Method for preparing composite sintered neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet material added with gadolinium, holmium and yttrium
A technology of composite addition and permanent magnetic materials, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic materials, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of low working temperature and temperature stability, low actual coercive force, poor corrosion resistance, etc., and achieve rare earth Total content saving, coercive force and working temperature increase, and the effect of improving toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
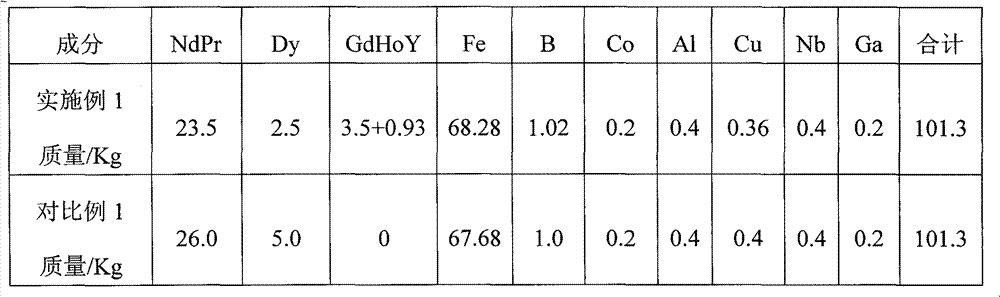
[0026] A method for preparing a sintered NdFeB permanent magnet material compounded with Gd, Ho, and Y, according to the formula described in the following table 1-1, a batch of 100Kg is carried out:
[0027] Table 1-1
[0028] Element
[0029] Among them, the mass percentage of Nd and Pr in the raw material is 75:25; the phase forms of Dy, B, and Nb are iron alloys with iron content of 25.0wt.%, 80.5wt.%, and 34.7wt.%, respectively; Gd, Ho , Y is compounded in the form of iron alloy with an iron content of 25.0wt.%, and its mass percentage is Gd:Ho:Y=40:50:10; the remaining Fe is added in pure iron metal.
[0030] Then adopt the following process steps to manufacture NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet materials:
[0031] The prepared raw materials are put into a vacuum melting furnace for melting to form molten alloy liquid. The melting temperature is 1500°C, and then the molten alloy liquid is rapidly solidified into master alloy flakes with a thickness of 0.3-0.5...
Embodiment 2
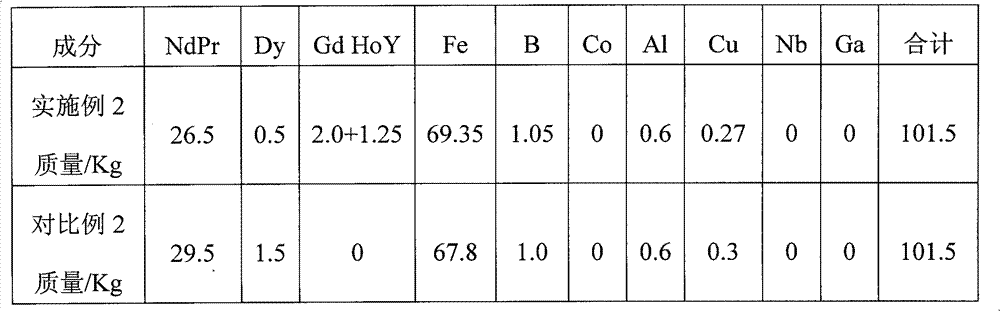
[0041] According to the formula described in the following table 2-1 and the steps in embodiment 1, carry out batching 100Kg once, wherein Gd: Ho: Y=50: 30: 20; other conditions are the same as embodiment 1.
[0042] table 2-1
[0043] Element
[0044] The prepared raw materials are put into a vacuum melting furnace for melting to form a molten alloy liquid from the raw materials. The melting temperature is 1550 ° C, and then the melted average particle size is that the alloy liquid is rapidly solidified into a master alloy sheet with a thickness of 0.3-0.5 mm; through Hydrogen crushing and jet milling crush master alloy flakes into fine powder with an average particle size of 3-5 μm; 100Kg master alloy powder and Gd with an average particle size of 0.5 μm 2 o 3 0.2Kg, Ho 2 o 3 0.6Kg, Y 2 o 3 0.7Kg, Cu 2 O 0.3Kg is uniformly mixed in a powder mixer; the uniformly mixed fine powder is pressed into a compact by molding and isostatic pressing; the compact is s...
Embodiment 3
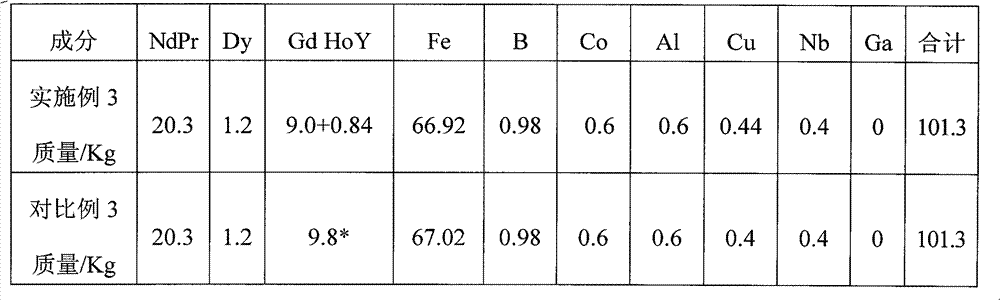
[0054] According to the formula described in the following table 3-1 and the steps in embodiment 1, carry out batching 100Kg once, wherein Gd: Ho: Y=60: 30: 10; other conditions are the same as embodiment 1.
[0055] Table 3-1
[0056] Element
[0057] The prepared raw materials are put into a vacuum melting furnace for melting to form a molten alloy liquid from the raw materials. The melting temperature is 1350 ° C, and then the melted average particle size is that of the alloy liquid, which is quickly solidified into a master alloy sheet with a thickness of 0.3-0.5 mm; through Hydrogen crushing and jet milling crush master alloy flakes into fine powders with an average particle size of 3-5 μm; add 100Kg of master alloy powder and Gd with an average particle size of 0.5 μm to the mixer 2 o 3 0.1Kg, Ho 2 o 3 0.5Kg, Y 2 o 3 0.4Kg, Cu 2 O 0.5Kg for secondary batching and powder mixing; the uniformly mixed fine powder is pressed into a compact by molding and is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com