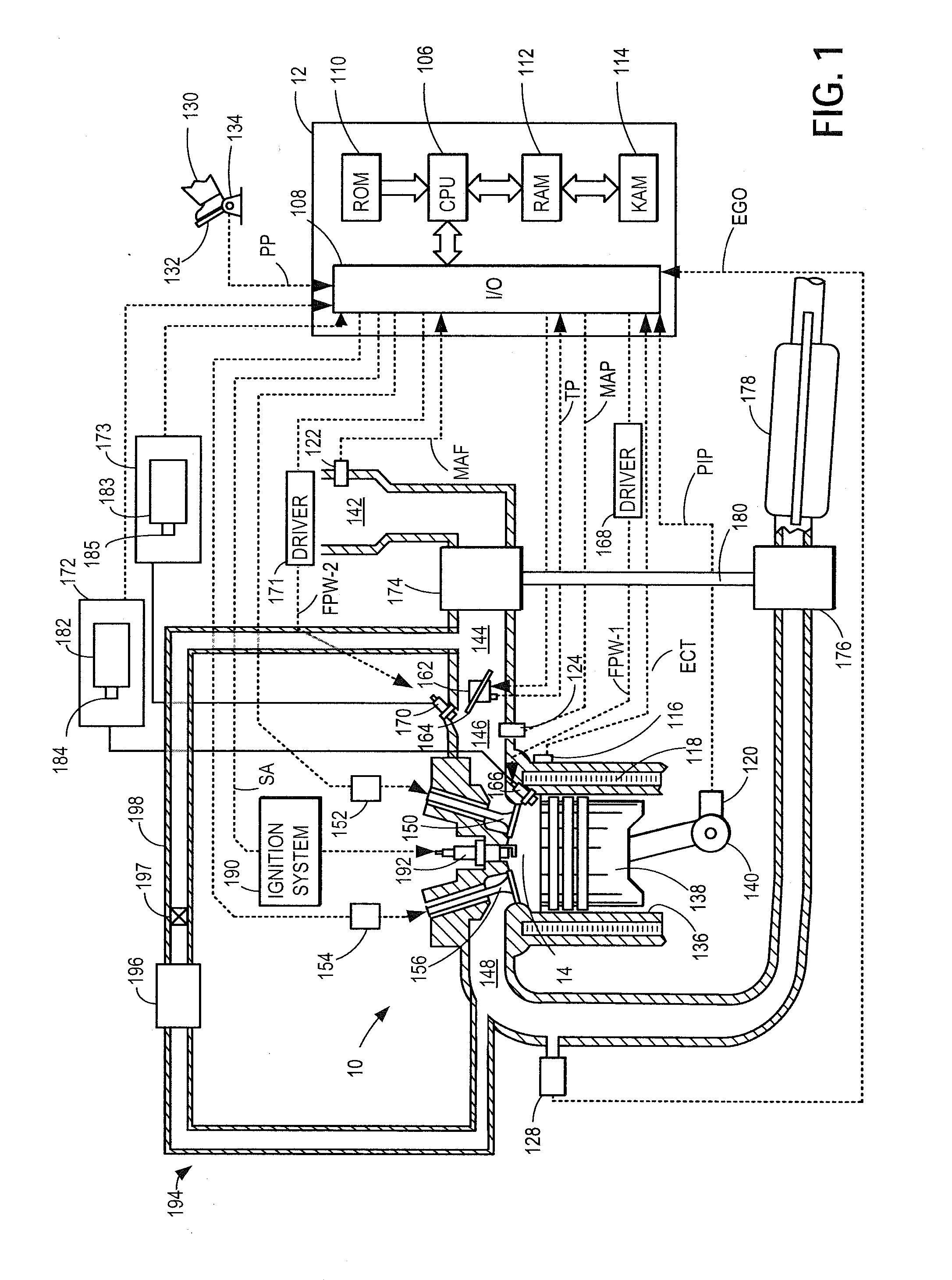
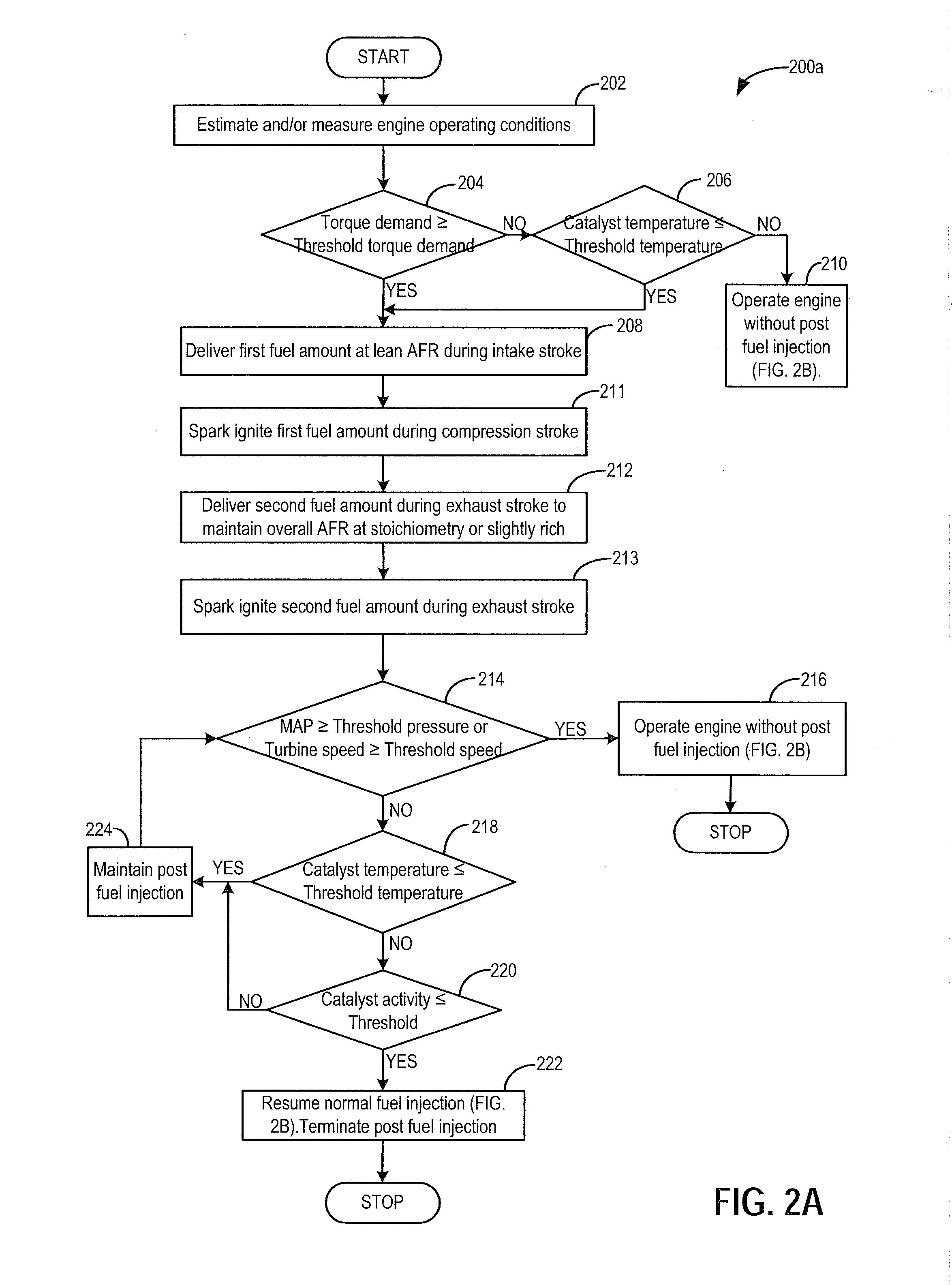
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
757results about "Automatic control with electric engine control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
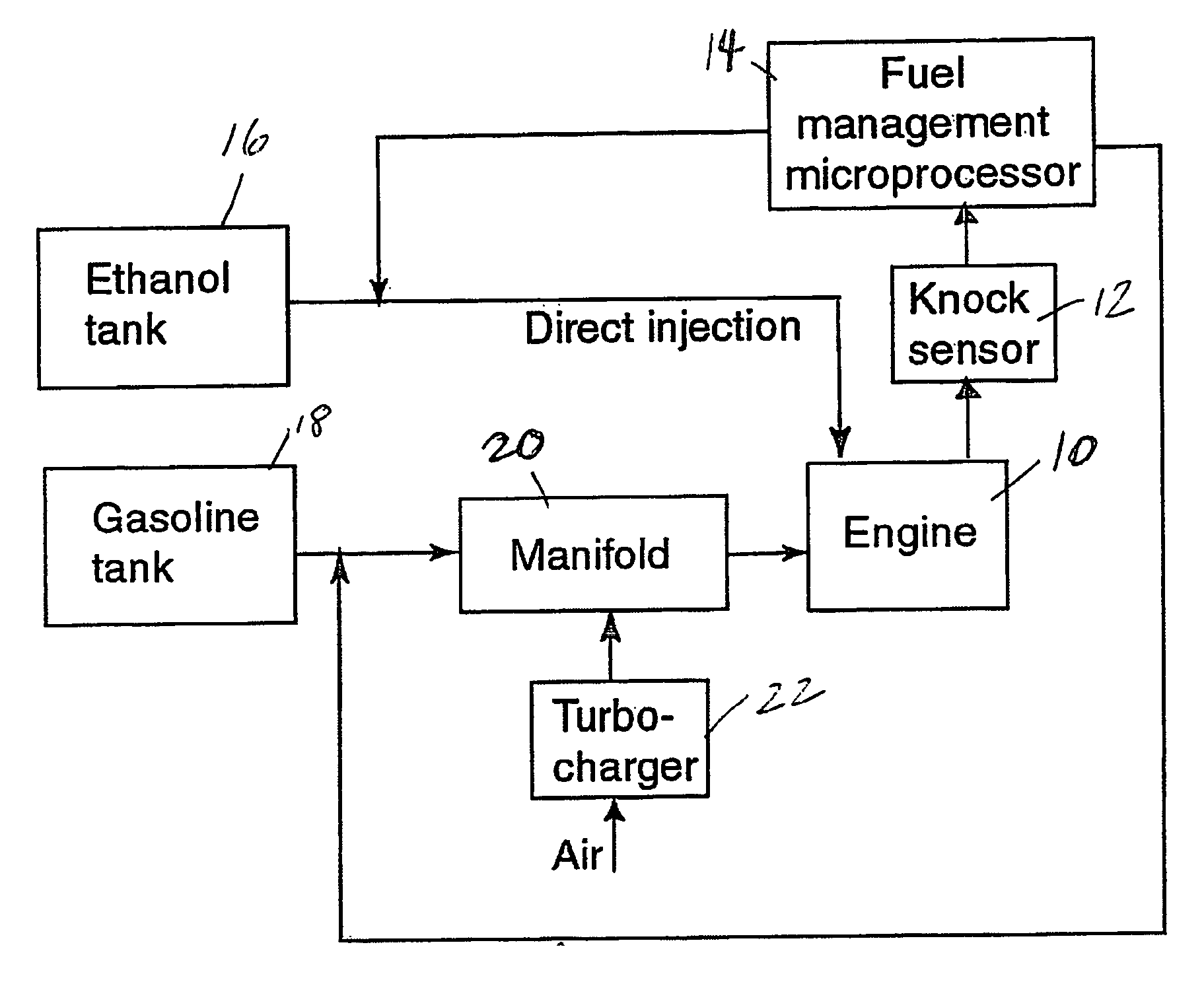
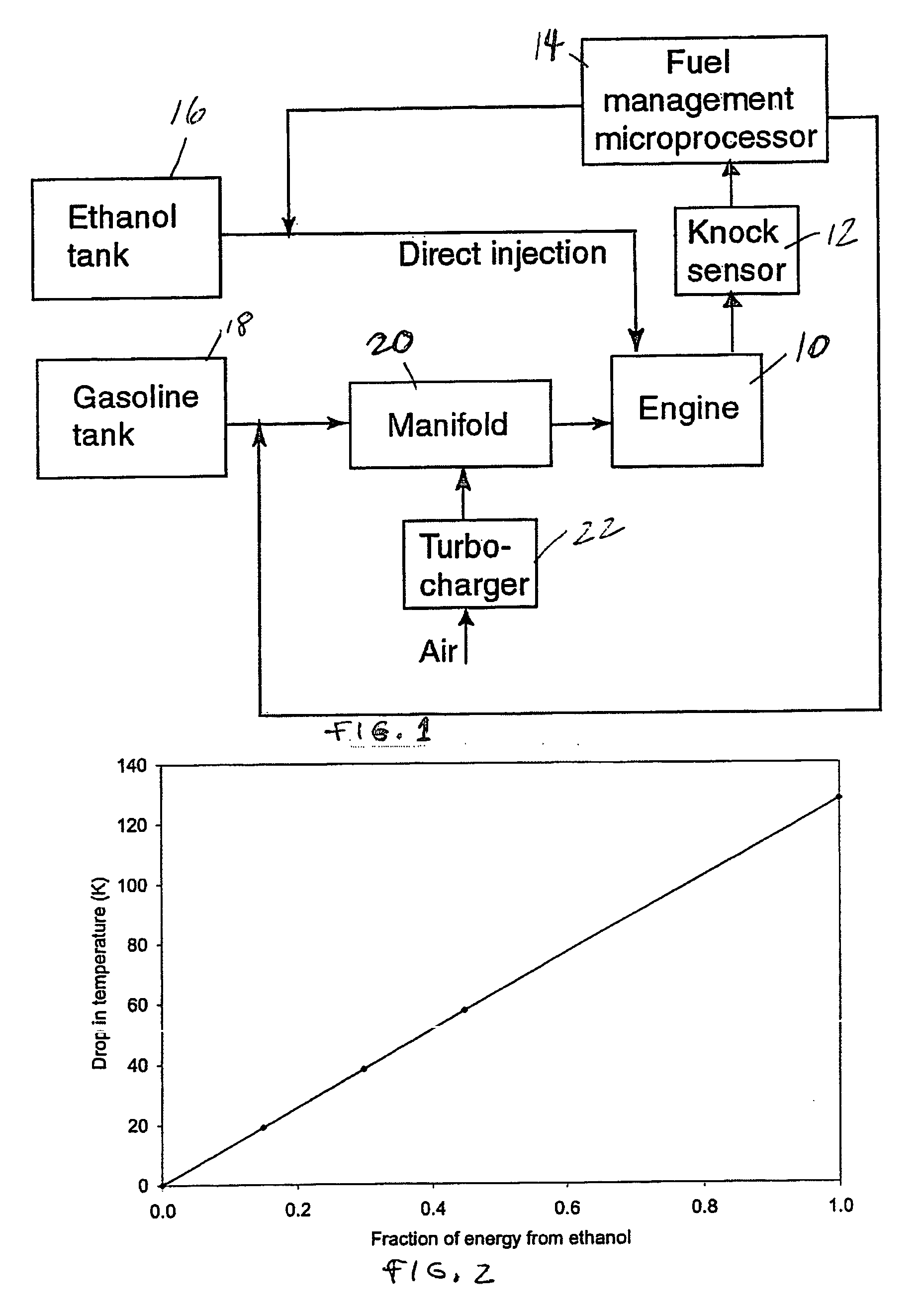
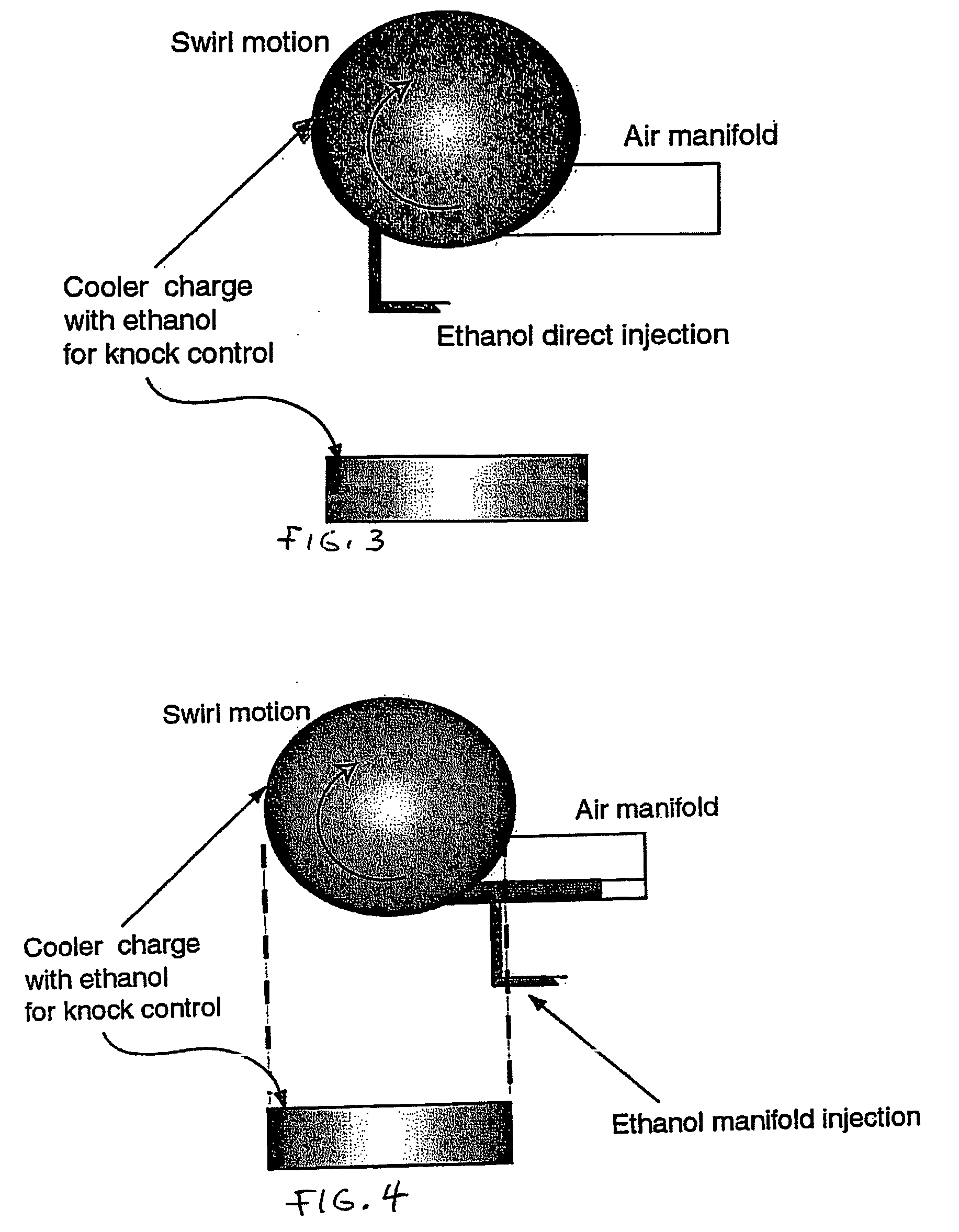
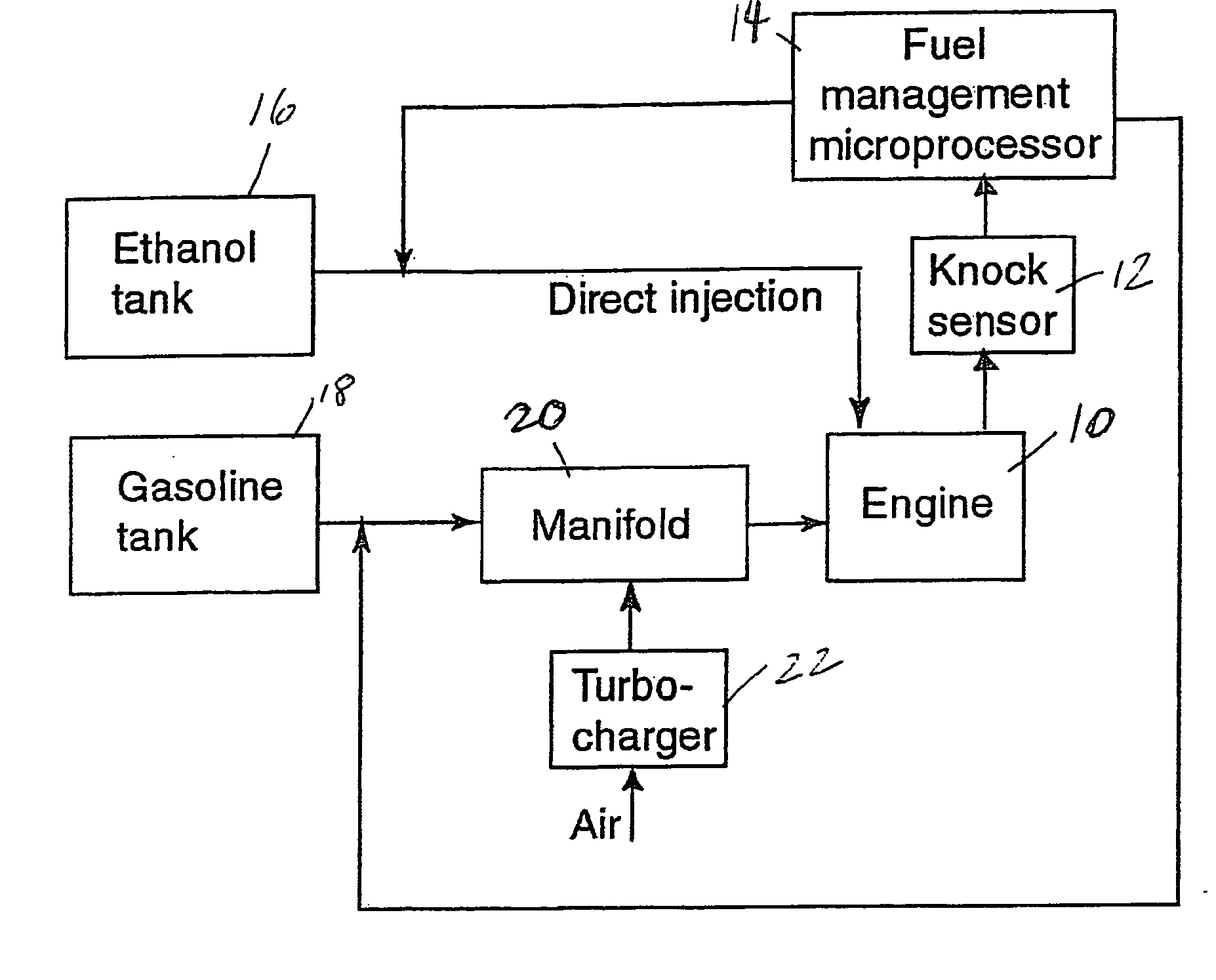
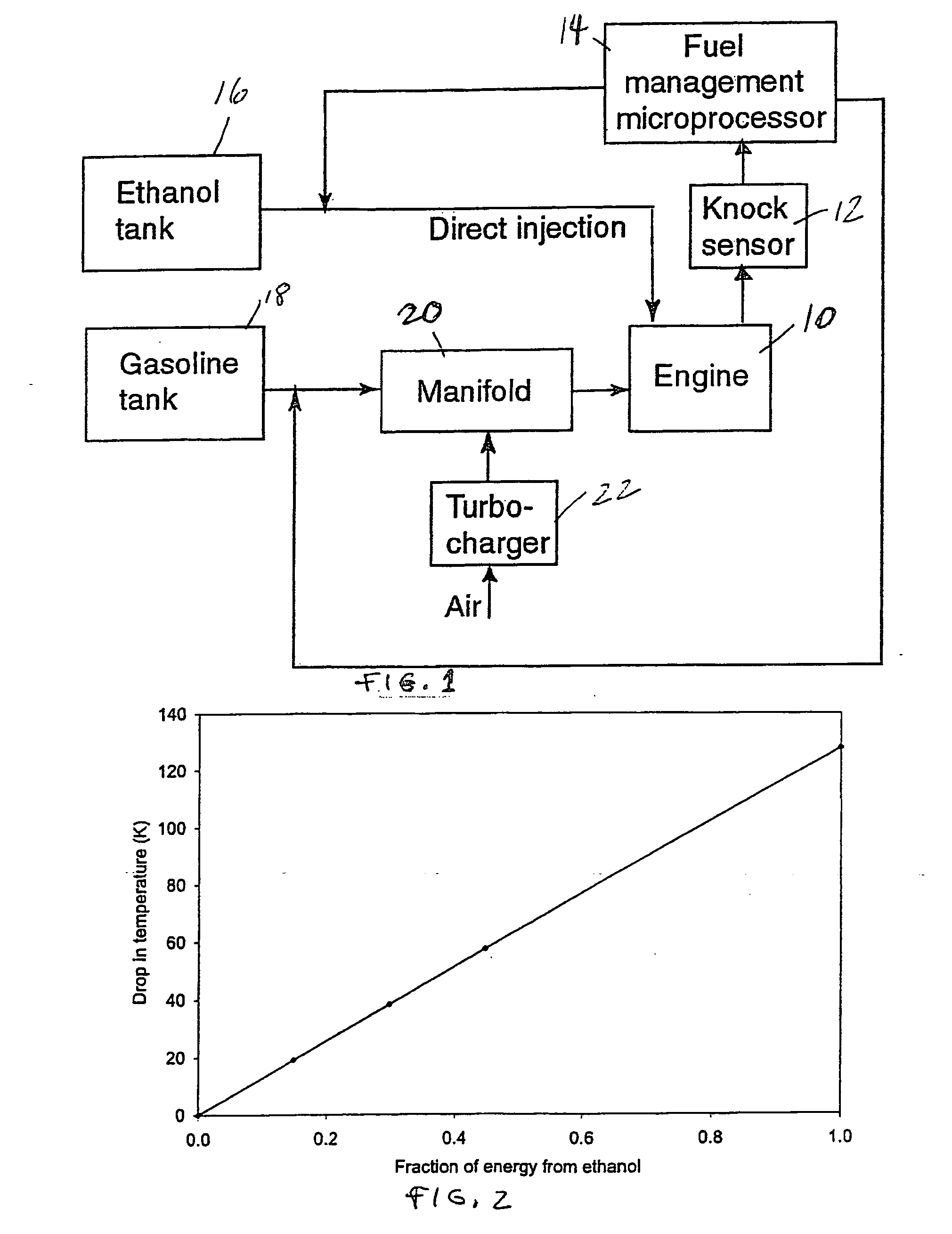
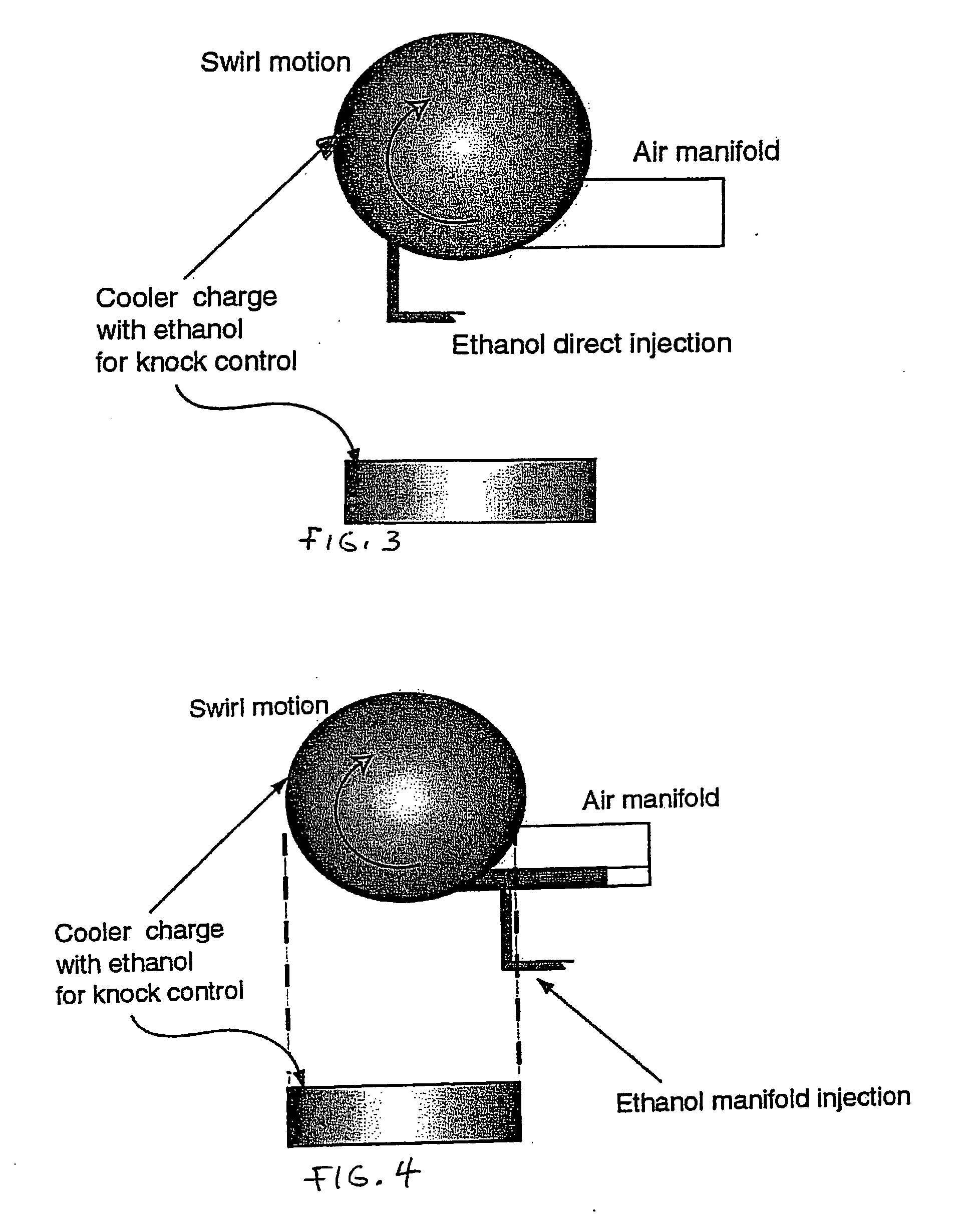
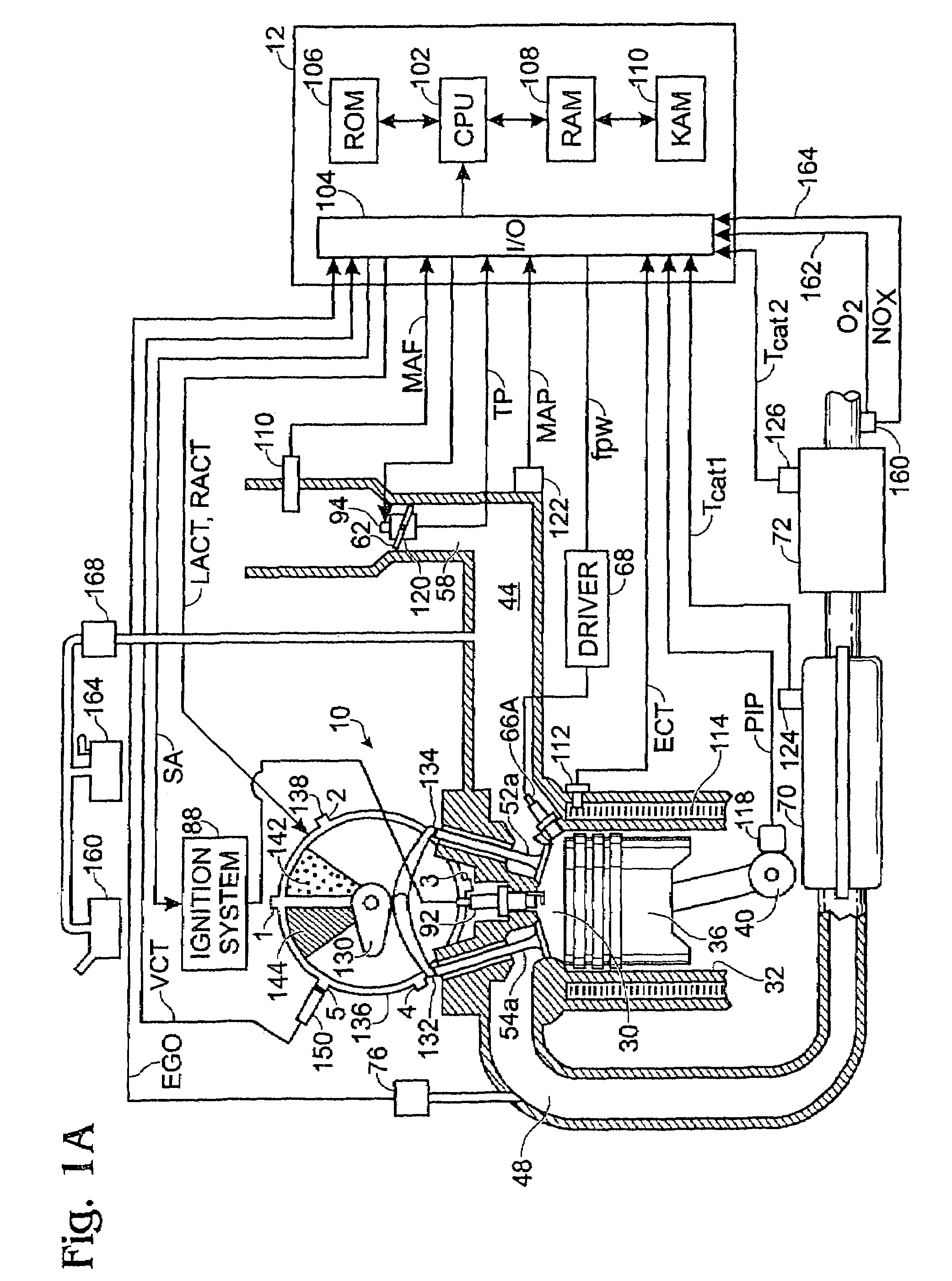
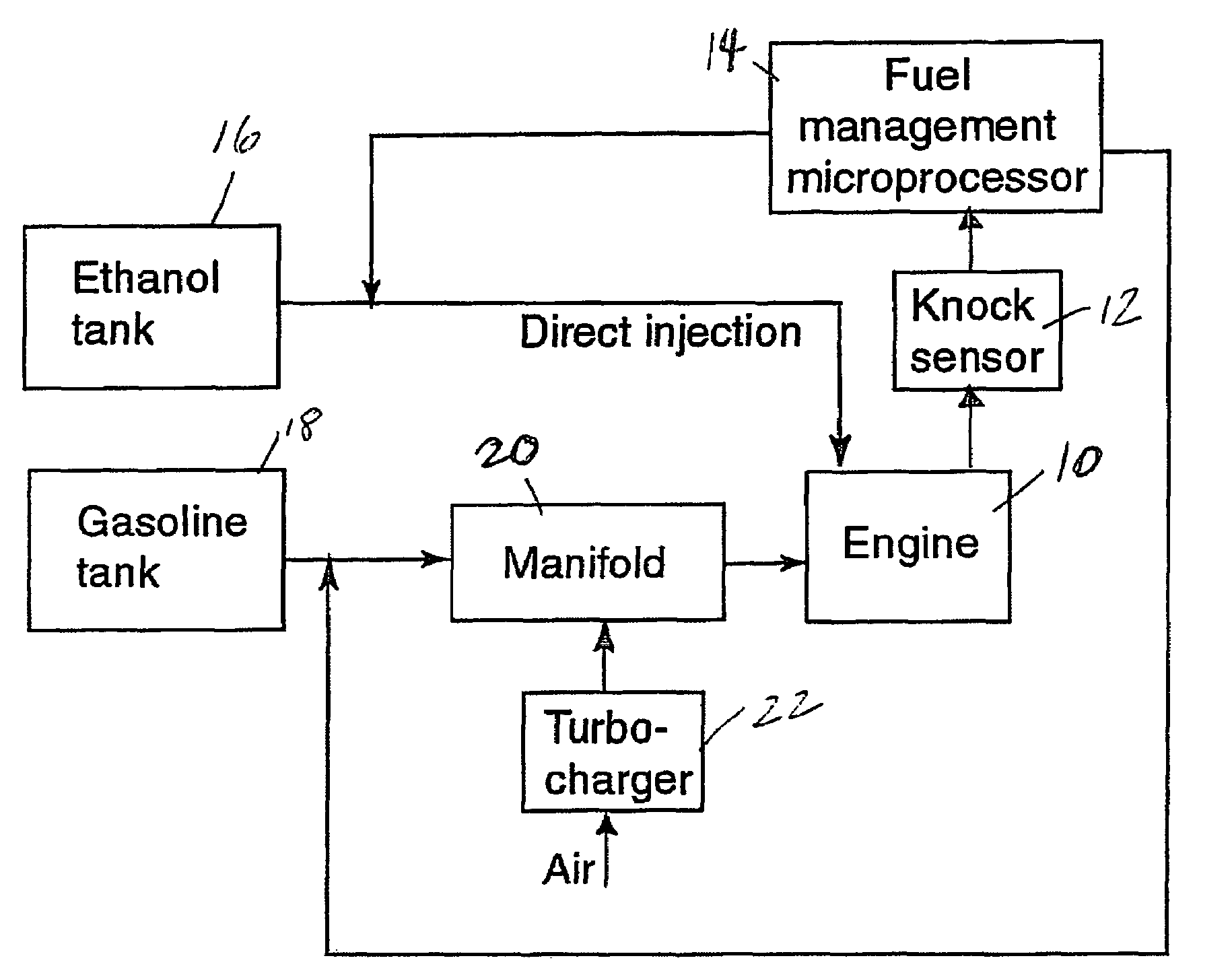
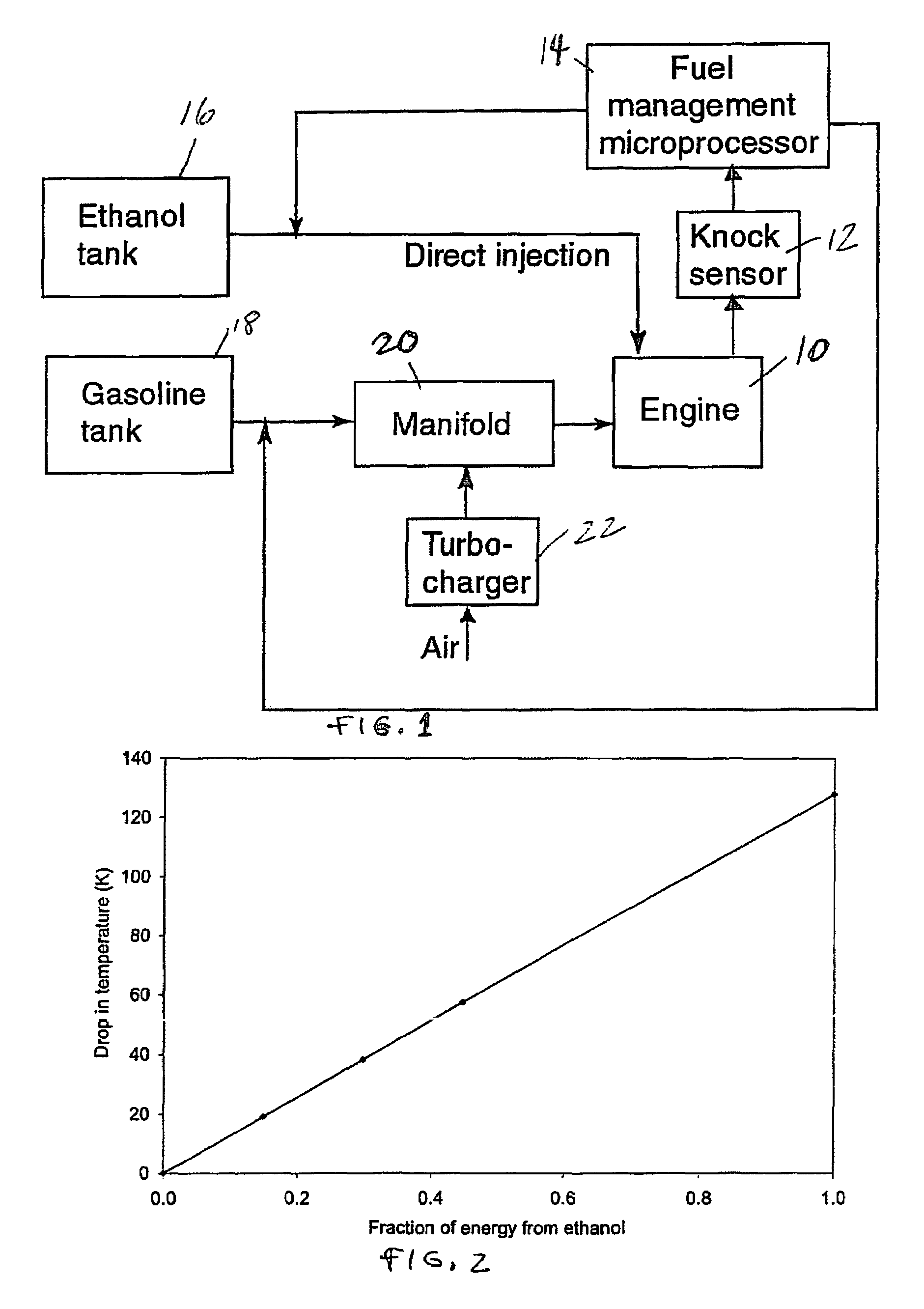
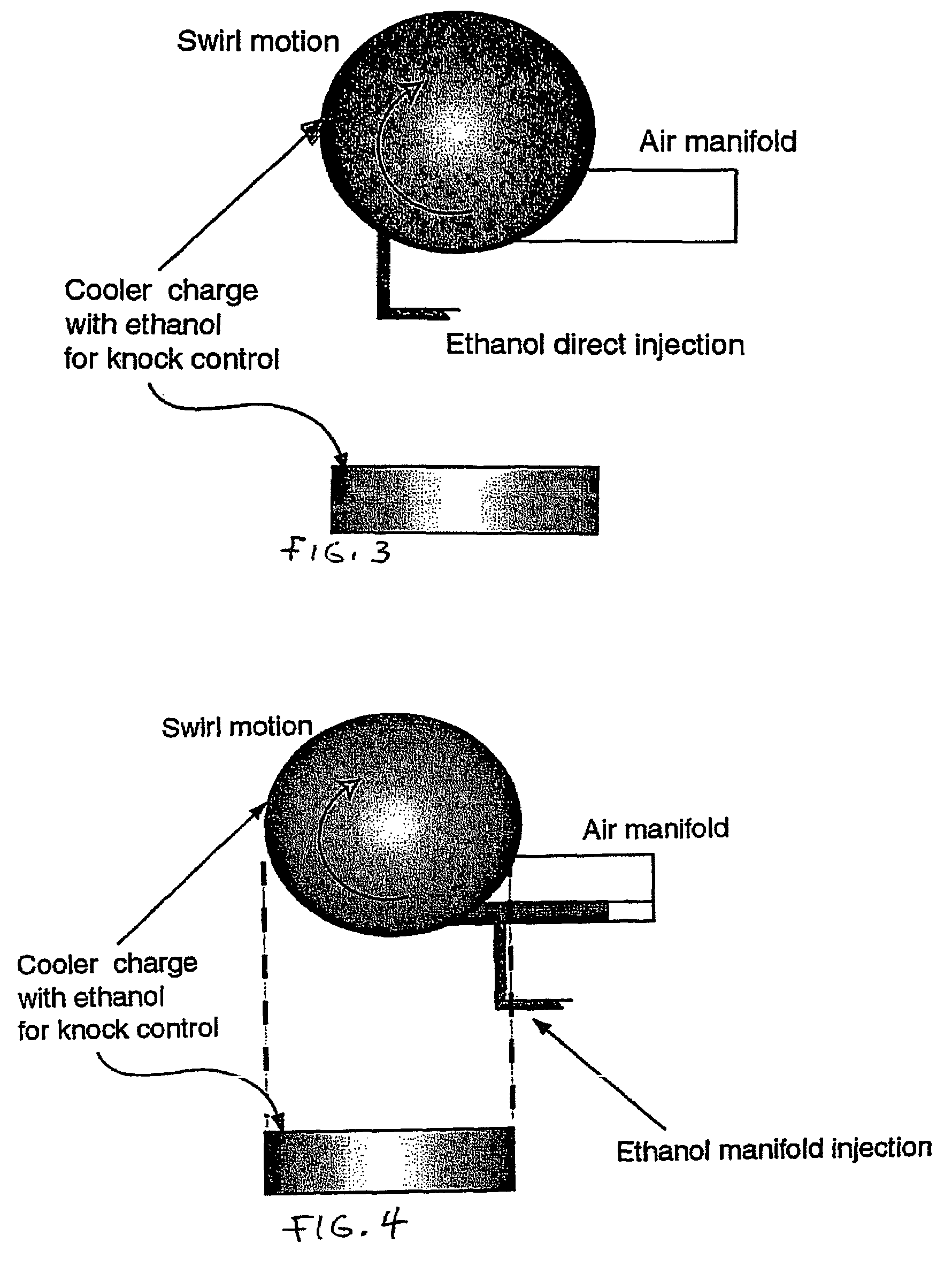
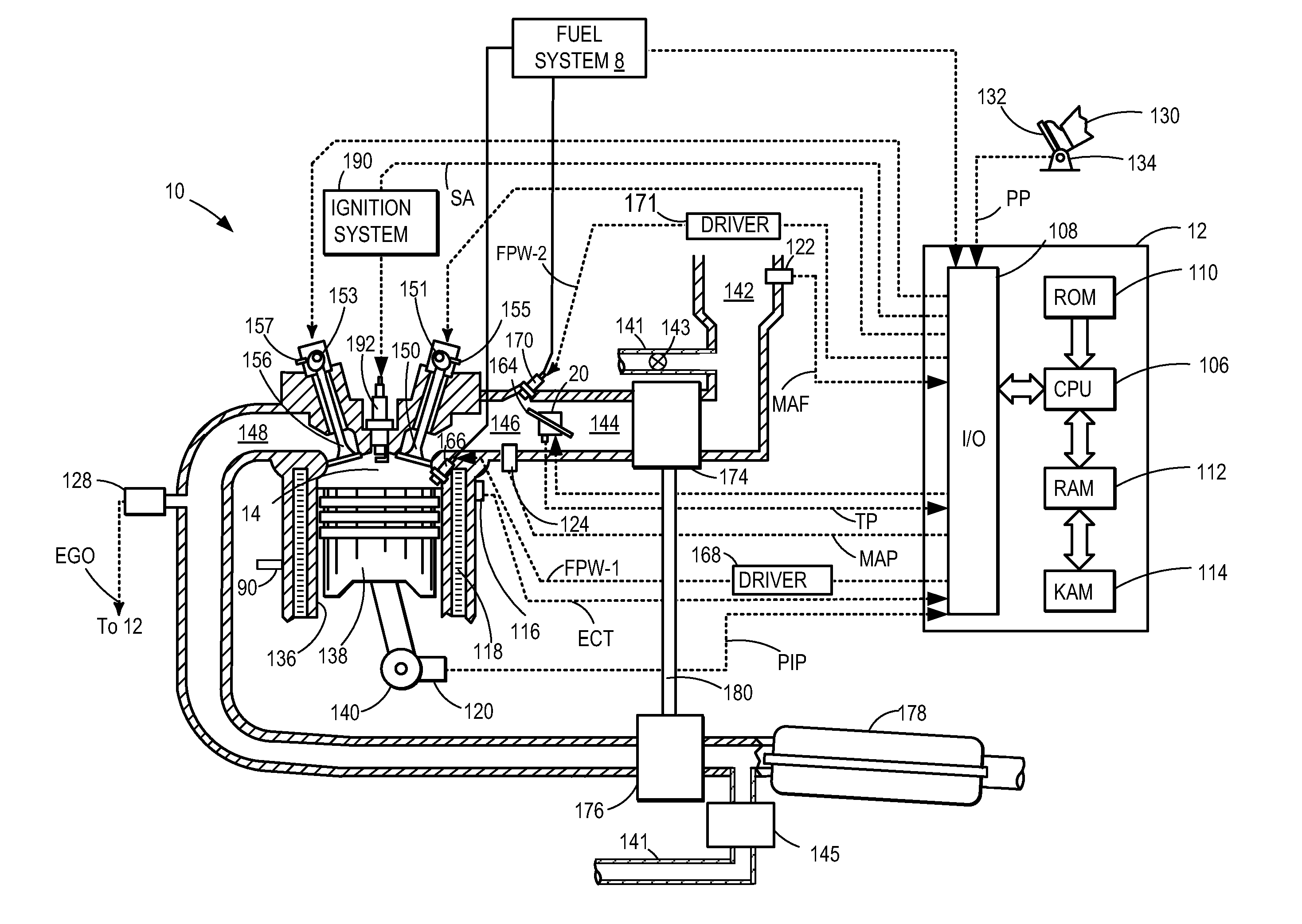
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancehment of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102145A1Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fuel management system for variable anti-knock agent octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS20060102146A1Increase heatReduces octane requirementElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEthanol InjectionEngineering
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
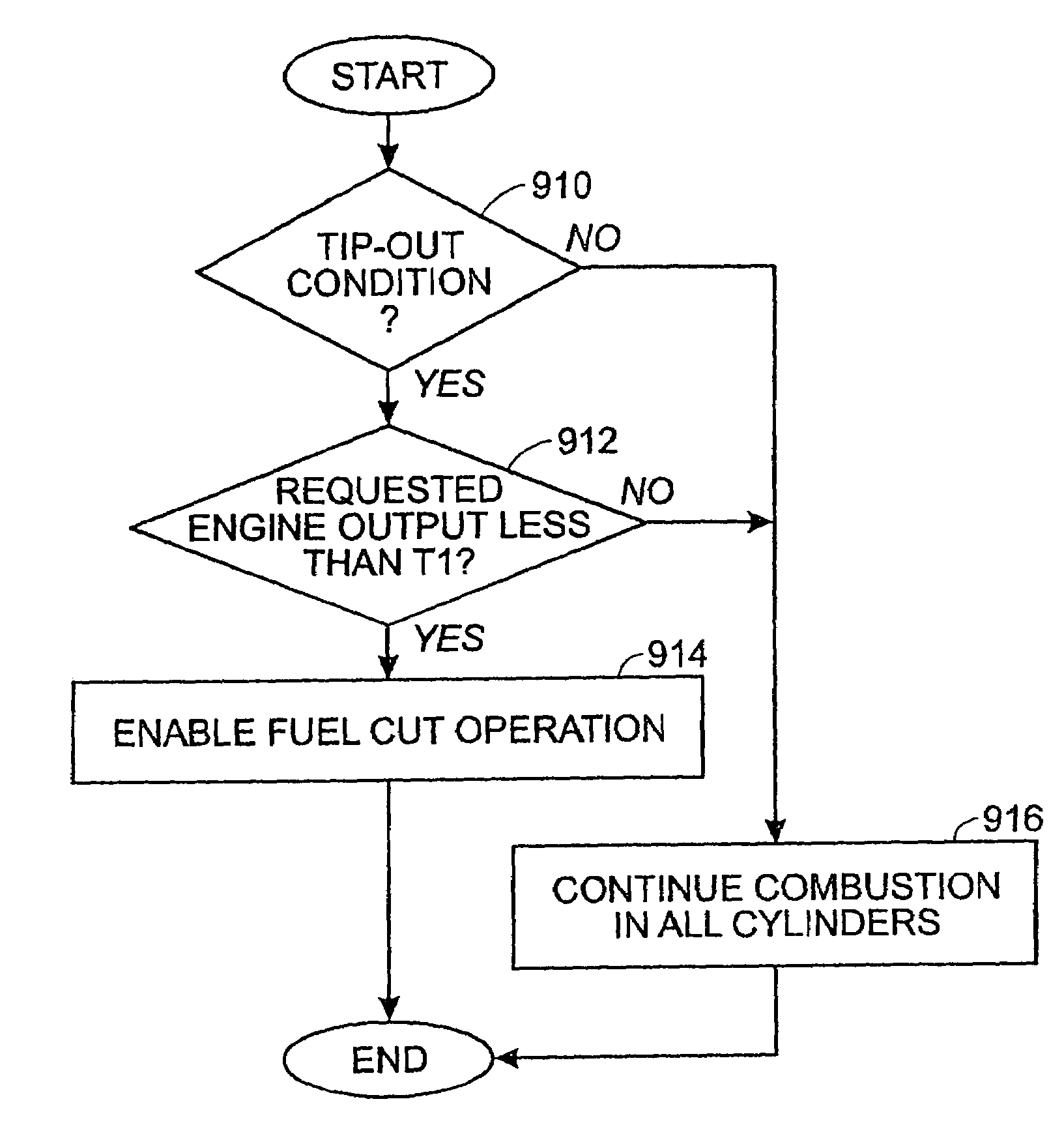
Engine system and method with cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS6978204B2Increase varietyEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSystems designFuel vapor
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fuel management system for variable ethanol octane enhancement of gasoline engines
InactiveUS7314033B2Increase heatMeet cutting requirementsElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringAntiknock agent
Fuel management system for efficient operation of a spark ignition gasoline engine. Injectors inject an anti-knock agent such as ethanol directly into a cylinder of the engine. A fuel management microprocessor system controls injection of the anti-knock agent so as to control knock and minimize that amount of the anti-knock agent that is used in a drive cycle. It is preferred that the anti-knock agent is ethanol. The use of ethanol can be further minimized by injection in a non-uniform manner within a cylinder. The ethanol injection suppresses knock so that higher compression ratio and / or engine downsizing from increased turbocharging or supercharging can be used to increase the efficiency of the engine.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Ignition and Knock Tolerance in Internal Combustion Engine by Controlling EGR Composition
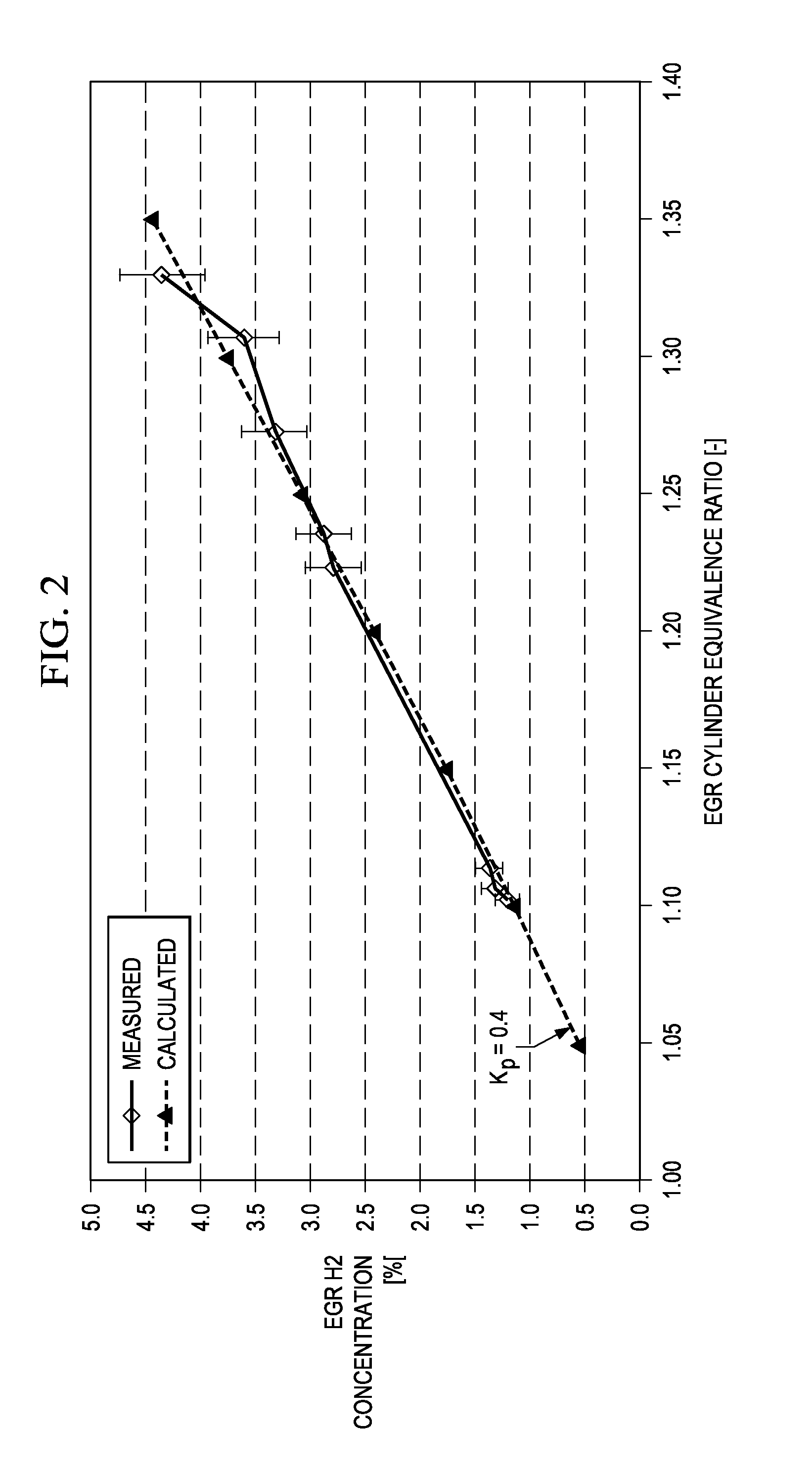
ActiveUS20140196702A1Improve efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHydrogenExhaust gas recirculation
A method for improving ignition of a spark ignited internal combustion engine by controlling the composition of recirculated exhaust gas. It is assumed that the engine has a spark ignition system and an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) loop such that at least one of the combustion cylinders is an EGR cylinder that generates an EGR stream carried by the EGR loop. Thus, the combustion charge is a mixture of air, fuel and recirculated exhaust. A first step is receiving combustibility data representing the current ignitability of the charge. It is then determined whether the energy of the ignition system is sufficient to ignite the charge. If not, the amount of hydrogen in the EGR stream is increased, which increases the ignitability of the charge.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Method and system for engine control
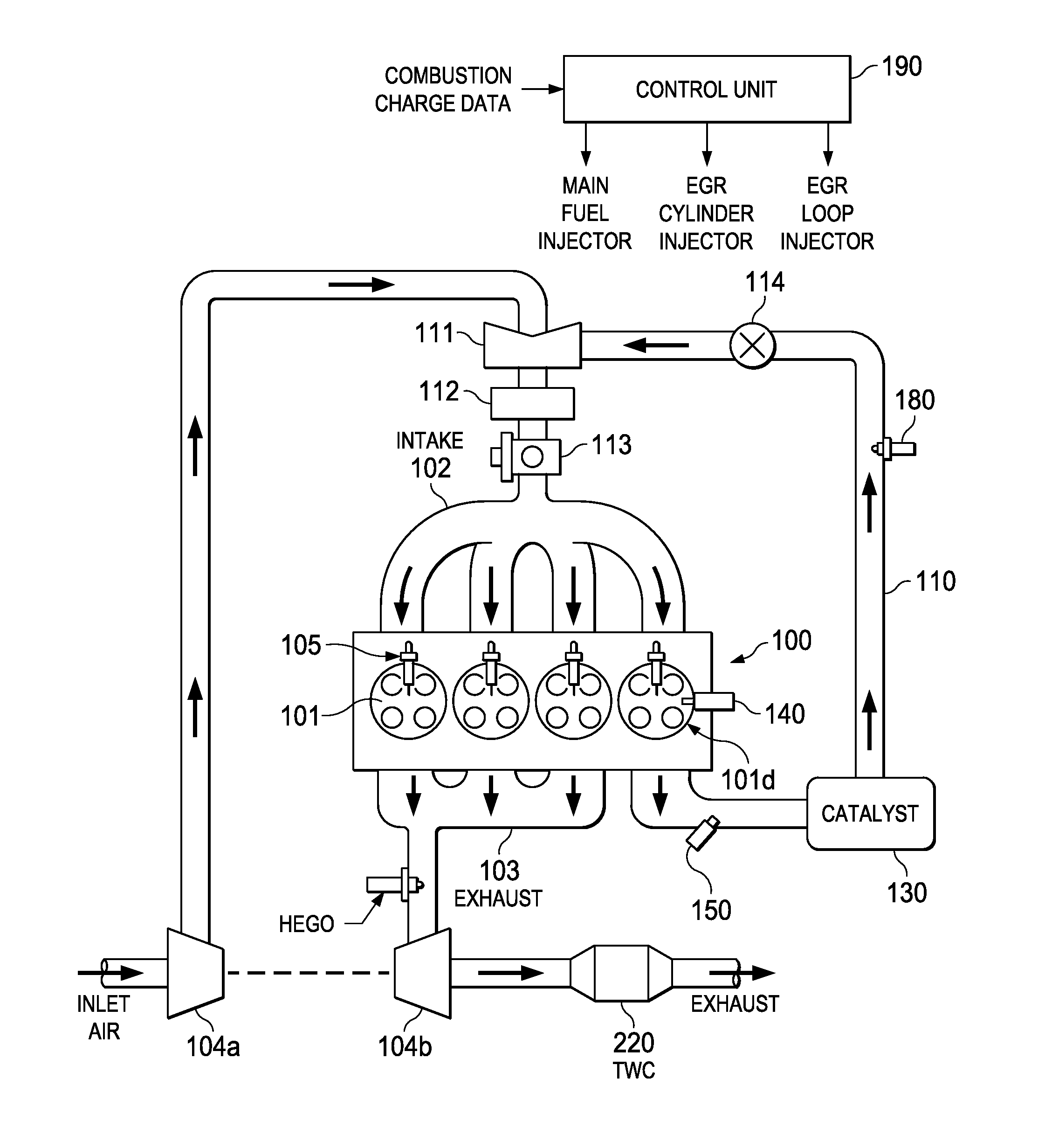
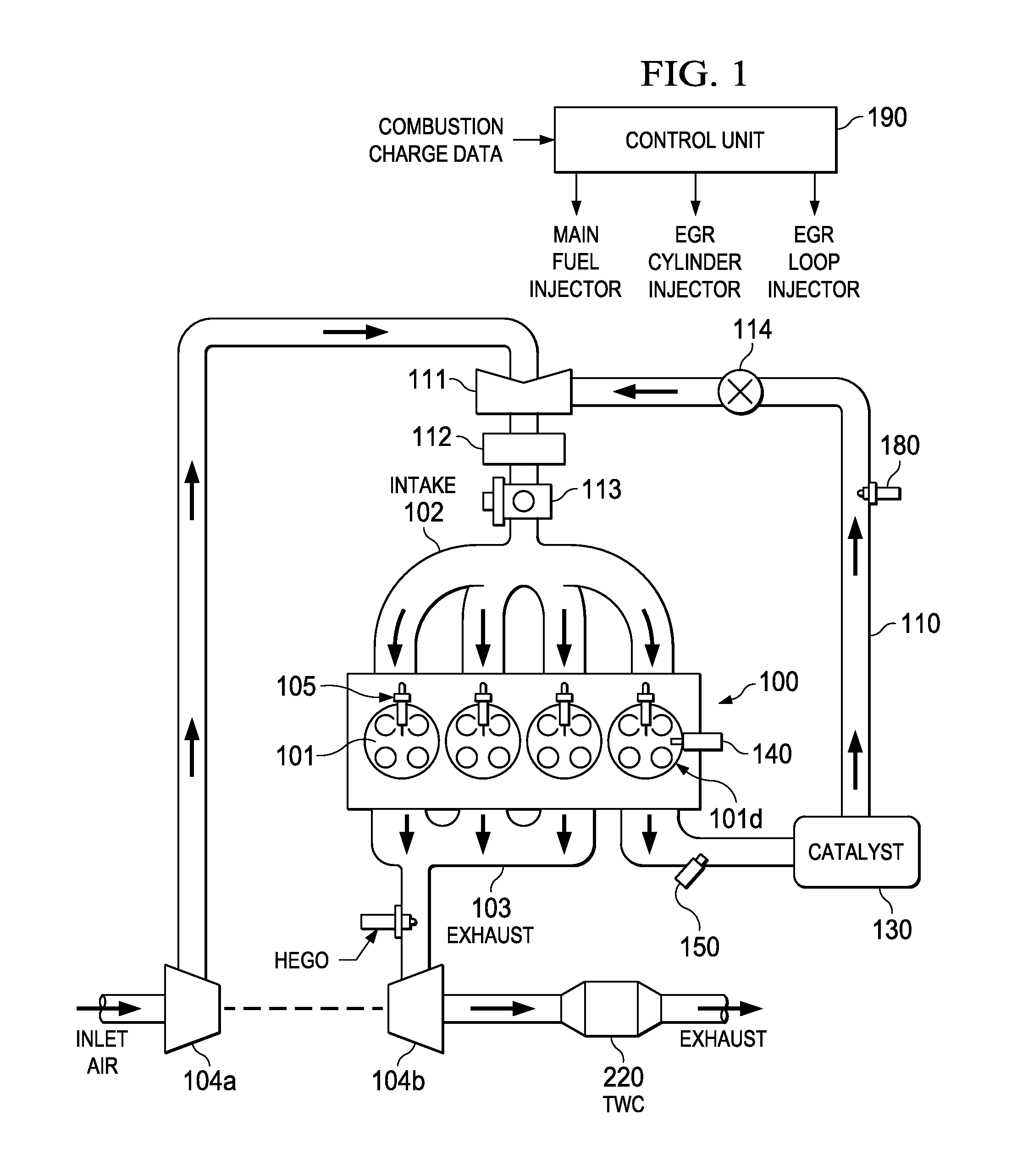
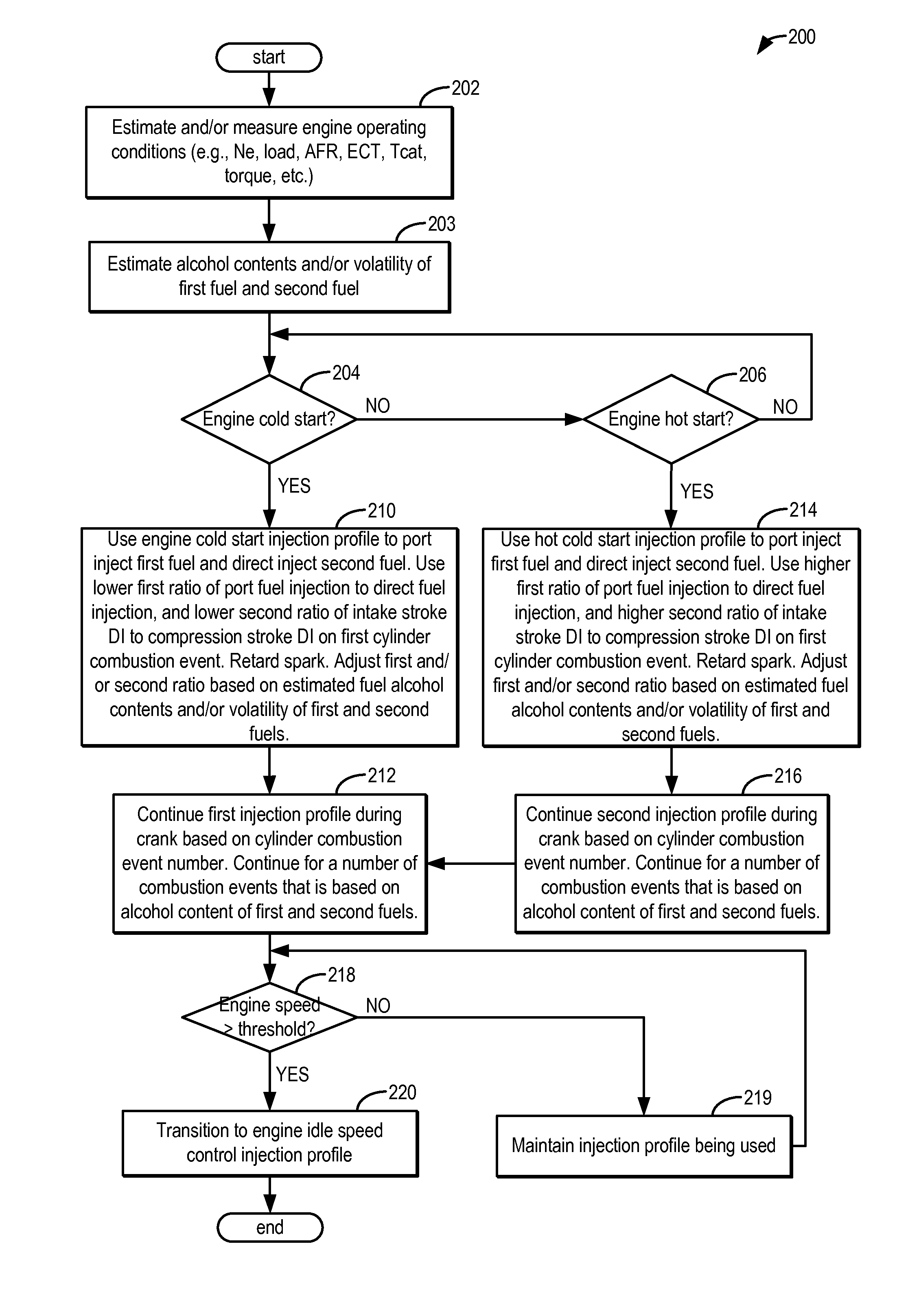
ActiveUS20140297159A1Improve cooling effectIncrease heatValve arrangementsElectrical controlAlcohol contentMultiple injection
Methods and systems are provided for controlling exhaust emissions by adjusting an injection profile for different fuels injected into an engine cylinder from different fuel injectors during engine start and crank. By splitting fuel injection during start and cranking so that fuel of lower alcohol content is port injected and fuel of higher alcohol content is direct injected as one or multiple injections, the soot load of the engine can be reduced and fuel economy can be improved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Abnormal combustion detection method for spark-ignition engine, and spark-ignition engine
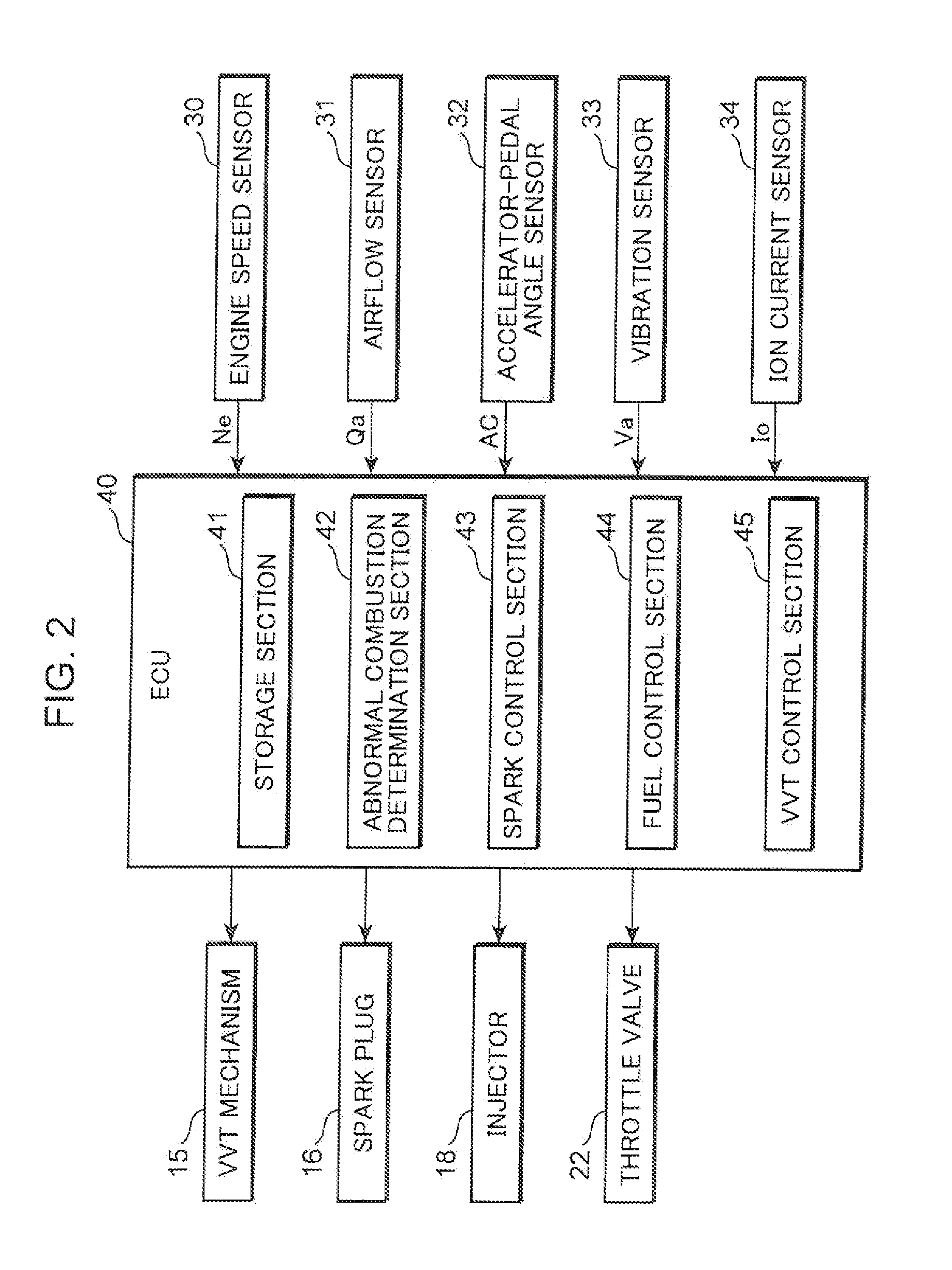
ActiveUS20110246049A1Enough can be detectedInternal-combustion engine testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesTop dead centerEngineering
When a maximum value of vibration intensity (maximum vibration intensity) (Vmax) acquired from a vibration sensor (33) in a low engine speed / high engine load (operating region (R)) is equal to or greater than a given threshold value (X), a spark timing of a spark plug (16) is shifted from a point set in a normal state on a retard side with respect to a compression top dead center, farther toward the retard side. Then, when a maximum vibration intensity (Vmax2) acquired after the spark timing retard is greater than a maximum vibration intensity (Vmax1) acquired before the spark timing retard, it is determined that preignition occurs. This technique makes it possible to reliably detect preignition using the vibration sensor, while distinguishing the preignition from knocking. An in-cylinder pressure sensor for detecting an in-cylinder pressure of an engine may be used to determine the presence or absence of the preignition, in the same manner.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Turbulent jet ignition pre-chamber combustion system for spark ignition engines
ActiveUS20150068489A1Promote flame quenchingHigh-drive cycle (part load) fuel economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemCombustion chamber
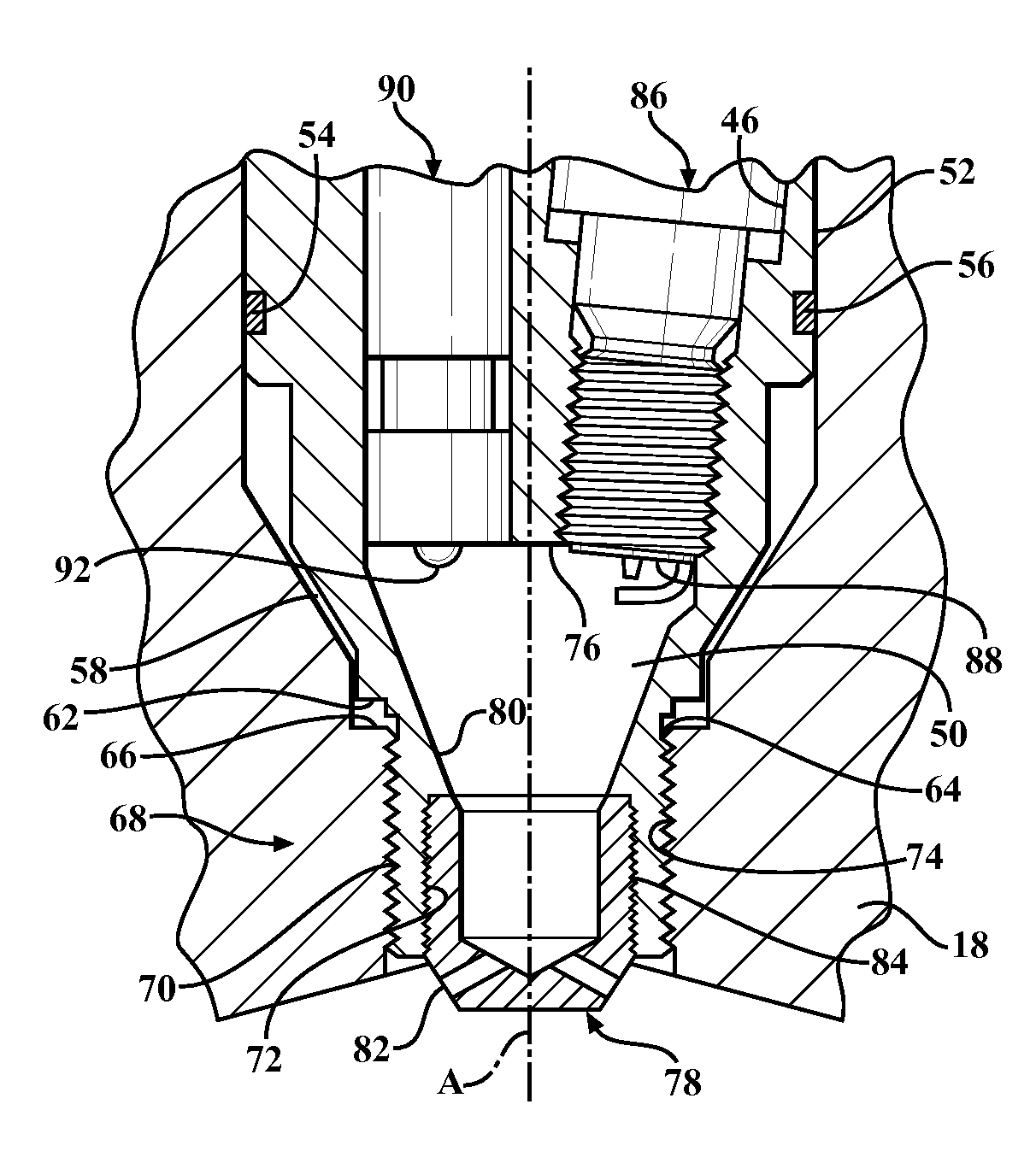
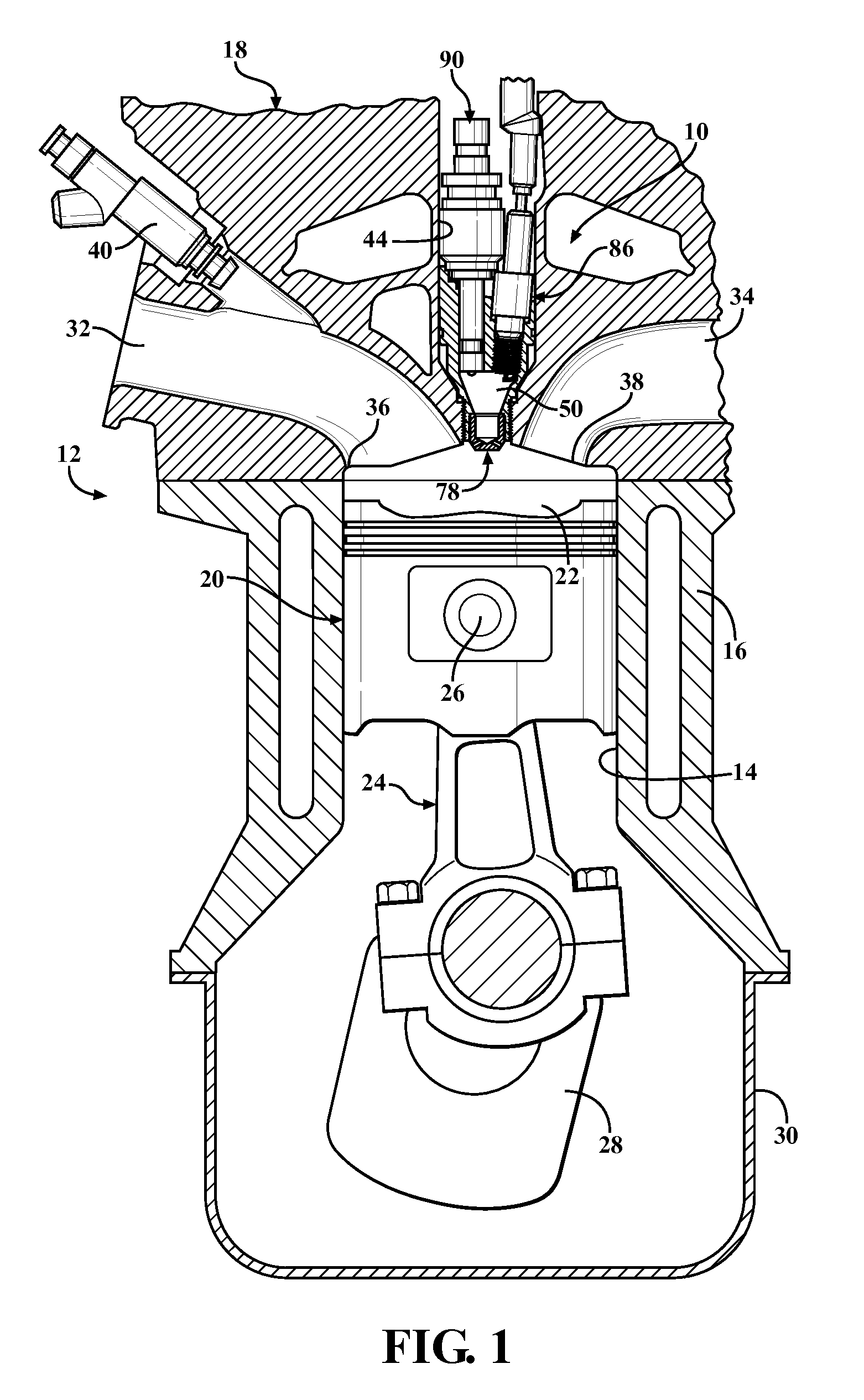
An ignition system for an internal combustion engine having at least one combustion chamber where the ignition system includes a housing, an ignition device, an injector, and a pre-chamber having a nozzle disposed spaced from the proximal portion of the pre-chamber. The igniter portion of the ignition device and the nozzle of the injector are operatively supported in the proximal portion of the pre-chamber and disposed flush therewith. The igniter portion ignites the fuel in pre-chamber such that partially combusted pre-chamber products are forced through orifices in the pre-chamber nozzle and extinguish, but dispersed through the combustion chamber so as to ignite the main fuel charge therein.
Owner:MAHLE POWERTRAIN
Method and system for controlling fuel usage
ActiveUS8127745B2Boost octaneVery high cooling effectValve arrangementsElectrical controlControl theoryThrottle
Methods and systems are provided for improving fuel usage while addressing knock by adjusting the use of spark retard and direct injection of a knock control fluid based on engine operating conditions and the composition of the injected fluid. One or more engine parameters, such as EGR, VCT, boost, throttle position, and CMCV, are coordinated with the direct injection to reduce torque and EGR transients.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and system for controlling fuel usage
ActiveUS20110174268A1Reduce exhaust emissionsHigh priceValve arrangementsElectrical controlControl theoryThrottle
Methods and systems are provided for improving fuel usage while addressing knock by adjusting the use of spark retard and direct injection of a knock control fluid based on engine operating conditions and the composition of the injected fluid. One or more engine parameters, such as EGR, VCT, boost, throttle position, and CMCV, are coordinated with the direct injection to reduce torque and EGR transients.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
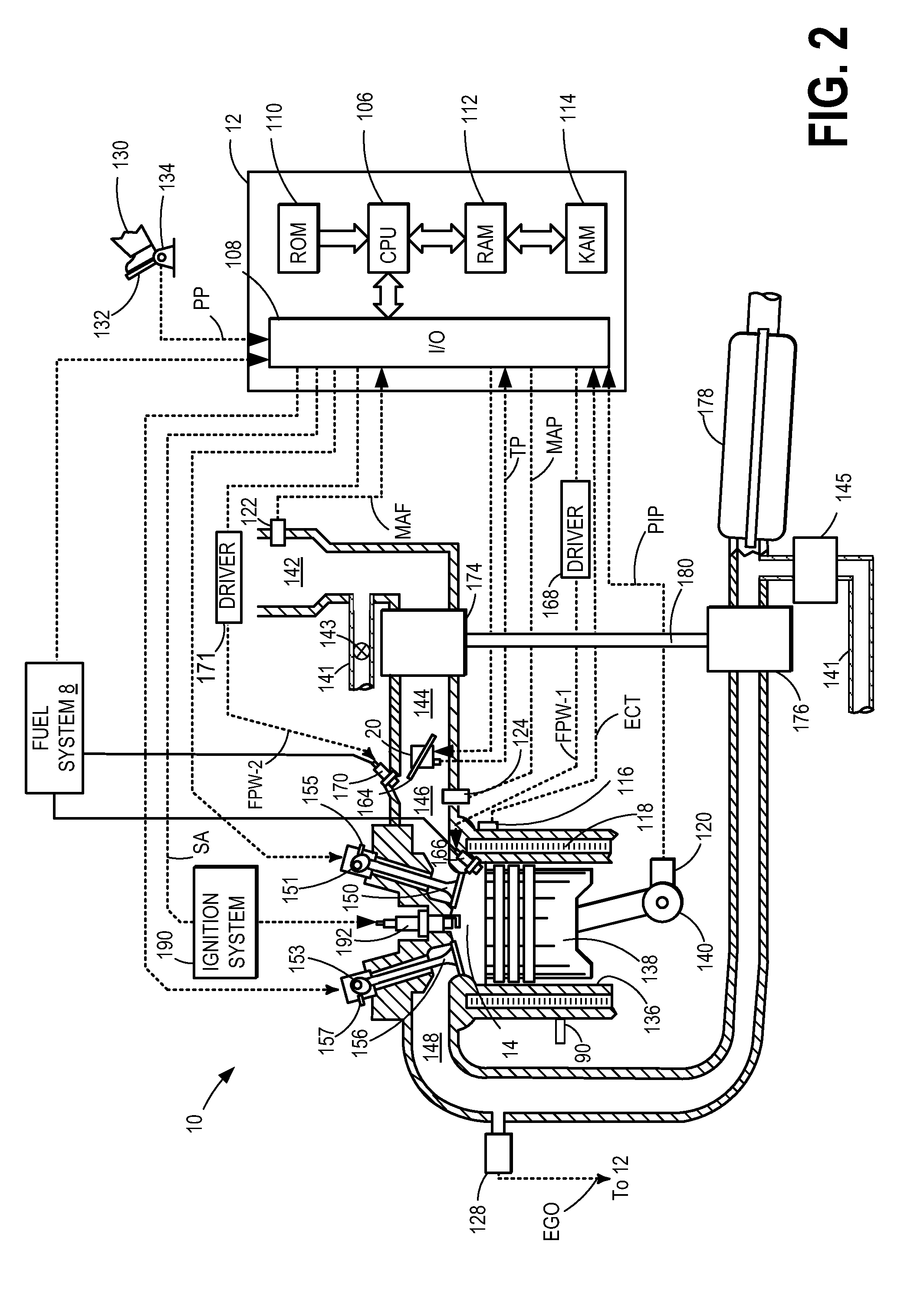
Ignition timing control system for light duty combustion engines
InactiveUS7000595B2Guaranteed uptimeAccelerate emissionsAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl systemNormal mode
A control system for a low cost, light duty combustion engine, where the control system generally utilizes engine speed and / or temperature input signals and independent operating sequences to determine a desired ignition timing and air-to-fuel ratio for a combustible mixture. There are several independent operating sequences, each one of which is designed to optimally control the engine under certain conditions. These operating sequences include a Cranking sequence that commences after the engine is initially turned on, a Warm Up sequence which follows the Cranking sequence, a Normal Mode sequence for typical operating conditions, an Acceleration sequence for certain increases in engine speed, a Come Down sequence for when a sufficient engine speed is followed by a certain decrease in speed, and a Recovery Bump sequence for when the engine speed dips below a predetermined level.
Owner:WALBRO LLC
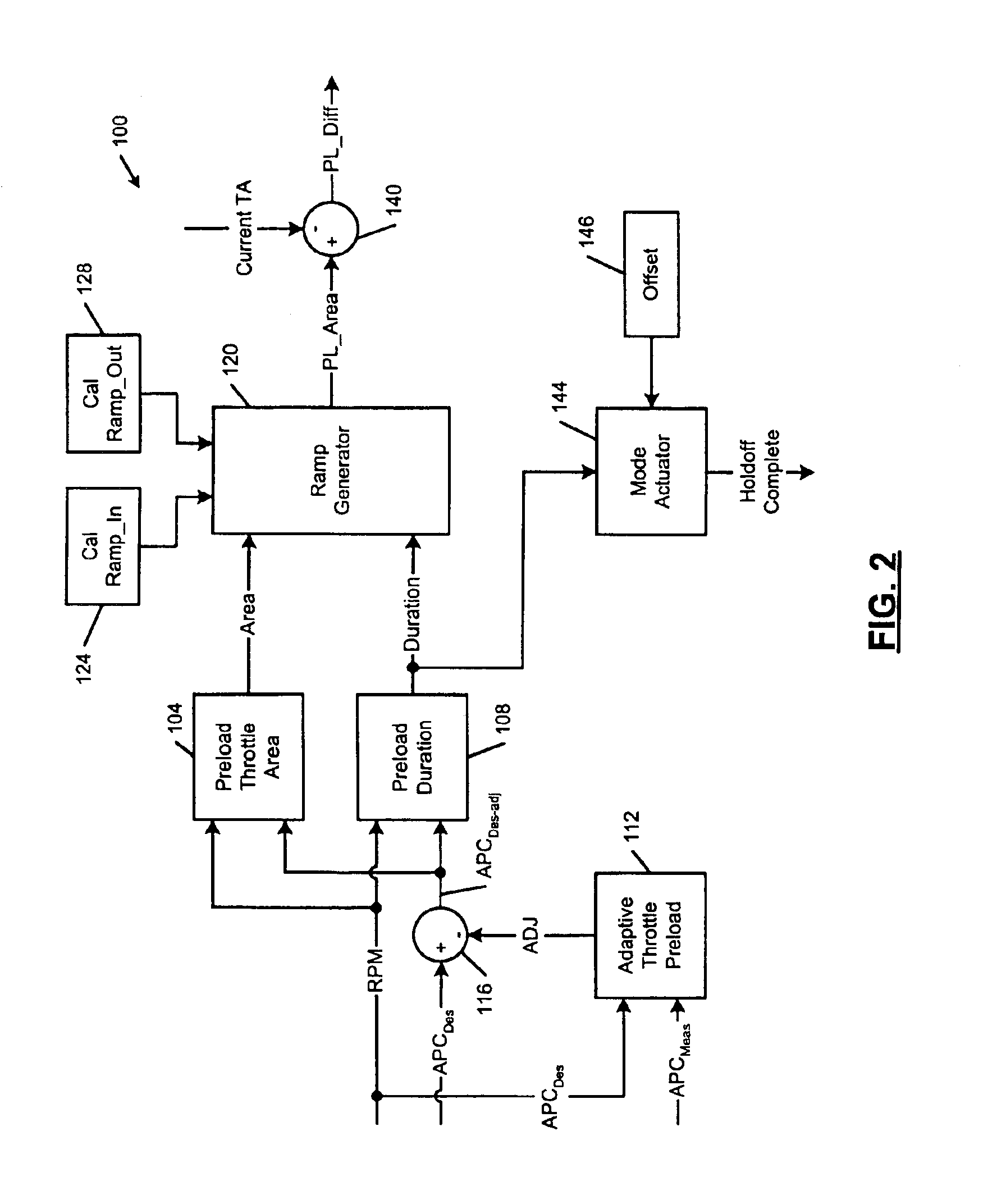
Engine control system with throttle preload during cylinder deactivation
InactiveUS6915781B2Reduce throttling noiseReduce noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineControl system
An engine control system and method for a displacement on demand internal combustion engine includes a throttle preload signal generator that outputs a throttle preload area signal having a base portion and ramp out portion. A combining circuit combines the throttle preload area signal with a current throttle area signal to generate a throttle preload difference signal that adjusts throttle area to smooth transitions during at cylinder deactivation. The engine control system smoothes the transition between activated and inactivated modes by increasing throttle area and manifold pressure when transitioning between activated and deactivated modes.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Engine system and method with cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS20050197759A1Increase varietyEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSystems designFuel vapor
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
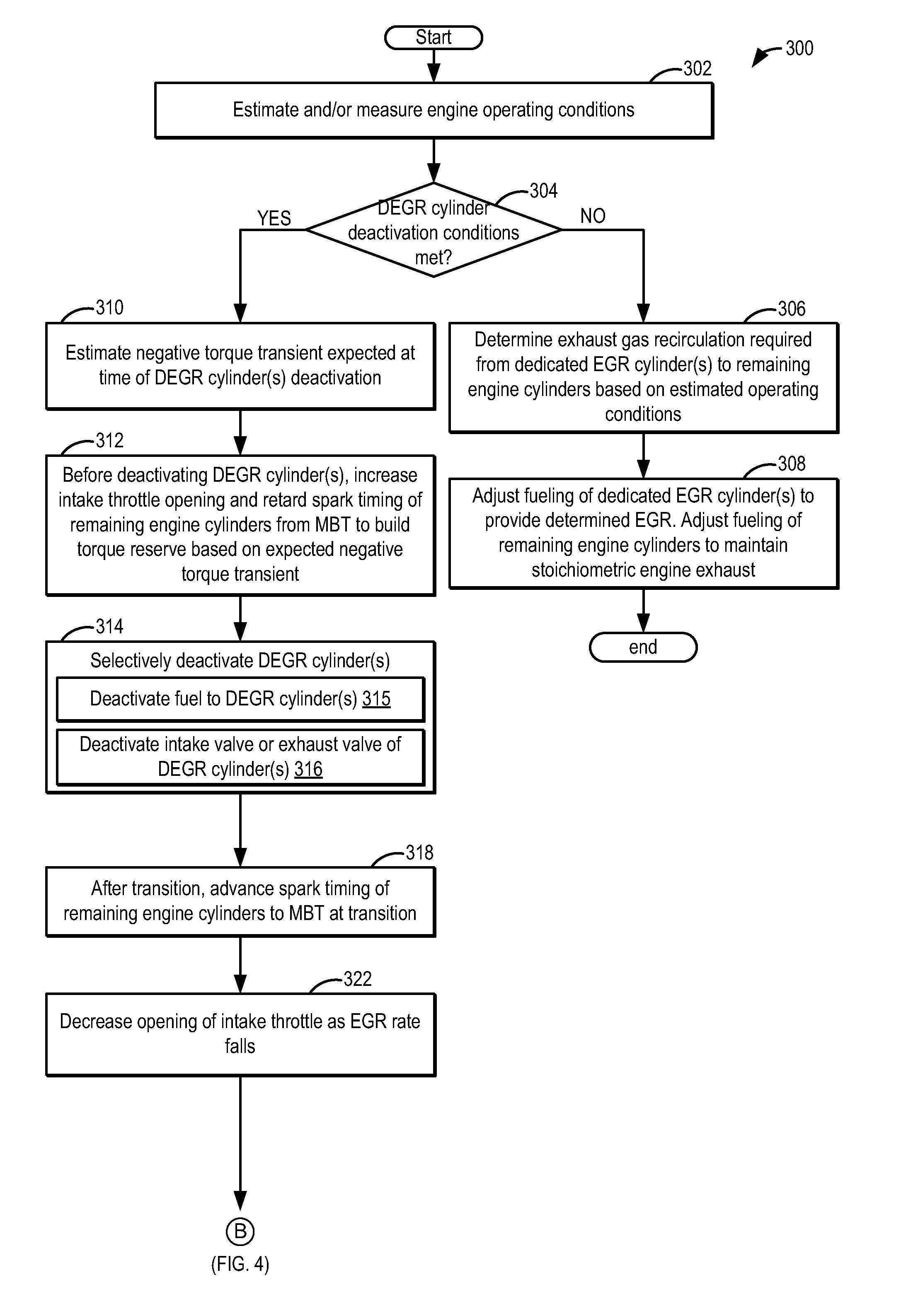
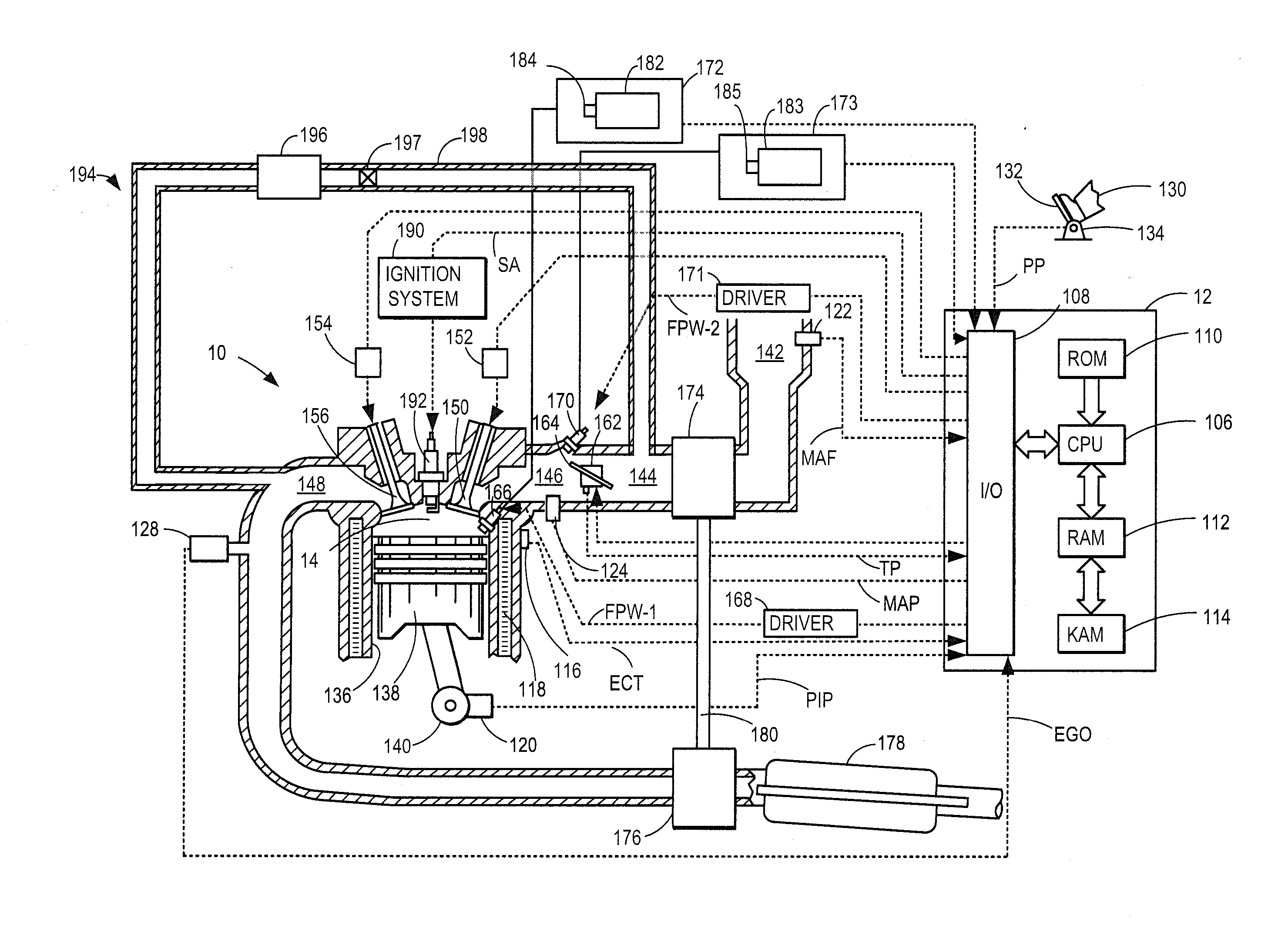
Systems and methods for egr control
InactiveUS20150354477A1Improve fuel economyImprove the level ofElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelControl theoryThrottle
Methods and systems are provided for reducing torque transients experienced when a dedicated EGR cylinder is deactivated to reduce EGR. Before deactivating the dedicated cylinder, an intake throttle position and spark timing of remaining engine cylinders is adjusted to build-up torque reserve in anticipation of a negative torque transient at deactivation. Then, the throttle position or spark timing is adjusted to reduce torque when a positive torque transient is expected.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of fuel injection for a variable displacement engine
ActiveUS20150345407A1Improve fuel economyReduce displacementValve arrangementsElectrical controlFuel injectionVariable displacement
Various systems and methods are described for controlling fuel injection in a variable displacement engine. One method for a deactivatable cylinder comprises, before deactivating the cylinder responsive to operating conditions, disabling a port injector and fueling the cylinder only via the direct injector. The method further comprises, when reactivating the cylinder from deactivation, enabling both the port injector and the direct injector, and injecting a higher amount of fuel via the direct injector while simultaneously injecting a lower amount of fuel via the port injector.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for selective cylinder deactivation
InactiveUS20160003168A1Improve fuel economyEasy loadingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringAir–fuel ratio
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Ignition Energy Control for Mixed Fuel Engine
InactiveUS20090114188A1Improve combustion qualityImprove the level ofElectrical controlOther installationsEnergy controlControl system
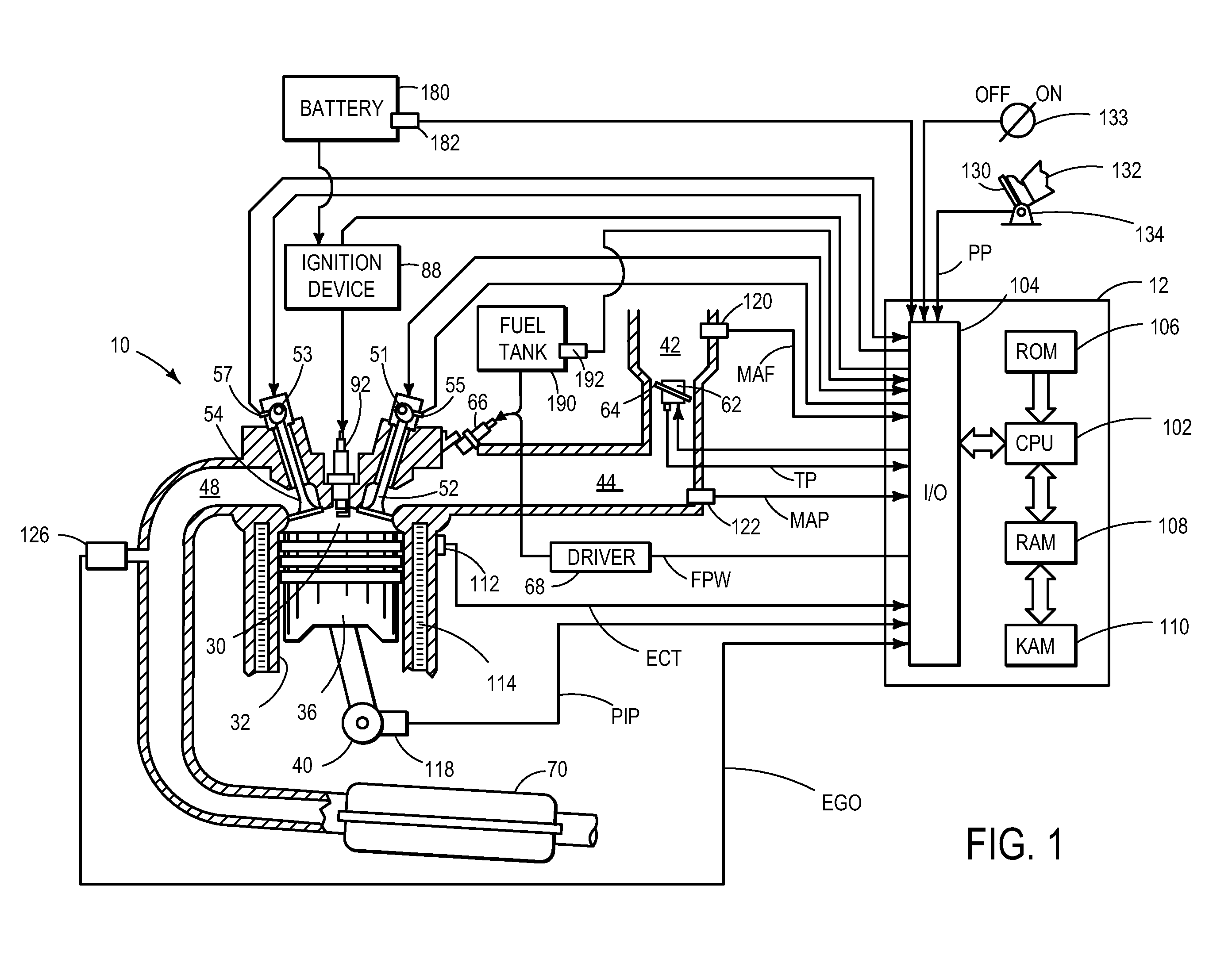
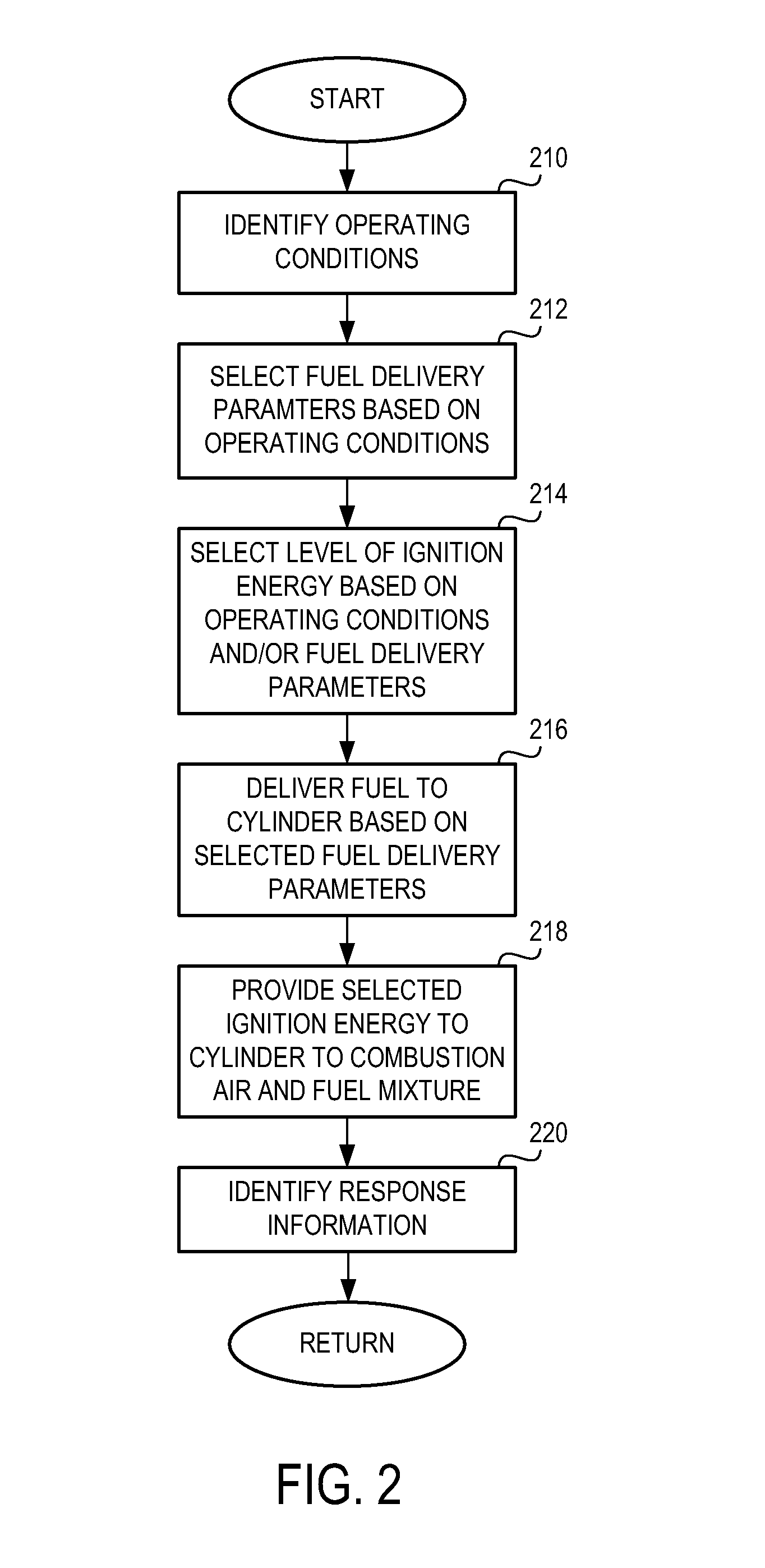
As one example, an engine system for a vehicle is provided, including an internal combustion engine having at least one cylinder; a fuel system configured to provide a fuel to the cylinder; an ignition system including at least a spark plug; a control system configured to vary a level of ignition energy provided to the cylinder via the spark plug in response to a composition of the fuel provided to the cylinder by the fuel system. A method of operating the engine system by varying a level of ignition energy provided to the engine after a start-up is also provided.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Turbulent jet ignition pre-chamber combustion system for spark ignition engines
ActiveUS9353674B2High-drive cycle (part load) fuel economyThermal efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemCombustion chamber
Owner:MAHLE POWERTRAIN
If method and system for engine knock control
ActiveUS9506411B2Large tendency to knockImprove knockingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
If method and system for engine knock control
ActiveUS20160108828A1Large tendency to knockImprove knockingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMechanical engineeringEngine knocking
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Systems and methods for injecting gaseous fuel during an exhaust stroke to reduce turbo lag
ActiveUS20150075492A1High power outputIncrease heightElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionLag
Methods and systems are provided for injecting and combusting an amount of gaseous fuel during an exhaust stroke of a cylinder combustion event in order to reduce turbo lag and reduce a duration of time required for an exhaust catalyst to light-off during transient events. In one example, when an increase in torque demand is greater than a threshold, a first amount of gaseous fuel may be combusted during a compression stroke of a cylinder combustion event and a second amount of gaseous fuel may be combusted during an exhaust stroke of the combustion event. The second amount may be adjusted based on the increase in torque demand.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Optimized flex fuel powertrain
InactiveUS7454285B2Minimize fuel economyImproved wide open throttle performanceAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlGasolinePowertrain
A fuel system and powertrain for a flexible fuel system vehicle utilizes a controller system to control variables in an engine and the final drive optimize operating efficiency of the vehicle while using an alcohol-gasoline blend. The controller system regulates engine operating variables such as fuel pressure, fuel flow, air-fuel flow, air-fuel temperature, and valve timing. The controller system regulates engine operating variables such as transmission gear selection and gear changing as well as differential ratio changes.
Owner:RICARDO INC
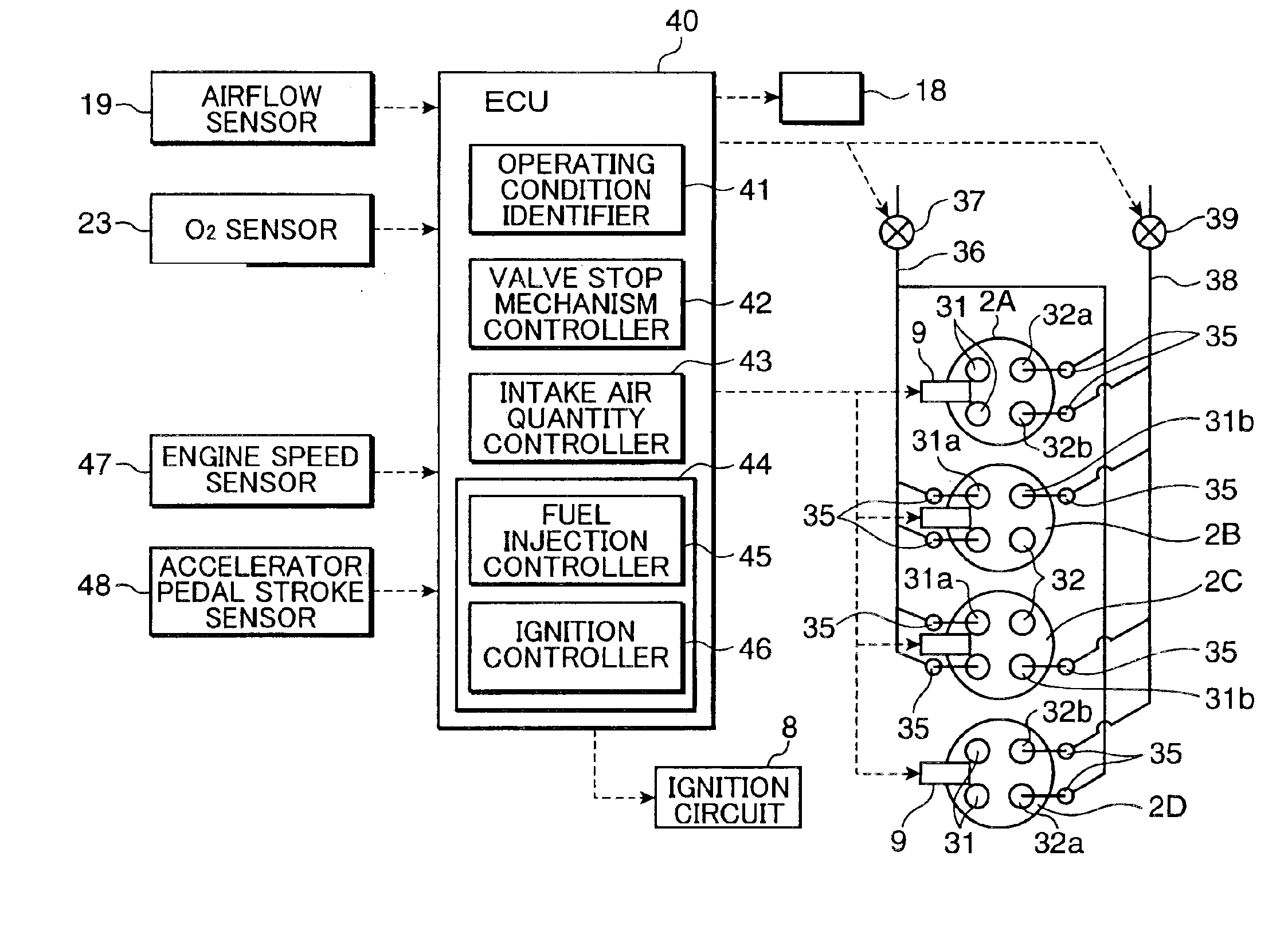
Spark ignition engine control device
InactiveUS7219634B2Effective contributionShorten speedValve arrangementsElectrical controlLow loadFuel efficiency
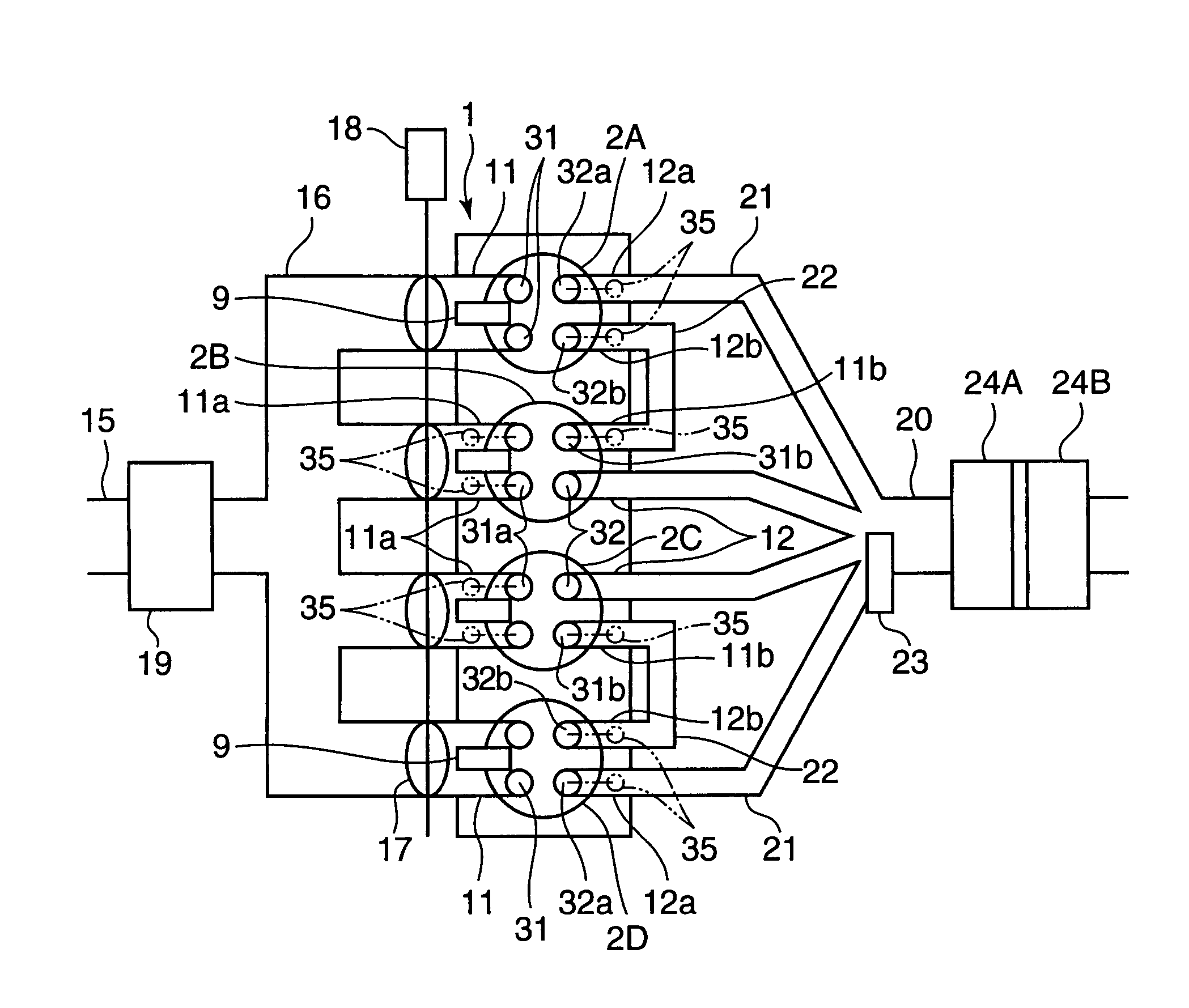
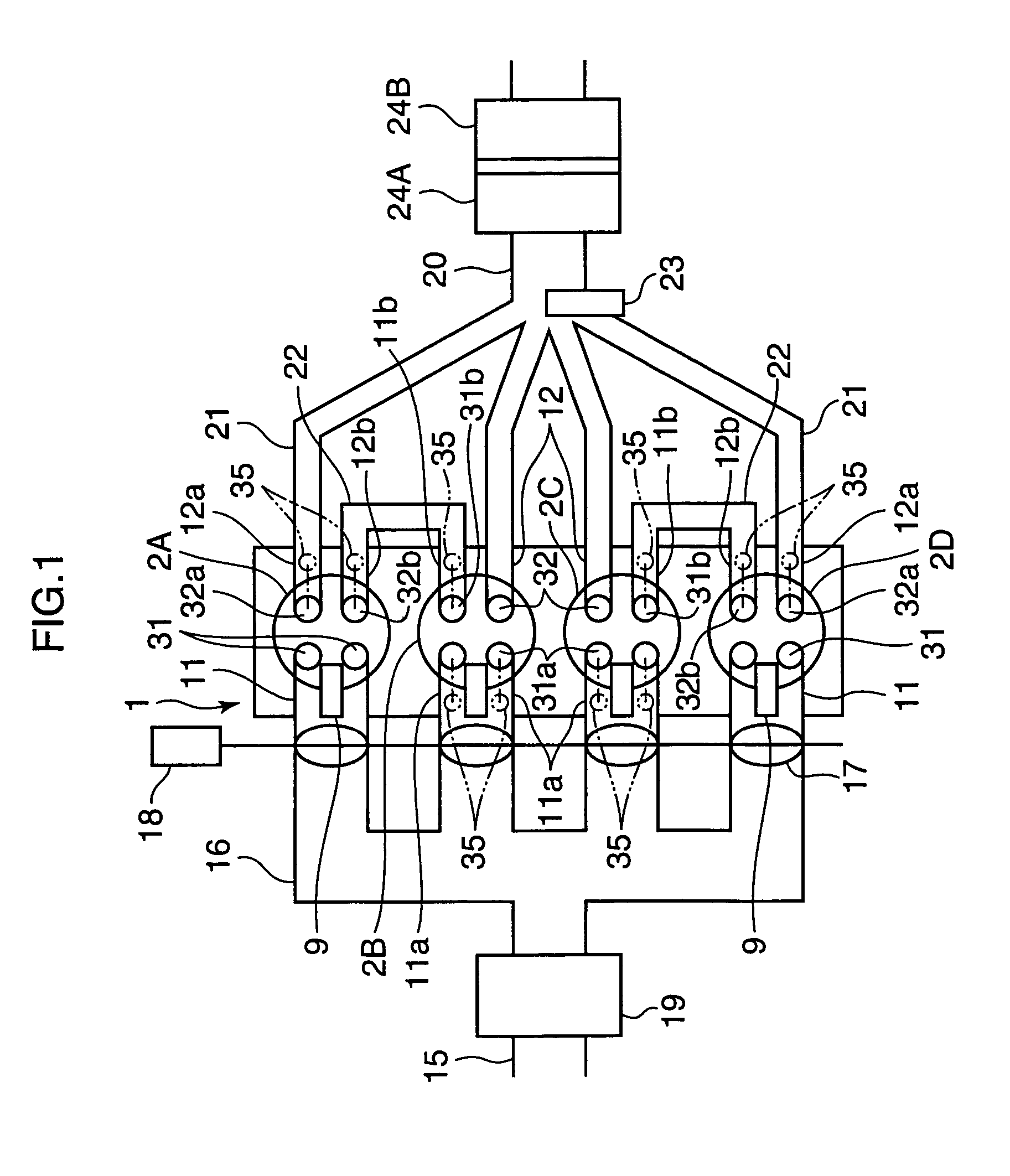
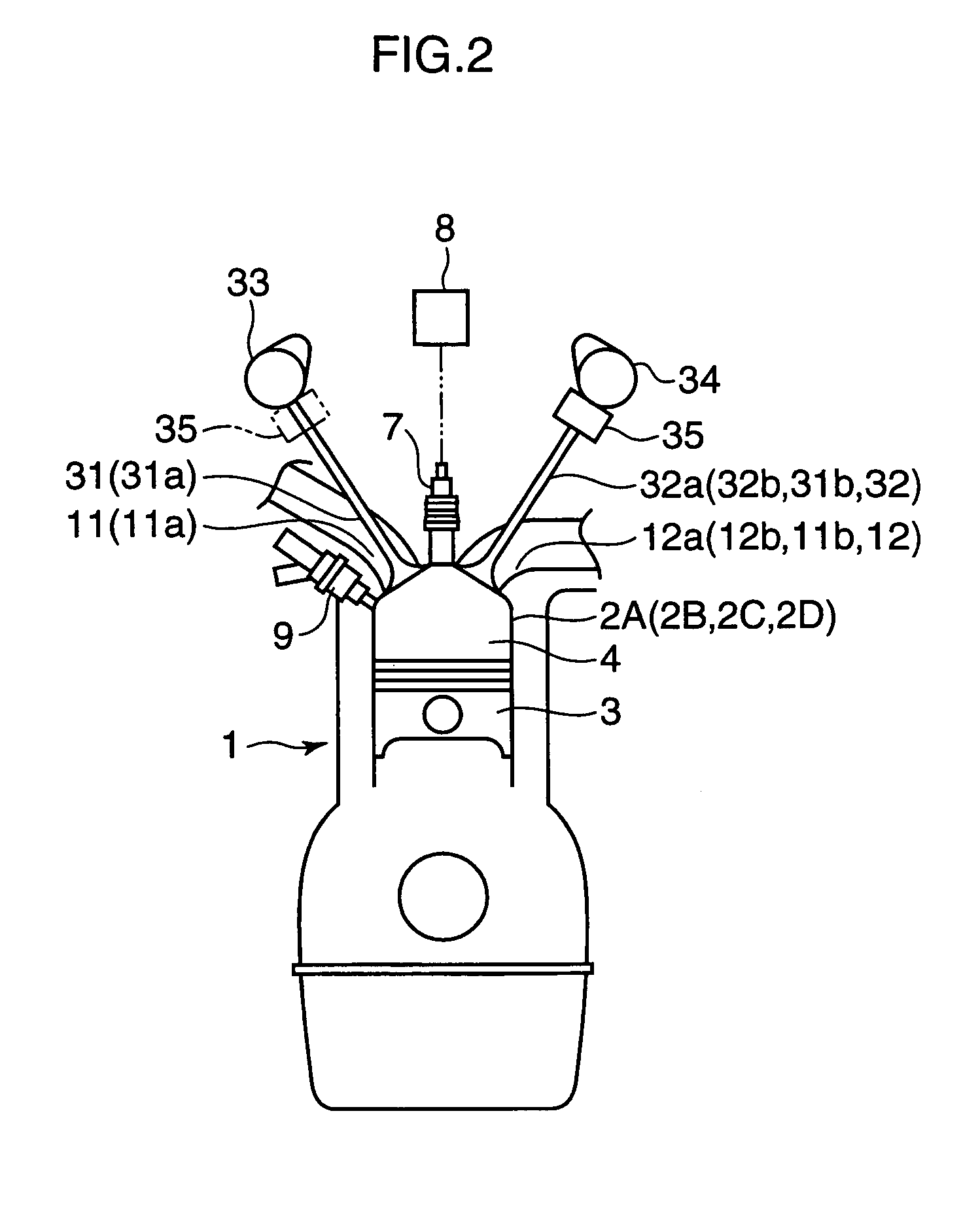
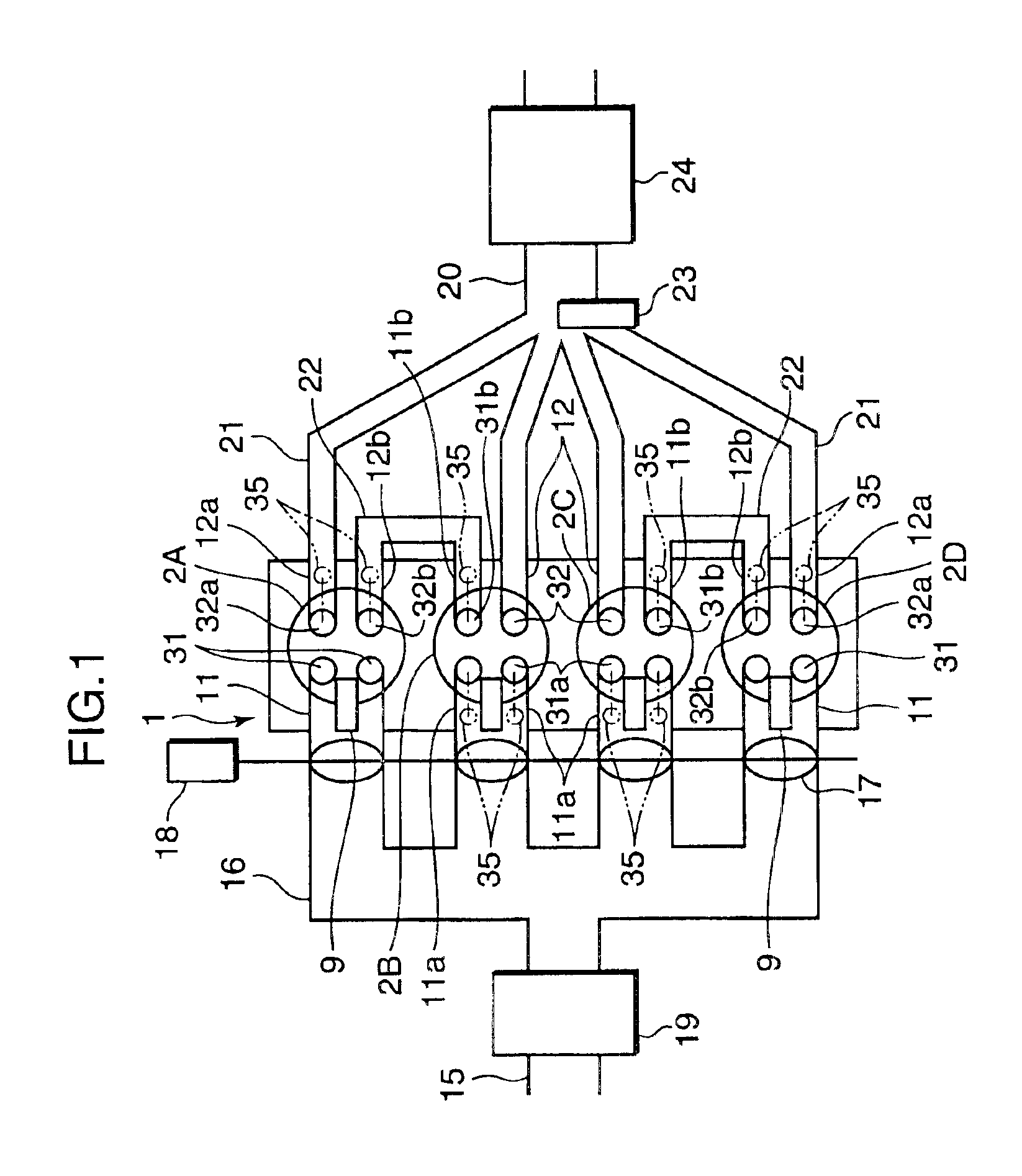
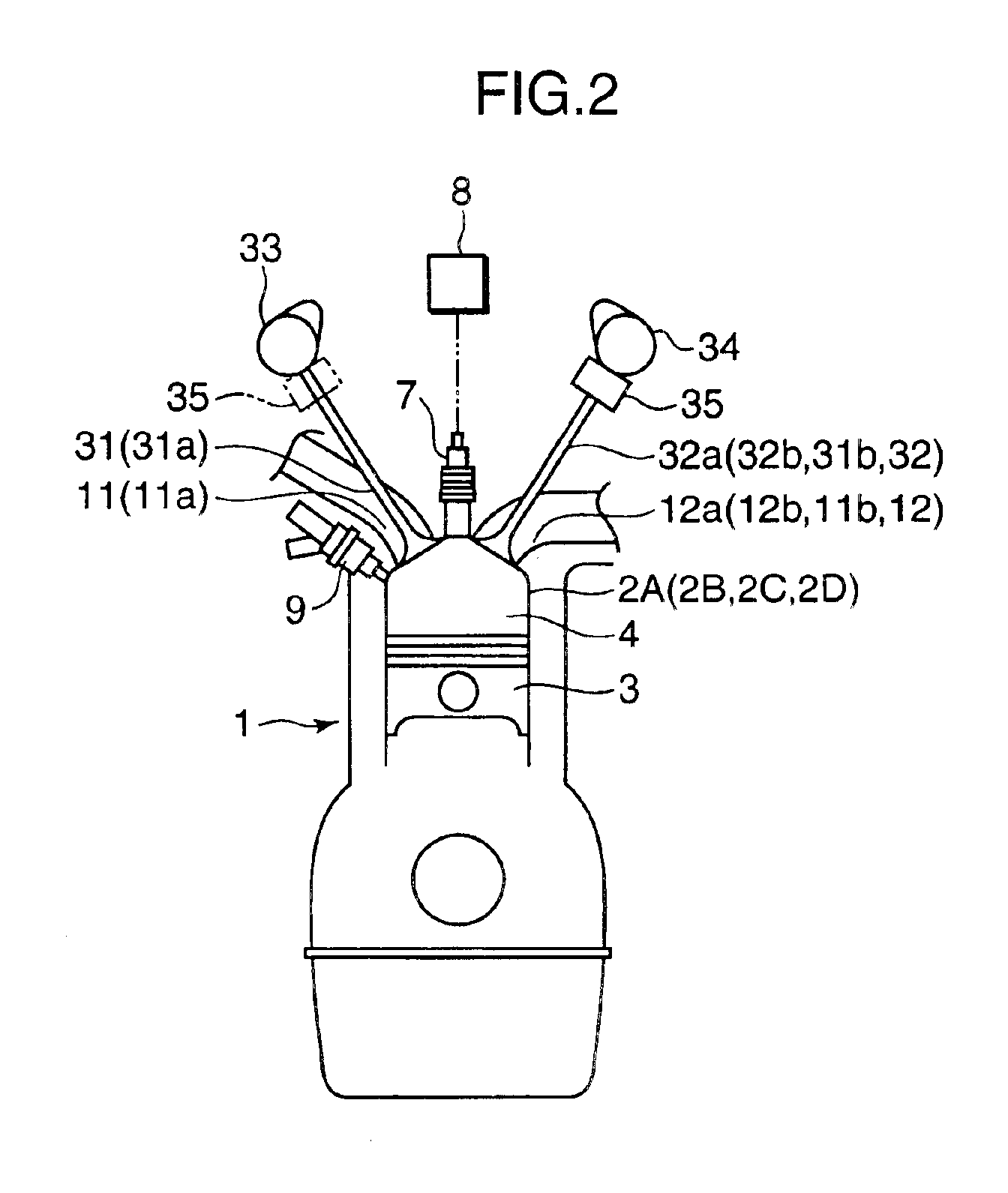
For the purpose of improving the fuel efficiency by lean combustion and enhancing the fuel efficiency improvement effects by performing compression ignition efficiently in some cylinders, a multi-cylinder spark ignition engine is constructed such that exhaust gas, that is exhausted from preceding cylinders 2A, 2D on the exhaust stroke side among pairs of cylinders whose exhaust stroke and intake stroke overlap in a low load, low rotational speed region, is directly introduced through an inter-cylinder gas passage 22 into following cylinders 2B, 2C on the intake stroke side and only gas exhausted from the following cylinders 2B, 2C is fed to an exhaust passage 20, which is provided with a three-way catalyst 24. Combustion controller is provided that controls the combustion of each of the cylinders such that combustion is conducted by forced ignition in a condition in which the air / fuel ratio is a lean air / fuel ratio which is larger by a prescribed amount than the stoichiometric air / fuel ratio in the preceding cylinders 2A, 2D and, in the following cylinders 2B, 2C, fuel is supplied to burnt gas of lean air / fuel ratio introduced from the preceding cylinders 2A, 2D and combustion is conducted by compression ignition.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
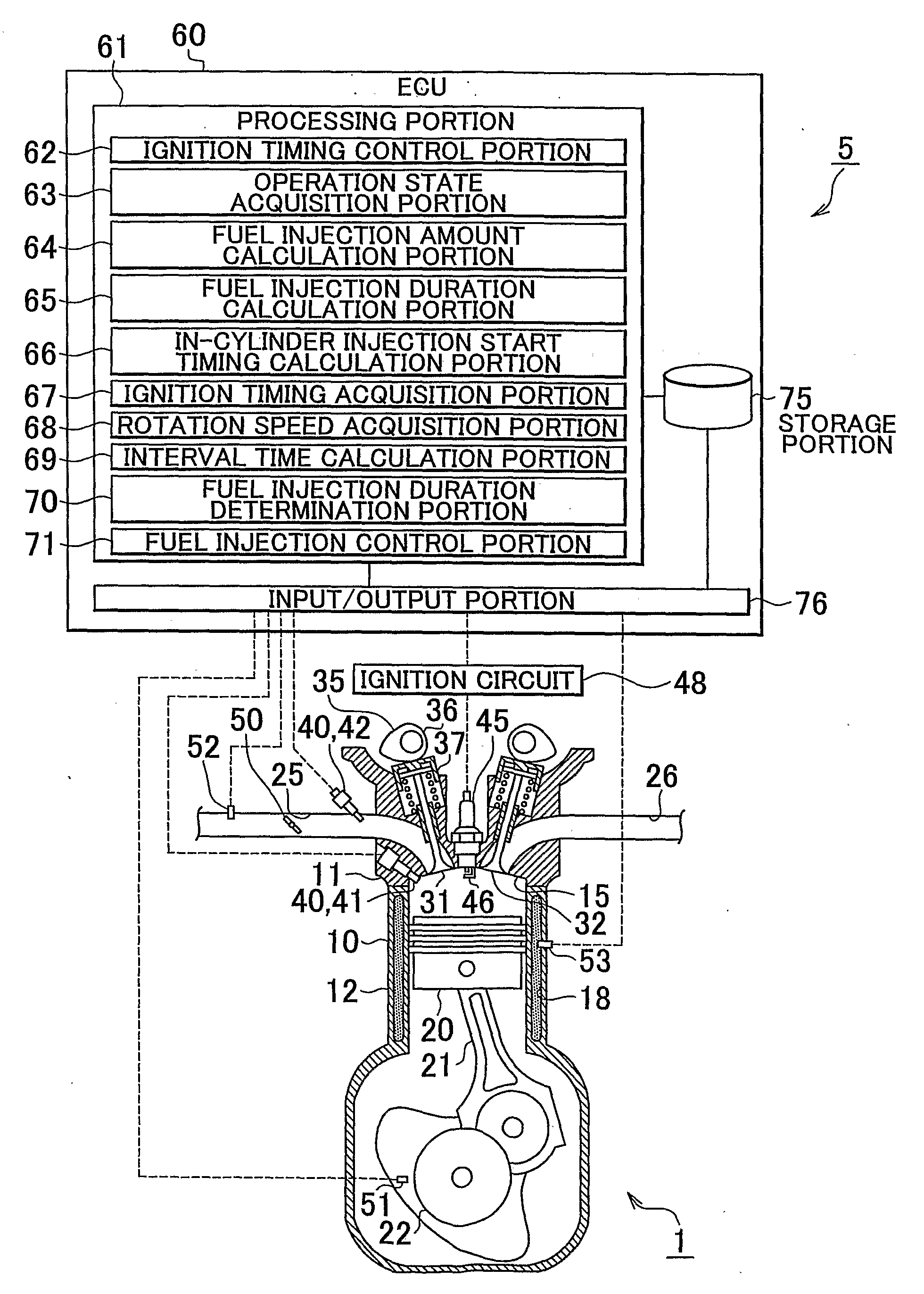
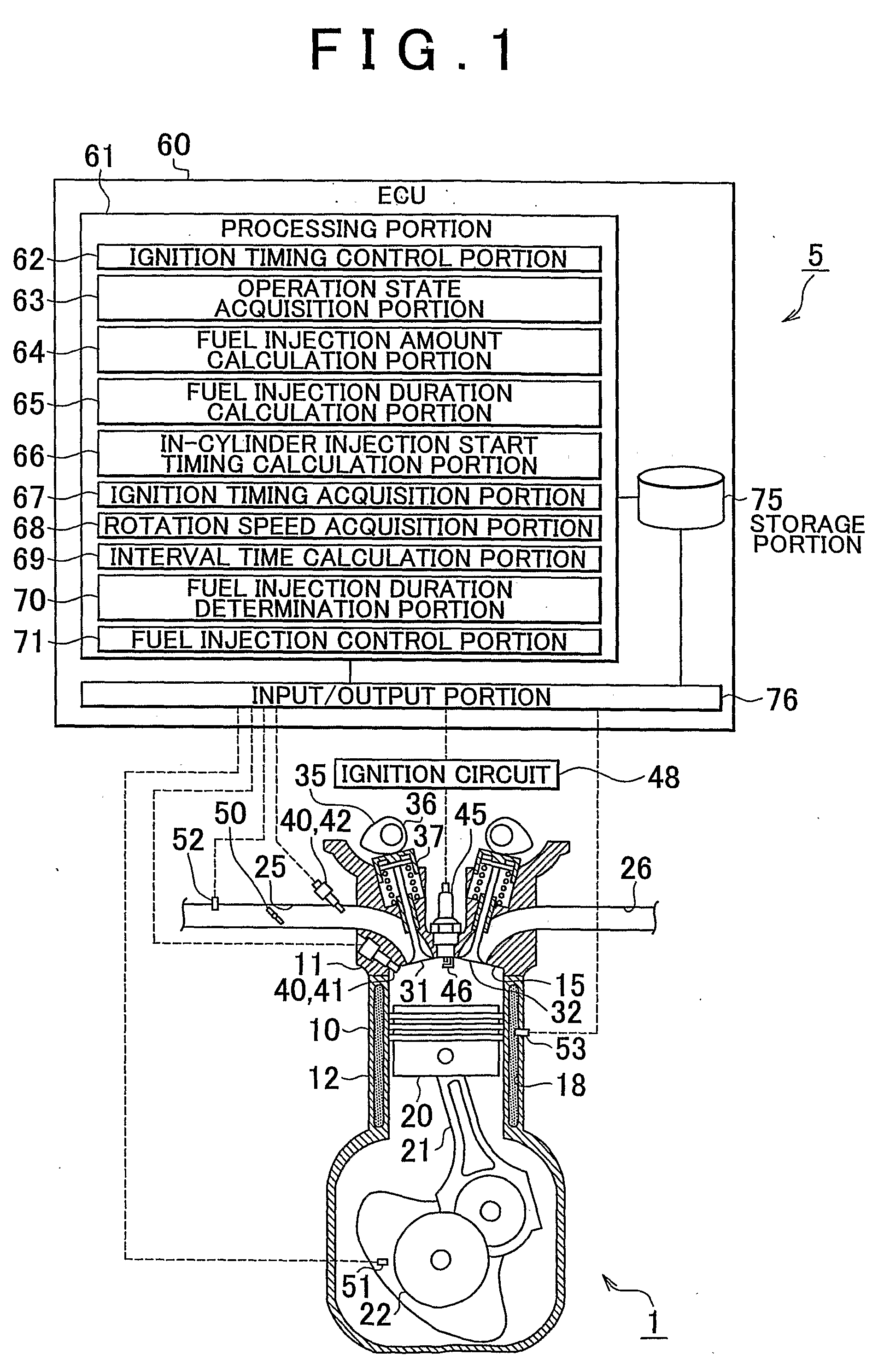
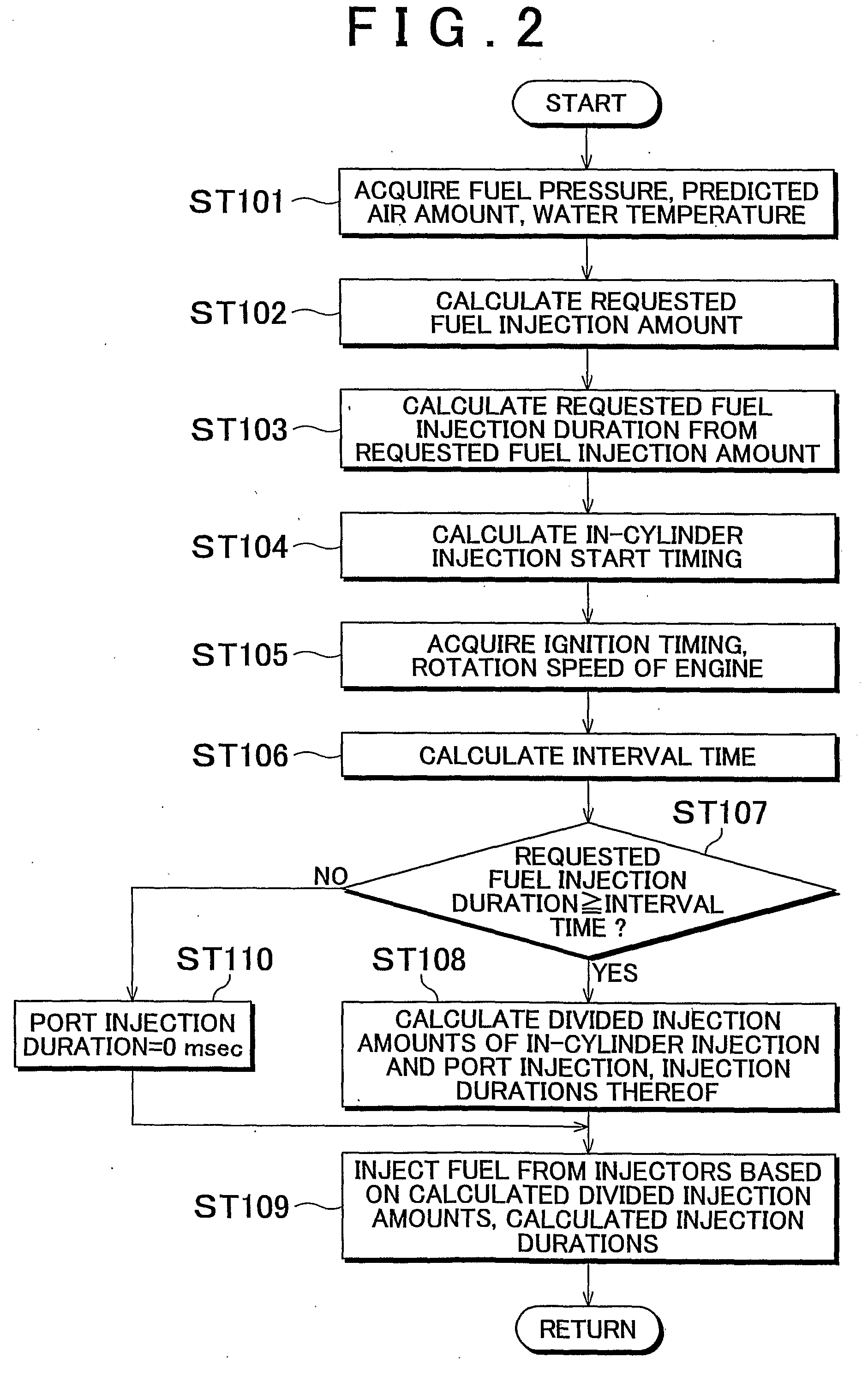
Fuel injection control device of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20090099756A1Emission reductionReduce the amount of fuelElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine including an in-cylinder injection injector and an intake port-injection injector. An ECU includes a fuel injection duration calculation portion that calculates a requested fuel injection duration and a fuel injection control portion that causes the in-cylinder injection injector to inject fuel during the compression stroke during the cold start of the engine, and that causes fuel to be injected also in a manner other than the fuel injection performed by the in-cylinder injection injector during the compression stroke if the requested fuel injection duration is longer than or equal to an interval time. Therefore, even if the requested fuel injection duration is longer than or equal to the interval time, the emissions can be reduced while a startability during a cold start of the internal combustion engine is secured.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Spark-ignition engine controller
InactiveUS6877464B2Large operating rangeImprove fuel economyValve arrangementsElectrical controlOperation modeFuel injection
Intake air / exhaust gas flow control is performed in an partial load range of an engine such that burned gas which is discharged from an exhaust stroke side preceding cylinder of a pair of cylinders having an overlapping exhaust stroke and intake stroke is introduced into an intake stroke side following cylinder through an intercylinder gas channel. In an operating range set as a special operation mode, a combustion condition controller executes control such that combustion is performed in the following cylinder by means of compression ignition. In an operating condition in which knocking is likely to occur within the compression ignition range of the following cylinder, control is executed by a fuel injection controller such that the timing of fuel injection into the following cylinder is retarded relative to that of an operating condition in which knocking is unlikely to occur.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
System and method for improving cylinder deactivation
ActiveUS20170356375A1Improving engine fuel economyReduce engine noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMotor fuelAutomotive engineering
Systems and methods for operating an engine with deactivating and non-deactivating valves are presented. In one example, estimates of engine fuel consumption for operating the engine with a plurality of cylinder modes or patterns while a transmission is engaged in different gears are determined and are used as a basis for deactivating engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control method for spark-ignition engines
InactiveUS6032640AReduction of the so called "throttling losses" sufferedLean conditionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectronThrottle
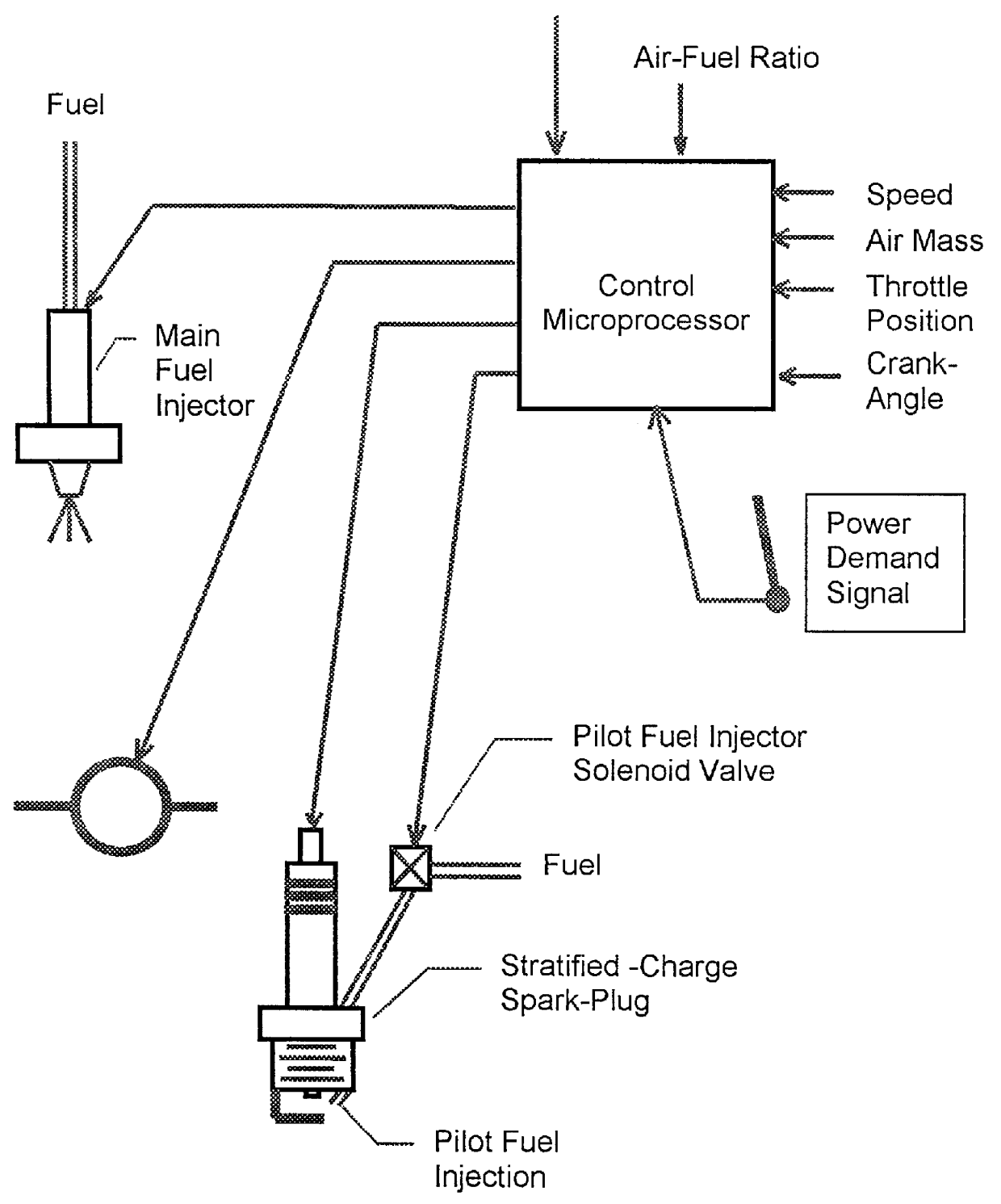
The control system disconnects the throttle from direct connection with the accelerator pedal, which sets the power requirements or demand. The demand signal passes to a computer control or microprocessor which electronically controls the throttle as a function of the engine operating conditions and pre-established values for controlled parameters stored in bitmaps in the microprocessor's memory. It is preferred to use a fuel injecting stratified charge spark plug in conjunction with the electronic control system and use the electronic control system to control the primary and auxiliary fuel injection systems as well as the ignition timing to permit the engine to run under very lean conditions to produce low levels of emissions such as nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide.
Owner:R L EVANS & ASSOC
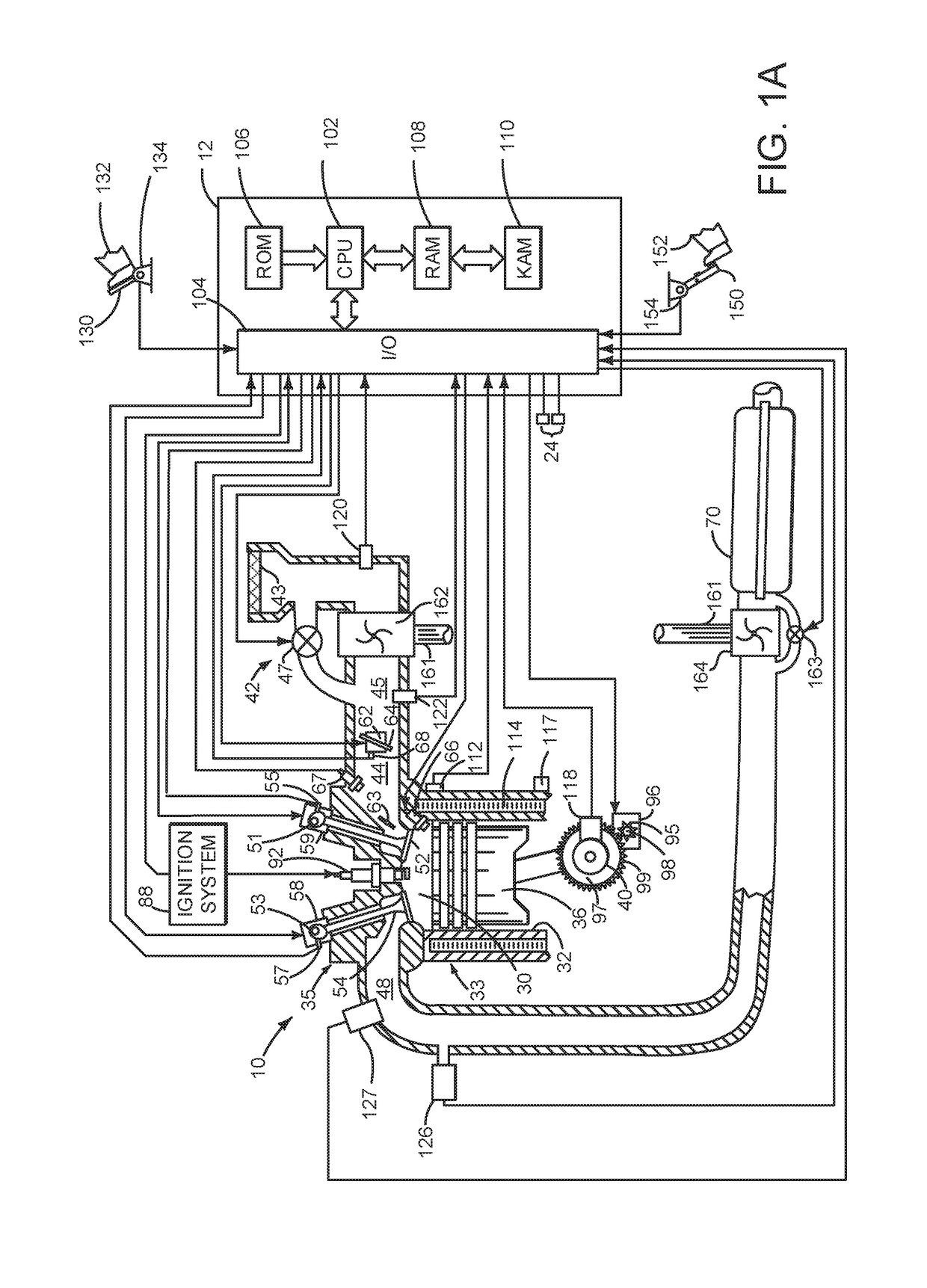
System and method for monitoring an ignition system
ActiveUS20130206106A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease volumeEngine controllersElectric motor startersElectricitySoot
A system for monitoring and cleaning a spark plug is disclosed. In one example, an amount of carbonaceous soot at the center electrode ceramic of the spark plug is determined in response to a voltage of a sense resistor that is in electrical communication with the spark plug. The system may institute spark plug cleaning after carbonaceous soot is detected so that the possibility of engine misfire may be reduced.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20140325983A1Secure performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineIgnition timing
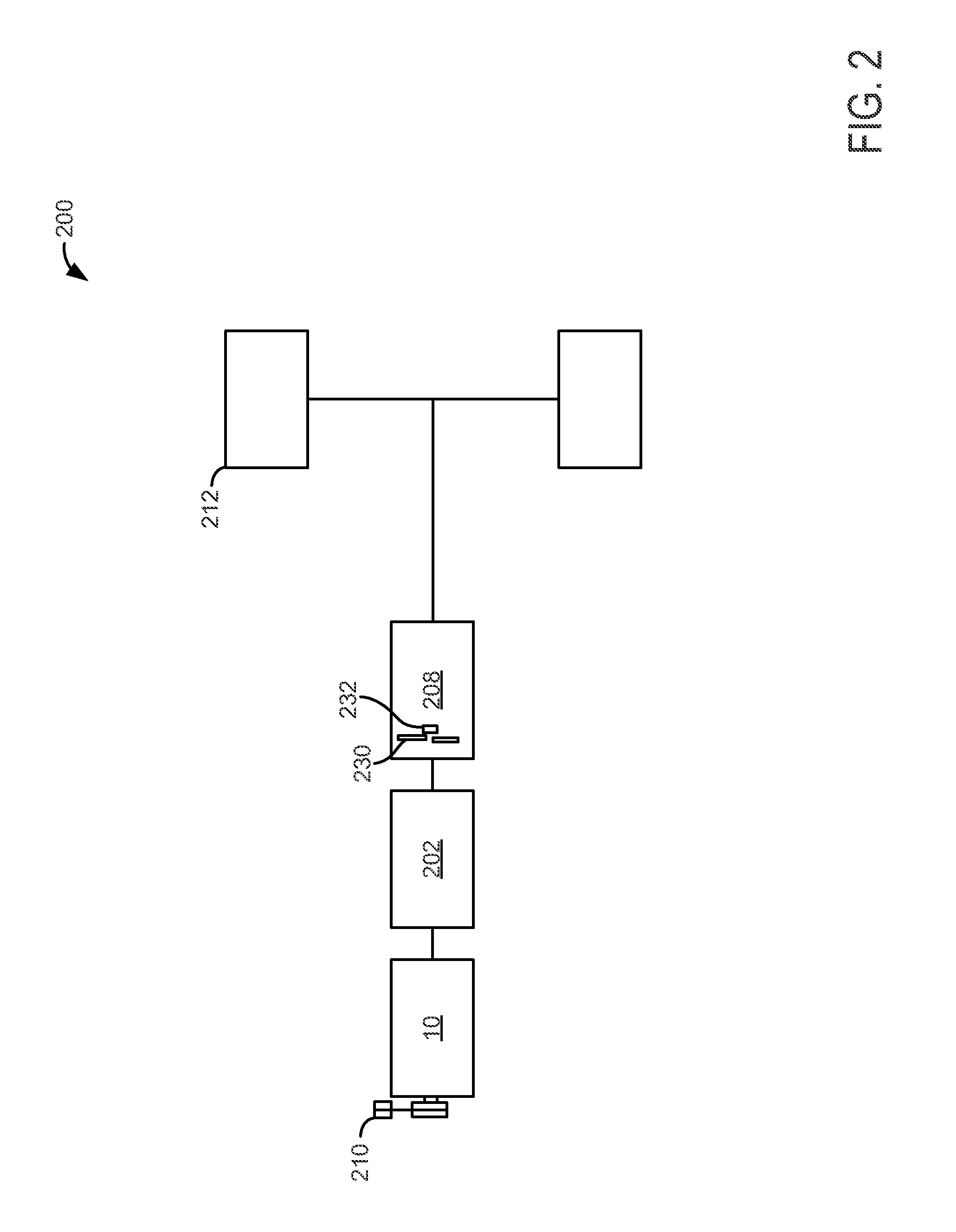
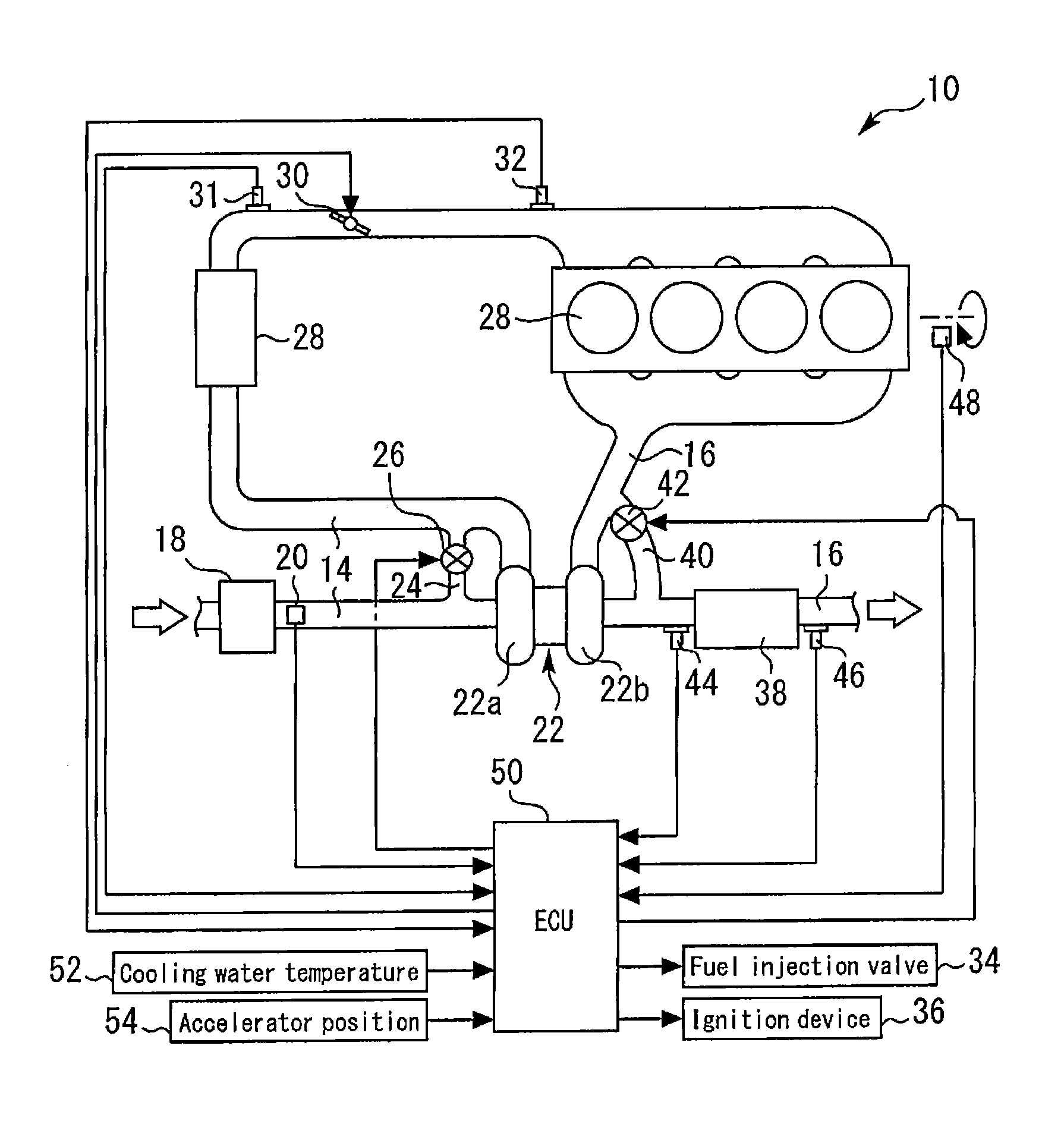
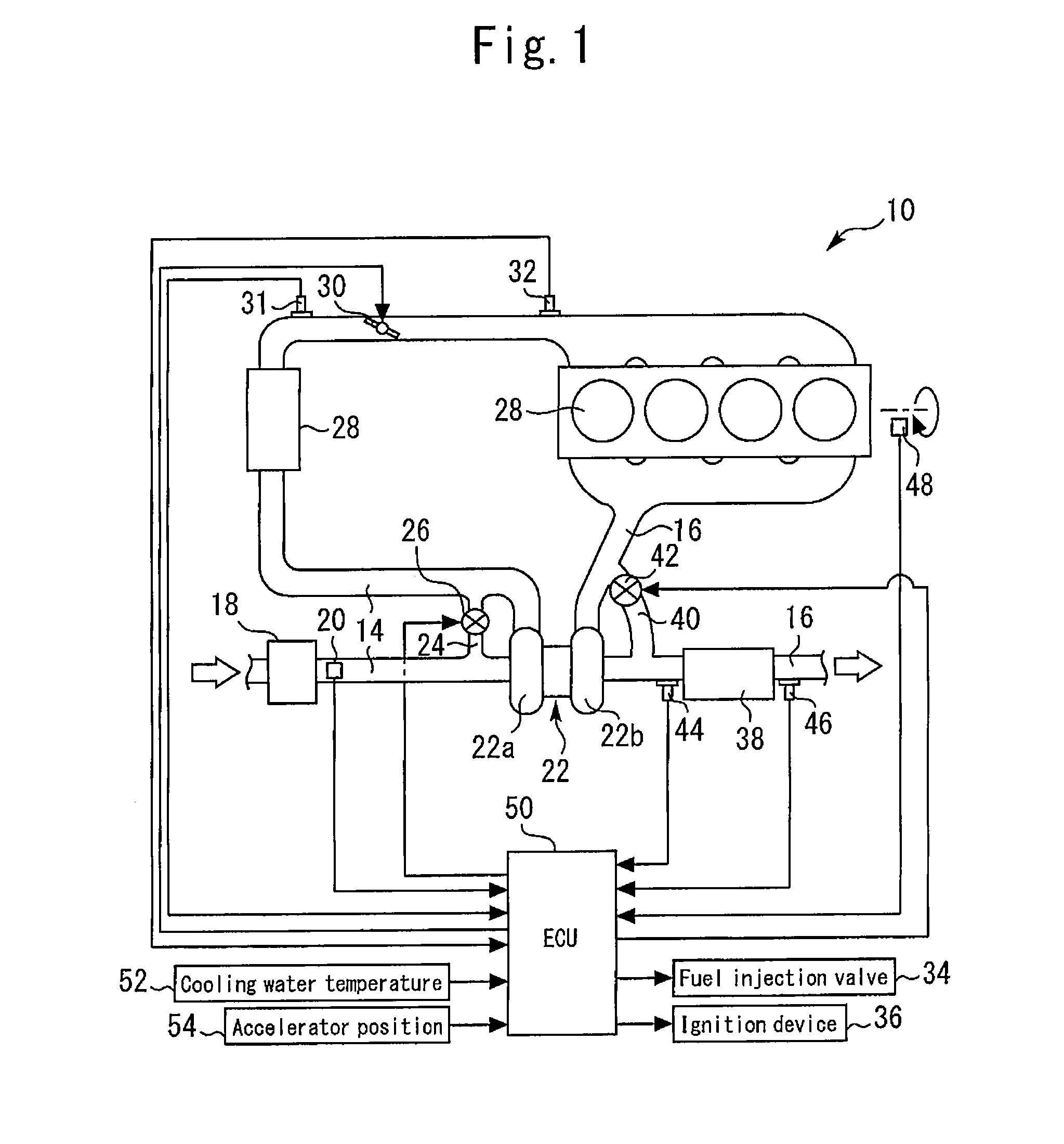
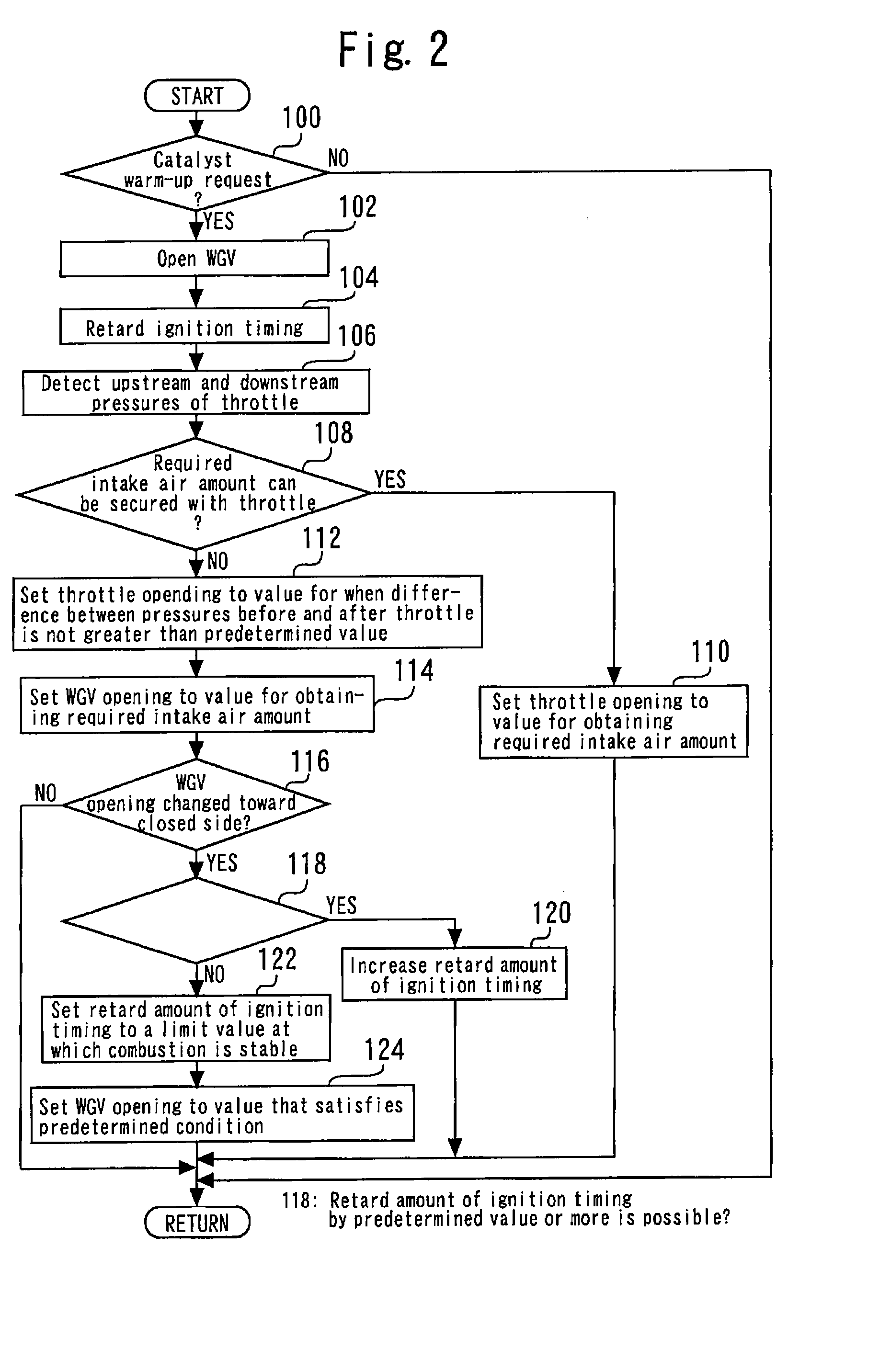
A control apparatus for an internal combustion engine of this invention includes: a turbo-supercharger; an exhaust gas purifying catalyst disposed in an exhaust passage on the downstream side of a turbine; and a WGV capable of opening and closing an exhaust bypass passage that bypasses the turbine. At the time of a catalyst warm-up request, catalyst warm-up control that opens the WGV and retards the ignition timing is executed. If the sensitivity of control of an intake air amount by a throttle valve is high, the intake air amount is controlled using the throttle valve during execution of the catalyst warm-up control. If the control sensitivity is low, the intake air amount is controlled using the WGV during execution of the catalyst warm-up control. When the WGV degree of opening is controlled toward a closed side during execution of the intake air amount control using the WGV, a retard amount of the ignition timing is increased.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Vehicle control apparatus
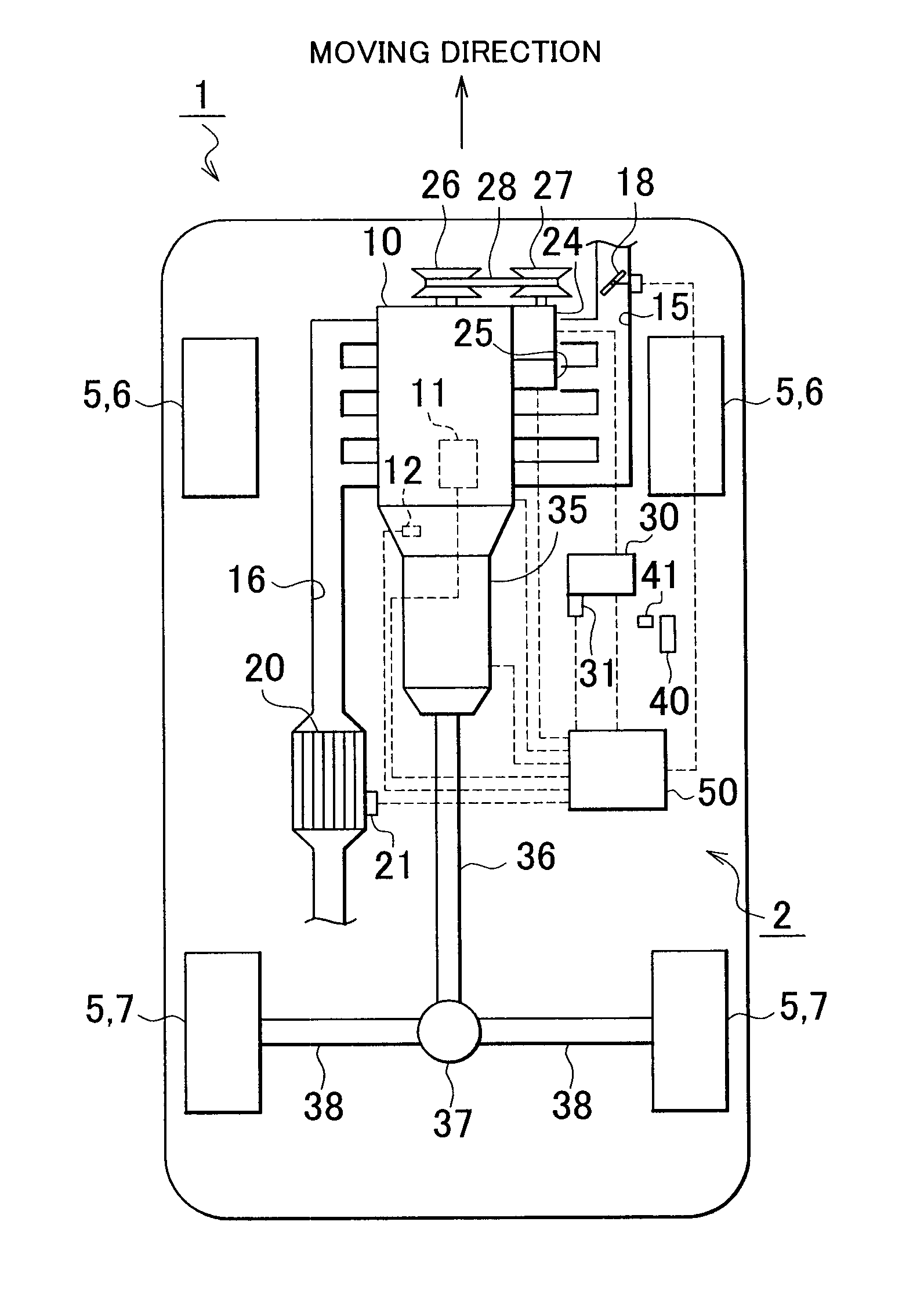
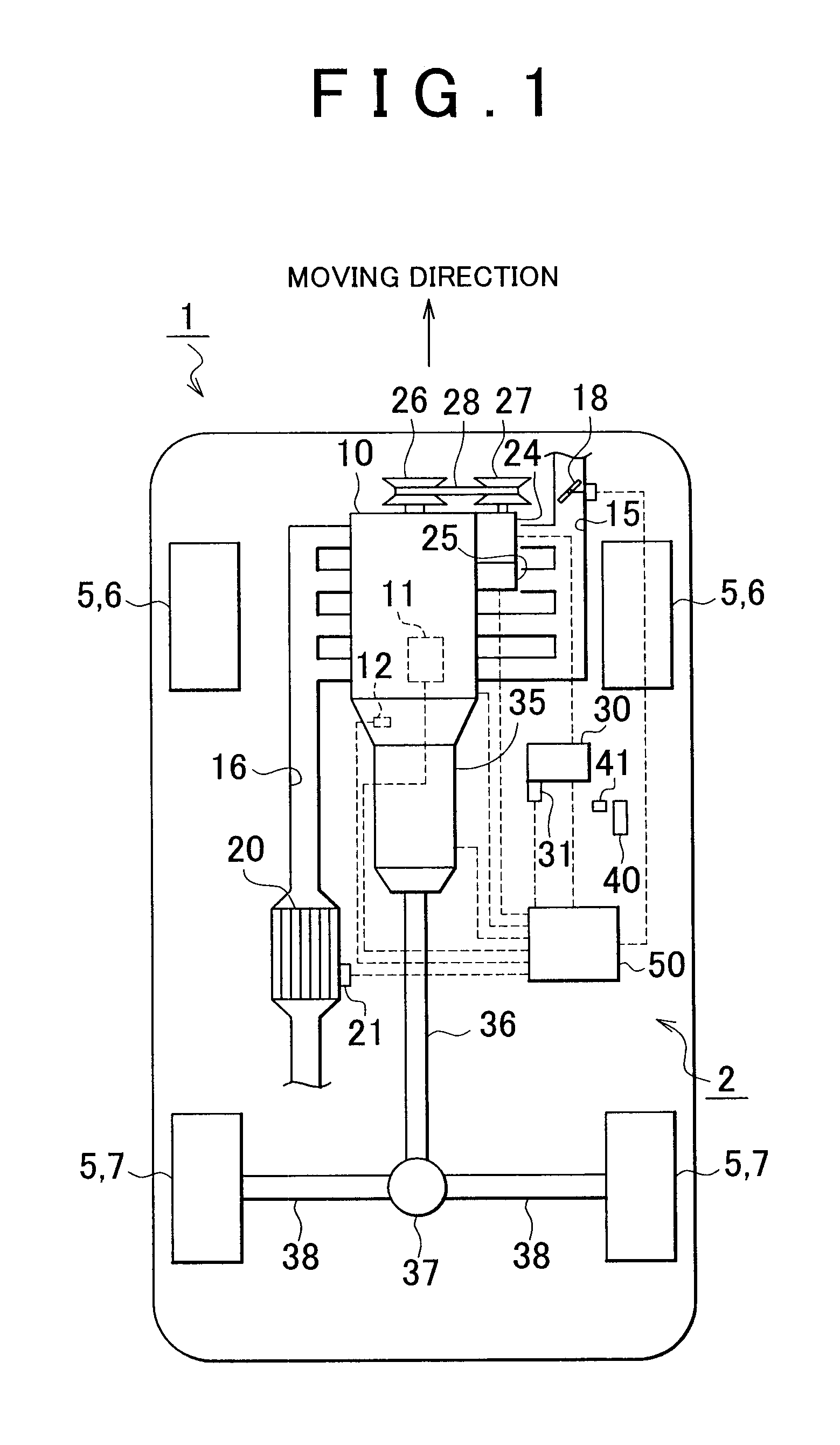
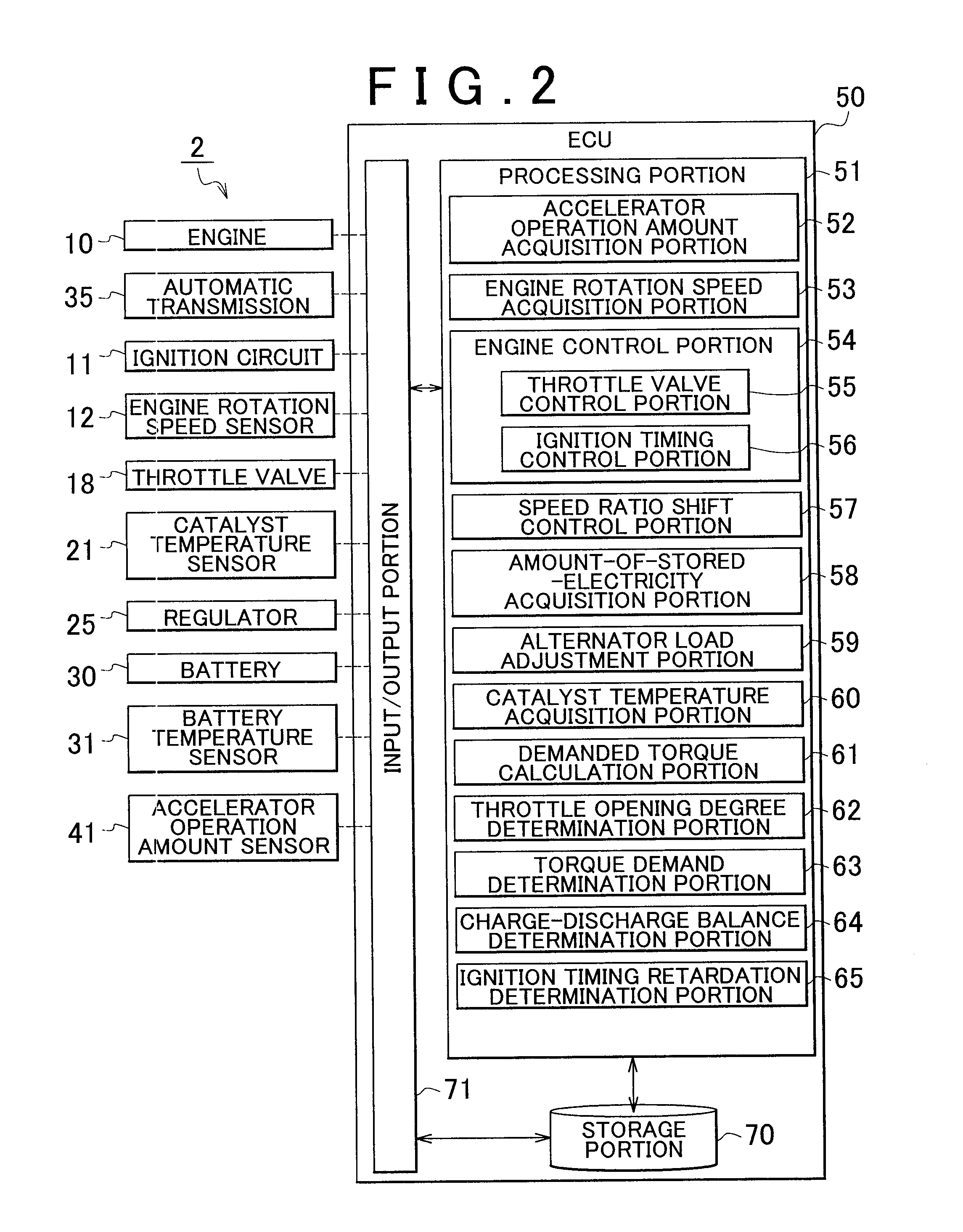
ActiveUS20110005212A1Lower latencyReduce storageAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineIgnition timing
A vehicle control apparatus includes: an accessory that adjusts torque that is output from an internal combustion engine, by giving load to the internal combustion engine; an ignition timing control portion that is provided so as to adjust ignition timing of the internal combustion engine, and that adjusts the torque output from the internal combustion engine by performing a retardation control of the ignition timing; an accessory load adjustment portion that adjusts an accessory load that is the load given from the accessory to the internal combustion engine; and a catalyst that purifies exhaust gas discharged from the internal combustion engine. The ignition timing control portion reduces the retardation of the ignition timing with increase in temperature of the catalyst. The accessory load adjustment portion increases the accessory load with increase in the temperature of the catalyst.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com