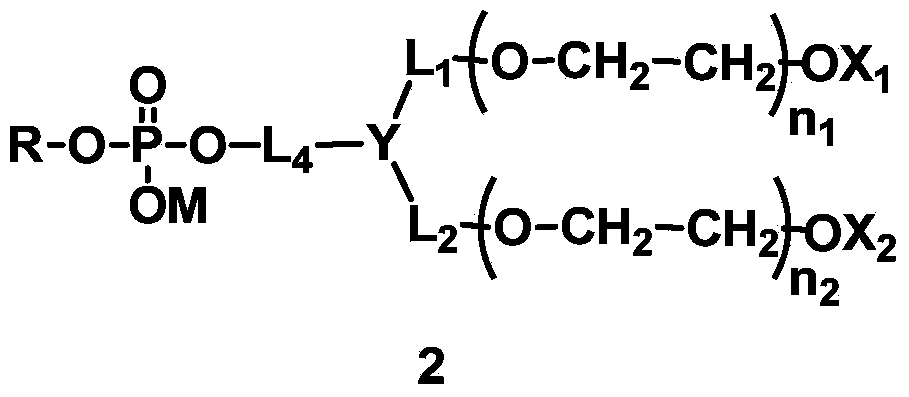
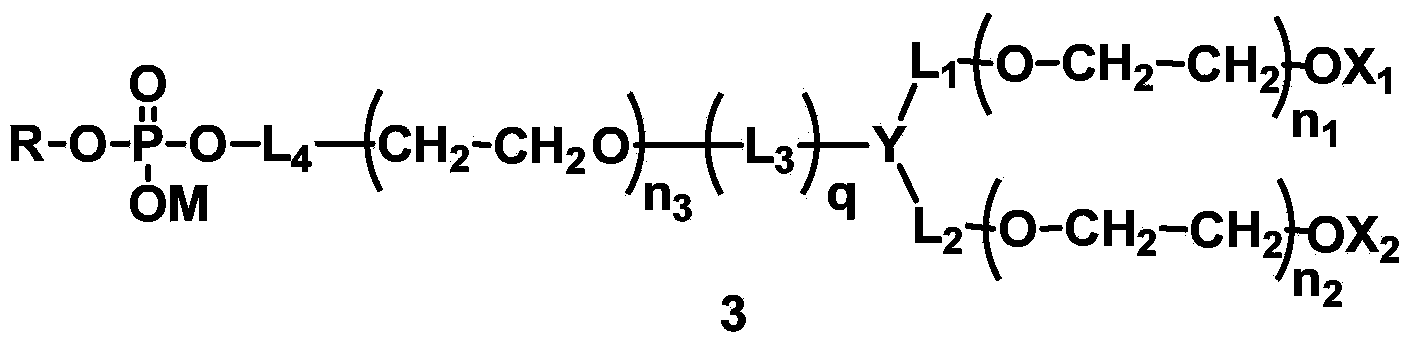Phospholipid derivatives for branching polyethylene glycol, and lipid membrane structural body composed of same
A technology of polyethylene glycol and derivatives, applied in liposome delivery, drug combination, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as poor retention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0228] Example 1: L 4 Preparation of amide bonds in
[0229] A. Condensation method
[0230] L 4 Synthesis of compounds (A1-1) containing amide bonds in which L 1 = L 2 = L 3 =CH 2 , Y=CH, X 1 =X 2 =CH 3 , q=1, R is dilauroyl glyceride residue, polyethylene glycol molecular weight is about 2000.
[0231]
[0232] After adding 40g of branched polyethylene glycol acetic acid and DLPE (13.9g, 1.2 equivalents) into a dry and clean 1L round bottom flask, nitrogen protection, adding the solvent dichloromethane (500mL), stirring at room temperature for 10min, then adding 20mL Dichloromethane solution of triethylamine and 20g of dicyclohexanecarbodiimide (DCC), reacted at room temperature for 24 hours, filtered to remove insoluble matter, concentrated, and recrystallized from isopropanol to obtain the compound containing amide bond in L4 ( A1-1).
[0233] The hydrogen spectrum data of compound A1-1 are as follows:
[0234] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 )δ (ppm): 0.95 (-CH 2 CH 3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0251] Example 2: L 4 Preparation of urethane linkages in
[0252] A, active ester synthesis method:
[0253] L 4 Synthesis of compounds containing carbamate bonds (A2-1) in which L 1 = L 2 =CH 2 CH 2 ,,L 3 =CH 2 CH 2 , X 1 =X 2 =CH 3 , Y is N, q=1, R is 1-stearyl-2-hydroxyglyceride residue, and the molecular weight of polyethylene glycol is about 1000.
[0254]
[0255] After adding branched polyethylene glycol succinimide carbonate active ester (20 g) and 1-stearyl-2-hydroxyglyceryl phosphatidylethanolamine (11.6 g, 1.2 equivalents) into a dry and clean 500 mL round bottom flask, Under nitrogen protection, add anhydrous dichloromethane (250mL), stir at room temperature for 10min, add 5mL triethylamine, react at room temperature for 24 hours, concentrate, and recrystallize from isopropanol to obtain the compound containing amino orthoester bond in L4 (A2-1).
[0256] The hydrogen spectrum data of compound A2-1 are as follows:
[0257] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 )δ (p...
Embodiment 3
[0264] Example 3: L 4 Preparation of ester bond (-OCO-) in
[0265] A:L 4 Synthesis of compounds containing ester bonds (A3-1), where L 1 = L 2 = L 3 =CH 2 ,X 1 =X 2 =CH 3 , Y is CH, q=1, R is the residue of dimyristyl phosphatidylglyceride. The designed total molecular weight is about 1500.
[0266]
[0267] After adding branched polyethylene glycol acetic acid (30 g) and dimyristyl phosphatidylglycerol (66.6 g, 5 equivalents) into a dry and clean 1L round-bottomed flask, nitrogen protection was added, and the solvent dichloromethane (500 mL) was added and kept at room temperature After stirring for 10 minutes, add 20 mL of triethylamine and 20 g of dicyclohexanecarbodiimide (DCC) in dichloromethane in sequence, react at room temperature for 24 hours, filter to remove insoluble matter, concentrate, dissolve in water, filter, and dialyze. A compound (A3-1) containing an ester bond in L4 was obtained.
[0268] The hydrogen spectrum data of compound A3-1 are as fol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com