Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80results about How to "Favorably corrected" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
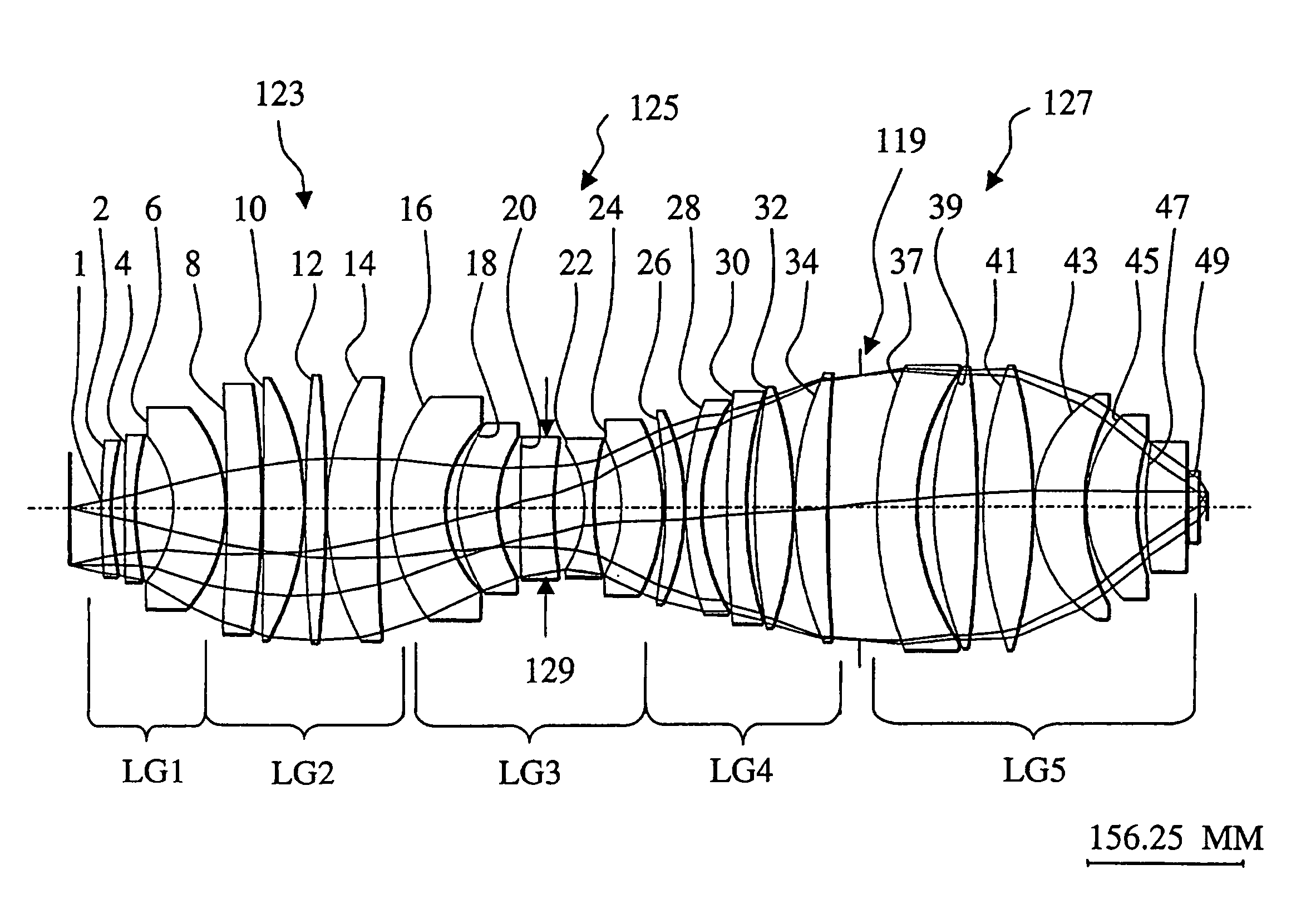
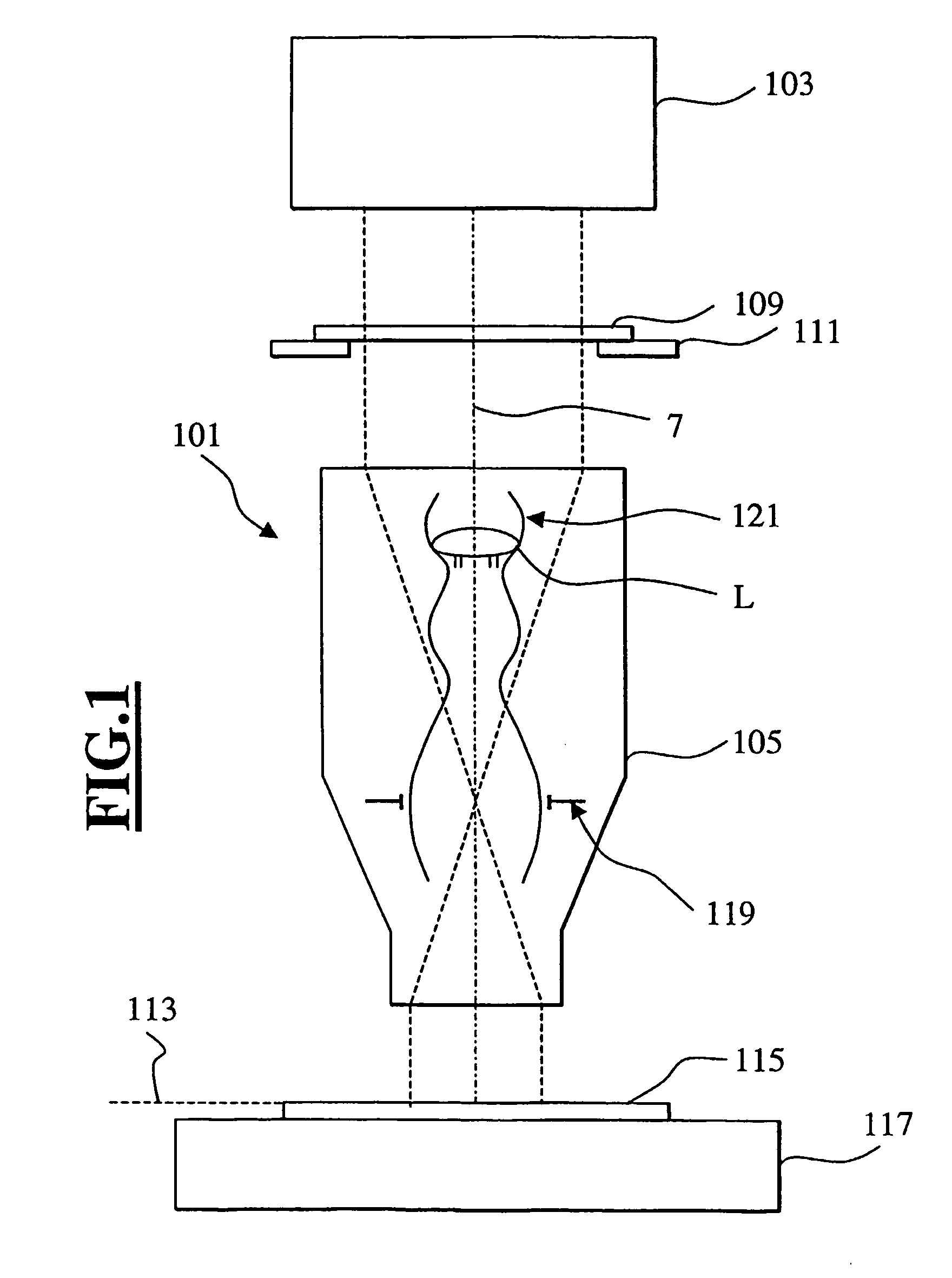
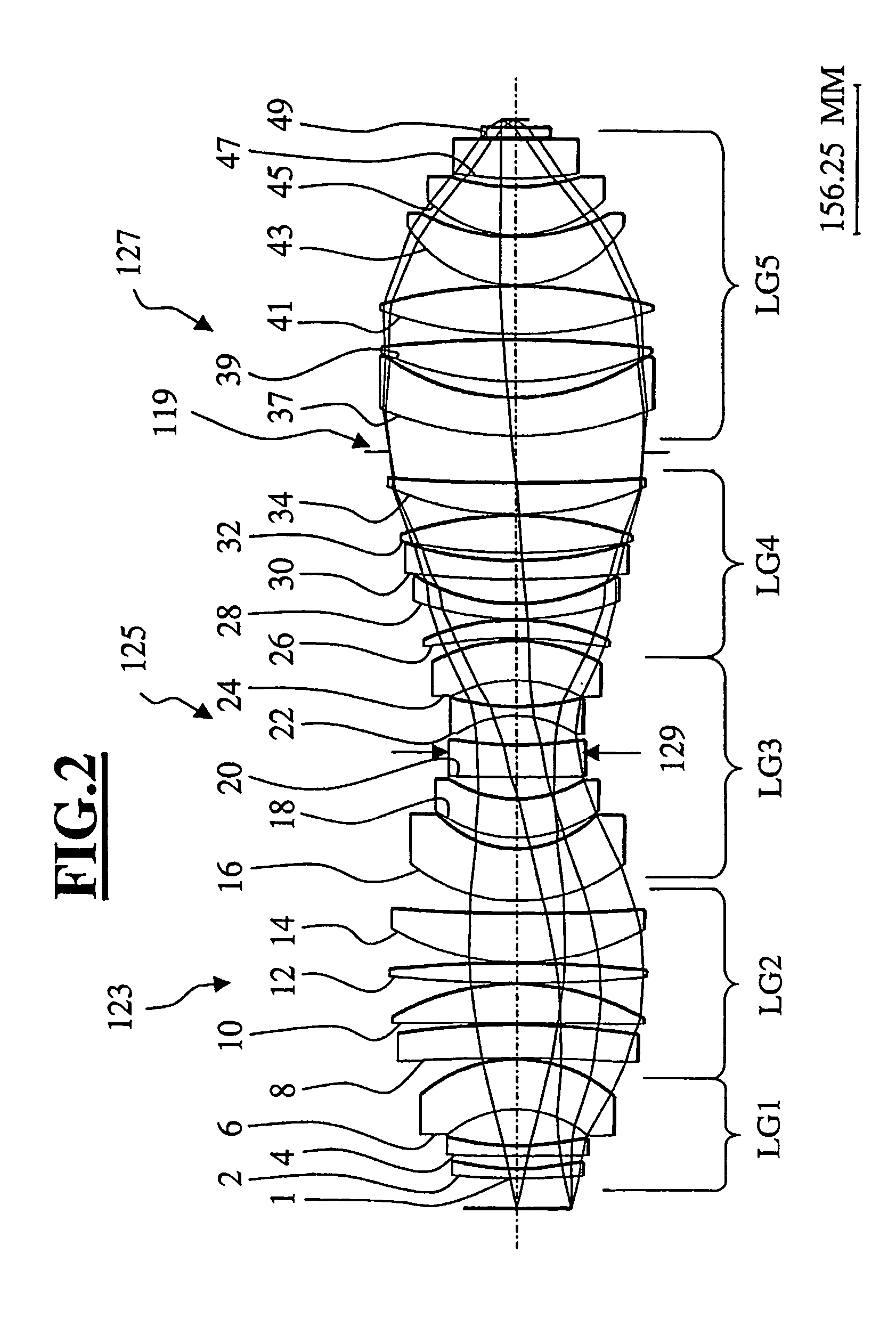
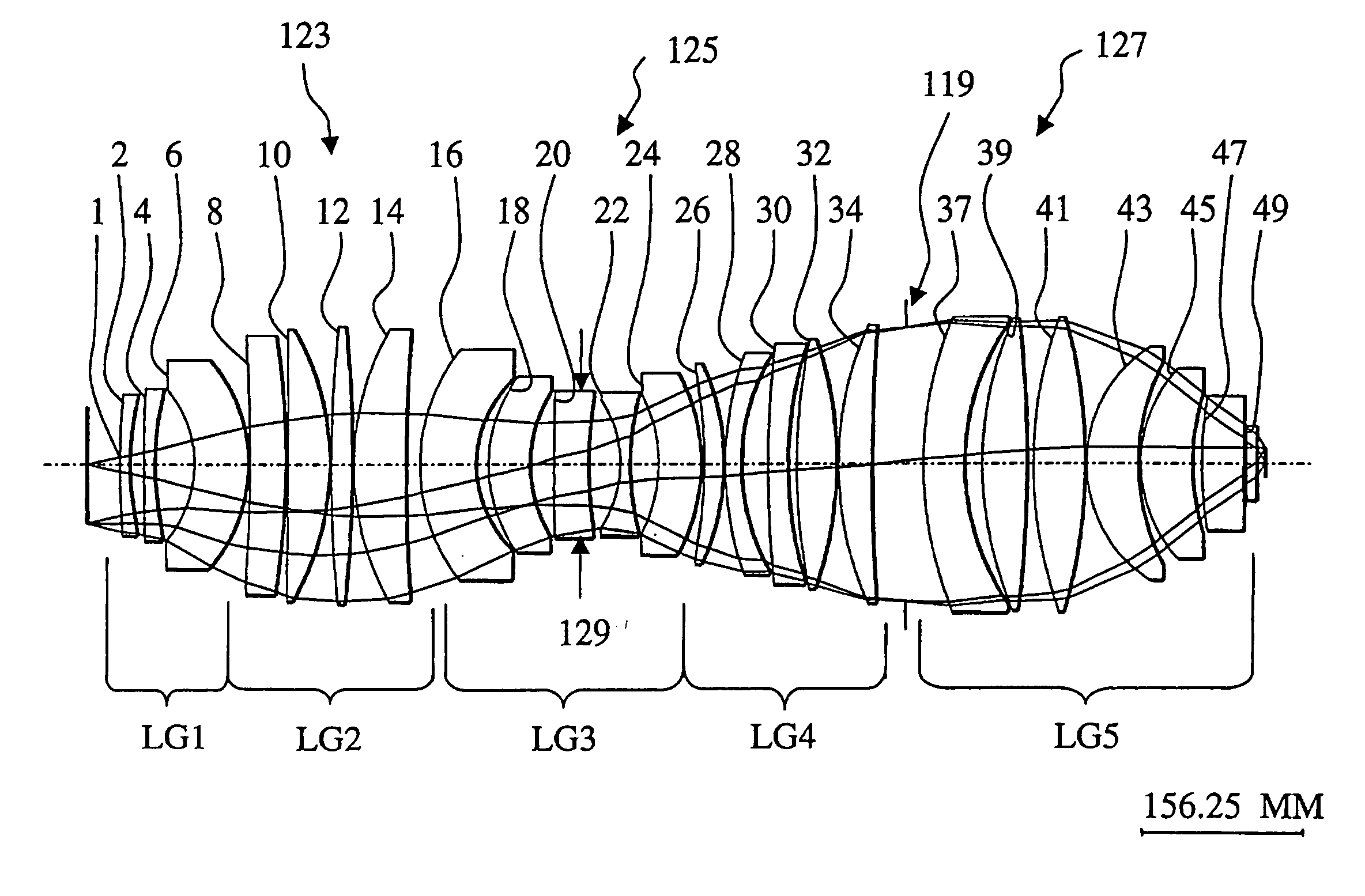
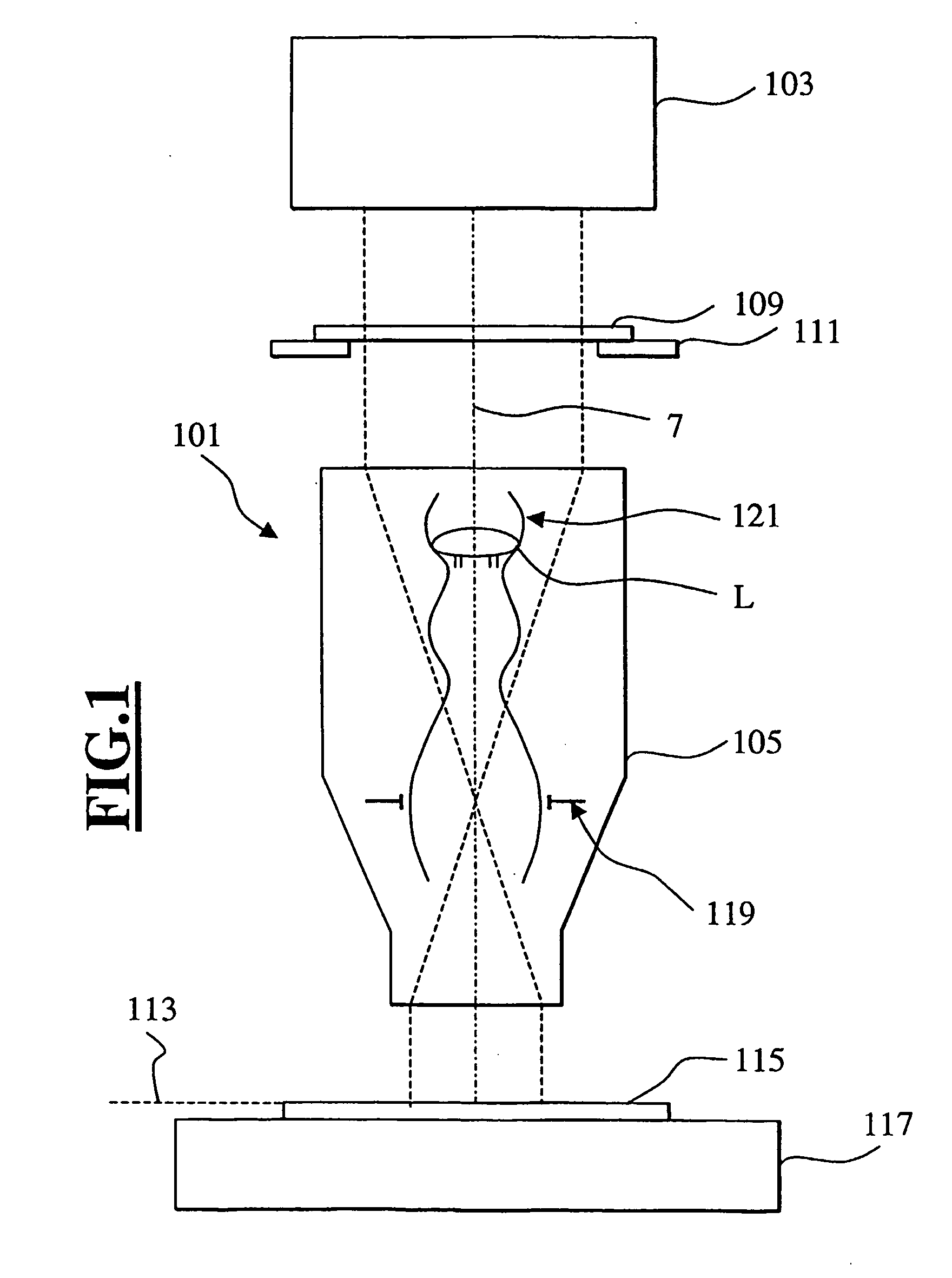
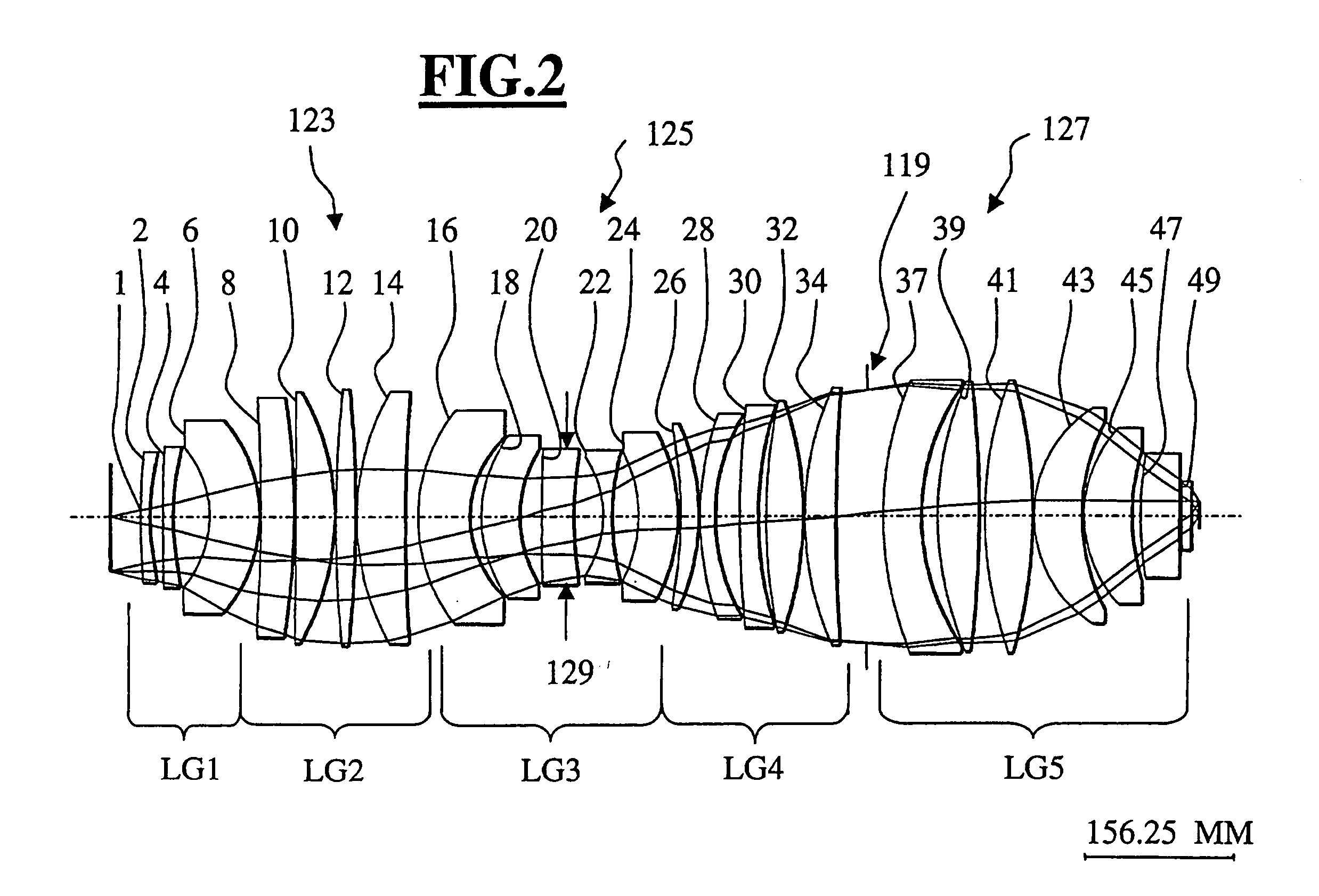
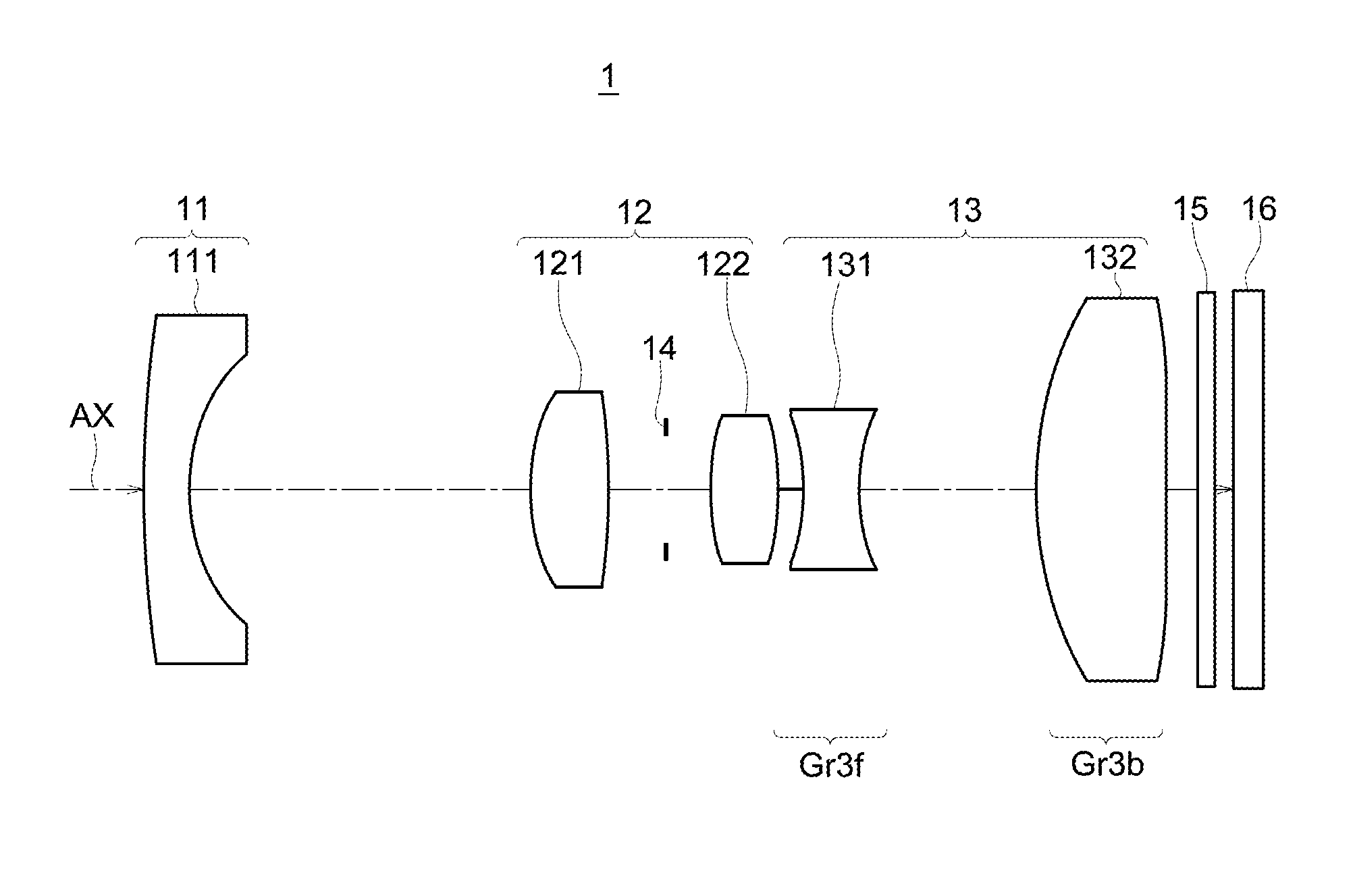
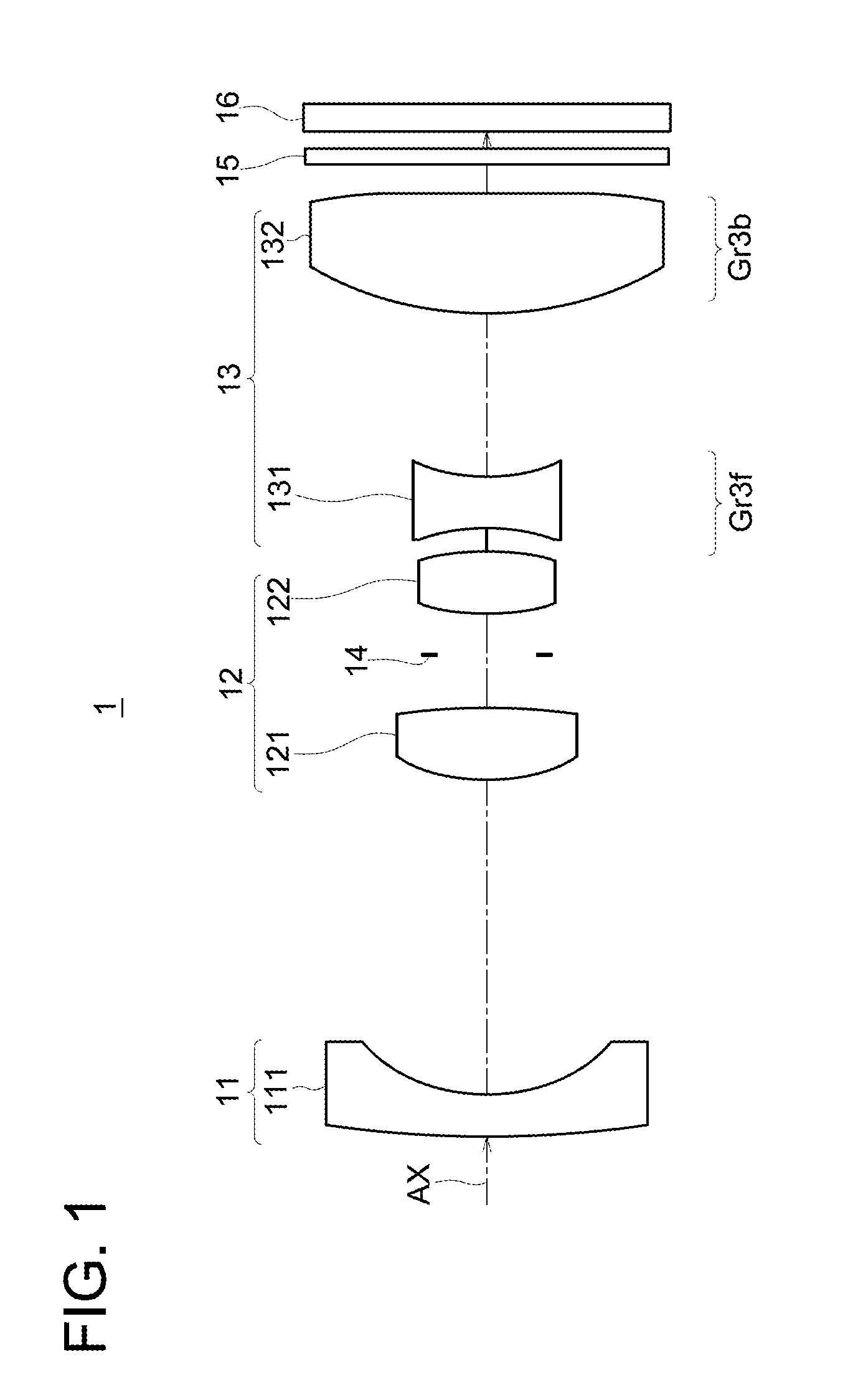
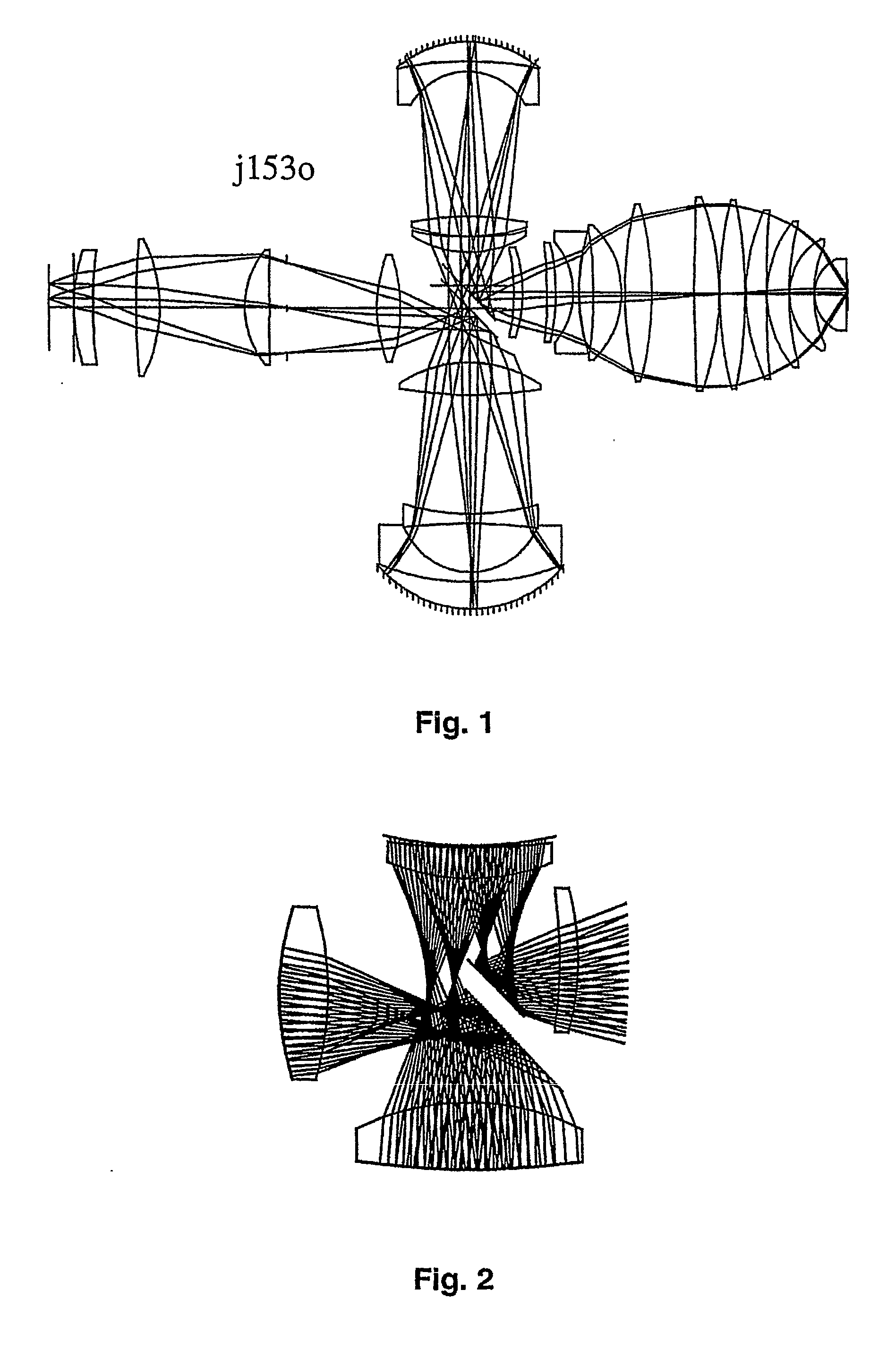
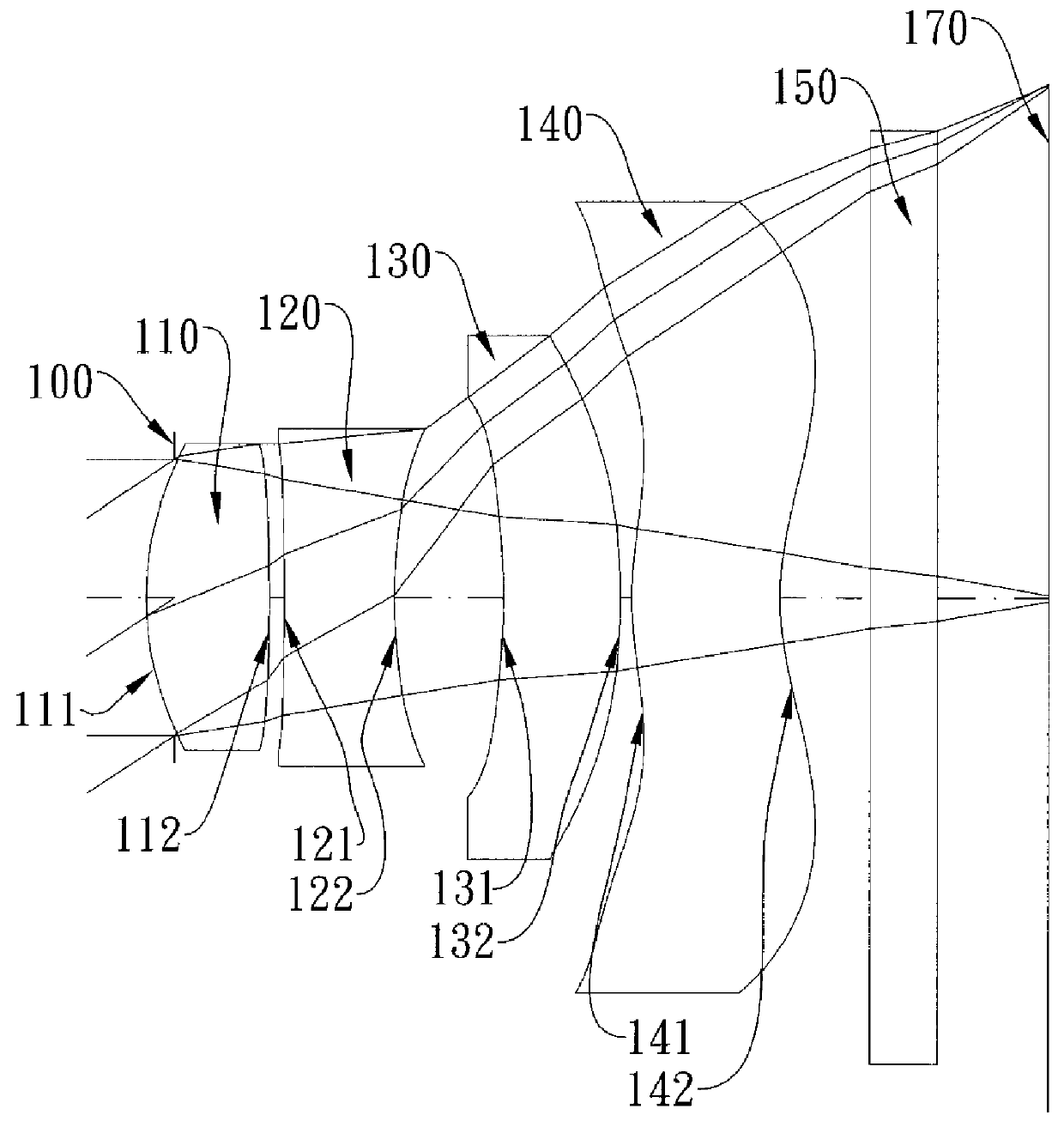
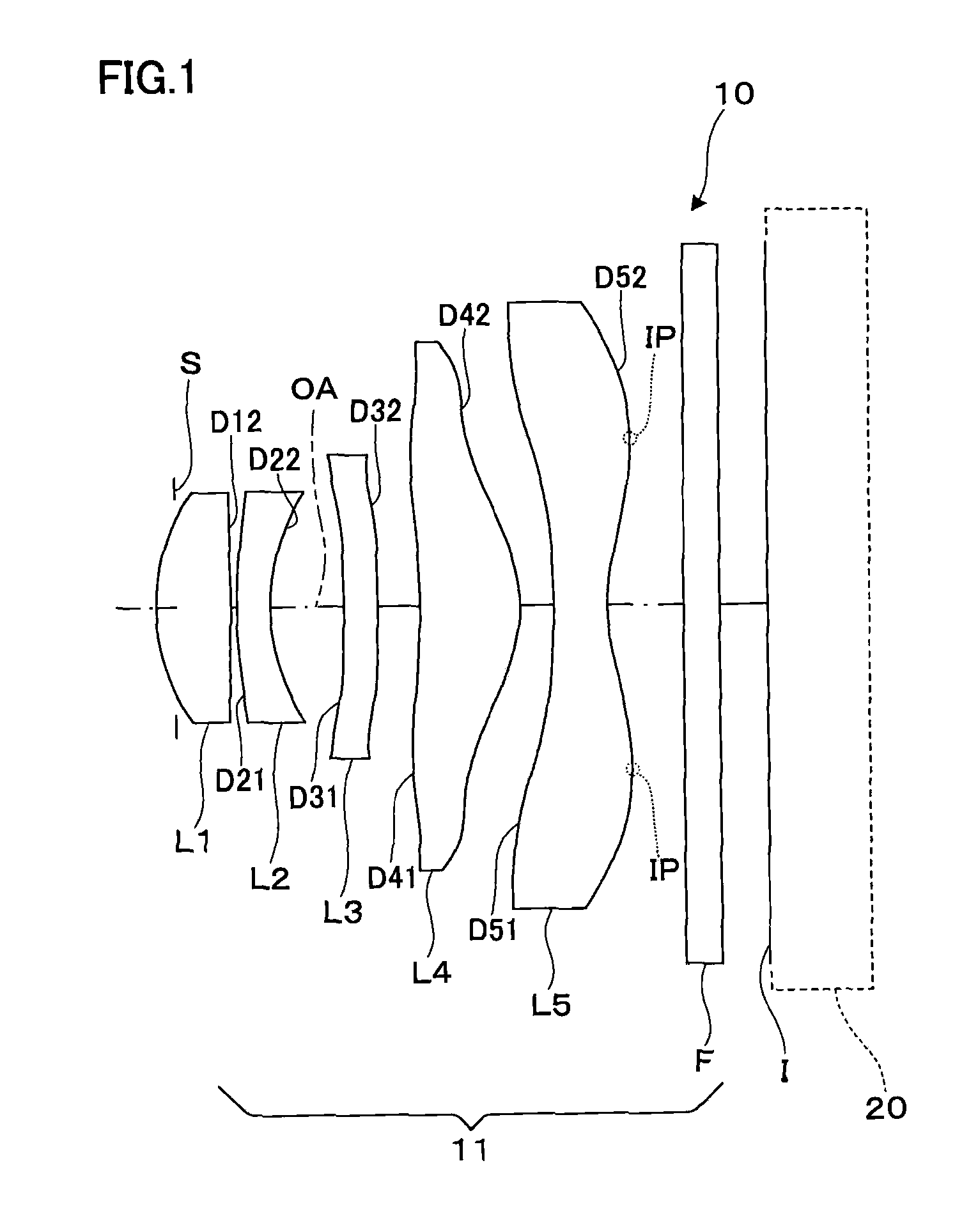
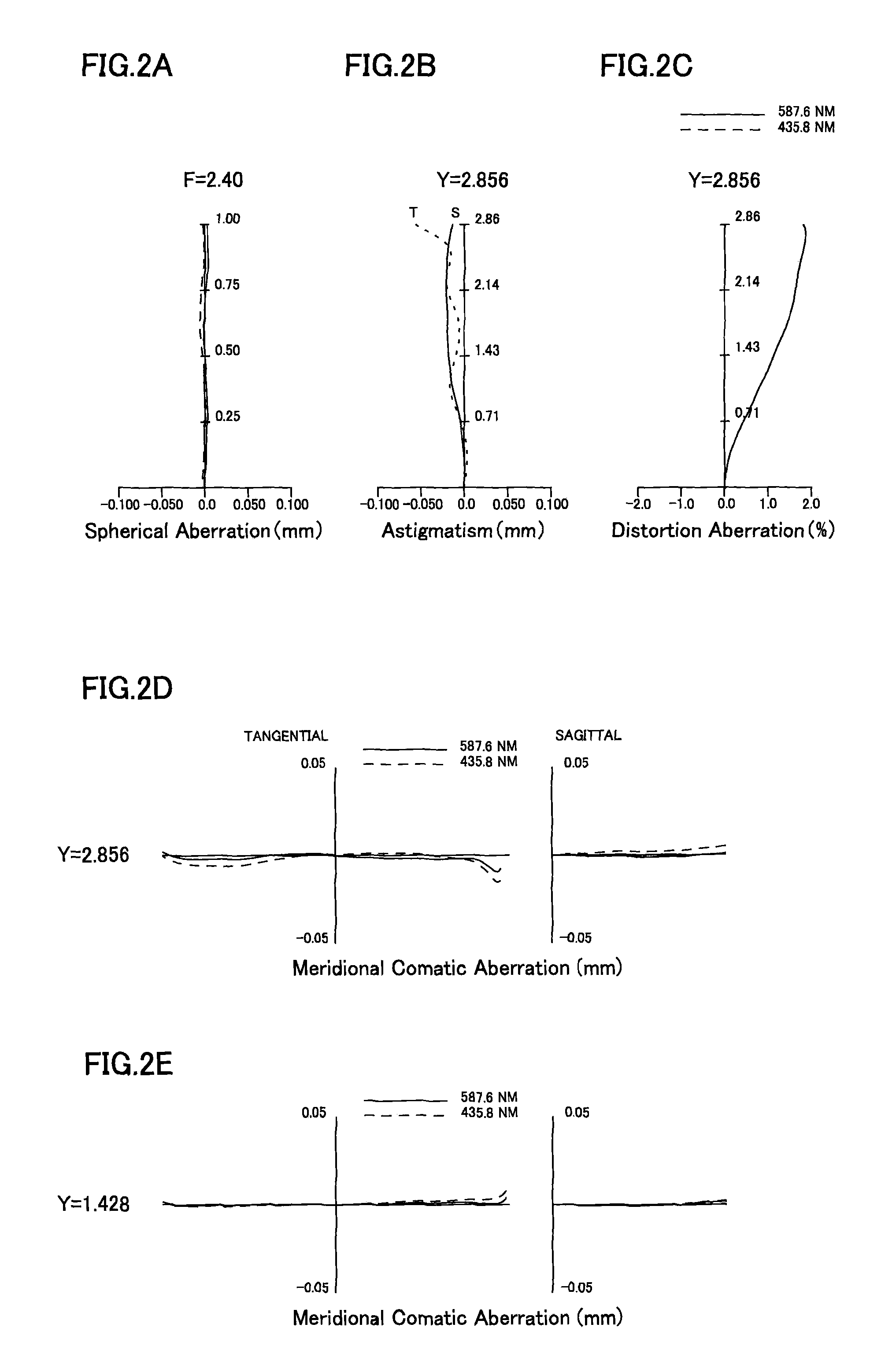
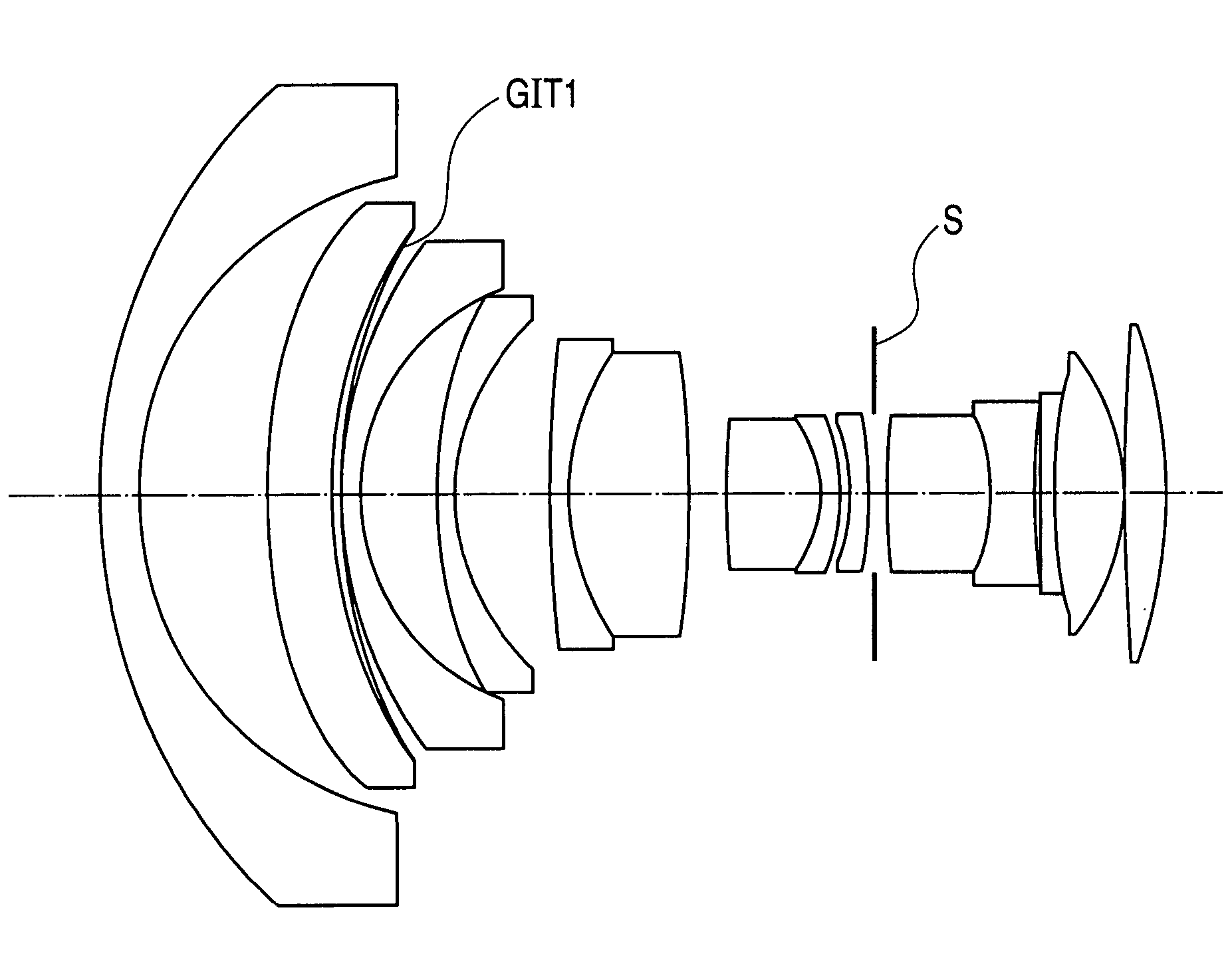
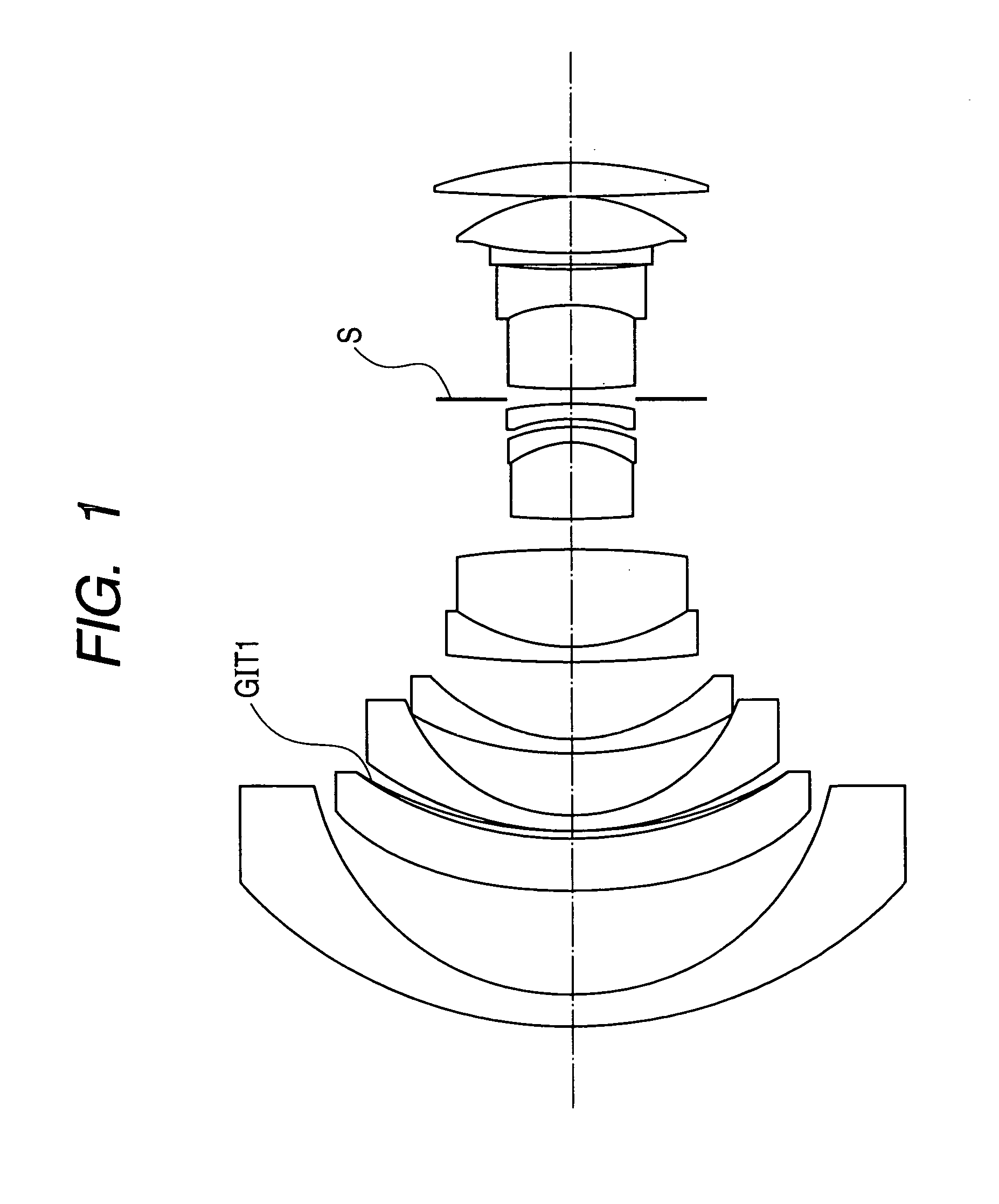
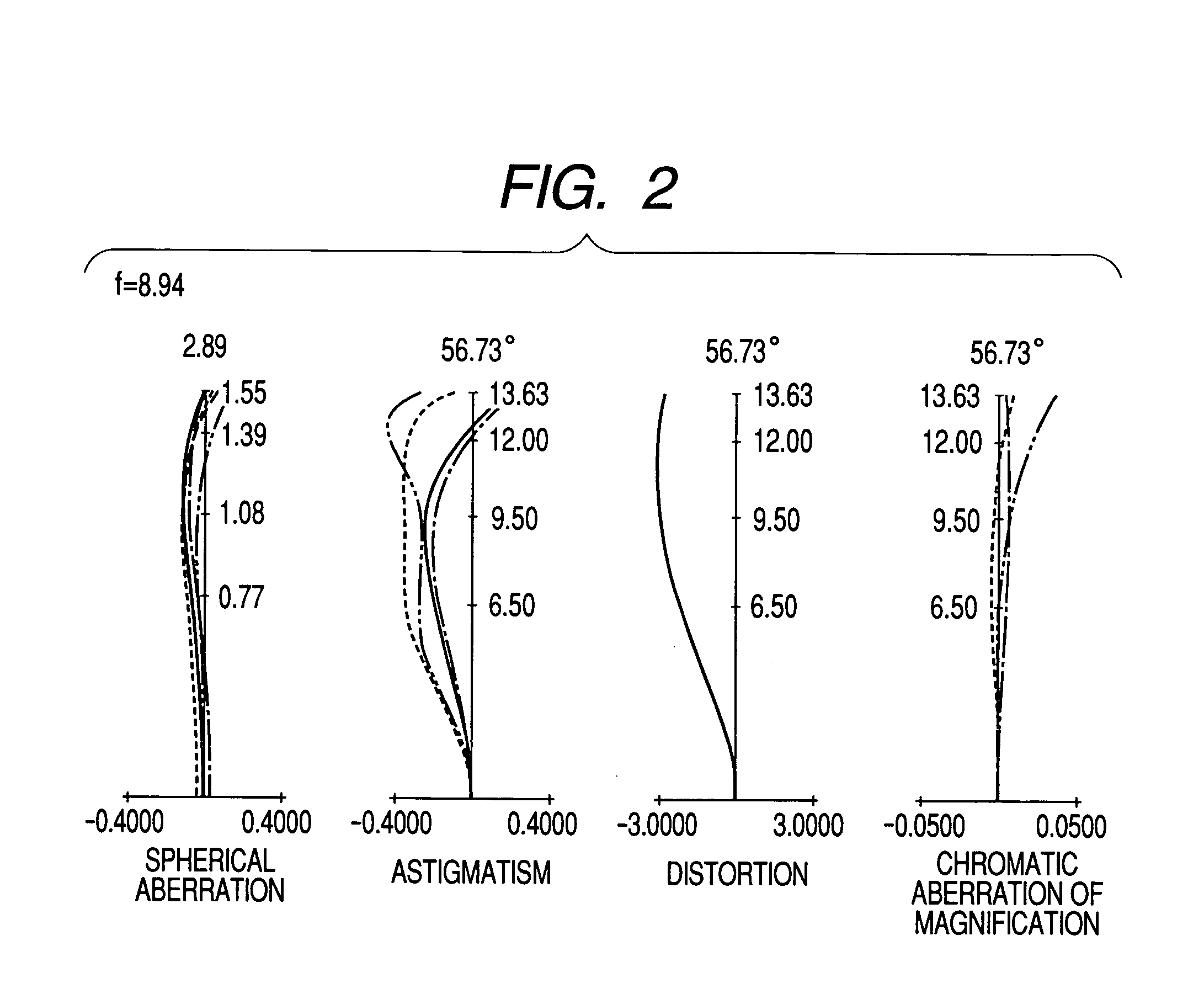
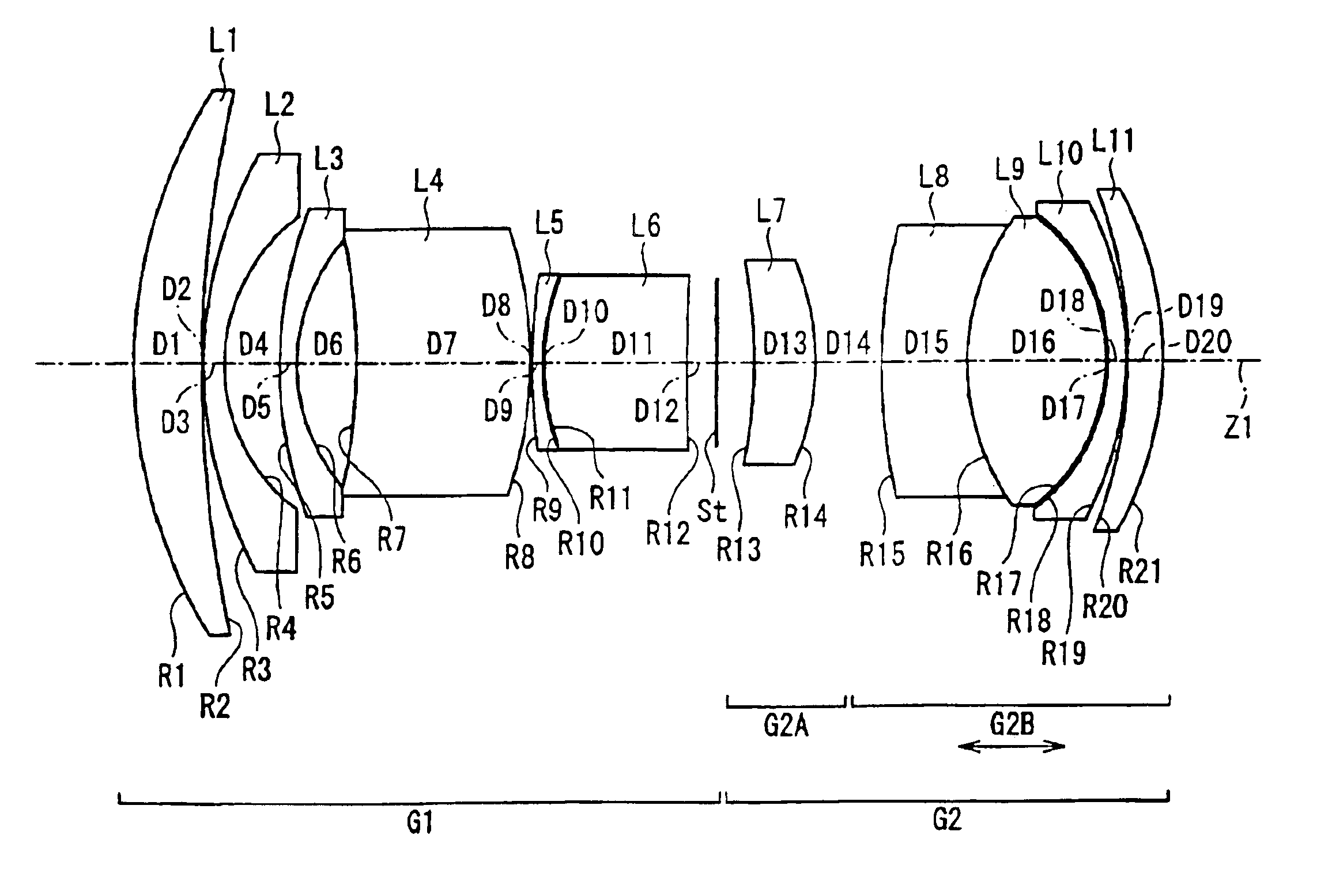
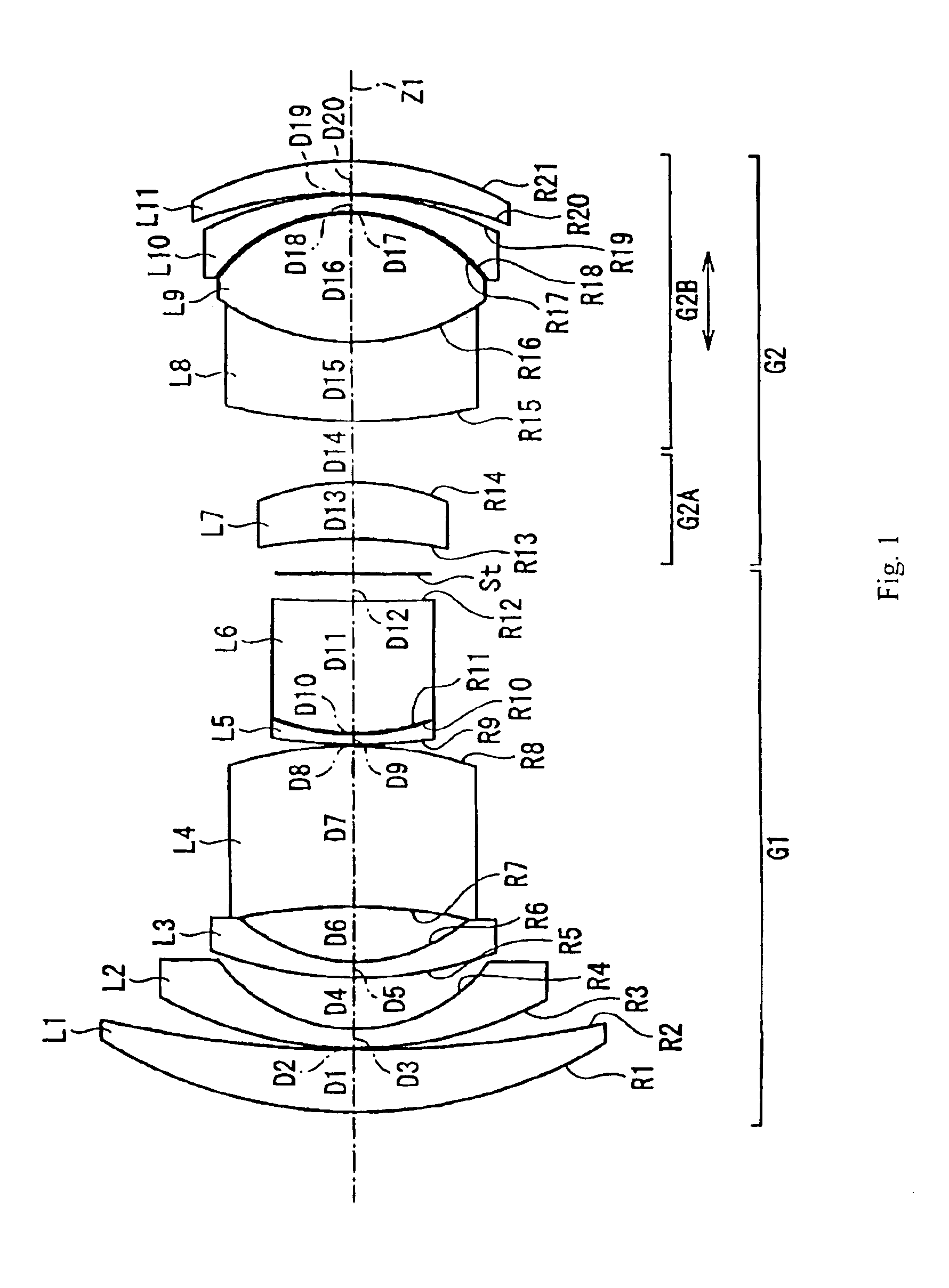
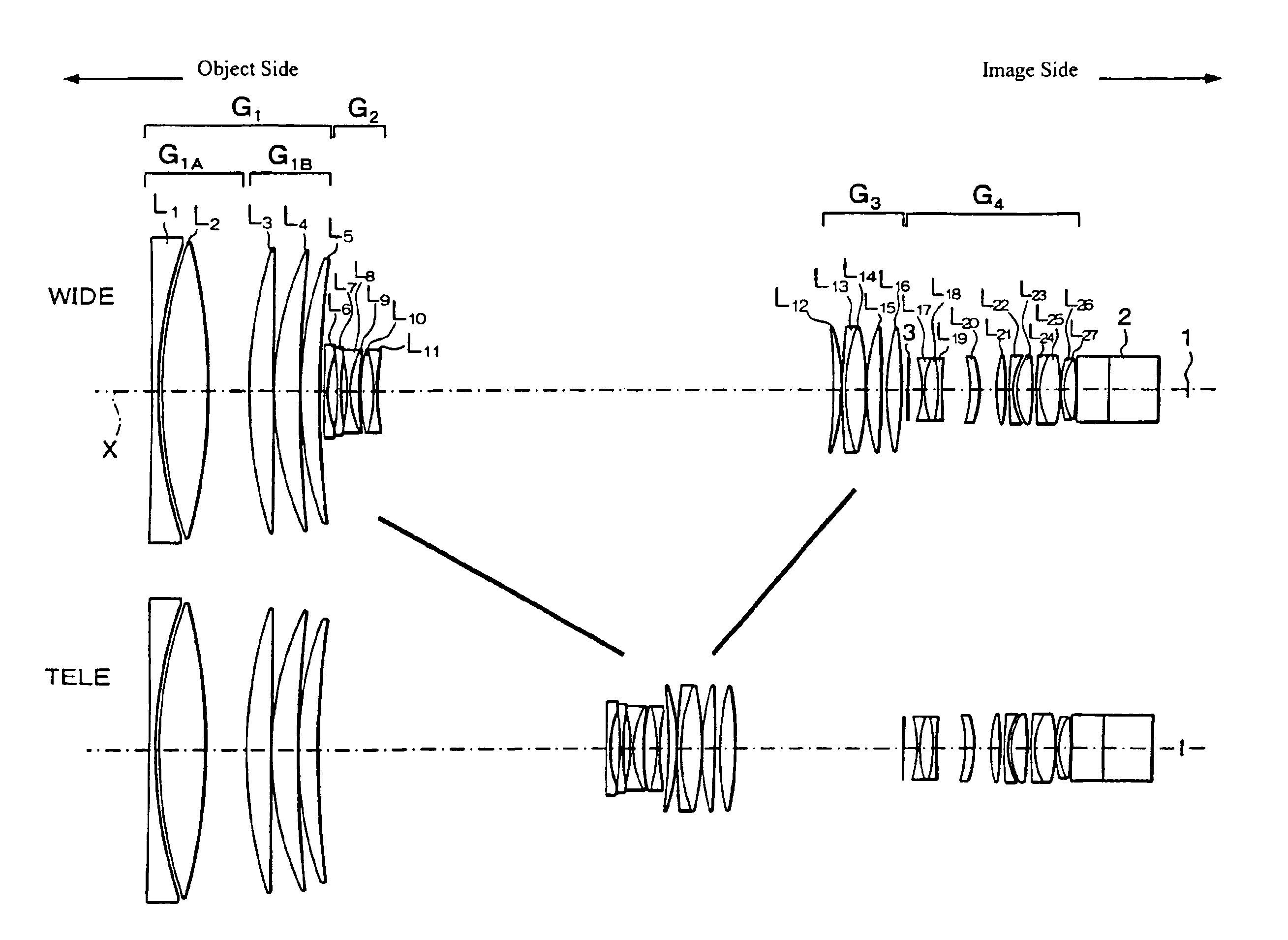
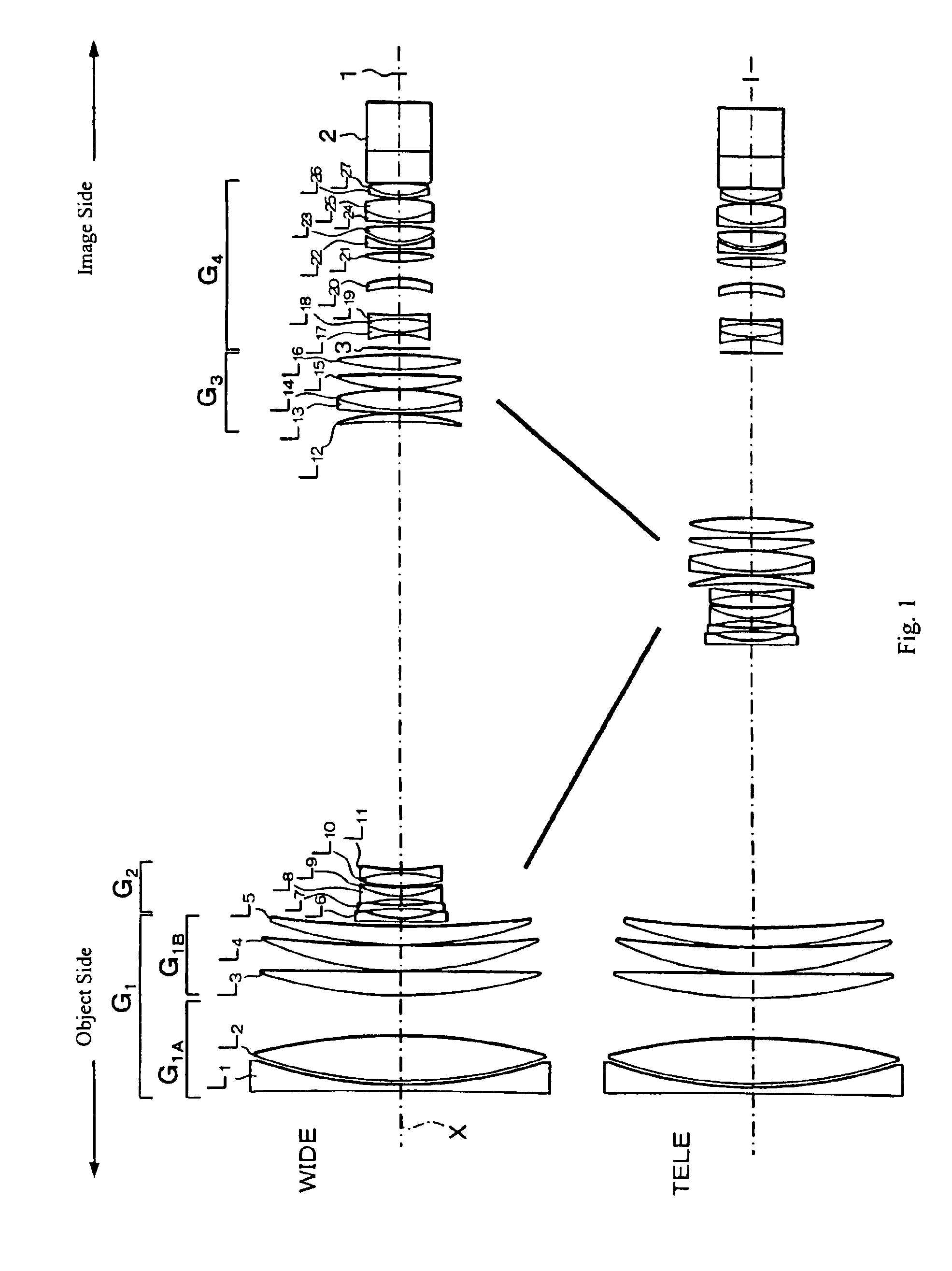
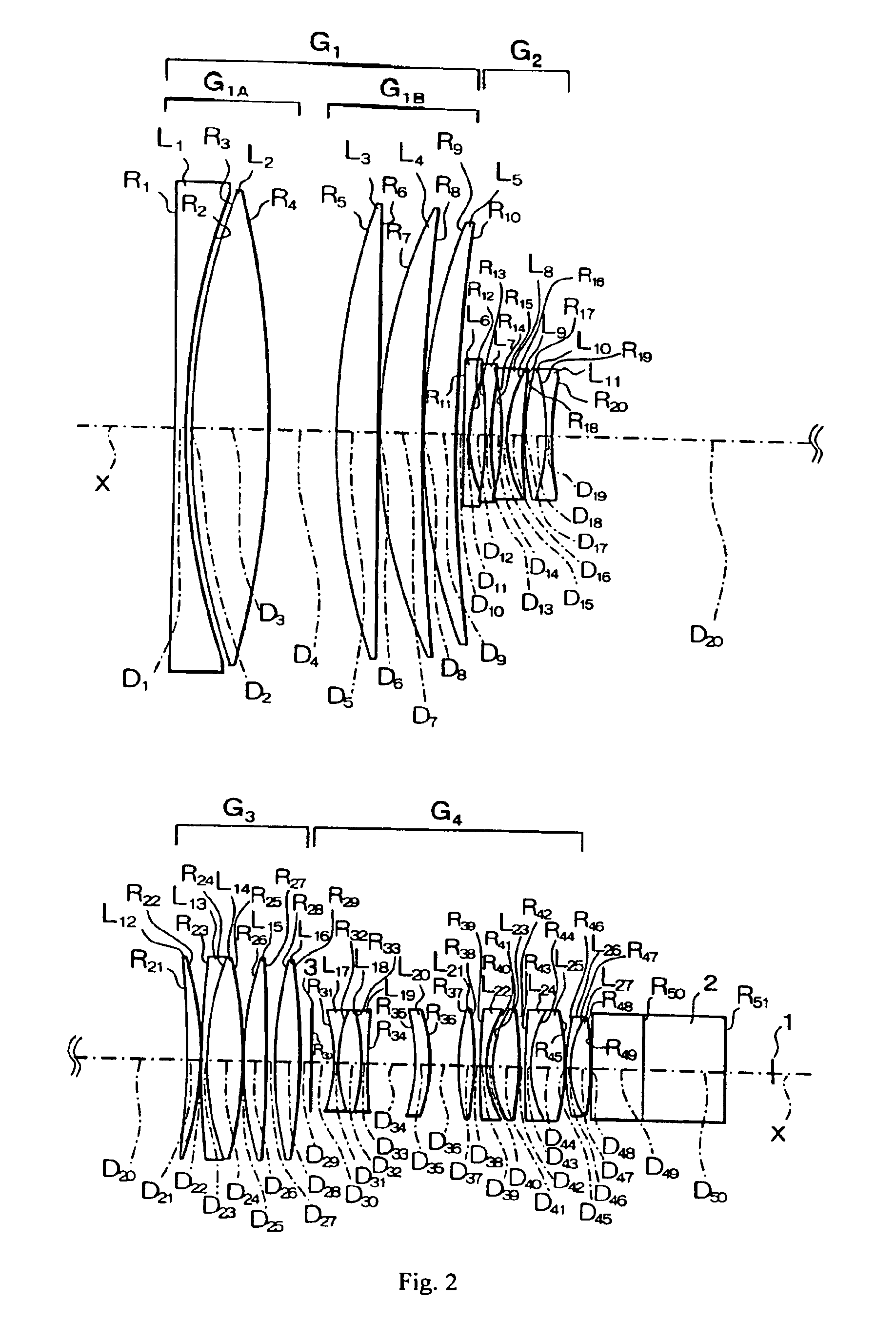
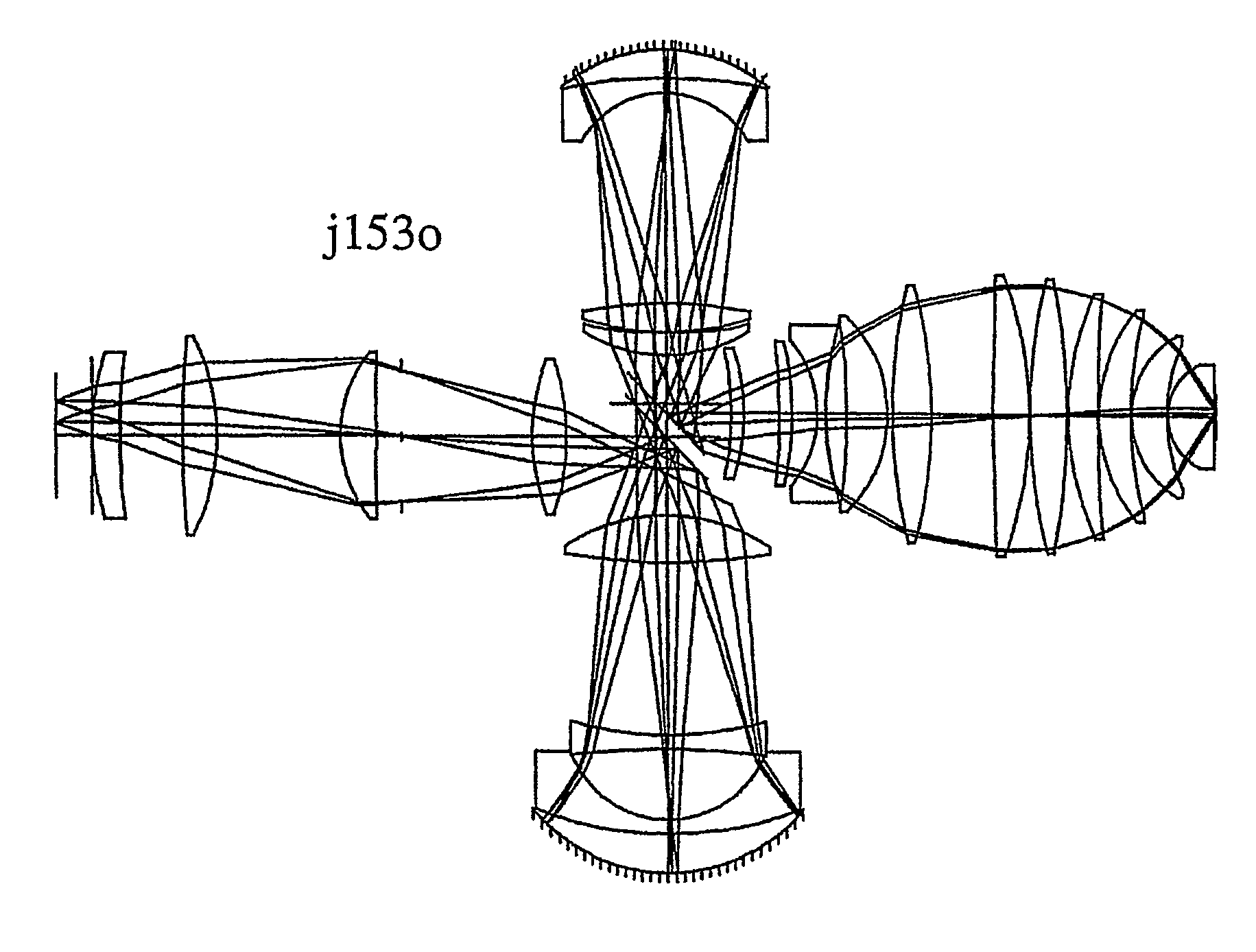
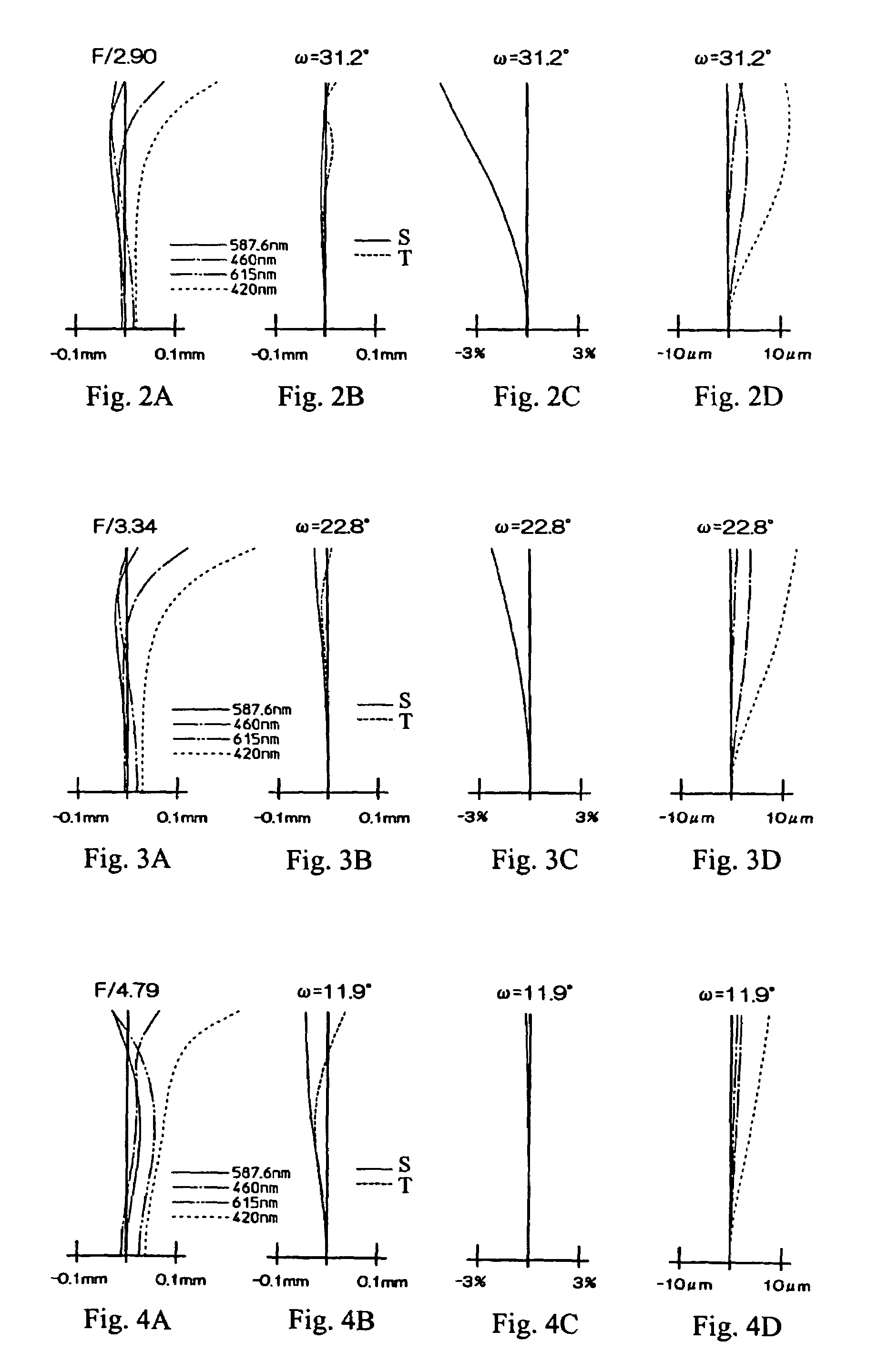
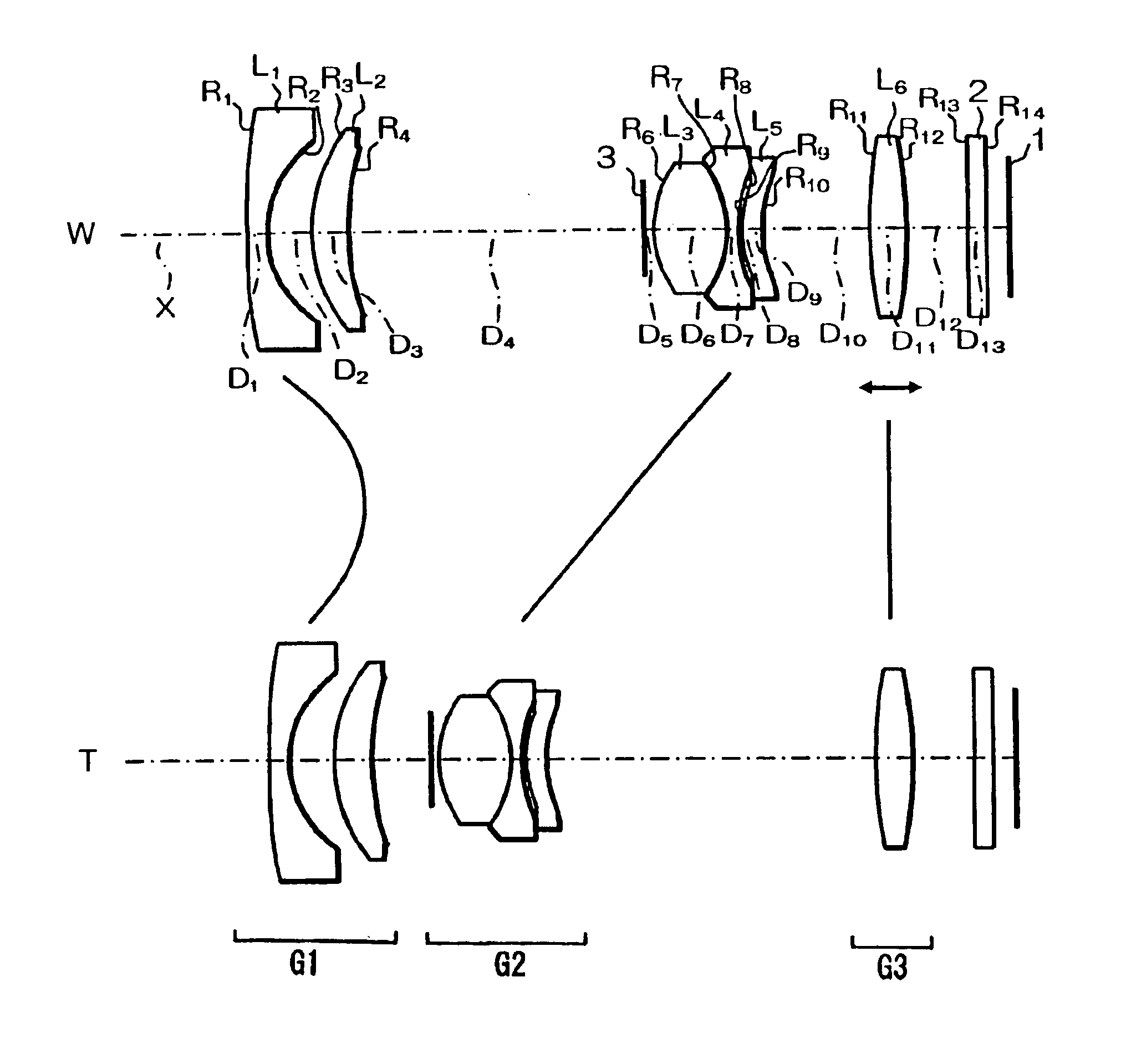
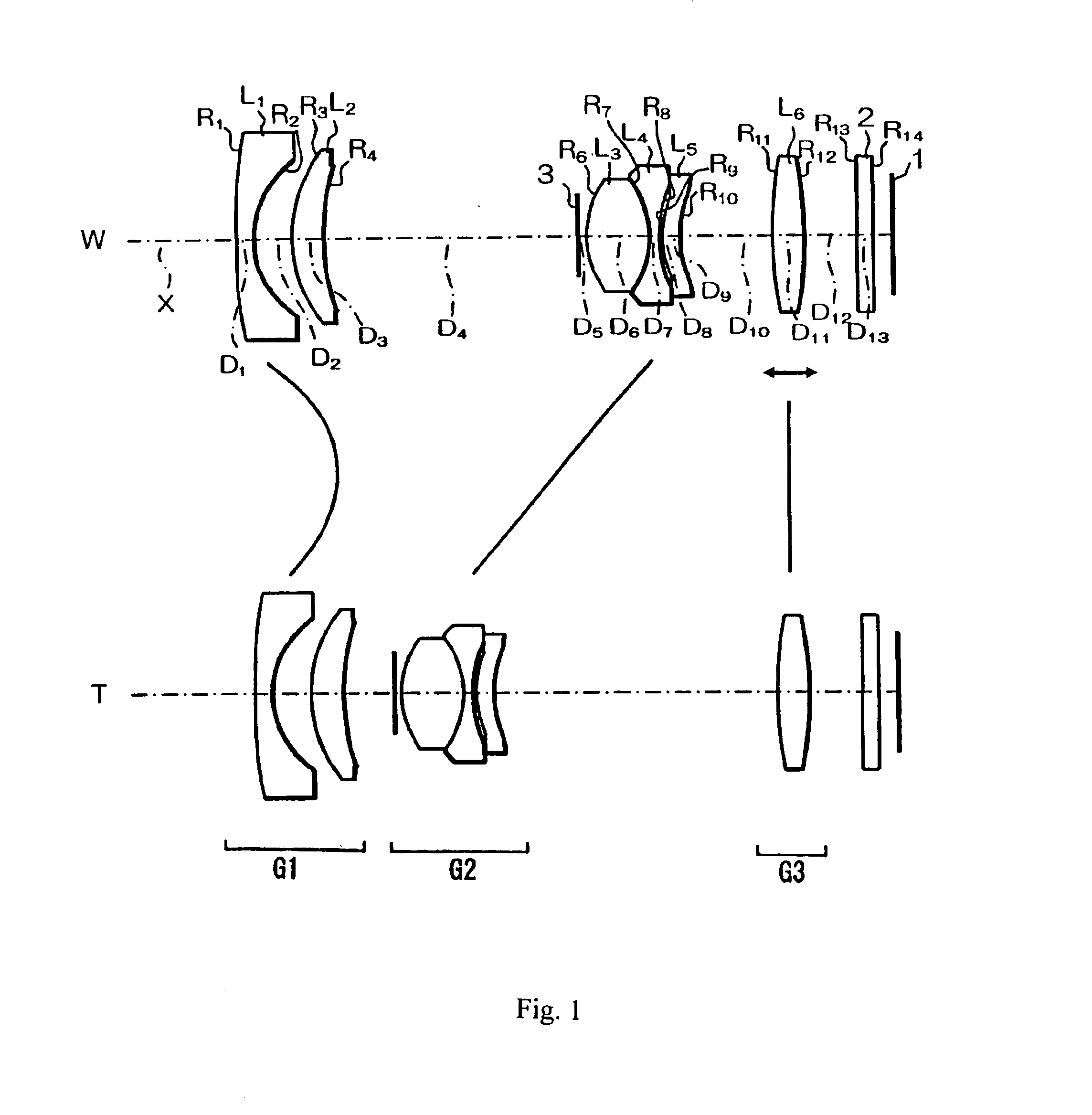
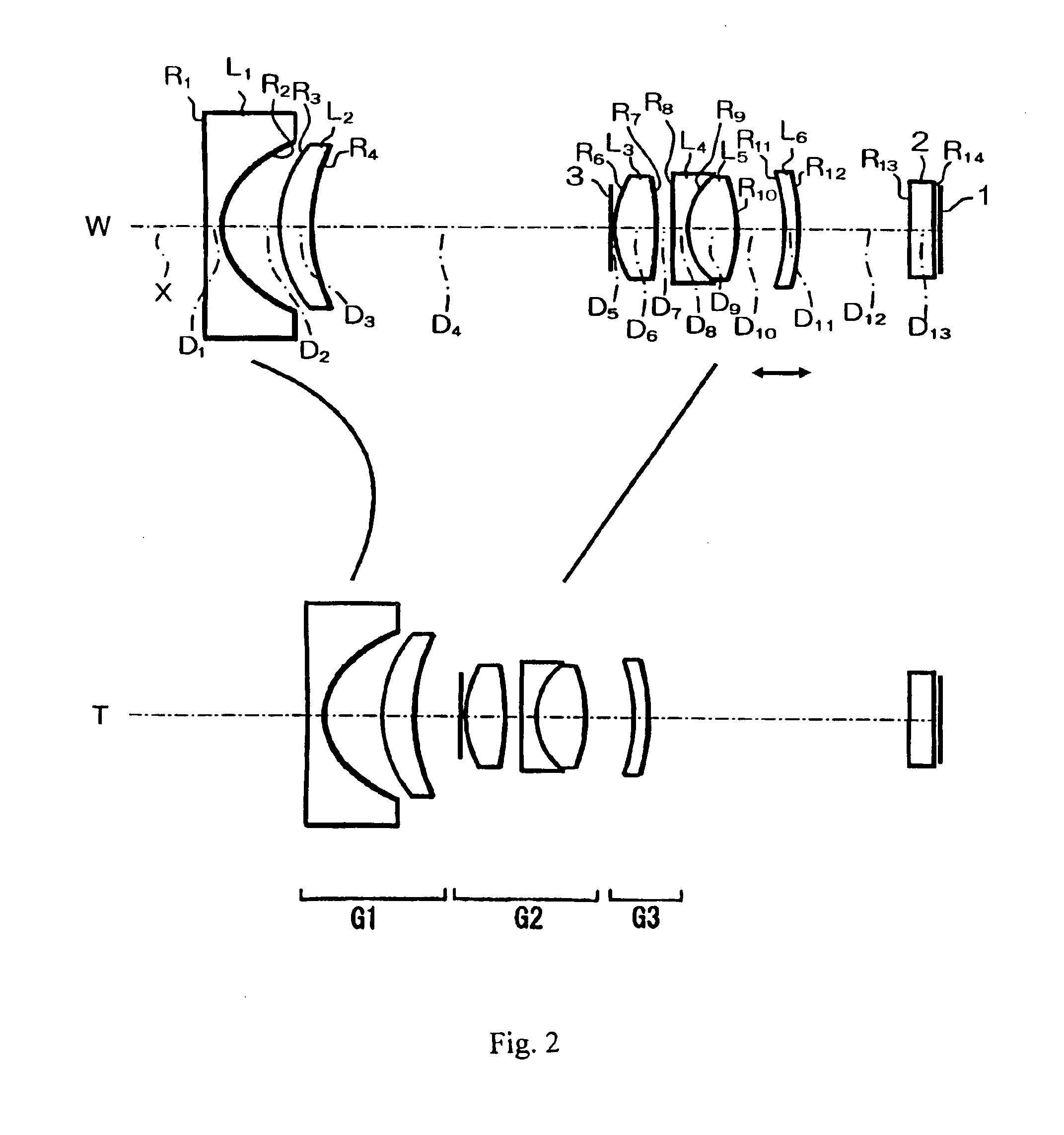
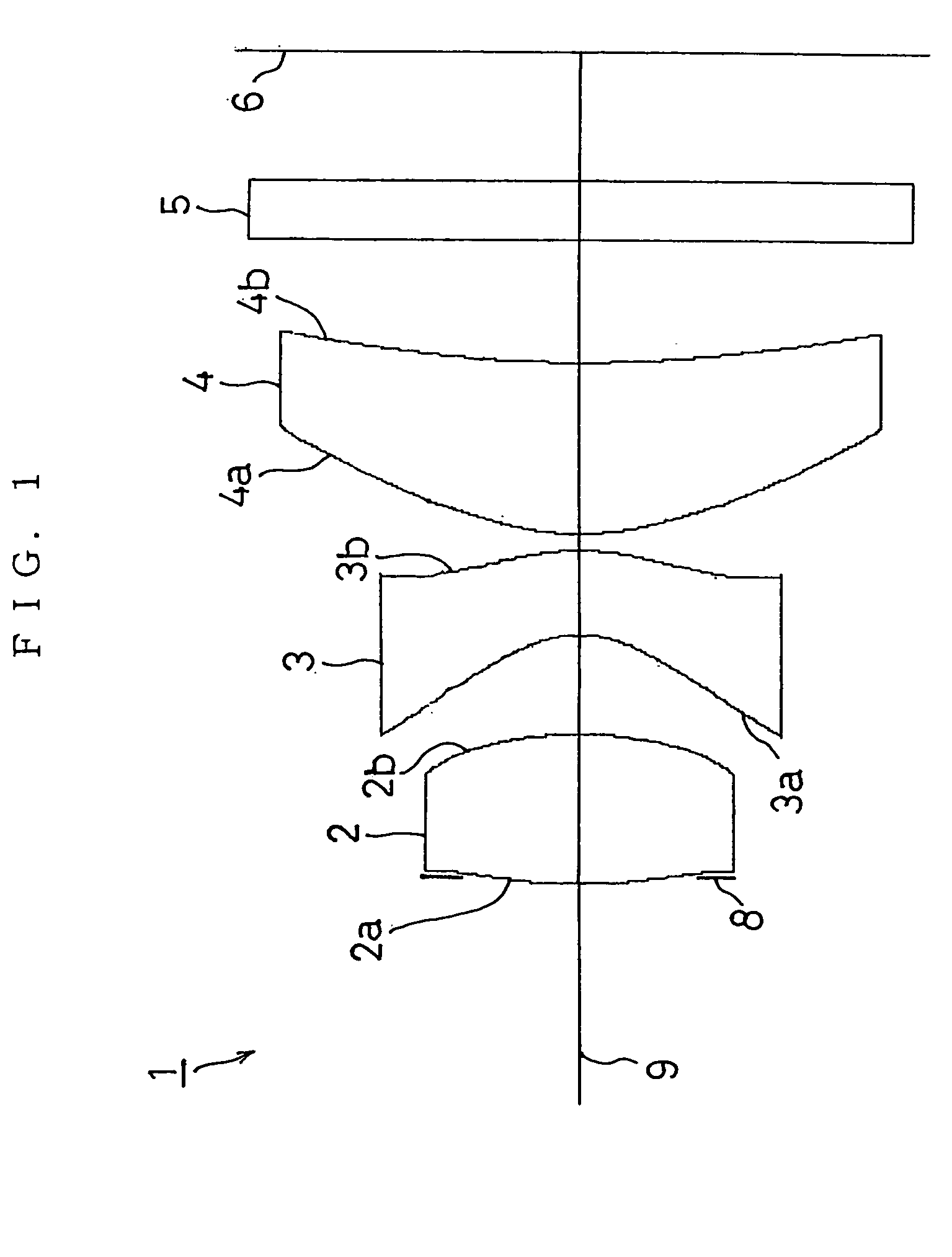
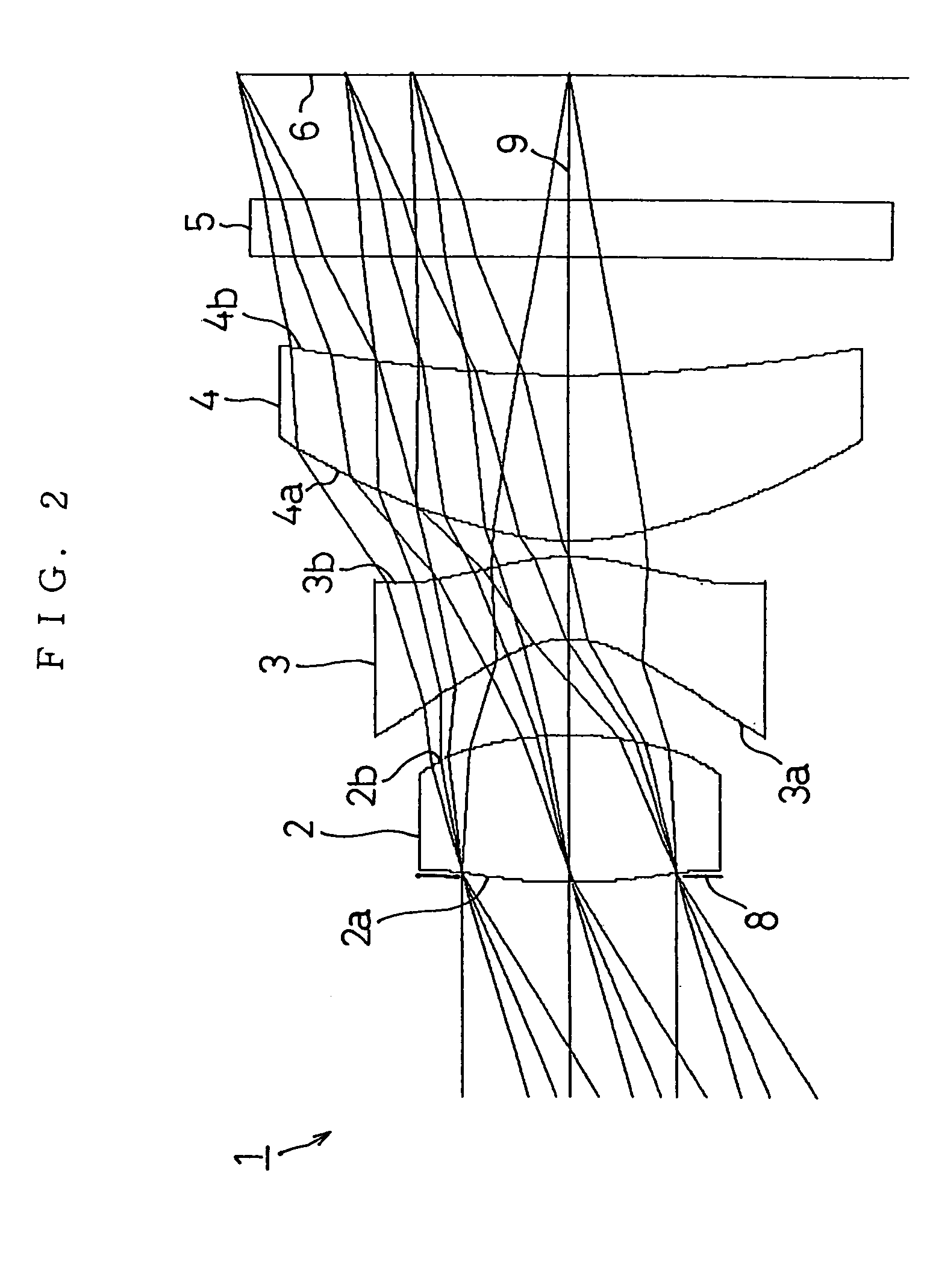
Refractive projection objective
InactiveUS7190527B2Low production costFavorably correctedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMaximum diameterSurgery
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
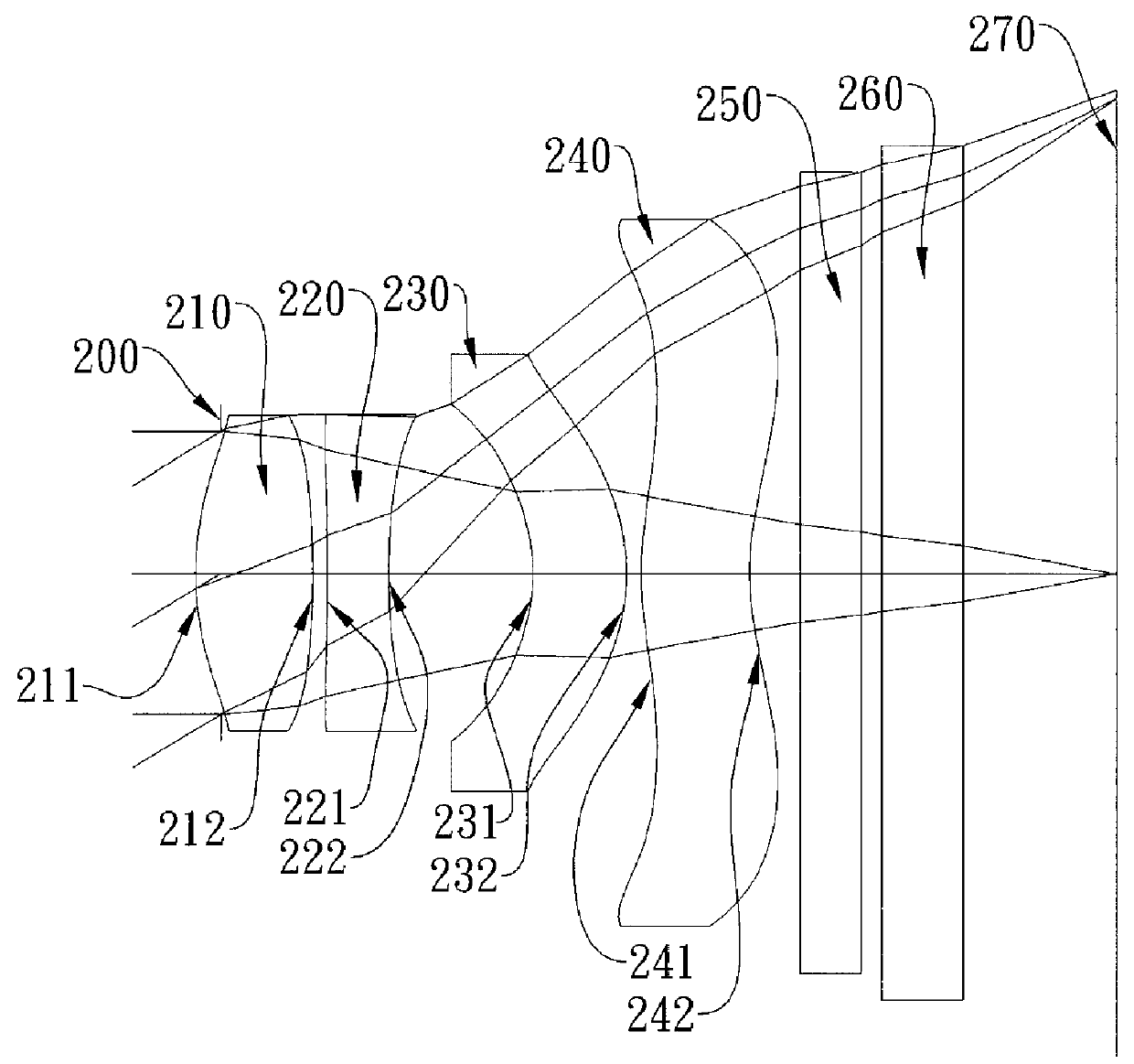
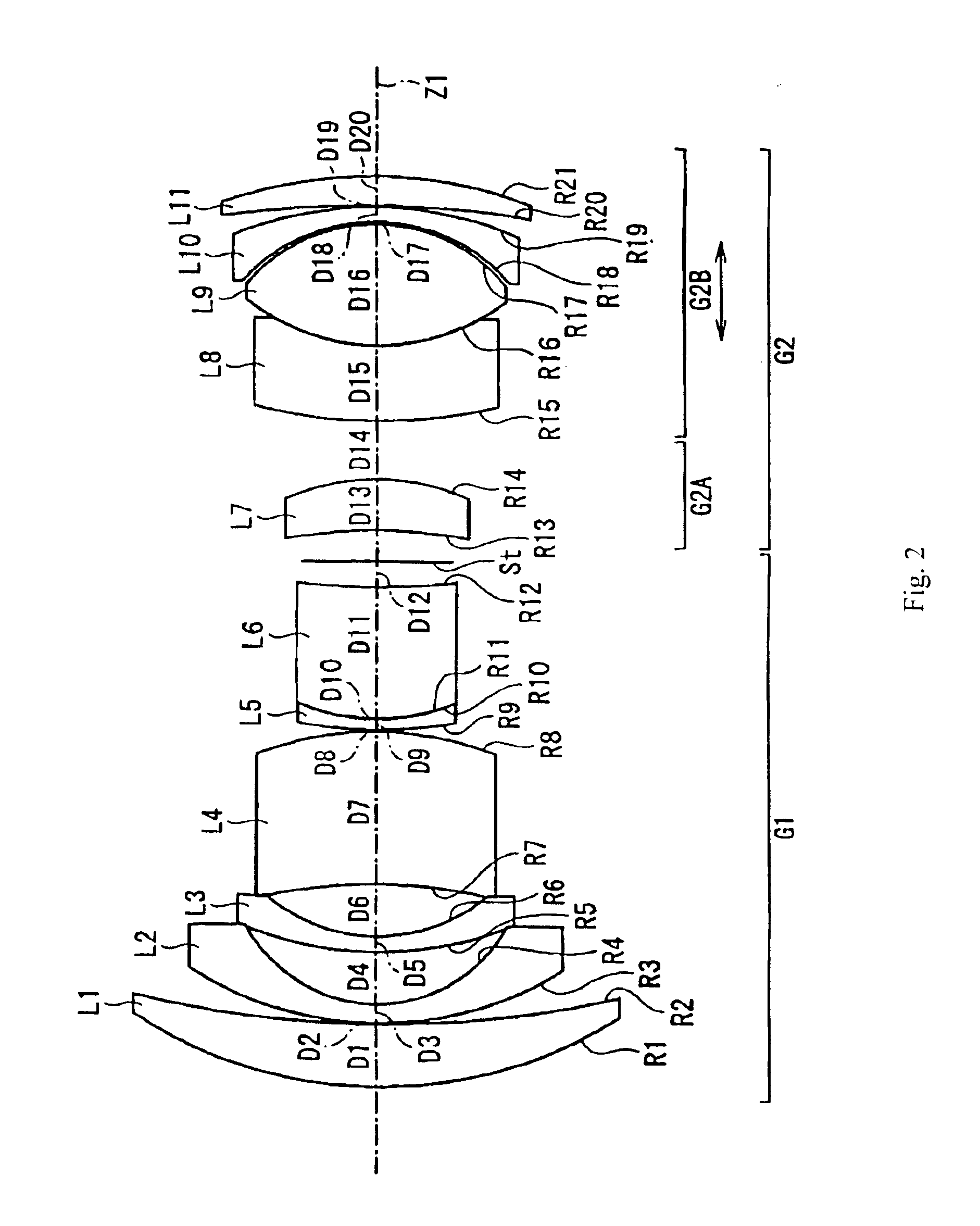
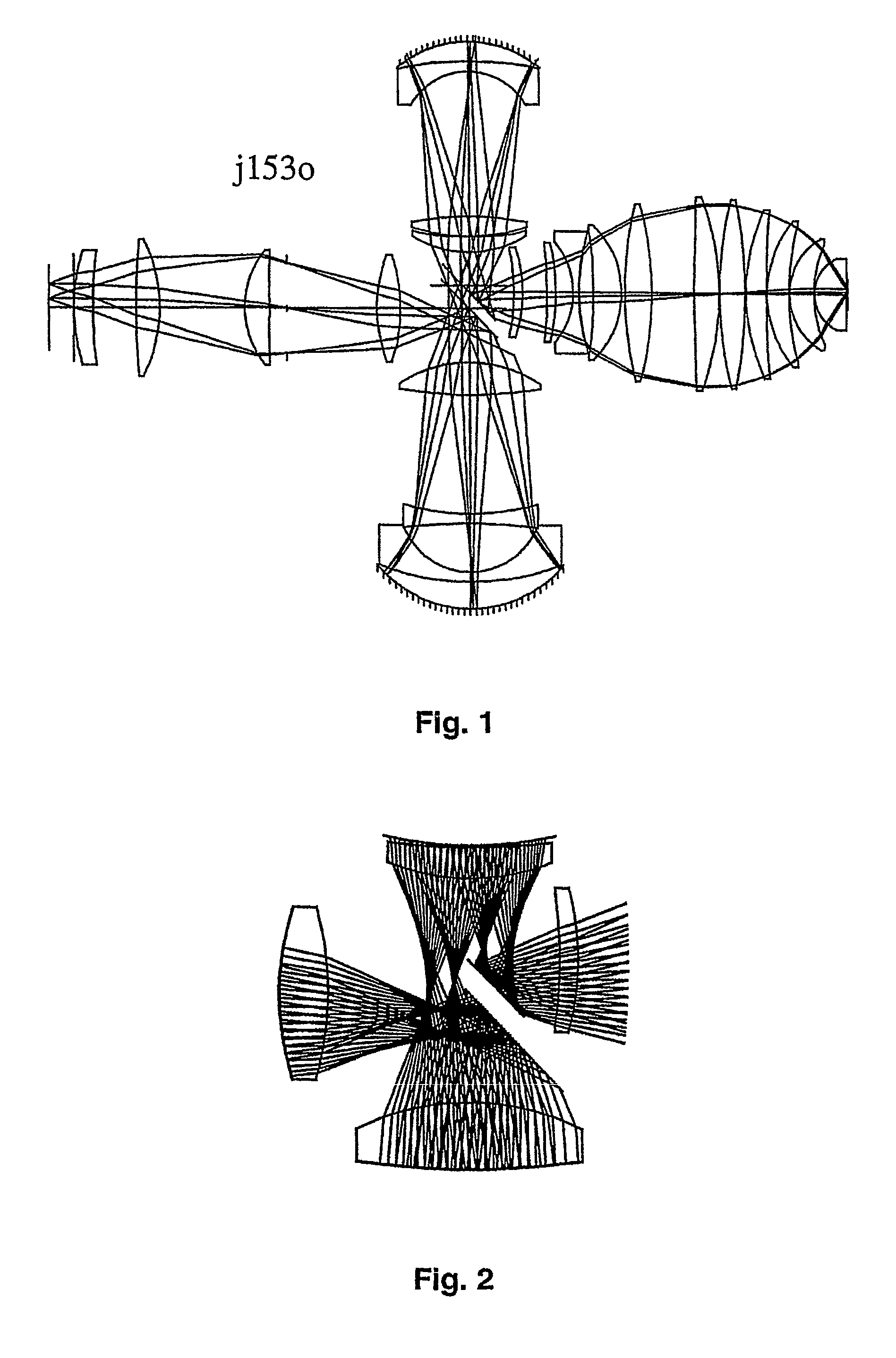
Refractive projection objective
InactiveUS20050231813A1Low production costEasy to correctPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMaximum diameterNumerical aperture
Refractive projection objective with a numerical aperture greater than 0.7, consisting of a first convexity, a second convexity, and a waist arranged between the two convexities. The first convexity has a maximum diameter denoted by D1, and the second convexity has a maximum diameter denoted by D2, and 0.8<D1 / D2<1.1.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
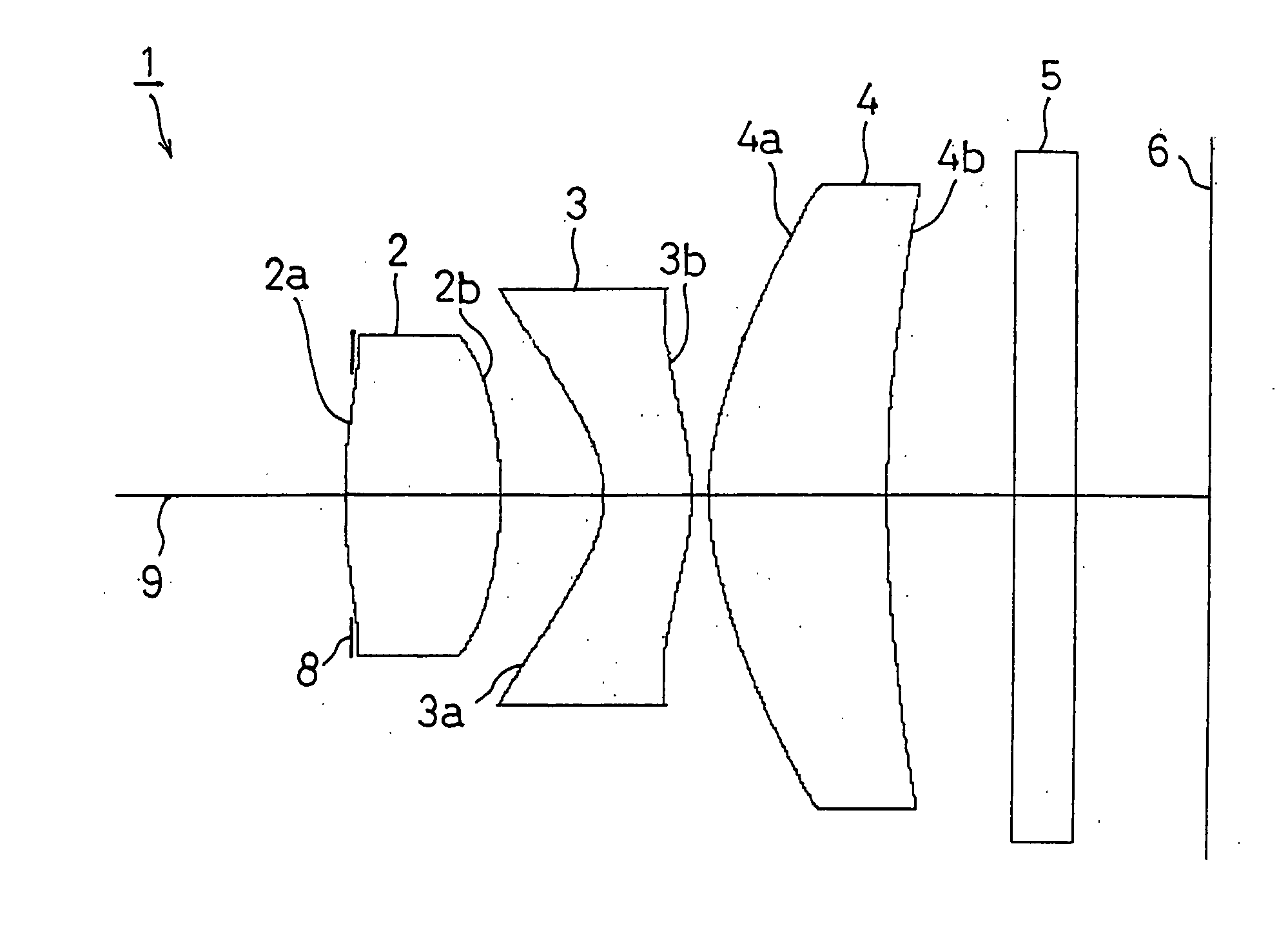
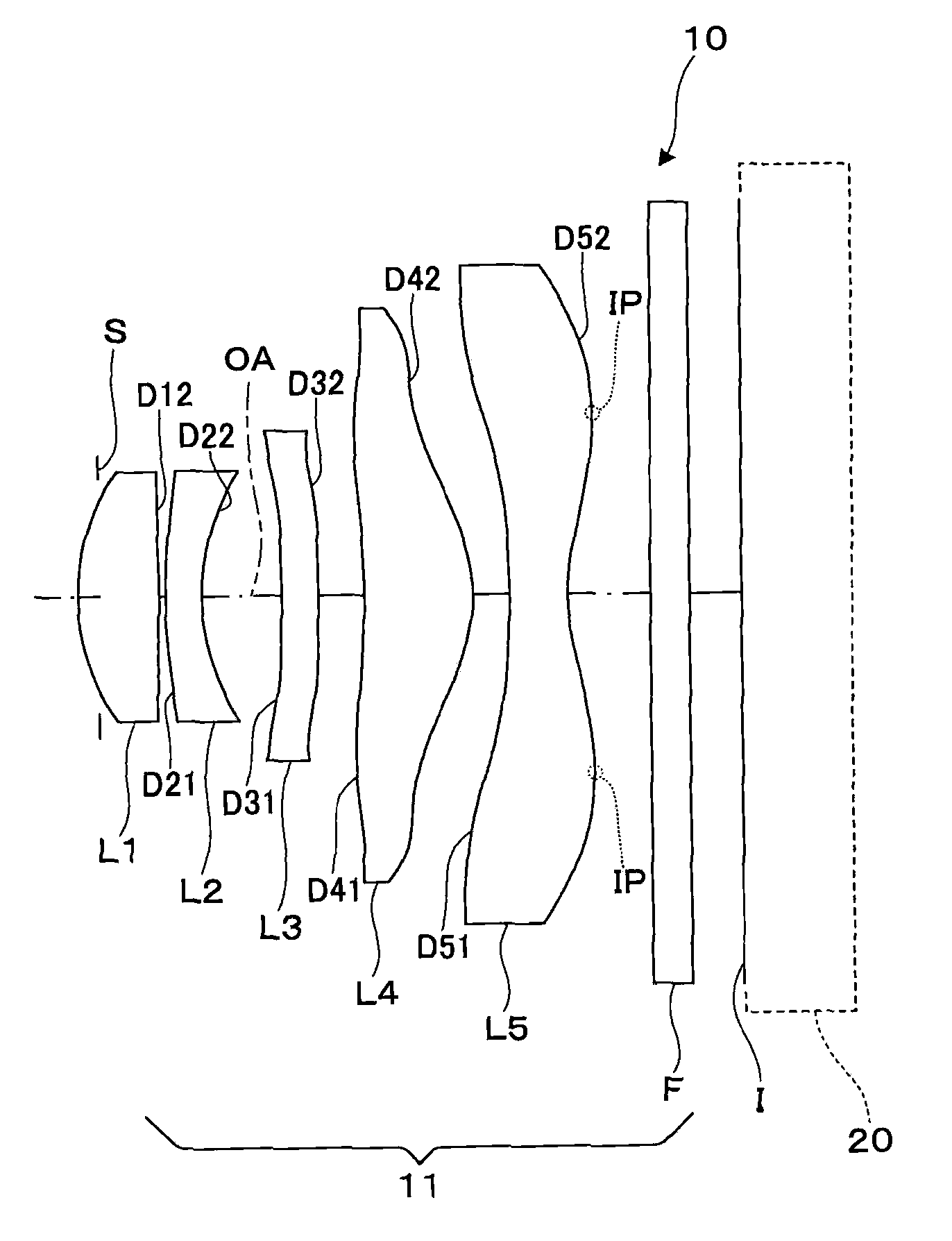
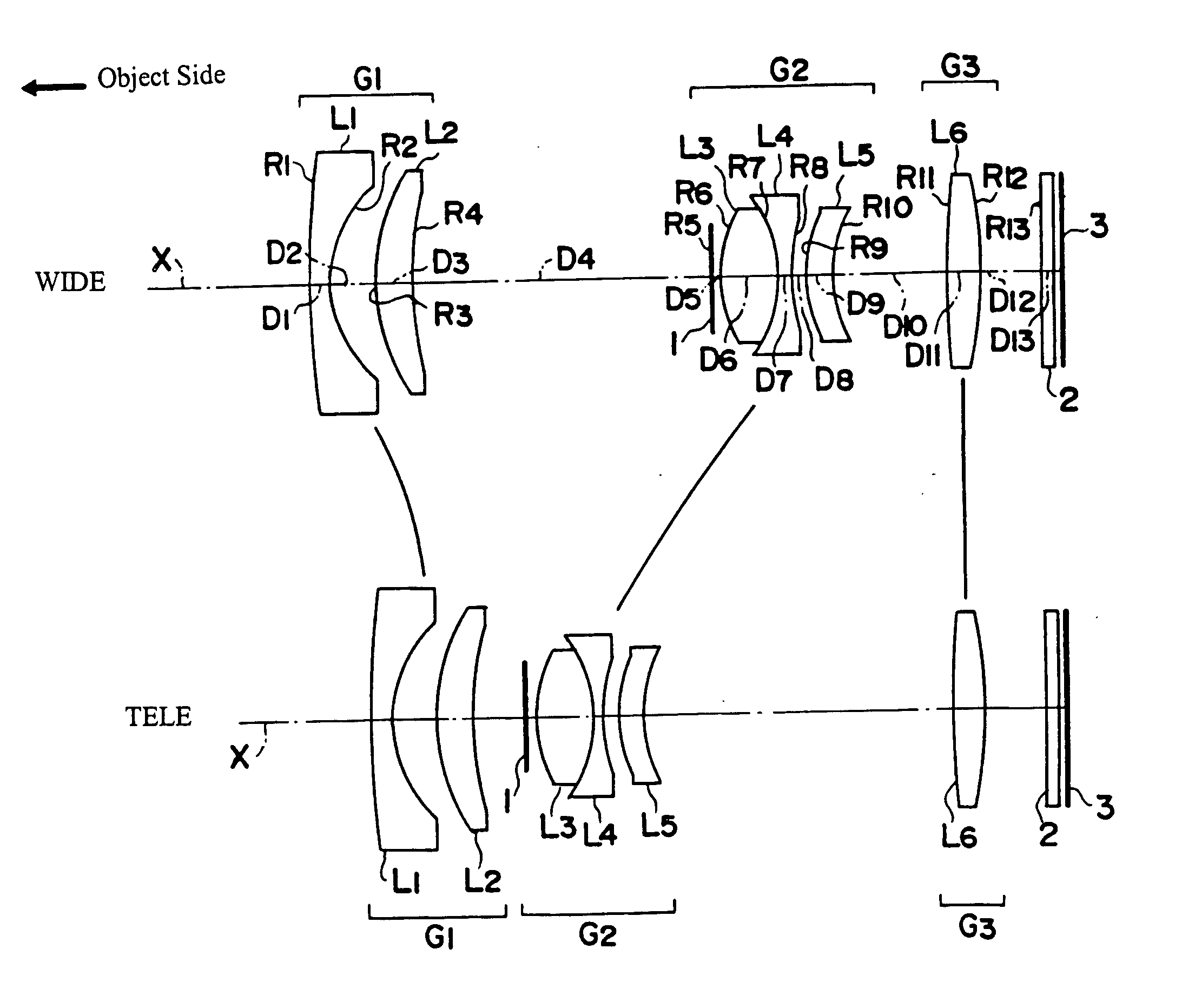
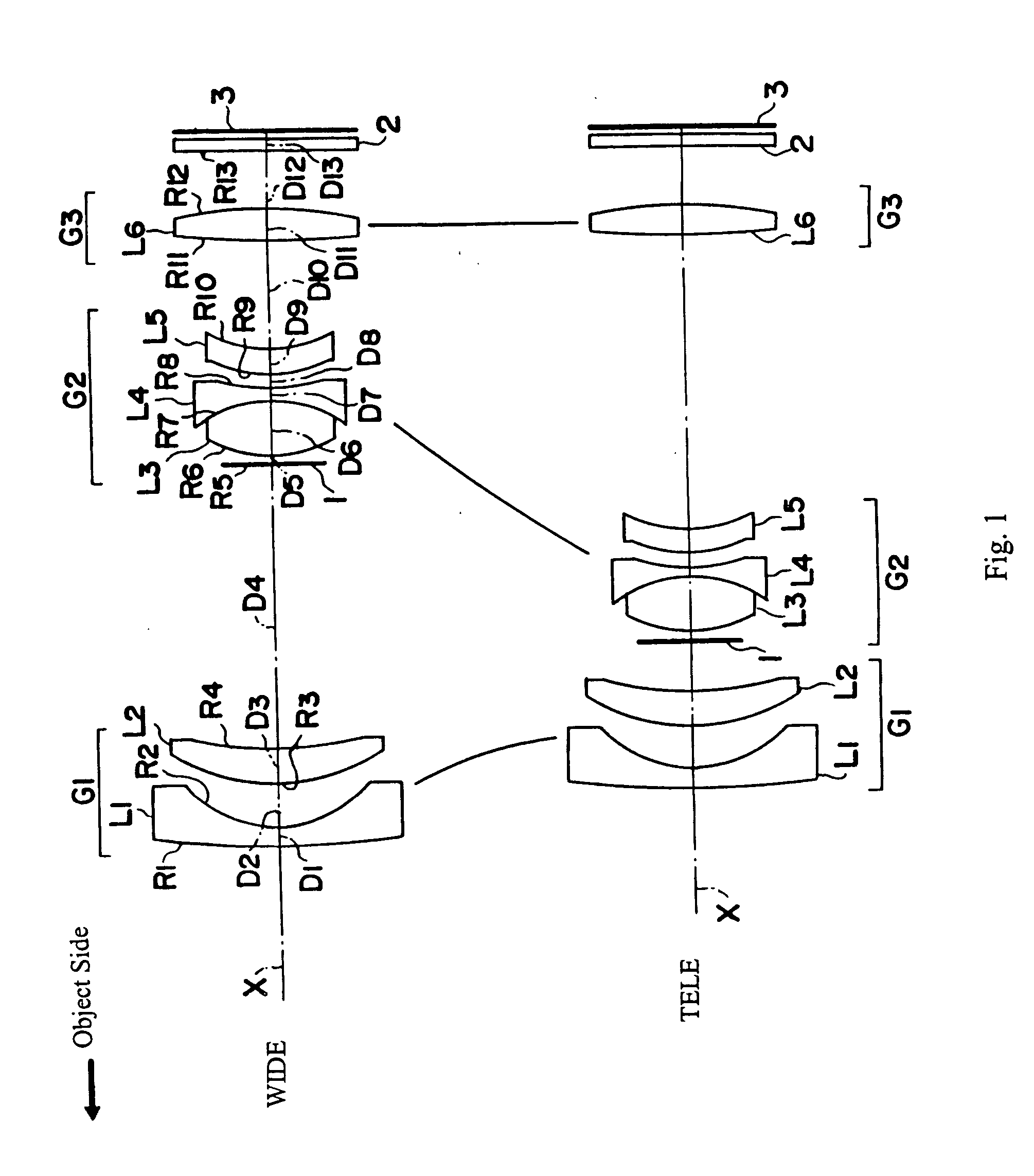
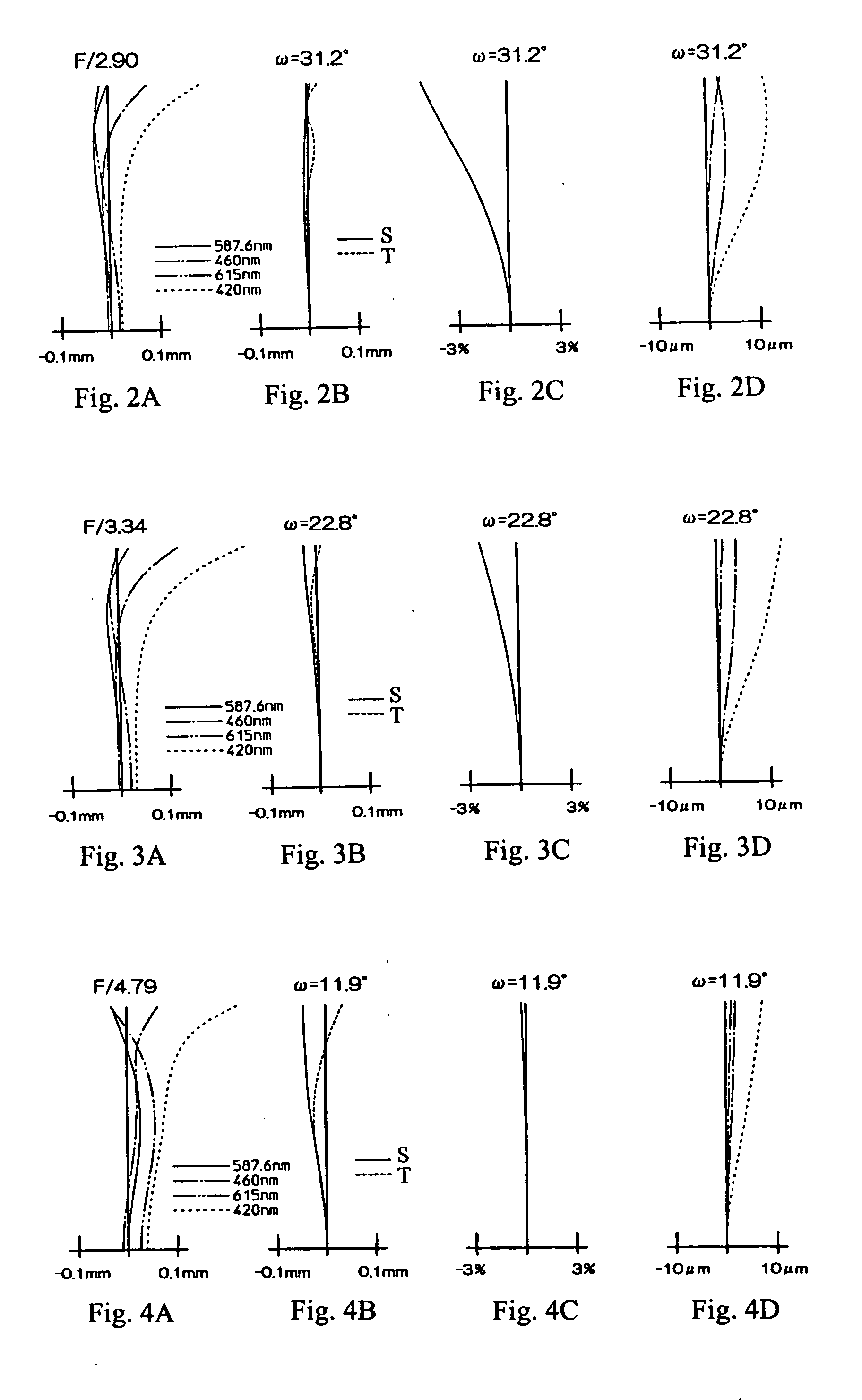
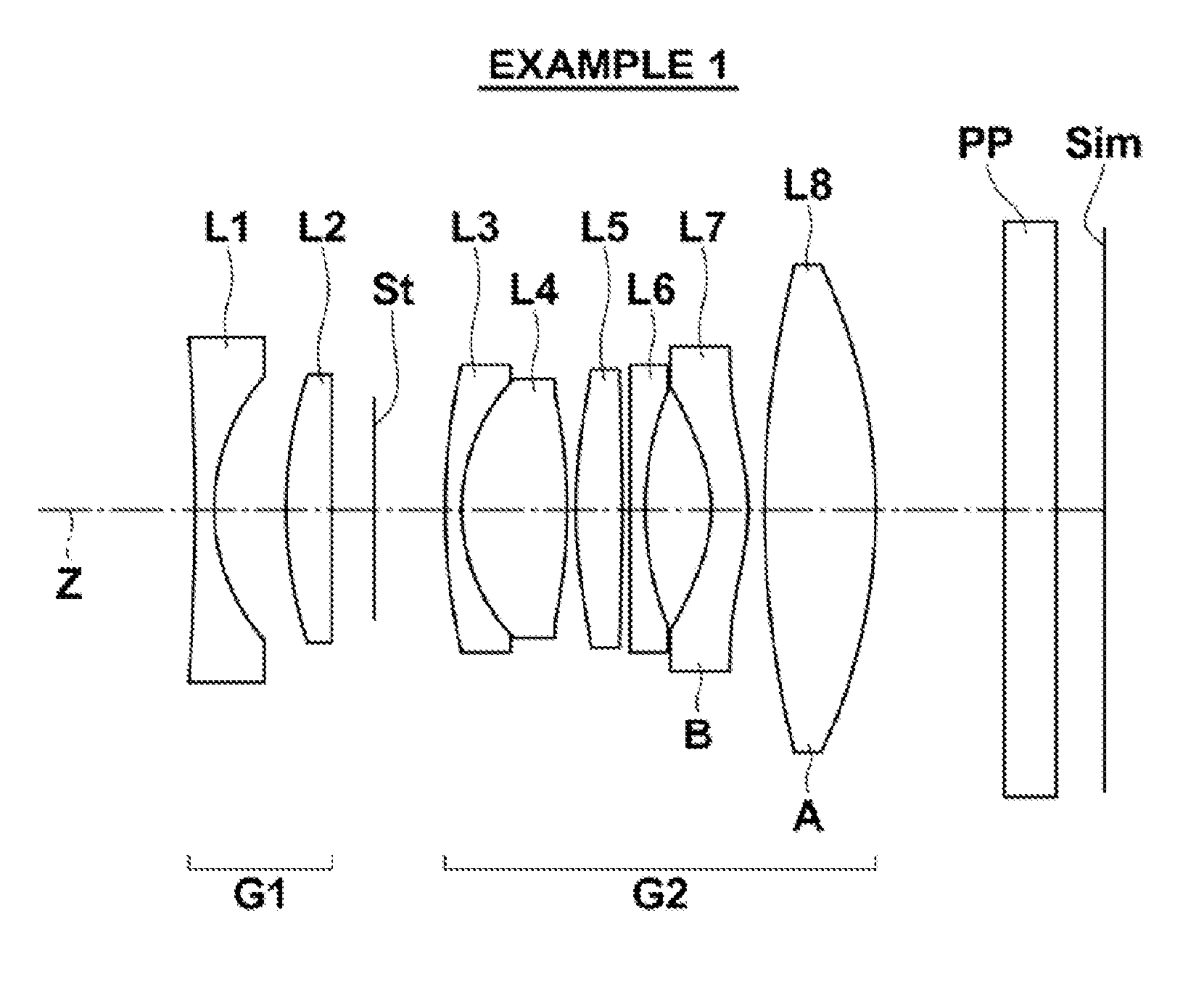
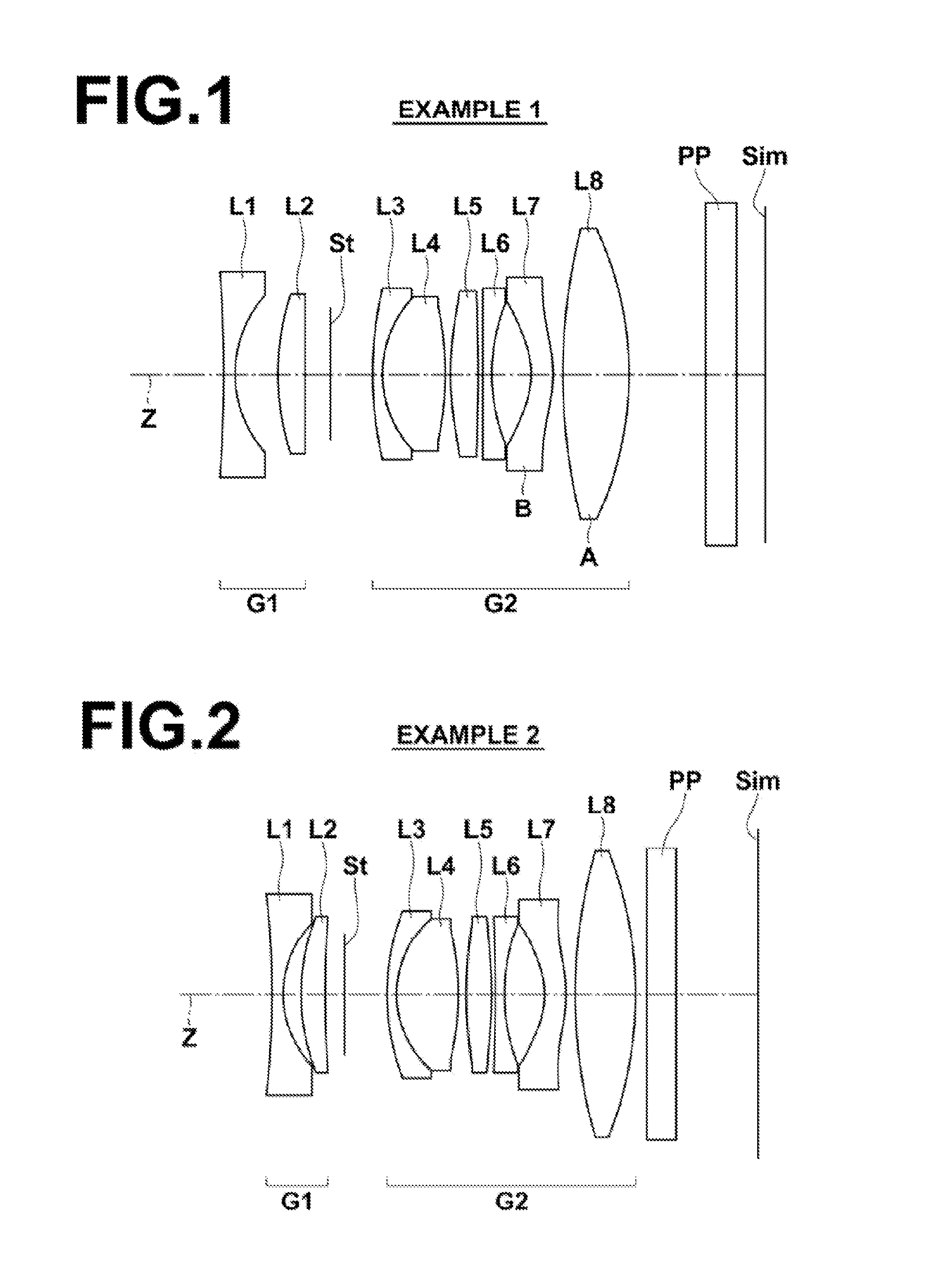
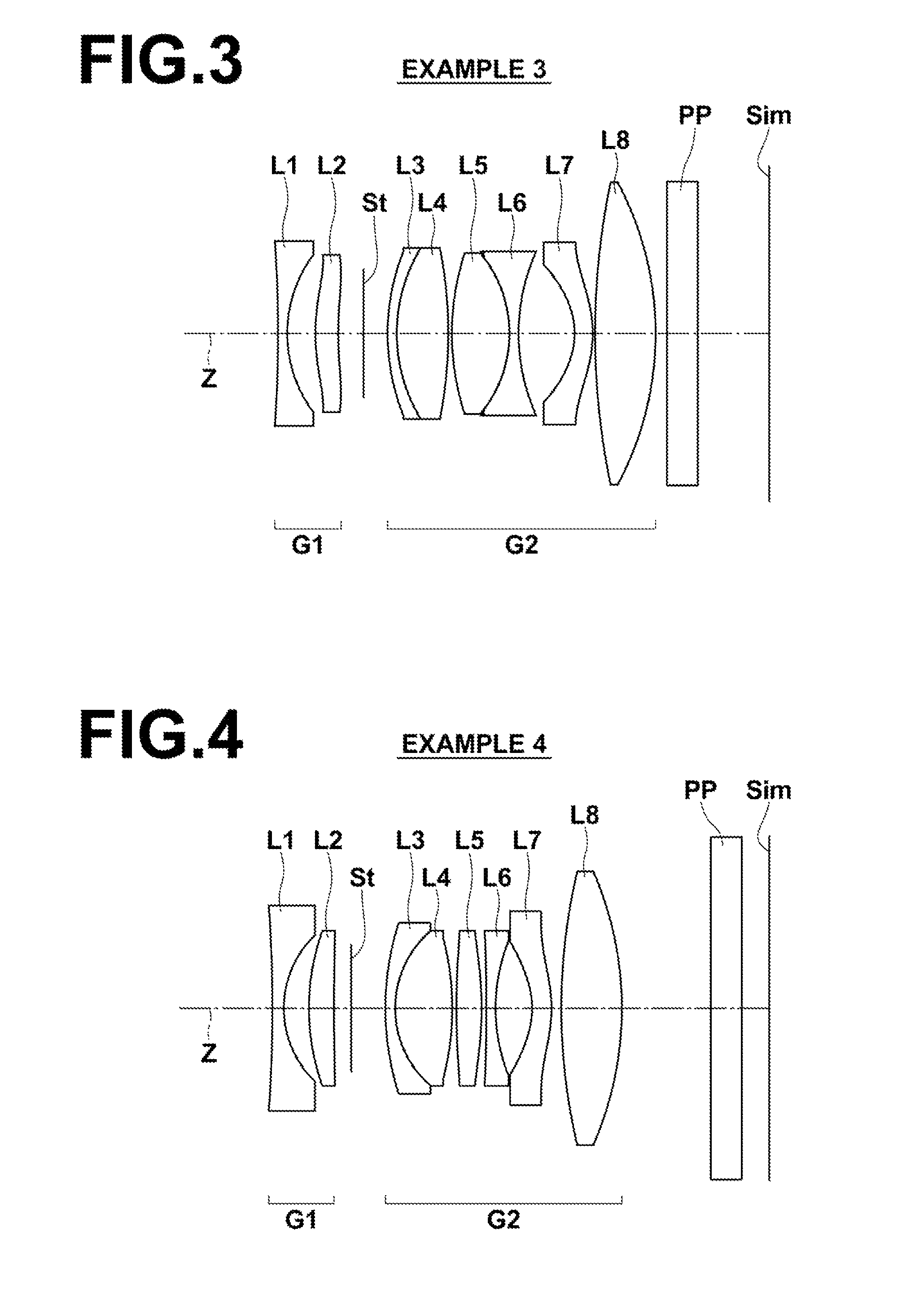
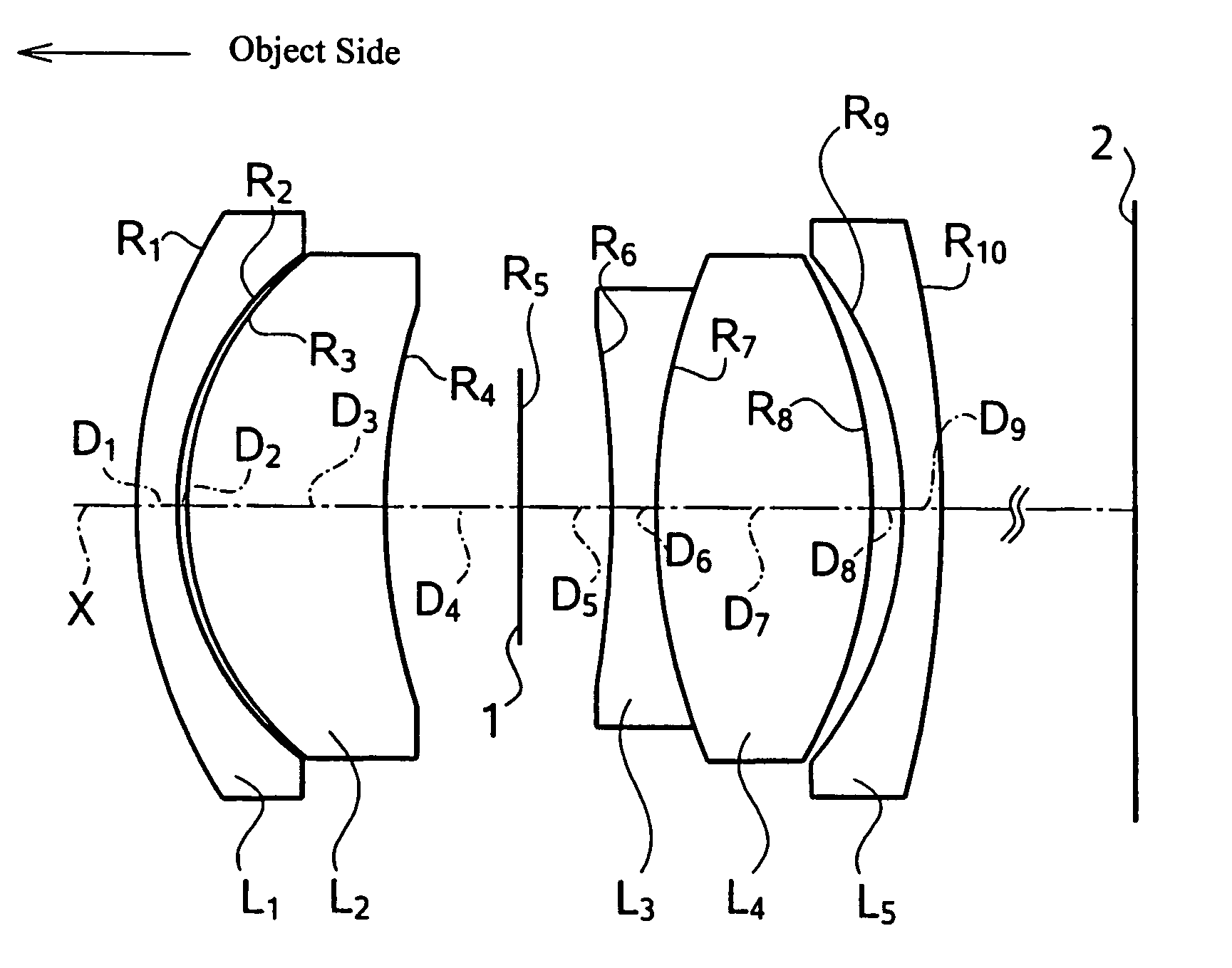
Imaging lens system
Provided is an imaging lens system comprising: a first lens having a main positive power whose convex surface facing an object side; a second lens in a meniscus shape having a negative power whose convex surface facing an image surface side; and a third lens having a positive power whose convex surface facing the object side. The three lenses are disposed in order from the object side to the image surface side.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
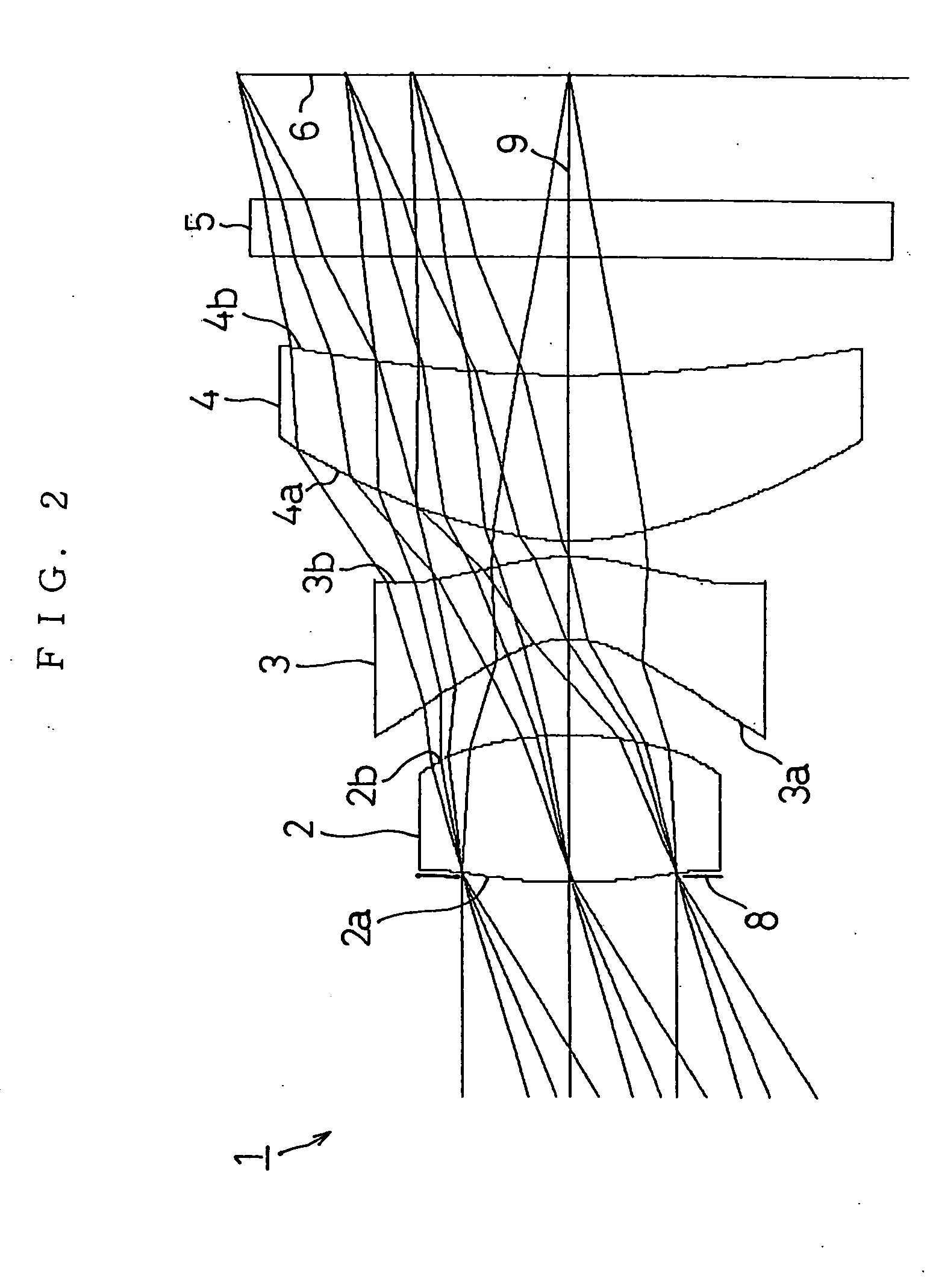
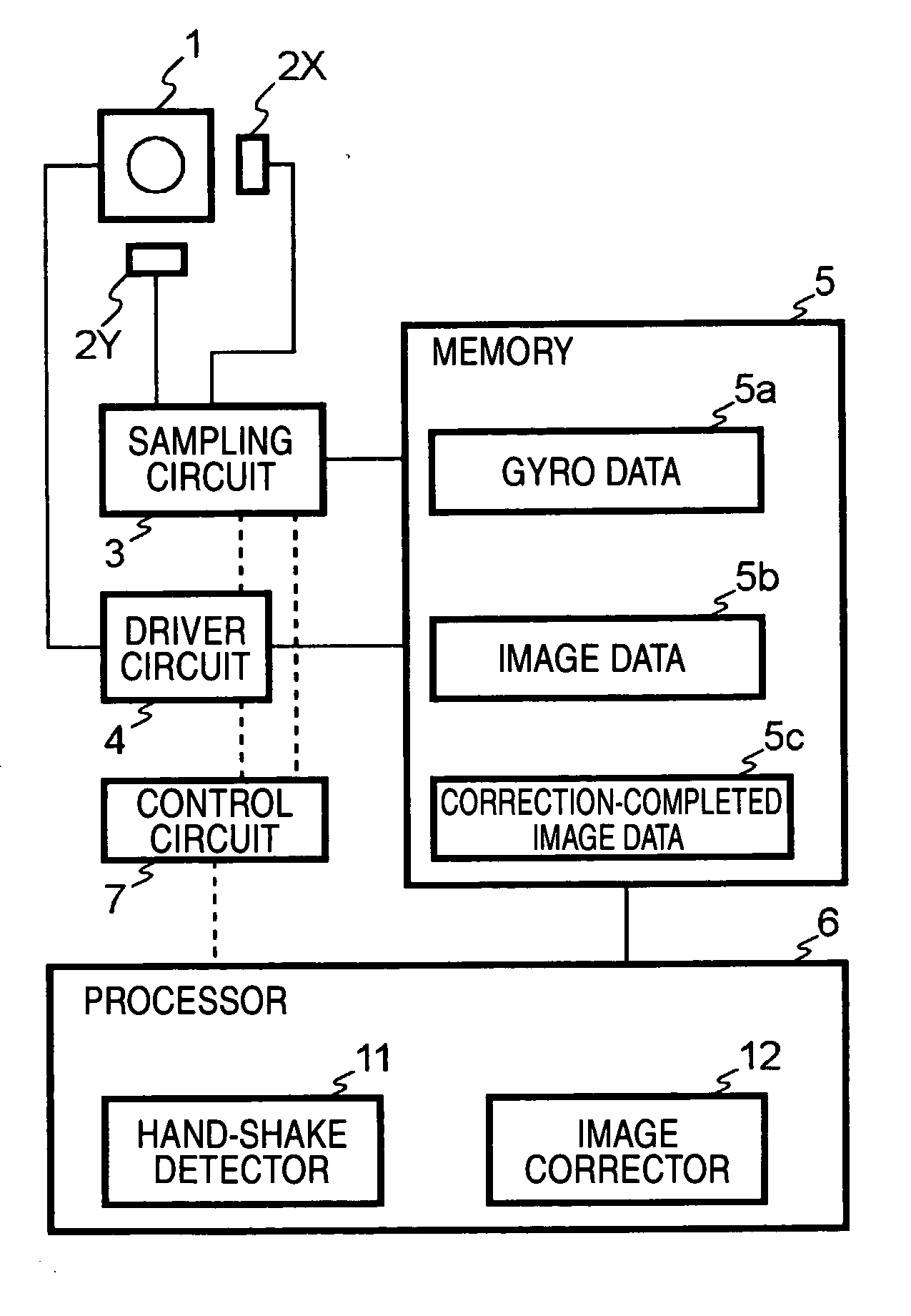
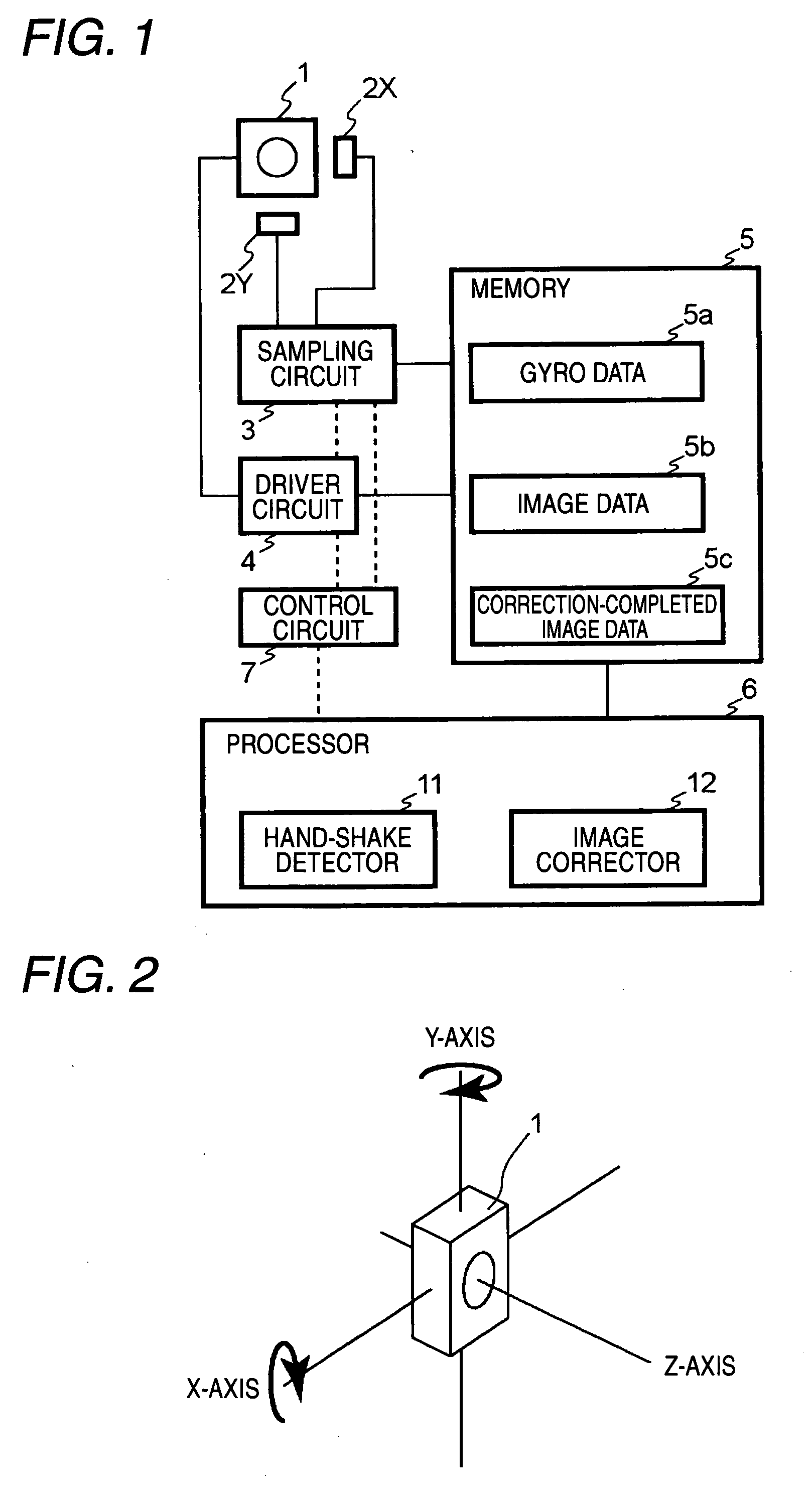
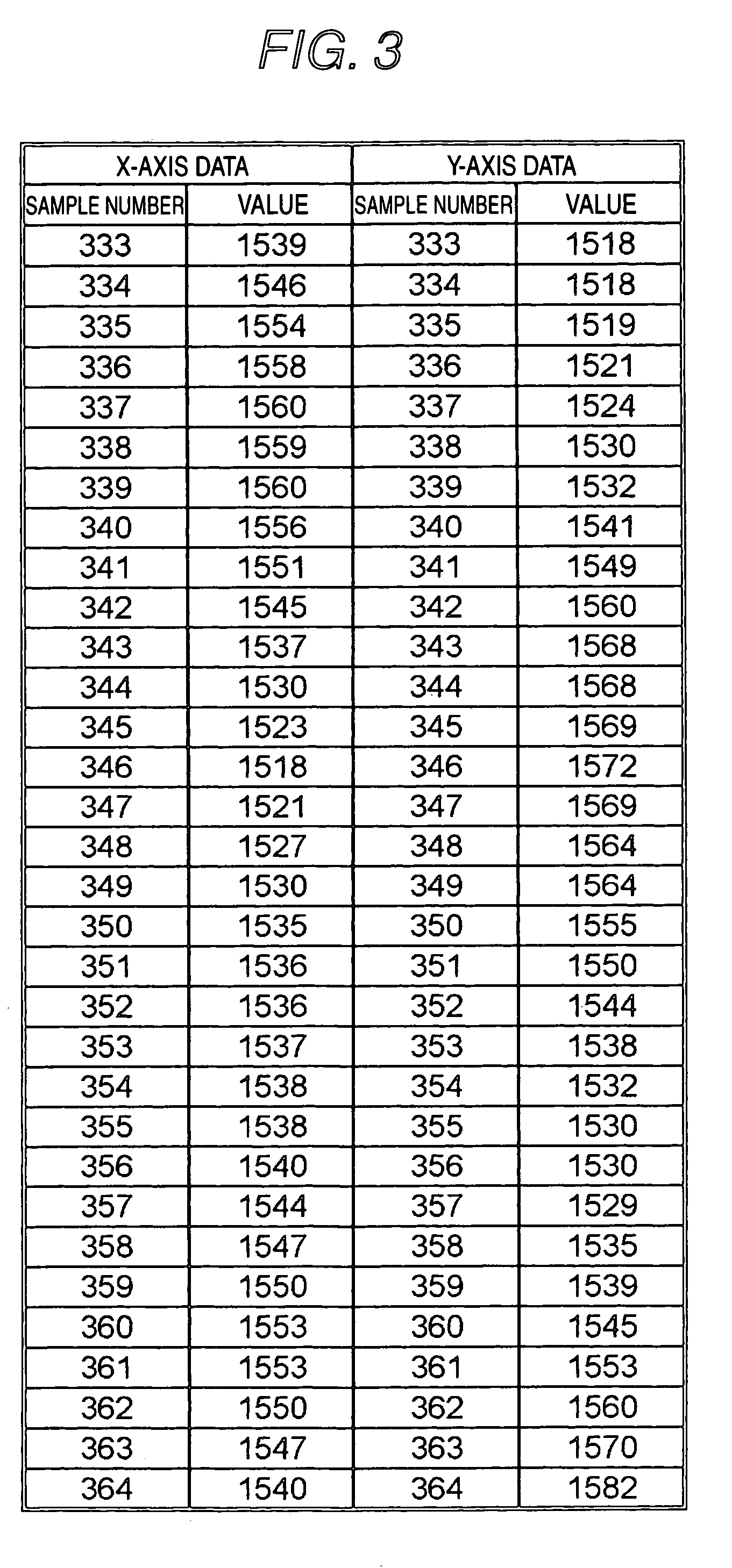
Image capturing device, correction device, mobile phone, and correcting method
ActiveUS20060170784A1Favorably correctedEasy to correctImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer visionCorrection method
An image capturing device is adapted to capture an object image and to generate an image data. Each of a plurality of image capturers is adapted to perform an image capturing of a part of the object image and to generate a partial image data which constitutes a part of the image data based on the part of the object image. Each of the image capturers has an optical axis. A detector is operable to detect movement of each of the image capturers in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis during the image capturing and to generate movement data based on the detected movement, for each of the image capturers. A processor is operable to correct the partial image data so as to compensate the movement during the image capturing based on the movement data.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
Variable power optical system, imaging device, and digital device
ActiveUS20100265380A1High power ratio and compactnessFavorably correctedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical powerImaging equipment
A variable power optical system (1) comprises a first lens group (11) having a negative optical power, a second lens group (12) having a positive optical power, and a third lens group (13). The first to third lens groups are arranged in order from the object side to the image side. The first lens group (11) is composed of one negative lens (111) and is fixed in variable power. The third lens group (13) includes at least one aspherical surface. When the third lens group is divided into a front group and a rear group with the largest air space in the third group, the front group has a negative optical power, and the rear group has a positive optical power.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
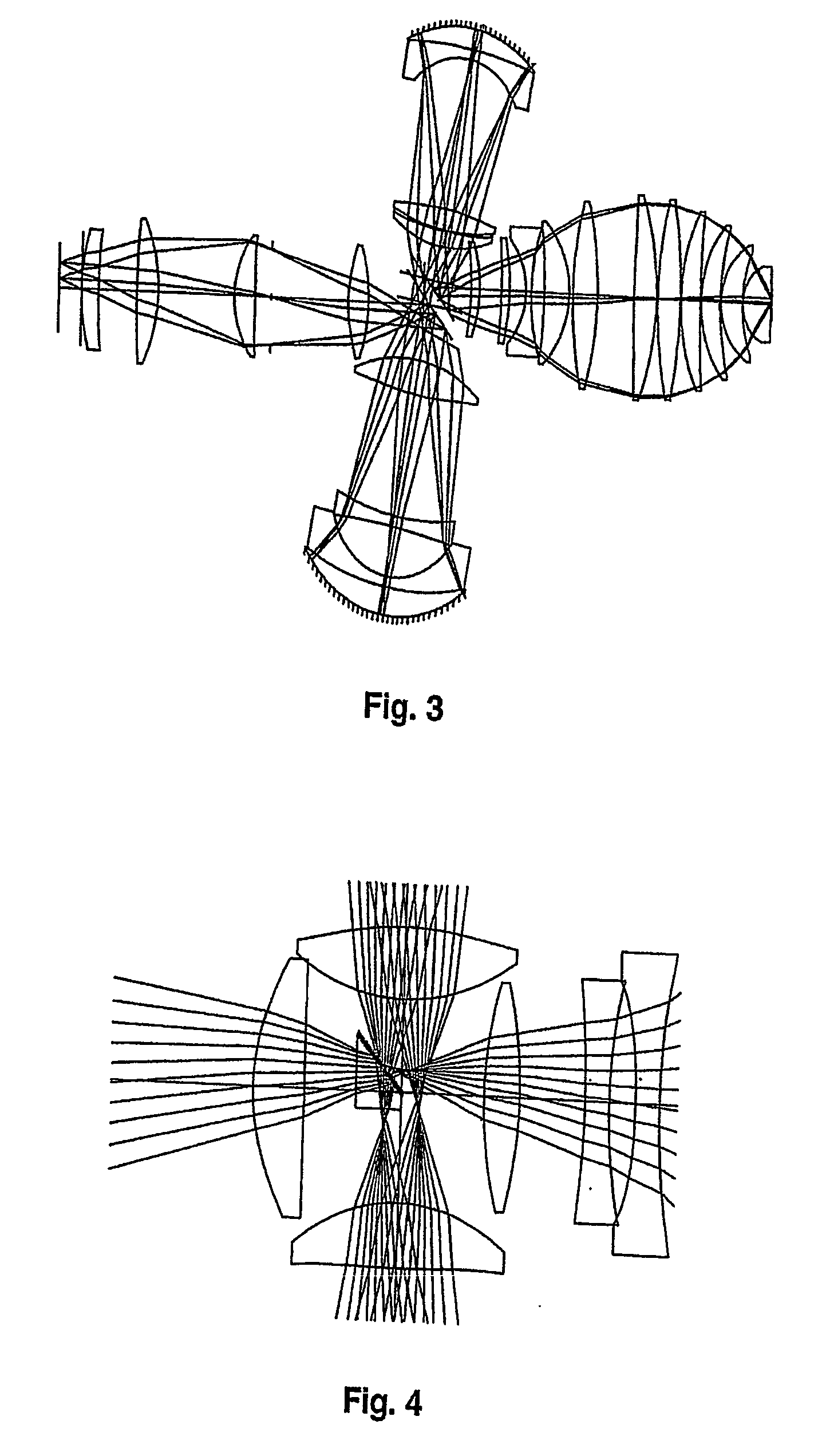
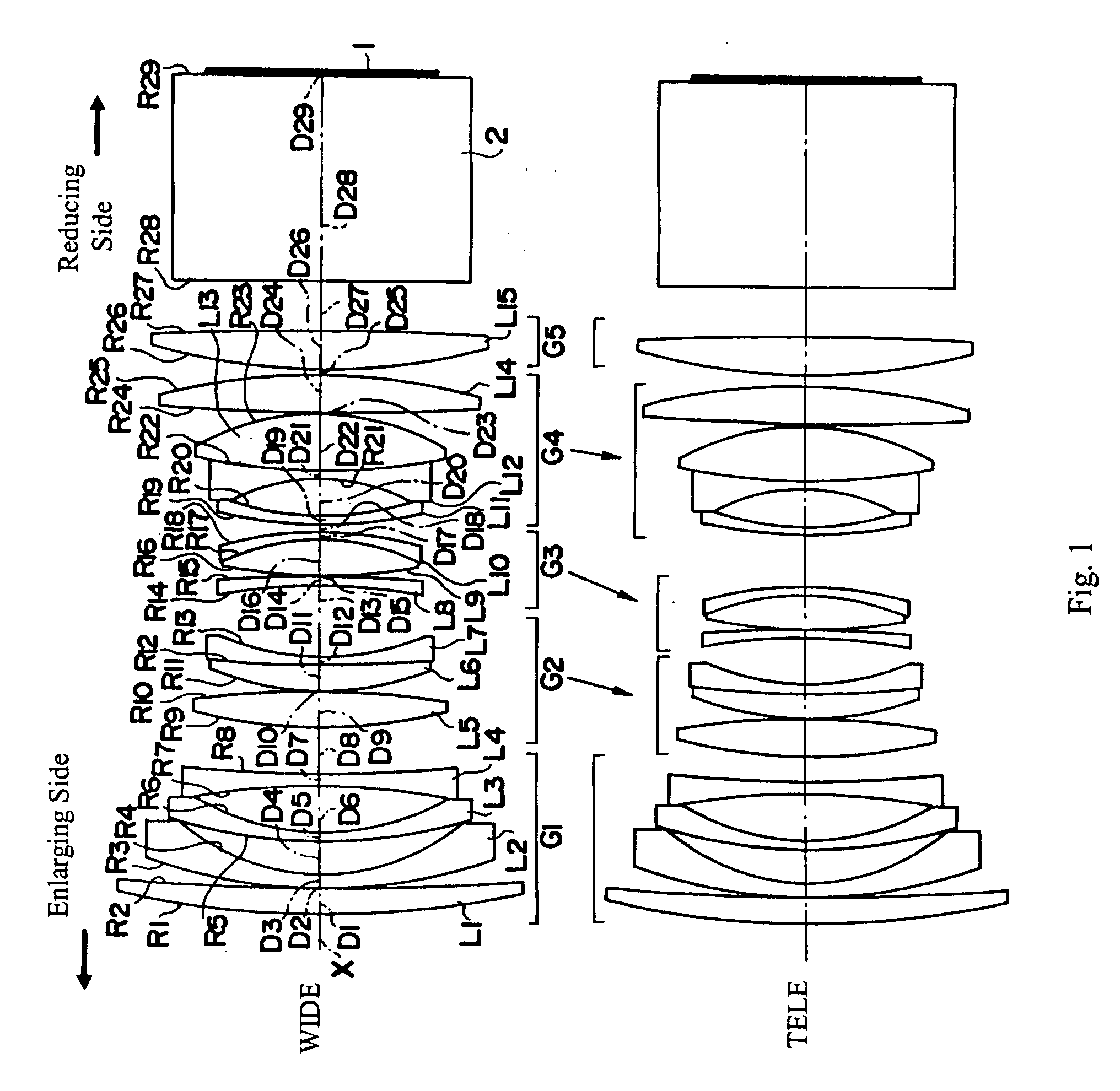
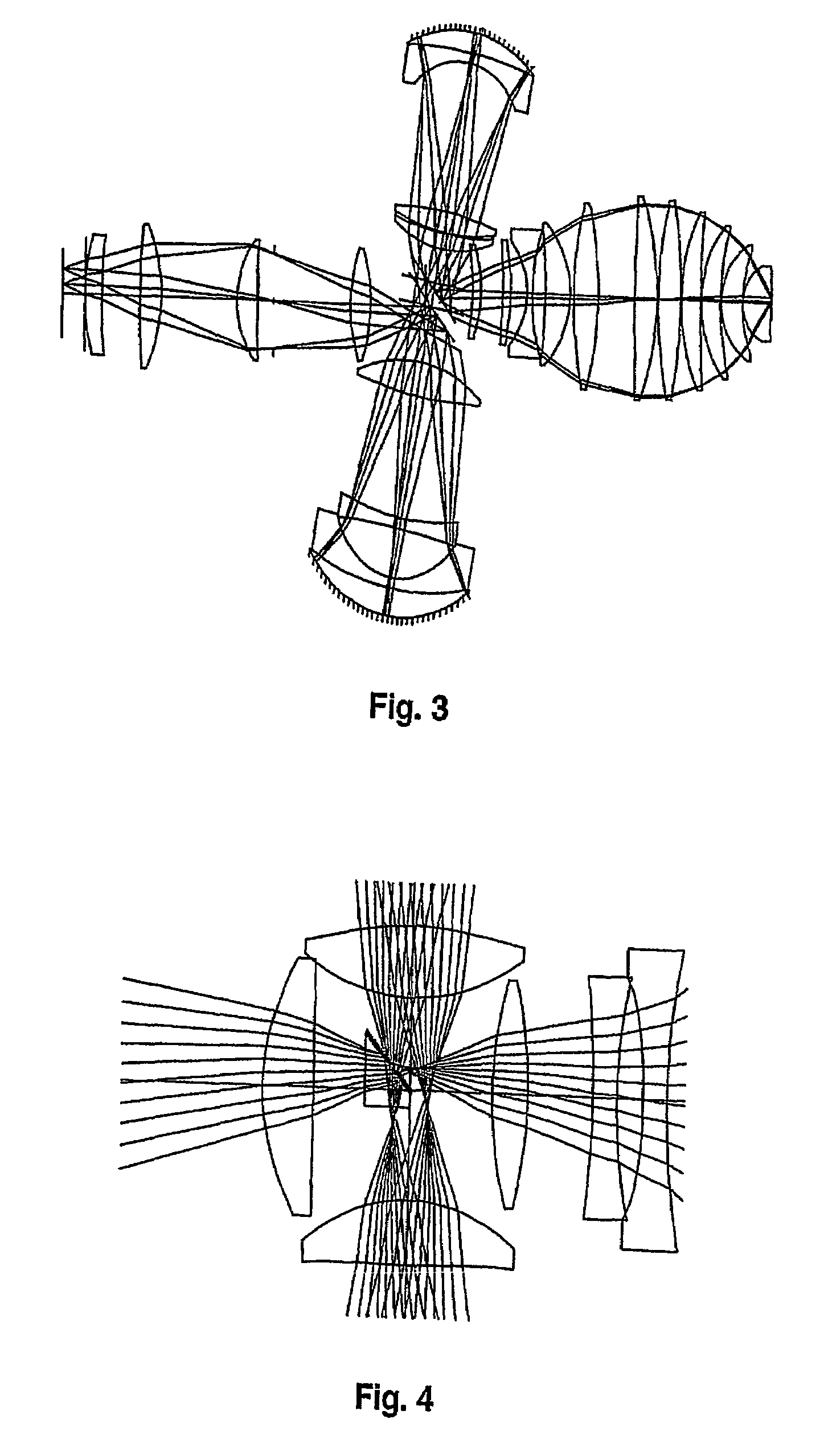
Catadioptric Projection Objective
InactiveUS20080037111A1Simple designEasy to correctMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageImage plane
A catadioptric projection objective for projecting a pattern arranged in the object plane of the projection objective into the image plane of the projection objective, having: a first objective part for projecting an object field lying in the object plane into a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for generating a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; a third objective part for generating a third real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the second objective part; and a fourth objective part for projecting the third real intermediate image into the image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Image pickup lens
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
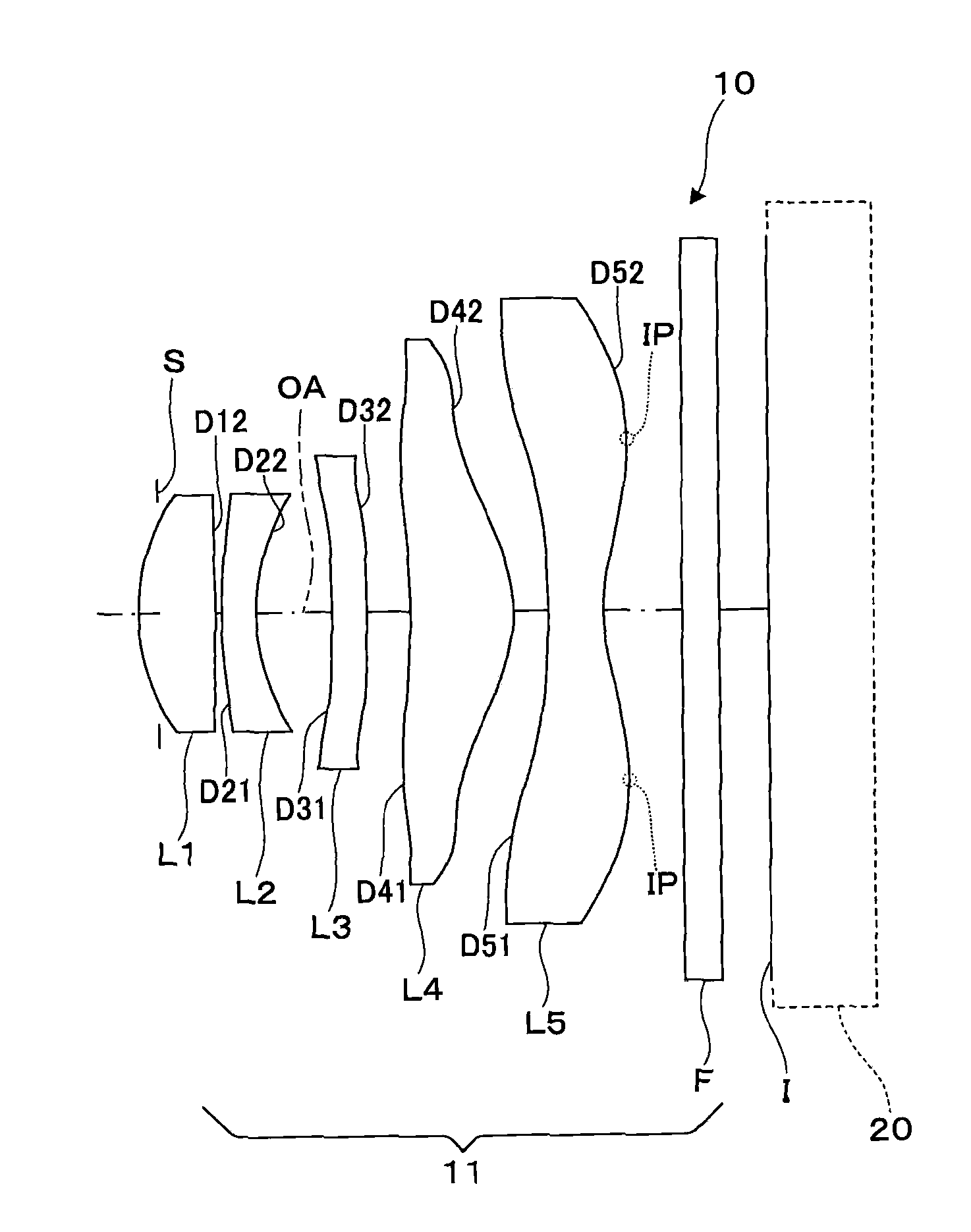
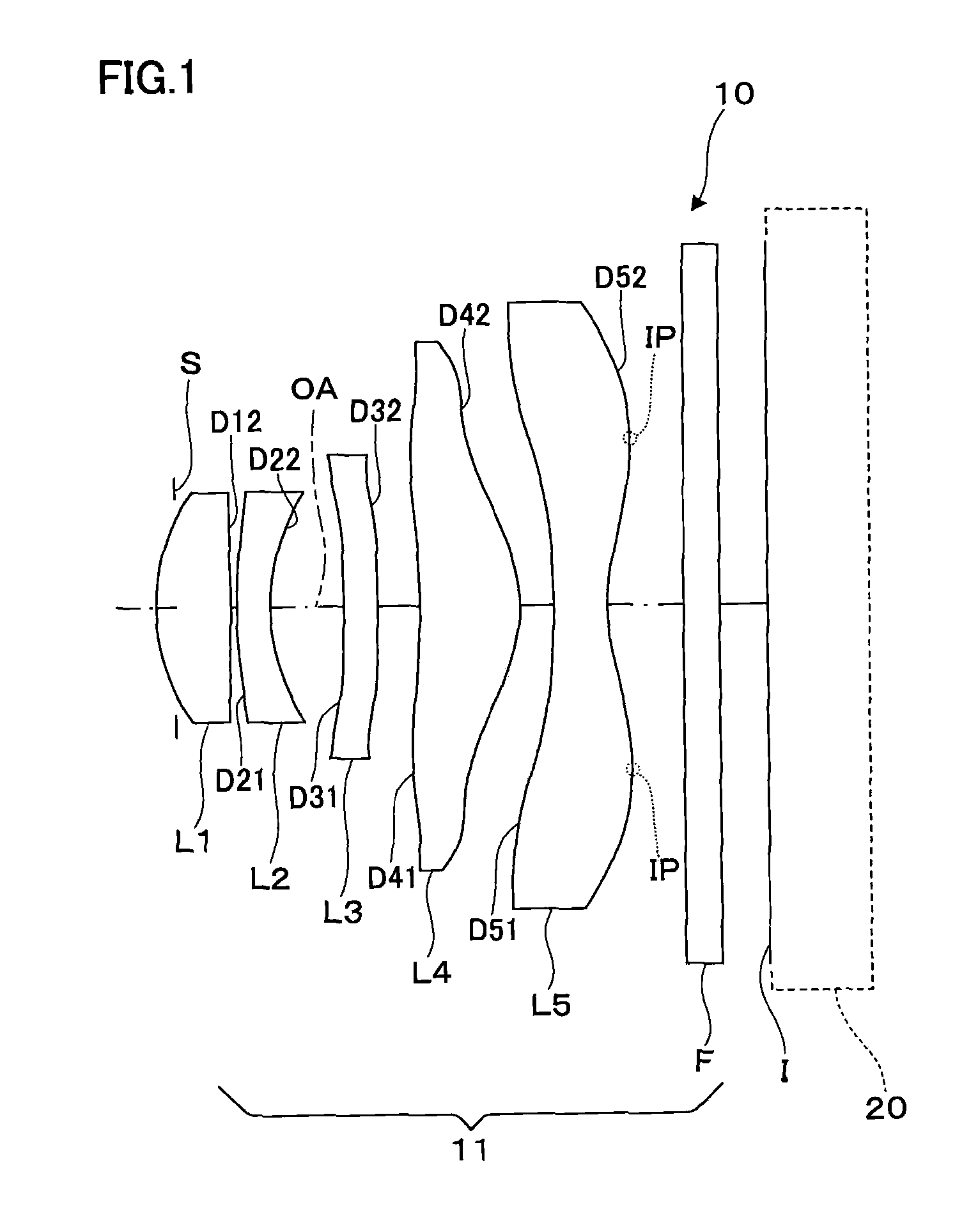
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
An imaging lens includes: a first lens group; an aperture stop; and a second lens group having a positive refractive power, in this order from an object side. The first lens group includes a negative first lens provided most toward the object side. The second lens group includes a positive lens, provided most toward an imaging surface, and a negative lens having a concave surface and an aspherical surface at least toward the object side. The following Conditional Formulae are satisfied:0.03<(|Sagsp1|−|Sagas1|) / Re1<0.35; and1.819≦NdAB wherein Sagsp1 is the sag of a reference spherical surface at the edge of the effective diameter of the object side surface of the negative lens, Sagas1 is the sag of the aspherical surface of the lens, Re1 is the effective diameter of the object side surface of the lens, and NdAB is the average refractive index of the positive lens and the negative lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photographing lens assembly
ActiveUS8169528B2Small sizeReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionPhysics
This invention provides a photographing lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a concave image-side surface; a third lens element with negative refractive power, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface on which at least one inflection point is formed; and an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the second lens element; wherein there are four lens elements with refractive power. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively reduce the size of the lens assembly, attenuate the sensitivity of the optical system and enable the lens assembly to obtain higher resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Image Pickup Lens
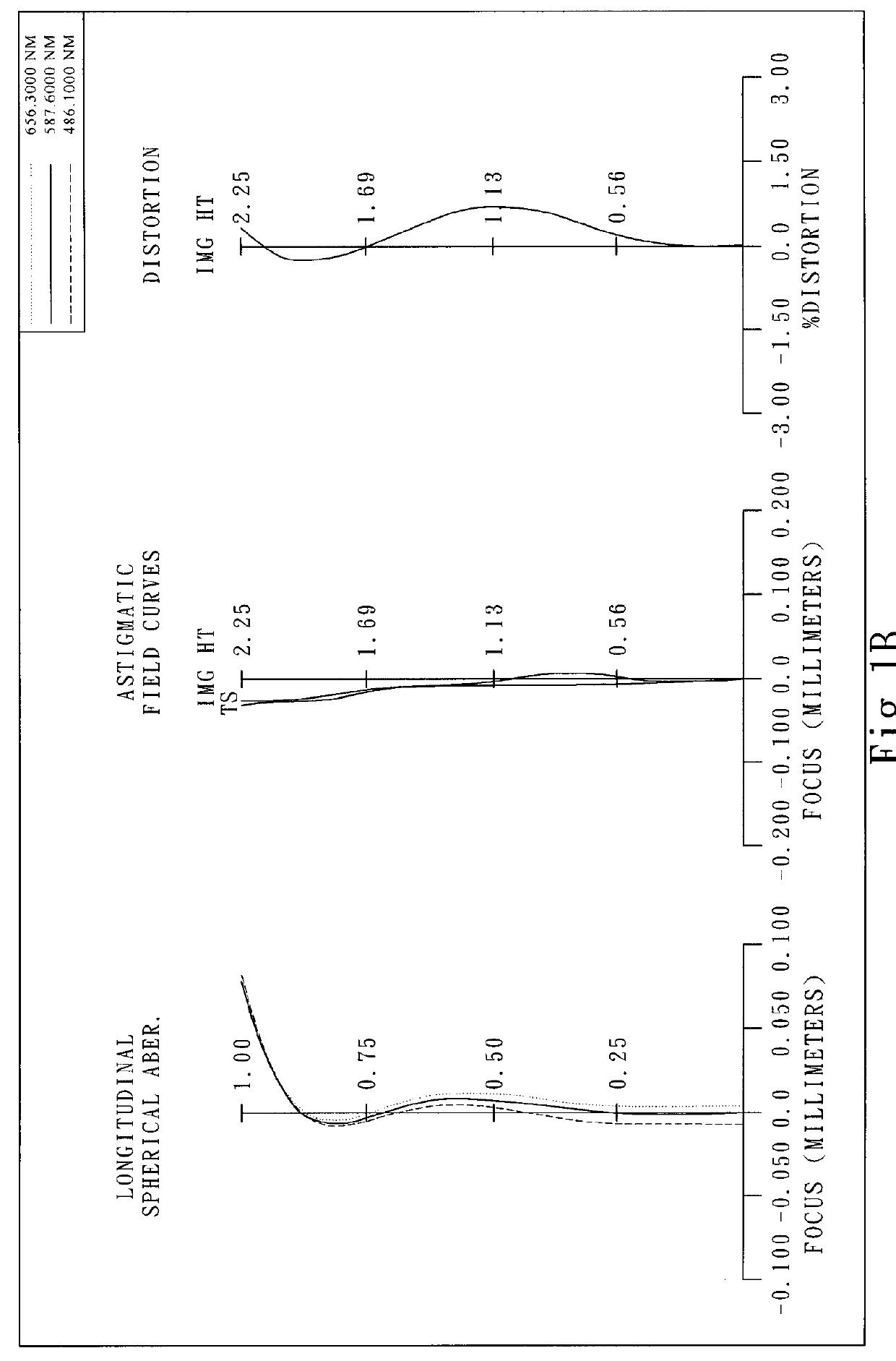
ActiveUS20130002920A1Reduce weight and sizeFavorably correctedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhysics
An image pickup lens has a configuration of five lenses whose aberrations are corrected favorably despite its compactness compared to a conventional type.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Imaging device
InactiveUS20110234861A1Biased shading can be preventedFavorably correctedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsViewpointsLuminous flux
An imaging device comprising a single photographing optical system, an image sensor having a plurality of pixels for obtaining a plurality of viewpoint images by photo-electrically converting a luminous flux passing through different regions of the photographing optical system, and a shading correction part for conducting a shading correction to the plurality of viewpoint images. The shading correction part varies the amount of shading correction based on light-reduction property for one viewpoint image among the plurality of viewpoint images with respect to the amount of shading correction based on light-reduction property for the other viewpoint image among the plurality of viewpoint images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiation correction method for electron beam lithography
InactiveUS6872507B2Readily commercially implementedOptimal correction for proximity effectsElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistLight beam
A method for forming a patterned microelectronics layer employing electron beam lithography in a sensitive material upon a substrate with optimal correction for proximity effects resulting from electron back scattering into the resist material. There is provided a substrate having formed thereon a layer of resist material sensitive to electron beam exposure. There is then exposed the sensitive layer to a vector scan shaped electron beam to write a primary pattern with dose correction of the beam dose for proximity effects due to electron scattering at each point in the primary pattern. There is then written a secondary pattern which is a negative reversed image of the primary pattern in a secondary exposure employing a vector scan shaped focused electron beam at an exposure dose substantially below the primary beam dose, there being provided a gap between the primary pattern and the secondary pattern. There is then developed the primary pattern in the sensitive resist layer to form the final corrected pattern on the substrate. The patterned layer of resist material may be employed directly on the substrate on which it is formed, or alternatively the patterned resist layer may be employed formed over an opaque layer upon the transparent substrate and subsequently the pattern etched into the opaque layer to form a photomask.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
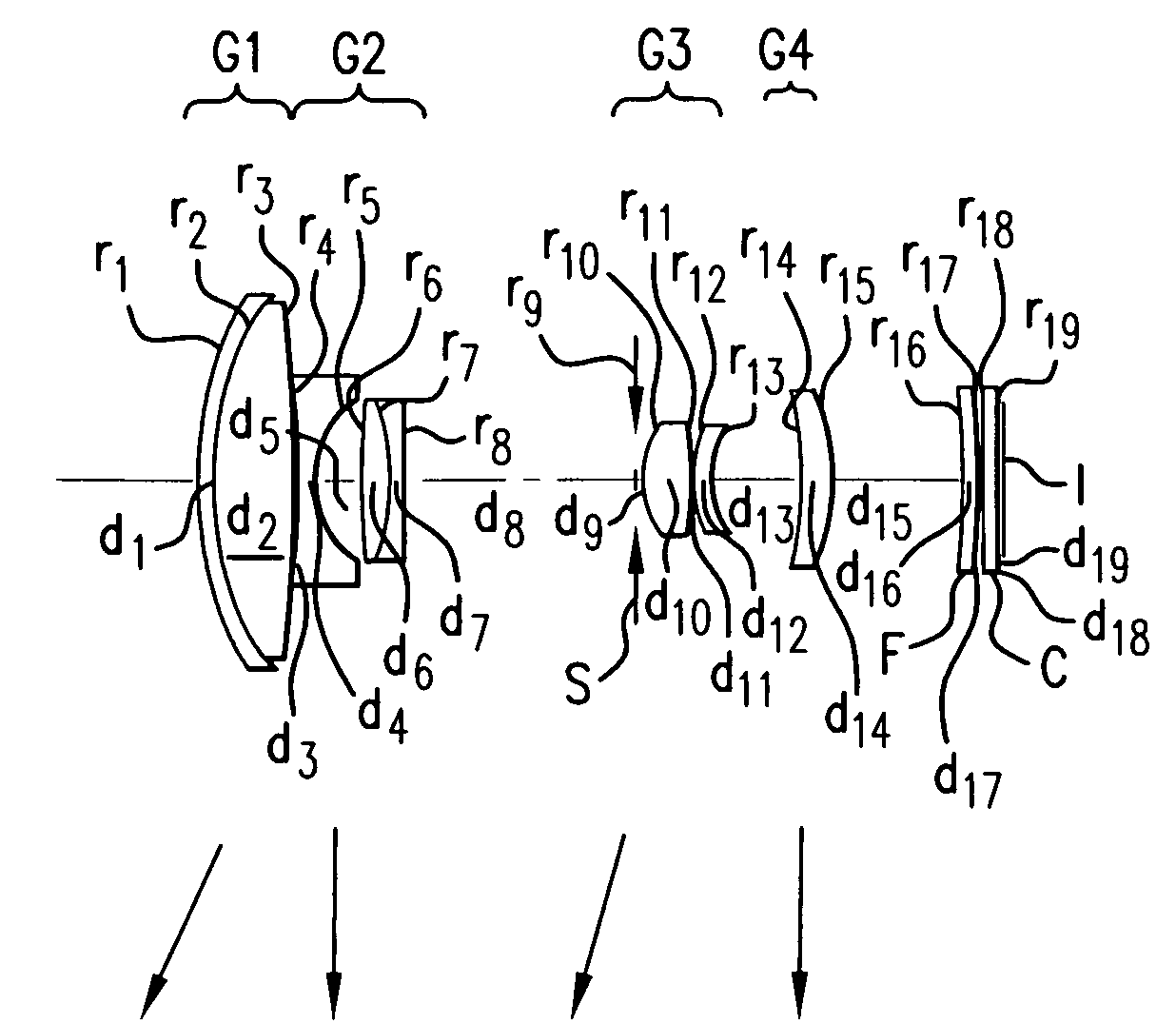
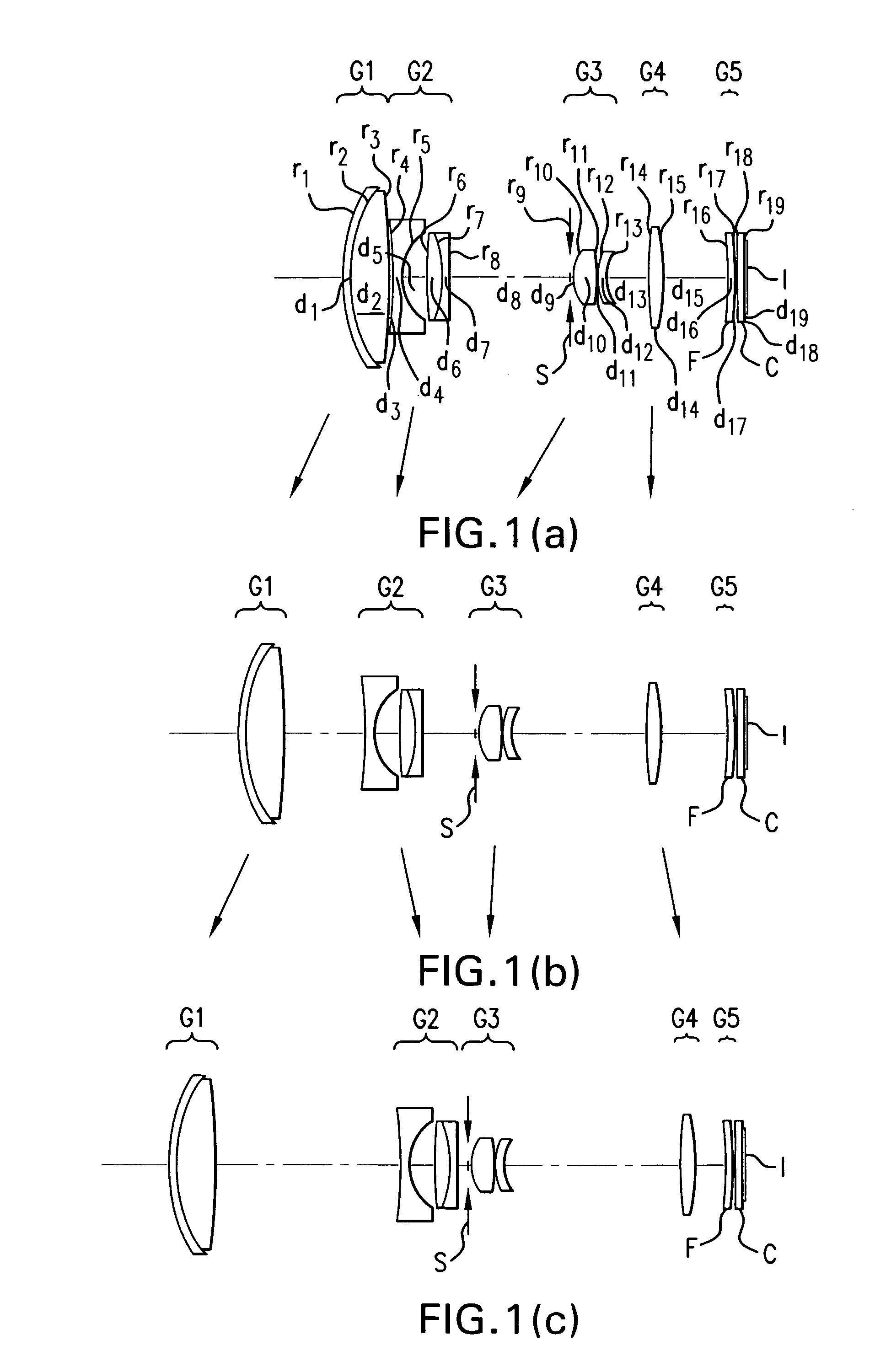
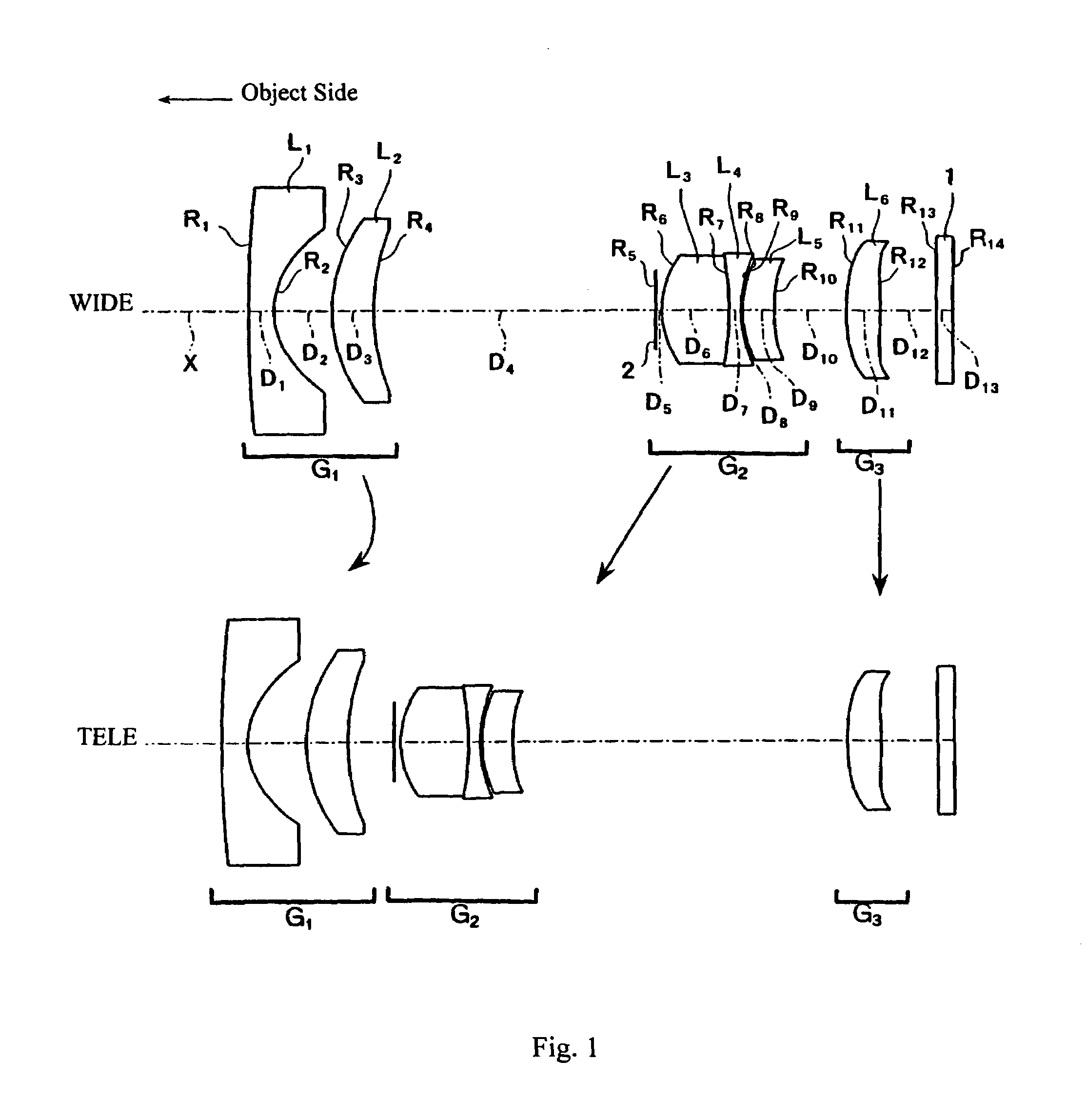
Three-group zoom lens
InactiveUS20050286140A1High resolution capabilityImprove picture qualityOptical elementsOptoelectronicsZoom lens
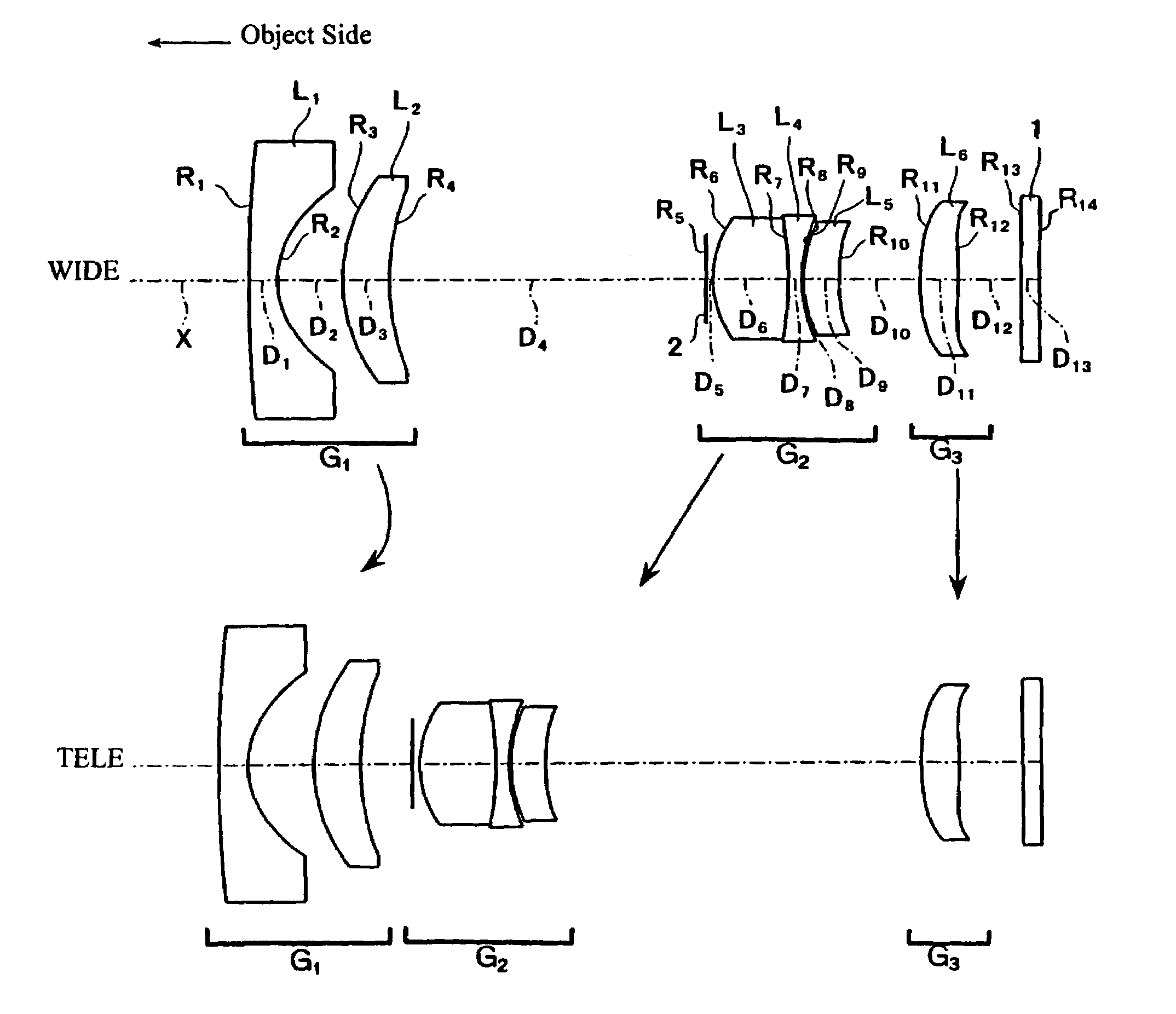
A three-group zoom lens includes five lens components and six lens elements. The first lens group from the object side has negative refractive power and both the second lens group, which includes a stop, and the third lens group from the object side have positive refractive powers. The first and second lens groups each include an aspheric surface. During zooming, the first lens group moves nearer the second lens group while the second lens group moves farther from the third lens group. The third lens group moves toward the object side when focusing from an object at infinity to a nearby object. The three lens groups have particular lens element constructions, and lens elements of the second and third lens groups satisfy certain conditions related to their focal lengths, Abbe numbers, and the focal length of the zoom lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Zoom lens and projection display device using the zoom lens
InactiveUS20060056043A1Shorten the lengthEasy to correctOptical elementsOptical axisProjection display
A zoom lens for a projection display device includes, in order from the enlarging side, a first lens group having negative refractive power and that is stationary during zooming, second and third lens groups having positive refractive power, a fourth lens group that has refractive power that is much weaker in absolute value than the refractive powers of the other lens groups, and a fifth lens group having positive refractive power and that is stationary during zooming. The second, third, and fourth lens groups move with coordinated movements continuously toward the enlarging side during zooming from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end of the zoom range. The zoom lens satisfies certain conditions related to focal lengths of the zoom lens and lens groups and distances along the optical axis. A projection display device uses the zoom lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Treatment device for the surgical correction of defective vision of an eye, method for producing control data therefor, and method for the surgical correction of defective vision of an eye
ActiveUS20140288538A1Avoid poor resultsEasy to implementLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsControl dataSurgical correction
A treatment device for the surgical correction of defective vision in an eye. The device includes a laser apparatus controlled by a controller. The controller determines a desired correction of defective vision from measurement data of the eye to produce control data for the laser, and to control the laser to emit radiation according to the control data, such that a lenticule-shaped volume is isolated in the cornea. The controller computes a lenticule-shaped intended volume, the removal of which from the cornea leads to an actual correction of defective vision in an optical zone in the eye which differs from the desired correction more at the edge of the optical zone than at the center of the optical zone. The thickness of the lenticule-shaped intended volume is less than the thickness of a lenticule-shaped comparison volume, the removal of which would bring about the desired correction of defective vision.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Retrofocus type optical system
InactiveUS20050243434A1Easy to correctEasy to manufactureMountingsLensRefractive indexComputational physics
Provided is a retrofocus type optical system including a lens or a layer made of a material satisfying the following conditions of the Abbe constant νd and partial dispersion ratios θgd and θgF, νd<30, θgd<−3.333×10−3·νd+1.40, θgF<−2.615−10−3·νd+0.67. In the case that this layer is disposed on the front side of the aperture stop, the layer is designed to have a positive refractive power, and in the case that the layer is disposed on the rear side of the aperture stop, the layer is designed to have a negative refractive index.
Owner:CANON KK
Retrofocus, wide-angle lens
A retrofocus, wide-angle lens includes a first lens group of negative refractive power, a stop, and a second lens group of positive refractive power. The first lens group includes, in order from the object side, a meniscus lens elements having positive refractive power, two meniscus lens elements having negative refractive power, and a thick lens element. The second lens group includes a cemented lens component that includes a lens element having negative refractive power and a biconvex lens element that is on the object side of a meniscus lens element having negative refractive power with its concave surface on the object side. The second lens group may include a meniscus lens component having positive refractive power on the object side of the biconvex lens element and a meniscus lens component having positive refractive power on the image side of the meniscus lens element having negative refractive power.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
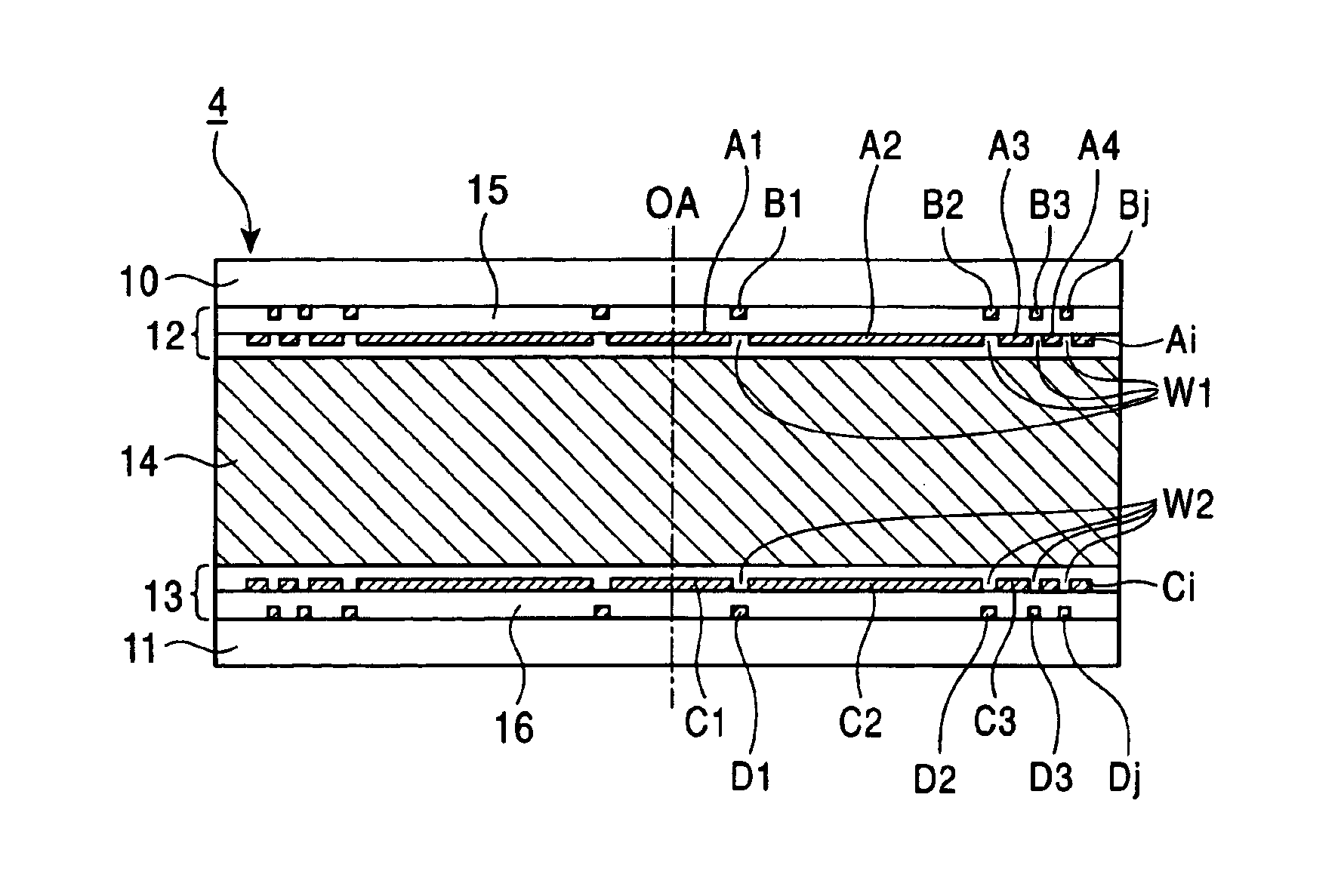
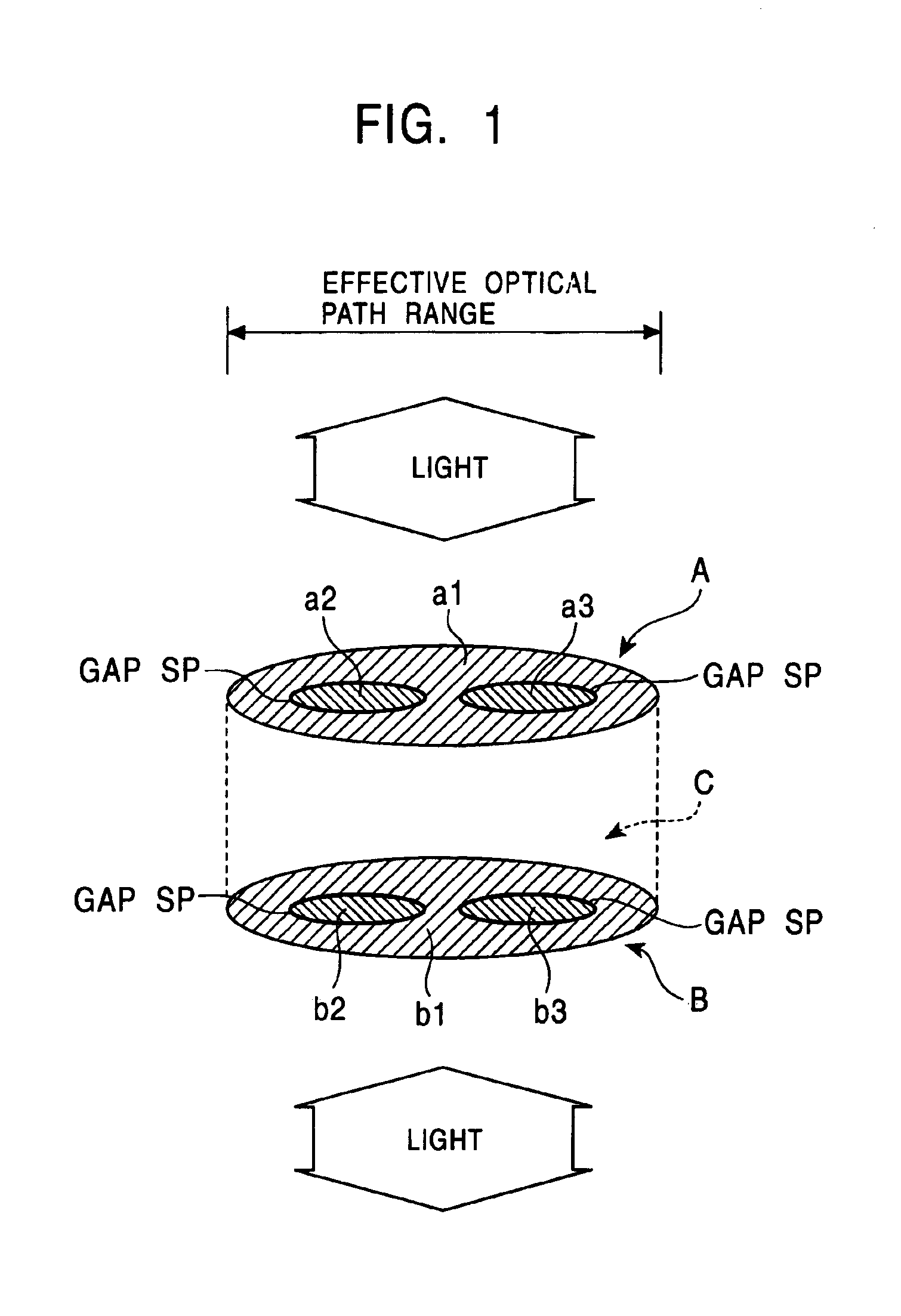
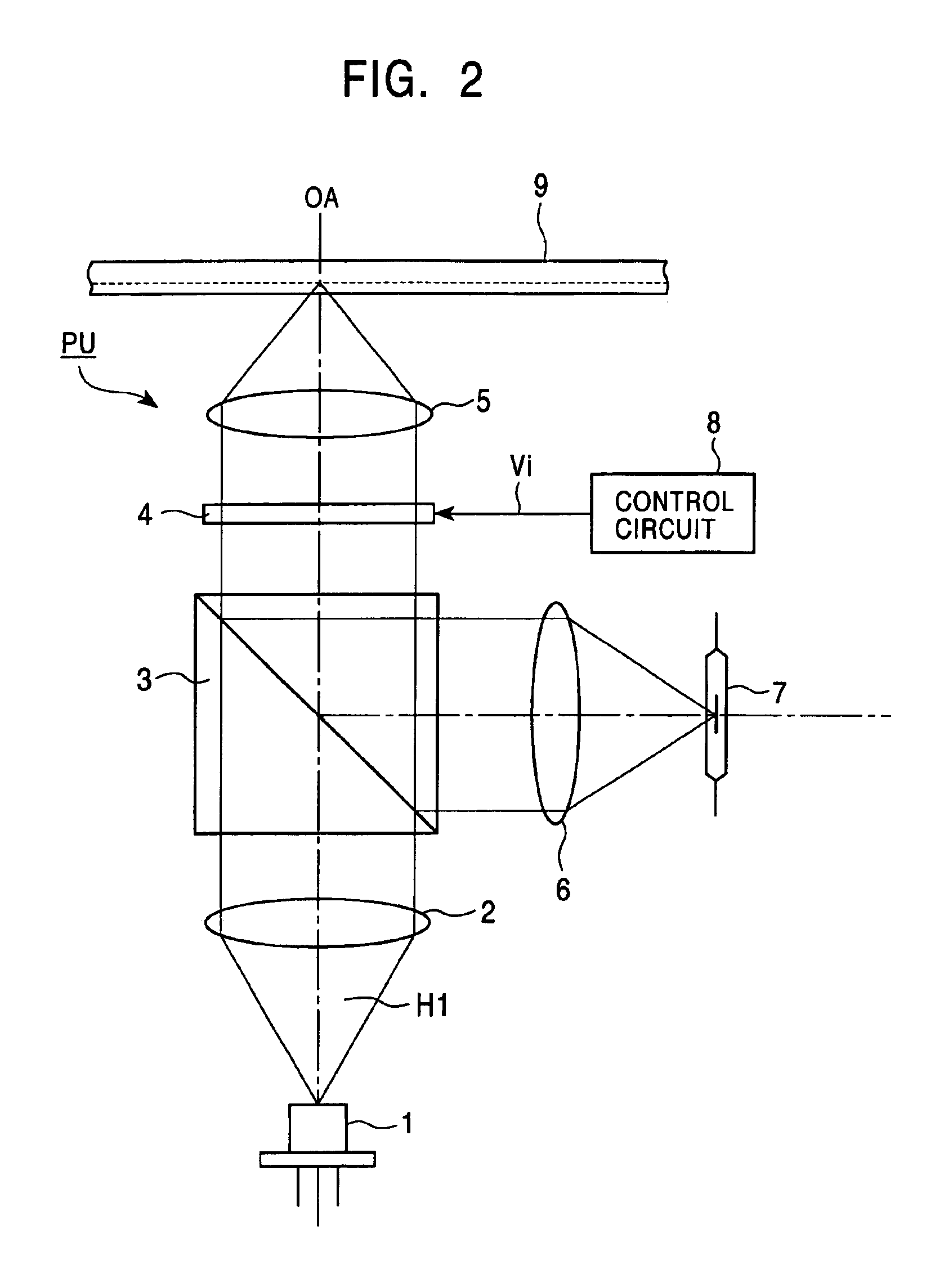
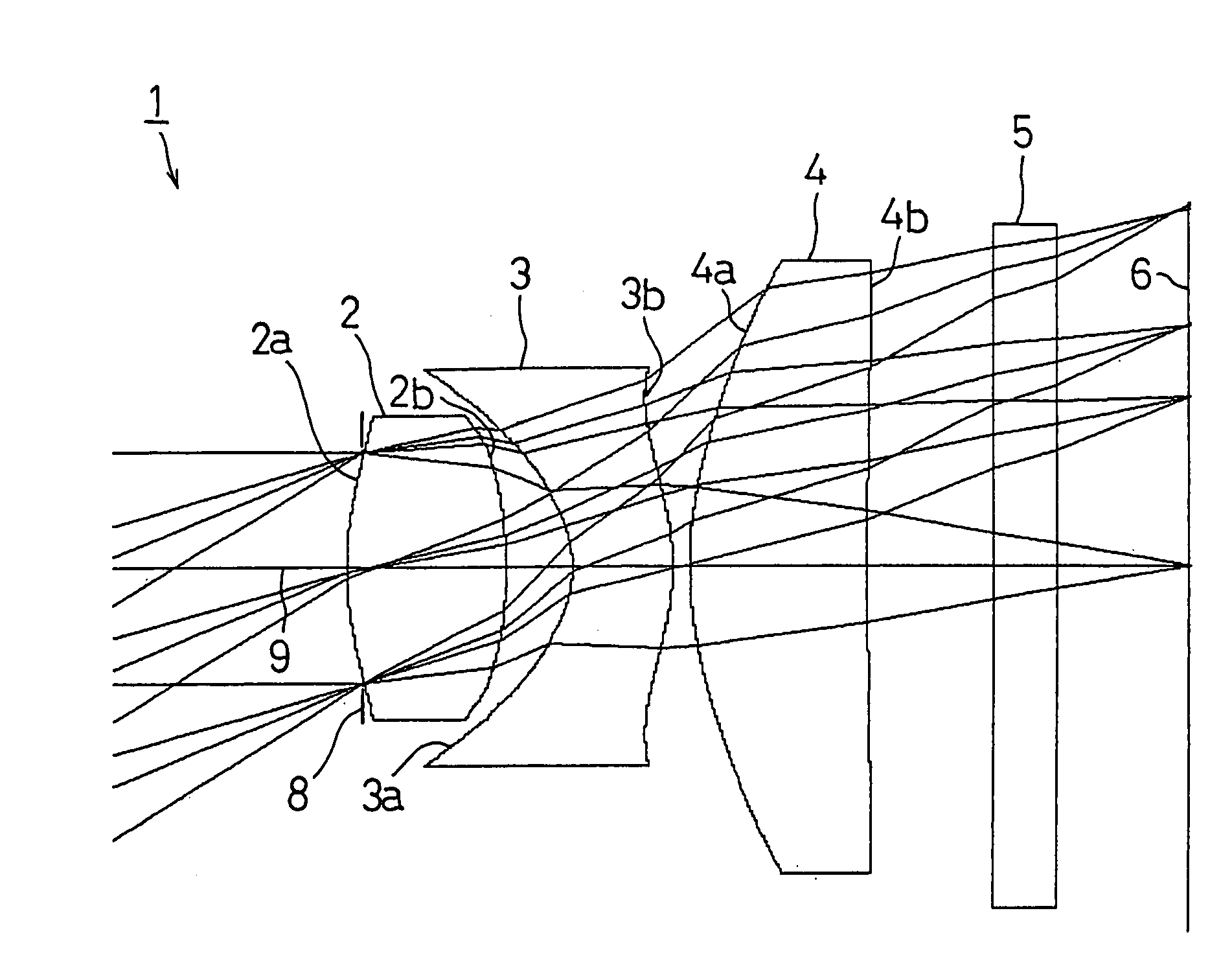
Aberration correcting optical unit, optical pickup apparatus and information recording/reproducing apparatus with single and multi-layer electrodes
InactiveUS6909686B2Accurate correctionFavorably correctedOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageElectricityOptical pickup
An aberration correcting optical unit includes an optical element for causing a phase change to light passing therethrough by the application of voltage and electrode layers for applying voltages to the optical element. The optical element is sandwiched between the electrode layers. At least one of the electrode layers includes a plurality of electrodes which are electrically isolated from one another. The plurality of electrodes are disposed such that an electric field generated in a portion of the optical element corresponding to a portion between the plurality of electrodes is larger than a predetermined intensity when a predetermined voltage is applied to the optical element.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
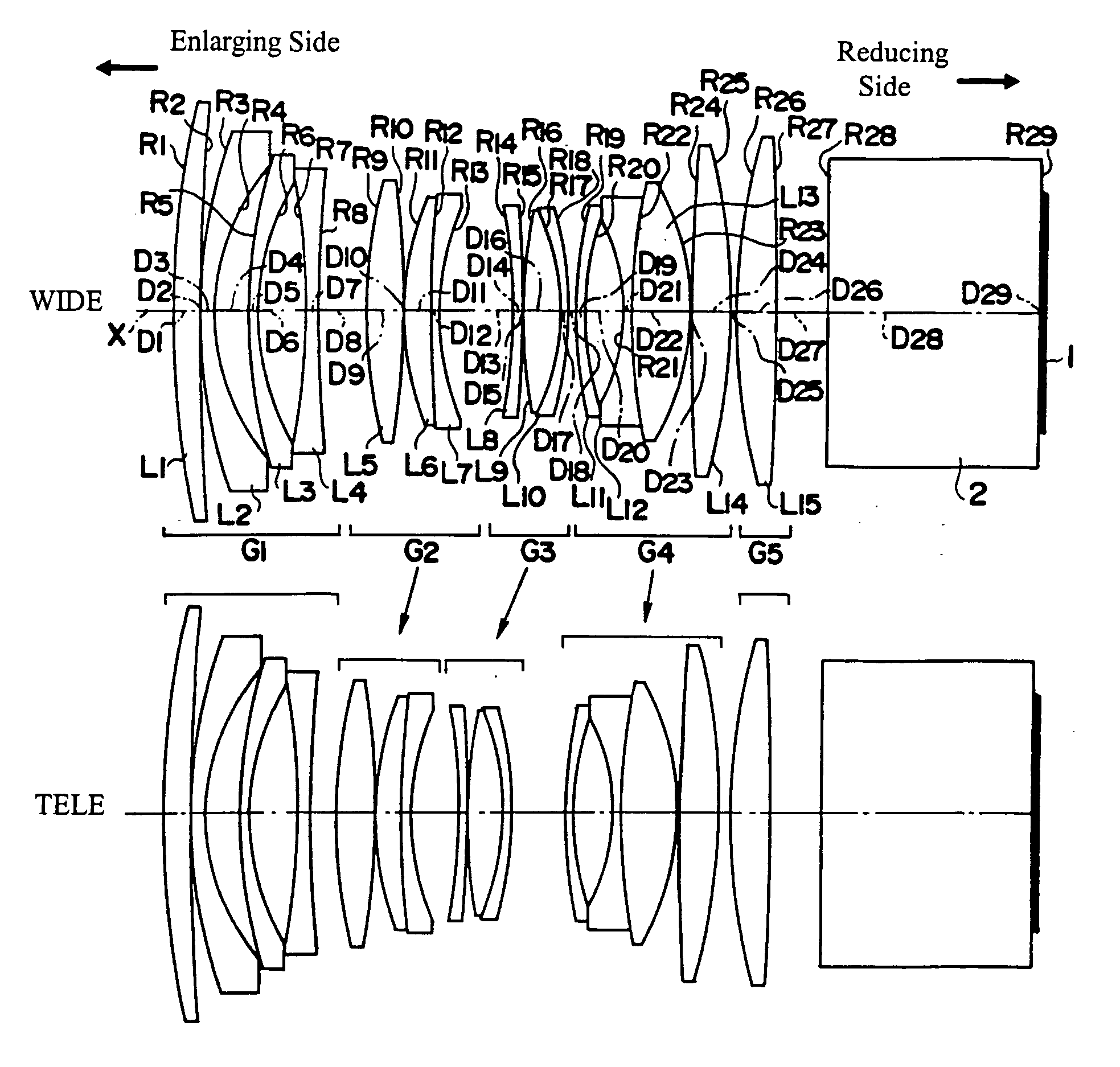
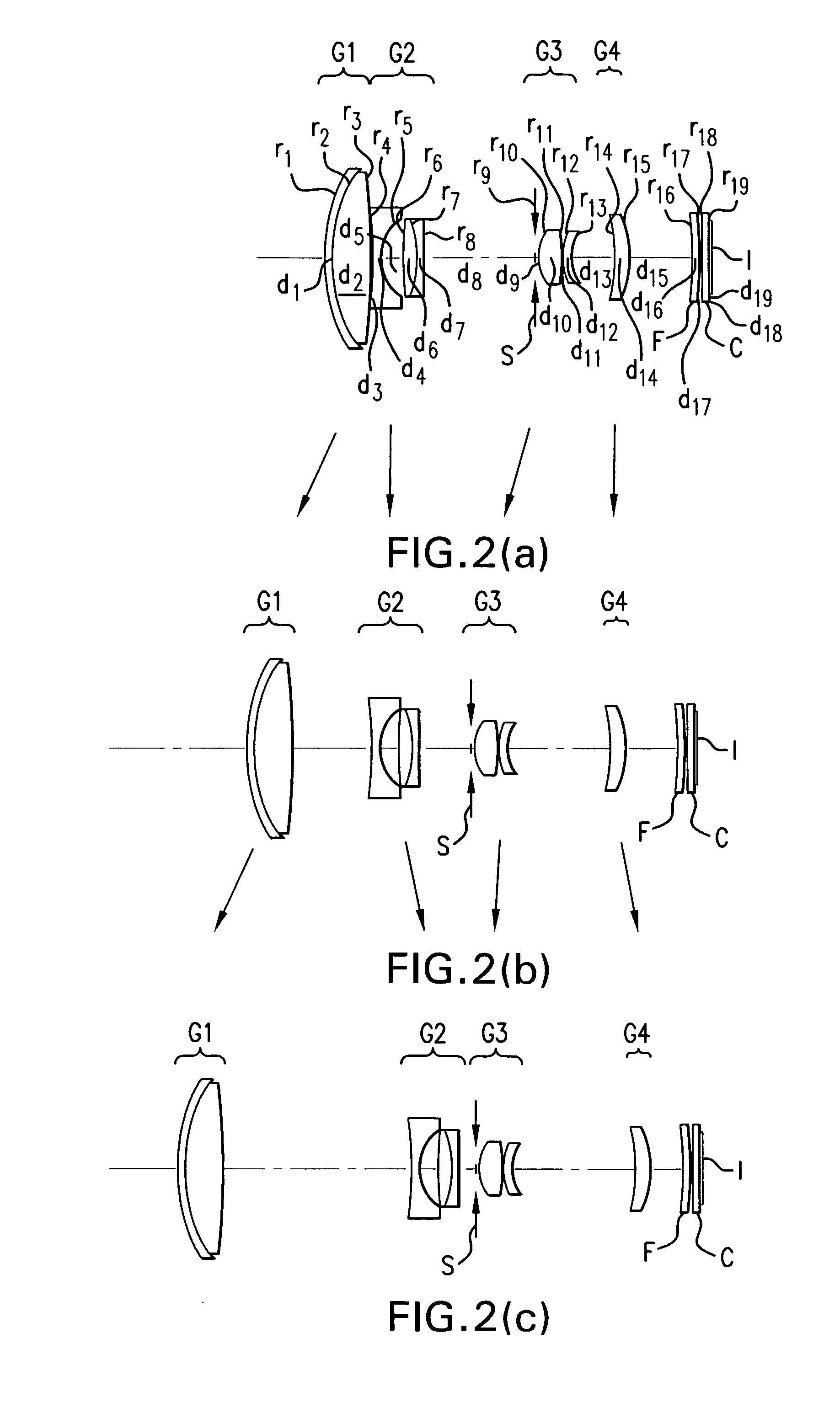
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus incorporating the same
ActiveUS20090103187A1Reduce in quantityCorrect chromatic aberrationOptical elementsRefractive indexImaging equipment
The invention relates to a zoom lens and an imaging apparatus incorporating the same, and more particularly to a zoom lens of small format that lends itself to imaging apparatus inclusive of video cameras and digital cameras. The zoom lens comprises, in order from its object side, a first lens group G1 of positive refracting power, a second lens group G2 of negative refracting power and a third lens group G3 of positive refracting power. Zooming is implemented by changing the space between the respective lens groups. The first lens group G1 comprises one negative lens and one positive lens in order from the object side. The zoom lens satisfies conditions (1) and (2):5.0<ft / fw<50.0 (1)1.4<Nd1p<1.7 (2)where fw is the focal length of the whole zoom lens system at a wide-angle end, ft is the focal length of the whole zoom lens system at a telephoto end, and Nd1p is the d-line refractive index of the positive lens in the first lens group.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
High magnification, four-group zoom lens
InactiveUS6956704B2High magnificationLarge zoom ratioDiffraction gratingsCamera lensRefractive index
A high magnification, four-group zoom lens formed of only four lens groups, namely, a first lens group of positive refractive power, a second lens group of negative refractive power, and third and fourth lens groups of positive refractive power. The first lens group includes, in order from the object side, a first lens subgroup that is fixed during focusing and a second lens subgroup that moves during focusing. The second lens group includes, in order from the object side, first and second lens elements having negative refractive power, and first and second doublet components with each formed of a lens element having positive refractive power and a lens element having negative refractive power. To suppress lateral color, specified conditions are satisfied for the Abbe numbers and the refractive indices of the positive refractive power lens elements that are included in the doublet components of the second lens group.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
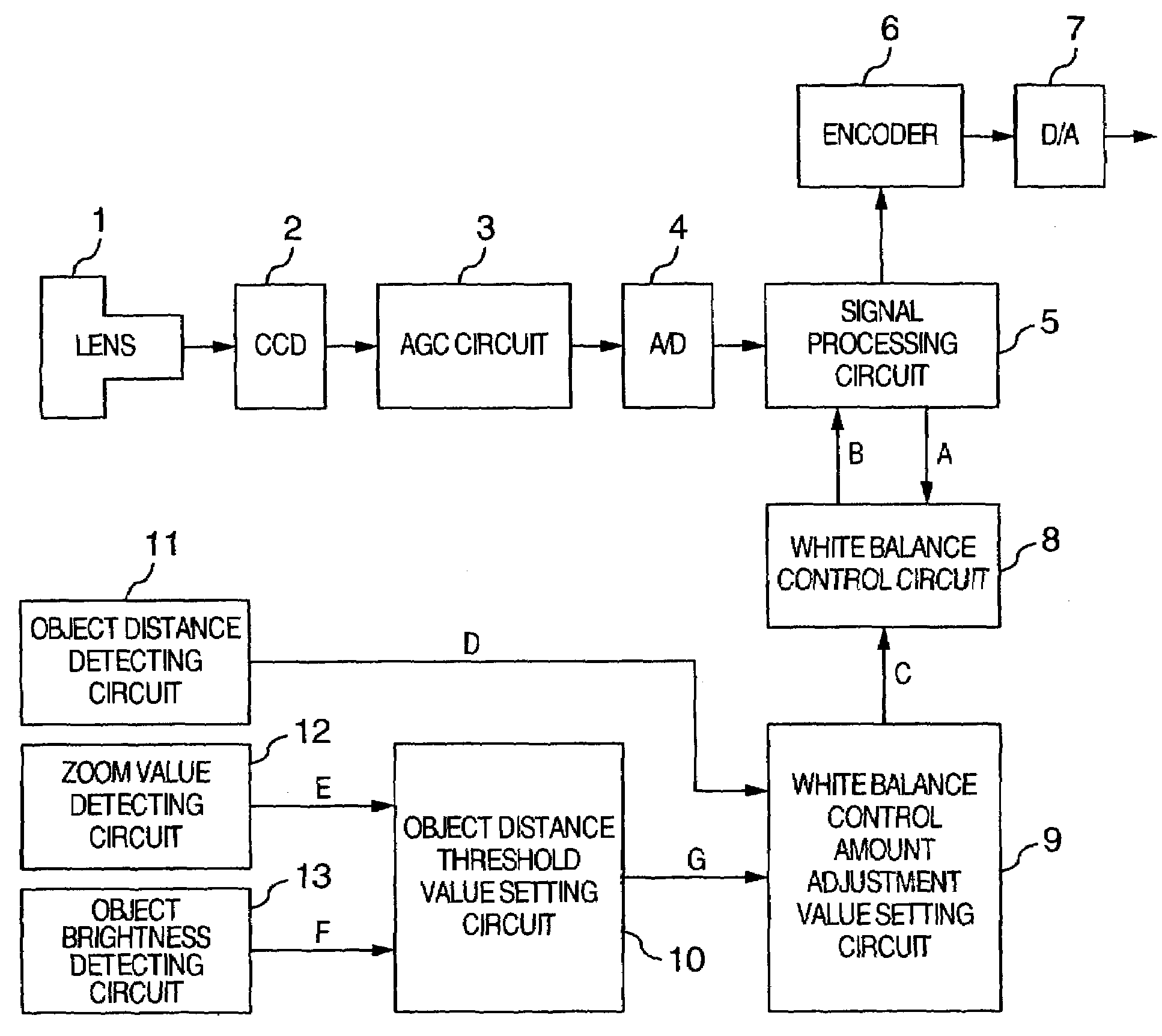
Imaging apparatus and method for controlling white balance
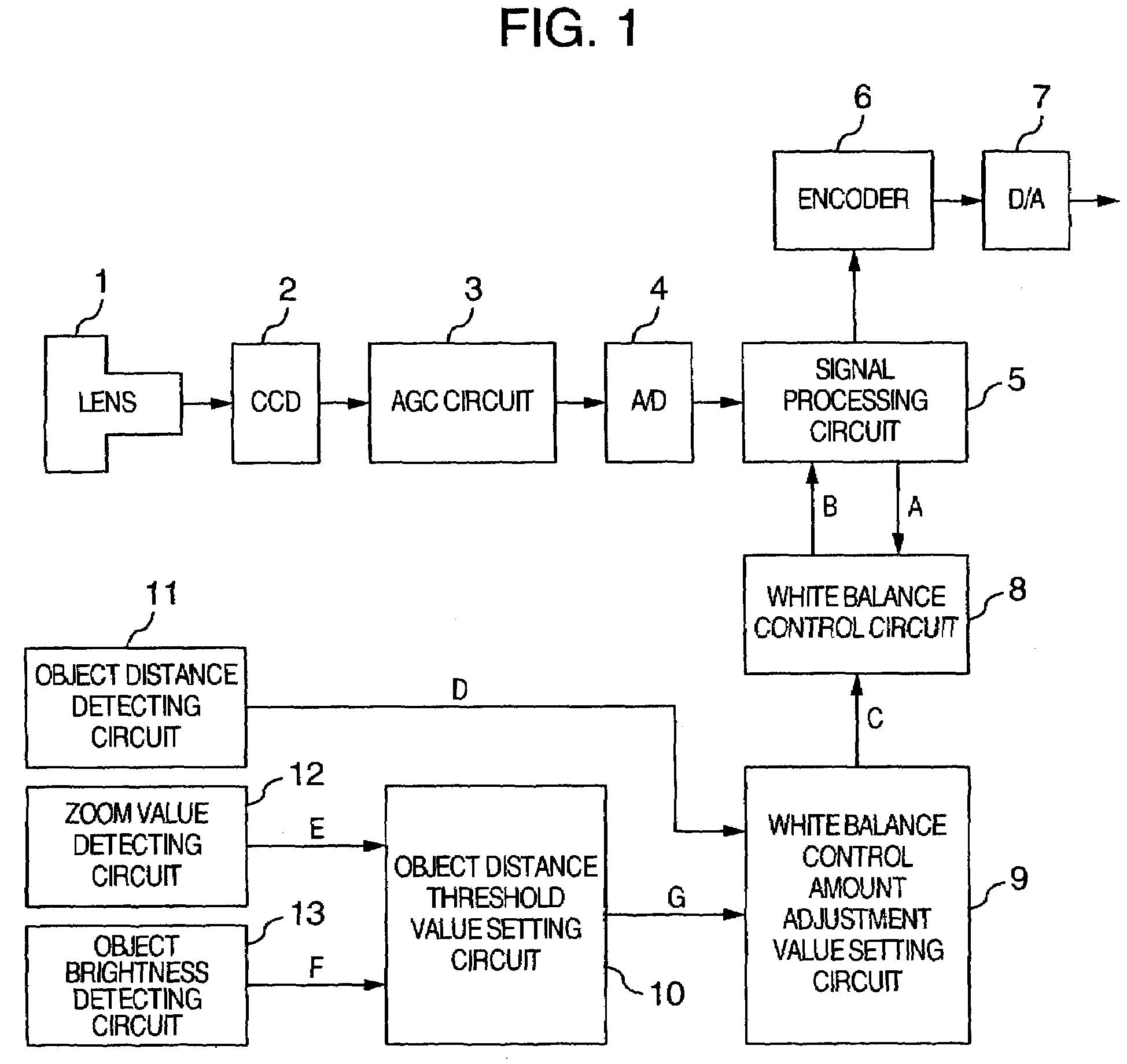
ActiveUS7199821B2Favorably correctedAccurate white balanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsValue setControl circuit
An imaging apparatus has: a white balance control circuit for detecting an achromatic portion of an image of an object and controlling gains of the chrominance; an object distance detecting circuit for detecting a distance to the object; and a zoom value detecting circuit for detecting a zoom value of the optical system. The imaging apparatus further has: an object brightness detecting circuit for detecting brightness of the object; and a white balance control amount adjustment value setting circuit for forming a white balance control amount adjustment value to adjust a control amount in the white balance control circuit on the basis of object brightness information, object distance detection information, and zoom value information, wherein the white balance control amount is adjusted on the basis of the white balance control amount adjustment value.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
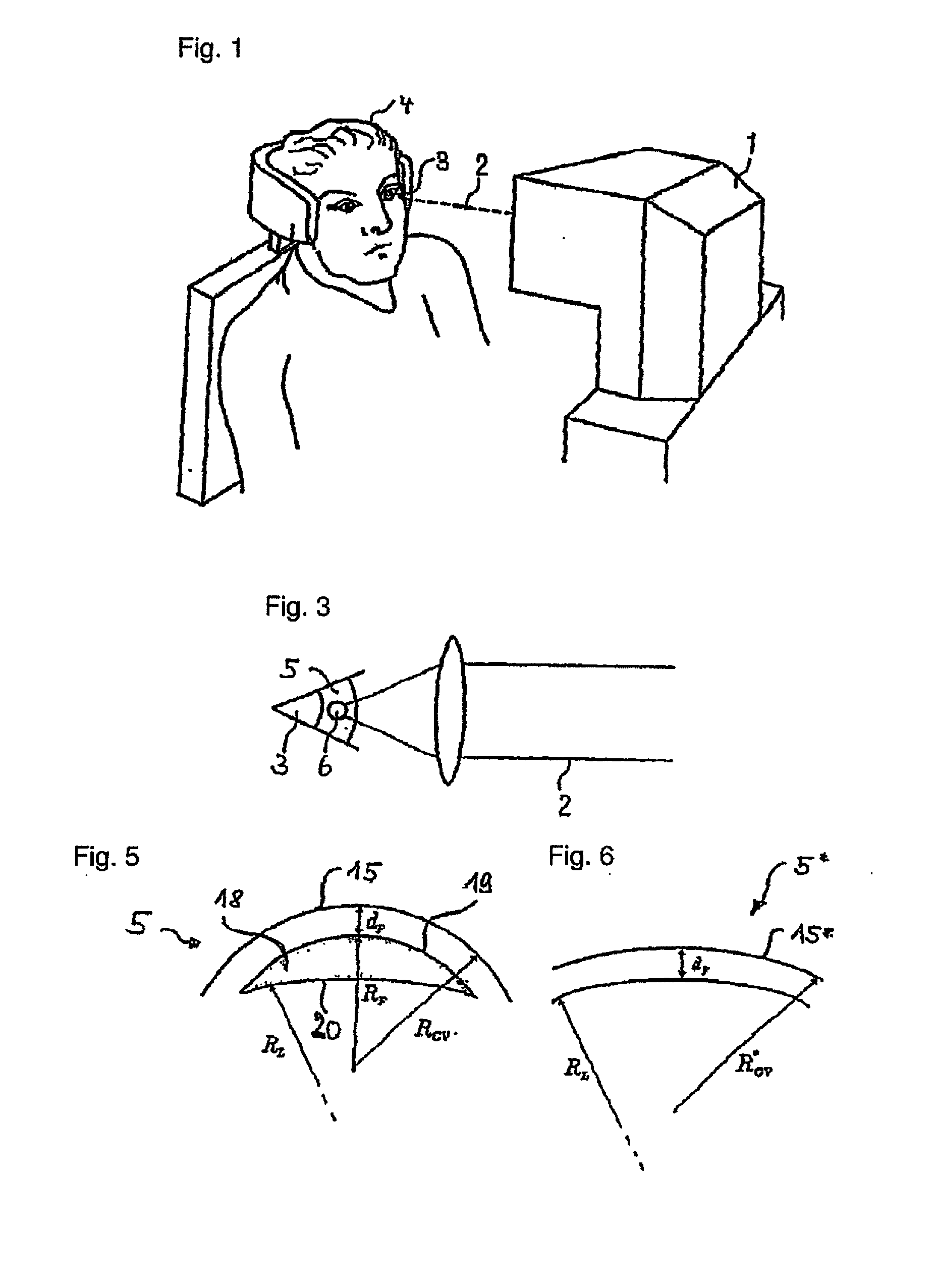
Objective phoropter system
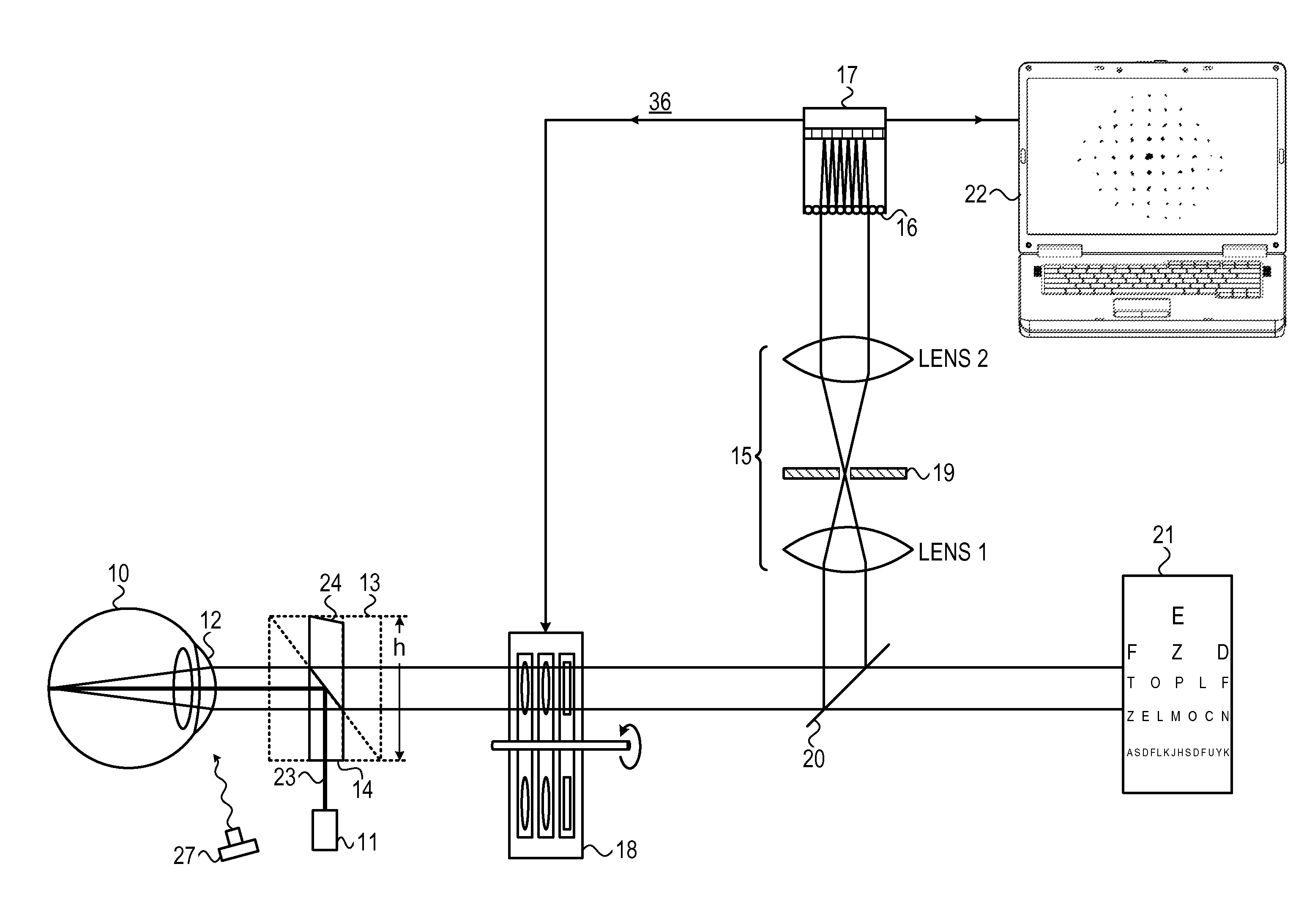
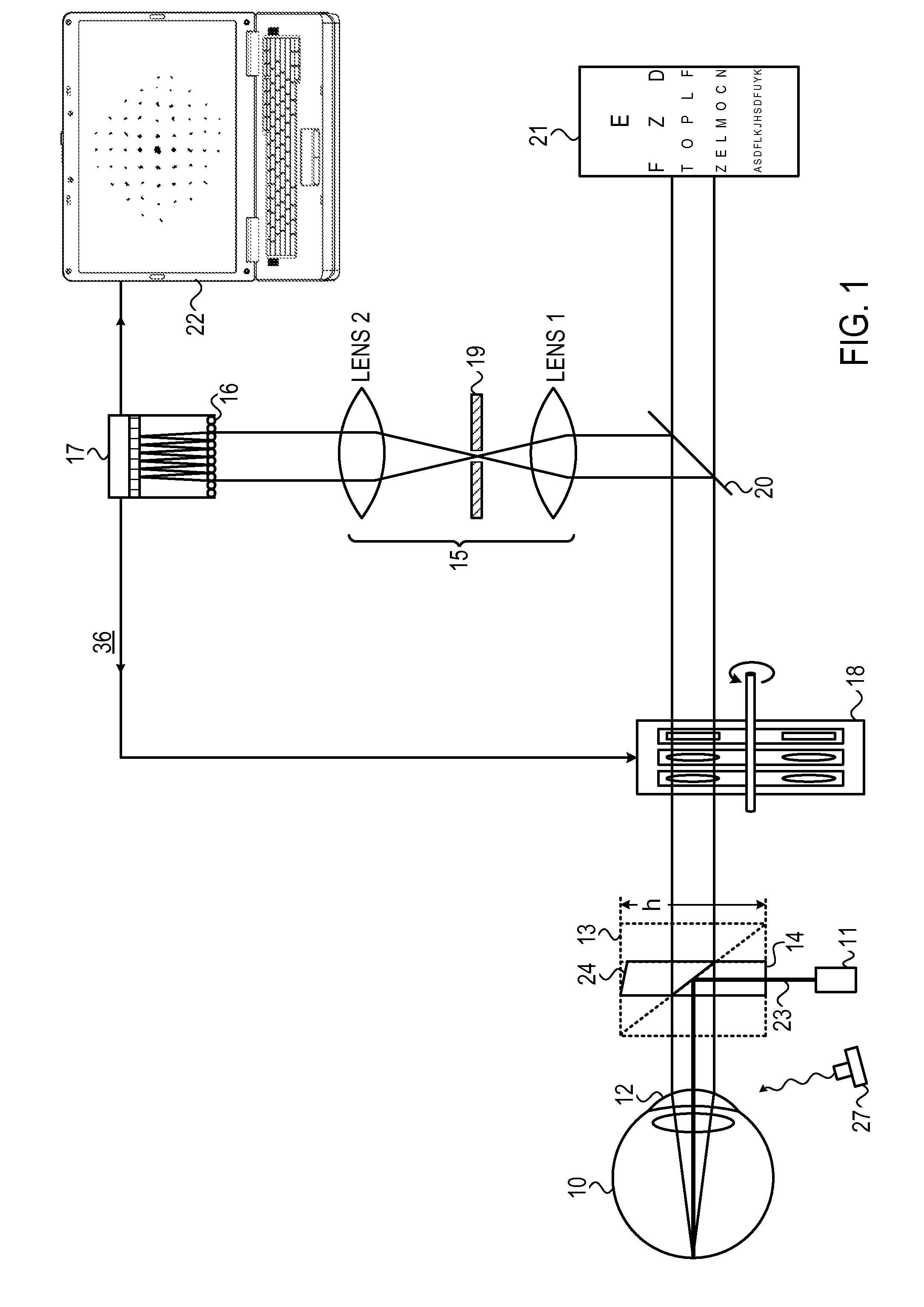
ActiveUS9462939B2Favorably correctedResidual aberrationMachines/enginesPump controlRefractive measurementsPupil
Systems for performing combined phoropter and refractive measurements to ascertain the aberrations present in the eye of a subject. The systems use a pair of phoropter wheel assemblies, one for each eye, each assembly comprising a number of lens wheels incorporating the series of lenses and wedges required to compensate for a range of refractive vision aberrations. The vision of each eye is corrected by a combination of a subjective phoropter measurement, iteratively performed with an objective wavefront analysis measurement to determine the residual aberrations existing after the initial phoropter correction. The system is able to automatically align the axes of each wavefront analyzer with is corresponding eye, by means of centering the pupil image in the wavefront analyzer camera, and to determine the pupil distance. By changing the focusing point on the wavefront analyzer of the light reflected from the eye, the corneal profile can be measured.
Owner:VISIONIX
Zoom lens
A zoom lens includes at least two lens groups that move for zooming. An object-side lens group is formed of a lens component having negative refractive power and a meniscus shape and a second lens component having positive refractive power and a meniscus shape, which may be in that order from the object side. Each of these lens components may be formed of a single lens element. Lens elements of the lens components satisfy certain conditions related to the half-field angle at the wide-angle end and the Abbe numbers of the lens elements. The zoom lens may include a third lens group, which may be stationary, with a middle lens group that moves nearer the object-side lens group and farther from the third lens group during zooming from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end. At least one surface of a lens component may be an aspheric surface.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
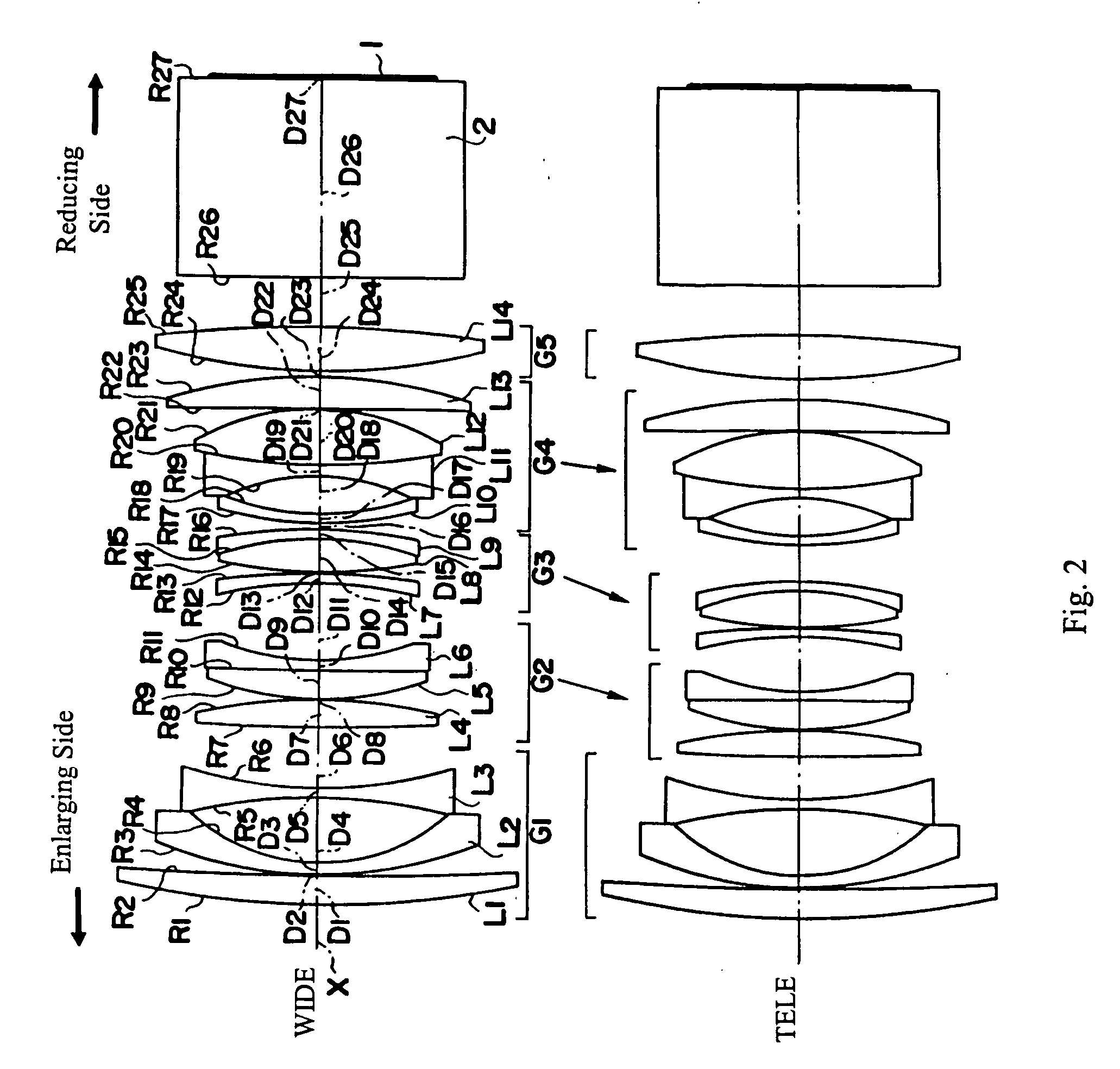
Catadioptric projection objective
InactiveUS7697198B2Favorably correctedSimple designMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageImage plane
A catadioptric projection objective for projecting a pattern arranged in the object plane of the projection objective into the image plane of the projection objective, having: a first objective part for projecting an object field lying in the object plane into a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for generating a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; a third objective part for generating a third real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the second objective part; and a fourth objective part for projecting the third real intermediate image into the image plane.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20050224724A1Uniform widthSufficient energyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsCritical dimension
A device manufacturing method using lithographic apparatus, in which method a patterned beam of radiation is projected on to a target portion of a substrate. Prior to exposing the substrate to the patterned beam of radiation a beam of compensating radiation is irradiated on to a predetermined area of the substrate, the beam of compensating radiation having an intensity which varies across said predetermined area. In the described embodiment the beam of compensating radiation is applied to an annular edge region of the substrate and has an intensity which is tilted across the cross-section of the beam so as to increase or decrease in intensity towards the edge of the substrate. This is done to improve the critical dimension (CD) uniformity across the substrate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Three-group zoom lens
InactiveUS7164539B2Favorably correctedImprove rendering capabilitiesOptical elementsOptoelectronicsZoom lens
A three-group zoom lens includes five lens components and six lens elements. The first lens group from the object side has negative refractive power and both the second lens group, which includes a stop, and the third lens group from the object side have positive refractive powers. The first and second lens groups each include an aspheric surface. During zooming, the first lens group moves nearer the second lens group while the second lens group moves farther from the third lens group. The third lens group moves toward the object side when focusing from an object at infinity to a nearby object. The three lens groups have particular lens element constructions, and lens elements of the second and third lens groups satisfy certain conditions related to their focal lengths, Abbe numbers, and the focal length of the zoom lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Three-group zoom lens including at least one aspheric lens surface
A three-group zoom lens includes first, second, and third lens groups, of negative, positive, and positive or negative refractive power, respectively. The second lens group includes a stop and the third lens group moves for focusing. When zooming from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end, the first and second lens groups become closer together. The zoom lens preferably satisfies specified conditions that ensure compactness, ease of manufacture, and favorable correction of aberrations. The zoom lens includes aspheric lens elements with lens surfaces defined by an aspheric lens equation that: (a) includes at least one non-zero coefficient of an even power of Y, and at least one non-zero coefficient of an odd power of Y, where Y is the distance of a point on the aspheric lens surface from the optical axis, and / or (b) includes at least one non-zero coefficient of Yi, where i is even and 16 or greater.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
An imaging lens includes: a first lens group; an aperture stop; and a second lens group having a positive refractive power, in this order from an object side. The first lens group includes a negative first lens provided most toward the object side. The second lens group includes a positive lens, provided most toward an imaging surface, and a negative lens having a concave surface and an aspherical surface at least toward the object side. The following Conditional Formula are satisfied: 0.03<(|Sagsp1|−|Sagas1|) / Re1<0.35; and 1.819≰NdAB wherein Sagsp1 is the sag of a reference spherical surface at the edge of the effective diameter of the object side surface of the negative lens, Sagas1 is the sag of the aspherical surface of the lens, Re1 is the effective diameter of the object side surface of the lens, and NdAB is the average refractive index of the positive lens and the negative lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
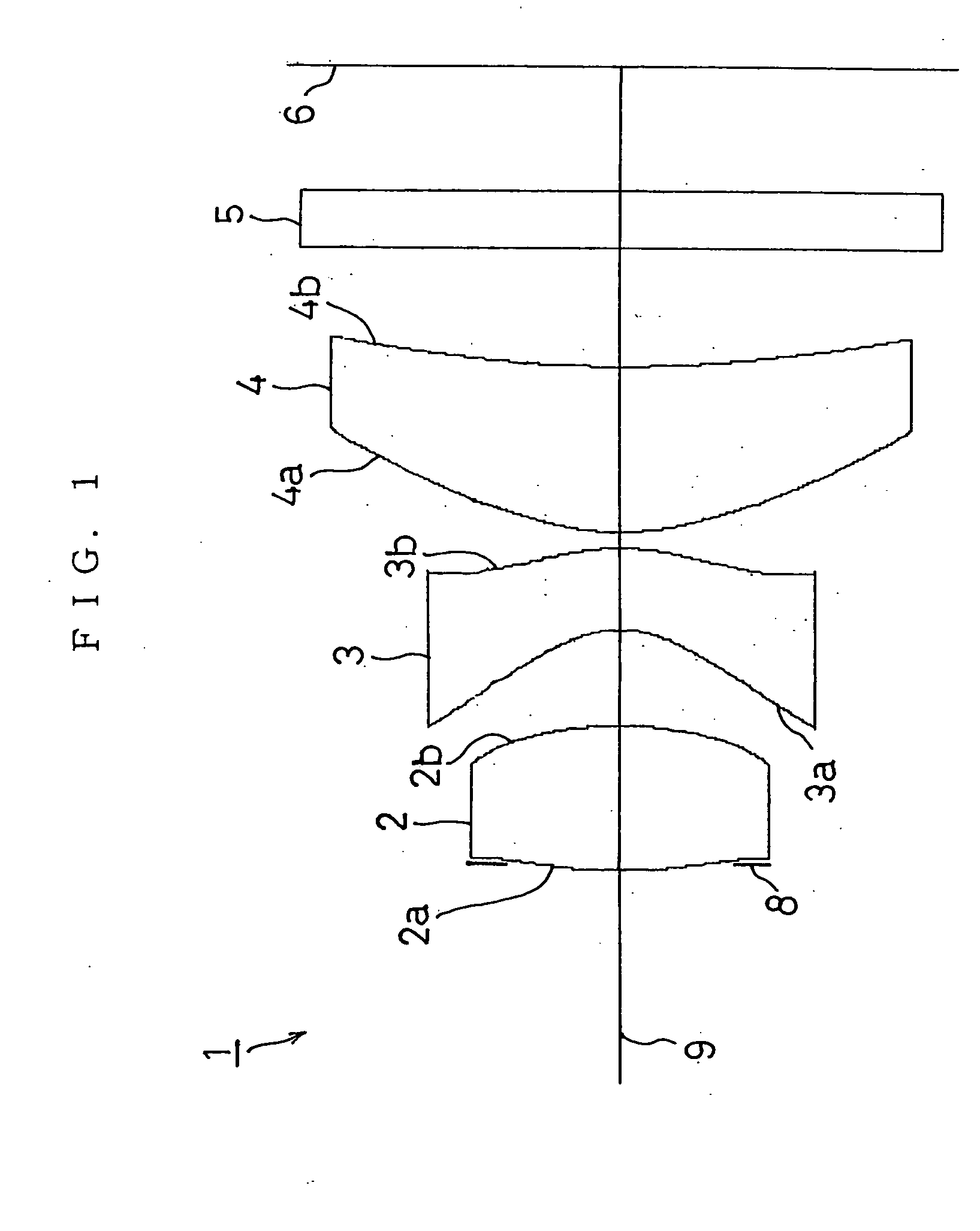
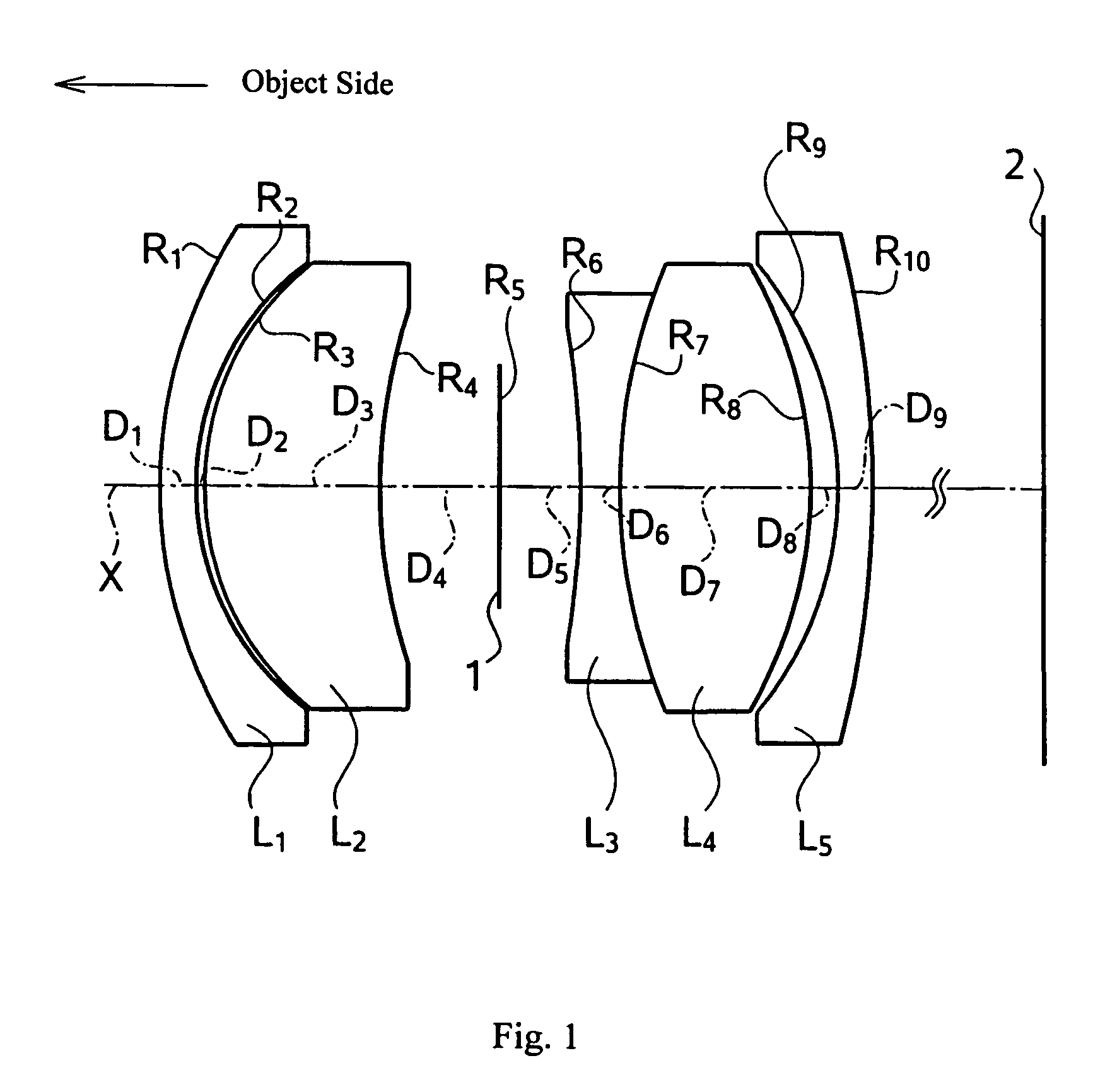
Imaging lens system
An imaging lens system including a first lens having a main positive power whose convex surface faces an object side, a second lens in a meniscus shape having a negative power whose convex surface faces an image surface side, and a third lens having a positive power whose convex surface faces the object side. The three lenses are disposed in order from the object side to the image surface side.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Image scanning lens and image scanning device that uses same
An image scanning lens includes four lens components that may include five lens elements as follows: a first lens element having negative refractive power and a meniscus shape with its convex surface on the object side, a second lens element having positive refractive power and a meniscus shape with its convex surface on the object side, a stop, a third biconcave lens element cemented to a fourth biconvex lens element, and a fifth lens element having negative refractive power and a meniscus shape with its concave surface on the object side. The image scanning lens satisfies certain conditions related to the focal lengths of the first, second, and third lens components of the image scanning lens and to the anomalous dispersion of the second lens element. An image scanning device, such as an image scanner, with an image pickup device, such as a CCD, uses the image scanning lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com