Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Preventing and delaying onset" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
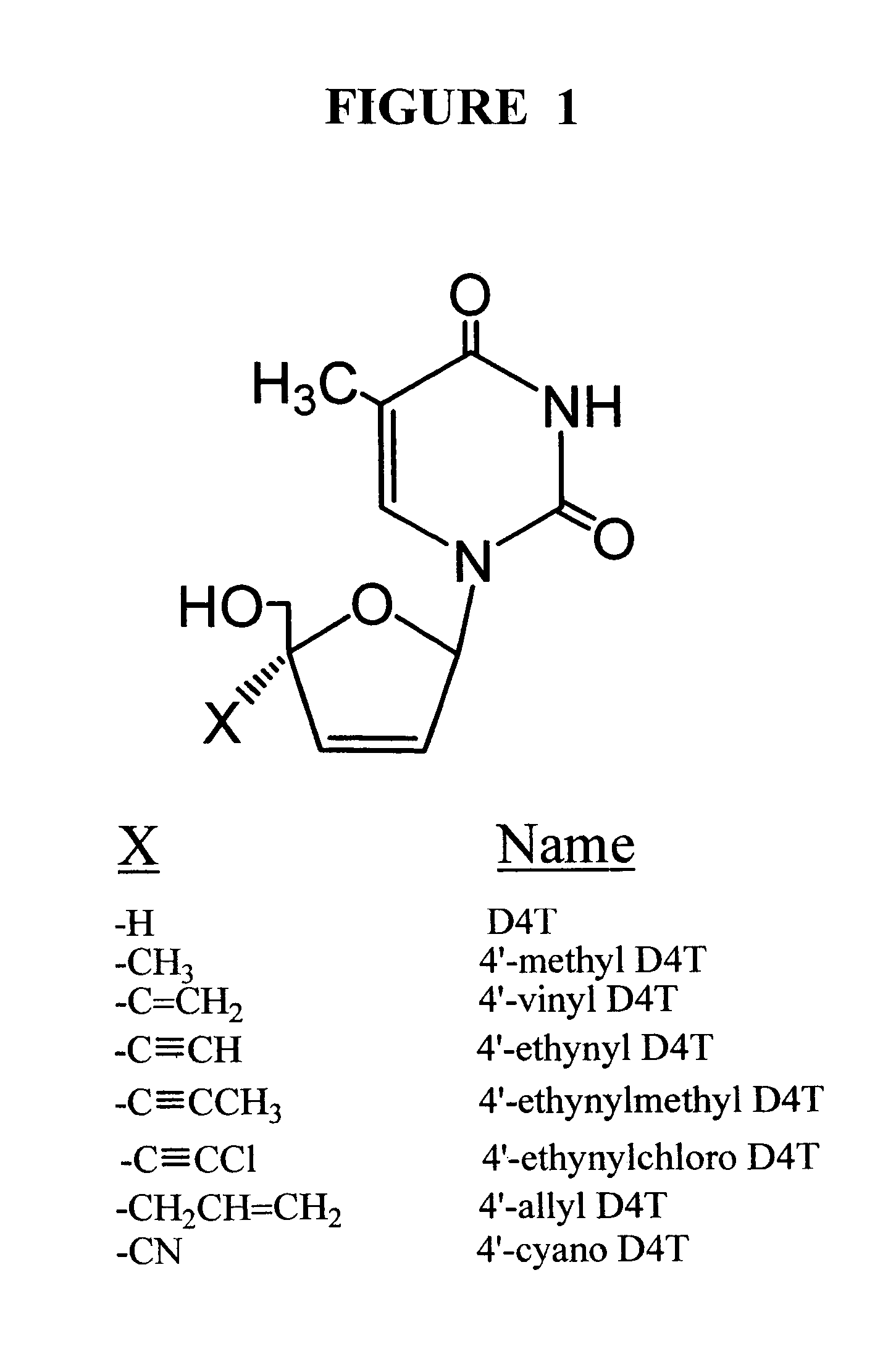
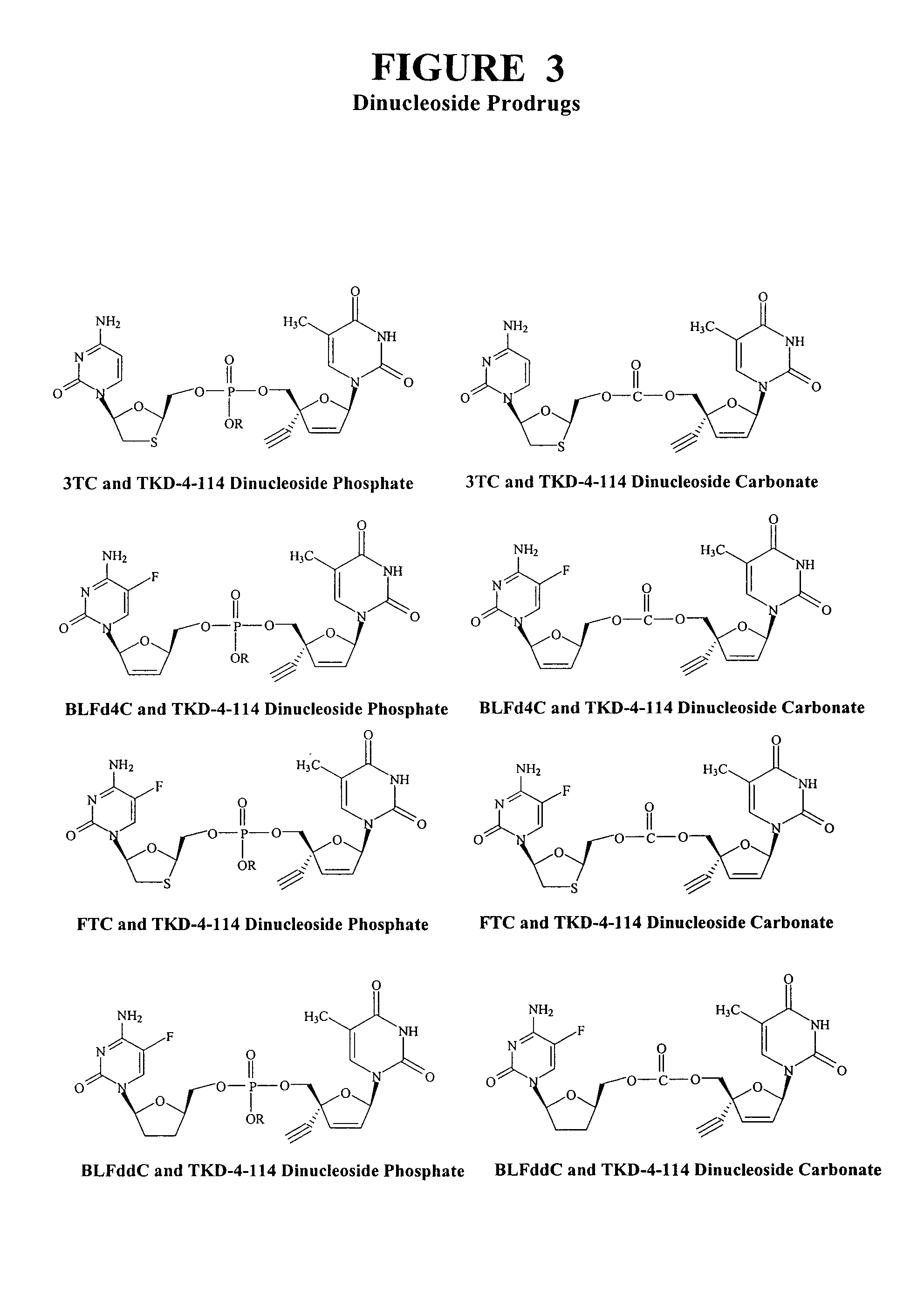
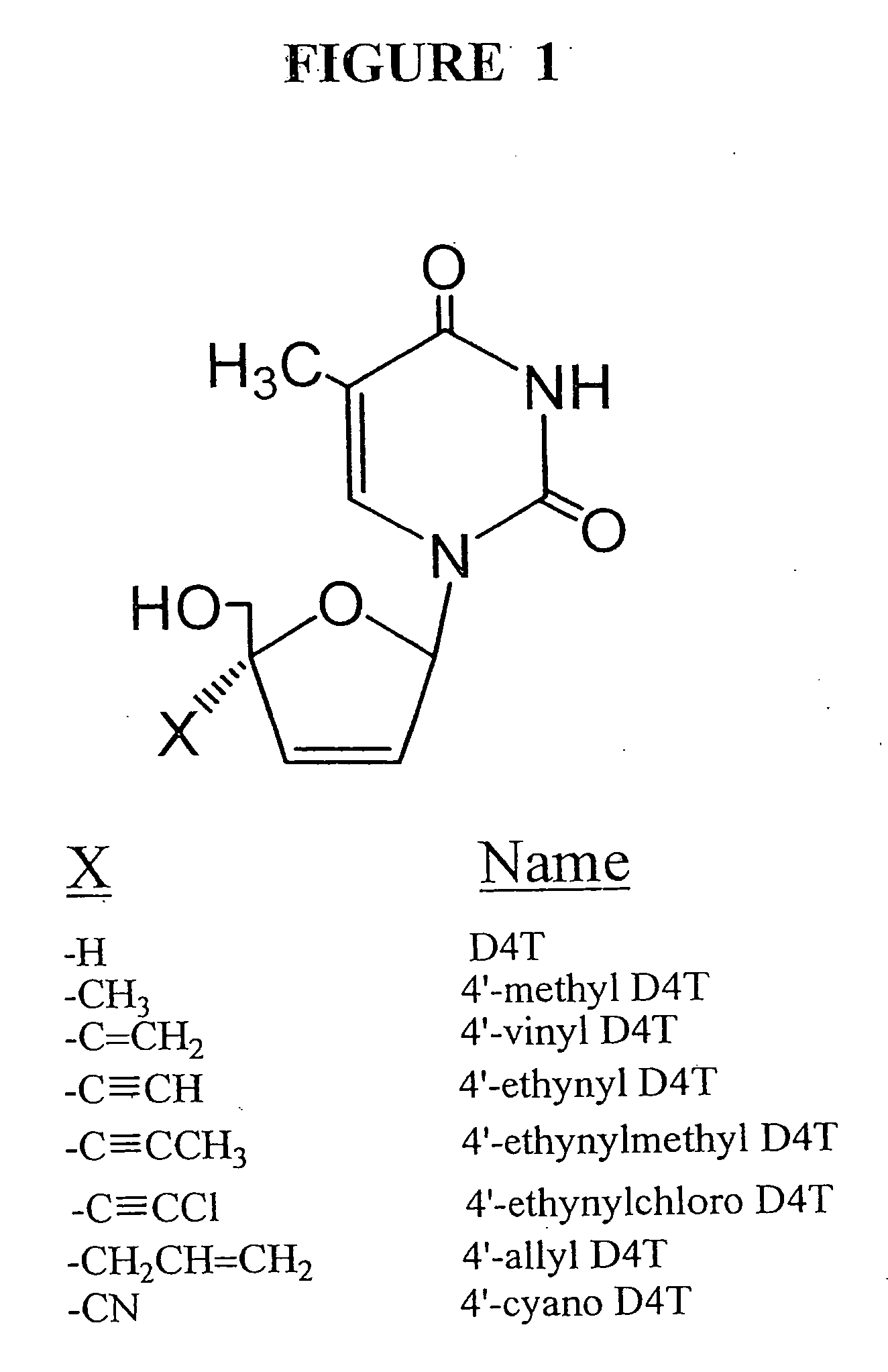
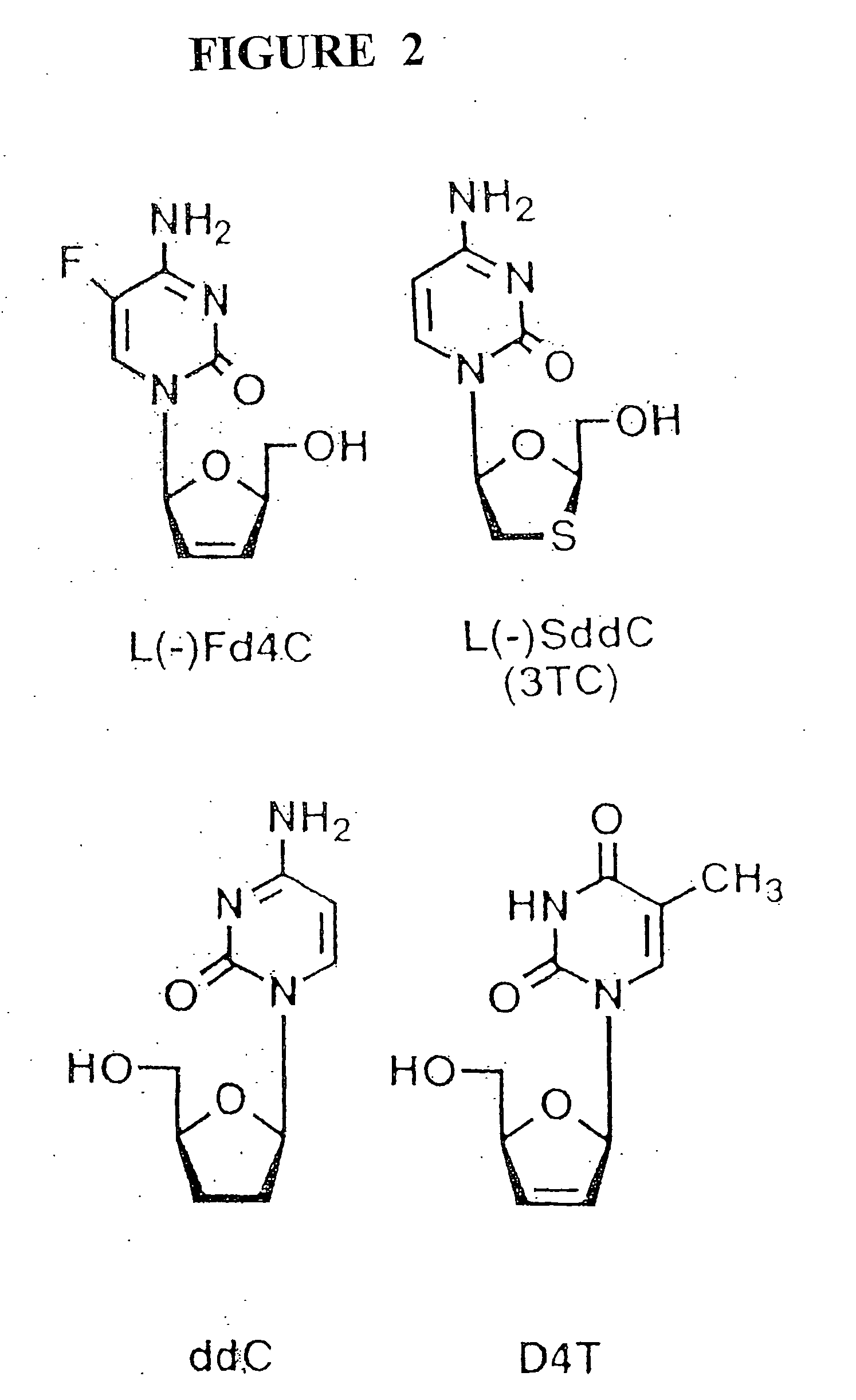
Anti-viral nucleoside analogs and methods for treating viral infections, especially HIV infections
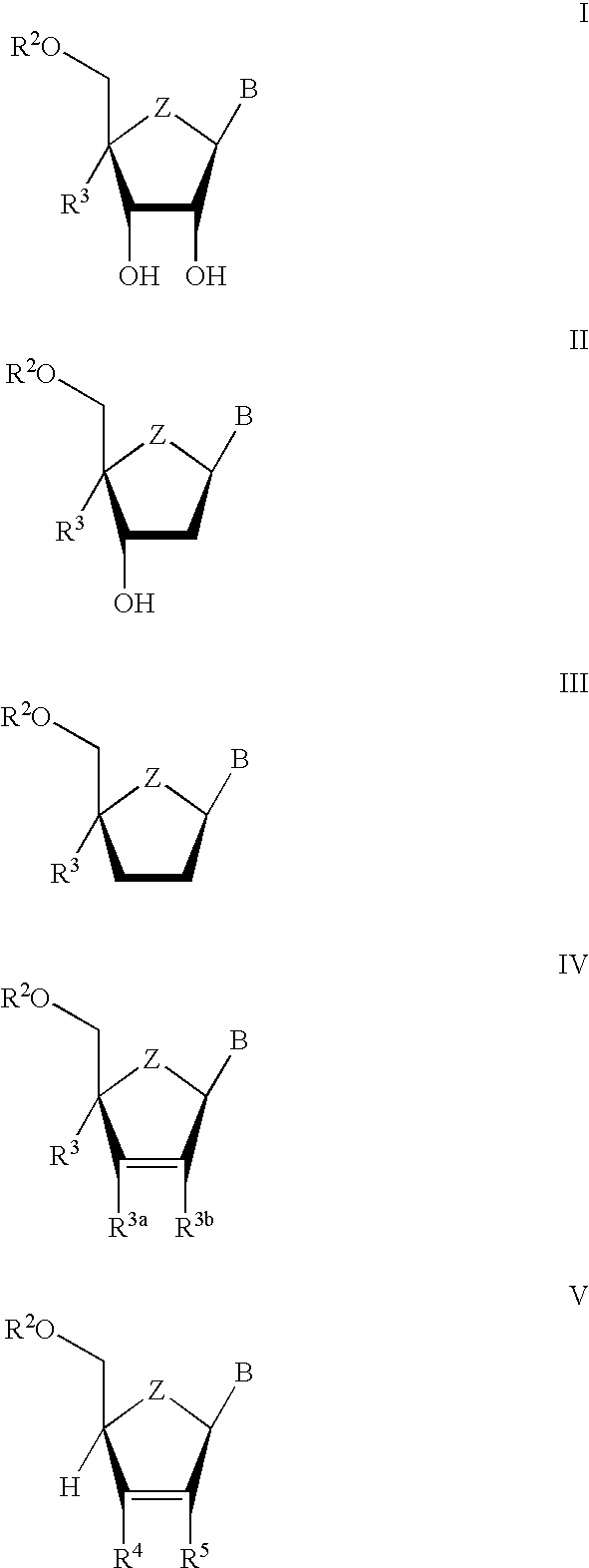
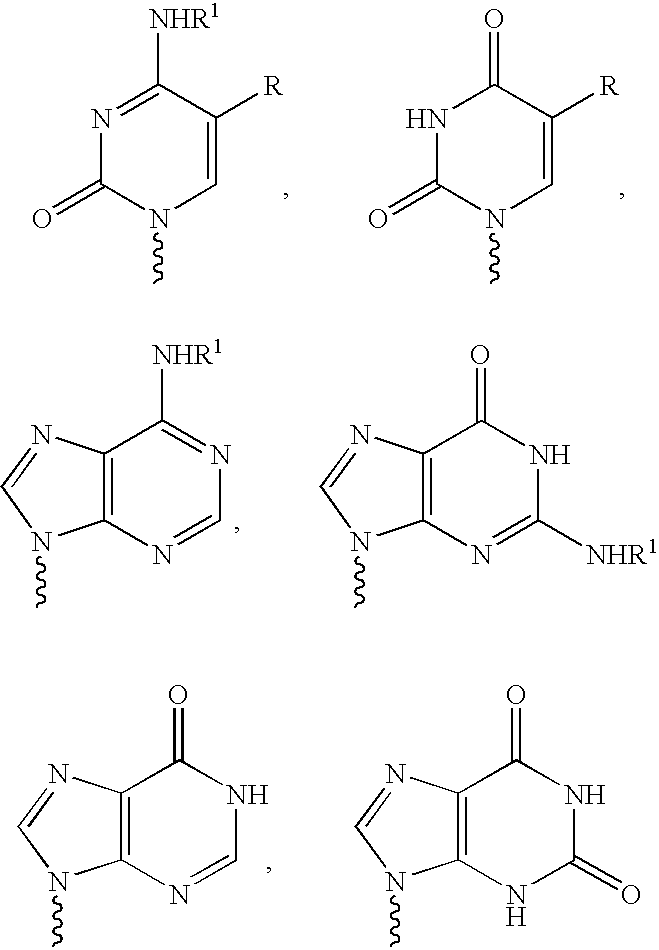
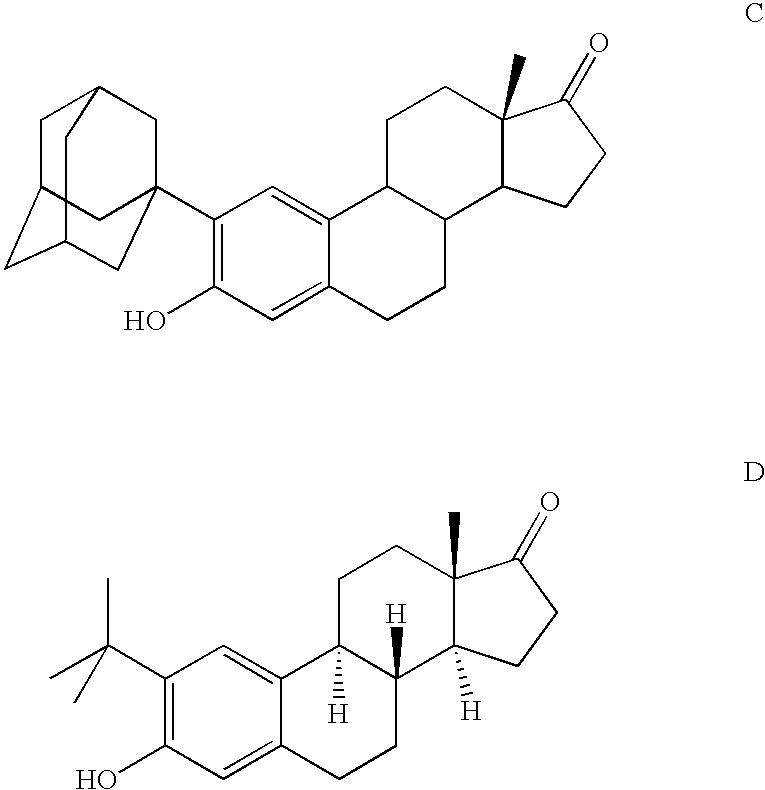
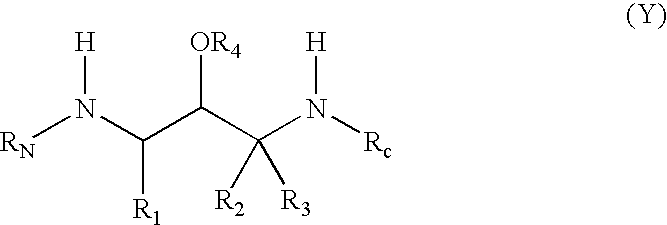
The present invention relates to novel compounds according to the to the general formulas I, II, III, IV or V: wherein B is nucleoside base according to the structure: R is H, F, Cl, Br, I, C1-C4 alkyl (preferably CH3), -C=N, -C=C-Ra, X is H, C1-C4 alkyl (preferably, CH3), F, Cl, Br or I; Z is O or CH2, with the proviso that Z is CH2 and not O when the compound is according to general formula II, R<3 >is -C=C-H and R<2 >is H or a phosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate or phosphotriester group; R<1 >is H, an acyl group, a C1-C20 alkyl or an ether group; R<2 >is H, an acyl group, a C1-C20 alkyl or ether group, a phosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate, phosphodiester group or a group; Nu is a radical of a biologically active antiviral compound such that an amino group or hydroxyl group from said biologically active antiviral compound forms a phosphate, phosphoramidate, carbonate or urethane group with the adjacent moiety; R<8 >is H, or a C1-C20 alkyl or ether group, preferably a C1-C12 alkyl group; k is 0-12, preferably, 0-2; R<3 >is selected from a C1-C4 alkyl (preferably, CH3), -(CH2)n-C=C-Ra, R<3a >and R<3b >are independently selected from H, F, Cl, Br or I; R<4 >and R<5 >are independently selected from H, F, Cl, Br, I, OH, C1-C4 alkyl (preferably, CH3), -(CH2)n-C=C-Ra, with the proviso that R<4 >and R<5 >are not both H; Ra is H, F, Cl, Br, I, or -C1-C4 alkyl, preferably H or CH3; Y is H, F, Cl, Br, I or -C1-C4 alkyl, preferably H or CH3; and n is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, preferably 0, 1 or 2; and their anomers, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, or polymorphs thereof.
Owner:YALE UNIV
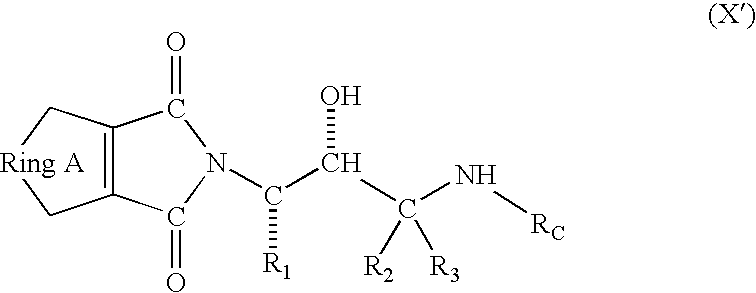
Compounds to treat alzheimer's disease
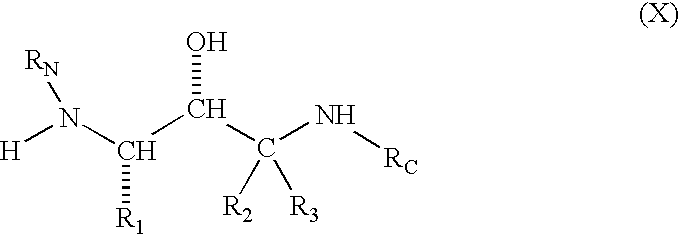
The present invention is substituted amines of formula (X) 1 and of the formula (X') 2 useful in treating Alzheimer's disease and other similar diseases.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO +1
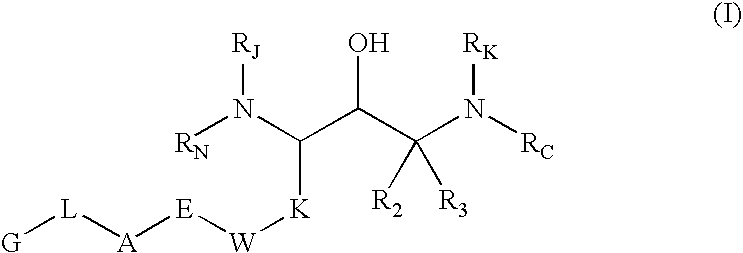
Substituted hydroxyethylamines
InactiveUS7312360B2Preventing and delaying onsetPrevent and delayBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseEnzyme
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC +1
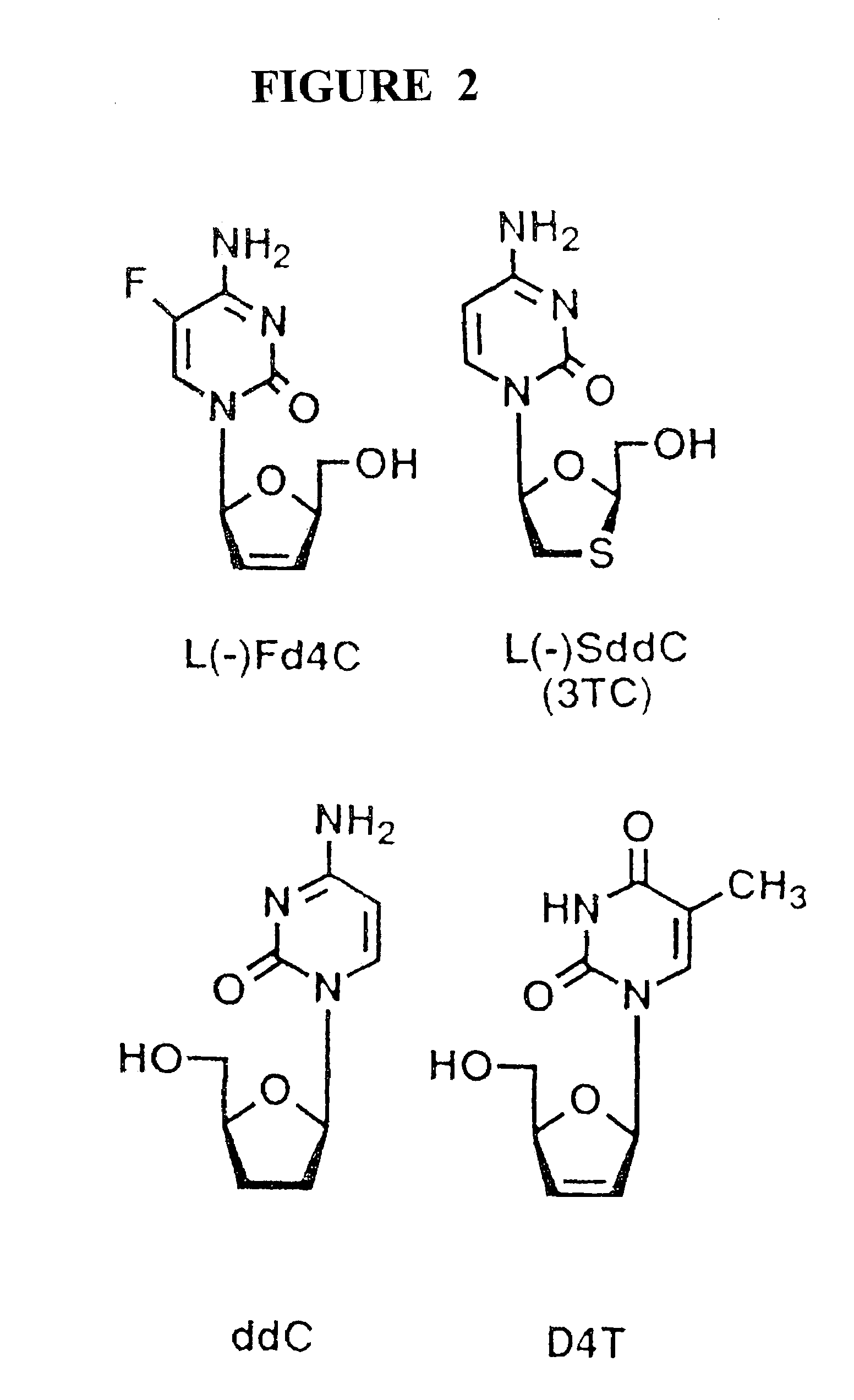
Anti-viral nucleoside analogs and methods for treating viral infections, especially HIV infections
ActiveUS7589078B2Preventing and delaying onsetReduce and prevent likelihoodBiocideSugar derivativesMedicineViral infection
The present invention relates to compounds according to the general formula:wherein B isorand the remaining variables are defined in the specification, and compositions comprising the compounds. The compounds are useful as anti-viral agents in viral therapy.
Owner:YALE UNIV
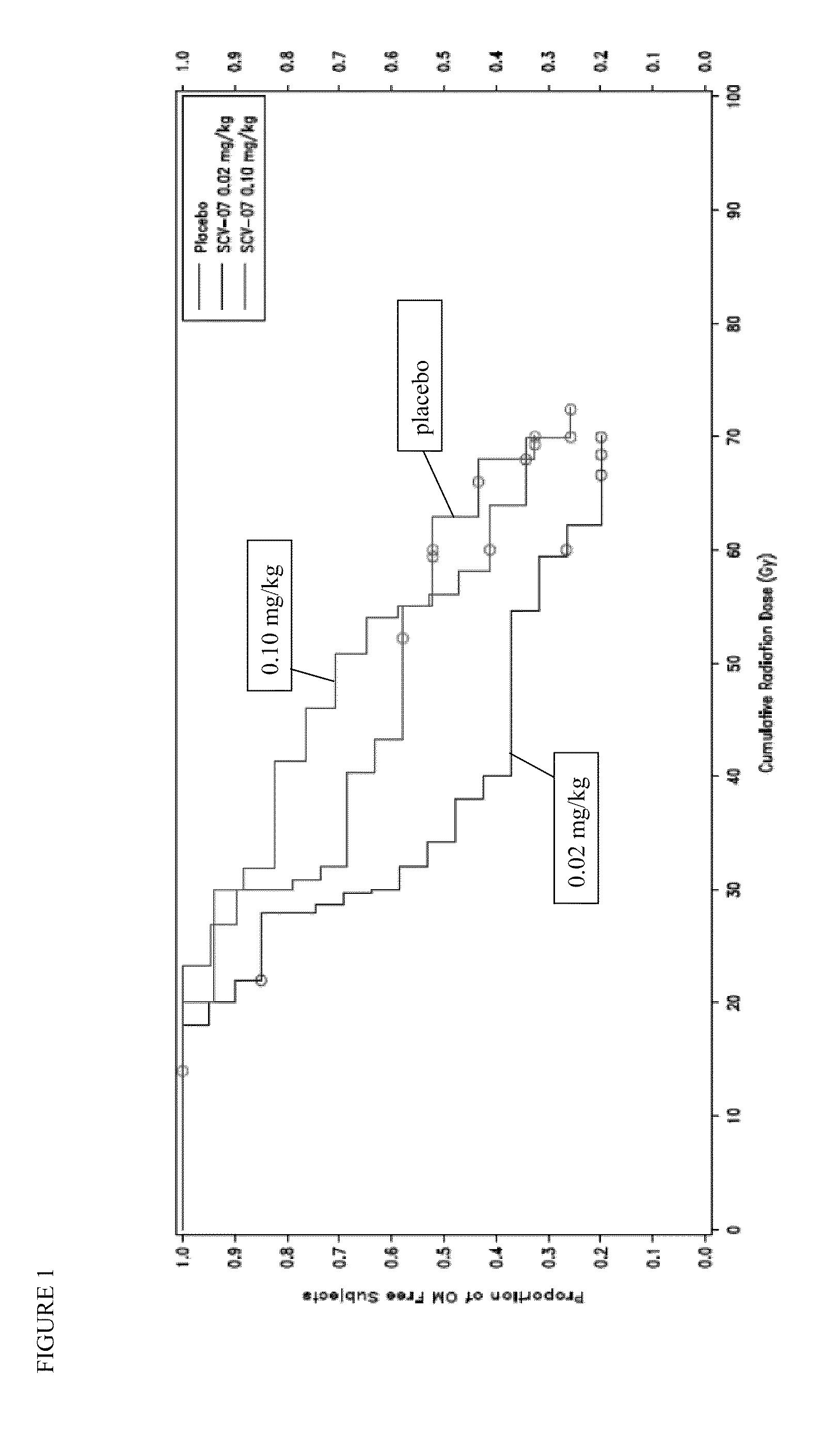
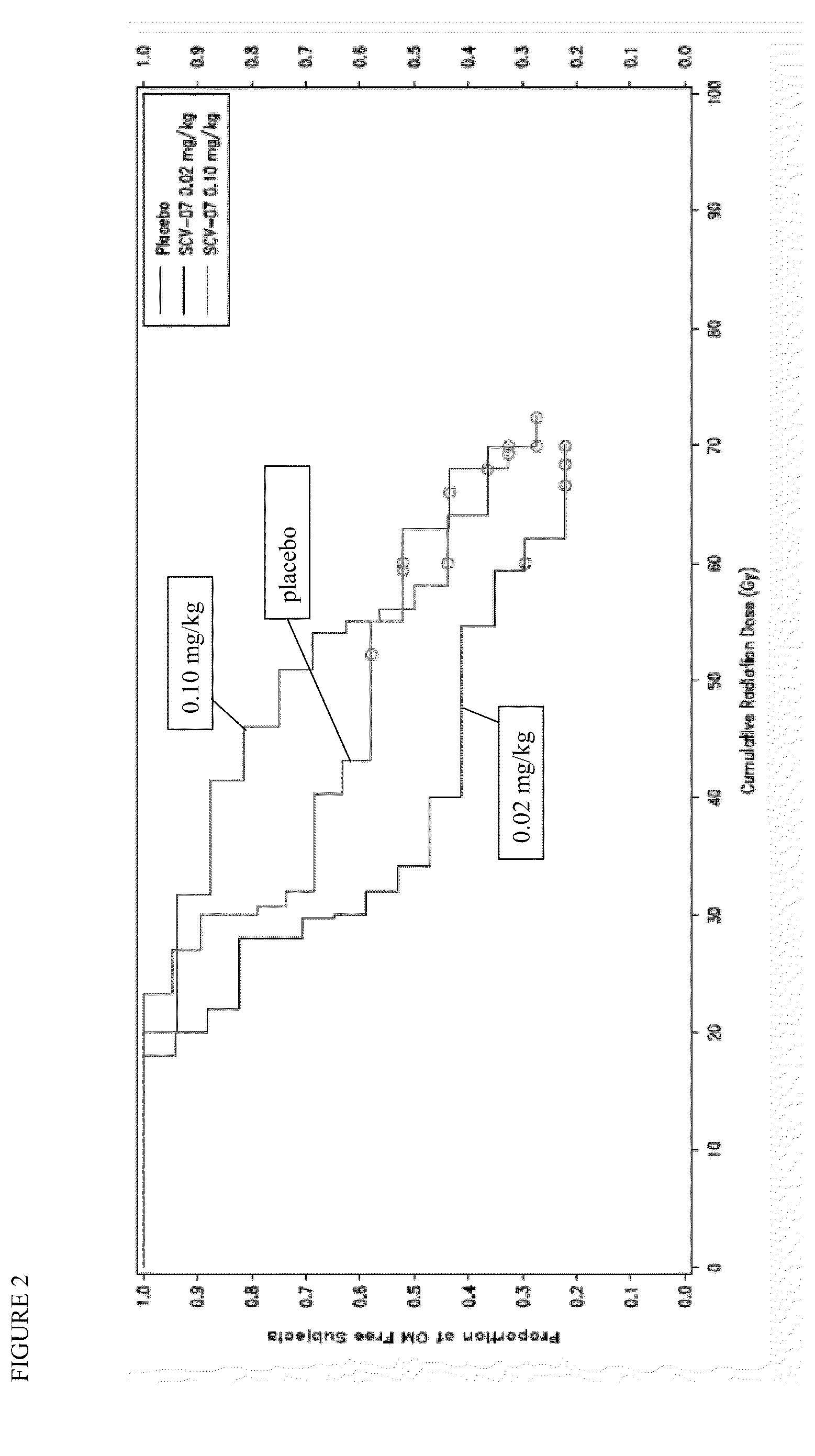
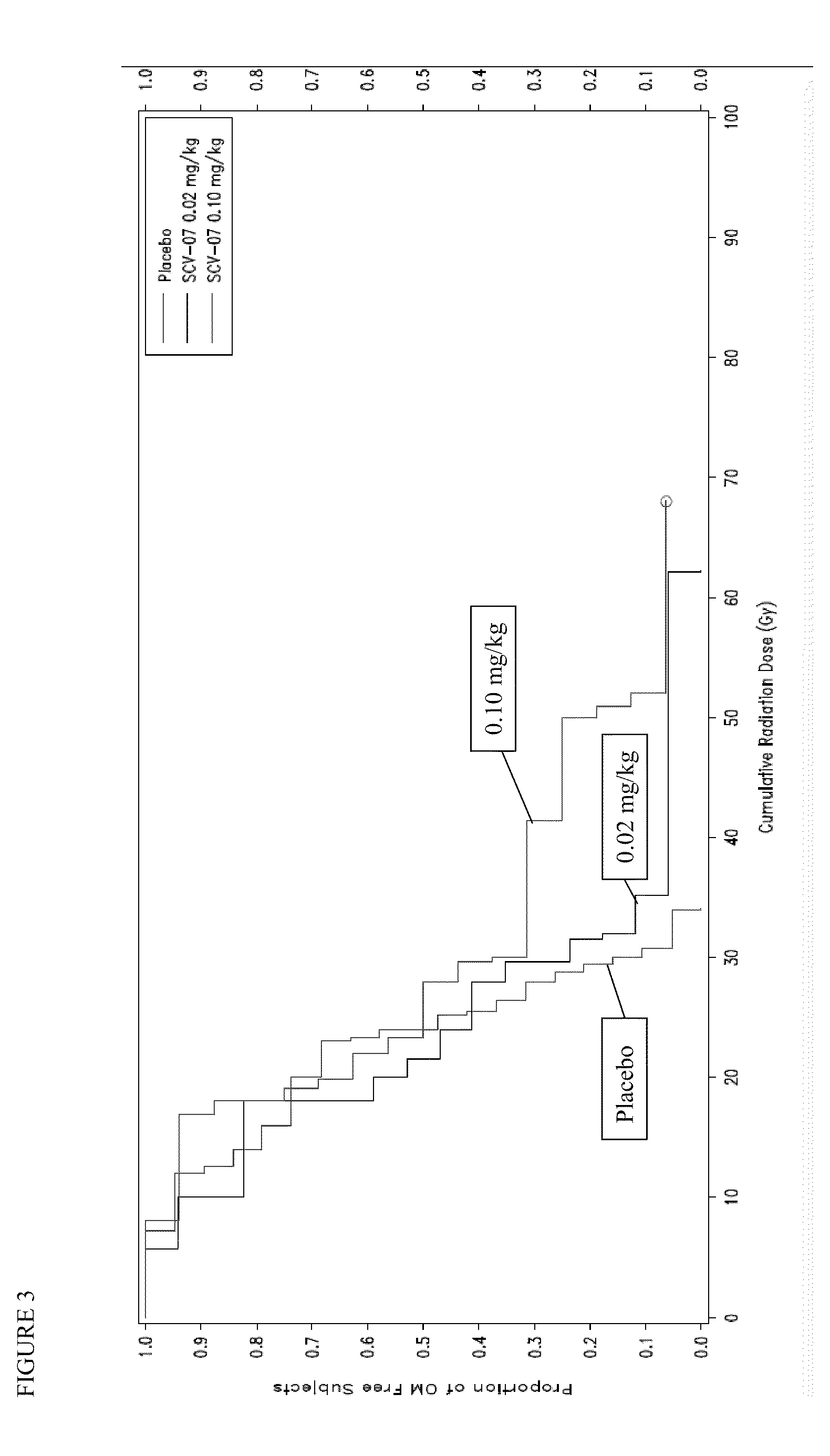
Prevention or delay of onset of oral mucositis
InactiveUS20110245316A1Prevents and delays onsetSatisfactory nutritional stateAntibacterial agentsBiocideRegimenPhysiology
The present invention provides a method for preventing or delaying the onset of oral mucositis, including the onset of ulcerative or severe OM, in a patient receiving cancer therapy. The method comprises administering to the patient an effective regimen of γ-D-glutamyl-L-tryptophan (SCV-07) over the course of therapy. The regimen, which includes scheduled doses of SCV-07 with respect to radiation exposure and / or chemotherapy, is effective for preventing or delaying the onset of OM. In accordance with the invention, the patient is more able to complete the planned course of cancer therapy (including chemotherapy and / or radiation therapy), by maintaining a sufficient nutritional state, and by avoiding the significant pain and discomfort associated with OM.
Owner:SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICAL INC
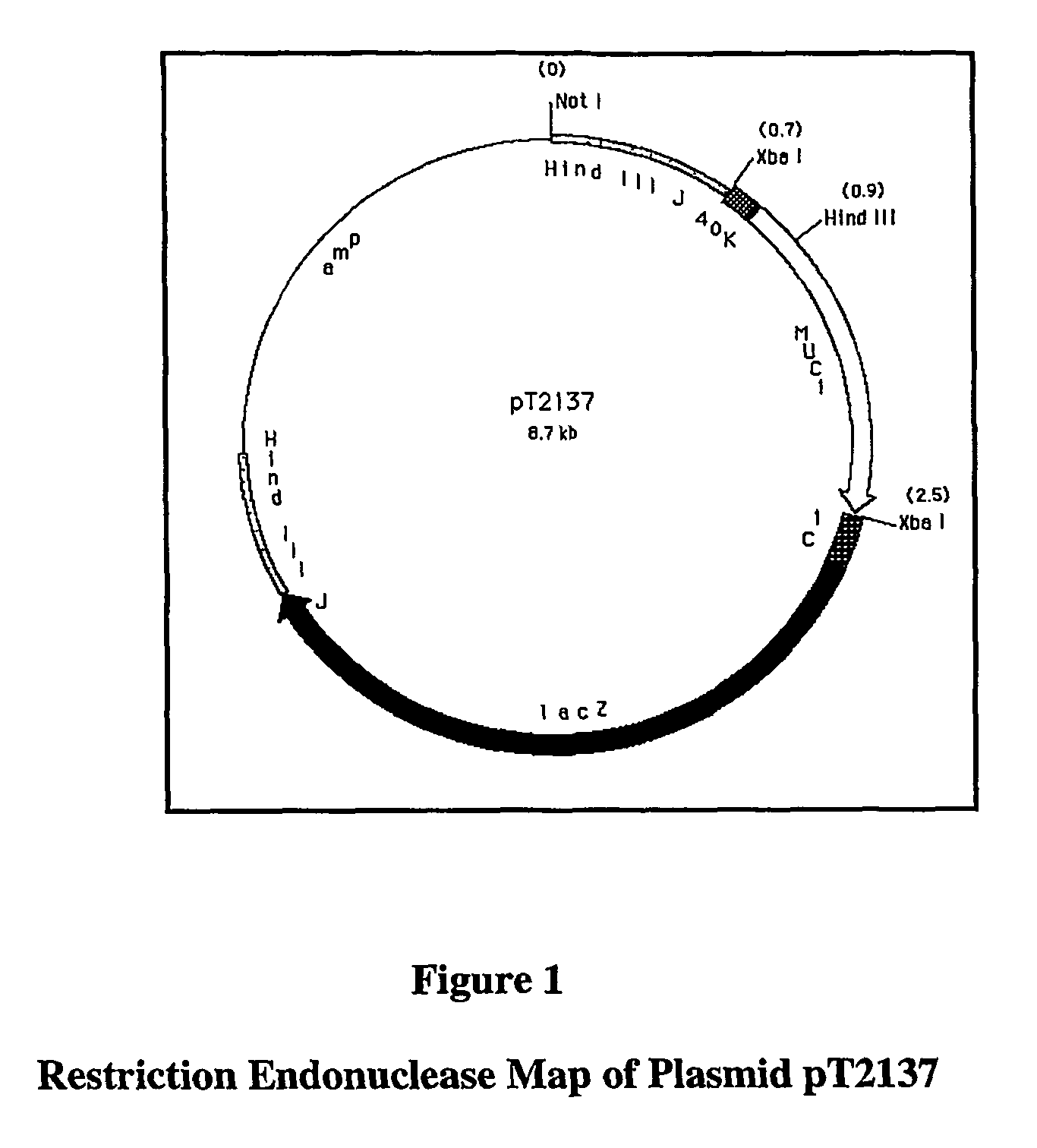
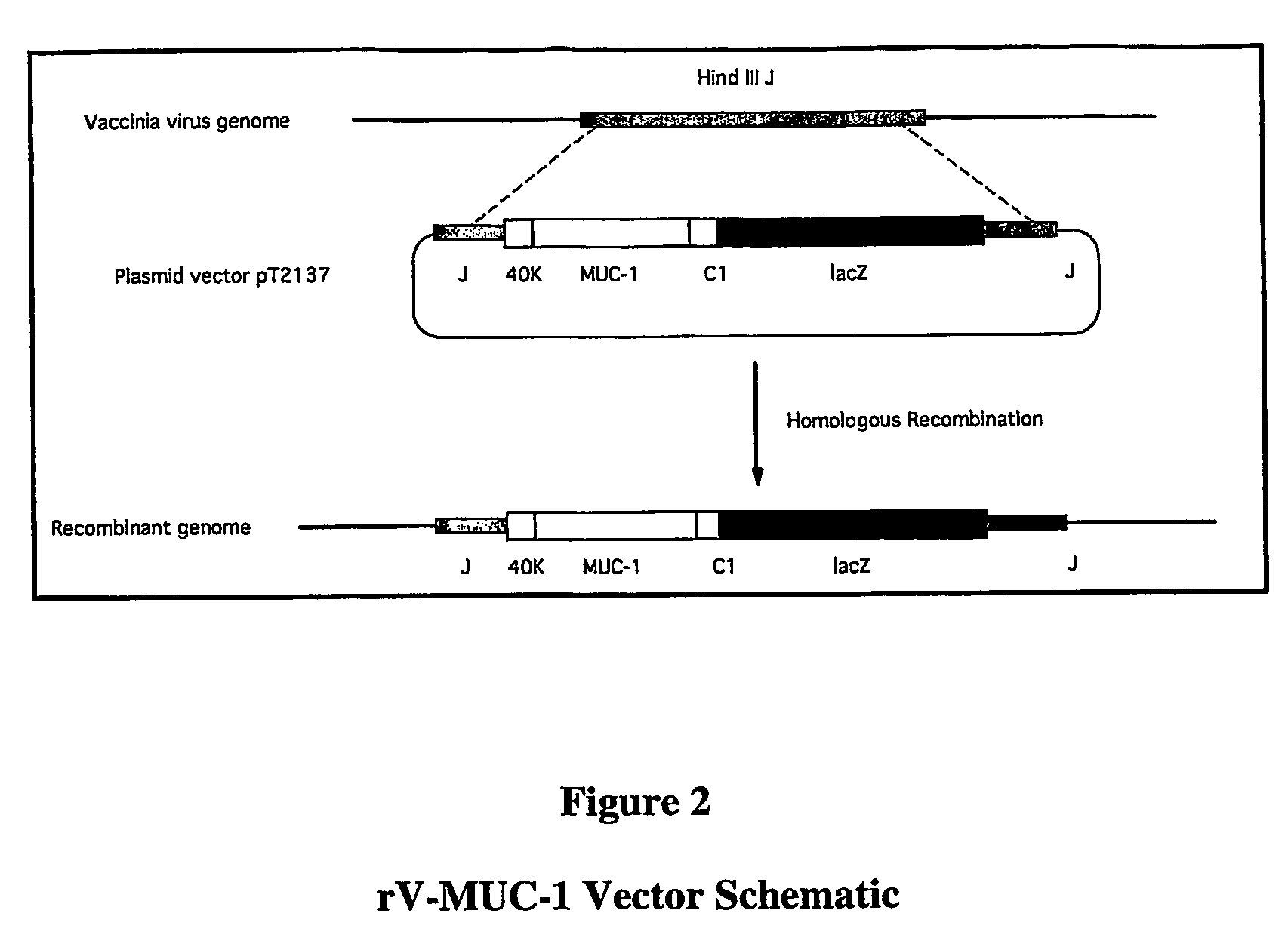
Custom Vectors for Treating and Preventing Pancreatic Cancer
ActiveUS20080166367A1Improve abilitiesPreventing and delaying onsetSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsAntigenOncology
The present invention is directed to a system for treating individuals at risk of developing or suffering from pancreatic cancer. The system comprises administering to the individual a recombinant poxvirus, where the poxvirus contains a foreign nucleic acid encoding at least one pancreatic tumor associated antigen (PTAA).
Owner:REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Treatment of opthalmic diseases
Owner:MIGENIX CORP
Method and composition for treating sarcopenia
PendingUS20180326026A1Reduce the total massDecline in muscle functionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansVertebrate antigen ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
A method of treating sarcopenia comprises immunizing a subject in need thereof against AGE-modified proteins or peptides of a cell. Immunizing a subject includes administering a vaccine that comprises an AGE antigen. Vaccines against AGE-modified proteins or peptides contain an AGE antigen, an adjuvant, optional preservatives and optional excipients.
Owner:SIWA CORP (US)
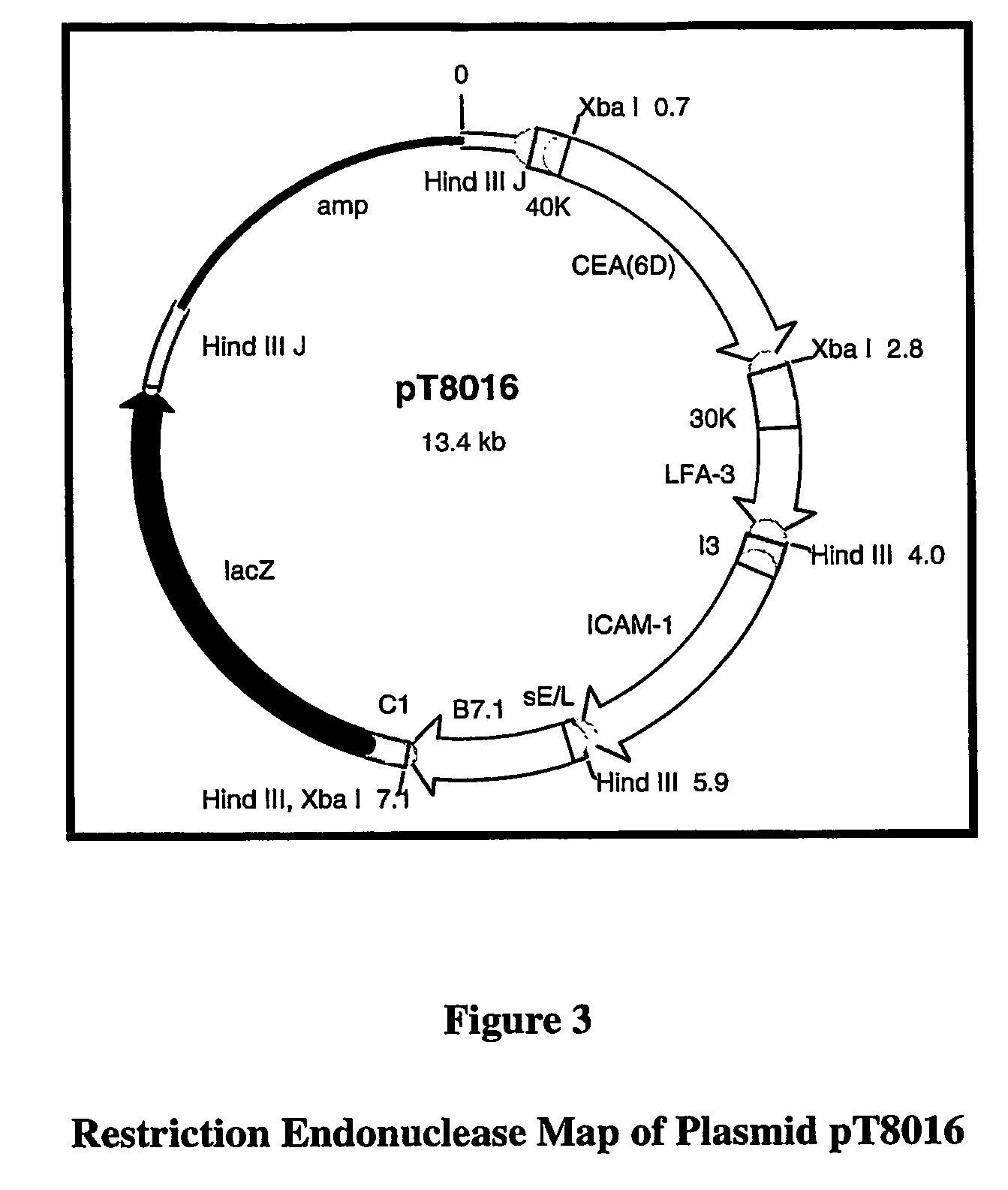
System for treating and preventing breast cancer
The present invention is directed to a system for treating individuals at risk of or suffering from breast cancer. The system comprises administering to the individual a recombinant poxvirus, where the poxvirus contains in a foreign nucleic acid encoding at least one breast cancer antigen.
Owner:THE GOVERMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES (SEE PF37) +1
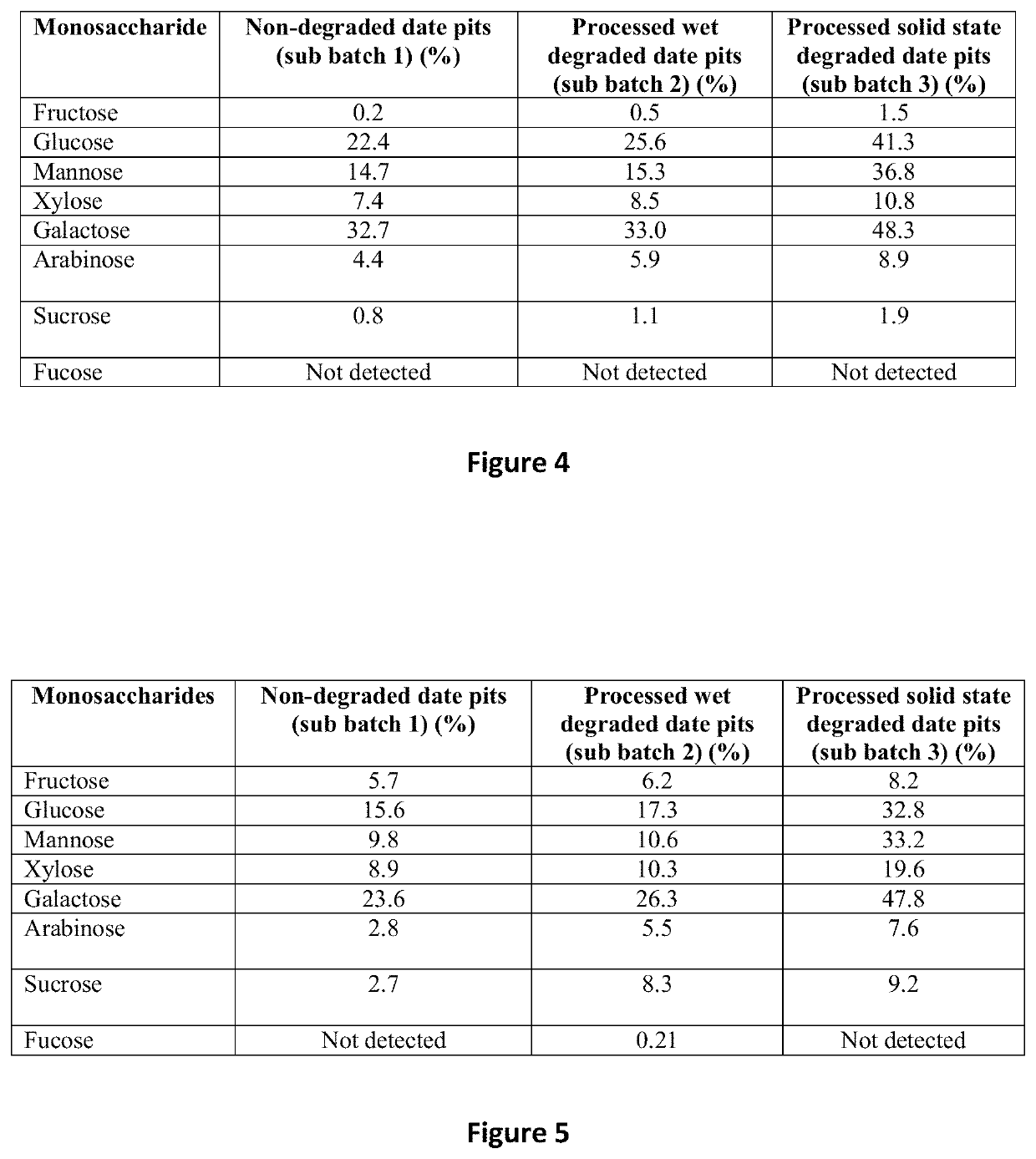
Antibacterial Peptide and Method of Treatment Using the Antibacterial Peptide
ActiveUS20170246240A1Treat and prevent bacterial infectionPreventing and delaying onsetPeptide/protein ingredientsFood processingStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
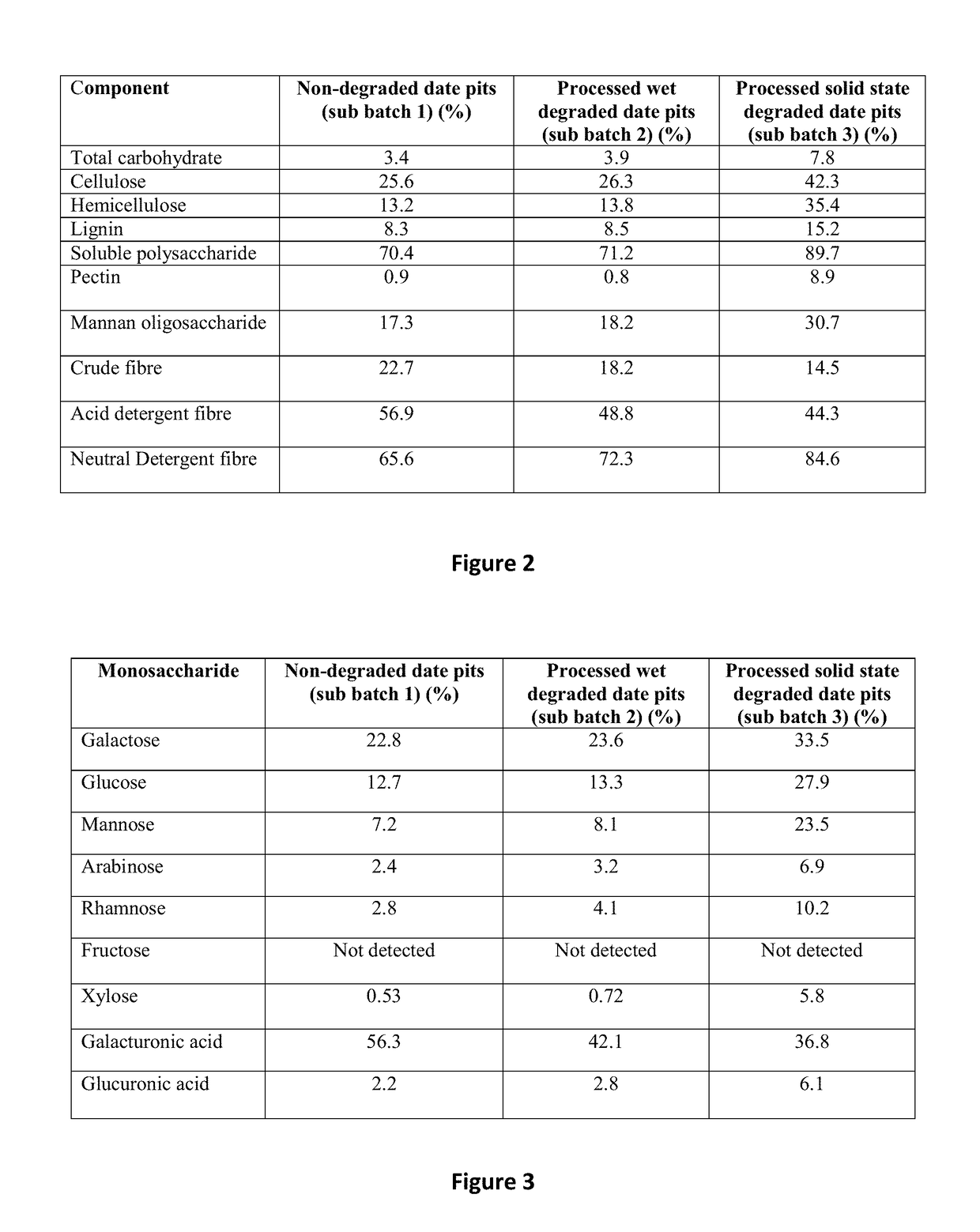
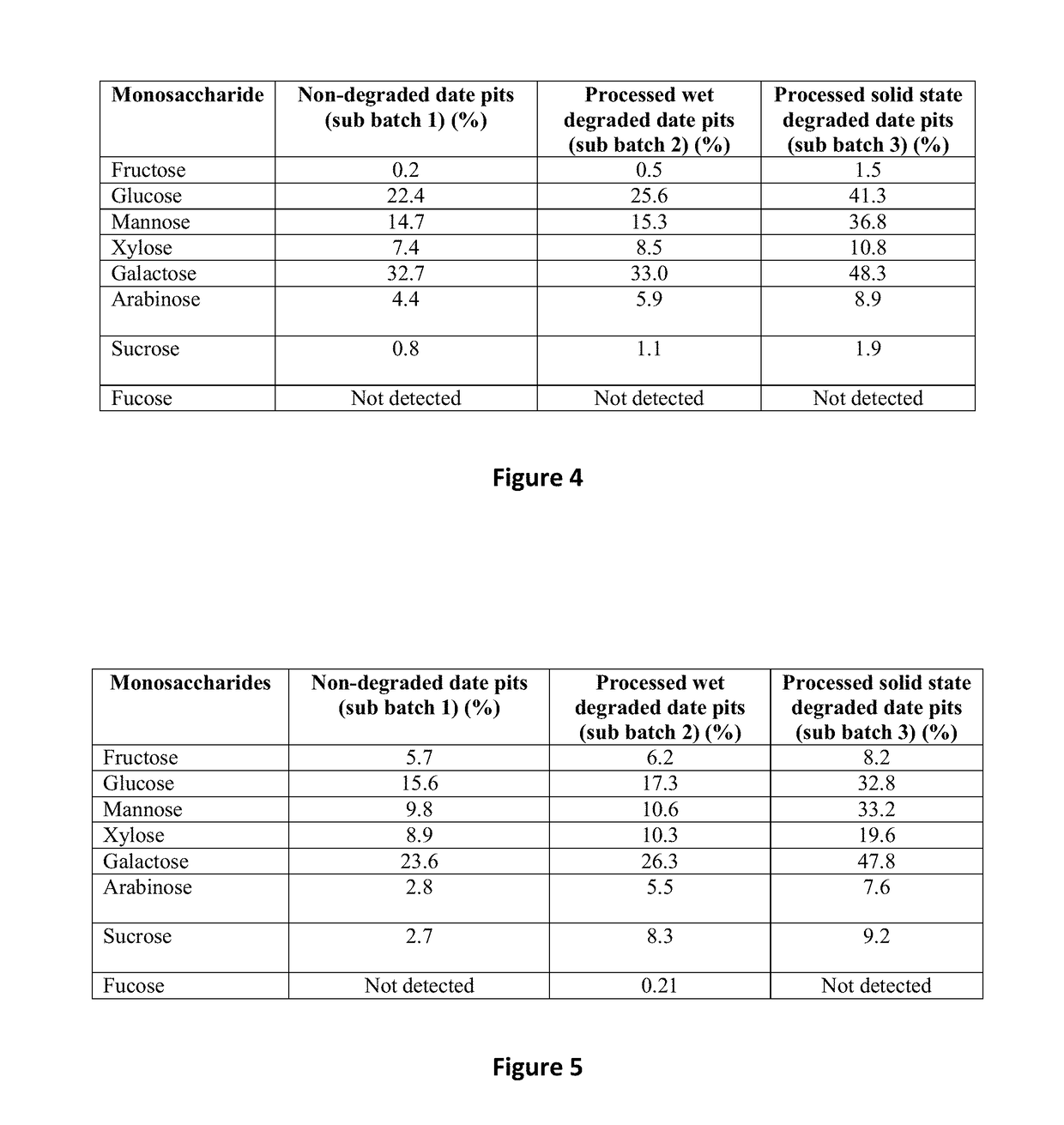
A method of treating or preventing a bacterial infection in an animal comprises administering to the animal an effective amount of an antibacterial peptide, the antibacterial peptide being derived from degraded date pits which are degraded by solid state degradation by a fungus, Trichoderma reesei. The antibacterial peptide has a molecular mass of less than 10 kDa and an amino acid sequence including (a) SEQ ID NO:4 or (b) SEQ ID NO:6. The bacterial infection is caused by a Gram-positive bacteria or a Gram-negative bacteria, for example, a Salmonella species, a Campylobacter species, a Shigella species, an Escherichia species, a Pseudomonas species, and a Staphylococcus species.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Formulations and methods for treatment of metabolic syndrome
ActiveUS20160213694A1Reduced pill burdenImprove efficacyPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsHypertension medicationsDisease
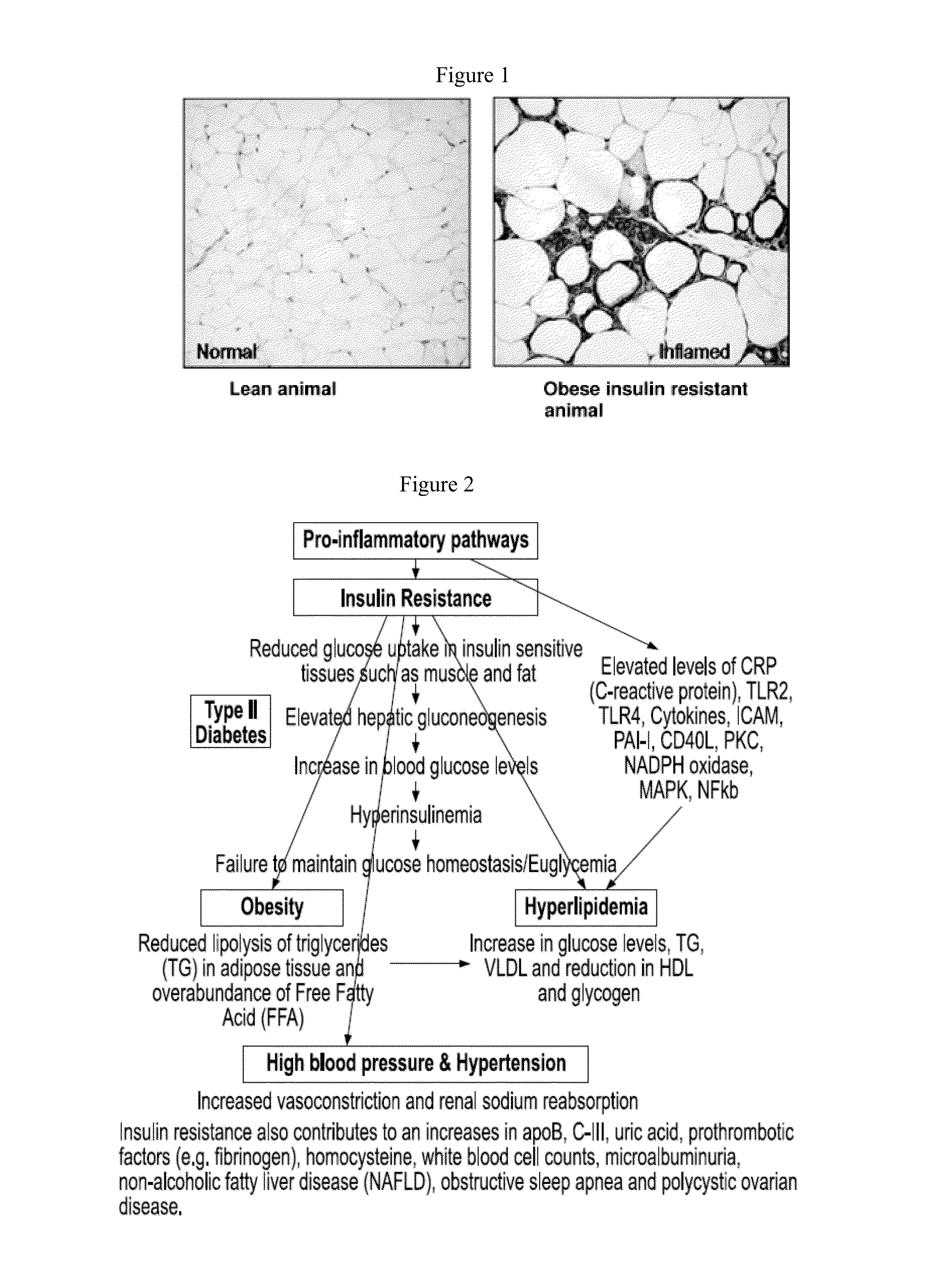
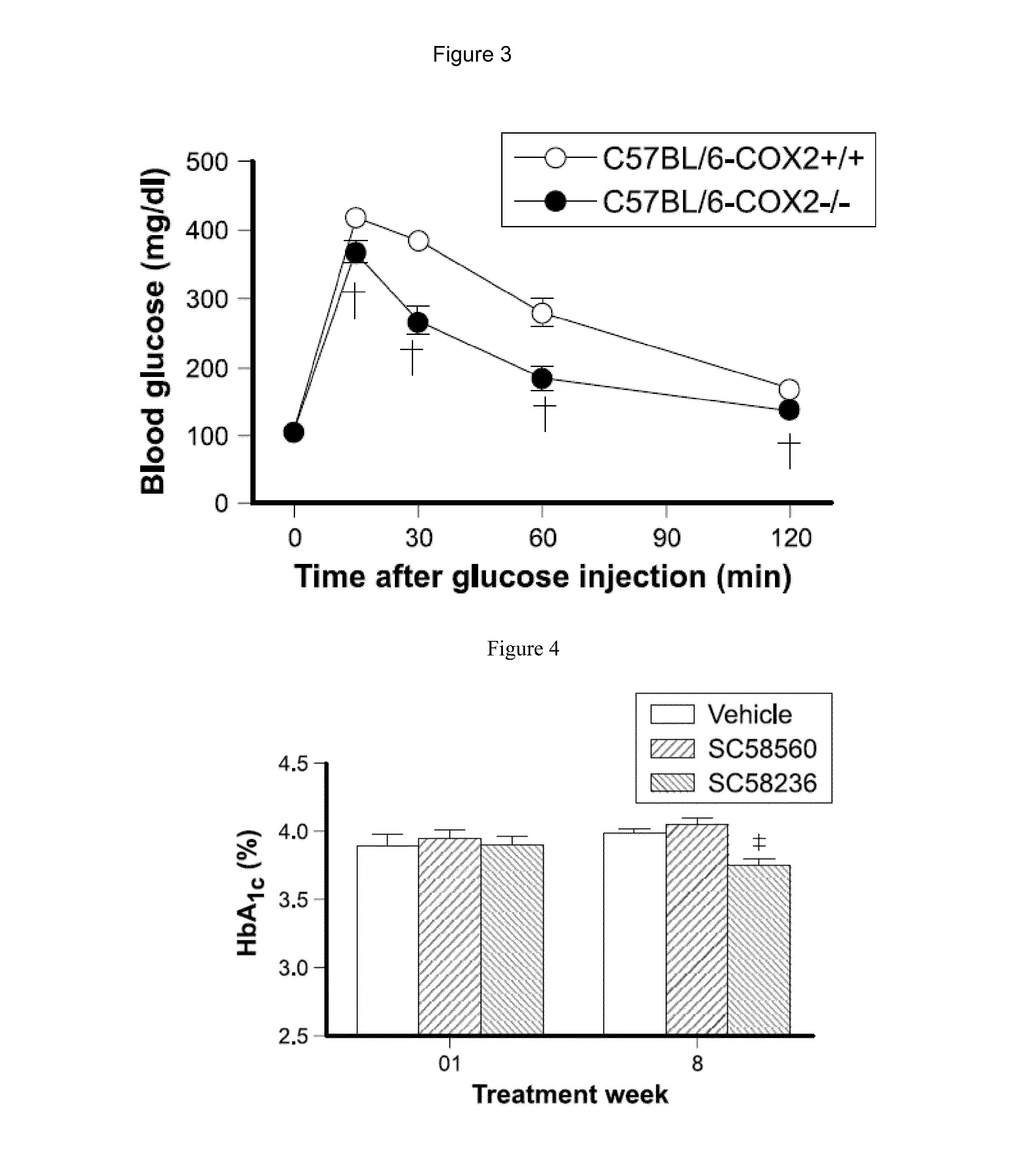
Formulations and methods of providing an orally-active anti-metabolic disease Fixed Dose Combinations (FDC) for use as personalized medicine to treat different components of the Metabolic Syndrome or Insulin resistance syndrome such as Type II diabetes, Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia and Obesity are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions of anti-inflammatory and pancreatic beta-cell centric drug formulations and methods comprising of NSAIDS in general and selective Cox-2 inhibitors in particular and one or more anti-T2DM or anti-hypertensive or anti-hyperlipidemic or anti-obesity drugs formulated to exhibit pre-determined modified release kinetics to achieve therapeutic as well as kinetic synergies are disclosed.
Owner:ARKAY THERAPEUTICS
Substituted hydroxyethylamines
InactiveUS20060106256A1Preventing and delaying onsetAvoid delayNervous disorderOrganic chemistryDiseaseStereochemistry
This invention relates to prodrugs of a class of amine compounds which are useful in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and similar diseases.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Anti-viral nucleoside analogs and methods for treating viral infections, especially HIV infections
ActiveUS20100048500A1Preventing and delaying onsetReduce and prevent likelihoodBiocideSugar derivativesPharmaceutical drugViral infection
The present invention relates to novel compounds according to the general formulas I, II, III, IV or V:wherein B is nucleoside base according to the structure:and the remaining variables as defined in the specification, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds. The compounds are useful interalia as anti-viral agents in viral therapy.
Owner:YALE UNIV
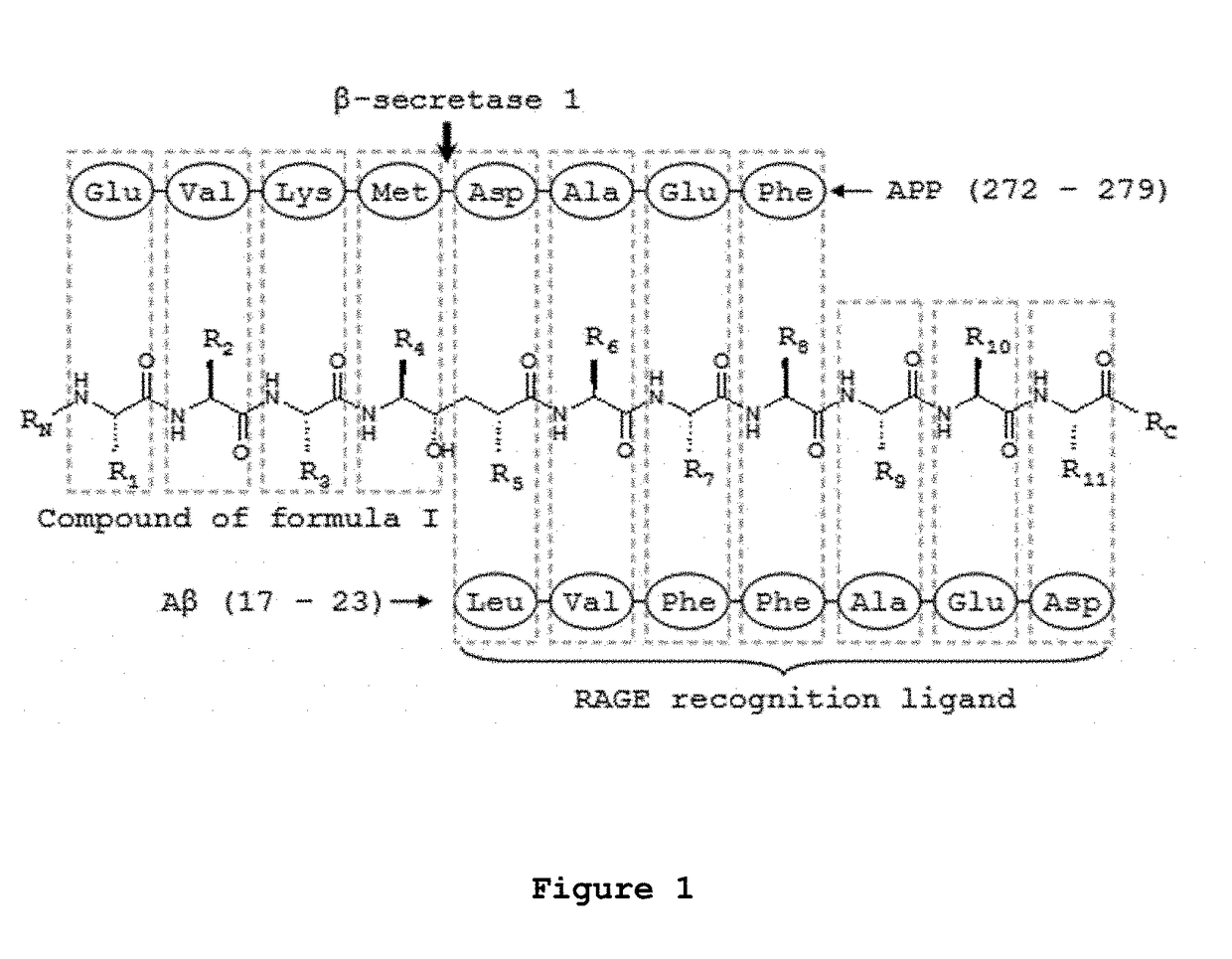
Brain permeant peptidomimetic beta-secretase 1 inhibitors for the treatment or prophylaxis of neurological disorders or conditions
InactiveUS9919021B2Preventing and delaying onsetEffective treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptides with abnormal peptide linkDiabetes mellitusAmyloid
The present application presents novel peptidomimetic substituted hydroxyethylene compounds, which are inhibitors of beta amyloid cleavage enzyme, capable to permeate the brain and to achieve therapeutic concentrations in the target organ, the brain. These compounds are incorporated in pharmaceutical compositions and applied in the treatment or prophylaxis of neurological disorders or conditions and also other disorders or conditions including Down's syndrome and diabetes.
Owner:INST DE BIOLOGIA EXPERIMENTAL E TECH IBET
System for treating and preventing breast cancer
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Date pit composition for the treatment of animals
ActiveUS8968729B2Preventing and delaying onsetReduce microbial loadAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMedicineTreated animal
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Vaccine Formulations That Induce A TH2 Immune Response
ActiveUS20160166663A1Reliable indicatorPreventing and delaying onsetNervous disorderTransportation and packagingKetoneAdjuvant
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such Alzheimer's disease, that are caused by misfolding, aggregating proteins. The compositions and methods of the present invention comprise a vaccine formulation comprising an antigen selected from the group consisting of i) amyloid-β or a peptide that has in its amino acid sequence part of the amyloid-β amino acid sequence, ii) hyperphosphorylated tau protein or one of its hyperphoshorylated peptides, or iii) a combination of antigens derived from groups i) and ii) and that are formulated with a non-acylated or deacylated, natural or synthetic, bidesmosidic triterpene glycoside carrying an aldehyde or ketone group, which acts as an adjuvant or immune agonist. These vaccine formulations are capable of stimulating a Th2 immunity or antibody response against antigens such as amyloid-β and tau derived antigens, but not a Th1 immune response.
Owner:QANTU THERAPEUTICS
Brain permeant peptidomimetic beta-secretase 1 inhibitors for the treatment or prophylaxis of neurological disorders or conditions
InactiveUS20170296618A1Preventing and delaying onsetEffective treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptides with abnormal peptide linkDiseaseAmyloid
The present application presents novel peptidomimetic substituted hydroxyethylene compounds, which are inhibitors of beta amyloid cleavage enzyme, capable to permeate the brain and to achieve therapeutic concentrations in the target organ, the brain. These compounds are incorporated in pharmaceutical compositions and applied in the treatment or prophylaxis of neurological disorders or conditions and also other disorders or conditions including Down's syndrome and diabetes.
Owner:INST DE BIOLOGIA EXPERIMENTAL E TECH IBET
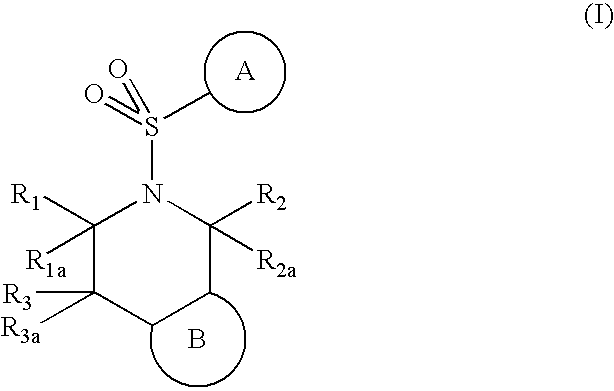
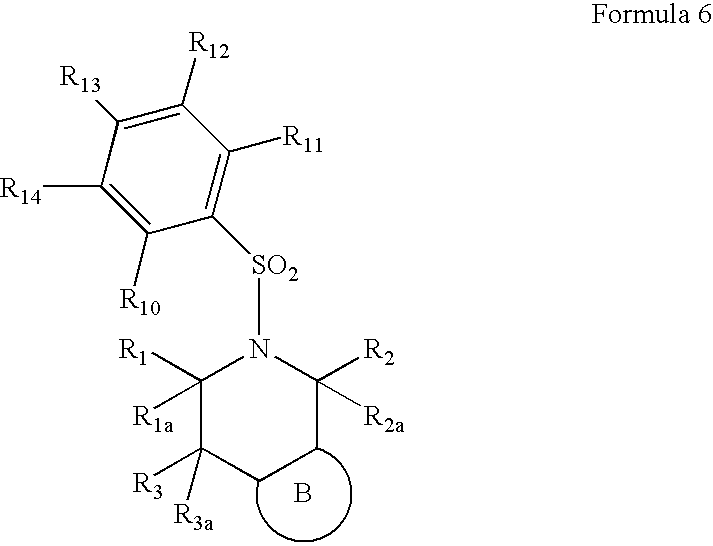
5-(arylsulfonyl)-pyrazolopiperidines
The invention provides N-cyclic sulfonamido compounds of Formula Iwherein A, B, R1, R1a, R2, R2a, R3 and R3a are as described in the specification. Compounds of Formula I are useful in treating or preventing cognitive disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease. The invention also encompasses pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds of Formula I, methods of preparing compounds of formula I, and methods of treating cognitive disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
Handlebar massage device
InactiveUS20180369063A1Preventing and delaying onsetDevices for pressing relfex pointsSteering deviceForearm musclePhysical therapy
A massage device for reducing arm pump is disclosed. The massage device includes a massage member disposed on a pair of handlebars used to steer a vehicle. The massage member can have various mounting methods to the handlebars. The massage member can include a variety of members having different dimensions and contours, and relieves the effects of arm pump when a rider presses his or her forearm against the massage device and moves it, either back and forth, or from side to side, thereby massaging the forearm muscle and relieving the effect of arm pump.
Owner:TORRES MICHAEL
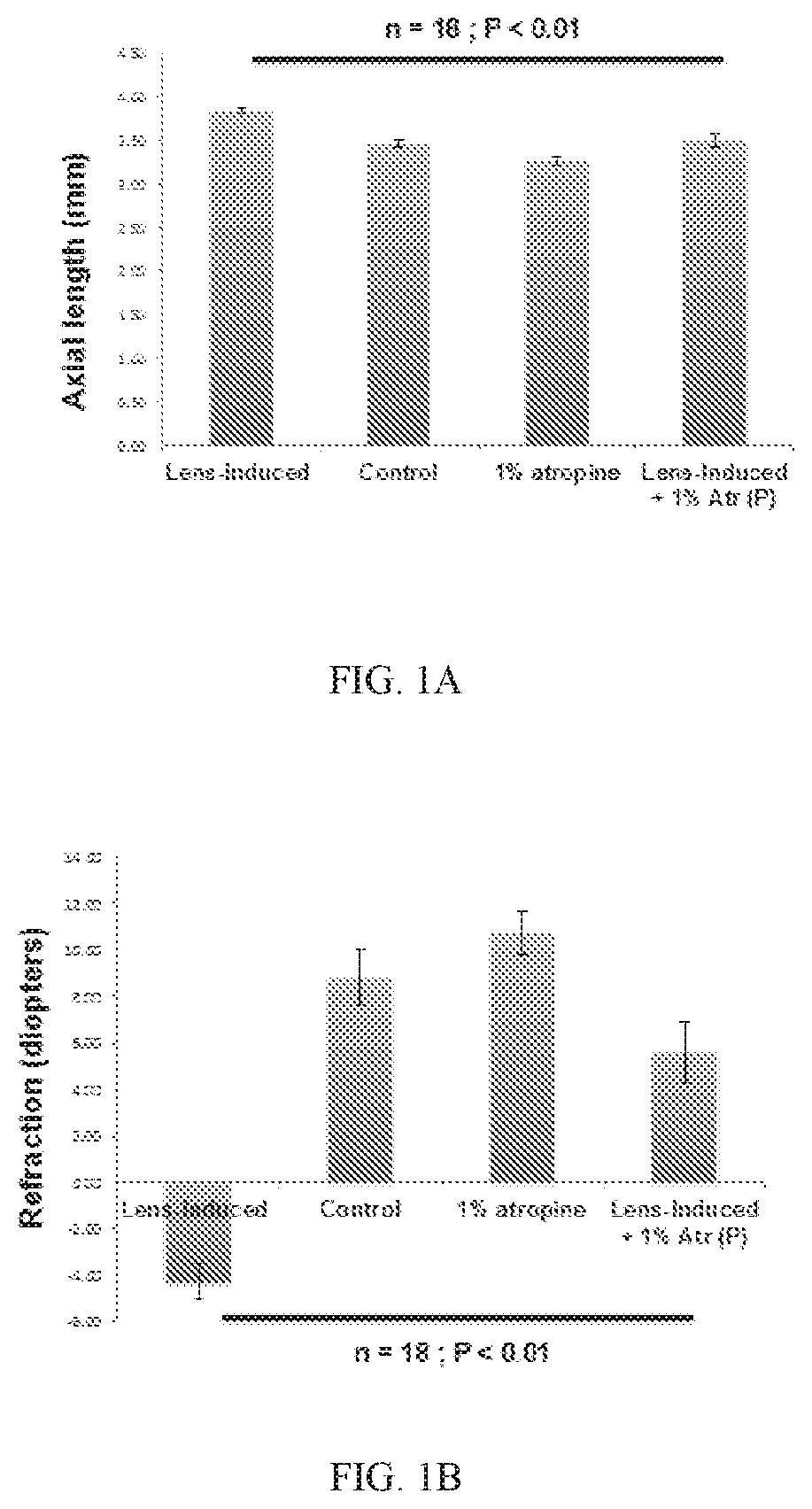
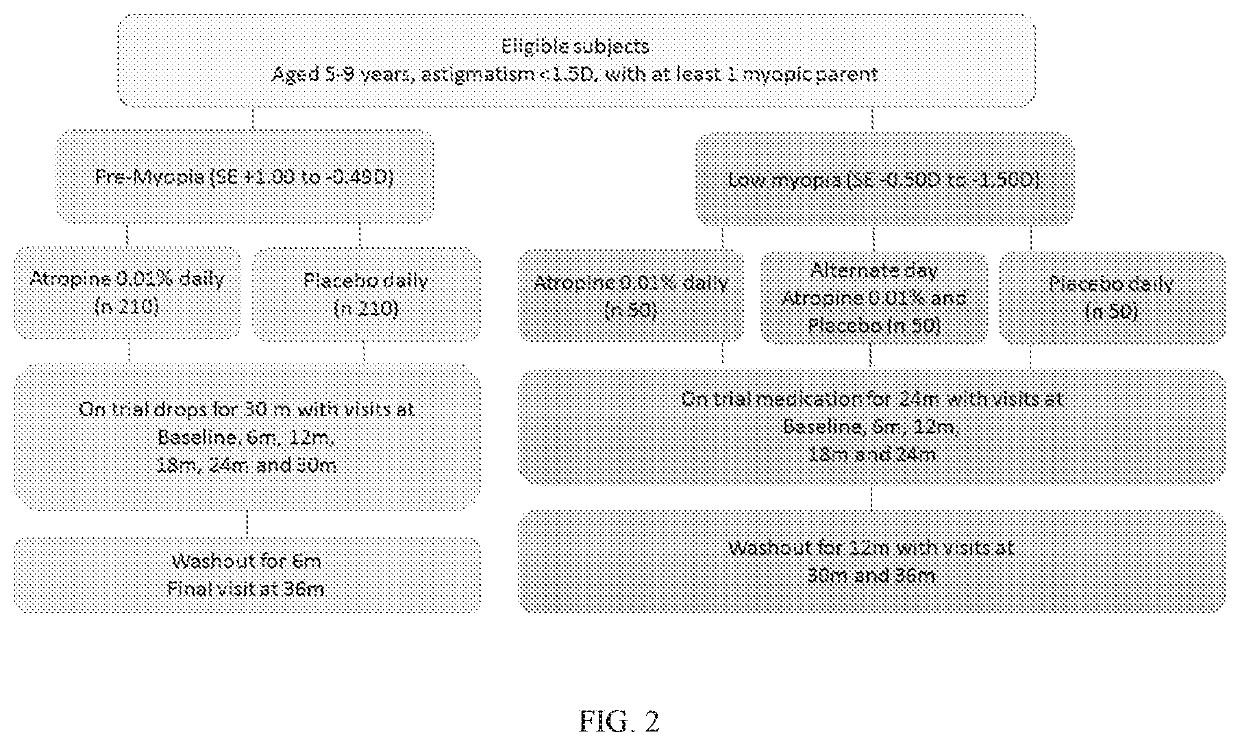
Composition and method for preventing or delaying onset of myopia comprising atropine
ActiveUS20200138801A1Prevent and delay onsetReducing and preventing progressionSenses disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOphthalmologySurgery
Methods of preventing or delaying onset of myopia in pre-myopic patients and also methods of reducing or preventing progression of myopia in patients having low myopia through the use of compositions comprising less than 0.025% of atropine are disclosed.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE
Antibacterial peptide and method of treatment using the antibacterial peptide
ActiveUS10517920B2Preventing and delaying onsetReduce microbial loadBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonasTrichoderma reesei
A method of treating or preventing a bacterial infection in an animal comprises administering to the animal an effective amount of an antibacterial peptide, the antibacterial peptide being derived from degraded date pits which are degraded by solid state degradation by a fungus, Trichoderma reesei. The antibacterial peptide has a molecular mass of less than 10 kDa and an amino acid sequence including (a) SEQ ID NO:4 or (b) SEQ ID NO:6. The bacterial infection is caused by a Gram-positive bacteria or a Gram-negative bacteria, for example, a Salmonella species, a Campylobacter species, a Shigella species, an Escherichia species, a Pseudomonas species, and a Staphylococcus species.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Custom vectors for treating and preventing pancreatic cancer
ActiveUS8901093B2Improve abilitiesPreventing and delaying onsetBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigenOncology
The present invention is directed to a system for treating individuals at risk of developing or suffering from pancreatic cancer. The system comprises administering to the individual a recombinant poxvirus, where the poxvirus contains a foreign nucleic acid encoding at least one pancreatic tumor associated antigen (PTAA).
Owner:REPRESENTED BY THE SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Materials and Methods for Reversing Type-1 Diabetes
InactiveUS20090162345A1Preventing and delaying onsetReduce and eliminate needMetabolism disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMedicineFunctional activity
Owner:ATKINSON MARK A +6
Date Pit Composition For The Treatment Of Animals
ActiveUS20130108615A1Treat and prevent bacterial infectionPreventing and delaying onsetAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMedicineTreated animal
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Type i diabetes therapy
PendingUS20200345815A1Increase productionInhibit progressOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPancreasType 1 diabetes
Owner:ST VINCENTS INST OF MEDICAL RES
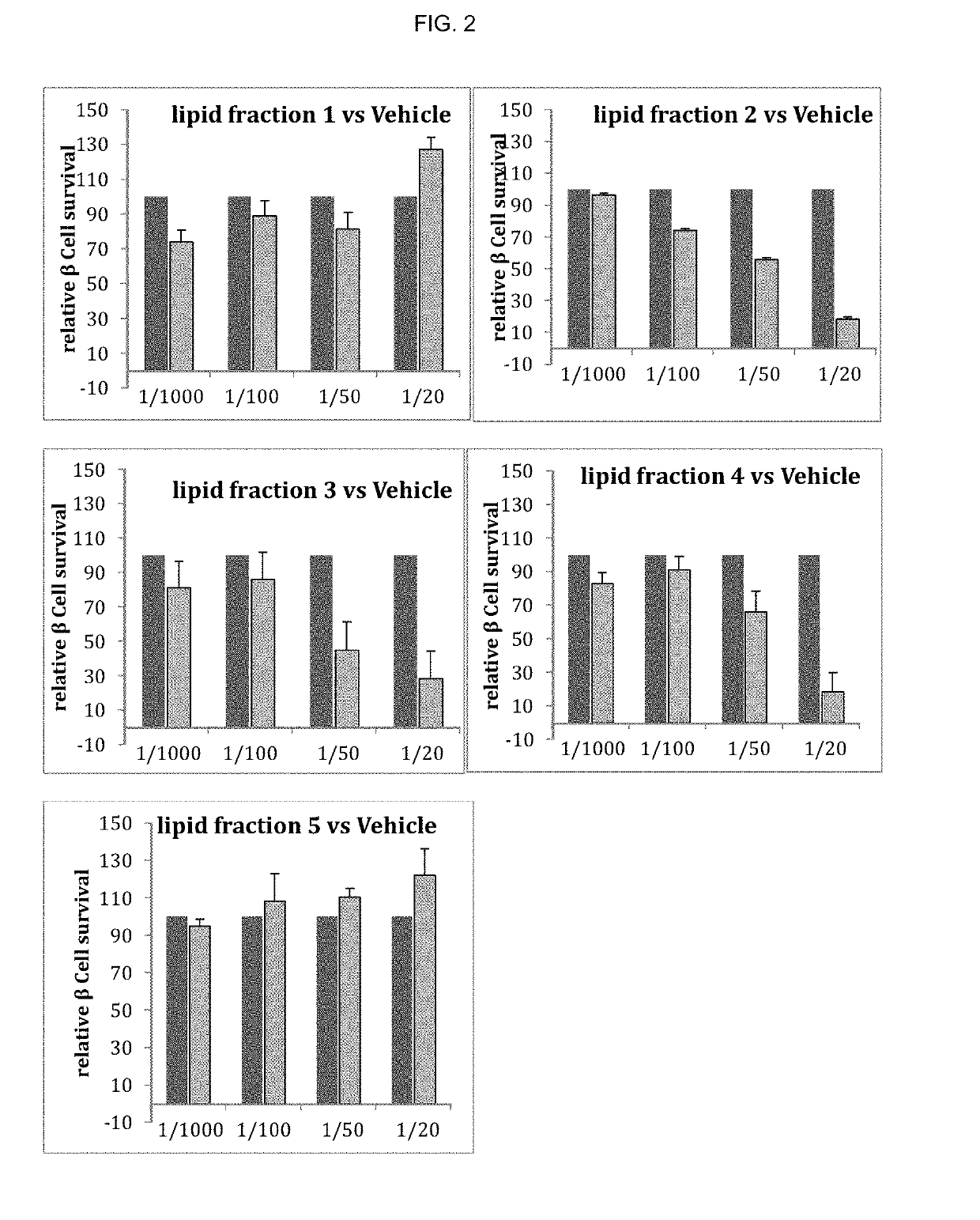
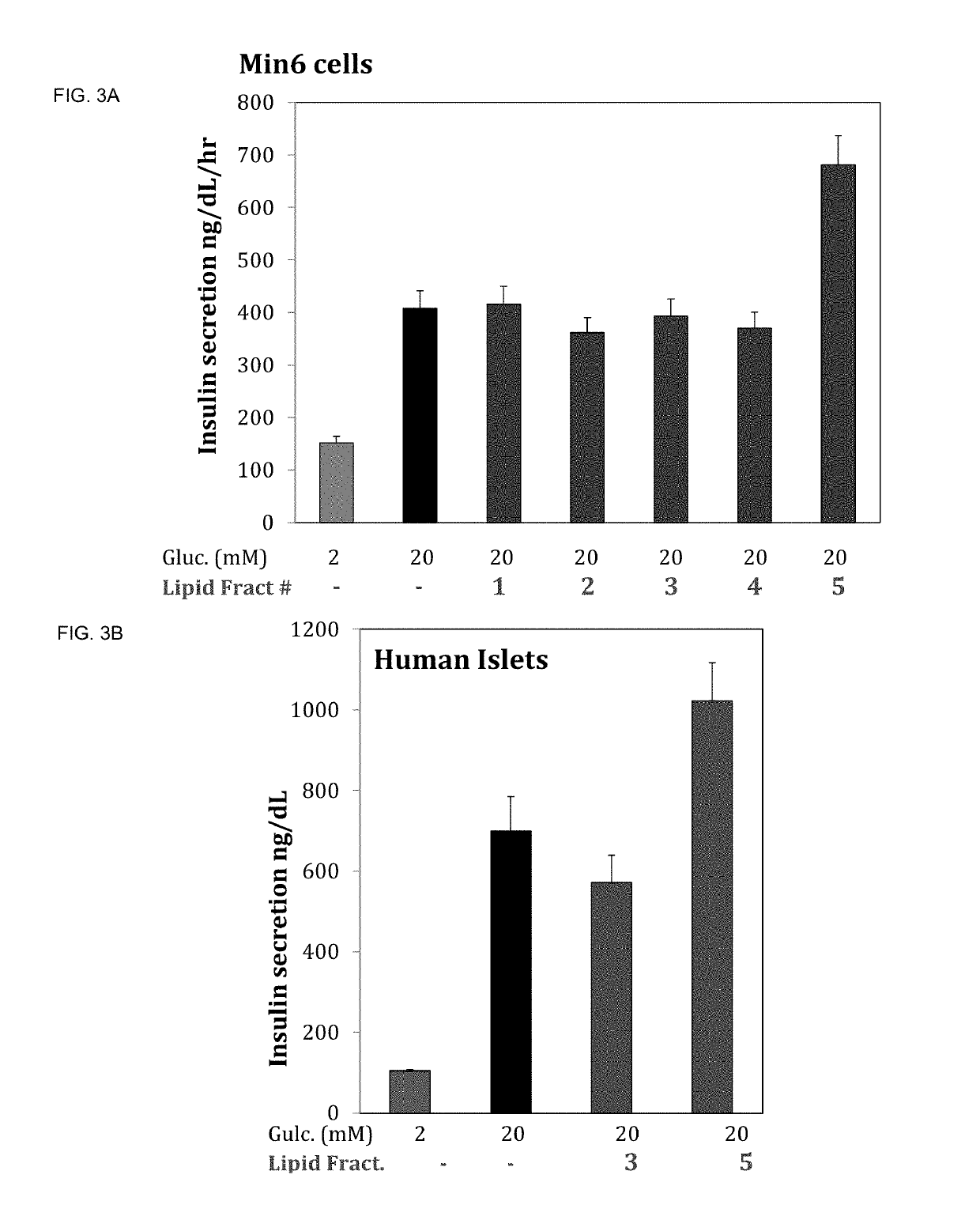
Uses of bioactive lipids
InactiveUS20190151277A1Preventing and delaying onsetImprove the level ofAntipyreticMetabolism disorderDiseaseGlycerol
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
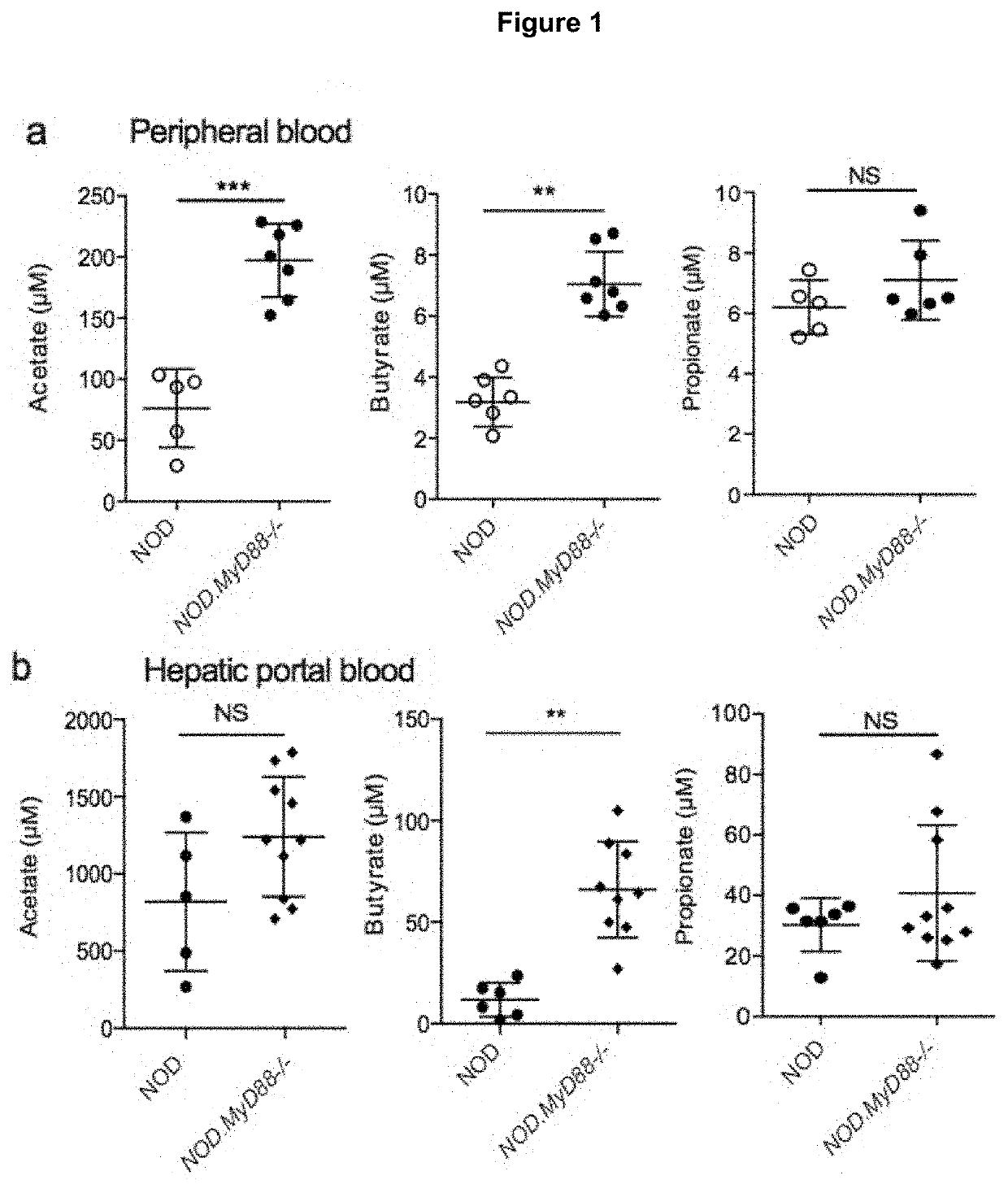
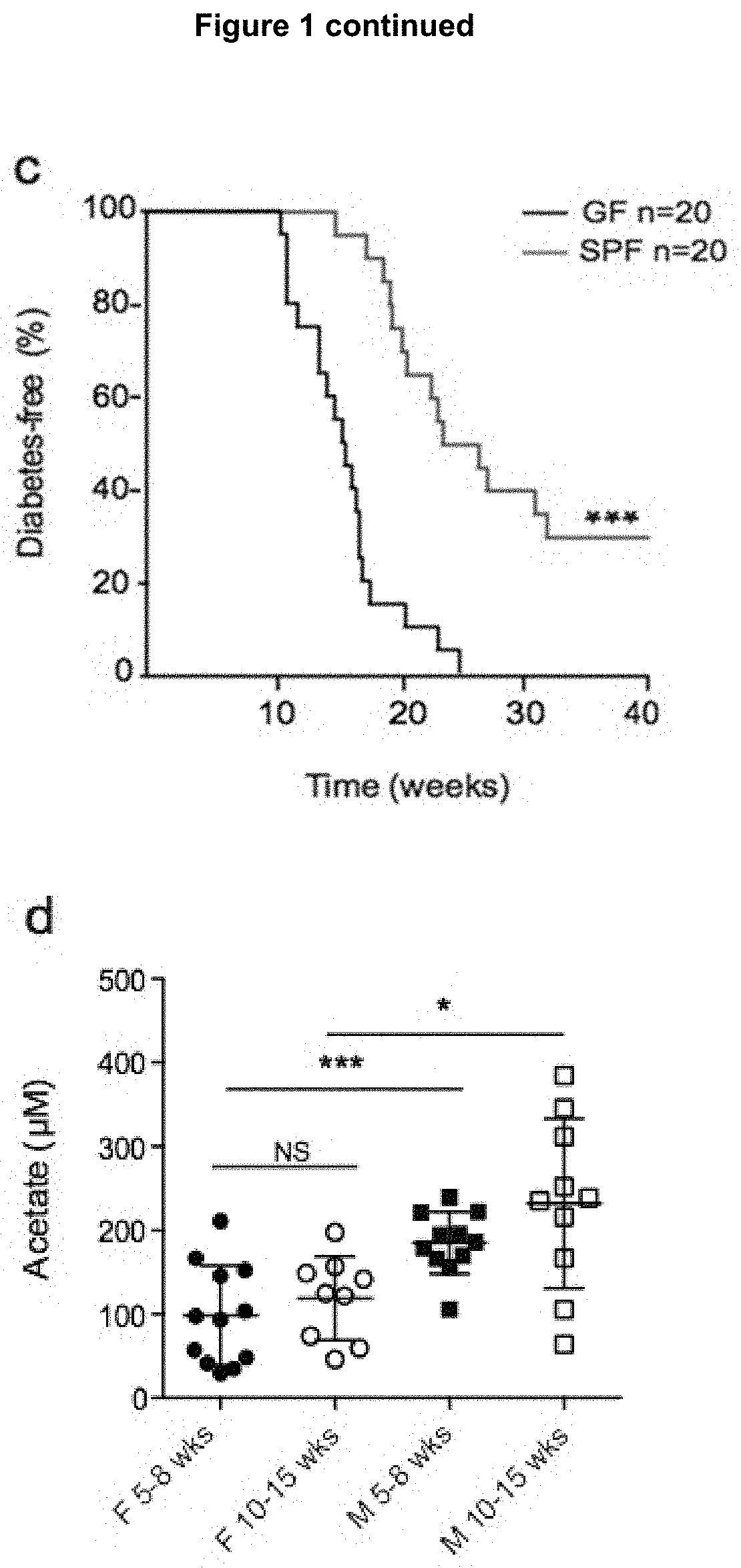
Metabolites for treatment and prevention of autoimmune disease
PendingUS20210244692A1Preventing and delaying onsetAvoid delayVitamin food ingredientsSuppositories deliveryAutoimmune conditionMetabolite
Owner:MONASH UNIV +1
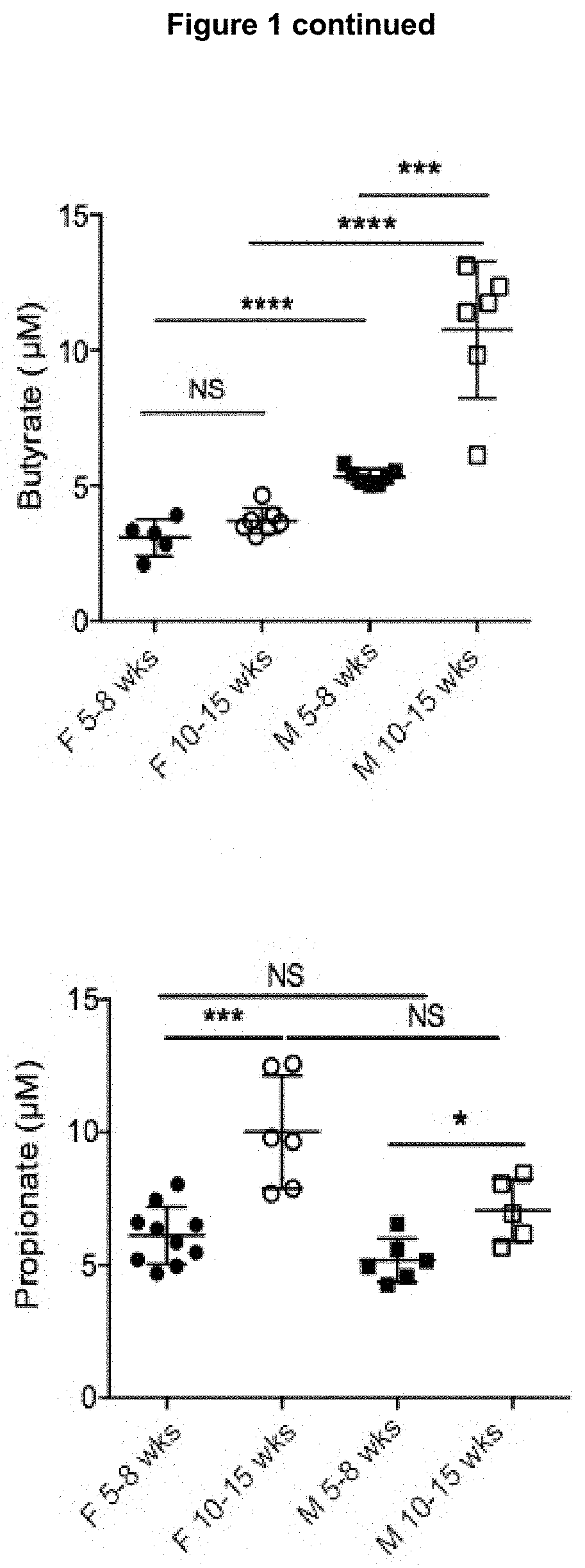
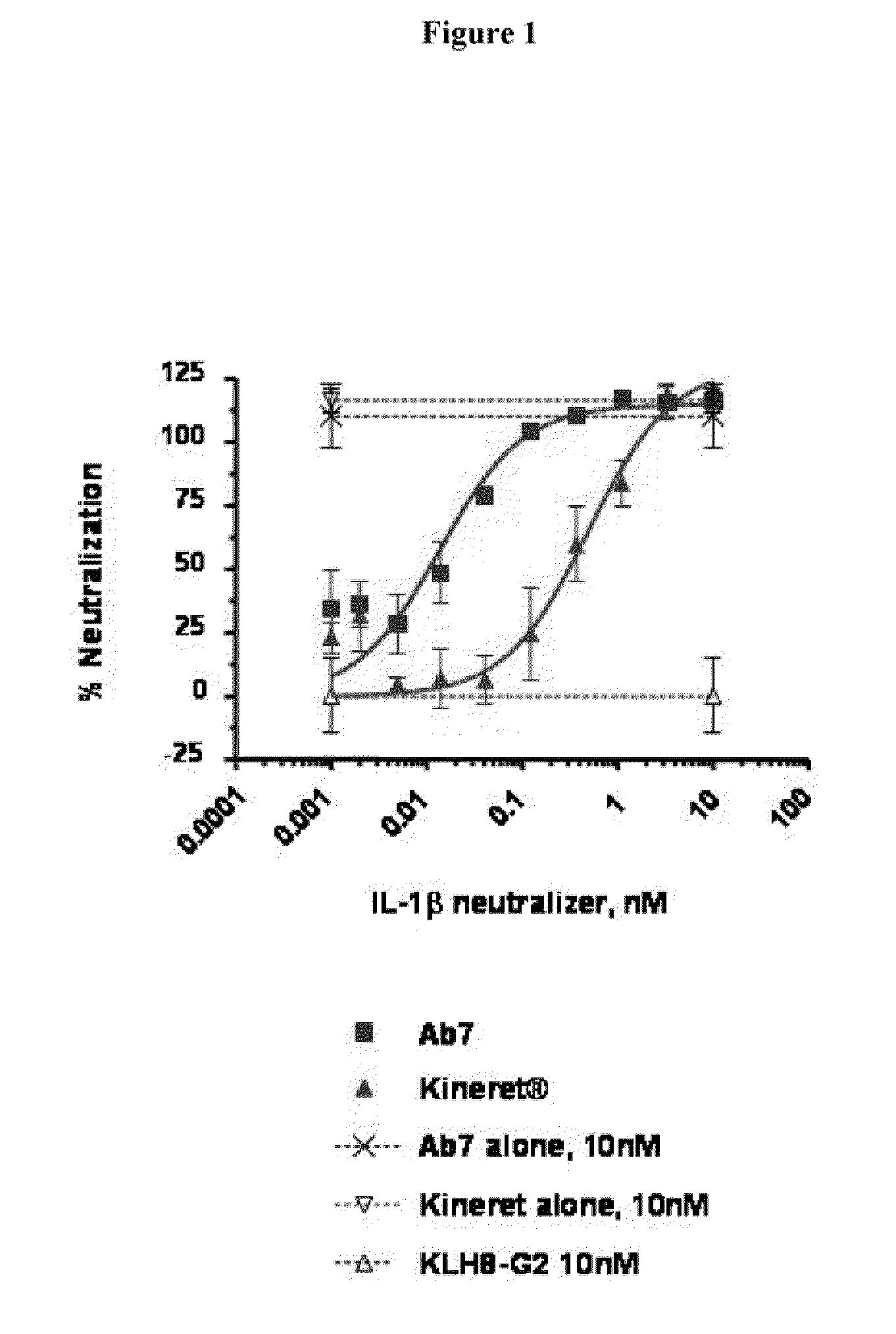
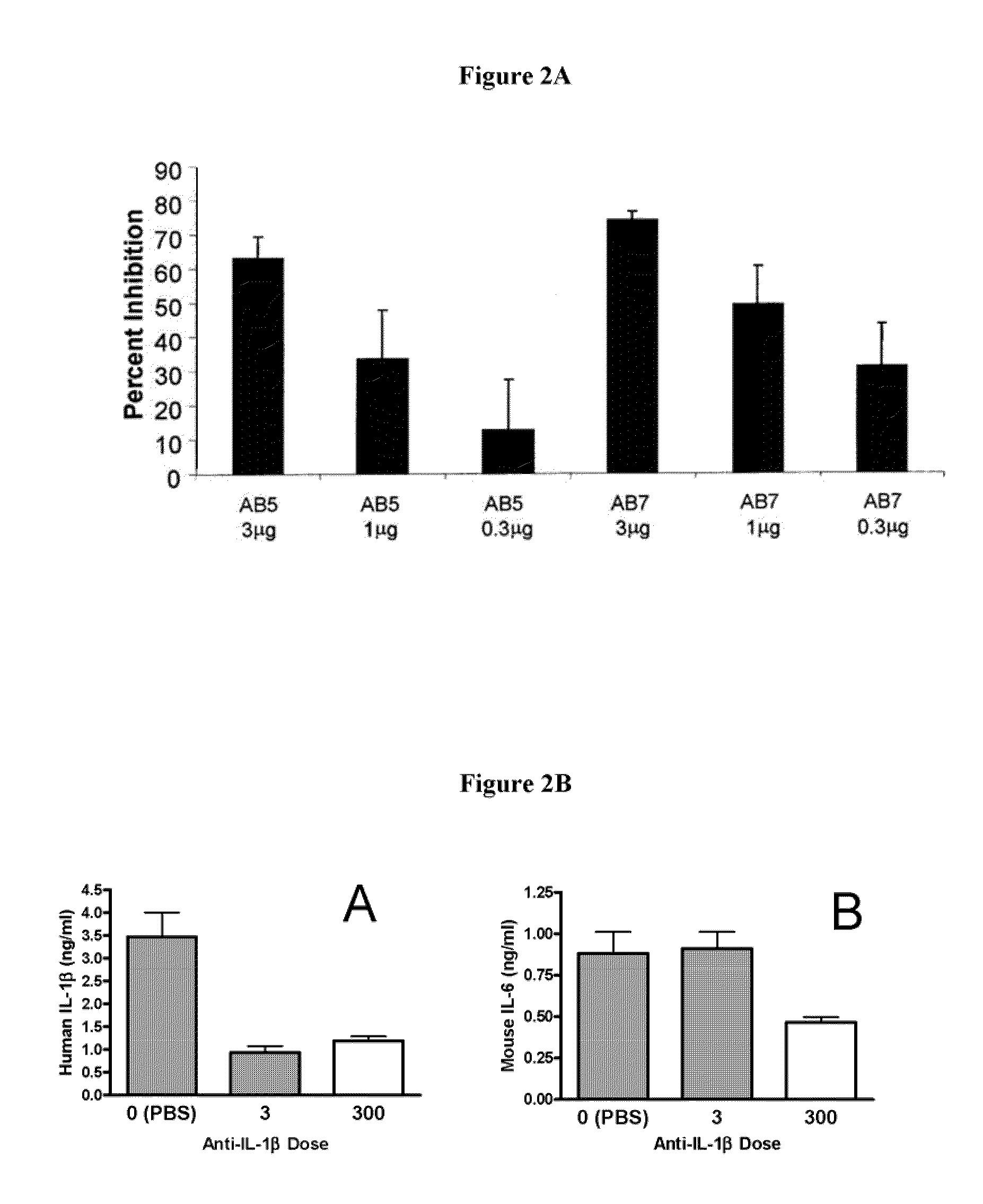
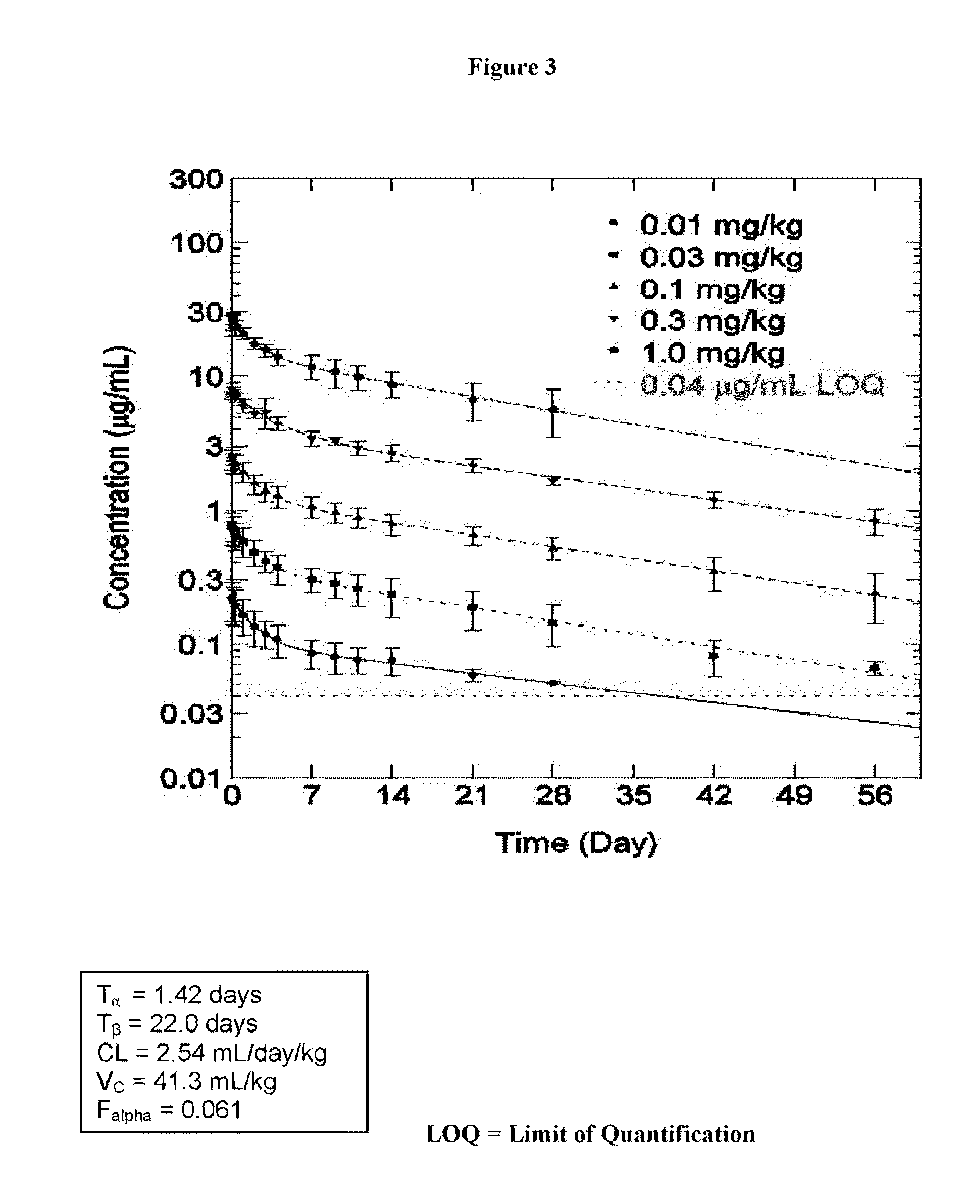
Methods for treating IL-1beta related diseases by administering an anti-IL-1beta antibody
ActiveUS8545846B2Preventing and delaying onsetLower Level RequirementsData processing applicationsMetabolism disorderDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Disclosed are methods for the treatment and / or prevention of Type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and disease states and conditions characterized by insulin resistance, decreased insulin production, hyperglycemia, hypoinsulinemia, metabolic syndrome, Type 1 diabetes and obesity, comprising administering to a subject an effective amount of anti-IL-1β antibody or fragment thereof.
Owner:XOMA (US) LLC
Interactive precision health care system related to high blood sugar
InactiveUS20190198145A1Preventing and delaying onsetHigh blood sugarMedical data miningDrug and medicationsTime scheduleDietary supplement
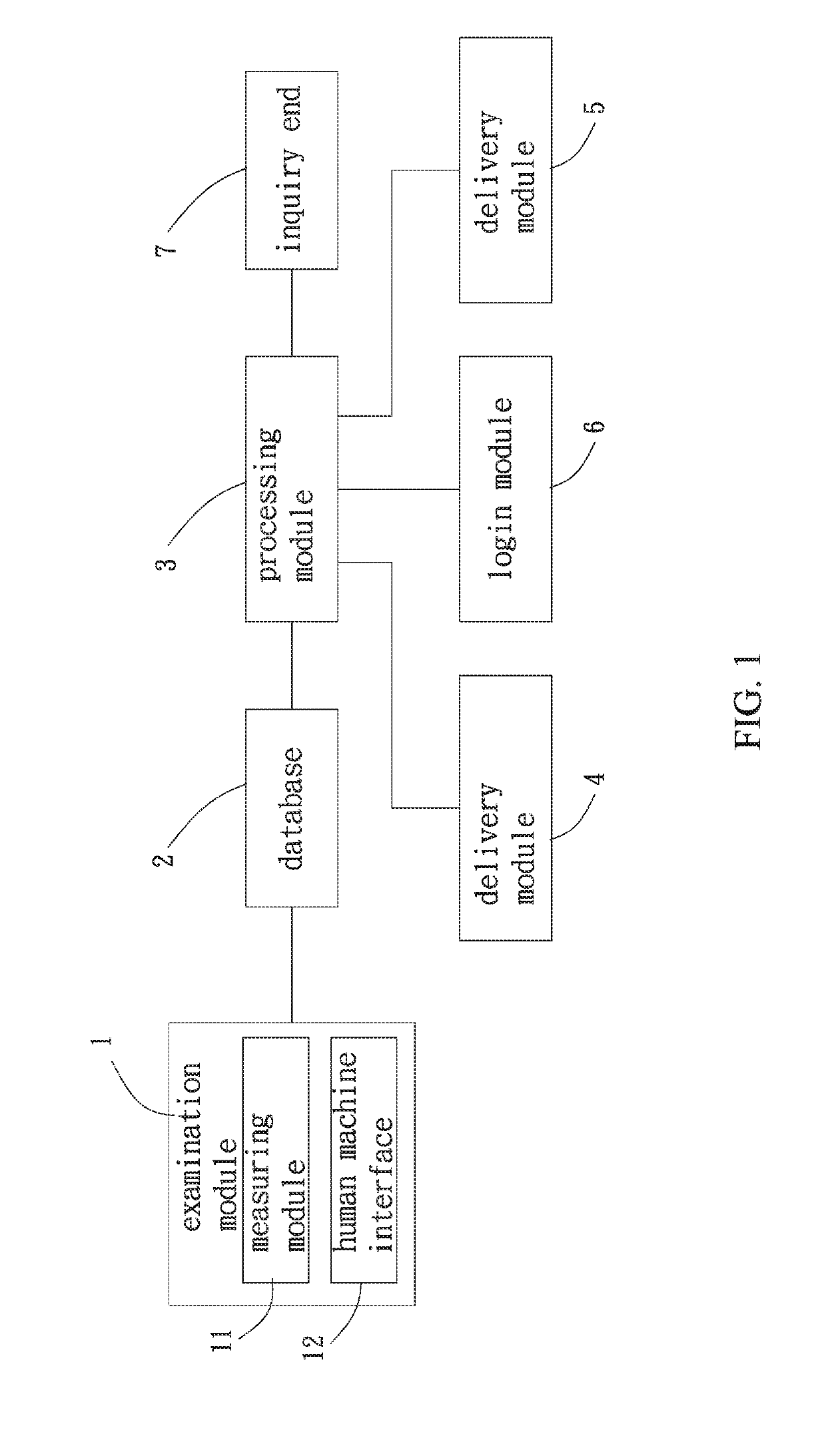
An interactive precision health care system related to high blood sugar includes an examination module generating an examination report, a database and a processing module. The database stores the examination report, a characteristic information, and a health care information. The characteristic information has a first range. The processing module receives and compares the examination report with the characteristic information. When a pre-meal blood sugar level falls within the first range, the processing module generates a dietary supplement product list including a product information and a time schedule of taking medicine. The processing module controls a delivery module to proceed with delivery. The processing module controls a reminding module to send out a message of taking medicine to obtain a new examination report. The processing module modifies the dietary supplement product list. The processing module controls the delivery module to proceed with delivery based on the modified dietary supplement product list.
Owner:PAN TZUNG SHIARN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com