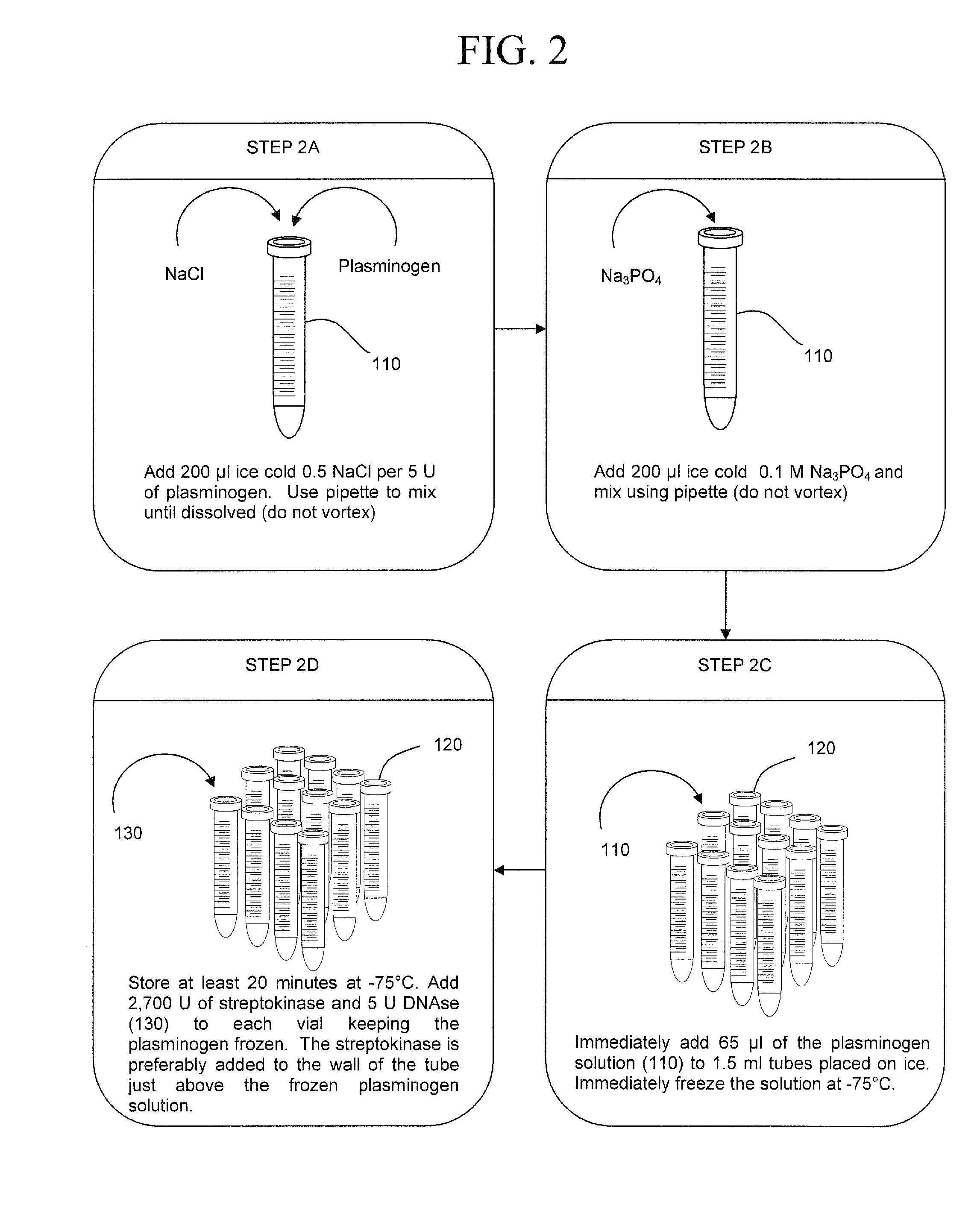
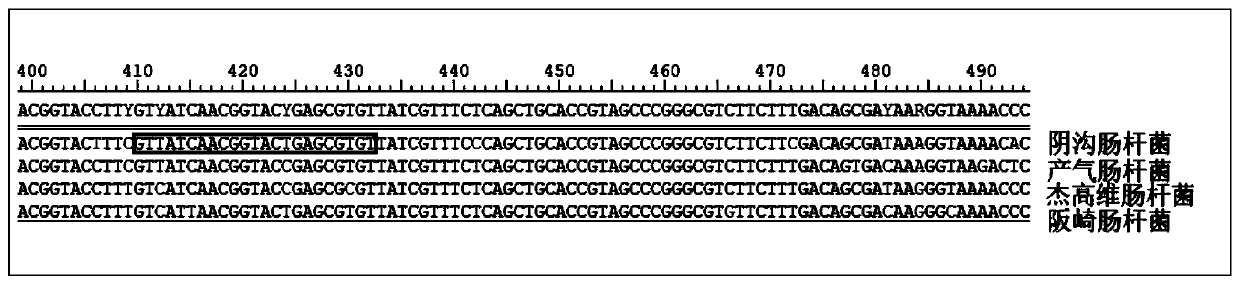
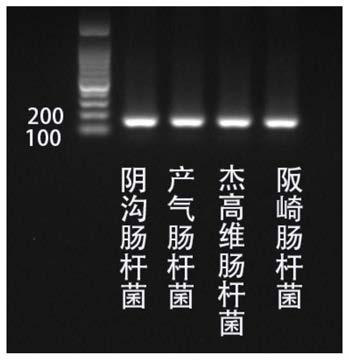
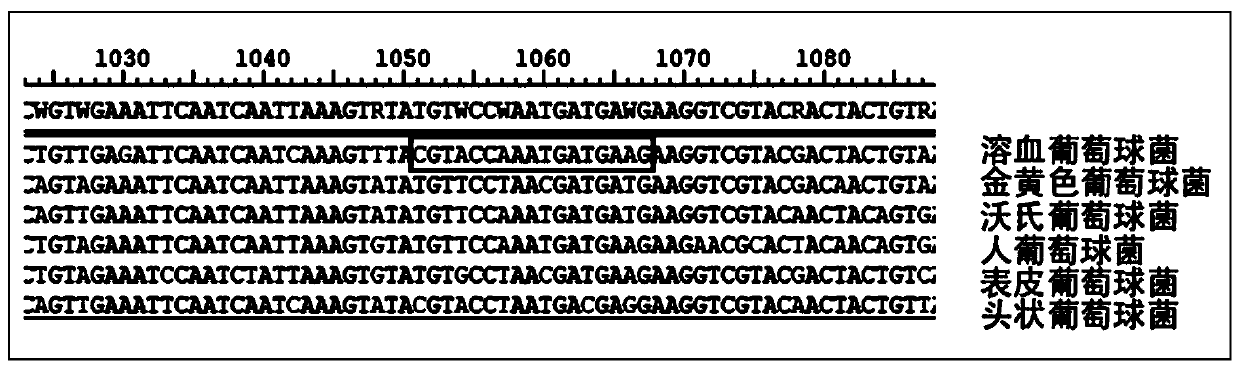
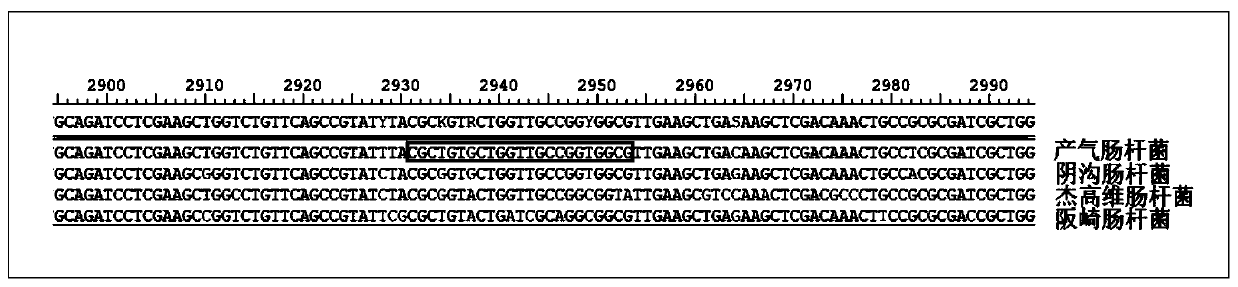
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Ribonuclease inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
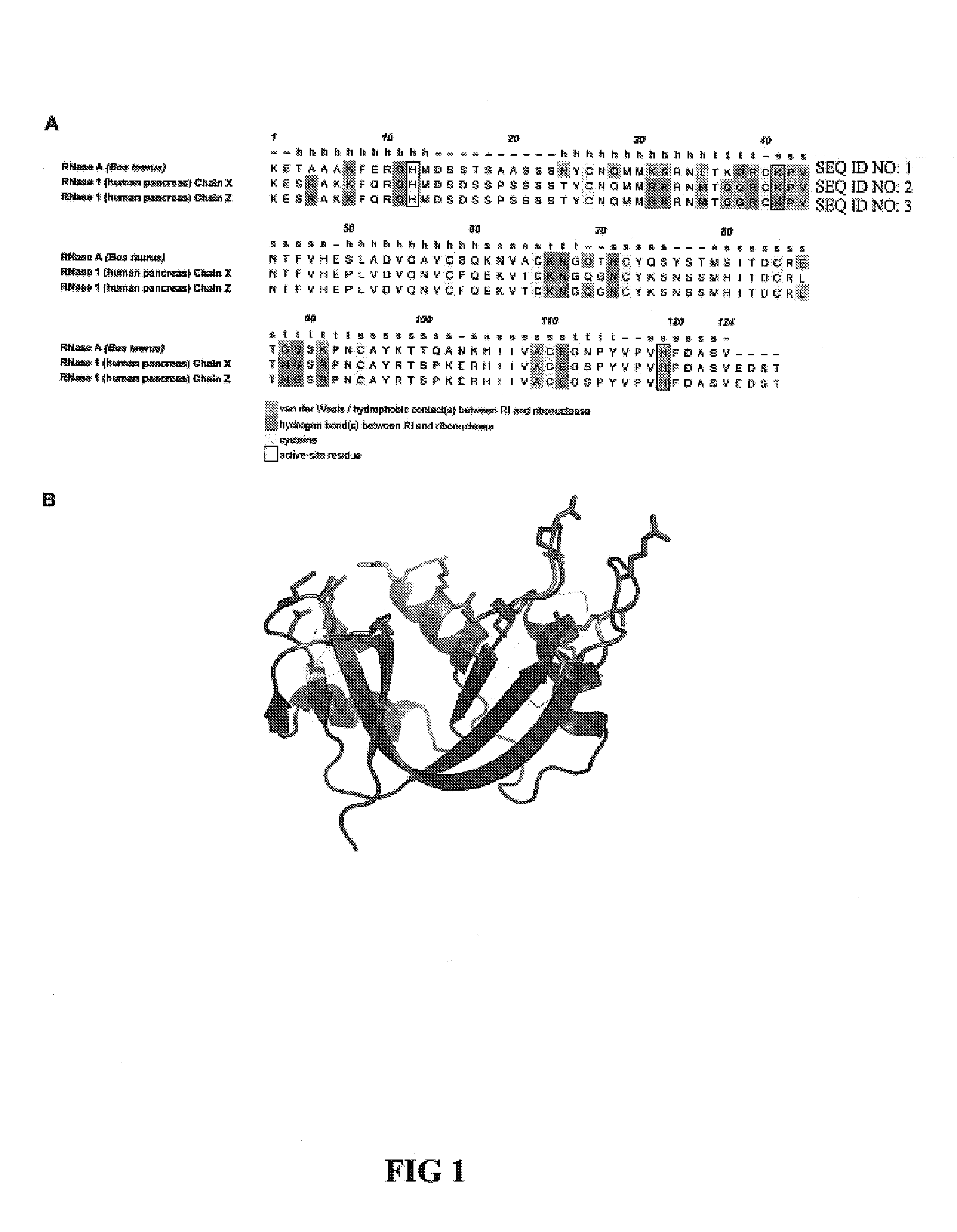
Ribonuclease inhibitor (RI) is a large (~450 residues, ~49 kDa), acidic (pI ~4.7), leucine-rich repeat protein that forms extremely tight complexes with certain ribonucleases. It is a major cellular protein, comprising ~0.1% of all cellular protein by weight, and appears to play an important role in regulating the lifetime of RNA.
Cytotoxic ribonuclease variants
This invention relates to altered forms of members of the RNase A superfamily. An RNase A can be modified to be cytotoxic by altering its amino acid sequence so that it is not bound easily by the ribonuclease inhibitor while still retaining catalytic properties. While earlier work had identified some modifications to RNase A that would result in cytotoxicity, the use of the FADE algorithm for molecular interaction analysis has led to several other locations that were candidates for modification. Some of those modifications did result in RNase A variants with increase cytotoxicity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Cytotoxic ribonuclease variants
ActiveUS20060292137A1High cytotoxic activityLow affinityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCytotoxicityRibonuclease inhibitor
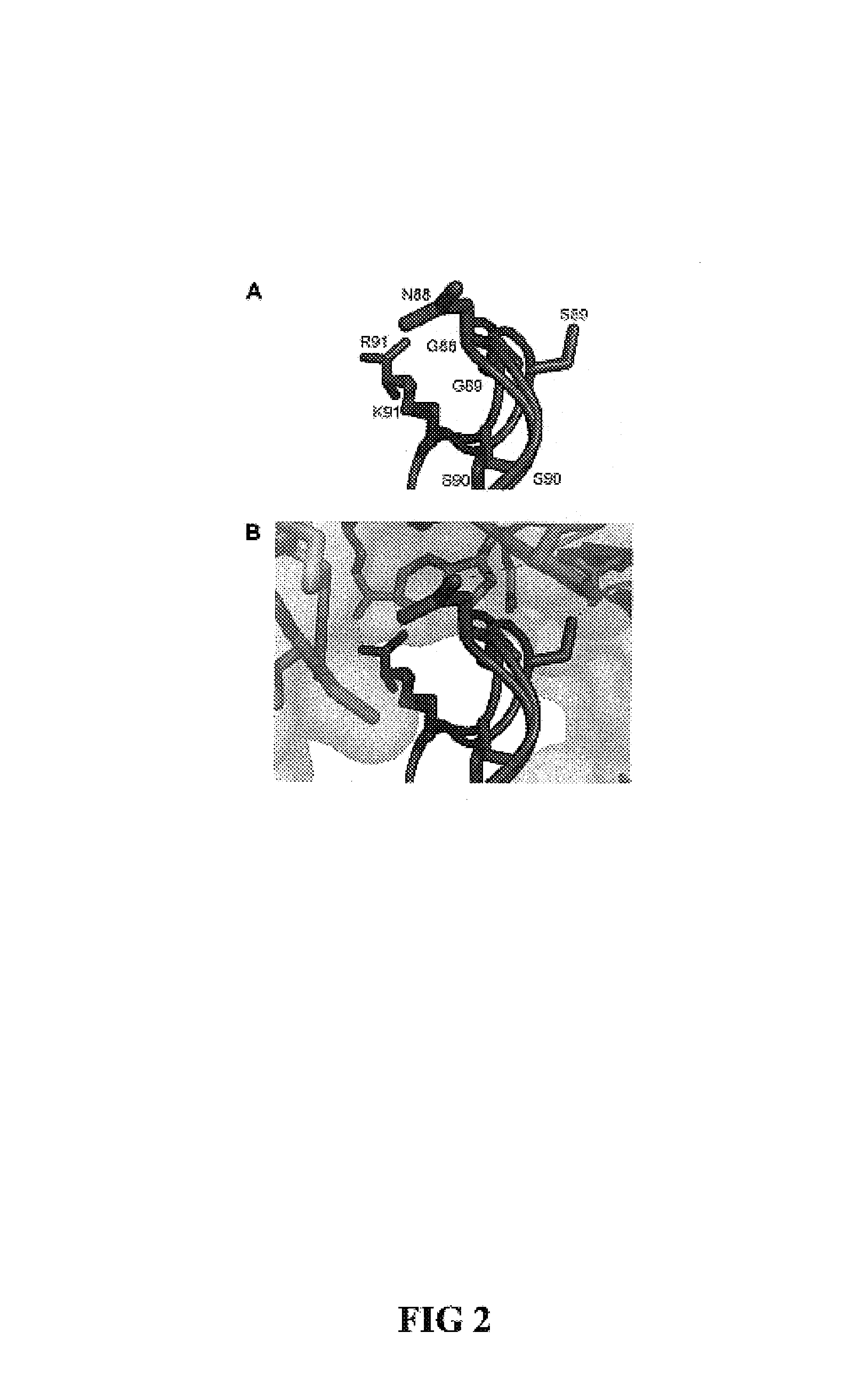
This invention relates to cytotoxic variants of human ribonuclease 1 (RNase 1) identified through analysis of the interaction between RNase 1 and the human ribonuclease inhibitor (hRI) as defined by the three dimensional (3-D) atomic structure of the RNase 1 hRI complex. Also disclosed is the 3-D structure of the hRI.RNase 1 complex and methods for designing the RNase 1 variants.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cytotoxic ribonuclease variants
ActiveUS7655757B2Low affinityHigh cytotoxic activityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesRNase PHCytotoxicity
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Molecular and bioinformatics methods for direct sequencing
InactiveUS20160180018A1Fast and accurate methodMinimize degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisBiotechnologyRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The present invention relates to methods for preparing an isolated biological sample containing at least one of DNA and RNA, such that the DNA and / or RNA is preserved in the sample at ambient temperatures for at least thirty days, the method comprising: contacting the isolated biological sample with a composition comprising a chaotropic agent, and subjecting the contacted sample to microbial cell lysis; and optionally, contacting the lysed biological sample with a slurry of size-selected silicon dioxide to form at least one of DNA-silicon dioxide complexes or RNA-silicon dioxide complexes in the sample; isolating at least one of DNA-silicon dioxide complexes or RNA-silicon dioxide complexes from the sample; and, separating at least one of DNA and RNA from the silicon dioxide and collecting at least one of the DNA and RNA.The present invention further relates to methods for preparing an isolated biological sample, the method comprising, separating the components in an isolated biological sample according to their size, wherein the components are at least one of DNA and RNA; purifying and isolating SSU rRNA from the biological sample using a composition comprising a ribonuclease inhibitor and a deoxyribonuclease to remove DNA from the sample, reverse transcribing the SSU rRNA into ds cDNA using random primers for SSU rRNA.The present invention also relates to computer implemented methods comprising, receiving an isolated sample prepared according to the methods of the invention, sequencing the sample, and providing the sequence with a sequence identifier (ID), the sequence comprising a plurality of groups of k-mers, each group of k-mers defining a node in a multi-level hierarchy which defines the relationship between the groups of k-mers; providing each group of k-mers with a respective group identifier (ID), determining the frequency of the k-mers in each group; generating a group signature array for each group of k-mers, each group signature array comprising the k-mers in each group that have the most increased frequency compared with the sibling k-mers; generating a signature map comprising each group signature array and at least one of the identifiers, the identifier of at least one parent group and the identifier of at least one child group; and outputting the signature map to be used to classify the sequence.
Owner:16S TECH INC
Oxidation-resistant ribonuclease inhibitor
InactiveUS7560248B1Reduce oxidationEfficient use ofHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsAngiogeninWild type
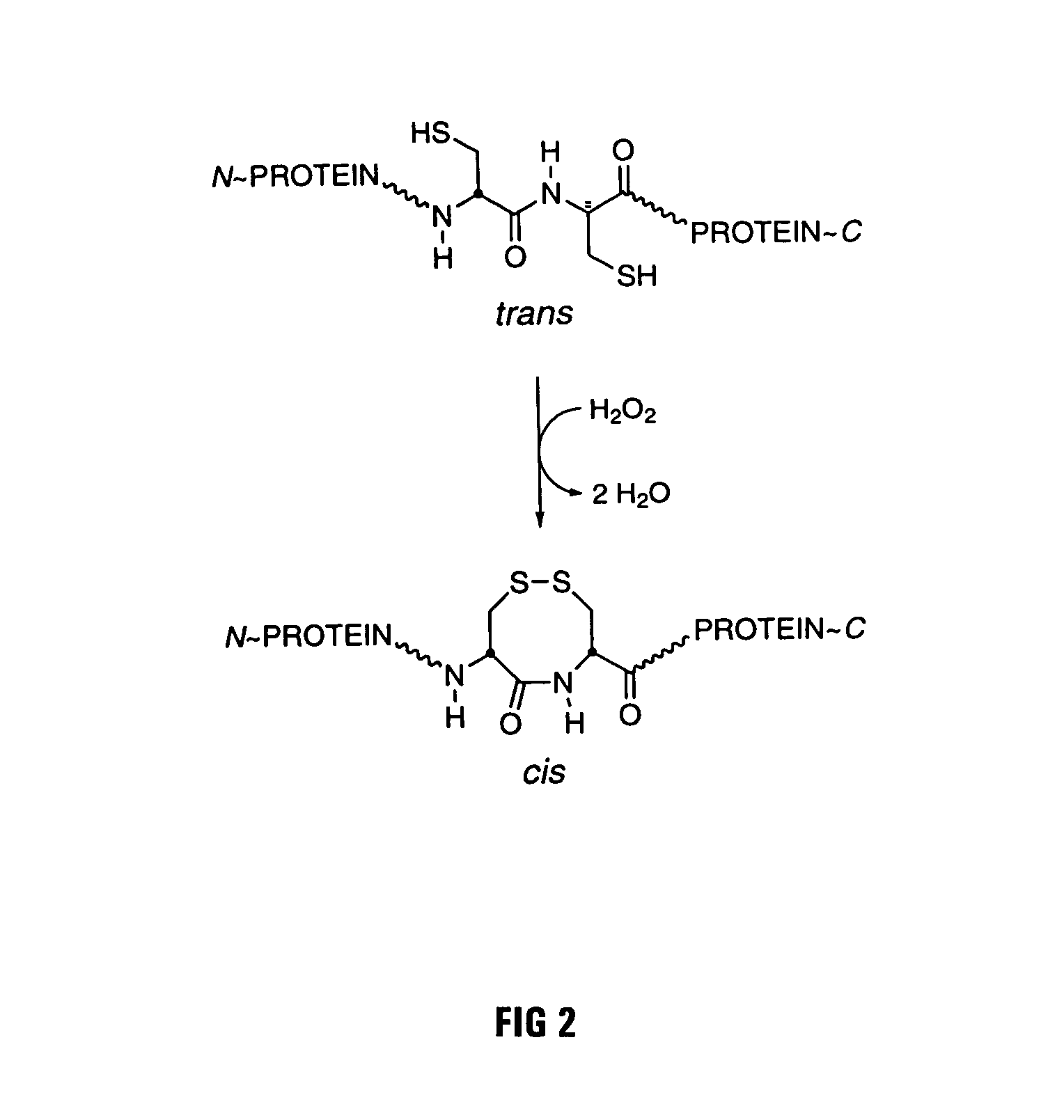
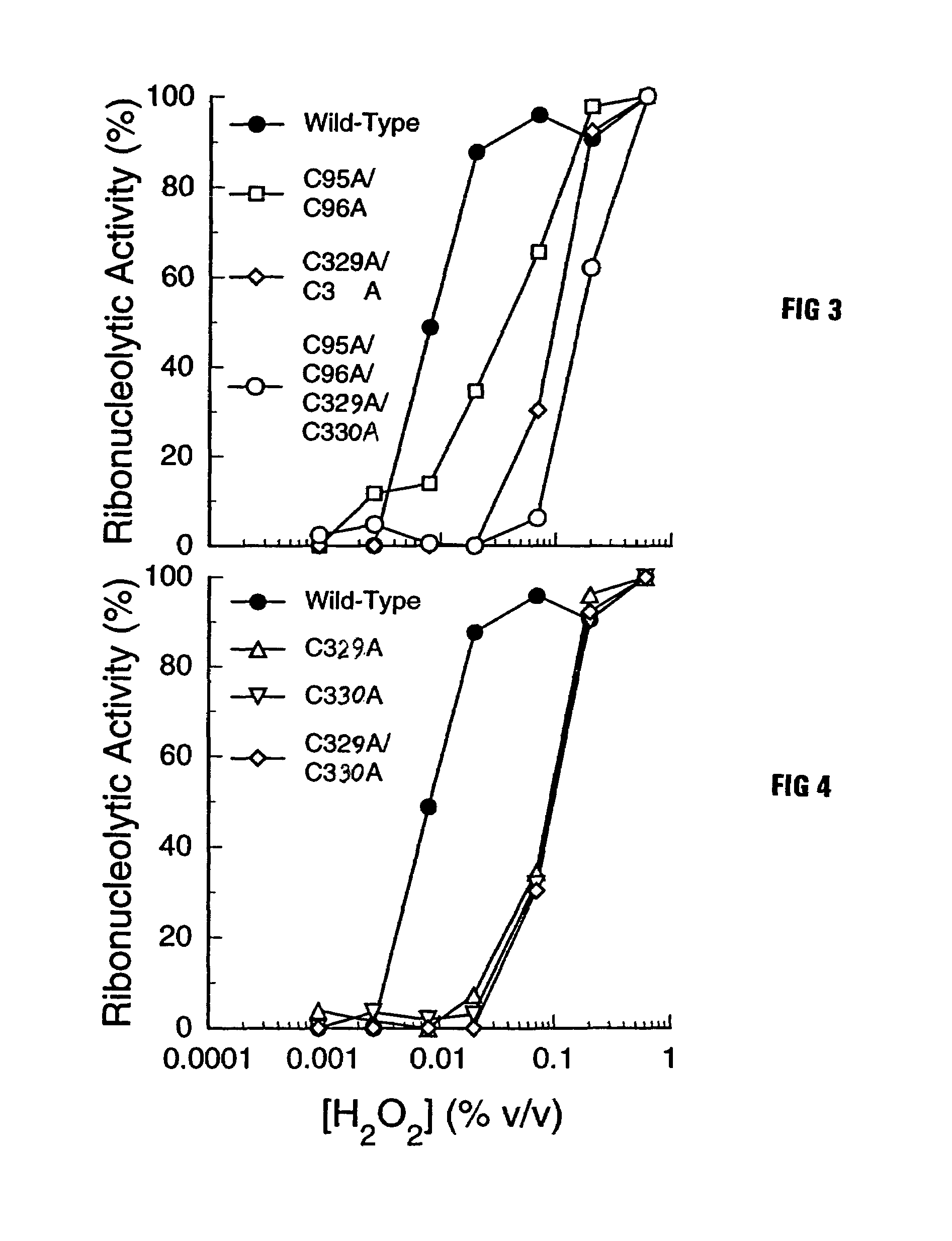
Mutant forms of ribonuclease inhibitor are described which are rendered more resistant to oxidation while retaining affinity for both ribonuclease and angiogenin. The mutant forms have another amino acid, typically an alanine, substituted for one or more of the adjacent cysteine residues in the wild-type sequence to prevent the formation of unwanted disulfide bonds which can disrupt the effectiveness of the molecule.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Post protein hydrolysis removal of a potent ribonuclease inhibitor and the enzymatic capture of DNA
ActiveUS20050277130A1Facilitate pathogen DNA extractionEasily damagedMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationLysisAurintricarboxylic acid
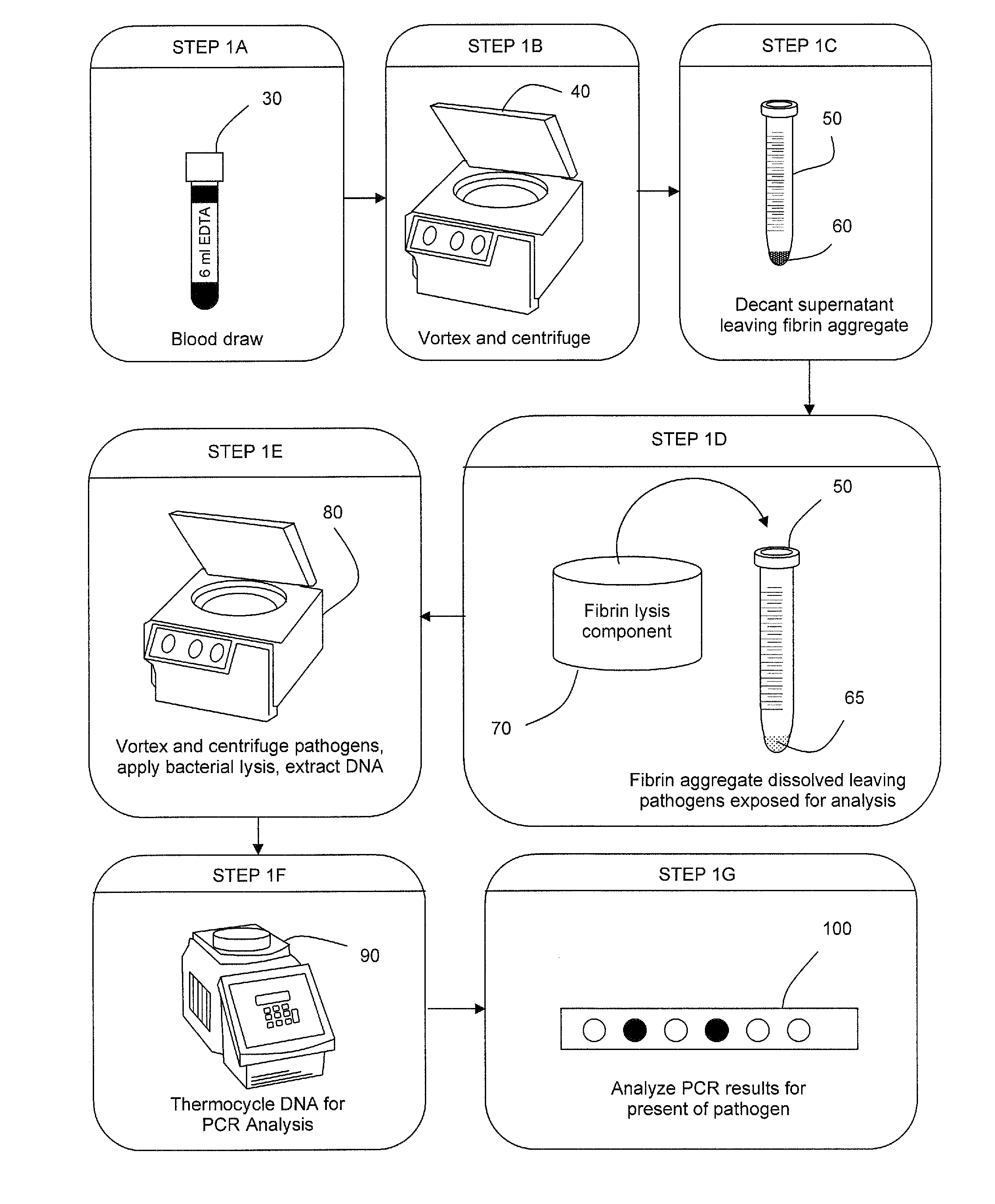
The present invention concerns compositions and methods of extracting infectious pathogens from a volume of blood. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of creating a fibrin aggregate confining the pathogens and introducing a fibrin lysis reagent to expose the pathogens for analysis. The present invention also concerns materials and methods for removing aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) from a sample.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Post protein hydrolysis removal of a potent ribonuclease inhibitor and the enzymatic capture of DNA
ActiveUS7416843B2Facilitate chemical and physical disruptionEasy extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationLysisAurintricarboxylic acid
The present invention concerns compositions and methods of extracting infectious pathogens from a volume of blood. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of creating a fibrin aggregate confining the pathogens and introducing a fibrin lysis reagent to expose the pathogens for analysis. The present invention also concerns materials and methods for removing aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) from a sample.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Post Protein Hydrolysis Removal of a Potent Ribonuclease Inhibitor and the Enzymatic Capture of DNA
InactiveUS20120164714A1Facilitate chemical and physical disruptionEasy extractionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLysisAurintricarboxylic acid
The present invention concerns compositions and methods of extracting infectious pathogens from a volume of blood. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of creating a fibrin aggregate confining the pathogens and introducing a fibrin lysis reagent to expose the pathogens for analysis. The present invention also concerns materials and methods for removing aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) from a sample.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Kit for real-time fluorescence quantification RT-qPCR detection of hepatis c viral nucleic acid by means of one-step method
ActiveCN106119415AShorten the lengthReduce the chance of being degraded by enzymesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a kit for real-time fluorescence quantification RT-qPCR detection of hepatis c viral nucleic acid by means of a one-step method. The kit comprises a viral nucleic acid extraction reagent, a probe containing detection target polynucleotide and an internal control, RT-qPCR reaction buffer used for amplification of a target polynucleotide primer, an RT-PCR enzyme mixture containing warm start DNA polymerase, Revert AidTM M-MLV reverse transcriptase and RiboLockTM ribonuclease inhibitor, and a quantitative criterion reference containing virus-like particles. By the adoption of the novel hepatitis c virus target sequence probe and primer, a secondary structure and an incision enzyme site which cause degradation easily in a hepatis c virus 5'-UTR area are avoided innovatively, original viral load can still be reflected to the maximum degree even if viral nucleic acid is unstable, all six genotypes of hepatis c viral nucleic acid RNA in samples subjected to improper acquisition, transportation, storage and treatment can be tested, and accurate basis is provided for auxiliary diagnosis of hepatis c virus infection and monitoring of drug therapy of infectors.
Owner:山东探克生物科技股份有限公司
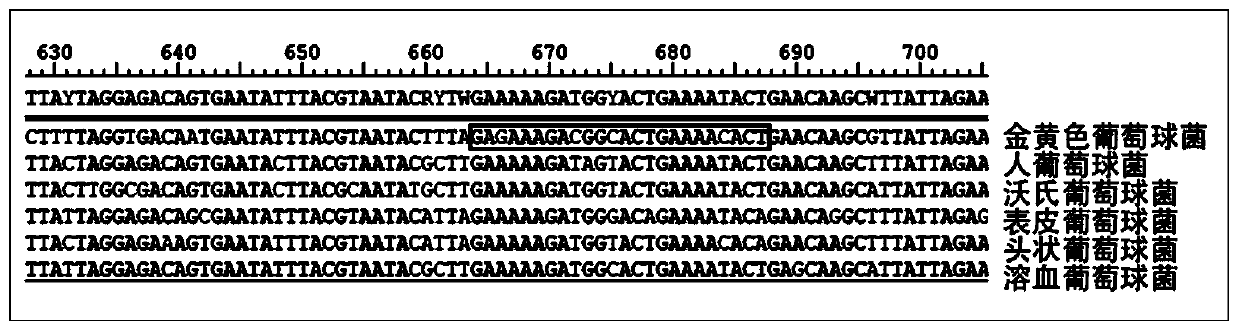
Kit used for staphylococcus aureus detection
InactiveCN110079586ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus haemolyticus
The invention provides a kit used for staphylococcus aureus detection. The kit used for staphylococcus aureus detection contains guide RNA of a specific targeted staphylococcus aureus rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), Ribonuclease Inhibitor and buffer liquid. By using the kit for staphylococcus aureus detection, the detection specificity is high, and staphylococcus aureus and other staphylococcus, including staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri,staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus, can be separated. Meanwhile, by using a RNA sequence for detection, elapsed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instruments are used, the equipment requirements are low, and are significantly lower than that of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical application valve is large.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cytotoxic ribonuclease variants
ActiveUS20090311784A1Low affinityHigh cytotoxic activityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsBiochemistry
This invention relates to cytotoxic variants of human ribonuclease 1 (RNase 1) identified through analysis of the interaction between RNase 1 and the human ribonuclease inhibitor (hRI) as defined by the three dimensional (3-D) atomic structure of the RNase1 hRI complex. Also disclosed is the 3-D structure of the hRI•RNase 1 complex and methods for designing the RNase 1 variants.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
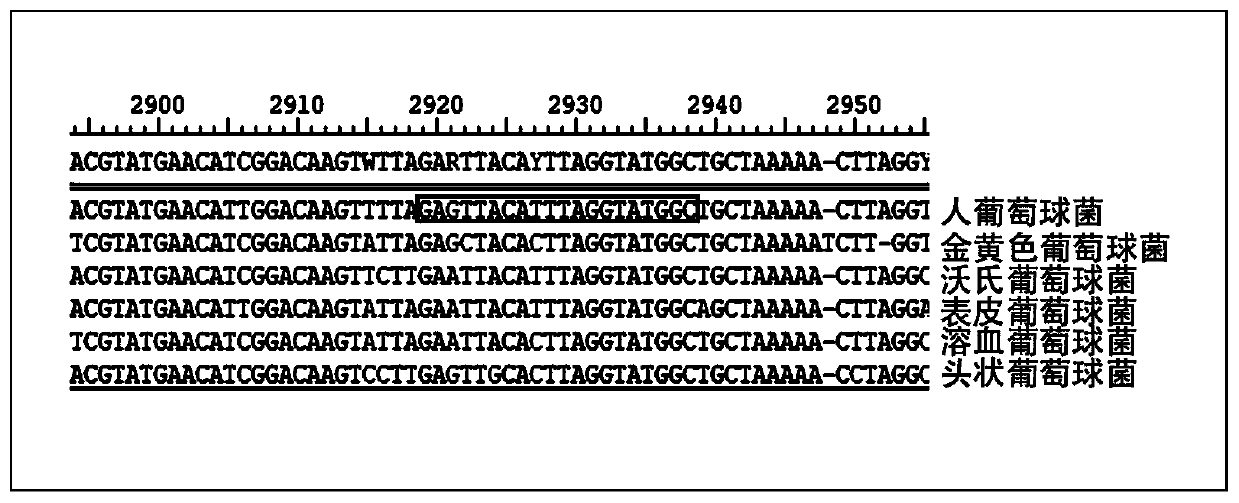
Kit for detecting staphylococcus hominis
InactiveCN110157821ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus hominis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus hominis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus hominis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus hominis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kit for detection of Enterobacter cloacae
InactiveCN110241239AStrong specificityLow equipment requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesRNA SequenceSingle strand dna
The invention provides a kit for the detection of Enterobacter cloacae, including guide RNAs specifically targeting the rpoB gene of the Enterobacter cloacae, a primer pair for amplification, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a proteins, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), Ribonuclease Inhibitor and buffer. The kit can be used to detect the Enterobacter cloacae with high specificity, and can distinguish the Enterobacter cloacae from other Enterobacter bacteria, including Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter gergoviae and Enterobacter sakazakii. At the same time, the method using the RNA sequence described in the invention for detection takes about 1 hour, does not need any PCR instruments, and has low requirements for equipment; and time consumption of the method is significantly lower than that of the conventional bacterial culture method or the PCR sequencing method, with great clinical practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus
InactiveCN110129462ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus. The kit comprises guide RNA specifically targeting staphylococcus haemolyticus rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-chain DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus haemolyticus, high detection specificity is achieved, and the staphylococcus haemolyticus can be distinguished from other staphylococcus such as staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus epidermidis. Meanwhile, when the RNA sequence is used to perform detection, detection time is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, equipment requirements are evidently lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and a high clinical practical value is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ribonuclease inhibitor inclusion body renaturation method
The present invention relates to a ribonuclease inhibitor (RI) inclusion body renaturation method. According to the present invention, RNase A is used during the renaturation so as to substantially improve the renaturation rate of RI, and is easily removed with the inorganic salt with a certain concentration under the slightly acidic condition in the subsequent purification process, and RI can bebound to the purification column through proper purification, such that the purification can be conveniently performed to obtain the high-purity RI.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHAOWEI TECH DEV
Reagent kit for detecting enterobacter aerogenes
InactiveCN110241237AStrong specificityLow equipment requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesRpoBSingle strand dna
The invention provides a reagent kit for detecting enterobacter aerogenes. The reagent kit contains a guide RNA specifically targeted to an enterobacter aerogenes rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, a hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying ball, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the reagent kit is used for detecting the enterobacter aerogenes, the detection specificity is high, and the enterobacter aerogenes can be distinguished from other enterobacter bacteria including enterobacter cloacae, enterobacter gergoviae and enterobacter sakazakii. Besides, when the RNA sequence is used for detection, time consumption is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, requirements for equipment are low and are notably lower than those by a traditional bacteria culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and the clinical use value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kit, primer, and probe for detecting Japanese encephalitis virus via real-time fluorescence isothermal amplification
ActiveCN104894112AGuaranteed specificityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerFluorescence
The invention discloses a kit, a primer, and a probe for detecting Japanese encephalitis virus via real-time fluorescence isothermal amplification. The kit comprises the following components: 100mM of Tris-HCl, 100mM of KCl, 20mM of MgCl2, 20mM of DTT, 20% of DMSO, 4mM of NTP, 1mM of dNTP, 0.125MuM of each of Primer-1 and Primer-2, 0.25MuM of a molecular beacon probe, 1.6U / MuL of an AMV reverse transcriptase, 8U / MuL of T7RNA polymerase, 0.04U / MuL of rnase h, 2U / MuL of ribonuclease inhibitor, and 0.1% of BSA. According to the invention, a specific forward primer, reverse primer, and molecular beacon probe are optimizedly selected via design and via combination with clinical sample screening; three different areas of the encephalitis virus are synchronously recognized; amplification specificity is ensured; the encephalitis virus RNA, which is of single copy number, contained in a sample can be detected; and sensitivity of detecting encephalitis is improved.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Efficient soluble expression method of active recombinant ribonuclease inhibitor
The invention provides an efficient soluble expression method of an active recombinant ribonuclease inhibitor, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention discloses an effective method for obtaining an active recombinant ribonuclease inhibitor, which is simple and easy to implement and has low cost. A recombinant plasmid vector of a coding gene for expressing a mouse ribonuclease inhibitor (mRI) is converted into engineering bacteria with protease gene defect phenotypes, and soluble expression of higher-level active products can be obtained by appropriate induction.
Owner:WEIZHI LANSI MEDICAL TECH BEIJING
Light emitting system of ribonuclease and inhibitor sieving of ribonuclease, preparation method and application of light emitting system
PendingCN109777794AThe identification method is intuitiveEasy to operateHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsLuminous intensity
The invention relates to a light emitting system of ribonuclease and inhibitor sieving of ribonuclease, a preparation method and application of the light emitting system. Gold nanometer clusters are based on good biocompatibility and emit red light, and are prepared from chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) under mild conditions, with ribonucleic acid (RNA) and mercaptoundecanoic acid being a microenvironment and with ascorbic acid being a mild reducing agent. The bright red fluorescent light is emitted, and the wavelength of the emitted light is about 630 nm. In the system, if a ribonucleic acid shear enzyme (such as RNase A) exists, the RNA structure is destroyed, the gold nanometer clusters cannot be formed, or the light-emitting intensity is low, and therefore the aim of quantitatively and qualitatively determining the activity of the ribonuclease is realized. The system can be further used for sieving the ribonuclease inhibitor. The preparation condition of the gold nanometer clusters is that a water bath is conducted at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C, and the volume ratio of the chloroauric acid to the RNA to the ascorbic acid to the mercaptoundecanoic acid is 0.8-1.2:6-10:8-15:0.8-1.2.Through the light-emitting intensity of the light emitting system, the ribonuclease can be quantitatively and qualitatively detected, wherein the quantitative detection range is 0-2.5*10-4 U / mL.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus epidermidis
InactiveCN110157822ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus epidermidis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus epidermidis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydratedTwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus epidermidis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus epidermidis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kit for detecting staphylococcus warneri
InactiveCN110144416ALower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The present invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus warneri. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus warneri rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying spheres, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), an ribonuclease inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcuswarneri and high in detection specificity, and can separate the staphylococcus warneri from other staphylococci, including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. At the same time, the use of the RNA sequence for the detection takes about 1 hour, does not require a PCR instrument, has low requirements on equipment, and is significantly lower than a conventional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method and large in clinical practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reagent kit for detecting streptococcus pyogenes
InactiveCN110241238AStrong specificityLow equipment requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementStreptococcus pyogenesRpoB
The invention provides a reagent kit for detecting streptococcus pyogenes. The reagent kit contains a guide RNA specifically targeted to a streptococcus pyogenes rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, a hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying ball, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the reagent kit is used for detecting the streptococcus pyogenes, the detection specificity is high, and the streptococcus pyogenes can be distinguished from other streptococcus including streptococcus dysgalactiae and streptococcus agalactiae. Besides, when the RNA sequence is used for detection, time consumption is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, requirements for equipment are low and are notably lower than those by a traditional bacteria culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and the clinical use value is large.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Japanese encephalitis virus real-time fluorescent isothermal amplification detection kit and its primers and probes
ActiveCN104894112BGuaranteed specificityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerT7 RNA polymerase
The invention discloses a Japanese Japanese encephalitis virus real-time fluorescent isothermal amplification detection kit and its primers and probes. The kit includes the following components: 100mM Tris-HCl, 100mM KCl, 20mM MgCl2, 20mM DTT, 20% DMSO, 4mM NTP, 1mM dNTP, 0.125μM each of Primer-1, Primer-2, and 0.25μM Molecular Beacon Probe; 1.6U / μL AMV Reverse Transcriptase, 8U / μL T7 RNA Polymerase, 0.04U / μL RNase H, 2U / μL Ribonuclease Inhibitor, 0.1% BSA. In the present invention, the specific forward primers, reverse primers and molecular beacon probes are designed and optimized in combination with clinical sample screening to simultaneously identify three different regions of Japanese encephalitis virus, ensuring the specificity of amplification ; Can detect single-digit copy number of JE virus RNA contained in the sample, which improves the sensitivity of JE detection.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Pretreatment method, pretreatment solution, kit and use thereof for viral nucleic acid detection
ActiveCN110982876BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionViral nucleic acid
The invention relates to the field of virus nucleic acid detection. Specifically, the present invention provides a pretreatment method for viral nucleic acid detection, the method comprising mixing a pretreatment solution containing a sample with a nucleic acid releasing agent and a qPCR amplification reagent, wherein the pretreatment solution includes: Tris-HCl, EDTA-2Na, sodium chloride, ribonuclease inhibitors and antibiotics; wherein the pH of the pretreatment solution is 6.5 to 8.0. The nucleic acid detection reaction solution prepared by the method of the present invention can directly perform qPCR, improve the detection efficiency, and shorten the detection time.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Detection kit and detection method for 3 species of food-borne viruses in marine products
InactiveCN101570798BHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementFood borneRotavirus RNA
The invention discloses a detection kit and a detection method for 3 species of food-borne viruses in marine products. The kit comprises reverse transcription Tag DNA polymerase with a concentration of 5U / mu L, inverse transcriptase with a concentration of 5U / muL and an RT-PCR reaction solution, wherein the RT-PCR reaction solution contains 10 millimols of Tris.HCl, 50 millimols of KCl, 25 millimols of MgCl2, 10 millimols of dNTP, a ribonuclease inhibitor with a concentration of 40 U / mu L, and 20 mu mols of downstream primer pair and 20 mu mols of upstream primer pairs of the food-borne viruses. The kit can synchronously detect hepatitis A viruses, rotaviruses and norwalk viruses. The kit has extremely high sensitivity, can detect 1*10<-7> nano gram of viral nuclei and is superior to the prior reported detection method for viruses in the marine products. In addition, the method is short in detection time, simple and quick, and suitable for quick detection.
Owner:曹际娟 +2
A test kit for human staphylococcus detection
InactiveCN110157821BLower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus hominis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus hominis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus hominis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus hominis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kit for detecting Enterobacter cloacae
InactiveCN110241239BStrong specificityLow equipment requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSingle strandBacilli
The invention provides a kit for the detection of Enterobacter cloacae, including guide RNAs specifically targeting the rpoB gene of the Enterobacter cloacae, a primer pair for amplification, hydrated TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a proteins, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), Ribonuclease Inhibitor and buffer. The kit can be used to detect the Enterobacter cloacae with high specificity, and can distinguish the Enterobacter cloacae from other Enterobacter bacteria, including Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter gergoviae and Enterobacter sakazakii. At the same time, the method using the RNA sequence described in the invention for detection takes about 1 hour, does not need any PCR instruments, and has low requirements for equipment; and time consumption of the method is significantly lower than that of the conventional bacterial culture method or the PCR sequencing method, with great clinical practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kit for detecting hemolytic staphylococcus
InactiveCN110129462BLower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus haemolyticus. The kit comprises guide RNA specifically targeting staphylococcus haemolyticus rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, LbCas12a protein, a single-chain DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. When the kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus haemolyticus, high detection specificity is achieved, and the staphylococcus haemolyticus can be distinguished from other staphylococcus such as staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus epidermidis. Meanwhile, when the RNA sequence is used to perform detection, detection time is about 1 hour, a PCR instrument is not needed, equipment requirements are evidently lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method, and a high clinical practical value is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A test kit for staphylococcus epidermidis detection
InactiveCN110157822BLower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus epidermidis. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus epidermidis rpoB gene, amplification primer pairs, hydratedTwistAmp basic kit reaction drying balls, an LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), a Ribonuclease Inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcus epidermidis, the detection specificity is high, and the staphylococcus epidermidis can be distinguished from other staphylococcocci including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus warneri, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. The RNA sequence is used for detection, the consumed time is about 1 hour, no PCR instrument is needed, the requirements for equipment are low and significantly lower than those of a traditional bacterial culture method or PCR sequencing method, and the clinical practical value is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of test kit for Staphylococcus wauserii detection
InactiveCN110144416BLower requirementStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus haemolyticusRpoB
The present invention provides a kit for detecting staphylococcus warneri. The kit comprises a guide RNA specifically targeting a staphylococcus warneri rpoB gene, an amplification primer pair, hydration TwistAmp basic kit reaction drying spheres, LbCas12a protein, a single-stranded DNA probe (ssDNA), an ribonuclease inhibitor and a buffer solution. The kit is used for detecting the staphylococcuswarneri and high in detection specificity, and can separate the staphylococcus warneri from other staphylococci, including staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus hominis, staphylococcus epidermidis, staphylococcus capitis and staphylococcus haemolyticus. At the same time, the use of the RNA sequence for the detection takes about 1 hour, does not require a PCR instrument, has low requirements on equipment, and is significantly lower than a conventional bacterial culture method or a PCR sequencing method and large in clinical practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com