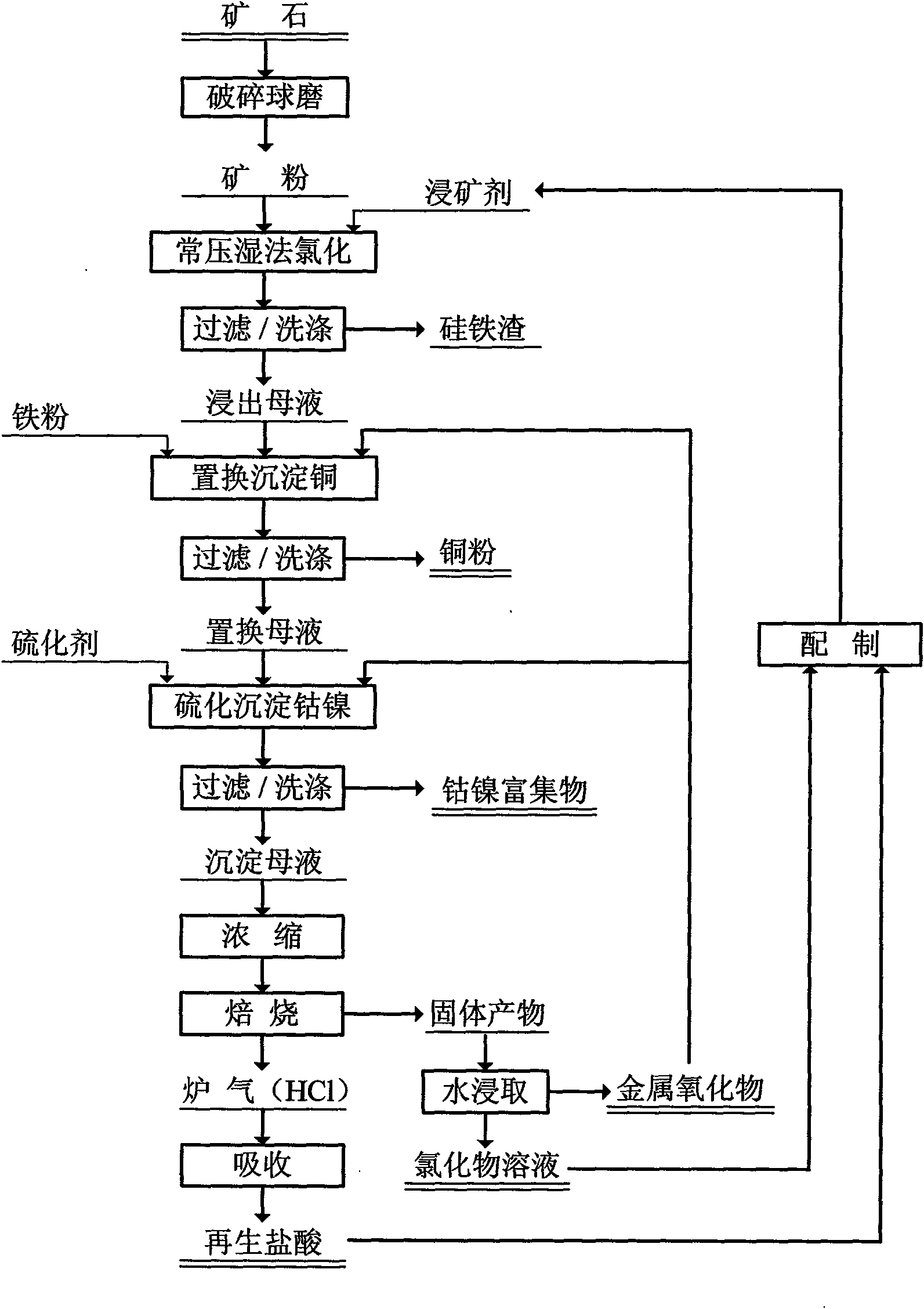
Method for separating and extracting copper and cobalt-nickel in low-grade complex mixed copper-cobalt ore
A low-grade and complex technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of insufficient comprehensive utilization of resources and weak versatility, and achieve the effects of complete solution, cost saving and high leaching rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1 heating ore leaching
[0060] A. Take the copper-cobalt ore slurry and pump it into the stirred reactor, the ratio of liquid to solid is 4.0:1, the ratio of acid to material (weight) is 1.2~1.4:1, and the ratio of salt (solid ferric chloride hexahydrate) to material is 0.28~ 0.30:1 Add hydrochloric acid (HCl content above 28%), solid ferric chloride hexahydrate, add water; heat, stir and leaching.
[0061] B. Control of leaching conditions: stirring and leaching for 1.0 hour at 60-70°C and 0.1MPa.
[0062] C. Filter and wash the residue.
[0063] The comprehensive leaching rates of valuable metals are: Cu 94.7%; Co+Ni 92.7%; Mg 96.2%; Fe42.7%.
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2 ore leaching at normal temperature
[0065] A. Take -100 mesh slurry and pump it into the stirred reactor, according to the liquid-solid ratio of 3.0:1, the ratio of acid to material (weight) is 0.8 to 1.0:1, and the salt (solid ferric chloride hexahydrate + magnesium chloride hexahydrate) material The ratio is 0.35-0.38: 1. Add hydrochloric acid (HCl content above 28%), solid ferric chloride hexahydrate, and add water; carry out stirring and leaching.
[0066] B. Control of leaching conditions: stirring and leaching for 3.0 hours at room temperature and 0.1 MPa.
[0067] C. Filter and wash the residue.
[0068] The comprehensive leaching rates of valuable metals are: Cu 93.7%; Co+Ni 93.1%; Mg 95.4%; Fe31.6%.
[0069] The mixed copper-cobalt ore is leached with a salt mixed leaching agent. The main metal element contents (g / L) of the leachate are: Cu8.70; Ni+Co 2.62; Mg+Ca 8.47 Fe 21.01; the acidity of the leachate is: H + 0.72mol / L. The following exam...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3 Normal Temperature Replacement Precipitated Copper
[0071] A. Adjustment of the pH value of the leachate: pump the leachate into the stirring reactor, stir at room temperature, slowly add the water leaching residue of the roasted solid product at a uniform speed, so that the pH of the leachate rises to 1.0-1.5, stop feeding, and continue stirring for 0.5 hours; the pH of the solution Value continues to rise; filter.
[0072] B. Reduction and precipitation extraction of copper powder: pump the adjustment solution into the stirring reactor, stir at room temperature, slowly and uniformly add reduced iron powder; according to the reduction chemical reaction metering of the amount of copper in the solution and the content of high-valent iron, the amount of iron powder added is 1.1 times the theoretical amount, the addition time is 2.0 hours, and the stirring reaction time is 2.5 hours.
[0073] C. Separation and extraction of copper powder: filter; collect the fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com