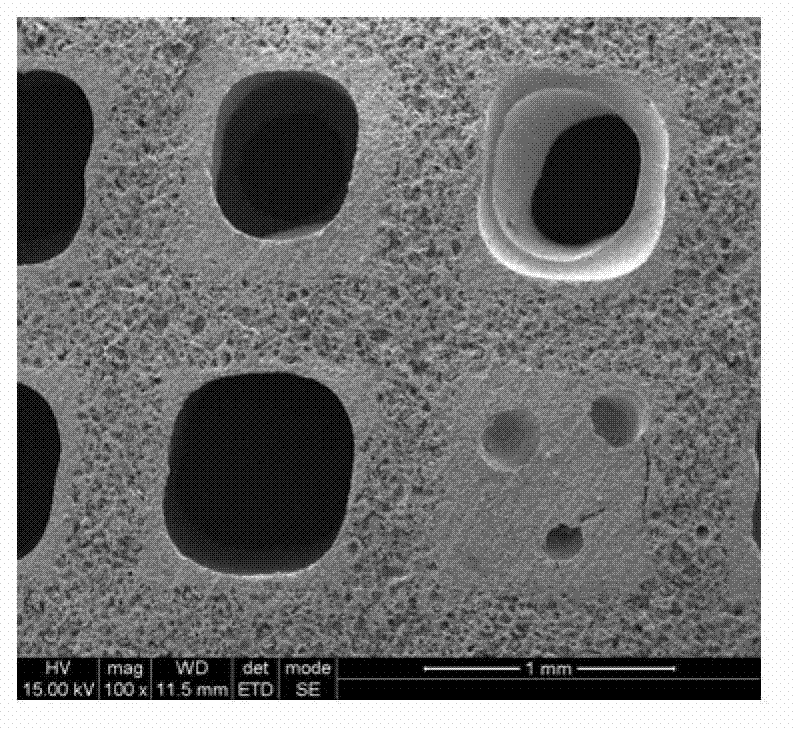
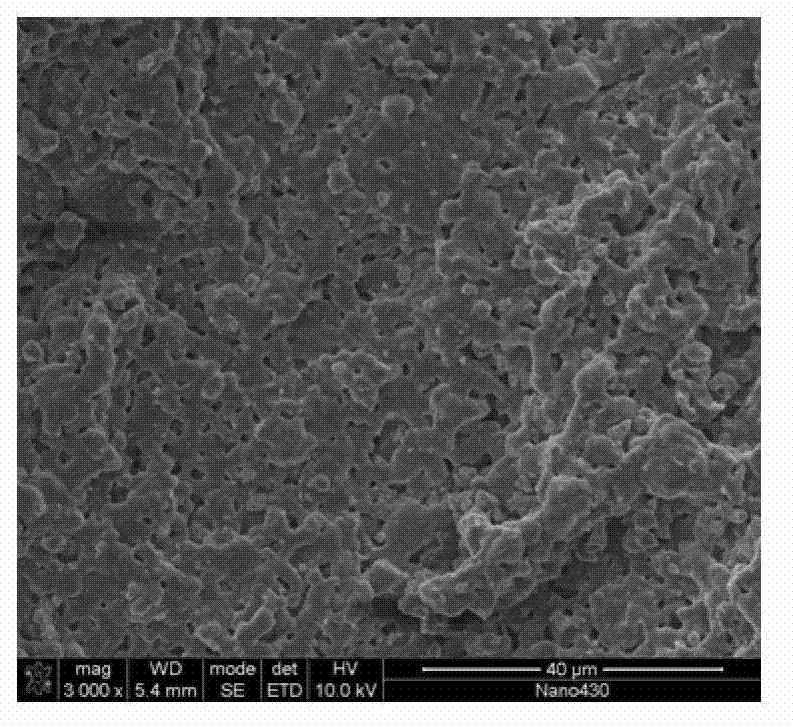
Preparation method and application of hierarchical porous bioactive ceramic
A bioactive ceramic and bioactive technology, applied in the field of bone defect repair medical materials, can solve the problems of short molding time, limited material form, high mechanical strength, and achieve the effects of high degree of mechanical forming, easy mechanical cutting, and high degree of automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Using methyl cellulose as a binder, ethylene glycol as a plasticizer, deionized water as a solvent, charcoal powder as a pore-forming agent and sodium polyacrylate 30% as a dispersant to prepare the steps of the multi-level porous bioactive ceramics include:
[0040] (1) Mix 5g of methylcellulose M450 (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., F20061011, analytically pure), 10g of ethylene glycol (Guangzhou Qingqin Chemical Co., Ltd., analytically pure) and 20mL of deionized water at 95°C, and use a mixer Mix for 25 minutes until methylcellulose and ethylene glycol are completely dissolved to obtain an additive emulsion;
[0041] (2) Add 4g of carbon powder (Shandong Guanxian Carbon Powder Factory, chemically pure) to the additive emulsion prepared in step (1), and continue mixing for 15 minutes until the carbon powder is evenly dispersed to obtain a carbon powder viscous liquid;
[0042] (3) Add 100g of β-tricalcium phosphate powder (Ensai Huaken (Beijing) Technology Co., ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Using dextrin as a binder, glycerin as a plasticizer, deionized water as a solvent, stearic acid as a pore-forming agent and polyacrylic acid as a dispersant to prepare the steps of the multi-level porous bioactive ceramics include:
[0052] (1) Mix 10g dextrin (China Pharmaceutical (Group) Shanghai Chemical Reagent Company, F20030310, analytically pure), 5g glycerol (Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co., Ltd., analytically pure) and 25mL deionized water at 60°C, and use a mixer Mix for 20 minutes until the dextrin and glycerin are completely dissolved to obtain an additive emulsion;
[0053] (2) Add 15g of stearic acid (Shanghai Lingfeng Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., 20101101, analytically pure) to the additive emulsion prepared in (1), and continue mixing for 10 minutes until the stearic acid is uniformly dispersed to obtain stearin acid viscous liquid;
[0054] (3) Add 100g of α-tricalcium phosphate powder (Ensai Huaken (Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd., 20100203, analytically...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Using polyvinyl acetate as binder, liquid paraffin as plasticizer, petroleum ether (Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co., Ltd., 110217) as solvent, polyethylene glycol as pore-forming agent and dodecylpyrrolidone as dispersion The steps of preparation of hierarchical porous bioactive ceramics include:
[0064] (1) Mix 5g polyvinyl acetate (Shenyang Shudeli Chemical Development Co., Ltd., chemically pure), 15g liquid paraffin (Shanghai Runjie Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., chemically pure) and 40mL petroleum ether (Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. Company, 110227) and mixed with a mixer at room temperature for 40 minutes until the polyvinyl acetate and liquid paraffin were completely dissolved to obtain an additive emulsion;
[0065] (2) Add 4g of polyethylene glycol 4000 (Shanghai Pudong Gaonan Chemical Factory, 090305, analytically pure) to the additive emulsion prepared in (1), and continue mixing for 20 minutes until the polyethylene glycol is uniformly dispersed to obtai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com