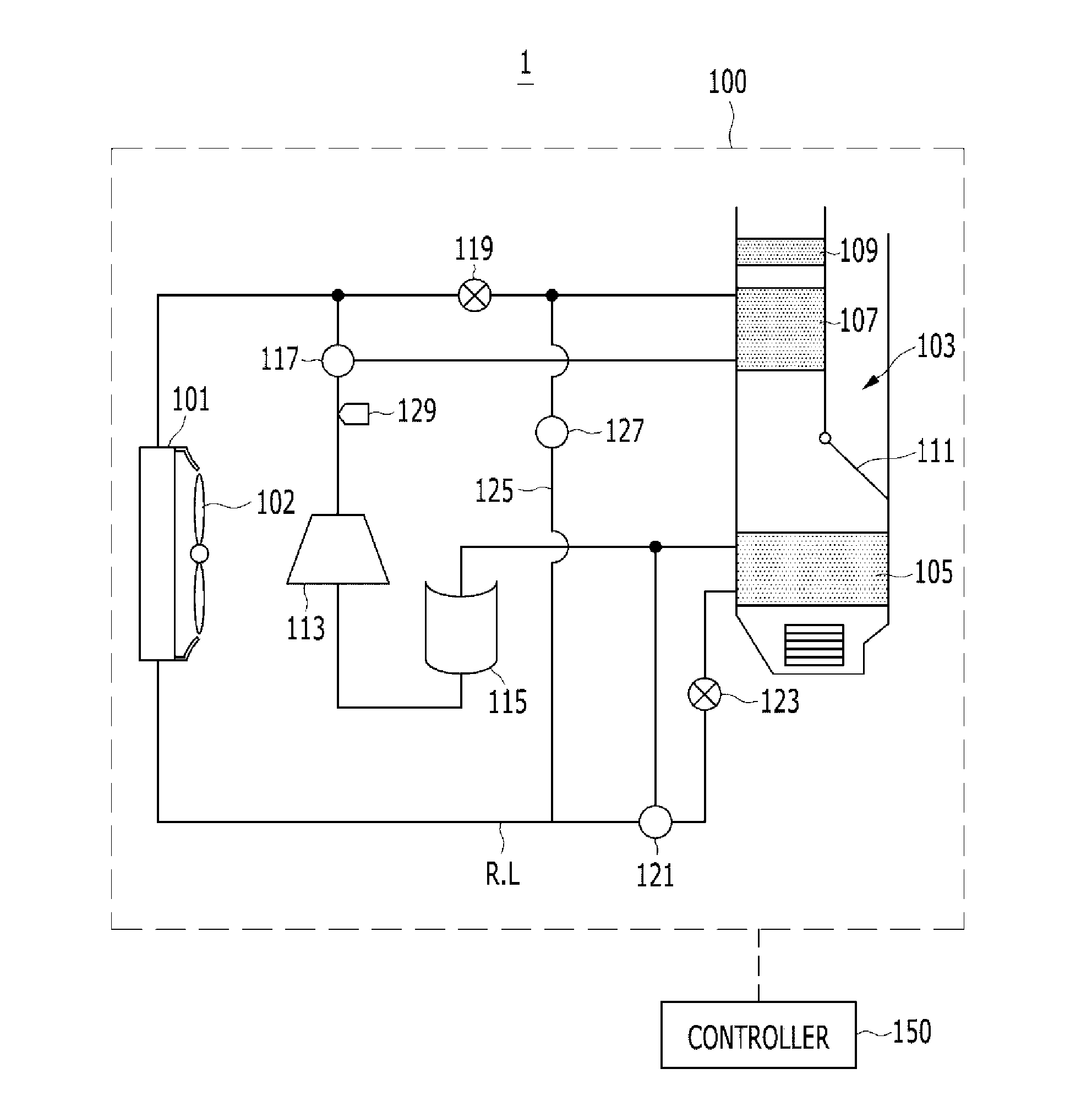
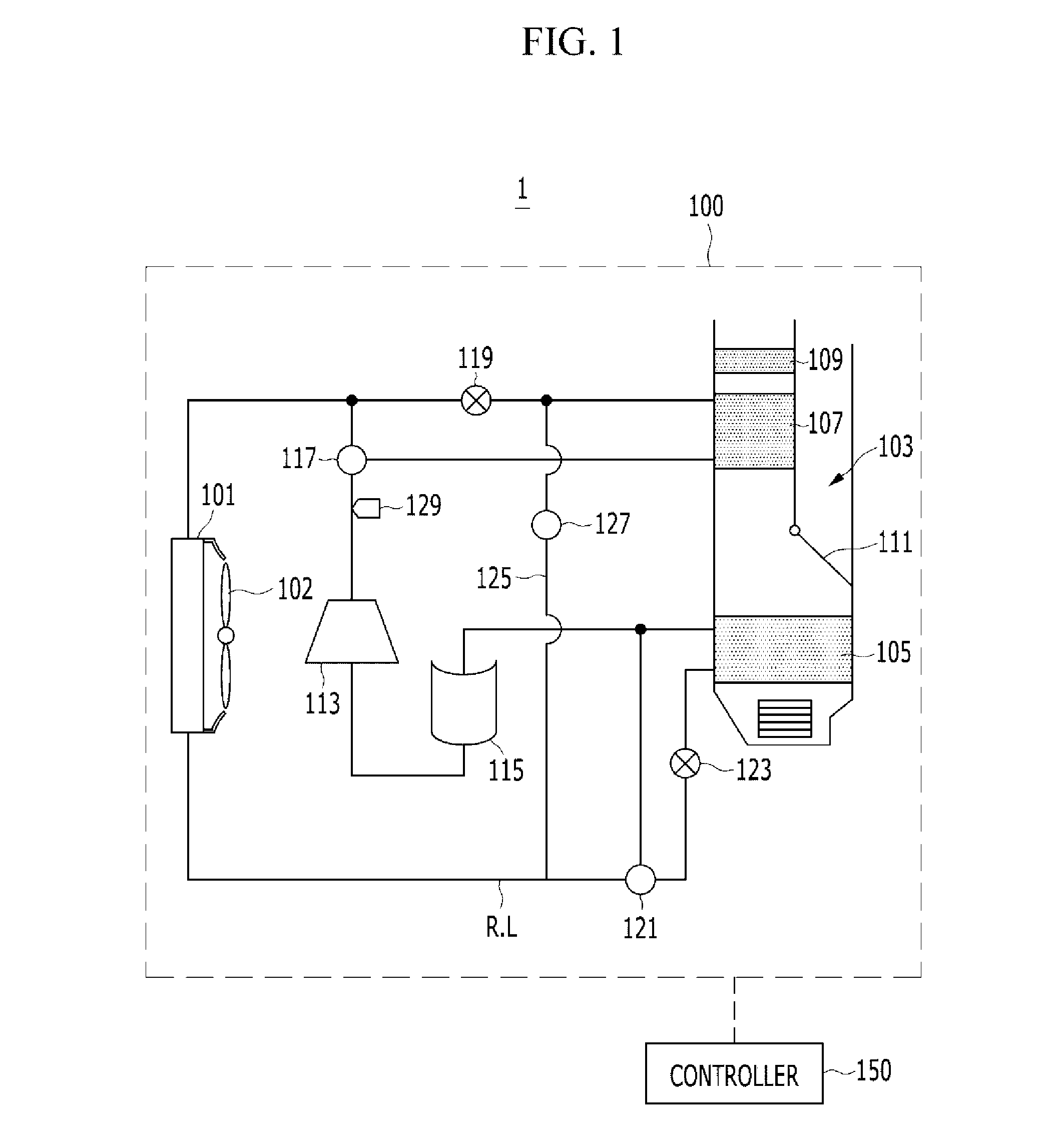
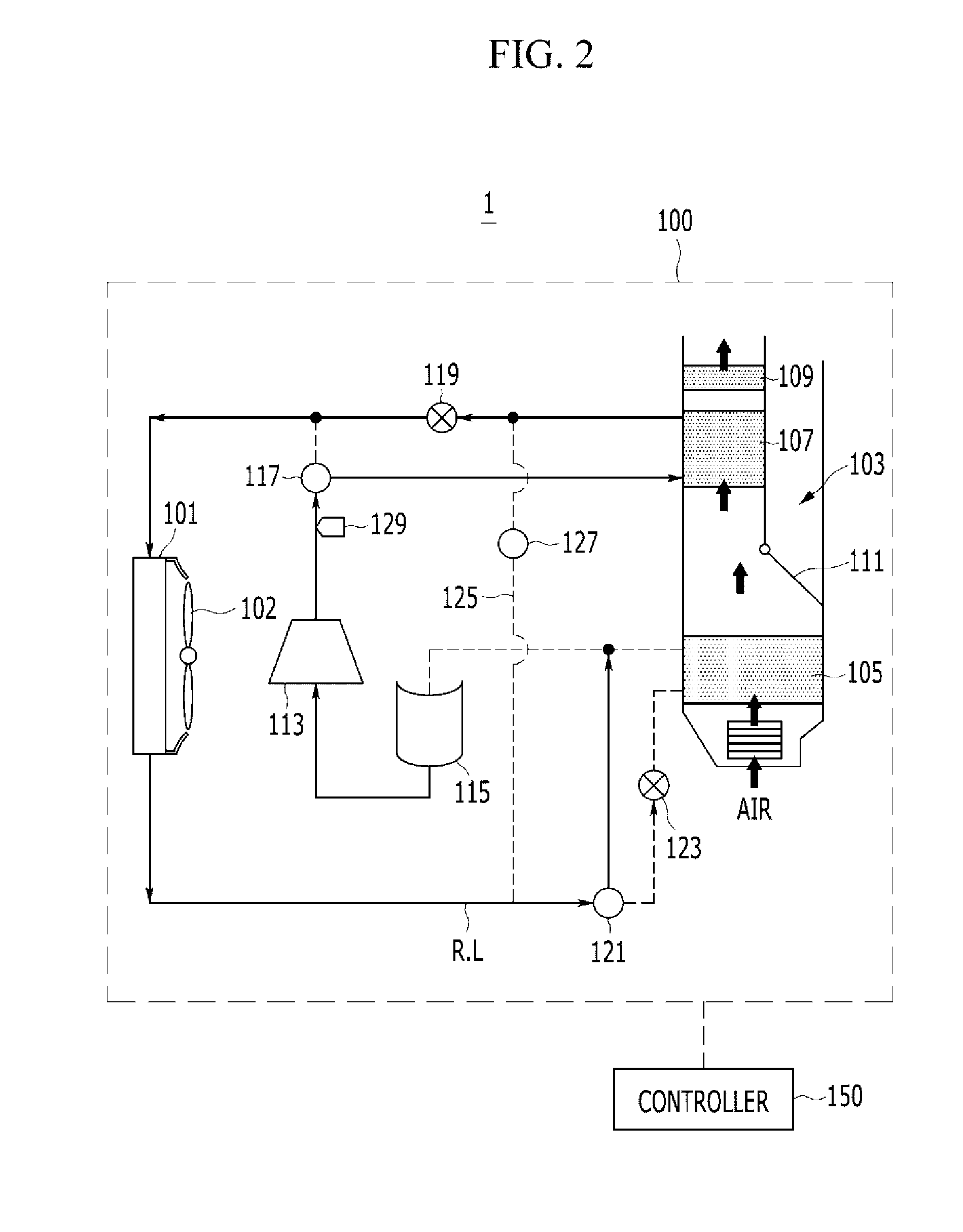
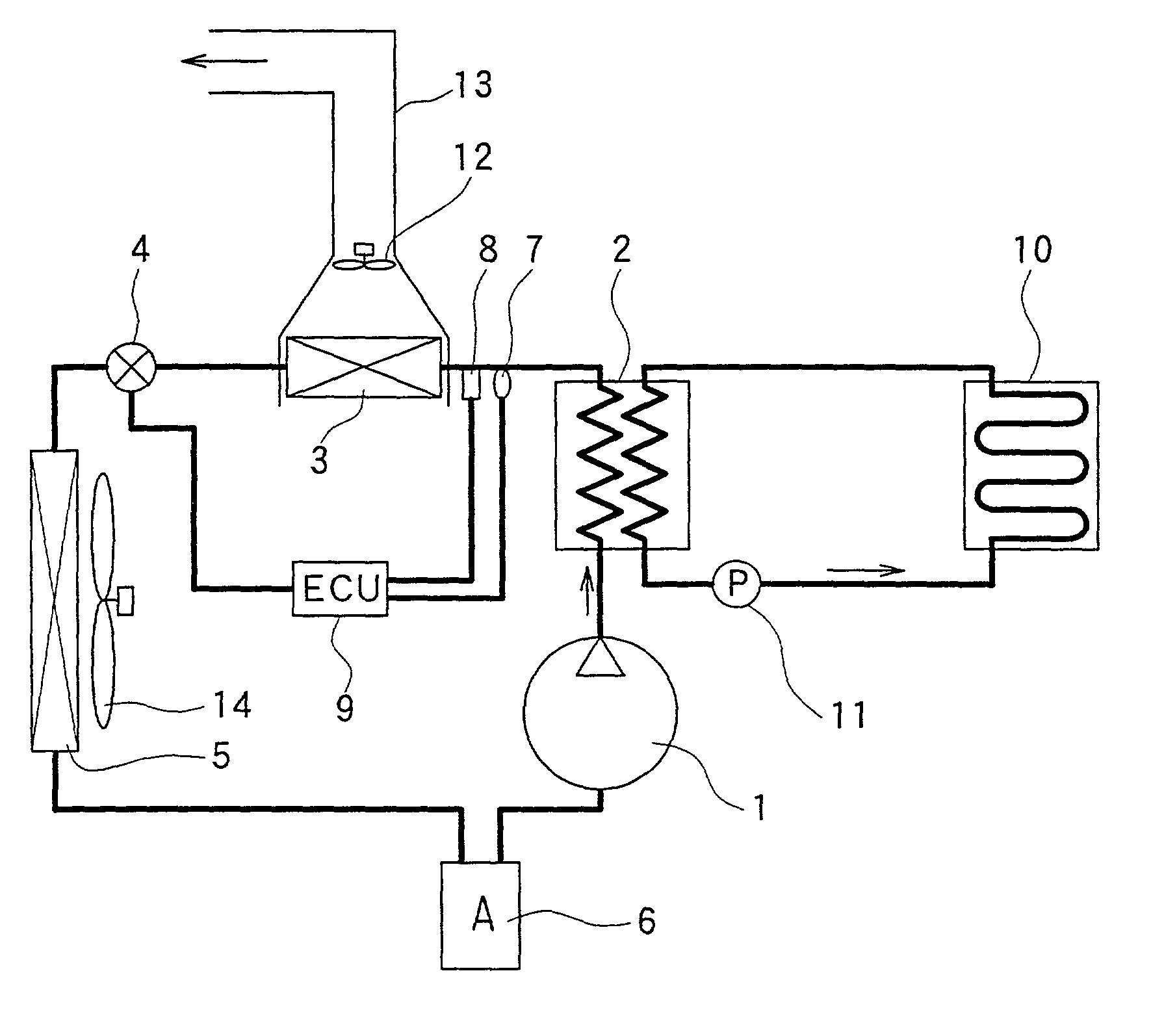
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1127results about "Compression machines with several condensers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heat engine
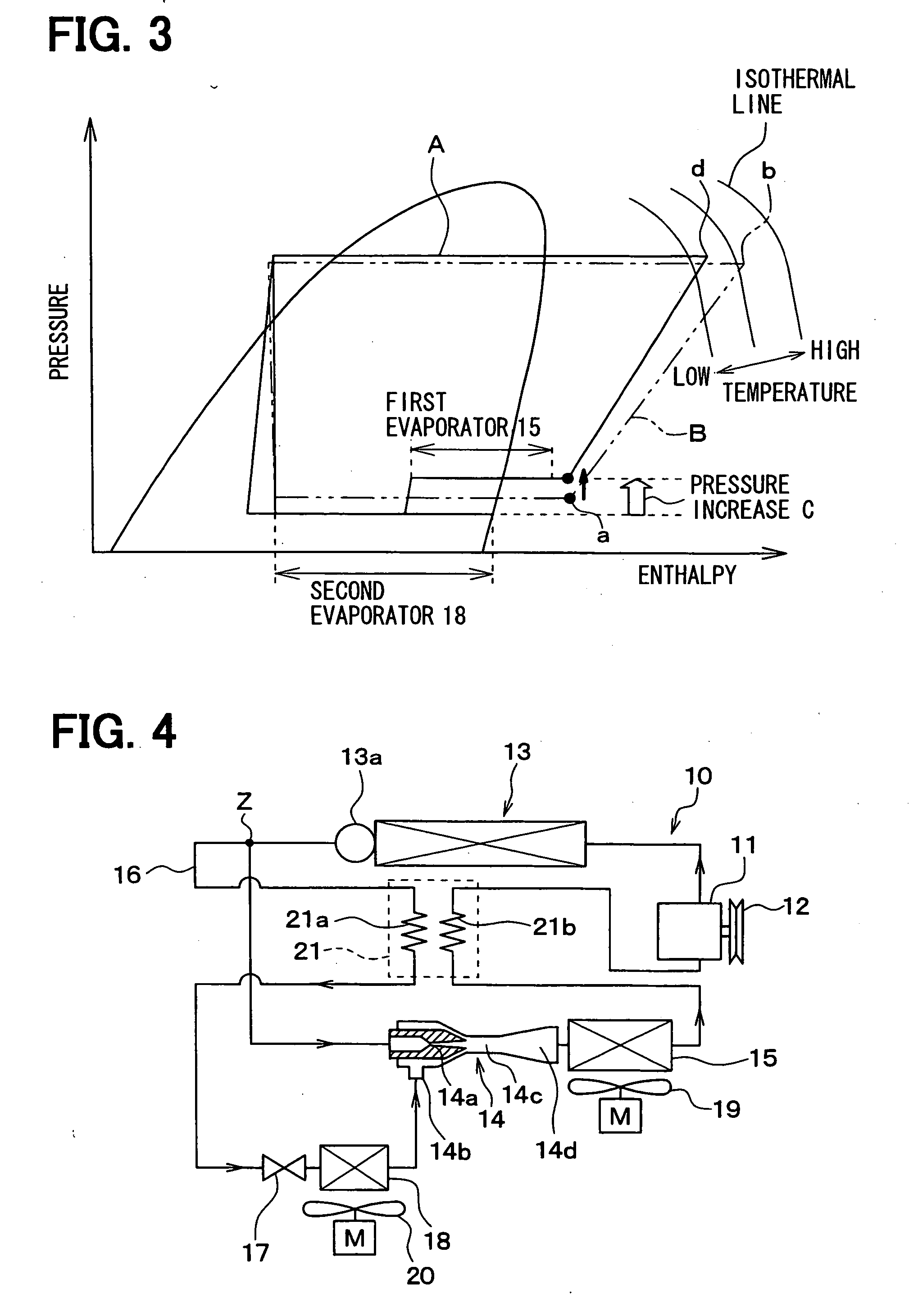
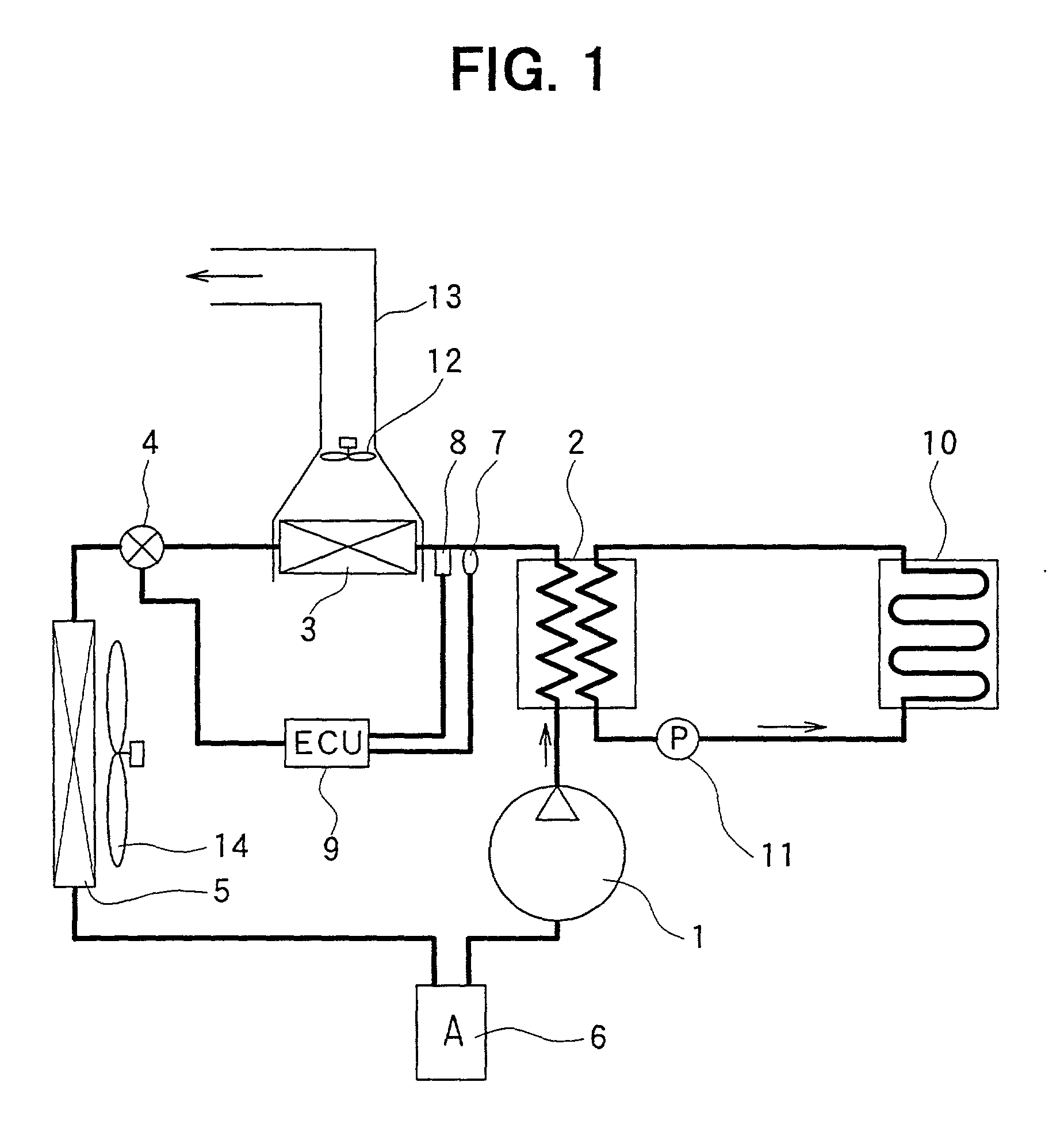
InactiveUS20030000213A1Easy to operateBoilers/analysersClimate change adaptationWorking fluidEngineering
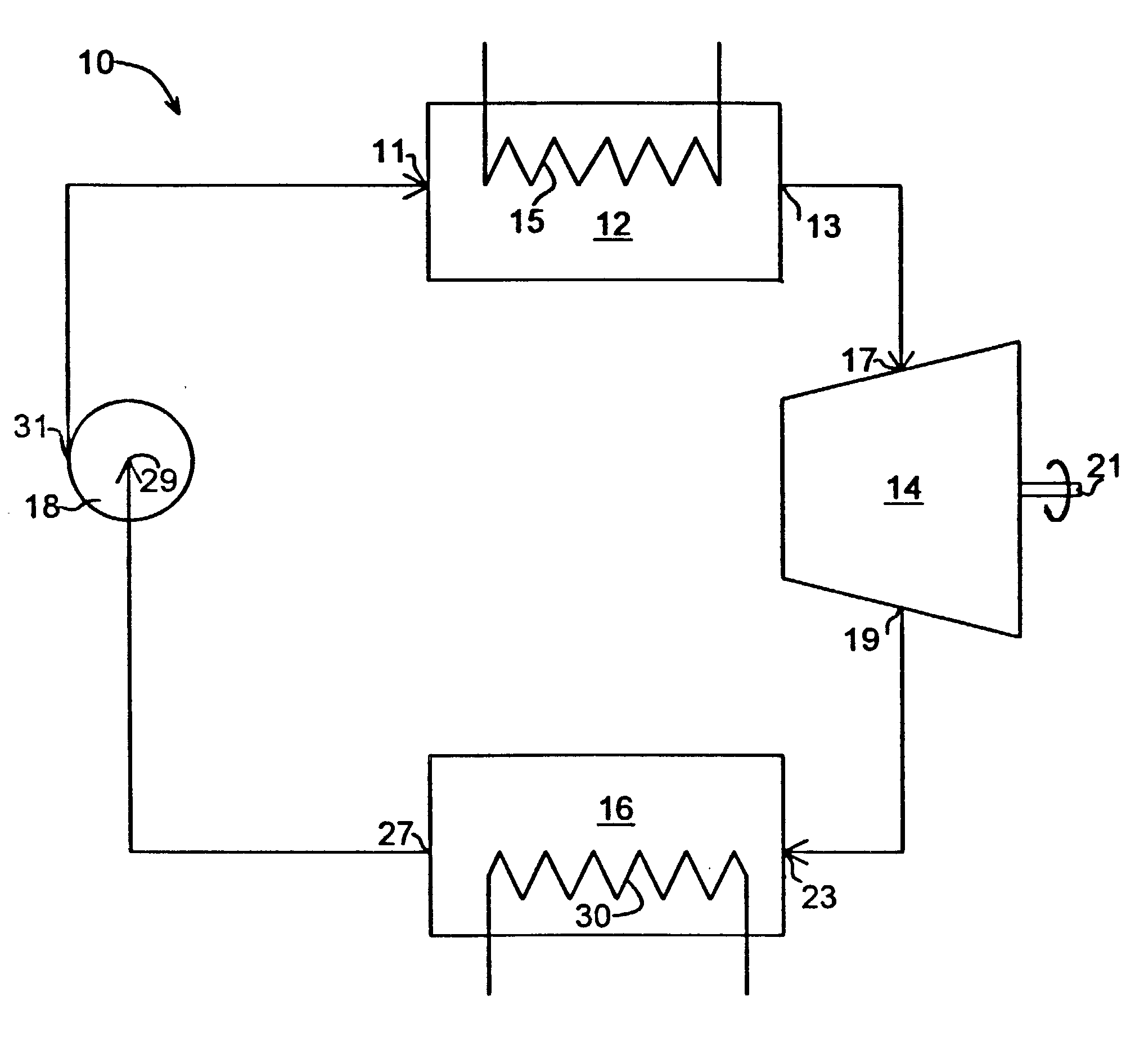
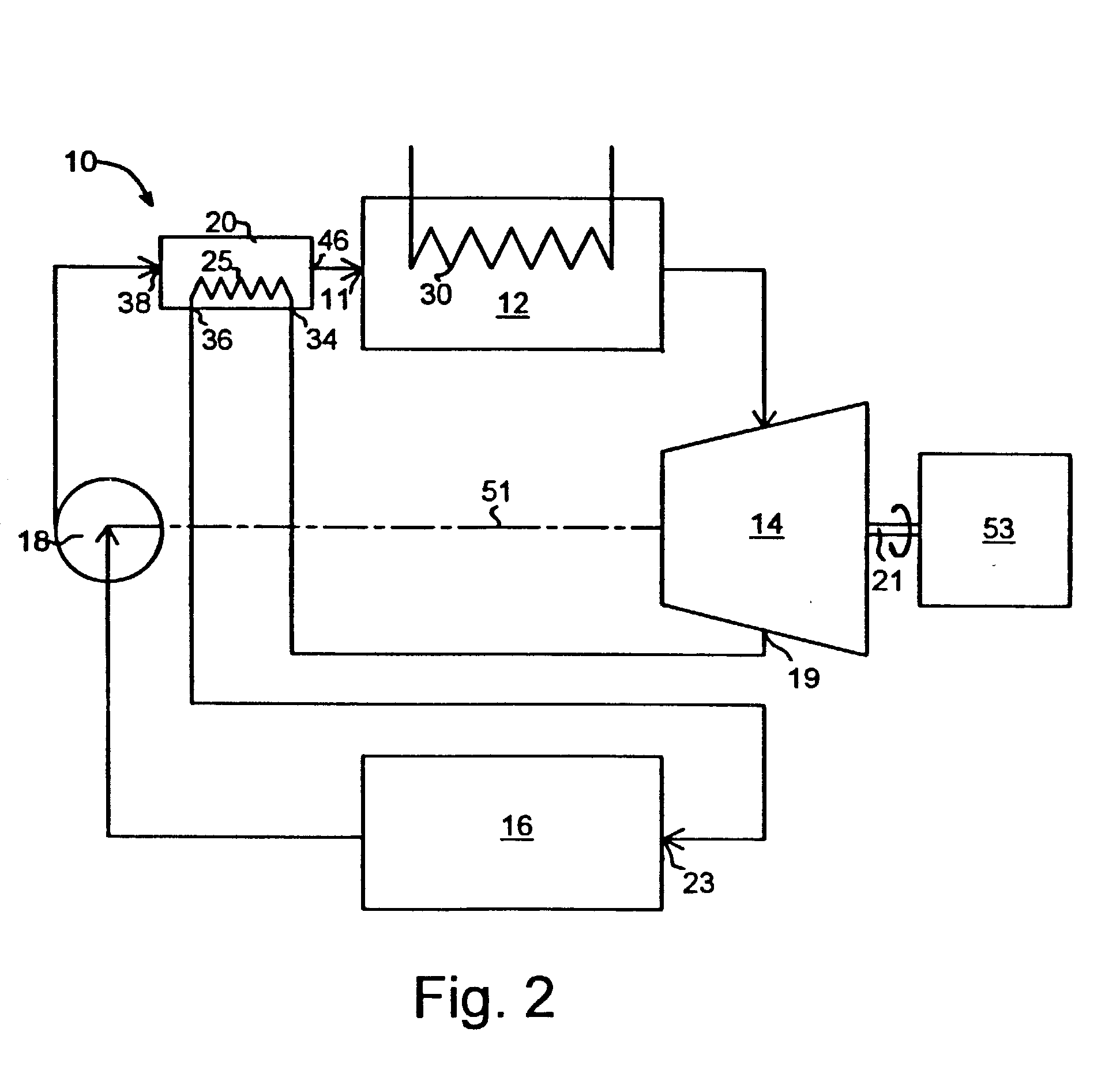
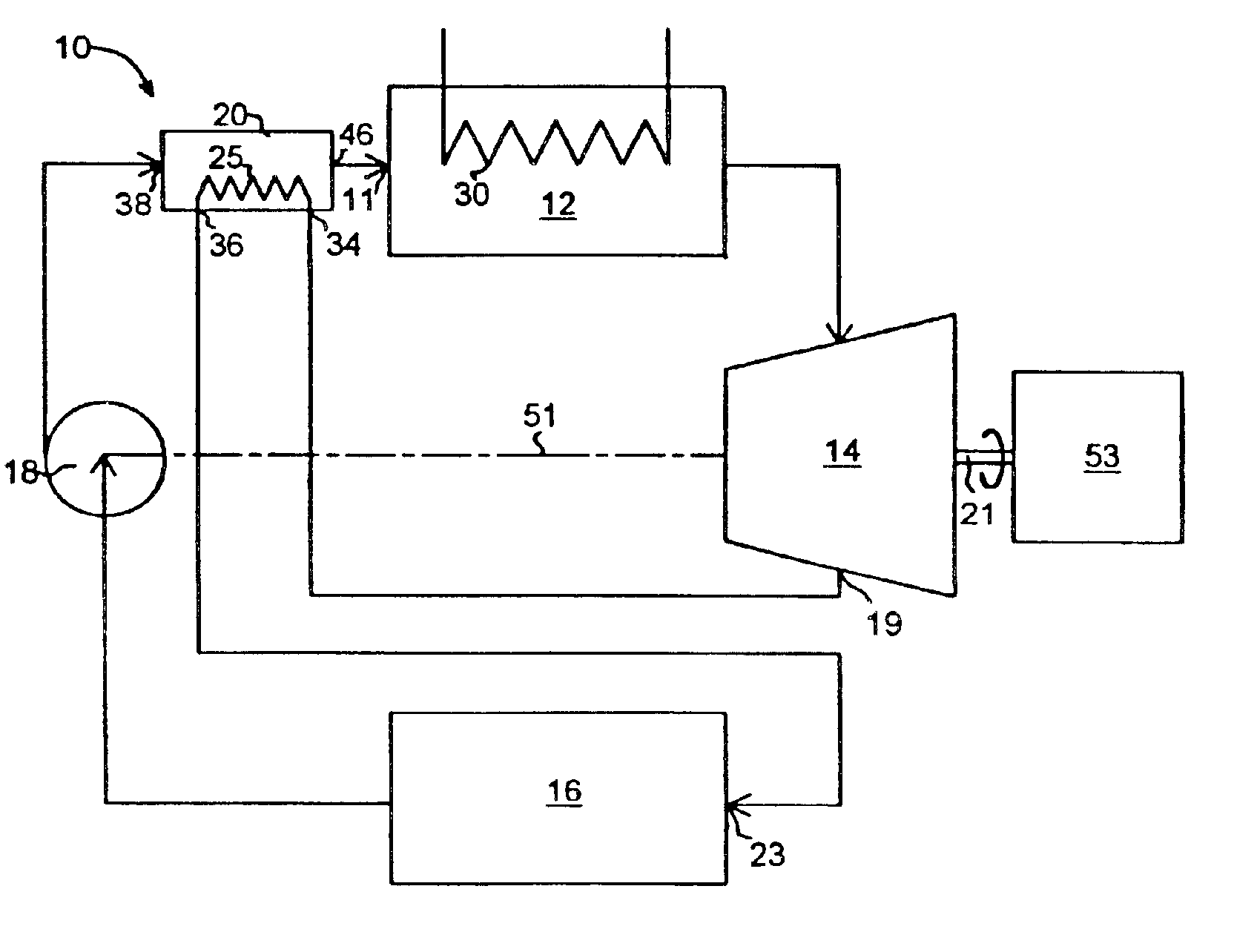
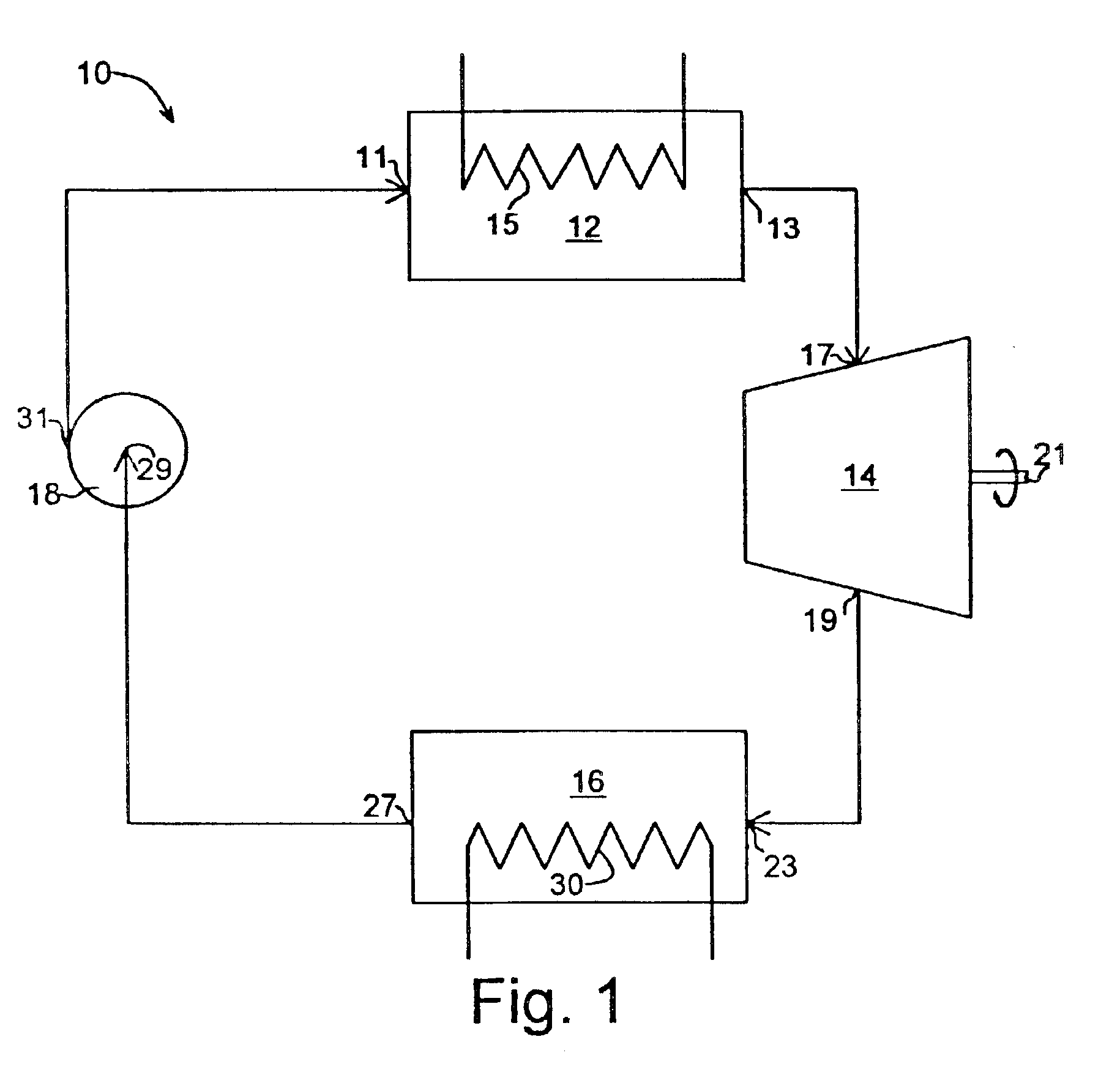
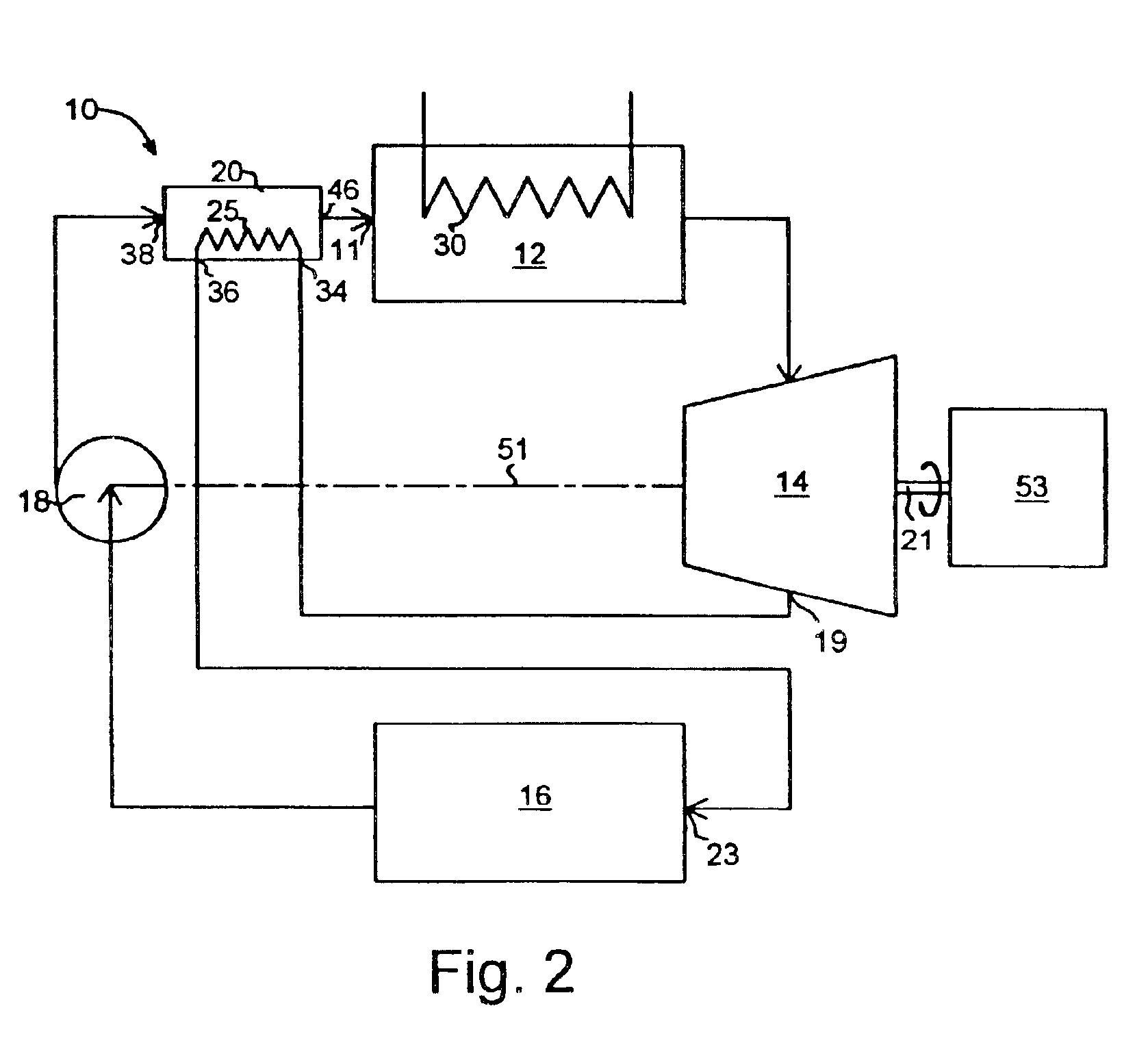
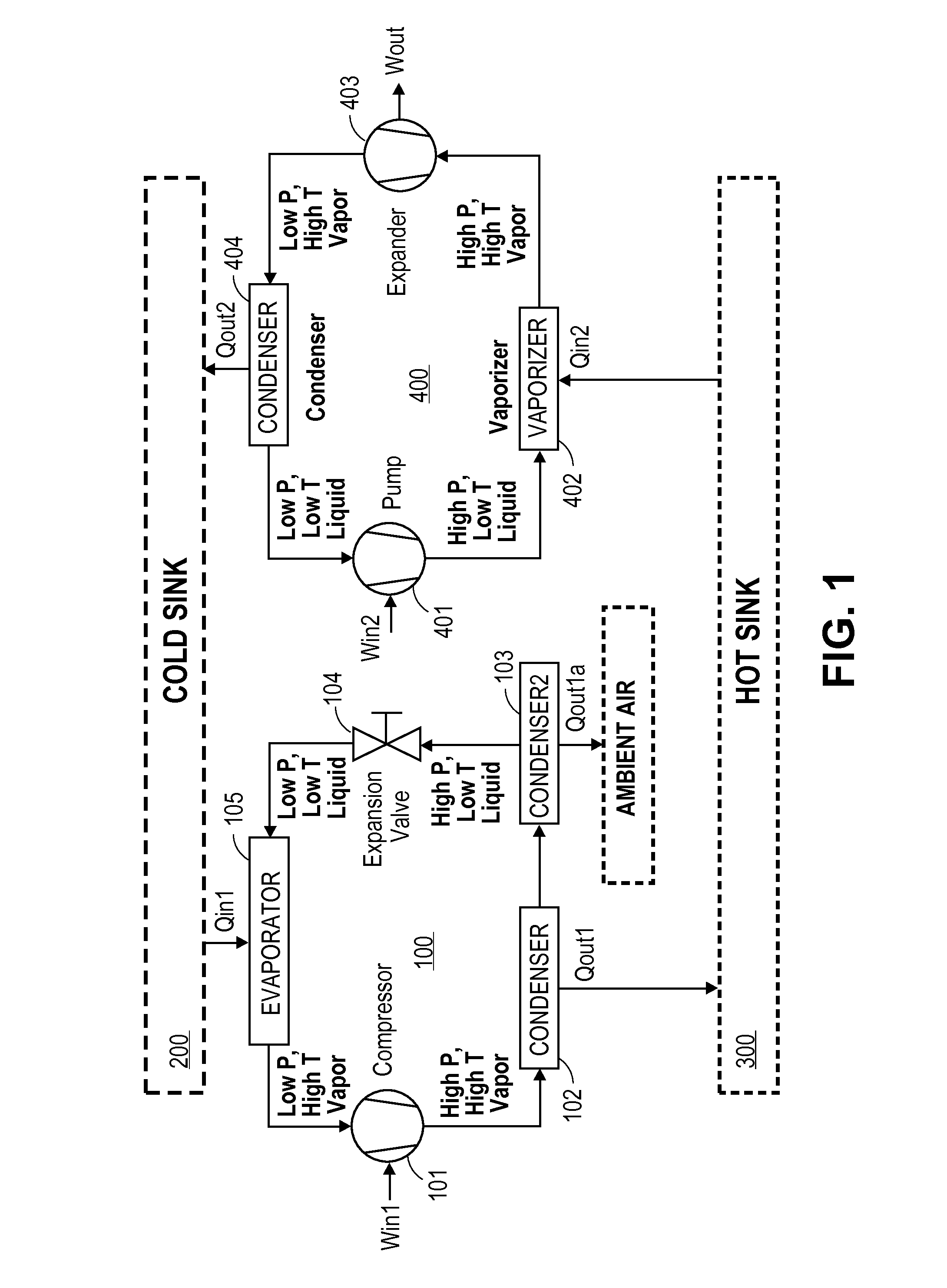
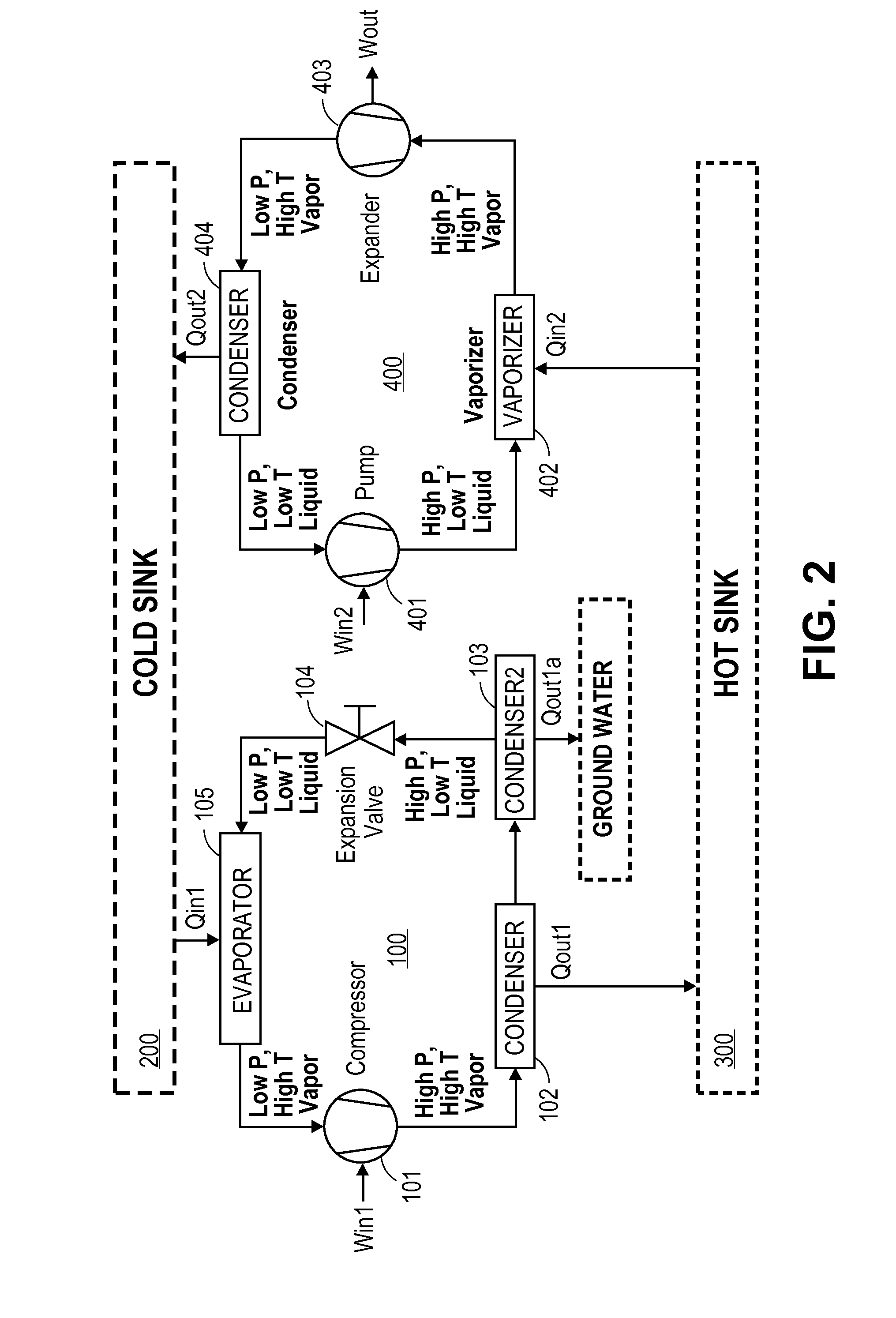
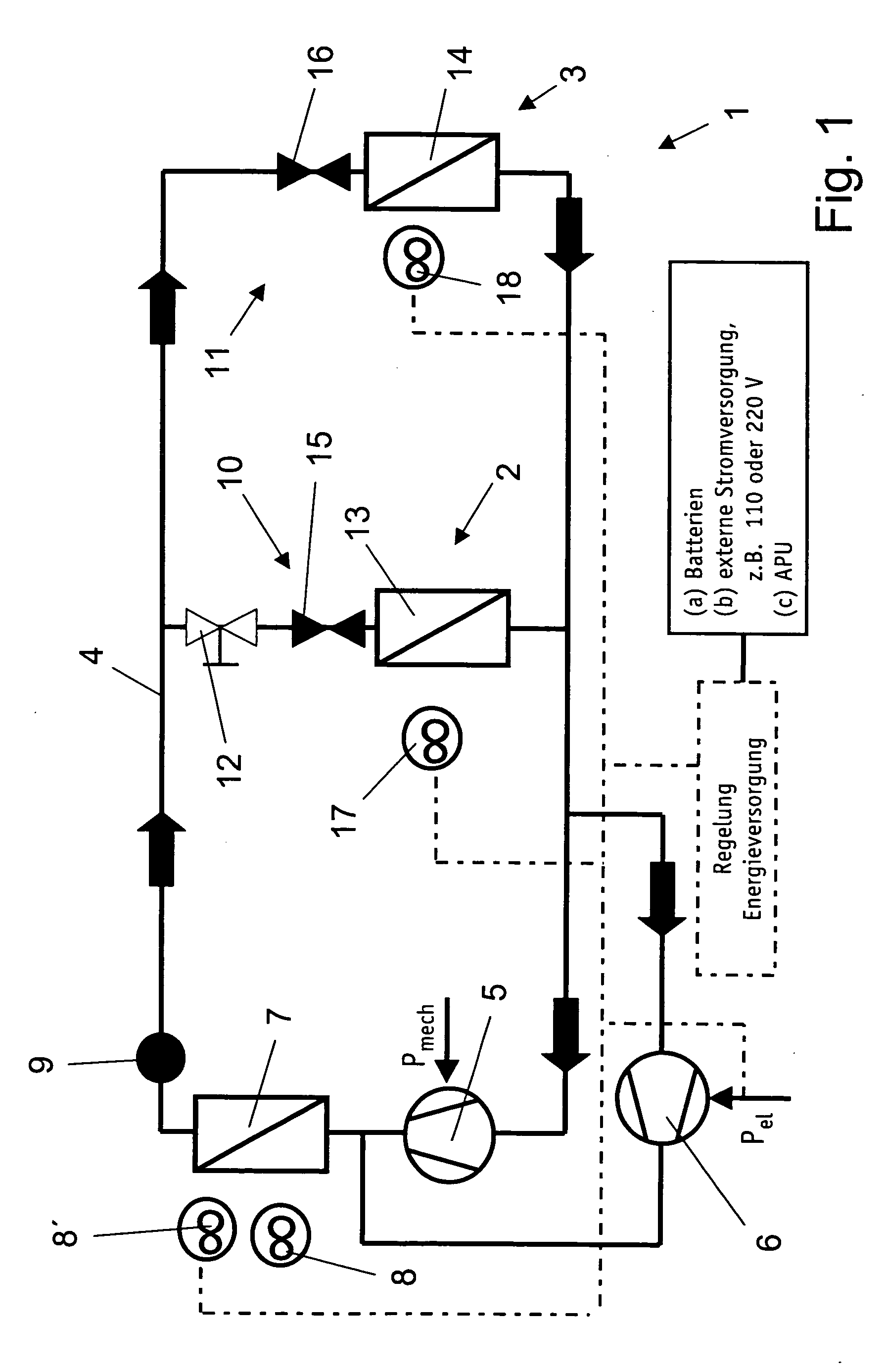
A heat engine (10) achieves operational efficiencies by: 1) recovering waste heat from heat engine expander (14) to preheat heat-engine working fluid, 2) using super-heated working fluid from compressor (402) to pre-heat heat-engine working fluid, and 3) using reject heat from condenser (93) and absorber (95) to heat the heat-engine boiler (12). A dual heat-exchange generator (72) affords continuous operation by using gas-fired heat exchanger (212) to heat generator (72) when intermittent heat source (40), e.g., solar, is incapable of heating generator (72). The combination of heat engine (10) and absorption and compression heat transfer devices (60, 410) allows use of low-temperature heat sources such as solar, bio-mass, and waste heat to provide refrigeration, heating, work output including pumping and heating of subterranean water and electrical generation.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
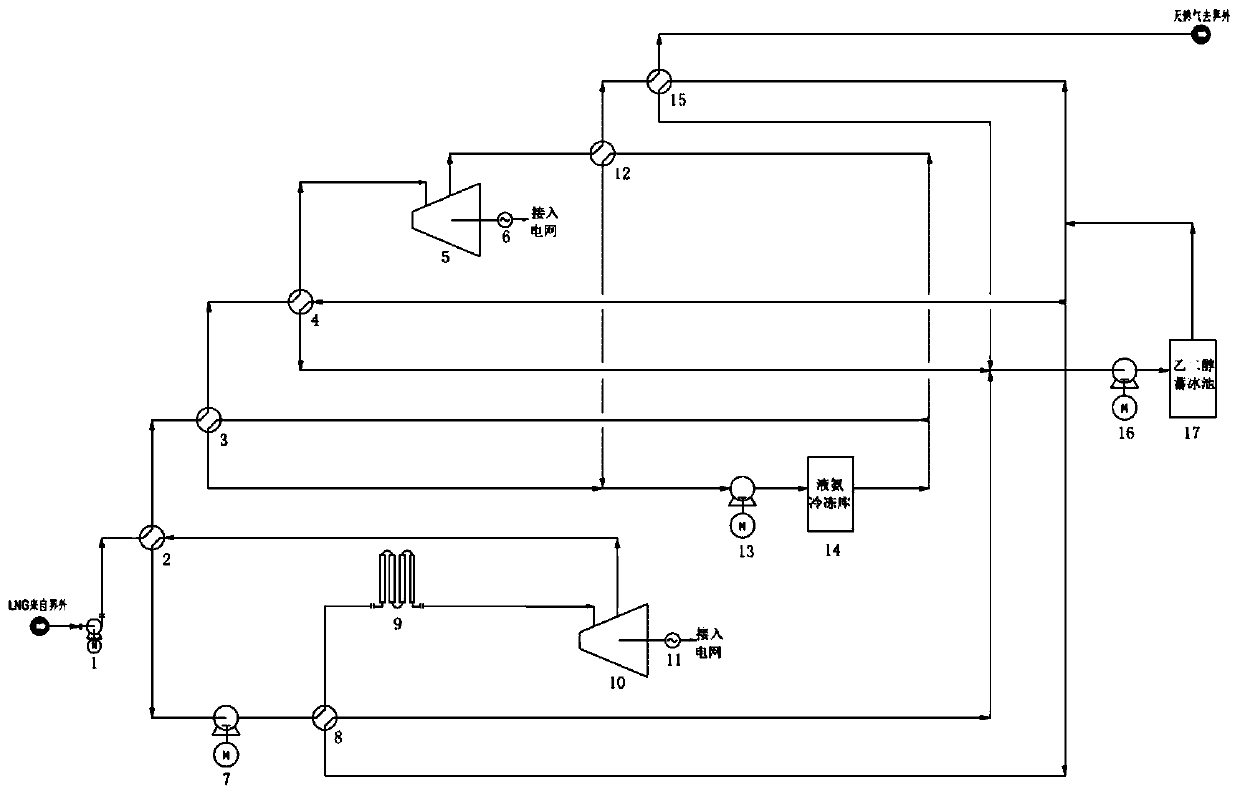
System for comprehensively utilizing LNG cold energy for power generation and cold supply
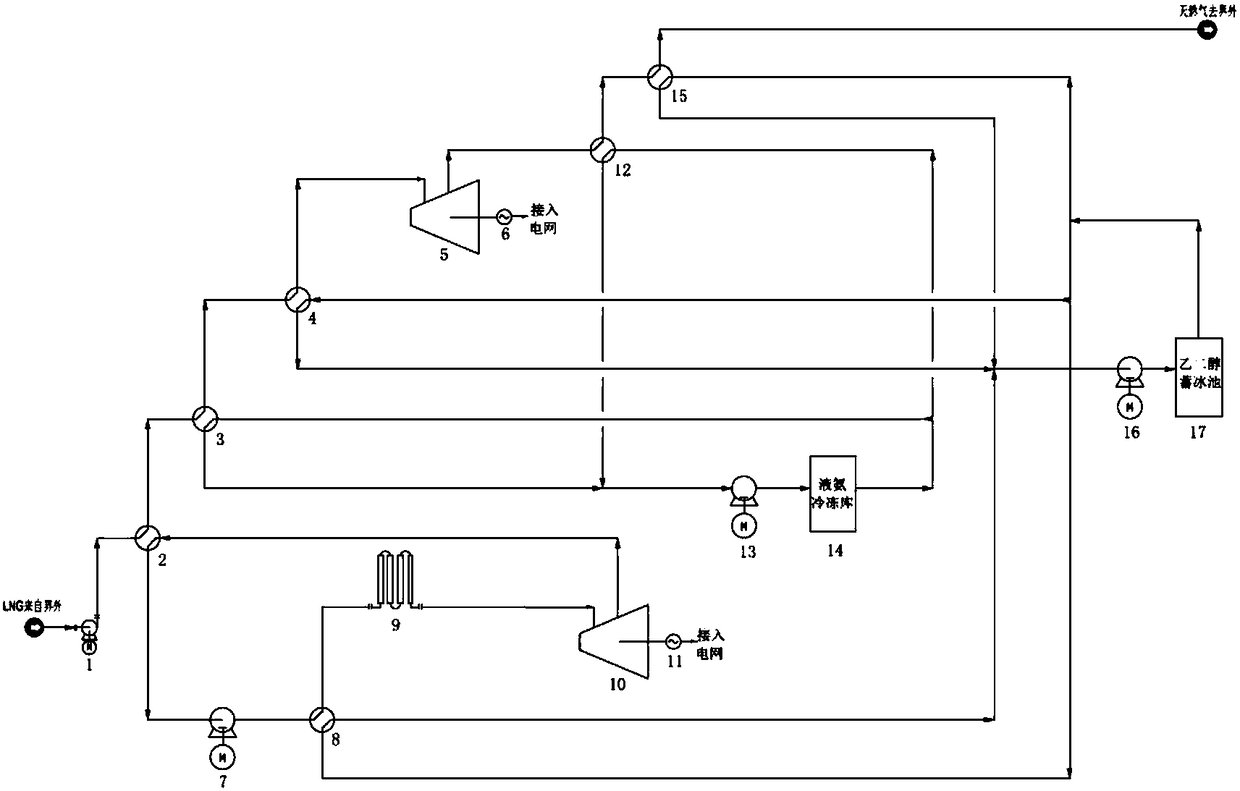
ActiveCN108087050AImprove utilization efficiencyClimate change adaptationCompression machines with several condensersIce storageRefrigeration
The invention relates to a system for comprehensively utilizing LNG cold energy for power generation and cold supply. The system comprises a LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation system, a mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation system, a liquid ammonia refrigeration house cold supply system and an ethylene glycol ice storage bath air conditioner cold supplycirculation system. The cold energy released in the LNG gasification process is utilized; high-grade electric energy is generated through LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation and mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation; cold is supplied to a refrigeration house through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ammonia recycling; and cold is supplied to an air conditioner through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ethylene glycol ice storage bath recycling. By means of the system, gradient utilization of the LNG cold energy is achieved, and the cold energy utilization efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN HENGRI GAS ENG CO LTD
A system for comprehensive utilization of lng cold energy for power generation and cooling
ActiveCN108087050BImprove utilization efficiencyClimate change adaptationCompression machines with several condensersIce storageEngineering
The invention relates to a system for comprehensively utilizing LNG cold energy for power generation and cold supply. The system comprises a LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation system, a mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation system, a liquid ammonia refrigeration house cold supply system and an ethylene glycol ice storage bath air conditioner cold supplycirculation system. The cold energy released in the LNG gasification process is utilized; high-grade electric energy is generated through LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation and mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation; cold is supplied to a refrigeration house through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ammonia recycling; and cold is supplied to an air conditioner through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ethylene glycol ice storage bath recycling. By means of the system, gradient utilization of the LNG cold energy is achieved, and the cold energy utilization efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN HENGRI GAS ENG CO LTD
Air conditioner
InactiveUS6035653AMinimizing temperature overshootMinimization needsAir-treating devicesMechanical apparatusResponsivityEngineering
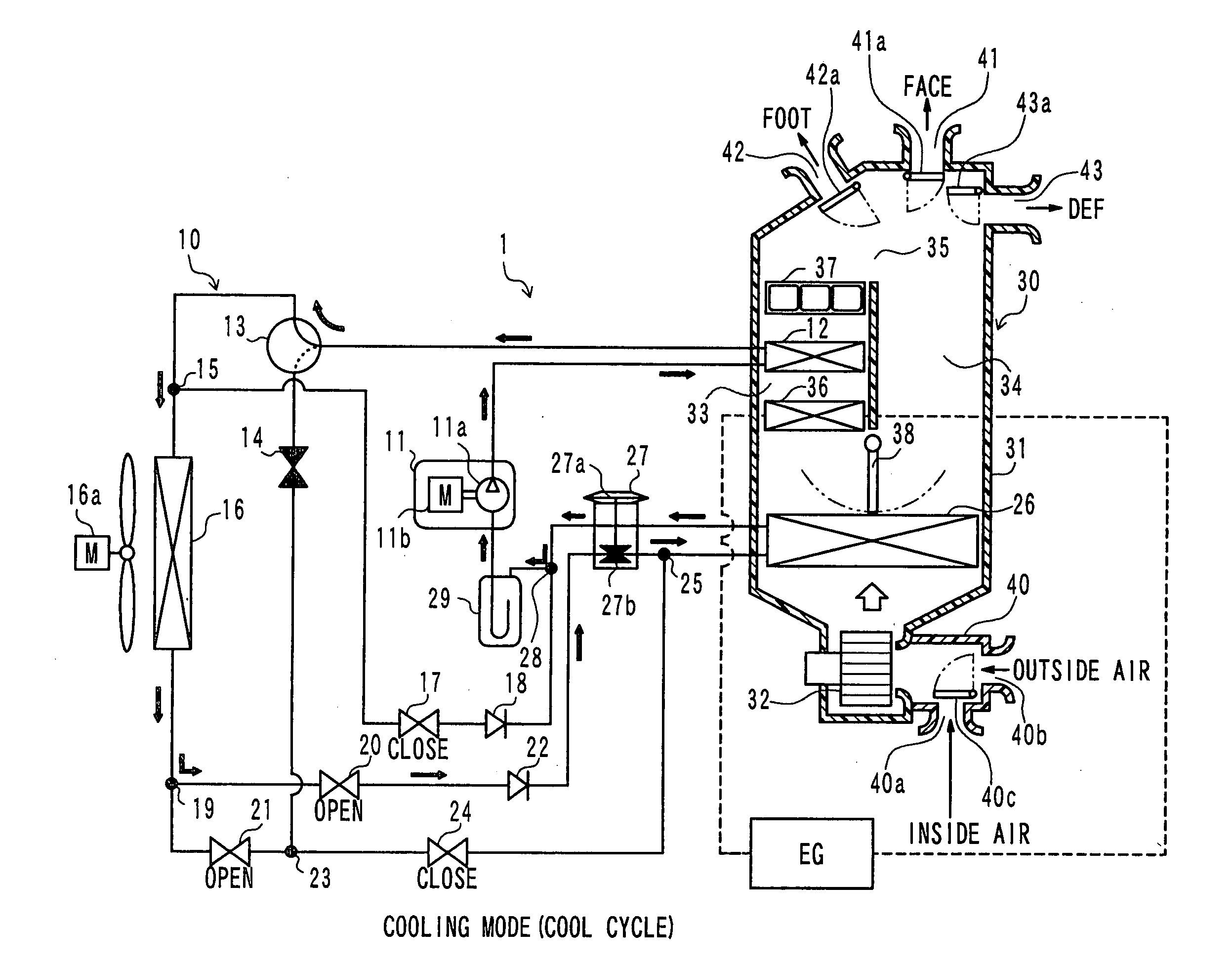
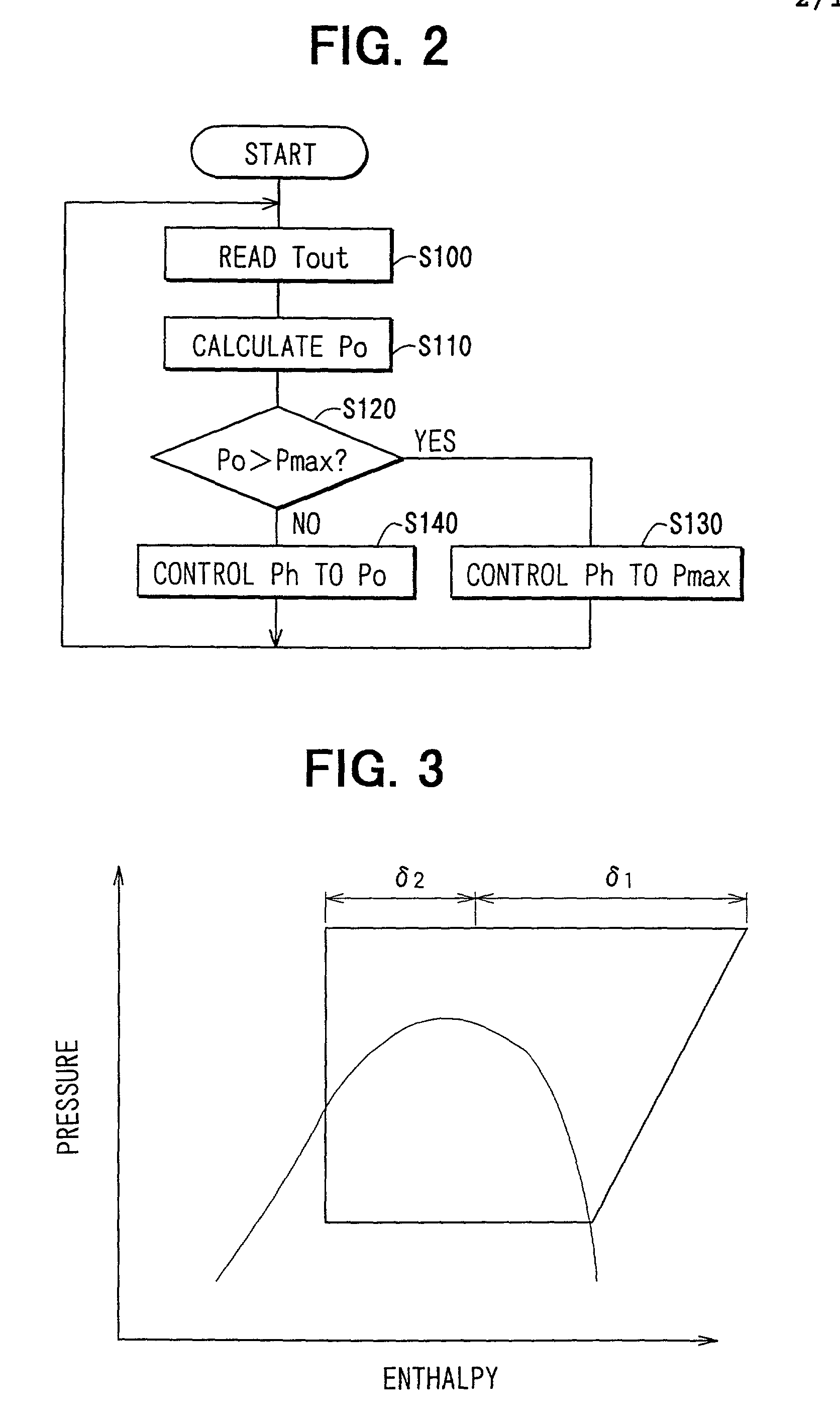
An air conditioner capable of enhancing responsivity of a blowout temperature of conditioned air while preventing occurrence of an overshoot or undershoot condition of the blowout temperature when a user gives an instruction to change the blowout temperature in a dehumidifying operation mode. In a control state, if a set temperature level is adjusted to increase a blowout temperature of conditioned air by increasing the target condenser outlet temperature, the rotating speed of the refrigerant compressor is increased, while the restriction opening of the heating expansion valve is maintained. Thus, the condenser outlet temperature is regulated to the target temperature with minimal undershoot or overshoot of the target temperature.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Heat engine
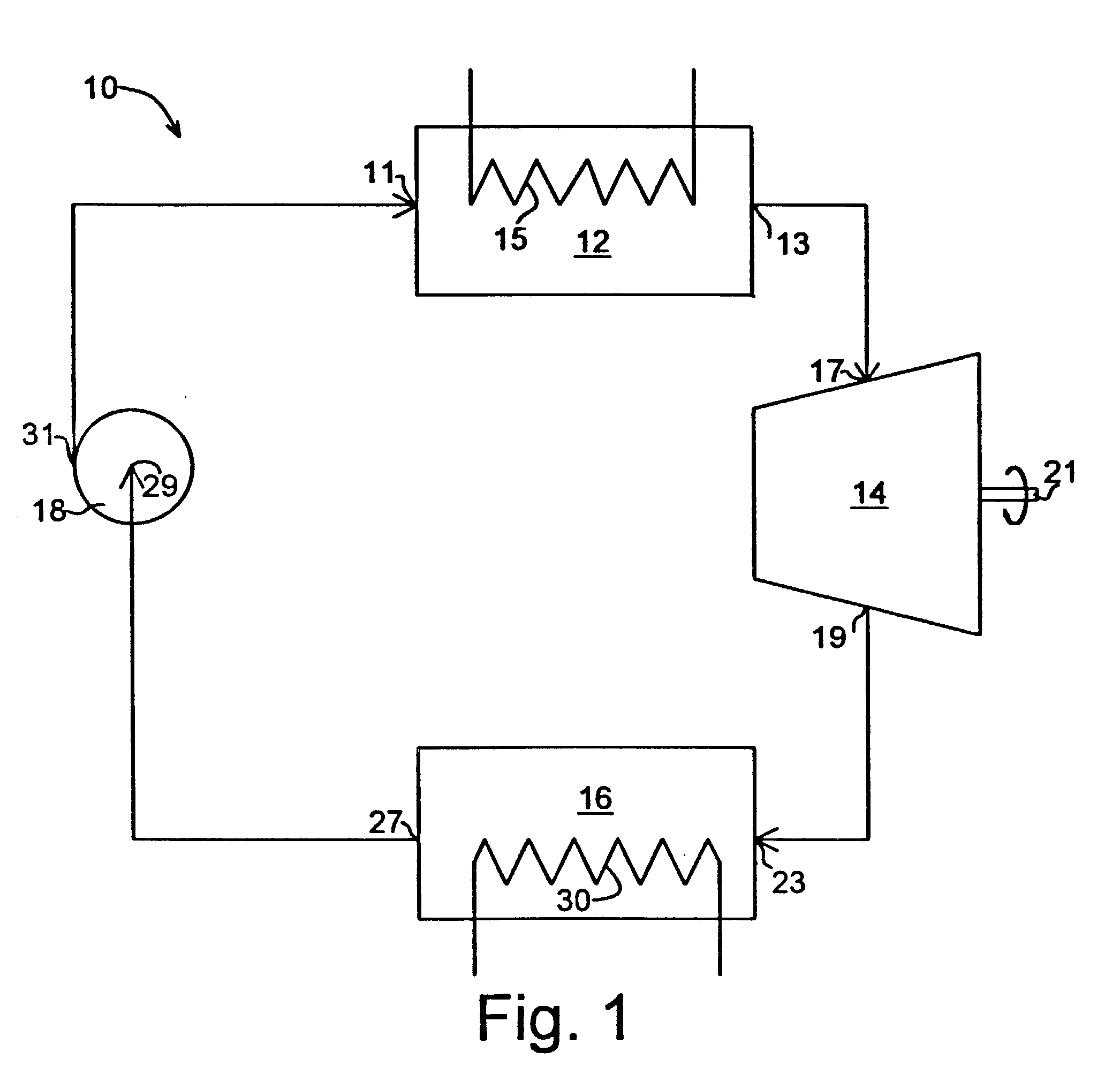
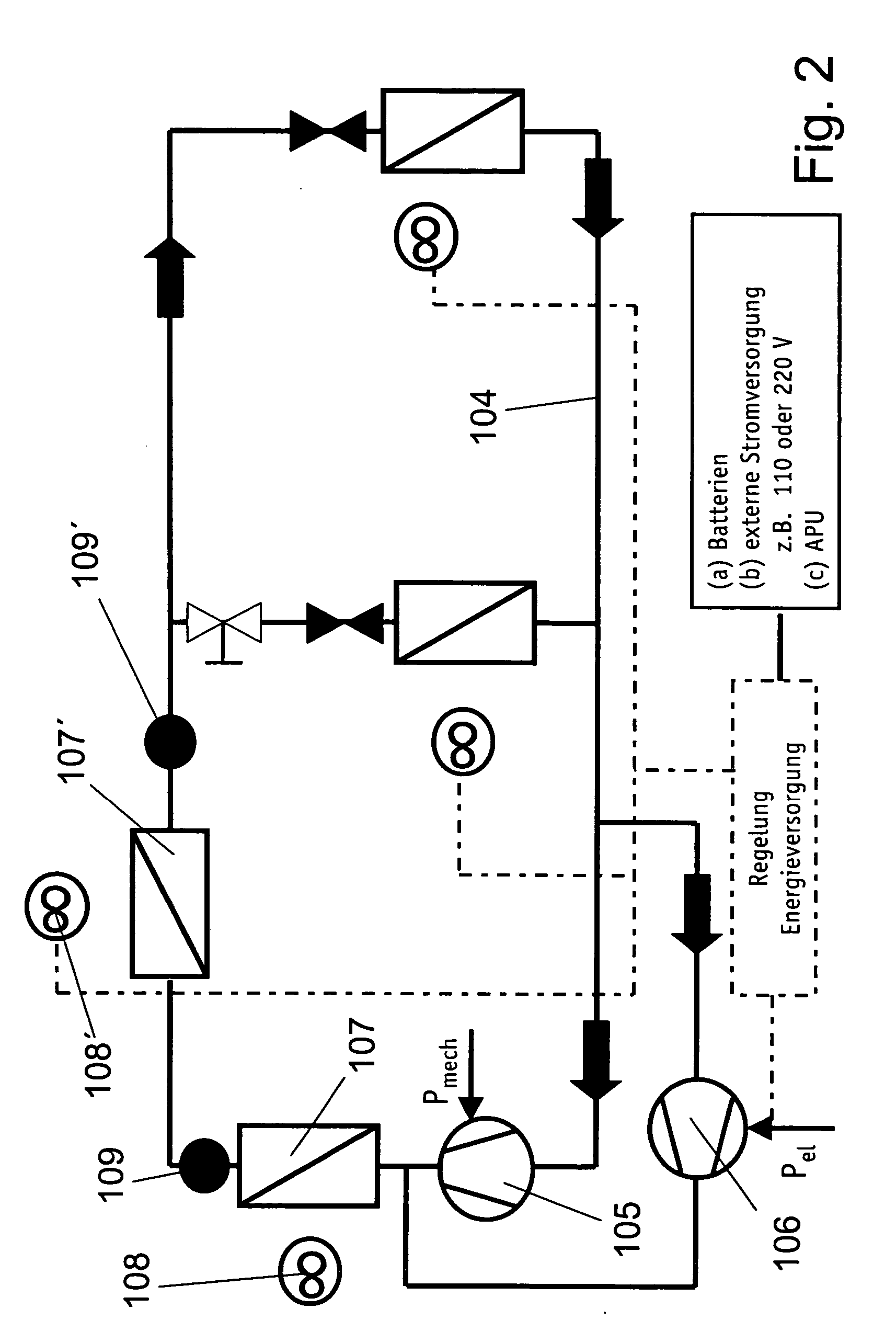
InactiveUS7062913B2Improve efficiencyBoilers/analysersClimate change adaptationWorking fluidEngineering
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
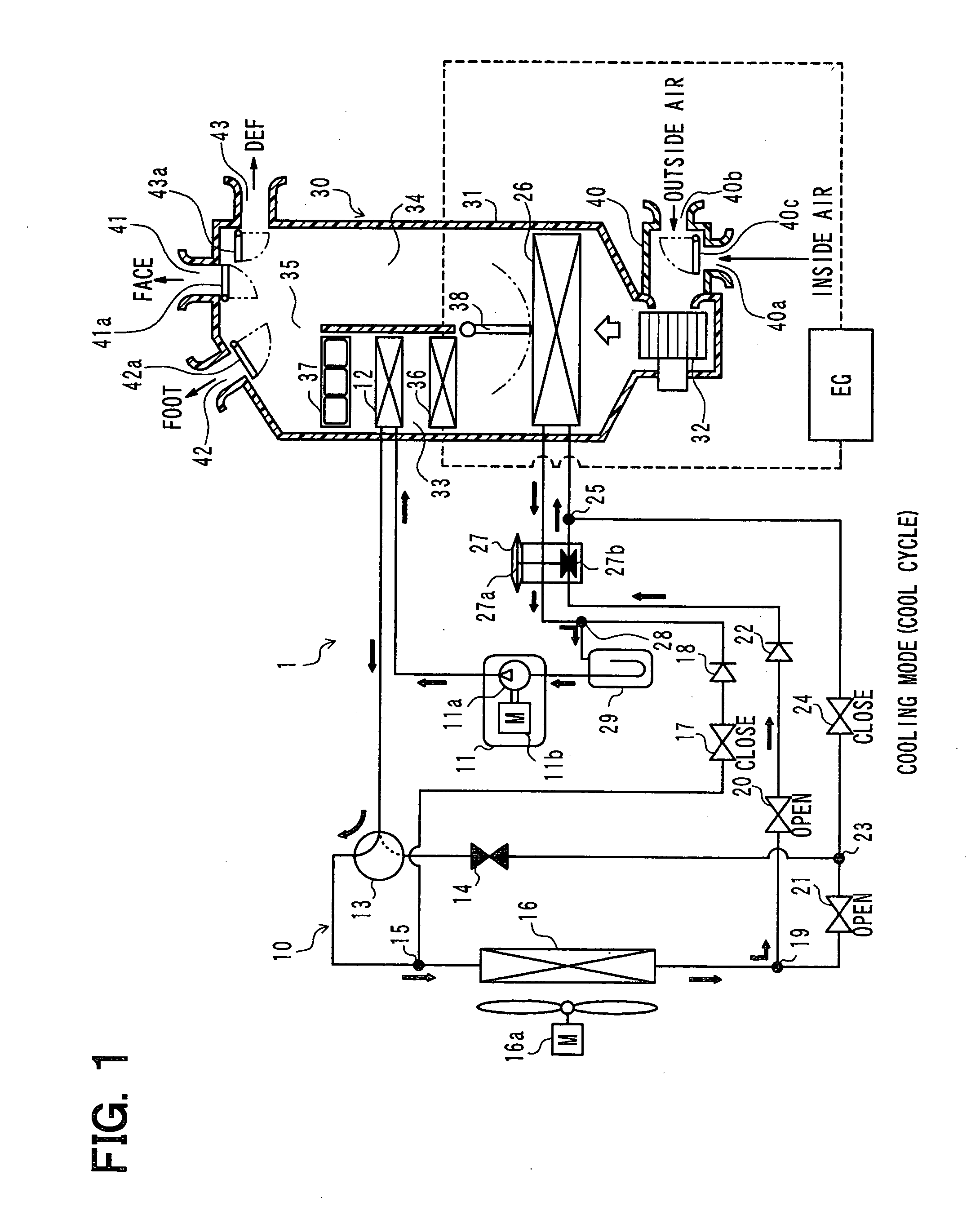
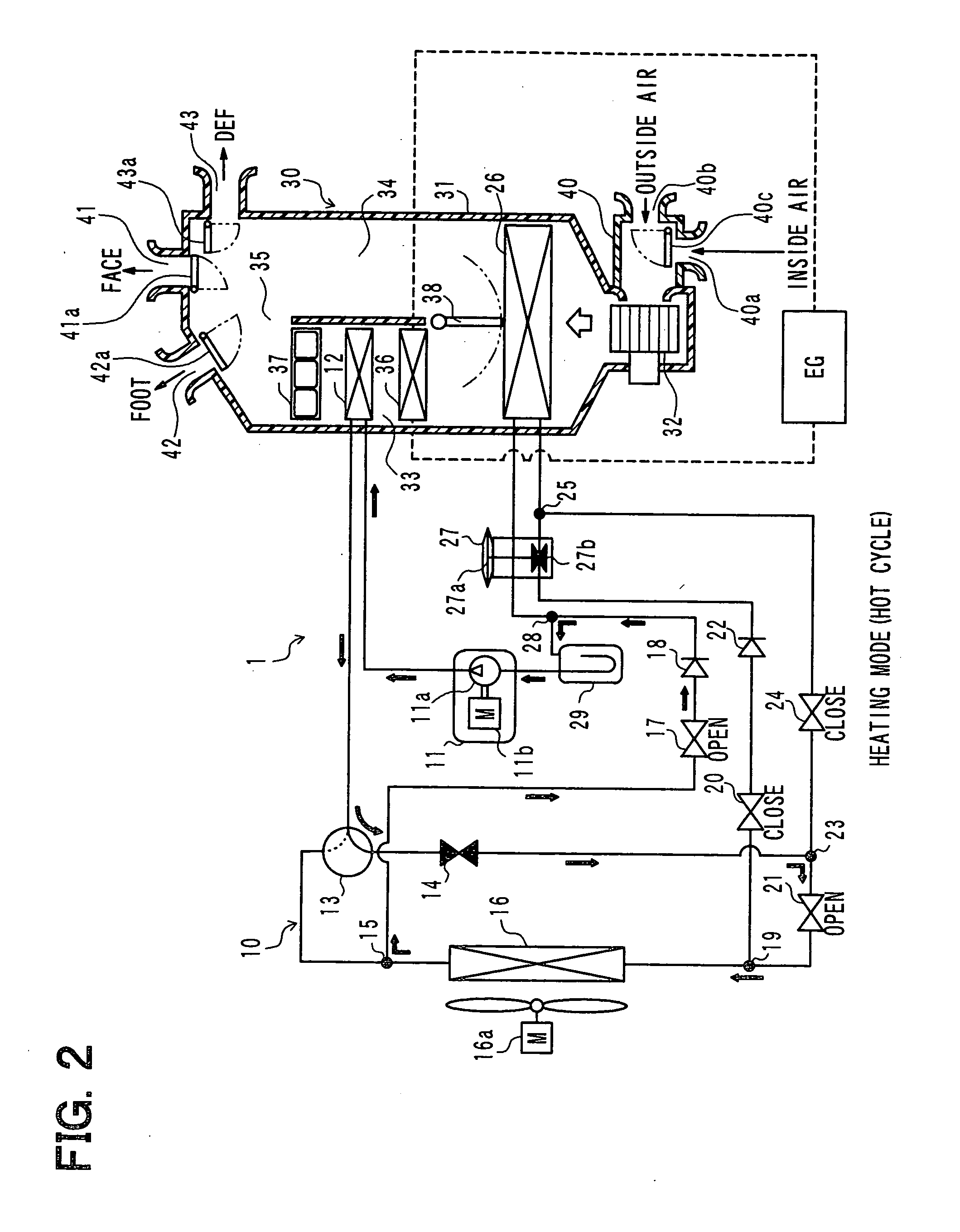
Air conditioner for vehicle with heat pump cycle
InactiveUS20100326127A1Effectively reducing fuel consumptionPrevent heating capacity being excessiveMechanical apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringInternal combustion engine
An air conditioner for a vehicle includes a vapor compression refrigeration cycle configured to have a heat pump cycle for heating air to be blown into an interior of a vehicle compartment, and a heating member for heating the air using a coolant of an internal combustion engine of the vehicle as a heat source. In the air conditioner, an operation request signal is output by an air conditioning controller to the internal combustion engine when an outside air temperature is lower than a predetermined threshold.
Owner:DENSO CORP
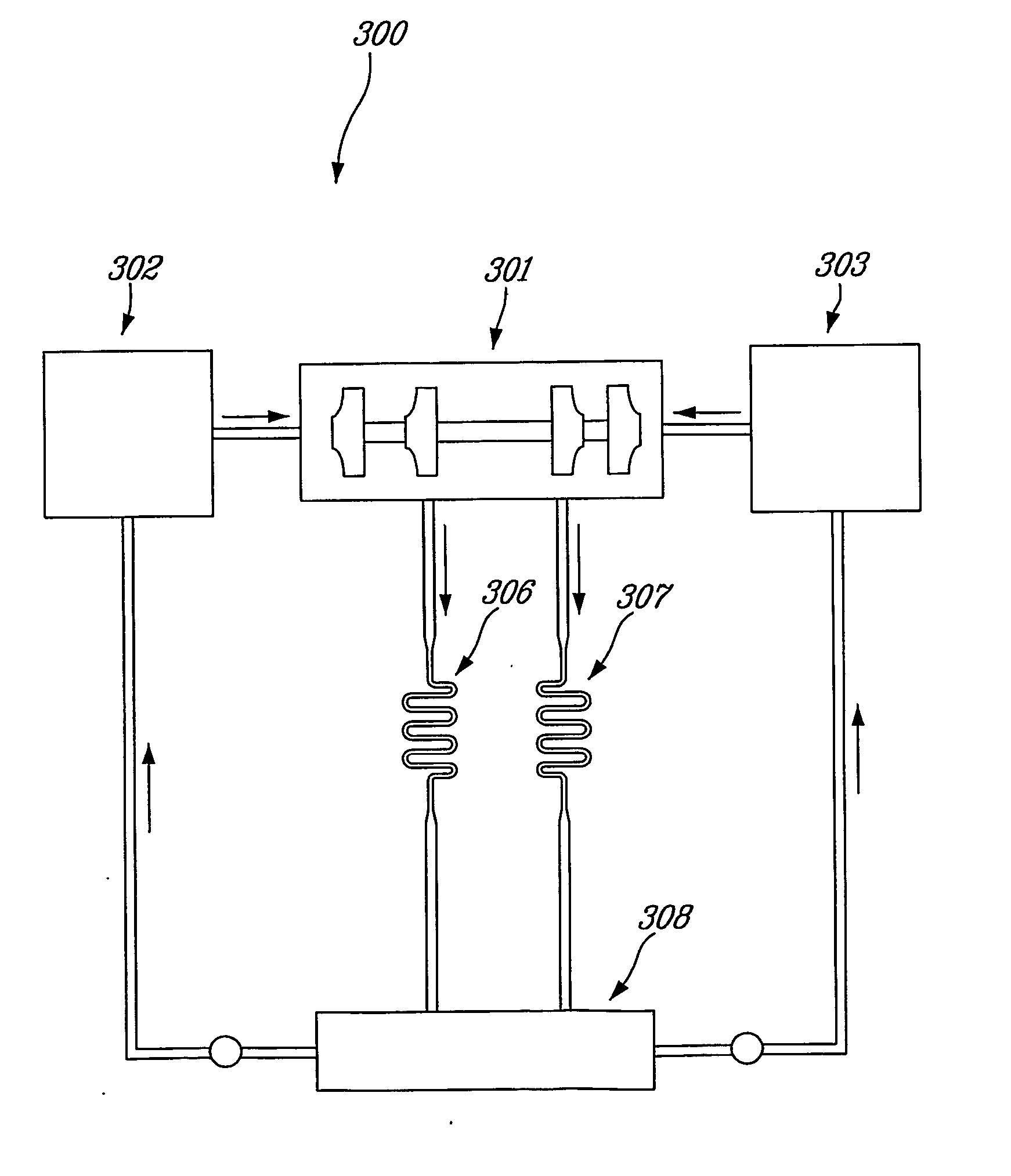
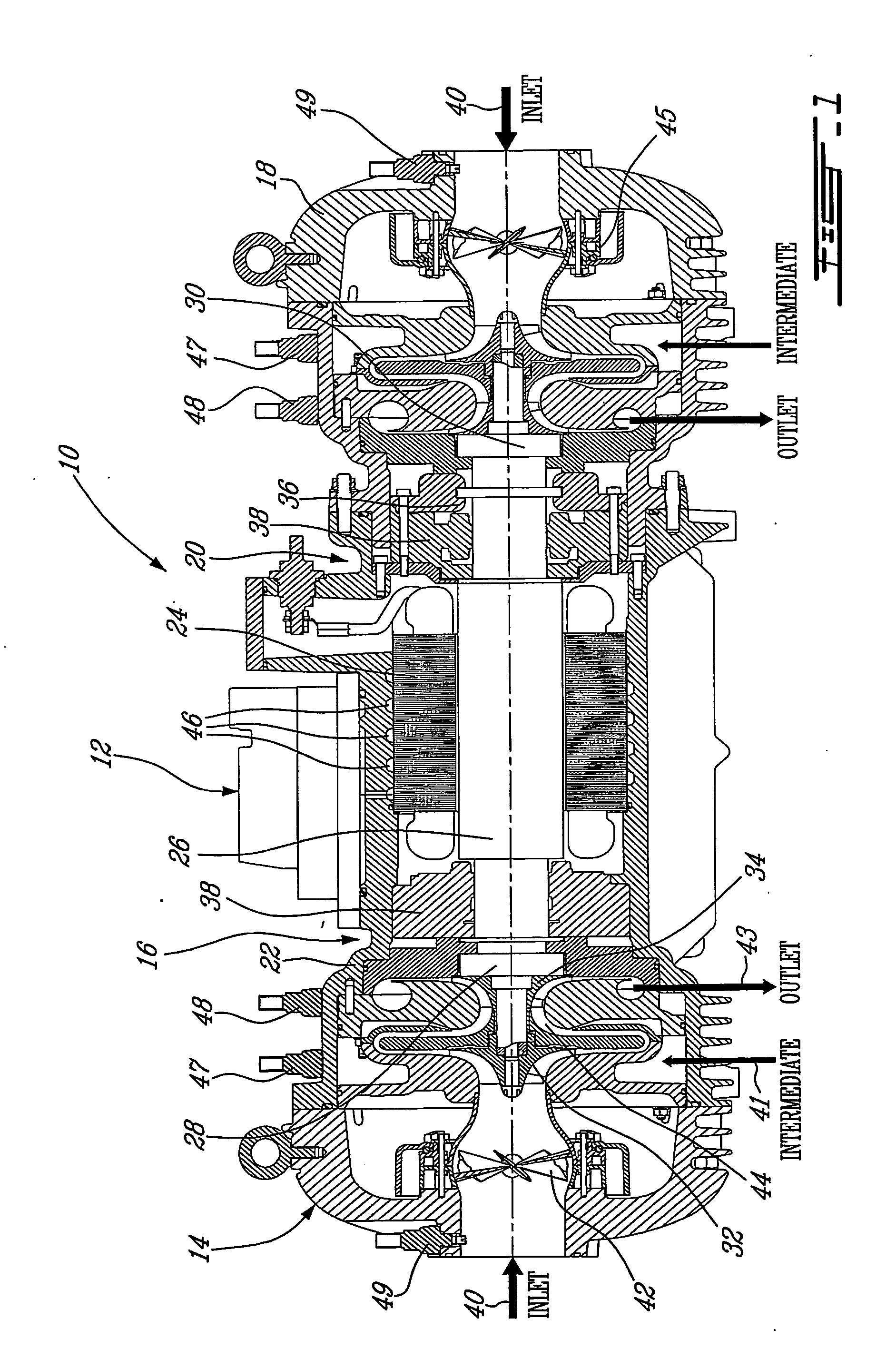
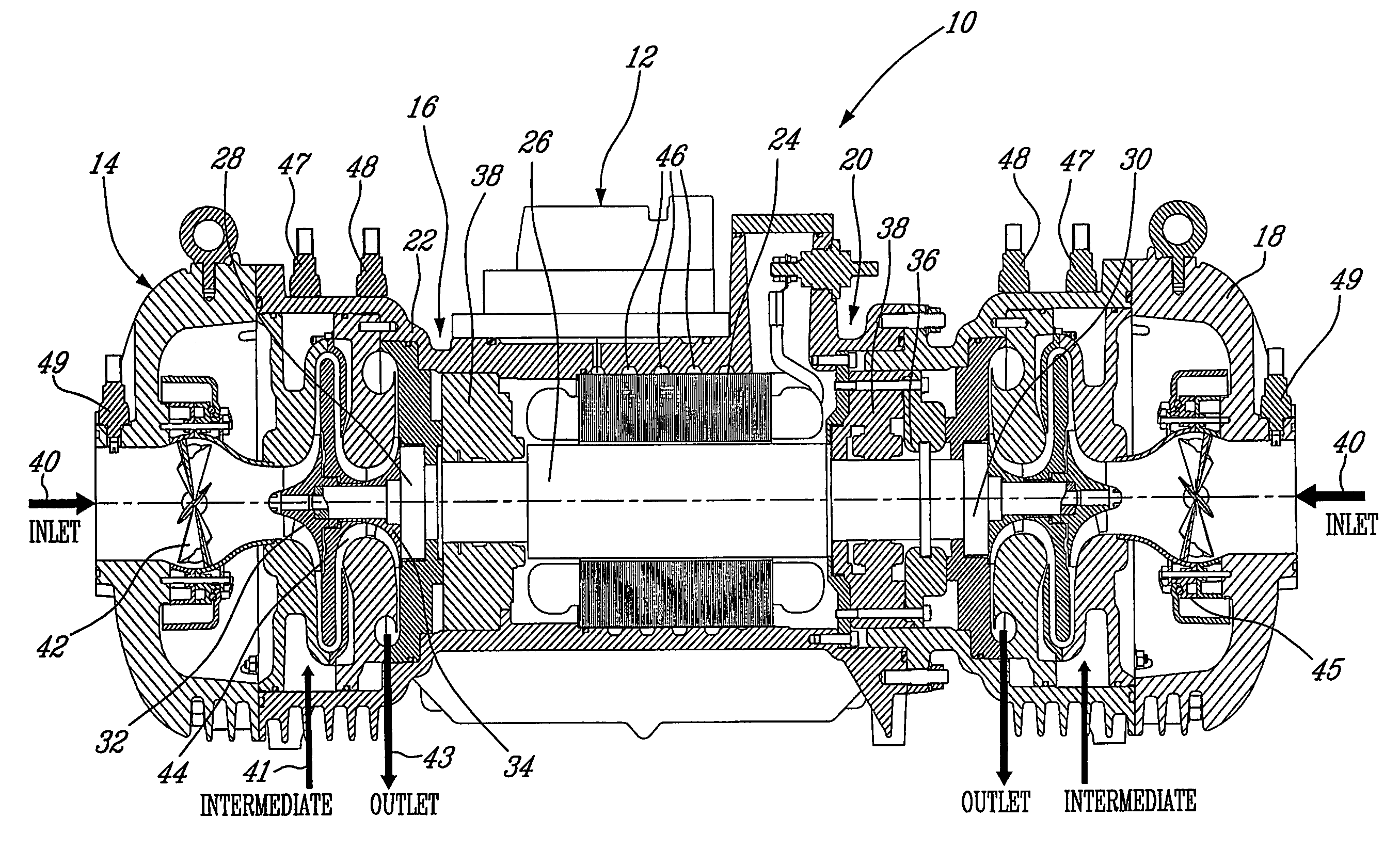
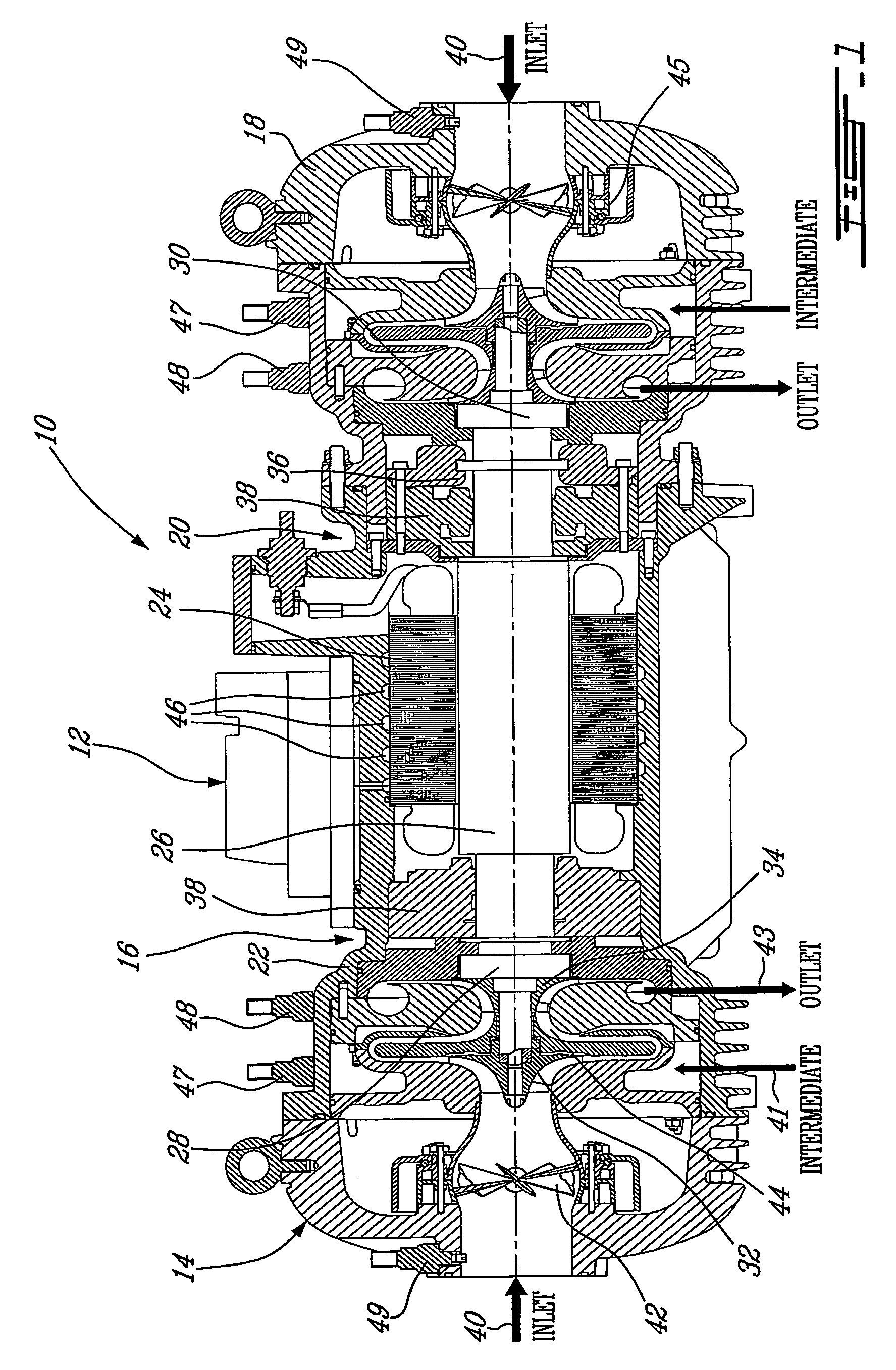
Centrifugal compressor
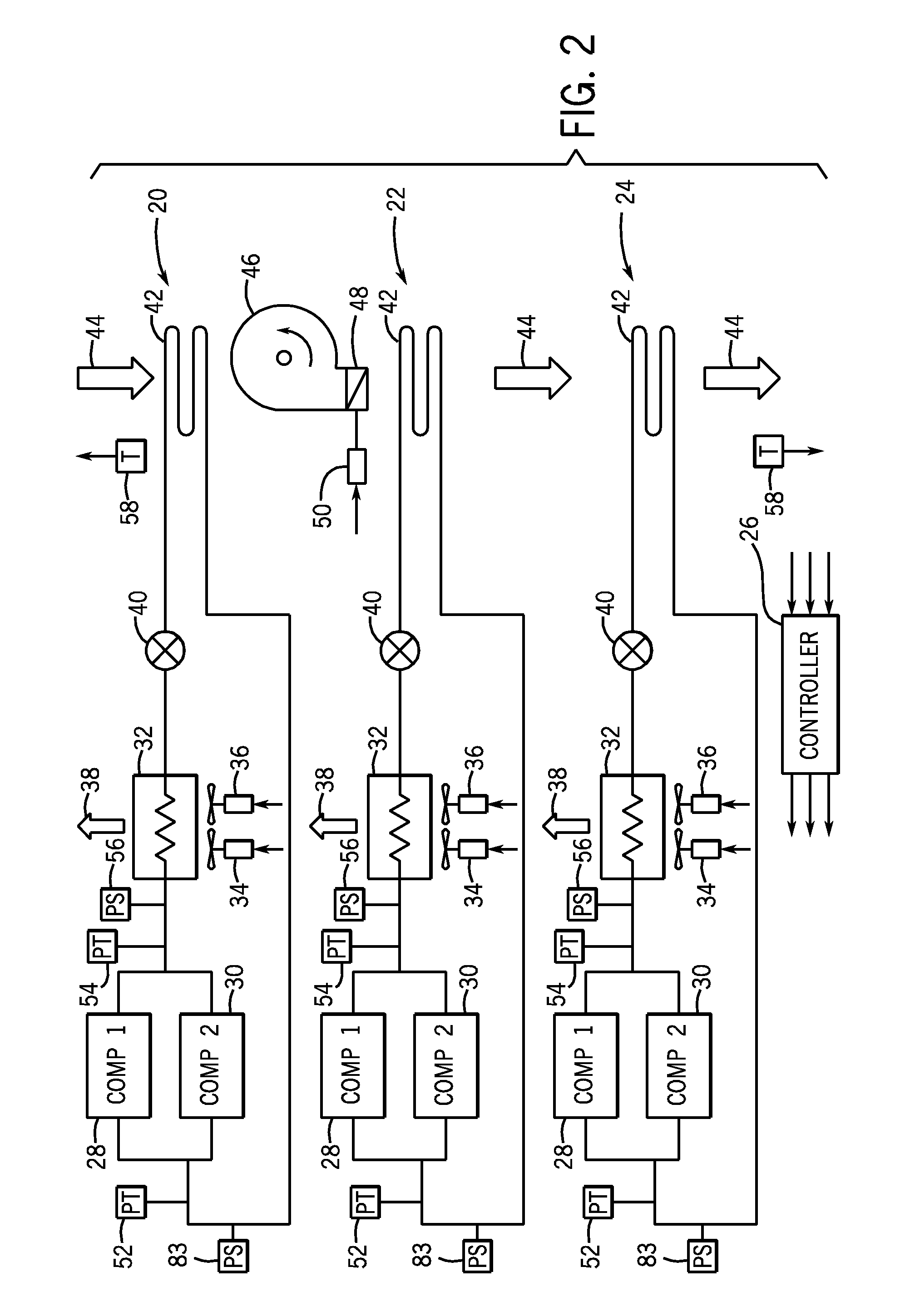
ActiveUS20050223737A1Improved centrifugal compressorCompressorPump componentsMagnetic bearingControl system
A compact and efficient compressor is provided, based on using magnetic bearing technology, which can operate at high speed and comprises a reliable control system. The compressor of the present invention makes use of two separate compressors mounted on a single common motor, thus sharing a single drive. The balancing of the thrust at high RPM is improved by using a pair of electromagnetic bearings.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
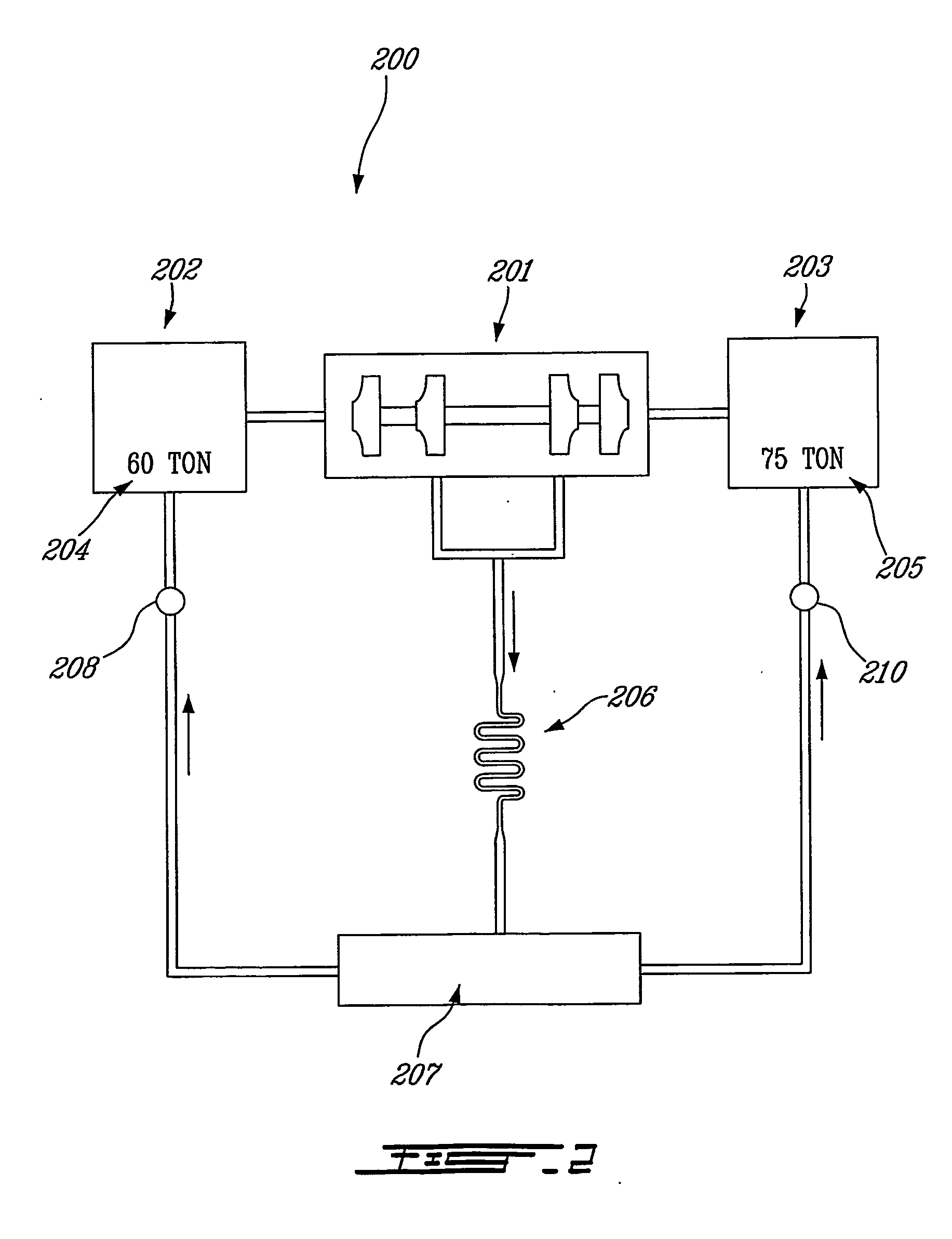
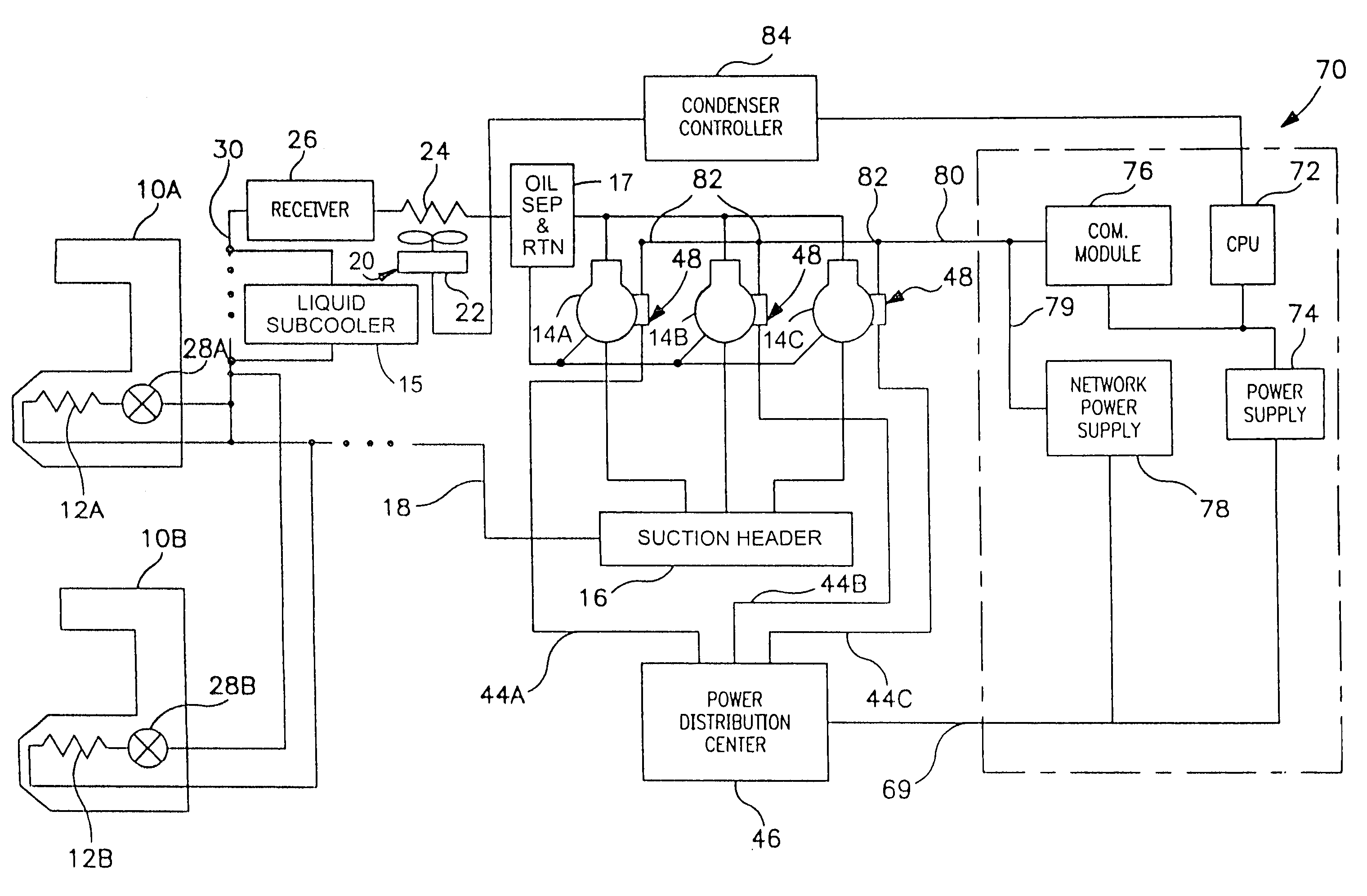
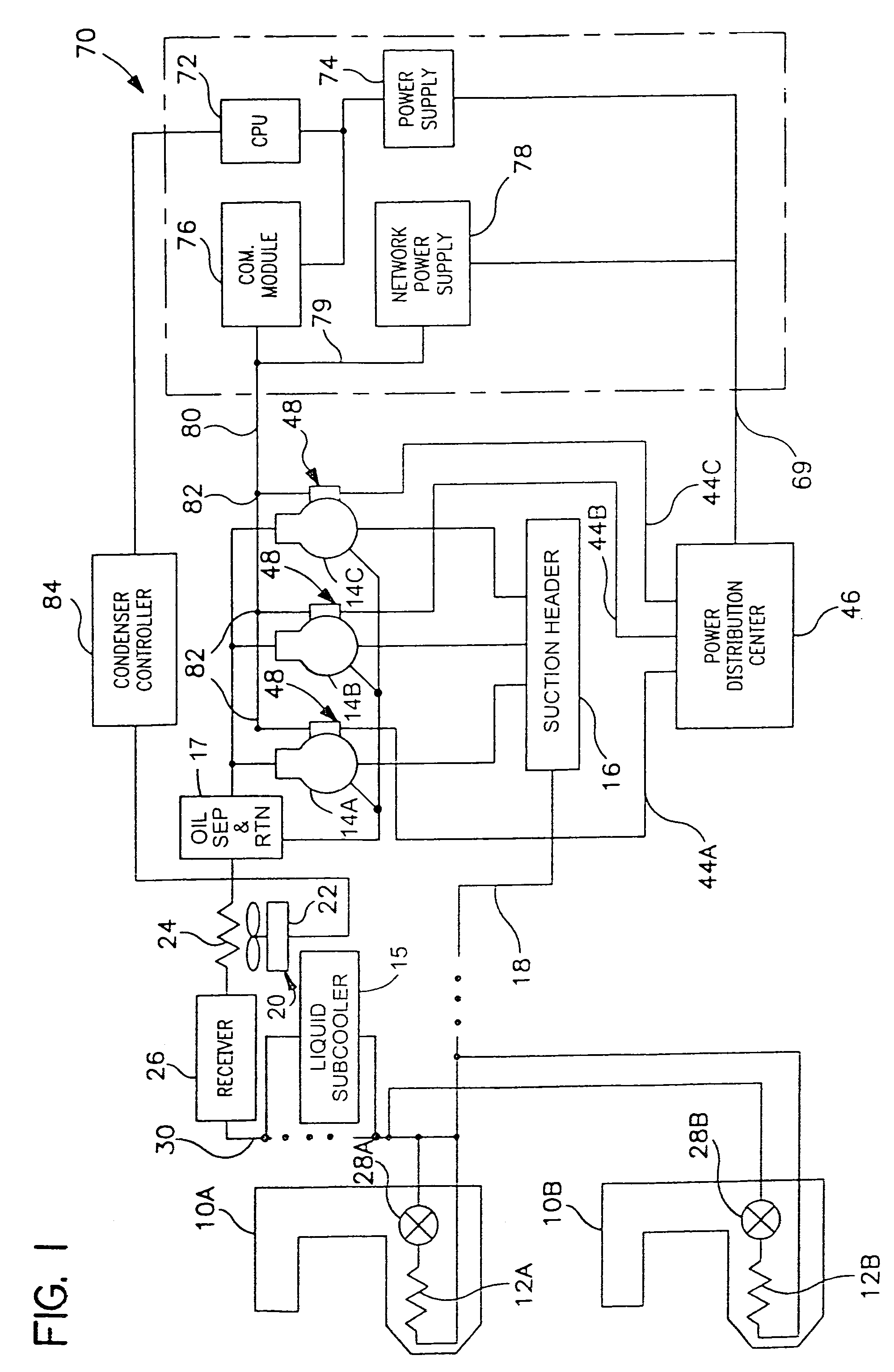
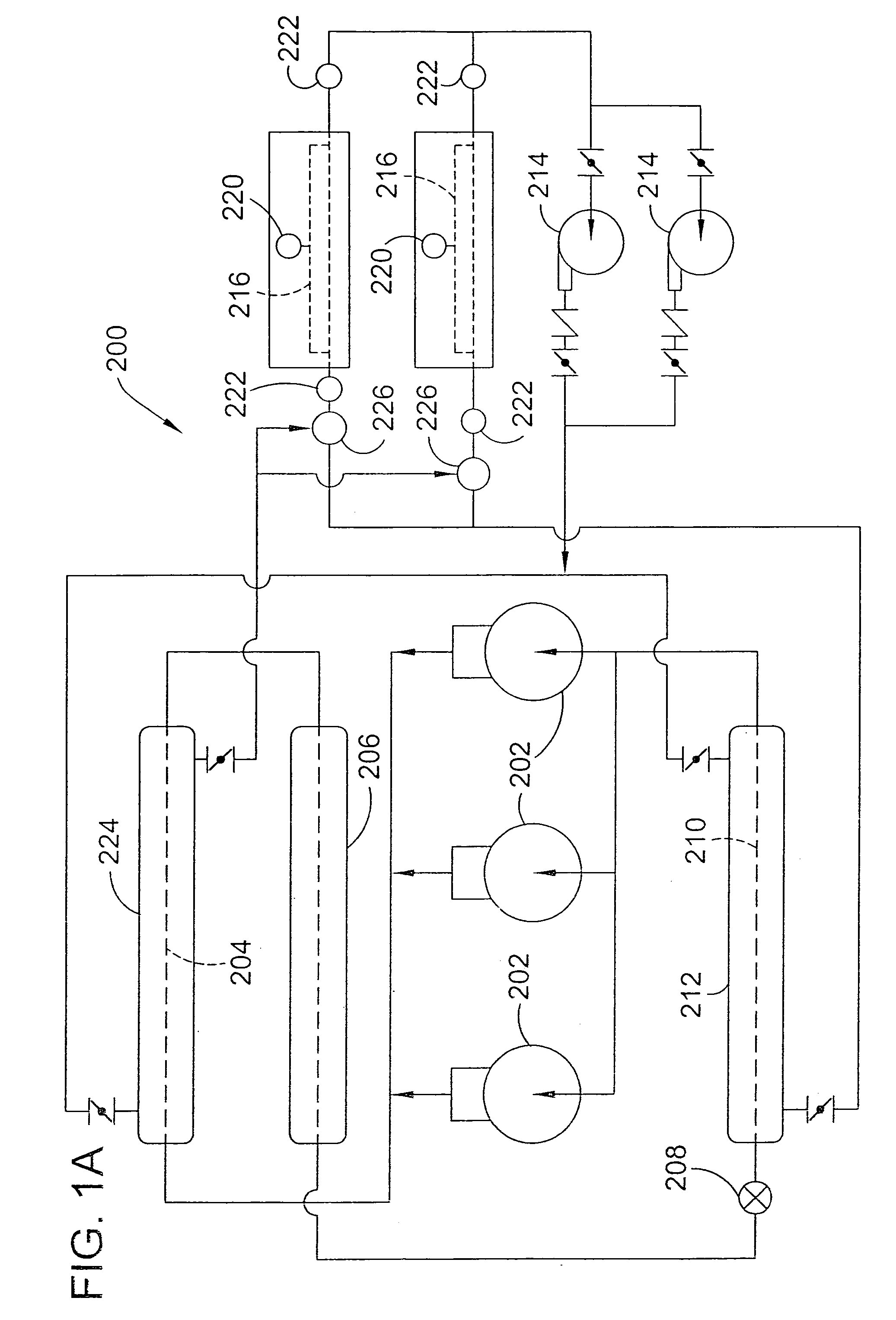
Distributed intelligence control for commercial refrigeration
InactiveUS7270278B2Easy to assembleEasy to installMechanical apparatusEfficient regulation technologiesDistributed intelligenceControl theory
A commercial refrigeration system including a compressor, a condenser, a valve, and an evaporator coil, all of which are in fluid communication. The refrigeration system further including a fixture adapted to be cooled by the evaporator coil, a system controller operable to control operation of the refrigeration system, and a subsystem controller in communication with the system controller. The subsystem controller being operable to monitor at least one parameter of a subsystem having at least one of the compressor, condenser, valve, and fixture, and being further operable to execute a command from the system controller to affect the operation of the subsystem.
Owner:HUSNN
Cooling system for electronic equipment
InactiveUS7855890B2Reduce the required powerTemperatue controlDigital data processing detailsCooling towerServer room
In a cooling system for an electronic device of the present invention, server rooms in which a plurality of servers are placed, an evaporator which is provided close to each of the servers, and cools exhaust air from the server by vaporizing a refrigerant with heat generating from the server, a cooling tower which is provided at a place higher than the evaporator, cools the refrigerant by outside air and water sprinkling, and condenses the vaporized refrigerant, and a circulation line in which the refrigerant naturally circulates between the evaporator and the cooling tower. According to the cooling system, an electronic device which is required to perform a precise operation with a heat generation amount from itself being large, such as a computer and a server, can be efficiently cooled at low running cost.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
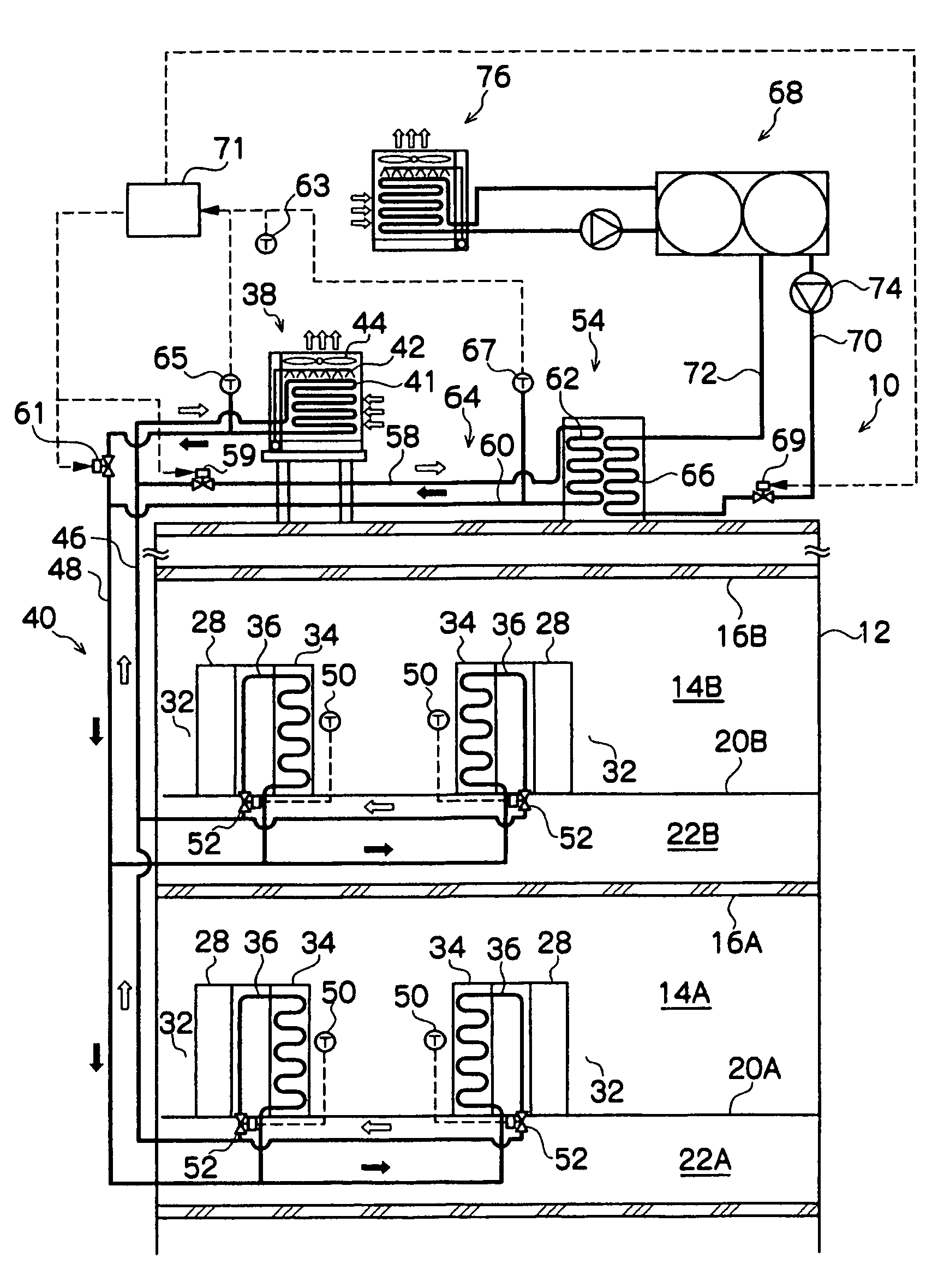
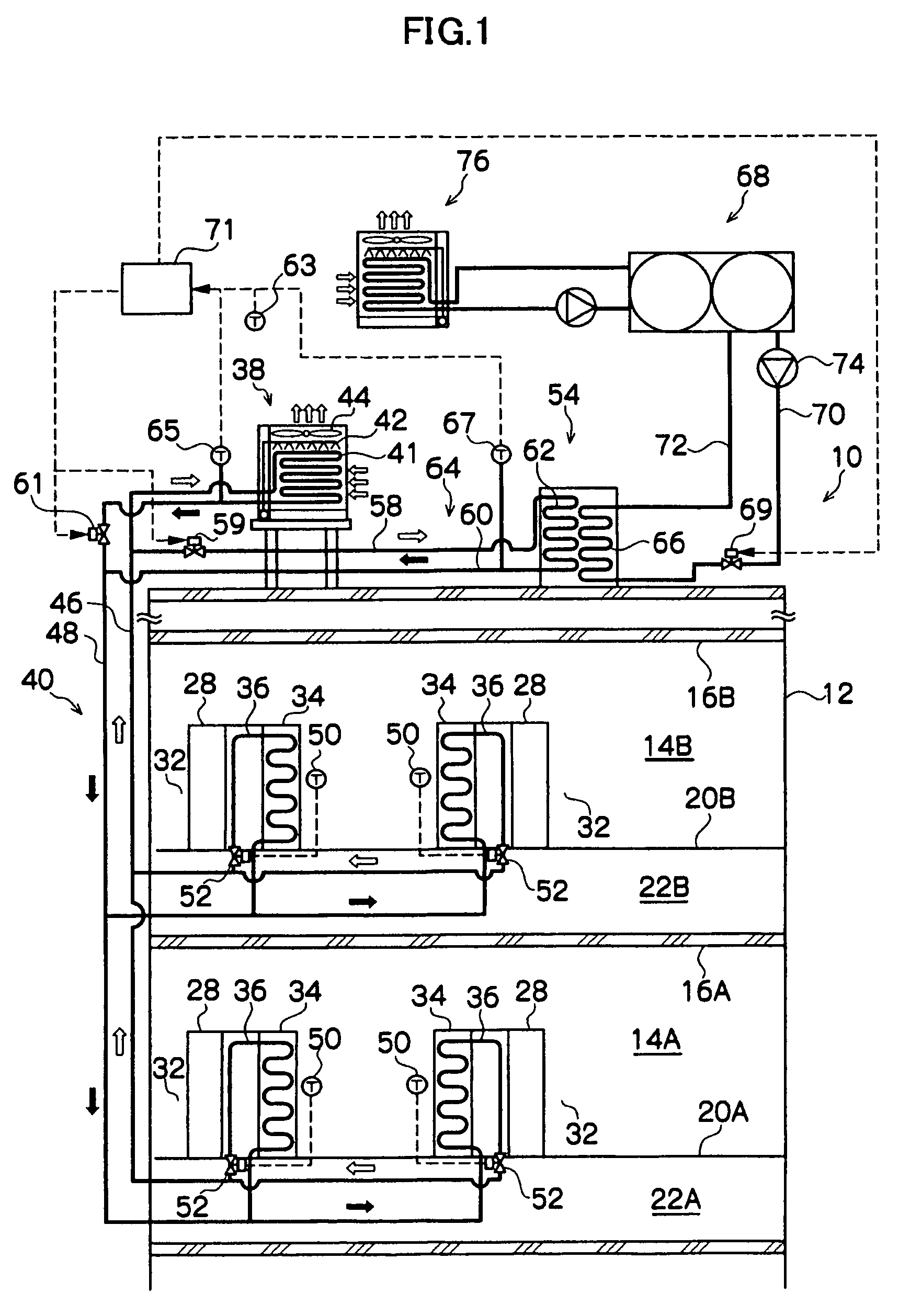
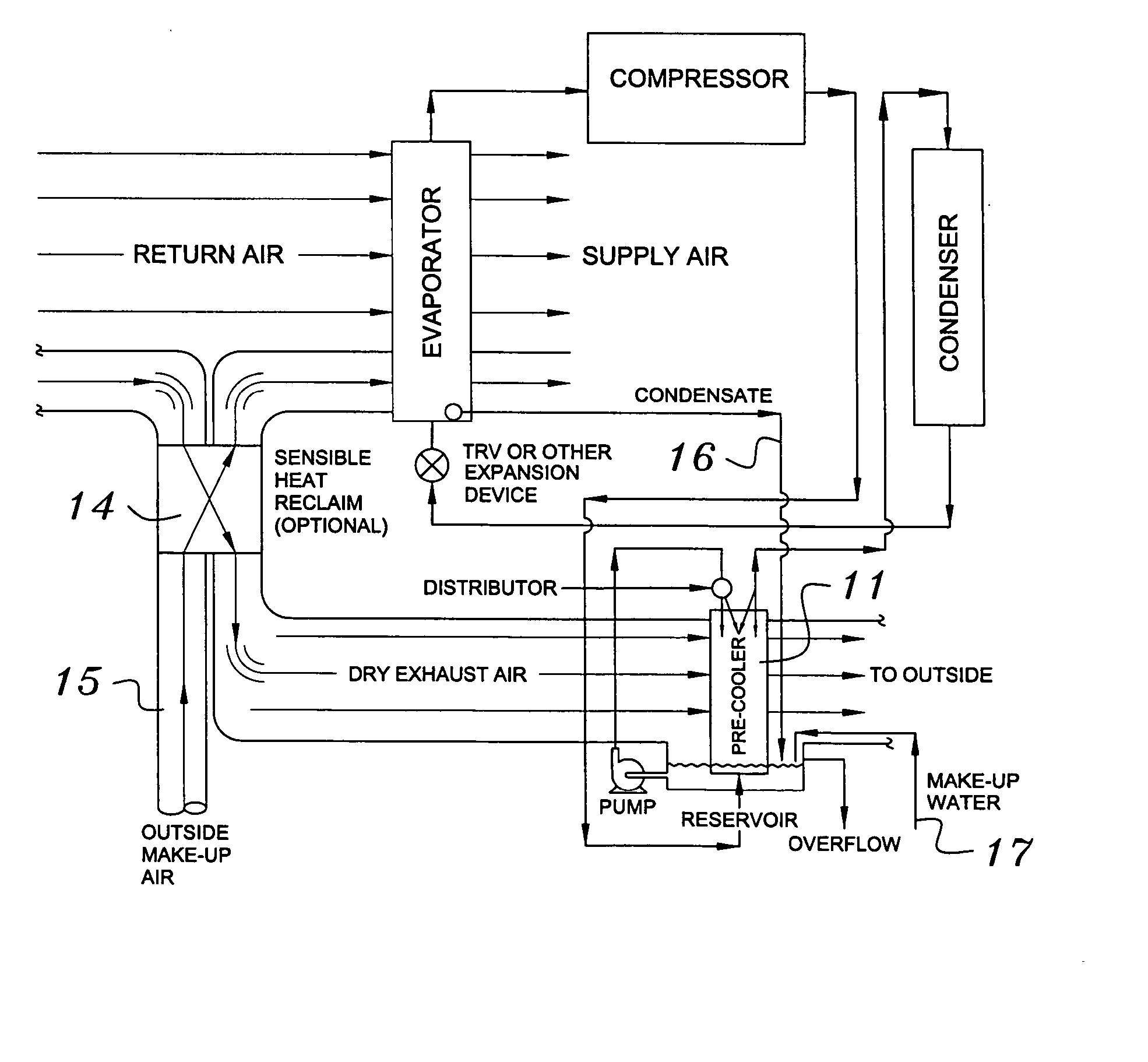
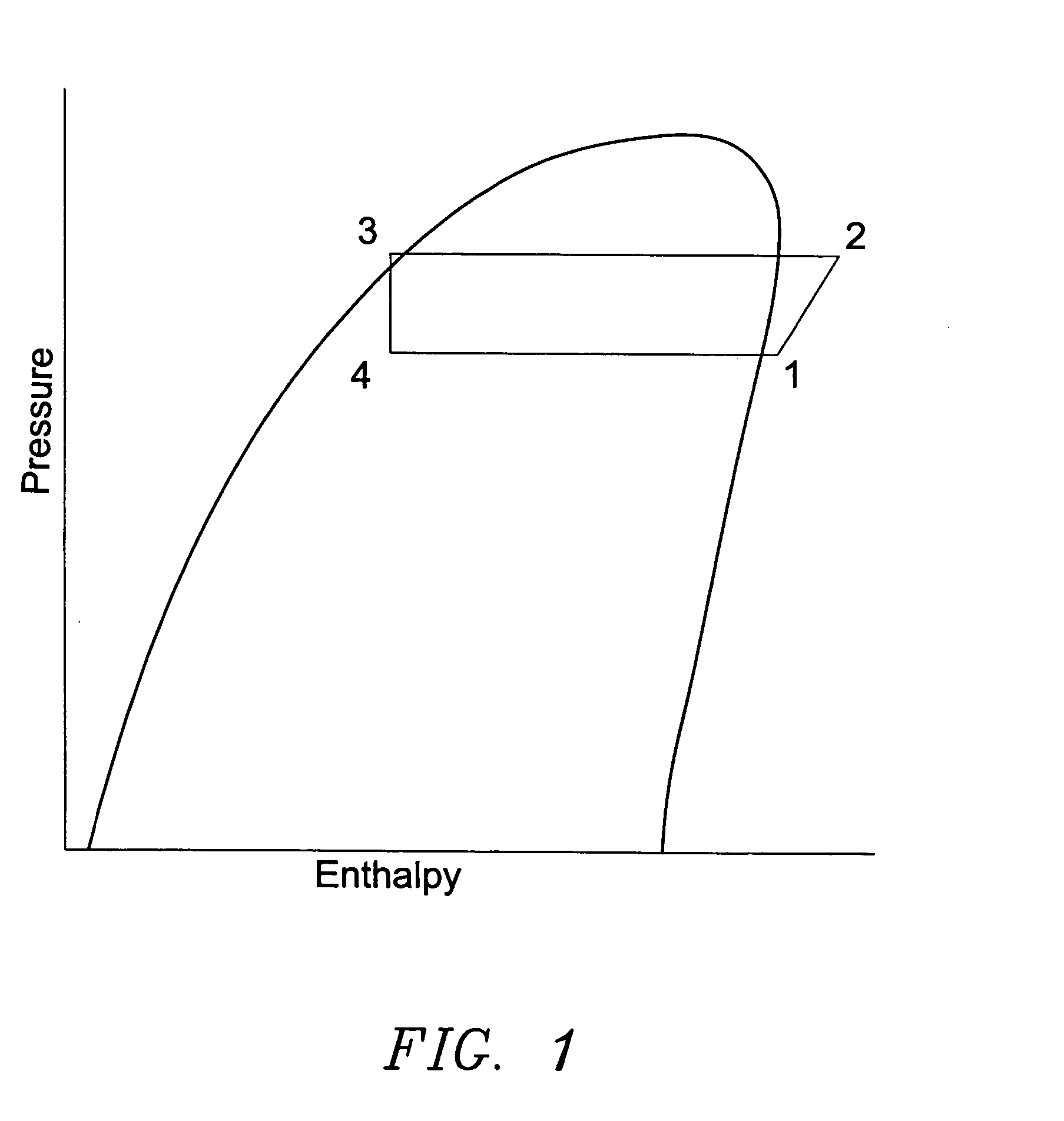
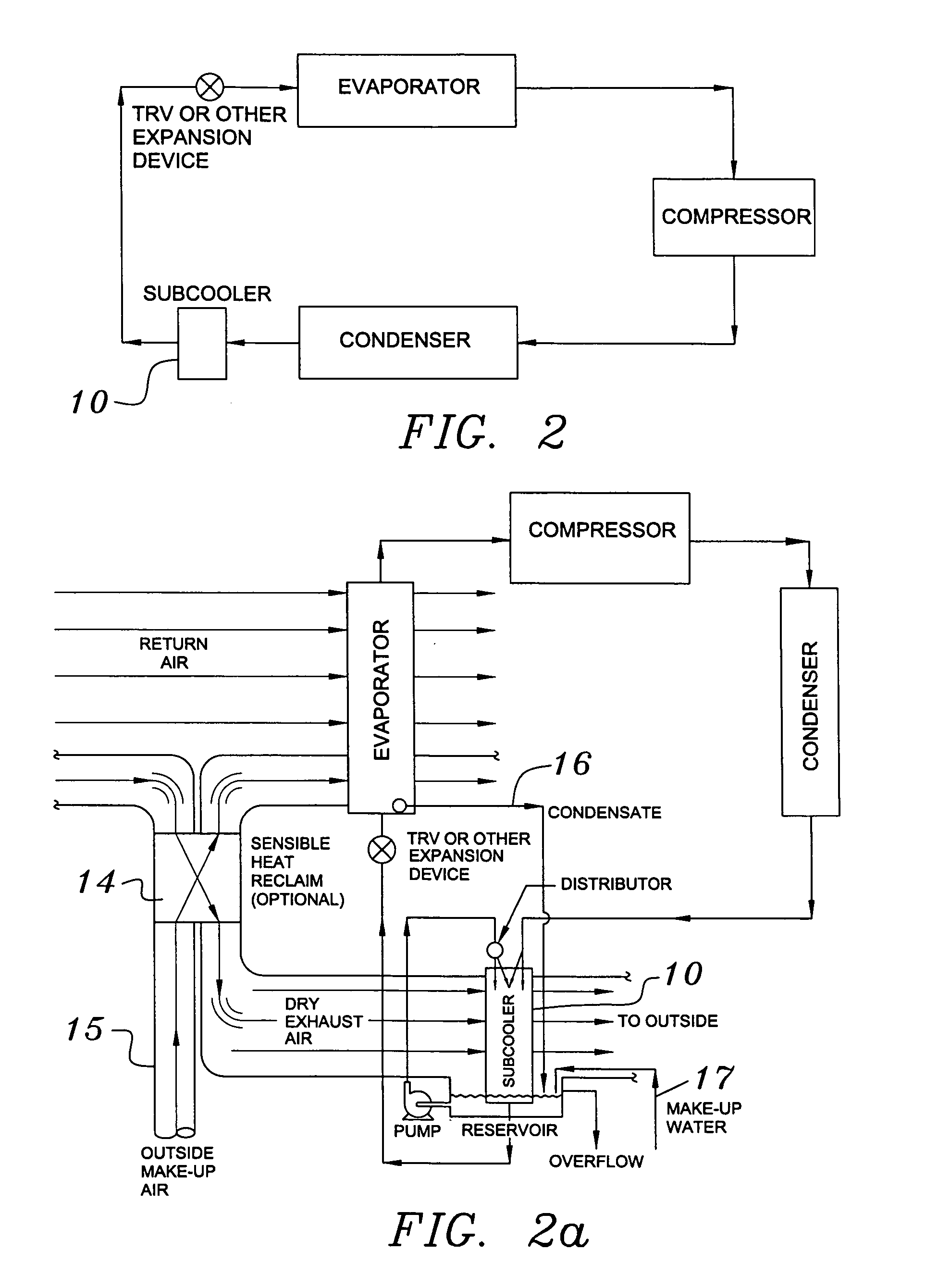
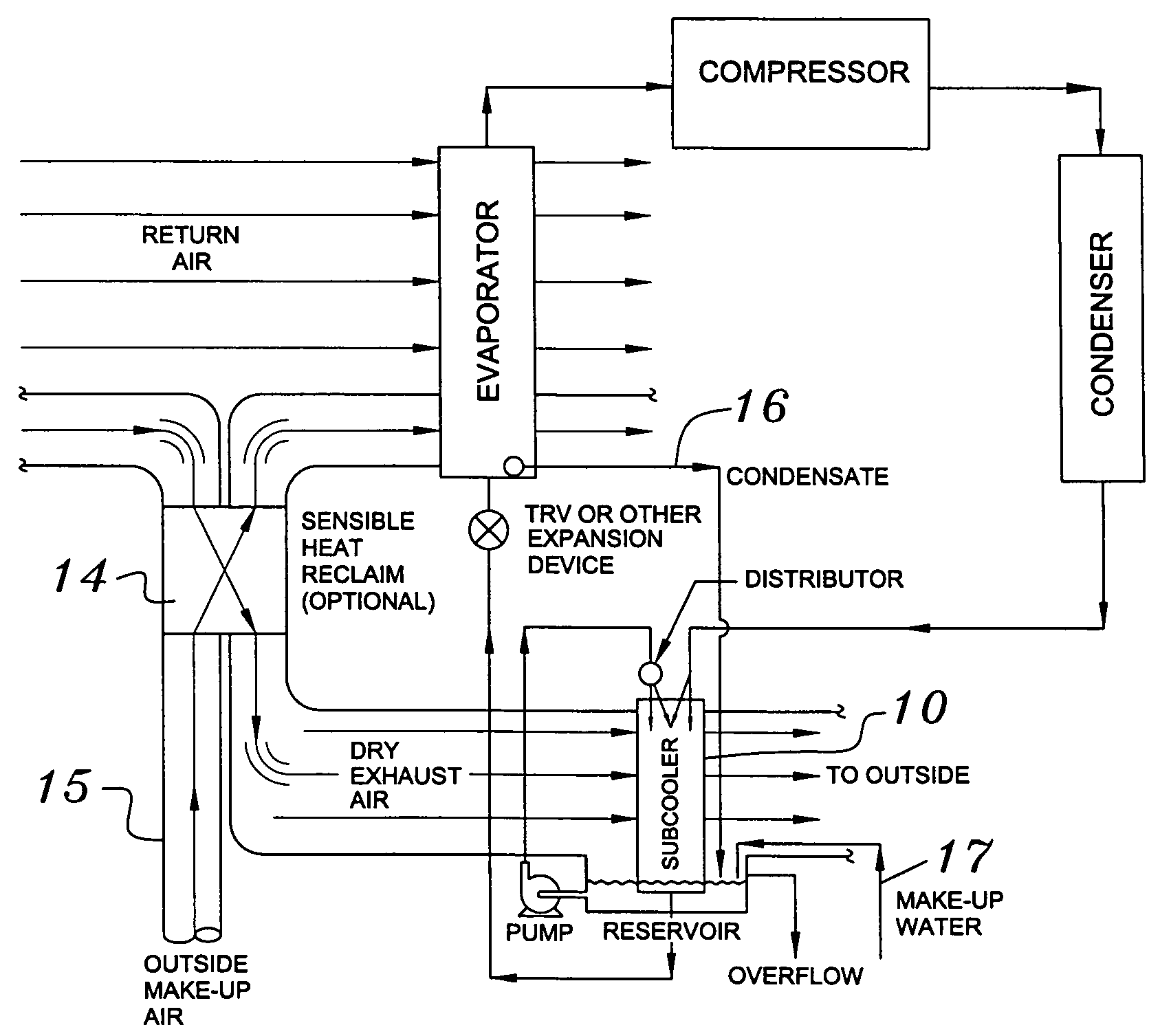
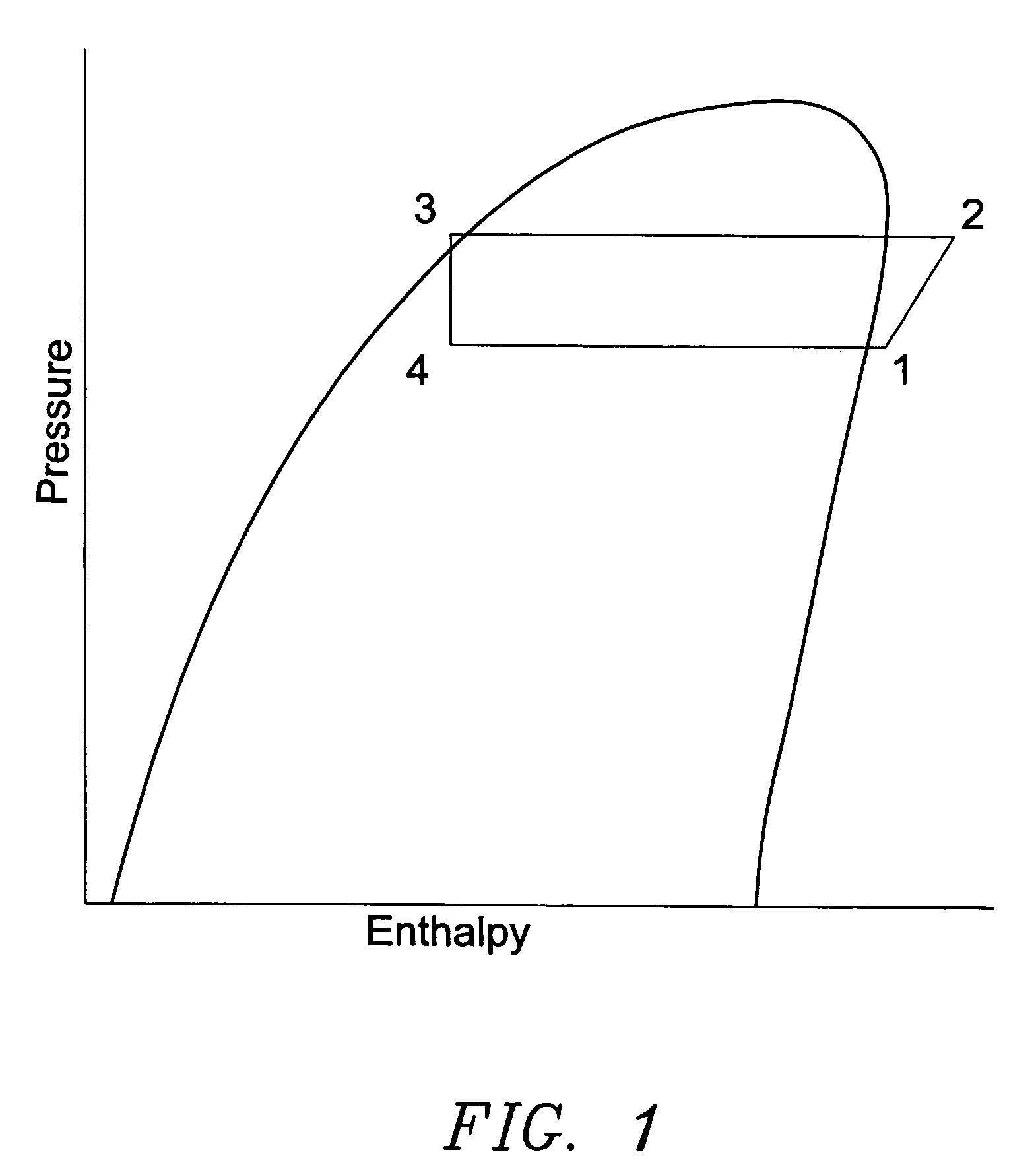
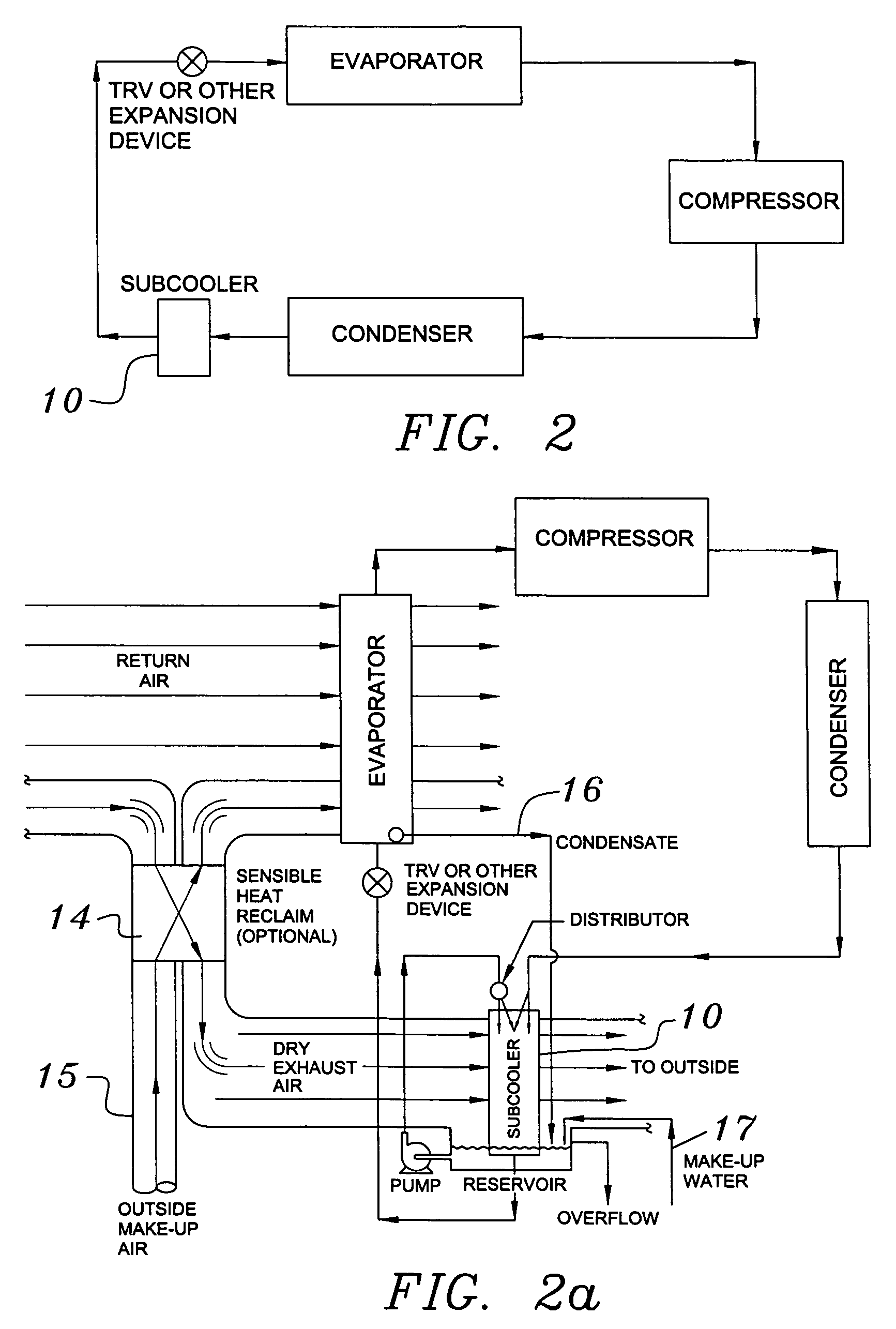
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS20050028545A1Improve cooling effectReduce power consumptionEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingDomestic cooling apparatusWater wetWater source
A system for providing liquid refrigerant subcooling by means of evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said air conditioner, refrigeration / heat pump system and / or other water supply to wet the surface of the subcool heat exchanger and pass the dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the subcool heat exchanger. A system for providing hot gas discharge refrigerant precooling into the primary condenser of an air conditioner, refrigeration or heat pump system by evaporative cooling utilizing the condensate water of said system and / or other water supply to wet the surface of the precool heat exchanger and then passing the cold, dry exhaust air across the wetted surface of the precool heat exchanger. A combination subcooler / precooler system where the cold dry building exhaust air is used to evaporatively subcool the liquid refrigerant in the water wetted (or dry) subcooler and then used to conductively cool the hot gas refrigerant.
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
Centrifugal compressor
ActiveUS7240515B2Improved centrifugal compressorCompressorPump componentsMagnetic bearingControl system
A compact and efficient compressor is provided, based on using magnetic bearing technology, which can operate at high speed and comprises a reliable control system. The compressor of the present invention makes use of two separate compressors mounted on a single common motor, thus sharing a single drive. The balancing of the thrust at high RPM is improved by using a pair of electromagnetic bearings.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
Heat pump cycle system
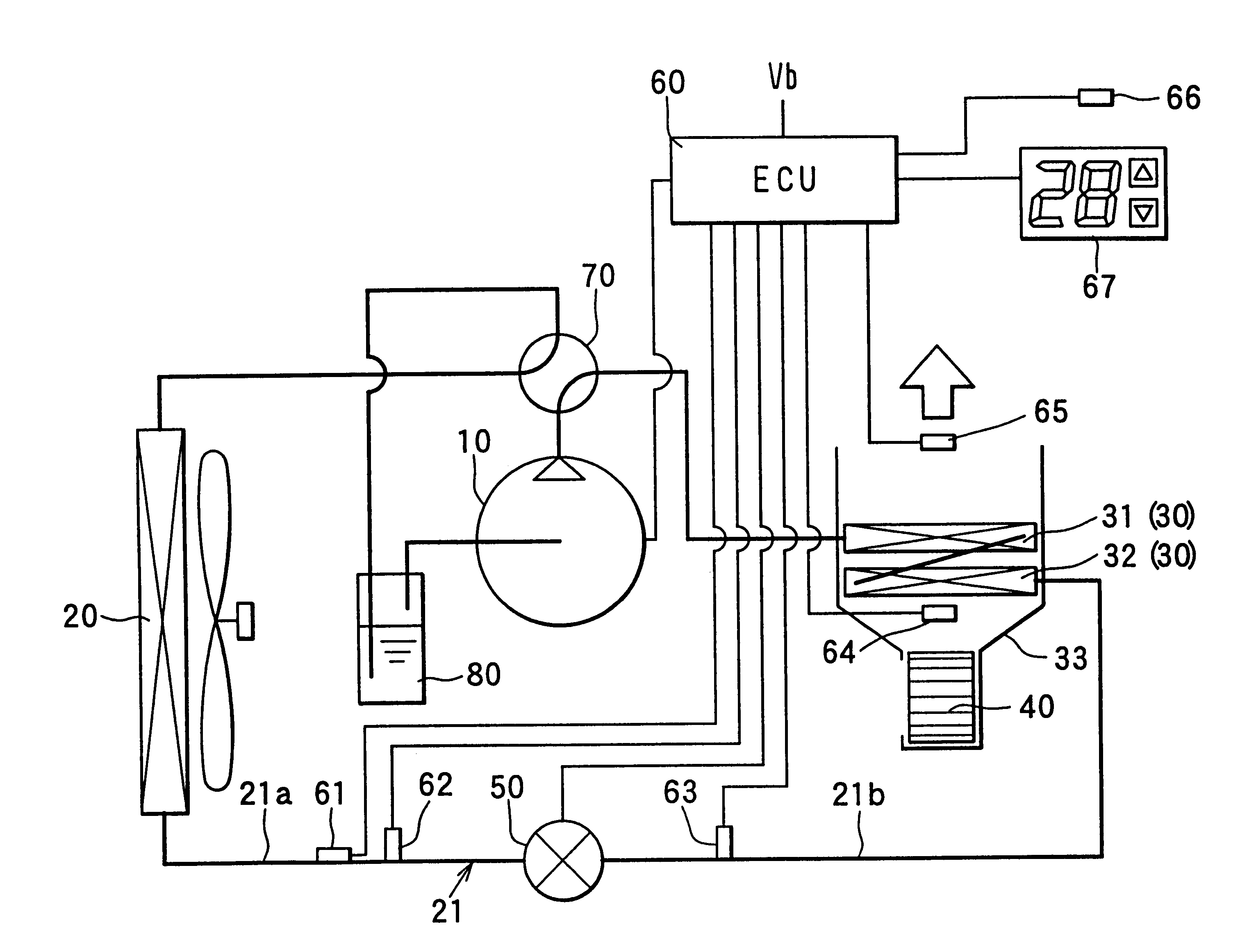
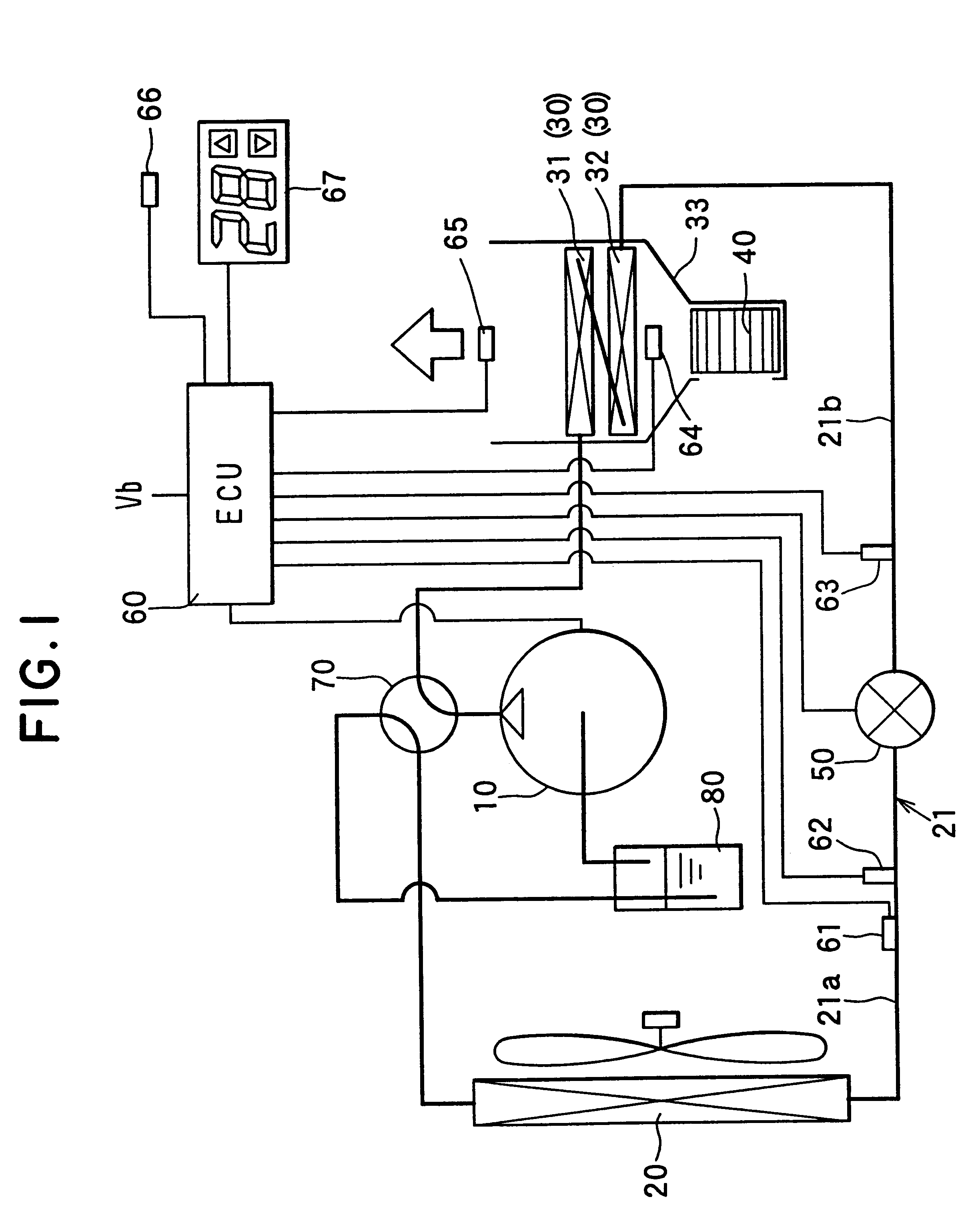
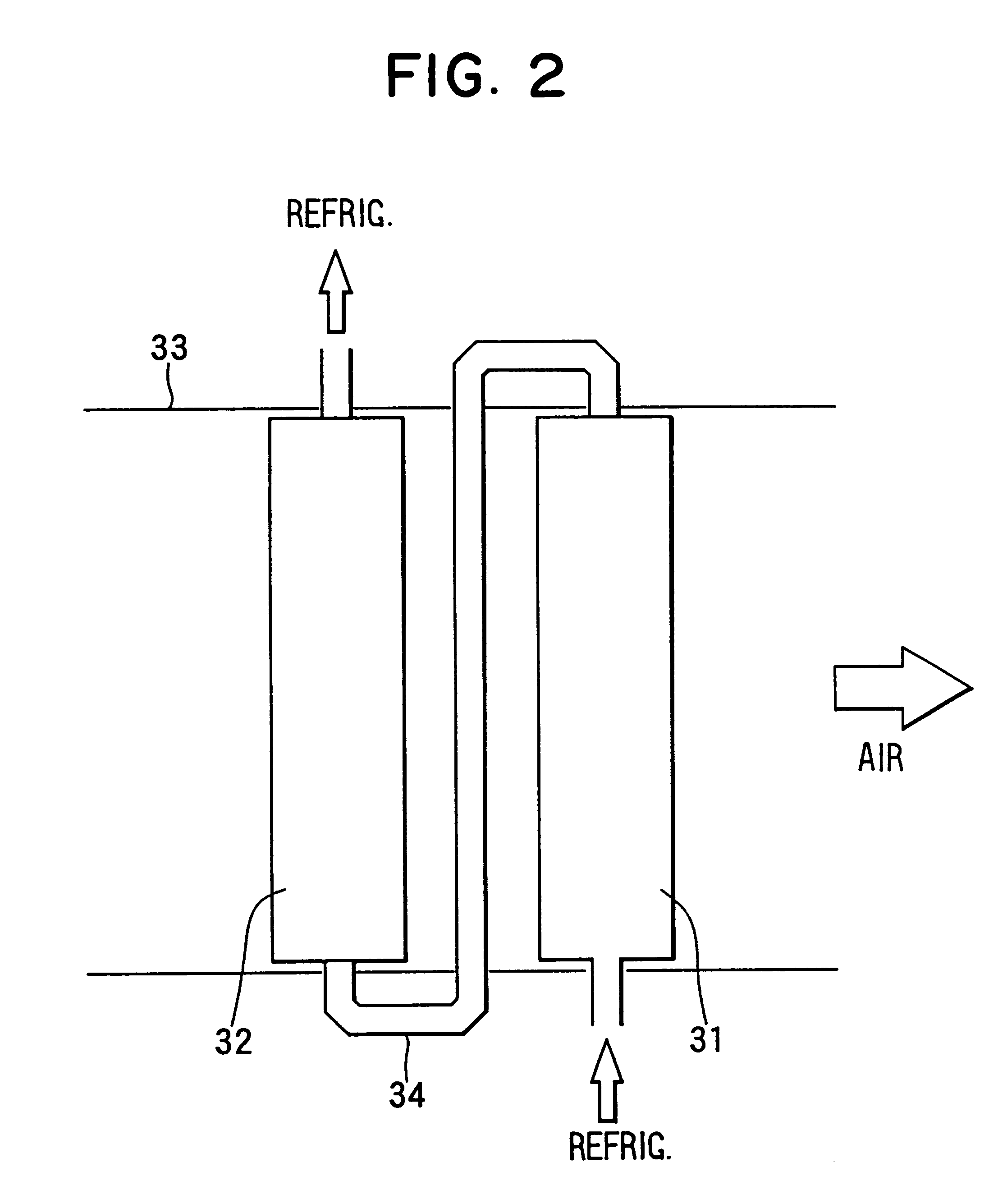
InactiveUS6230506B1Improve the heating effectImprove the overall coefficientMechanical apparatusAir-treating devicesLower limitEngineering
A heat pump cycle system which can switches cooling operation and heating operation for a compartment includes a first inside heat exchanger and a second inside heat exchanger disposed in an air conditioning case. The first inside heat exchanger is disposed in the air conditioning case at a downstream air side of the second inside heat exchanger, while being arranged in line in a flow direction of refrigerant. The first inside heat exchanger is upstream from the second inside heat exchanger in the flow direction of refrigerant during the heating operation. In the heat pump cycle system, an expansion valve is controlled so that coefficient of performance in each operation becomes approximately maximum. Thus, during the heating operation of the heat pump cycle system, a lower limit temperature of air blown from the inside heat exchangers can be increased so that temperature of air blown into the compartment is increased, while the coefficient of performance is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Cooling system for electronic equipment
InactiveUS20090201645A1Reduce the required powerDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlCooling towerEngineering
In a cooling system for an electronic device of the present invention, server rooms in which a plurality of servers are placed, an evaporator which is provided close to each of the servers, and cools exhaust air from the server by vaporizing a refrigerant with heat generating from the server, a cooling tower which is provided at a place higher than the evaporator, cools the refrigerant by outside air and water sprinkling, and condenses the vaporized refrigerant, and a circulation line in which the refrigerant naturally circulates between the evaporator and the cooling tower. According to the cooling system, an electronic device which is required to perform a precise operation with a heat generation amount from itself being large, such as a computer and a server, can be efficiently cooled at low running cost.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
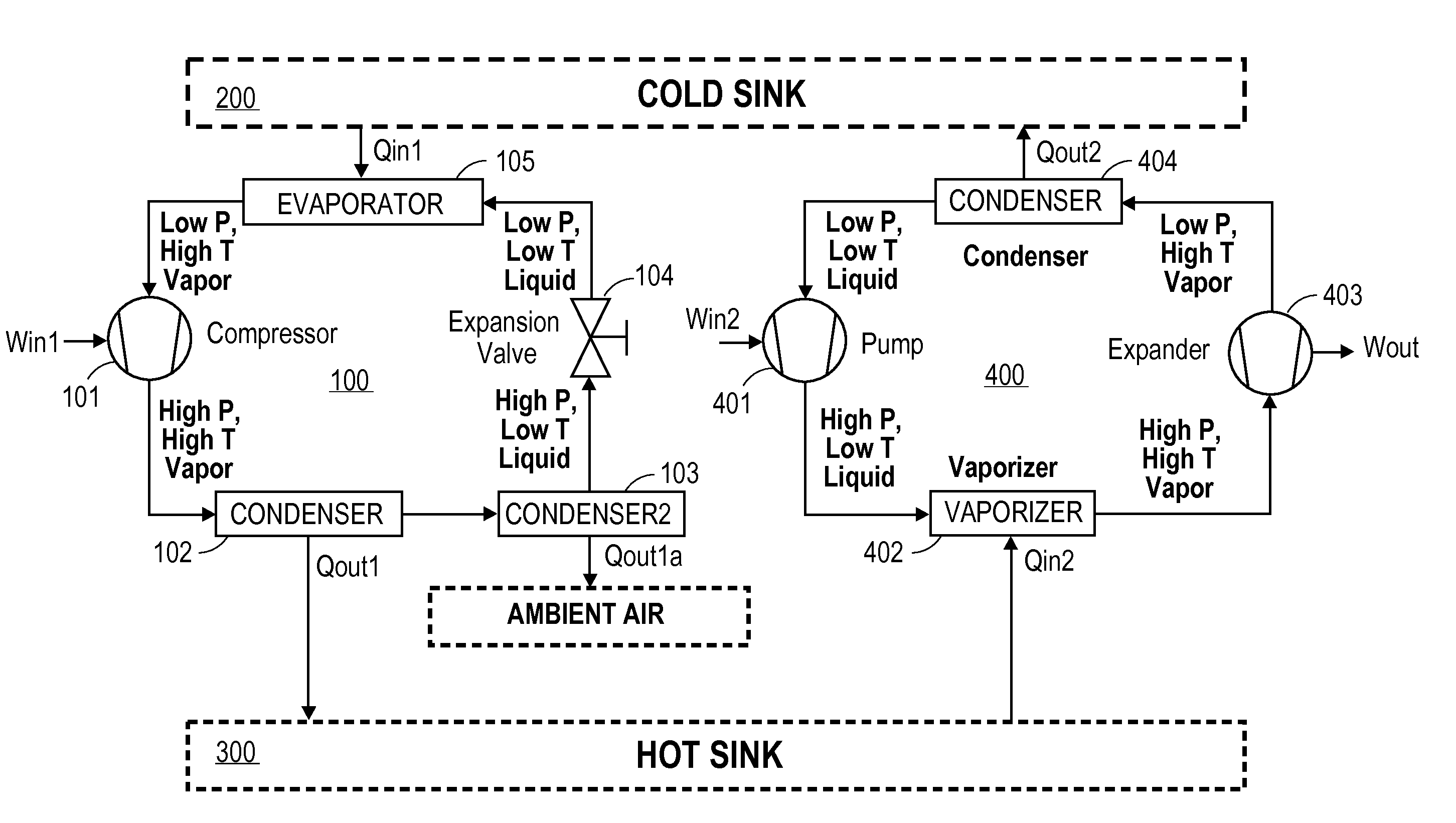
Energy storage systems
ActiveUS20110204655A1Compression machines with non-reversible cycleDomestic refrigeratorsThermal energyStored energy
The present invention provides an energy storage device that utilizes a cold sink that undergoes cycles of freezing and thawing. The device converts electrical energy to stored thermal energy, and then re-converts the stored thermal energy to electrical energy, as needed or desired. The device can store energy on a large scale (e.g., on the order of megawatts or greater) and for an extended period of time (e.g., for at least 12 hours, or longer, as needed).
Owner:PHASE CHANGE STORAGE
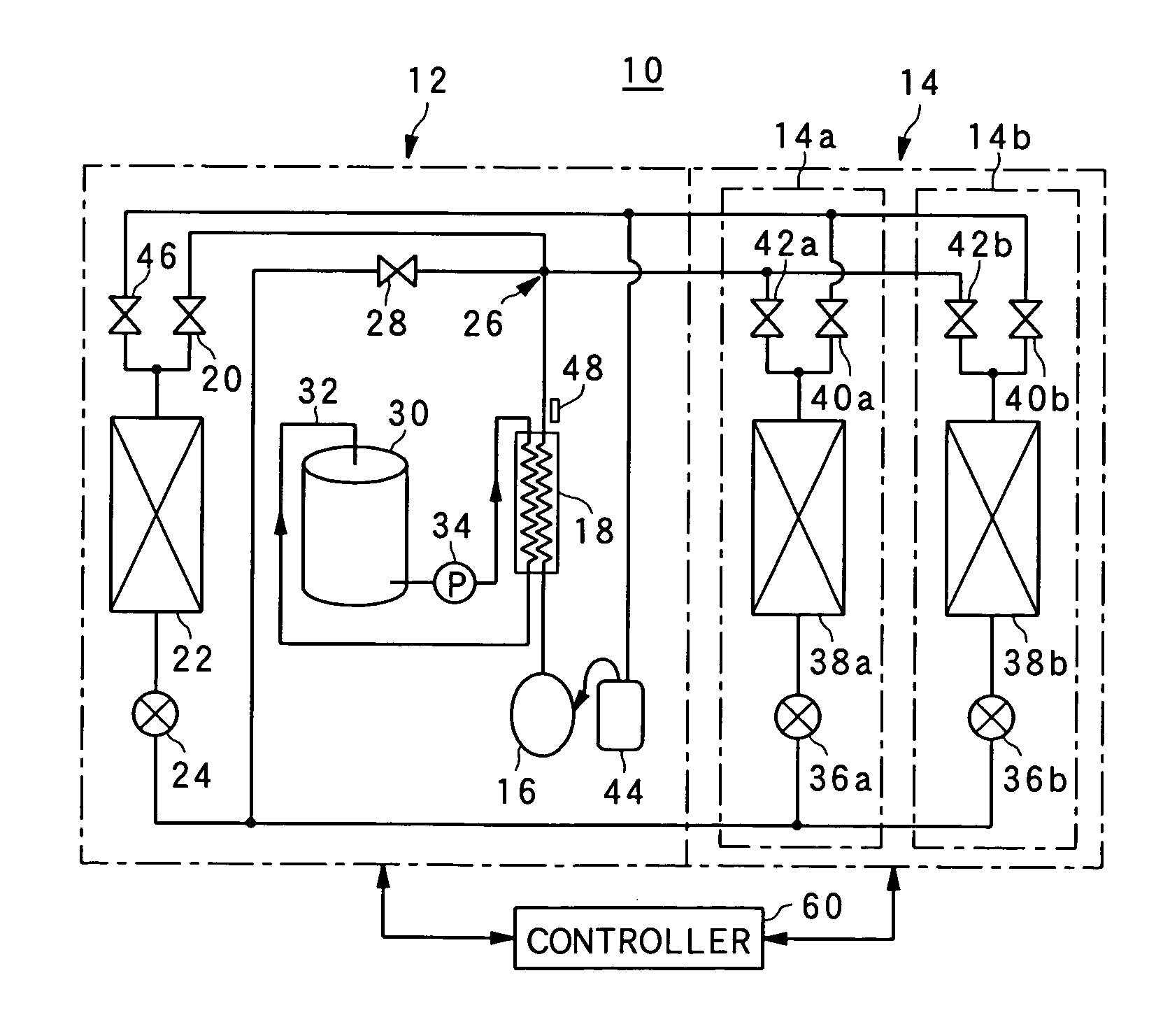
Multi-Part Heat Exchanger
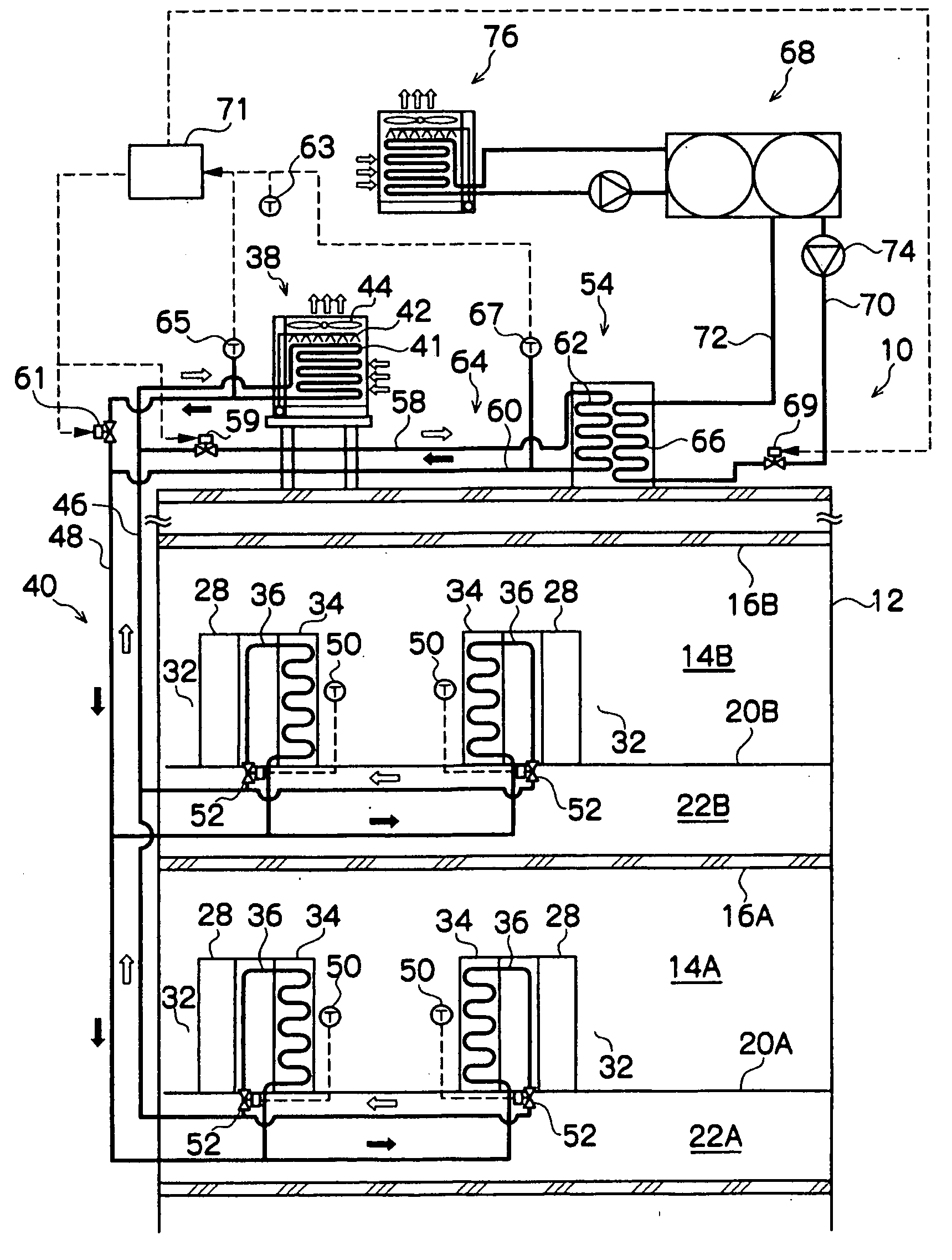
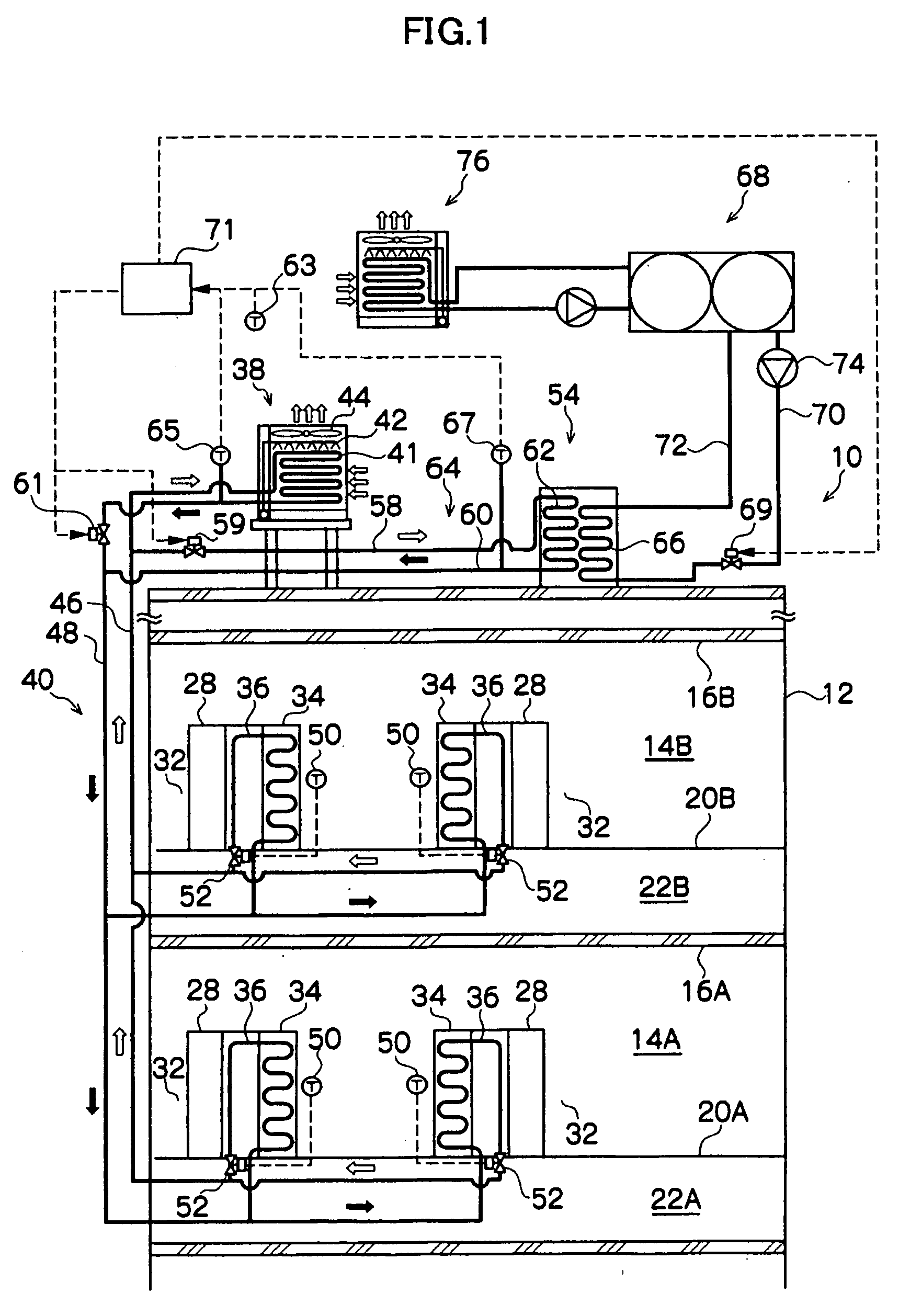
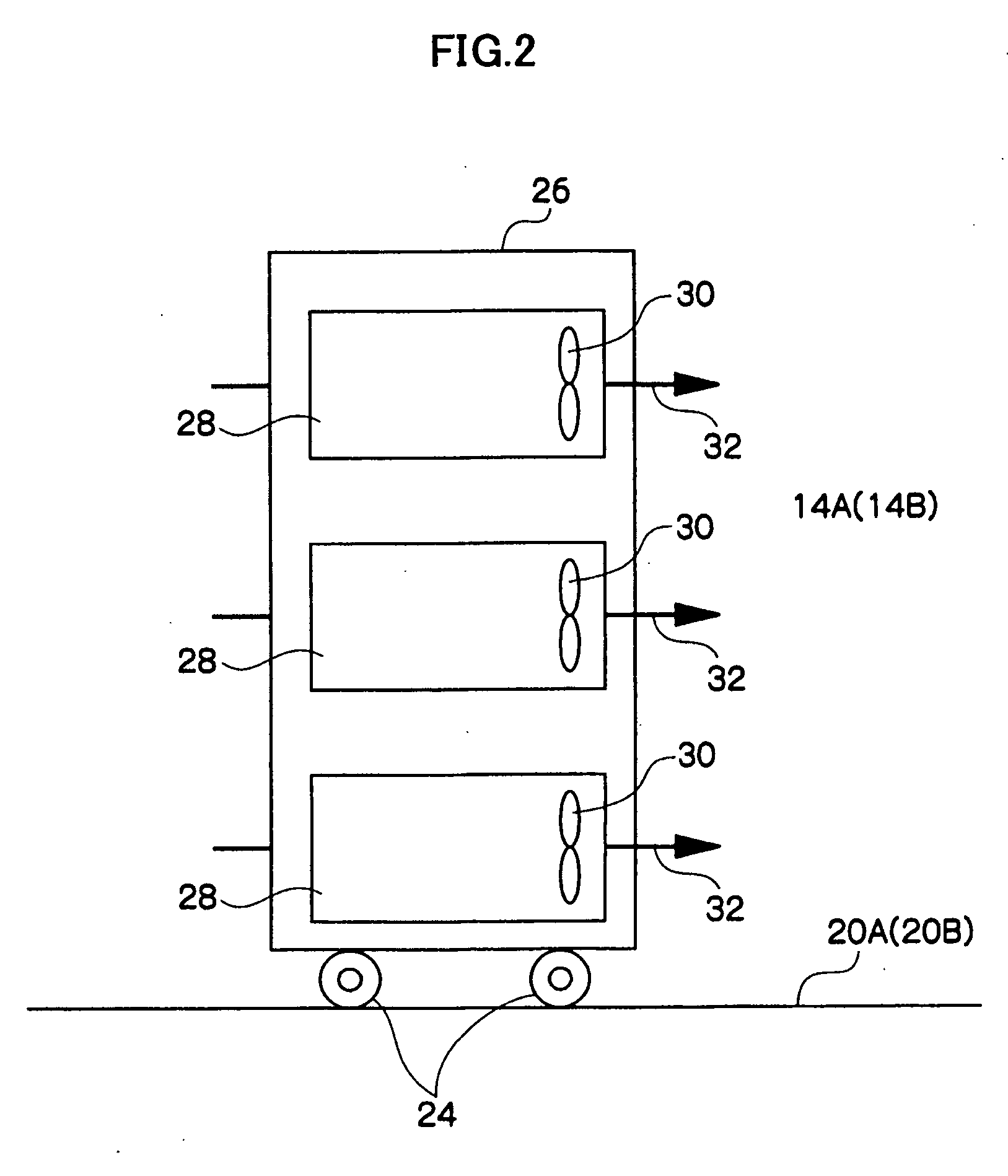
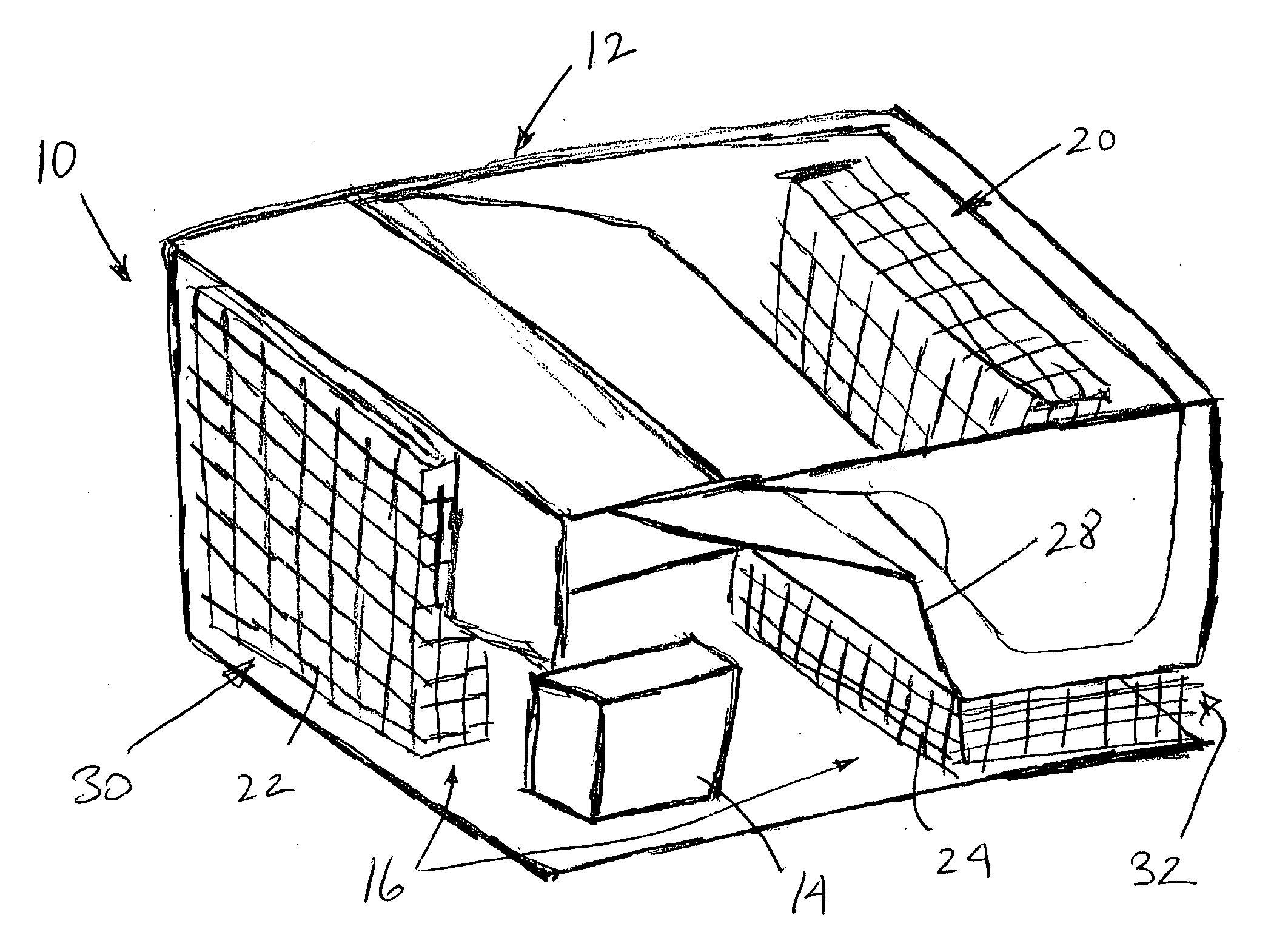
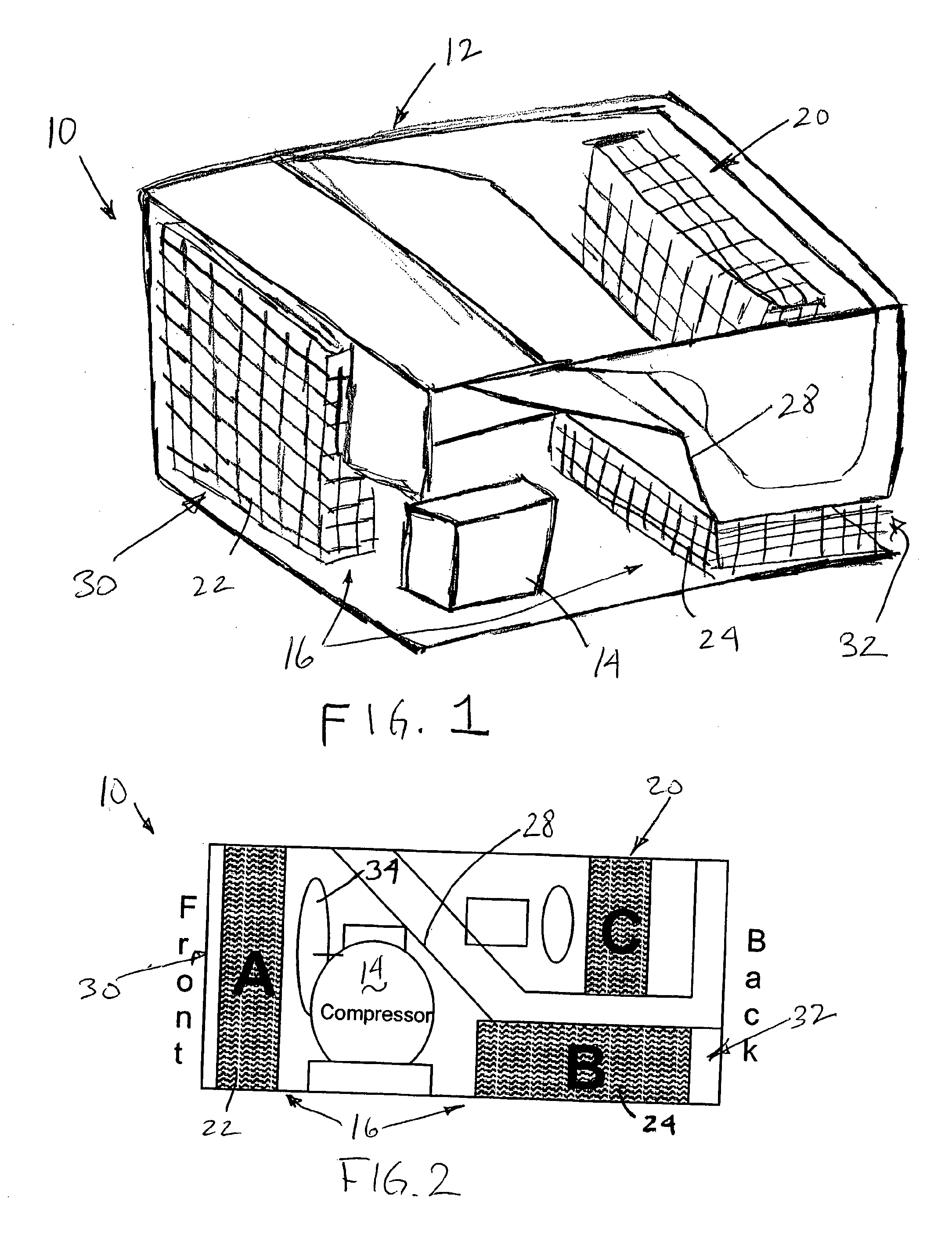
InactiveUS20080184731A1Use space moreEasy to useCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCompression machines with several condensersEngineeringRefrigerant
A refrigeration system includes a compressor for driving a refrigerant along a flow path in at least a first mode of system operation; a first heat exchanger along the flow path downstream of the compressor in the first mode; a second heat exchanger along the flow path upstream of the compressor in the first mode; and a pressure regulator or expansion device in the flow path downstream of the first heat exchanger and upstream of the second heat exchanger in the first mode, wherein the first heat exchanger comprises a plurality of heat exchanger components arranged along a flow path of heat exchange fluid for the first heat exchanger. The heat exchanger components can be positioned in smaller available areas within the unit and thereby use space more efficiently.
Owner:CARRIER COMML REFRIGERATI
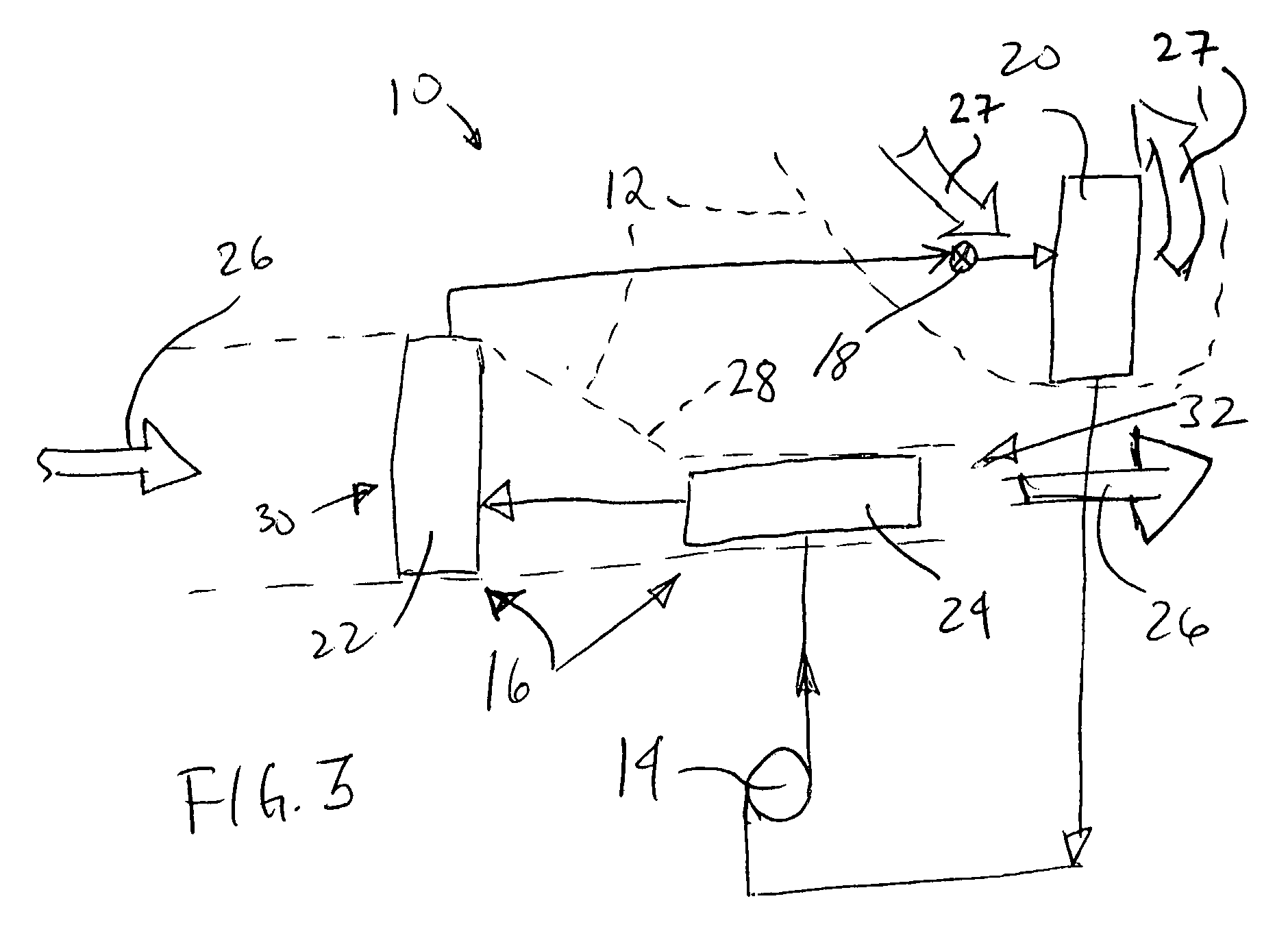
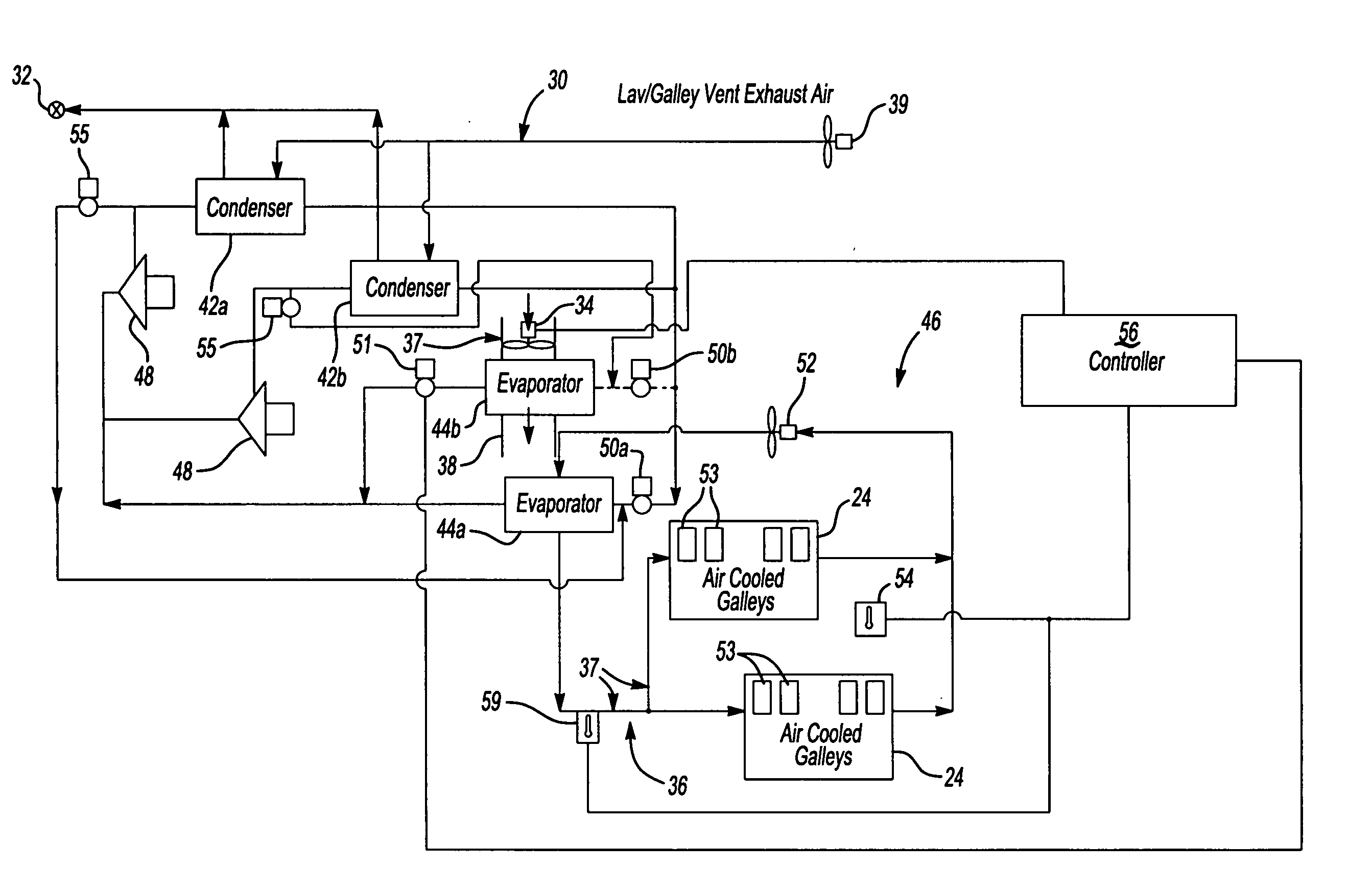
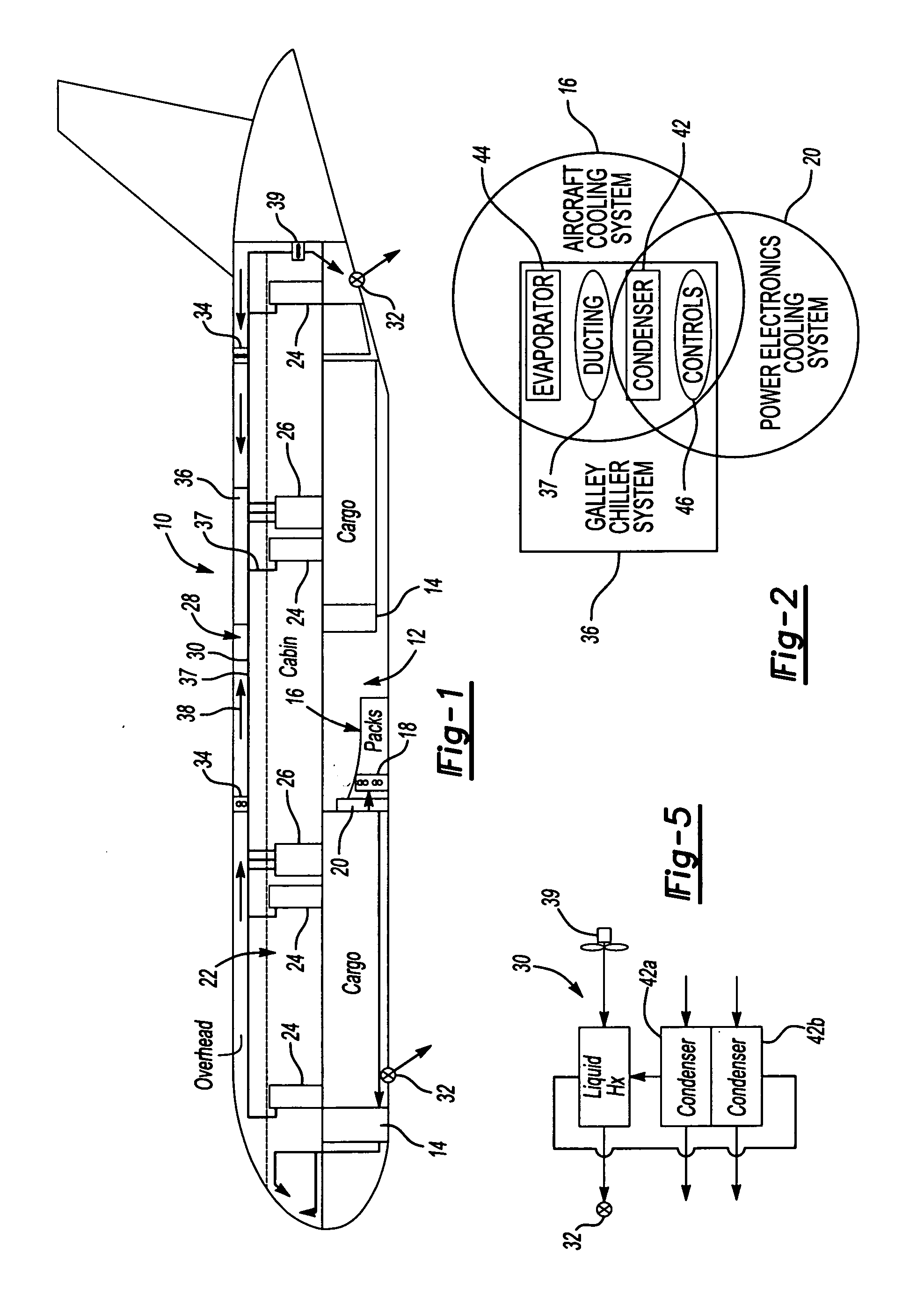
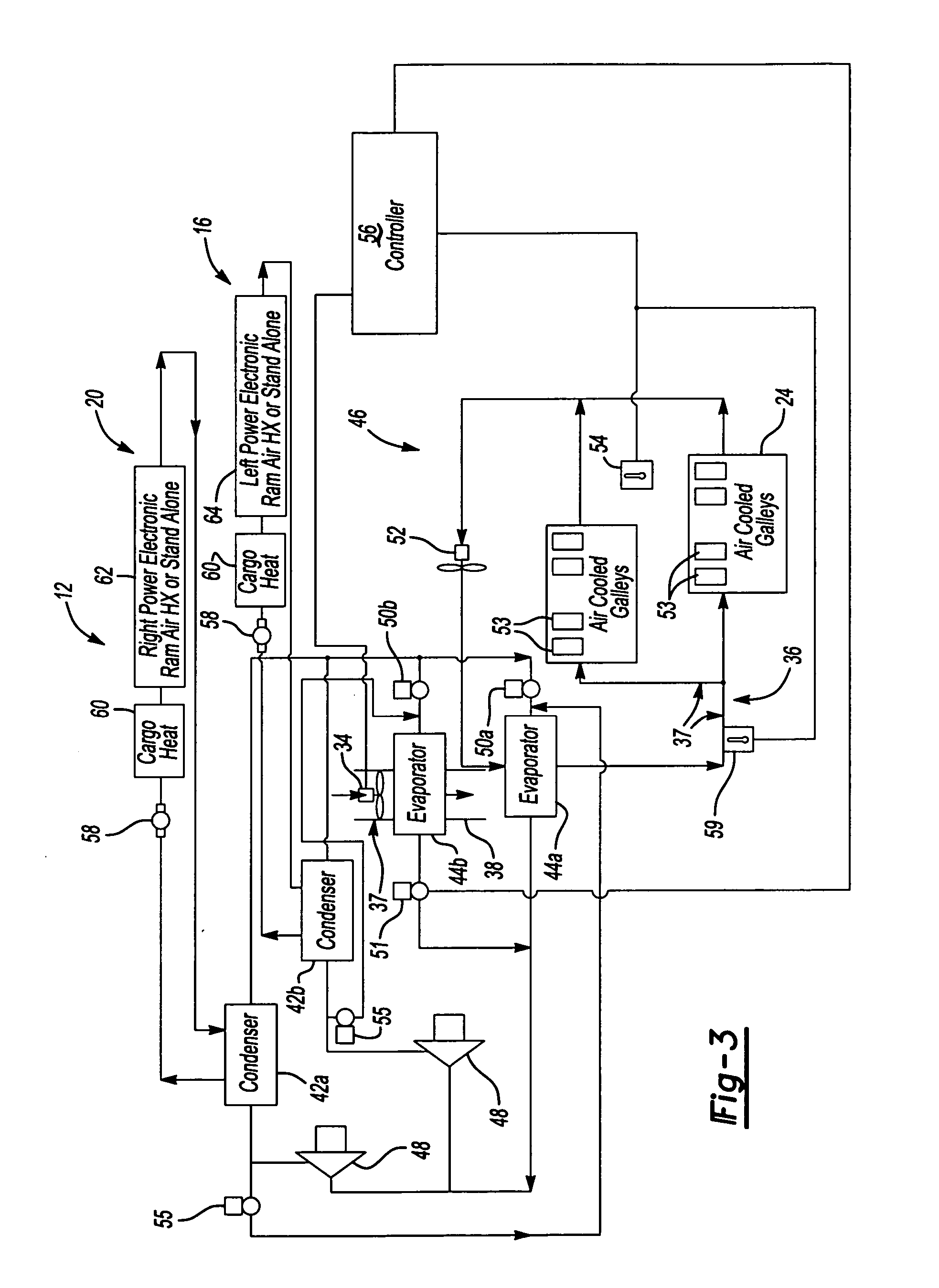
Aircraft galley chiller system
ActiveUS20050061012A1Lower requirementEasy to useMechanical apparatusAir-treating devicesEngineeringChiller
A galley chiller system for an aircraft includes at least one condenser having a refrigerant fluid. The fluid within the condenser rejects heat to a first surrounding environment. To more efficiently use the condenser of the galley chiller system and reduce the requirement on other cooling systems within an aircraft, the condenser may reject its heat to a desired location using a heat exchanger. The galley chiller system includes at least one evaporator that receives fluid from the condenser. A first evaporator absorbs heat from a galley, which may include a bank of carts. The first evaporator is arranged in ducting that carries cooled air to the carts. A second evaporator may absorb heat from a cabin recirculation air duct of the aircraft cooling system. In this manner, the evaporators of the inventive galley chilling system cools not only the galley carts but also provides supplemental cooling to the aircraft cooling system thereby reducing its cooling requirements.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Refrigeration cycle device
InactiveUS20070199337A1Improve cooling effectSecure amount of heatingEvaporators/condensersCompression machines with several condensersEngineeringRefrigerant
In a refrigeration cycle device in which heat generated by heat absorption of an evaporator is used for heating in a condenser, a disadvantage that a cooling capacity of the evaporator deteriorates owing to shortage or drop of an amount of the heat to be rejected from the condenser is securely avoided and a cooling function is maintained. In the refrigeration cycle device which is provided with a refrigerant circuit including a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve and an evaporator and which exhibits a heating function by the heat rejected from the condenser and which exhibits the cooling function by the heat absorption of the evaporator, an operation to secure a predetermined amount of the heat to be rejected from the condenser is executed in order to maintain the cooling function of the evaporator based on an index capable of grasping the amount of the heat to be rejected from the condenser.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Ejector type refrigerating cycle
ActiveUS20060218964A1Easy to adjustImprove performanceCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCompression machines with several condensersEngineeringHigh pressure
An ejector type refrigerating cycle comprises a compressor, a heat radiating device, an ejector, and a first vaporizing device, which are connected in a circuit to form a refrigerating cycle. A bypass passage is provided between an inlet port and a suction port of the ejector, so that a part of the refrigerant is bifurcated to flow through the bypass passage. A second vaporizing device is provided in the bypass passage. An internal heat exchanger is further provided between an outlet side of the heat radiating device and the inlet side of the ejector, so that the enthalpy of the high-pressure refrigerant from the heat radiating device is reduced, to thereby increase an enthalpy difference between the inlet side and outlet side of the first and second vaporizing devices. As a result, the cooling capability by the both vaporizing devices can be improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
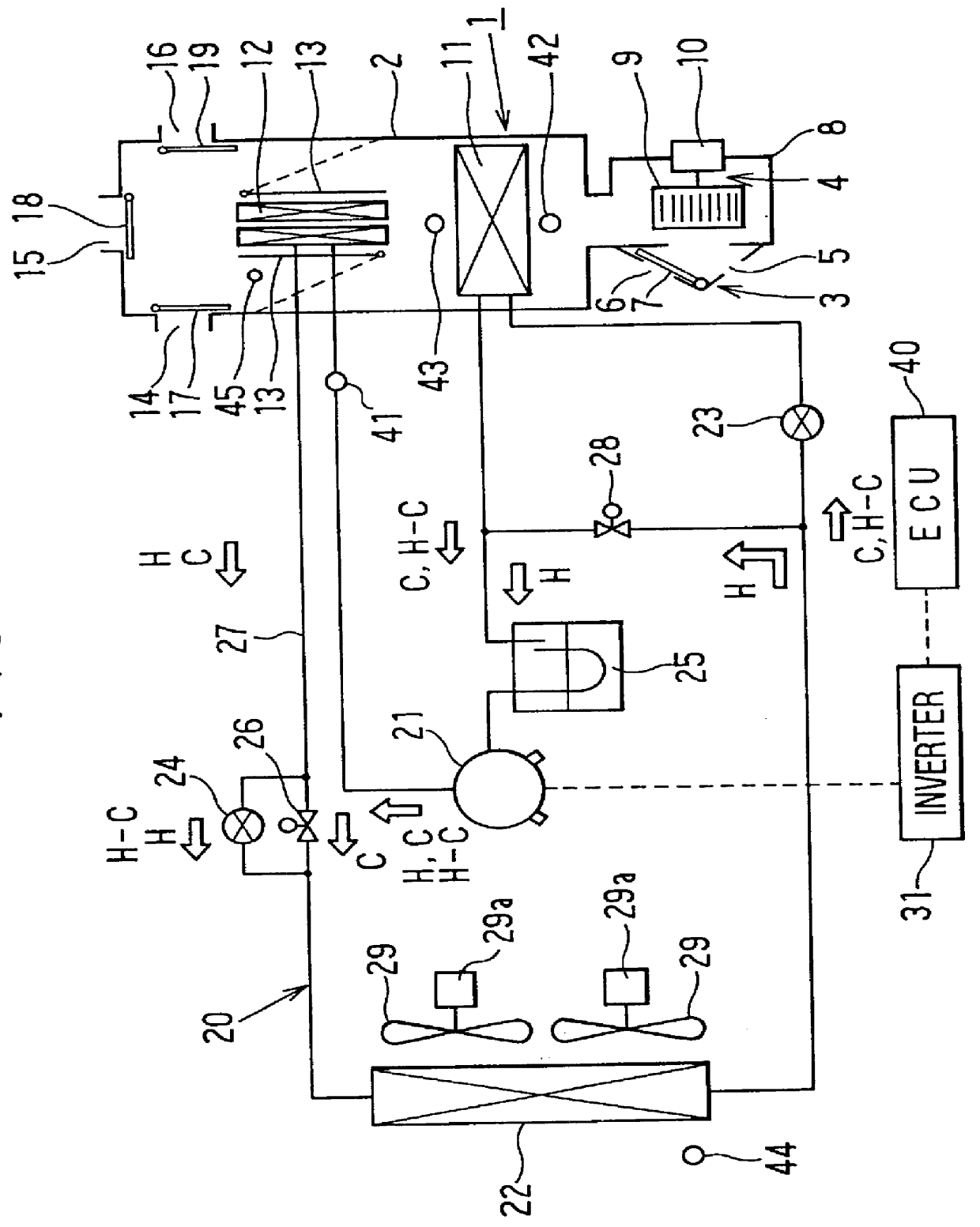
Heat pump system for vehicle and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20140069123A1Improve heating performanceImproving performance dehumidificationMechanical apparatusHeat pumpsEngineeringRefrigerant
A heat pump system for a vehicle may include a cooling apparatus that supplies and circulates coolant to a motor and an electrical equipment through a cooling line, wherein the cooling apparatus includes a radiator, a cooling fan that ventilates wind to the radiator, and a water pump connected to the cooling line, and an air conditioner apparatus connected through a refrigerant line, wherein the air conditioner apparatus includes a water-cooled condenser connected to the cooling line to change a temperature of the coolant using a waste heat that has occurred in the motor and the electrical equipment according to each mode of the vehicle and that is connected to the refrigerant line to enable an injected refrigerant in the refrigerant line to exchange a heat with the coolant at the inside thereof, and an air-cooled condenser connected in series to the water-cooled condenser through the refrigerant line.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Heat pump cycle
ActiveUS20140318170A1Improve performanceSuppression of of improvedHeat pumpsEvaporators/condensersEngineeringHigh pressure
A heat pump cycle includes a refrigerant circuit and a coolant circuit. A first heat exchanger and a second heat exchanger are disposed between the refrigerant circuit and the coolant circuit. The first heat exchanger includes an exterior heat exchanger that functions as an evaporator in a heating operation, and a radiator for radiating heat of a coolant. The second heat exchanger transmits a heat of high-pressure refrigerant to the coolant in the heating operation. A temperature of refrigerant within the second heat exchanger is higher than a temperature of refrigerant within the first heat exchanger. The heat obtained from the second heat exchanger is supplied to the first heat exchanger through the coolant. Further, the heat obtained from the second heat exchanger is stored in the coolant. In defrosting operation, the coolant that has stored the heat therein is supplied to the first heat exchanger.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Stationary vehicle air conditioning system and method
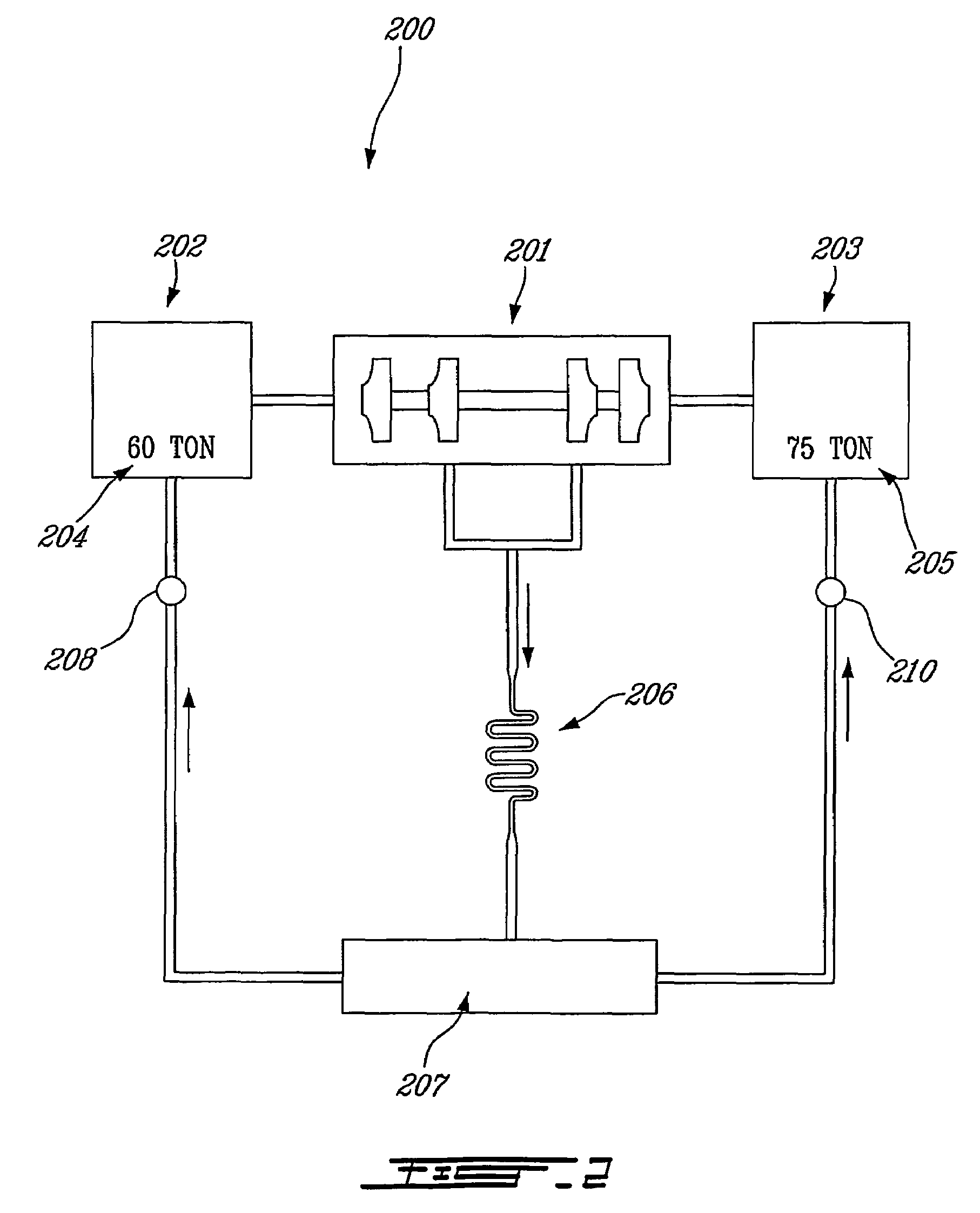
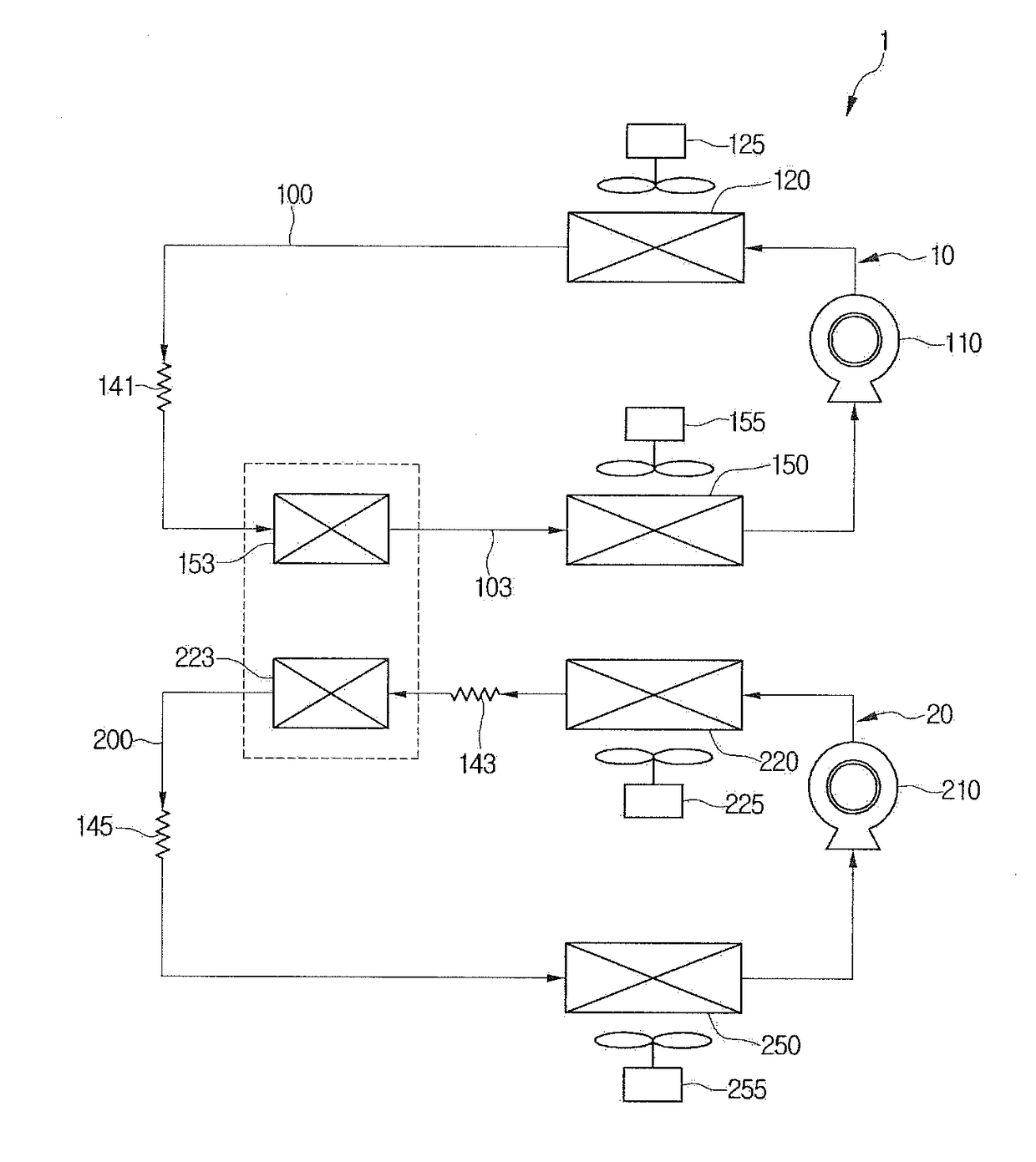
ActiveUS20060042284A1Simple regulationImprove overall utilizationAir-treating devicesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleMechanical energyAir conditioning
The invention pertains to a stationary vehicle air conditioning system with a refrigerant circuit, in which a compressor circulates refrigerant through a refrigerant circuit including at least one condenser. The one compressor may be powered by the vehicle's mechanical power, by an electrical source, or by a combination of these driving forces. Depending on desired operating characteristics, a plurality of condensers may be arranged in a series or parallel configuration within the circuit, and a second compressor also may be added, which second compressor may be powered by a source other than the mechanical energy of the vehicle's engine. A plurality of fans may be positioned and selectively operable to provide cooling air streams to one or more of the condensers, with the vehicle engine mechanically driving one fan and an electrical power source driving another fan. At minimum, at least one fan is provided to provide a cooling air stream to one or more condensers, wherein the fan is a hybrid drive unit that is capable of being driven through mechanical or electrical means.
Owner:BEHR GMBH & CO KG
Parked aircraft climate control system and method
InactiveUS20090084120A1Reducing heat-removal capacity of systemMaintaining system operationAir-treating devicesMechanical apparatusEngineeringHigh pressure
A conditioned air delivery system is provided for parked aircraft. The system can accommodate elevated thermal loads while maintaining operation, albeit with reduced flow rates or slightly elevated temperatures. When temperature set points are not reached or cannot be maintained, a second compressor of a refrigeration unit is operated in parallel with a first compressor. When refrigerant pressure becomes excessive, a second fan is operated that is associated with a condenser of the system. Still higher pressures, indicative of higher thermal loads, can cause the system to shut down operation of one of the compressors, reducing the overall cooling capacity of the system, while maintaining the supply of refrigerated air to the aircraft. The airflow may be reduced to maintain an air temperature at or near the desired temperature. Coordination of several parallel and redundant refrigeration units may be provided with a single blower and coordinated control.
Owner:HOBART BROS
Low-condensing-pressure deep supercooling efficient dehumidifier
ActiveCN104019574AReduce condensing pressureReduce power consumptionCompression machines with several condensersBusiness efficiencyThermal bridge
The invention provides a low-condensing-pressure deep supercooling efficient dehumidifier. The low-condensing-pressure deep supercooling efficient dehumidifier comprises an air flue, a first draught fan and a refrigerating and dehumidifying system. The refrigerating and dehumidifying system comprises an evaporator, a first condenser, a second condenser, a compressor and a throttling device. According to the low-condensing-pressure deep supercooling efficient dehumidifier, a bypass airflow channel is additionally arranged in the air flue between the first condenser and the second condenser, so that the ventilation quantity of the first condenser is increased, and the condensing pressure of refrigerating fluid gas in the condensers is reduced; the first condenser is used for heat release and cooling of a sensible heat portion of the overheated refrigerating fluid gas and heat release, condensation and liquefaction of the refrigerating fluid gas, and the second condenser is used for cooling and supercooling of refrigerating fluid; since a finned thermal bridge between the first condenser and the second condenser is disconnected, the supercooling degree of the refrigerating fluid at the tail end of the second condenser is improved, the vaporization ratio of the refrigerating fluid in the throttling device can be lowered, the evaporation and heat absorption capacity of the refrigerating fluid in the evaporator is improved, and the energy efficiency ratio of the dehumidifier is increased substantially.
Owner:HANGZHOU PREAIR ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE IND
Heat pump system for vehicle and control method thereof
ActiveUS20130019615A1Improve heating performanceImproving performance dehumidificationMechanical apparatusHeat pumpsAir conditioningRefrigerant
A method for controlling a heat pump system is provided with air conditioning means connected to a controller and including a plurality of valves and expansion valves connected to each other through a refrigerant line and a bypass line, a compressor, an accumulator, an evaporator, an exterior condenser, an interior condenser, and an HVAC module having a PTC heater and a door at a warming mode, a cooling mode, a dehumidification mode, a dehumidification / defrosting mode, or an extremely low temperature dehumidification / defrosting mode according to selection of a driver.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Heat Pump Cycle
InactiveUS20020007943A1Coefficient of performance (COP) of the heat pump from becoming worseIncrease temperatureHeat pumpsFuel cell auxillariesEngineeringHigh pressure
In a heat pump cycle, a first high-pressure side heat exchanger is disposed to perform a heat exchange between refrigerant discharged from a compressor and a first fluid, and a second high-pressure side heat exchanger is disposed to perform a heat exchanger between refrigerant from the first high-pressure side heat exchanger and a second fluid having a temperature lower than that of the first fluid. Accordingly, a heat quantity obtained from the heat pump cycle is the sum of a heat amount obtained from the first high-pressure side heat exchanger and a heat amount obtained from the second high-pressure side heat exchanger.
Owner:NIPPON SOKEN +1
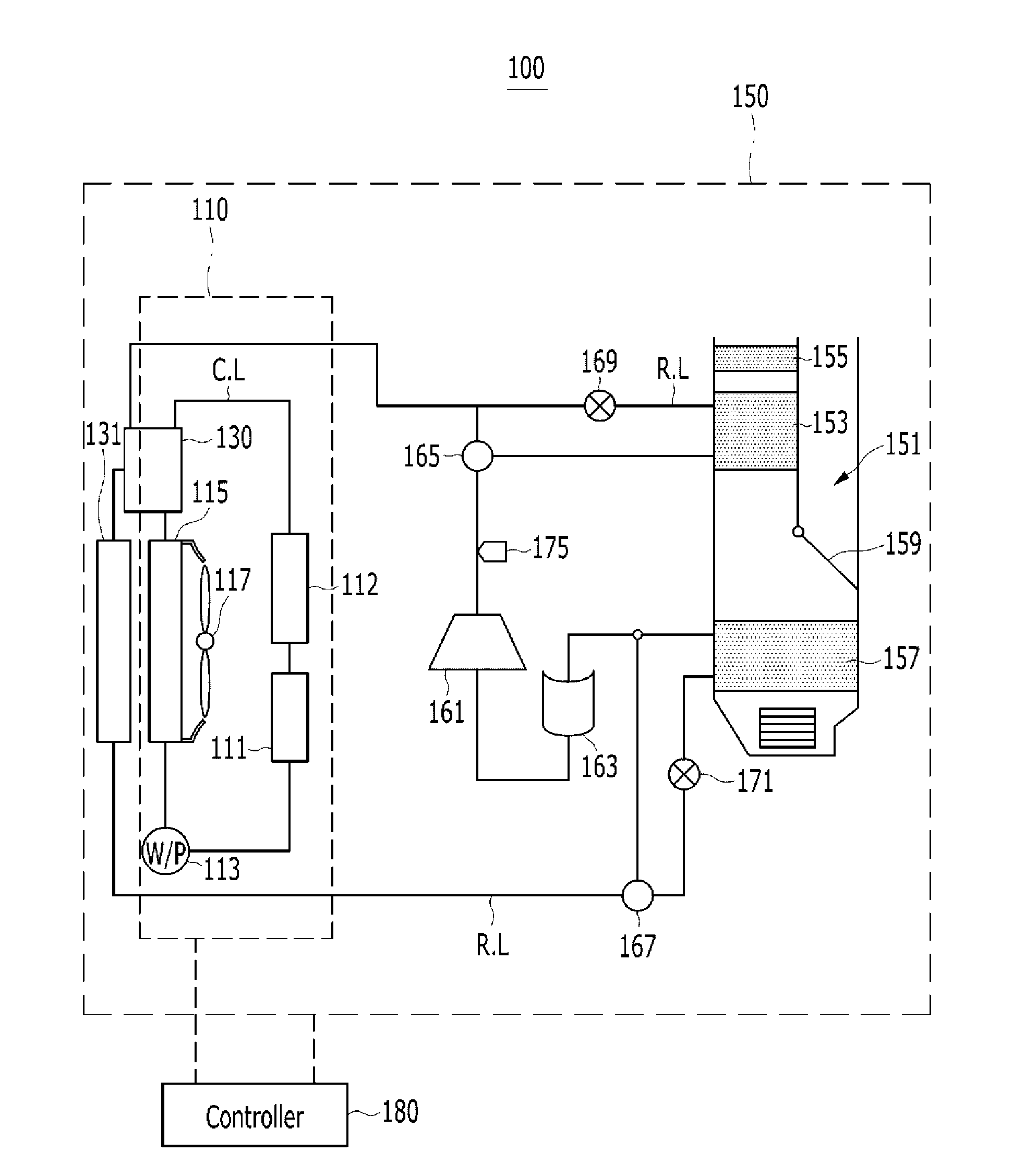
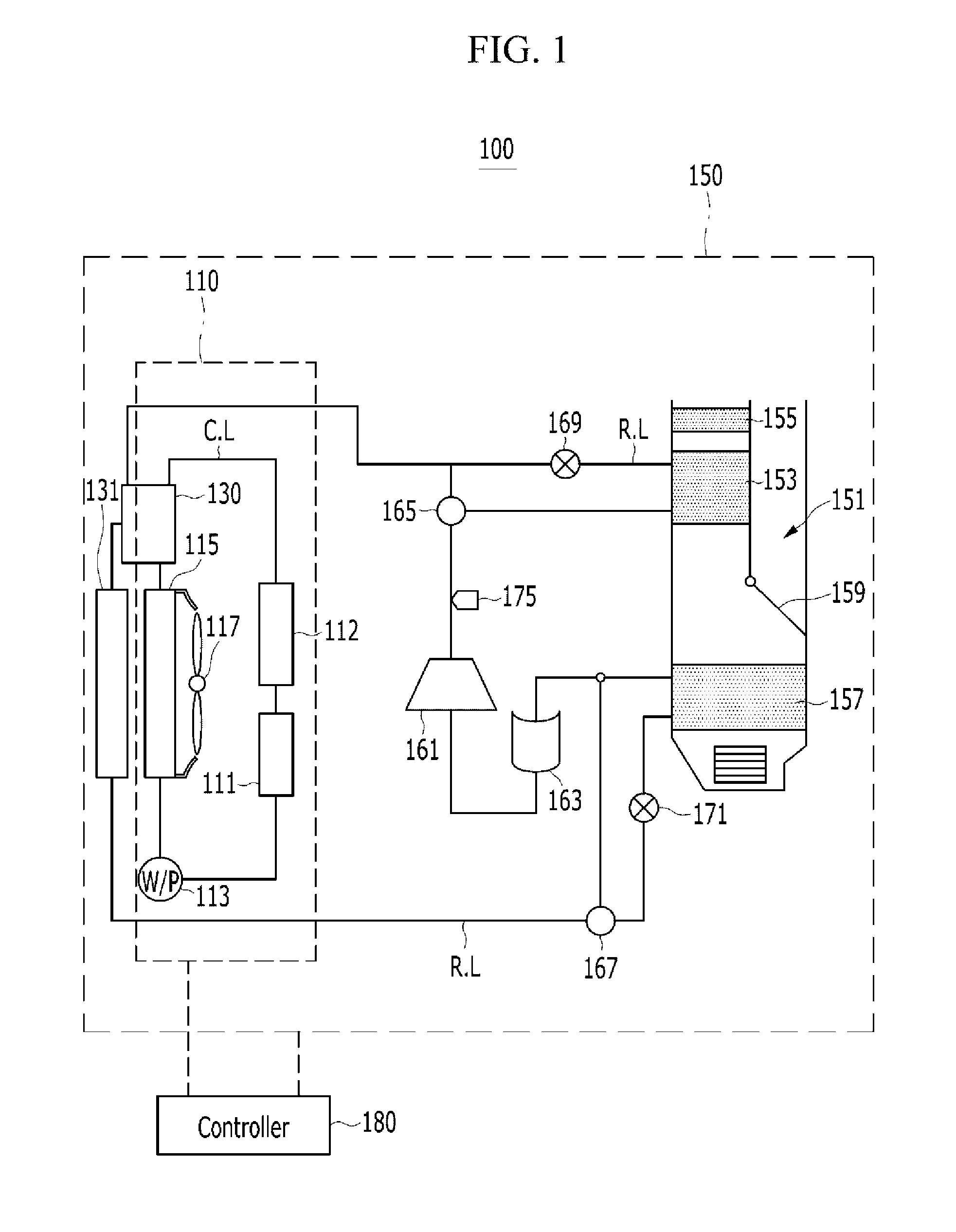
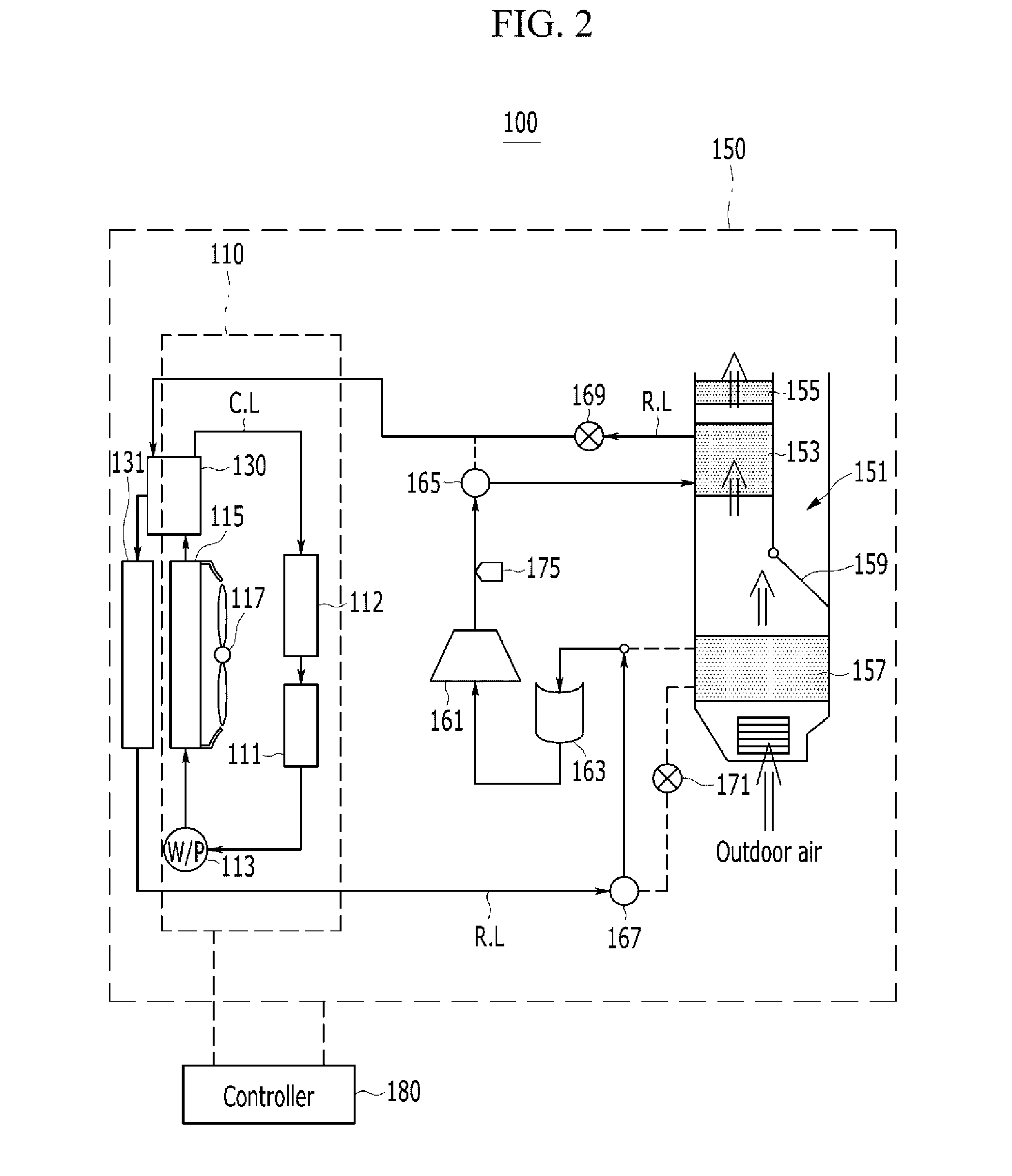
Refrigerator and control method thereof
ActiveUS20170176083A1Improve refrigeration cycle efficiencyImprove cooling efficiencyMechanical apparatusCompression machines with several condensersEvaporationEngineering
Disclosed are a refrigerator and a control method thereof. The refrigerator according to one aspect includes a main body having a storage chamber; a compressor configured to compress a refrigerant; a condenser configured to condense the refrigerant compressed by the compressor; an evaporation expander configured to depressurize the refrigerant condensed by the condenser; a first evaporator configured to evaporate the refrigerant depressurized by the evaporation expander and thus to cool the storage chamber; a condensing expander installed between the condenser and the evaporation expander and configured to depressurize the refrigerant condensed by the condenser; and a subsidiary condenser installed between the condensing expander and the evaporation expander and configured to condense the refrigerant depressurized by the condensing expander.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Stationary vehicle air conditioning system
ActiveUS7350368B2Improve performanceSimple designCompression machines with several condensersEvaporators/condensersMechanical energyAir conditioning
The invention pertains to a stationary vehicle air conditioning system with a refrigerant circuit, in which at least one compressor circulates the refrigerant to at least two condensers. The at least one compressor may be powered by the vehicle's mechanical power, by an electrical source, or by a combination of these driving forces. Depending on desired operating characteristics, the condensers may be arranged in a series or parallel configuration. A second compressor also may be added, which second compressor may be powered by a source other than the mechanical energy of the vehicle's engine.
Owner:BEHR GMBH & CO KG
Building exhaust and air conditioner condensate (and/or other water source) evaporative refrigerant subcool/precool system and method therefor
InactiveUS7150160B2Improve pumping efficiencyReduce power consumptionCondensate preventionDomestic cooling apparatusWater wetWater source
Owner:OLIVE TREE PATENTS 1
Refrigerant circuit and heat pump type hot water supply apparatus
InactiveUS20050066678A1Cutting costsInferior cycle efficiencyHeat pumpsCompression machines with non-reversible cycleEngineeringRefrigerant
In a heat pump type hot water supply apparatus having a compressor (16), an outdoor heat exchanger (22), an expansion valve (24) and at least one indoor heat exchangers, and a water heat exchanger (18) for heat-exchanging refrigerant and water to achieve hot water, the water heat exchanger (18) is equipped in the refrigerant circuit so as to be connected to the outdoor heat exchanger (22) in series in the refrigerant circuit.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Refrigeration cycle device
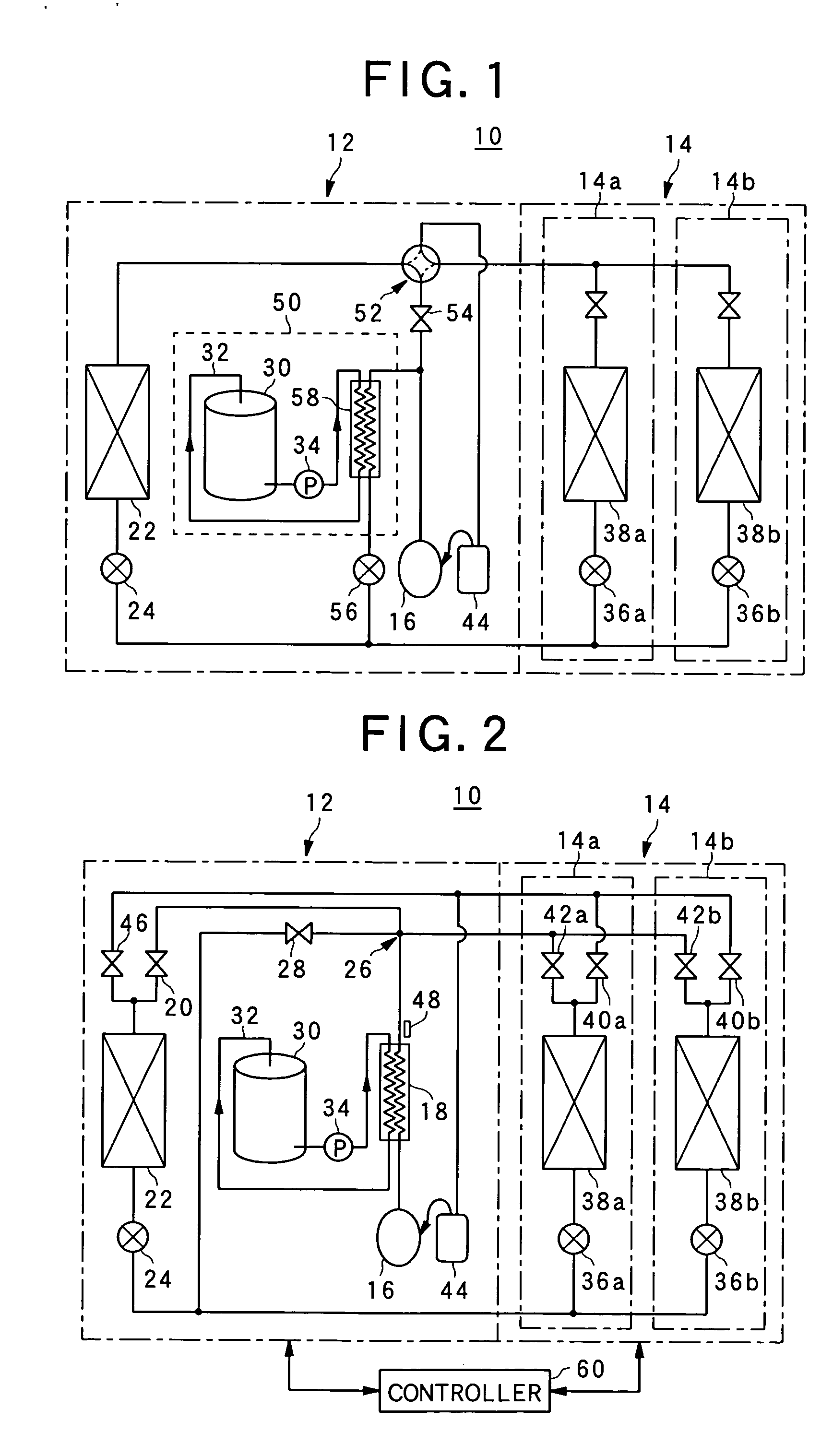
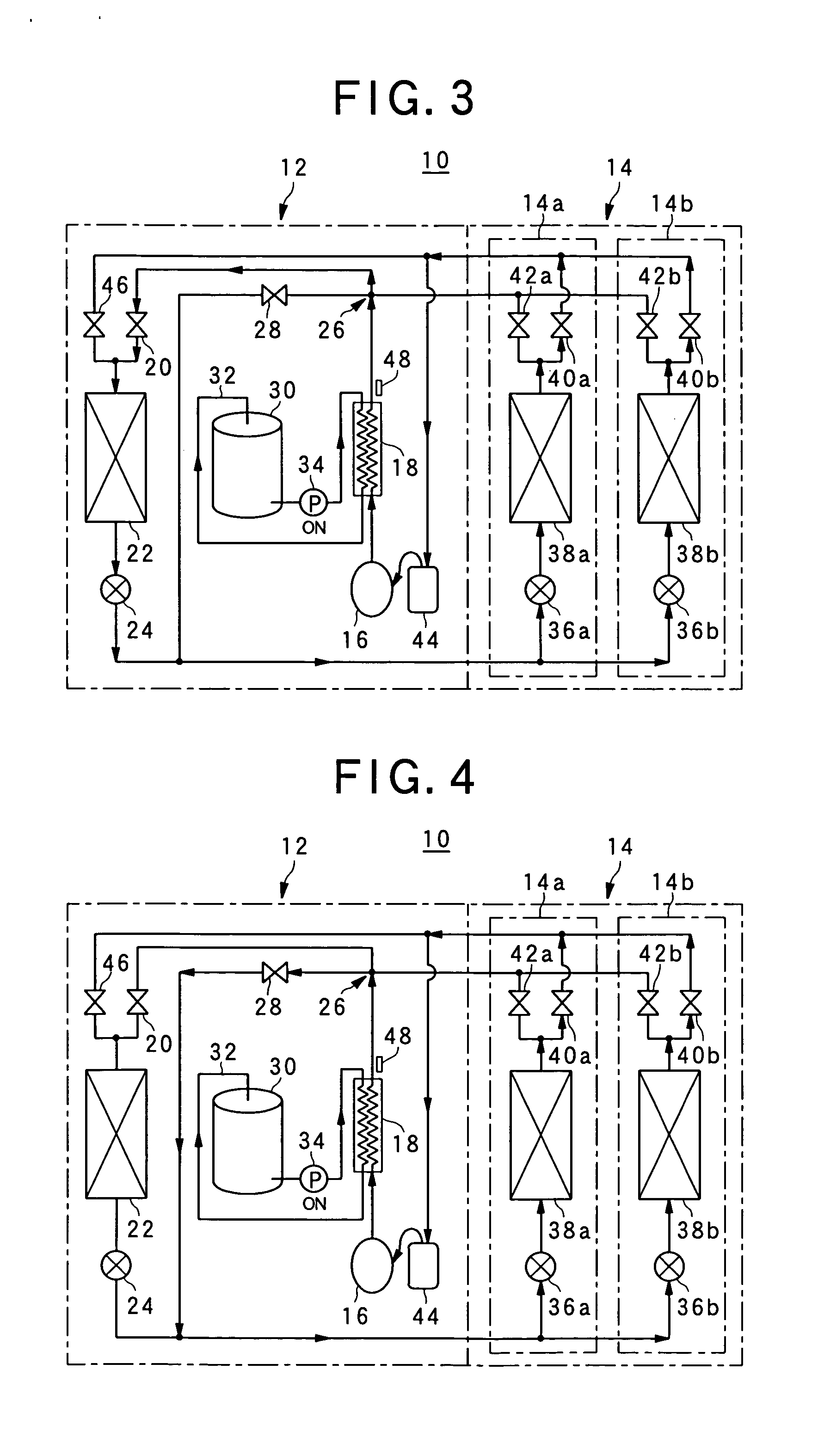
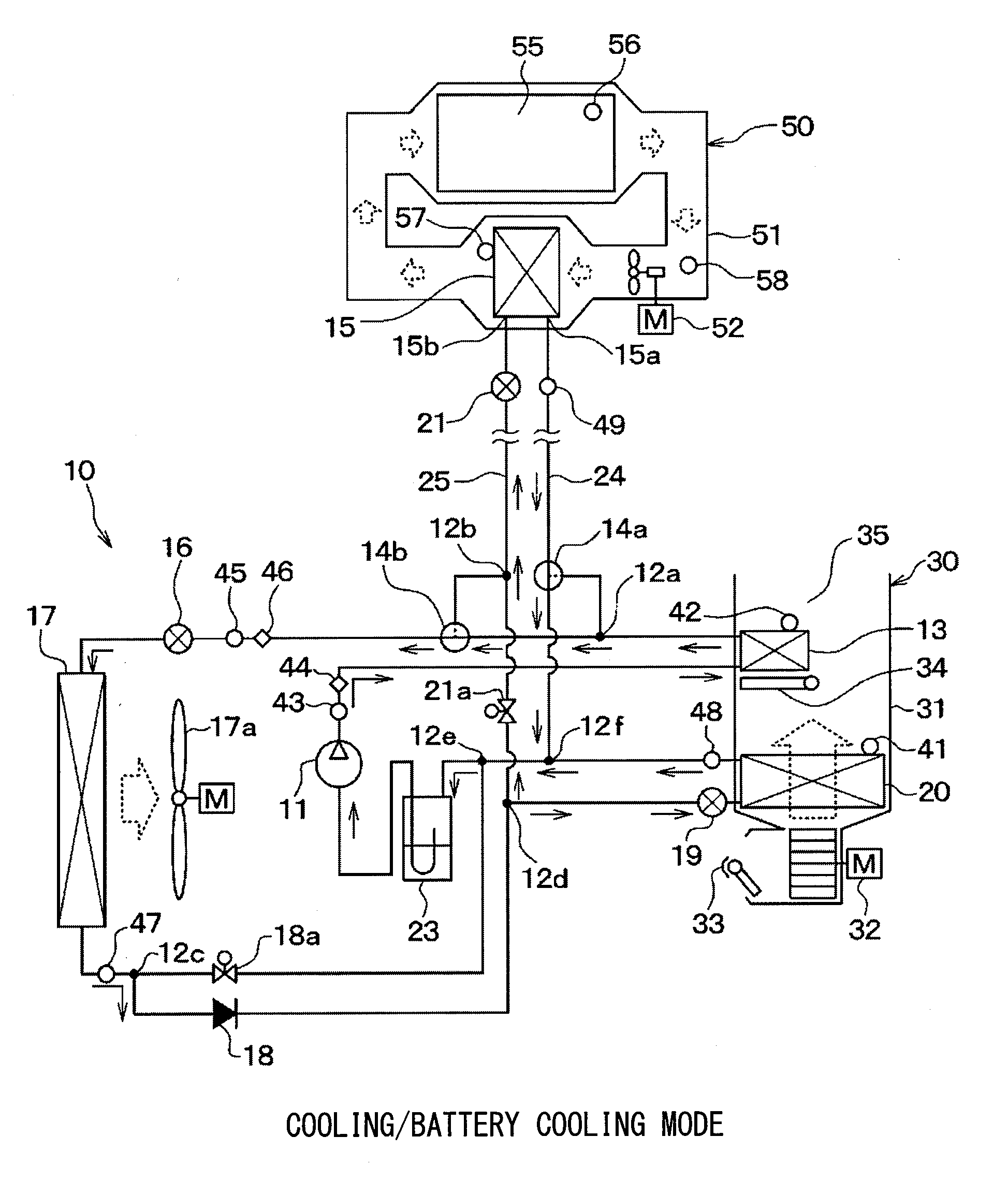
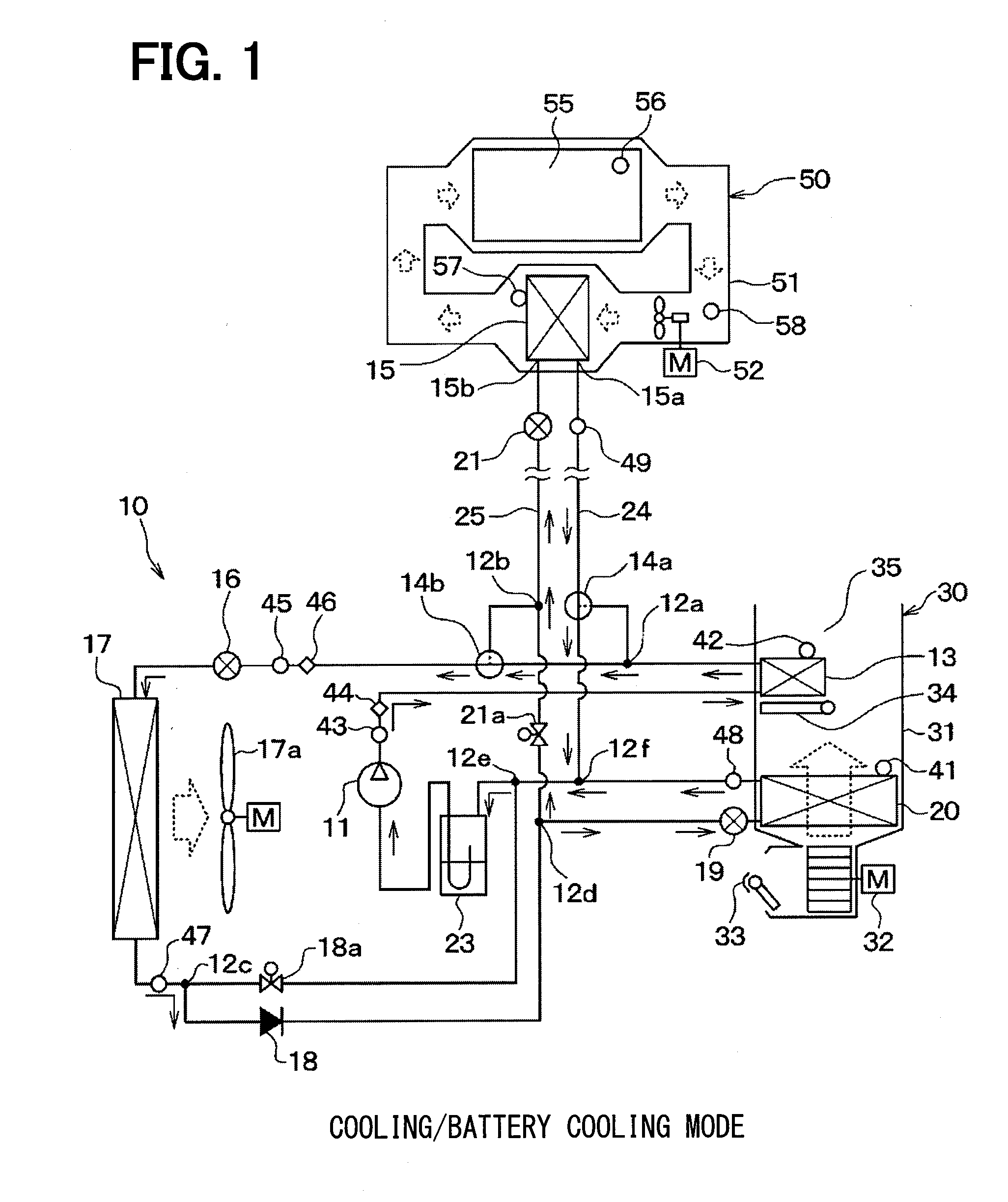
ActiveUS20150295285A1Small passage cross-sectional areaLarge passage cross-sectional areaMechanical apparatusPower to auxillary motorsEngineeringOperation mode
In an operation mode for heating battery air, a refrigerant passage switching portion switches over to a first refrigerant passage in which a refrigerant including gas refrigerant flowing out of an interior condenser flows into an auxiliary heat exchanger through a first pipe having a relatively large passage cross-sectional area and a liquid refrigerant flowing out of the auxiliary heat exchanger flows to an inlet of an exterior heat exchanger through a second pipe having a relatively small passage cross-sectional area. Meanwhile, in an operation mode for cooling the battery air, the refrigerant passage switching portion switches over to a second refrigerant passage in which a liquid refrigerant flowing out of the exterior heat exchanger flows into the auxiliary heat exchanger through the second pipe and a gas refrigerant flowing out of the auxiliary heat exchanger flows to a suction port of a compressor through the first pipe.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com