Preparation method for medical porous metal material for replacing dentale
A porous metal and dental bone technology, applied in metal processing equipment, medical science, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of mechanical properties such as ductility, compressive strength, insufficient bending strength, and affect the processing of porous tantalum materials, etc., to improve Biocompatibility and biosafety, good pore size uniformity of the finished product, and the effect of pore distribution connectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
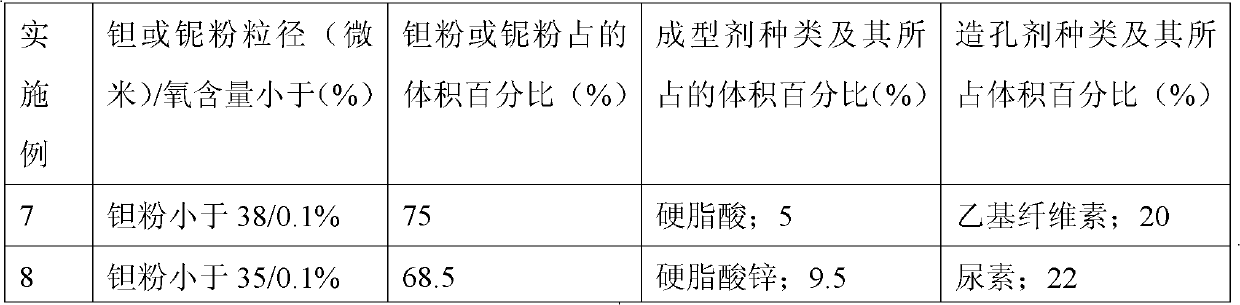
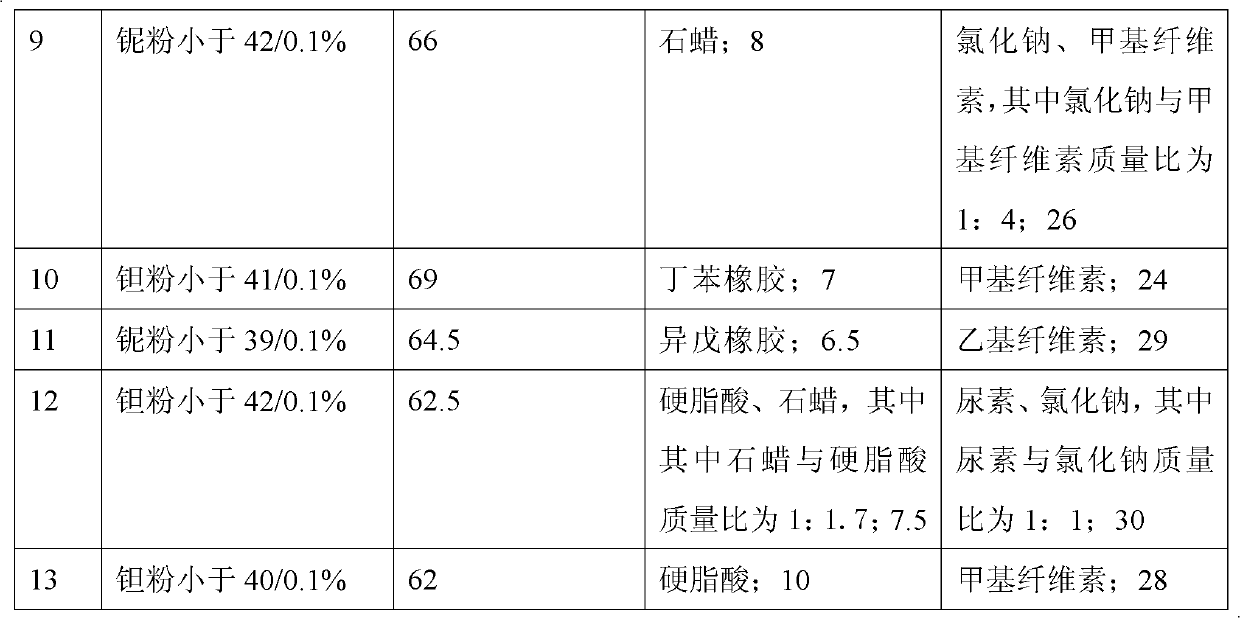
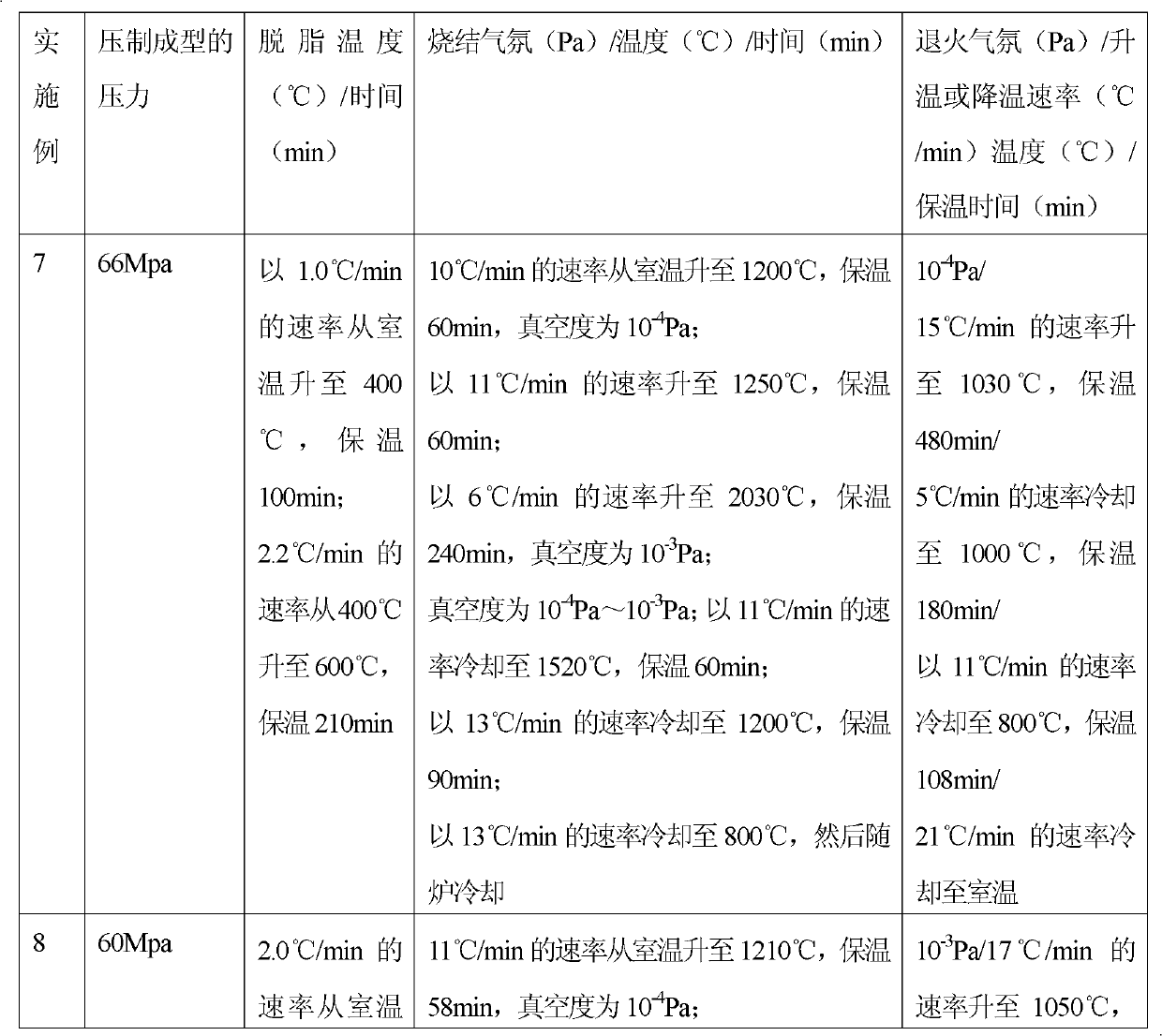
[0024] A kind of preparation method of the medical porous metal material that replaces dental bone is to select molding agent, pore-forming agent (the molding agent is one or more arbitrary combinations in stearic acid, zinc stearate, paraffin, synthetic rubber , the pore-forming agent is one or more of urea, sodium chloride, ethyl cellulose, and methyl cellulose in any combination) mixed with tantalum powder with an average particle size of less than 43 microns and an oxygen content of less than 0.1%. Mixed powder, the mixed powder is pressed into an organic foam at 50-100Mpa to form, and then degreased, sintered, cooled and heat-treated to obtain a porous tantalum material. The formed porous tantalum is tested to have a porosity of 20-30%, and a pore diameter of 5-30 μm.
[0025] More specifically, the above-mentioned porous tantalum is composed of 5-10% (by volume percentage) of the above-mentioned forming agent, 20-30% (by volume percentage) of the above-mentioned pore-for...
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: take by weighing zinc stearate, average particle diameter less than 43 micron oxygen content less than 0.1% tantalum powder and methyl cellulose and mix uniformly into mixed powder, wherein zinc stearate accounts for 6%, methyl cellulose accounts for 23%, and tantalum powder accounted for 71%, all calculated by volume percentage. Pressure molding: Add the above mixed powder into an injection molding machine and press it into a polyurethane foam (pore diameter 0.48-0.89mm, density 0.015g / cm2) at 62Mpa 3 ~0.035g / cm 3 , hardness greater than 50°) in molding. Degreasing treatment: vacuum degree 10 -4 Pa, from room temperature to 400°C at a heating rate of 1.5°C / min and hold for 110 minutes; then at a heating rate of 2.5°C / min from 400°C to 700°C for a holding time of 210 minutes. Vacuum sintering: sintering in a vacuum furnace, the sintering temperature is 2000°C, the heat preservation is 2 hours, and the vacuum degree is 10 -4 Pa, the sintering process is...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: take by weighing paraffin, average particle diameter less than 43 microns, oxygen content less than 0.1% niobium powder and urea and mix uniformly into mixed powder, wherein paraffin accounts for 5%, ethyl cellulose accounts for 30%, and niobium powder accounts for 65%, All are calculated by volume percentage. Compression molding: Add the above mixed powder into an injection molding machine and press it under 65Mpa to a hole diameter of 0.56-0.72mm and a density of 0.025g / cm 3 , molded in polyurethane foam with a hardness of 50°-80°. Degreasing treatment: vacuum degree 10 -4 Pa, raise the temperature from room temperature to 400°C at a heating rate of 2°C / min, and hold for 100 minutes; then raise the temperature from 400°C to 800°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, and hold for 200 minutes. Vacuum sintering: sintering in a vacuum furnace, the sintering temperature is 2100°C, the heat preservation is 4 hours, and the vacuum degree is 10 -4 Pa, the sintering ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com