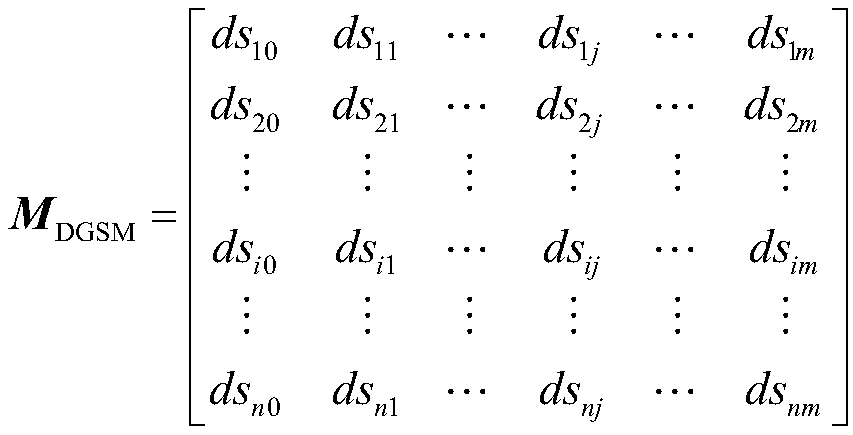Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64results about How to "Line selection is accurate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low current neutral grounding system fault route selecting method by wavelet package decompose and correlation analysis
InactiveCN101162838ARealize correct line selectionStrong anti-arc grounding abilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectric power systemDecomposition
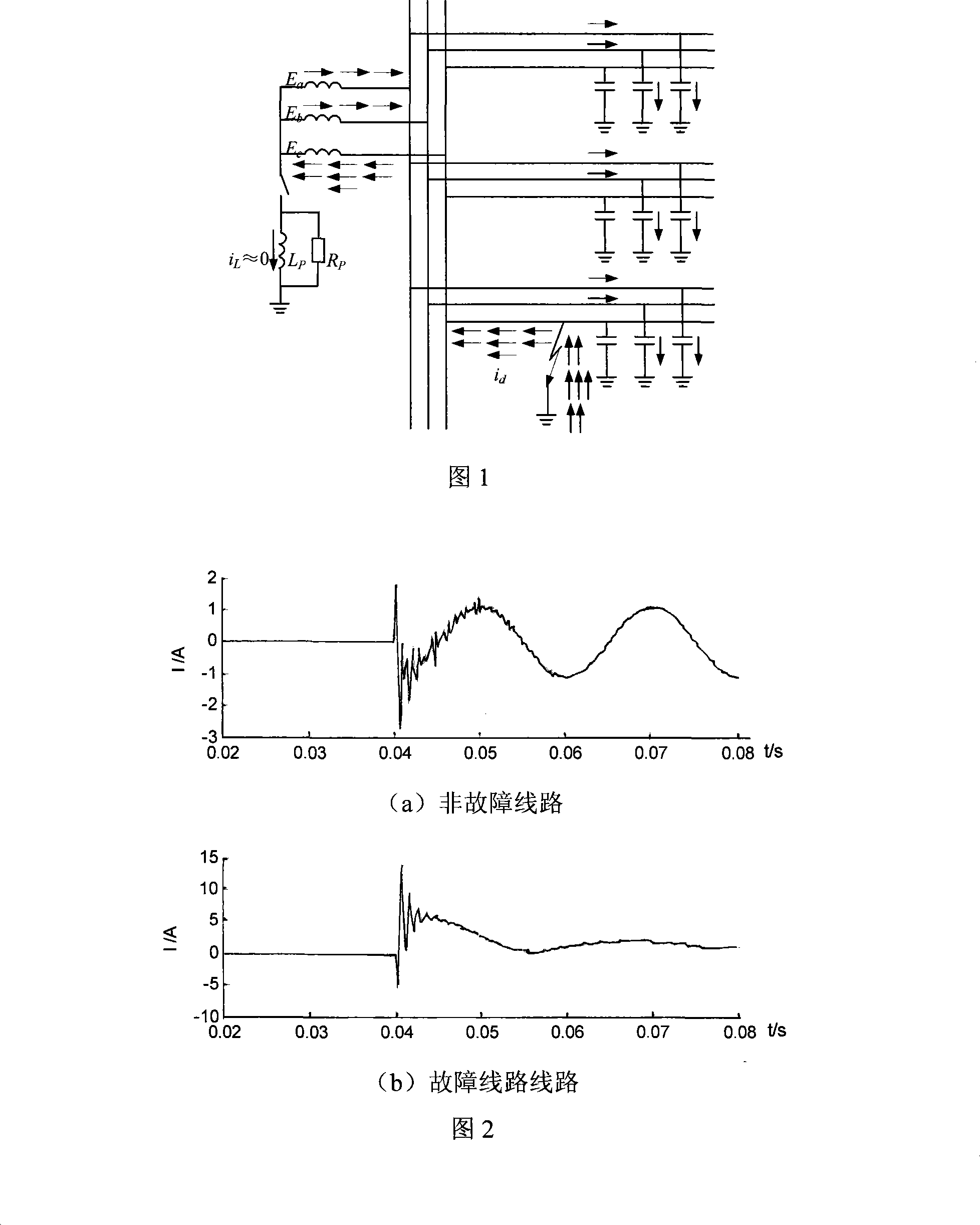
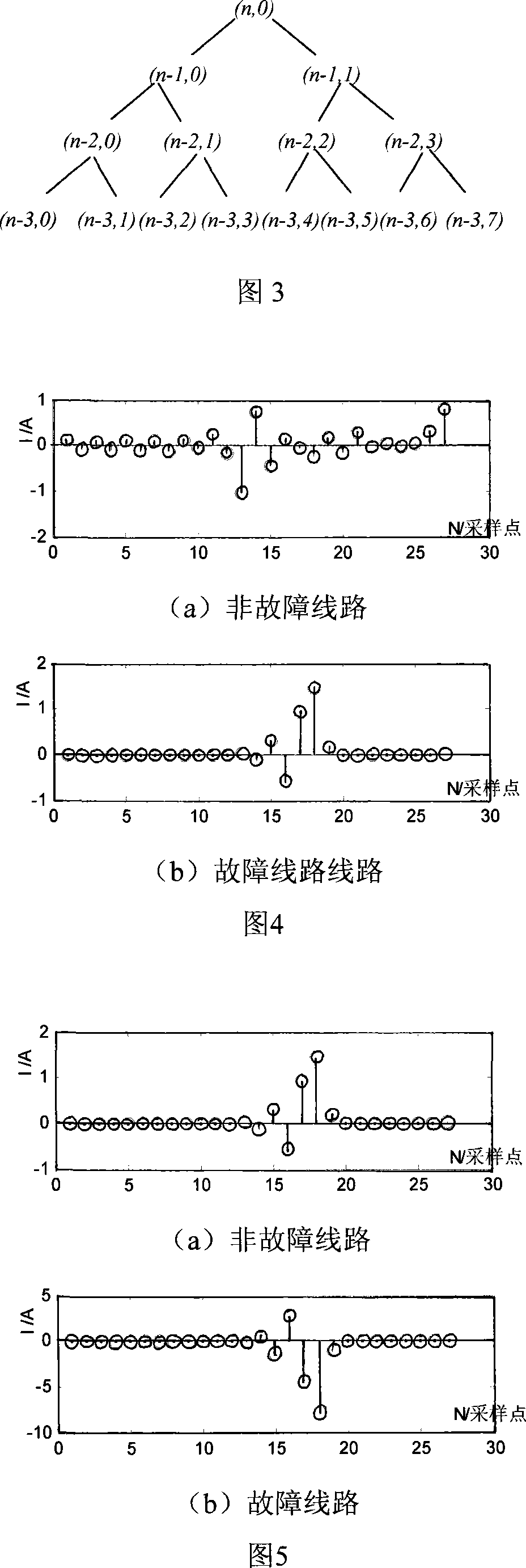
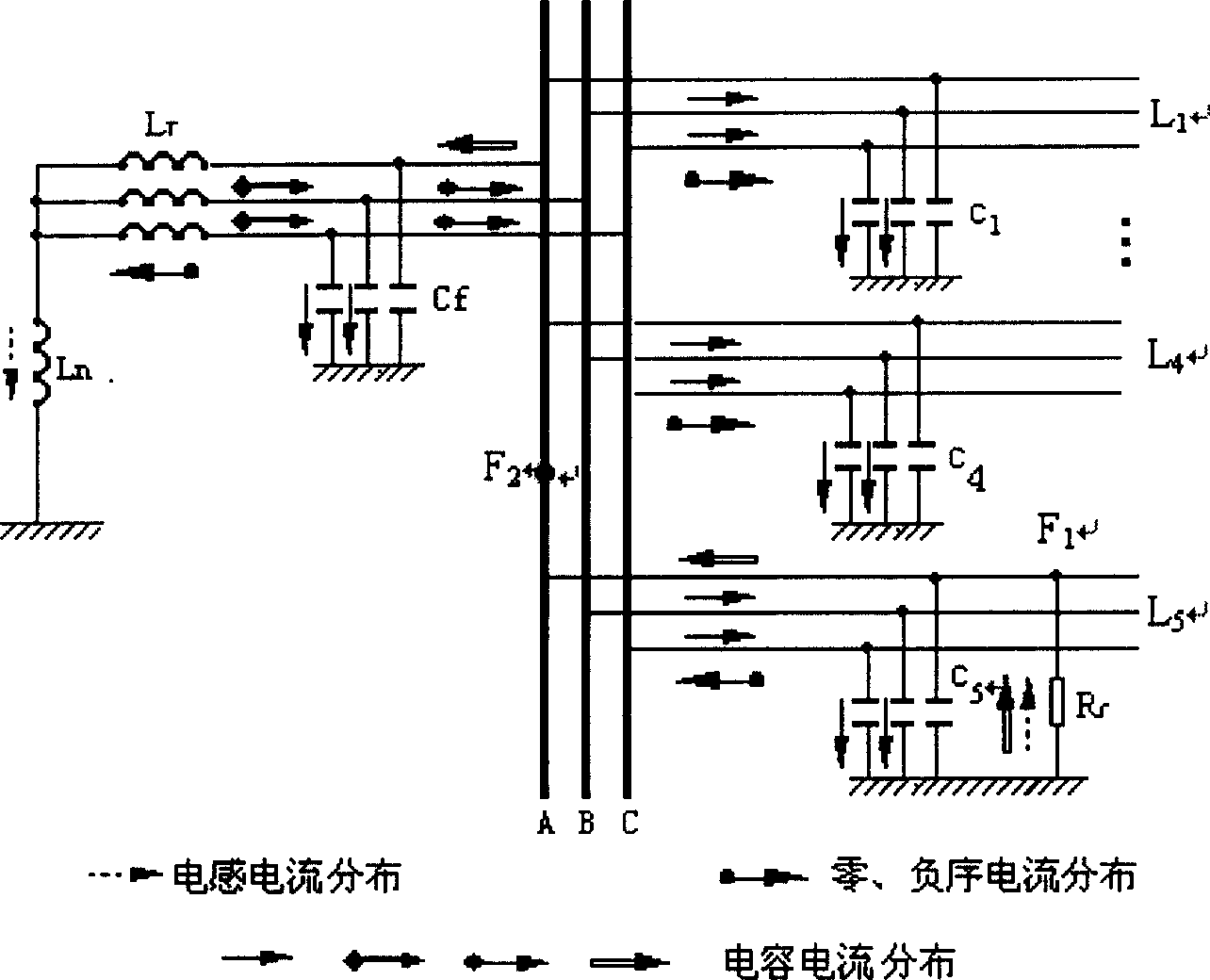
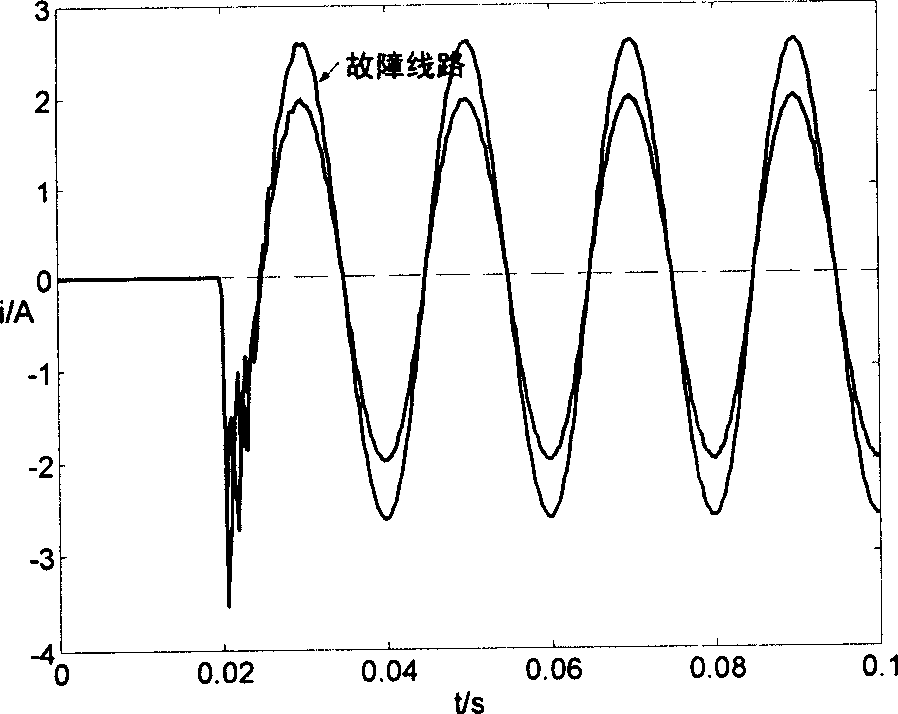
The present invention relates to a small current grounding system fault line selecting method by wavelet package decomposition and relevant analysis, belonging to the power system relay protection technical field. The method comprises: starting the fault line selecting device and recording wave to acquire transient zero-order current on each of the feeder lines when bus zero-order voltage transient value exceeds limit; calculating energy on each of frequency bands of the transient zero-order current after wavelet package decomposition, summing the energy of transient zero-order current on all the lines according to frequency bands and selecting the frequency bands with the maximum and secondary value of energy and values as the characteristic frequency bands, applying relevant analysis method to line transient zero-order current on the selected characteristic frequency bands in order; and finally determining fault point integrating the relevant analysis results of two frequency bands. The method uses wavelet package decomposition and relevant analysis, thereby effectively using information (amplitude and phase) contained in fault transient process and reflecting differences between fault line and non-fault line to maximum degree. Principle analysis and simulations demonstrate that the method has precise and reliable line selection.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Distribution network feed out circuit fault circuit selection method by using HHT detection technology
The present invention is a distribution network cable-line mixed fault circuit selection method by using HHT detection technology. The invention uses HHT singularity detection technology to calibrate fault occurring time accurately, and implements circuit selection according to a principle that, when a fault occurs transient fault zero-sequence current component of the fault circuit and the regular circuit is opposite in direction. The specific method is using HHT to proceed EMD decomposition to the sampling signal of before and after 1 / 4 period each circuit fault zero-sequence current that is morphological filter pretreated, obtaining highest frequency IMF component of each circuit fault zero-sequence current and proceeding a first-order backward difference treatment to the IMF component, comparing the polar mutation of the fault zero-sequence current IMF component at fault moment, and then forming a circuit selection criterion. Analysis and simulation of the principle shows that, using fault information of 1 / 4 period after the fault to select circuit can provide an accurate and reliable circuit selection result and avoid effects of paraphrase and CT saturation on circuit selection accrracy.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Overhead power transmission line optimized line selection method based on airborne laser radar data
InactiveCN101335431ARealistic 3D visualizationReduce configuration requirementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationApparatus for overhead lines/cablesAviationSimulation
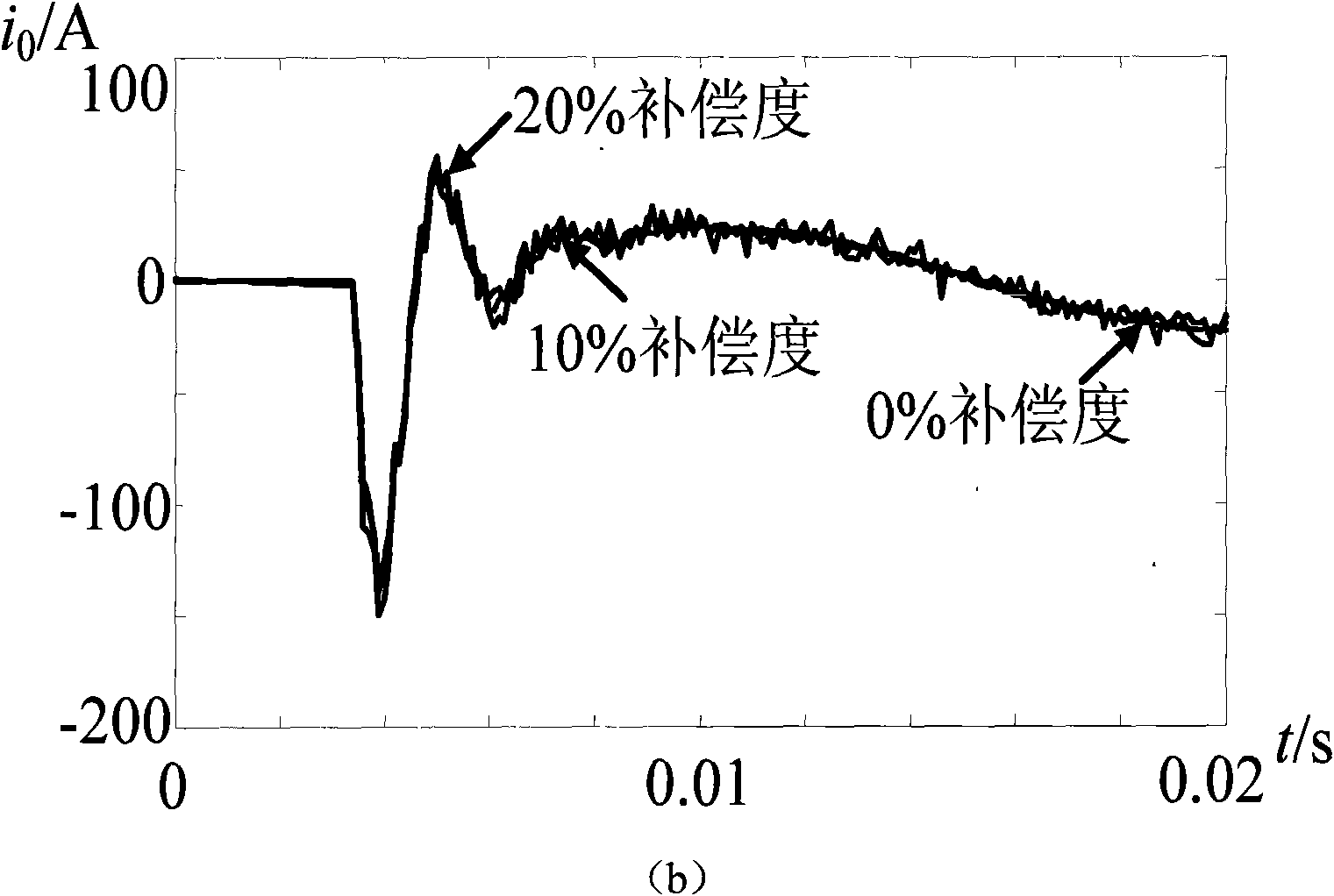
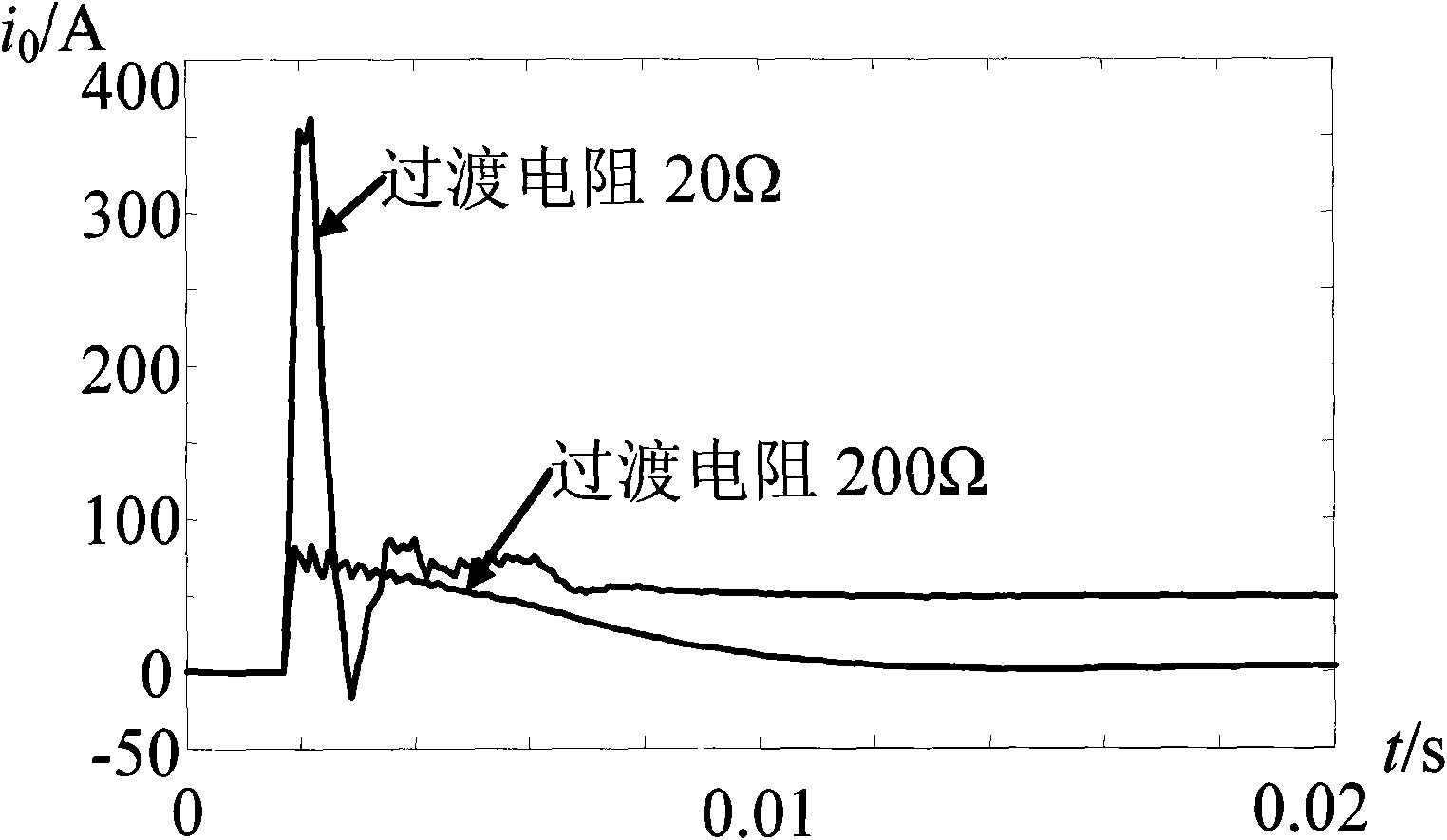
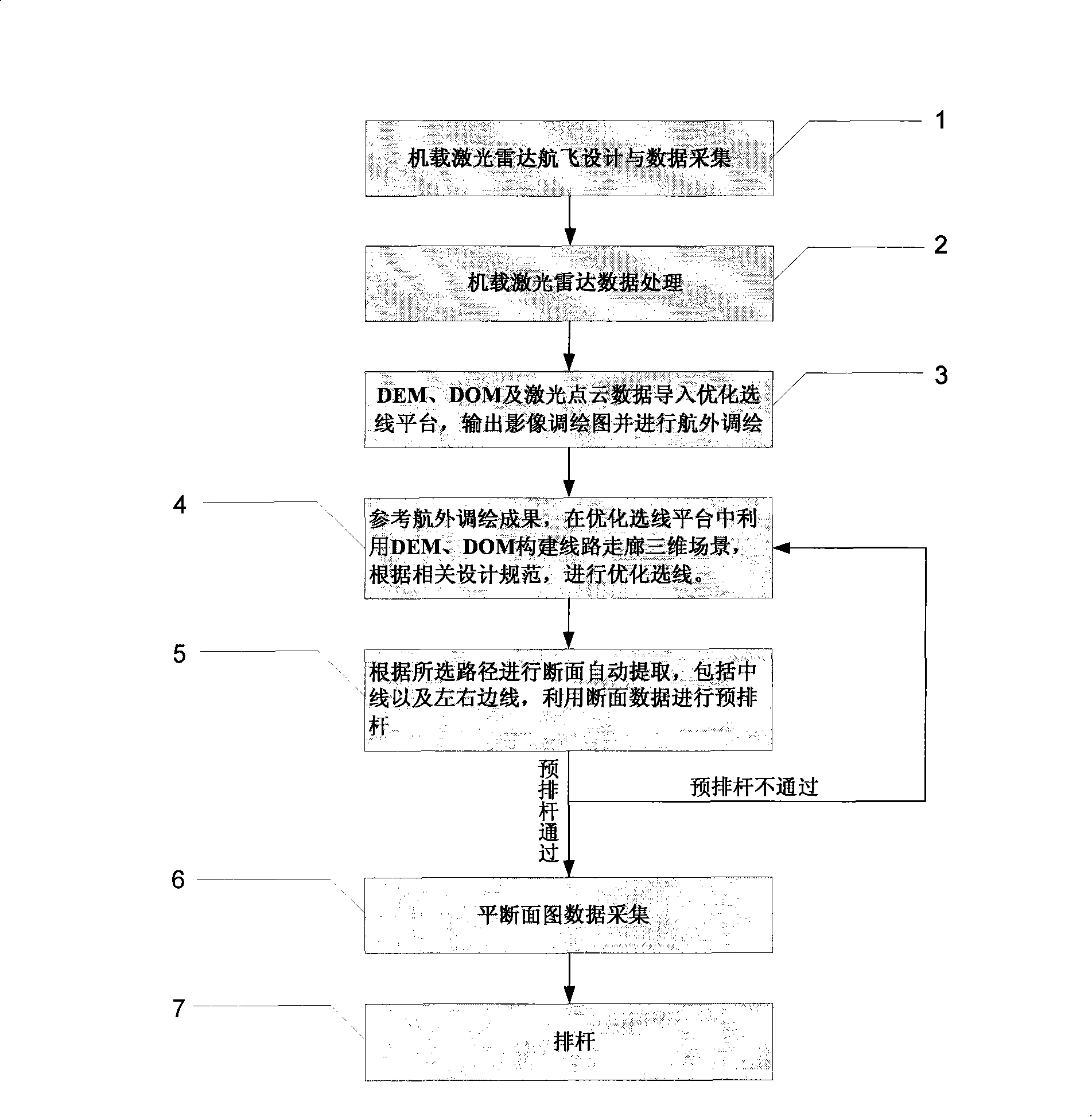
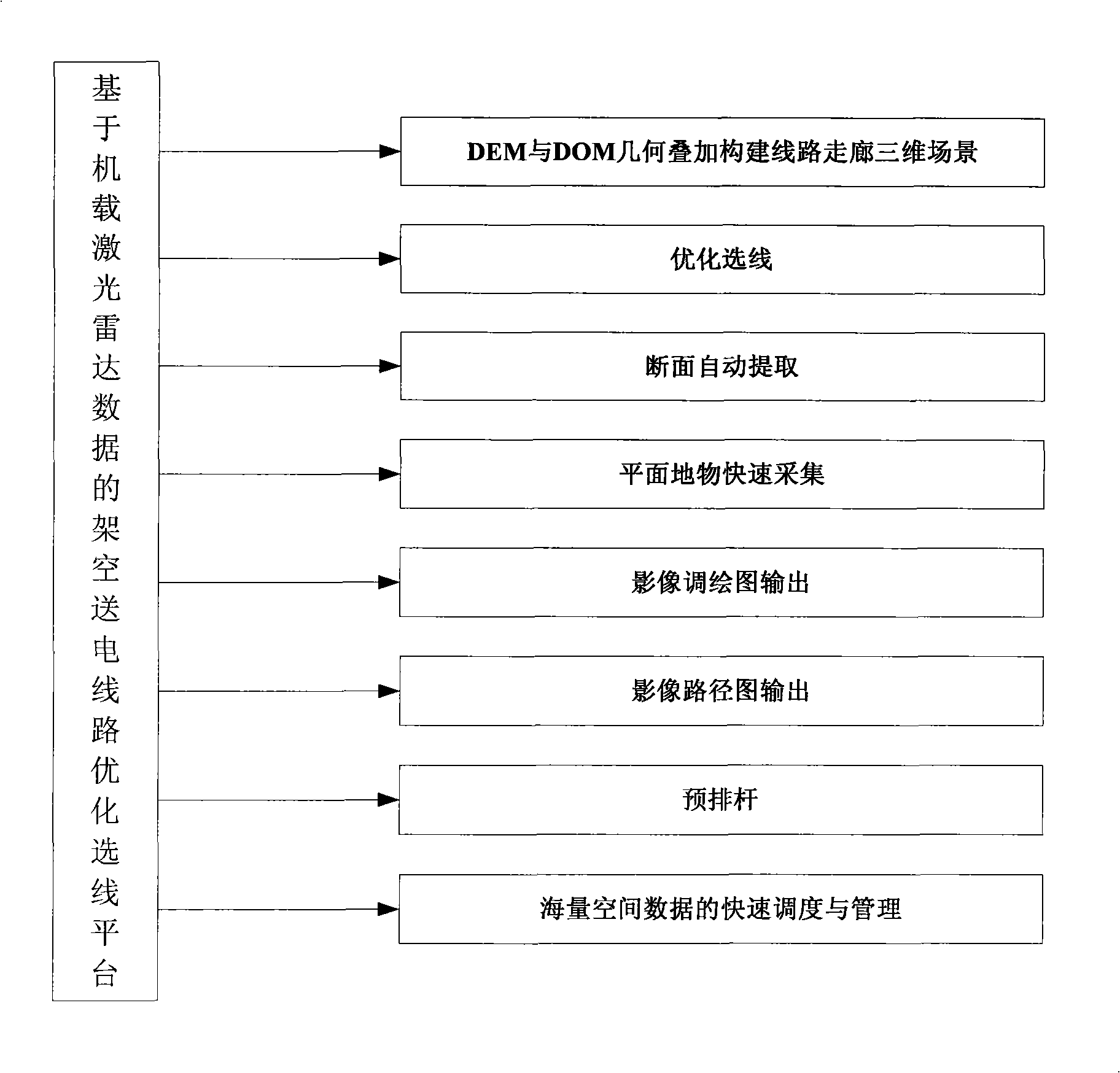
The invention discloses an optimal route selection method for overhead transmission line route. Onboard lidar equipment is adopted to acquire laser point cloud data and aerial digital photo data of the transmission line route corridor range; the onboard lidar data is processed after the wave filtering and the sorting of the laser point cloud data, and the points of the ground surface are made into a digital elevation model with high precision; then data processing is carried out by utilizing the data of the digital elevation model with high precision and ortho-rectification is carried out to the aerial photo by utilizing the internal and external orientation elements of the aerial digital photo to generate digital orthophoto maps; through the overlying of the digital elevation model and the digital orthophoto maps, the tridimensional visualization of the transmission line route corridor can be realized to optimize the transmission line route selection; finally prearrangement of power pole and power pole arrangement are carried out according to the data of plane cross sections. The route selection platform of the invention has simple operation and lifelike tridimensional scene, thus being convenient for full roaming and multi-view observation and greatly improving the efficiency of the inner plane cross section survey operation. Compared with the optimal route selection technology based on the aerial photographing measuring method, the efficiency of the inner plane cross section survey operation can be improved by about 75 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI ELECTRIC POWER IND INVESTIGATION DESIGN & RES INST
Novel faulty line selection method in low current faulty grounding system
InactiveCN101701998ALine selection is accurateOvercome the problem of low accuracy of fault line selectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationHarmonicSelection criterion
The invention discloses a novel faulty line selection method in a low current faulty grounding system, which judges whether a ground fault happens or not by detecting zero sequence voltage and phase voltage of a system bus, determines to judge grounded fault circuit adopting different faulty line selection methods according to the different characteristics of zero sequence fundamental wave and zero sequence quintuple harmonic current generated according to that arc suppression coil exists in a system when single-phase grounding fault happens on the premise that ground fault occurs, combines with some assistant line selection criteria to perform comprehensive judgment so as to select the circuit with a fault correctly, thus overcoming the problem of low accuracy of faulty line selection in a low current grounding system. The invention has the characteristics of reasonable method steps, high accuracy of faulty line selection and convenient operation and application.
Owner:山东泰开自动化有限公司
Failure line selection method of small current ground system by using simulation after zero mode current measure
InactiveCN101242097AOvercome the influence of small fault transient currentRealize correct line selectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides a fault route-selecting method by using small current grounding system simulated by measured zero-mode current. The method includes following steps: when a generatrix zero-mode voltage instantaneous value is over the limit, a fault route-selecting is started and recorded immediately; zero-phase shift digital wave filter is used to obtain a high-frequency transient weight of each feed line zero-mode current; orderly the feed line is supposed to be fault feed line, the rest of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current is quantificationally solved by using the measured simulative method according to the supposed high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current and each feed line zero-order distributing capacitance parameter; the actual-measured wave shape and simulative wave shape of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current are analyzed and a average relative coefficient of the actual-measured wave shape and simulative wave shape of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current are solved, the route-selecting criterion is formed to achieve the fault route selection. The principle analysis and simulation indicate that route selection of this method is accurate and reliable.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Test simulation method for failure line selection of small current ground system
ActiveCN101188354AOvercome the influence of small fault transient currentRealize correct line selectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceElectric power system
The invention relates to a measuring post simulation method of the fault wire selection for a low current grounding system. The invention belongs to the technical field of the power system relay protection. The method is realized by that when the instantaneous value of the voltage of a bus zero exceeds the limit, a fault wire selection device is started immediately and used for recording the wave. The invention adopts a digital filter algorithm to obtain the bus zero voltage and the transient pure fault components of zero current on each feedback line. When a low current grounding system takes place a single-phase earth fault, the waveform of the zero current is quantitatively solved by using measuring post simulation according to the transient pure fault component of the measured value of the bus zero voltage and the feeder zero distribution capacitor parameter under the assumption premise of the perfect feeder of every feeder. The invention carries out correlativity analysis to compare the measured waveform of the current of every zero current with the transient pure fault component solved by the measuring simulation method under a definite data window and calculate both correlative coefficients, thereby the invention forms a line selecting criterion 1 and 2 and can carry out line selection to the system according to the line selecting criterion. The principle analysis and the simulation show that the line selection method has the advantages of accuracy and reliability.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for fault line selection of electric distribution network by using S transformation energy relative entropy
ActiveCN101546906AAvoid the influence of fault line selection accuracyStrong anti-arc grounding abilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationTransient stateEngineering
The invention relates to a self-adaptive method for single-phase grounding fault line selection of an electric distribution network by using S transformation energy relative entropy. The method comprises the following steps: when the zero-sequence voltage instantaneous value of a bus is out of limit, starting a fault line selection device immediately; performing S transformation on zero-sequence current in 1 / 4 cycle after the fault of each line, and calculating transient energy under each frequency of the zero-sequence current of each line by using a complex matrix obtained by the S transformation; and calculating the S transformation energy relative entropy under each frequency of each line and solving the comprehensive S transformation energy relative entropy of each line by using the super-strong recognition capability of the relative entropy to slight differences between signals, and self-adaptively selecting out the fault line by comparing the size of the comprehensive S transformation energy relative entropy of each line under all frequencies. Theoretical analyses and a large number of emulations show that the method effectively avoids the influence caused by a CT saturation discontinuous angle on the line selection, and is applicable to the cable-wire mixed line, pure cable lines and pure aerial lines.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
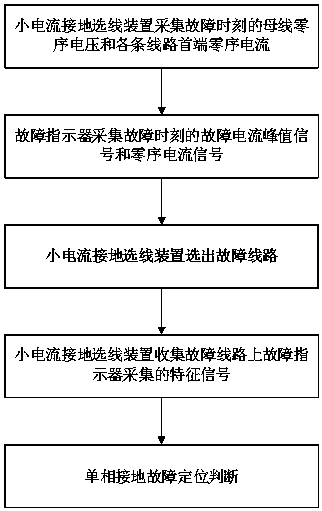
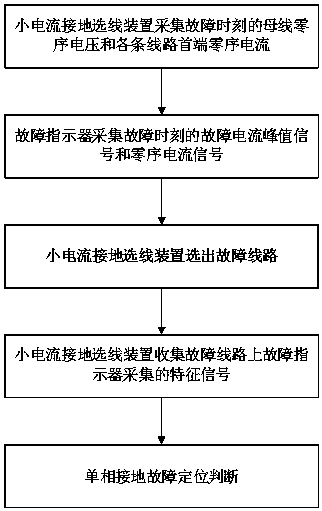
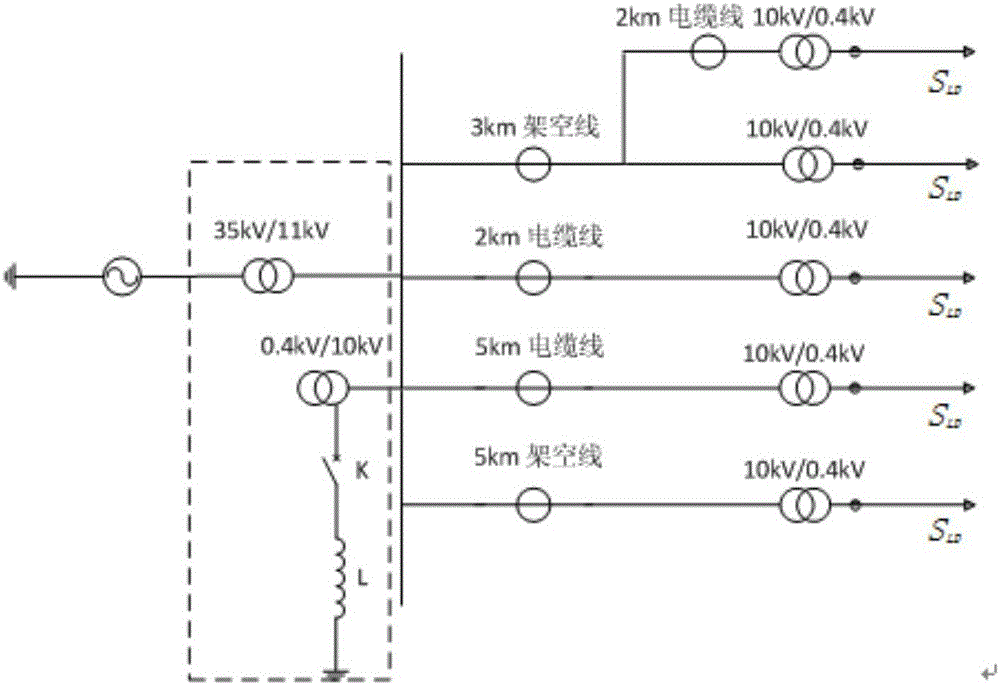
Small-current grounding fault line selection device-based power distribution network grounding fault location method
ActiveCN107144762AImprove power supply reliabilityImprove processing efficiencyFault location by conductor typesCurrent measurements onlyFault indicatorTransient state
The present invention belongs to the power system power distribution network single-phase grounding fault detection technical field and relates to a small-current grounding fault line selection device-based power distribution network grounding fault location method. The method specifically includes the following steps that: (1) a small-current grounding fault line selection device acquires bus-bar zero-sequence voltage and the zero-sequence current of the head end of each line at a fault time point; (2) a fault indicator acquires fault current peak signals and zero-sequence current signals at the fault time point; (3) the small-current grounding fault line selection device selects a fault line; (4) the small-current grounding fault line selection device collects characteristic signals acquired by the fault indicator on the fault line; and (5) and single-phase grounding fault location judgment is performed. With the method of the invention adopted, the single-phase grounding fault of a power distribution network can be accurately located; and the small-current grounding fault line selection device applies transient signal characteristic frequency band line selection theory, and therefore, the line selection accuracy of the small-current grounding fault line selection device can be higher than 98%, and transient signals can be accurately captured, fault analysis and traceability can be realized, and load on-line measurement, statistics and analysis are supported.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD +1
One-phase grounding clustering line selection method of resonant grounding system
ActiveCN103454562AAvoid artificial experience selection thresholdStable algebraic featuresFault locationSingular value decompositionCapacitance
The invention relates to a resonant grounding system fault line selection method with clustering achieved by means of time-frequency matrix singular values. The resonant grounding system fault line selection method comprises the steps that empirical mode decomposition is carried out on the transient-state zero-sequence current waveform of each circuit and the transient-state zero-sequence current waveform of a bus after a fault occurs to obtain a plurality of IMF components; Hilbert conversion is carried out on the IMF components to obtain a two-dimensional Hilbert gray-scale time-frequency spectrogram of transient-state zero-sequence currents; a time-frequency matrix of the transient-state zero-sequence current waveforms is constructed by means of HHT band-pass filtering; singular value decomposition is carried out on the time-frequency matrix to obtain a series of singular values which can reflect time-frequency characteristics of the waveforms, and the singular values serve as the characteristic quantity of transient-state zero-sequence currents of each circuit and the bus; vague C mean value clustering is carried out on the singular values to select a fault line. According to the resonant grounding system fault line selection method, influence of distributed capacitance and currents of a sound long line is avoided when a short line breaks down, and accurate line selection can be achieved under the conditions of high resistance grounding, noise interference, arc faults and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Power distribution network outgoing feeder fault route selecting method by S transform amplitude detection
ActiveCN101587159AAvoid line selection failureNot affected by compensationVoltage-current phase angleFault locationS transformEngineering
The invention relates to a power distribution network outgoing feeder fault route selecting method by S transform amplitude detection, namely, when the power distribution network generates single-phase ground fault, the bus zero sequence voltage before and after the fault can be performed for S transform to find out the moment corresponding to a module maximal value on the S transform highest frequency component position for accurately calibrating the fault moment; the each line zero sequence current before and after the fault moment can be performed for S transform to obtain the S transform complex matrix of each line zero sequence current; the amplitudes of highest frequency component at fault moment in the each line zero sequence current S transform complex matrix can be worked out, and the amplitude difference can be worked out; the integrative amplitude difference of each line zero sequence current can be worked out; the fault route selecting can be implemented by comparing the size of the integrative amplitude difference. The invention can avoid the route selecting failure caused by CT saturation and phase alternation, the invention implements the route selecting by using high-frequency components, without being influenced by arc-suppression coil compensation degree. The accurate route selecting under different fault conditions comprising small fault angle can be implemented.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Small current grounding system single-phase grounding fault wire selection method based on transient zero-module current
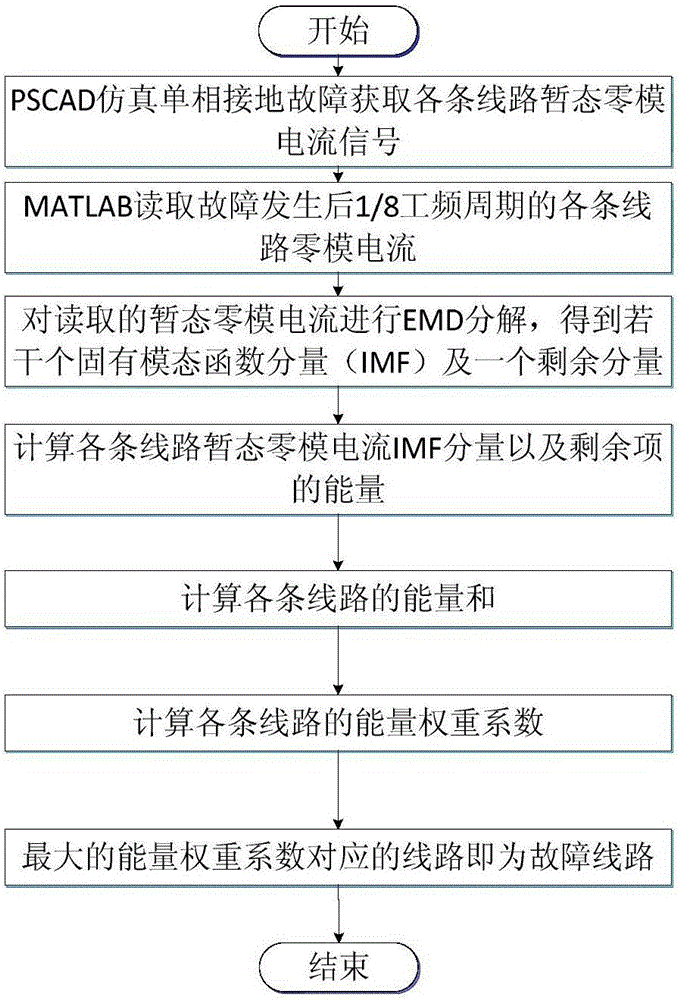
InactiveCN105866634AEconomicalLine selection is accurateFault location by conductor typesSingle phasePower grid
The invention discloses a single-phase grounding fault line selection method for a small current grounding system based on transient zero-mode current. Three-phase modeling is performed on the power grid, and different fault conditions are selected for single-phase grounding fault simulation experiments to obtain various lines Transient zero-mode current; extract the above data; perform empirical mode decomposition EMD on the above data; calculate the time-domain energy of multiple IMFs and residual components; add the energy of IMF and residual components to obtain the energy sum of a line , repeat the above steps to obtain the energy sum of all lines; calculate the energy weight coefficients of each line, compare the energy weight coefficients of each line, and the line corresponding to the maximum energy weight coefficient is the faulty line. Comparing the peak value and polarity of the first zero-mode current pulse and the polarity of the first instantaneous power peak value, the zero-mode current amplitude of the faulty line is larger than that of the non-faulty line, and the polarity of the two is opposite. The invention is not affected by arc suppressing coils and fault conditions and can accurately select fault lines.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
Small current earth fault line selection method for radial distribution network
InactiveCN103308822ASmall amount of calculationEigenvalue increaseFault locationUltrasound attenuationTransient state
The invention relates to a small current earth fault line selection method for a radial distribution network. The small current earth fault line selection method for the radial distribution network comprises the steps that firstly, the line reference values of fault lines and non-fault lines are calculated according to the number of branch lines of a current radial distribution network system; secondarily, taking a Gabor atom dictionary as the index, a matching tracing algorithm is utilized to carry out time frequency atomic decomposition on transient zero-sequence current of each fault branch line within the first one quarter cycle, and attenuation sinusoidal quantity atoms representing the fault feature information of branch lines are further obtained; thirdly, an improved gray correlation analytic method is adopted to carry out correlation degree analysis on the attenuation sinusoidal quantity atom of each branch line, so that the feature value of each branch line is obtained; and finally, Euclidean distance is obtained by using the feature value of each branch line and the reference values of the fault lines and the non-fault lines, the Euclidean distances are compared, so that the accurate line selection is realized through the comparison of the Euclidean distances. The small current earth fault line selection method for the radial distribution network realizes low calculated amount and high line selection accuracy and is particularly applicable to radial distribution network systems with multiple branch lines.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Adaptive approach for route selection of grounded system connected to arc suppression coil
InactiveCN1696724AIntuitive theoretical basisSimple methodFault locationElectric power systemGround system
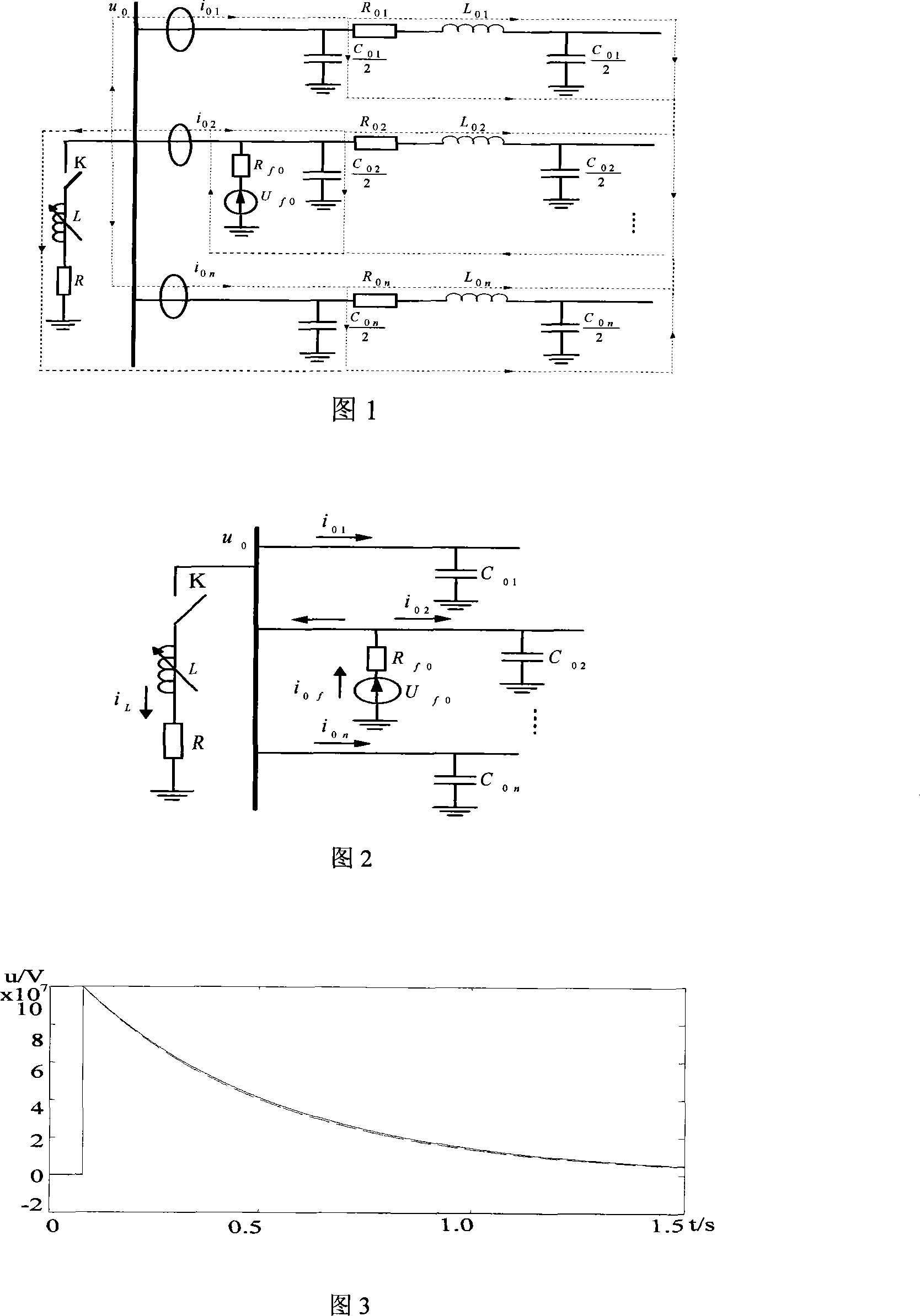
An adaptive method of fault wire selection includes starting up fault wire selection device to record zero sequence current and voltage of each outlet on two cycles before fault and three cycles after fault when bus zero sequence transient voltage value uo ( t ) is over KuUn as Ku value of 0.35 and Un referring to bus rated voltage; searching sample point with value being less than 0.01 Un on bus; finding out corresponding time when single phase earthing fault is occurred; calculating phase angle theta uo and each line I DC to obtain criteria 1, 2, 3 and 4; selecting wire for system fault as per criteria.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power distribution network cable-line commingle line fault route selection anastomosing method using extension theory
InactiveCN101227086ARealize correct line selectionStrong anti-arc grounding abilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceTransient state
The invention relates to a fault line selection fusion method of a power distribution network cable-line mixing line which utilizes an extensive theory, and belongs to the electric power system relaying protection technology field. The application of a distribution network cable-line mixing line is increased in cities, a cable in a unit length has larger capacitance for the earth than a trolly wire, frequency dependent character of a cable parameter is serious, and a voltage current fault transient state component is more distinct when the cable-line mixing line is connected with the ground in a single phase way. Perceptual decay direct current component characteristic of each feeding outgoing line fault zero-sequence current is fused with a disintegrating and integrating relative coefficient of a transient component small waving bag through utilizing the extensive theory. Possible fault line assembly, fault characteristic assembly and an amount domain which is set by the characteristic are used as three factors for the extendable merging matter, and the decay direct current component and the small waving bag disintegrating and integrating relative coefficient are used as the characteristic assembly. A weight function can be objectively confirmed according to the size of a fault close angle, a fault confident degree of each line can be calculated through utilizing the extensive correlation function, and the fault outgoing line is judged according to the confident degree. A great number of artificial results indicate that the line chosen by the method is accurate and reliable.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-phase-to-ground fault line selection method for small current
InactiveCN109884464AAvoid interferenceAvoid chanceSpectral/fourier analysisFault locationDecompositionSingle phase
A single-phase-to-ground fault line selection method for small current comprises the following steps of first determining a signal sampling period, using an A / D converter to collect the zero-sequencevoltage of a bus and the zero-sequence current of feeders of the system, monitoring the zero-sequence voltage of the bus in real time, and starting a line selection algorithm when the zero-sequence voltage is greater than a set voltage; performing smoothing pre-treatment on the transient zero-sequence current spectrum of each of the extracted feeders, carrying out empirical wavelet transform decomposition to extract an intrinsic mode function that best characterizes the original signal, calculating energy relative entropies by using the amplitude of the signal obtained after Hilbert transform,selecting the line with the largest relative entropy as the fault candidate line, determining that the line with the largest relative entropy is faulty if the line with the largest relative entropy is larger than the sum of the relative entropies of the line with the second largest relative entropy and the line with the third largest relative entropy, and otherwise determining that the bus is faulty. The single-phase-to-ground fault line selection method is accurate in line selection and good in real-time performance without being affected by the neutral point grounding mode, the fault distance, the initial fault angle or the transition resistance fault condition.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Fault line selection method based on phase current transient characteristic
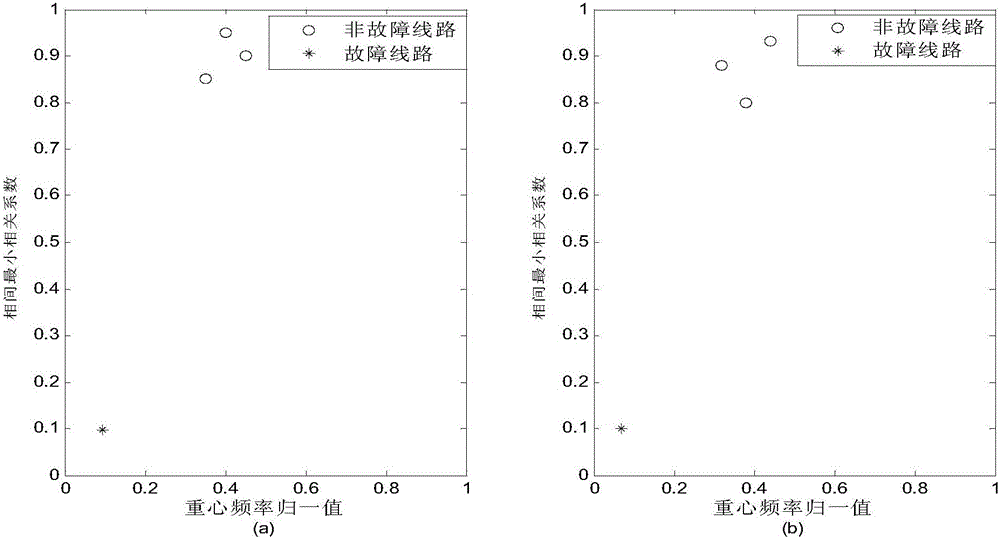
ActiveCN105974264AEfficient discriminationLine selection is validFault locationPhase currentsCorrelation coefficient
The method discloses a fault line selection method based on a phase current transient characteristic. The method comprises the following steps of S1, continuously measuring a distribution line outlet zero sequence voltage value and determining whether a power distribution network generates a grounding fault; S2, processing collected phase current data, extracting a transient phase-current sudden-change amount of each line, and carrying out interphase pairwise correlation analysis so as to obtain an interphase minimum correlation coefficient rhok min; S3, carrying out spectral analysis on each line fault phase current and calculating a gravity frequency fkg; S4, carrying out normalization processing on a fault characteristic quantity and acquiring normalization values, establishing a two-dimensional coordinate system based on the normalization values, and determining each line fault characteristic coordinate point; and calculating a fault characteristic distance dk between each line fault characteristic coordinate point and a reference point (0, 0) so as to determine a bus fault. The method possesses advantages that a principle is simple; practicality is high; an anti-interference capability is good; accuracy is high and so on.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Device for single-phase earth fault line selection and method thereof
InactiveCN101865967AAvoid errorsAvoid interferenceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides a method for single-phase earth fault line selection and a method thereof. The device comprises an automatic line selection device, a disturbance source and a zero sequence current transformer, wherein the disturbance source is arranged on a system neutral point and transmits the disturbance to a zero sequence circuit of the system after receiving a disturbance command transmitted by the automatic line selection device; and the zero sequence current transformer is arranged on each line, is connected with the automatic line selection device and is used for sampling the disturbed zero sequence circuit current. The invention is not limited by the magnitude of the system capacitance current, earth types and other factors and can be used for reliably and accurately selecting an earth fault line.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHIGUANG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Single-phase grounding fault locating method for distribution network without master station
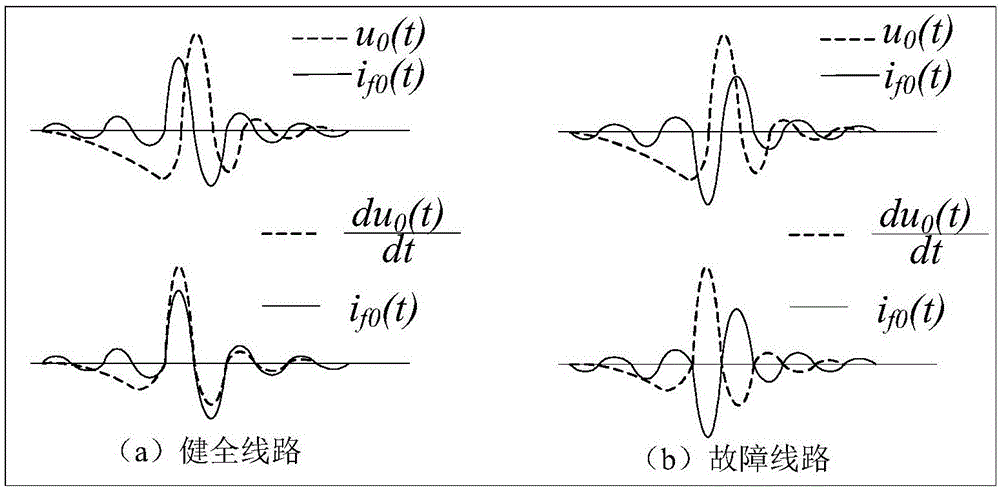
InactiveCN106501683AAccurate analysis of flow directionLine selection is accurateFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemMaster stationElectrical polarity
A single-phase grounding fault locating method for a distribution network without a master station of the invention comprises the following steps: (1) each distribution terminal detects the zero sequence voltage value of a distribution network, and judges whether there is a single-phase grounding fault; (2) when there is a single-phase grounding fault, each distribution terminal takes the derivative of zero sequence voltage, compares the polarity of transient zero sequence current with the polarity of the derivative of zero sequence voltage, and identifies a single-phase grounding fault line; (3) a line meeting the condition that the polarity of transient zero sequence current and the polarity of the derivative of zero sequence voltage are opposite is selected as a fault line, and each distribution terminal sends a grounding fault locking signal containing level information to a higher-level line distribution terminal; (4) the distribution terminal at the fault point does not receive a grounding fault locking signal, and acts first to remove the grounding fault, and the distribution terminals upstream of the fault do not malfunction; and (5) if the distribution terminal at the fault point fails to remove the fault in time, the higher-level feeder distribution terminal delays the action exit gradually according to the received locking signal. Through the method, a grounding fault point can be located accurately even when a distribution terminal on a switch loses communication connection with a distribution monitoring master station system.
Owner:NANJING INTELLIGENT APP
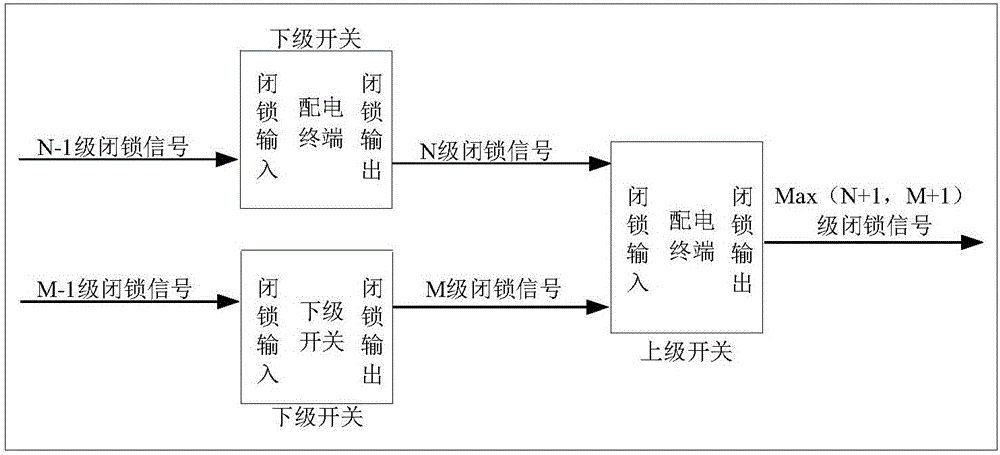
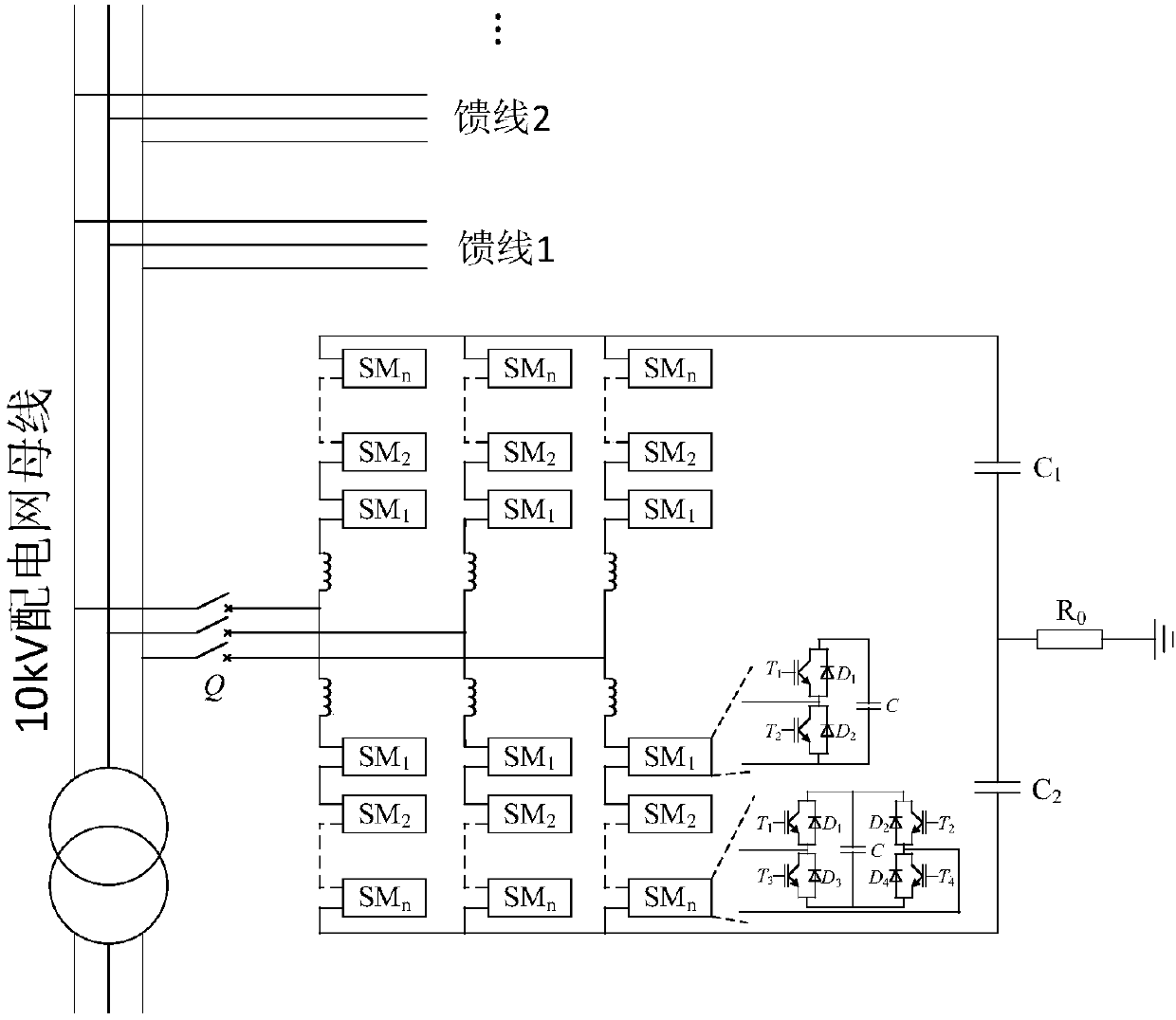
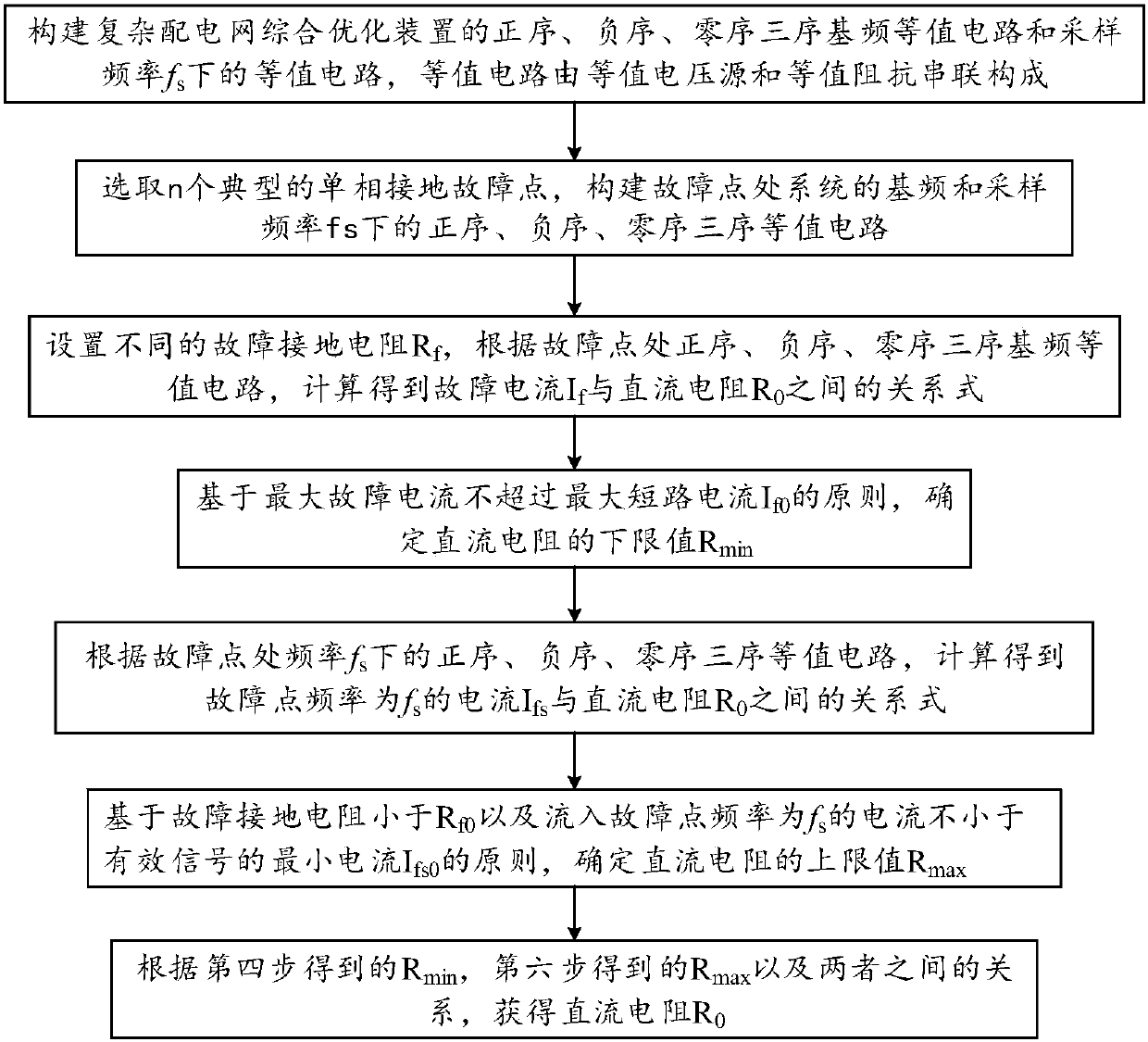
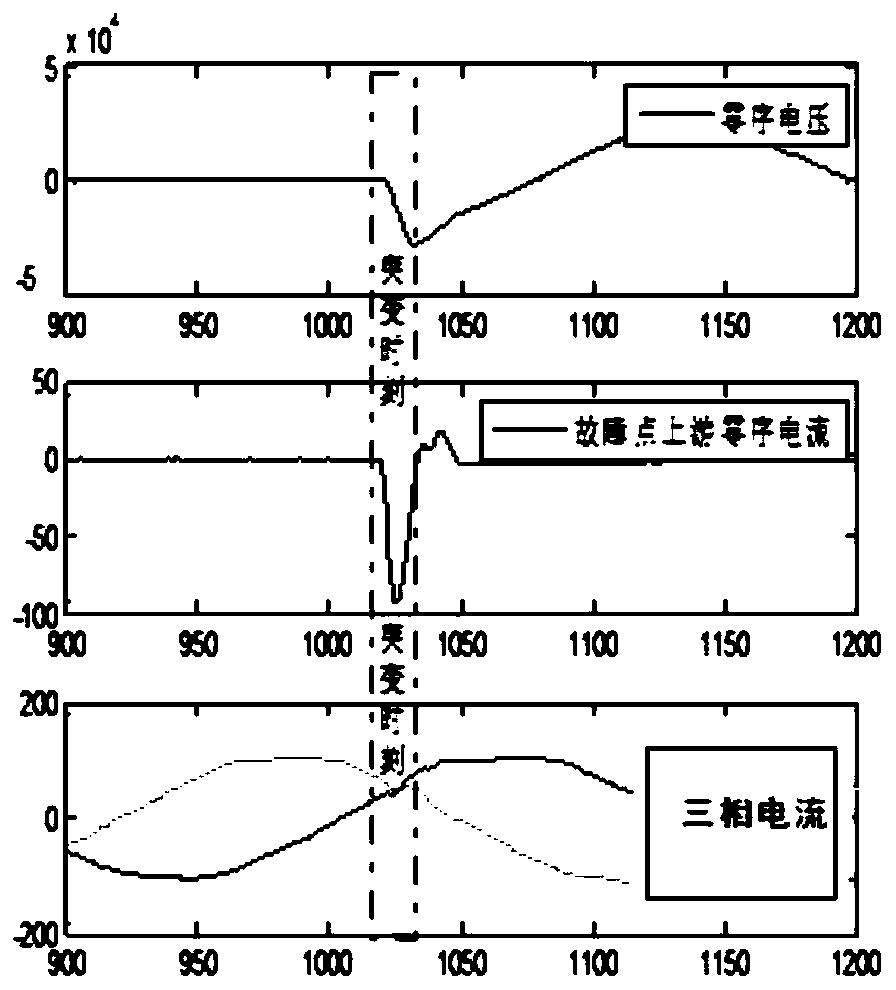
DC resistance selection method and system for complex power distribution network comprehensive optimization device
ActiveCN108120878AImprove controlAchieve substitutionResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingDistribution power systemEngineering
The invention discloses a DC resistance selection method and system for a complex power distribution network comprehensive optimization device. The DC resistance selection method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence three-sequence fundamental frequency equivalent circuits and equivalent circuits at a sampling frequency for the complex power distribution network comprehensive optimization device; 2) constructing positive-sequence, negative-sequence and zero-sequence three-sequence equivalent circuits at a fundamental frequency anda sampling frequency of a power distribution system at a fault point; 3) calculating to obtain a relationship between fault current and DC resistance; 4) determining a lower limit value of the DC resistance; 5) calculating to obtain a relationship between the current of the sampling frequency at the fault point and the DC resistance; 6) determining an upper limit value of the DC resistance; and 7) obtaining the DC resistance according to the lower limit value and the upper limit value as well as a relationship between the lower limit value and the upper limit value. The DC resistance selection method and system disclosed by the invention have the benefits that a selected DC resistance value can take into account effective arc suppression and accurate line selection of the power distribution system, effectively improve the control performance of the comprehensive optimization device and realize the substitution effect on an arc suppression coil.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +1
Single-phase ground fault locating method based on zero sequence voltage starting
InactiveCN110426593ANo wiring pull wires requiredConstruction saves time and effortFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemFault indicatorEngineering
The invention relates to a single-phase ground fault locating method based on zero sequence voltage starting. Zero sequence voltage is adopted as a single-phase ground fault break variable starting component, when a ground fault appears, a bus zero sequence voltage starting device can record zero sequence voltage waveforms at the break moment T, three-phase current waveforms of all high-precisiontransient wave recording type fault indicators installed along a transformer substation outgoing line at the same moment are called, and finally fault positioning is achieved based on wide area synchronous information. The purpose of single-phase ground fault locating in an existing power distribution network is achieved.
Owner:苏州银蕨电力科技有限公司
Fault selecting method by attenuated DC component
InactiveCN1584613AIntuitive theoretical basisSimple methodFault locationSingle phaseUltrasound attenuation
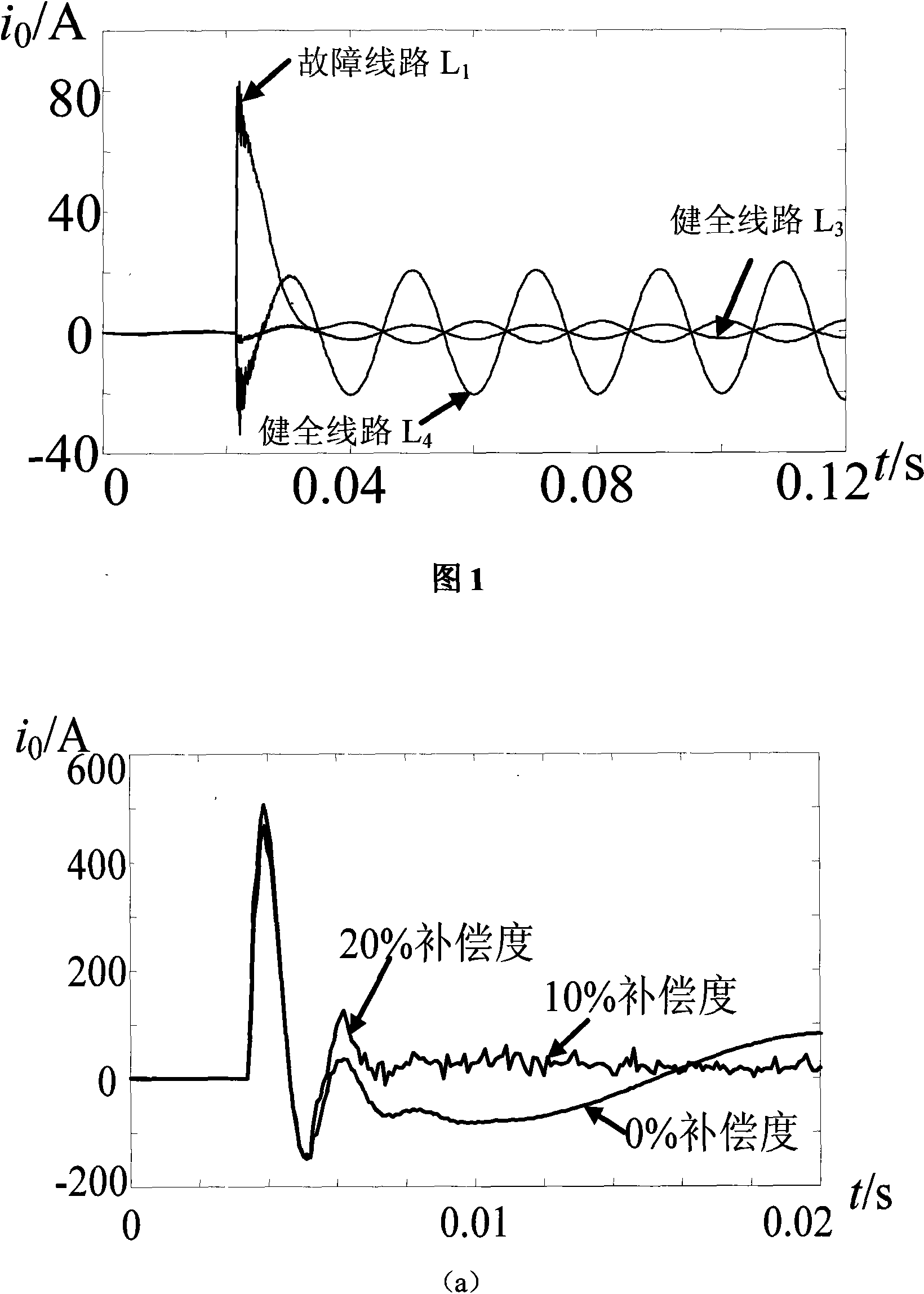
A method for selecting out fault circuit in small earthing current system uses DC constituent of the first cycle after the fault to replace attenuation DC constituent for calculation and selects out fault circuit of small earthing current system with arc suppression coil based on DC constituent size. The rationale of the method is also listed in the present invention.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Resonant earthed system fault line selection method with invariant moments
The invention relates to a resonant earthed system fault line selection method with invariant moments. The method comprises the following steps that S1, zero-sequence current waveforms measured at the head ends of all circuits within a working frequency period are recorded after a fault occurs; S2, the point gray levels of curves of all the measured zero-sequence current waveforms are one, the other point gray levels are zero, and an image gray level distribution function F(t, i) is obtained; S3, the image gray level distribution function F(t, i) of the obtained zero-sequence current waveforms is substituted in an invariant moment formula, 11 invariant moments reflecting image characteristics are obtained, and four invariant moment characteristic quantities, psi4, psi6, psi9 and psi11 expressing an image axial symmetry relation are extracted; S4, spectrum clustering analysis is carried out on the invariant moment characteristic quantities, psi4, psi6, psi9 and psi11, and a cluster tree is output; S5, according to cluster validity indexes, the optimal cluster tree is selected out, and fault line selection is carried out. The method is accurate in line selection, and can improve reliability of power distribution network fault line selection.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Single-phase grounding fault line selection method applied to flexible grounding system
InactiveCN110488155AImprove the accuracy of line selectionReduce misjudgmentFault location by conductor typesCapacitanceCorrelation coefficient
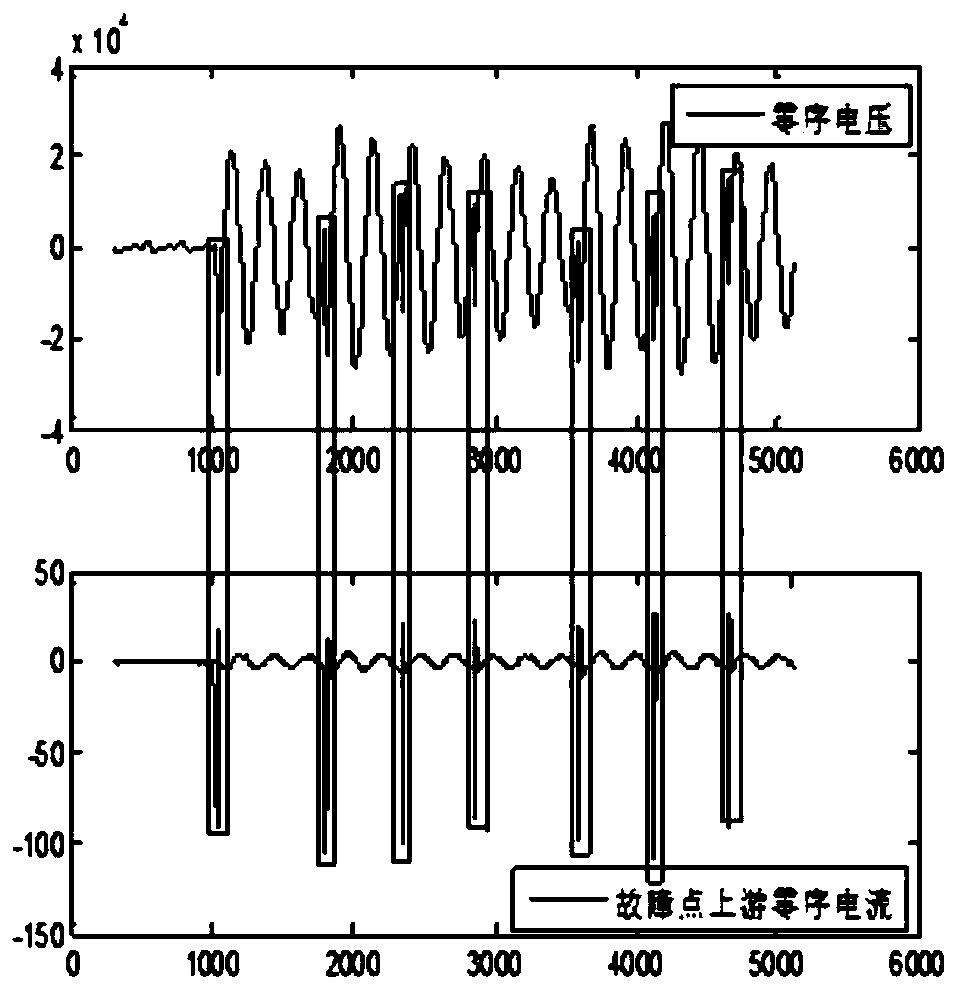
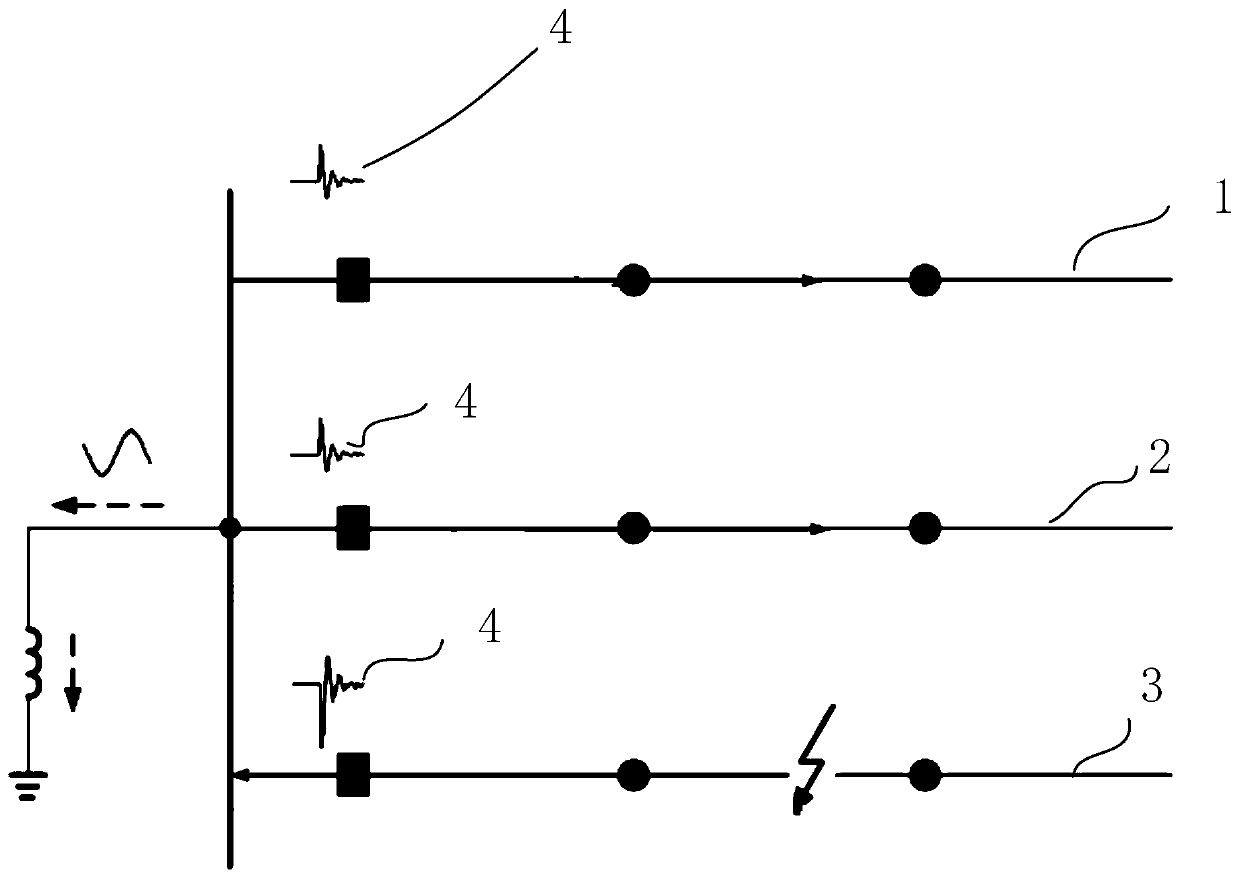
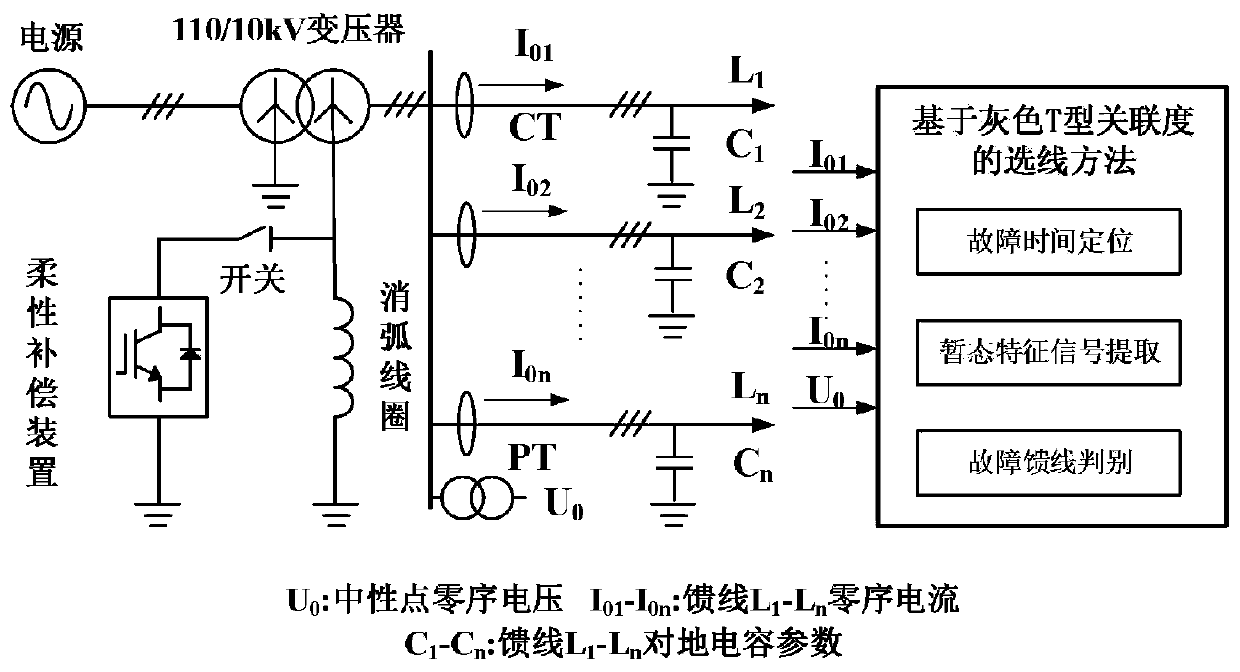
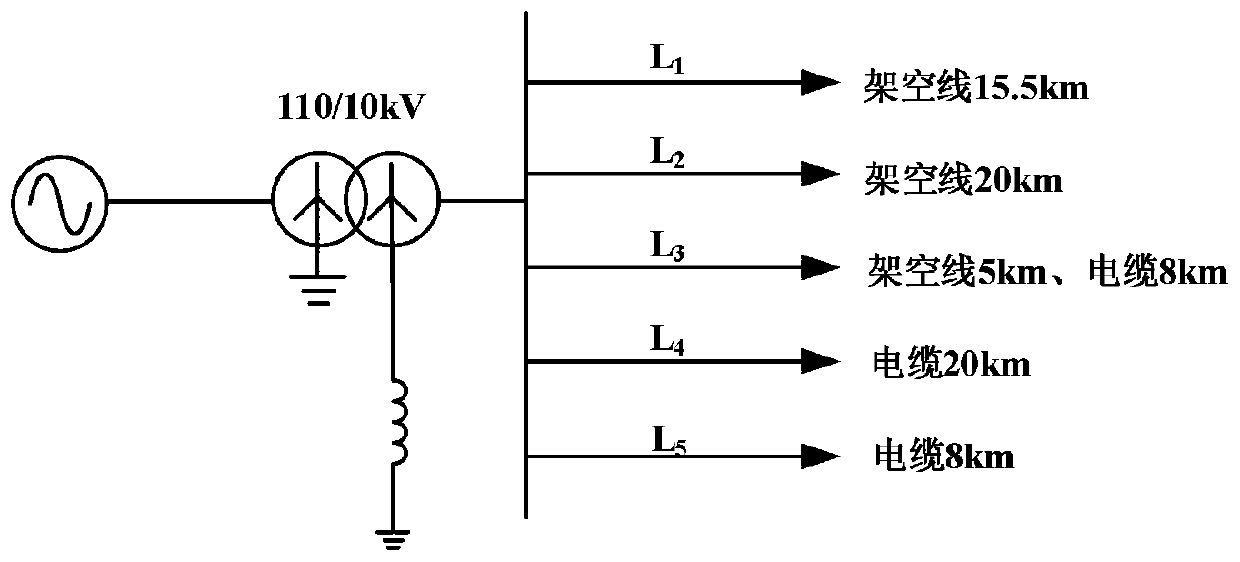
The invention discloses a single-phase grounding fault line selection method applied to a flexible grounding system. The method comprises three steps of fault time positioning, transient characteristic signal extraction and faulty feeder discrimination, and specifically comprises the steps of 1) carrying out wavelet packet decomposition on a zero sequence voltage signal of a neutral point, and taking a time point corresponding to a modulus maximum point as the actual fault time; 2) selecting feeder zero-sequence current signals of 1 / 4 and 3 / 4 periods before and after the actual fault time, carrying out wavelet packet decomposition and reconstruction, and extracting transient characteristic waveforms; and 3) calculating a comprehensive gray T-shaped correlation coefficient of the transientcharacteristic waveform of each feeder, and comparing the comprehensive gray T-shaped correlation coefficient with a threshold value to determine a faulty feeder. According to the method, the relevance of the dynamic change trend of the overhead line and the dynamic change trend of the cable is effectively reflected, the misjudgment caused by the difference between the capacitance values of the cable and the overhead line to the ground is reduced, the requirements of a flexible grounding system for the rapidity and accuracy of line selection are met, and the method has feasibility and practical value.
Owner:LIYANG RES INST OF SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Line selection method based on FastICA for low current grounding system in single-phase grounding fault
The invention relates to the technical field of grounding fault identification, in particular to a line selection method based on a FastICA for a low current grounding system in a single-phase grounding fault. According to the method, the FastICA method is utilized to process zero-sequence current of the grounding fault, three observation channels are arranged to separate fault steady-state components, transient-state components and noise signals from observation signals, the line fault characteristics are obvious after processing, and accurate line selection can be conducted on a fault line according to the energy of line separation variables. Because the noise signals are separated at the same time, the method is reliable, high in anti-interference capability and capable of not being affected by interference signals; meanwhile, for different initial phase angles of the fault, satisfactory line selection results can all be obtained by means of the method. By using the method to decompose and analyze the zero-sequence current of the fault, the cancellation or compensation among the components of the signals can be avoided, so that the fault characteristics are obvious to achieve the accurate line selection, and the method is widely applicable to the low current grounding system.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Small current line selection method using correlation analysis
InactiveCN110542821ALine selection is accurateHigh speedFault location by conductor typesComplex mathematical operationsCurrent sampleTransient state
The invention discloses a small current line selection method using correlation analysis. The method comprises following steps of first, starting a line selection device, then recording more zero-sequence current sampling data, that is, recording sampling data of each line zero-sequence current of one cycle before a fault and ten cycles after a fault; second, for each line fault zero-sequence current, deducting sampling data of the first cycle before a fault from sampling data of the first cycle after the fault correspondingly, then deducting sampling data of the tenth cycle after the fault correspondingly; and third, obtaining a transient pure fault component of a zero-sequence current, then performing correlation analysis by using the transient pure fault component of the zero-sequence current rather than the zero-sequence current, so as to realize fault line selection. The method can detect a fault line by analyzing similarity of line zero-sequence currents, and selects a line accurately and rapidly.
Owner:江苏莱尔曼电气科技有限公司
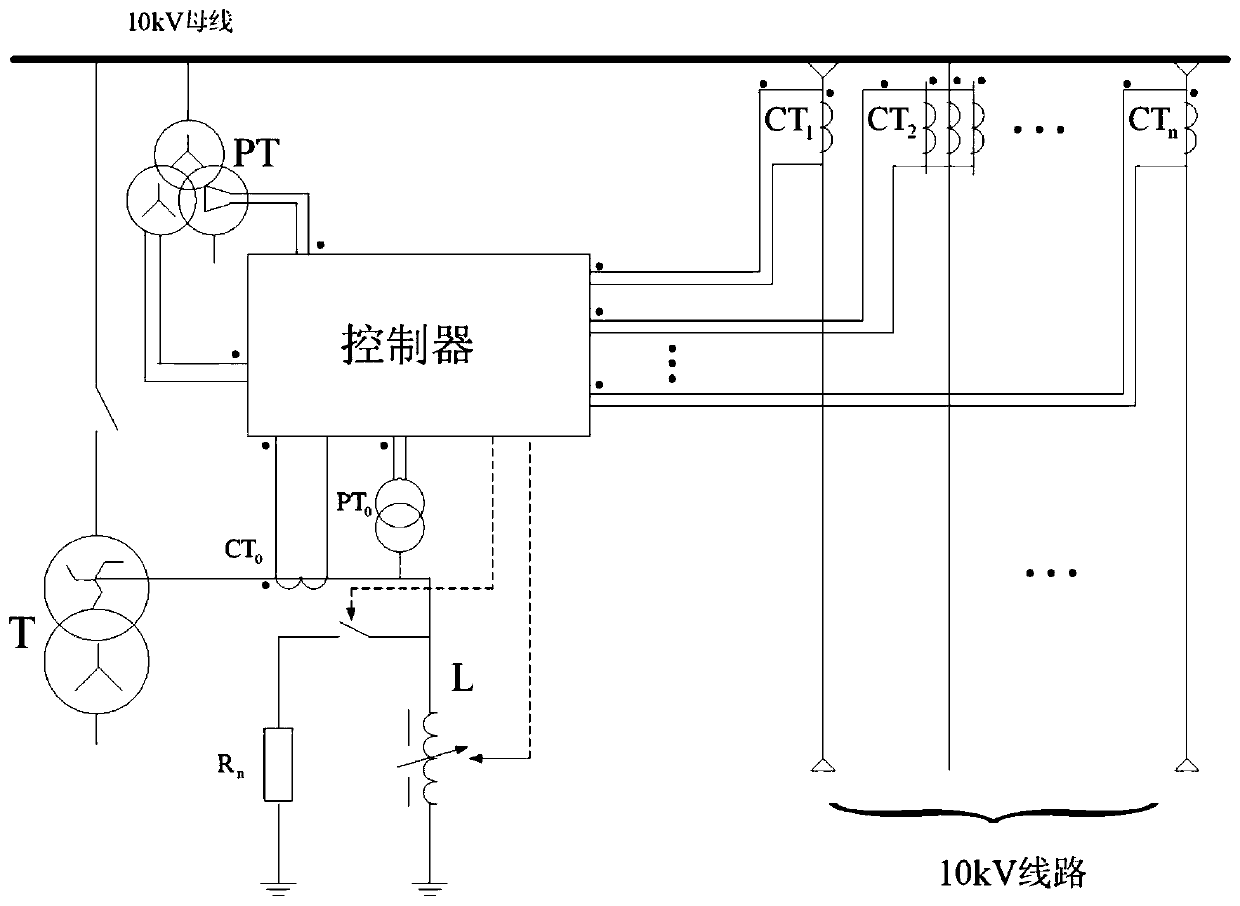
Neutral-point grounding control equipment medium-voltage power grid
PendingCN110416990AReduce residual flowGuarantee safe operationEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPower gridEngineering
The invention discloses neutral-point grounding control equipment of a medium-voltage power grid. The neutral-point grounding control equipment comprises a bus voltage transformer, a grounding transformer, a circuit zero-sequence current transformer and a controller, wherein the bus voltage transformer is connected with a bus and the controller, the grounding transformer is connected with the busand an arc extinguishing coil, a neutral point current transformer and a neutral point voltage transformer are arranged between the grounding transformer and the arc extinguishing coil and are connected with the controller, a branch is arranged between the neutral voltage transformer and the arc extinguishing coil and is connected with a resistor by a switch connected with the controller, the controller is connected with at least two branch lines by the circuit zero-sequence current transformer, and the branch lies are connected with the bus. The advantages of two grounding modes of neutral-point resonant grounding and resistance grounding are combined, the advantage that a line can be accurately selected by resistance grounding is maintained, residual current of a grounding point also canbe reduced, an arc light grounding overvoltage is limited, an appropriate working mode can be selected according to different conditions of a short-term grounding fault or a permanent grounding fault, the safety running of the line is guaranteed, and the power supply reliability is also improved.
Owner:赵子云 +1
An arc grounding overvoltage limiting device applied to medium voltage power distribution system
InactiveCN102290805AEliminate arc flash overvoltage to groundEliminate overvoltageEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentDistribution systemVaristor
The invention discloses an arc grounding overvoltage limiting device applied to a medium-voltage power distribution system, which includes a single-phase fast electronic switch controlled by an intelligent controller and a high-energy nano-zinc oxide energy-absorbing arc extinguishing device; the single-phase fast electronic switch is three Only, the main circuits of the three single-phase fast electronic switches are connected in a star shape, and the three high-voltage terminals are respectively connected to the three-phase busbar of the system, and the other ends are connected in parallel to the upper end of the high-energy nano-zinc oxide energy-absorbing arc-extinguishing device The high-energy nano-zinc oxide energy-absorbing arc-extinguishing device is composed of a high-energy zinc oxide linear resistor, a nano-damping absorber, a high-energy zinc oxide non-linear resistor and a high-voltage thyristor, wherein the high-voltage thyristor is connected in parallel to the high-energy zinc oxide Linear resistors and nano-damping absorbers at both ends. Compared with the prior art, the invention can effectively limit the single-phase intermittent arc grounding overvoltage in various operating modes of the 3-35KV neutral point non-directly grounded power grid.
Owner:四川电器集团股份有限公司
Distribution line single-phase earth fault line selection method and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN111007427ALine selection is accurateAc/pulses peak value measurementsFault location by conductor typesComputational physicsThree-phase electric power
The invention provides a distribution line single-phase earth fault line selection method based on phase current traveling wave comparison. The method comprises the following steps: collecting three-phase current traveling waves on a distribution line, and taking a bus pointing line as a current positive direction; when a single-phase earth fault occurs in the distribution line, comparing the amplitude and the polarity relationship of the difference before and after the three-phase current traveling wave fault; when the amplitude of one phase of current traveling wave difference is greater than the amplitude of the other two phases of current traveling wave differences by more than 1.5 times, and the polarity of the phase of current traveling wave difference with the maximum amplitude is opposite to the polarity of the other two phases of current traveling wave differences, judging that the fault occurs on the line on the load side of the measurement point and the phase with the maximum current traveling wave difference amplitude is a fault phase; and if the three-phase current traveling wave difference amplitudes are the same and the polarities are the same, judging that the faultoccurs on the line at the power supply side of the measurement point. Through the technical scheme of the invention, accurate line selection of the single-phase earth fault of the distribution line can be realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Distribution network small current neutral grounding line selection method based on multi-source information fusion
ActiveCN108919043ALine selection is accurateImprove adaptabilityFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemAgricultural engineeringDistribution grid
The invention discloses a distribution network small current neutral grounding line selection method based on multi-source information fusion. The distribution network small current neutral groundingline selection method comprises the steps that a distribution network grounding line selection switch matrix (DGSM) is established to describe feeder and outlet switch models of related buses of all grounding substations in the distribution network; a feeder switch pull path sequence table (FSST) is established to describe the brake separating action sequence of each feeder and outlet switch on the bus; priority adjustment rules are established to perform necessary adjustments on the switch sequence in the feeder switch pull path sequence table (FSST); and according to the distribution networkgrounding line selection switch matrix (DGSM) and the adjusted feeder switch pull path sequence table (FSST), the distribution network grounding fault is subjected to comprehensive line selection processing until a grounding fault feeder is found. The distribution network small current neutral grounding line selection method has good adaptability to a substation line selection device under the conditions of accurate and inaccurate of line selection.
Owner:WEIHAI POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY
Low-current earthing line-selection method based on tabu search optimization RBF network
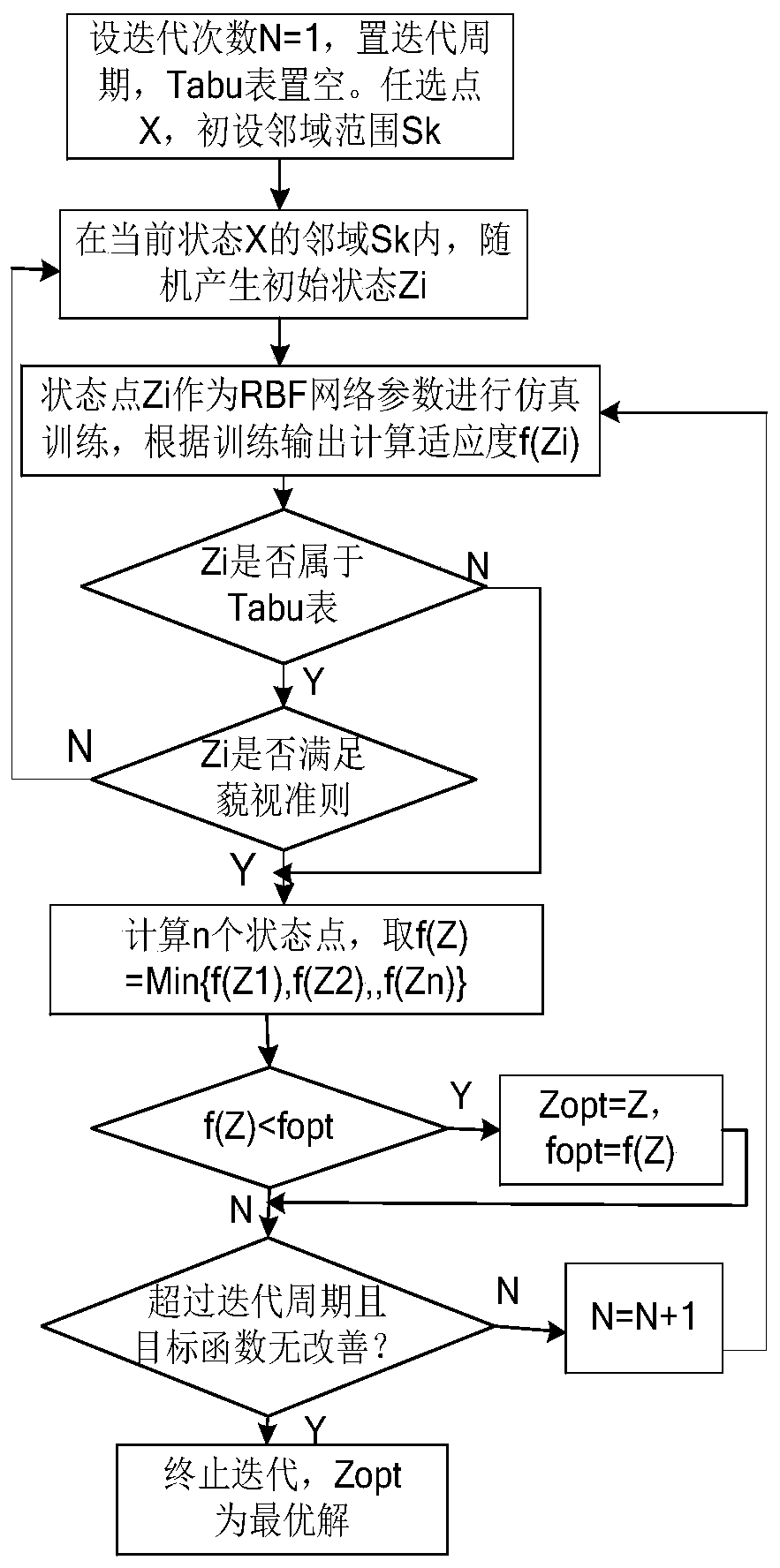
ActiveCN110221170AFast convergenceImprove robustnessFault location by conductor typesPower flowSimulation
The invention discloses a low-current earthing line-selection method based on tabu search optimization RBF network. A tabu algorithm is adopted, undermined RBF network structural parameters are trained so as to ensure that the RBF network structural parameters trend to optimal, and the optimized RBF network is used as a line selection model, so that low-current earthing fault comprehensive line selection is realized, automatic and quick determination of fault lines is realized, and stable operation of a power grid and safe equipment can be ensured.
Owner:GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com