Method for detecting embryo chromosome abnormalities by using blastula-stage embryo cells
A technology for chromosomal abnormalities and embryonic cells, which is applied in the field of chromosomal abnormality detection, can solve the problems of affecting experimental results, small number of templates, cumbersome operations, etc., and achieve the effect of improving amplification effect, increasing success rate, and high detection throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Isolation of blastocyst trophectoderm cells
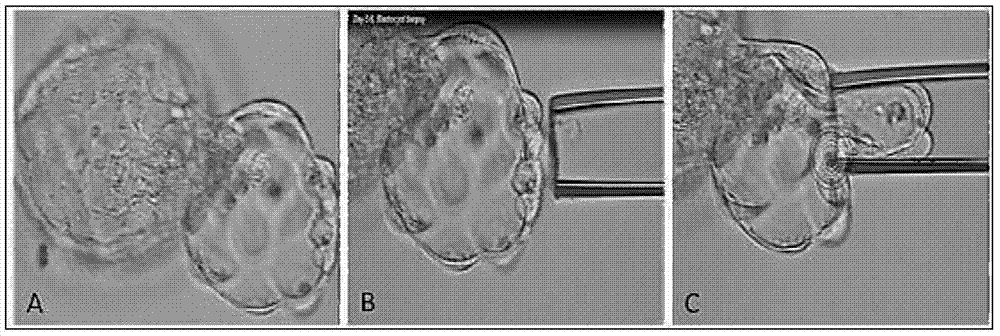
[0021] Select in vitro fertilized embryos from high-risk groups (age ≥ 35, repeated implantation failure, repeated miscarriage) in IVF, and obtain blastocyst trophectoderm cells by conventional embryo biopsy methods; when the embryo develops to the D3 stage, the zona pellucida is used to infiltrate Well, continue to culture until D5 stage, when trophectoderm cells extrude the zona pellucida, such as figure 1 , absorb part of the trophectoderm cells (5-10) with a flat micromanipulator needle, and cut off with a laser; the absorbed cells are transferred to PBS solution and washed 3 times.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Cell Lysis and Single Cell Expansion
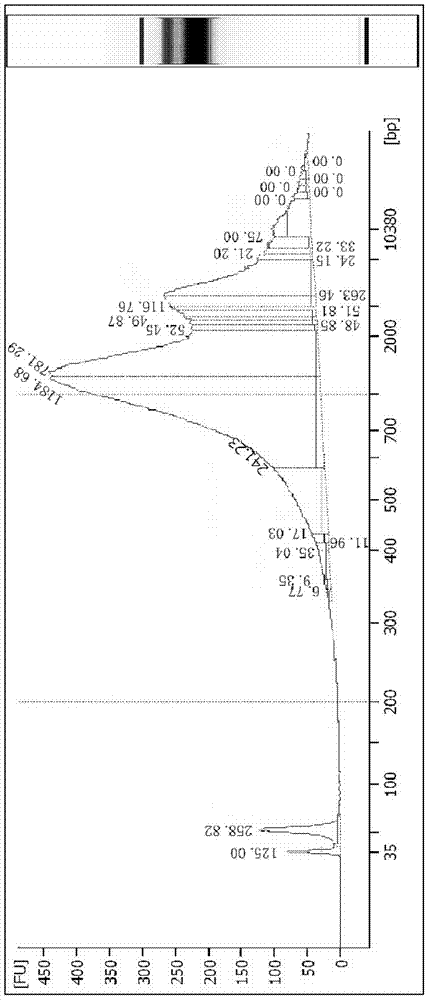
[0025] Transfer the washed cells to a 0.2mL PCR tube. According to the number of samples, mix the cell lysis buffer and cell lysis enzyme, and add the mixture to the cell samples. The reaction system for a single sample is shown in Table 1 below:
[0026] Table 1
[0027] components
Reaction volume (μL)
single cell sample
<2
Cell Lysis Buffer
5
Cytolytic enzyme
0.1
Total amount of reaction system
<7.1
[0028] Incubate the samples in a preheated PCR machine under the conditions shown in Table 2 below:
[0029] Table 2
[0030]
[0031] (2) Pre-amplification
[0032] According to the number of samples, mix the pre-amplification buffer and pre-amplification enzyme, and add the mixture to the reaction tube in the previous step. The single-sample reaction system is shown in Table 3 below:
[0033] table 3
[0034] components
Reac...
Embodiment 3
[0048] DNA fragmentation
[0049](1) DNA Fragmentation Use NEB's Fragmentation Enzyme Kit, briefly centrifuge the DNA fragmentation enzyme for 3 seconds, place it on an ice box, and configure the system shown in Table 7 below in a 1.5mL EP tube:
[0050] Table 7
[0051] components
Reaction volume (μL)
Purified DNA samples
X (500ng)
fragmentation buffer
2
water
16-X
Fragmentase
2
Total amount of reaction system
20
[0052] Place the EP tube in a thermostatic metal bath at 37°C for 30 min; after the reaction, add 5 μL of stop reaction buffer.
[0053] (2) DNA purification after fragmentation
[0054] Add 30 μL of water to the reaction system to make the volume of the system reach 50 μL, add 75 μL of XP magnetic beads, shake the Votex or blow it with a gun to mix the reaction system, and let it stand at room temperature for 5 minutes; put it into the magnetic stand, wait until the magnetic beads are co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com