Titanium alloy integral blade disc with composite performance and fabricating method thereof
An integral blade, titanium alloy technology, applied in the parts of the pumping device for elastic fluid, liquid fuel engine, metal material coating process, etc. Large and other problems, to achieve high-temperature fracture toughness and creep resistance, improve utilization and structural efficiency, and achieve the effects of small particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: TC4 titanium alloy material was prepared by laser melting deposition on TC4 titanium alloy substrate by laser melting deposition method.
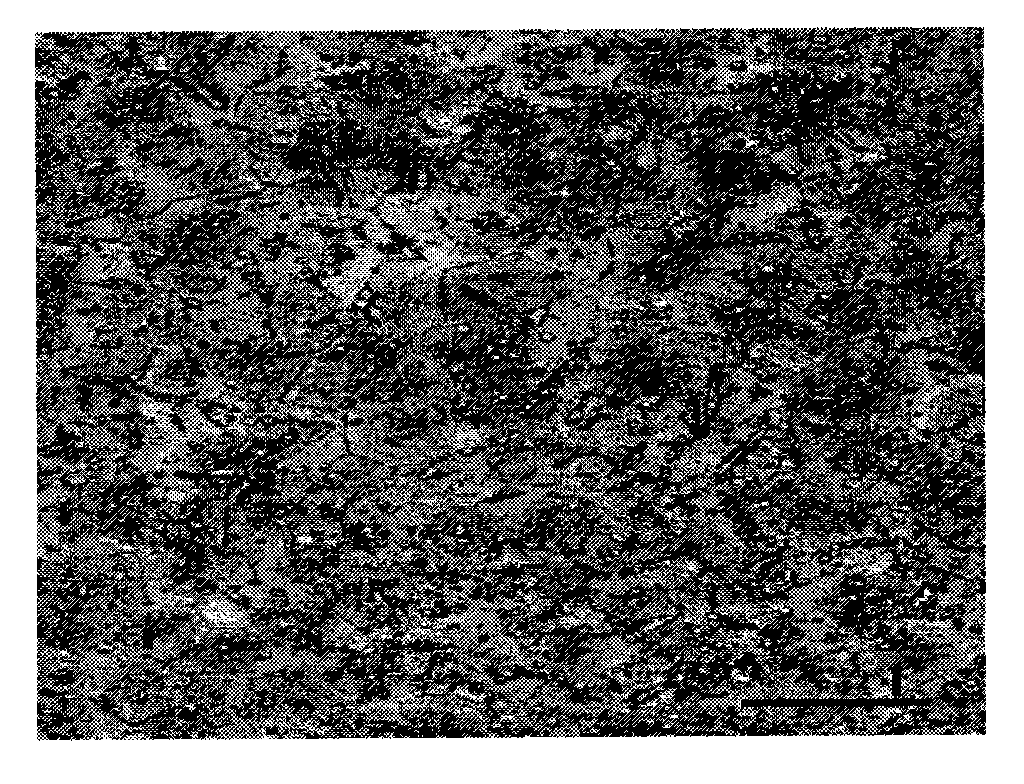
[0056] The TC4 titanium alloy powder transported synchronously by laser melting was used to deposit thin-walled samples on the TC4 titanium alloy substrate layer by layer, and the tensile samples were obtained by mechanical processing, and the room temperature static load tensile test was carried out. The test results are shown in Table 1. , and the tensile mechanical properties of other forming processes are also given in Table 1. It can be seen that the mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy formed by laser deposition are equivalent to those of forging annealed state. The laser power used for laser melting deposition is 2.0kW, the scanning speed is 5.0mm / s, the beam diameter is 3.0mm, the powder feeding rate is 4.5g / min, and the powder particle size is 50-150μm. figure 1Photograph of the internal structure of TC4...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2: Preparation of TA15 titanium alloy material by laser melting deposition on TA15 titanium alloy substrate by laser melting deposition method
[0061] The TA15 titanium alloy powder transported synchronously by laser melting was used to deposit thin-walled samples on the TA15 titanium alloy substrate layer by layer, and the tensile samples were obtained by mechanical processing, and the room temperature static load tensile test was carried out. The test results are shown in Table 2. , and the tensile mechanical properties of other forming processes are also given in Table 2. It can be seen that the mechanical properties of TA15 titanium alloy formed by laser deposition are equivalent to those of forging annealed state. The laser power used for laser melting deposition is 2.5kW, the scanning speed is 5.0mm / s, the beam diameter is 3.0mm, the powder feeding rate is 5.0g / min, and the powder particle size is 50-105μm. figure 2 Photograph of the internal structure o...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Laser melting deposition of TC4+Cr on TC4 titanium alloy substrate by laser melting deposition method 3 C 2 Obtain in-situ TiC reinforced titanium matrix composites.
[0066] 90wt% TC4 powder and 10wt% Cr 3 C 2 Powder pre-mixed; pre-mixed TC4+10wt%Cr by laser melting deposition method 3 C 2 The powder is melted layer by layer by laser and deposited on the surface of TC4 titanium alloy substrate to prepare in-situ TiC reinforced titanium matrix composite material. The reaction process is 2Ti+Cr 3 C 2 =3Cr+2TiC, the laser power used is 3.0kW, the spot diameter is 3.0mm, the scanning speed is 4.0-6.0mm / s, the powder feeding rate is 4.2g / min, the powder particle size of TC4 titanium alloy is 50-105μm, Cr 3 C 2 The particle size of the powder is 45-75 μm. The hardness of the prepared titanium-based composite material is HRC 47-49. Laser Melting Deposition TC4+10wt%Cr 3 C 2 The microstructure analysis results of in-situ TiC reinforced titanium matrix com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com