Method combining oxidizing composite reagent and activated carbon to remove arsenic in water
A technology of compounding agent and activated carbon is applied in the field of water treatment to achieve good removal effect, ensure water quality safety and facilitate management.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0028] Specific Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, the method for removing arsenic in water by the combination of new oxidizing compound agent and activated carbon is carried out in the following manner: add new oxidizing compound medicament to the water and stir, and after 10 minutes of contact oxidation, use activated carbon to adsorb again, which is completed Removal of arsenic in water; among them, the new oxidizing compound agent is composed of potassium ferrate, chlorine dioxide, sodium peroxide, potassium persulfate, potassium monopersulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate, and hydroxylamine hydrochloride. The dosage of oxidizing compound agent The amount is added according to the molar equivalent ratio of arsenic in water to 5:1.
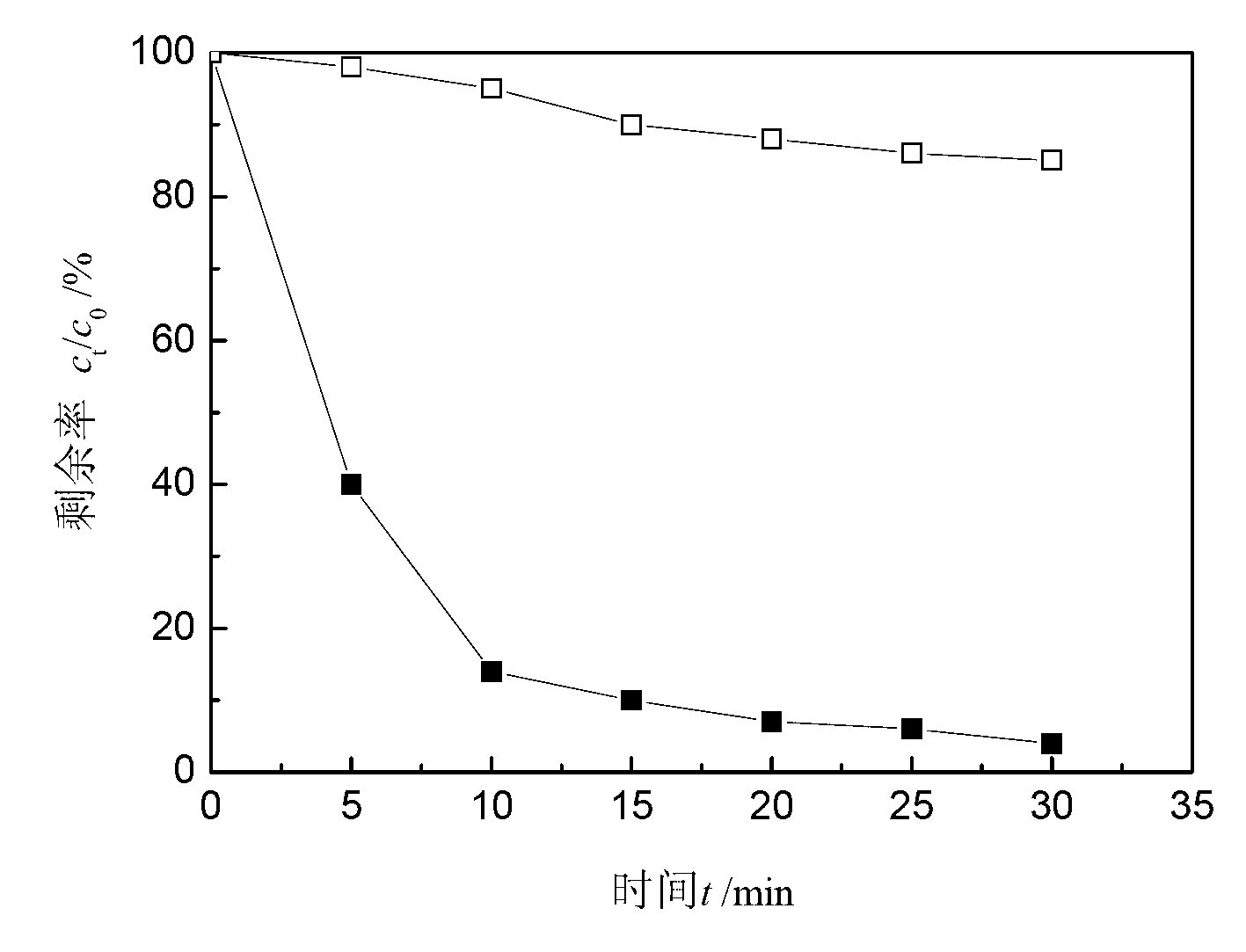
[0029] In this embodiment, sodium arsenite is added to certain surface water, and the initial total arsenic concentration is 50 μg / L, as the treated raw water. The removal effect of arsenic in water is shown in figure 1 . It can be seen th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, the arsenic-containing water is exposed to air or oxygen to ensure that the dissolved oxygen in the water is 4-40 mg / L, and the pH of the water body is controlled to be 6-9 .
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that a new type of oxidation compound agent and activated carbon are added to the water at the same time, and the stirring reaction is oxidized for 3 to 30 minutes to realize the removal of arsenic.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com