Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Vertebral surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
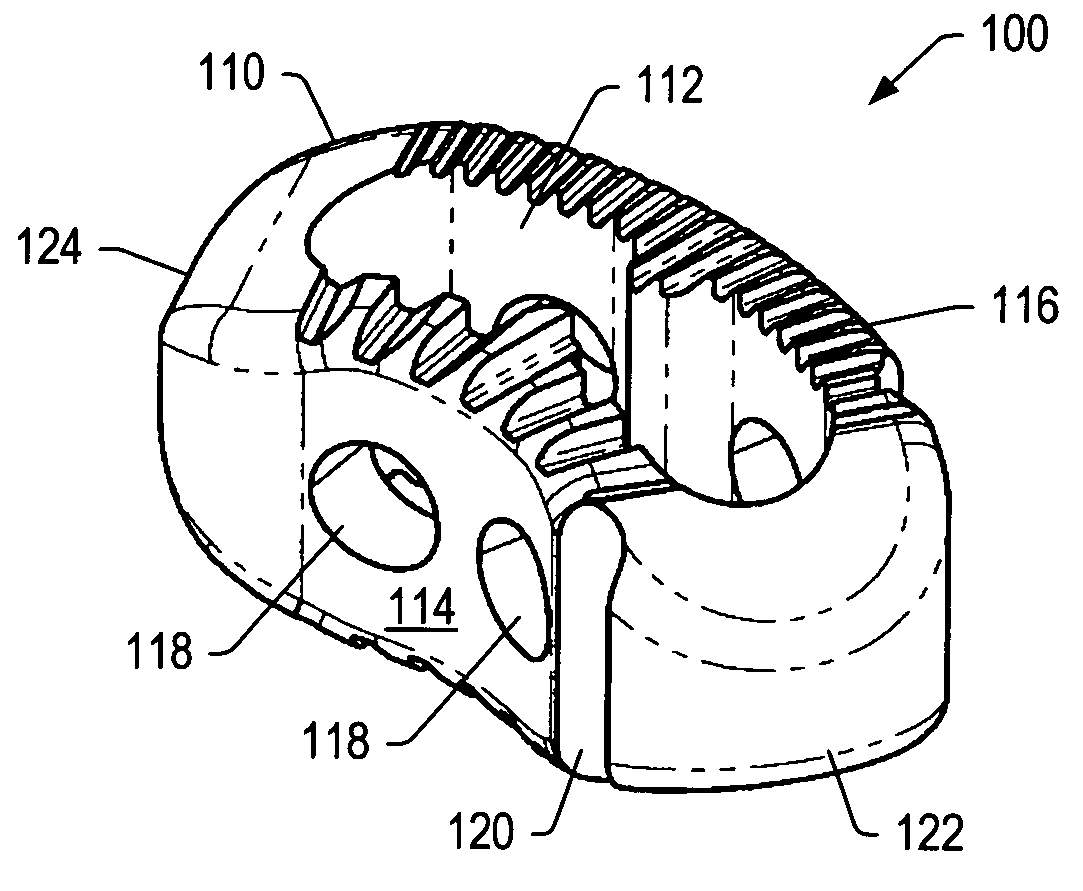
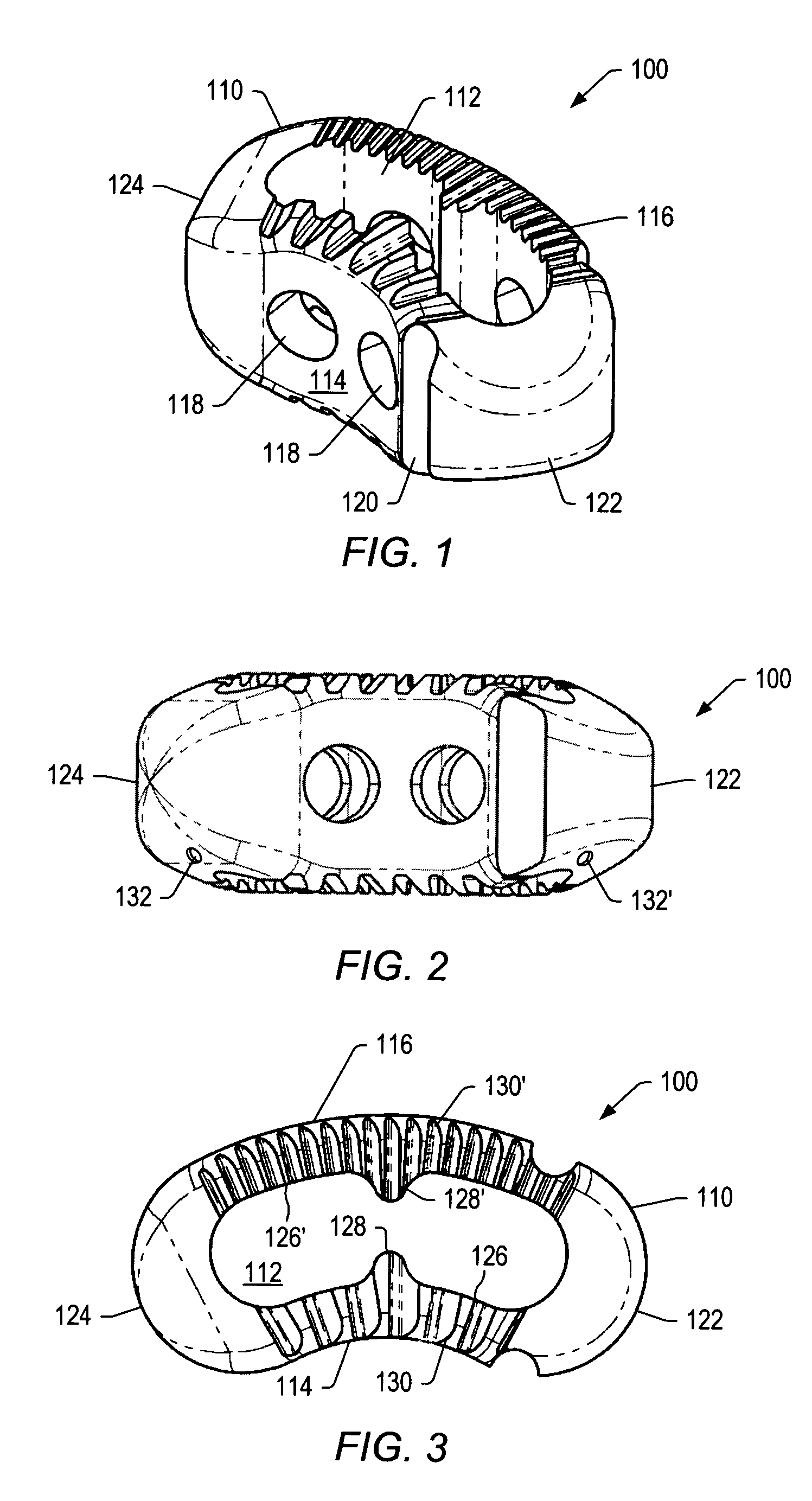
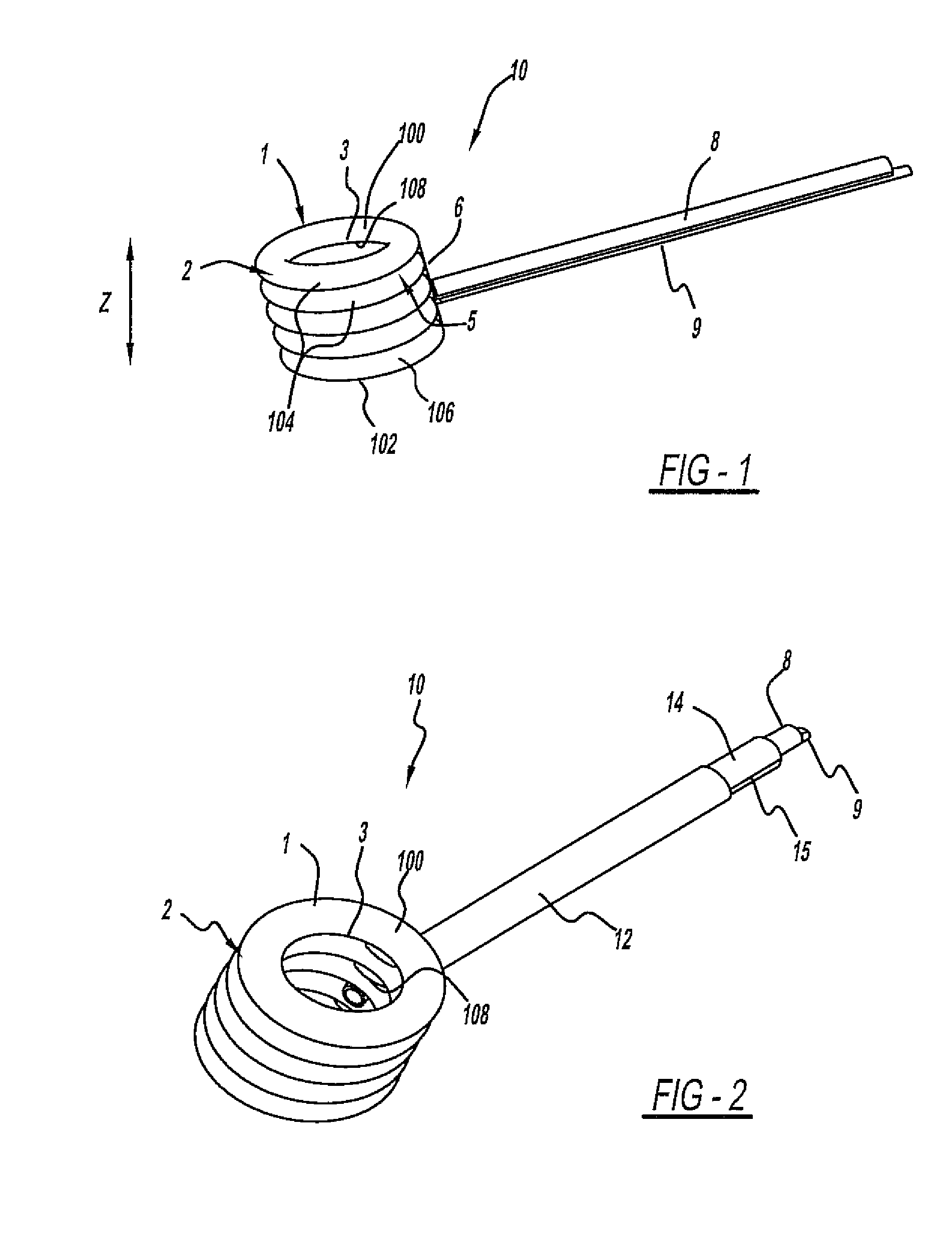
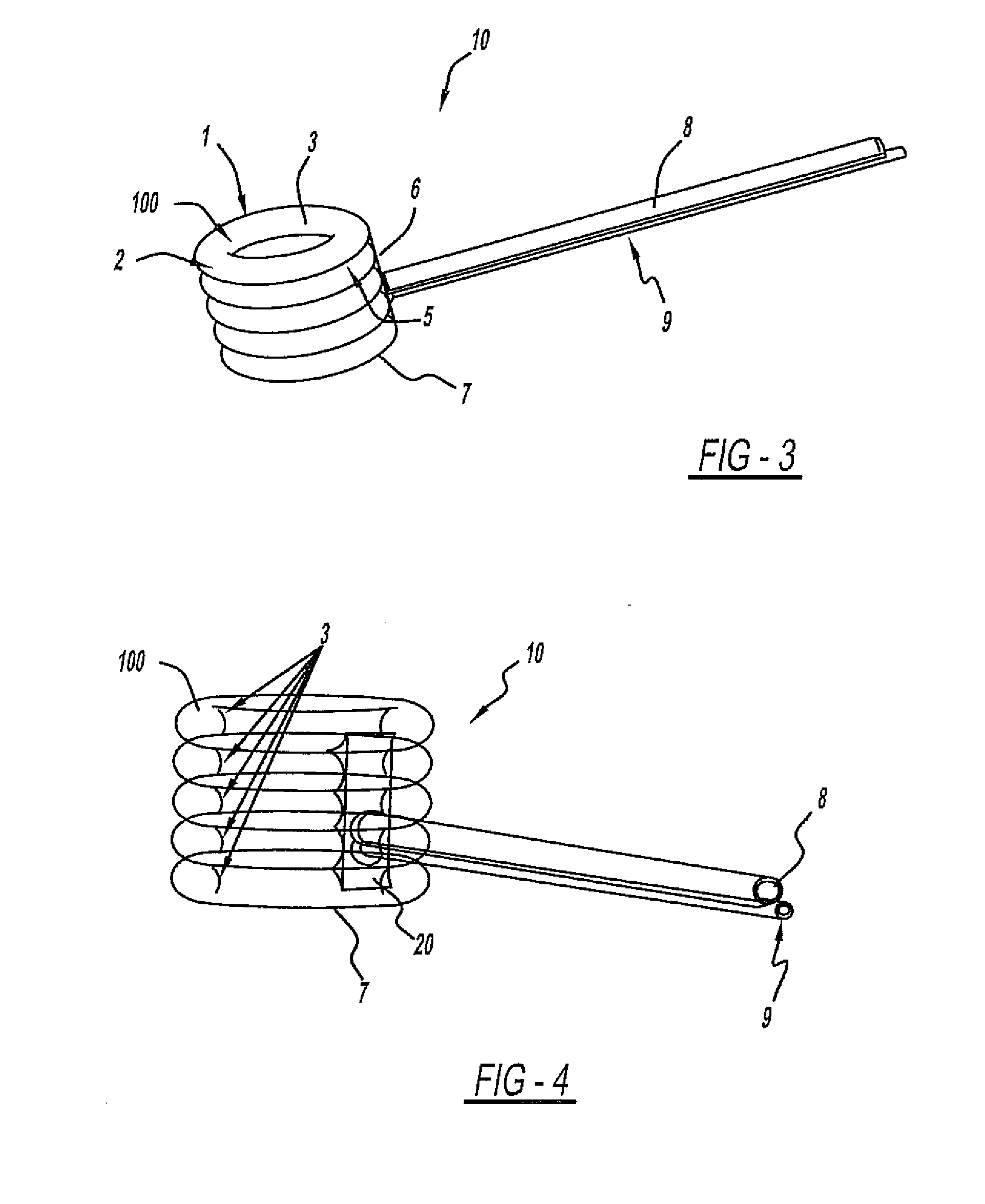
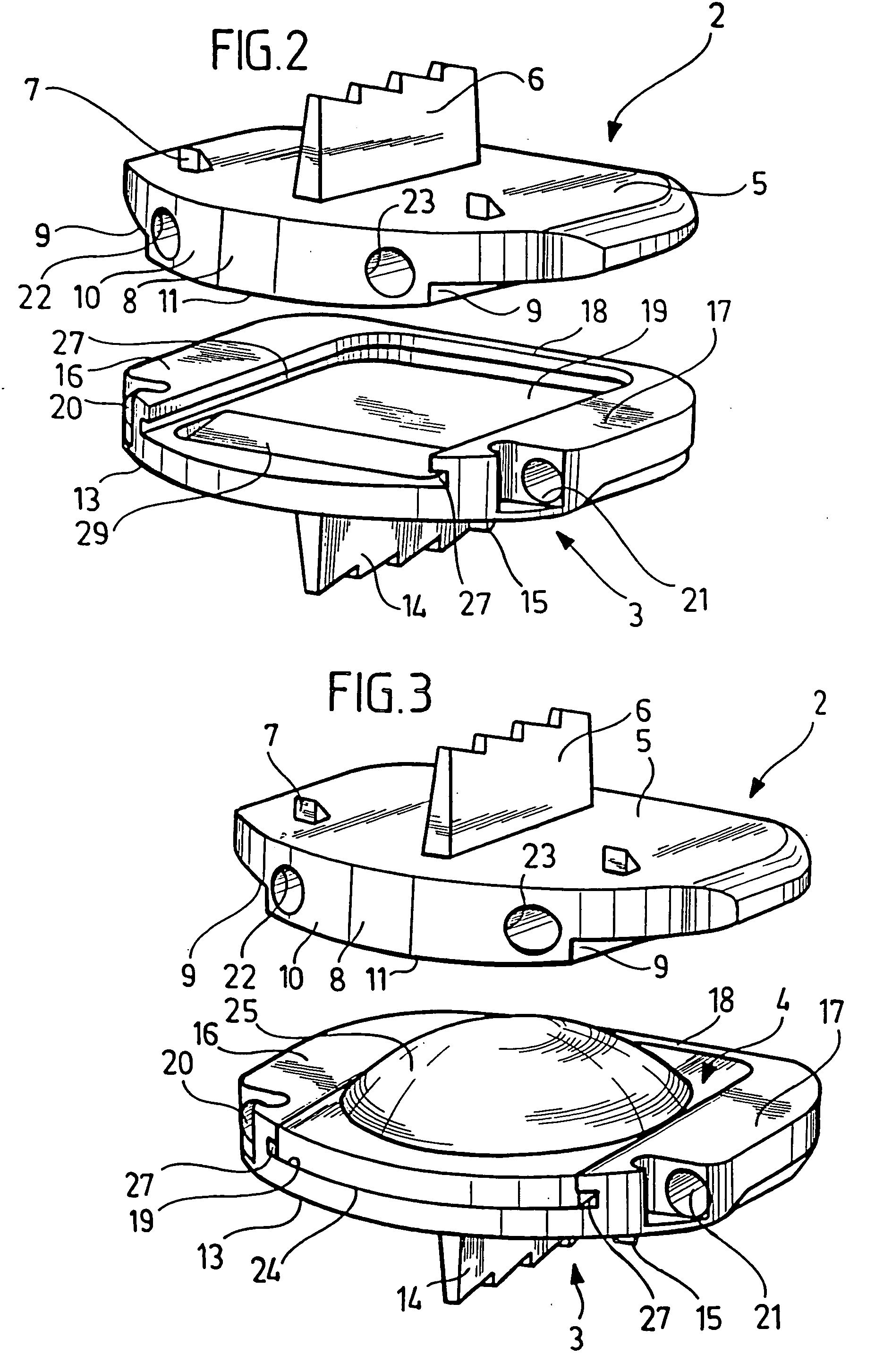
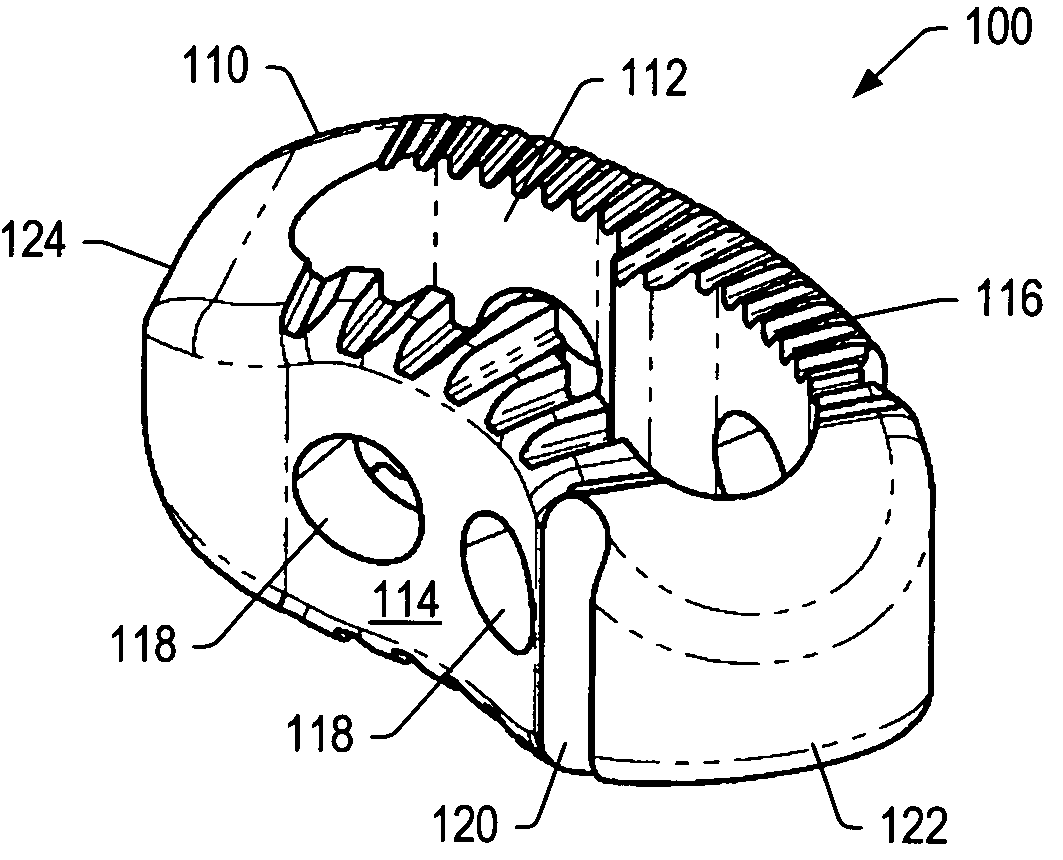
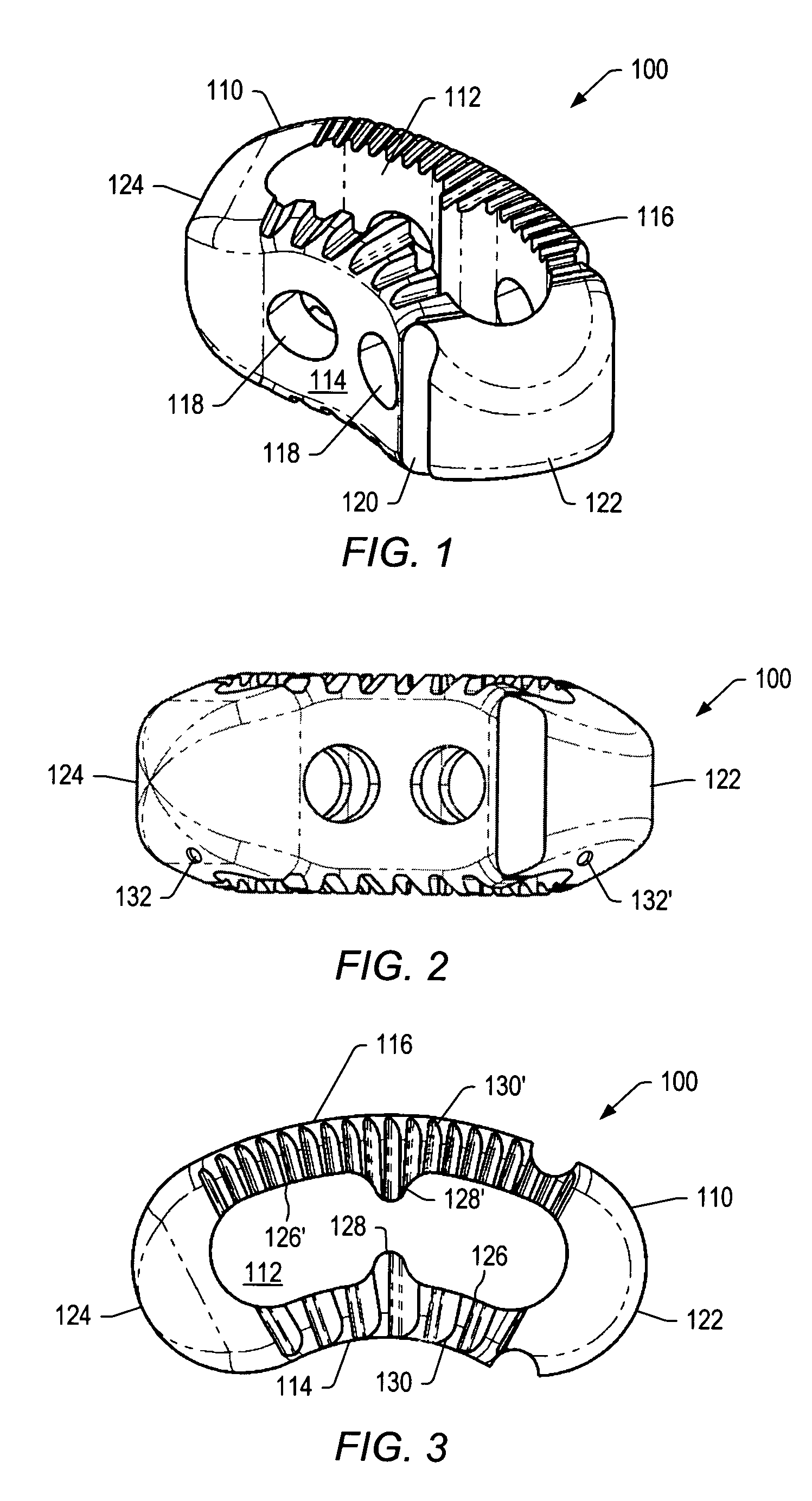
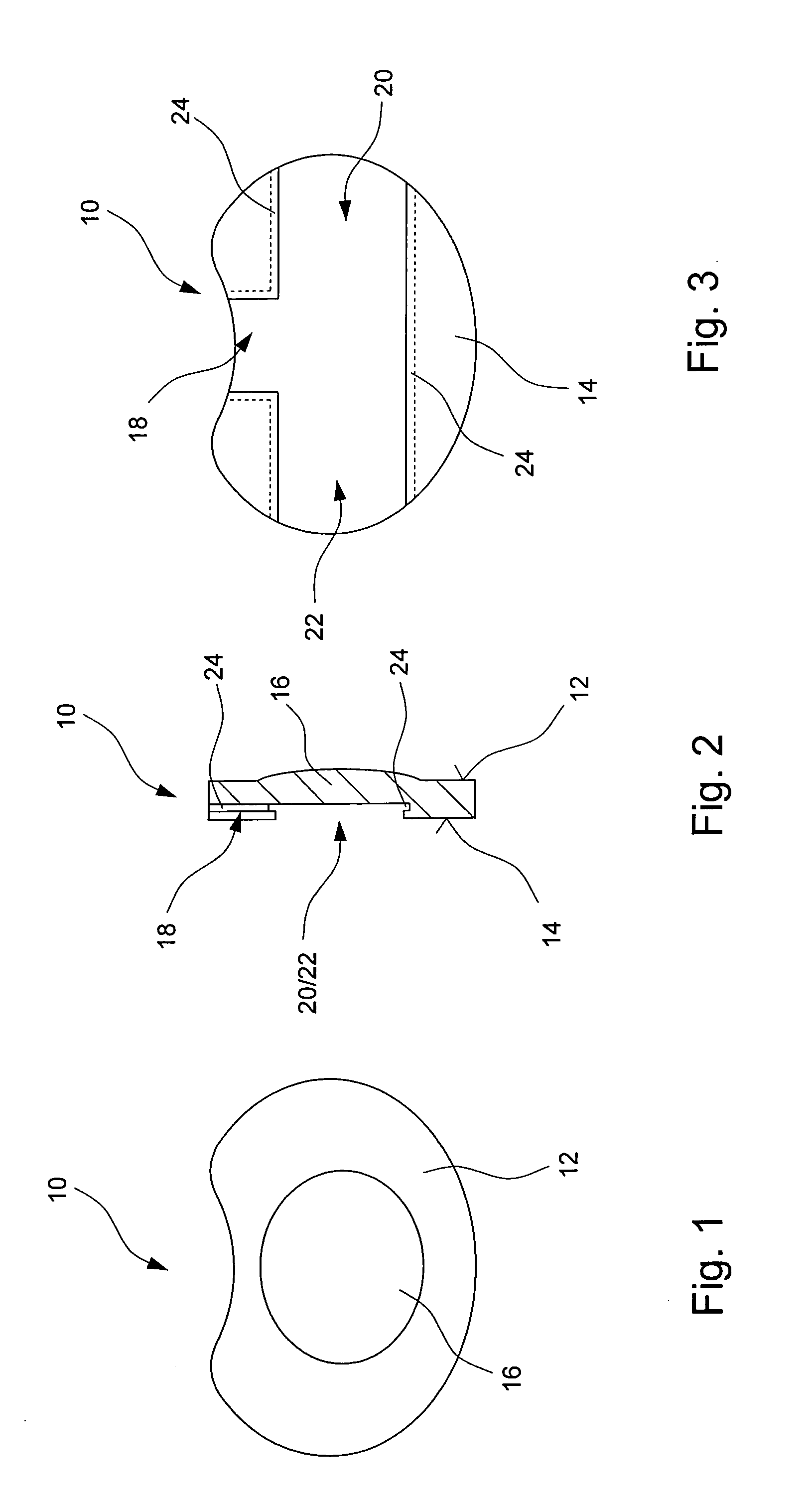
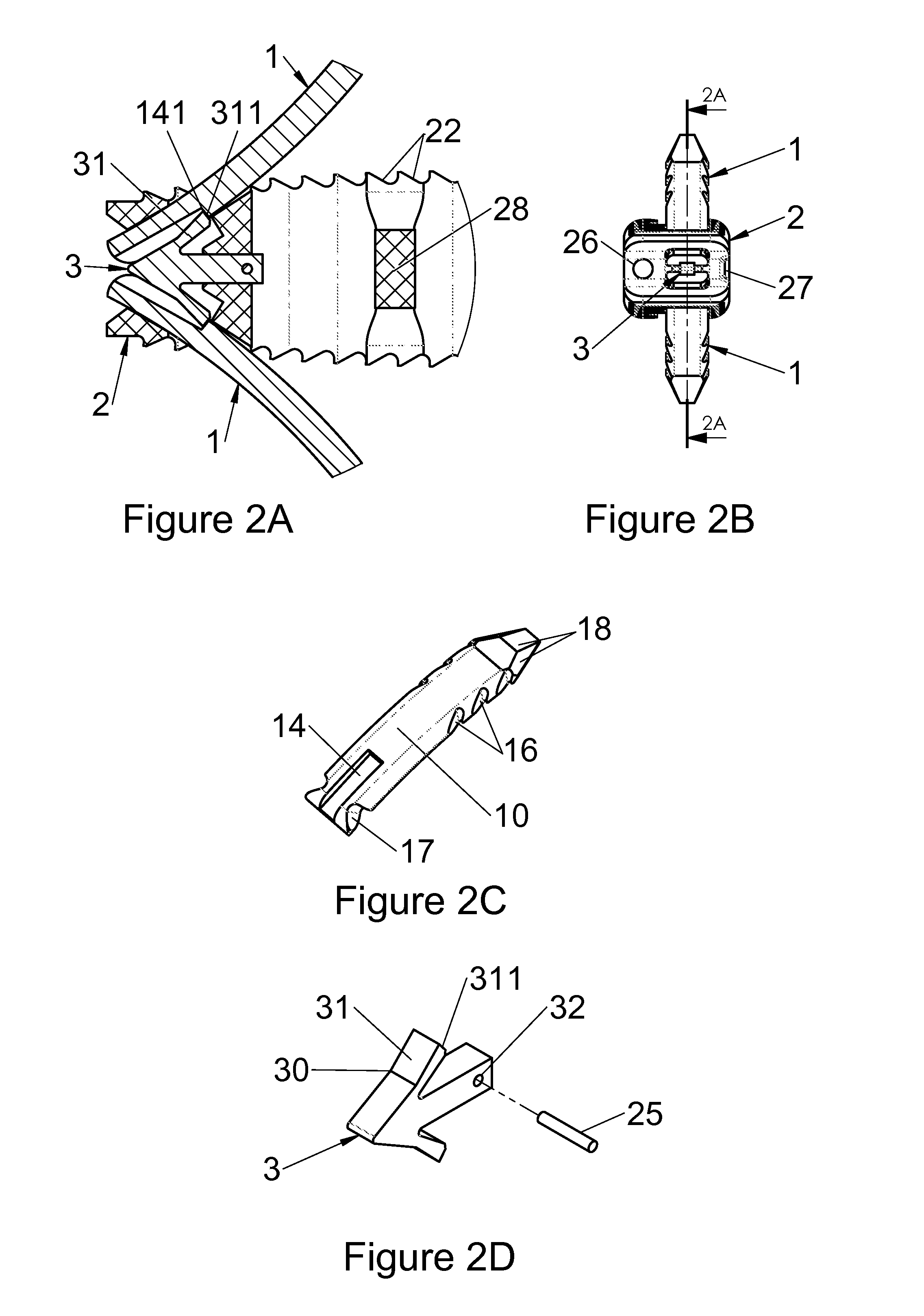
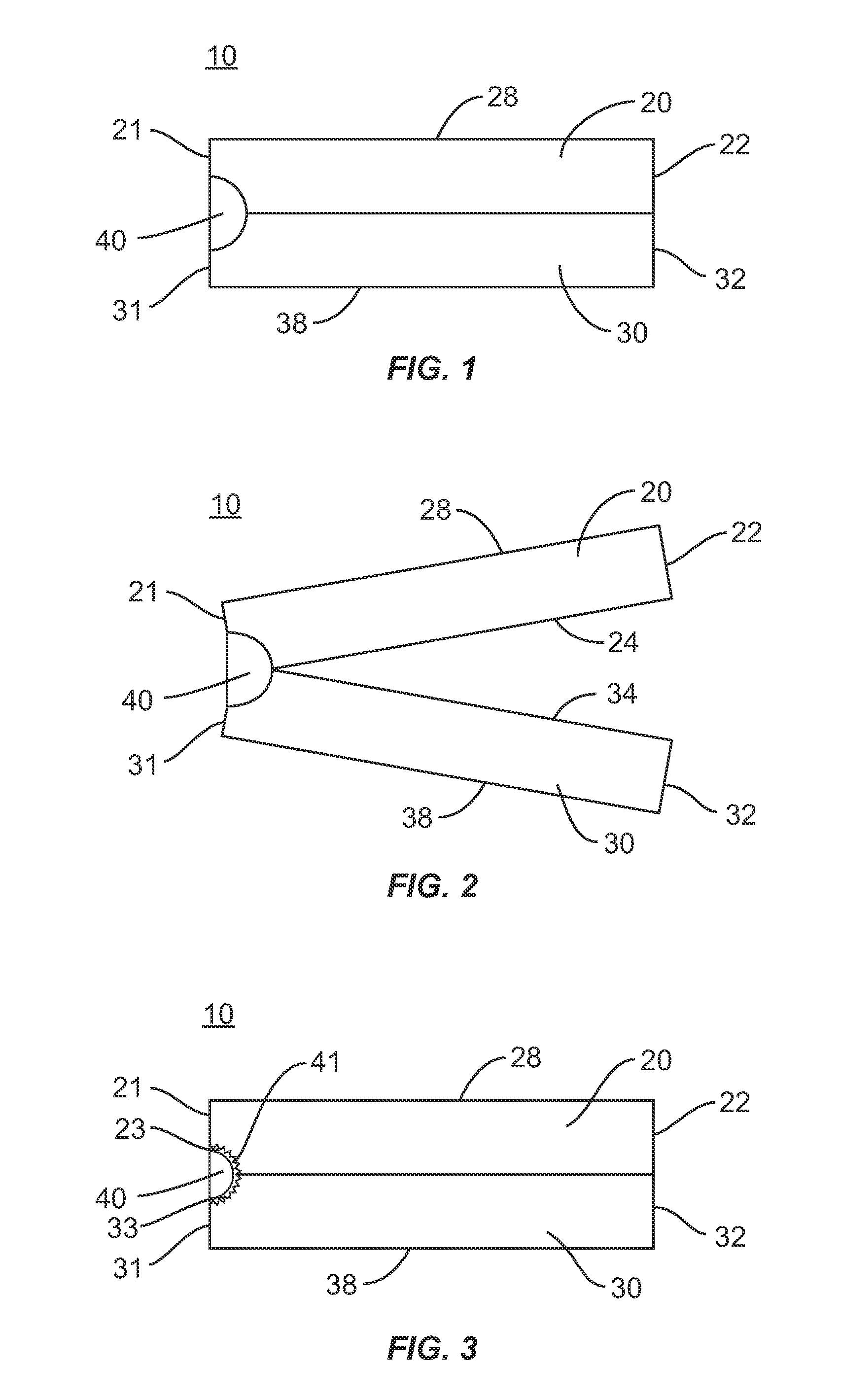
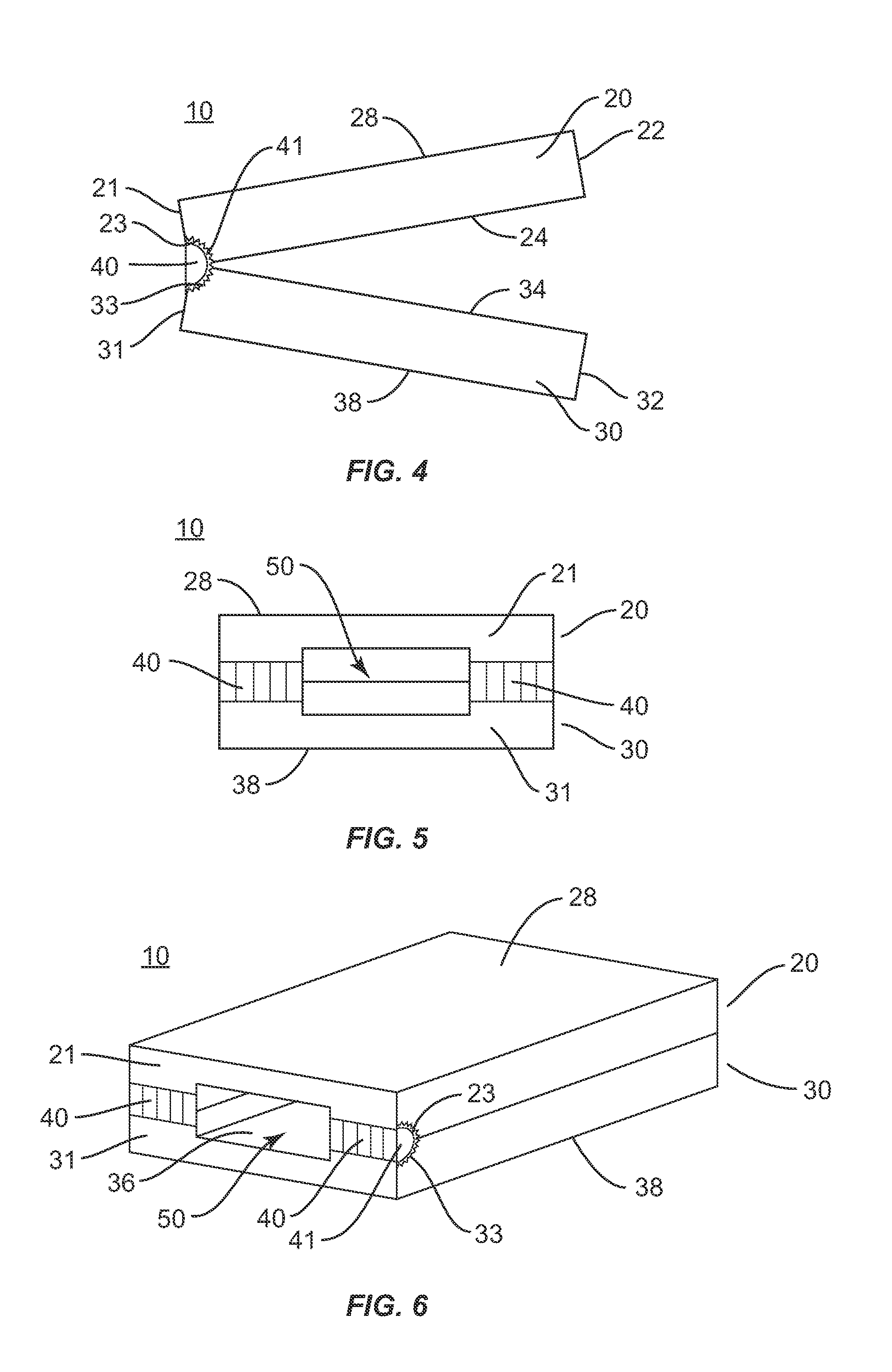
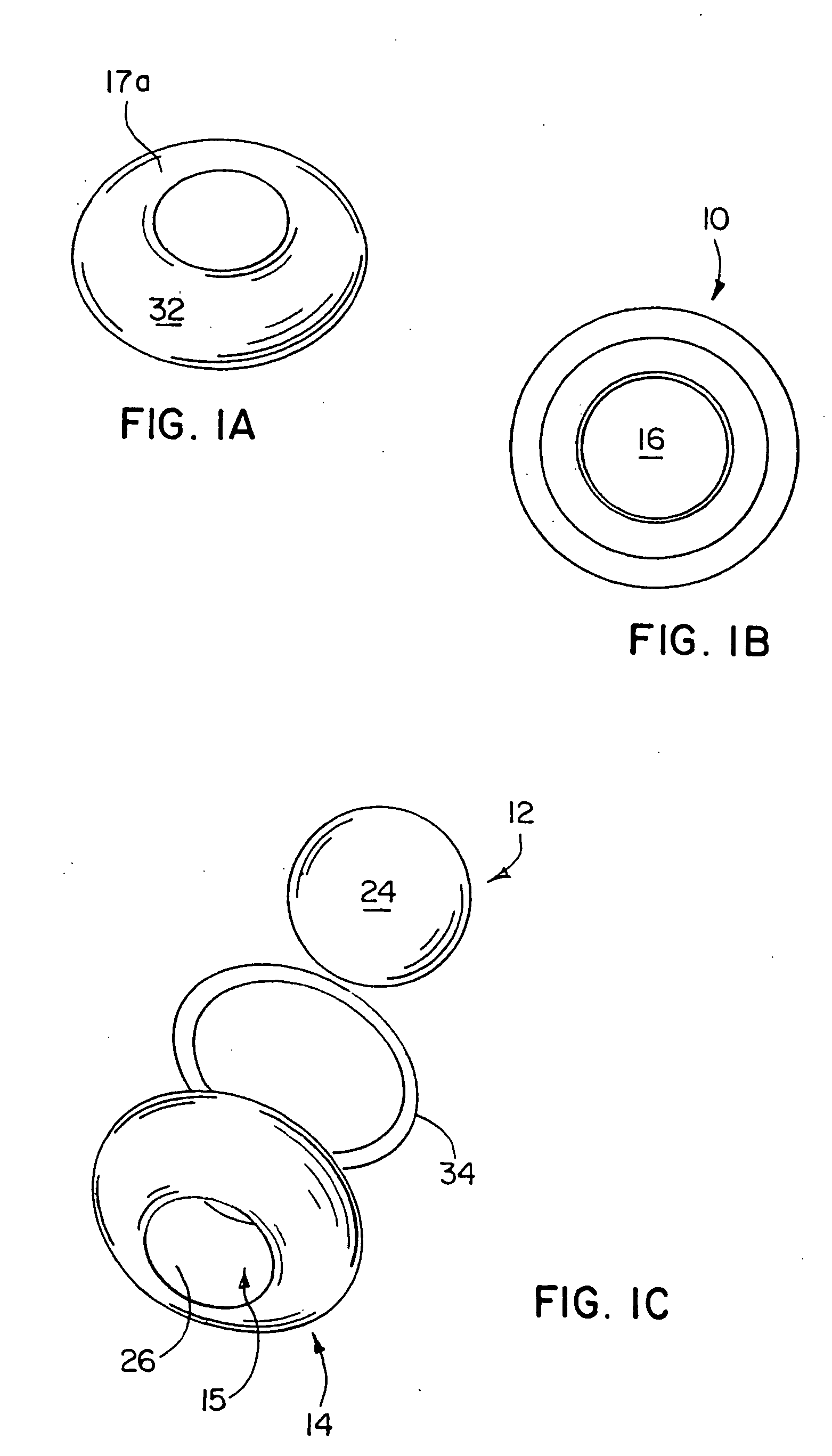
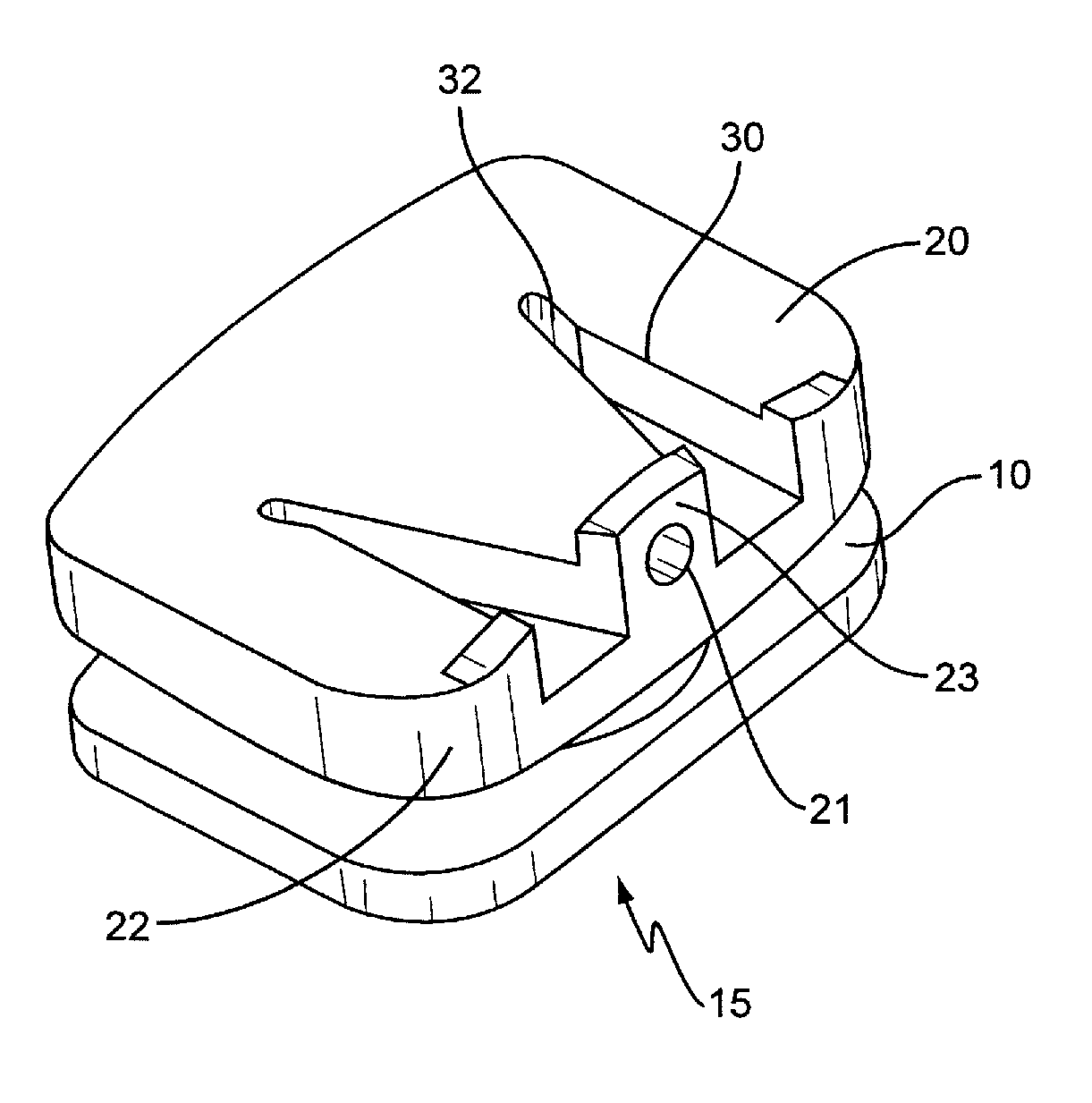
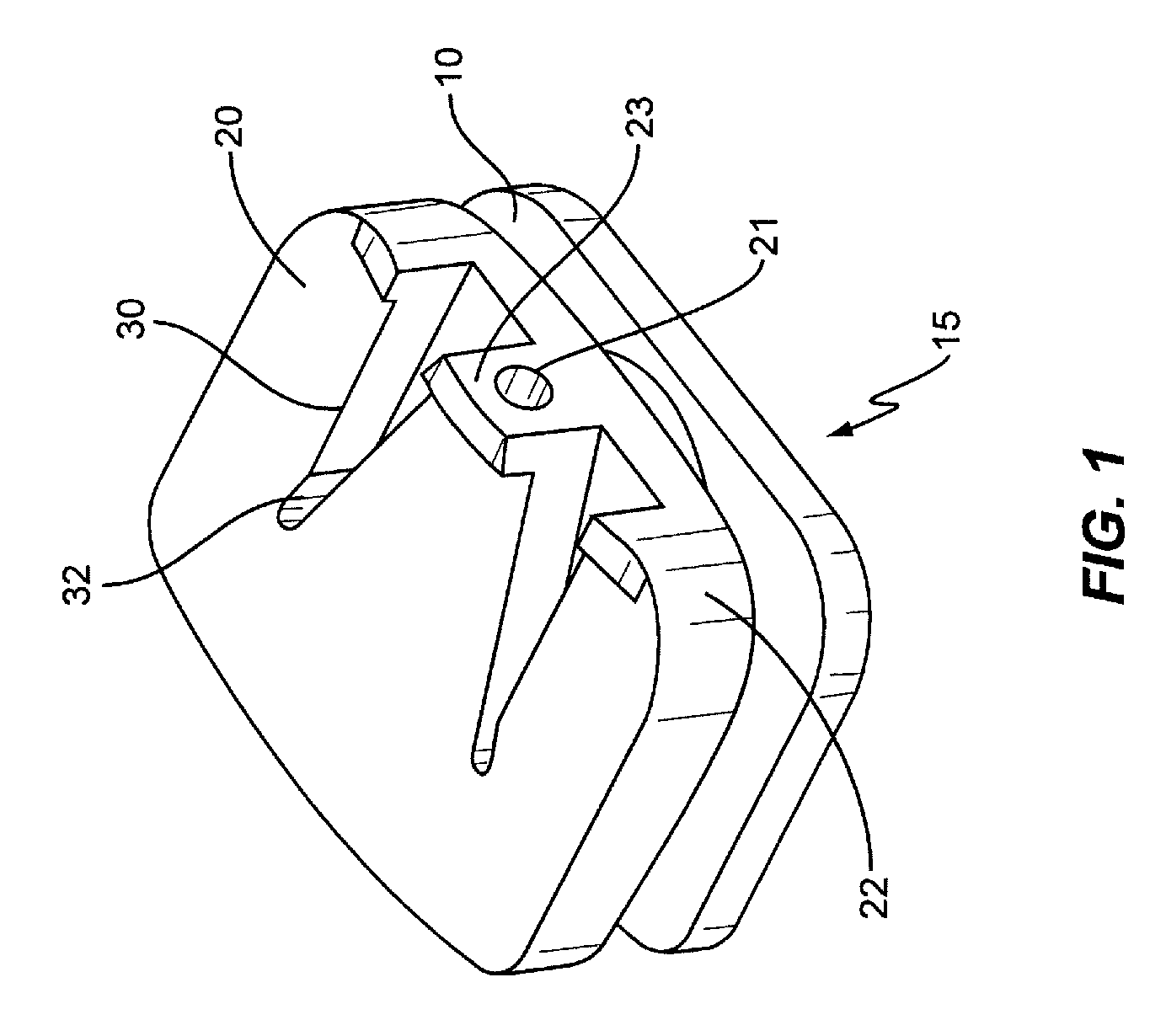
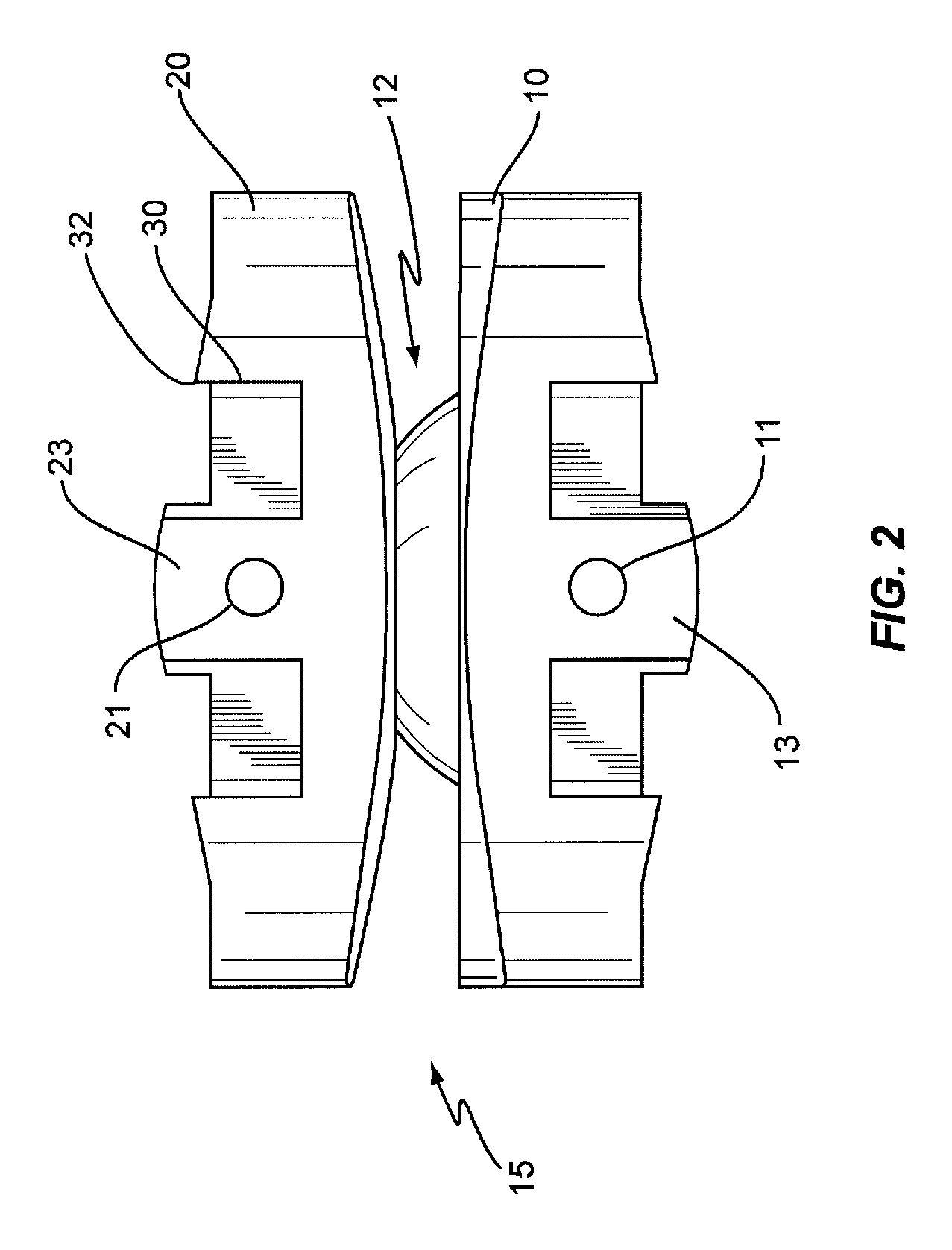
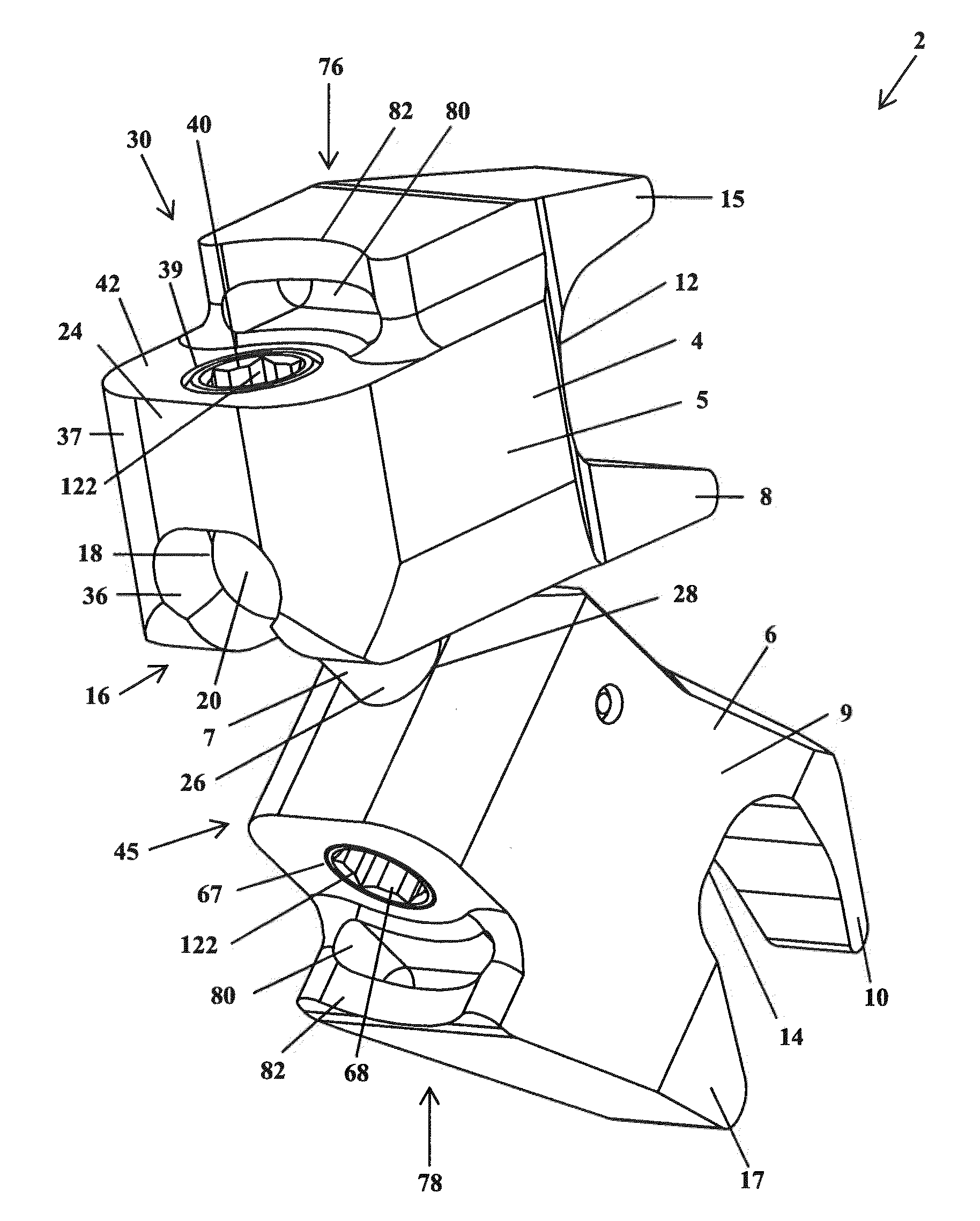
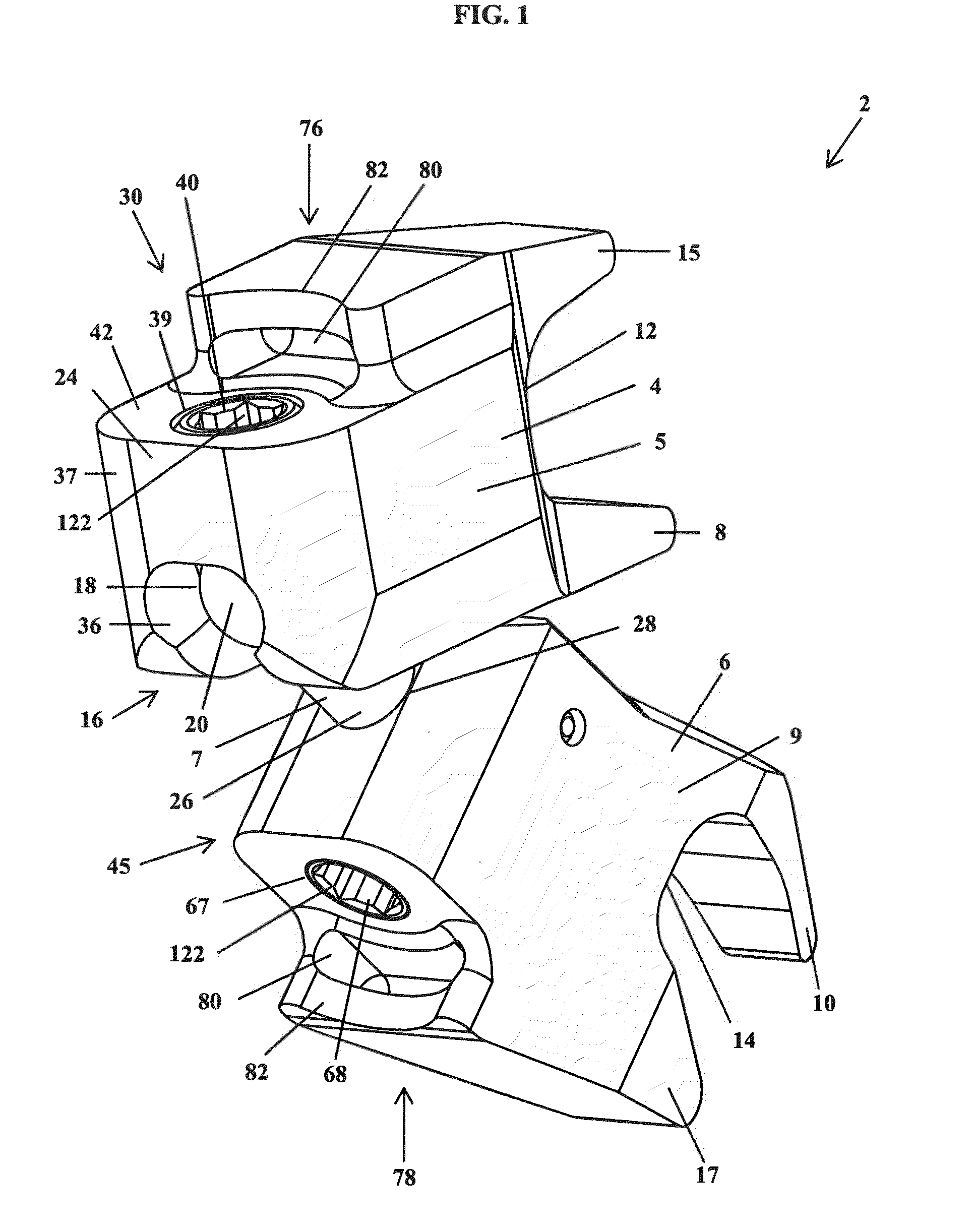
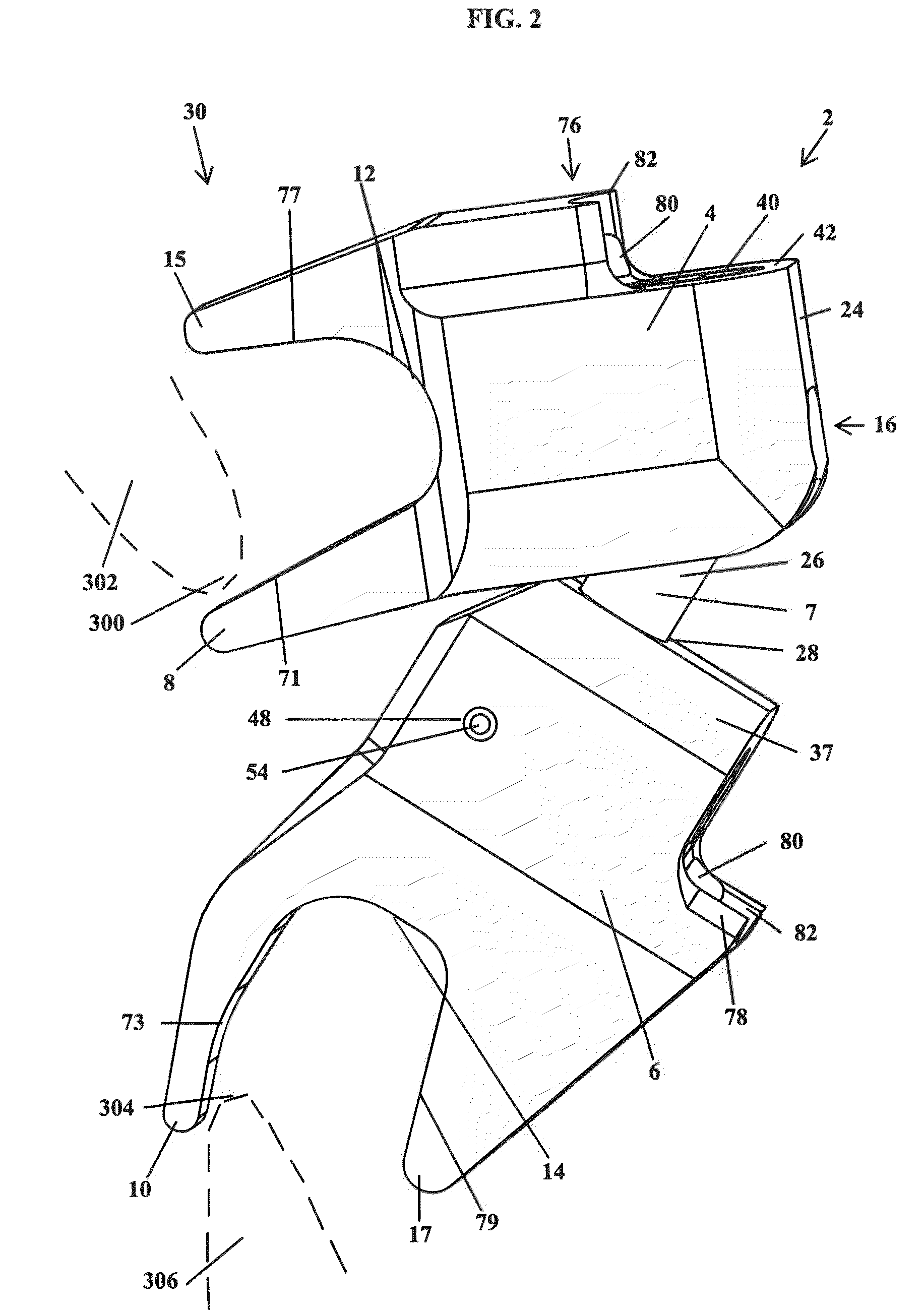
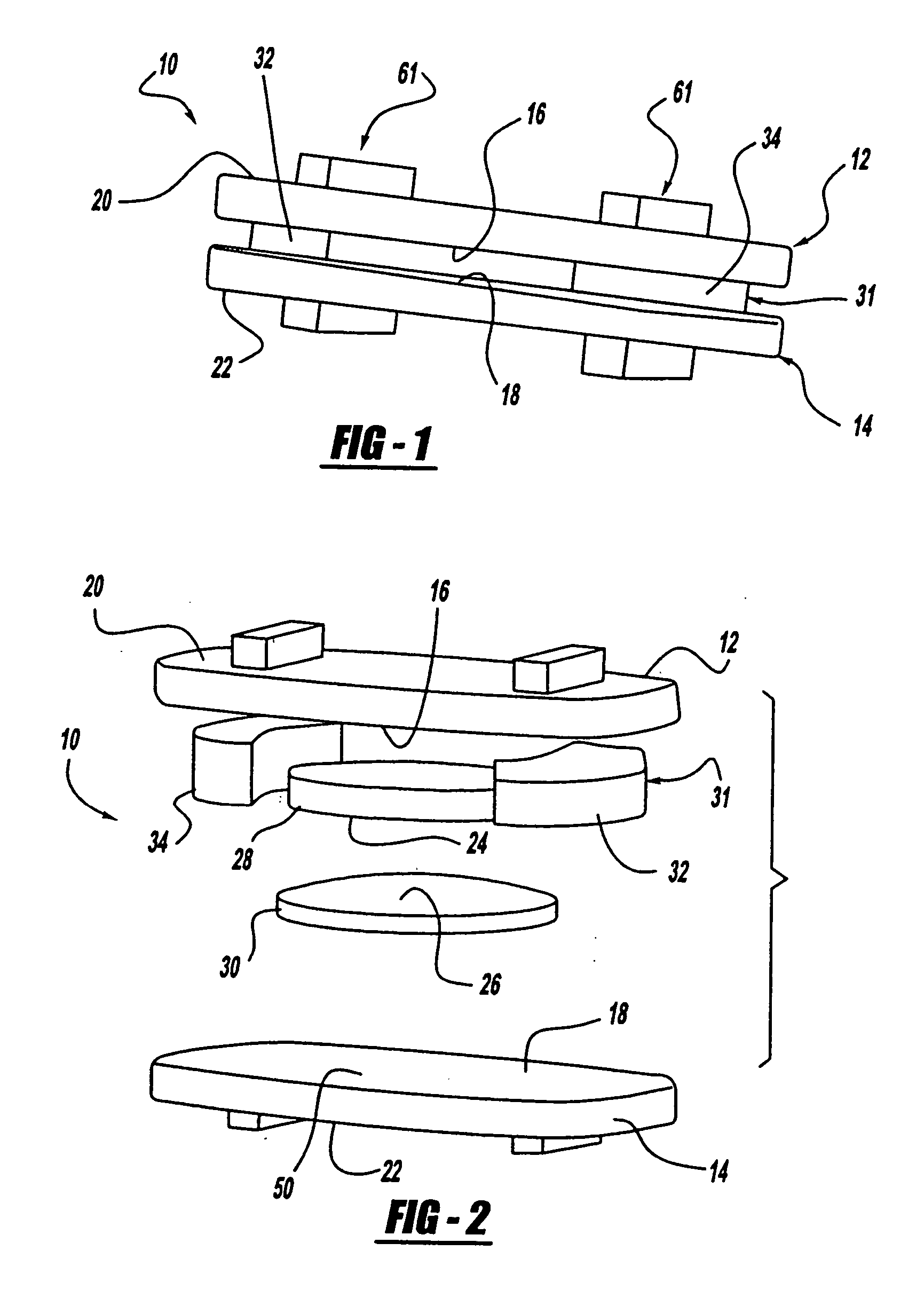
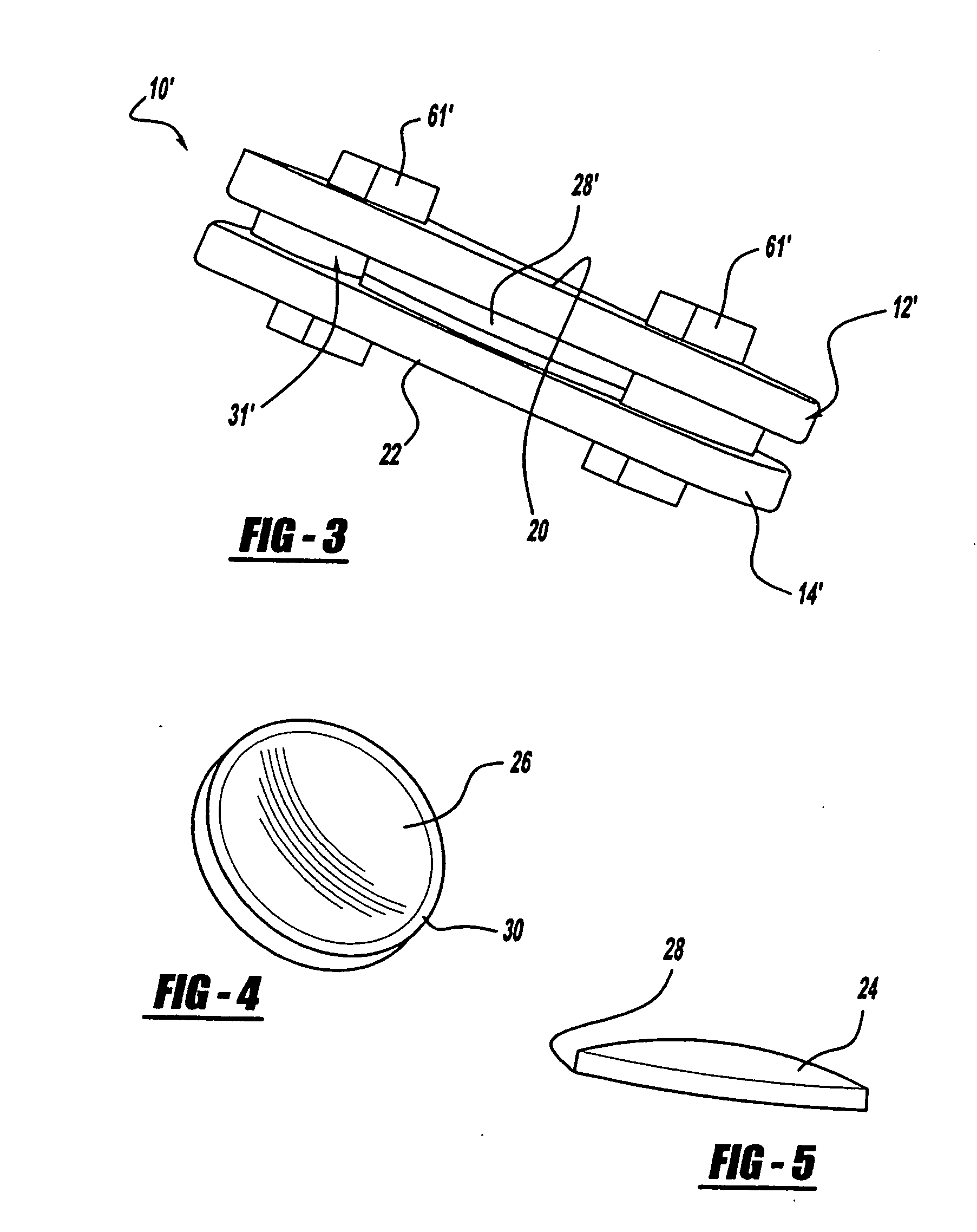
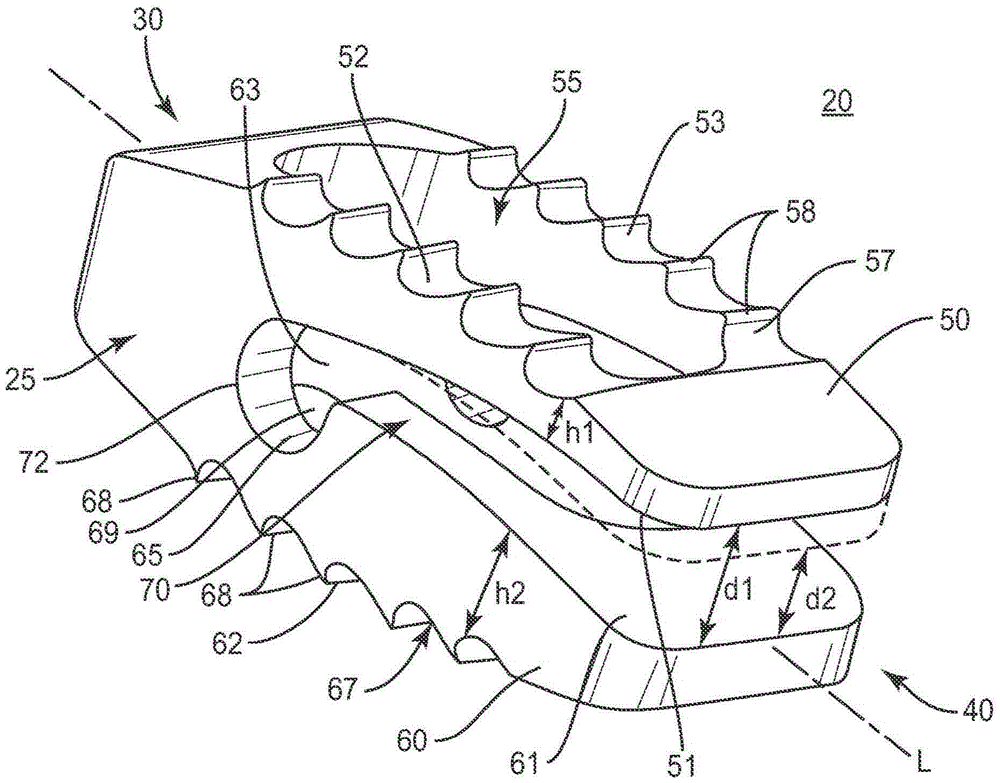
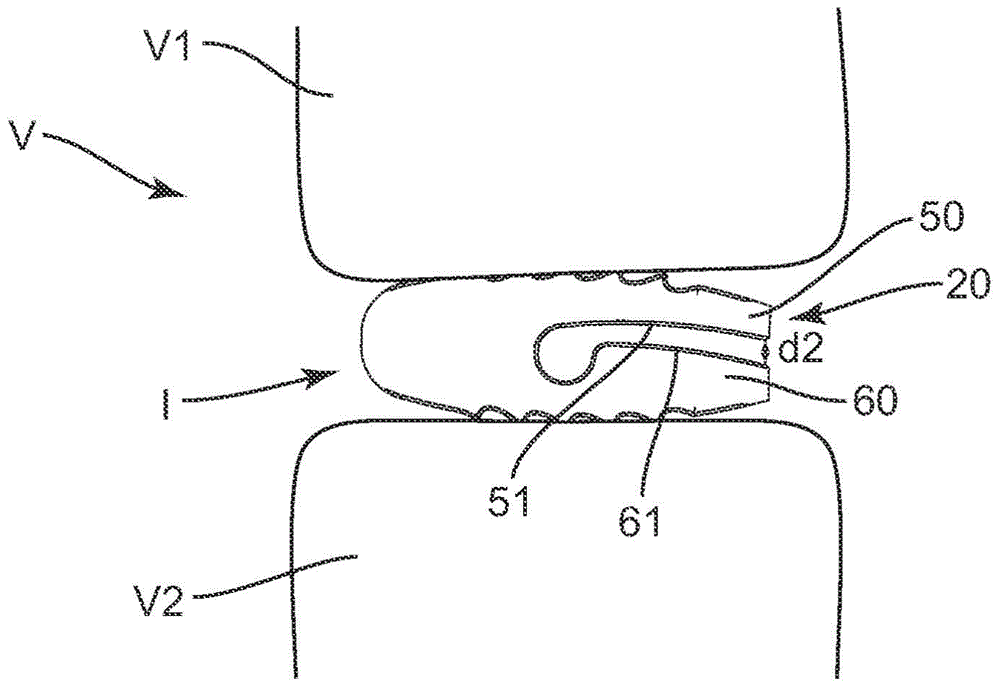
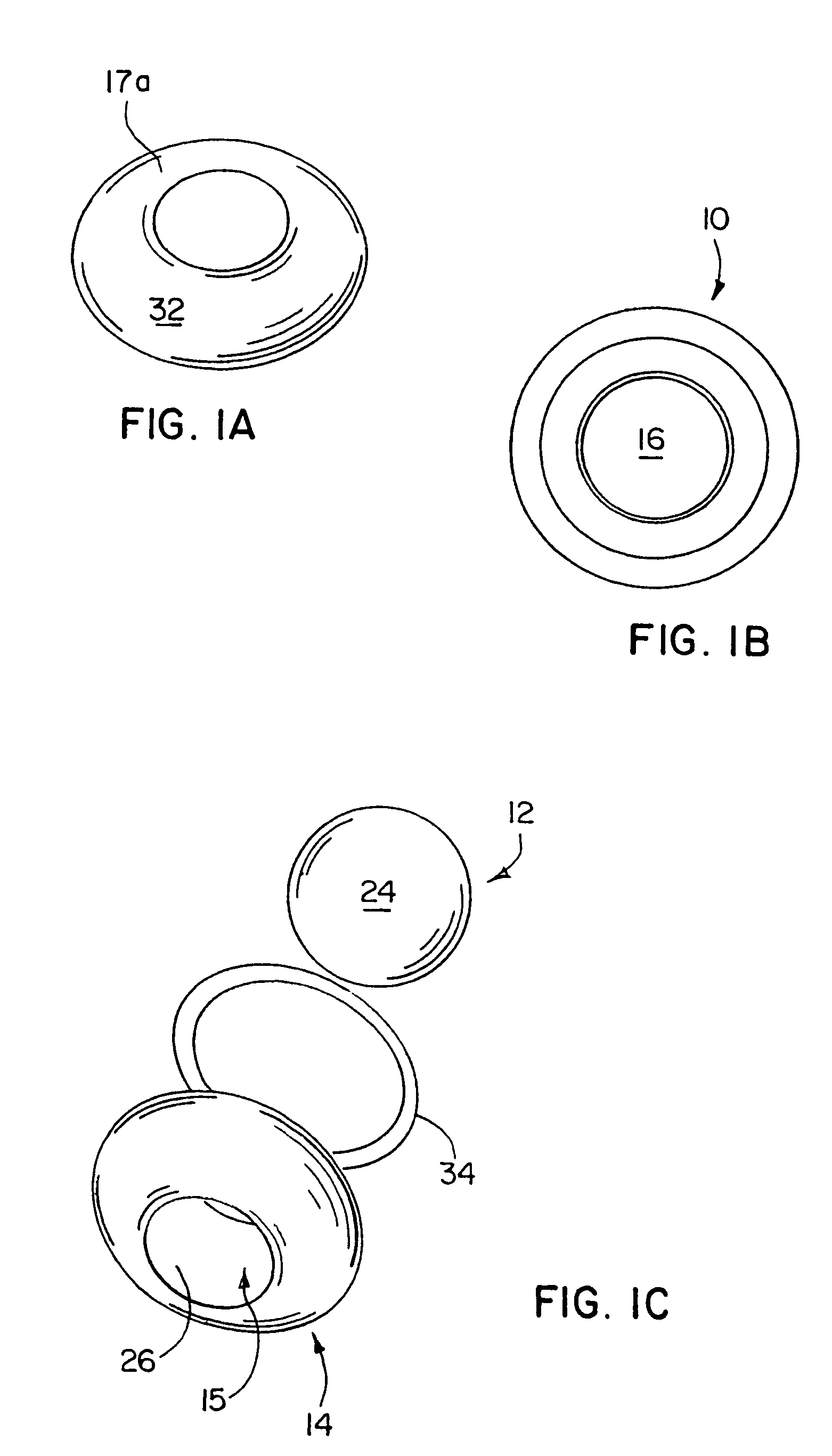
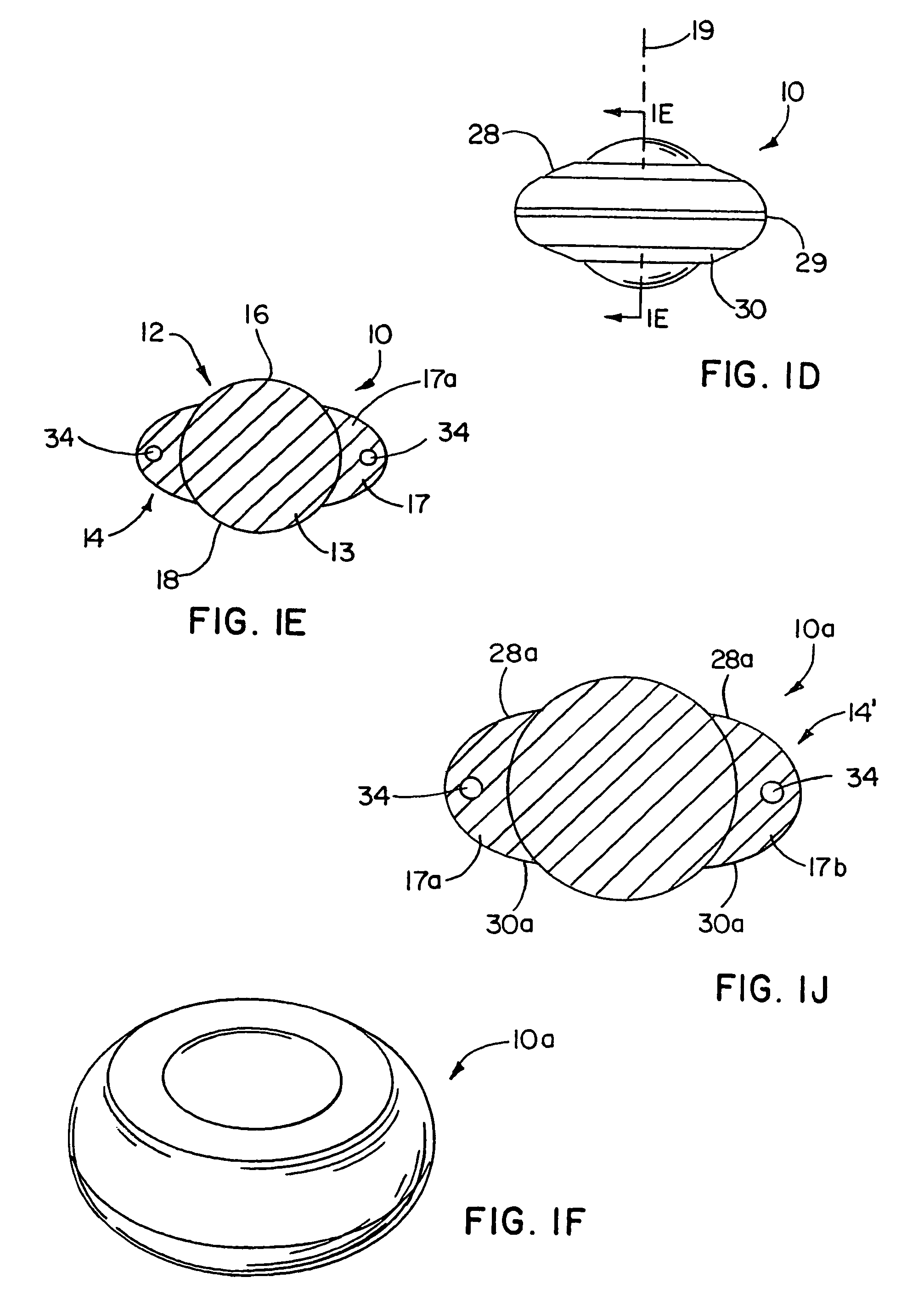
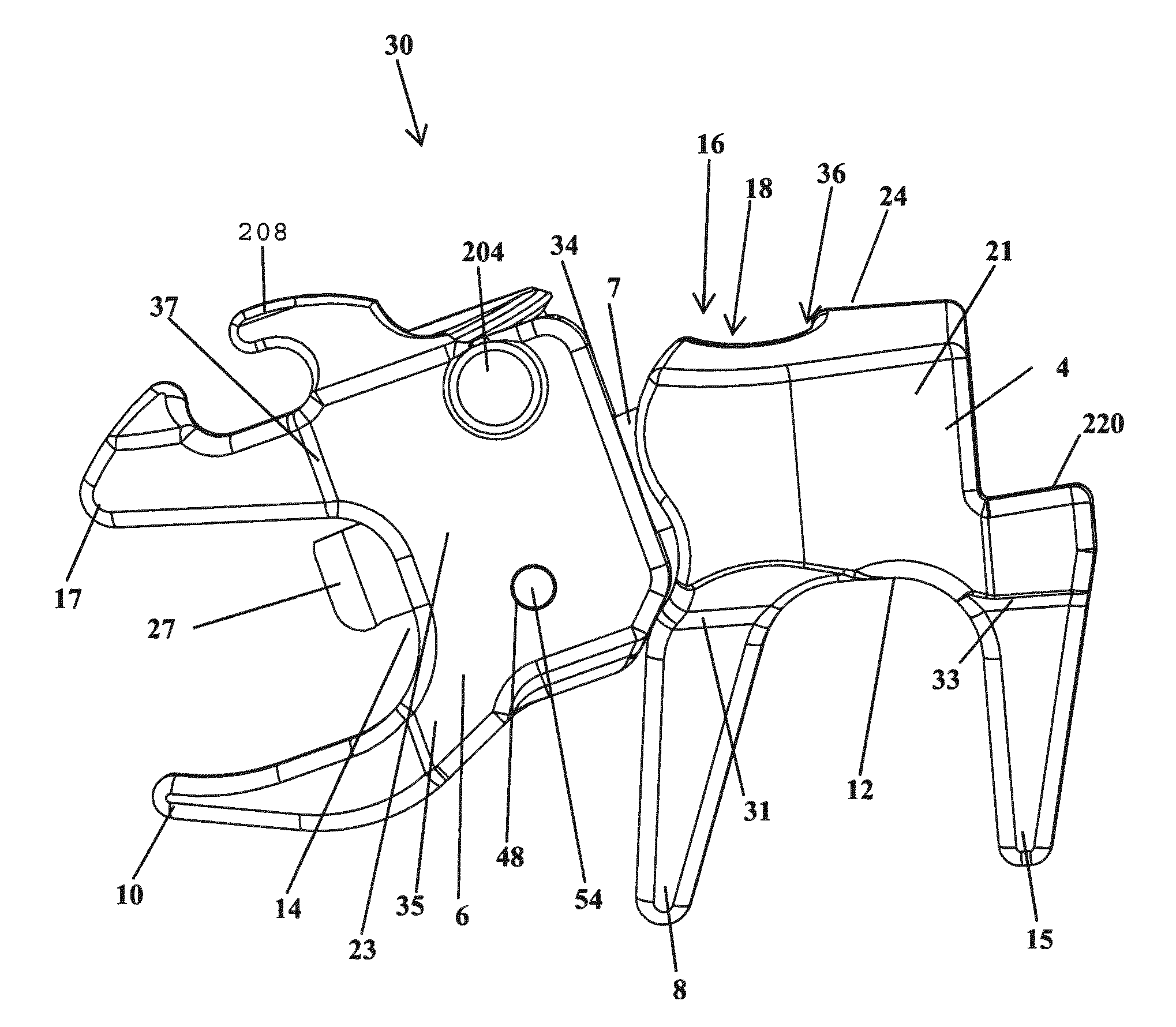
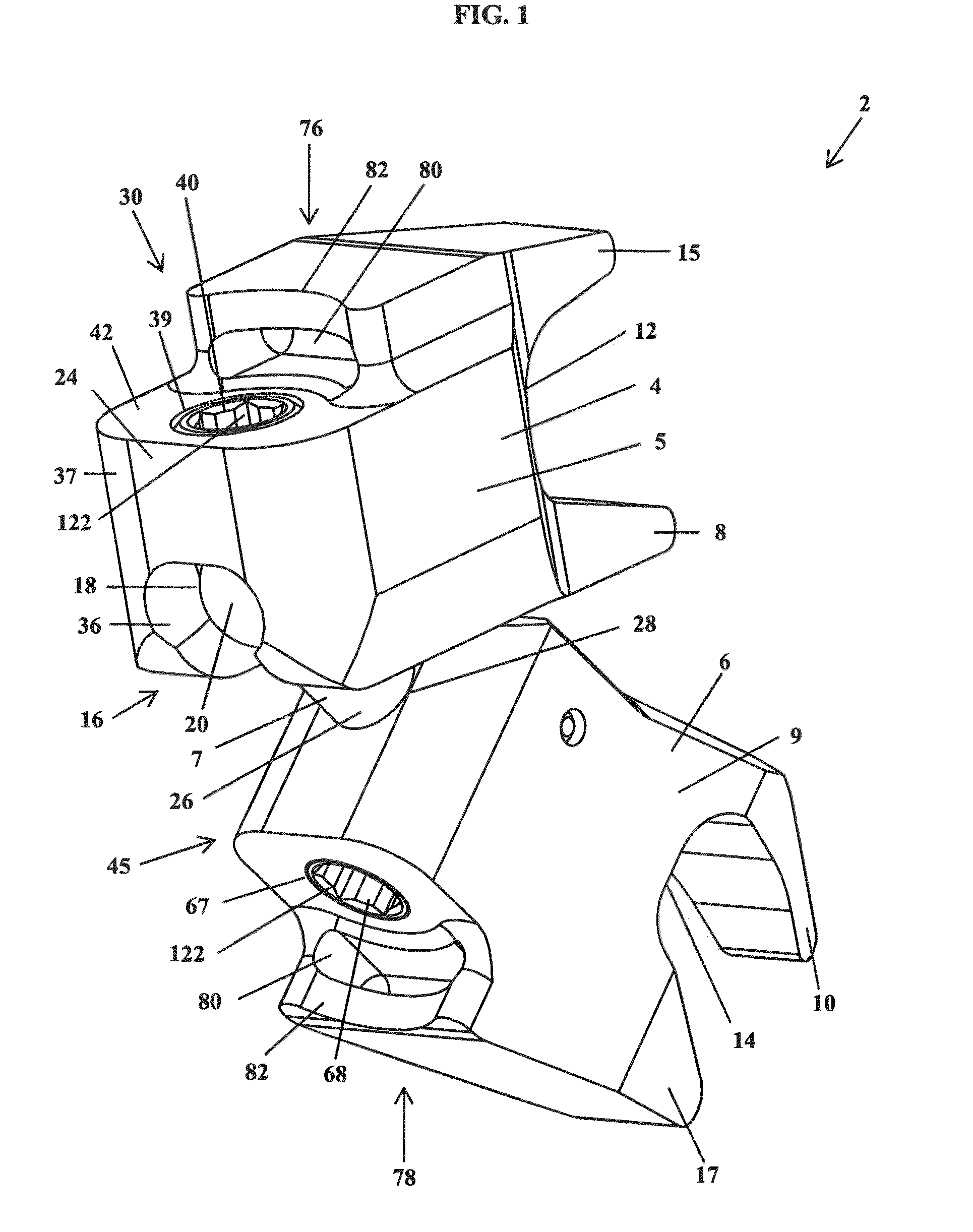
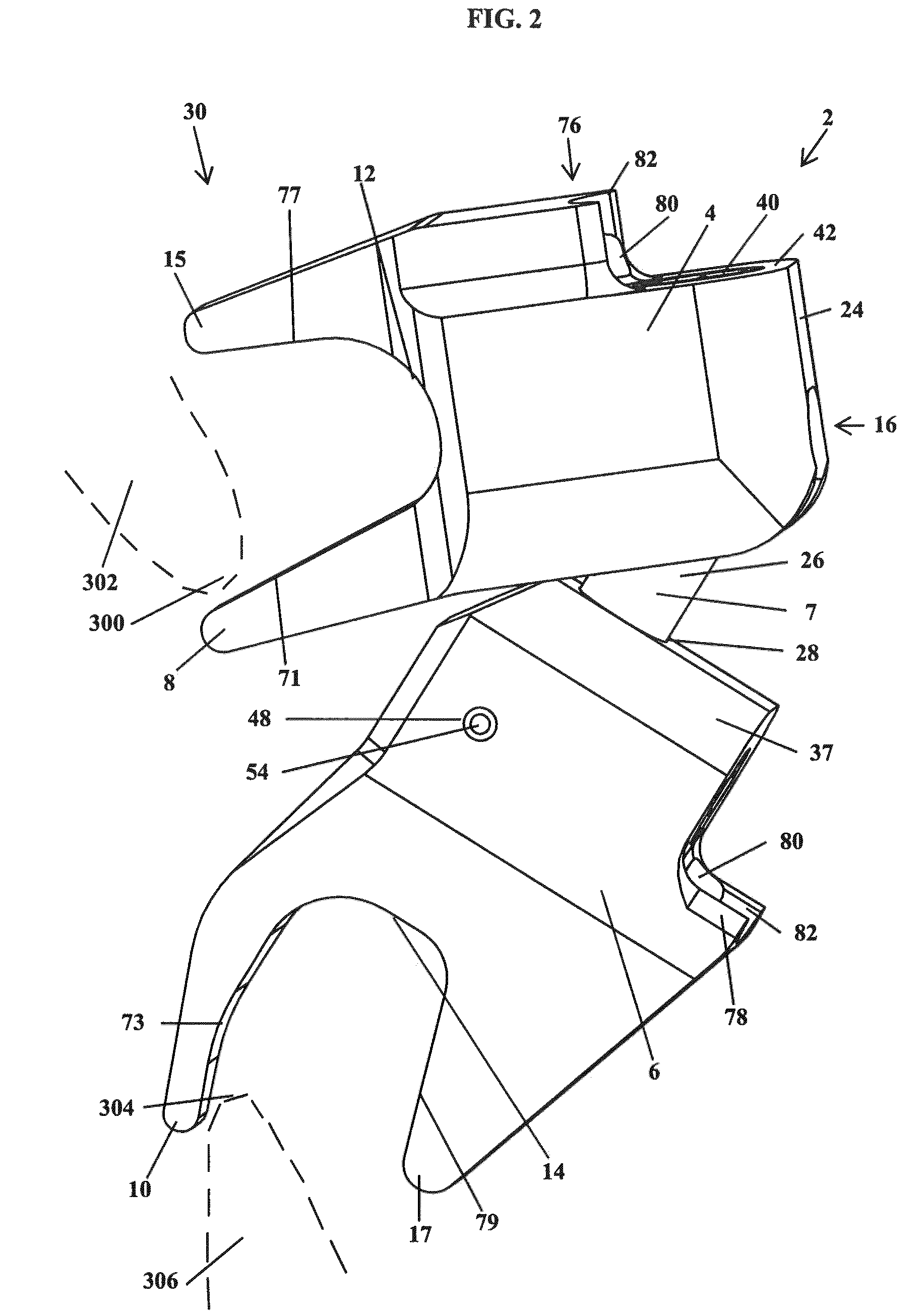
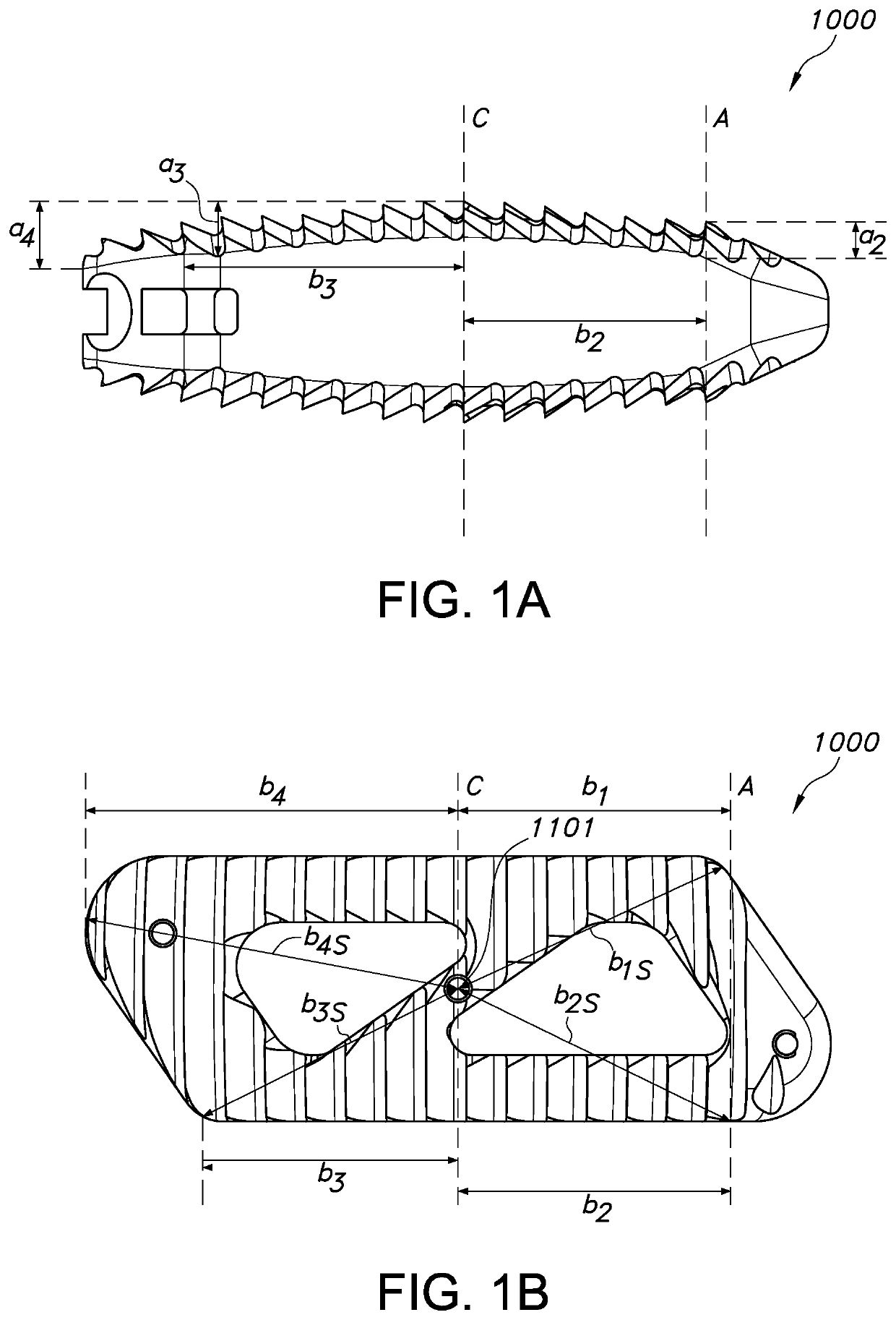
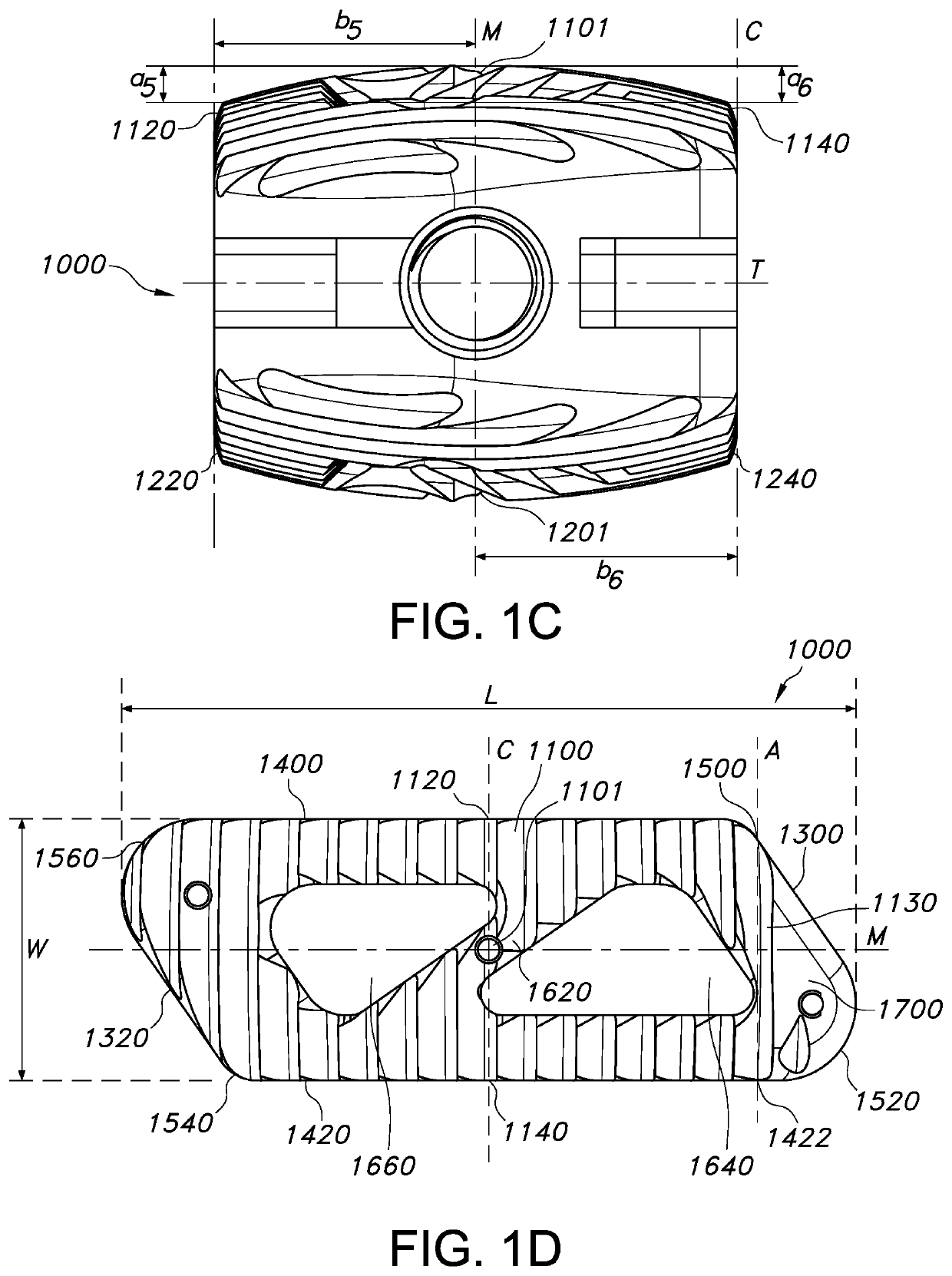
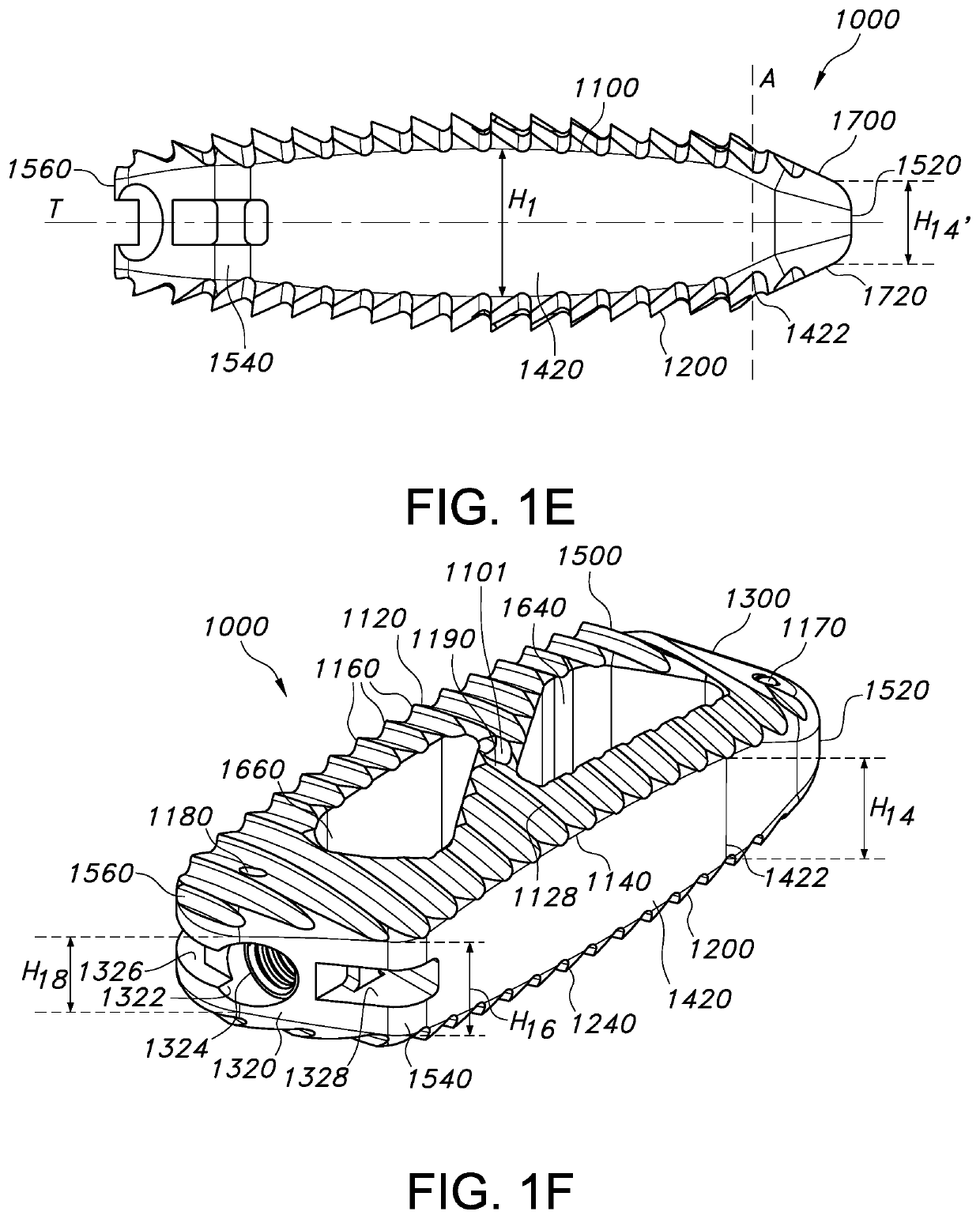
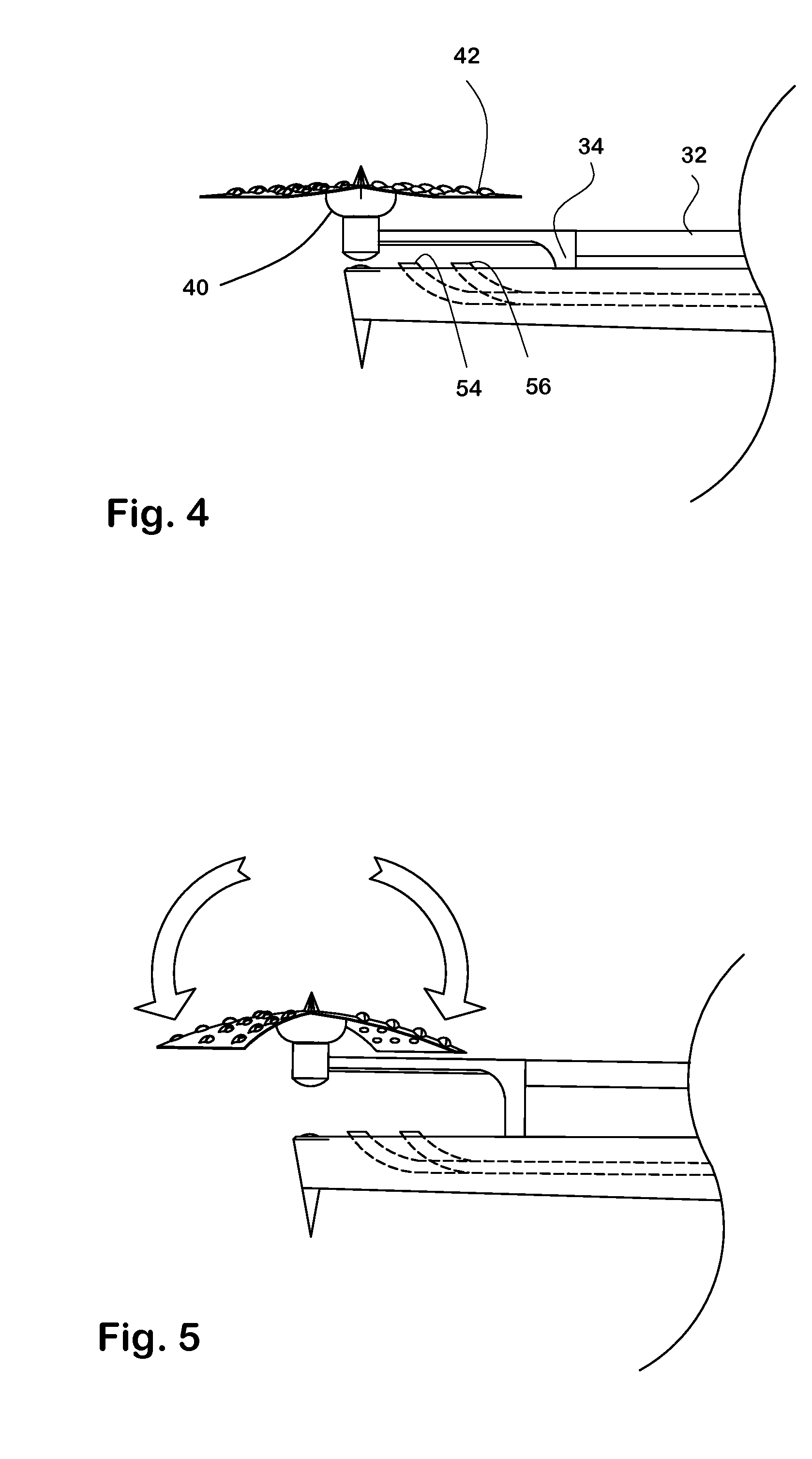
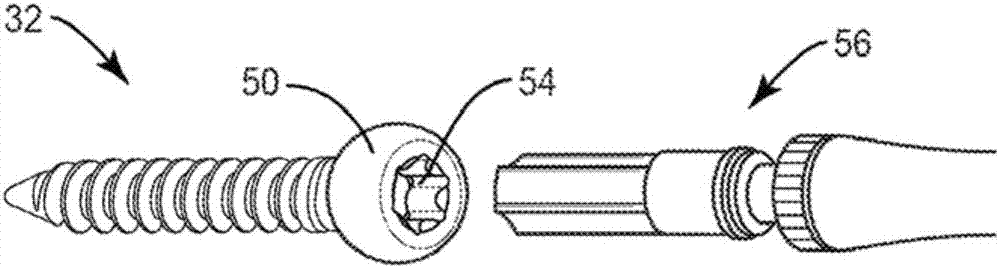
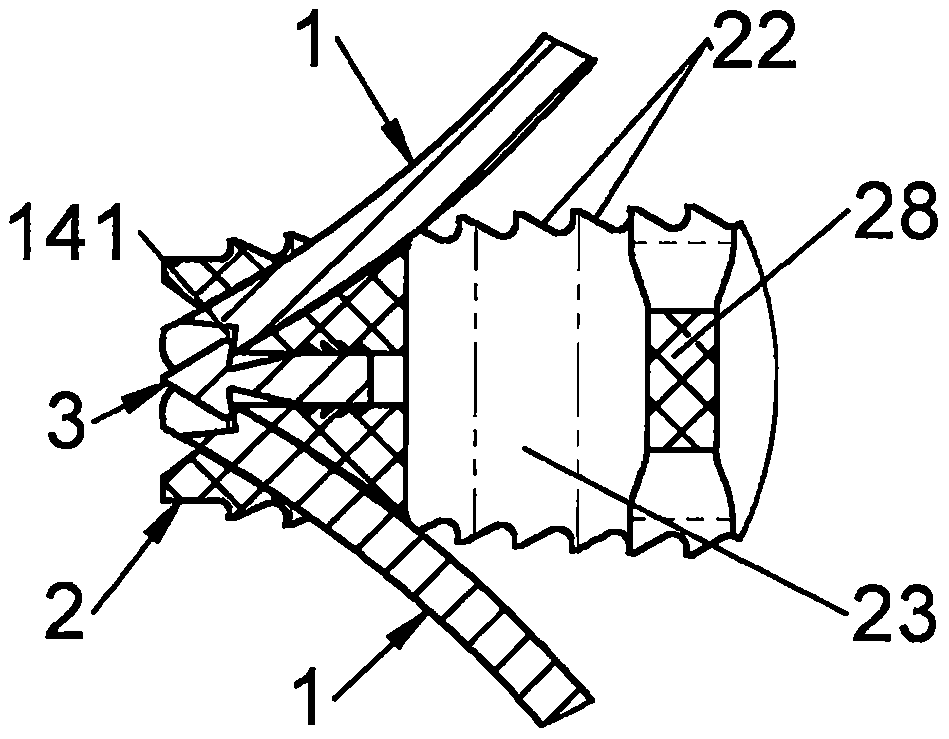
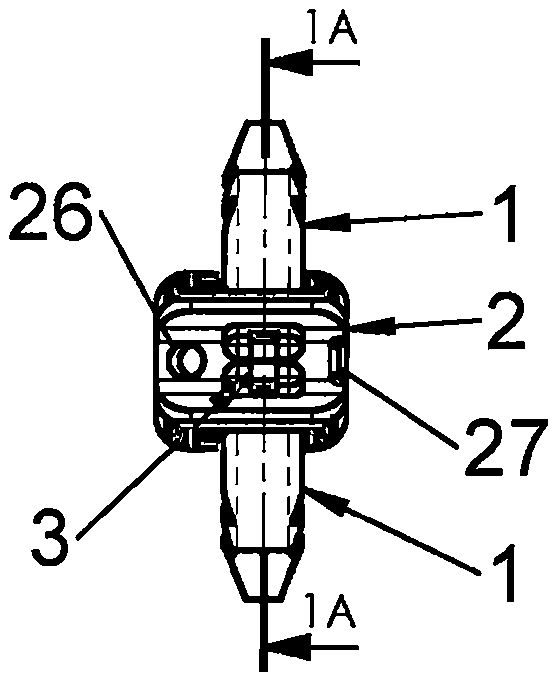
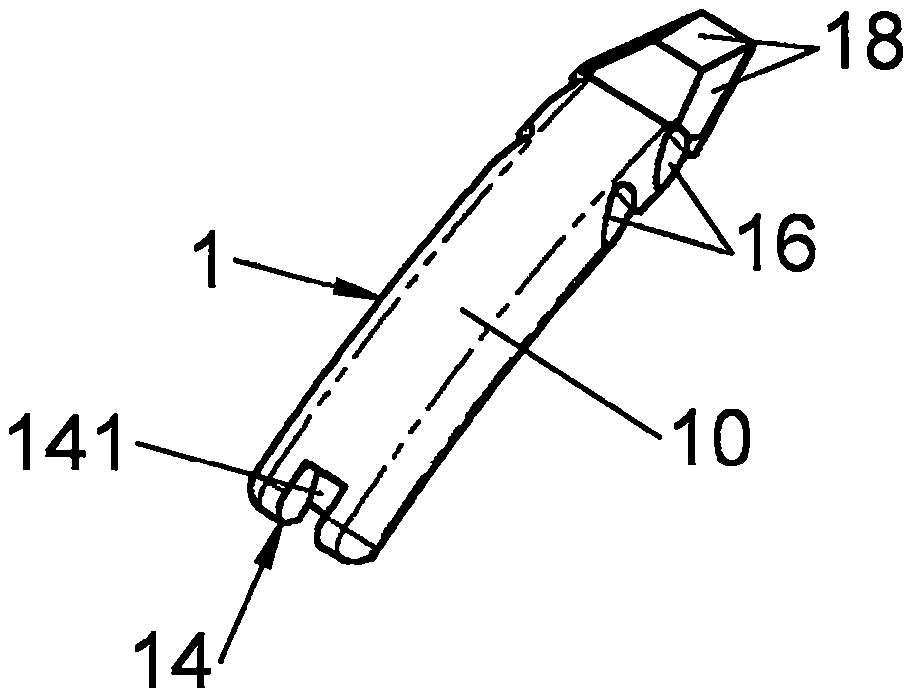
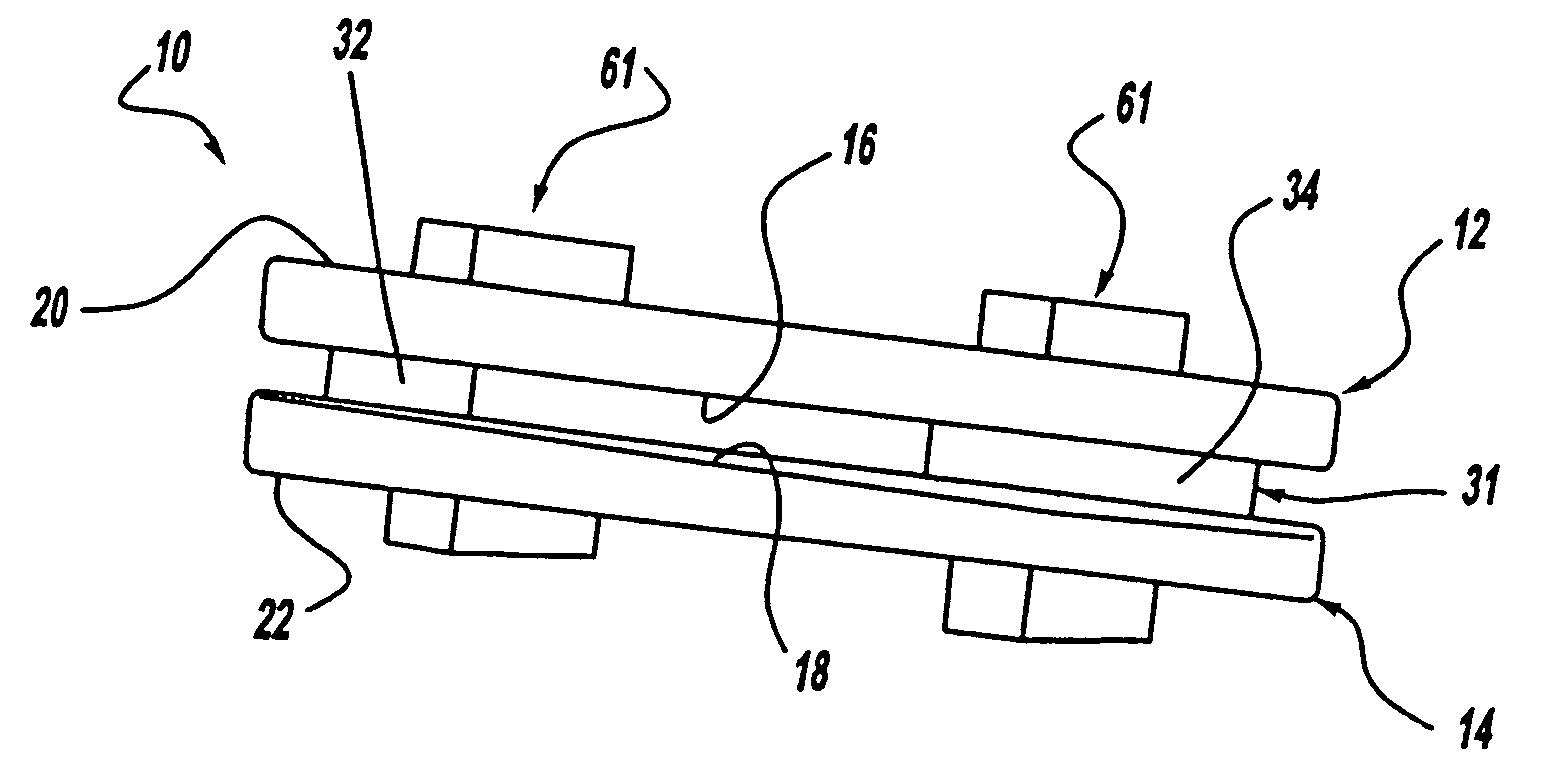
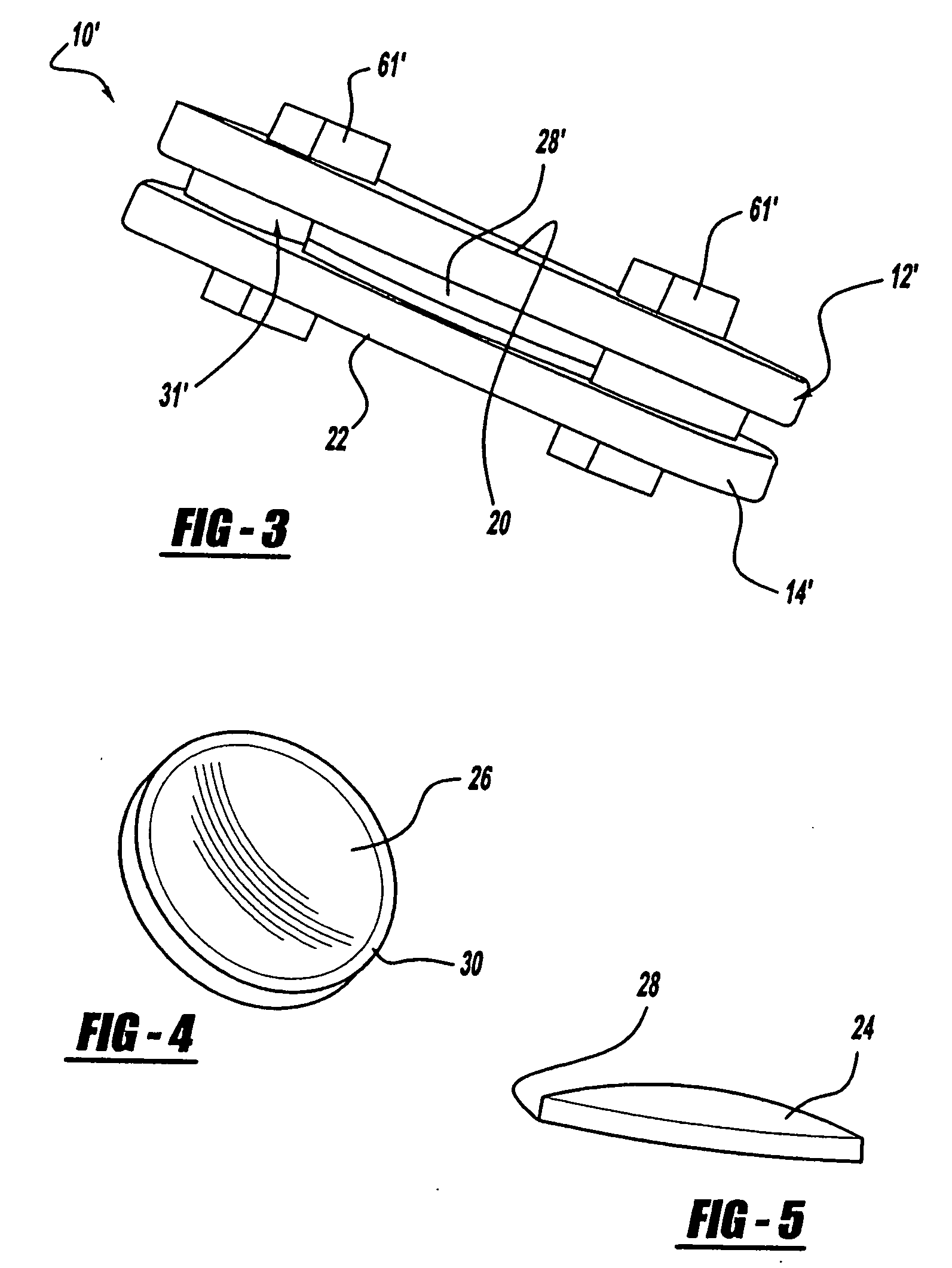
Spinal implant
ActiveUS20050027360A1Easy to integratePromote bone growthDiagnosticsBone implantRaspIntervertebral disk
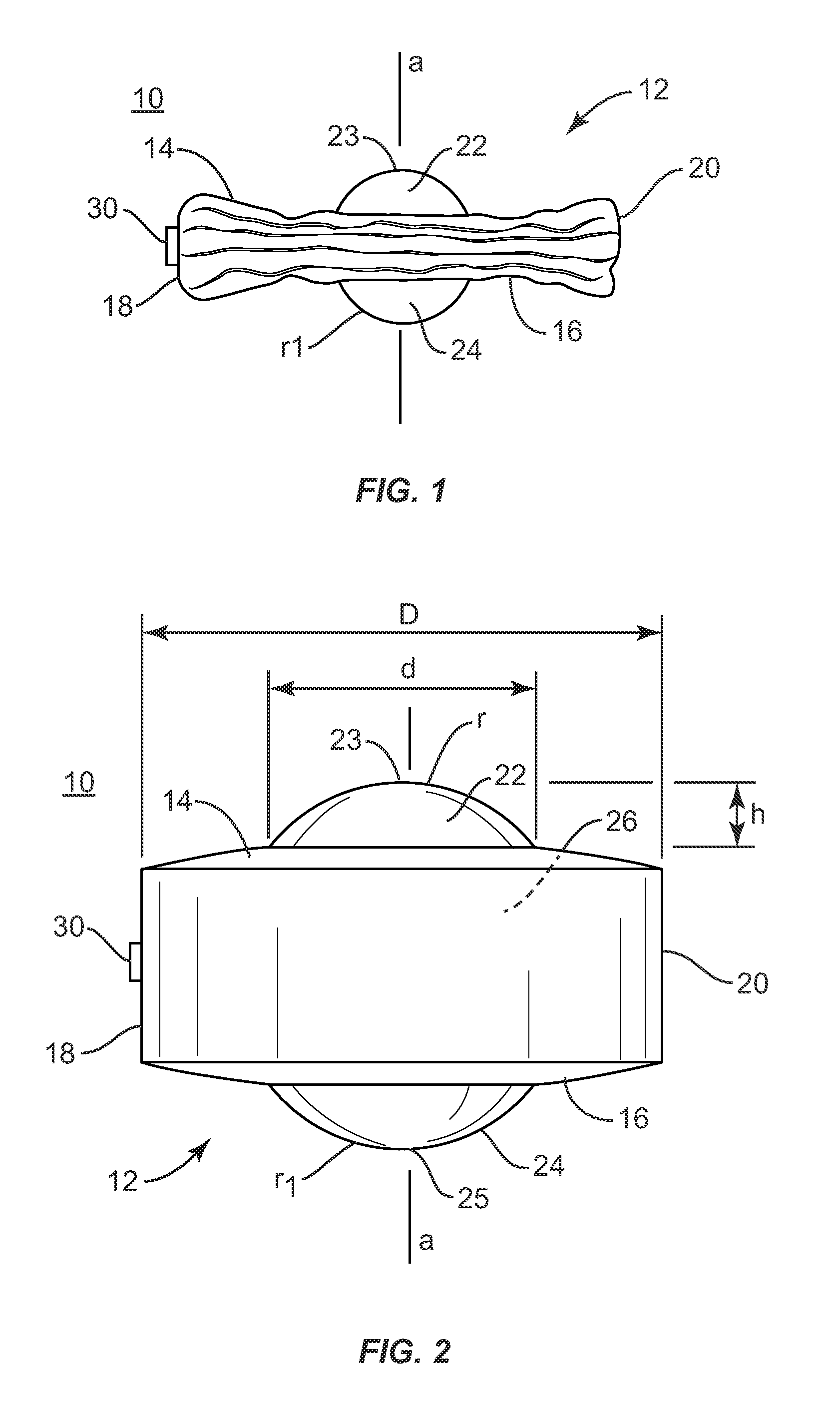
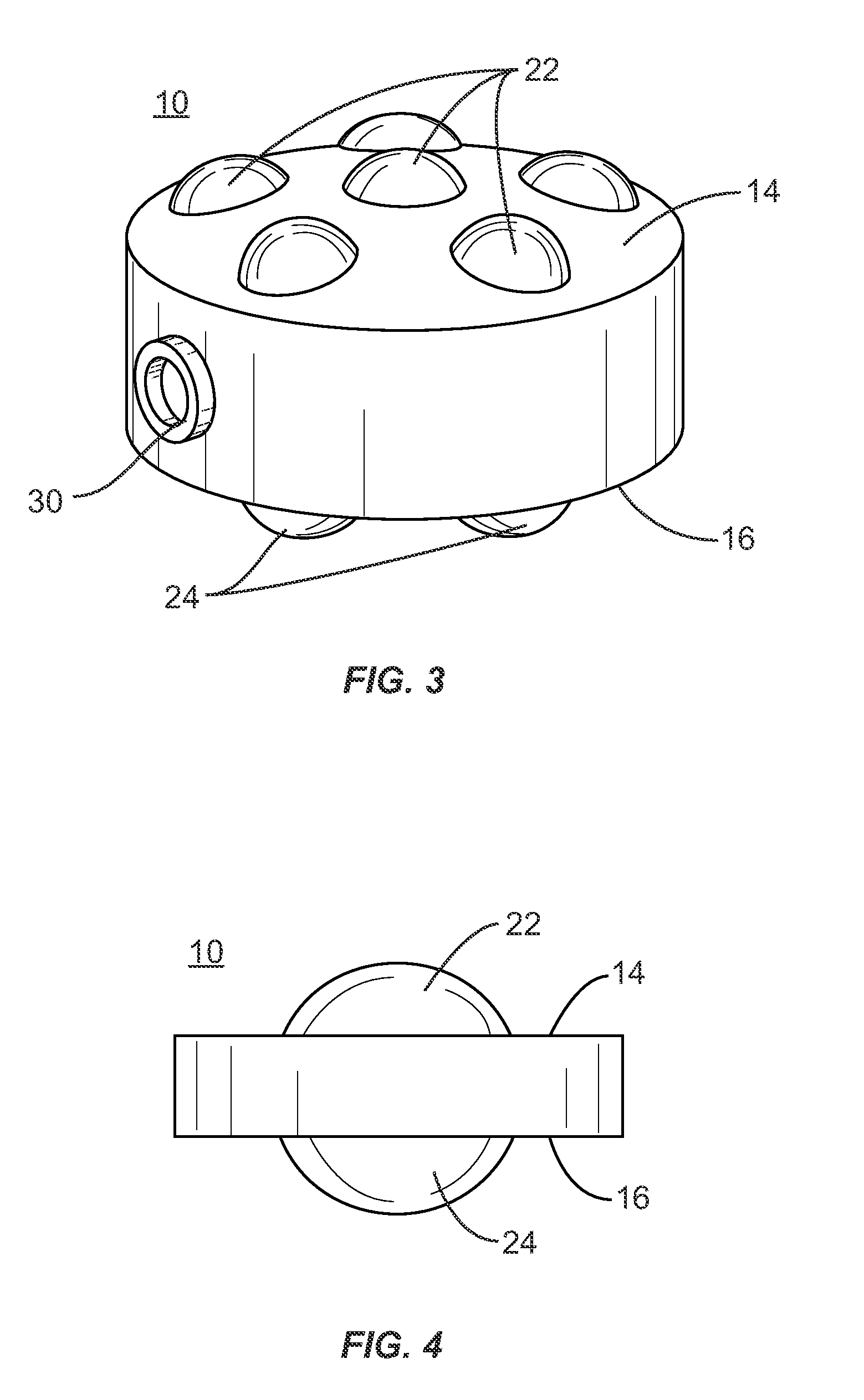
A spinal implant may be used to stabilize a portion of a spine. The implant may promote bone growth between adjacent vertebrae that fuses the vertebrae together. An implant may include an opening through a height of a body of the implant. The body of the implant may include curved sides. A top and / or a bottom of the implant may include protrusions that contact and / or engage vertebral surfaces to prevent backout of the implant from the disc space. A variety of instruments may be used to prepare a disc space and insert an implant. The instruments may include, but are not limited to, a distractor, a rasp, and one or more guides. The implant and instruments may be supplied in an instrument kit.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Vertebral device for restoration of vertebral body height
An intra-vertebral body height restoring device includes a body for insertion into an intra-vertebral space. The body includes top and bottom surfaces for engaging opposing vertebral surfaces defining the intra-vertebral space. The body includes at least two layers extending along a width of the body and having a fully expanded and fully collapsed height relative thereto. A reversible expansion mechanism selectively and reversely expands and collapse the height of the layers and including the fully expanded and collapsed heights to restore a selected height to the intra-vertebral space.
Owner:RICHELSOPH MARC E
Intervertebral Implant
InactiveUS20050267581A1Easy to insertMinimum structural heightSurgeryJoint implantsDetentIntervertebral space
An intervertebral implant comprises first and second parts having outer surfaces engaging adjacent vertebral surfaces. An insert between these parts provides relative movement therebetween. The first and / or second parts may have engagement means in the form of apertures for engagement with insertion instruments. The first and second parts may nest together, in the absence of the insert, for insertion into the intervertebral space. The boundaries of the implant may form a working space which would include insertion instruments therein. A detent and detent recess may be provided for engagement of the insert and one of said first and second parts.
Owner:CENTINEL SPINE LLC
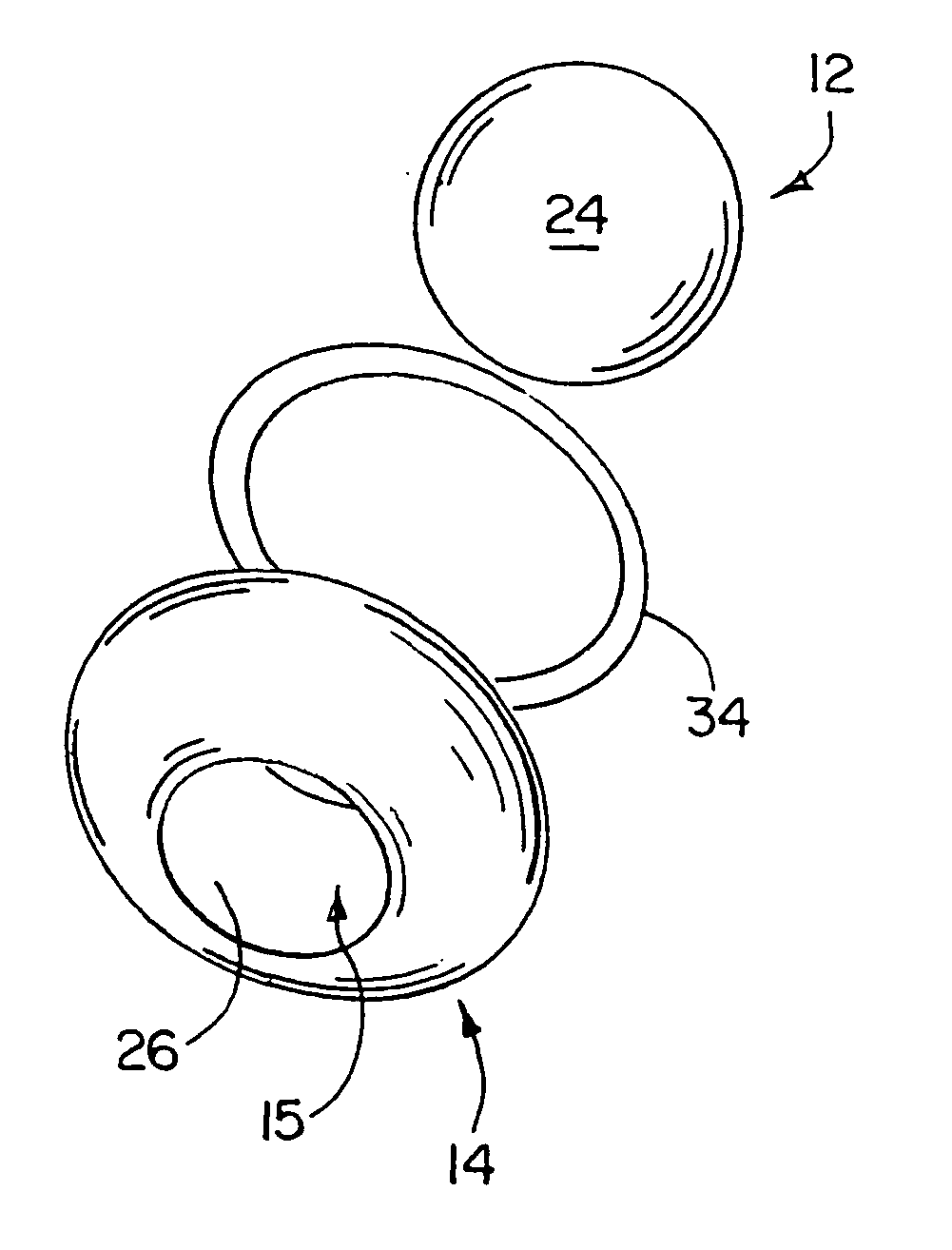
Artificial intervertebral disc device
InactiveUS7001433B2Improve distributionImprove shock absorptionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBall bearingBiomechanics
Artificial disc devices are disclosed that restore correct anatomical intervertebral spacing for damaged discs while maintaining a substantially normal range of biomechanical movement for the vertebrae between which they are implanted. The disc devices include center bearing and outer or annular bearing portions with the center bearing portion including generally axially extending locating surfaces which cooperate with the facing vertebral surfaces to resist migration. The outer bearing portion is for load bearing or load sharing with the center bearing portion and includes surfaces that extend radially toward the periphery of the vertebrae so that subsidence about the center bearing portion is minimized. Alternate forms of the disc devices include one with an axially enlarged center ball bearing having an annular ring bearing extending thereabout and another having upper and lower plate members with a central bumper member and a surrounding resilient annular member therebetween.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Spinal implant
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
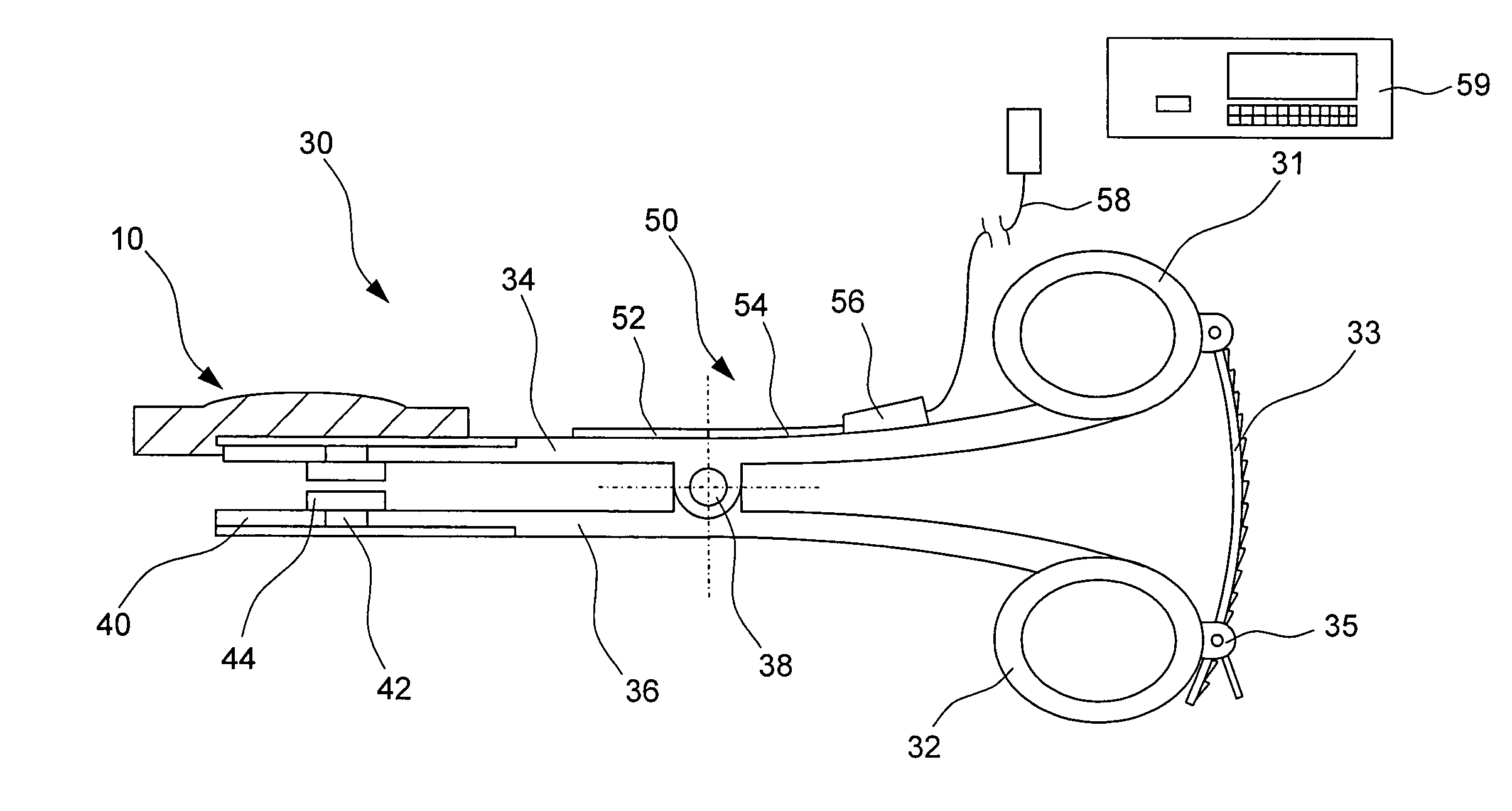
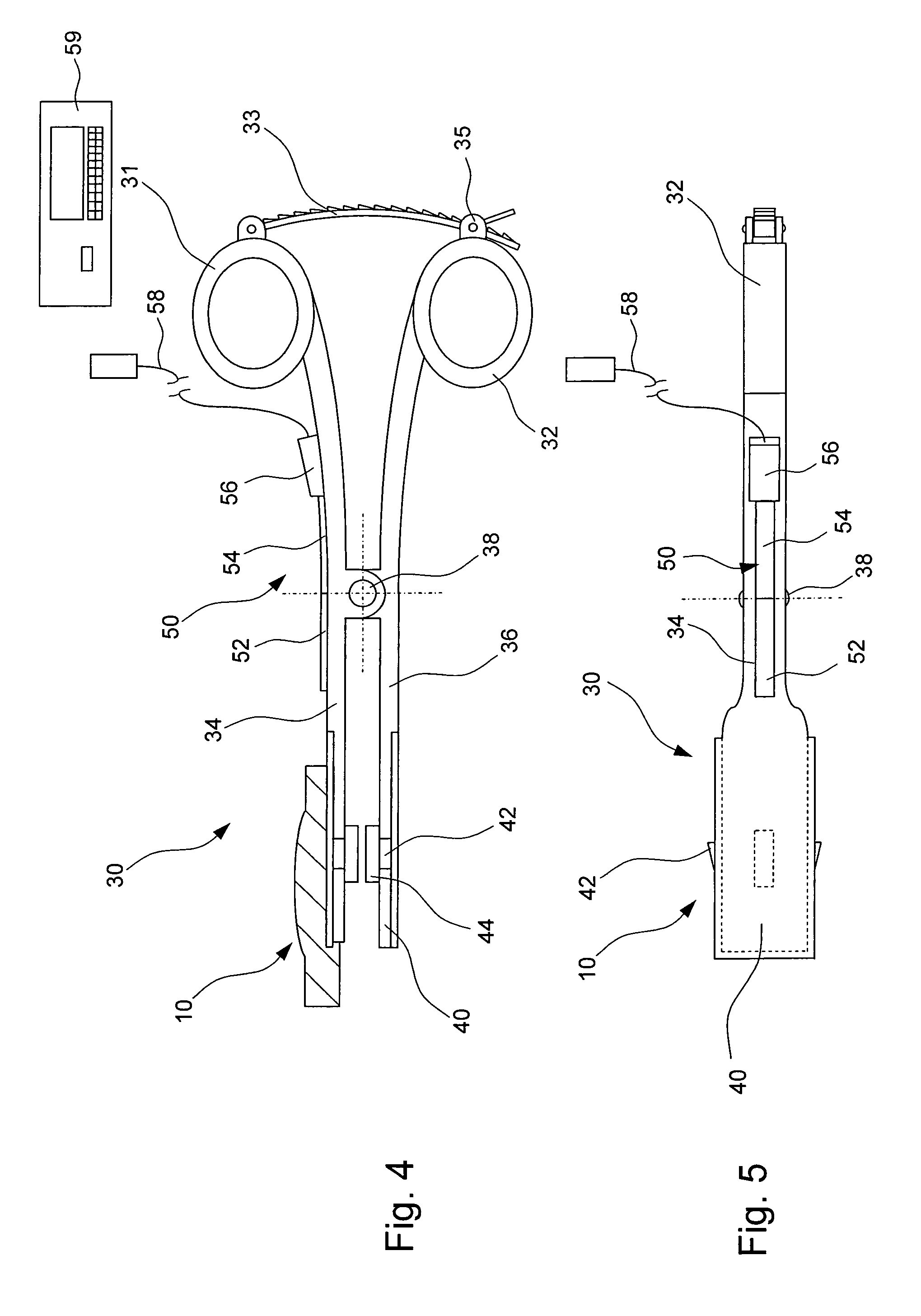
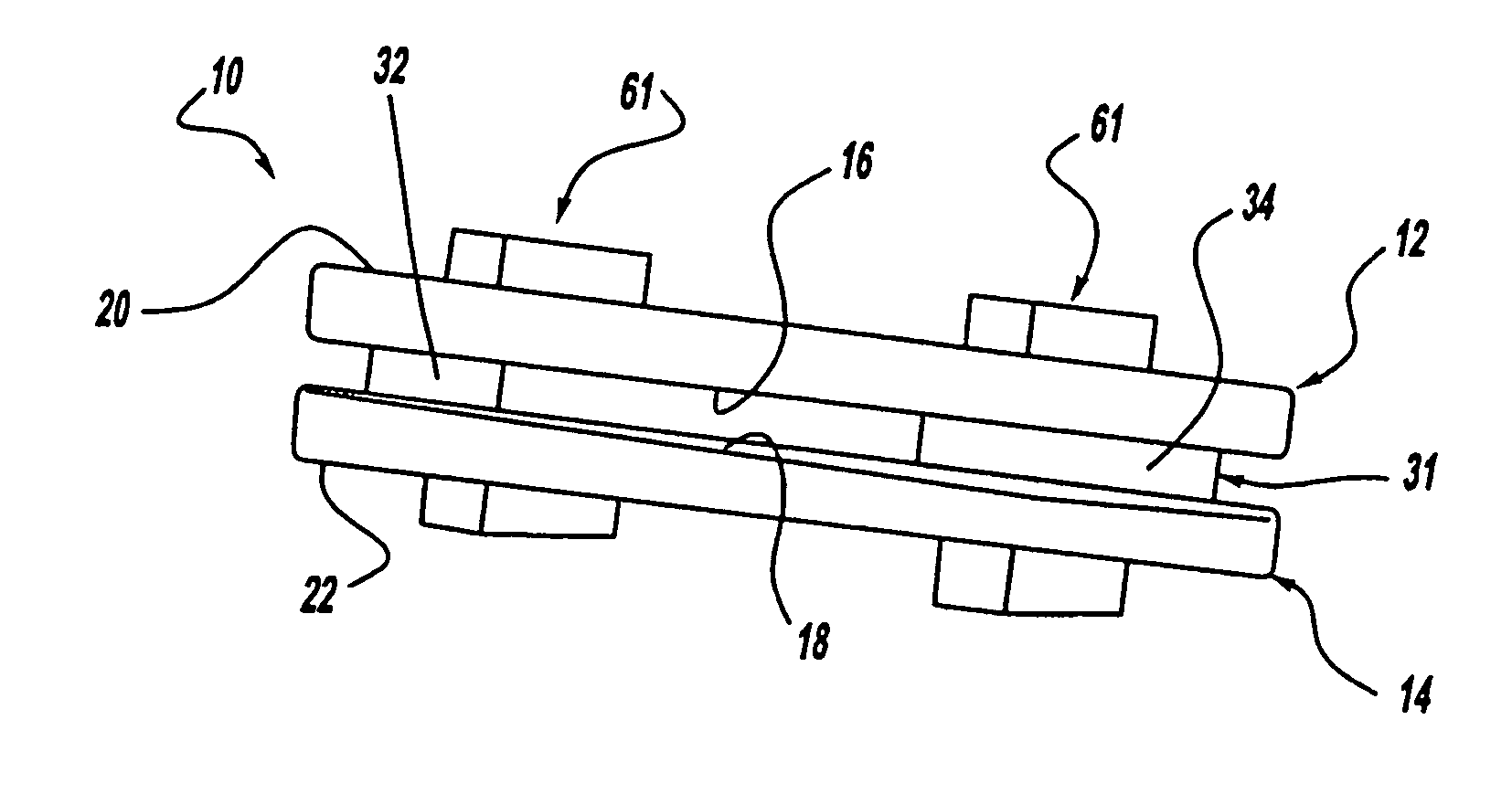
Instrument for measuring the distraction pressure between vertebral bodies
An instrument for measuring the distraction pressure between vertebral bodies comprises a control device (34, 36; 64, 66) for introducing a pressure force onto surfaces of opposing vertebral bodies and a measuring device (50; 84) associated with the control device (34, 36; 64, 66) for determining the pressure force applied onto the vertebral bodies. According to the invention, at least one end region of the control device (34, 36; 64, 66) carries a support body (10), which is designed for engaging in a concave dome that is surrounded by a bone ring of the vertebral bodies. The support body can be pivoted about at least one pivoting axis with respect to the control device and / or has a convex support surface, so that the support body when engaging into the dome can be pivoted in a sliding manner with respect to the vertebral body about at least one pivoting axis.
Owner:COPF JR FRANZ
Anchoring device for a spinal implant, spinal implant and implantation instrumentation
ActiveUS20150209089A1Reduce riskLow risk of damageInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsLocking mechanismAbutment
Anchoring devices for rachidian implants, implants, surgical instruments, and surgical systems and methods are disclosed. In some embodiments, an anchor comprises a stiff plate with a longitudinal axis, configured for penetration of its anterior end into a vertebral surface while its posterior end remains engaged with the implant. An implant may include a locking mechanism for the anchor. An anchor may include an abutment configured to abut a complementary abutment of an implant. In some configurations, inserting an anchor in a passage of an implant may displace a locking mechanism, which may resile and lock the anchor in the implant with complementary abutments of the anchor and implant abutting.
Owner:LDR MEDICAL
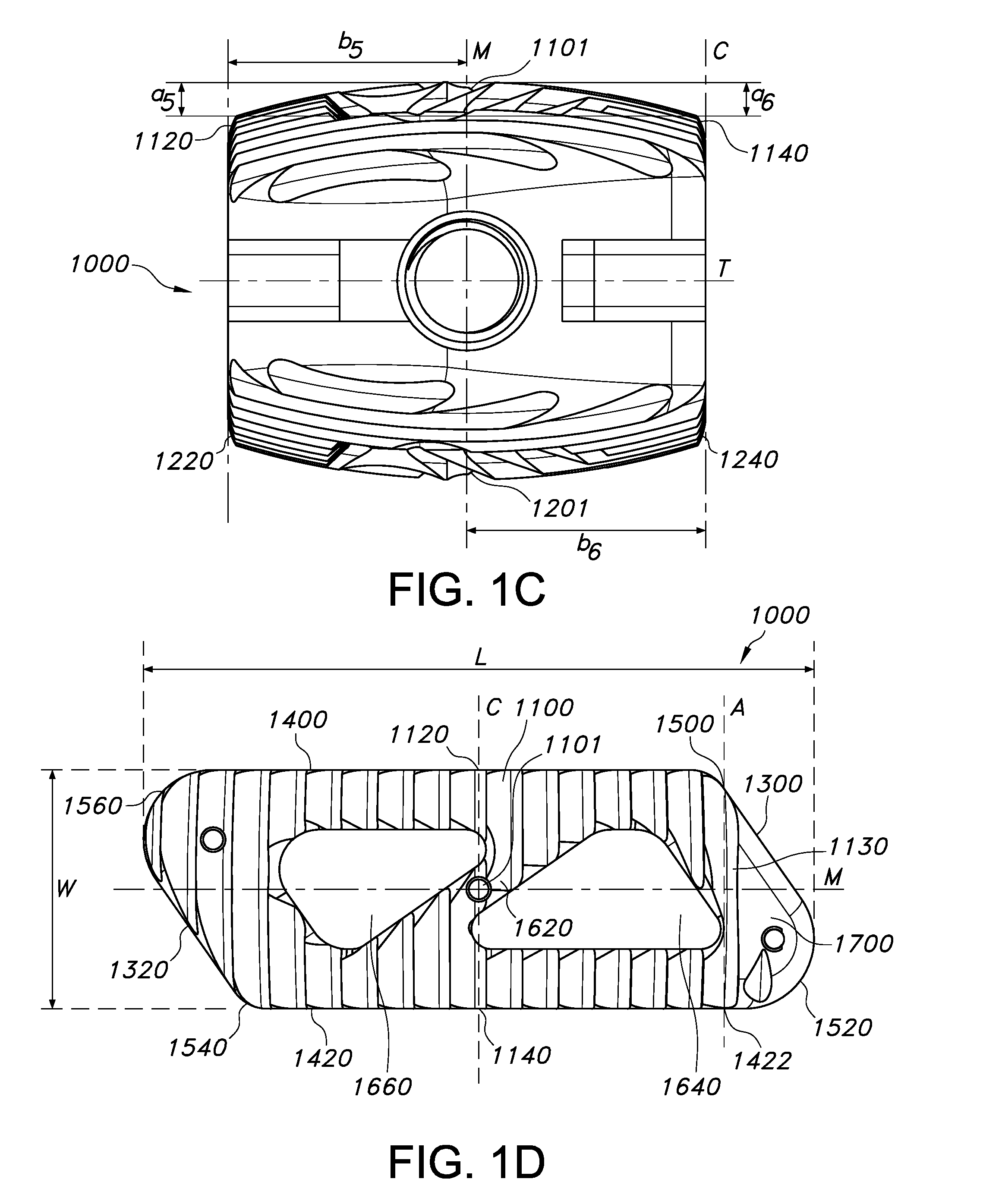
Spinal fusion implant for oblique insertion
Intervertebral spinal fusion implants for interbody fusion of the anterior column of the spine are described. The implants have a substantially bi-convex or a substantially offset bi-convex shape. The implants are placed through a transforaminal or posterior approach at an oblique insertion angle. The implants have an outermost point on the superior convex surface and an outermost point on the inferior convex surface and four edges of differing heights. The outermost superior and inferior points of the implants are connected with the four edges with convex surfaces of different curvatures. The curvatures of the convex surfaces of the implants are designed to match the curvatures of concave vertebral surfaces when the implants are inserted at an oblique insertion angle.
Owner:CAMBER SPINE TECH
Expandable implant system and methods of use
A spinal implant includes a first component including a first surface configured for engagement with a first vertebral surface and a second surface configured to define at least a portion of an implant support cavity. A second component is connected to the first component and includes a first surface configured for engagement with a second vertebral surface and a second surface configured to define at least a portion of the implant support cavity. A removable intermediate component is configured for disposal in the implant support cavity. The intermediate component is inflatable to move the first component relative to the second component to expand the interbody implant from a first configuration to a second, expanded configuration. At least one agent is configured to replace the intermediate component in the implant support cavity in the second configuration. Methods of use are disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Expandable implant system and methods of use
A spinal implant includes a first component including a first surface configured for engagement with a first vertebral surface and a second surface configured to define at least a portion of an implant support cavity. A second component is connected to the first component and includes a first surface configured for engagement with a second vertebral surface and a second surface configured to define at least a portion of the implant support cavity. A removable intermediate component is configured for disposal in the implant support cavity. The intermediate component is inflatable to move the first component relative to the second component to expand the interbody implant from a first configuration to a second, expanded configuration. At least one agent is configured to replace the intermediate component in the implant support cavity in the second configuration. Methods of use are disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Artificial disc device
InactiveUS20050256581A1Improve distributionImprove shock absorptionSurgeryJoint implantsBall bearingEngineering
Artificial disc devices are disclosed that restore correct anatomical intervertebral spacing for damaged discs while maintaining a substantially normal range of biomechanical movement for the vertebrae between which they are implanted. The disc devices include center bearing and outer or annular bearing portions with the center bearing portion including generally axially extending locating surfaces which cooperate with the facing vertebral surfaces to resist migration. The outer bearing portion is for load bearing or load sharing with the center bearing portion and includes surfaces that extend radially toward the periphery of the vertebrae so that subsidence about the center bearing portion is minimized. Alternate forms of the disc devices include one with an axially enlarged center ball bearing having an annular ring bearing extending thereabout and another having upper and lower plate members with a central bumper member and a surrounding resilient annular member therebetween.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
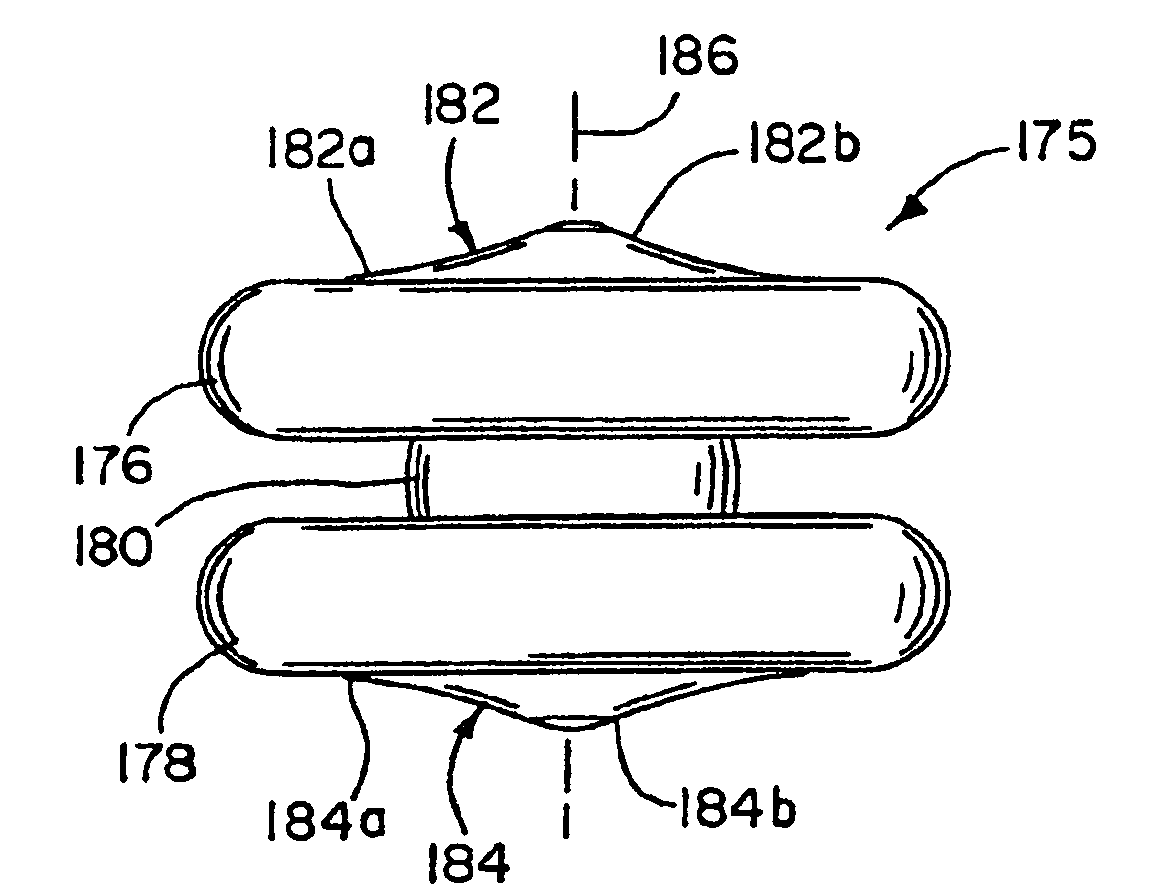
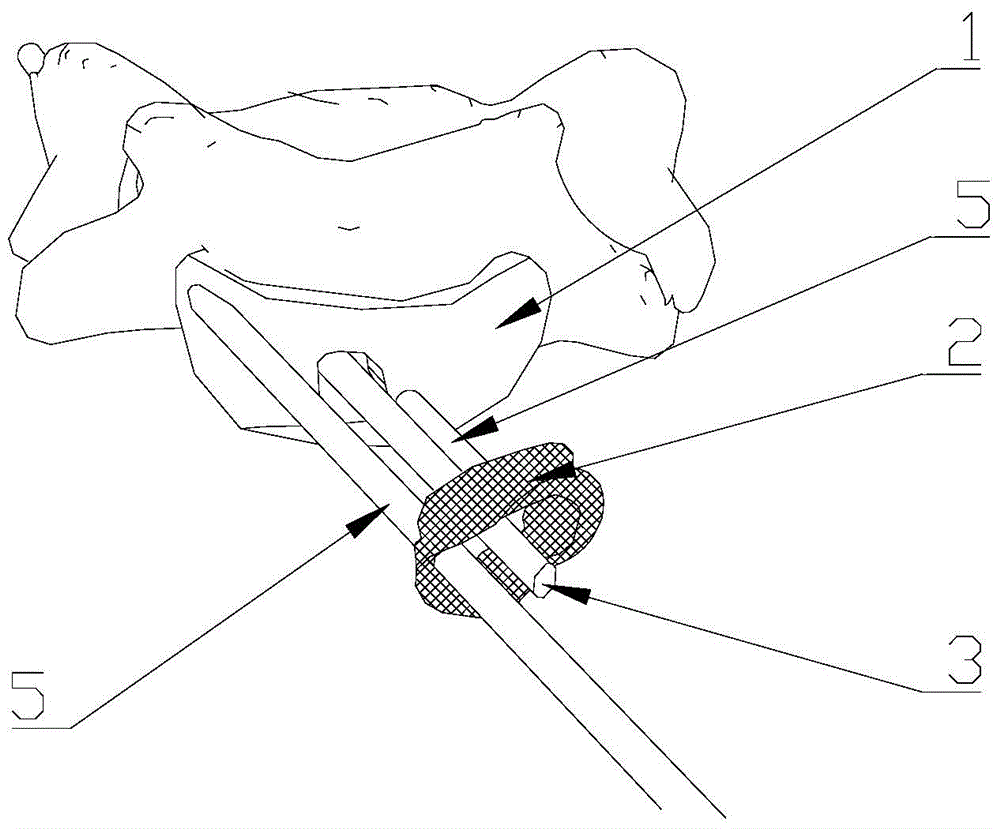
V-shaped staple for spinal prosthesis
An intervertebral implant system for positioning between an upper vertebra and a lower vertebra is provided. The implant system comprises an intervertebral implant and a staple. The implant comprises an inferior plate and a superior plate, while the superior plate has a vertebral surface facing the upper vertebra and the inferior plate has a vertebral surface facing the lower vertebra. There are two grooves on at least one vertebral surface extending at an angle outward from a centerline on the vertebral surface as they extend from the anterior portion of the plate toward the posterior portion of the plate. When in use, the staple is associated with the two grooves for maintaining stability of the intervertebral implant and preventing backing out of the intervertebral implant. The staple also has two arms and has a generally rectangular shape prior to use.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
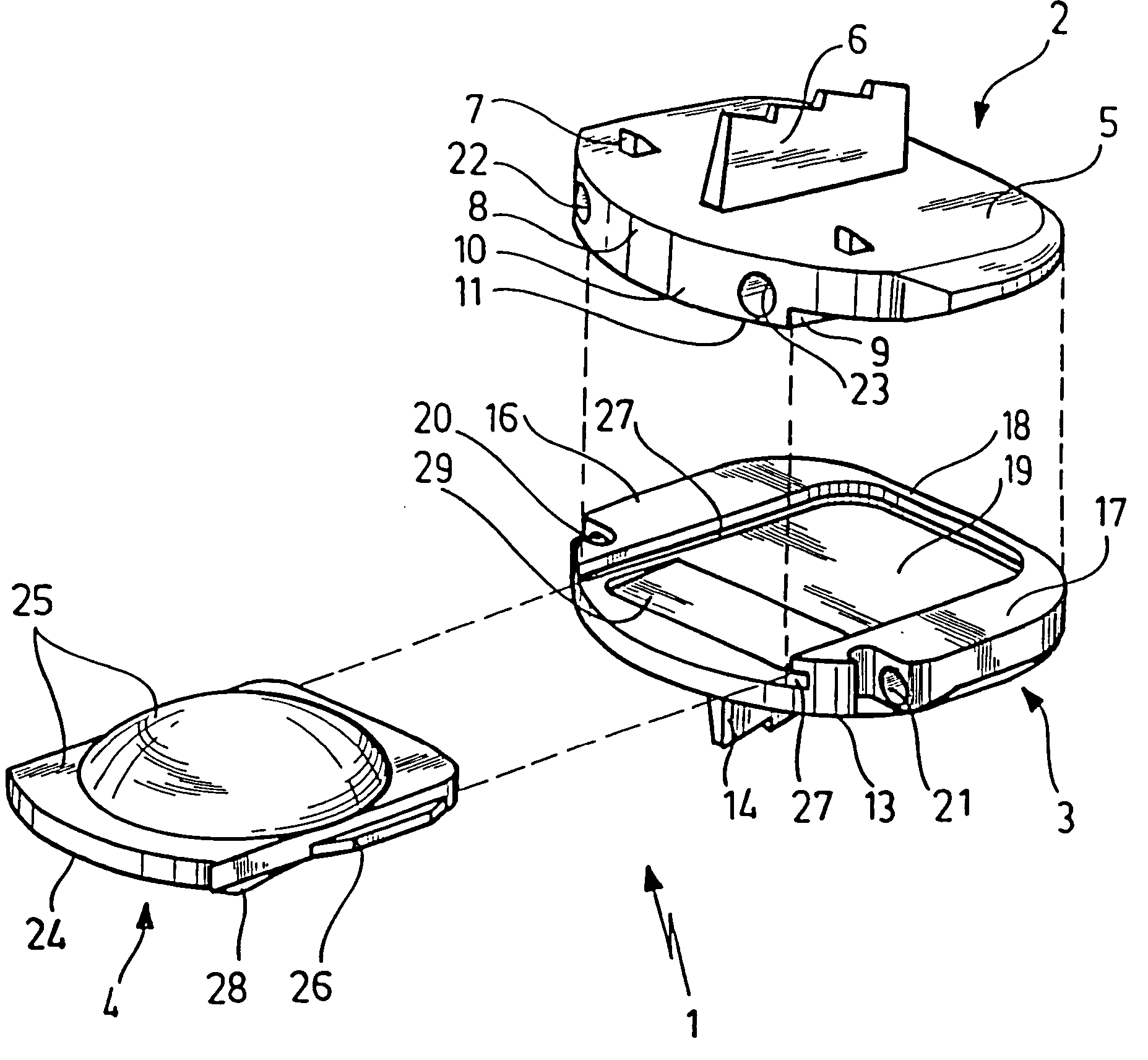
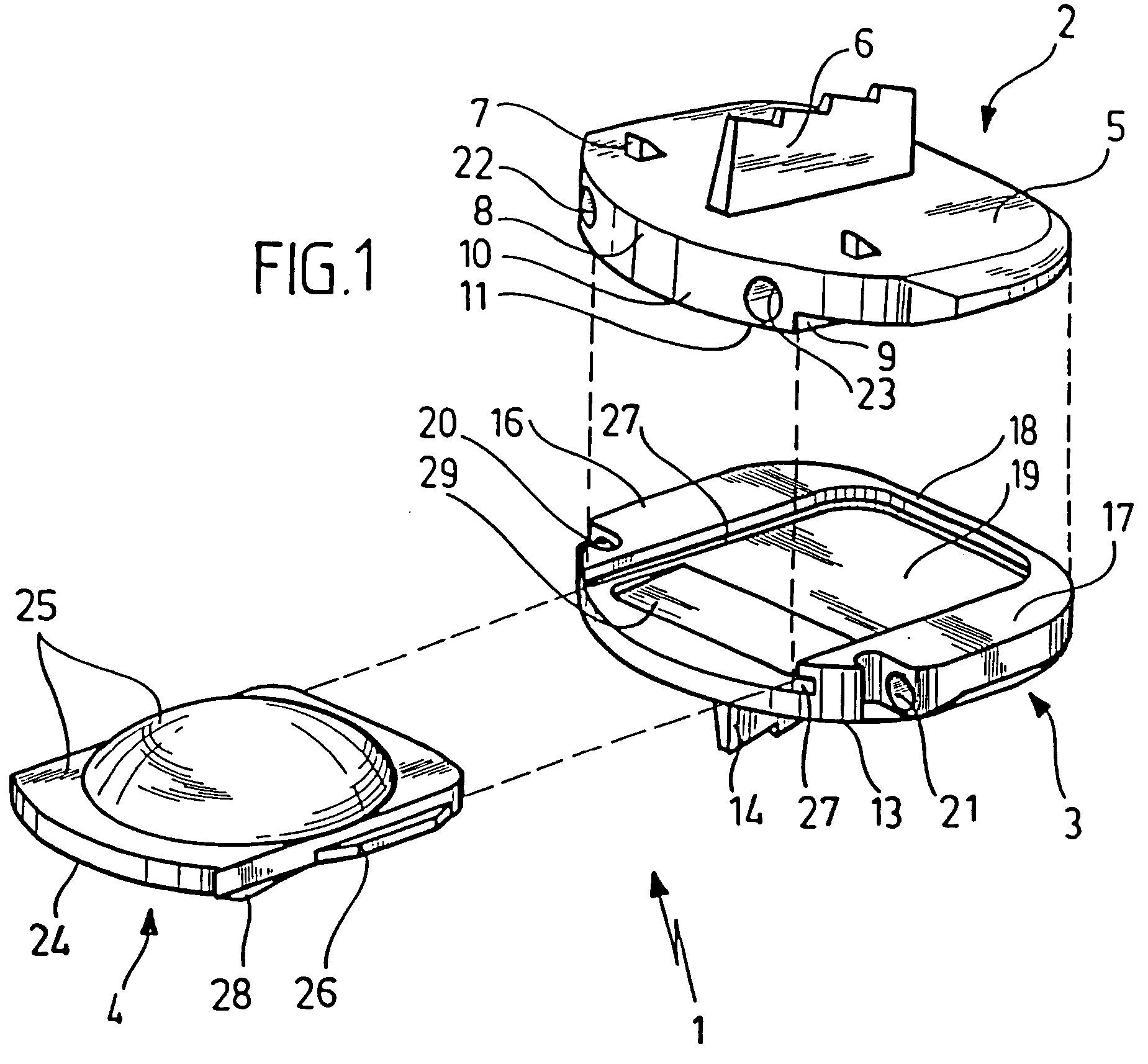
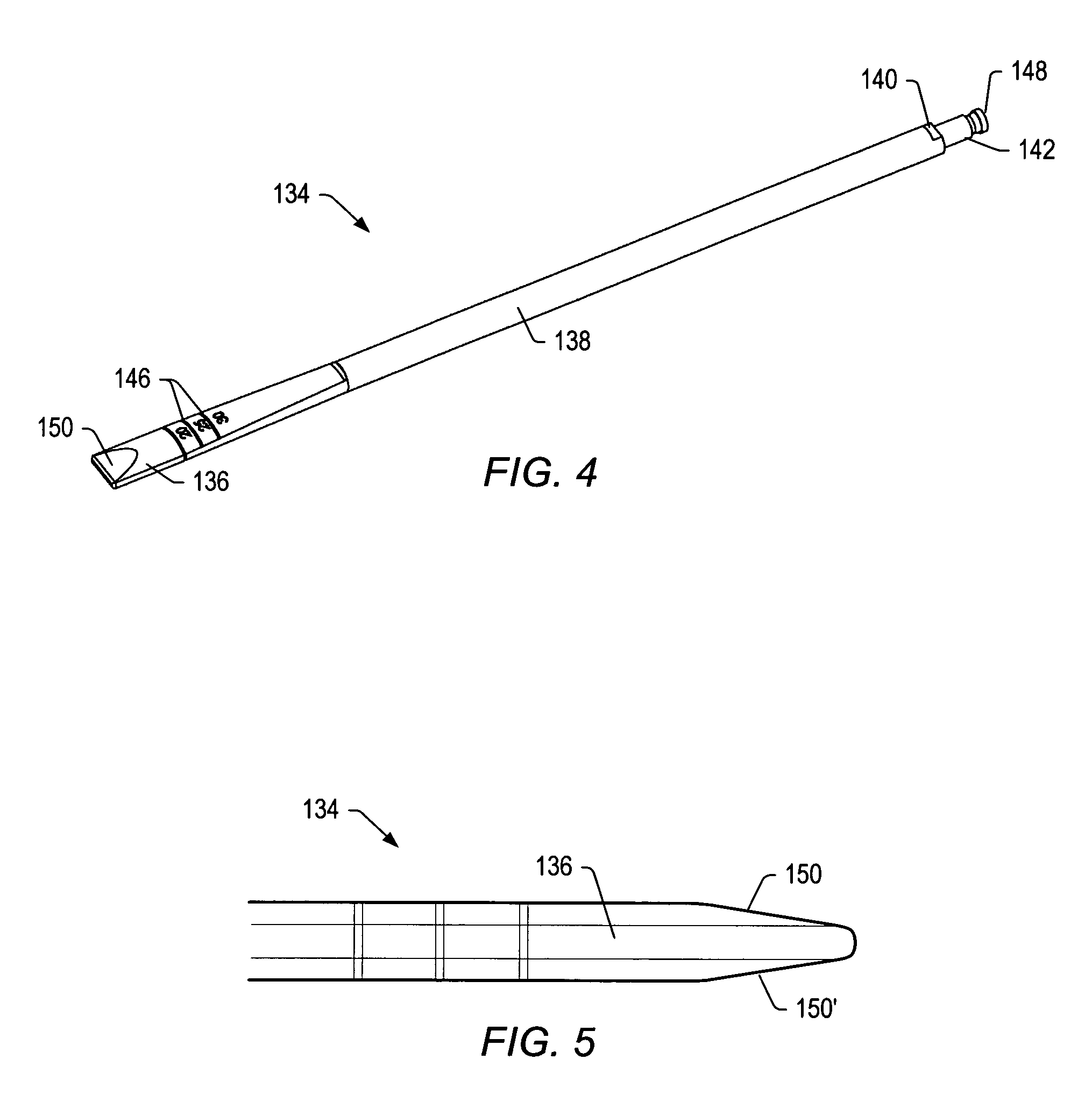
Intervertebral Implant Devices And Methods For Insertion Thereof
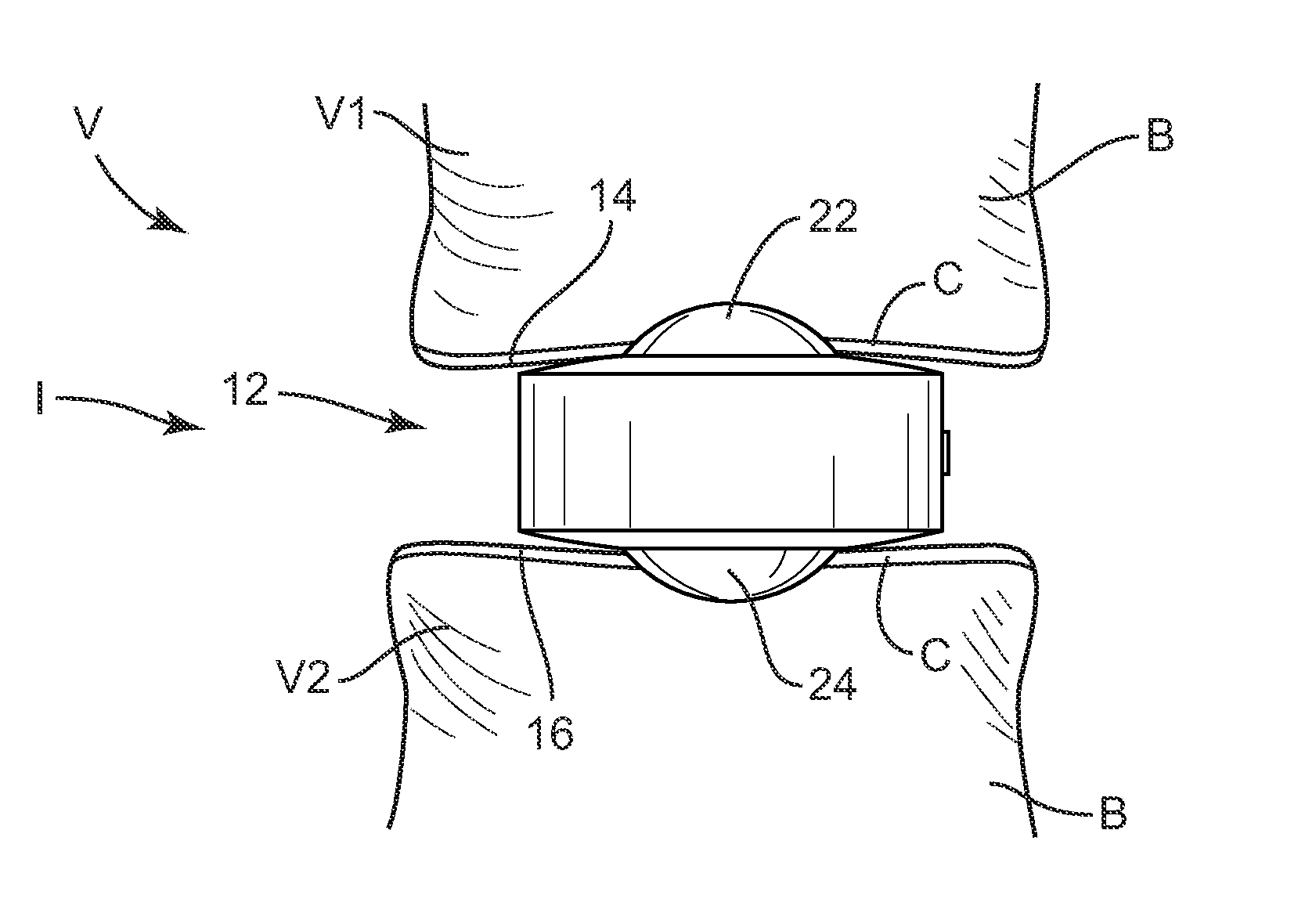
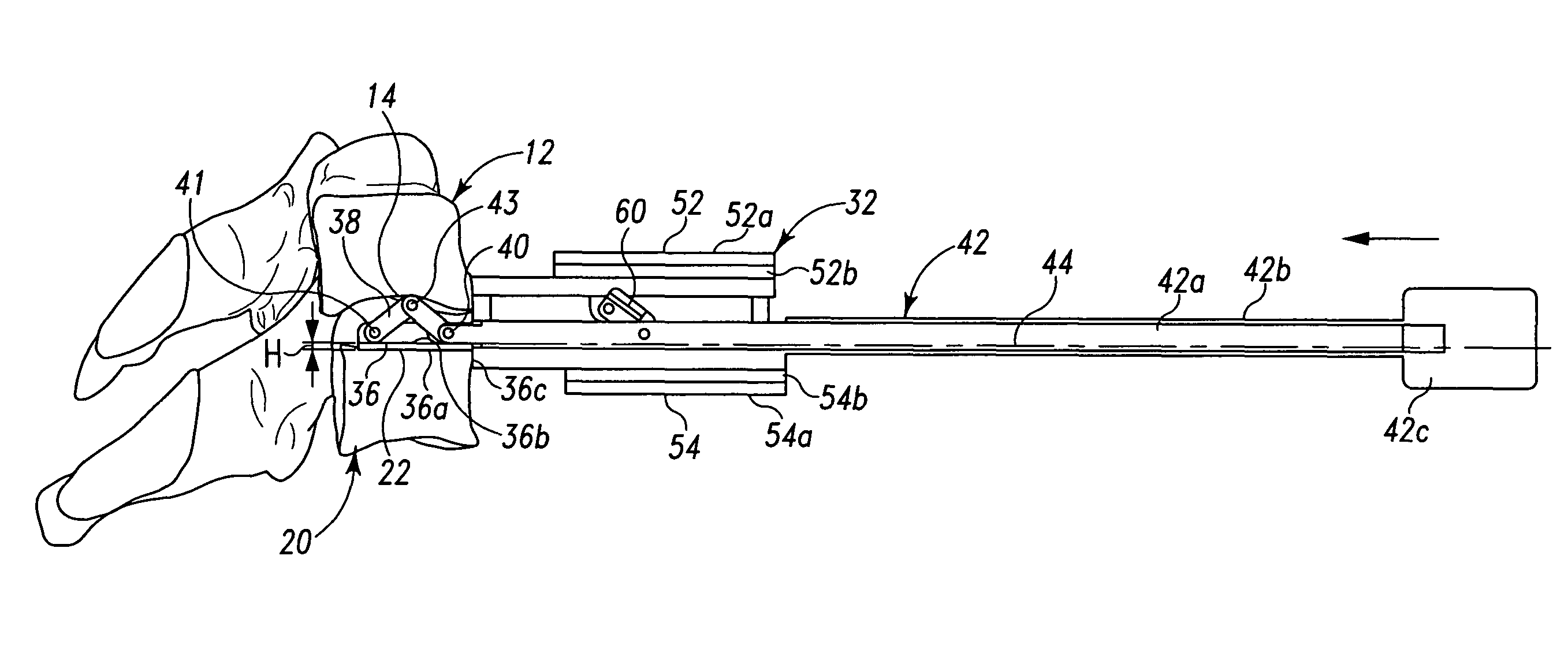
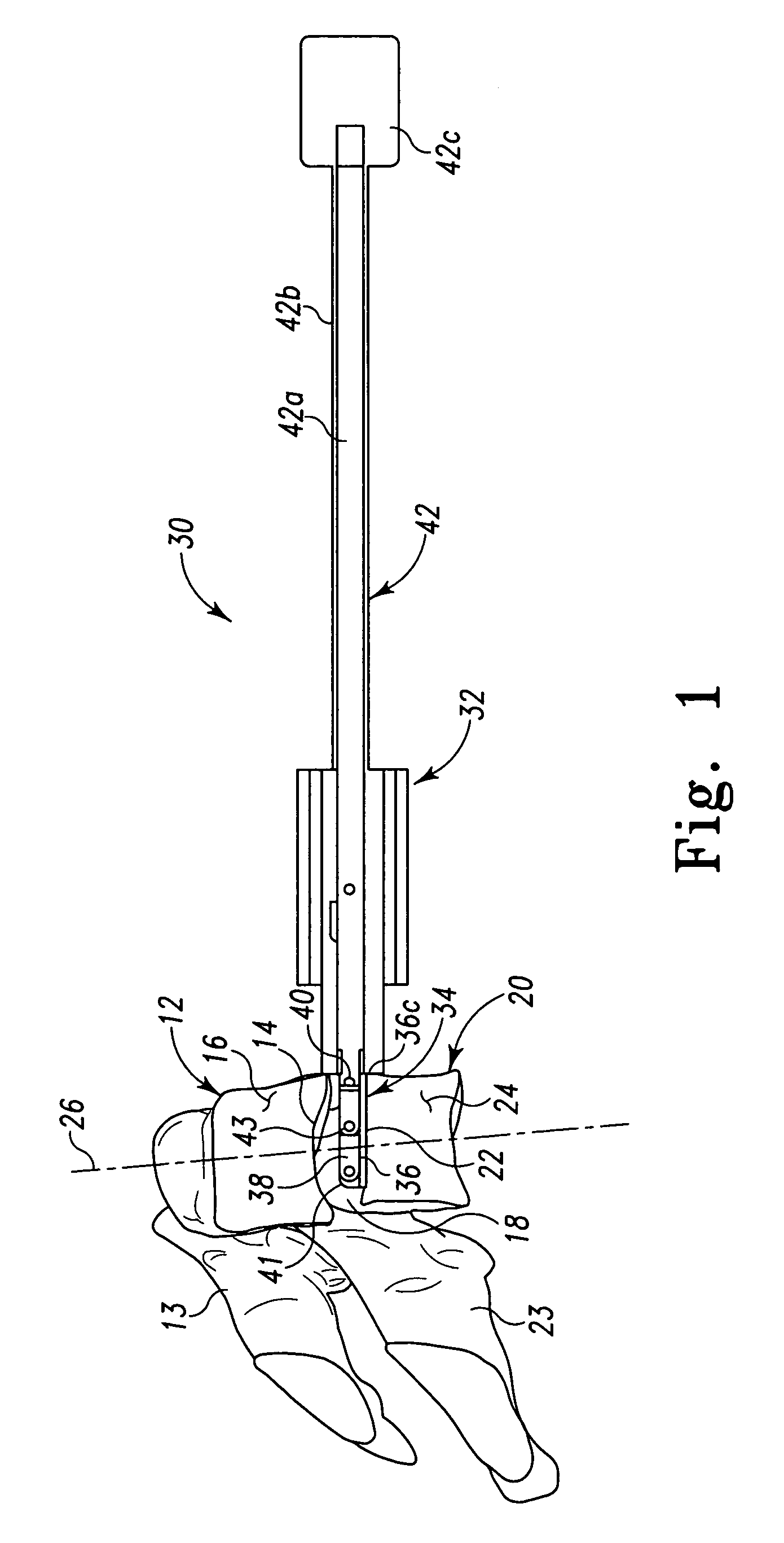
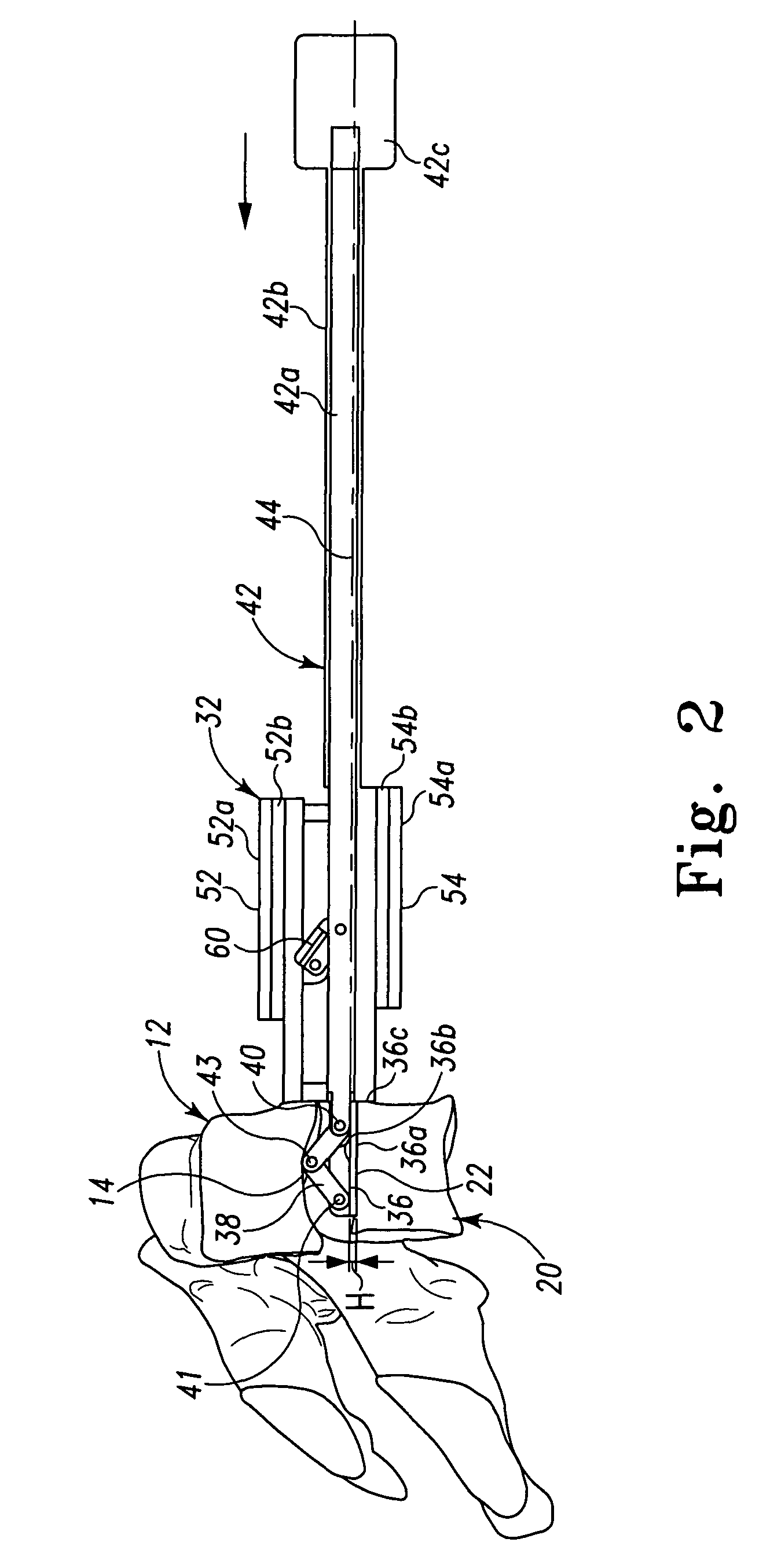
InactiveUS20110118788A1Compact configurationEasy to removeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsImplanted deviceVertebral surface
An implant device includes a pair of hook devices and an elongate guide device. The hook devices are configured to be disposed between and engage adjacent vertebral bodies. The elongate guide device is connected to the hook devices and allows for relative movement of at least one of the hook devices to adjust for the geometries of the vertebral surfaces to be engaged by the hook devices.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Artificial intervertebral disc
InactiveUS20060265072A1Reduce frictionRestrict movementBone implantJoint implantsEngineeringIntervertebral disk
Owner:AESCULAP IMPLANT SYST
Adaptable interbody implant and methods of use
An intervertebral fusion implant comprises a body defining a longitudinal axis and extending between a first end and a second end. The body defines a first wall configured for engaging a first vertebral surface and a second wall configured for engaging a second vertebral surface. The first wall is connected to the second wall. The first wall is movable relative to the second wall such that the body is deformable from a first, initial implanted configuration such that the body is disposed between the first vertebral surface and the second vertebral surface for fixation thereof and a second configuration such that the body is deformed relative to the first configuration to adapt to an orientation of the first vertebral surface and the second vertebral surface. Methods of use are disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Interbody implant system and methods of use
An interbody implant spacer includes a flexible body defining a first surface configured for engagement with a first vertebral surface and a second surface configured for engagement with a second vertebral surface. The first surface includes at least one pre-formed protrusion extending outwardly therefrom. The body is expandable between a first, non-expanded configuration such that the at least one protrusion extends outwardly from the first surface and a second, expanded configuration such that the at least one protrusion extends outwardly from the first surface to engage the first vertebral surface and at least a portion of the second surface engages the second vertebral surface. Methods of use are disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Artificial disc device
InactiveUS8262731B2Improve distributionImprove shock absorptionSurgeryJoint implantsBall bearingEngineering
Artificial disc devices are disclosed that restore correct anatomical intervertebral spacing for damaged discs while maintaining a substantially normal range of biomechanical movement for the vertebrae between which they are implanted. The disc devices include center bearing and outer or annular bearing portions with the center bearing portion including generally axially extending locating surfaces which cooperate with the facing vertebral surfaces to resist migration. The outer bearing portion is for load bearing or load sharing with the center bearing portion and includes surfaces that extend radially toward the periphery of the vertebrae so that subsidence about the center bearing portion is minimized. Alternate forms of the disc devices include one with an axially enlarged center ball bearing having an annular ring bearing extending thereabout and another having upper and lower plate members with a central bumper member and a surrounding resilient annular member therebetween.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Navigation template for vertebral pedicle locating and real-time screw path monitoring and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104905869AMonitor location in real timePlace stableOsteosynthesis devicesVertebral pedicleVertebral surface
The invention discloses a navigation template for vertebral pedicle locating and real-time screw path monitoring and a manufacturing method thereof. The navigation template comprises a vertebral surface attachment template body and an external vertebral pedicle template body, at least one connecting rod is arranged between the vertebral surface attachment template body and the external vertebral pedicle template body, a screw inlet area is arranged on the vertebral surface attachment template body, the vertebral surface attachment template body is obtained by thickening after needed surgical vertebral surface data are extracted, the external vertebral pedicle template body is obtained through a mirror image vertebral pedicle template, and the vertebral pedicle template is obtained by thickening after needed surgical vertebral pedicle surface data are extracted. The vertebral surface attachment template body is obtained by thickening after the needed surgical vertebral surface data are extracted, and therefore in the screw arrangement process, the navigation template is placed firmly. The external vertebral pedicle template body is obtained through the mirror image vertebral pedicle template, therefore, the position of a screw in the vertebral pedicle can be monitored in real time, and screw inlet accuracy is improved. The navigation template is suitable for the field of medical instruments.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Intervertebral implant devices and methods for insertion thereof
InactiveUS8603141B2Compact configurationEasy to removeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsImplanted deviceVertebral surface
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Spinal fusion implant for oblique insertion
Intervertebral spinal fusion implants for interbody fusion of the anterior column of the spine are described. The implants have a substantially bi-convex or a substantially offset bi-convex shape. The implants are placed through a transforaminal or posterior approach at an oblique insertion angle. The implants have an outermost point on the superior convex surface and an outermost point on the inferior convex surface and four edges of differing heights. The outermost superior and inferior points of the implants are connected with the four edges with convex surfaces of different curvatures. The curvatures of the convex surfaces of the implants are designed to match the curvatures of concave vertebral surfaces when the implants are inserted at an oblique insertion angle.
Owner:CAMBER SPINE TECH
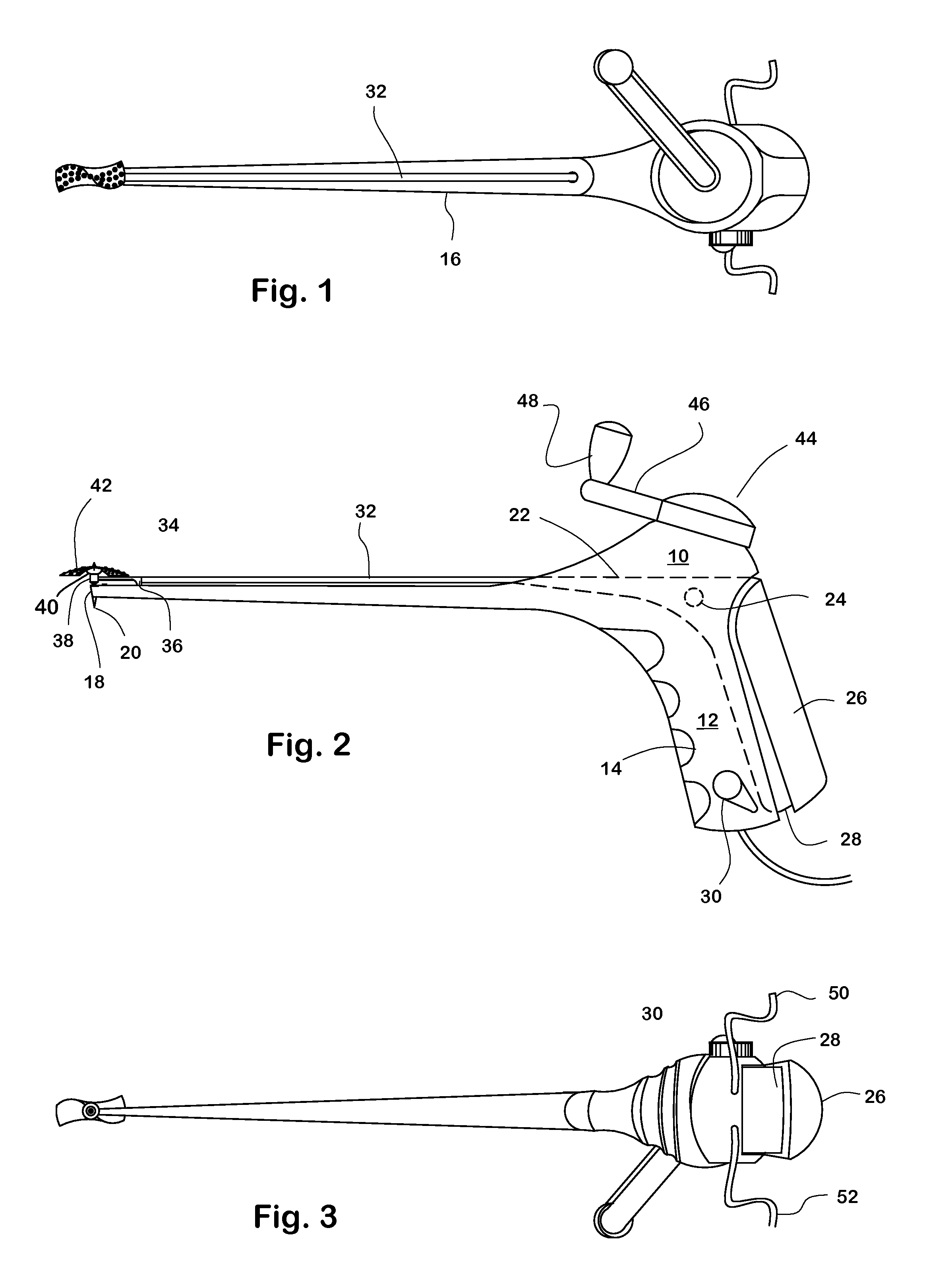
Disk preparation tool
A tool for preparing vertebral surfaces following a discectomy has a body and a rotary cutting tool mounted at the distal end of a lever which extends through the body. The proximal end of the lever can be squeezed toward the body to force the cutting tool against the vertebral surface facing it, while the tool is rotated by turning a crank supported on the tool body, or by a motor. The cutting tool is preferably a flexible rasp or blade which can conform to and control the convexity of the prepared surface.
Owner:SUDDABY LOUBERT
Vertebral surface preparation instrument
Provided is an instrument for preparing a surface of a vertebra, such as a vertebral endplate, for receipt of a spinal disc implant. The instrument includes a working tool with implements on one or more surfaces of the working tool that act on the vertebral surface. The instrument includes a rotary-to-linear translation system to cause the working tool to move; for example, from side-to-side, top-to-bottom, or along a path that includes side-to-side and top-to-bottom aspects. The rotary-to-linear translation system may include a drive shaft having a cam pin at a distal end, and a cam follower slot at an anterior end of the working tool.
Owner:RANIER LIMITED
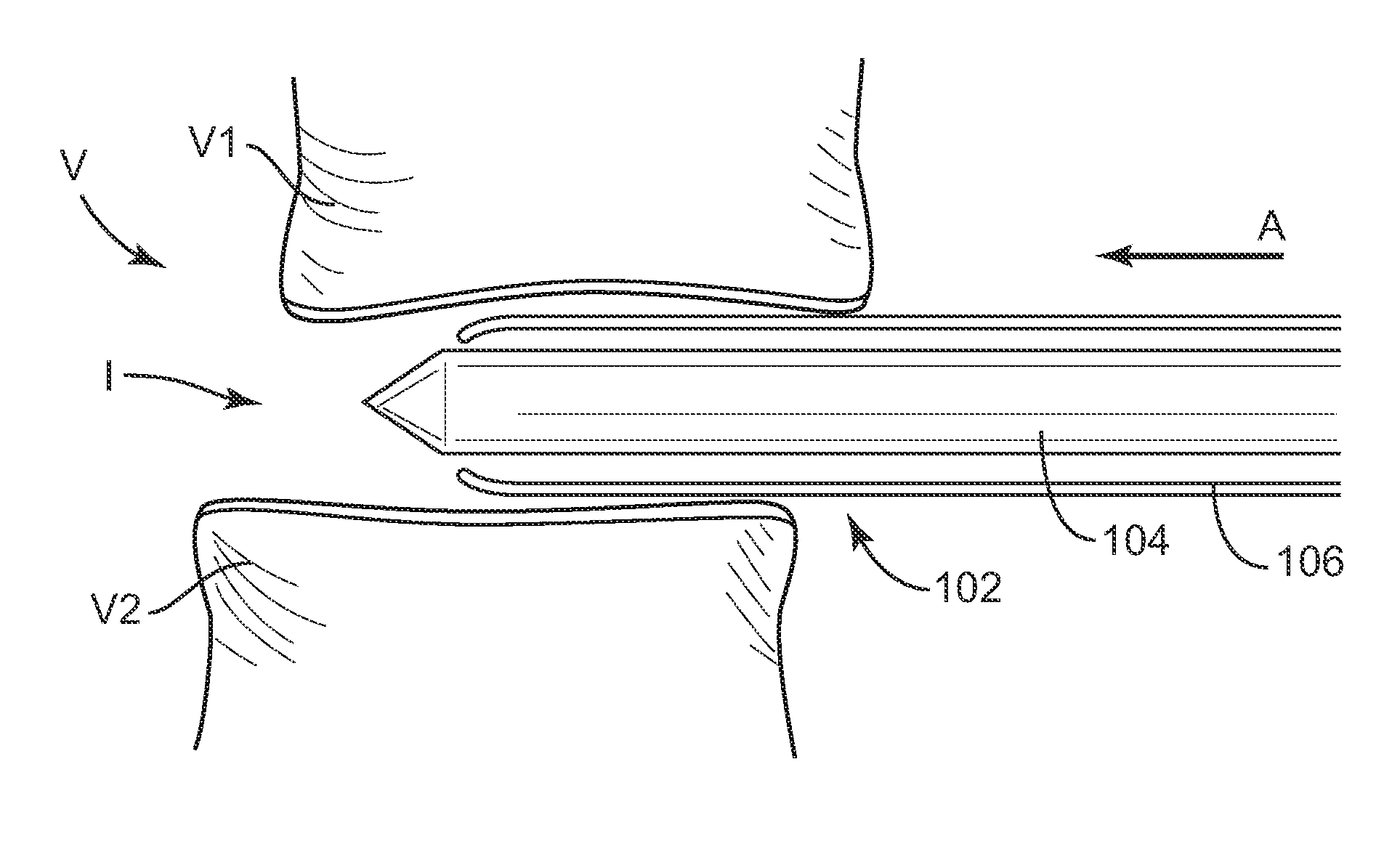
Instruments and techniques for guiding instruments to a spinal column
Systems and methods of shaping surfaces of vertebral bodies include a reference guide instrument that can be positioned relative to a disc space between vertebral bodies and referenced to the caudally located endplate of the disc space. The reference guide instrument can then be employed to guide preparation instruments to the vertebral bodies in an orientation and spacing referenced to the caudal endplate of the subject disc space to shape vertebral surfaces to receive an implant.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Spinal implant system and method of use
A method for treating a spine is provided. The method includes the steps of: disposing an interbody implant adjacent a first vertebral surface and a second vertebral surface of an intervertebral discspace, the interbody implant engaging the vertebral surfaces at a selected angular orientation; connecting the interbody implant with at least one of the vertebral surfaces via at least one fastener that is engaged with the interbody implant and fixed with the vertebral surface such that the at least one fastener is movable to a plurality of axial orientations relative to the interbody implant; and manipulating the vertebral surfaces such that the at least one fastener is fixed relative to the interbody implant. Spinal implants, surgical instruments and systems are disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Adjustable interbody fusion device
InactiveCN105997311AReduced risk of collapseIncrease the footprintSpinal implantsStress distributionIntervertebral space
The invention relates to an adjustable interbody fusion device and belongs to the technical field of body insertions of medical instruments. The adjustable interbody fusion device comprises a front fixed structure, a back fixed structure, a movable structure and a fastening structure. The movable structure is arranged in the middle portion of the front fixed structure and the middle portion of the back fixed structure, and after the front fixed structure and the back fixed structure are connected through the movable structure, in the implanting process, the front fixed structure, the movable structure and the back fixed structure can be further fastened into a whole through the fastening structure. The adjustable interbody fusion device can be implanted into intervertebral space through a small incision or a path. The adjustable interbody fusion device has the advantages that the contact area between the device and implanted sclerotin and centrum surface is large, stress distribution is wide, and supporting is high, and the adjustable interbody fusion device can be used for cases such as a cervical lumbar vertebrae degenerative disease. The adjustable interbody fusion device solves the problems that various interbody fusion devices adopted at present cannot be implanted with the small path, or after an operation, the fusion devices shift or get out of the positions, the centrum collapses, and nonunion rate of the planted sclerotin is high.
Owner:李照文
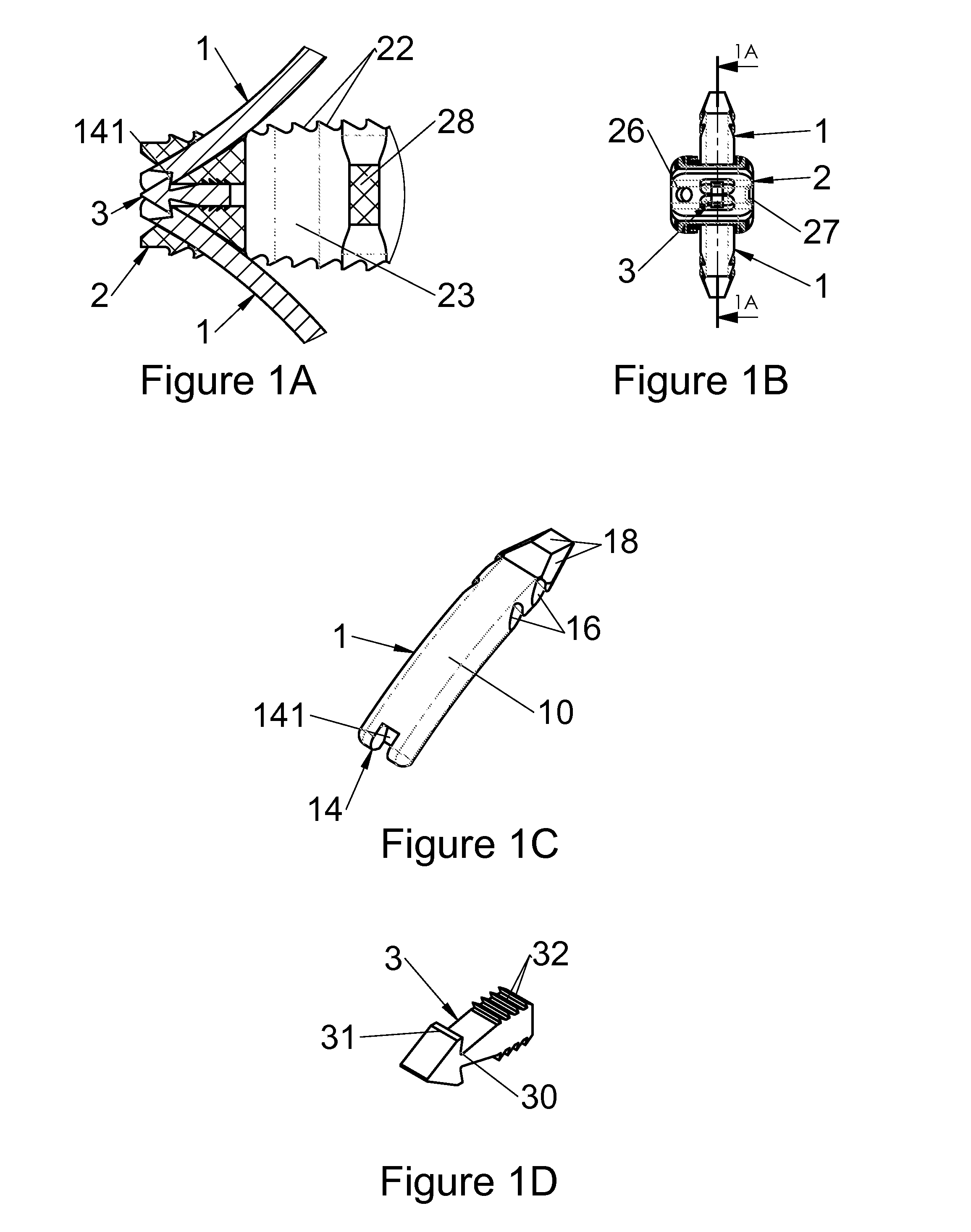
Anchoring device for a spinal implant, spinal implant and implantation instrumentation
The present invention relates to an anchoring device (1) for a rachidian implant (2), to an implant (2), to surgical instrumentation for the latter and to a rachidian surgery system, the anchoring device (1) comprising at least one stiff plate (10) with a longitudinal axis, configured so that its anterior end penetrates into at least one vertebral surface while its posterior end remains in a passage of the implant (2), characterized in that the implant (2) includes at least one means (3) for locking the device (1) relative to the implant (2) and in that the anchoring device (1) includes at least one abutment (14), said locking means (3) at least one flexible portion (30) and at least one abutment (31 ), cooperating with said abutment (14) of the device (1), the insertion of the anchoring device (1) into the passage allowing said abutment (31) of the locking means (3) to be pushed back by the flexibility of said flexible portion (30) which also allows mutual engagement of both abutments (14, 31) when they are found facing each other, by the elastic return of the flexible portion (30).
Owner:LDR MEDICAL SAS
Artificial intervertebral disc
InactiveUS20060265071A1Reduce frictionRestrict movementBone implantJoint implantsIntervertebral diskBearing surface
An artificial intervertebral disc includes housing members including spaced inner surfaces facing each other and oppositely facing outer surfaces for engaging spaced apart vertebral surfaces. Bearing surfaces extend from each of the inner surfaces for engaging each other while allowing for low friction and compression resistant movement of the housing members relative to each other while under compression. Load sharing pads are disposed between the inner surfaces and about at least a portion of the bearing surfaces for sharing absorption compressive loads with the bearing surfaces while limiting the relative movement of the housing members.
Owner:AESCULAP IMPLANT SYST
An osteogenic, rapidly absorbing hemostatic bone wax
ActiveCN108744019BAvoid bleedingGood hemostasisSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSpinal columnSurgical operation
Owner:中国人民解放军海军军医大学第一附属医院
Method for determining and verifying screw channel for bone surgery based on three-dimensional modeling
PendingCN112022344AQuick extractionEasy to determineComputer-aided planning/modellingCoronal planeVertebral surface
The invention discloses a method for determining and verifying a screw channel for bone surgery based on three-dimensional modeling. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining original CT scanning data of a bone, storing the original CT scanning data in a Dicom format, importing the original Dicom data into three-dimensional modeling software, building a two-dimensional mask of a bone needing to be operated, separating the mask of the bone needing to be operated from a mask of an adjacent bone, independently separating out the two-dimensional mask of the bone needing to be operated,and filling the mask with bone substances completely; reconstructing a three-dimensional model of the vertebral body based on the two-dimensional mask of the bone; in a high perspective mode of the three-dimensional model of the vertebral body, obtaining the form of the screw channel on the vertebral body; and projecting a vertebral arch channel to a median coronal plane or sagittal plane to obtain a screw channel projection, fitting the maximum inscribed circle of the screw channel, recording the radius of the inscribed circle, and obtaining the position of the circle center projected to thesurface of the vertebral body, namely the optimal screw feeding point. By establishing the three-dimensional model, the screw channel is rapidly extracted, the screw placement accuracy is high, the cost is low, and popularization is facilitated.
Owner:ZIGONG NO 4 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
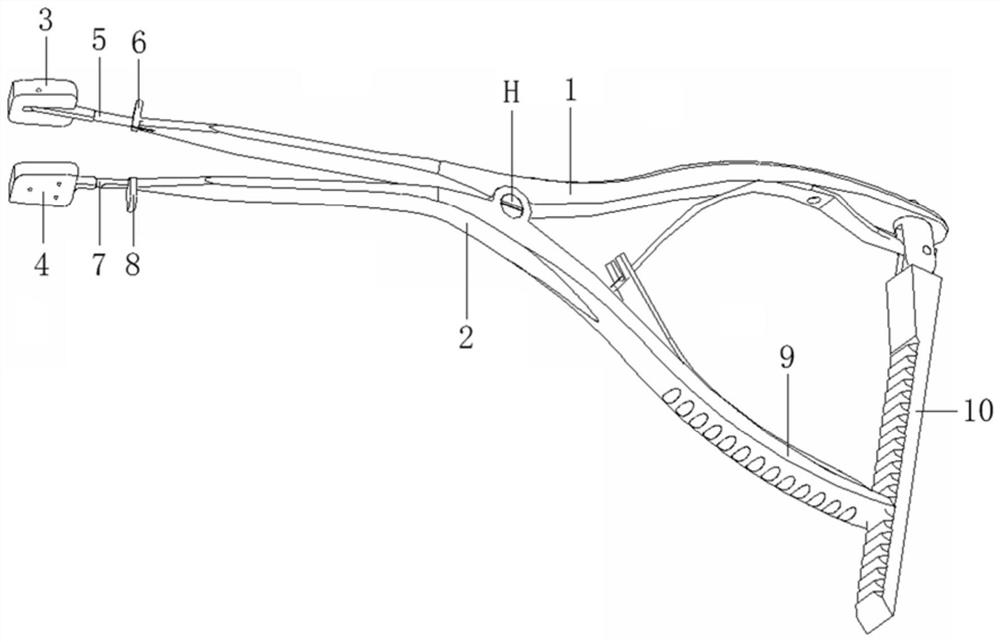
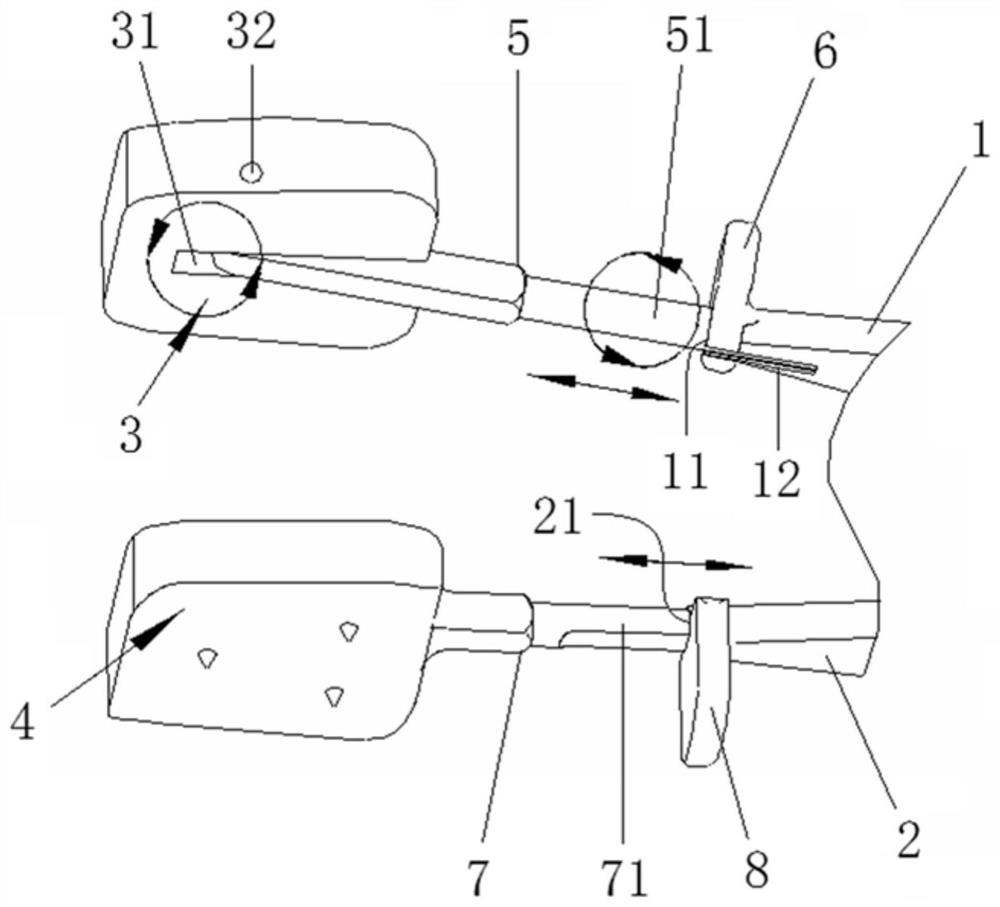
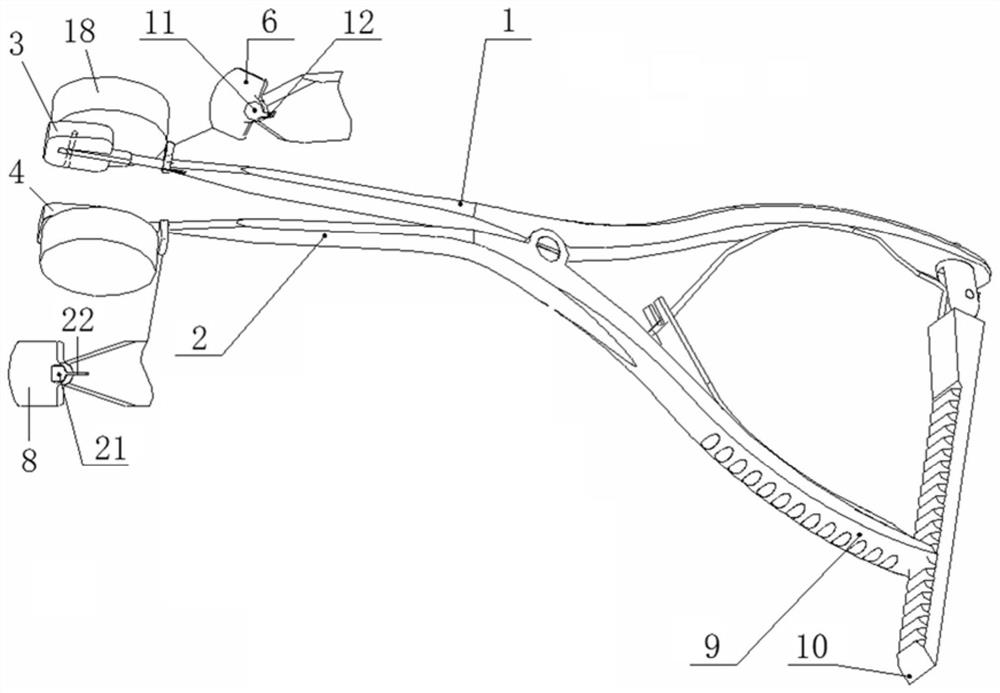
Self-adaptive angle distraction forceps
The invention discloses self-adaptive angle distraction forceps and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The self-adaptive angle distraction forceps is in the form of a pair of torsion type distraction forceps and comprises an upper forceps body and a lower forceps body, the middle parts of the upper forceps body and the lower forceps body are hinged, the front end of the upper forceps body is hinged with a movable distraction piece, and the front end of the lower forceps body is connected with a fixed distraction piece. The self-adaptive angle distraction forceps are used for distraction between vertebral bodies of the spine and are mainly used for distraction of the intervertebral space in an anterior cervical surgery, the distraction angle of the self-adaptive angle distraction forceps can be automatically adjusted along with changes of the included angle between the vertebral bodies, the distraction pieces are more attached to the surfaces of the vertebral bodies, the intervertebral space can be distraction in the maximum range, posterior longitudinal ligaments behind the spine can be conveniently relaxed. The diseased intervertebral disc and the rear diseased posterior longitudinal ligament are cleaned. The distraction pieces and the vertebral body are tightly attached (in surface contact), the pressure on the surface of the vertebral body can be dispersed to the whole contact surface. The situation that the end plate and vertebral body sclerotin are crushed due to pressure concentration at a point is avoided.
Owner:胡建华
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com