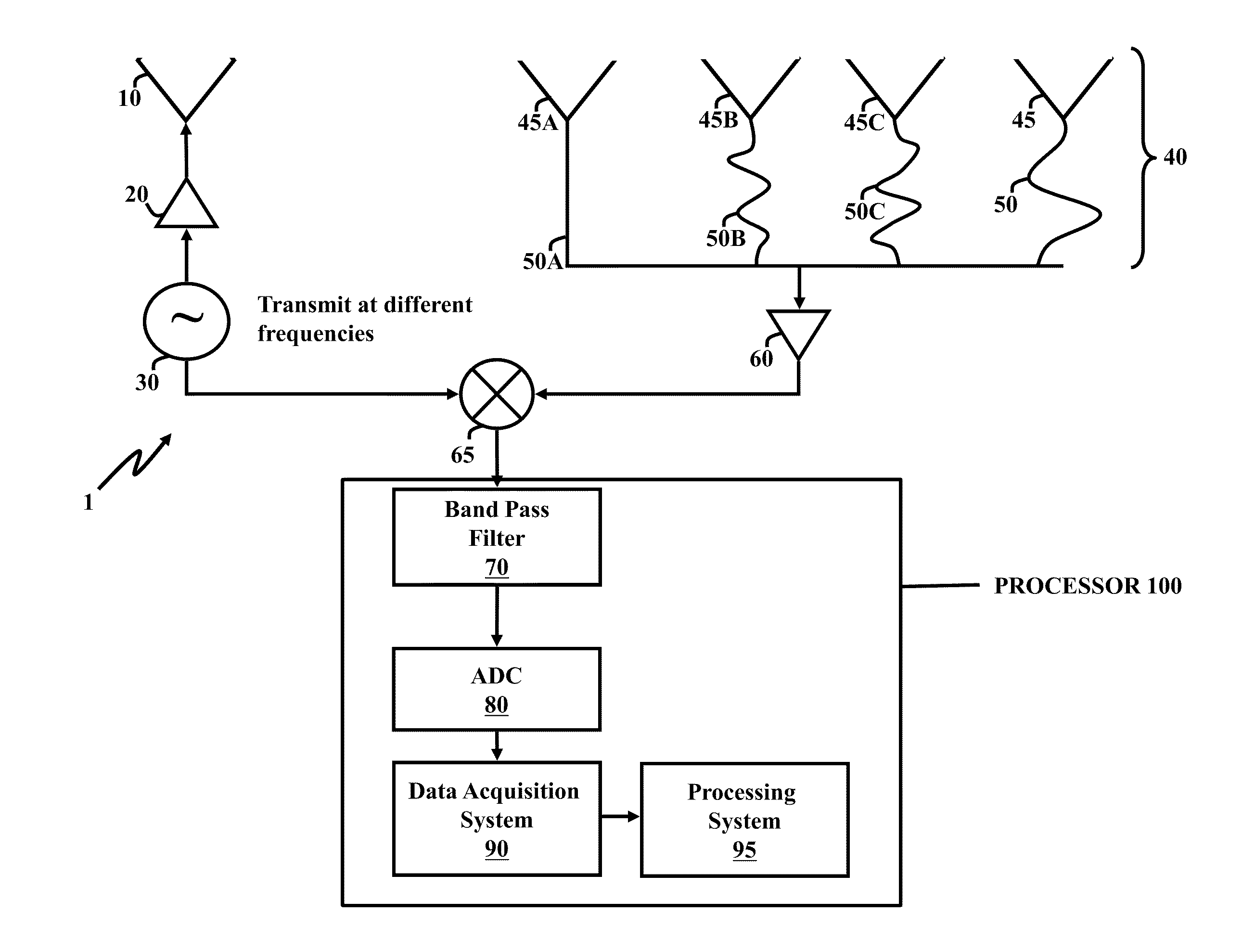
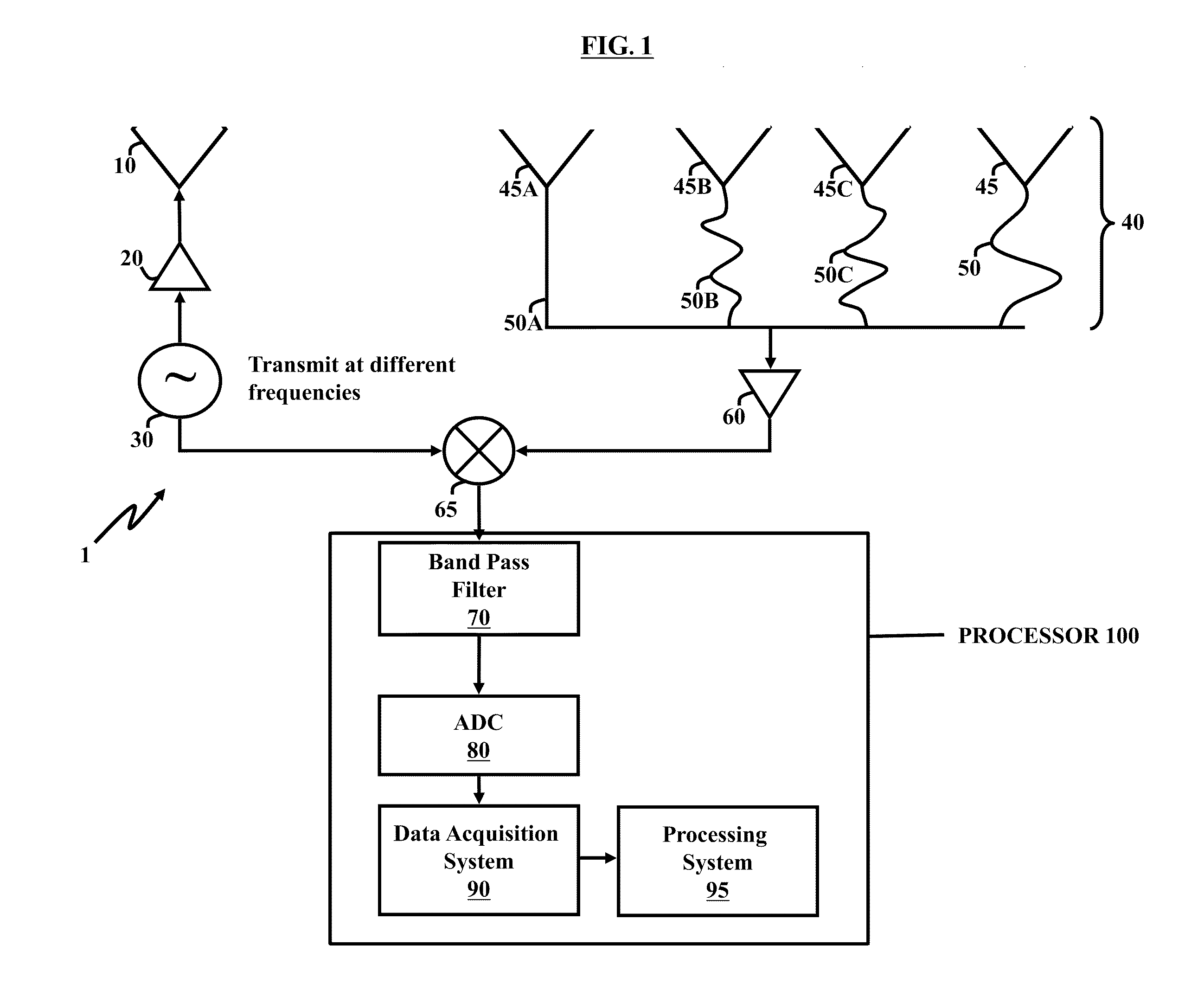
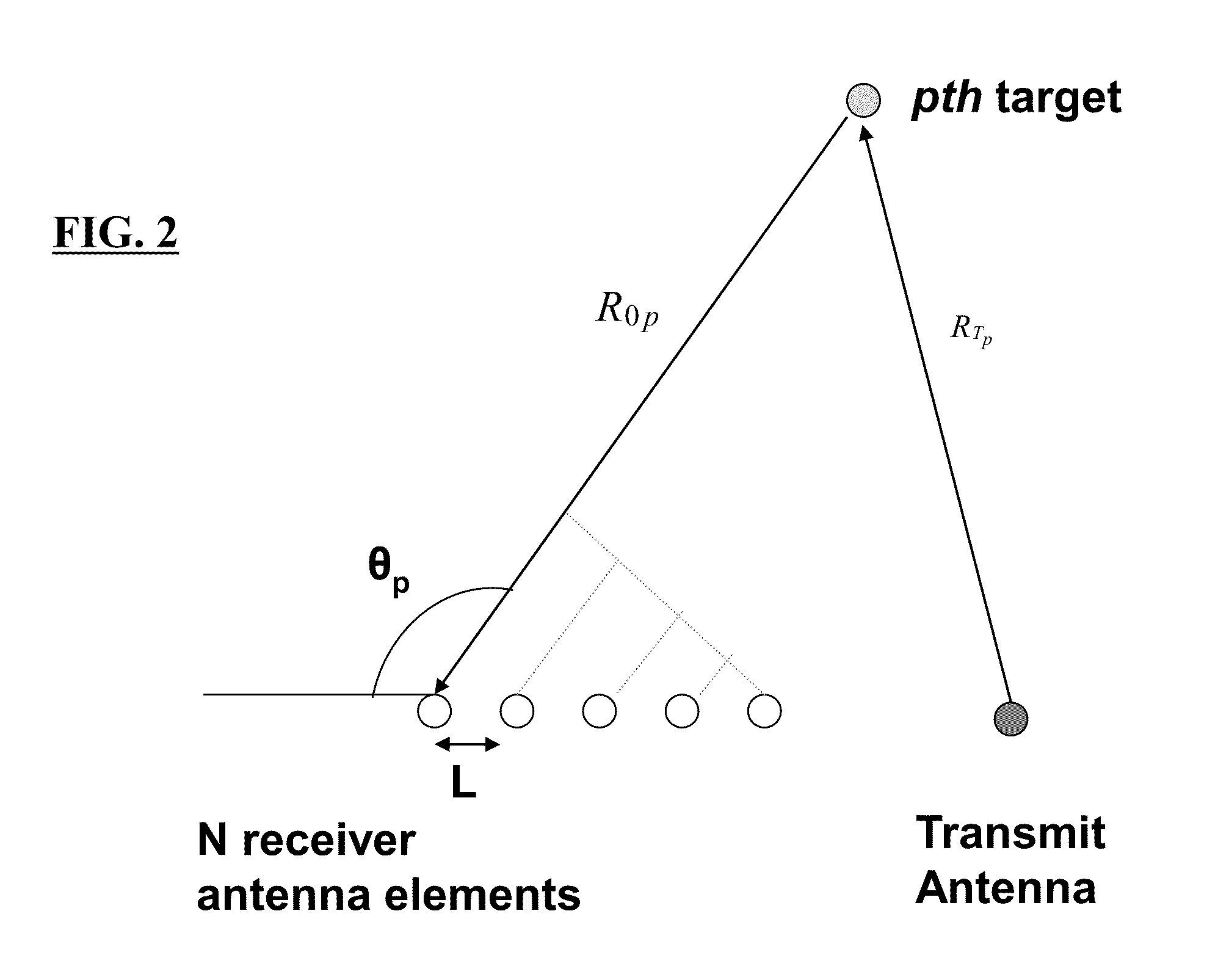
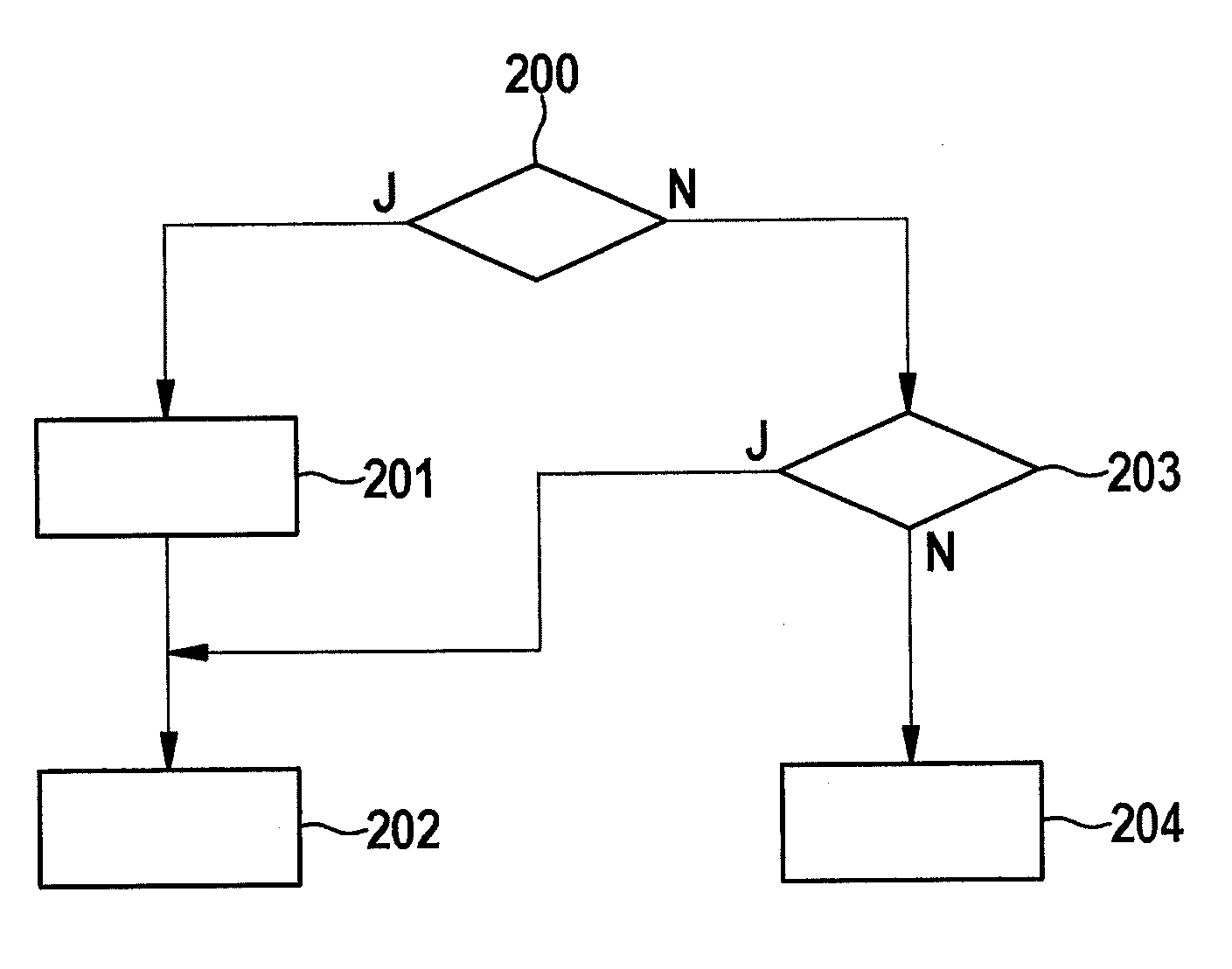
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
389 results about "Radar transmitter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
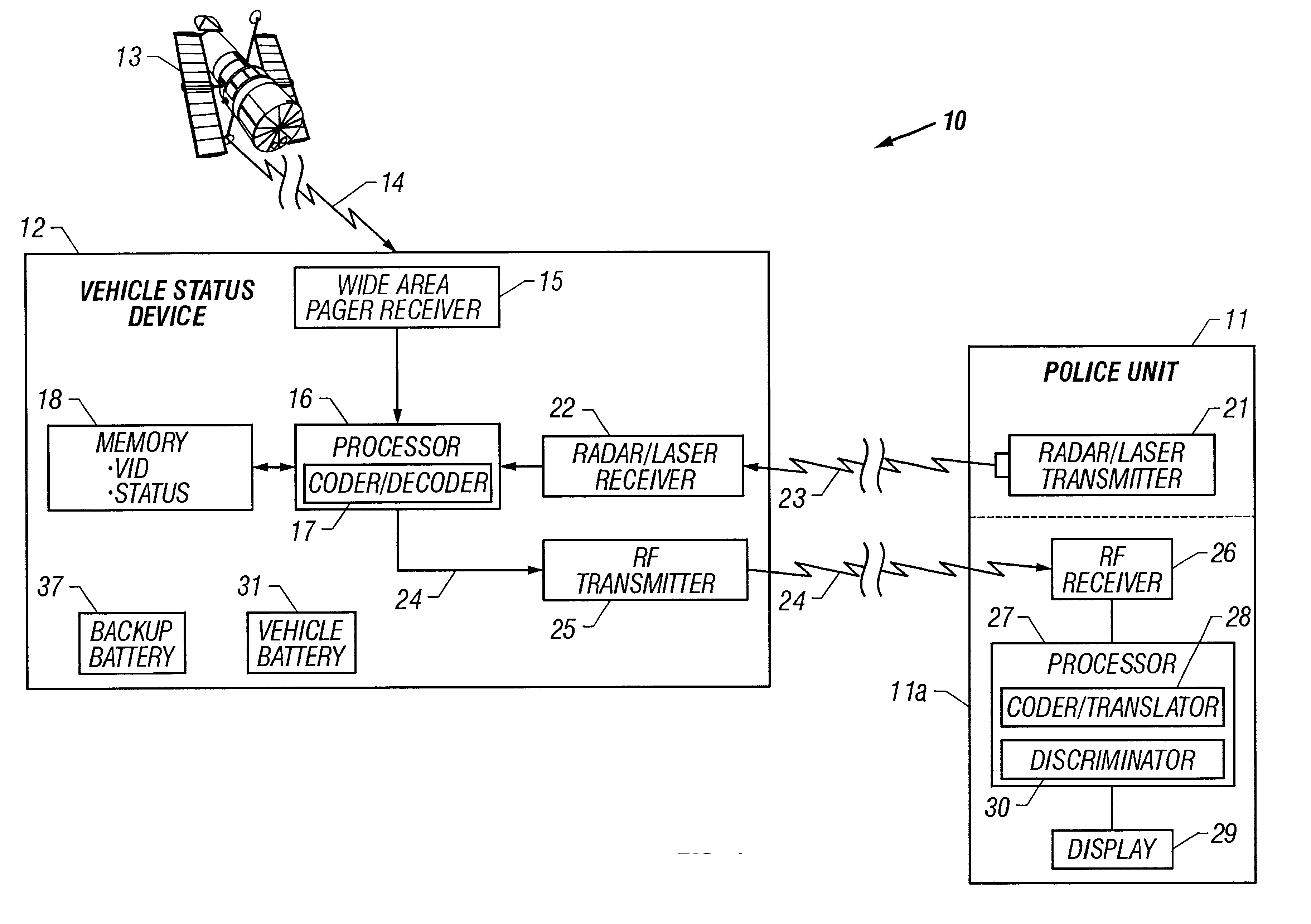
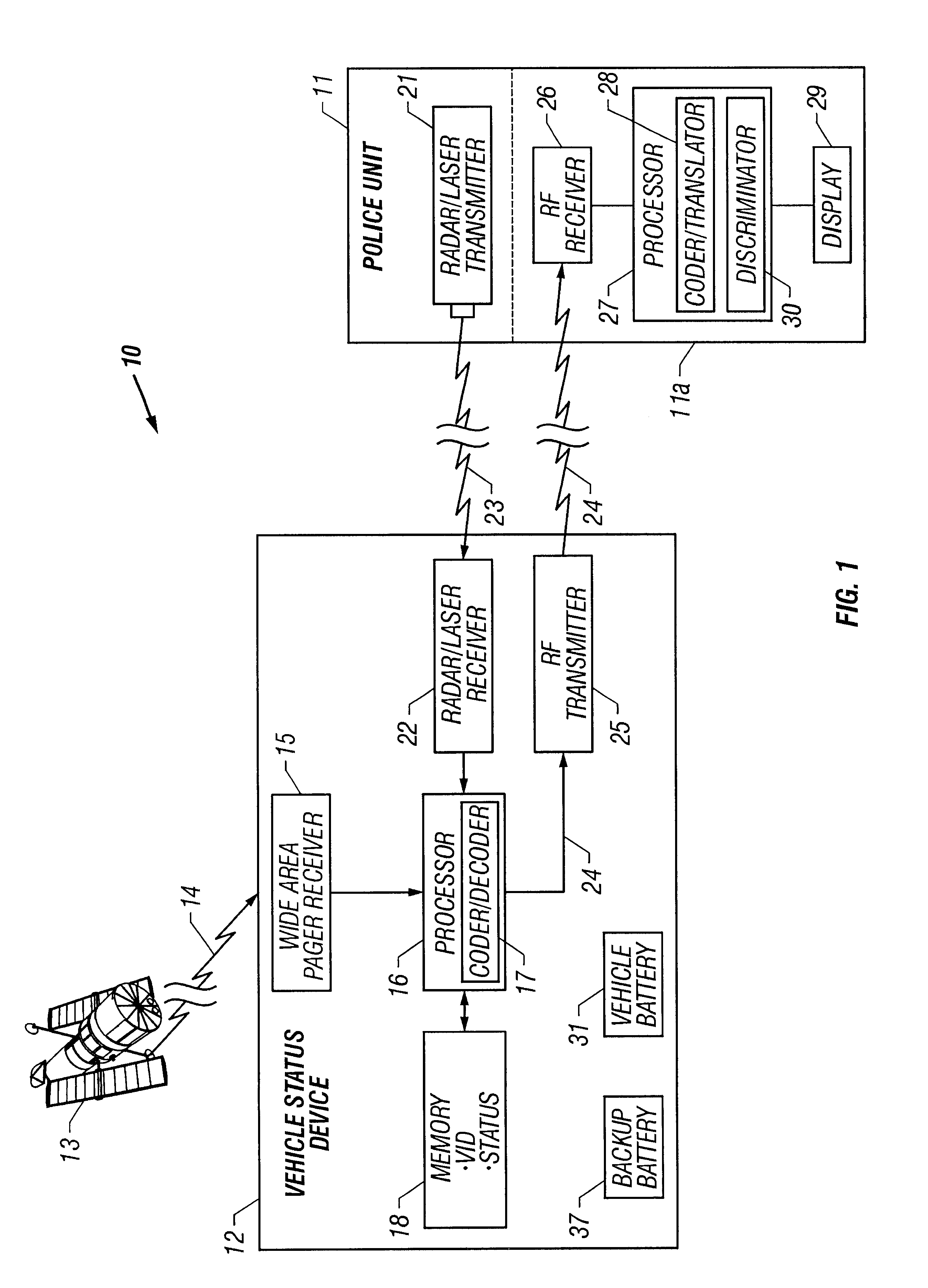
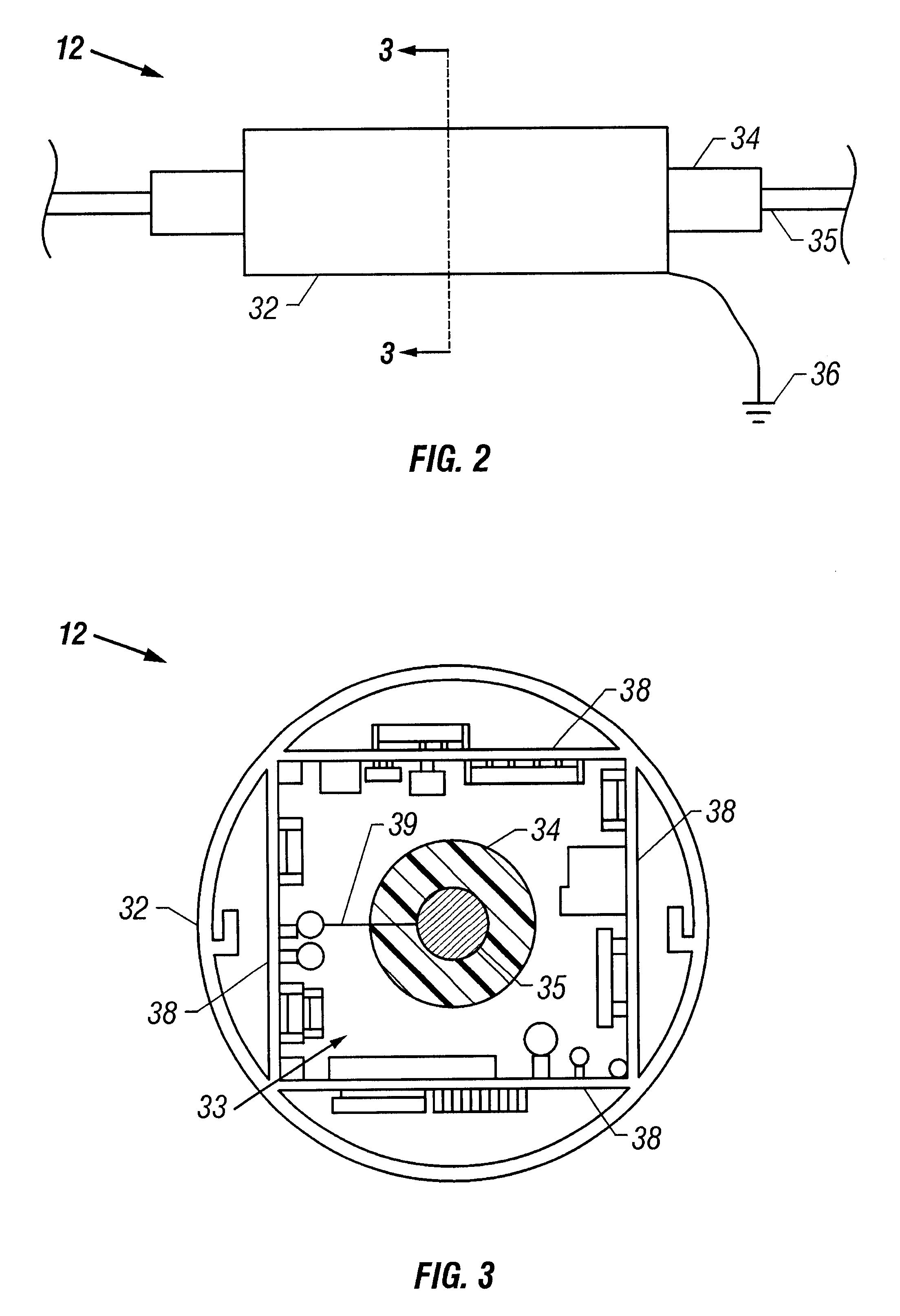
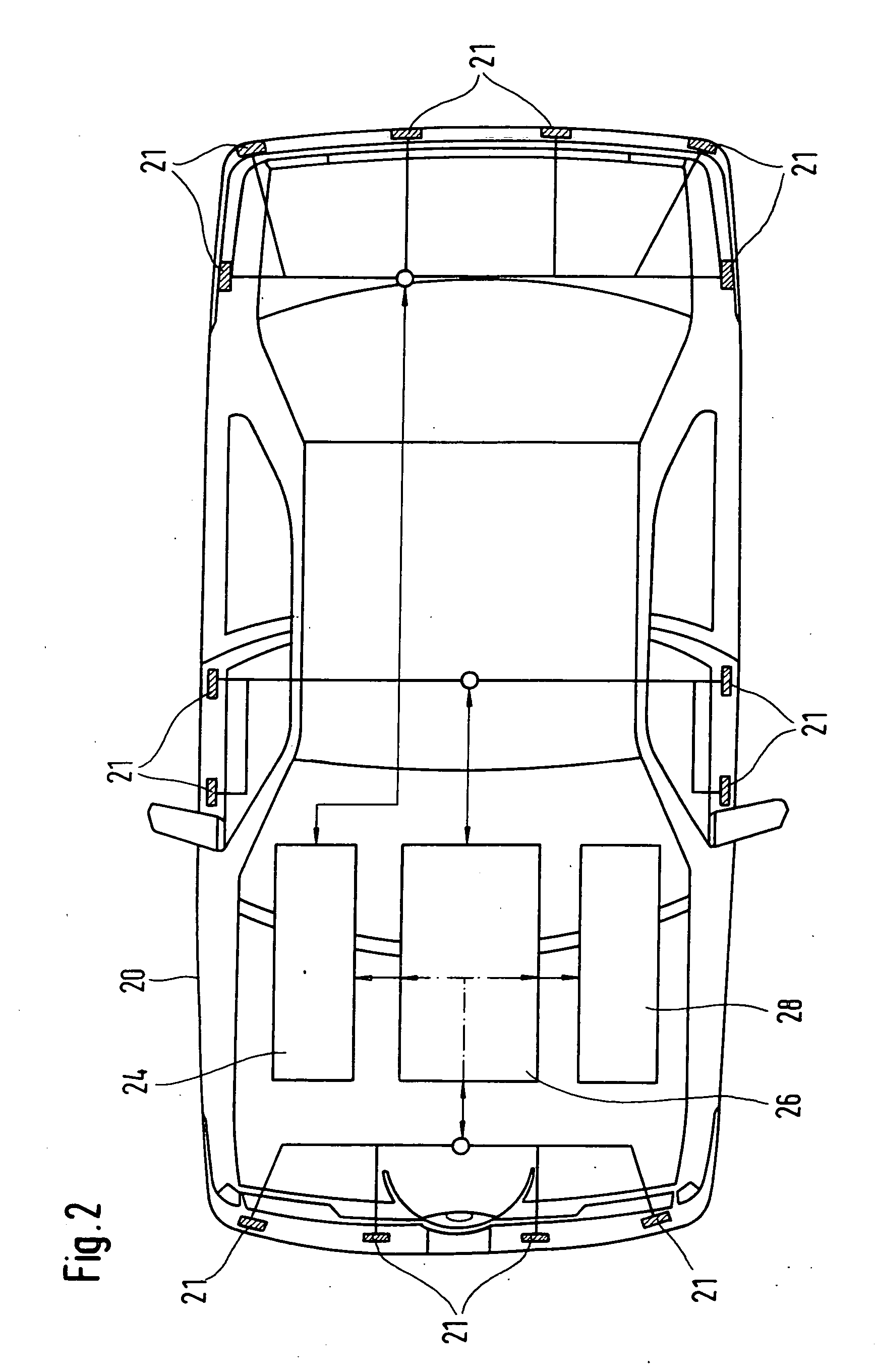
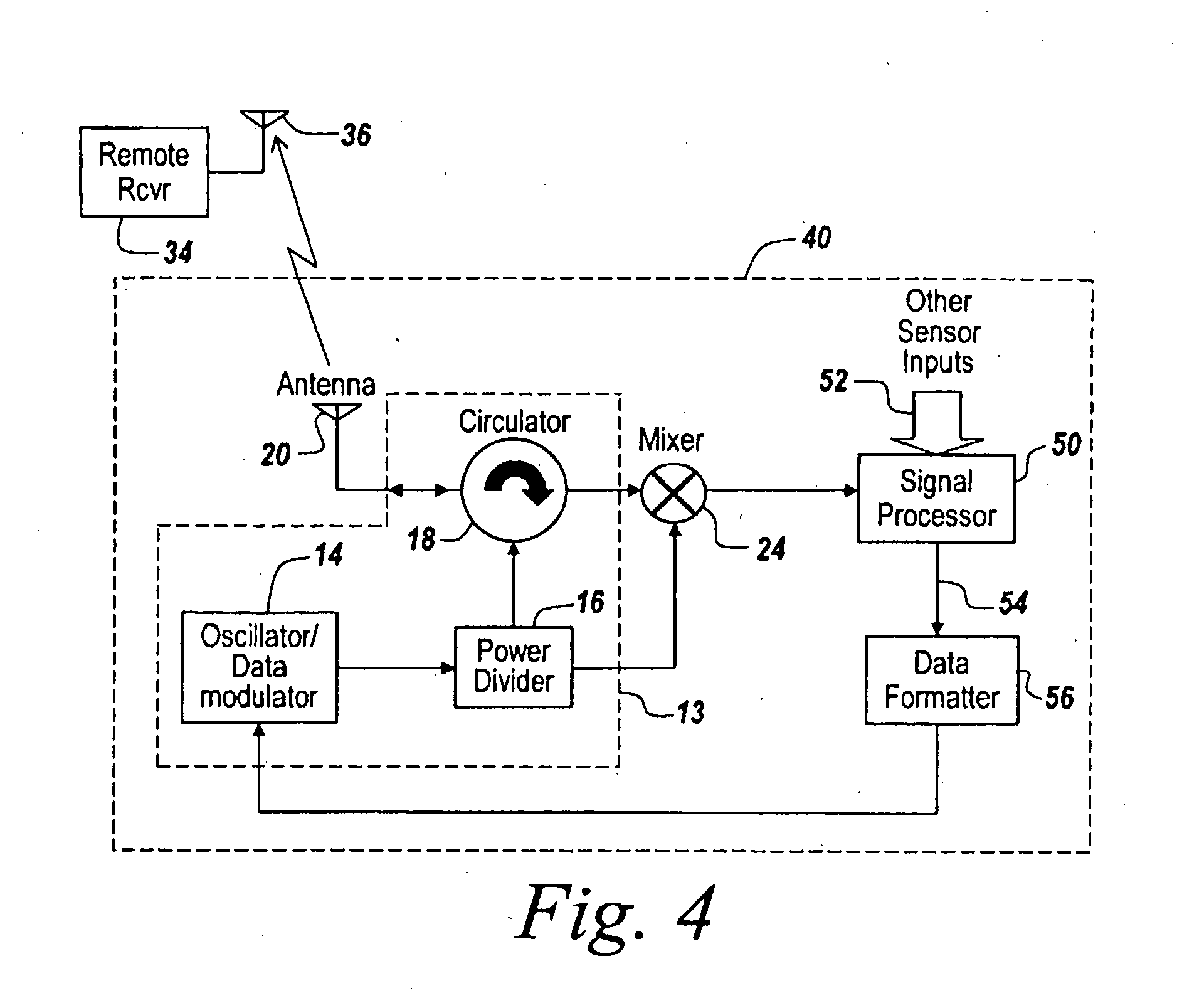
Vehicle-status device and system for remotely updating and locally indicating the status of a vehicle
A vehicle status device and system for remotely updating and locally indicating the status of a vehicle. The vehicle status device is located in a vehicle and indicates status information for the vehicle on a vehicle-status indicator on the vehicle when the device is interrogated by an interrogating unit. The device includes a database of status information for the vehicle and owner. An update receiver in the device receives encoded updated information from a wide area paging network for storage in the database. An interrogation receiver receives an interrogation signal from the interrogating unit, and a processor decodes the status information and sends it to the status indicator in response. The system also includes an interrogating unit which includes a police radar transmitter or a laser transmitter for transmitting the interrogation signal to the vehicle status device. The status indicator includes a set of summary status lights and may also include an LCD display for detailed status information. In an alternative embodiment, the device uses a wireless Internet access device to access external databases and download the vehicle status information either periodically or on demand. The information may be passed directly to the status indicator without the need for an internal database.
Owner:INTELLIGENT VEHICLE SYST
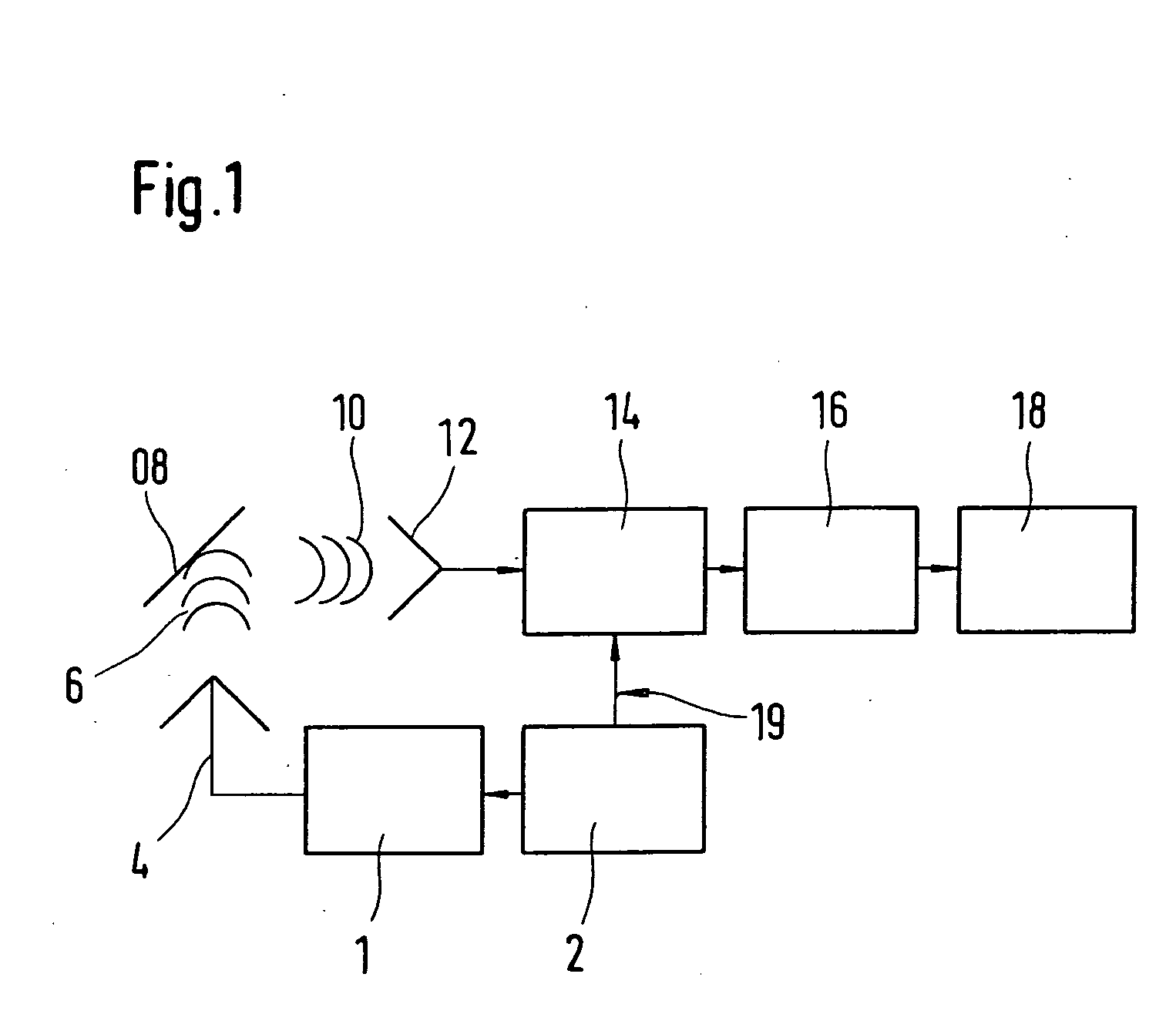
Method and device for the adaptive regulation of power
InactiveUS20060109170A1Minimizes signal irregularityLess interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBraking systemsControl powerIn vehicle
A method and a device for adaptively controlling power in a radar device having a radar transmitter and a radar receiver are provided, in particular for applications in vehicles. The radar signals are emitted, and radar signals reflected off of target objects are received and checked for irregularities. The transmitting power of the radar transmitter is reduced when irregularities occur which are attributable to interference caused by neighboring radar transmitters.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
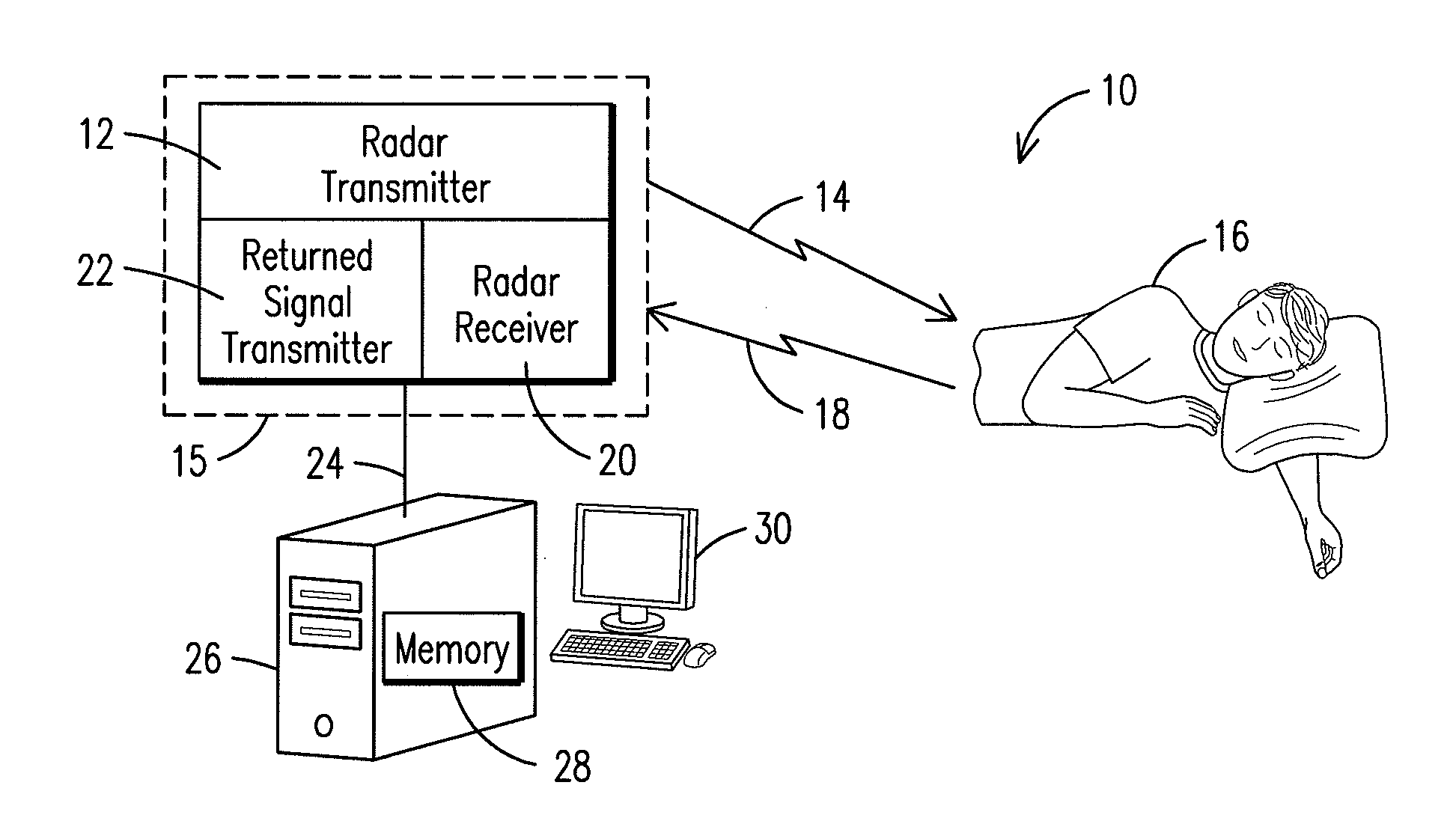
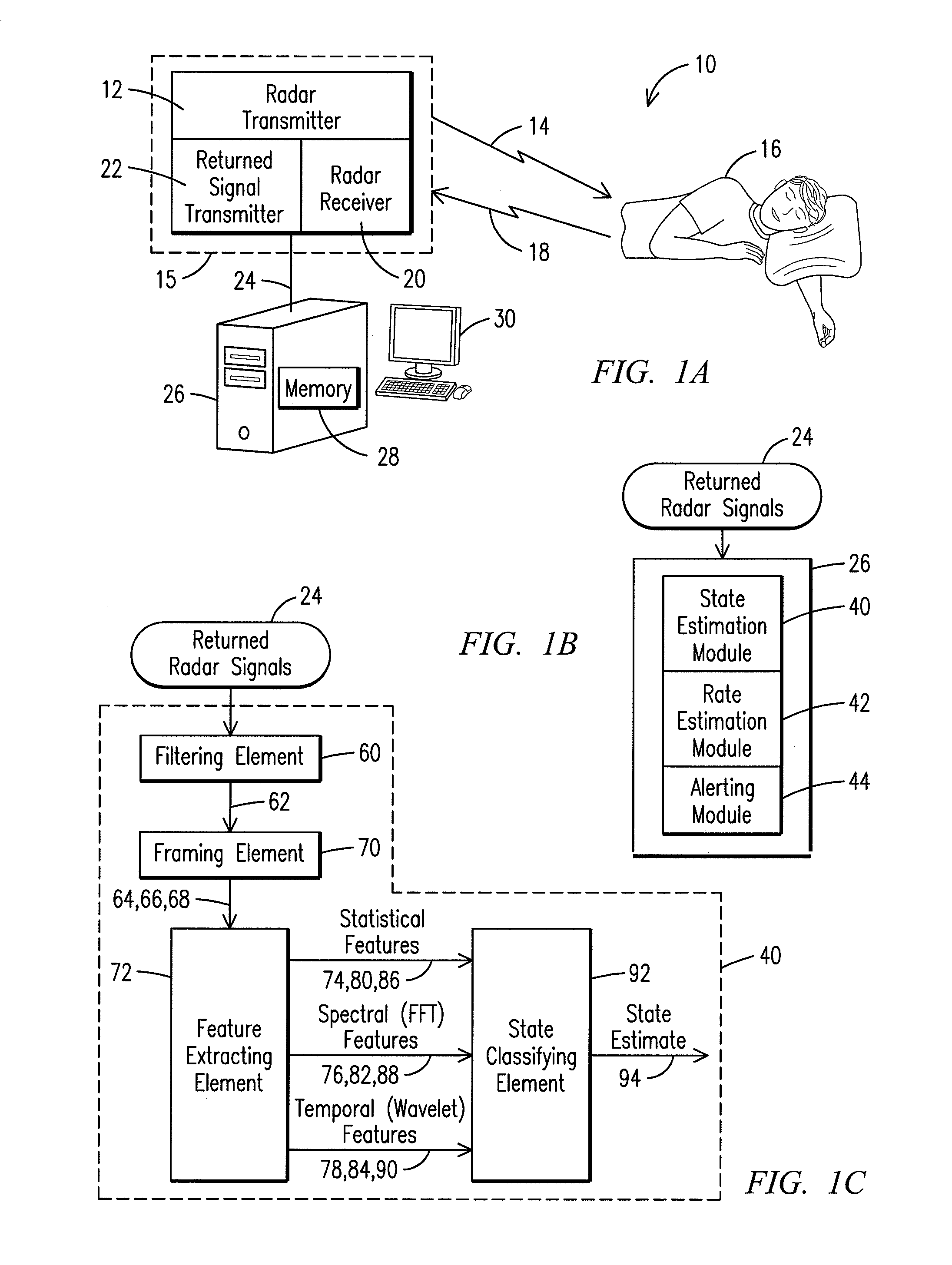
Physiology Monitoring and Alerting System and Process
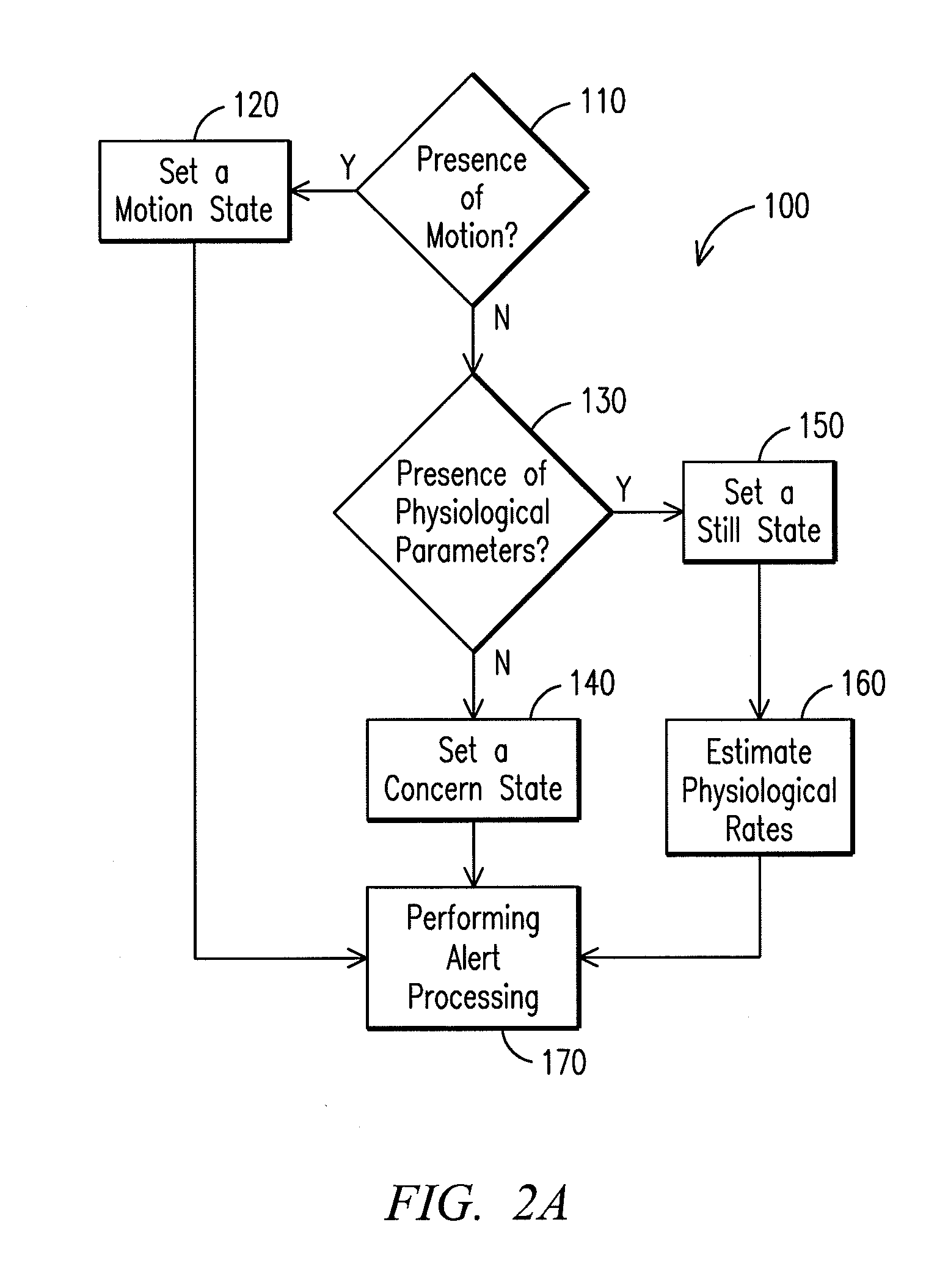
A system for monitoring physiology, having: a RADAR transmitter and a RADAR receiver; a state estimation module configured to process a returned RADAR signal to detect a presence of motion and set a motion state upon said presence of motion, said state estimation module configured to detect a presence of one or more physiological parameters including heartbeat and respiration, and said state estimation module configured to assign a still state or a concern state based on said presence of physiological parameters; a rate estimation module configured to estimate one or more estimated physiological rates including an estimated respiration rate and an estimated heart rate; and an alerting module configured to provide an alert if an alert value exceeds an alert value threshold, wherein the alert value is derived from at least one of the motion state, concern state, still state and the estimated physiological rates.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
3D terrain imaging system of interferometric synthetic aperture radar and elevation mapping method thereof
InactiveCN101551455AReal-time quick-look observationAchieve observationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
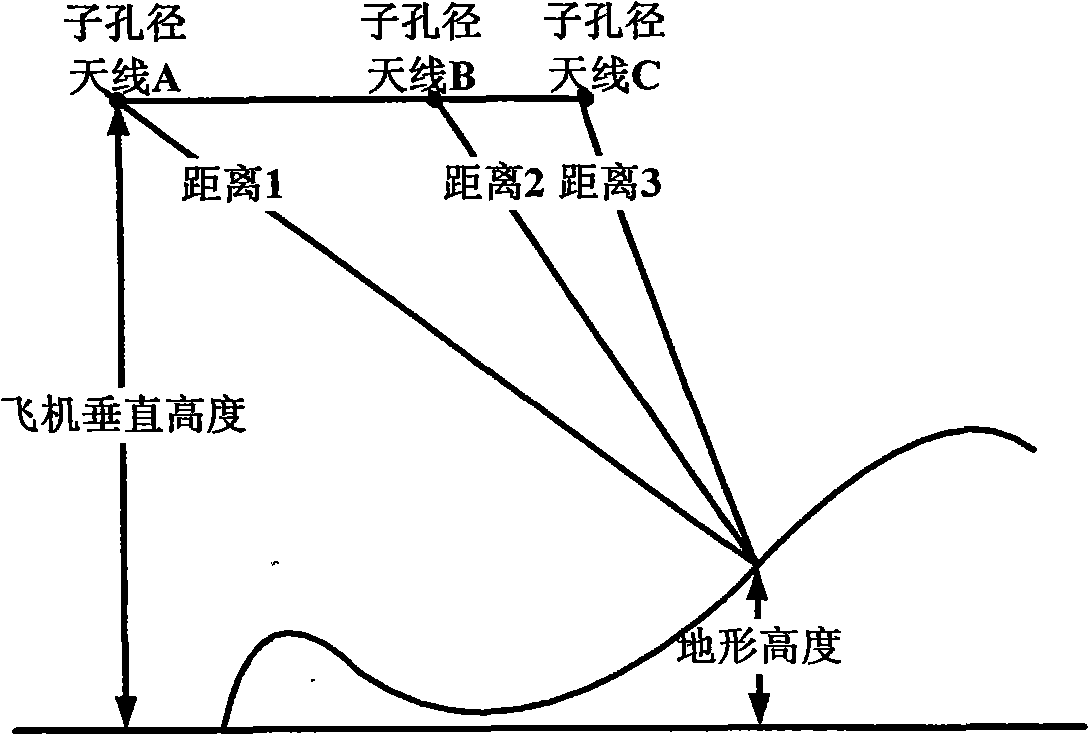
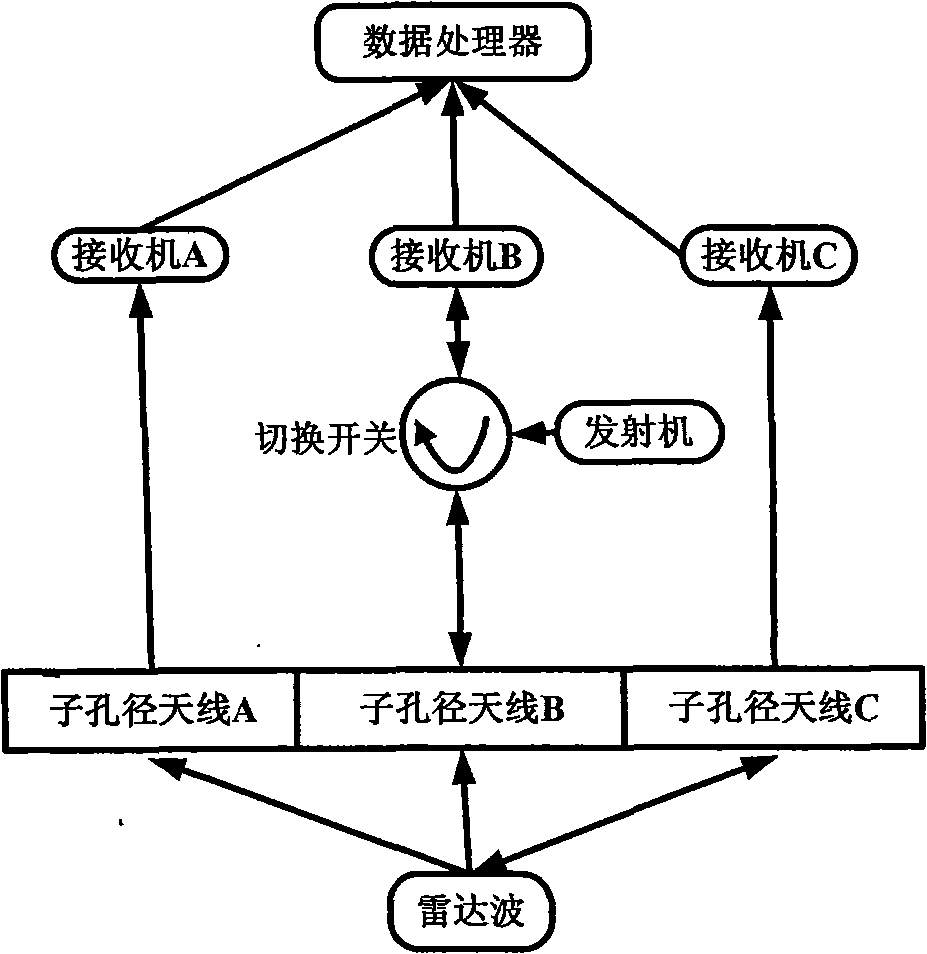
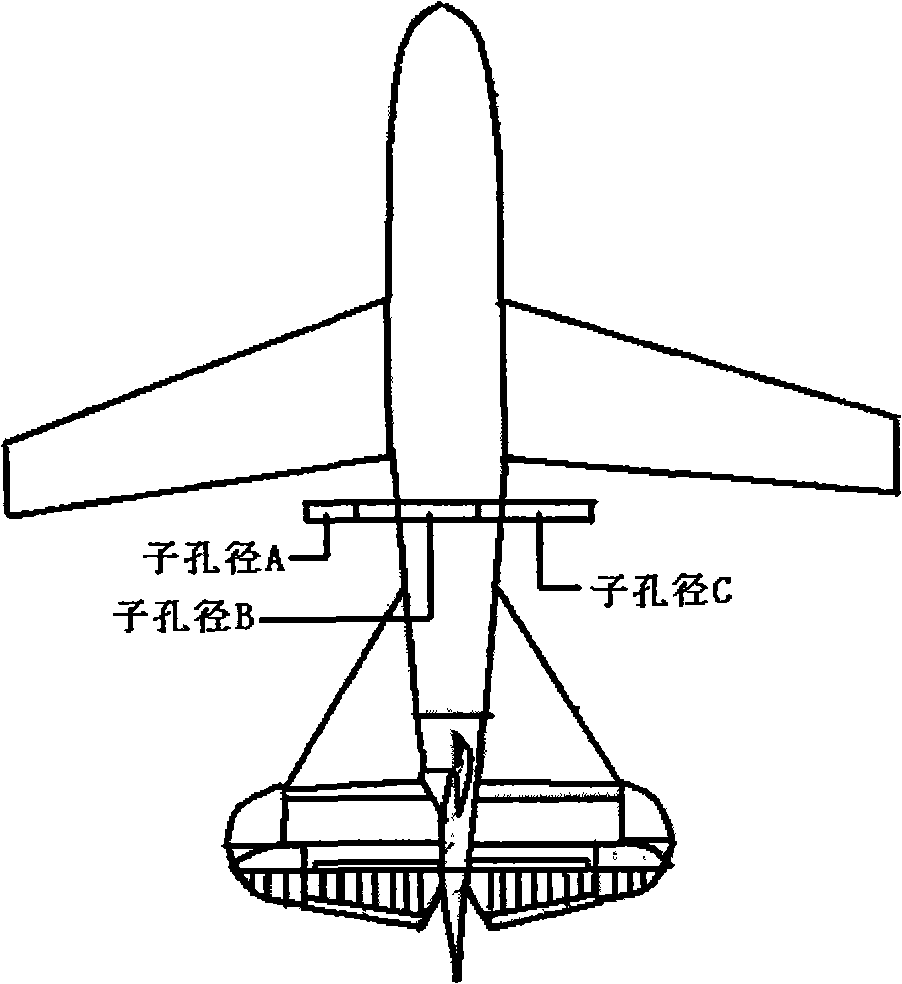
The invention discloses a 3D terrain imaging system of the interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and an elevation mapping method thereof, which mainly solve the problems that the existing InSAR has bad imaging pragmaticality and can not implement 3D elevation mapping on the fast-changing terrain and the transilient terrain. The system comprises three sub-aperture antennas, a radar transmitter, a radar receiver and an imaging data processor; the imaging signal processor comprises a SAR image processing unit and an InSAR image processing unit. The invention receives radar echo through the three sub-apertures, then conducts SAR imaging process on the radar echo respectively received by the three sub-apertures, and then conducts InSAR imaging process on the obtained SAR complex pattern, wherein the InSAR imaging process comprises image registration, phase filtering and phase unfolding based on cluster analysis. The processed InSAR phase unfolded image is processed with an elevation inversion to recover a three dimensional digital elevation map. The invention has the advantages of wide adaptability to mapped terrains, and high imaging effectiveness, therefore, the invention can be used in the mapping of the 3D terrain.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
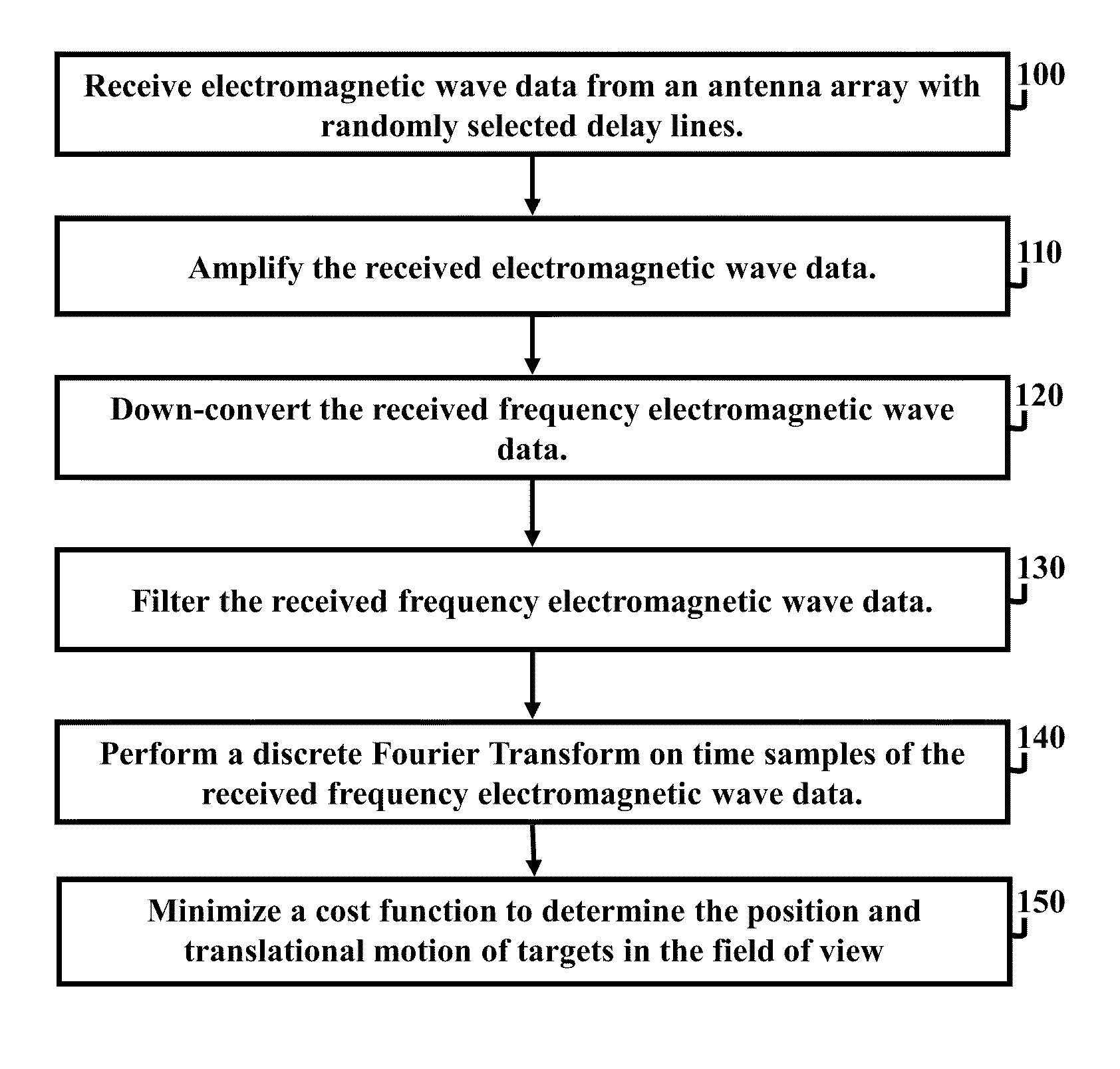
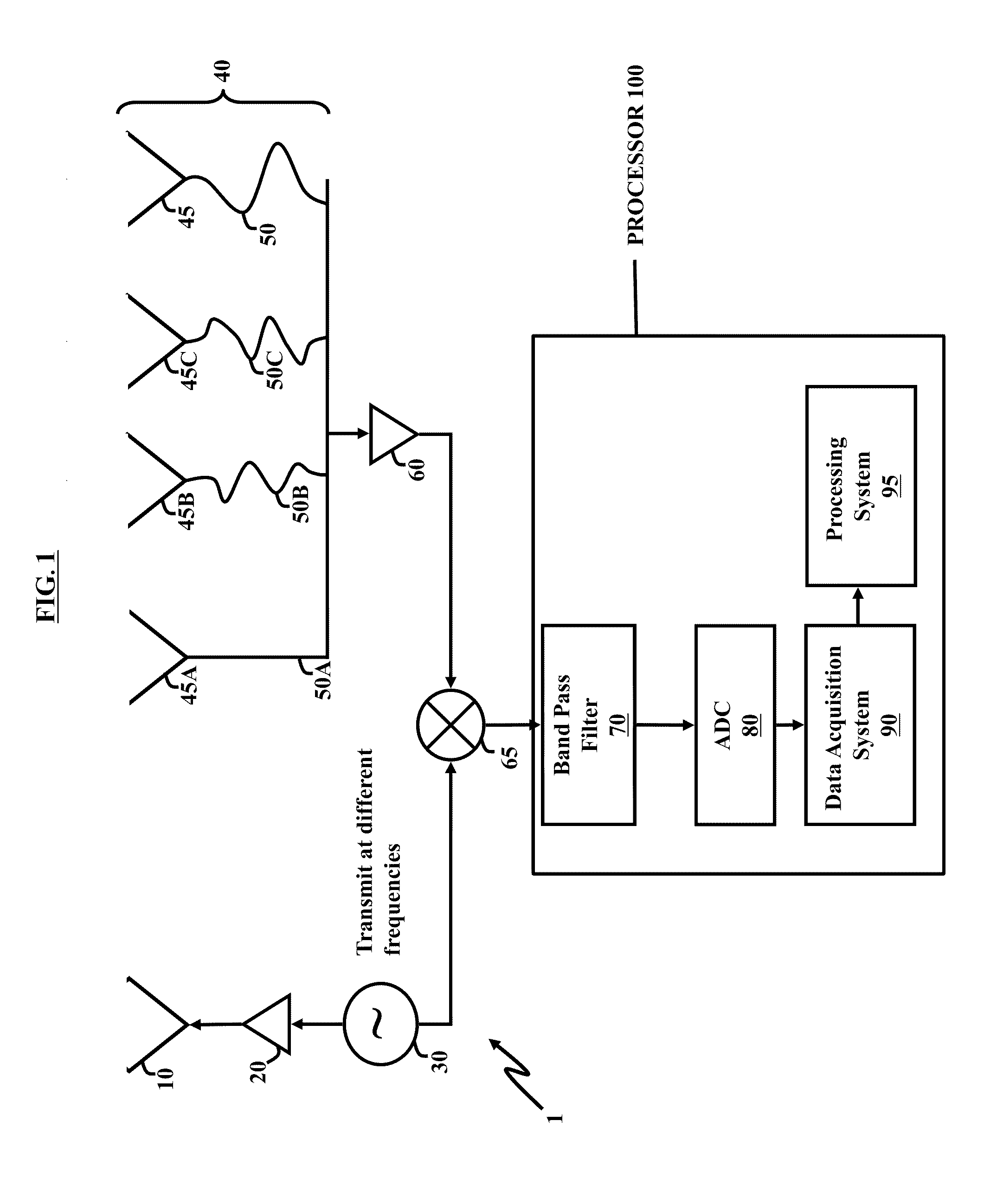
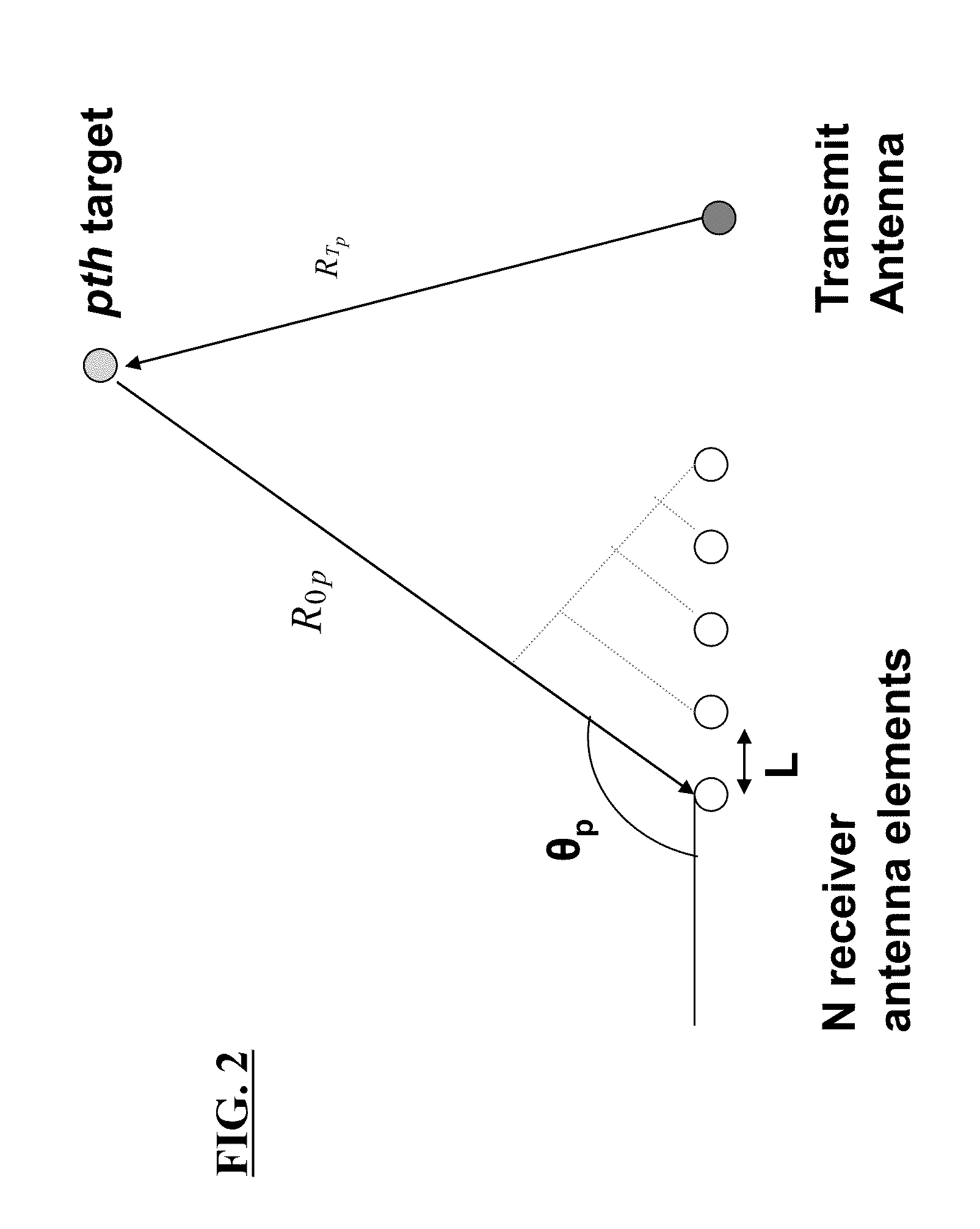
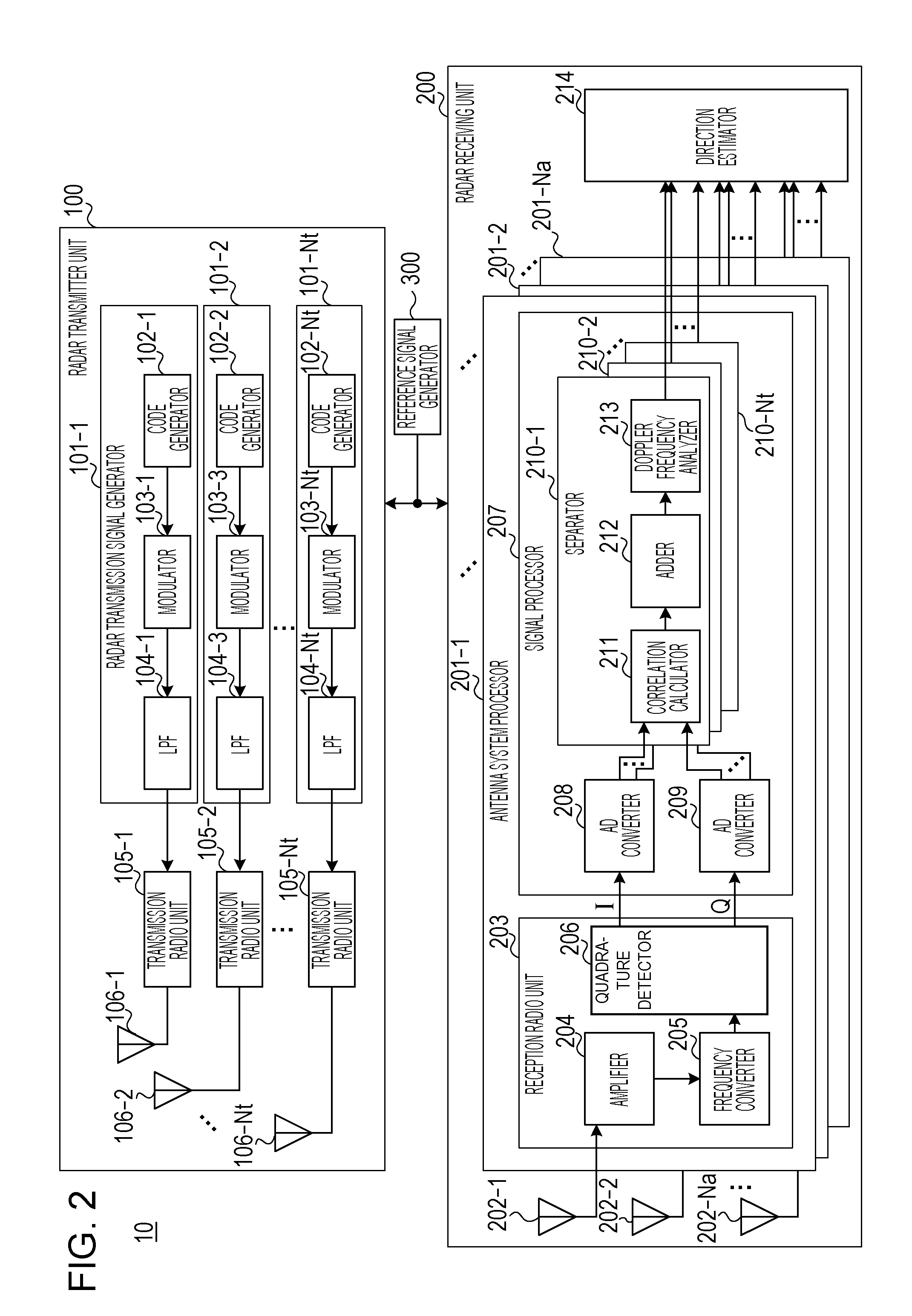
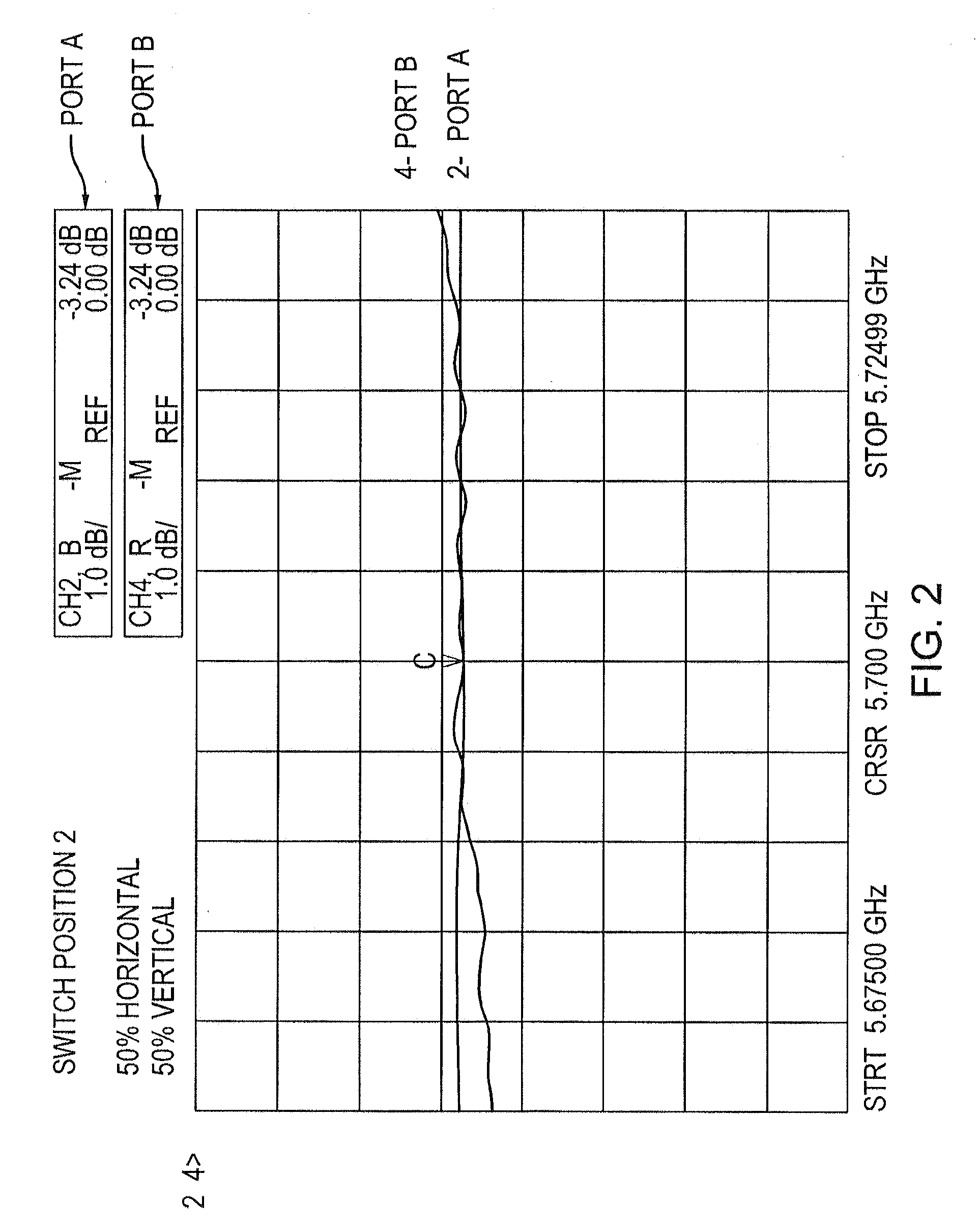
Radar system and antenna with delay lines and method thereof
InactiveUS8330650B2Good range and angular resolutionLow costDirection findersAntennasRadar systemsBeam pattern
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
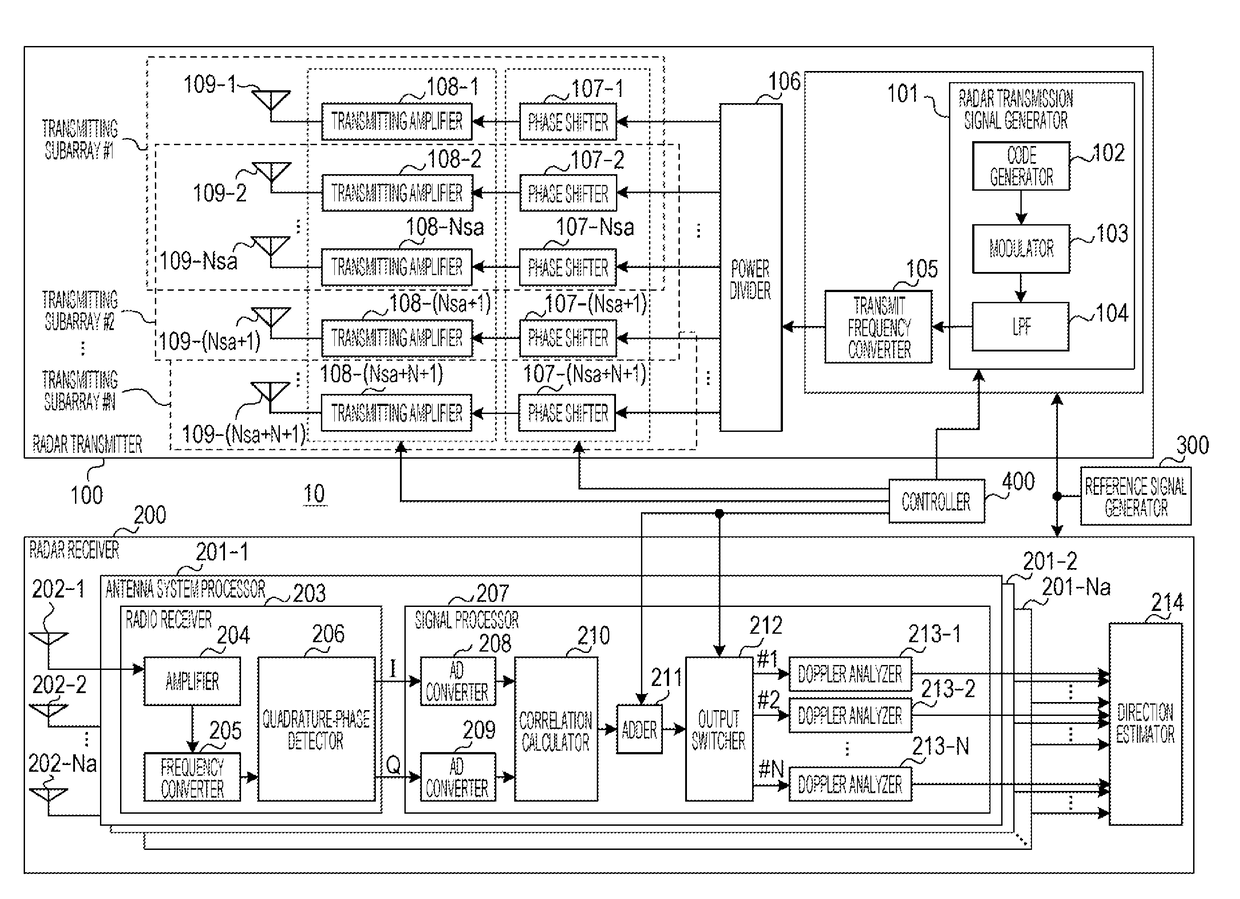
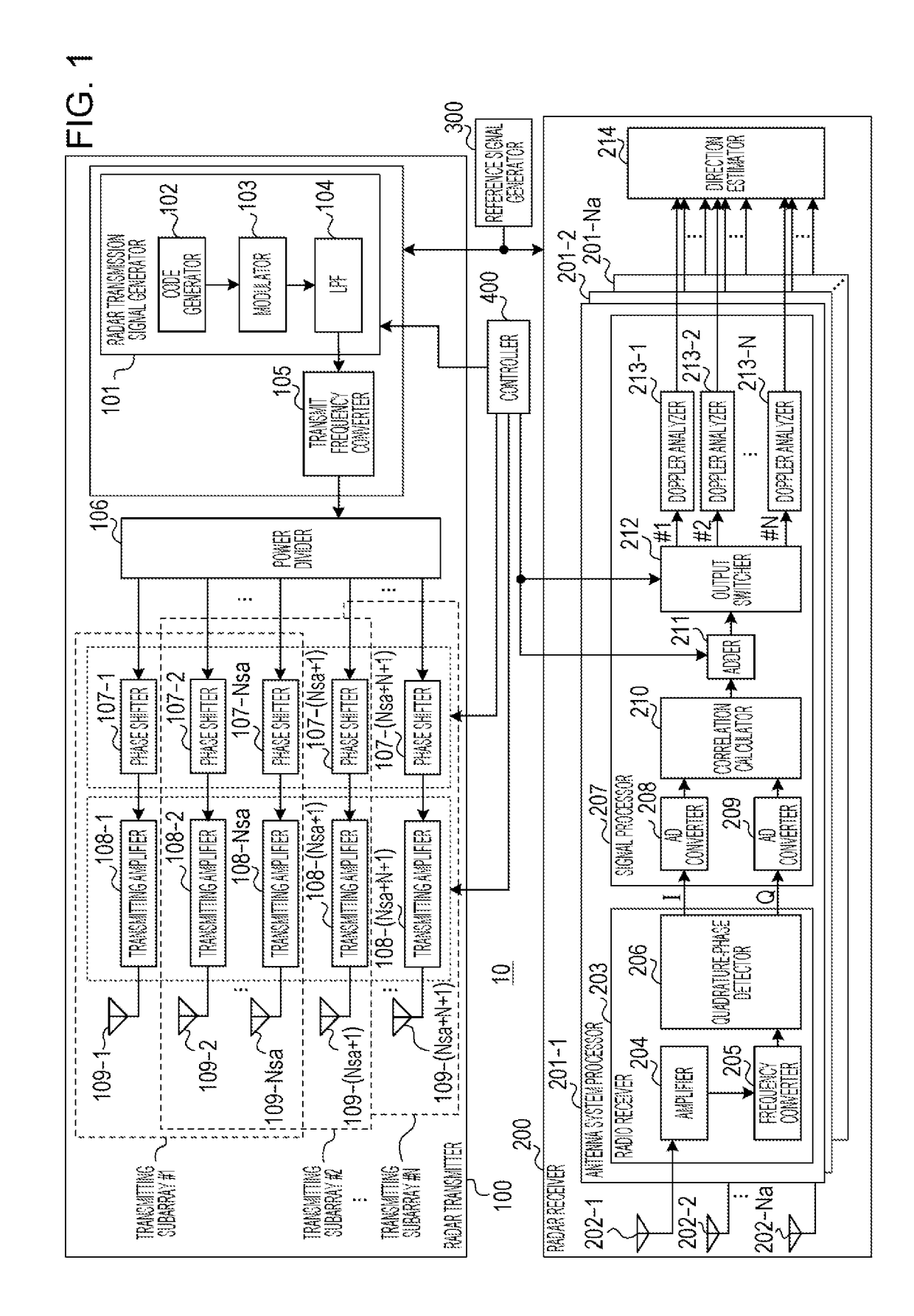
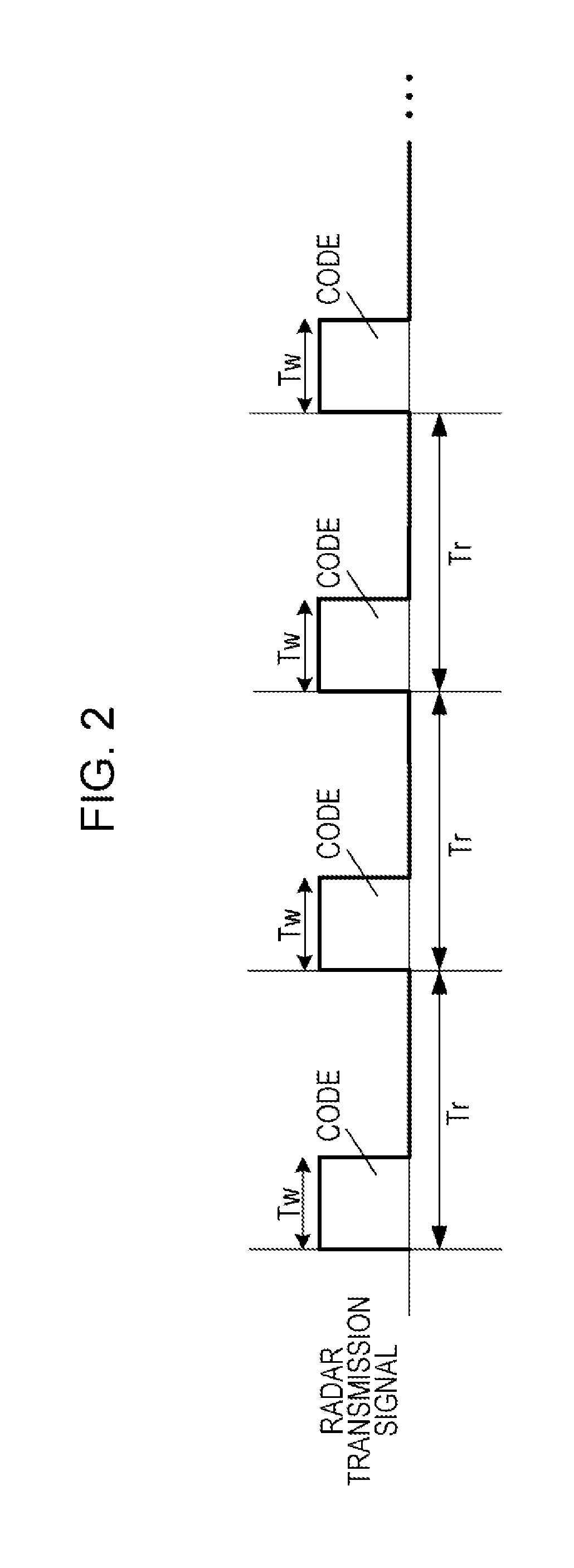
Radar apparatus
ActiveUS20180088224A1Reduce circuit sizePolarisation/directional diversityIndividually energised antenna arraysReflected wavesRadar signals
A radar apparatus includes: a radar transmitter that transmits a plurality of radar signals while switching among a plurality of transmitting subarrays; and a radar receiver that receives reflected-wave signals produced by the plurality of radar signals being reflected by a target, the plurality of radar signals being transmitted from the respective transmitting subarrays. In the radar apparatus, each of the plurality of transmitting subarrays includes a plurality of transmitting antennas, and adjacent ones of the plurality of transmitting subarrays share at least one of the plurality of transmitting antennas with each other.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System for sensing aircraft and other objects
InactiveUS20110169684A1Reduce RF NoiseReduce noisePosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCommunications systemFlight vehicle
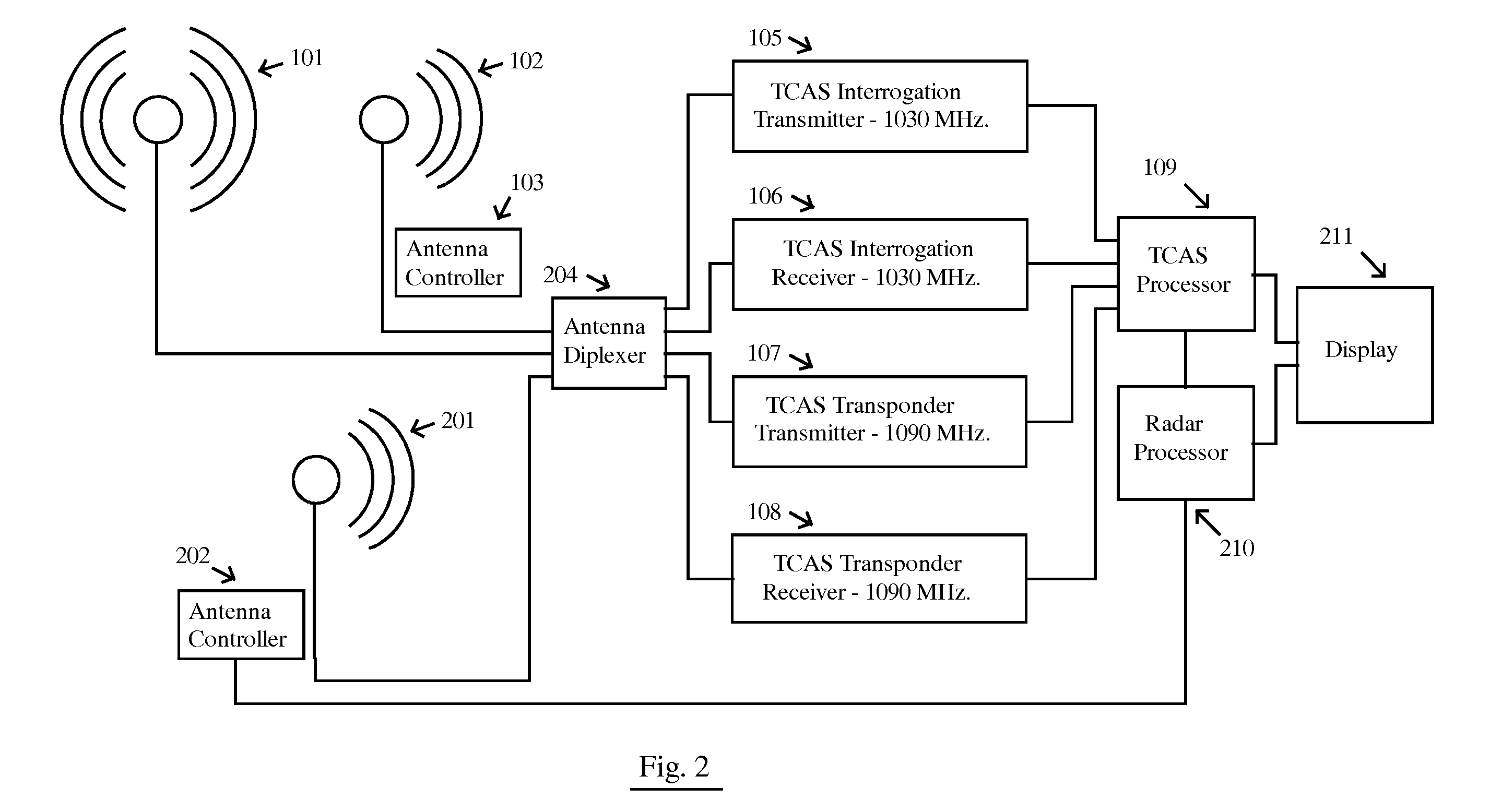
A system for sensing aircraft and other objects uses bistatic radar with spread-spectrum signals transmitted from remotely located sources such as aircraft flying at very high altitudes or from a satellite constellation. A bistatic spread spectrum radar system using a satellite constellation can be integrated with a communications system and / or with a system using long baseline radar interferometry to validate the digital terrain elevation database. The reliability and safety of TCAS and ADS-B are improved by using the signals transmitted from a TCAS or ADS-B unit as a radar transmitter with a receiver used to receive reflections. Aircraft and other objects using spread spectrum radar are detected by using two separate receiving systems. Cross-Correlation between the outputs of the two receiving systems reveals whether a noise signal is produced by the receiving systems themselves or is coming from the outside.
Owner:MARGOLIN JED
Radar device
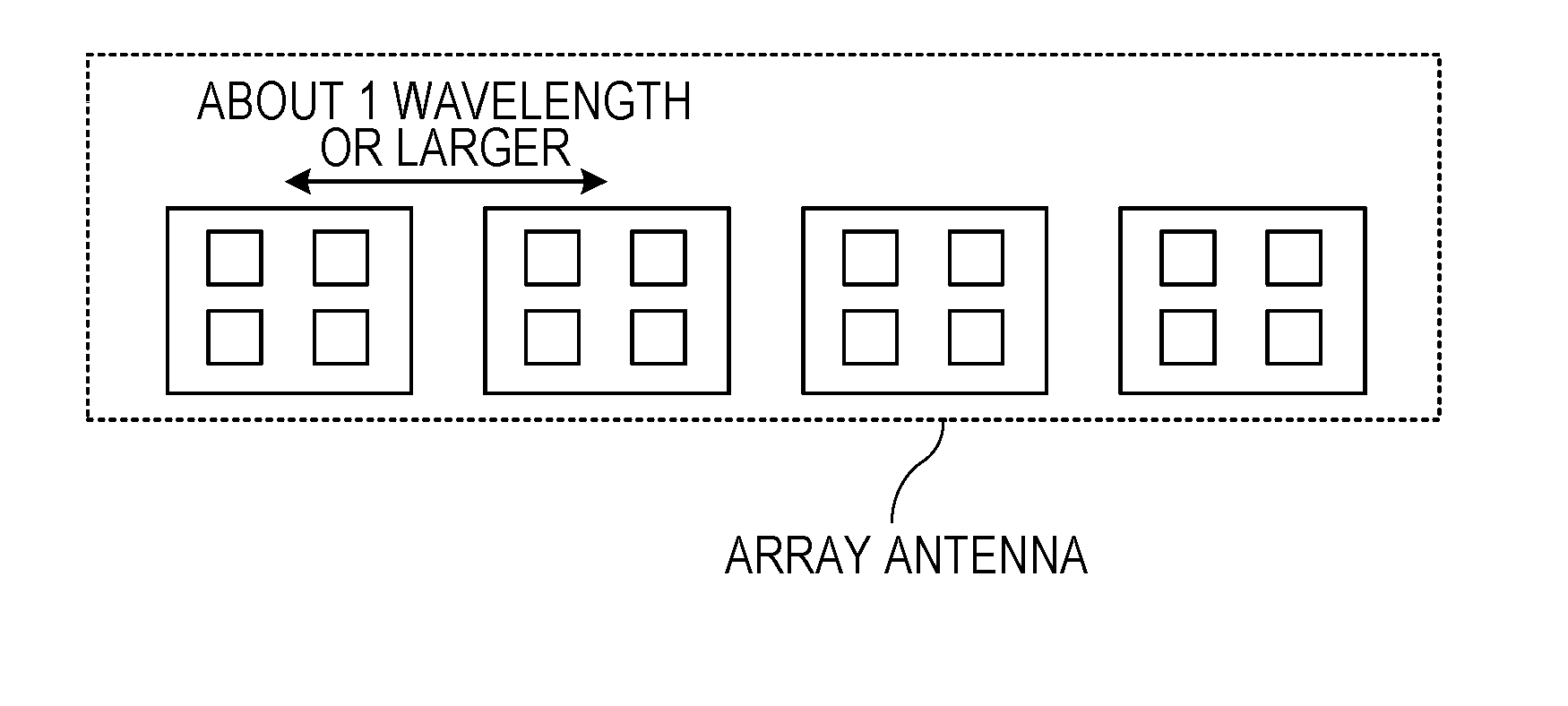
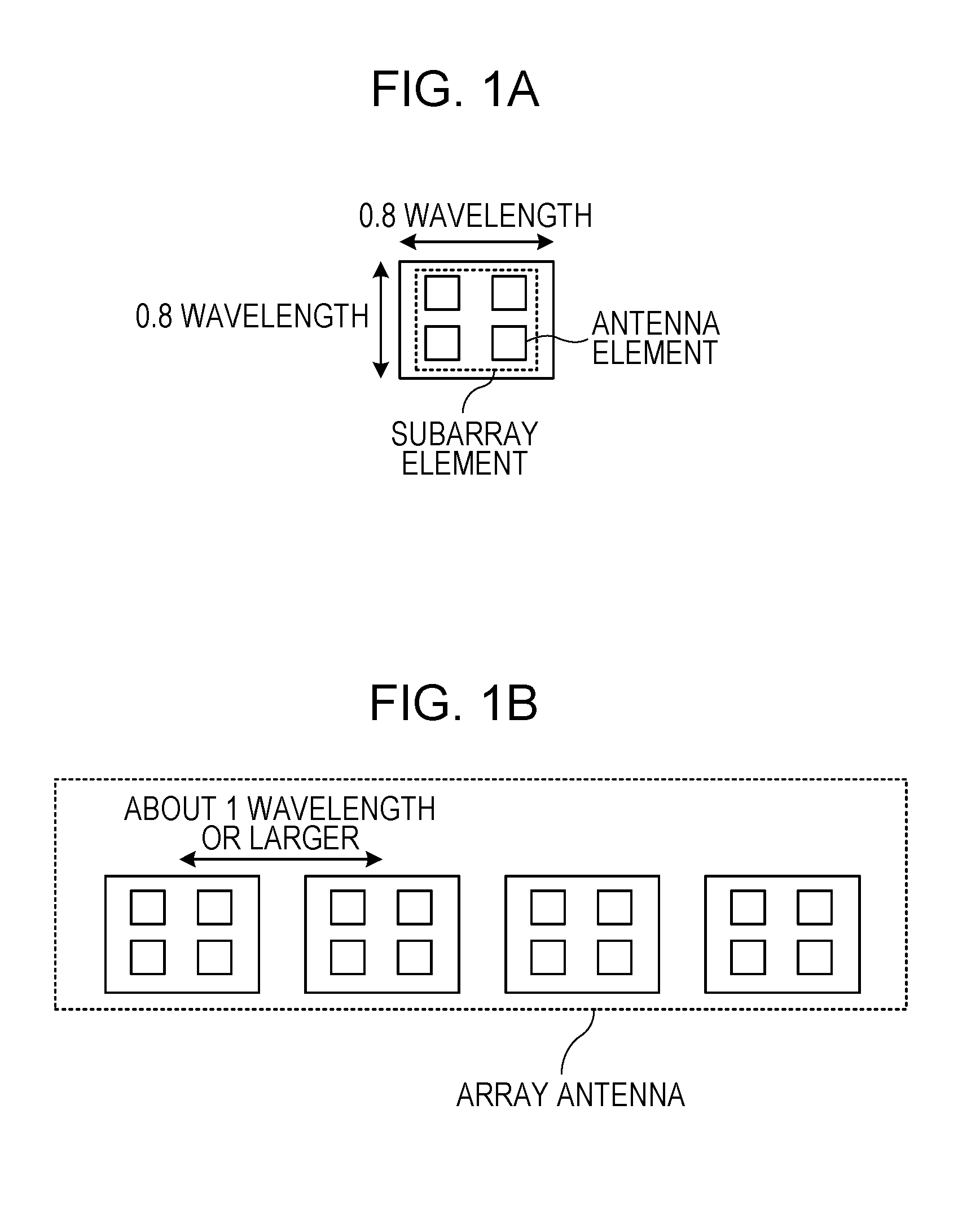
ActiveUS20160285172A1Avoid it happening againDesired directivityIndividually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna elementTransmit array
A radar transmitter transmits a radar signal through a transmitting array antenna at a predetermined transmission period, and a radar receiver receives a reflected wave signal which is the radar signal reflected by a target through a receiving array antenna. A transmitting array antenna and a receiving array antenna each include multiple subarray elements, the subarray elements in the transmitting array antenna and the receiving array antenna are linearly arranged in a first direction, each subarray element includes multiple antenna elements, the subarray element has a dimension larger than a predetermined antenna element spacing in the first direction, and an absolute value of a difference between a subarray element spacing of the transmitting array antenna and a subarray element spacing of the receiving array antenna is equal to the predetermined antenna element spacing.
Owner:PANASONIC HLDG CORP
Radar system and antenna with delay lines and method thereof
InactiveUS20110273325A1Good range and angular resolutionLow costDirection findersAntennasRadar systemsBeam pattern
A radar system, apparatus, and method includes at least one radar transmitter for transmitting an electromagnetic waveform; a receiving antenna comprising a plurality of receiving antenna elements and delay lines, each of the plurality of receiving antenna elements receiving the return signal operatively associated with a predetermined delay line; each delay line having a delay length which produces a different phase delay in the return signal; the different phase delays producing substantially different antenna patterns for the received signal at a given frequency; at least one processor operatively connected to receive data from the plurality of delay lines; the at least one processor operating to analyze the substantially different beam patterns for a given frequency; whereby the processing of the data produces results indicating the presence and location of a target.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Method for operating a MIMO radar
ActiveUS20140347211A1Easy to operateExclude influenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionObject motionCovariance
In a method for operating a MIMO radar, an influence of an object motion on an angle estimate is substantially eliminated, and a time multiplex schema having a transmission sequence and transmission instants of transmitters of the MIMO radar is identified by optimizing the following mathematical relationship: d _ pulses , opt = arg max d _ pulses [ Var S ( d _ pulses ) - ( Cov S ( d _ pulses , t ) ) 2 / Var S ( t _ ) ] in which: dpulses,opt is optimized positions of the transmitters in the sequence in which they transmit; dpulses is positions of the transmitters in the sequence in which they transmit; t is transmission instants; VarS is sample variance; and CovS is sample covariance.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Heating element on the polymer inside surface of a motor vehicle front-end module/bumper in an operative connection to a radar transmitter/receiver unit
InactiveUS20060086710A1Excellent radar transmittingExcellent receiving characteristicVehicle seatsDielectric heating circuitsMobile vehicleElectrical conductor
A heating element for an inside surface of a front-end module / bumper for a motor vehicle. The heating element is operatively connected to a radar transmitting / receiving unit. The heating element comprises a heating film formed of a polymer, an array of conductor strips integrated into the heating film, and an electronic control element that controls the conductor strips. The array of conductor strips is divided into an inner region through which a radar beam from the radar transmitting / receiving unit is transmitted, and an outer region through which the radar beam is not transmitted. The conductor strips in the inner region are inclined by angles of about 45° to about 90° relative to a polarization plane of the radar beam. The conductor strips in the outer region are arranged in a meandering pattern.
Owner:REHAU AG & CO
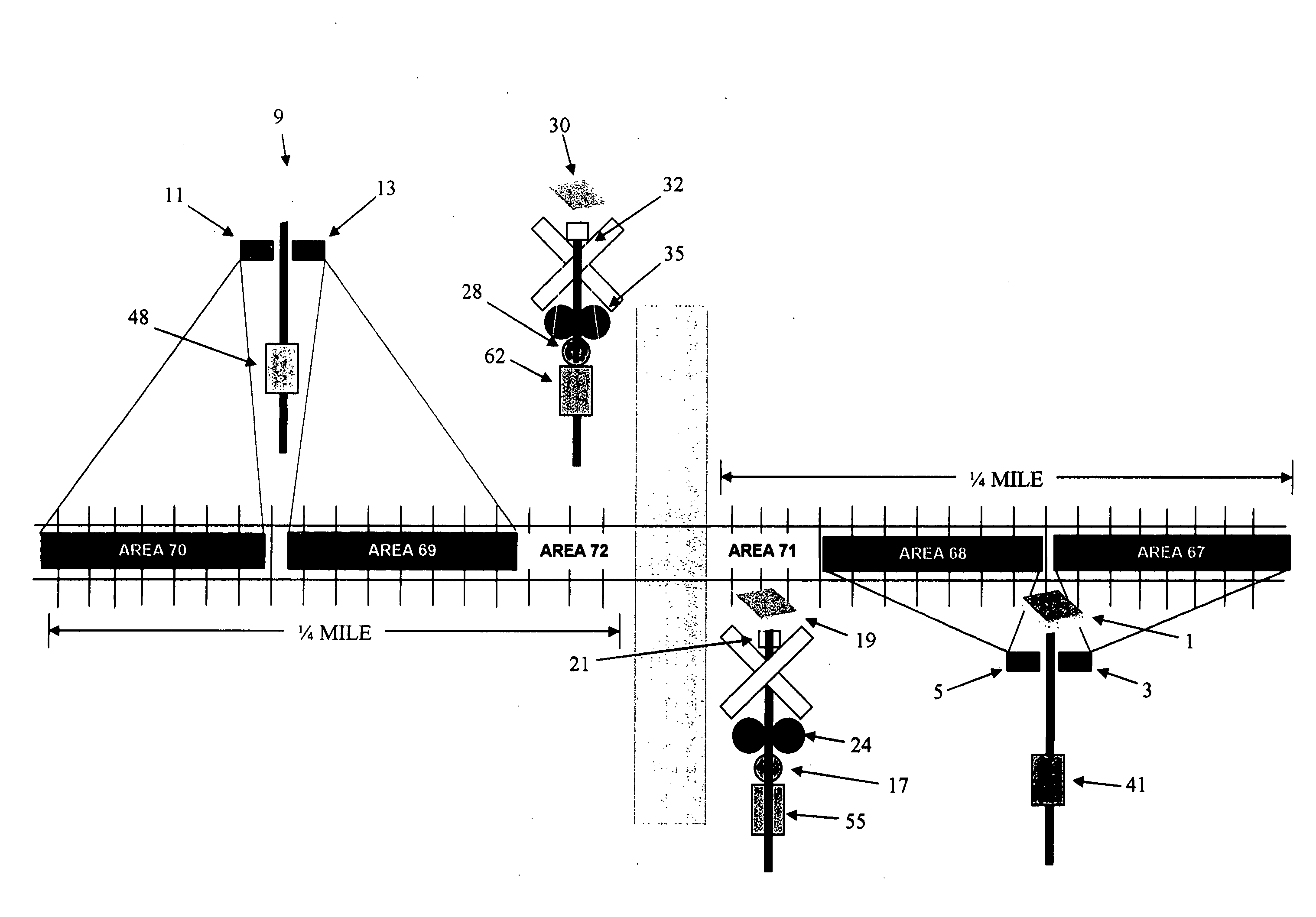
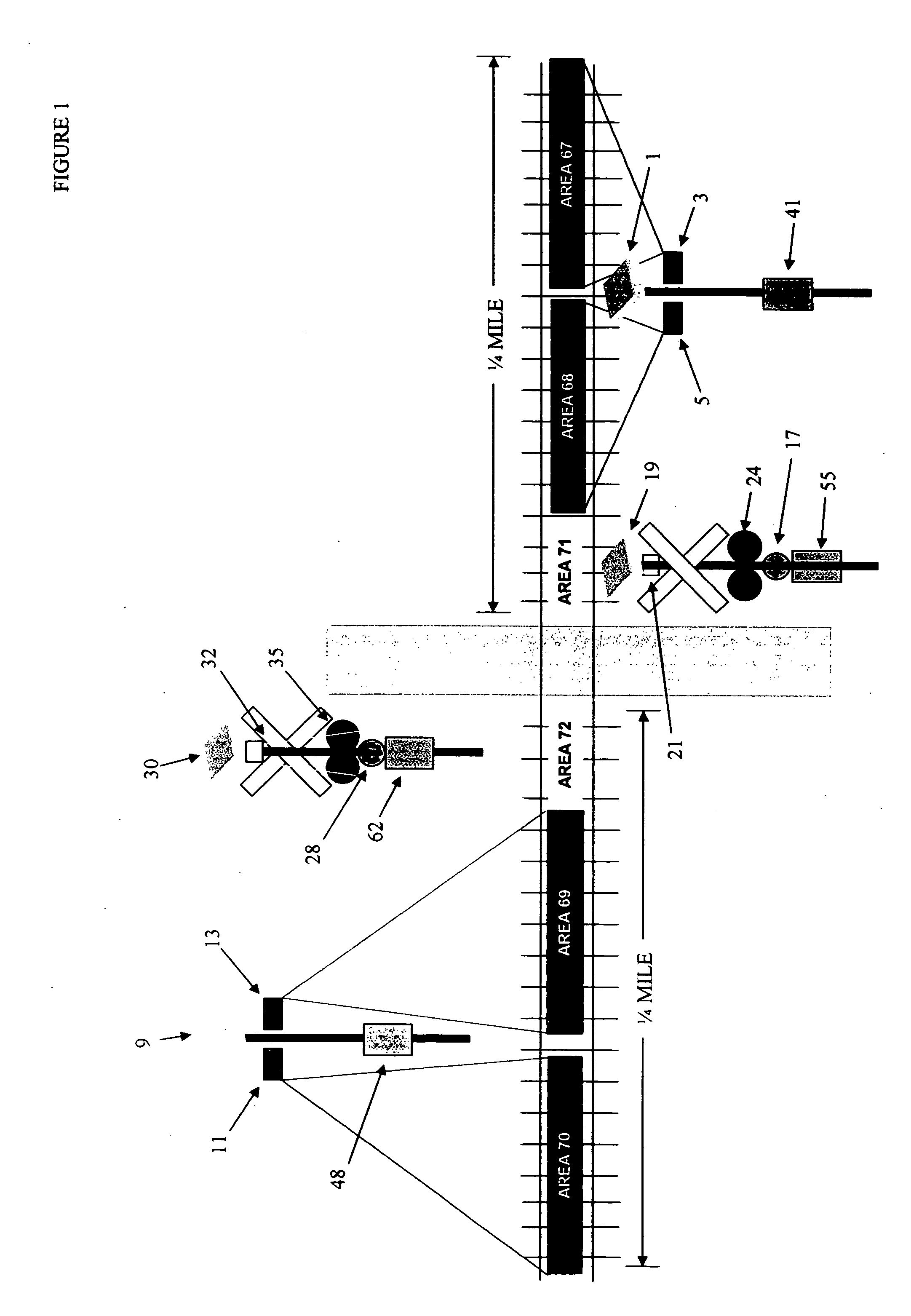
Railroad crossing warning system
InactiveUS20050184883A1Easy to useAvoid utilizationControlling traffic signalsDetection of traffic movementLevel crossingVisual perception
A highway / railroad crossing detection and warning system which uses sets of Doppler radar transmitters and receivers to detect the approach of a train coming from either direction toward a highway crossing. The Doppler radar sets are located an extended distance from the crossing with each set detecting movement toward and away from its location. Presence detectors are located at the crossing and sense moving or stationary trains. All detector devices transmit signals to warning equipment to provide aural and visual indications to approaching motorists or work crews.
Owner:GRAHAM KEVIN M
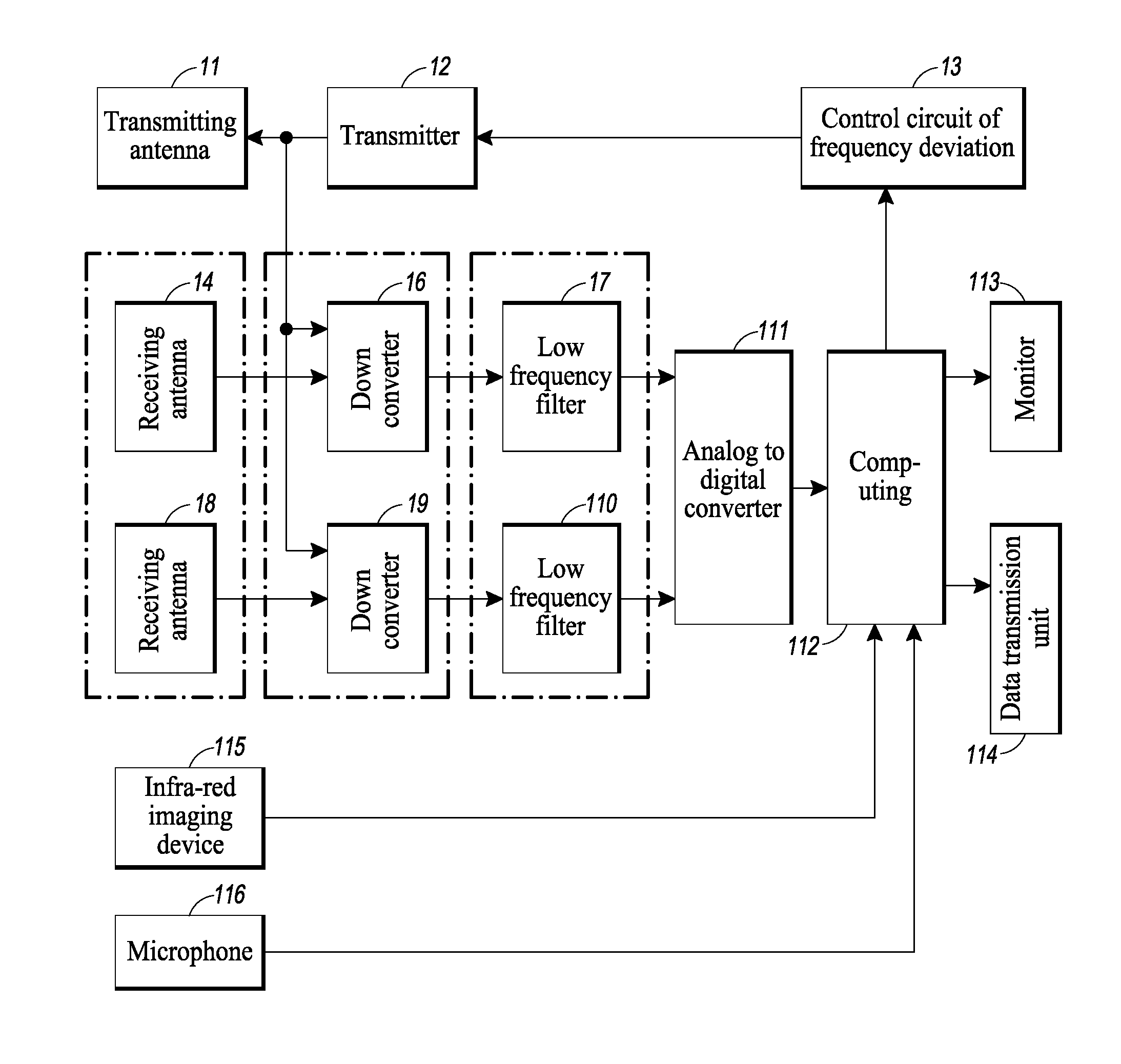
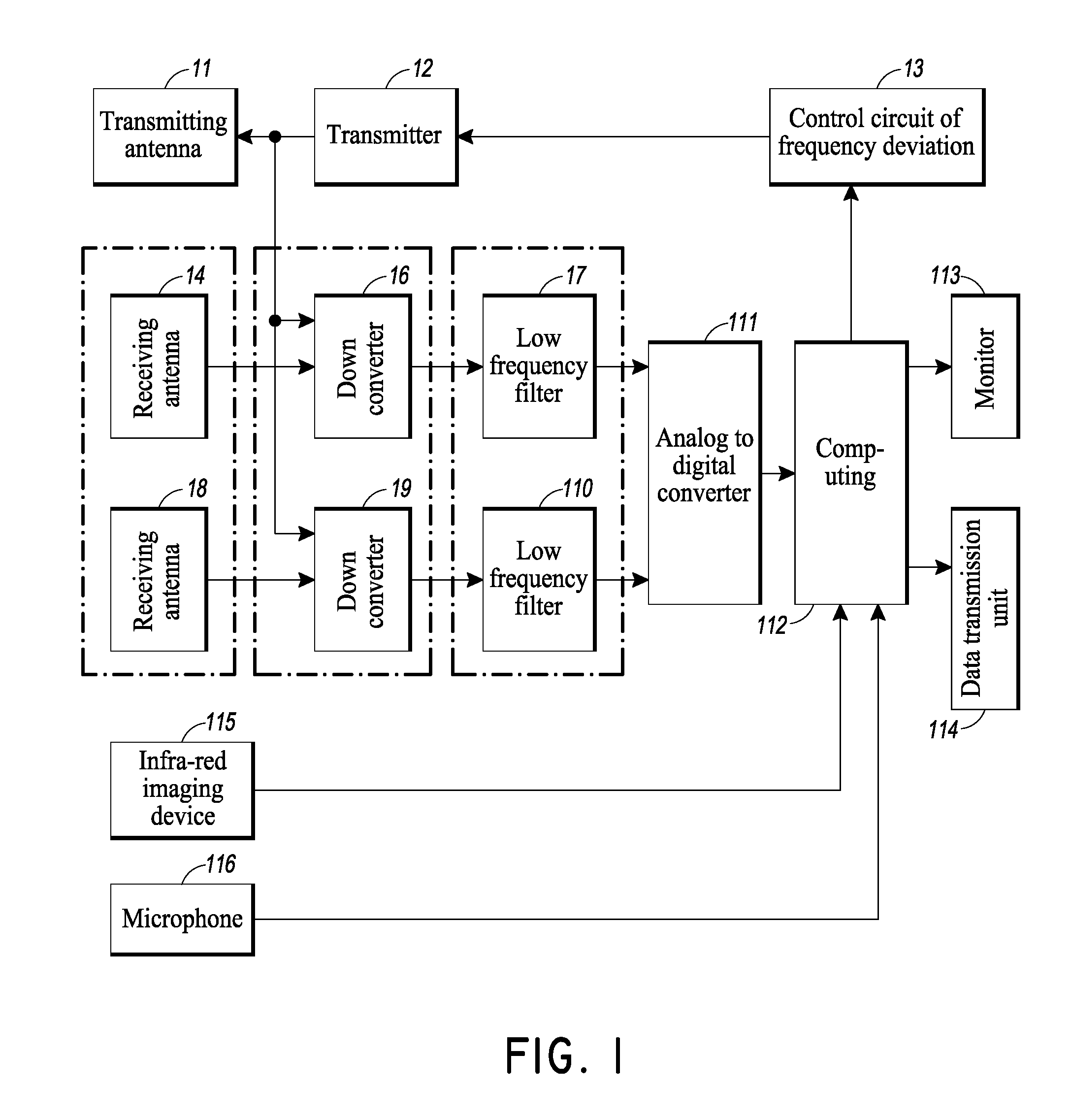
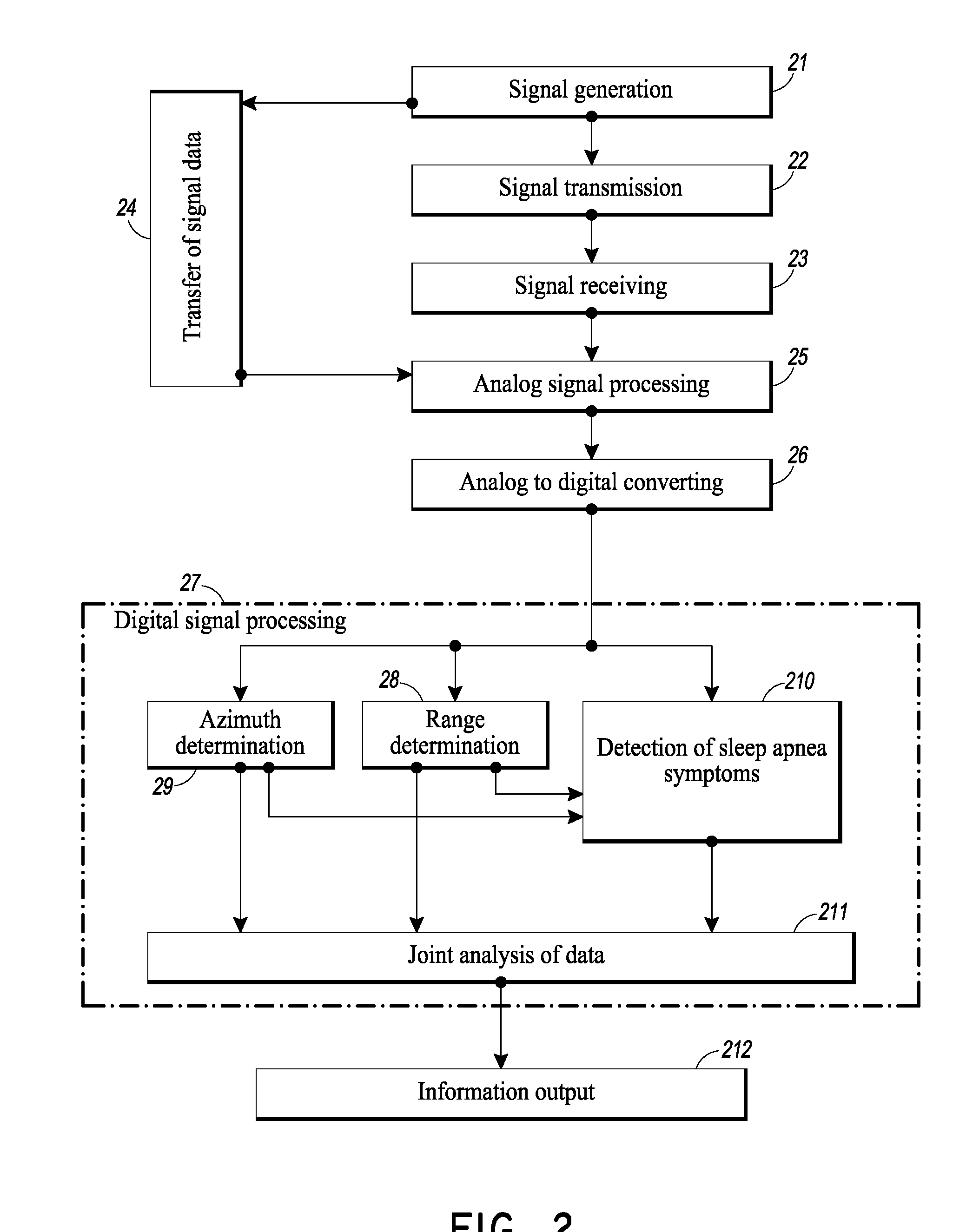
An apparatus for remote contactless monitoring of sleep apnea
InactiveUS20160022204A1Eliminate damageProvide convenienceInertial sensorsAuscultation instrumentsAccelerometerRadio frequency signal
An apparatus for remote contactless monitoring of sleep apnea, comprising a radar transmitter having a transmitting antenna for radiation of radio frequency signal towards a human body, and a radar receiver for receiving a signal reflected from the human body. The radar receiver comprises a receiving antenna positioned at a predefined distance from the transmitting antenna. The apparatus further comprises an accelerometer adapted to be placed on a human body, a microphone and a signal processor. Respective outputs of the radar receiver, accelerometer and microphone are connected to the input of the signal processor which is configured for extracting and processing apnea-specific physiological parameters of the at least one human body from the inputted signals of the receiver, accelerometer, and microphone.
Owner:MOSTOV KIRILL
Digital radio frequency tag
InactiveUS20020196178A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionAcoustic wave reradiationSoftware designElectromagnetic shielding
A digital RF tag (10) for providing an automatic reply to an electromagnetic signal. The system includes a radar receiver (11, 20); signal and data processors (50, 64) for analyzing the electromagnetic signal to extract data with respect thereto and for synthesizing a second electromagnetic signal; and a radar transmitter (11, 20). The radar receiver (11, 20) is a narrow band radar receiver. The use of a narrow band receiver minimizes power consumption and extends battery life. The inventive RF tag (10) tracks the received radar signal. The data processor (50) includes a microprocessor adapted to execute software designed to implement the tracking function. While the received radar signal is being tracked, type and timing data are extracted and used to synthesize a reply signal. The use of a synthesized reply signal, as opposed to a recorded and modified transmit signal as a reply signal, allows for the transmission of the cleaner (noise free) reply signal. In addition, other data including voice and video may be impressed onto the reply signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
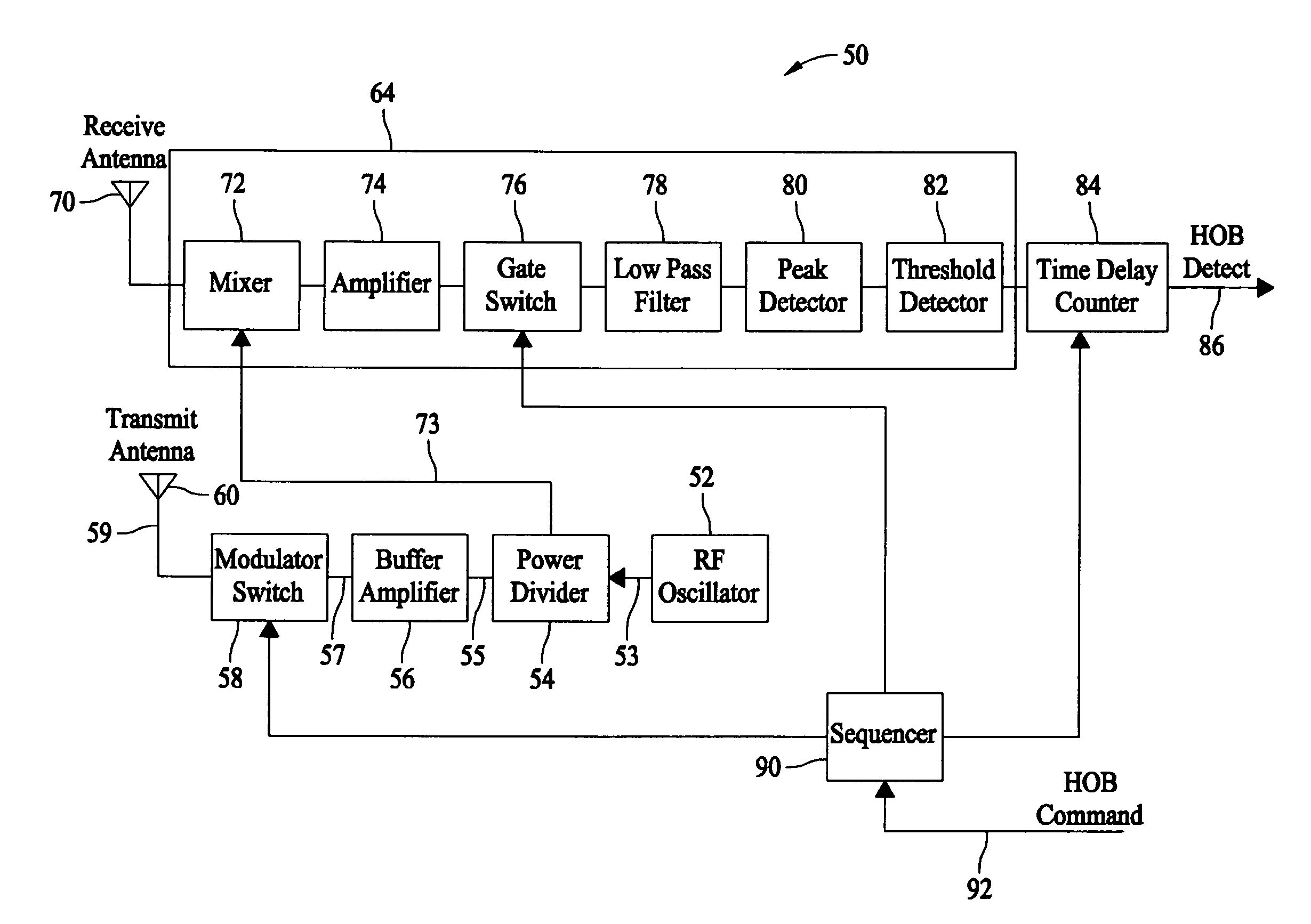
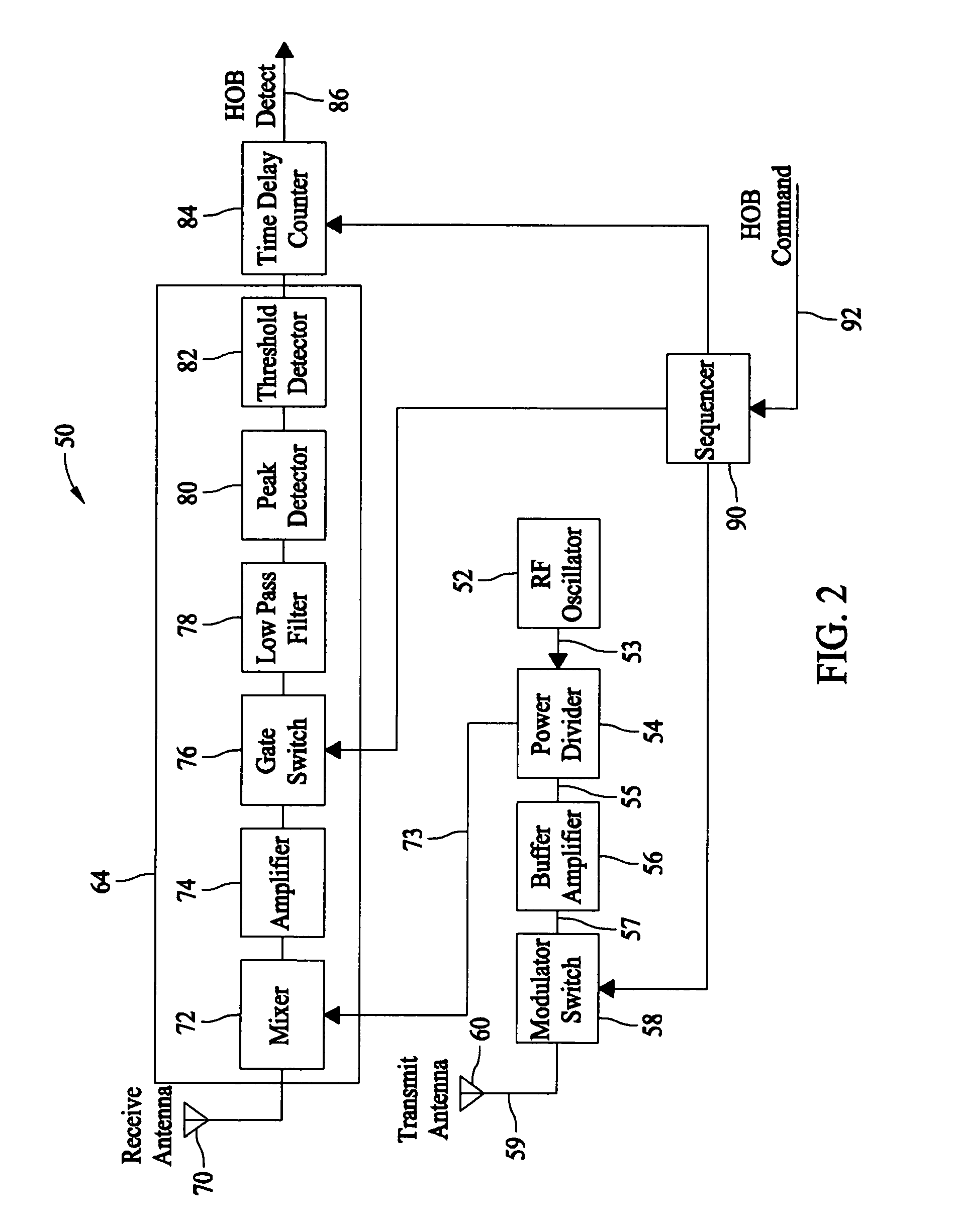
Methods and systems for controlling a height of munition detonation
A unit is described that is configured to control detonation of a munition such that the munition is detonated at a desired altitude. The unit includes a radar transmitter, a radar receiver that includes a radar range gate, and a sequencer. The sequencer is configured to receive a detonation altitude and set the range gate based on the received detonation altitude. The unit is also configured to output a detonation signal when radar return pulses received by the receiver aligned with gate delay pulses from the range gate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Measurement arrangement
InactiveUS6531881B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceUsing wave/particle radiation meansMeasurement deviceEngineering
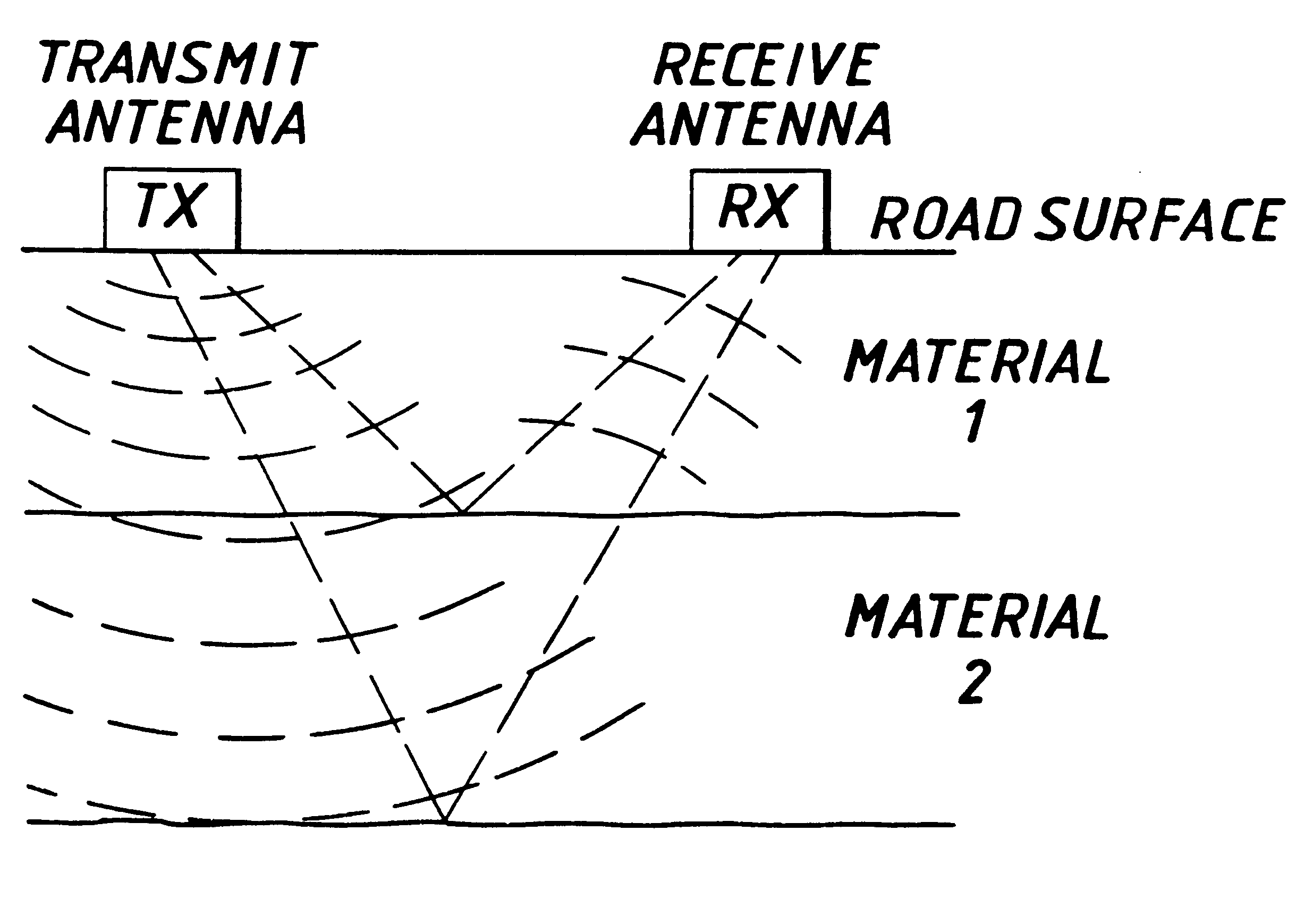
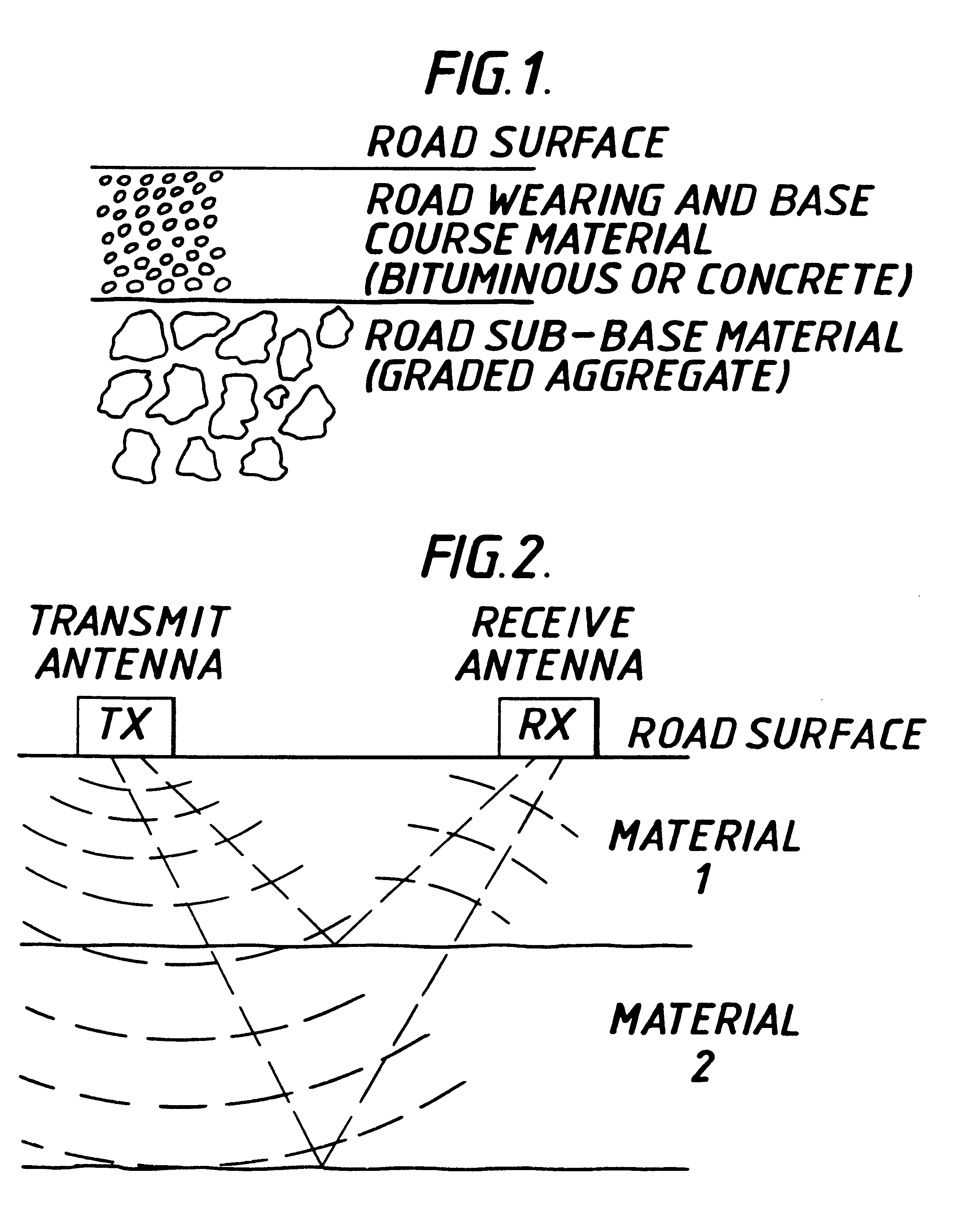
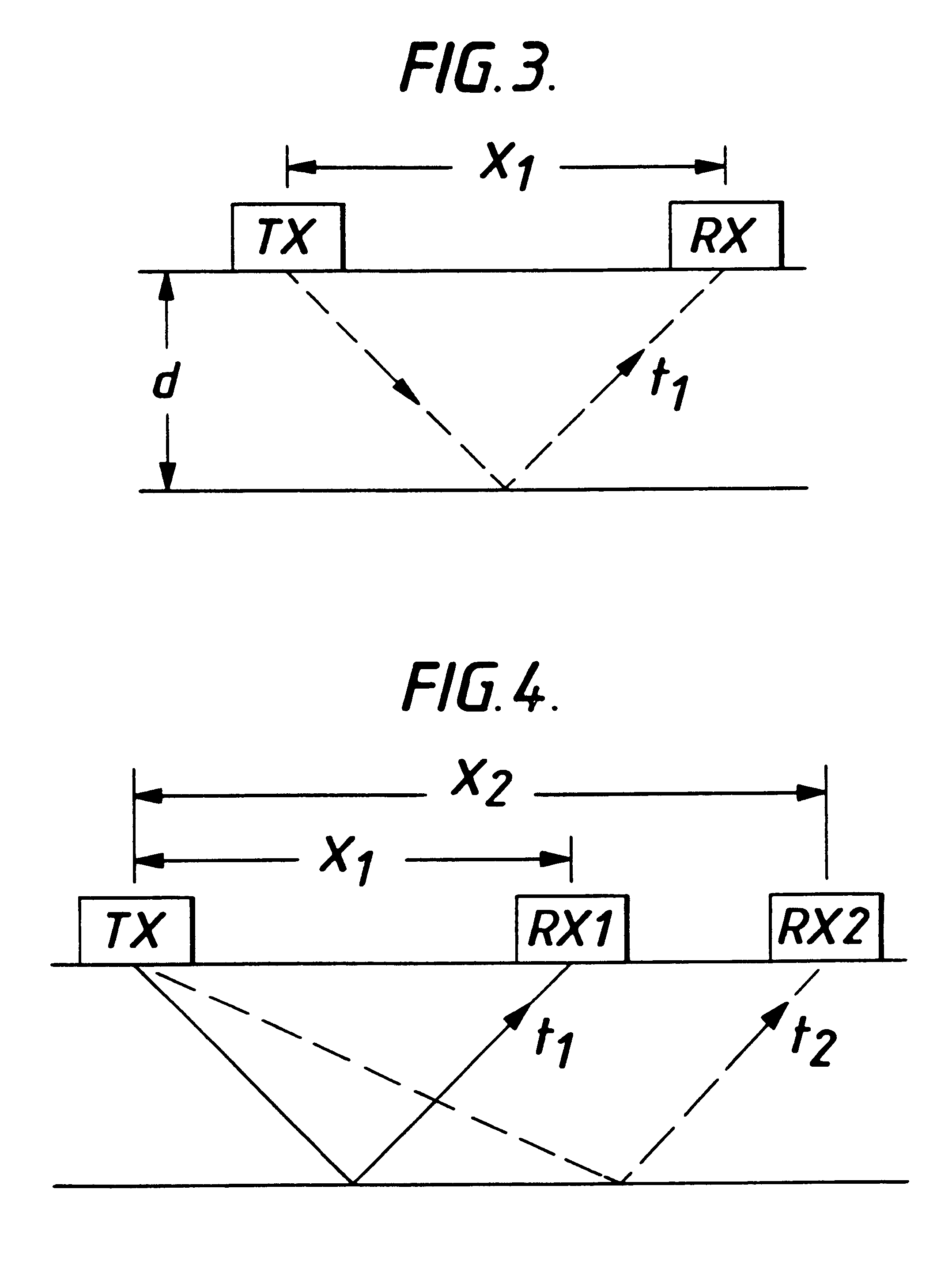
A measuring device for determining the thickness of a non-homogeneous medium such as the thickness of a road structure. The device includes a radar transmitter and two spaced receivers. Information on the timing of the transmitted signal as well as the signals received by the two receivers is used to calculate the material thickness while eliminating signal drift.
Owner:TRANSCO PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY
Marine radar systems and methods
ActiveUS7688257B1High sensitivityHigher effective system bandwidthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsImage resolution
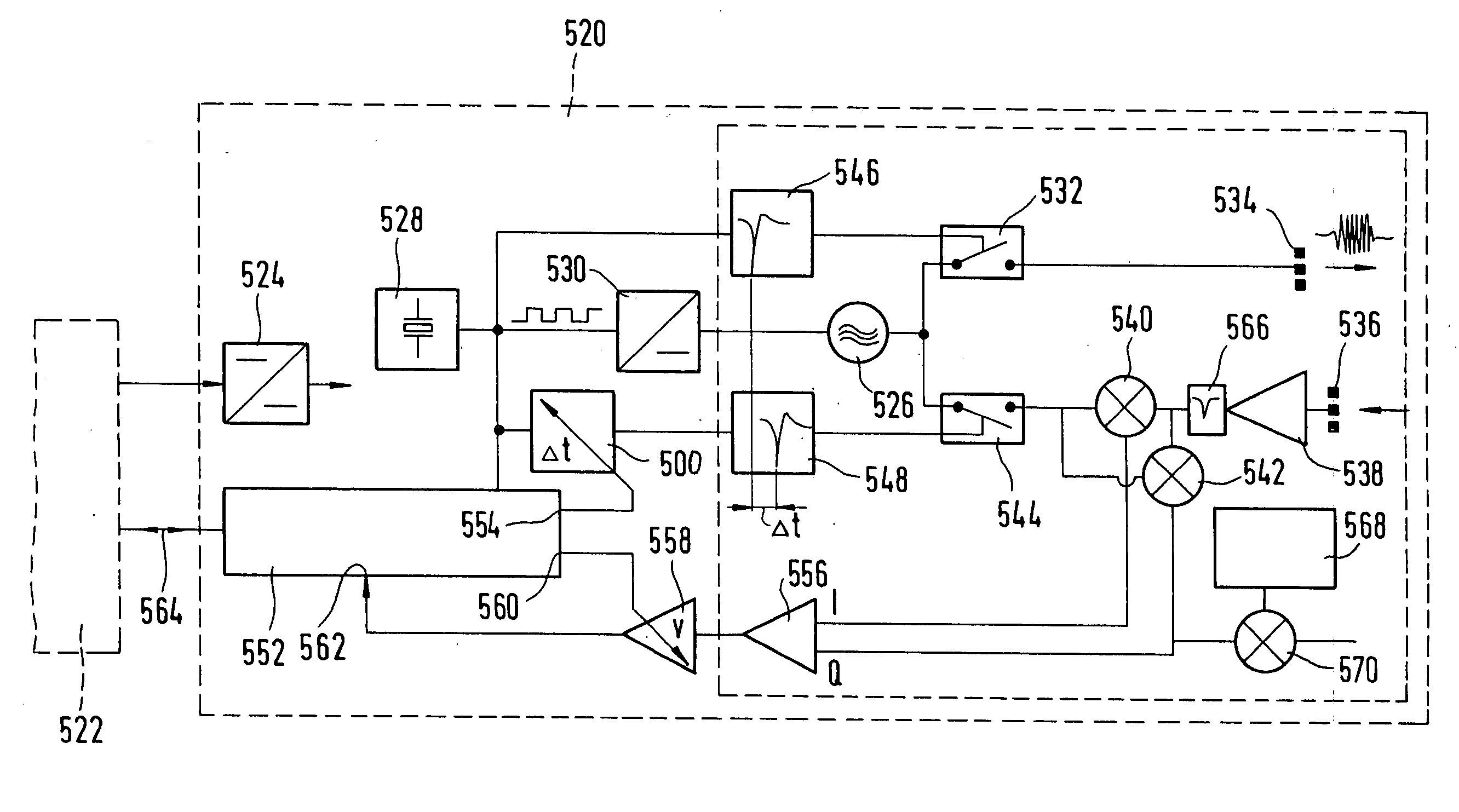
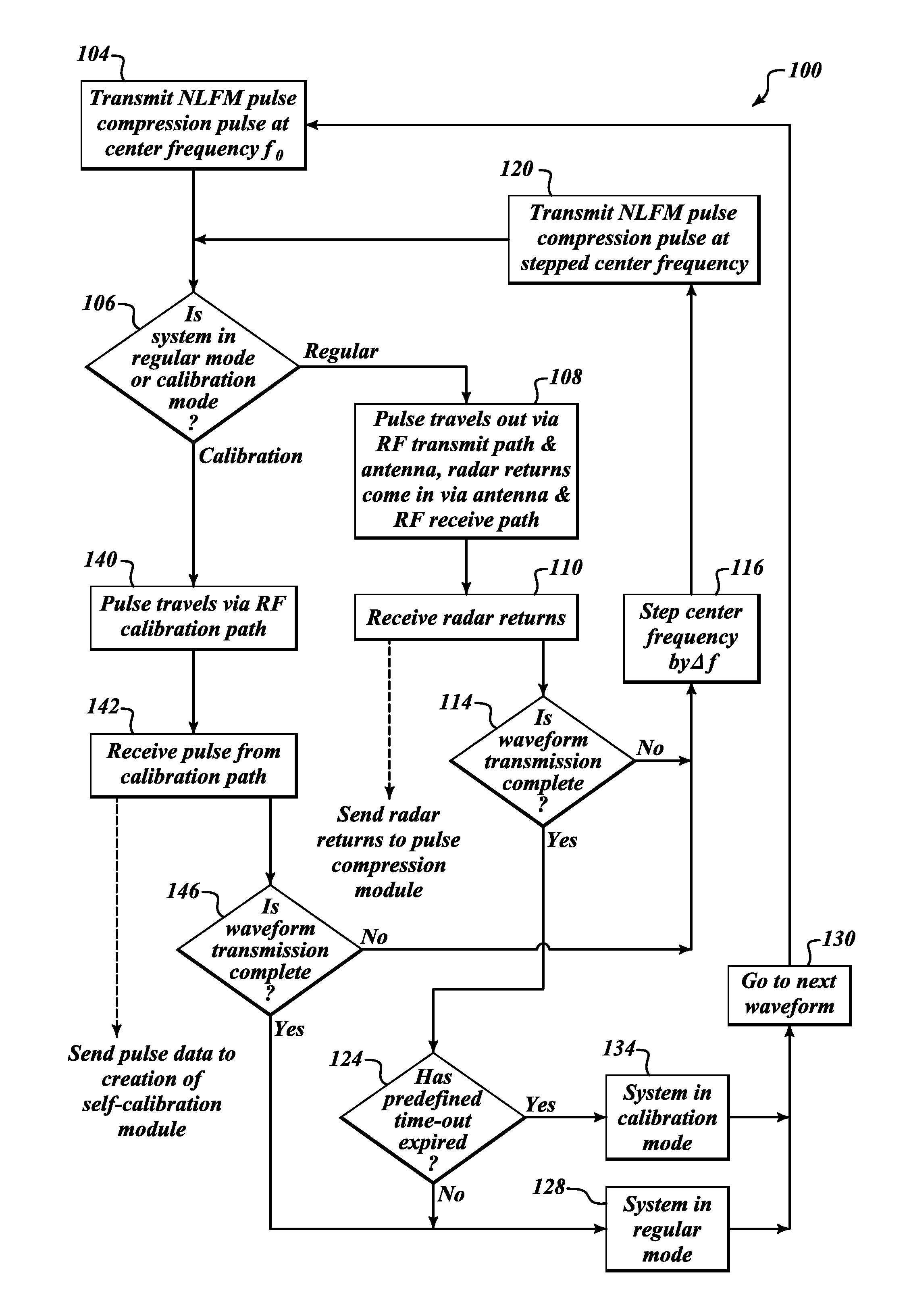
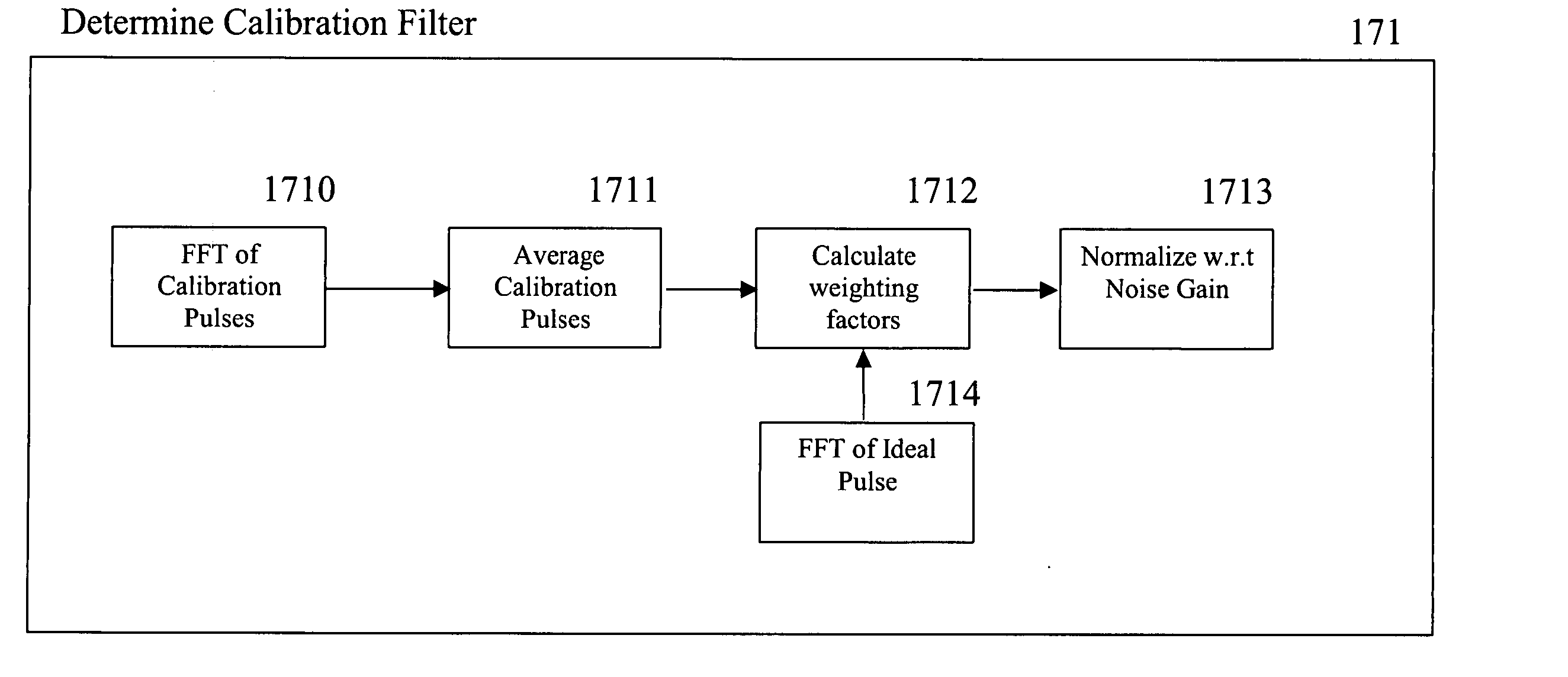
Marine radar systems and methods for producing low power, high resolution range profile estimates. Non-linear Frequency Modulation (NLFM) pulse compression pulses are frequency stepped to form a low power, wide-bandwidth waveform. Periodically, calibration filters are determined and applied to return signals for correcting non-ideal effects in the radar transmitter and receiver.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Horizontally polarized wide-angle radar object detection
A radar includes fixed beam radar transmitter and receiver antennae that utilize mixed polarization to optimize the object detection field-of-view through an intervening plastic fascia. The transmitter antenna transmits radar energy with slant polarization, a first receiver antenna designed for short-range wide-angle object detection passes only horizontally polarized radar energy, and a second receiver antenna designed for long-range narrow-angle object detection passes only vertically polarized radar energy.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Radar radiation source identification method based on phase noise unintentional modulation characteristic
InactiveCN104809358AAccurate identification and judgmentGood recognition and classificationWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsPhase noisePrincipal component analysis
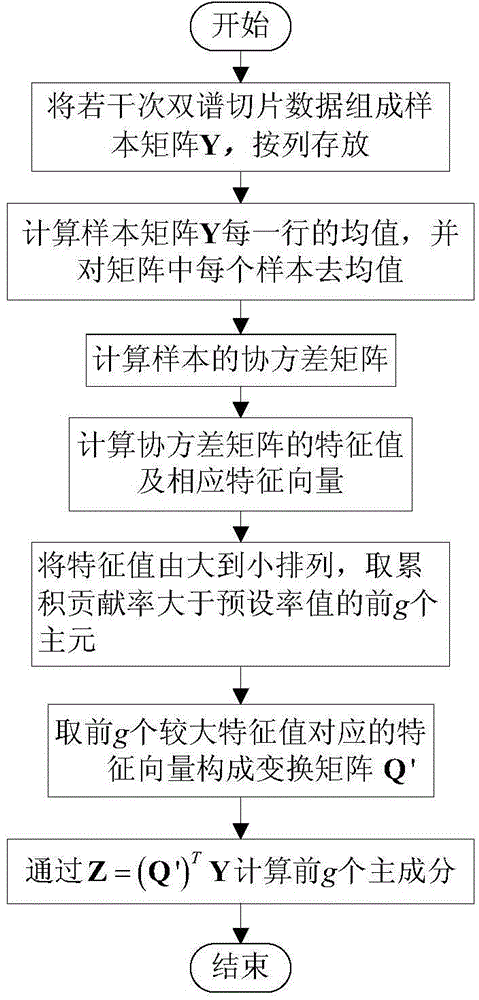
The invention discloses a radar radiation source identification method based on phase noise unintentional modulation characteristic, relates to an identification method of a radar radiation source, and aims to solve the problem that the identification rate of an existing radiation source identification method based on phase noise is not high. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of analyzing the structure of a phase-lock frequency synthesizer in a radar transmitter system; building a model of phase noise generated by the phase-lock frequency synthesizer; calculating a bispectrum diagonal slice characteristic and a bispectrum non-diagonal slice characteristic; forming a characteristic matrix Y by using a bispectrum diagonal slice characteristic matrix A1 and a bispectrum non-diagonal slice characteristic matrix B1; performing PCA (Principal Component Analysis) dimensional reduction and building a type-known transmitter vector machine model; identifying a transmission signal of a type-unknown transmitter by utilizing the built vector machine model so as to realize the identification of a radar radiation source. The method disclosed by the invention is applicable to the identification of the radar radiation source.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Operational bistatic radar system synchronization
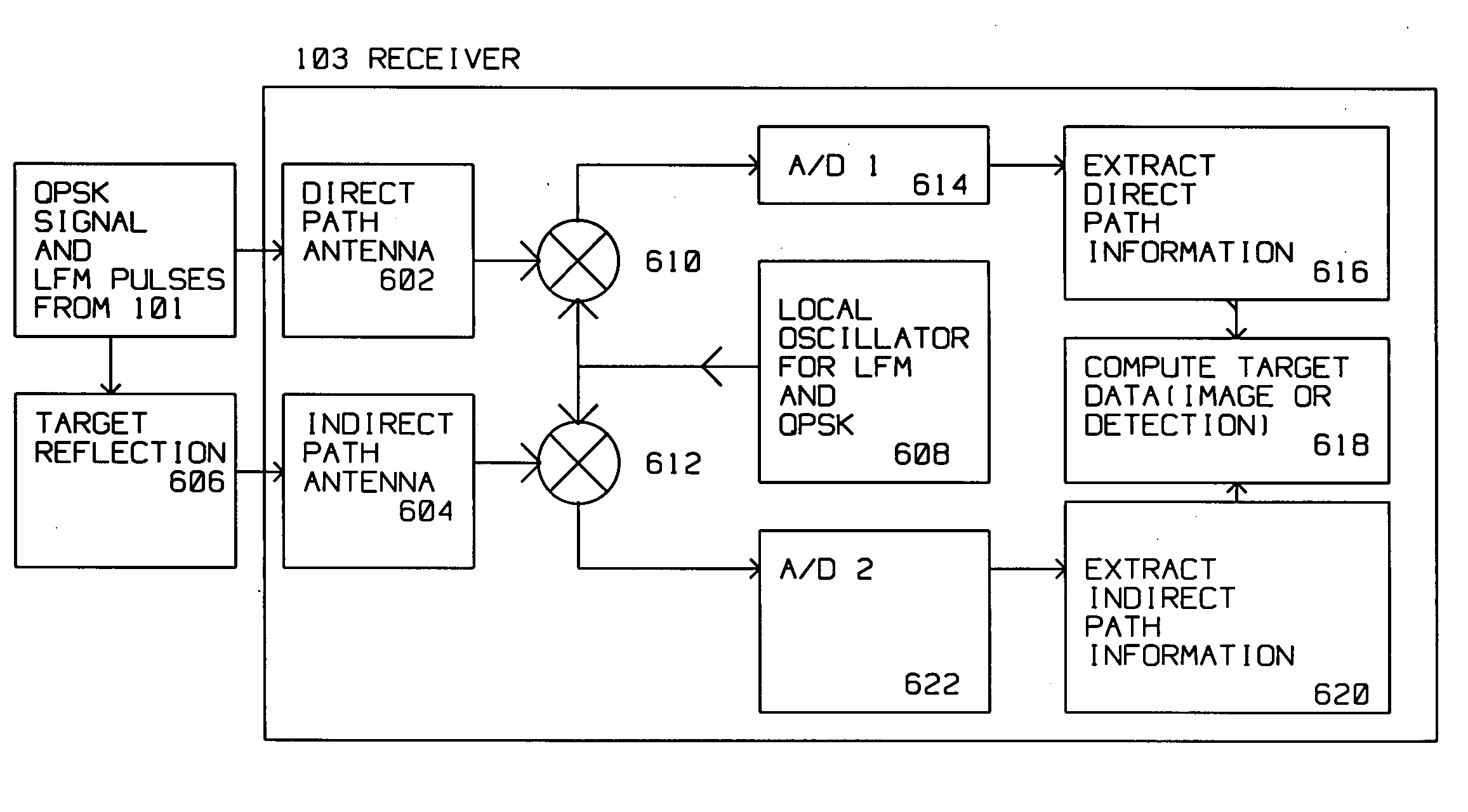
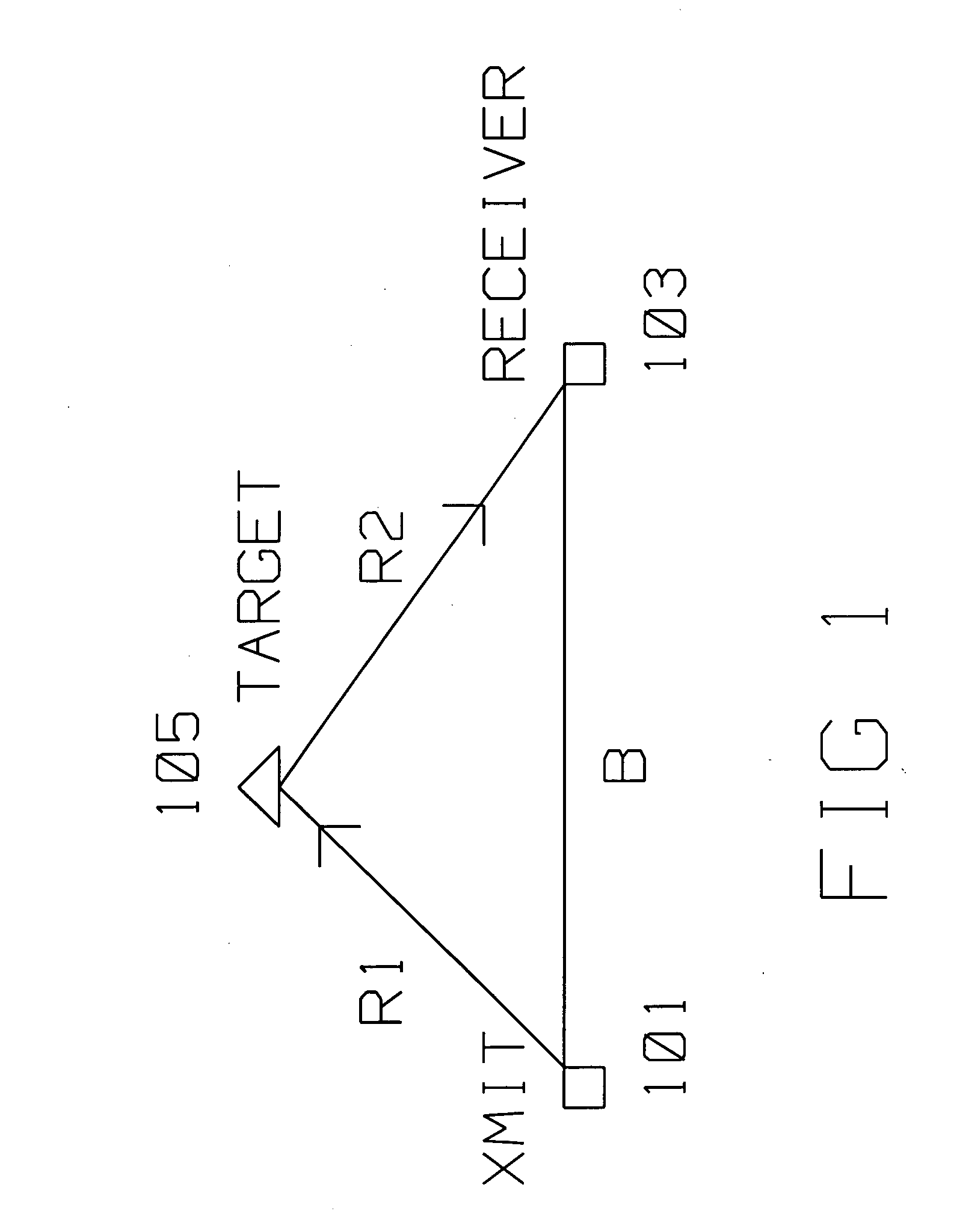
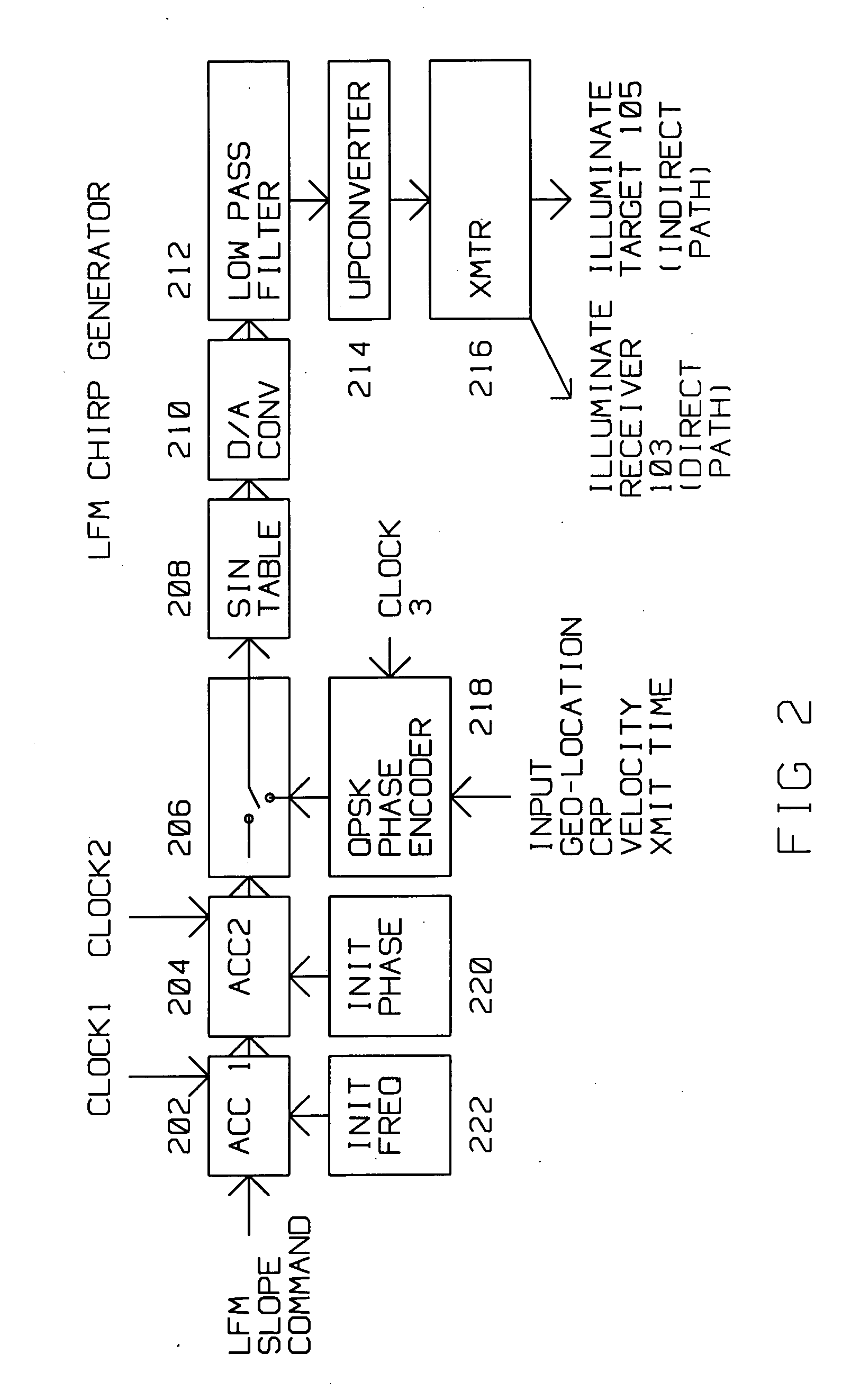
A bistatic radar has a radar transmitter at a first location on a moving platform having a motion and a radar receiver at a second location, remote from the first location. The transmitter illuminates a target along an indirect path with an encoded radar signal. The target reflects the encoded radar signal to the radar receiver. The transmitter concurrently provides the encoded radar signal to the radar receiver along a direct path. The encoded radar signal is radiated at a start time from a central reference point, and contains the first location, the pulse start time, the central reference point and the motion of the moving platform. Bit synchronization codes are also included. The radar receiver receives the encoded radar signal from the radar transmitter along the direct path during a first time interval, and the same encoded radar signal reflected from the target along the indirect path during a second time interval. The radar receiver decodes first information contained in the encoded radar signal from the direct path received during the first time interval to extract direct path information. The radar receiver also decodes second information contained in the encoded radar signal from the indirect path received during the second time interval to extract indirect path information. The radar receiver combines the direct path information and the indirect path information to to generate a target image or perform target detection. Linear Frequency Modulated (LFM) pulse coherency is maintained by extracting from the direct path pulse phase corrections and applying the phase correction to the indirect received LFM pulses.
Owner:RAYTHEON COMPANY INTPROP & LICENSING
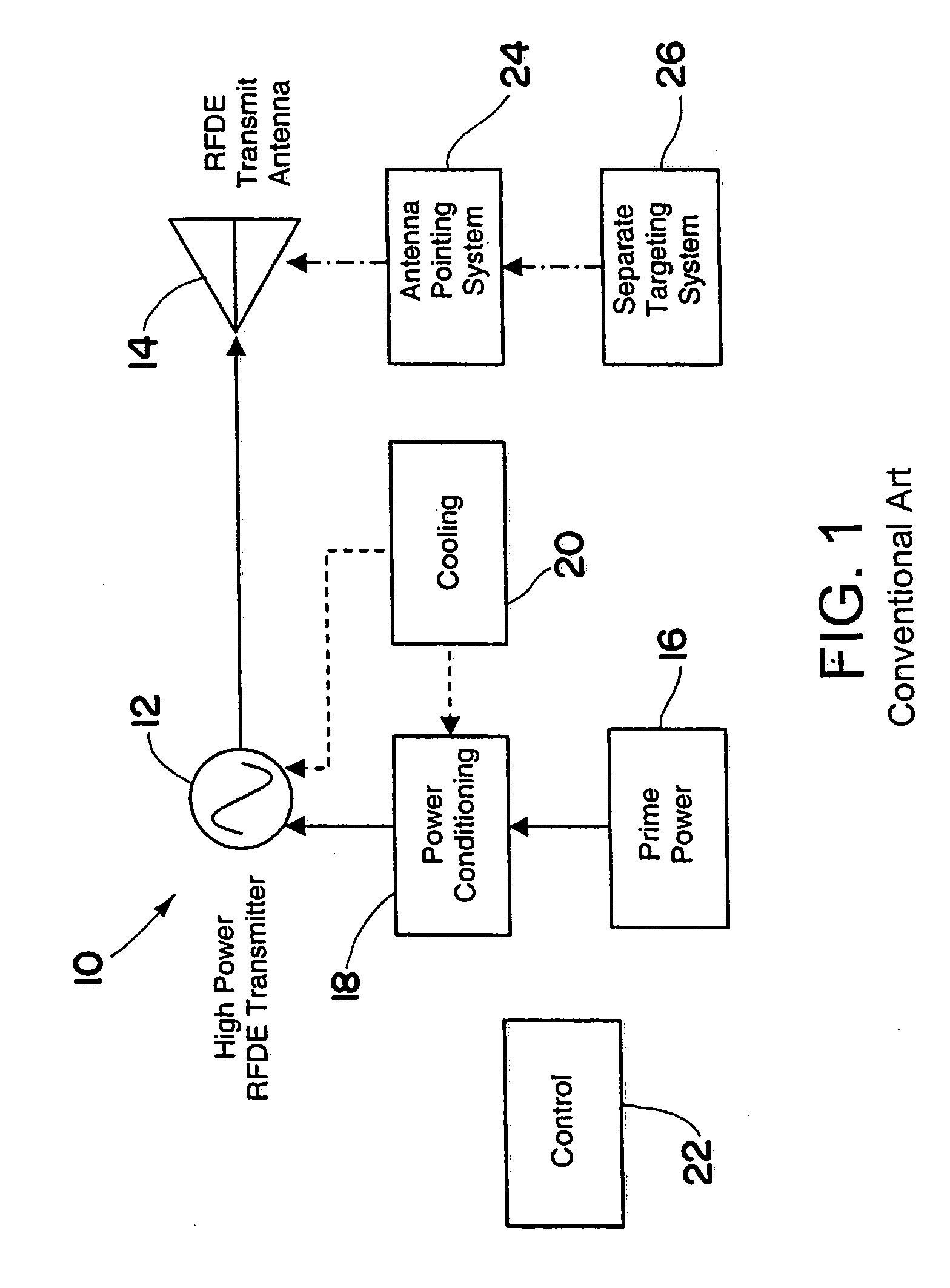
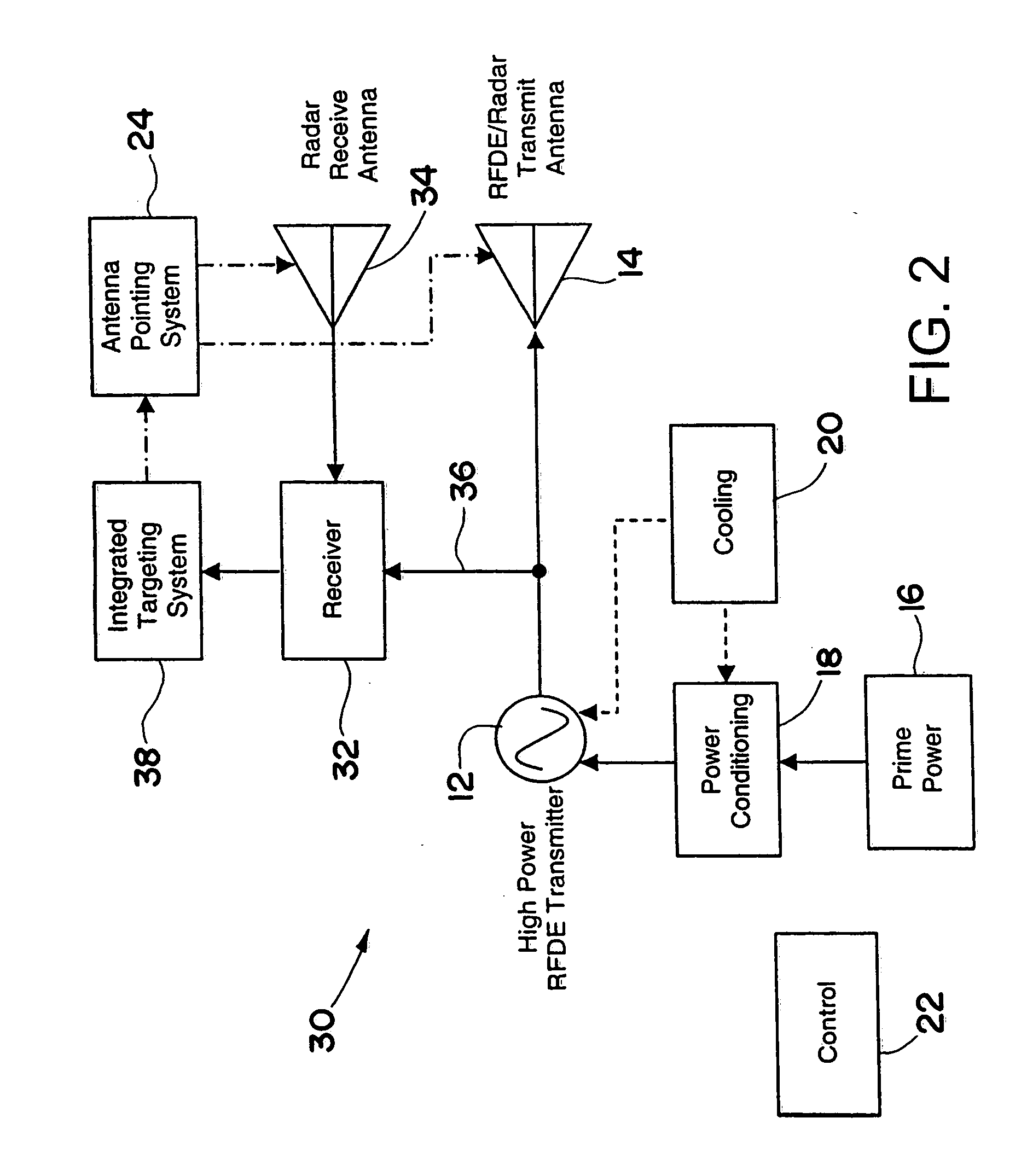
Multifunctional radio frequency directed energy system
InactiveUS20070139247A1Reduce system costEliminate needCommunication jammingWeapons typesHigh energyEngineering
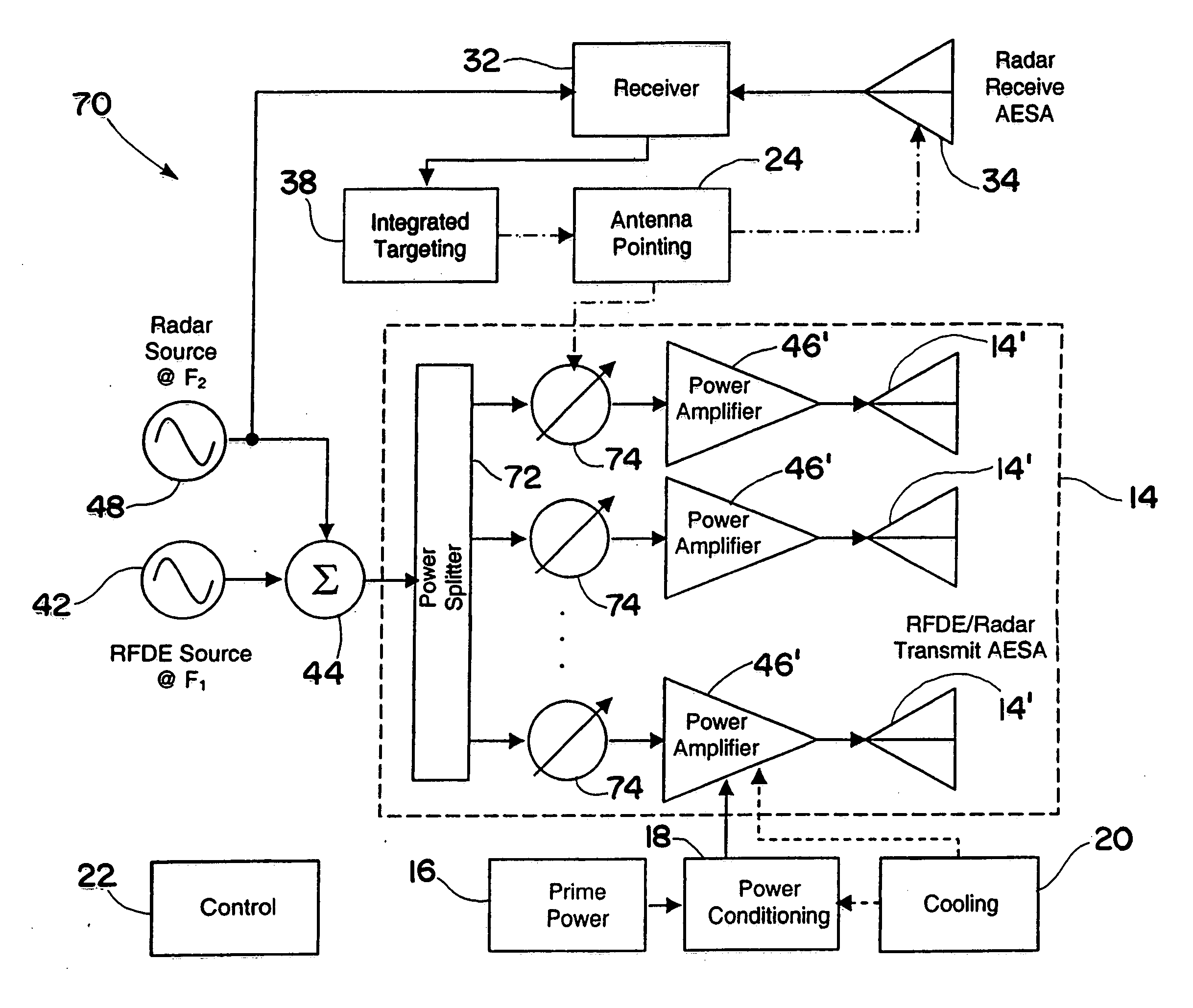
An RFDE system includes an RFDE transmitter and at least one RFDE antenna. The RFDE transmitter and antenna direct high power electromagnetic energy towards a target sufficient to cause high energy damage or disruption of the target. The RFDE system further includes a targeting system for locating the target. The targeting system includes a radar transmitter and at least one radar antenna for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic energy to locate the target. The RFDE system also includes an antenna pointing system for aiming the at least one RFDE antenna at the target based on the location of the target as ascertained by the targeting system. Moreover, at least a portion of the radar transmitter or the at least one radar antenna is integrated within at least a portion of the RFDE transmitter or the at least one RFDE antenna.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Combined Radar and communications link
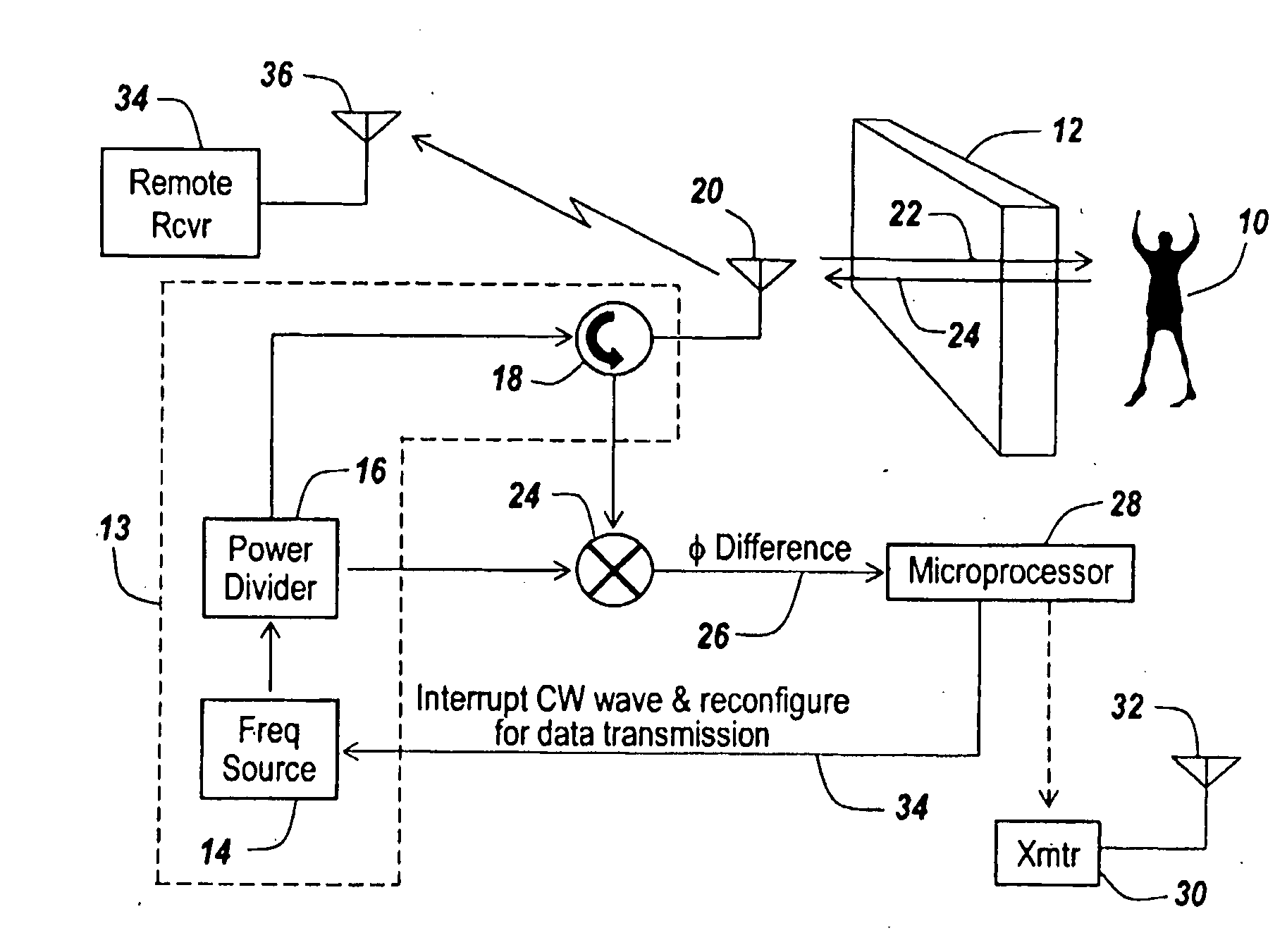
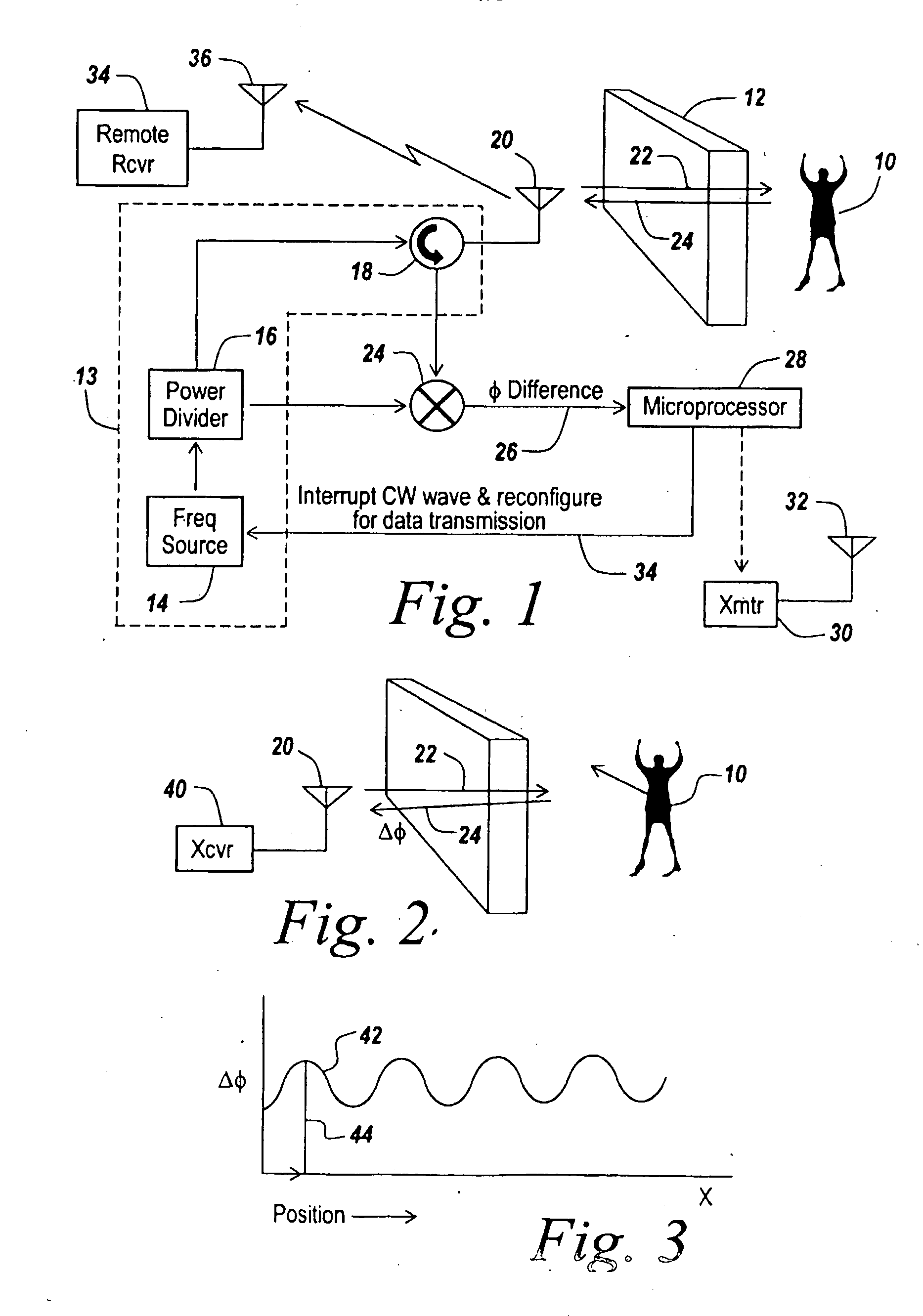
InactiveUS20090135044A1Improve accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBurglar alarm short radiation actuationMotion detectorRadar systems
In a CW radar system for detecting motion behind a wall (12) involving modulation of the radar transmission, means (34) are provided to interrupt the CW wave when motion is detected and to use the same radar transmitter (30) to transmit a serial digital message to a remote monitoring receiver (34). The encoding can include a receiver wakeup message to turn on the receive only when motion has been detected. In one embodiment, a microprocessor (28) is used to detect when motion exists behind a wall and to provide a tailorable message to modulate the radar's transmitter in the period when the CW signal from the radar is turned off after the motion detector.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
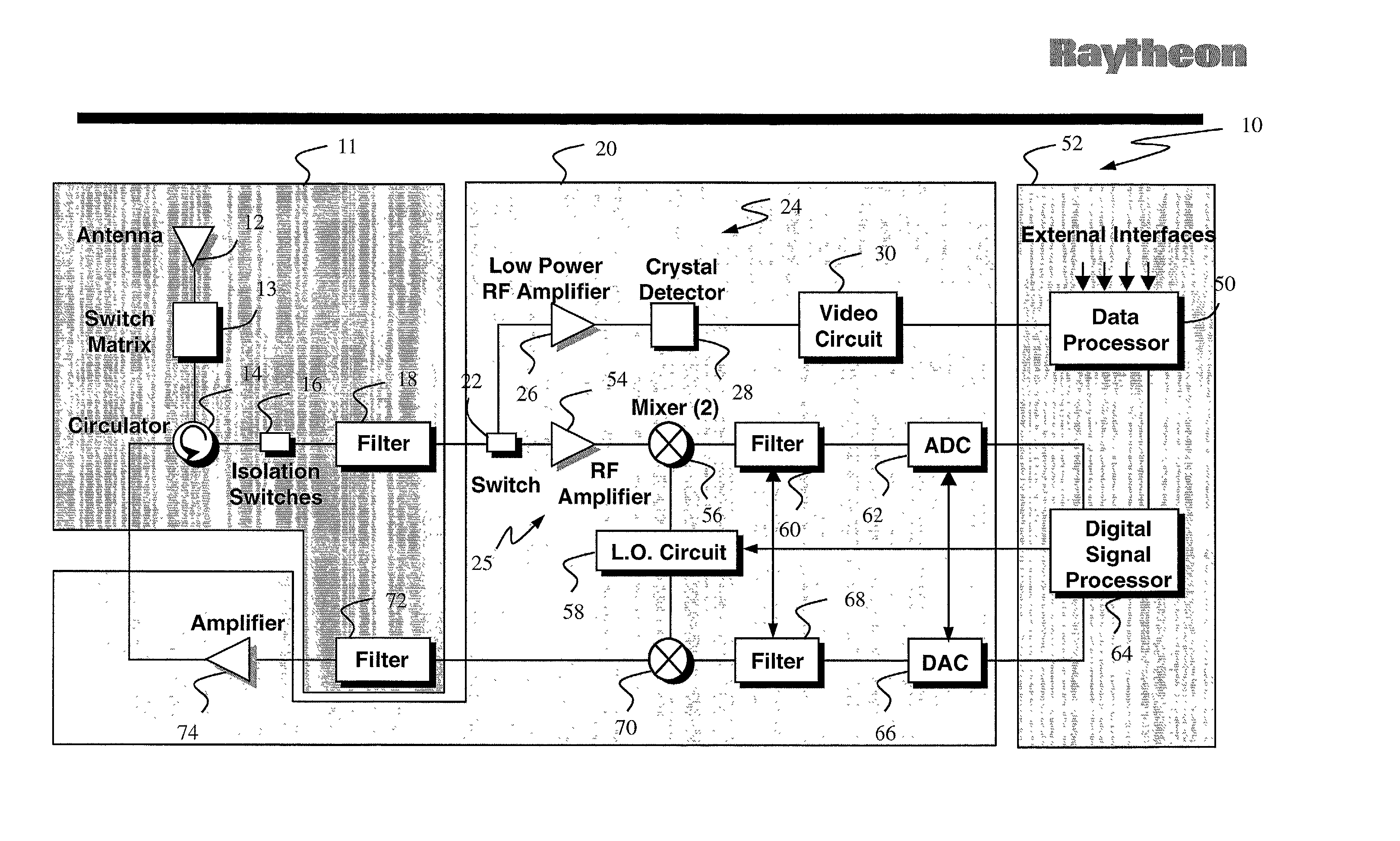
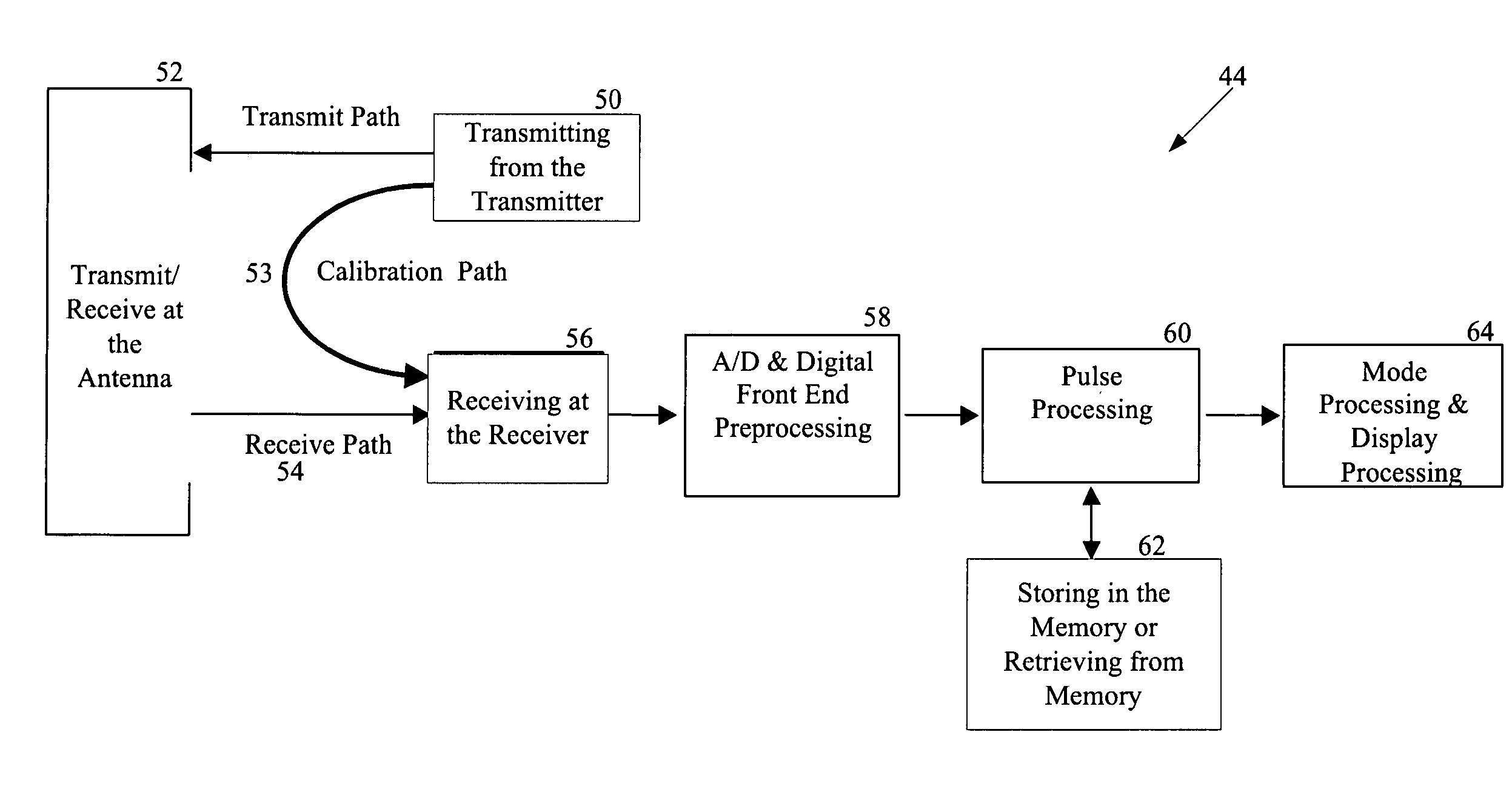
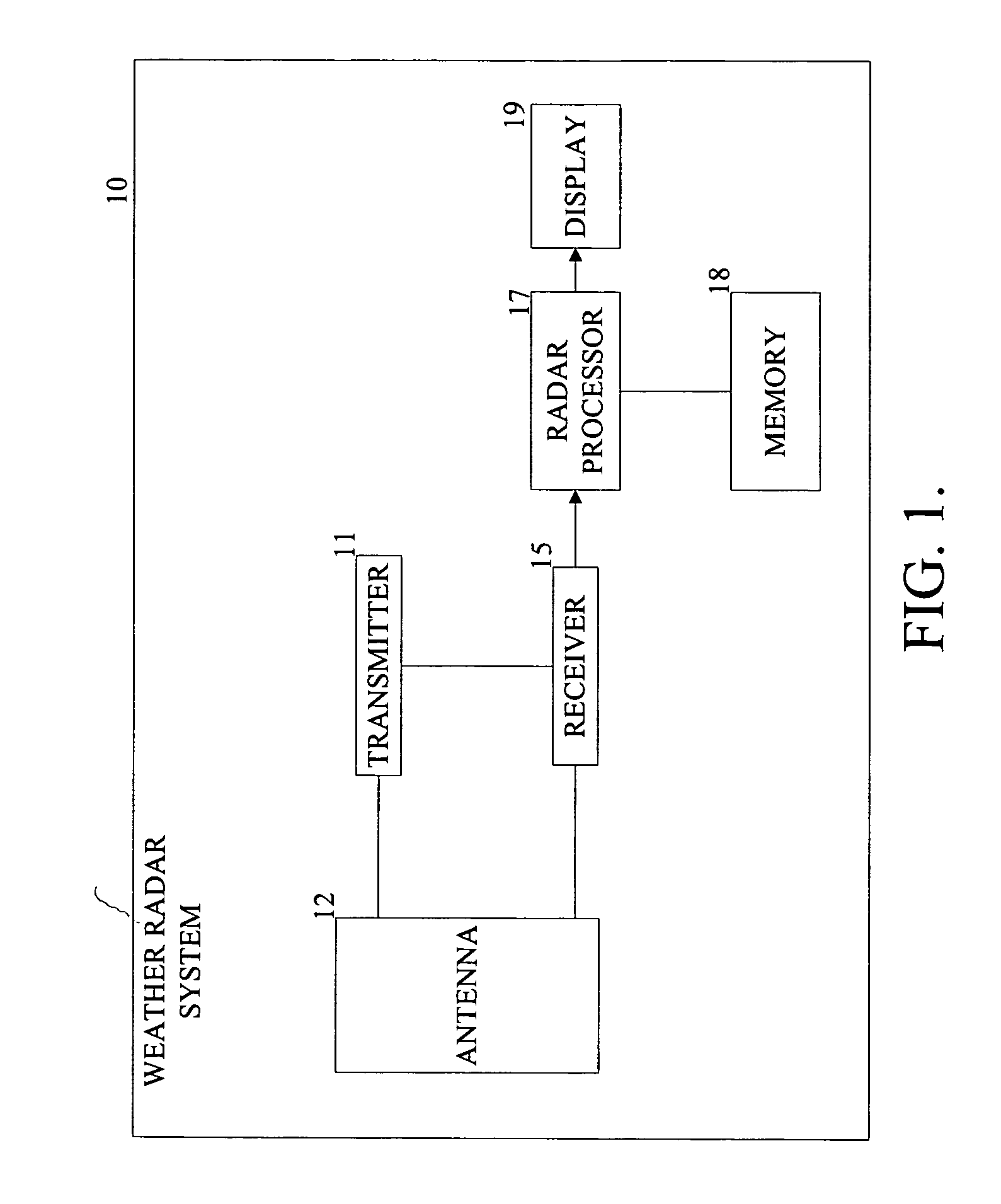
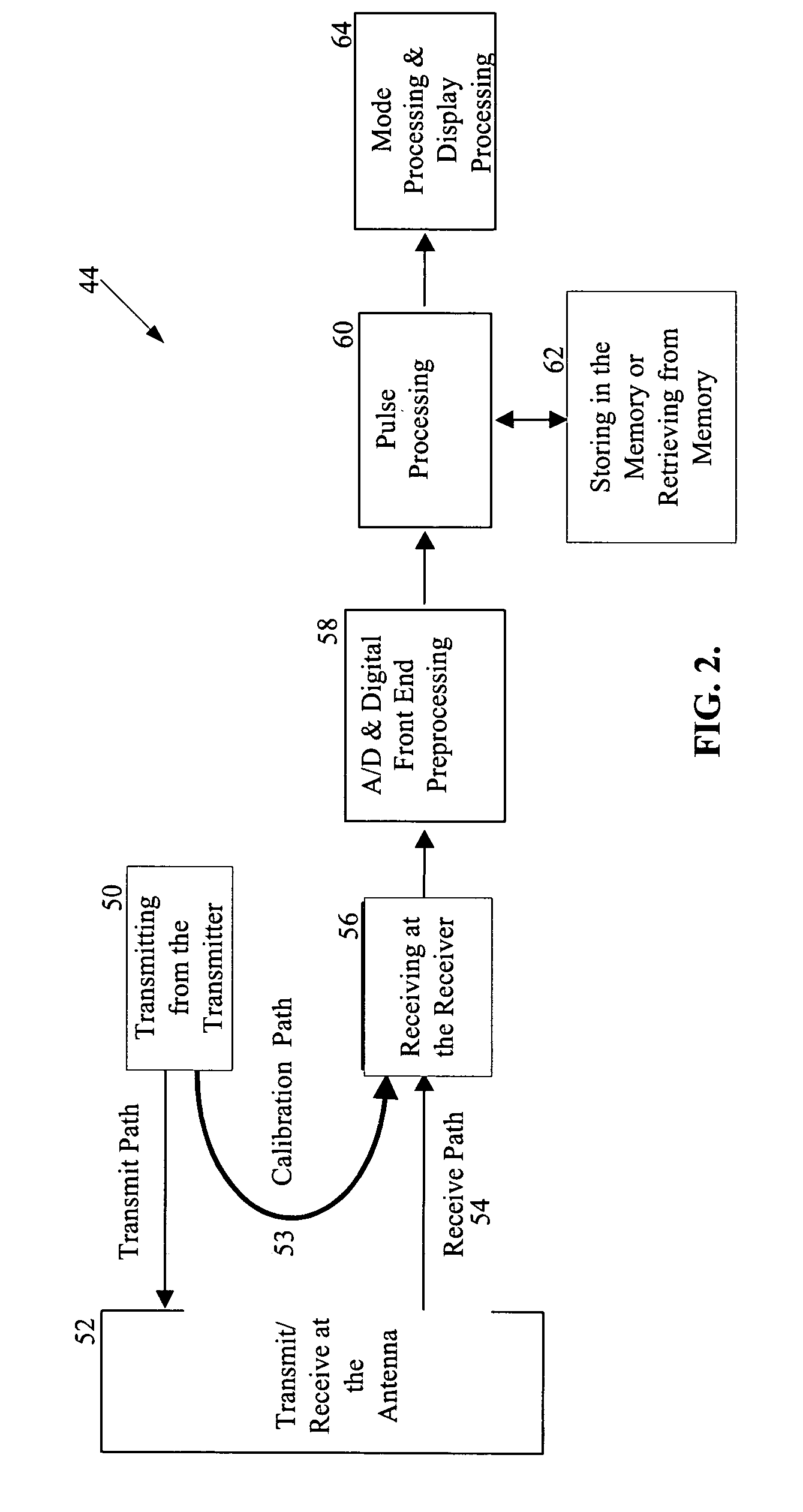
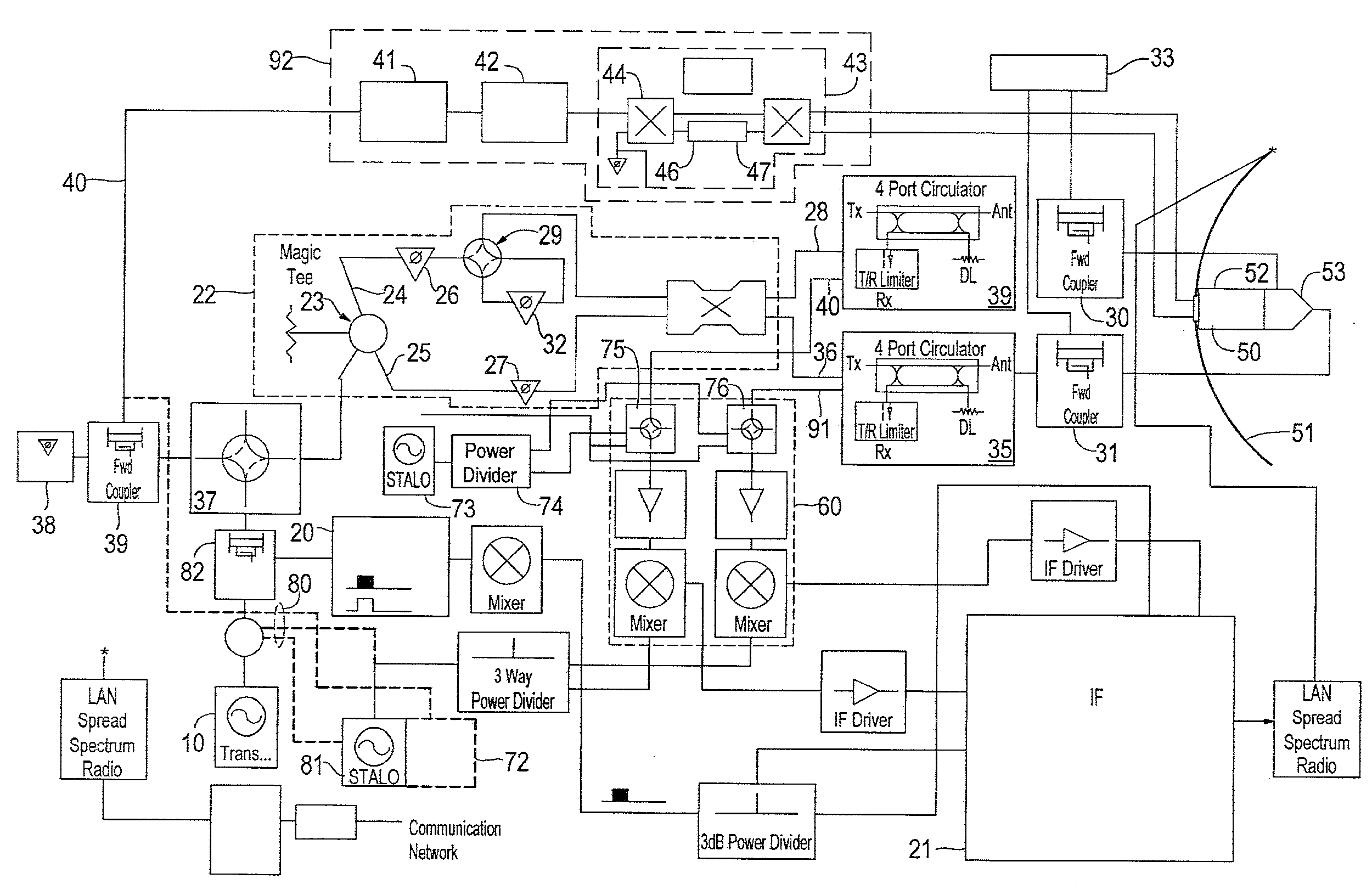
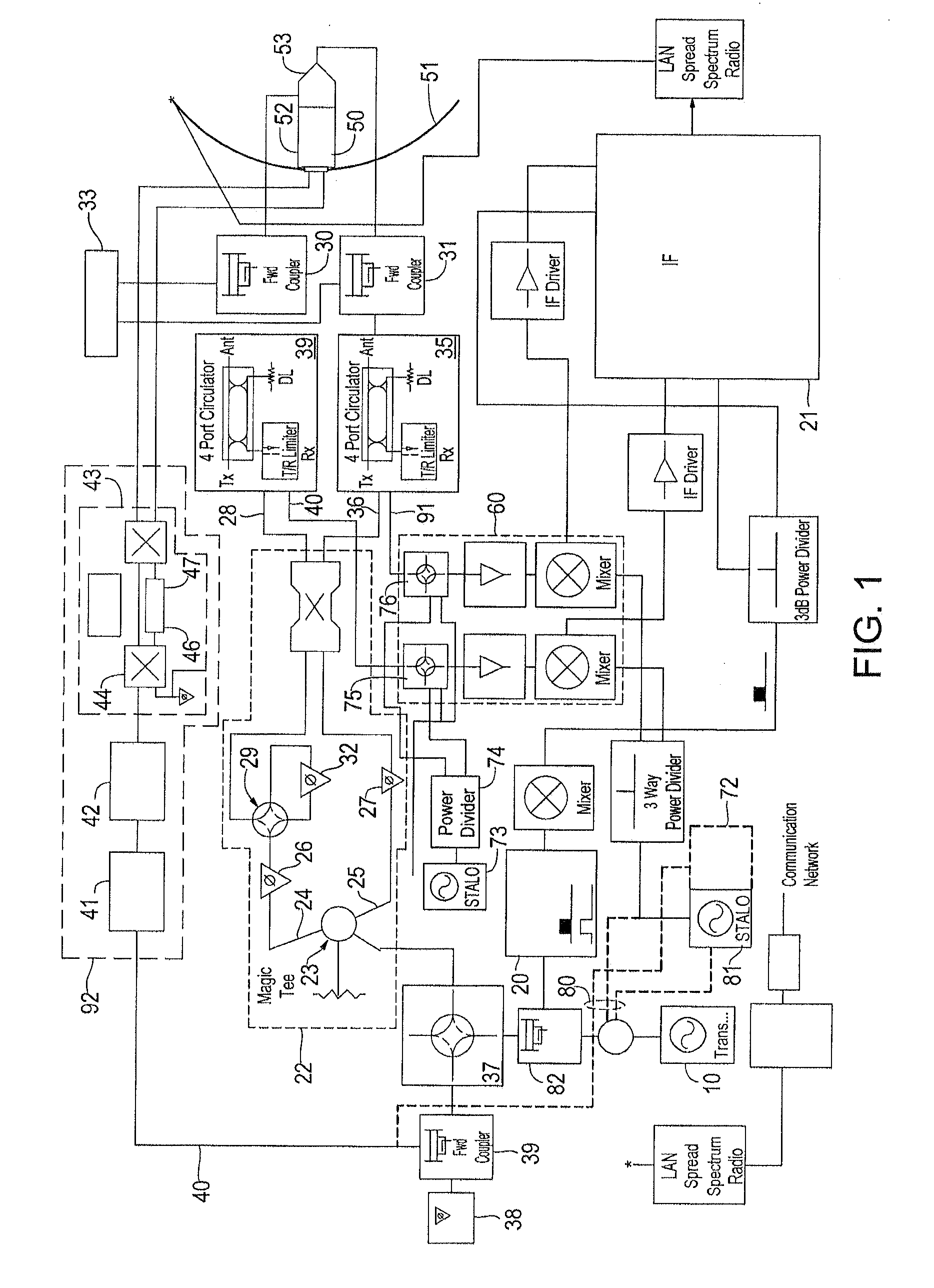
RF channel calibration for non-linear FM waveforms
ActiveUS7019686B2ICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar signal processingRadar signals
A system, method, and computer program product that performs self-calibration of pulse-compression radar signals. The system includes an antenna, a receiver, a transmitter, and a radar signal processor. Under normal (non-calibration) operation the radar transmitter generates a pulse compression waveform and transmits it via the antenna. Any reflections from this waveform are detected by the same antenna and processed by the receiver. The received radar signal then undergoes pulse compression followed by more mode-specific processing (windshear, weather, ground map, etc.) by the radar processor. During calibration, the radar transmitter generates a similar pulse compression waveform (i.e., calibration pulses), but the calibration pulses bypass the antenna and go directly to the receiver via a “calibration path” built into the hardware. The resulting calibration pulses are used to generate a calibration filter. The calibration filter is applied to the received radar signals in the frequency domain either before or after pulse compression.
Owner:NAVICO
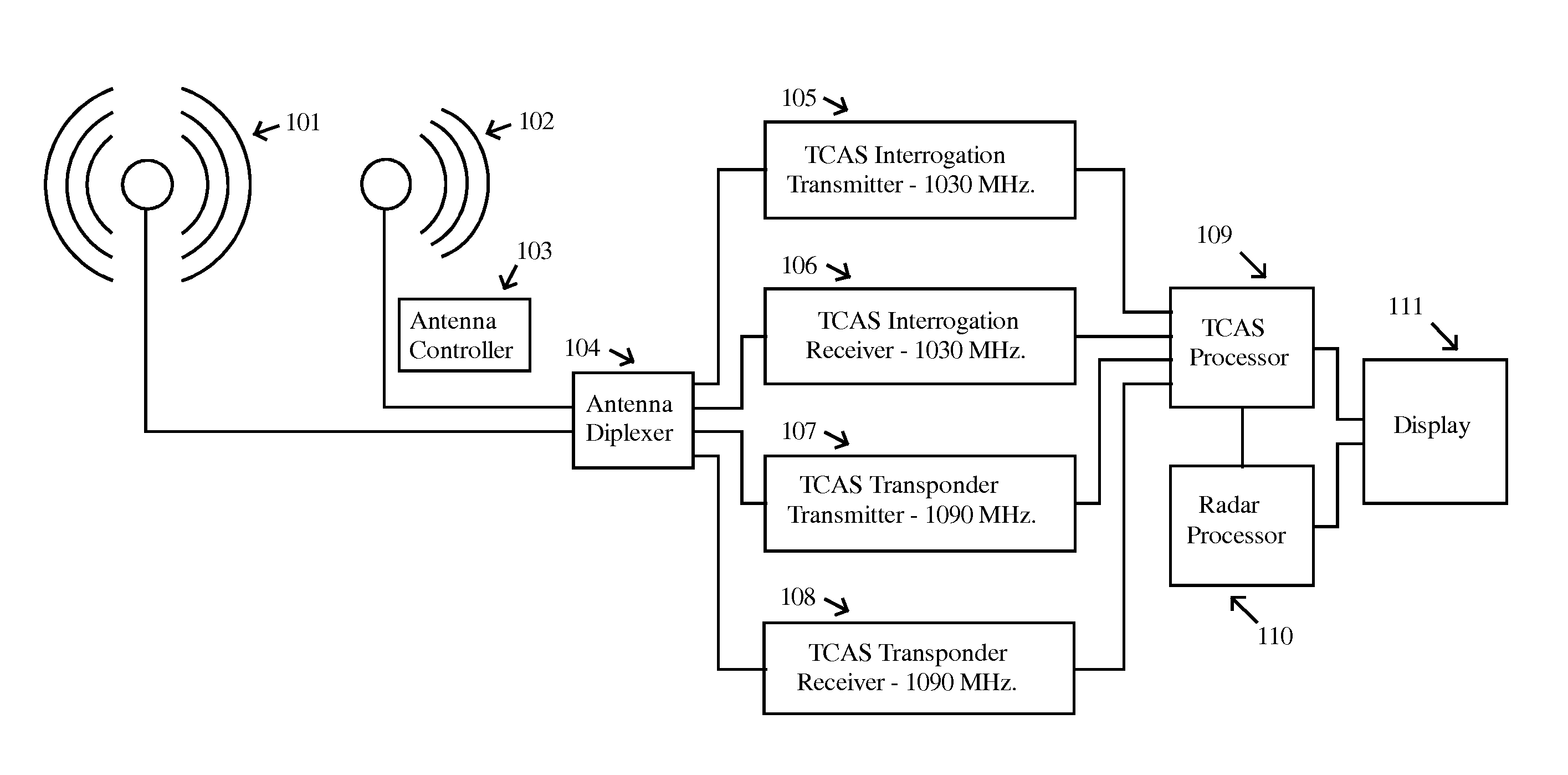
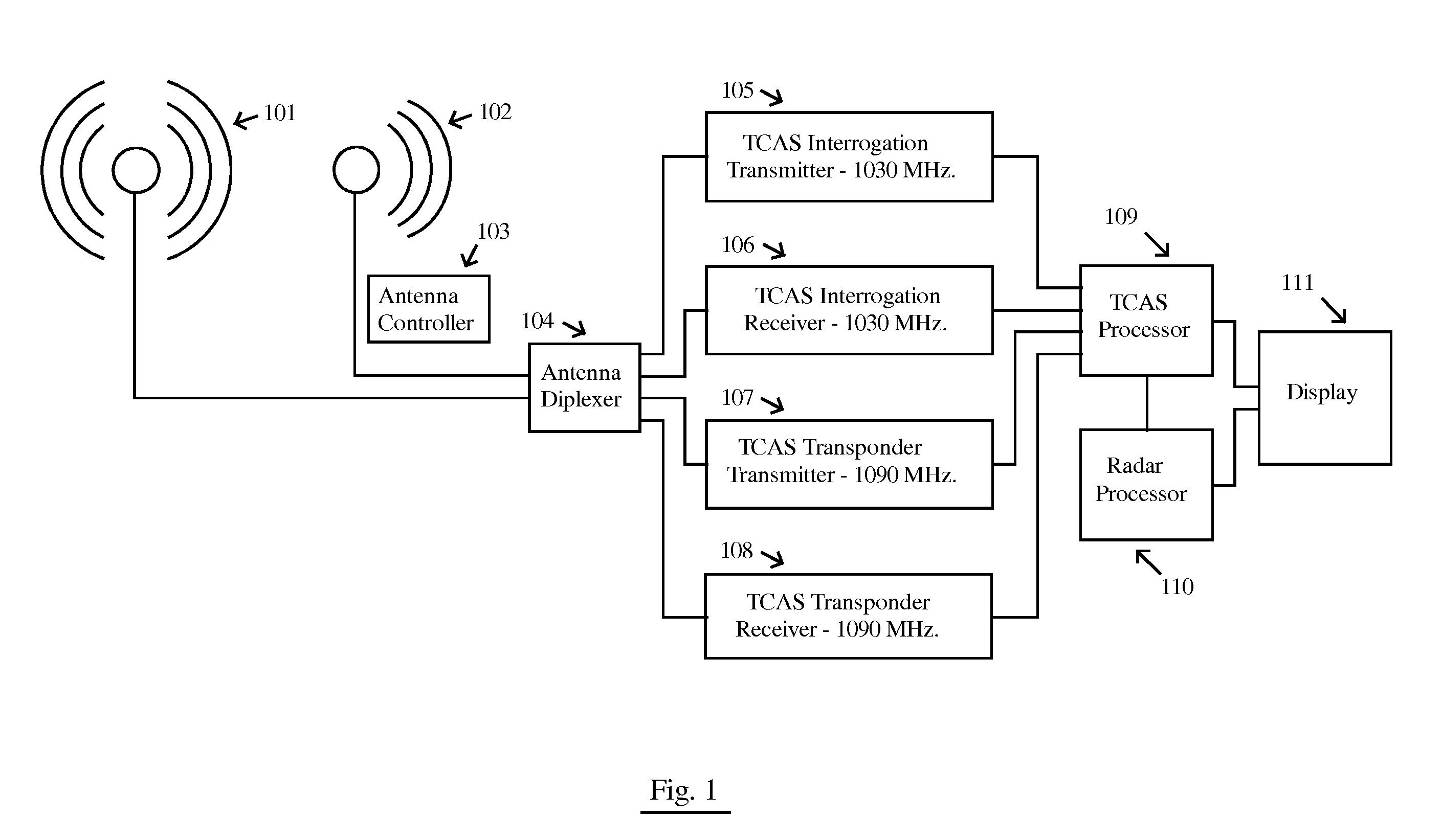
Aircraft bird strike avoidance method and apparatus using transponder
InactiveUS8279109B1Reduce difficultyMaximizes antenna to receive antenna isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTarget signalEngineering
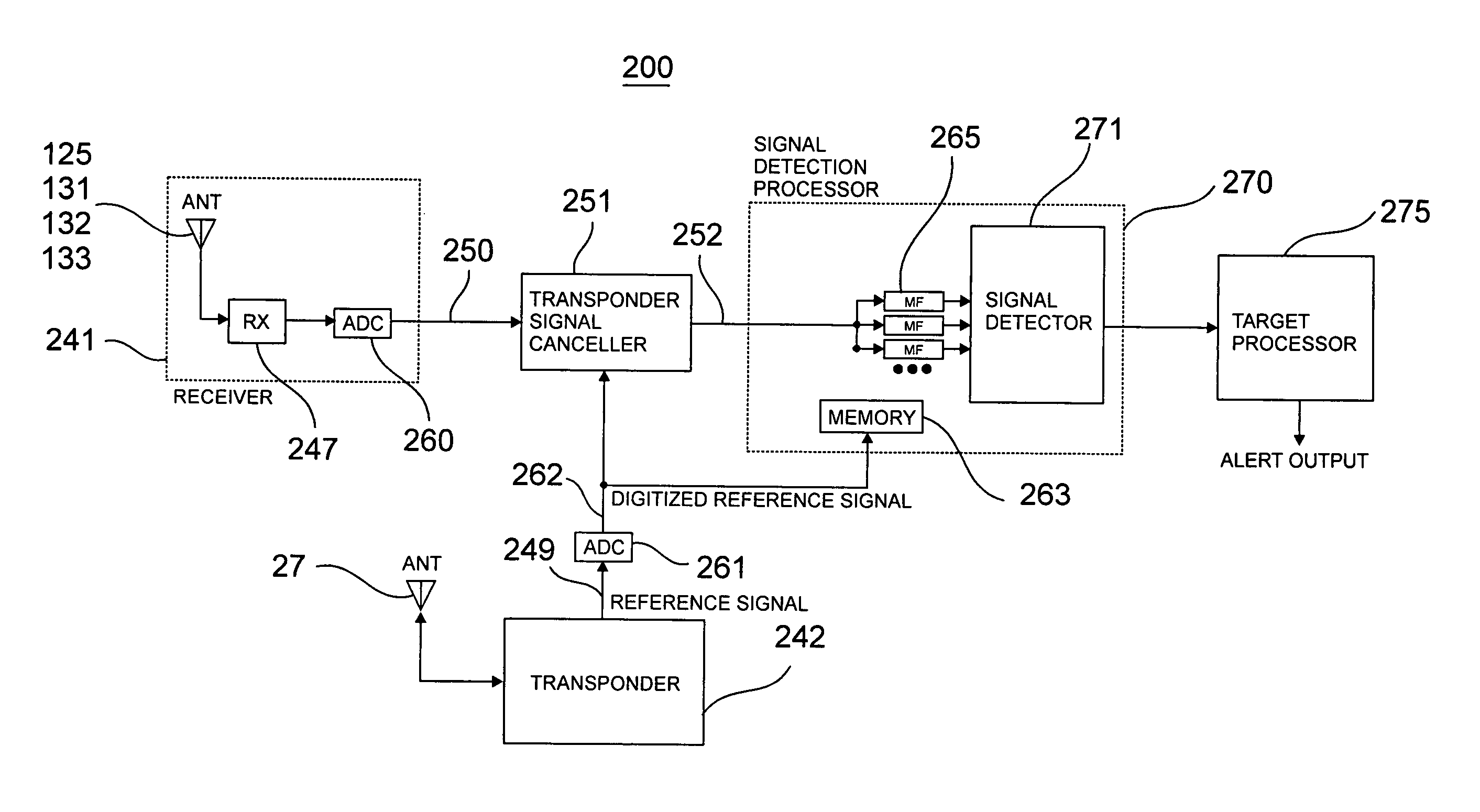
An aircraft avian radar is implemented using an existing aircraft transponder, Mode S, or TCAS installation as the radar transmitter. To eliminate self jamming of low level avian target signals by high level transmitter signals, the ending period of the transmission signal is digitized and cross correlated with the ending period of reflected avian target signals received after the transmission signal has ended. In a first implementation, the current transponder antenna is used for both transmission and reception. In a second implementation, an external receive only antenna is mounted in a position that maximizes the transmit antenna to receive antenna isolation. In a third implementation, a signal canceller and sample of the transmit signal are used to cancel or null out as much transmit signal as possible that couples directly to the receive antenna.
Owner:PIESINGER GREGORY HUBERT
High-performance coherent high-frequency radar multi-frequency detection method
ActiveCN106226761AImprove performanceLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase shiftedEmission channeling
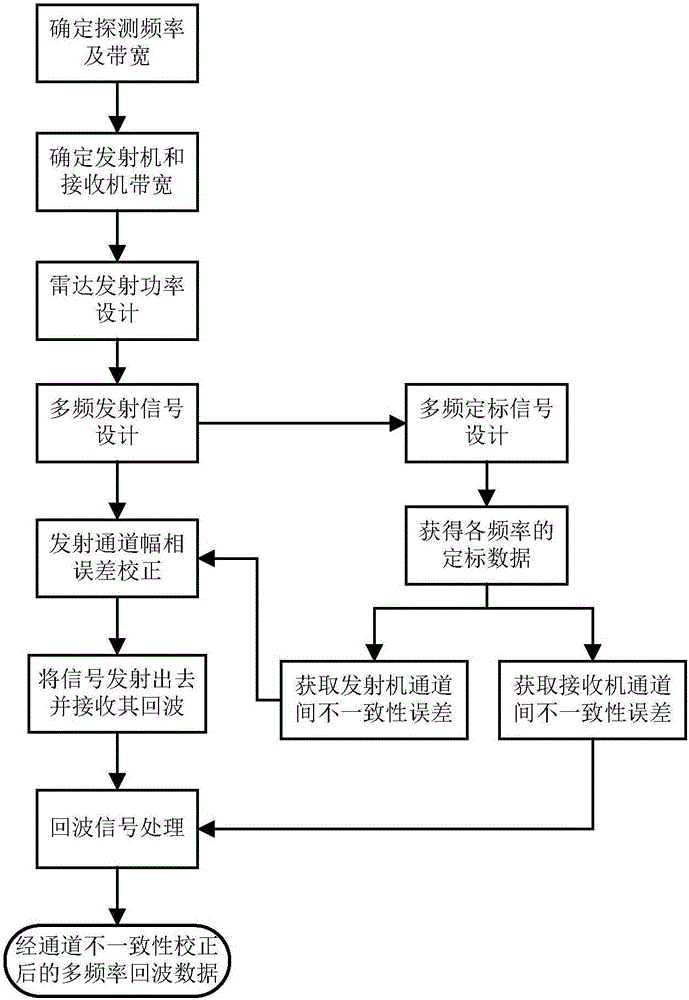
The present invention provides a high-performance coherent high-frequency radar multi-frequency detection method. The method comprises the steps of 1) assigning the frequency values of a plurality of frequencies and an observation wave beam of each frequency, and according to the direction of the observation wave beam, determining the phase shift increment of each frequency to thereby design an emission signal of each channel of a radar emitter; designing a calibration signal, obtaining an inconsistency error between emission channels and an inconsistency error between reception channels, namely, an amplitude error and a phase error, by taking a first channel as the reference; utilizing the inconsistency error between the emission channels to carry out the amplitude compensation and the phase compensation on the emission signals to thereby correct the inconsistency between the emission channels; 2) using the emitter to filter and amplify the compensated emission signals, and then using an antenna to emit the signals out; then, using the antenna and a radar receiver to receive the echoes of the signals; 3) carrying out the frequency separation on the echo digital signals, and utilizing the inconsistency error between the emission channels obtained in the step 1 to compensate the amplitude and the phase to thereby obtain the radar echo data.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
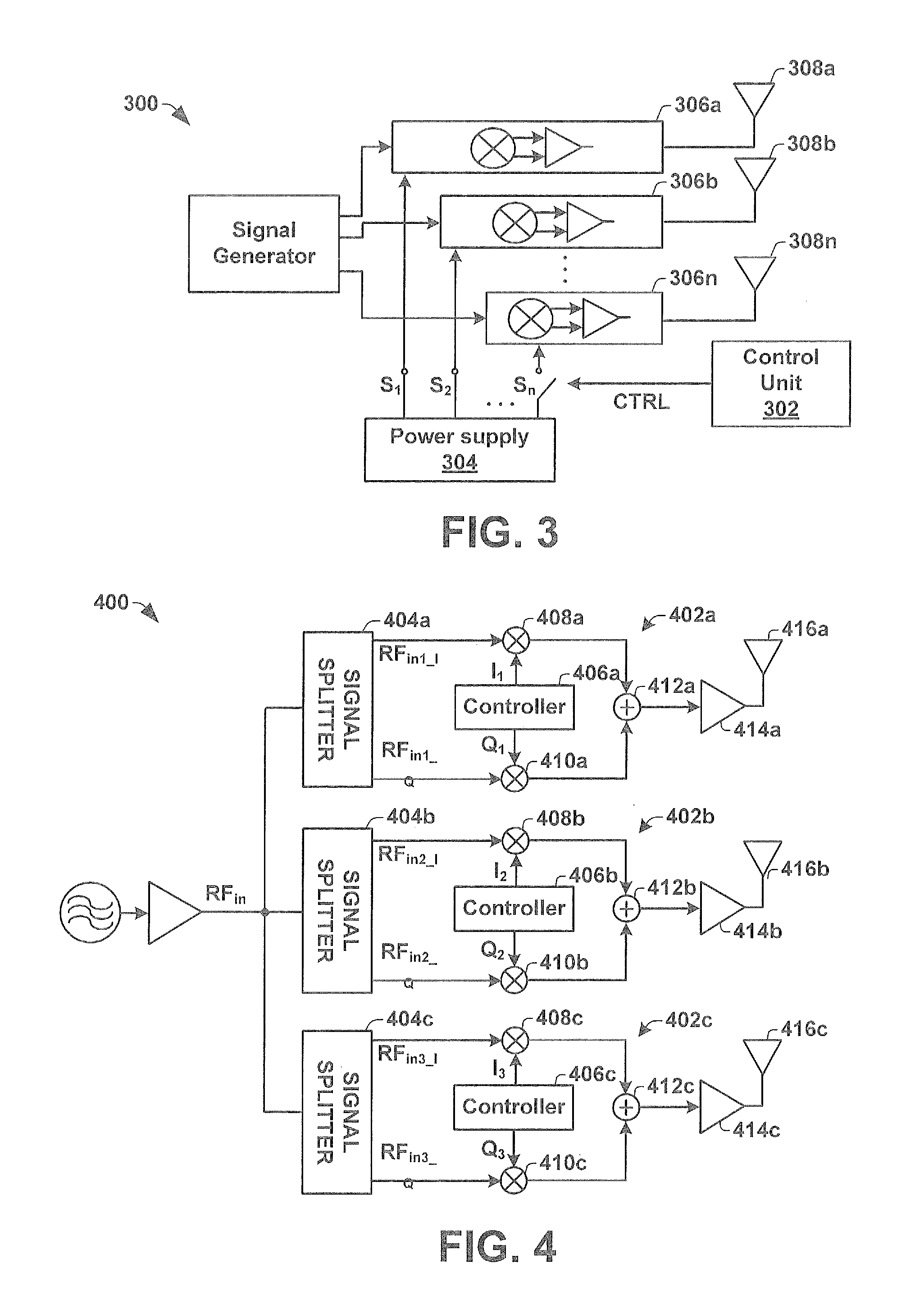
Automotive Radar Transmitter Architecture
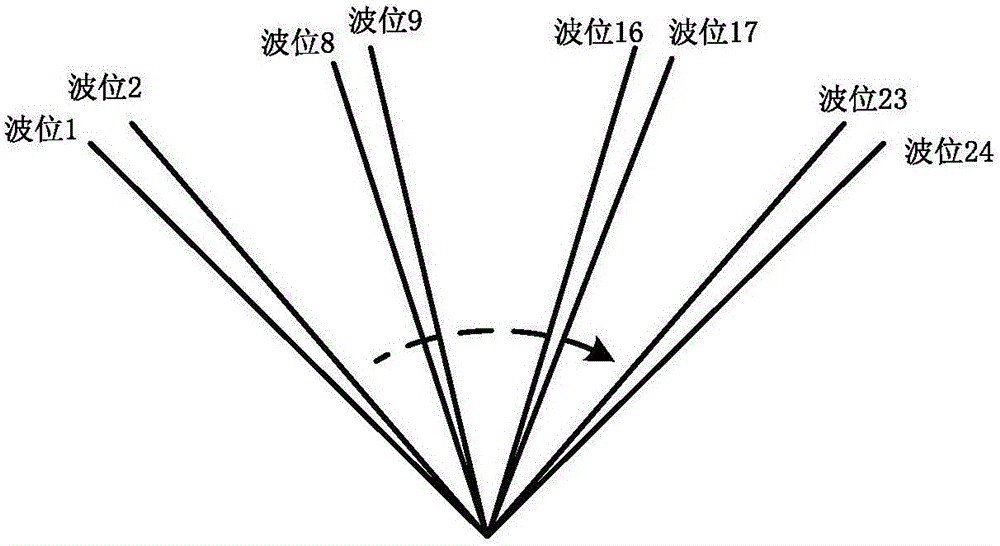
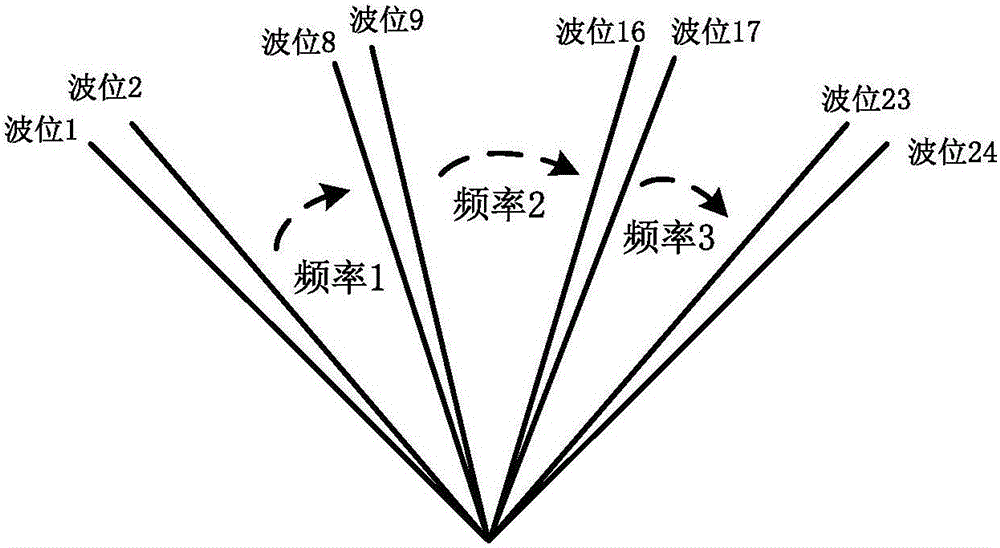
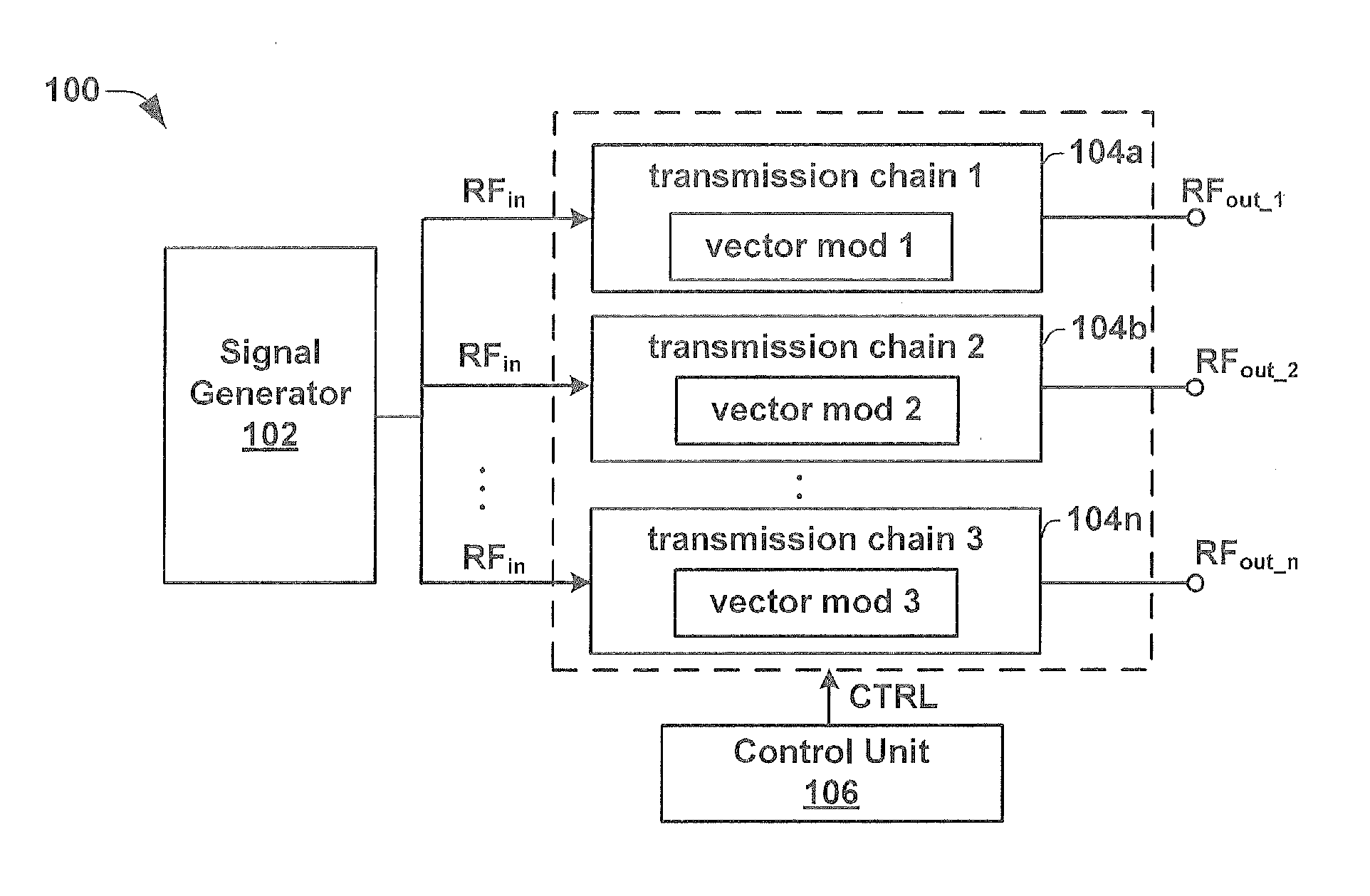
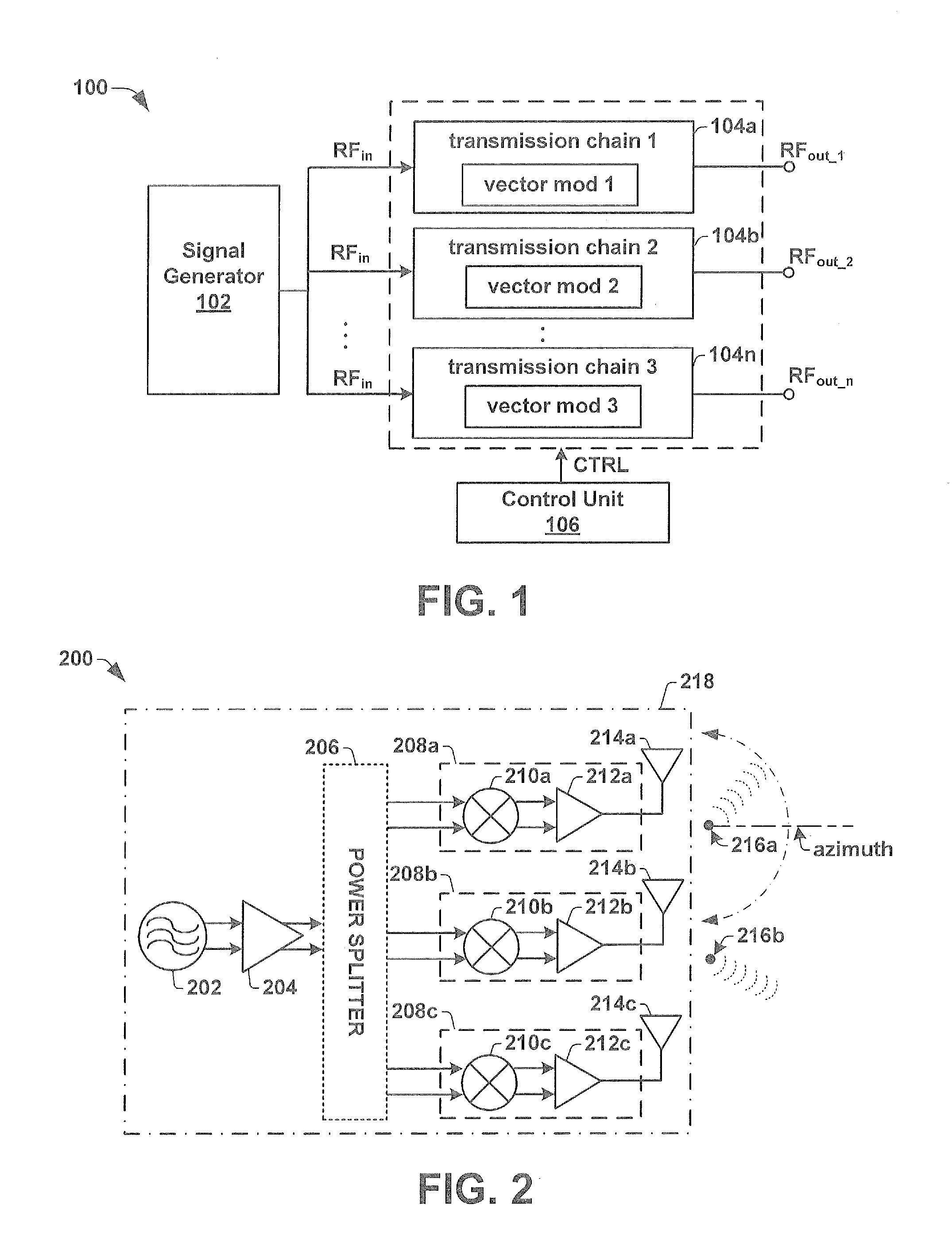
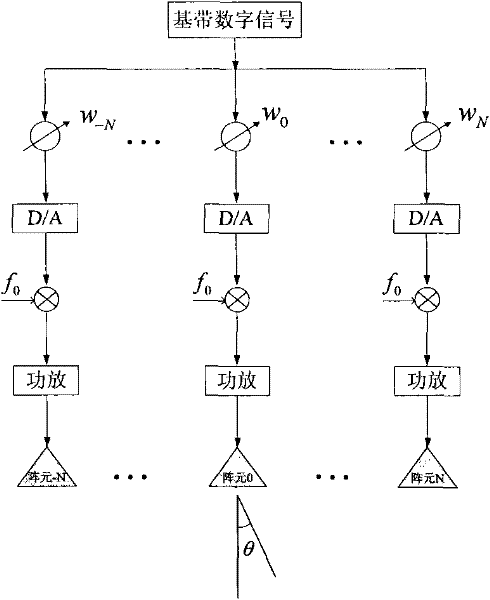
ActiveUS20130088383A1Radio transmissionIndividually energised antenna arraysBeam steeringEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a radar transmitter comprised within a single integrated chip substrate, which is capable of continuous beam steering of a transmitted radar beam as well as an option to change the physical position of the origin of the transmit radar beam. The radar transmitter has a signal generator that generates an RF signal. The RF signal is provided to a plurality of independent transmission chains, which contain independently operated vector modulators configured to introduce an individual phase adjustment to the high frequency input signal to generate separate RF output signals. A control unit is configured to selectively activate a subset of (e.g., two or more) the independent transmission chains. By activating the subset of independent transmission chains to generate RF output signals with separate phases, a beam steering functionality is enabled. Furthermore, the subset defines a changeable position of the transmitted radar beam.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Dual Polarization Radar with Automatic Built-In Test Equipment and Calibration
ActiveUS20090284409A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationUltrasound attenuationRadar systems
A calibration system for the receiver of a dual polarization radar system has been developed. The system includes a radar transmitter that transmits signals in horizontal and vertical polarizations and a radar receiver that receives the horizontal and vertical polarization signals. The system also includes a test signal generator that generates a continuous wave test signal. A calibration circuit for the radar receiver modifies the test signal to simulate weather conditions by adjusting the attenuation and Doppler phase shift of a continuous wave test signal.
Owner:BARON SERVICES
RF channel calibration for non-linear FM waveforms
ActiveUS20050190100A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationRadar signal processingSystems approaches
A system, method, and computer program product that performs self-calibration of pulse-compression radar signals. The system includes an antenna, a receiver, a transmitter, and a radar signal processor. Under normal (non-calibration) operation the radar transmitter generates a pulse compression waveform and transmits it via the antenna. Any reflections from this waveform are detected by the same antenna and processed by the receiver. The received radar signal then undergoes pulse compression followed by more mode-specific processing (windshear, weather, ground map, etc.) by the radar processor. During calibration, the radar transmitter generates a similar pulse compression waveform (i.e., calibration pulses), but the calibration pulses bypass the antenna and go directly to the receiver via a “calibration path” built into the hardware. The resulting calibration pulses are used to generate a calibration filter. The calibration filter is applied to the received radar signals in the frequency domain either before or after pulse compression.
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
Airborne three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging system based on transmitted beam scanning
InactiveCN102253386ALow costIncrease costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingBeam scanning
The invention discloses an airborne three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging system based on transmitted beam scanning. In the current three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging system, echo data volume is large, imaging processing is complex and timeliness is low. Using the airborne three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar imaging system of the invention can solve the above problems. In the invention, a radar transmitter generates narrow wave beams possessing different preset orientations in a vertical heading by using a transmitted beam forming technology. A phased-arrayantenna, which is arranged vertically to the heading in a flight plane, successively transmits the narrow wave beams generated by the radar transmitter one by one. Narrow wave beam scanning to the vertical heading can be performed in every direction at any time. The echo is received by a single array element of the phased-array antenna and is sent to a radar receiver so as to complete acquisitionof single channel echo data. An imaging processor can be used to three-dimensionally image the collected echo data. By using the invention, echo data volume is small, imaging processing is not complex and timeliness is strong. And the system has the ability of rapid three dimensional imaging an object scene, especially the complex object scene.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Wide area high resolution SAR from a moving and hovering helicopter
A hovering helicopter has a radar transmitter / receiver for transmitting radar pulses for illuminating a target for SAR imaging, and rotor blades for generating lift. Radar reflectors are on the rotor blades. The radar reflectors are oriented to reflect the radar pulses from the transmitter to the target as the rotor blades rotate. The radar pulses reflected by the moving reflector from the transmitter are timed to generate the synthetic aperture image using radar returns from the target. The receiver also receives blade returns directly reflected from the moving reflectors attached to the lift rotor blades. The receiver analyzes the blade returns to extract motion details of the reflectors and uses the motion details for motion compensation of target returns for SAR imaging.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com