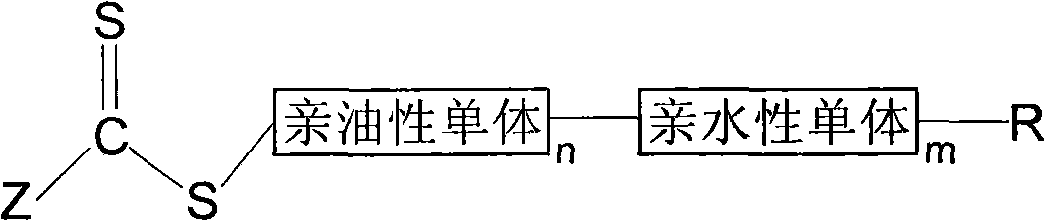
Implementation method of reversible addition fragmentation chain emulsion polymerization
A technology of addition cleavage and emulsion polymerization, applied in the field of emulsion polymerization, can solve the problems of long reaction polymerization inhibition period, molecular weight deviation from theoretical value, low final conversion rate, etc., to achieve short reaction polymerization inhibition period, save reaction time, and improve production The effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] 40 grams of water, 0.1 gram of amphiphilic macromolecular reversible addition and fragmentation chain transfer reagent (1), 4 grams of butyl acrylate, and 0.01 gram of small molecule reversible addition and fragmentation chain transfer reagent (1) are added to the reactor, Stir and mix, stir, pass nitrogen gas for 20 minutes, heat up to 80° C., add 0.004 g of ammonium persulfate to initiate polymerization, add 0.01 g of ammonia water after 20 minutes of reaction, and continue polymerization for 0.5 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0066] Mix 40 grams of water, 1 gram of amphiphilic macromolecular RAF chain transfer reagent (2), 5 g of styrene, 5 g of methyl methacrylate, and 0.01 g of small molecule RAF chain transfer Reagent (2) was added into the reactor, stirred and mixed, stirred, nitrogen gas was passed for 30 minutes, the temperature was raised to 70° C., 0.04 g of potassium persulfate was added to initiate polymerization, and the polymerization was carried out for 2 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0068] With 40 grams of water, 1.7 grams of amphiphilic macromolecular reversible addition and fragmentation chain transfer reagent (3), 5 grams of styrene, 5 grams of acrylonitrile, 0.1 gram of small molecule reversible addition and fragmentation chain transfer reagent (3 ) into the reactor, stirred and mixed, stirred, passed nitrogen for 20 minutes, heated to 50°C, added 0.01 g of ammonium persulfate to initiate polymerization, and added an aqueous solution containing 2 g of sodium bicarbonate when reacting for 3 hours, and continued to polymerize for 5 hours .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com