Iron agent used for producing aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
An aluminum alloy and iron agent technology, applied in the field of aluminum alloy iron additives and their preparation, can solve the problems of inability to melt the intermediate alloy, the quality of the aluminum alloy is reduced, and the energy consumption is increased, so as to reduce the formation of iron metal and aluminum metal oxide films. , Reduce the chance of exposure to oxygen, reduce the effect of fuel use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
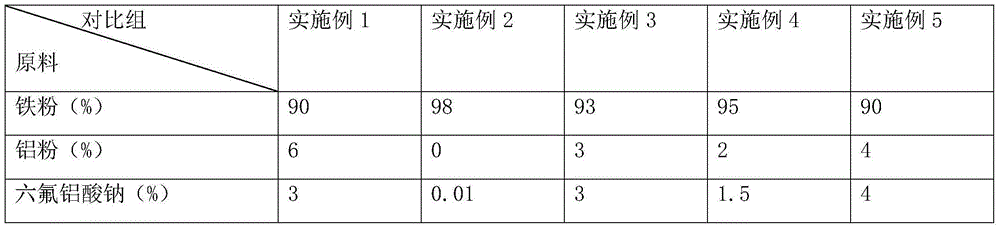
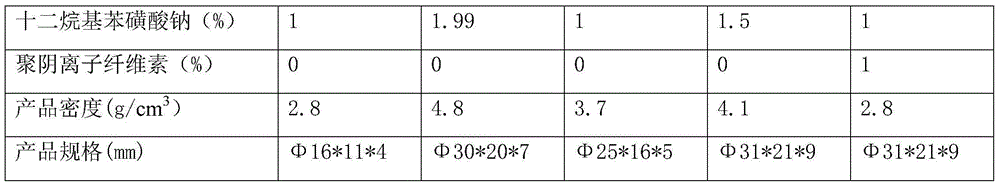
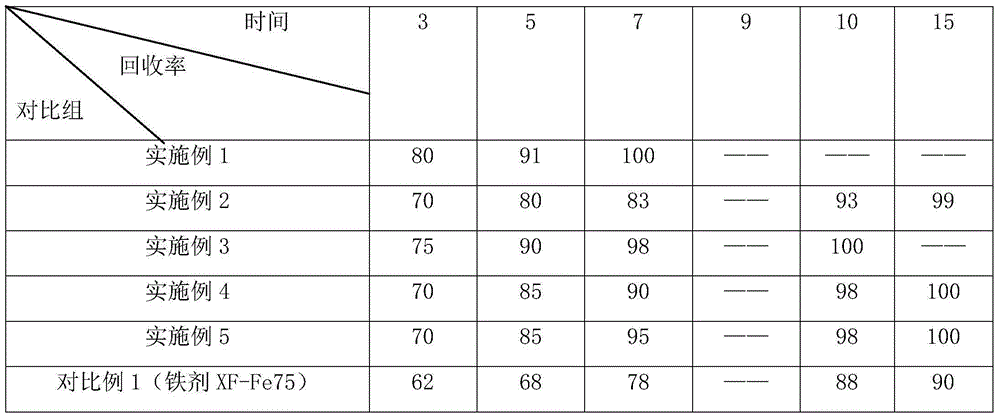
[0033] This example is used to produce the iron agent of aluminum alloy, made into rugby ball shape of Φ16mm*11mm*4mm, by mass percentage, iron powder 90%, aluminum powder 6%, sodium hexafluoroaluminate 3%, dodecane Sodium phenyl sulfonate 1%, the density after compression molding is 2.8g / cm 3 .
[0034] Above-mentioned additive is made according to the following method:
[0035] (1) Pulverization: Protected by inert gas, the iron metal, aluminum metal and sodium hexafluoroaluminate are respectively pulverized under the protection of inert gas, wherein the particle size range of the iron powder is 10-700 mesh, and the particle size range of the aluminum powder is 40-500 mesh, the powder particle size range of sodium hexafluoroaluminate is 40-500 mesh;
[0036] Among them, the particle size distribution of iron powder is 325-700 mesh iron powder accounts for 35-40% of the total iron powder content, 100-325 mesh iron powder accounts for 35%-45% of the total iron powder content...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference between the preparation method of this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0047] (2) Weighing: weighing the iron powder, aluminum powder and sodium hexafluoroaluminate powder obtained in step 1 according to the following weight ratio: 98% iron powder, 0.01% sodium hexafluoroaluminate powder;
[0048] (3) Preparation of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate solution: according to the total mass of weighing gained in step 2, prepare sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate solution according to a mass percentage of 1.99%;
[0049] (6) The density of the pressed product is 4.8g / cm 3 .
Embodiment 5
[0051] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0052] (2) Weighing: Weigh the iron powder, aluminum powder, and sodium hexafluoroaluminate powder obtained in step 1 according to the following mass percentages: 90% iron powder, 4% aluminum powder, and 4% sodium hexafluoroaluminate powder.
[0053] (3) Preparation of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate solution: according to the total mass obtained by weighing in step 2, prepare sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate solution according to 1% by mass.
[0054] (4) Preparation of binder solution: according to the total mass obtained by weighing in step 2, a polyanionic cellulose solution was prepared according to 1% by mass, and the concentration of the binder solution was 20%.
[0055] (6) step 3 and step 4 gained sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate solution and polyanionic cellulose solution are sprayed in the preliminary mixture of step 5 gained, open mixer, set its stirring frequency as 20- 30 revolutions per minute, an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com