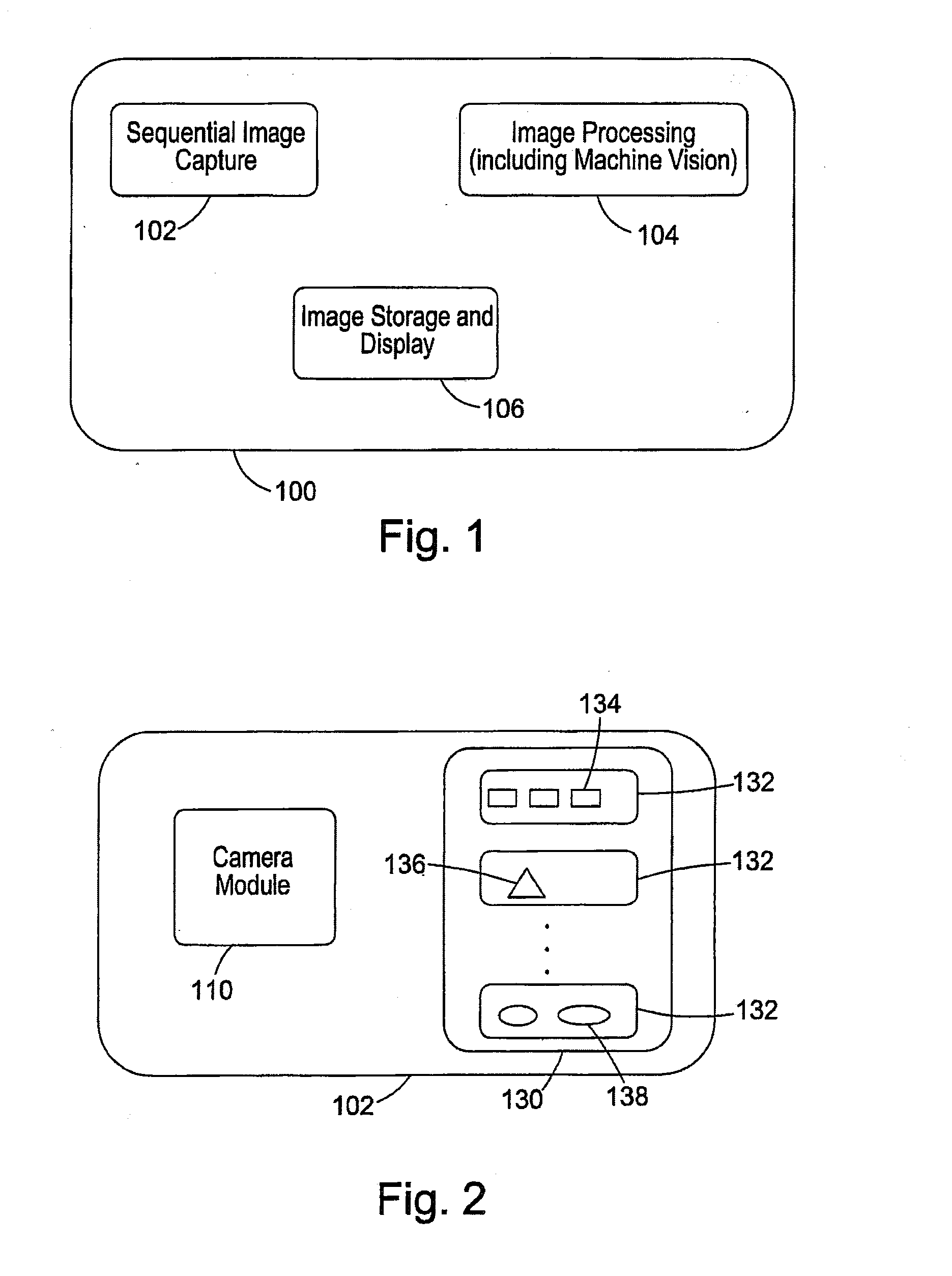
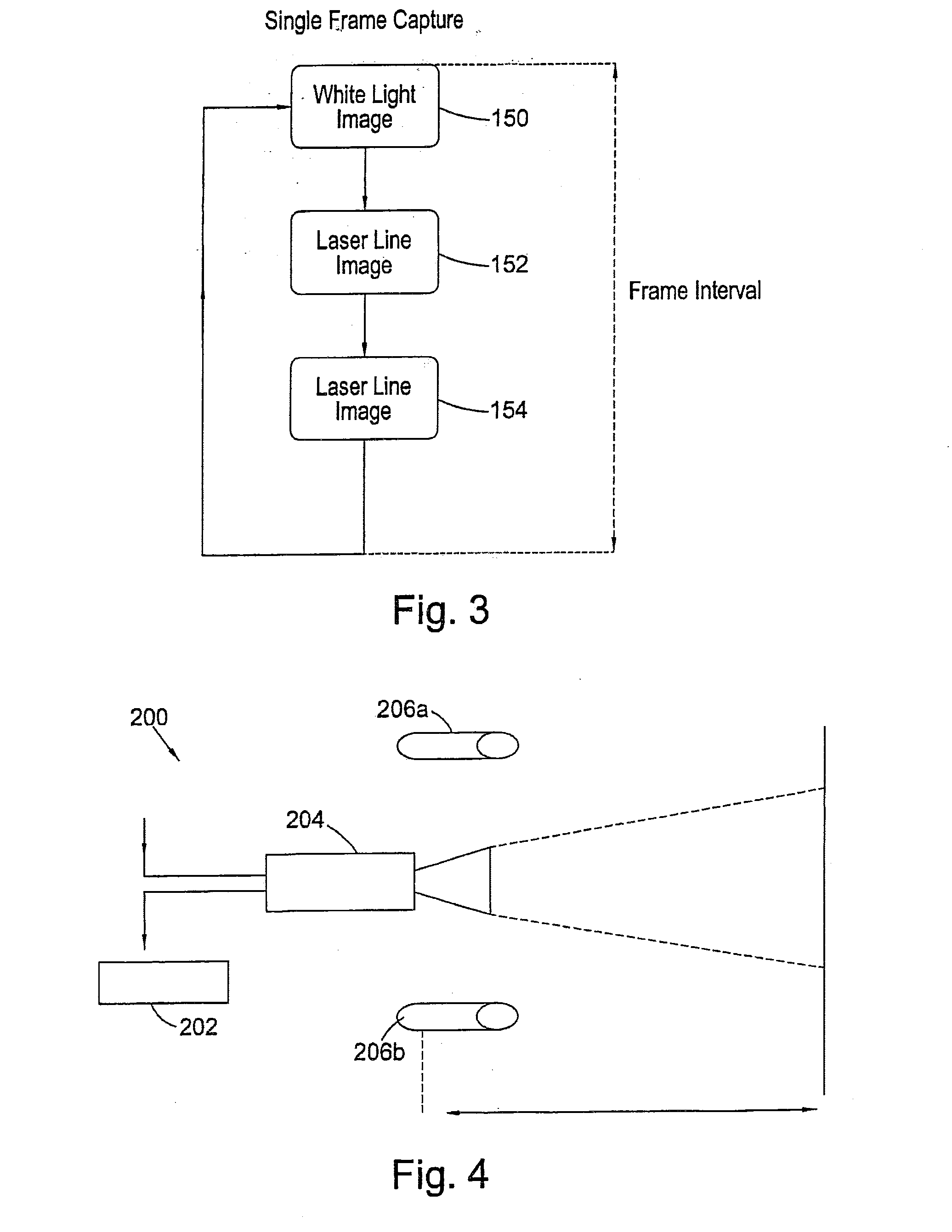
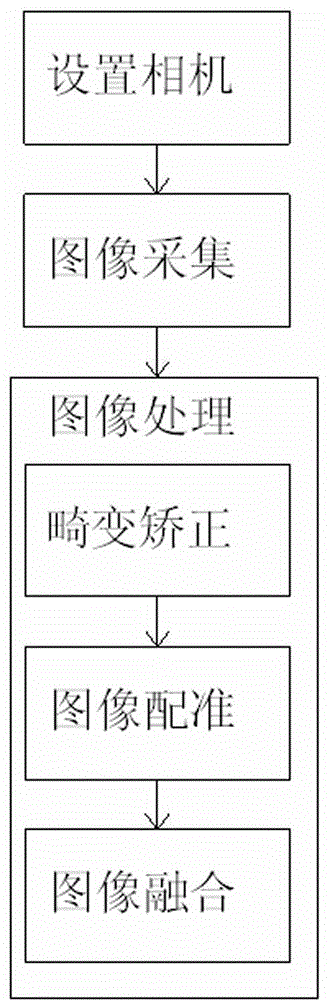
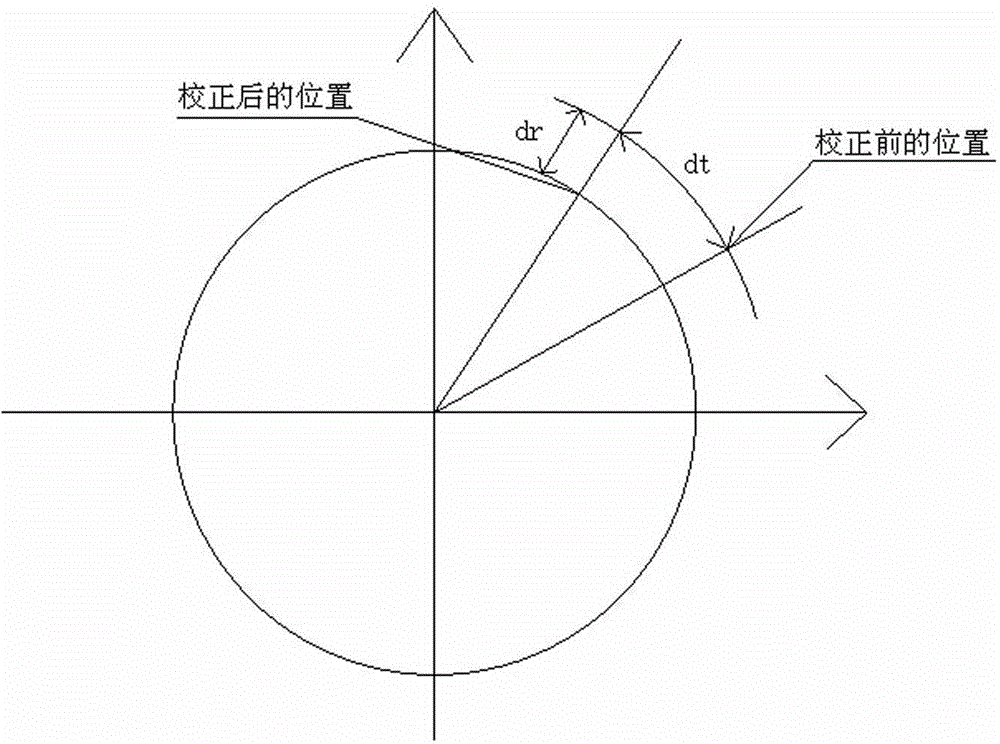
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1707results about "Details involving image mosaicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stereoscopic (3D) panorama creation on handheld device
A technique of generating a stereoscopic panorama image includes panning a portable camera device, and acquiring multiple image frames. Multiple at least partially overlapping image frames are acquired of portions of the scene. The method involves registering the image frames, including determining displacements of the imaging device between acquisitions of image frames. Multiple panorama images are generated including joining image frames of the scene according to spatial relationships and determining stereoscopic counterpart relationships between the multiple panorama images. The multiple panorama images are processed based on the stereoscopic counterpart relationships to form a stereoscopic panorama image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
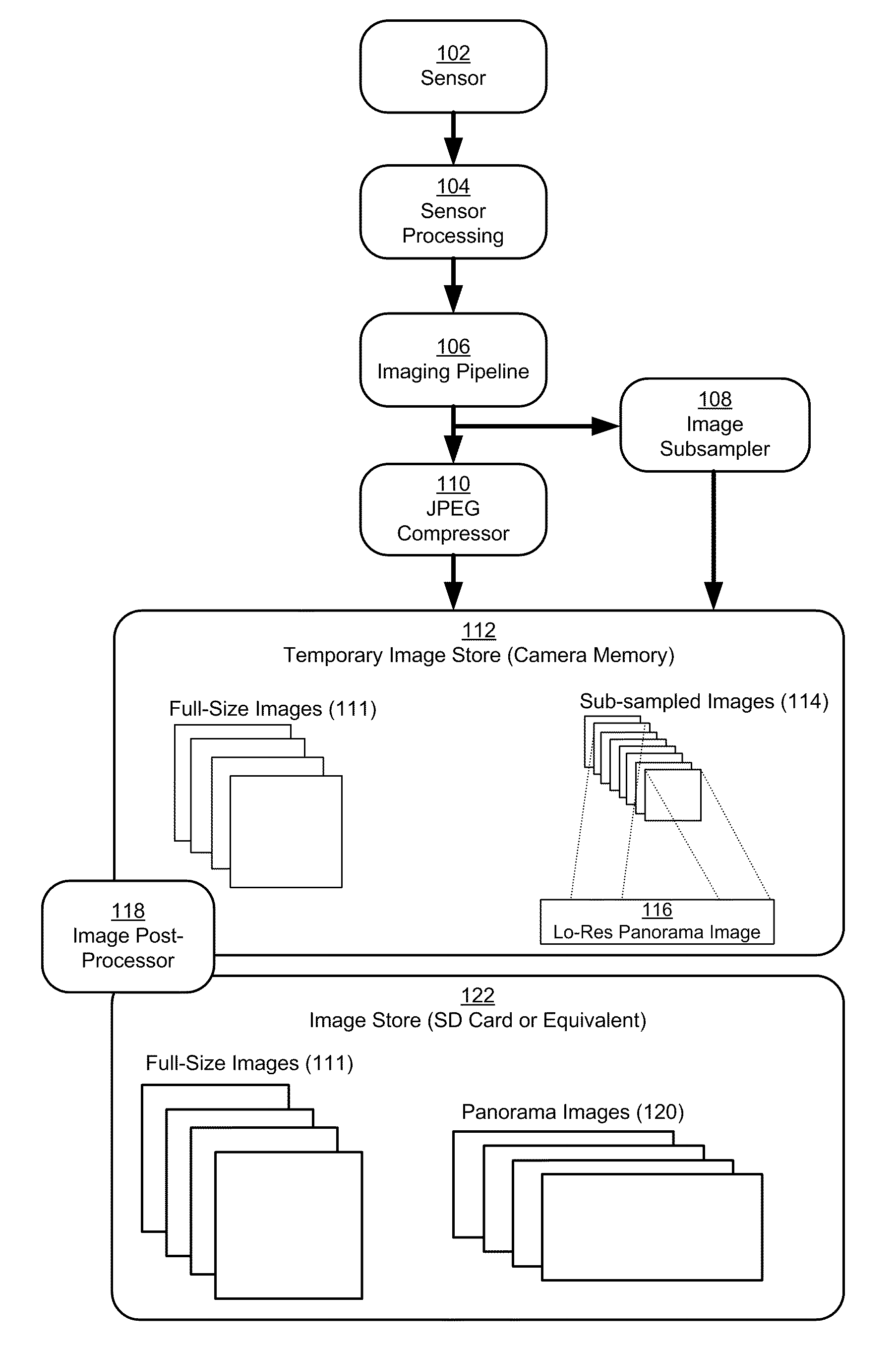
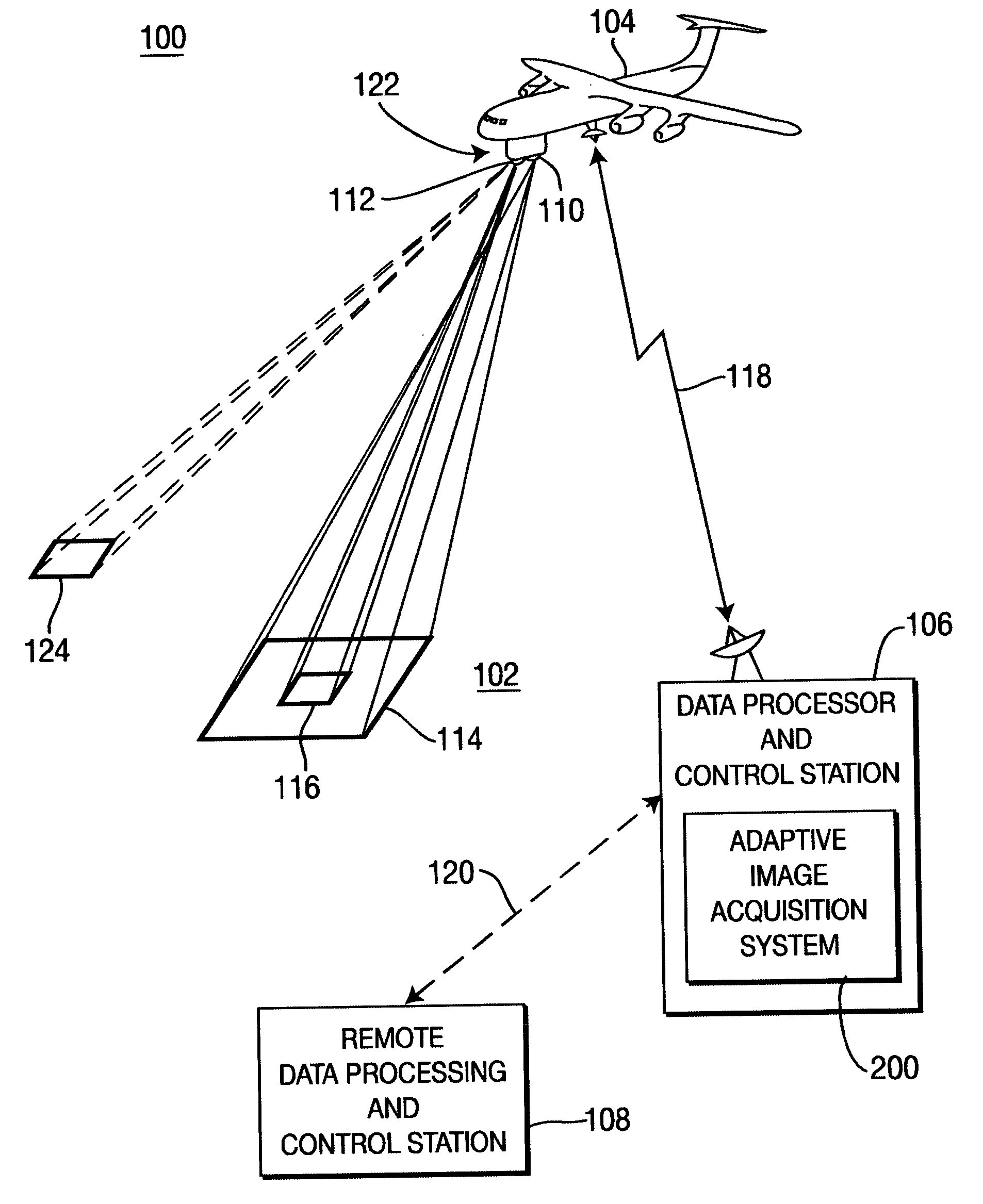
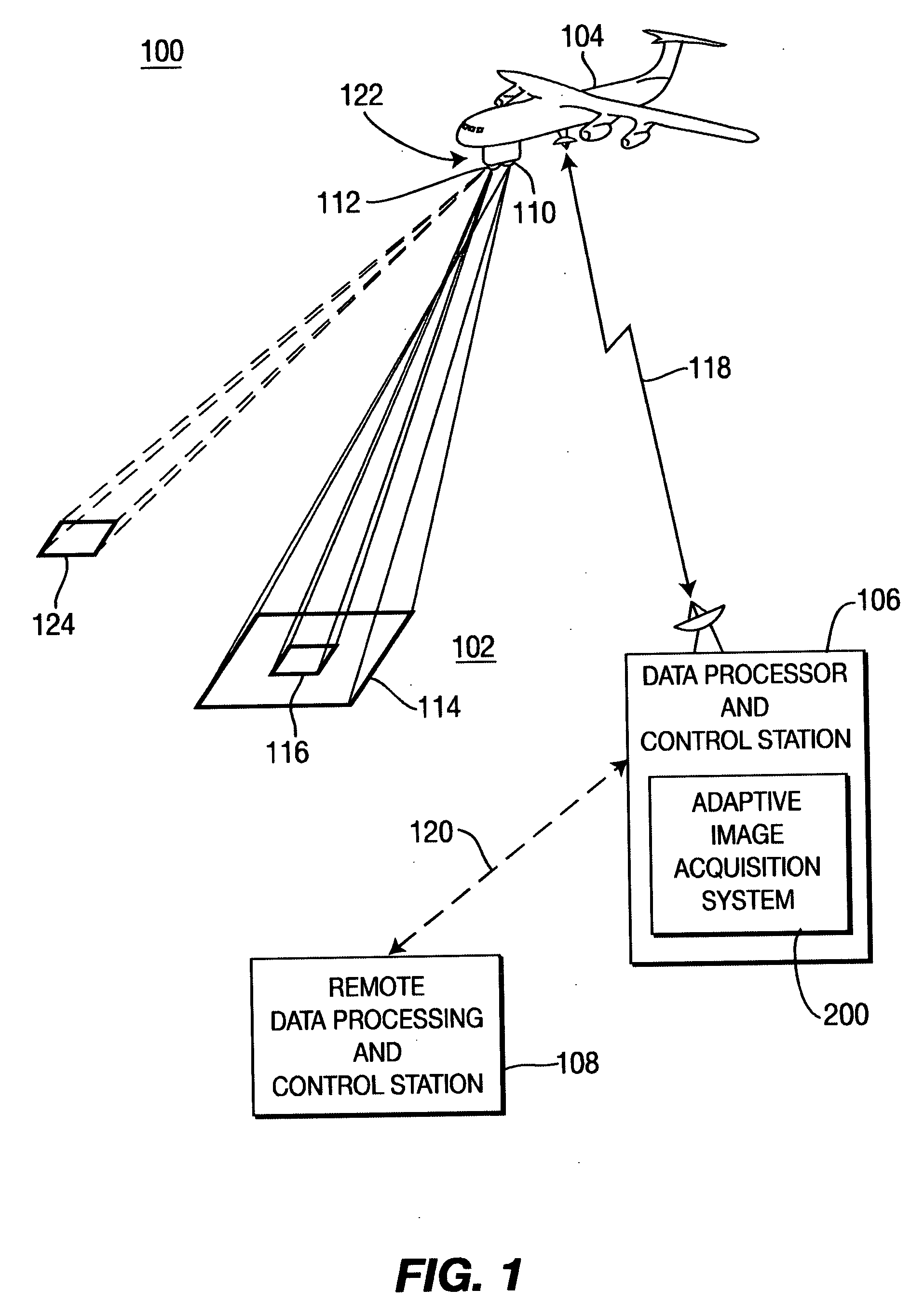
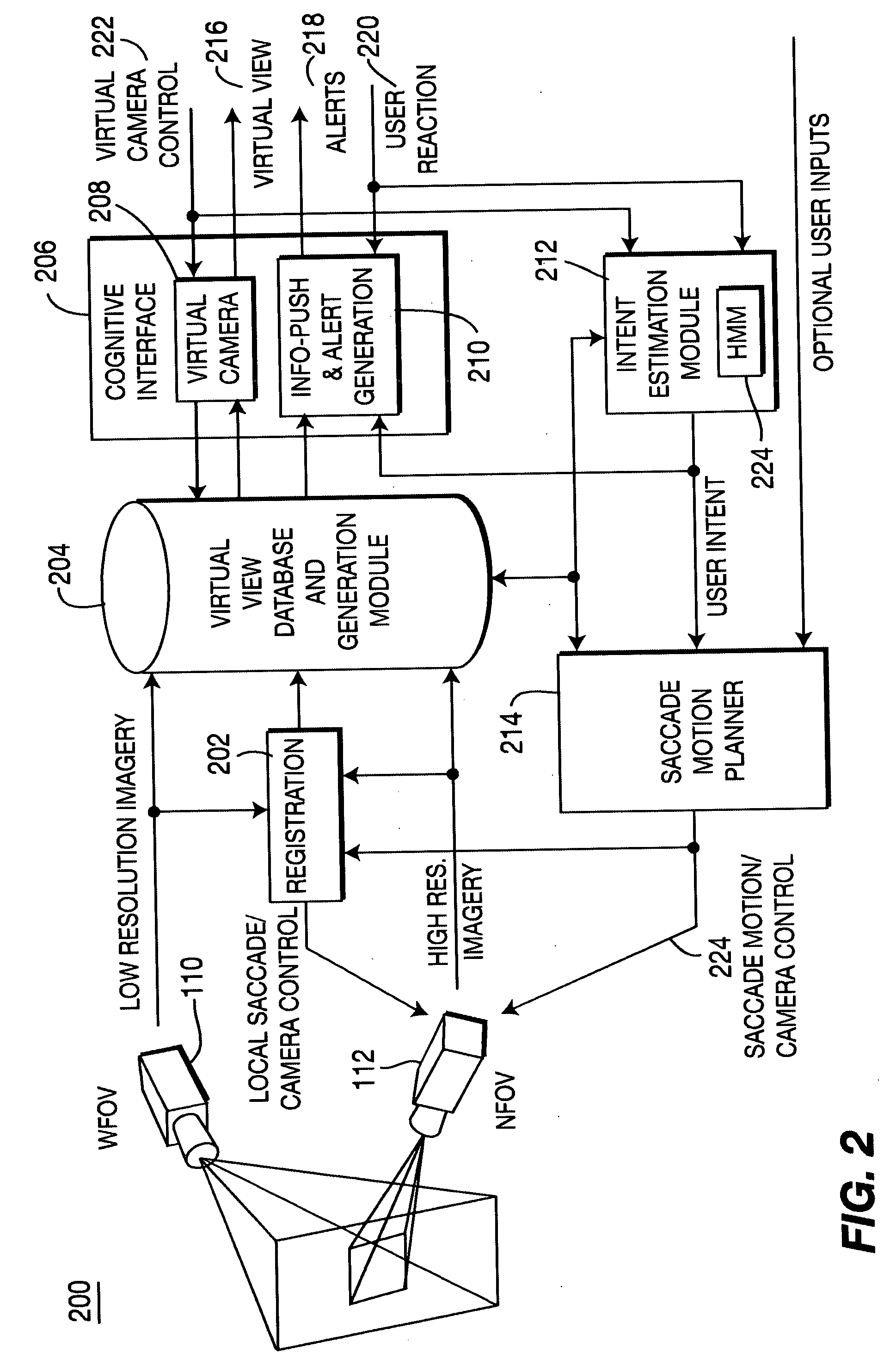
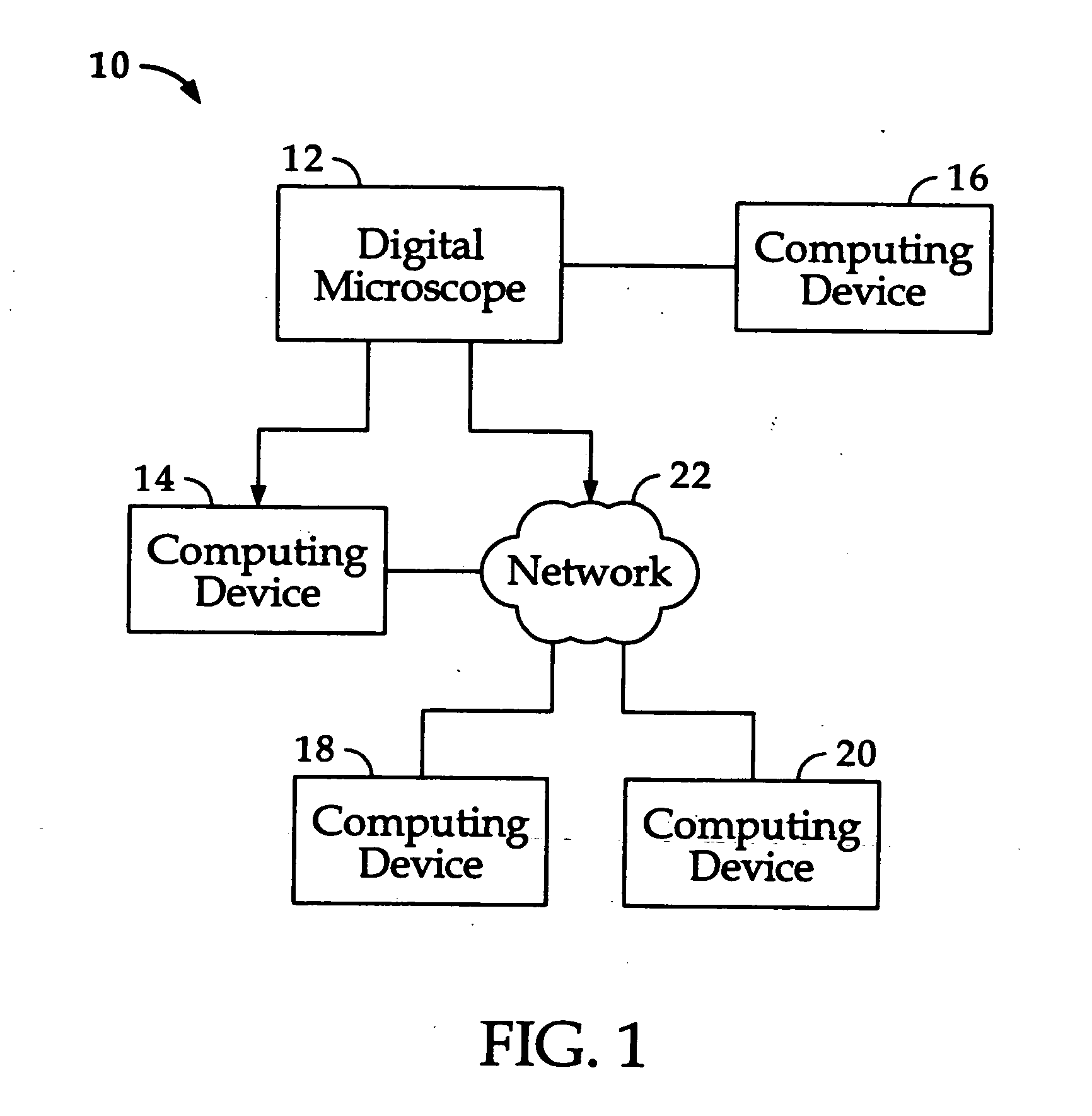
Method and system for performing adaptive image acquisition
ActiveUS20060077255A1High resolution imagingLow resolution imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionSaccade
An adaptive image acquisition system and method that generates virtual view of a surveillance scene to a user (operator), in which, the user operates the system. Through viewing the virtual view, the user controls sensors that create the virtual view. The sensors comprise at least one first sensor having a higher resolution than at least one second sensor. Images from the second sensor are processed to create an image mosaic that is overlaid with images from the higher resolution first sensor. In one embodiment of the invention, the first sensor is moved using Saccade motion. In another embodiment of the invention, a user's intent is used to control the Saccade motion.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method and apparatus for increasing field of view in cone-beam computerized tomography acquisition
ActiveUS9795354B2Cost of component being equalIncrease in sizeReconstruction from projectionRadiation diagnostic device controlTomographyField of view
A method and apparatus for Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography, (CBCT) is configured to increase the maximum Field-Of-View (FOV) through a composite scanning protocol and includes acquisition and reconstruction of multiple volumes related to partially overlapping different anatomic areas, and the subsequent stitching of those volumes, thereby obtaining, as a final result, a single final volume having dimensions larger than those otherwise provided by the geometry of the acquisition system.
Owner:CEFLA SOC COOP
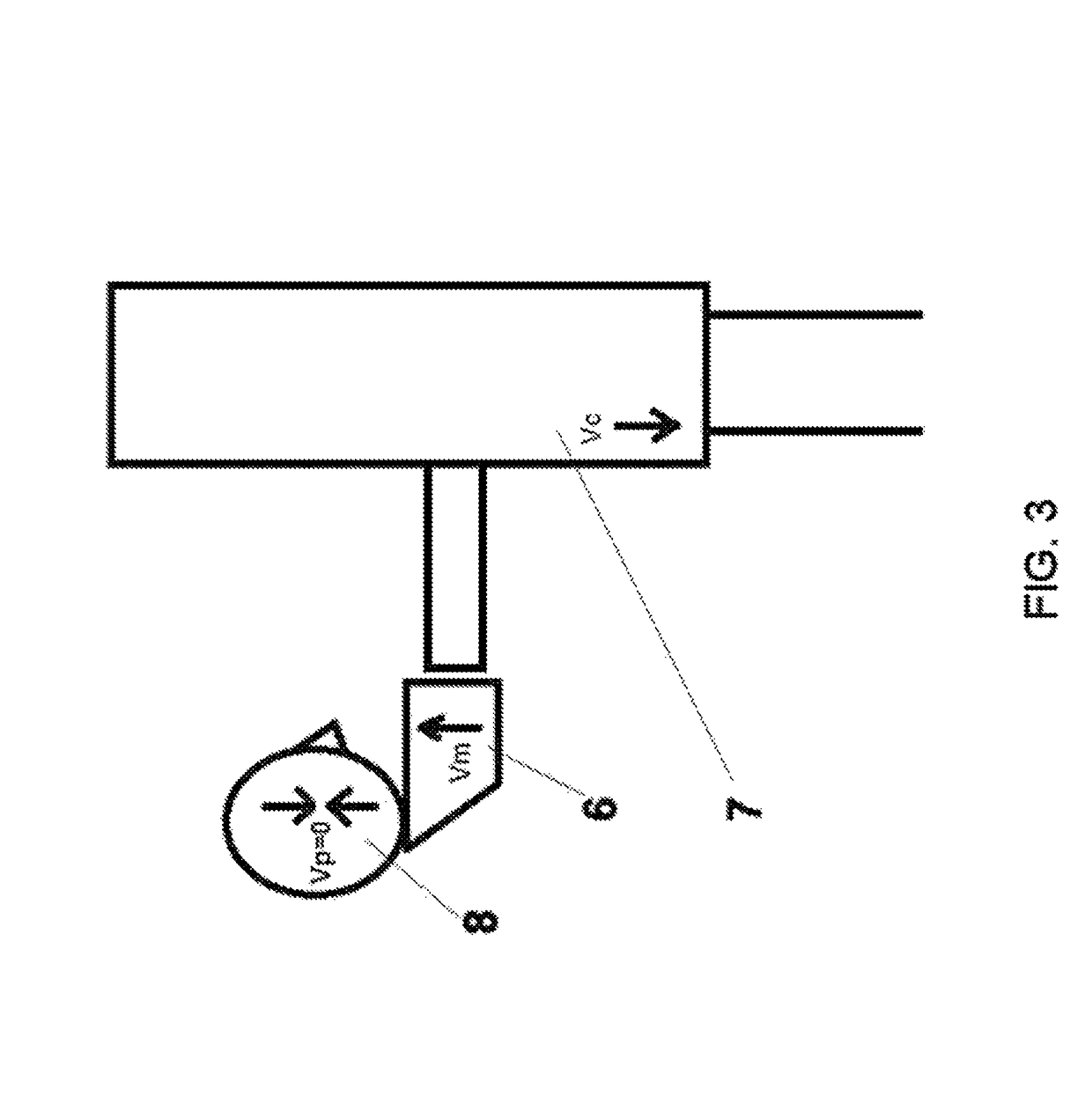
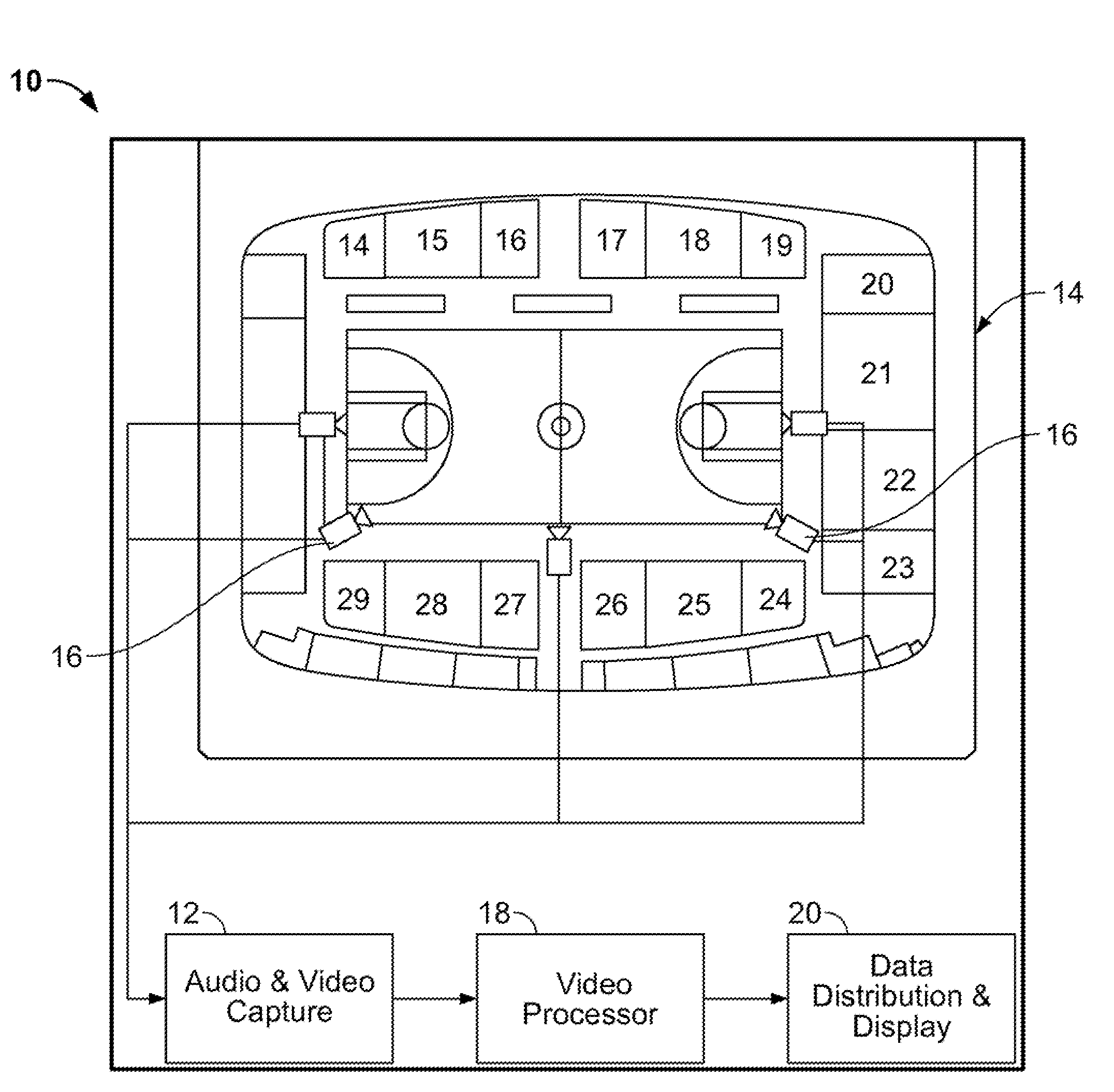
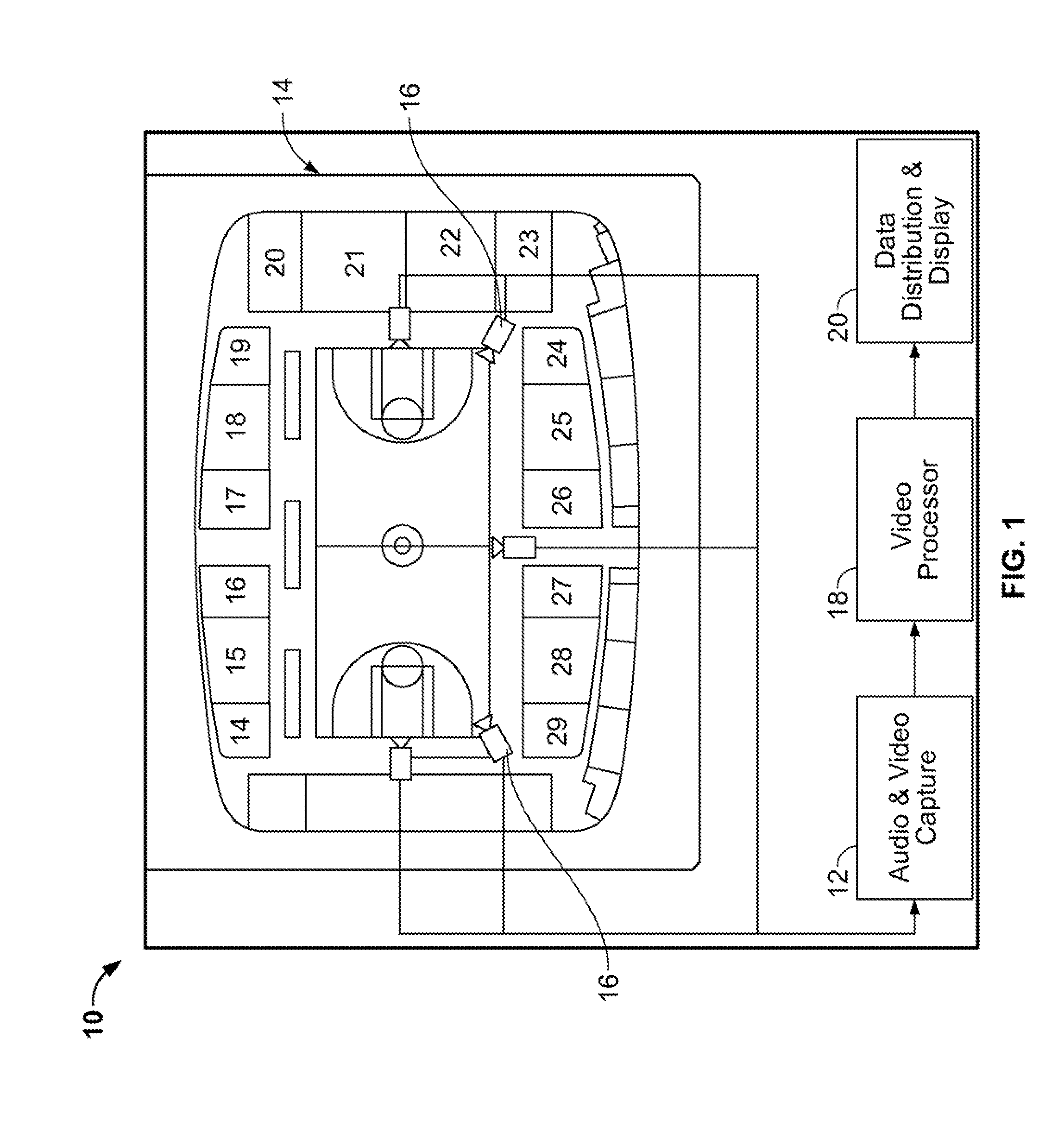
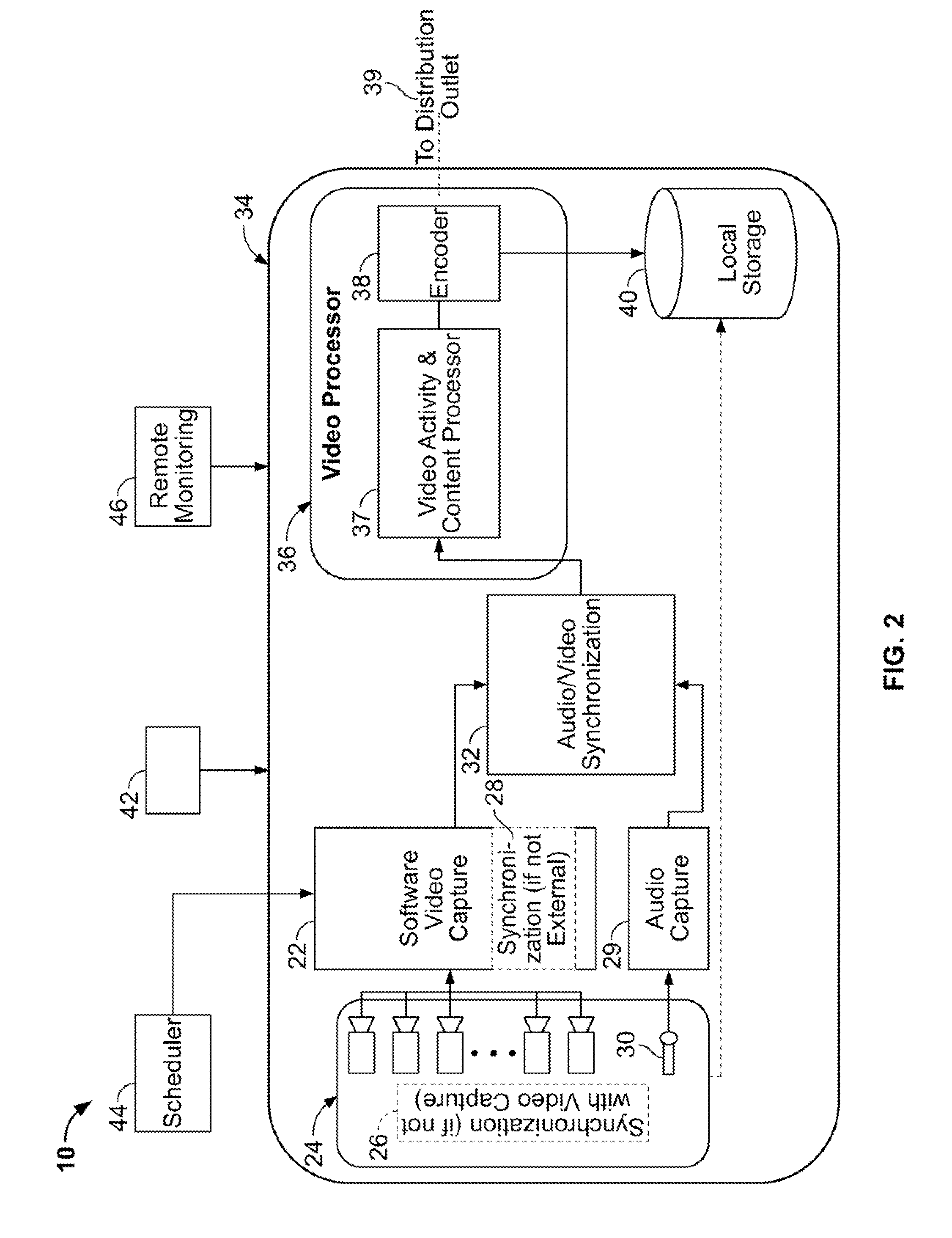
Apparatus for intelligent and autonomous video content generation and streaming
ActiveUS20090284601A1Remove distortionRemove parallaxImage enhancementTelevision system detailsRegion selectionViewpoints
A system for automatically capturing an event of interest in a venue is disclosed, comprising a plurality of cameras for capturing video images of the event; and at least one processor communicatively connected to said plurality of cameras and con figured to execute a plurality of modules, said modules comprising a rectification module for combining the video images to form a wide-angle view; at least one of a motion analysis module configured for tracking salient blobs that are not part of a background of the wide-angle view, an activity analysis module configured for extracting temporal and spatial patterns from the wide-angle view, and a shape and appearance module configured for selecting one or more objects in the wide-angle view based on descriptors that are scale and rotational invariant; and a region of interest selector for selecting a viewpoint from the wide-angle view based on output from at least one of the motion analysis module, the activity analysis module, and the shape and appearance module, wherein the region of interest selector outputs the selected viewpoint for display. The system further comprises at least one audio recording device for capturing audio from the event; and means for synchronizing the video images and audio.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
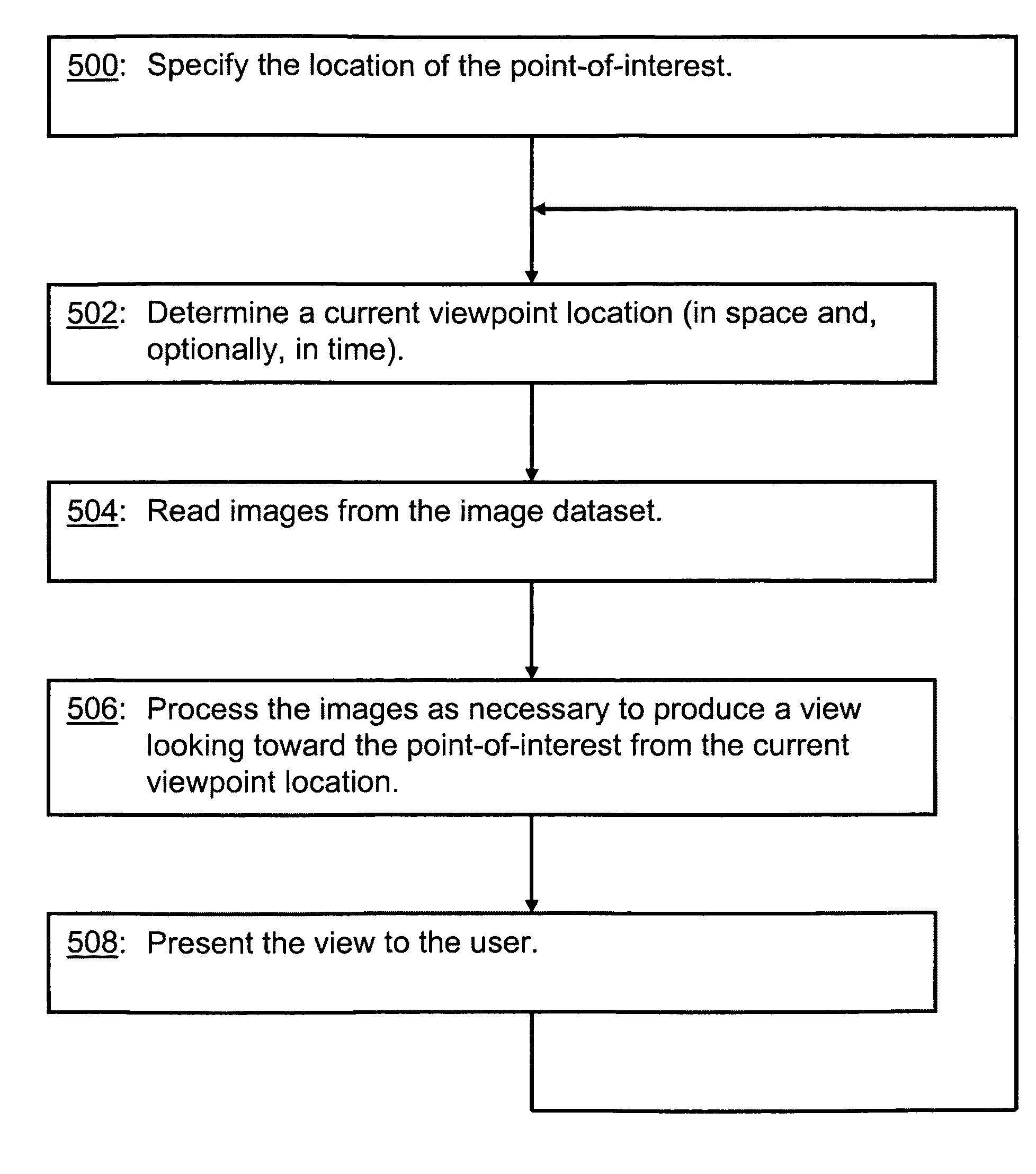
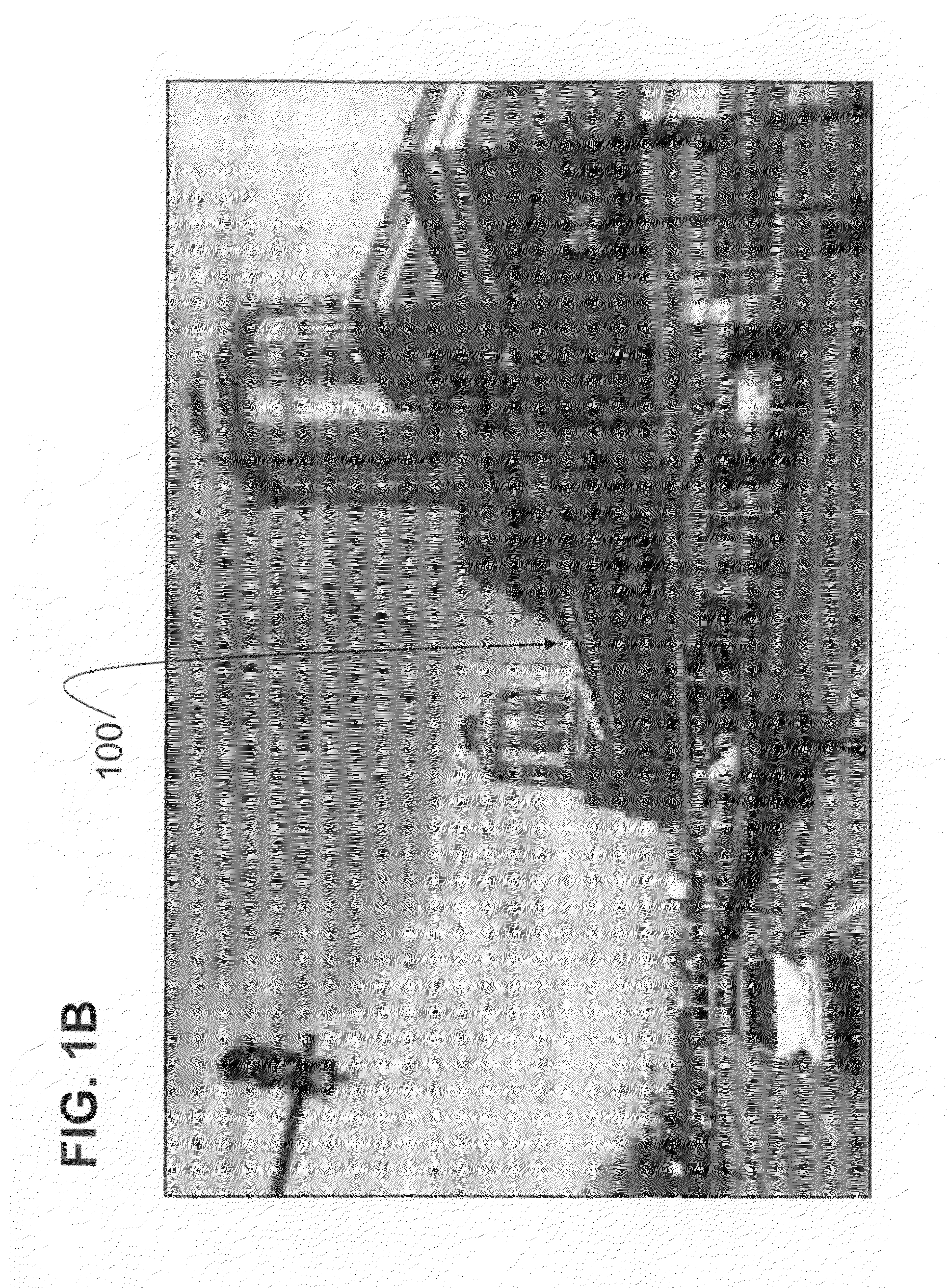
System and method for producing multi-angle views of an object-of-interest from images in an image dataset
ActiveUS20090153549A1Road vehicles traffic controlGeometric image transformationComputer animationData set
Disclosed are a system and method for creating multi-angle views of an object-of-interest from images stored in a dataset. A user specifies the location of an object-of-interest. As the user virtually navigates through the locality represented by the image dataset, his current virtual position is determined. Using the user's virtual position and the location of the object-of-interest, images in the image dataset are selected and interpolated or stitched together, if necessary, to present to the user a view from his current virtual position looking toward the object-of-interest. The object-of-interest remains in the view no matter where the user virtually travels. From the same image dataset, another user can select a different object-of-interest and virtually navigate in a similar manner, with his own object-of-interest always in view. The object-of-interest also can be “virtual,” added by computer-animation techniques to the image dataset. For some image datasets, the user can virtually navigate through time as well as through space.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Real-time infrared thermography inspection and control for automated composite material layup
ActiveUS20060191622A1Slight variationImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryComputer visionDigital image data
A real-time thermal imaging apparatus and method includes multiple digital infrared cameras mounted to an automated composite material layup device to record digital infrared images of the composite material surface on a real-time basis during a composite material layup process. The digital infrared cameras are triggered periodically to produce digital images of the composite material. The digital image data is sent to an image analyzer which detects edges of and anomalies in the composite material and generates alarm and other process control signals. The image analyzer also aggregates the digital images from the multiple cameras and the digital images recorded over a sequence in time to produce a continuous virtual digital image of the composite material surface. The digital image data and associated analysis results are saved and may be displayed on a real-time basis or at a later time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and Apparatus for Combining Panoramic Image
ActiveUS20130208997A1High resolutionSmall sizeImage analysisGeometric image transformationFold changePanorama
The disclosure discloses a method and an apparatus for combining panoramic image. The method includes: obtaining multiple original images of the same scene, performing folding change and coordinates transformation to the multiple original images, and determining an overlapping area of the multiple original images; establishing a mathematical model of the multiple original images, aligning the overlapping area of the multiple original images, and transforming the multiple original images to a coordinate system of a reference image; obtaining the space transformation relationship among / between the multiple original images according to the coordinate system of the reference image, selecting an appropriate image combining strategy, and completing the combining of the images. The solution can realize obtaining scene picture with large field of view without reducing image resolution.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for determining camera position from two-dimensional images that form a panorama
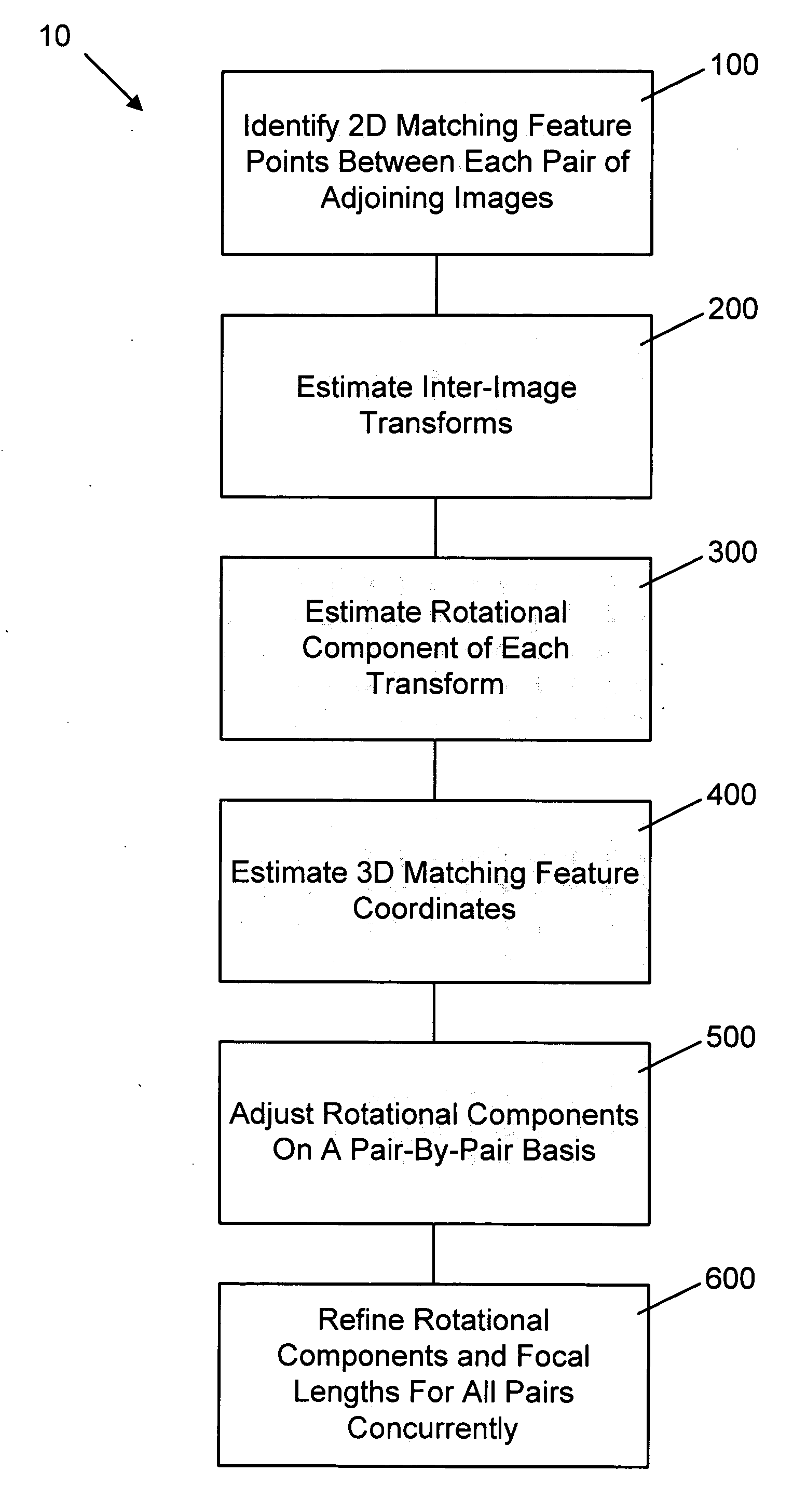
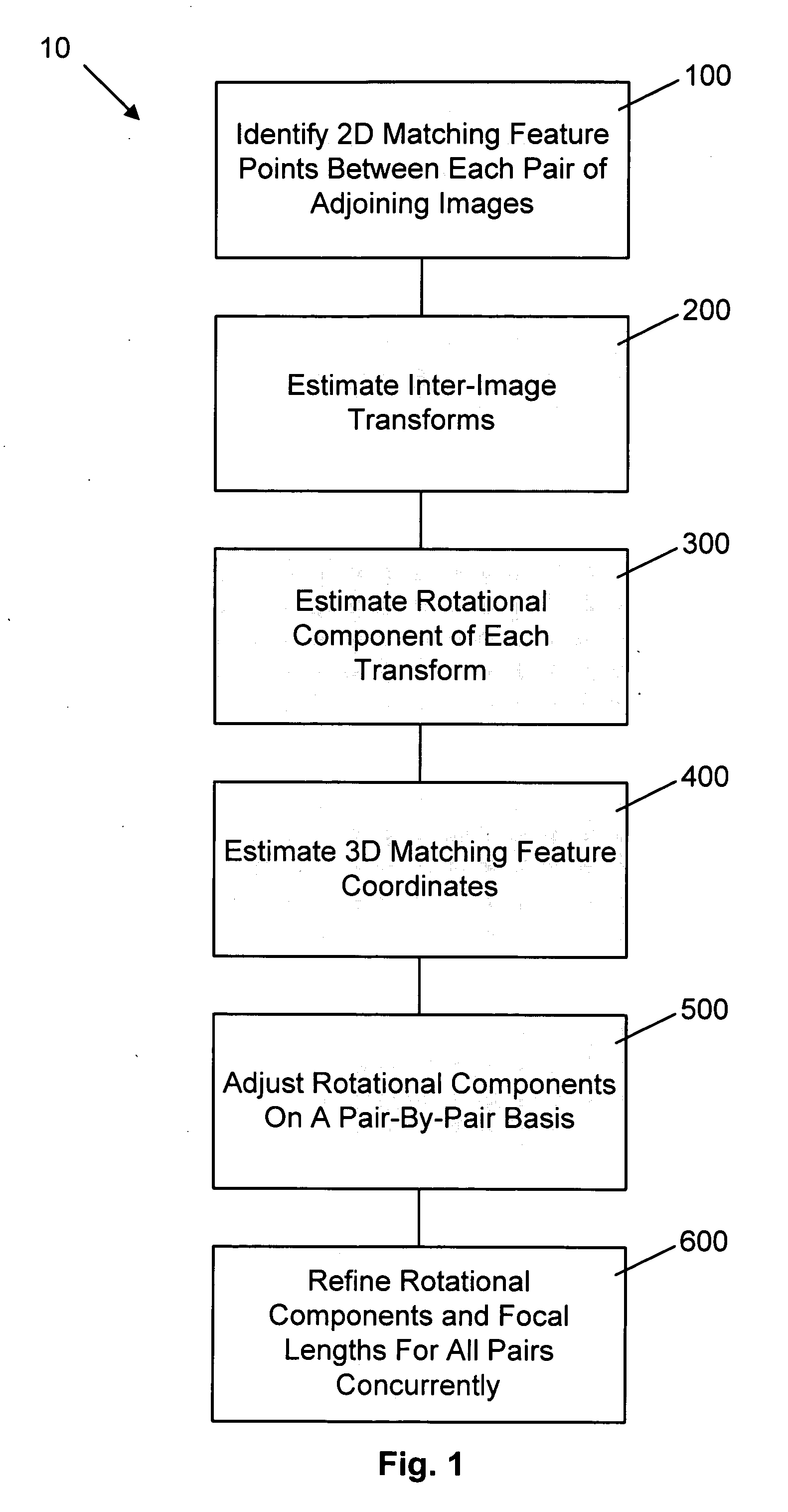
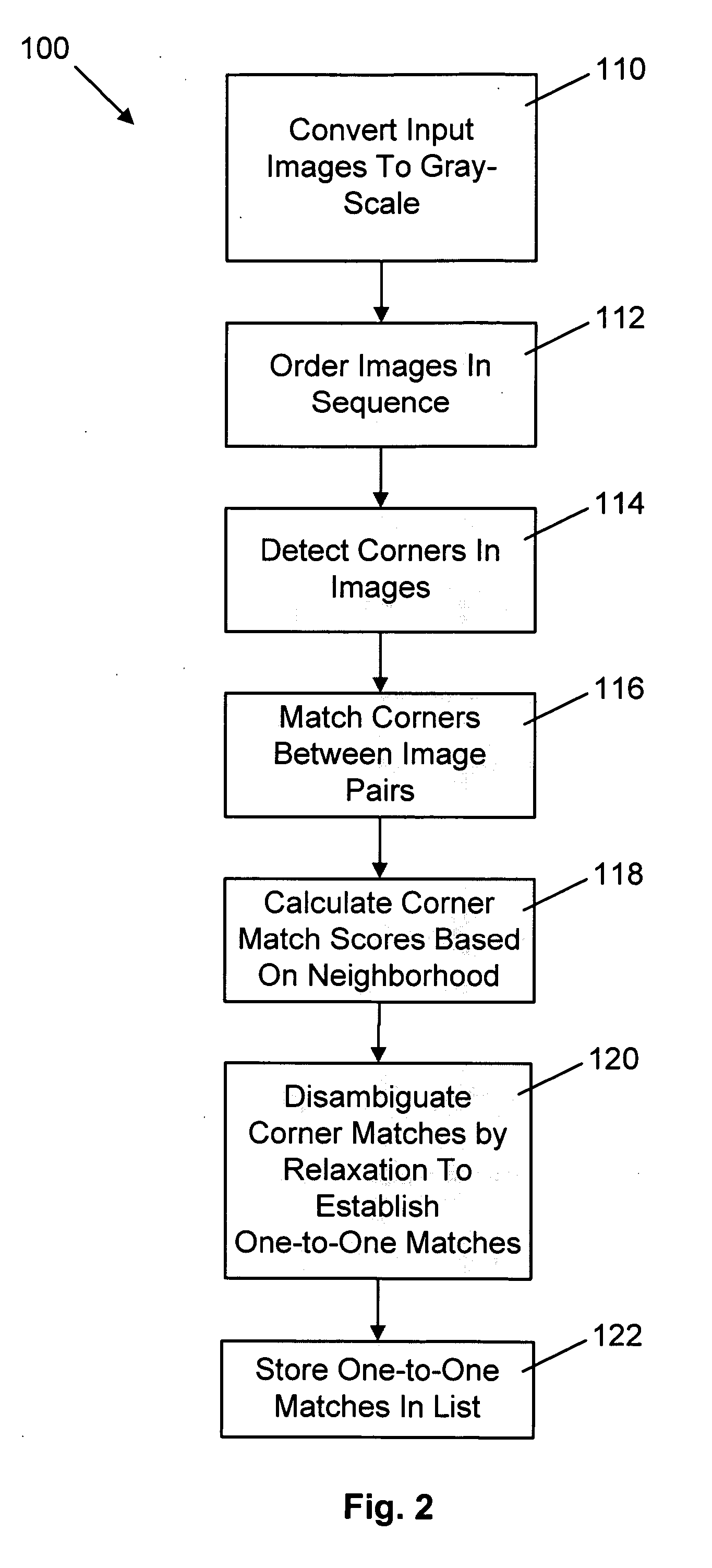
InactiveUS20070008312A1Save additional processing resourceShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisThree-dimensional spaceGlobal optimization
A method of estimating three-dimensional camera position information from a series of two-dimensional images that form a panorama employs common features in adjoining image pairs in the series to estimate a transform between the images in the pairs. The common features are subsequently employed to adjust an estimated rotational component of each transform by reducing error between coordinates corresponding to the common features in three-dimensional space in image pairs, on a pair-by-pair basis. A global optimization of the position estimation, used for long sequences of images such as 360 degree panoramas, refines the estimates of the rotational and focal length components of the transforms by concurrently reducing error between all 3D common feature coordinates for all adjoining pairs.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Apparatus and method for generating an overview image of a plurality of images using a reference plane
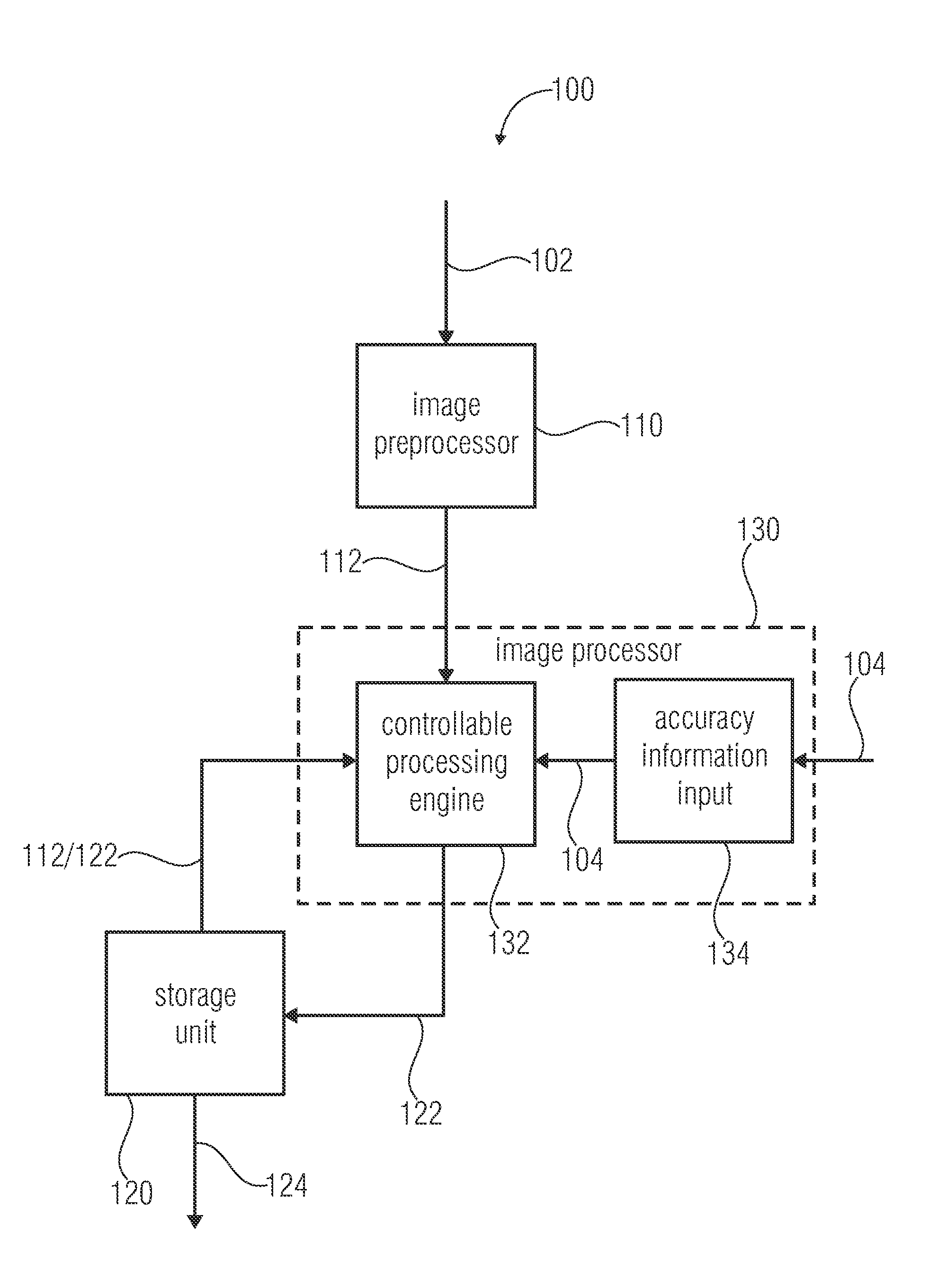
InactiveUS20120050525A1Quick buildImprove smoothnessImage enhancementImage analysisImage processorImage based
An apparatus for generating an overview image of a plurality of images comprises a storage unit and an image processor. The storage unit stores a plurality of processed images of the overview image and is able to provide the overview image containing the plurality of processed images at their assigned positions for displaying. The image processor determines feature points of a new image and compares the determined feature points of the new image with feature points of a stored processed image to identify common feature points and to obtain 3-dimensional positions of the common feature points. Further, the image processor determines common feature points located within a predefined maximum distance of relevance to a reference plane based on the 3-dimensional positions of the common feature points to identify relevant common feature points. Further, the image processor processes the new image by assigning the new image to a position in the overview image based on a comparison of an image information of each relevant common feature point of the new image with an image information of each corresponding relevant common feature point of the stored processed image without considering common feature points located beyond the predefined maximum distance of relevance to the reference plane.
Owner:LAKESIDE LAB
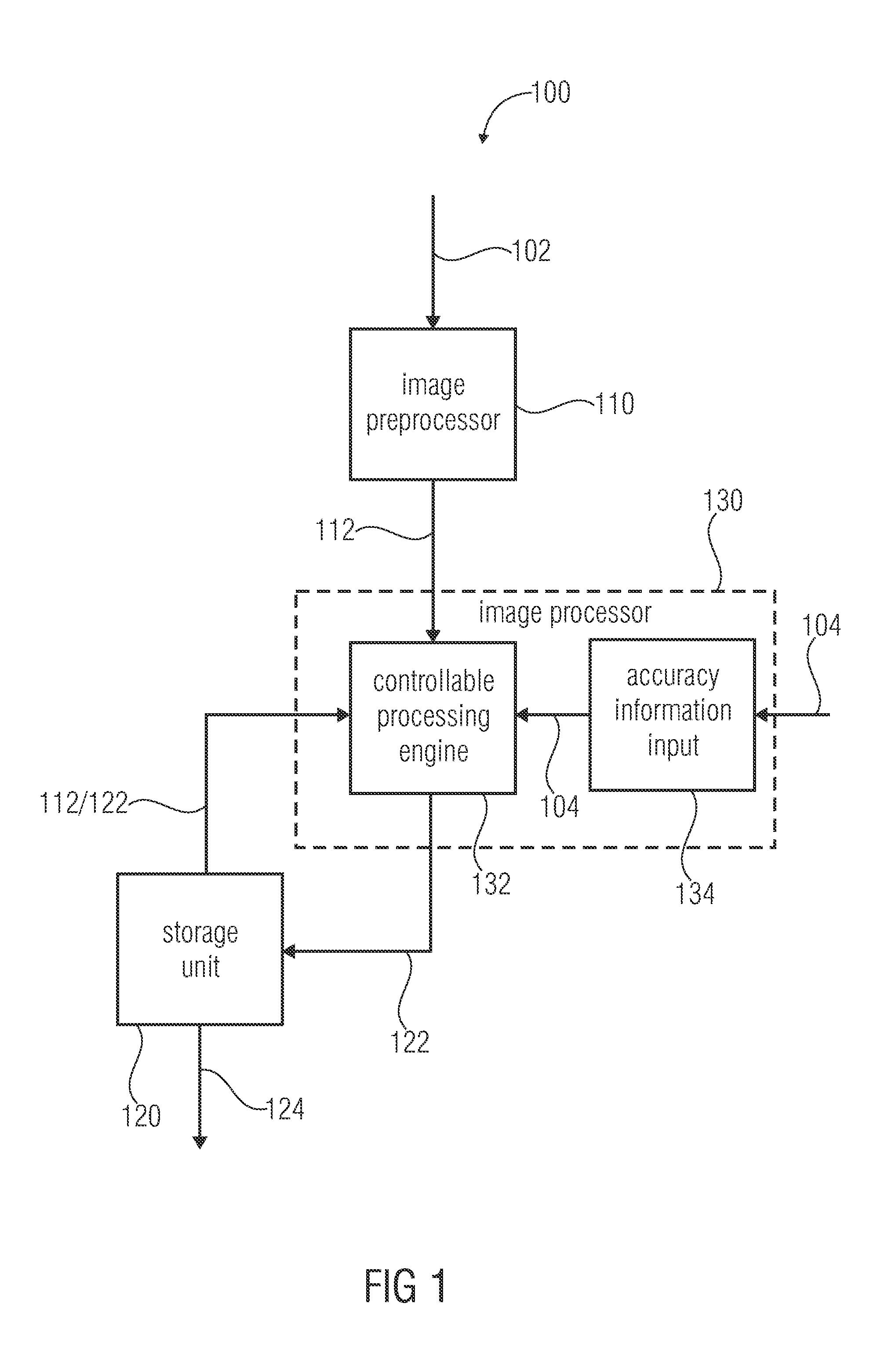
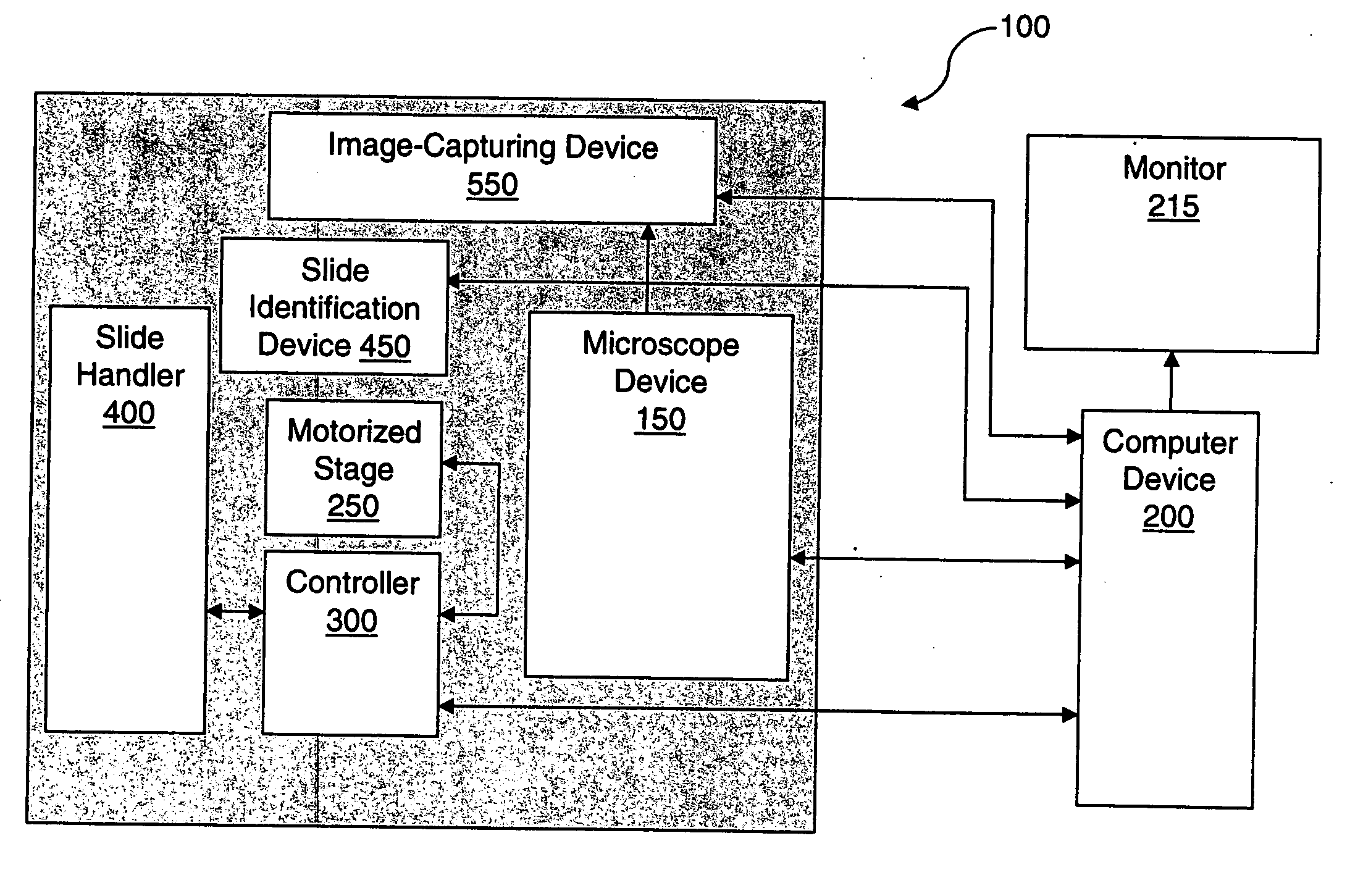
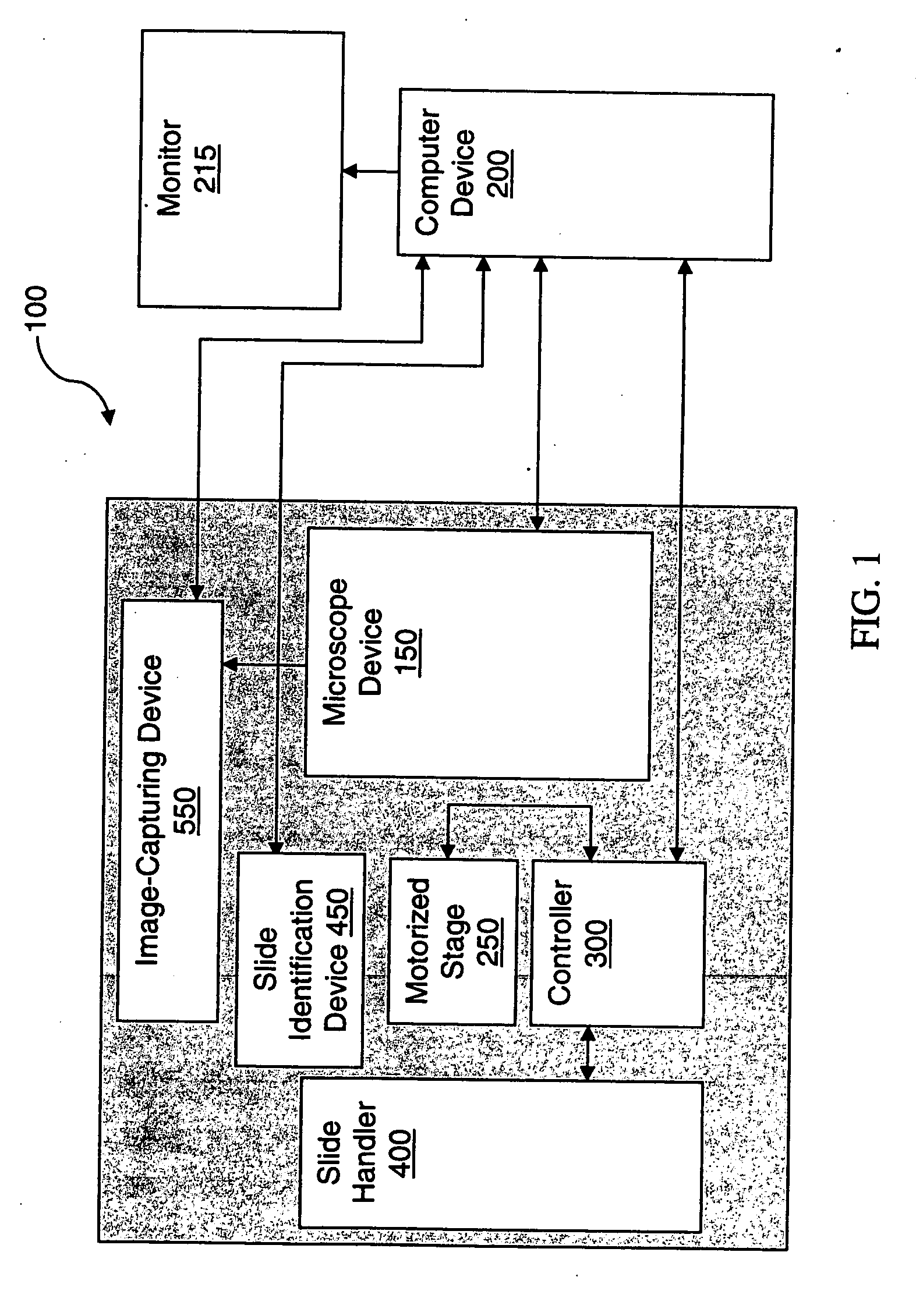
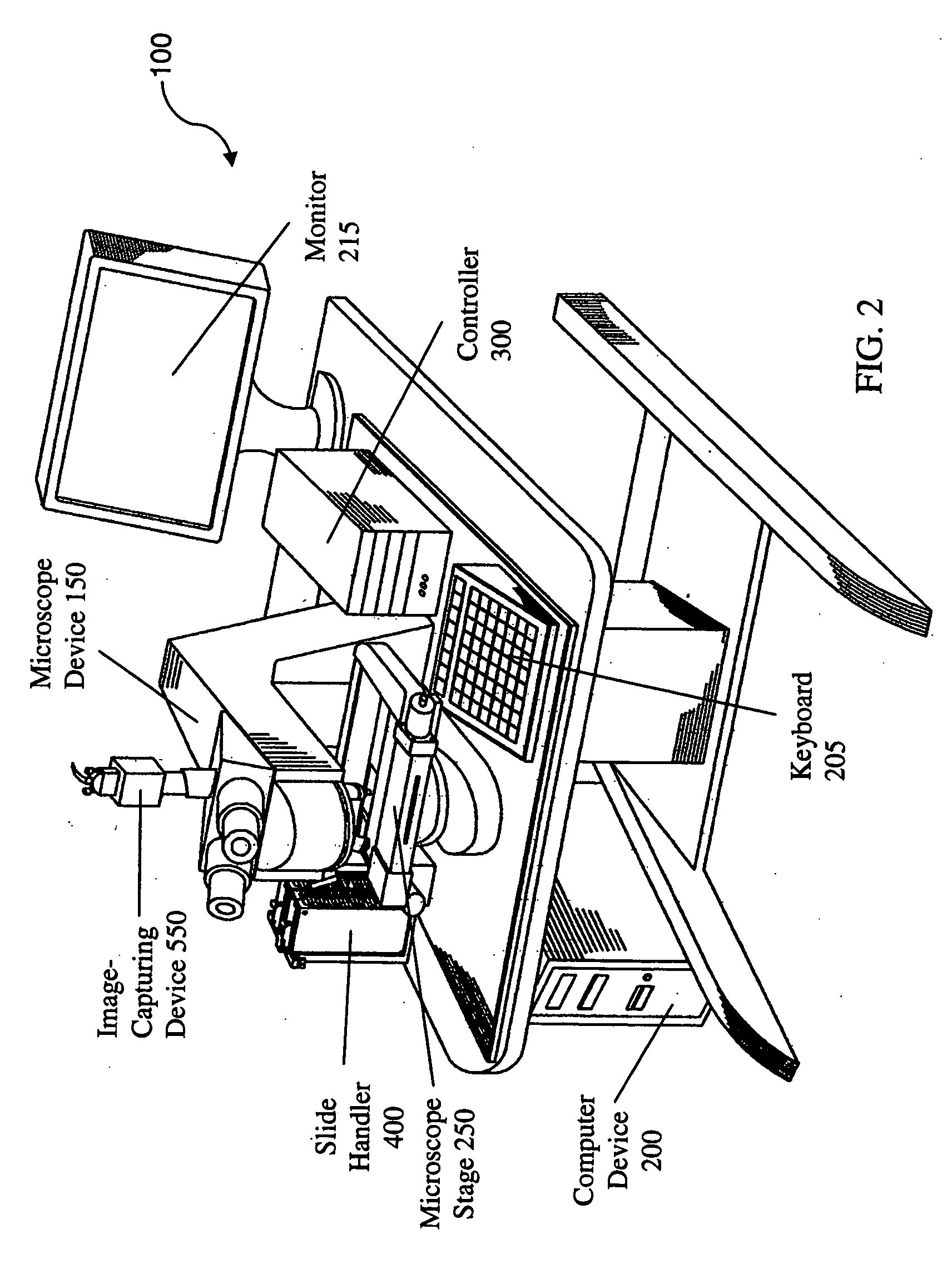
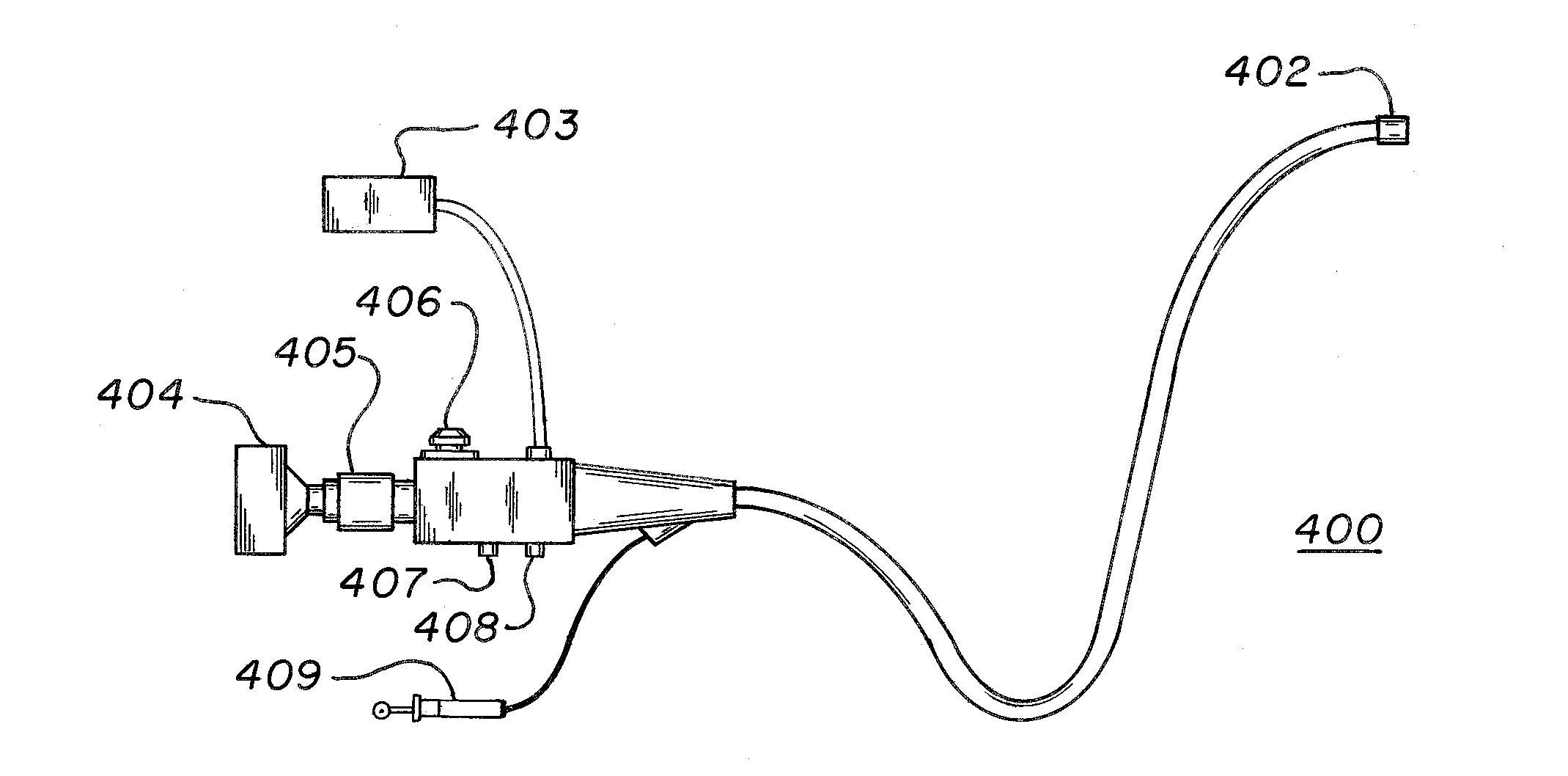
Systems and methods for stitching image blocks to create seamless magnified images of a microscope slide
Scanned image portions of a virtual slide are stored in accord with a positional index metric associated to each image's location in a mosaic representation of the entire physical slide and a normalized correlation search is performed on next neighbor regional image blocks. A set of relative positional offset values and a correlation coefficient is determined for a regional image block and a next neighbor regional image block. A portion of the regional image blocks is viewed as a field of view of a display and a composite of the portion of regional image blocks is stitched together in accord with the set of relative positional offset values and the correlation coefficient, such that only the blocks comprising the portion are stitched. Moving the field of view of the display causes additional regional image blocks to be displayed, where image stitching is subsequently performed only with respect to the additional regional image blocks brought into the new field of view.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROIMAGING AIS +1
Alternate Viewpoint Image Enhancement
ActiveUS20140002439A1High resolutionImprove viewing effectGeometric image transformation2D-image generationViewpointsImage resolution
In one embodiment, panoramic images, images bubbles, or any two-dimensional views of three-dimensional subject matter are enhanced with one or more alternate viewpoints. A controller receives data indicative of a point on the two-dimensional perspective and accesses a three-dimensional location based on the point. The controller selects an image bubble based on the three-dimensional location. The three-dimensional location may be determined according to a depth map corresponding to the point. A portion of the image bubble is extracted and incorporated into the two-dimensional perspective. The resulting image may be a seamless enhanced resolution image or include a picture-in-picture enhanced resolution window including subject matter surrounding the selected point.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
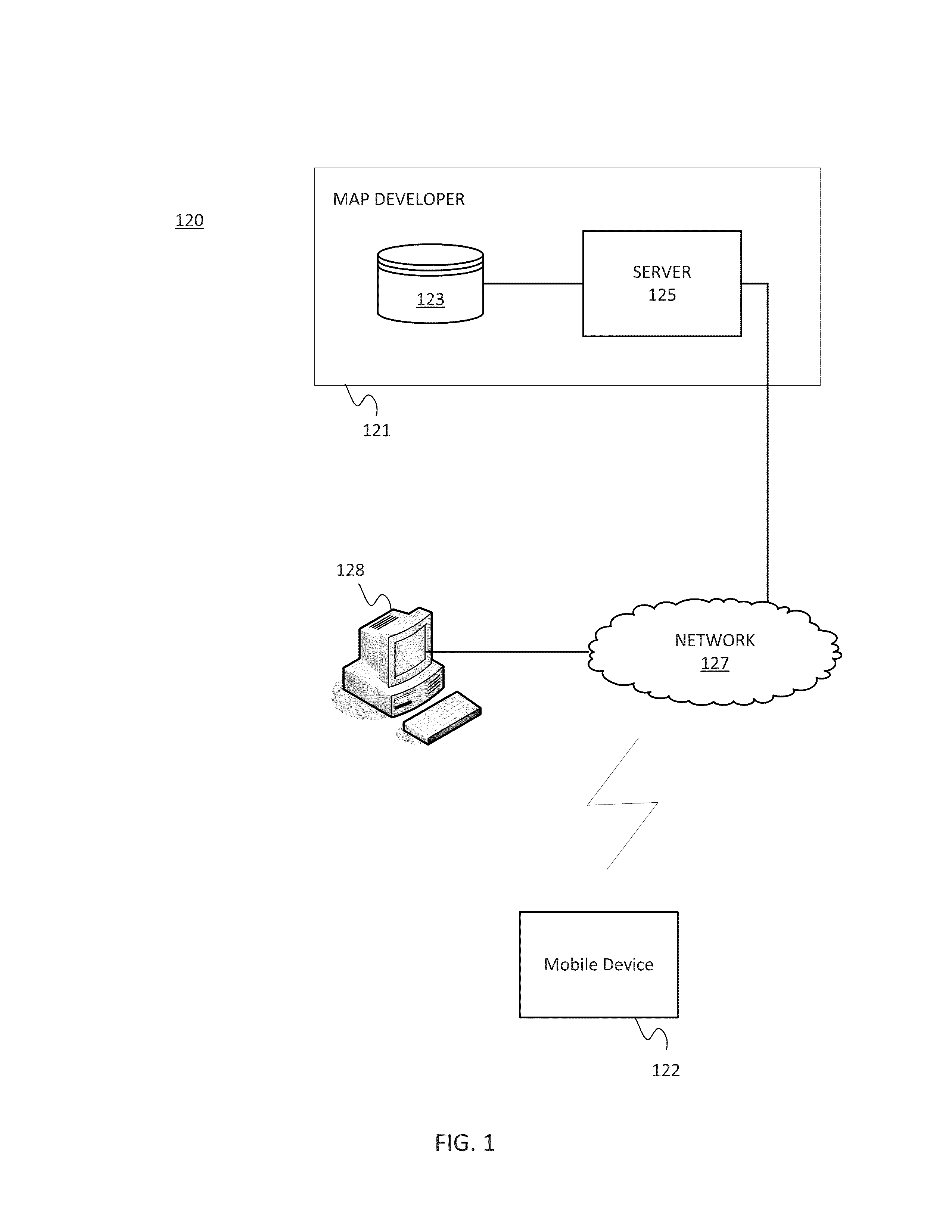
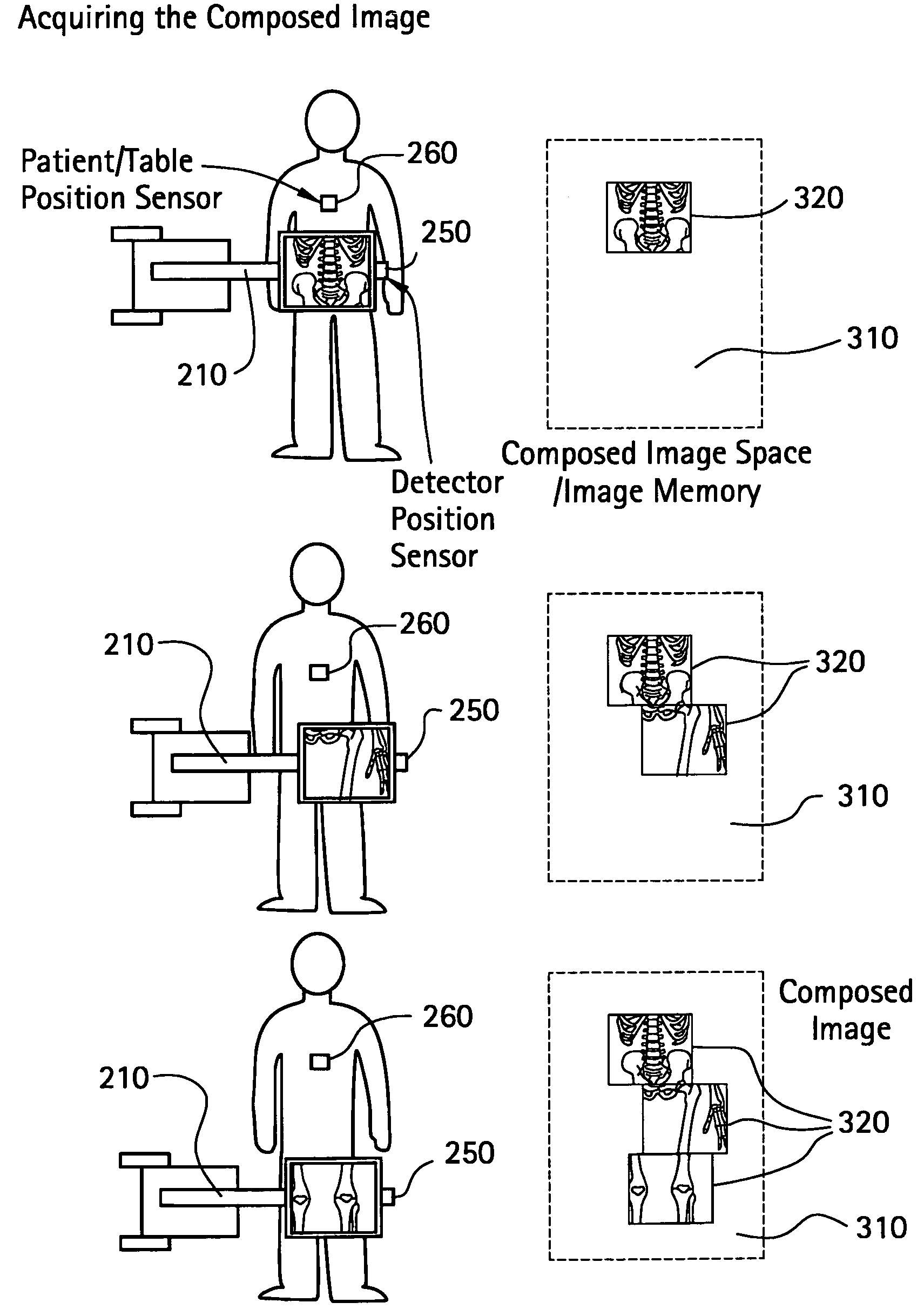
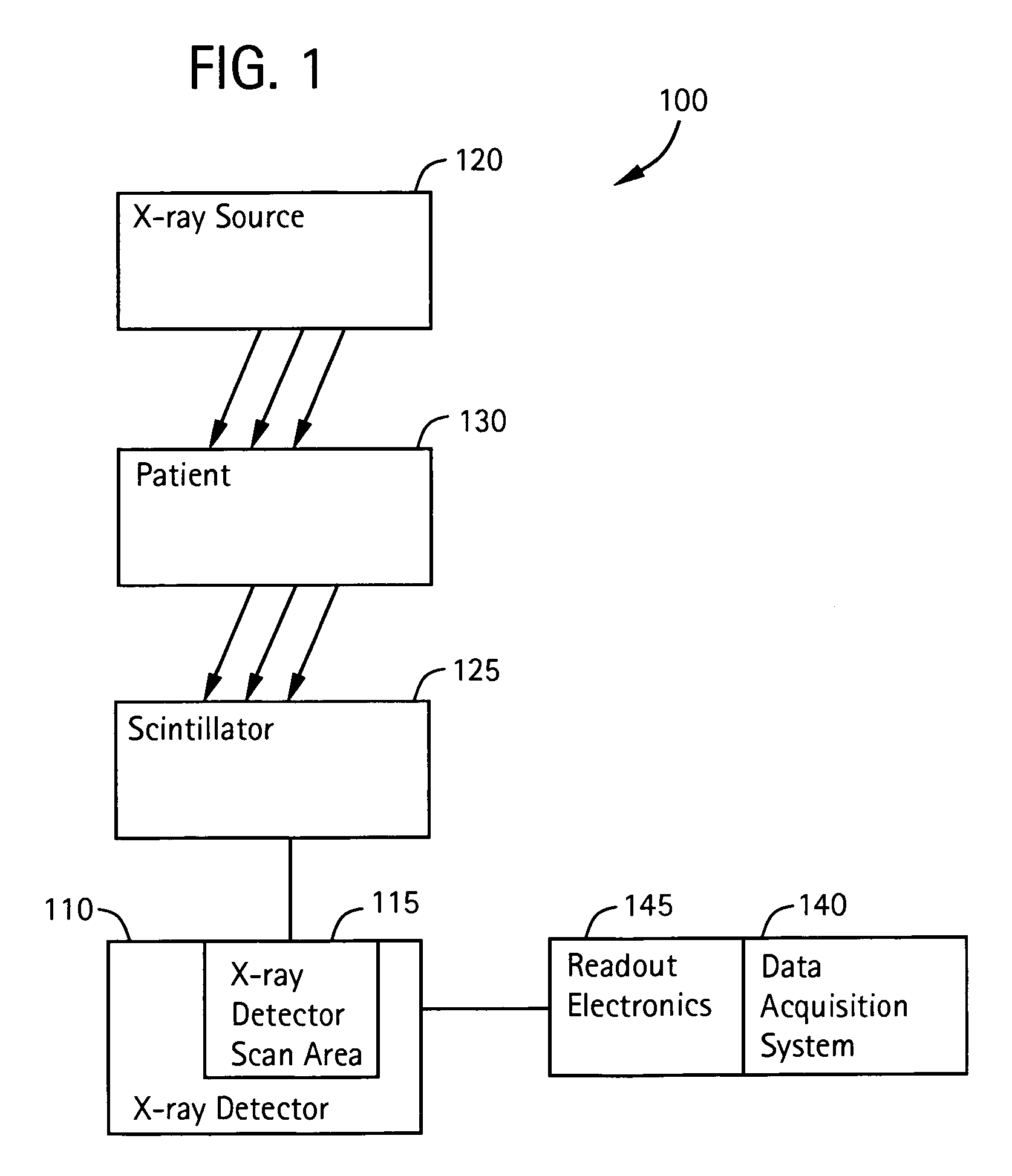
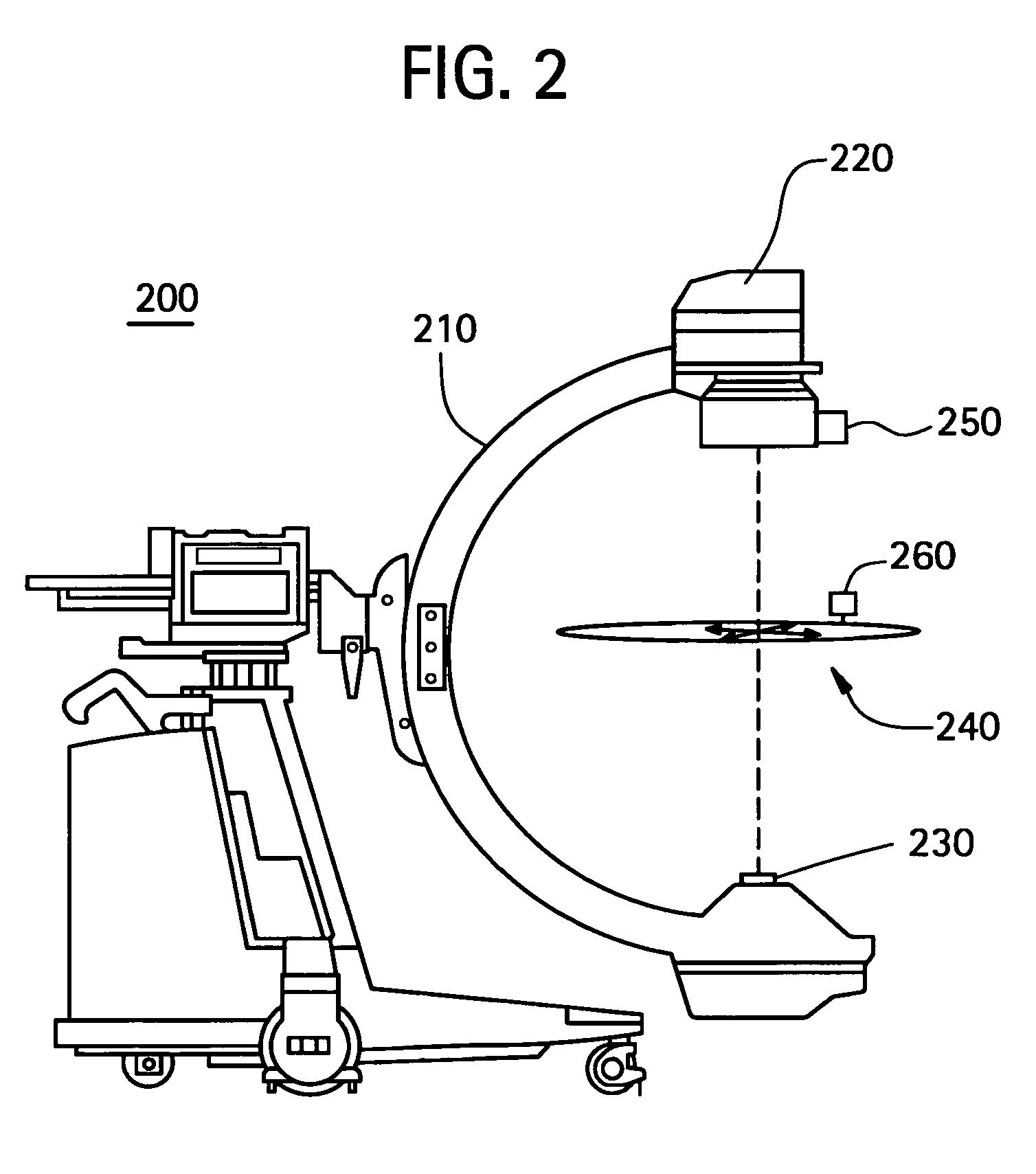
System and method for image composition using position sensors
InactiveUS7522701B2Facilitates digital subtraction angiographyImage enhancementImage analysisMemory mapPosition sensor
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for image composition. Certain embodiments include acquiring a first image of an object using an imager, obtaining first positional information for the imager with respect to the object, acquiring a second image of the object using the imager, obtaining second positional information for the imager with respect to the object, and creating a composed image using the first and second images. A spatial relationship between the images is maintained using the positional information. A composed image may be created by constructing a memory map of image data related to the object and inserting the images into the memory map based on the positional information, for example. A composed image may be created by combining the images based on the positional information, for example.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
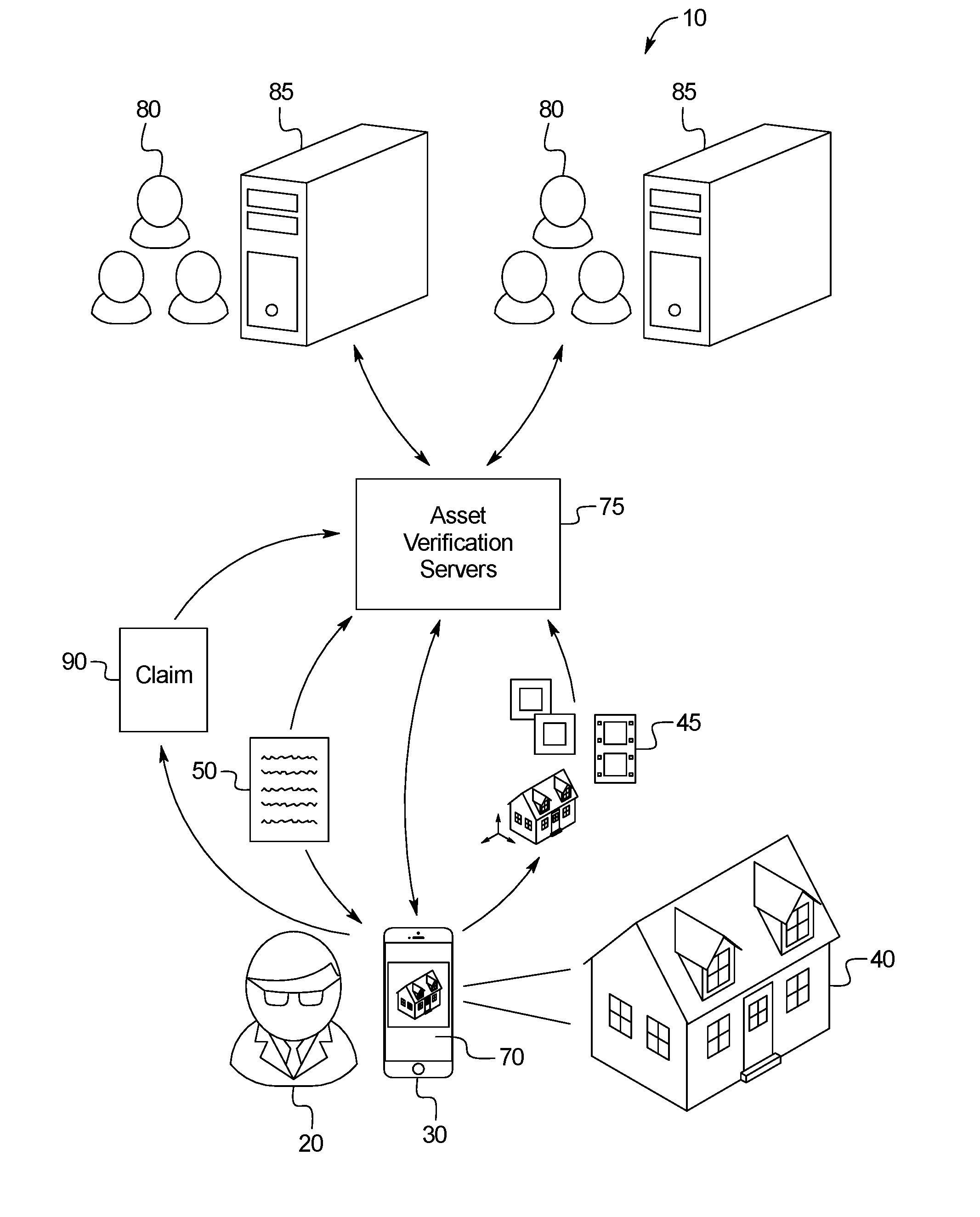
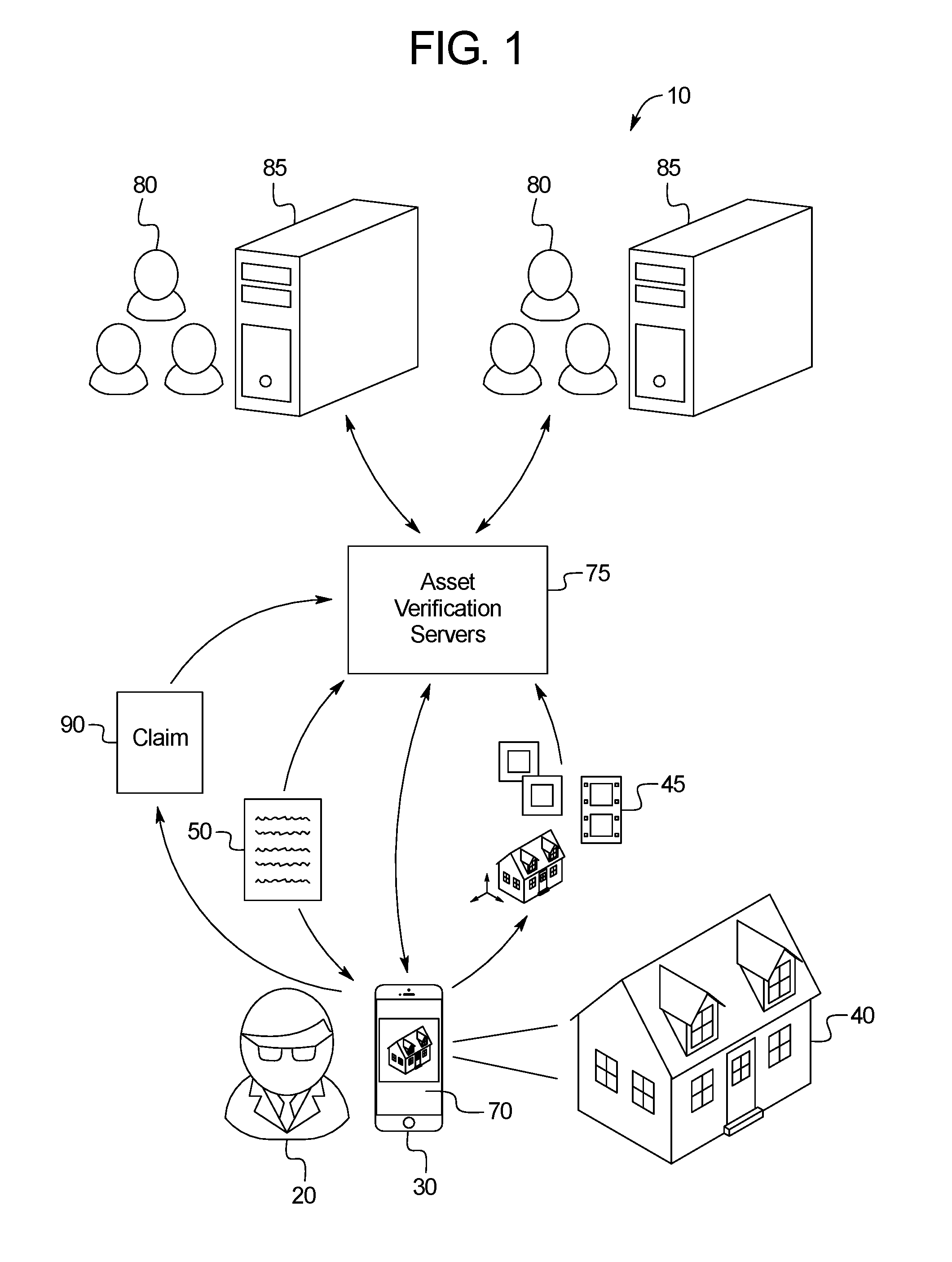
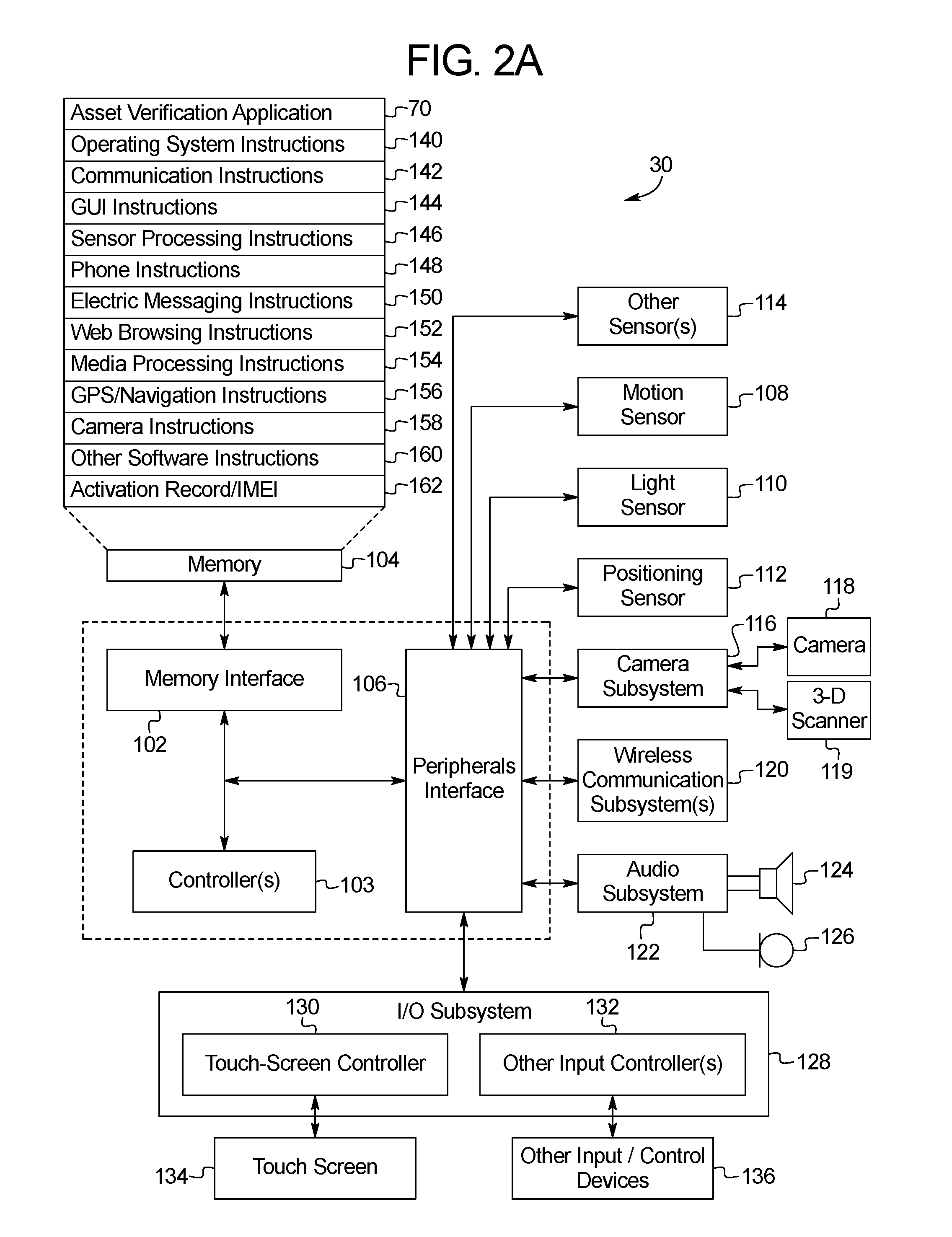
Insurance Asset Verification and Claims Processing System
PendingUS20160171622A1Precise processReasonable priceTelevision system detailsFinanceHandling systemVisual perception
A user interface system for providing insurance including: a media capture unit including a camera; a controller in communication with the media capture unit; and a memory in communication with the controller; wherein the memory includes first asset information previously captured by an asset verification process in which a user captures first visual media information including at least one visual media information including an asset shown from a perspective, wherein the memory additionally including an asset verification software application that, when executed by the controller, causes the controller to: in response to receiving a notification of a loss regarding the asset, prompt the user to capture second asset information using a media prompt including directions for capturing at least one image including a view of the asset from the perspective; and transmit the second asset information to an underwriting server.
Owner:LOSS OF USE
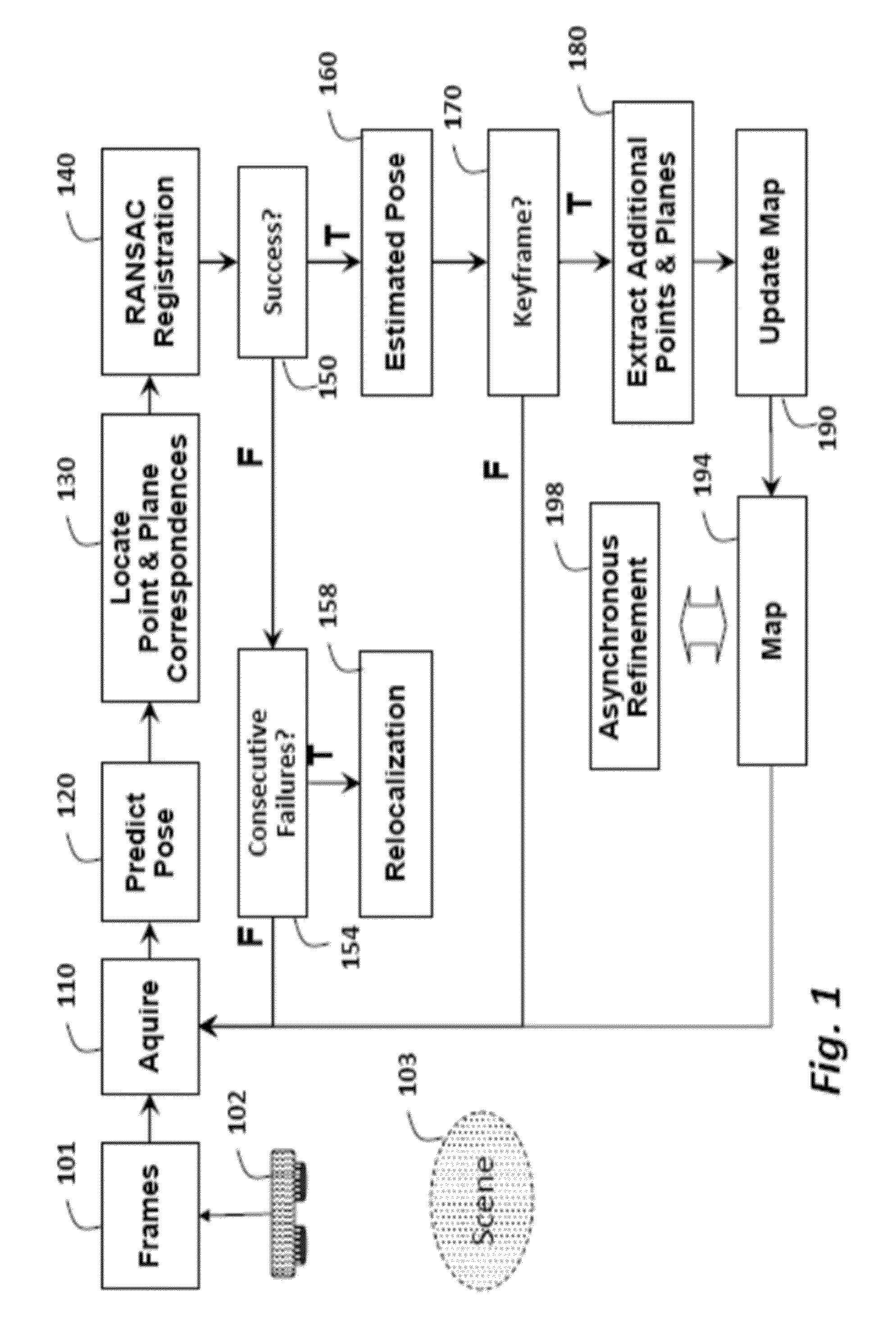
Tracking Poses of 3D Camera Using Points and Planes
ActiveUS20140002597A1Fast and accurate registrationMinimize failureImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraRegister data
A method registers data using a set of primitives including points and planes. First, the method selects a first set of primitives from the data in a first coordinate system, wherein the first set of primitives includes at least three primitives and at least one plane. A transformation is predicted from the first coordinate system to a second coordinate system. The first set of primitives is transformed to the second coordinate system using the transformation. A second set of primitives is determined according to the first set of primitives transformed to the second coordinate system. Then, the second coordinate system is registered with the first coordinate system using the first set of primitives in the first coordinate system and the second set of primitives in the second coordinate system. The registration can he used to track a pose of a camera acquiring the data.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
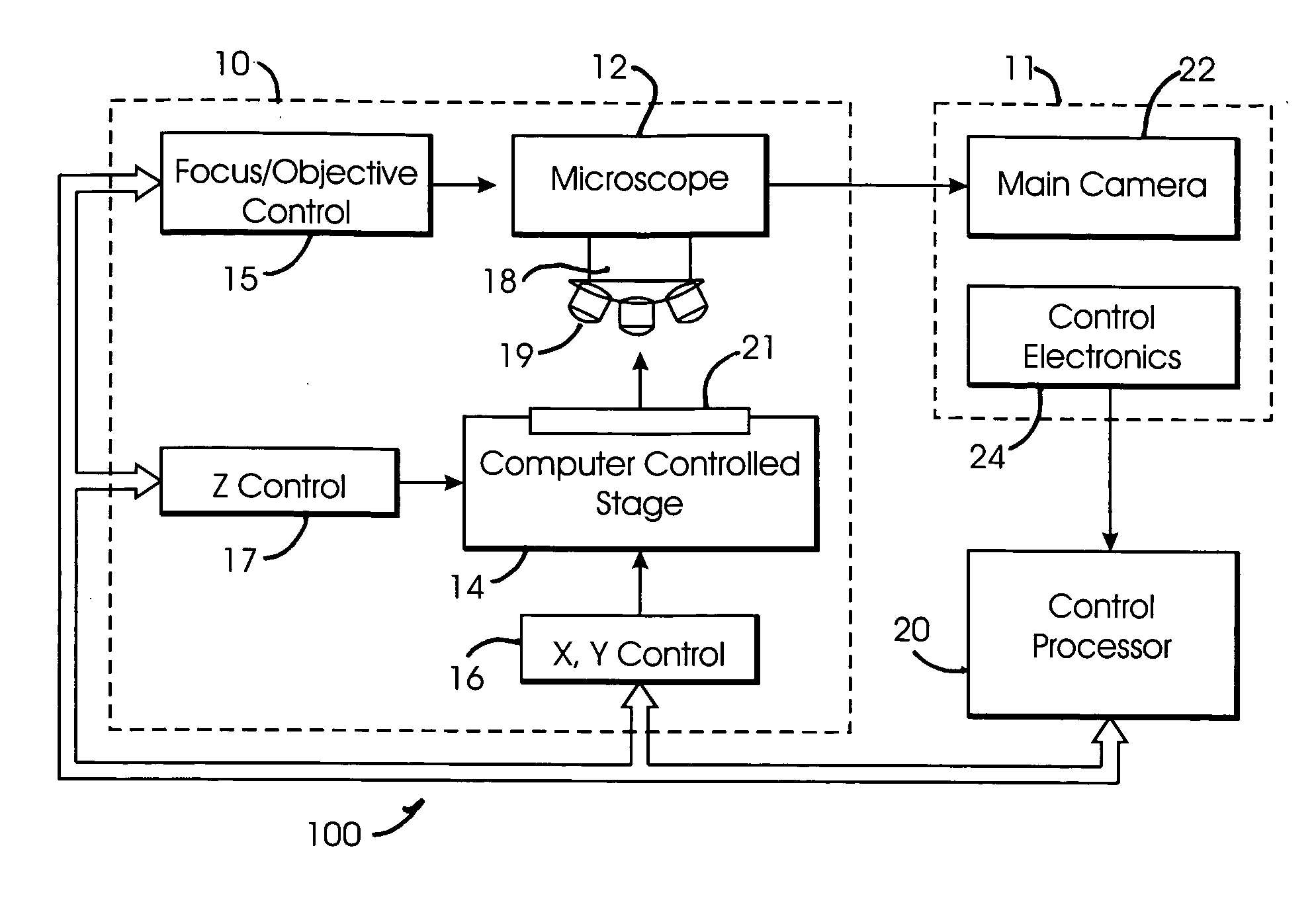
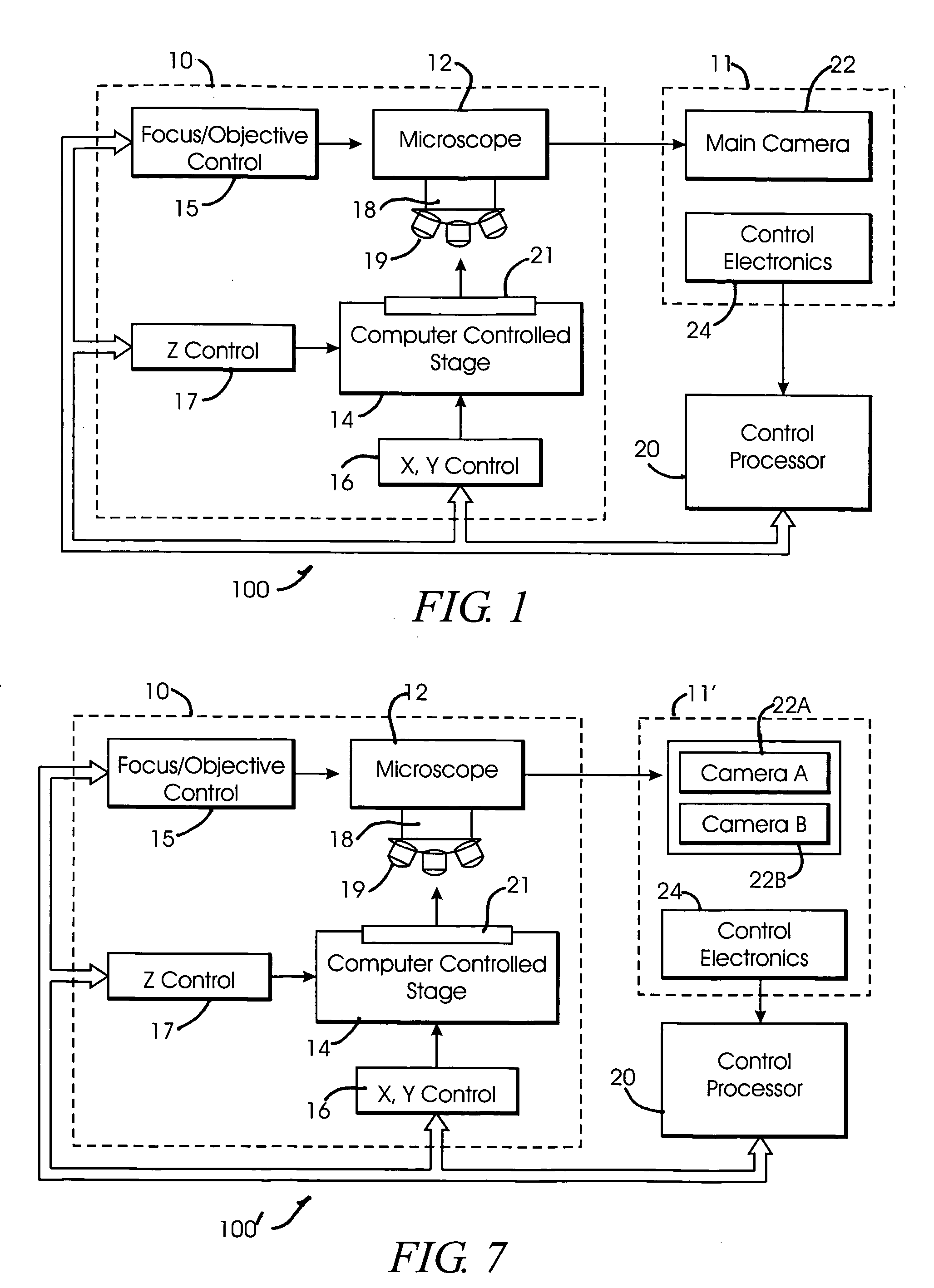
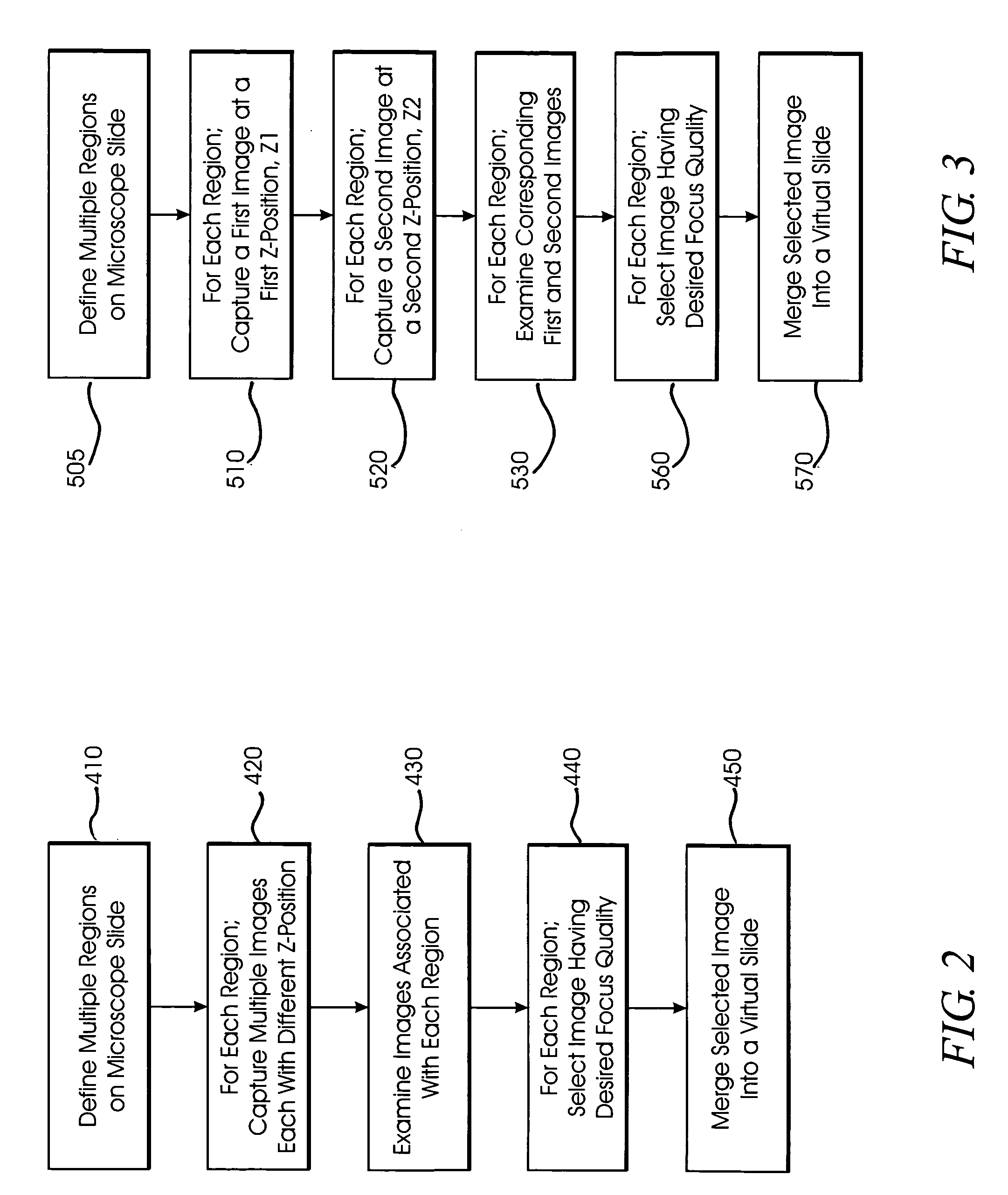
System and method for creating magnified images of a microscope slide
InactiveUS20060045505A1Optimum image quality characteristicImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscope slideRegion selection
A method and system for creating a digital, virtual slide having optimum image quality characteristics. Multiple regions of a physical slide are identified as well as at least two focus z-positions z1, and z2. Each region of the physical slide is scanned (imaged) at the first z position, so as to produce a first set of digital images of each defined region. Each region of the physical slide is also scanned (imaged) at the second z position, so as to produce a second set of digital images of each defined region. Each image of each set is evaluated against a focus quality metric and, for each region, either the first or second image, corresponding to that region, is selected that exhibits a focus quality metric corresponding to a desired focus quality. These images are then merged into a digital virtual slide. Additional focus z-positions may be included, and the multiple z-positions may be scanned seriatim, sequentially, and / or in overlapping fashion.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Using Image Content to Facilitate Navigation in Panoramic Image Data
ActiveUS20090213112A1Easy to navigateGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging dataMarine navigation
The present invention relates to using image content to facilitate navigation in panoramic image data. In an embodiment, a computer-implemented method for navigating in panoramic image data includes: (1) determining an intersection of a ray and a virtual model, wherein the ray extends from a camera viewport of an image and the virtual model comprises a plurality of facade planes; (2) retrieving a panoramic image; (3) orienting the panoramic image to the intersection; and (4) displaying the oriented panoramic image.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC +1
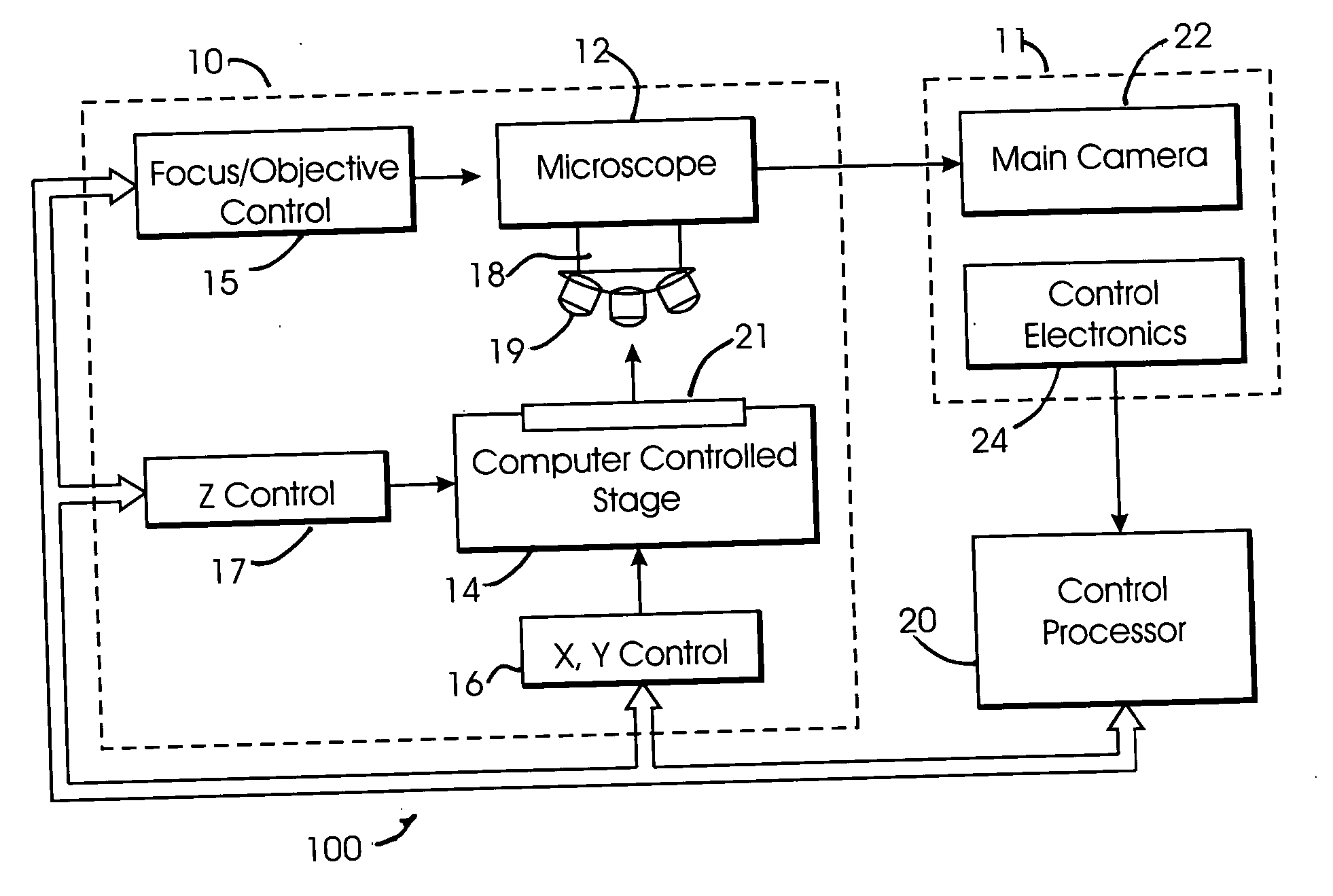
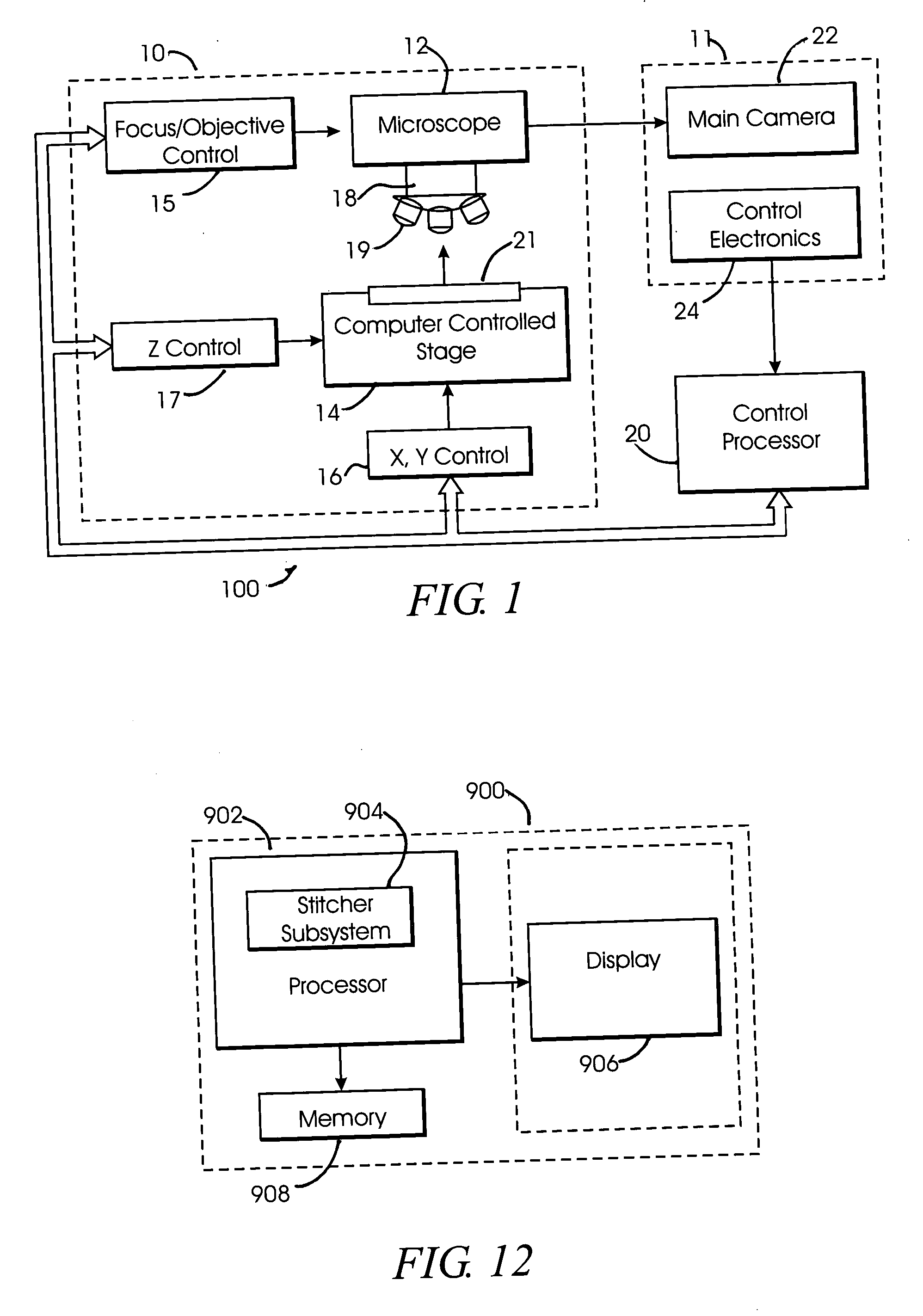
Microscopy system having automatic and interactive modes for forming a magnified mosaic image and associated method
InactiveUS20060133657A1Quality improvementMeet needsAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsMicroscopesInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
A scanning device for biological slides is provided, which can be operated in an interactive routine mode as well as in an unsupervised high speed automatic mode. In the first case, typical components, which the pathologist is used to operating manually, such as the microscope, the stage and the focus, and which have to be motorized for the automatic unsupervised system mode, are configured to simulate manual use, operation, and response. A non-interlaced area scan camera supports the interactive selection and acquisition of individual images in the manual mode, as well as the continuous high-speed scan motion for the rare event detection and virtual slide scan applications of the system. Due to the particular requirements to accommodate both operational modes, methods are described for constructing the virtual slide out of image tiles with varying overlap areas in the x- and y-directions.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
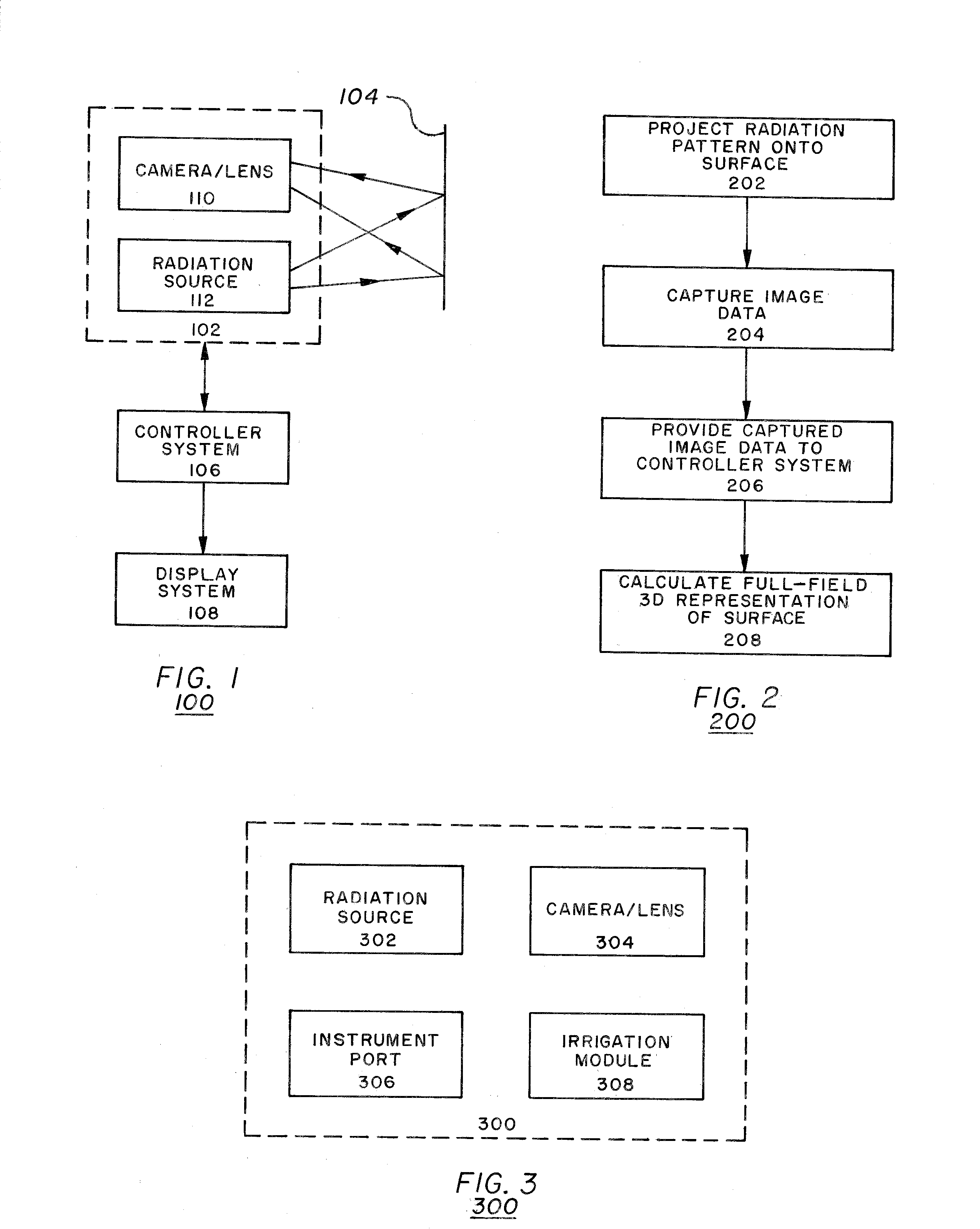
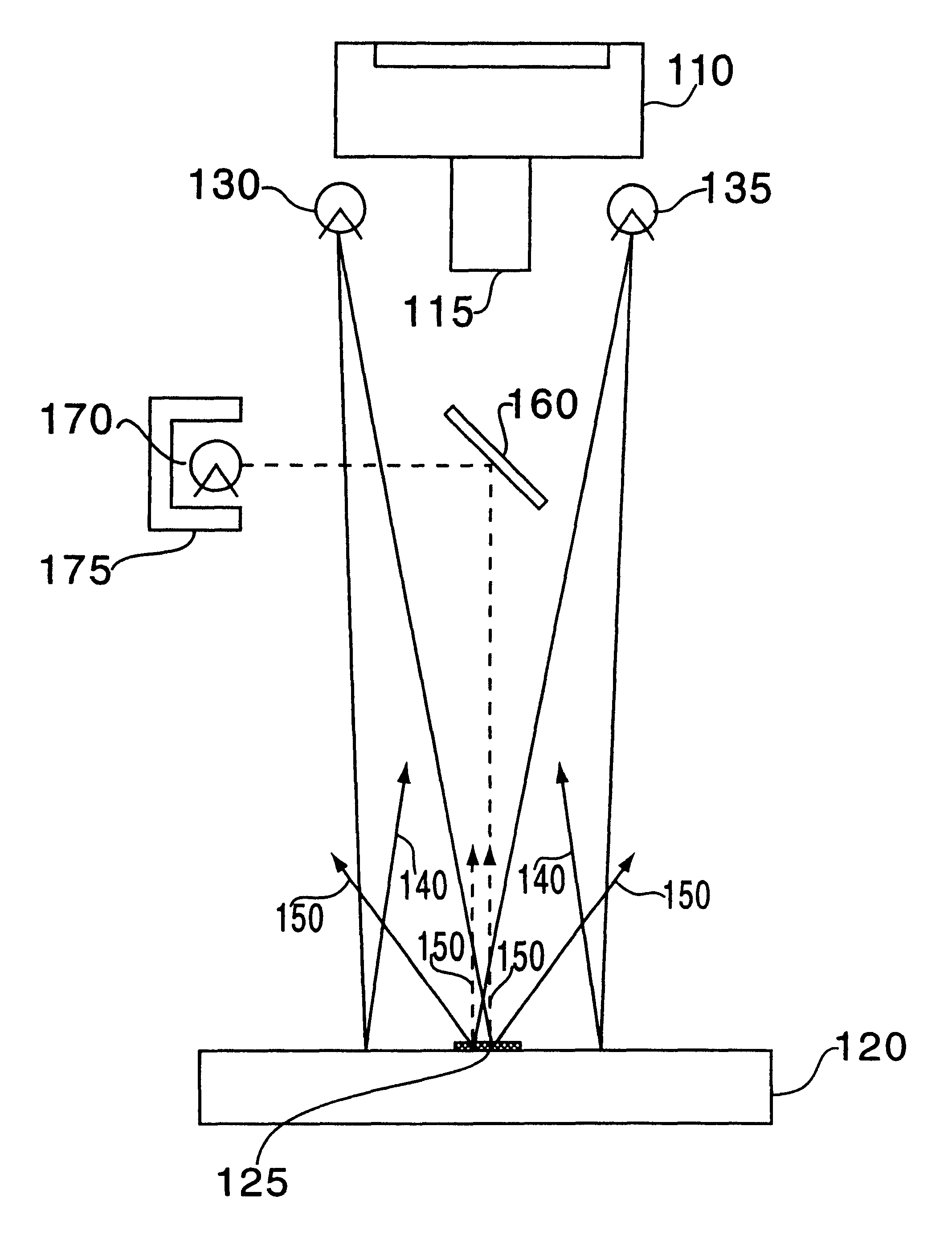
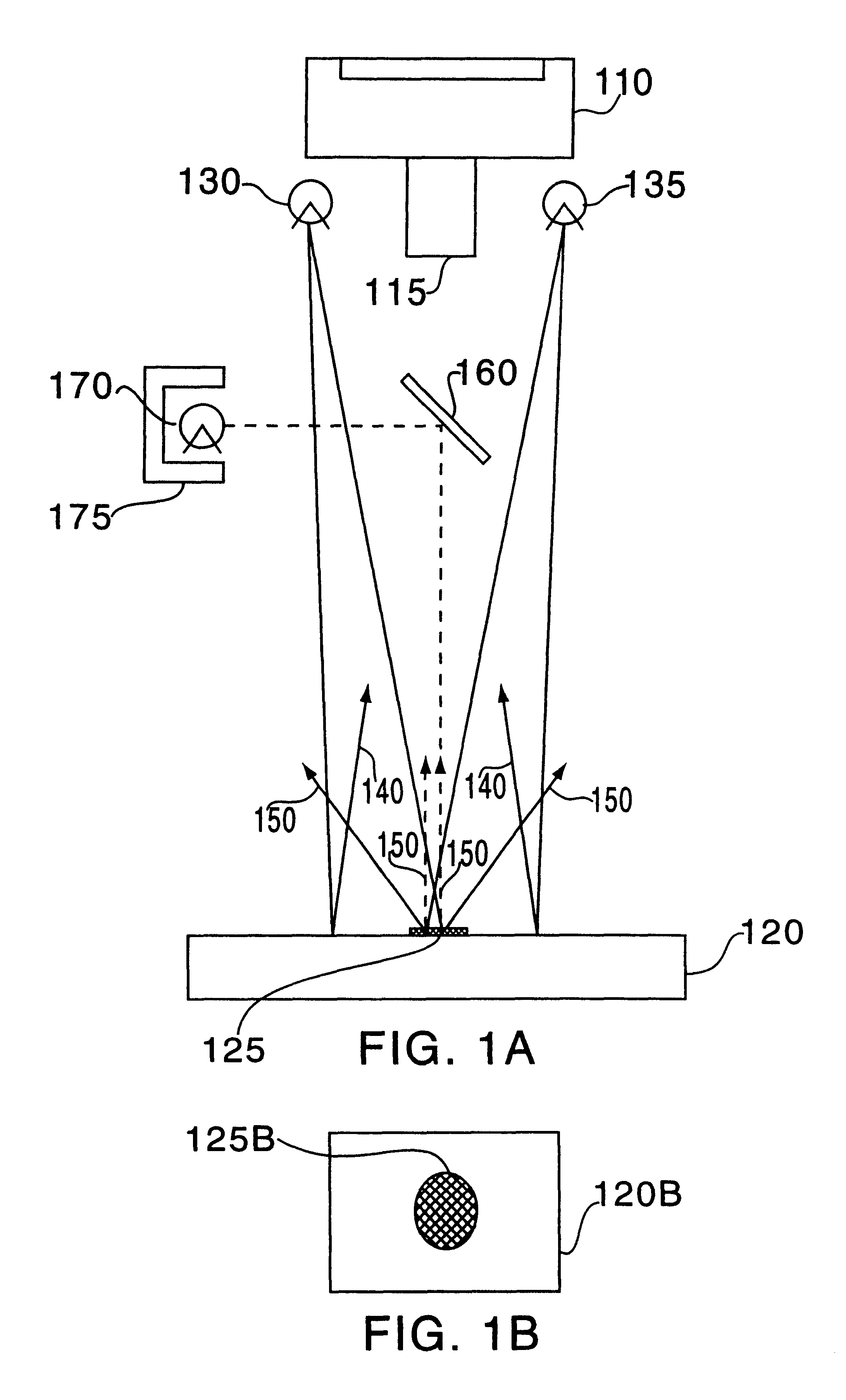
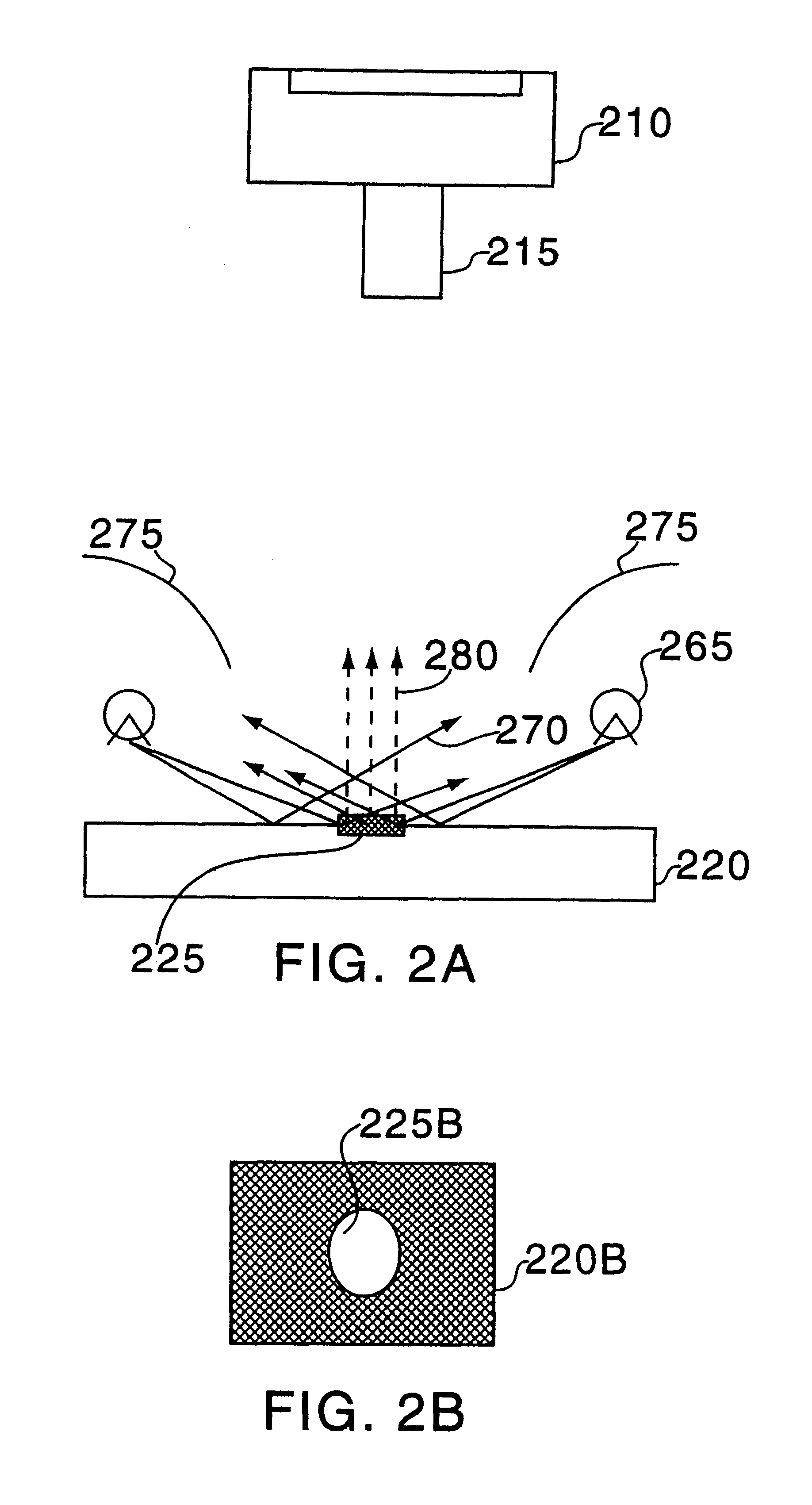
Full-field three-dimensional surface measurement
Embodiments of the present invention may be used to perform measurement of surfaces, such as external and internal surfaces of the human body, in full-field and in 3-D. Embodiments of the present invention may include an electromagnetic radiation source, which may be configured to project electromagnetic radiation onto a surface. The electromagnetic radiation source may be configured to project the electromagnetic radiation in a pattern corresponding to a spatial signal modulation algorithm. The electromagnetic radiation source may also be configured to project the electromagnetic radiation at a frequency suitable for transmission through the media in which the radiation is projected. An image sensor may be configured to capture image data representing the projected pattern. An image-processing module may be configured to receive the captured image data from the image sensor and to calculate a full-field, 3-D representation of the surface using the captured image data and the spatial signal modulation algorithm. A display device may be configured to display the full-field, 3-D representation of the surface.
Owner:VIRTUAL 3 D TECH CORP
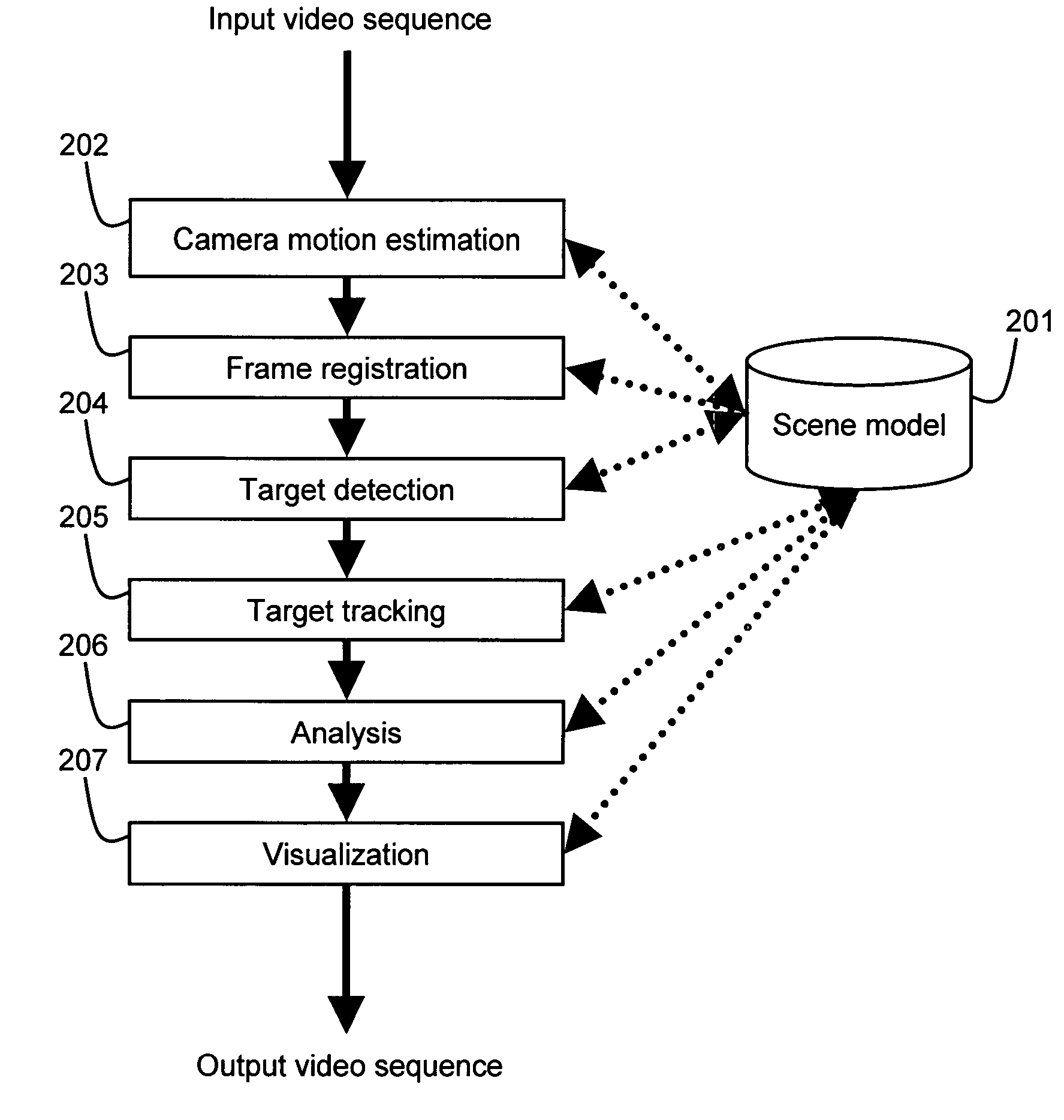
Enhanced processing for scanning video
A method of video processing may include registering one or more frames of input video received from a sensing unit, where the sensing unit may be capable of operating in a scanning mode. The registration process may project the frames onto a common reference. The method may further include maintaining a scene model corresponding to the sensing unit's field of view. The method may also include processing the registered frames using the scene model, where the result of processing the registered frames includes visualization of at least one result of processing.
Owner:OBJECTVIDEO
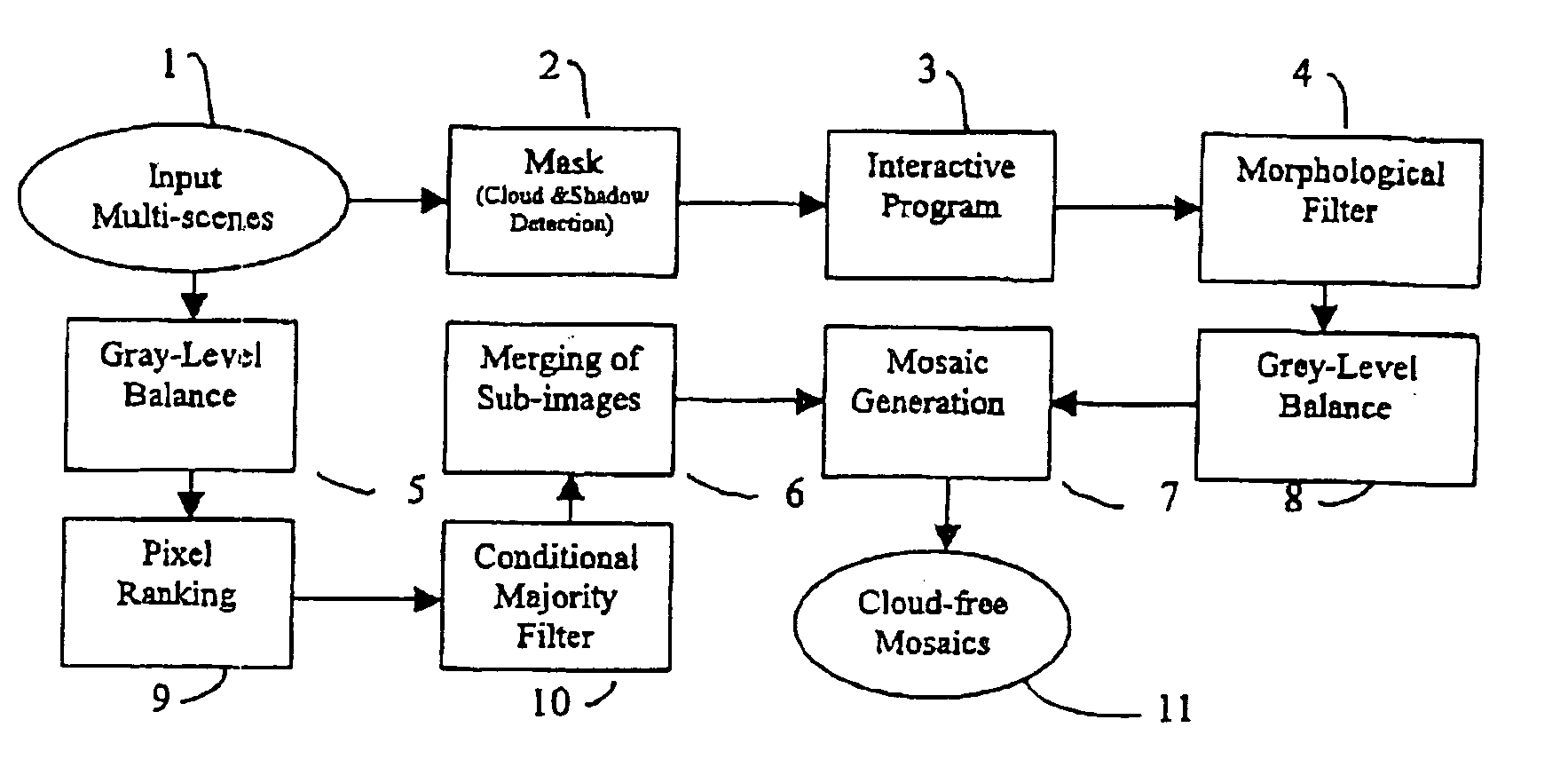
Method for producing cloud free and cloud-shadow free images
A method for generating a cloud free and cloud-shadow free image from a plurality of images of a region, the method including the steps of ranking pixels in order of cloudiness and shadowness, generating cloud and shadow masks by classifying a group of pixels as cloud, shadow, or noncloud-nonshadow, and creating a mosaic from the plurality of images to form the cloud free and cloud-shadow free image.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Method and system for imaging an object or pattern
A system and method for simultaneously obtaining a plurality of images of an object or pattern from a plurality of different viewpoints is provided. In an exemplary embodiment, proper image contrast is obtained by replacing the light sources of earlier systems with equivalent light sensitive devices and replacing the cameras of earlier systems with equivalent light sources. With such a system, bright-field images and dark-field images may be simultaneously obtained. In one aspect of the invention, a light source is positioned to illuminate at least a portion of an object. A plurality of light guides having input ends are positioned to simultaneously receive light reflected from the object and transmit the received light to a plurality of photodetectors. The light guides are arranged such that their respective input ends are spaced substantially equally along at least a portion of a surface of an imaginary hemisphere surrounding the object. The signals generated by the photodetectors (as a result of light detection) are processed and a plurality of images of the object are formed. Another aspect of the invention provides a method for generating composite images from simultaneously obtained images. Equivalent regions of each image (corresponding to geographically identical subpictures) are compared. The subpicture having the highest entropy is selected and stored. This process continues until all subpictures have been considered. A new composite picture is generated by pasting together the selected subpictures. In another aspect of the invention, the vector of relative light values gathered for each pixel or region of an object illuminated or scanned (i.e., one value for each photodetector) is used to determine reflectance properties of points or regions illuminated on the object or pattern. The reflectance properties may be stored in a matrix and the matrix used to read, for example, a Bar Code of a data matrix symbol.
Owner:RUDOLPH TECHNOLOGIES INC
Human body model obtaining method and network virtual fitting system based on depth camera
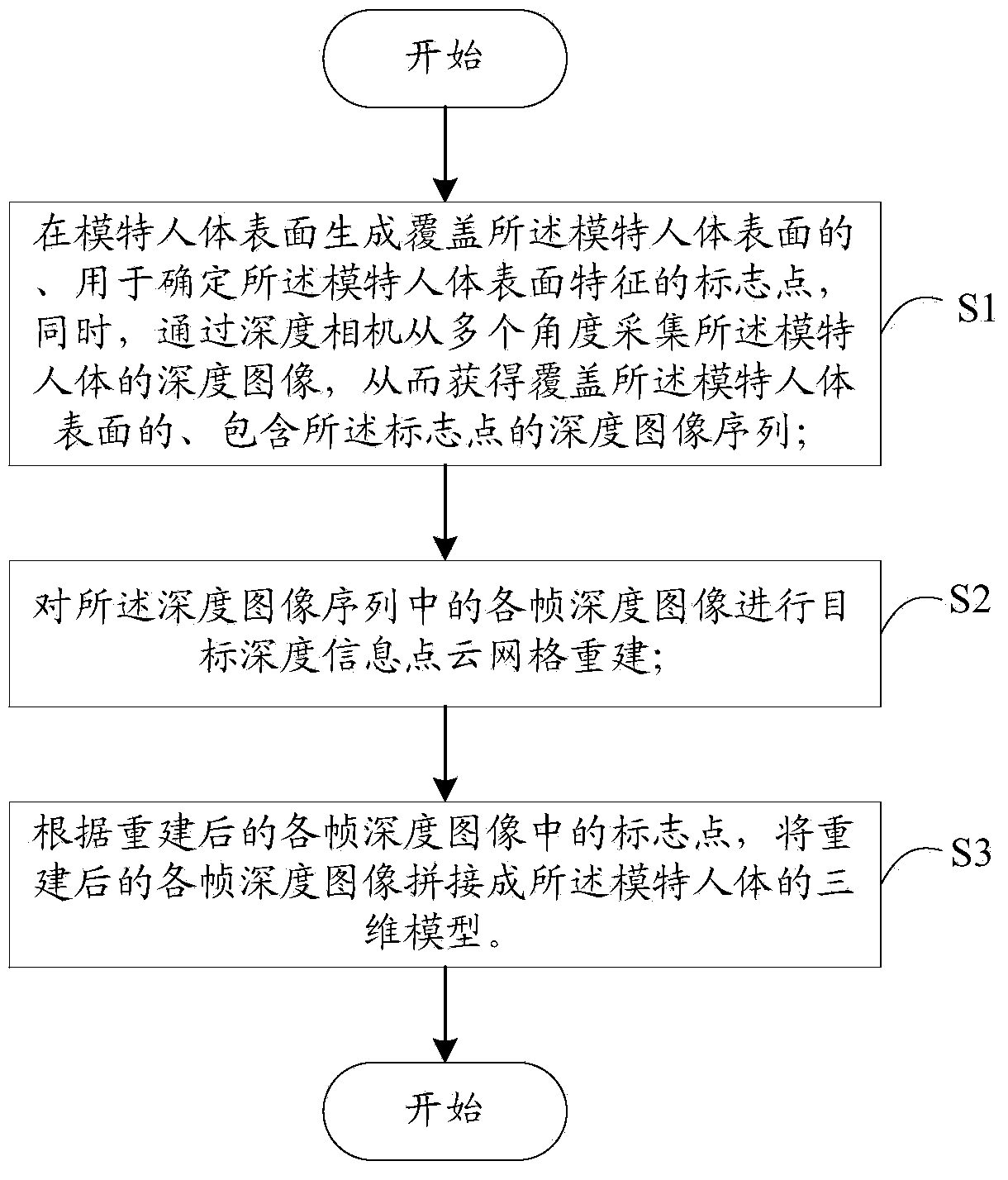
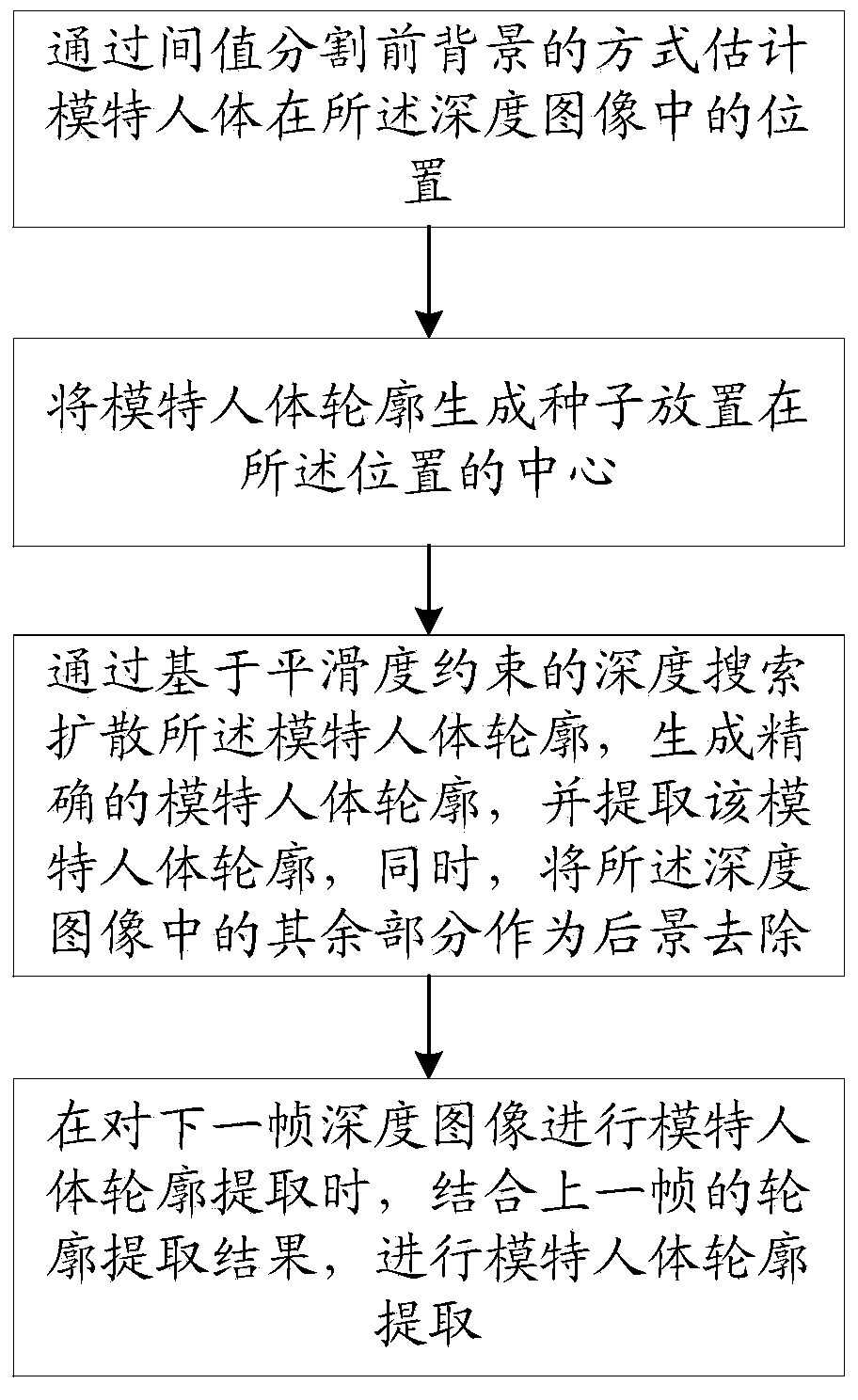
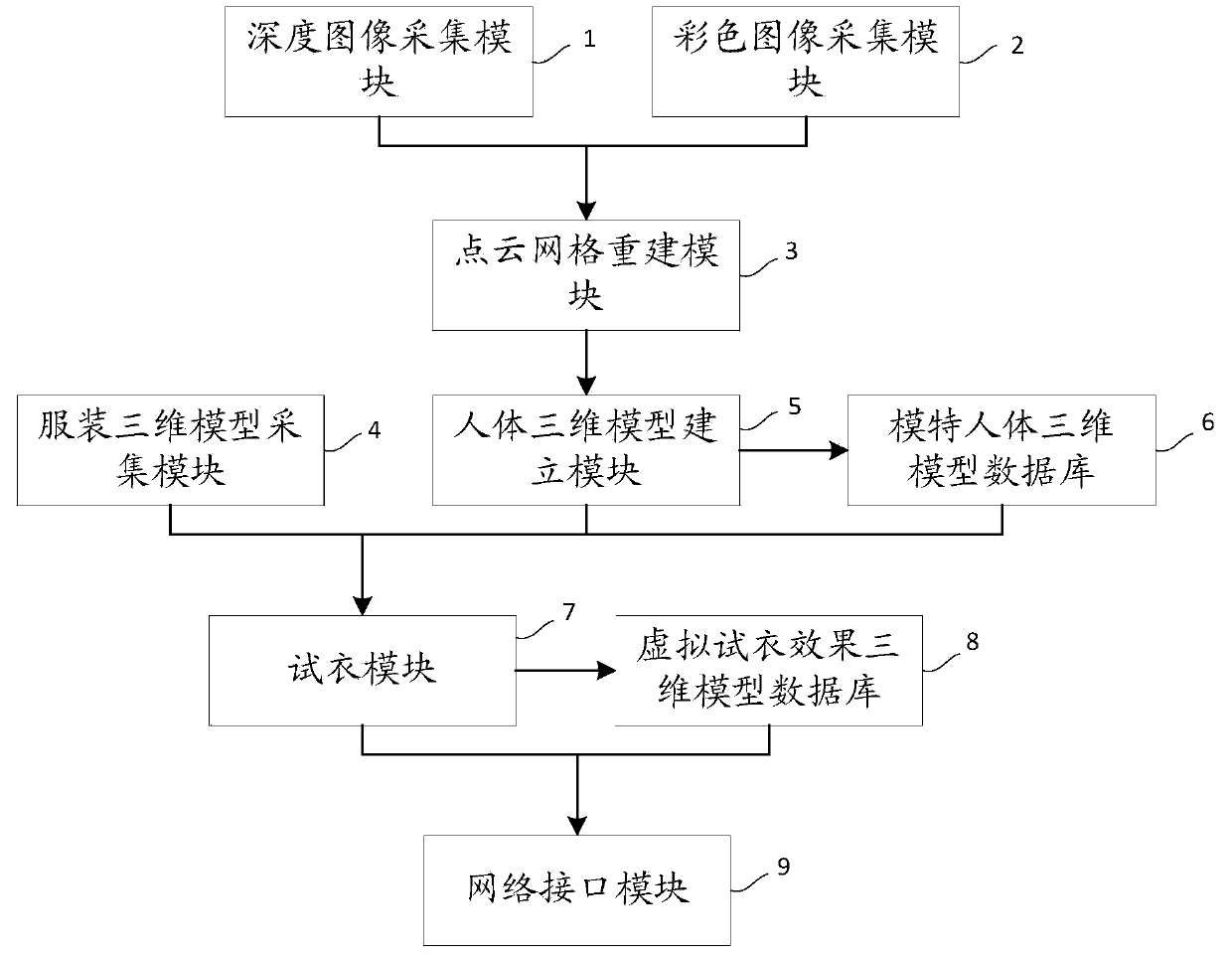
ActiveCN104008571AReal try-on effectDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementHuman bodyPoint cloud
The invention relates to a human body model obtaining method and a network virtual fitting system based on a depth camera. The method comprises the steps of 1, generating mark points on the surface of a model human body, meanwhile, collecting depth images of the model human body from multiple angles through the depth camera, and therefore obtaining depth image sequences covering the surface of the model human body and comprising the mark points, wherein the mark points cover the surface of the model human body and are used for determining characteristics of the surface of the model human body; 2, performing target depth information point cloud network reconstruction on each frame of depth images in the depth image sequences; 3, splicing the reconstructed depth images into a three-dimensional model of the model human body according to the reconstructed mark points in the depth images. Compared with the prior art, the human body model obtaining method and the network virtual fitting system based on the depth camera can obtain the accurate human body three-dimensional model and the garment three-dimensional model, virtual fitting is achieved according to the models, and the real fitting effect can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
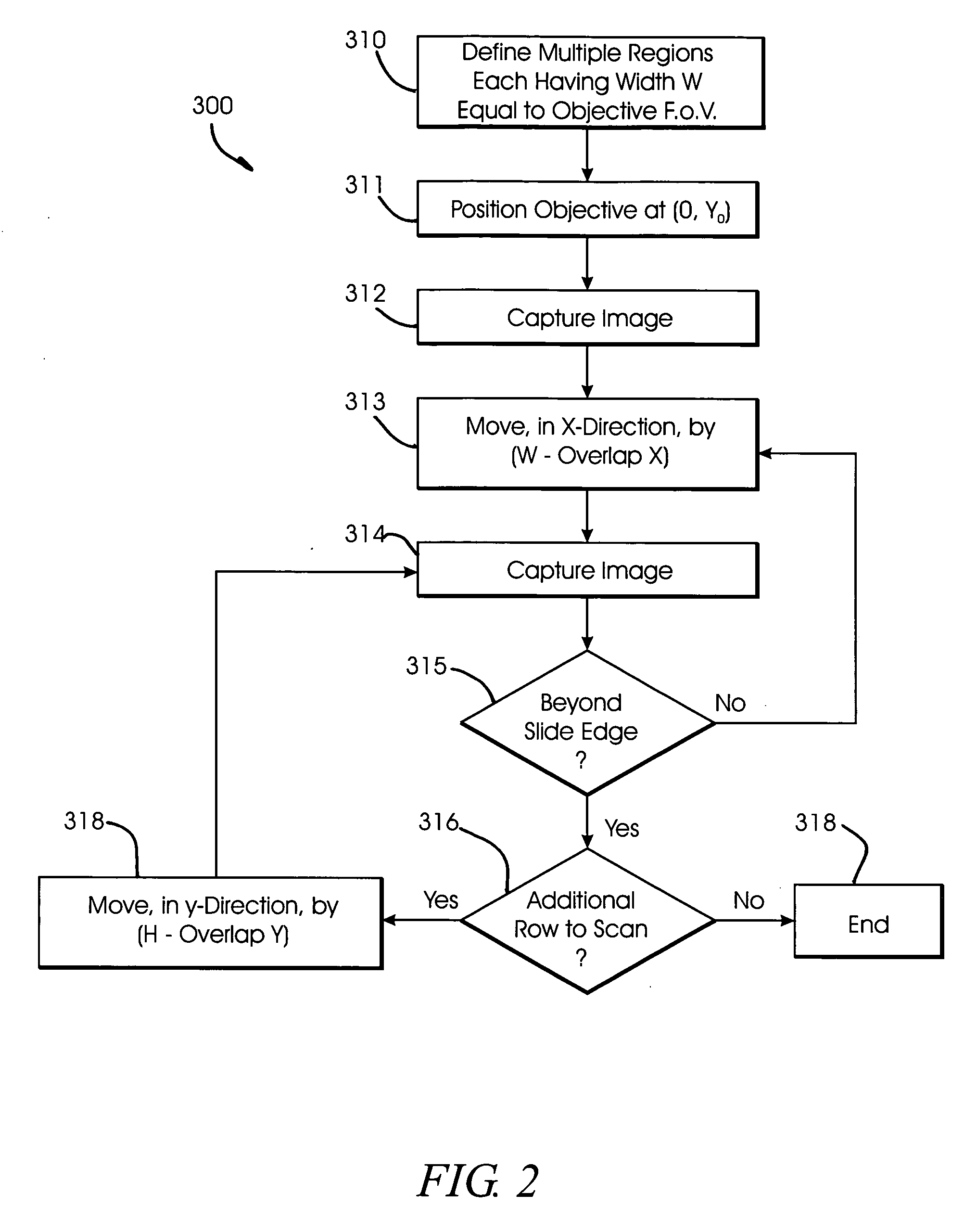
Method and apparatus of mechanical stage positioning in virtual microscopy image capture
ActiveUS20060034543A1Improve accuracyLarge image captureImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceMarine navigation
A method and apparatus for creating a magnified composite image of a microscope specimen comprises making error corrections for imprecise movements of the specimen relative to an objective lens when capturing data for first and second images. A correction offset is computed based on a comparison of data for overlapped portions of the first and second images and then the specimen is moved through a distance modified by the correction offset for capture of a subsequent tiled image. Image center portions are retained as the data structure tile. The area about the center portion is used to align images and to compensate for stage inaccuracies and to provide a feedback signal for a drive system. Differences in X,Y coordinates for macro and micro view images may be used as navigation offsets to view a selected point for the micro image marked on the macro image.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
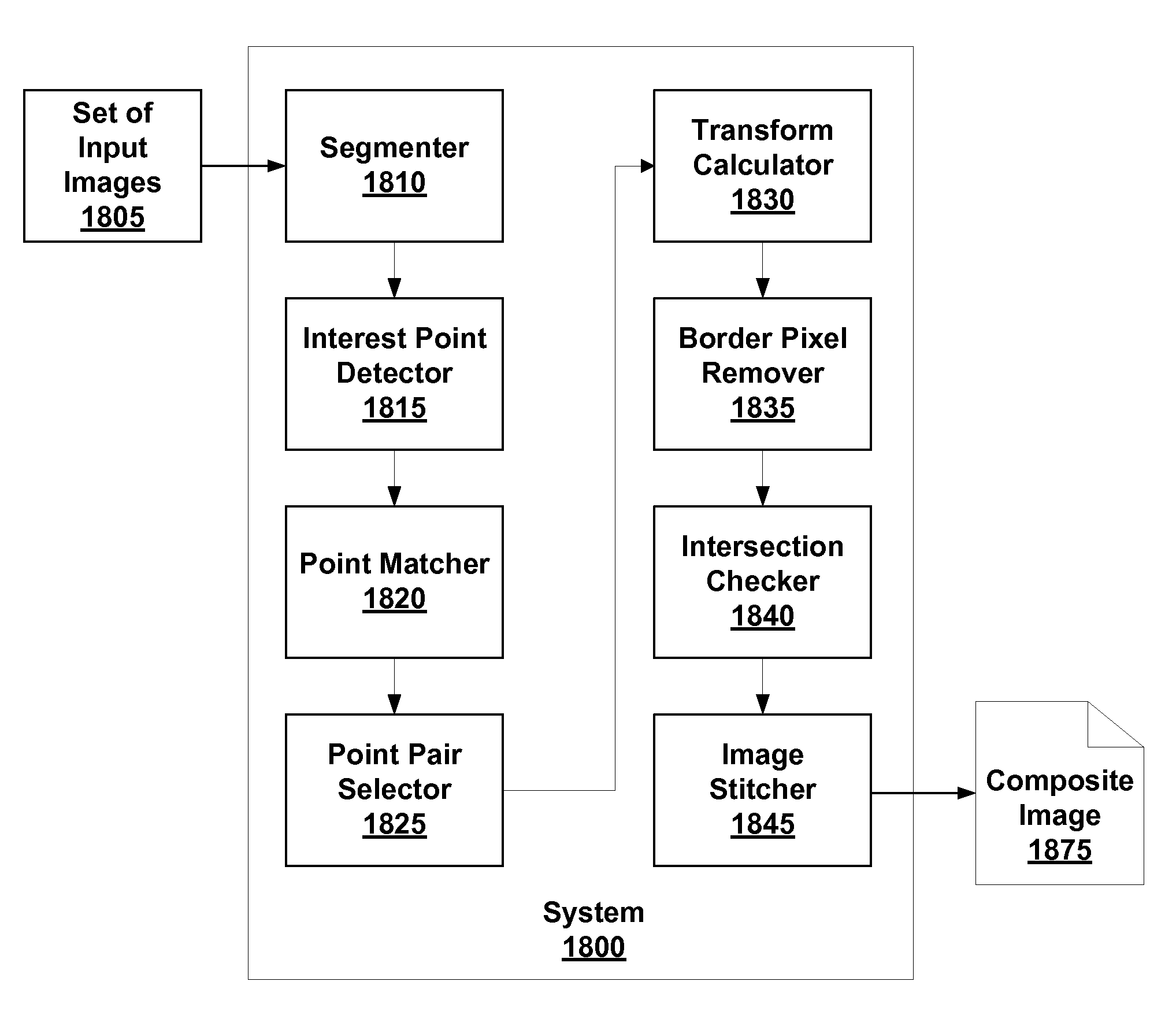
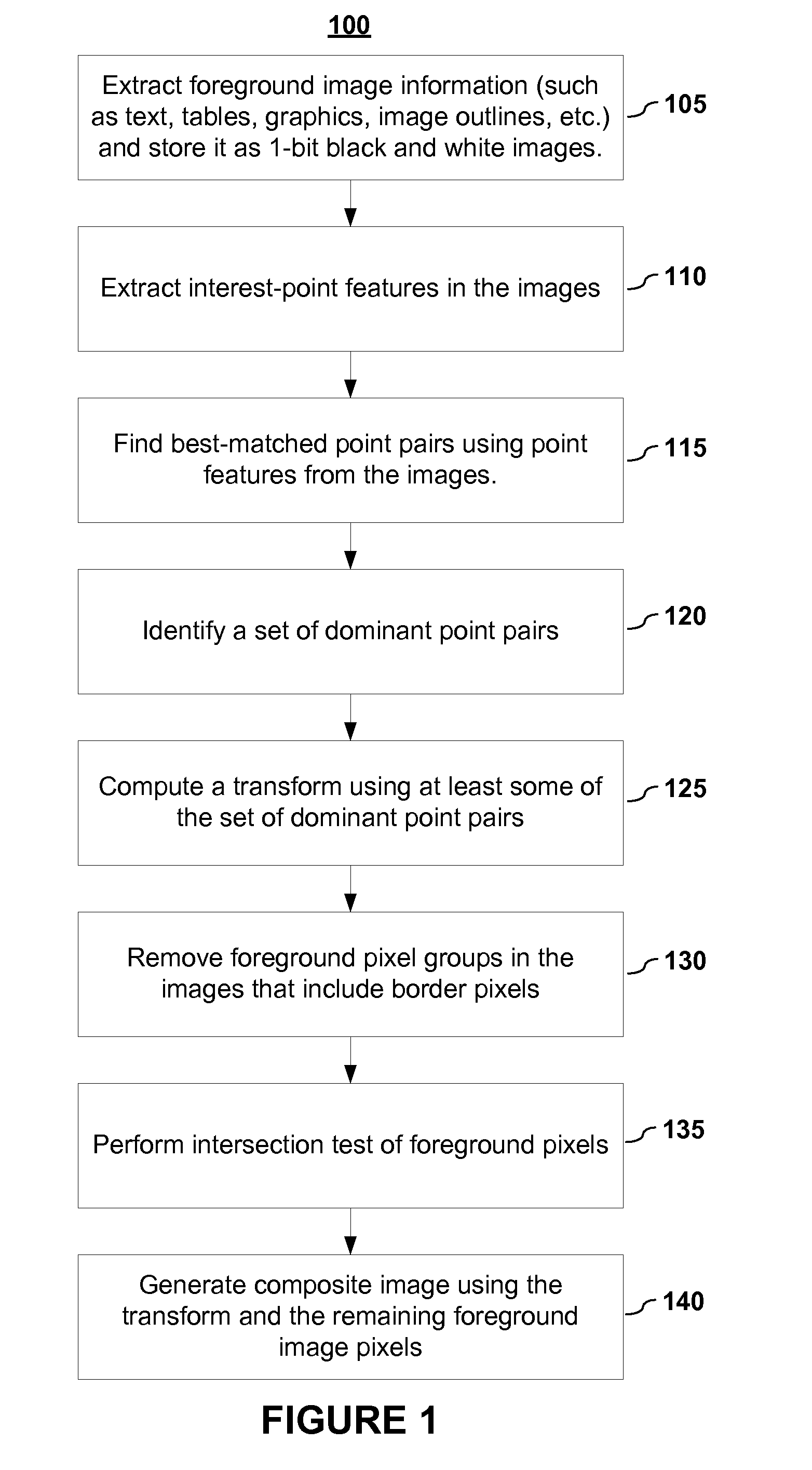
Image Stitching
InactiveUS20080298718A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisImage pairPoint pair
Disclosed are embodiments of systems and methods to stitch two or more images together into a composite image. By finding matching point pairs for a pair of images, a homography transform may be obtained for the pair of images. The homography transform may be used to generate a composite image of the image pair. In an embodiment, the process of identifying a homography transform may be iterated. In an embodiment, when forming the composite image, the transformed foreground regions may be selected such that there is no intersection of foreground pixel regions. In an embodiment, foreground pixel regions on the border of an image may be removed. The resulting composite image is a larger image generated from the selected regions from the input images. In embodiments, the process may be repeated for sets of images with more than two images.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and Method For Panoramic Image Stitching
ActiveUS20110102542A1Addressing slow performanceEasy to handleGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionBarcodeImage stitching
A system for capturing images of a target, such as a test tube, that is presented in front of an optical imager and rotated 360 degrees. The imager of the system captures a series of images which are then stitched together to form a panoramic image of the target. The panoramic image may then be processed to decode any barcode code information placed on the target, capture other information placed on the target, or obtain information about the target or the contents thereof.
Owner:NOVANTA CORP
Method and Apparatus of Taking Aerial Surveys
ActiveUS20100283853A1Extensive computationExtensive data collectionImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionAerial survey
A method of taking an aerial survey maps boundaries of a first image and a second image from a first plane to a second plane to determine boundaries of an output image in the second plane. For a plurality of pixels in the output image, the method determines a corresponding pixel of either the first image or second image in the first plane.
Owner:INTERGRAPH SOFTWARE TECH
Processing survey data of an underwater scene
ActiveUS20150363914A1Easy to connect in seriesImage enhancementTelevision system detailsField of viewMetadata
The present invention relates to method of processing survey data of an underwater scene comprising acquiring an augmented image of each of a plurality of fields of view within the scene, wherein each augmented image comprises at least a scene image of the scene, a location tag associated with that scene image, metadata associated with that scene image. This is useful is reviewing large.
Owner:CATHX RES
Method for acquiring panorama image by using two fish-eye camera lenses
InactiveCN104835118AReduce volumeReduce difficultyGeometric image transformationDetails involving image mosaicingCamera lensFisheye lens
The invention relates to the technical field of image communication, and particularly relates to a method for acquiring a panorama image by using two fish-eye camera lenses. The method comprises the following operation steps: (1) camera configuration: two fish-eye lenses with view angles of greater than 180 degrees are oppositely arranged on a camera, so that two ends of the view angles of the two fish-eye lenses are overlapped; (2) image acquisition: the camera is arranged in a panorama, and acquires a part of the panorama through one fish-eye lens to form a first image, and acquires the other part of the panorama through the other fish-eye lens to form a second image, and two ends of the first image and the second image are overlapped; (3) image processing: a processor of the camera splices the first image and the second image to form a 360-degree panorama image. According to the method provided by the invention, two images can be quickly obtained by the two fish-eye lenses, and combined into a panorama image, the operation is simple and convenient, and the combination effect is good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DETU NETWORK CO LTD
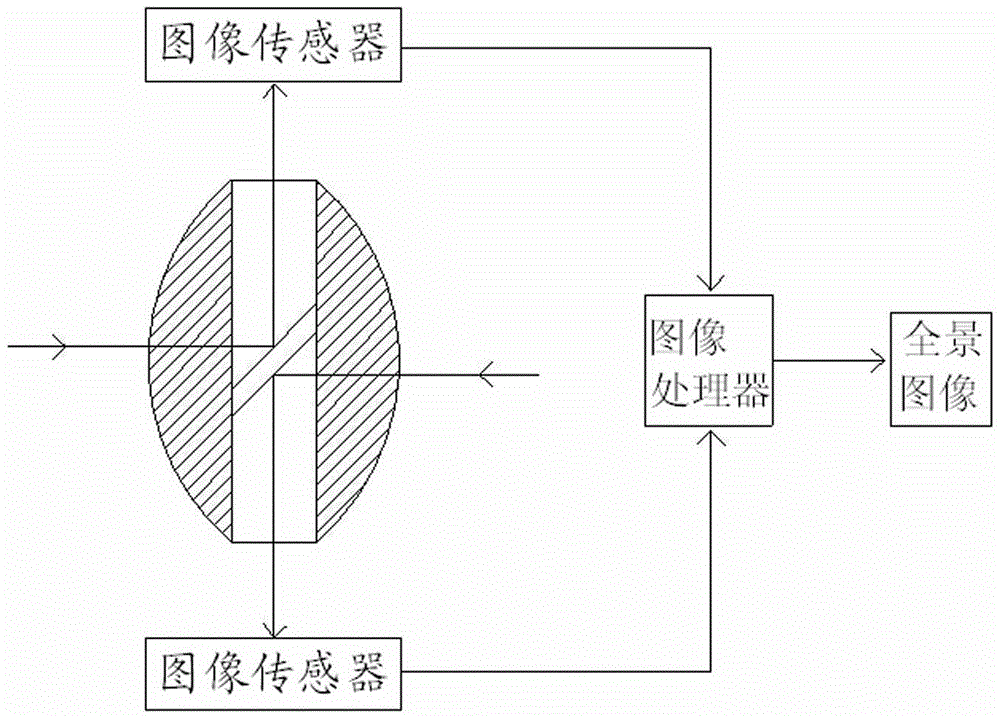
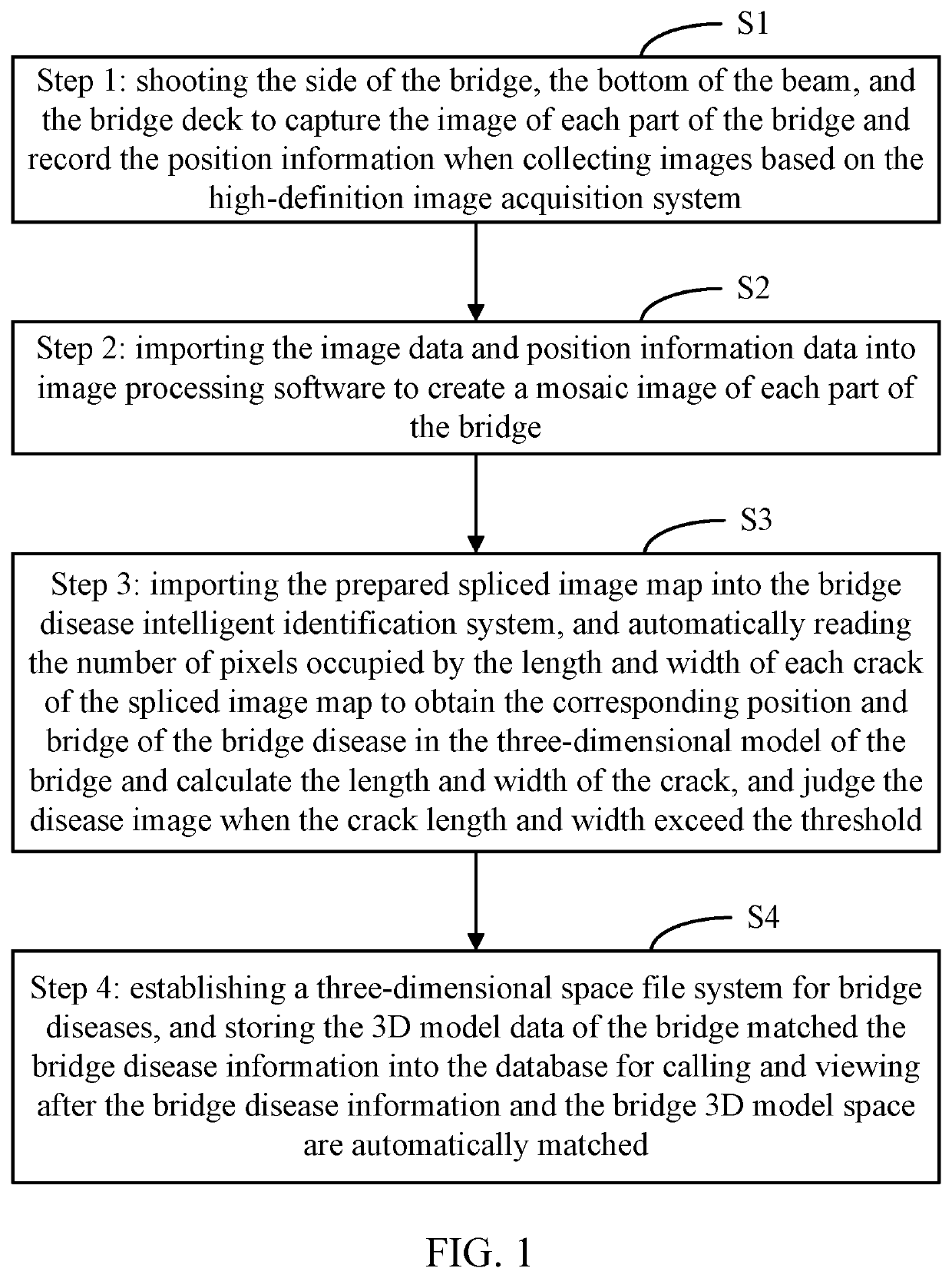
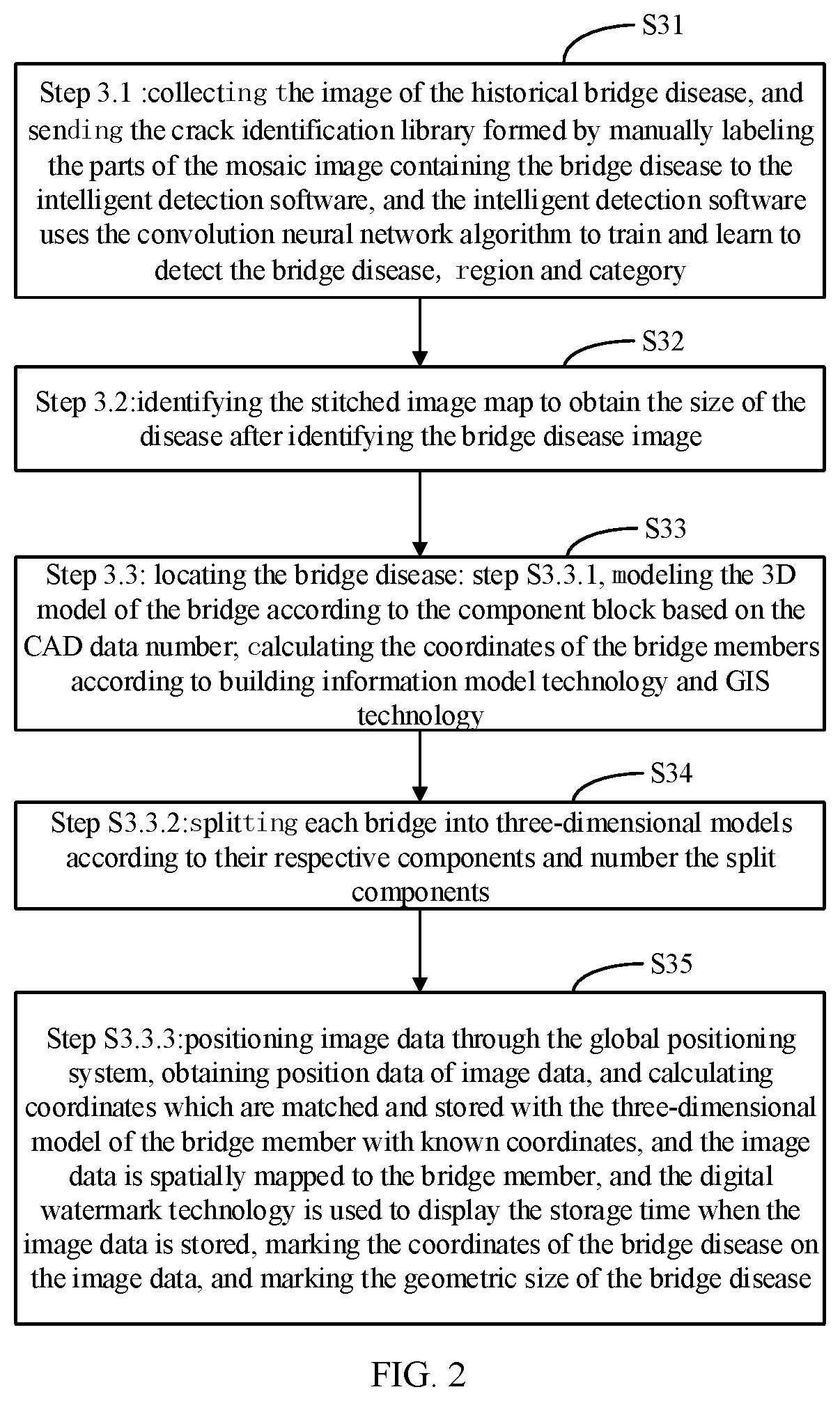
High-precision Intelligent Detection Method For Bridge Diseases Based On Spatial Position
ActiveUS20200098103A1Reduce workloadImprove detection efficiencyGeometric CADImage enhancementDiseaseImage processing software
A high-precision intelligent detection method for bridge diseases based on spatial position. The method comprising: collecting images based on the high-definition image acquisition system; importing the image data and position information data into image processing software to create a mosaic image of each part of the bridge; importing the prepared spliced image map into the bridge disease intelligent identification system; obtaining the corresponding position and bridge of the bridge disease in the three-dimensional model of the bridge; identifying the stitched image map to obtain the size of the disease after identifying the bridge disease image and locating the bridge disease. The high-precision intelligent detection method for bridge diseases based on spatial position realizes automatic collection and intelligent analysis of bridge inspection data, reduces the workload of the inspection technicians and improves the detection efficiency.
Owner:CHONGQING CONSTR ENG GRP
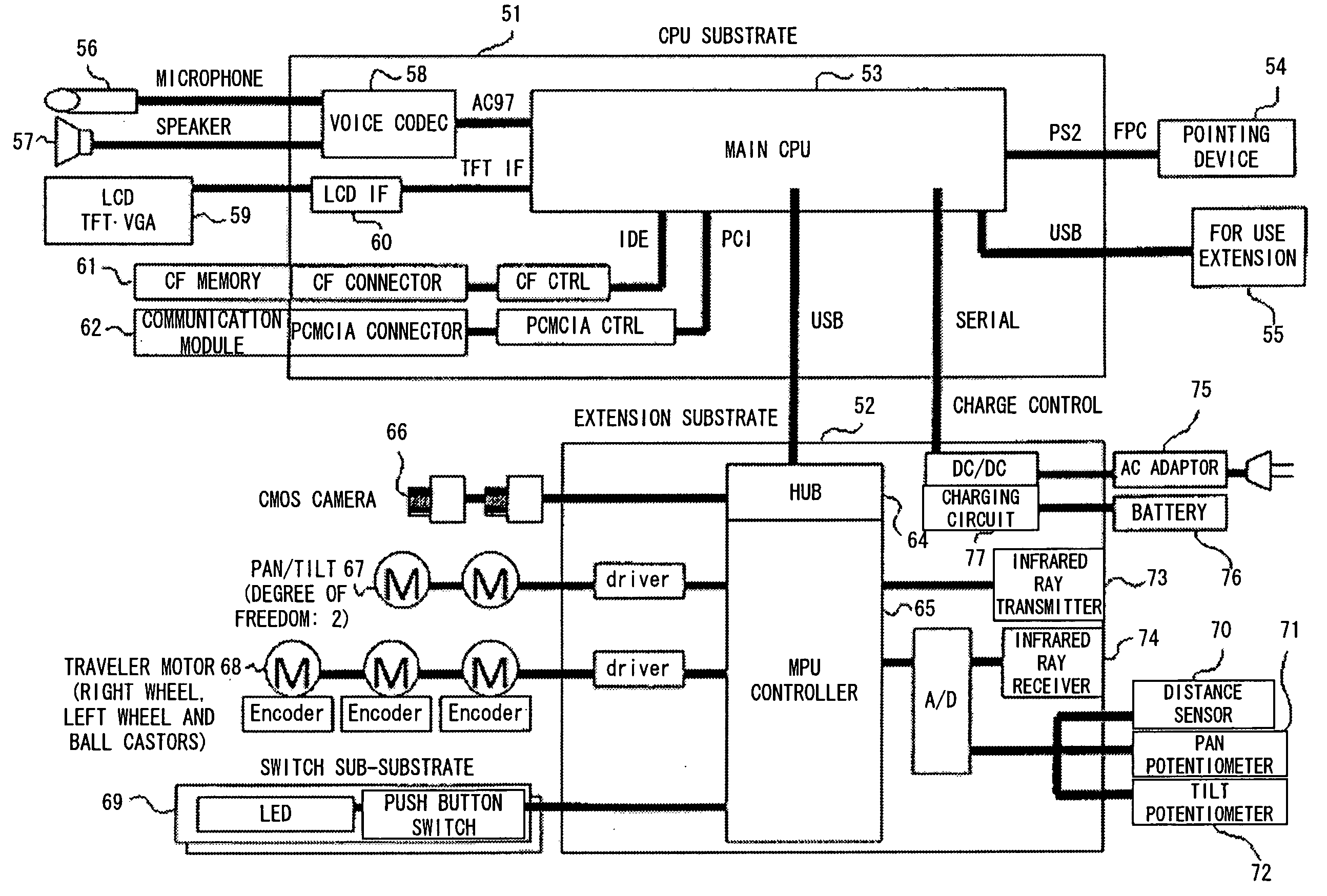
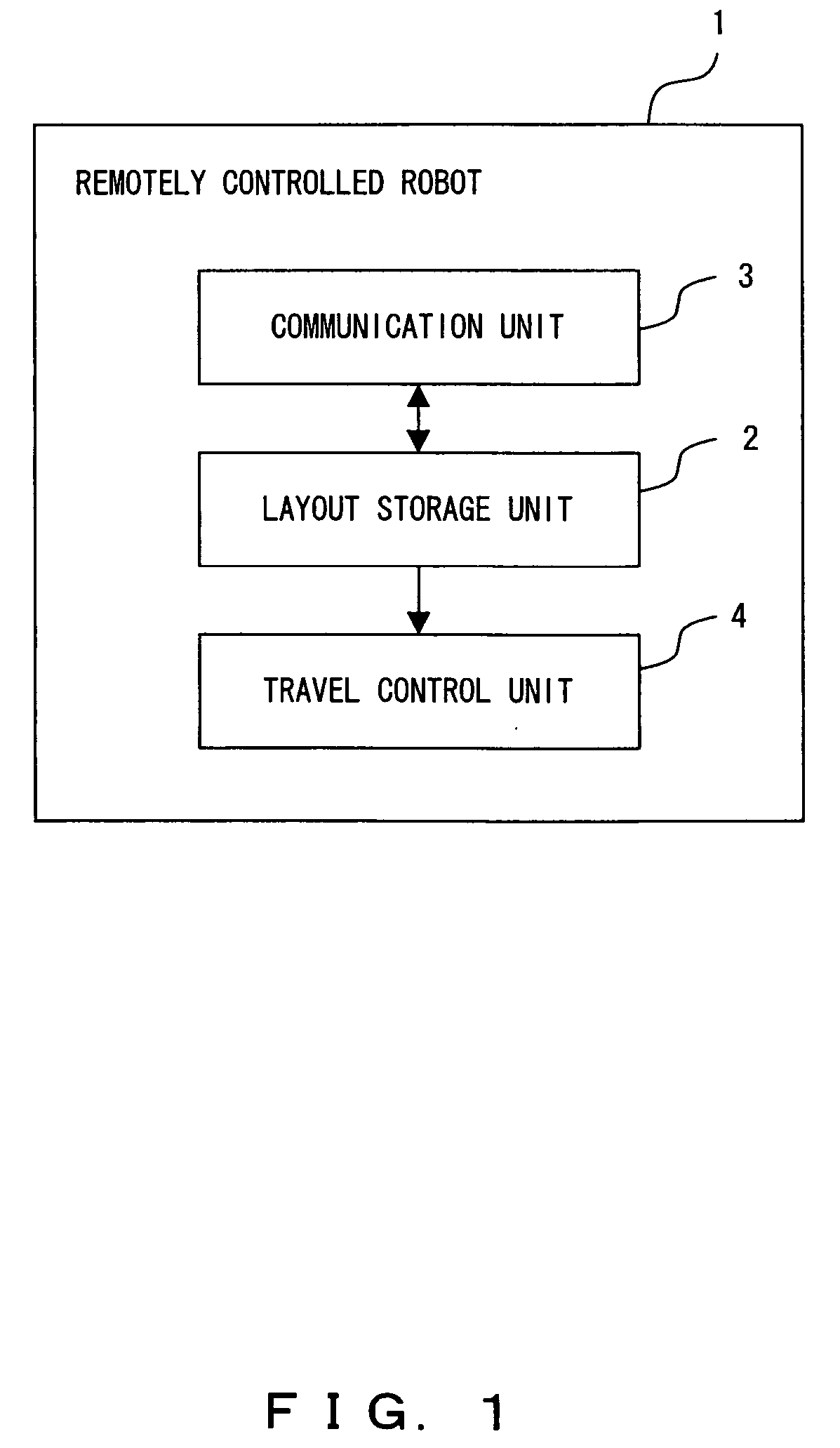
Remote-controlled robot and robot self-position identification method
A remotely controlled robot comprises a unit storing the layout plan of a building, a unit receiving a position remotely designated in the layout plan from a remote location and a unit controlling the travel of the robot to the designated position. A self-position identification method is implemented by a robot with a camera whose shooting direction can be changed. The robot takes in advance a panoramic picture of a room where the robot may travel, generates a reference picture by extracting a plurality of block pictures from the panoramic picture and identifies a room where the robot is located, by applying correlation and DP matching, using both a picture taken in the room where the robot is located and the reference picture.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com