Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Optical data disk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
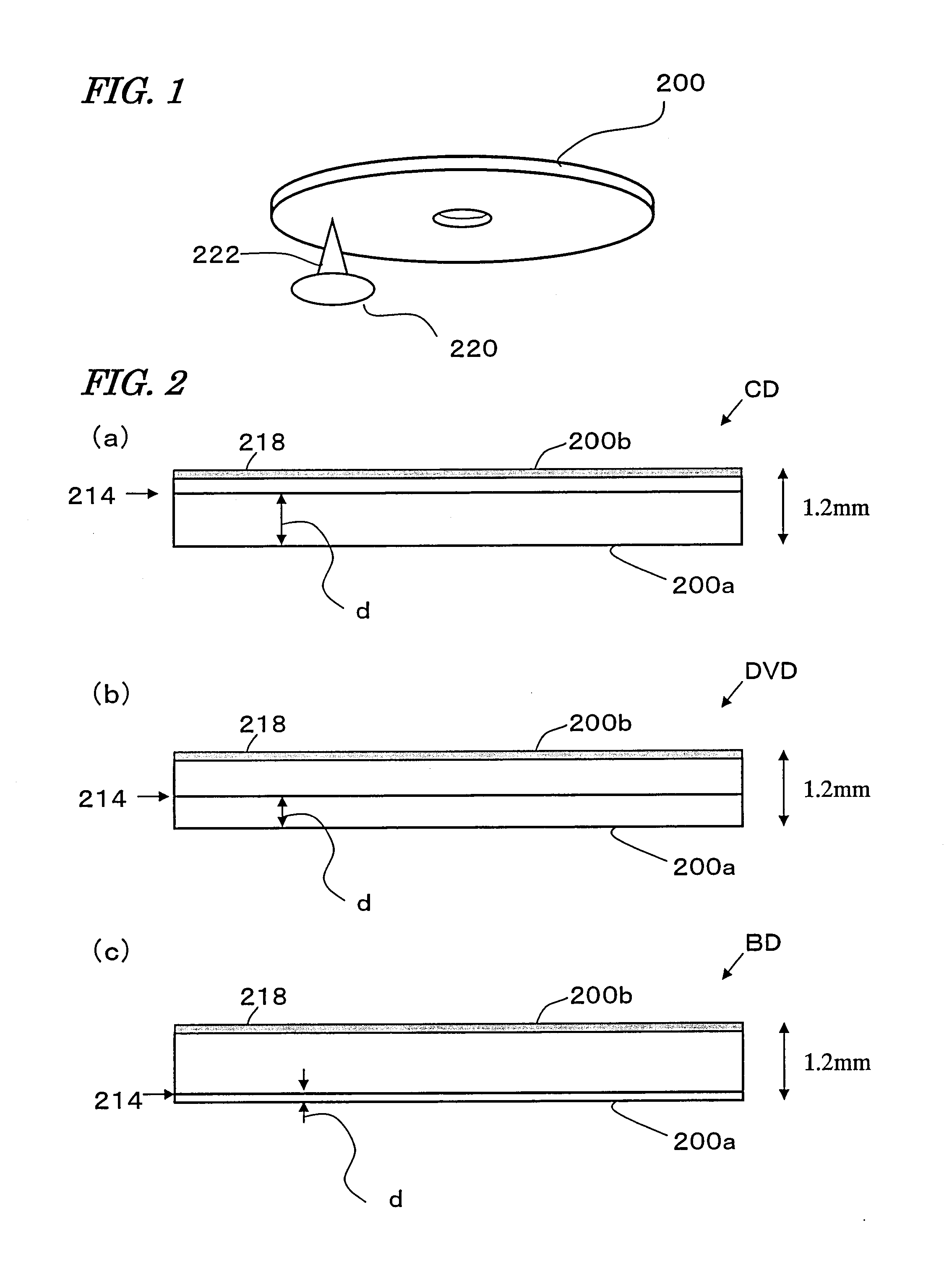
An optical disc is an electronic data storage medium that can be written to and read using a low-powered laser beam.
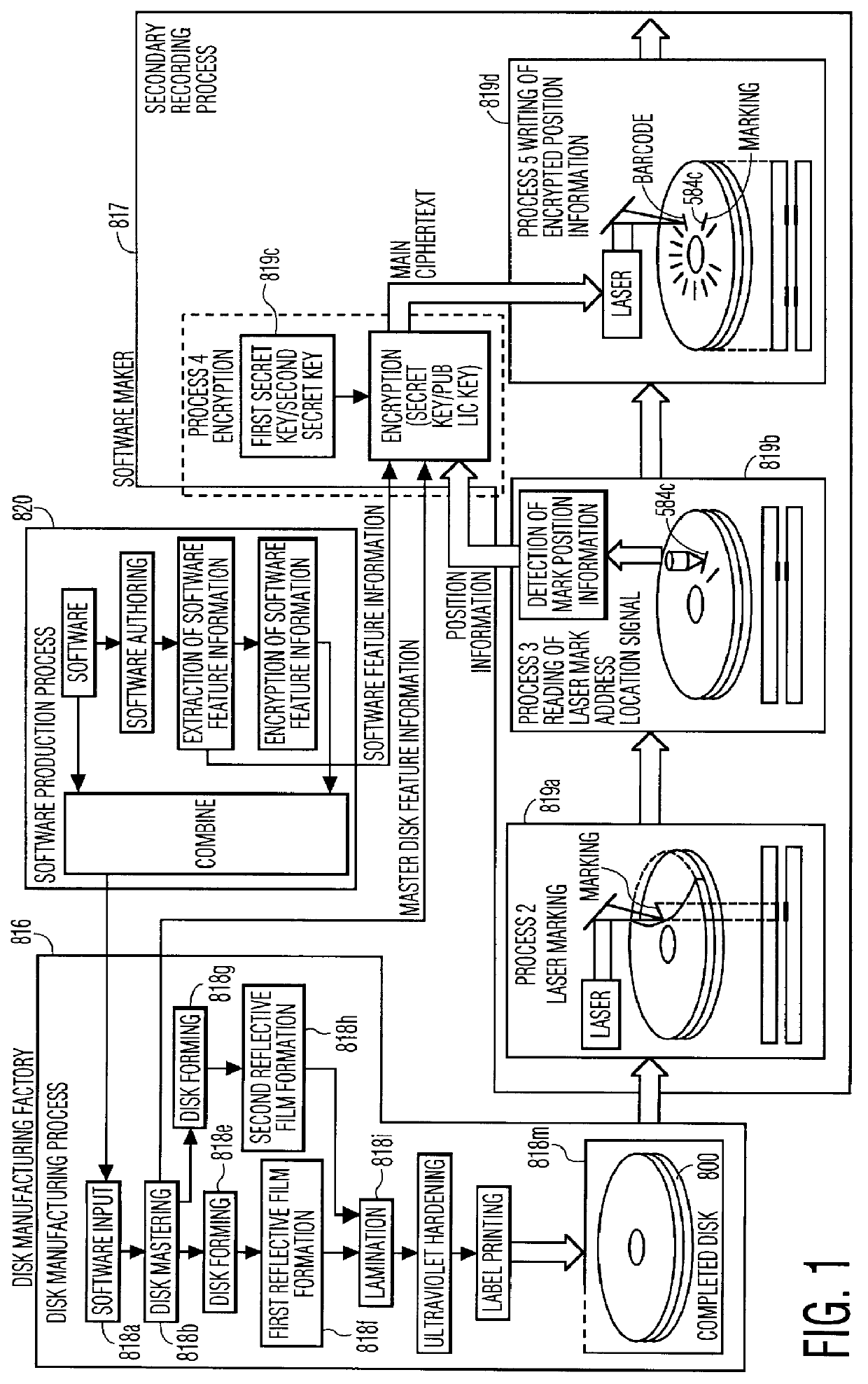
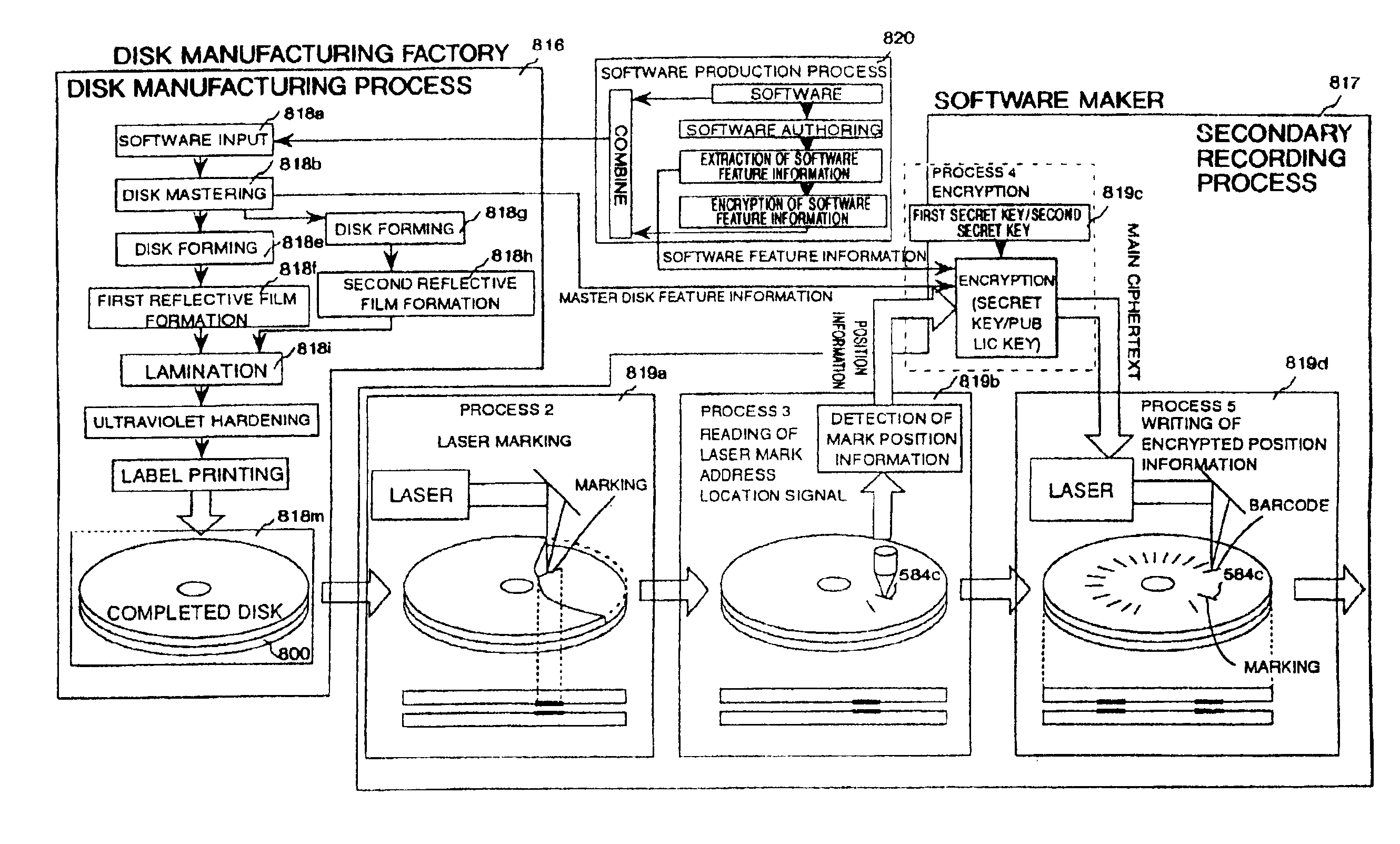
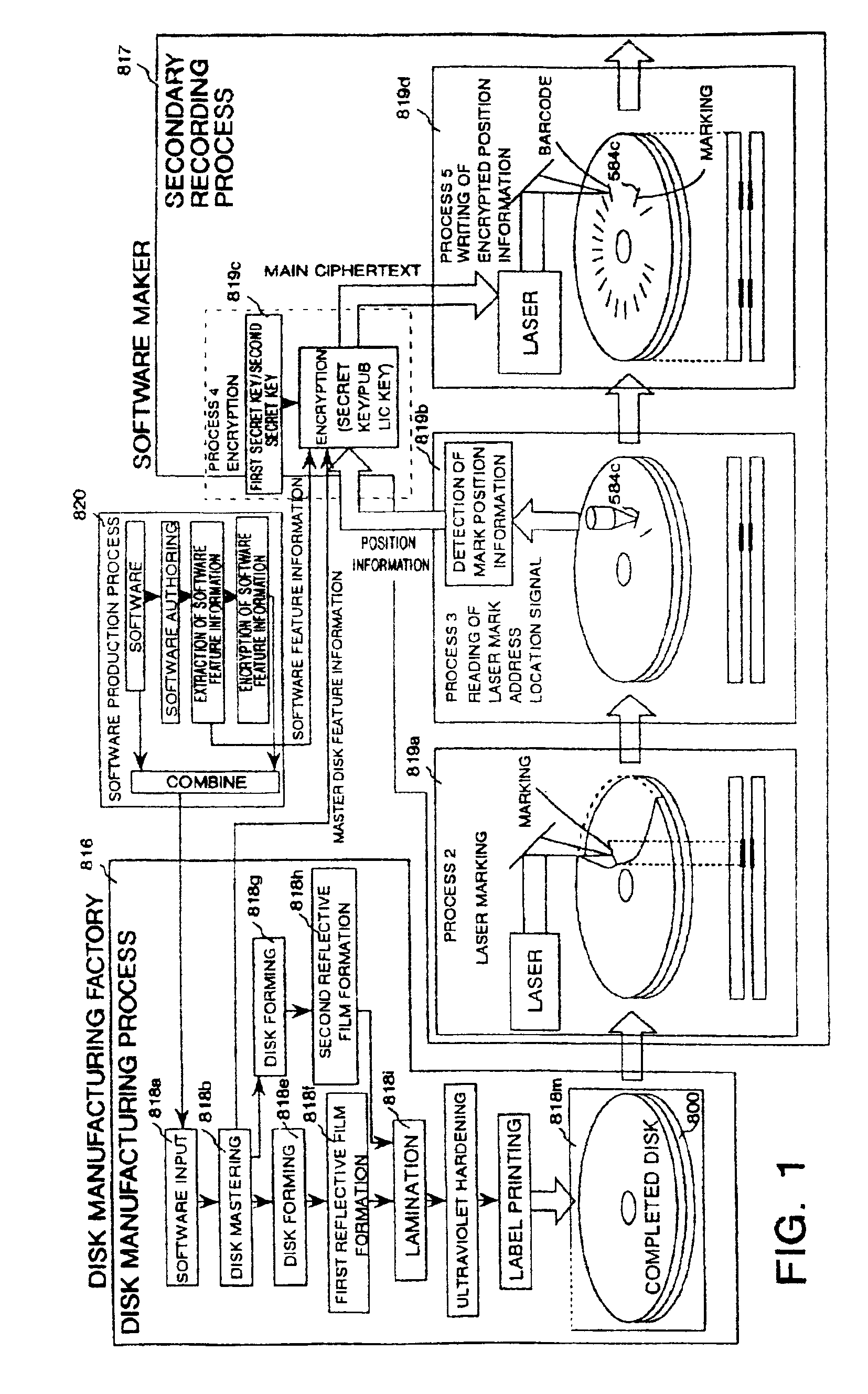
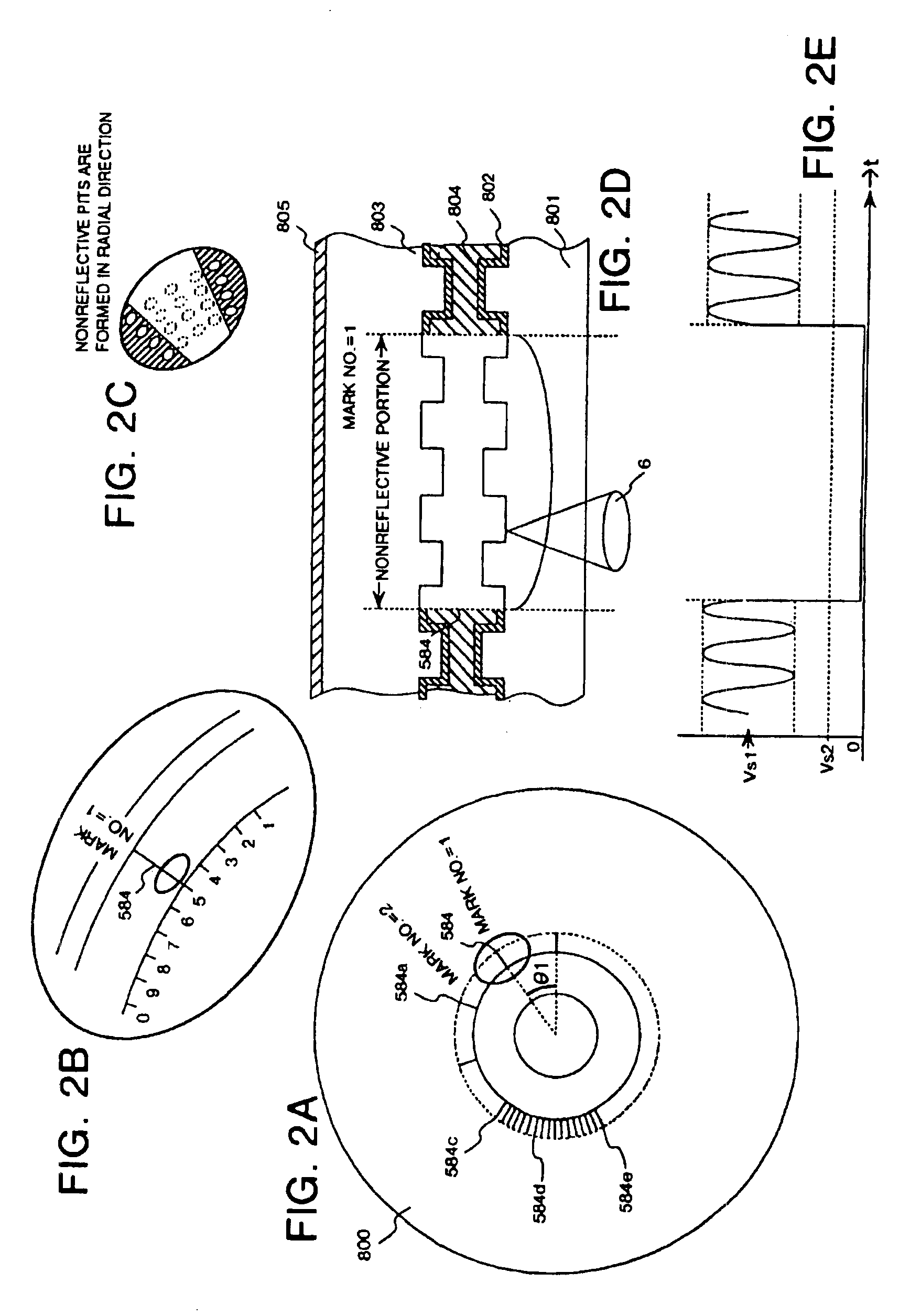
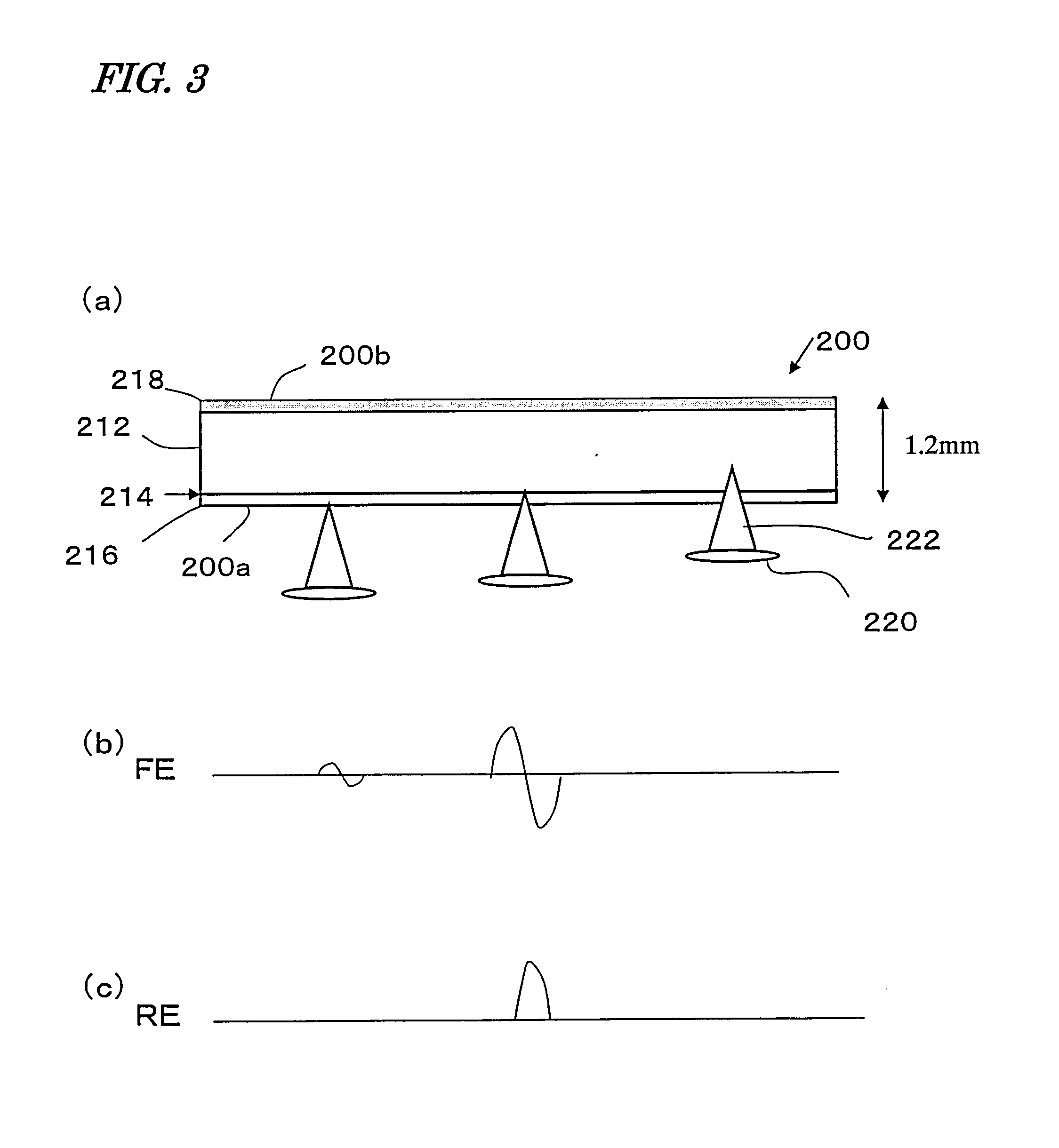
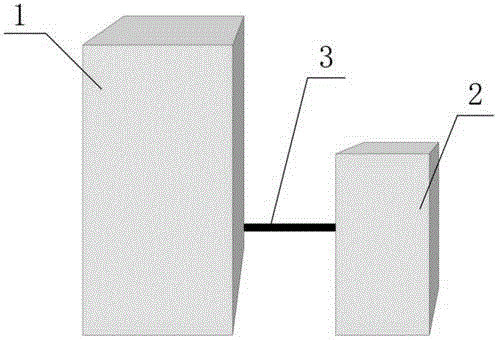
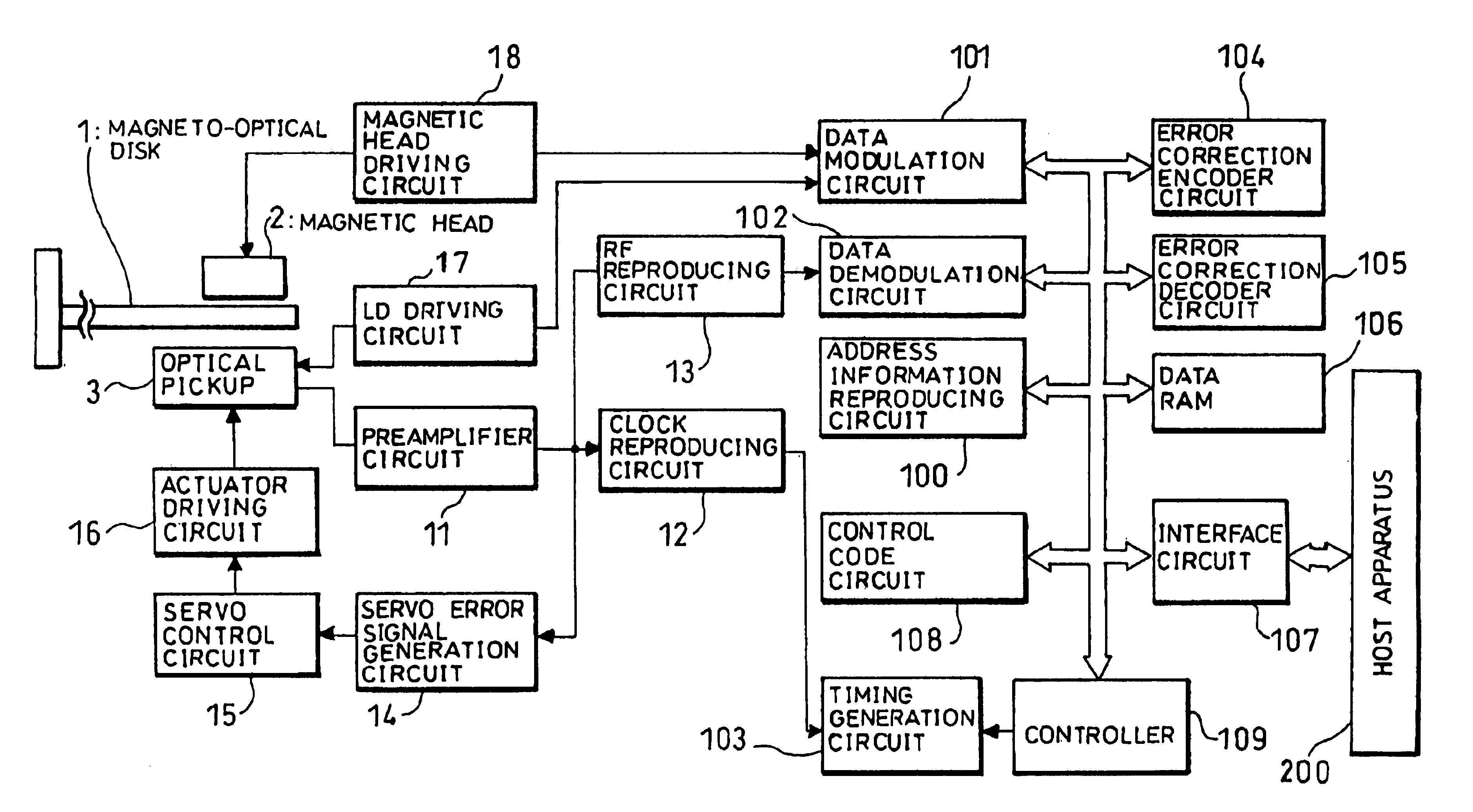
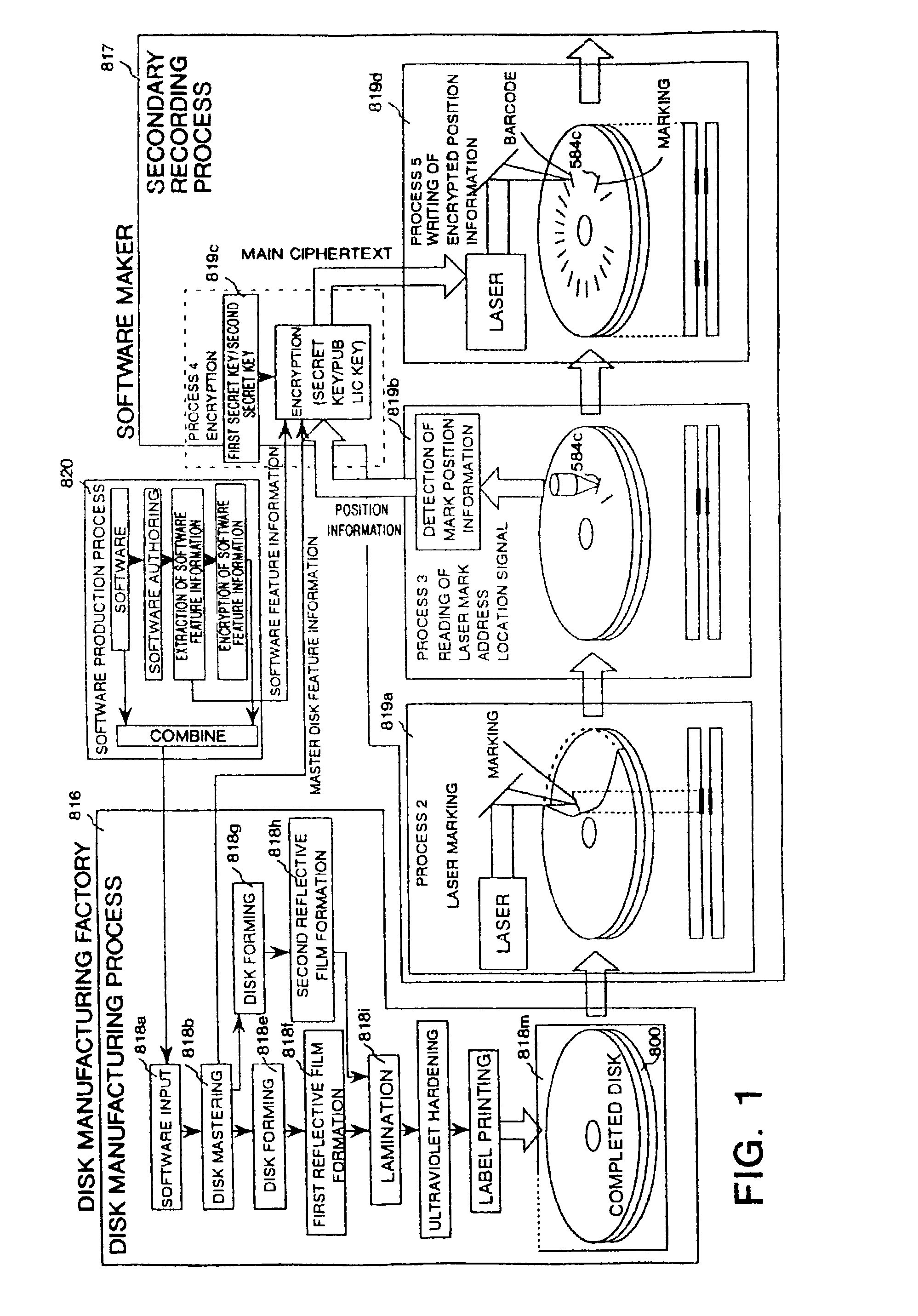
Optical disk, an optical disk barcode forming method, an optical disk reproduction apparatus, a marking forming apparatus, a method of forming a laser marking on an optical disk, and a method of manufacturing an optical disk
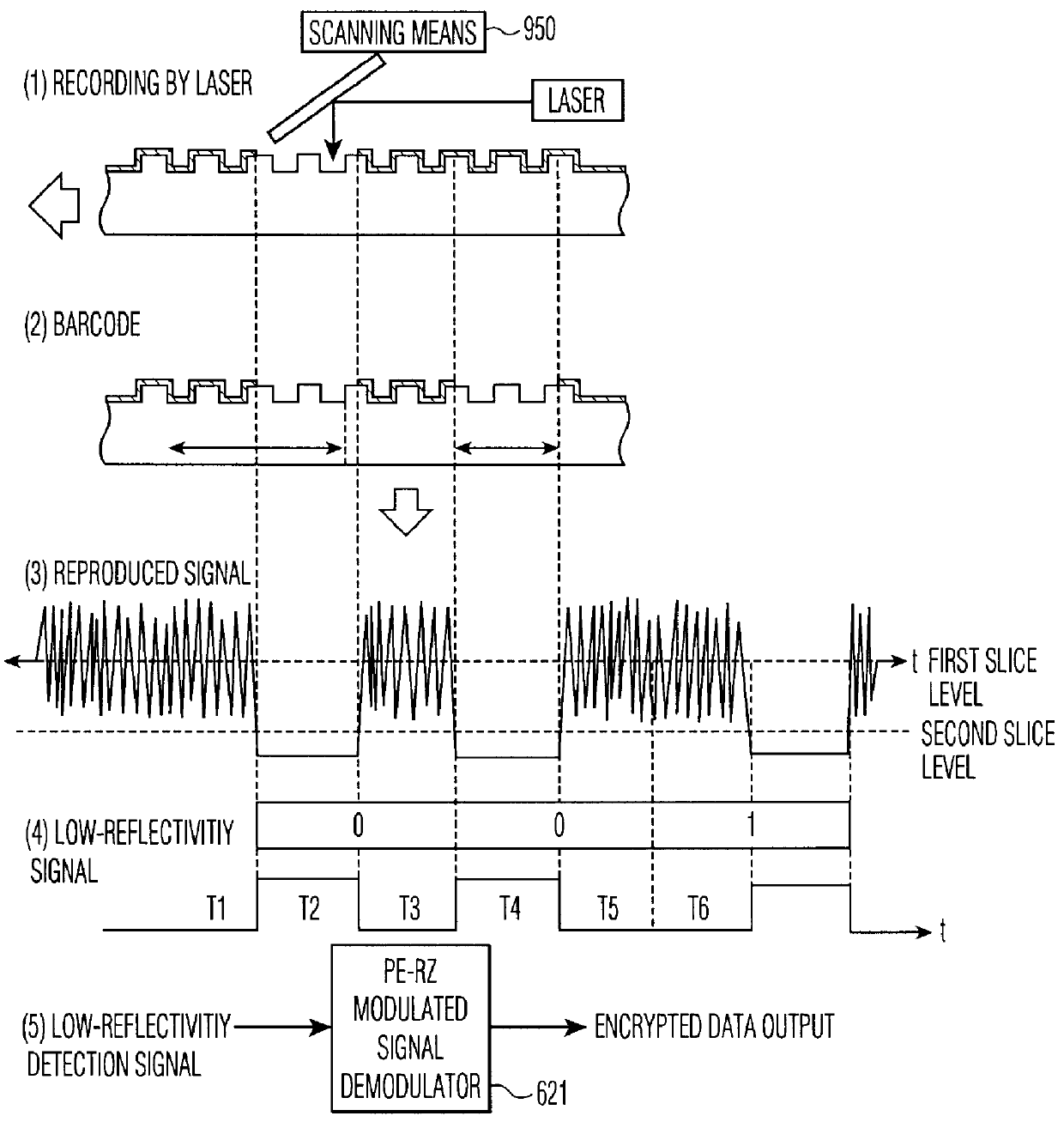
Disclosed is an optical disk barcode forming method wherein, as information to be barcoded, position information for piracy prevention, which is a form of ID, is coded as a barcode and is recorded by laser trimming on a reflective film in PCA area of an optical disk. When playing back the thus manufactured optical disk on a reproduction apparatus, the barcode data can be played back using the same optical pickup.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for bit prediction using a multi-pixel detector
InactiveUS20100157771A1Combination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersData Coding SchemeData encoding
The present techniques provide methods and systems for more reliable reading of optical data disks. In embodiments, a multi-pixel detector that is segmented into multiple areas, or detector segments, may be used to detect a pattern in the light reflected from an optical data disk. The pattern may include light scattered from a single bit that may be under a center detector, as well as light scattered from proximate bits. The detector system may then combine the quantized values from each of the detector segments mathematically to determine the presence or absence of a bit or bits of data. The mathematical combination may also use data that is known about the status of adjacent data bits (such as previously read bits, or bit patterns which are allowed or not allowed by specific data encoding schemes) to improve the accuracy of the bit prediction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Intelligent optical storage apparatus
InactiveCN105869662AStore data fastStore data securityOptical re-recordingRecord information storageOptical storageEnvironmentally friendly
The invention provides an intelligent optical storage device, including a hard disk, an optical disc cartridge, an optical drive, a processor, and a manipulator; Put the CD into the CD-ROM drive, burn the data read into the hard disk to the CD-ROM through the CD-ROM drive, or copy the data from the CD-ROM to the hard disk through the CD-ROM drive, and finally take the CD-ROM out of the CD-ROM drive and put it back into the CD-ROM box through the manipulator; The hard disk, the CD box, and the CD-ROM drive are arranged sequentially from top to bottom, and the manipulator is arranged on one side of the opening of the CD-ROM box. The intelligent optical storage device provided by the present invention reads the data input from the outside into the hard disk, and then stores the data in the hard disk in the optical disk copied by the optical drive, or transfers the required data to the hard disk through the optical drive through the optical disk, and then The data is read out through the hard disk, and the device stores data quickly and safely, and does not consume power, energy, energy, and environmental protection.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for drawing visible image on optical disk by vibrating laser beam focus
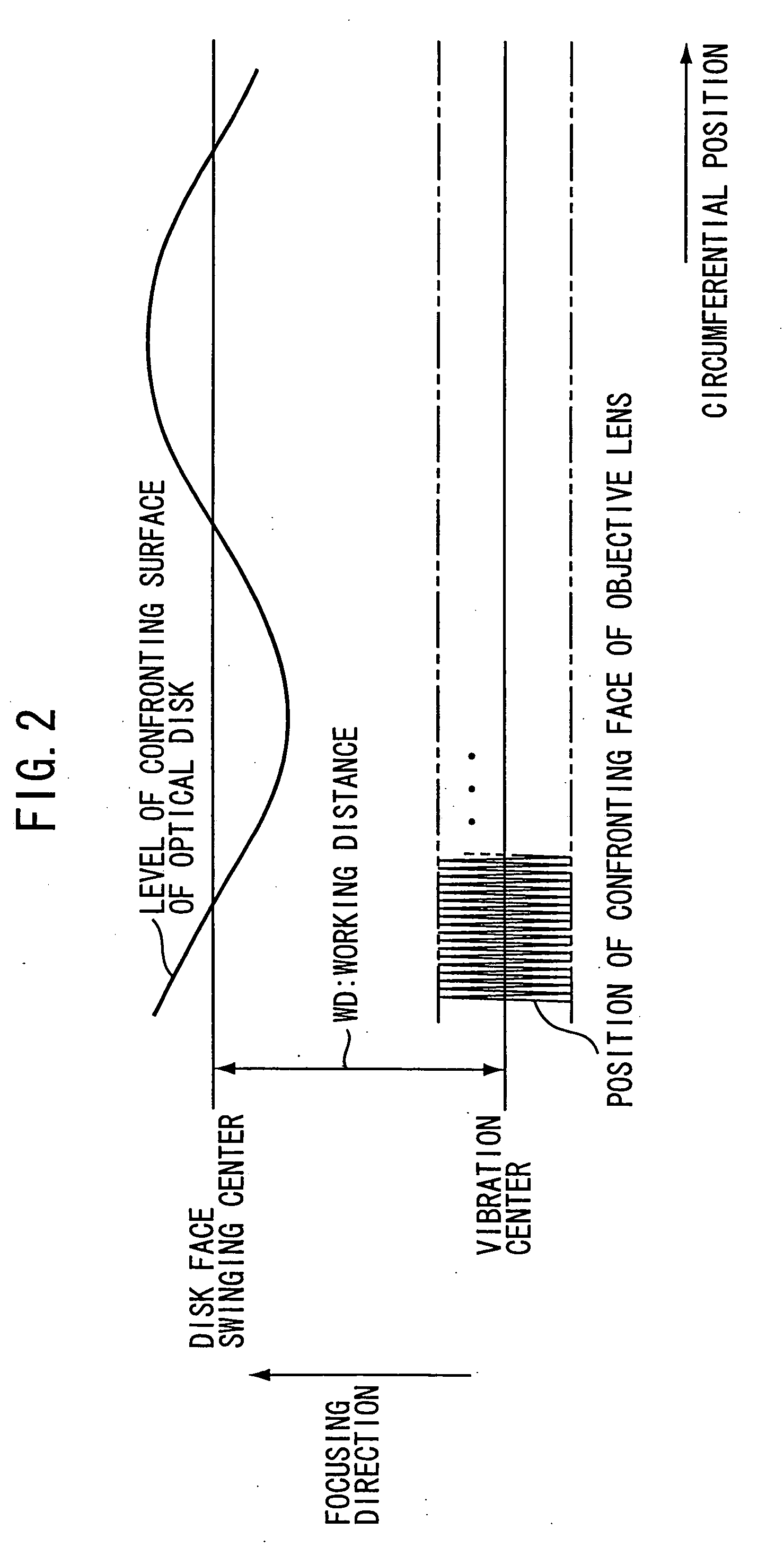
A method is designed for drawing a visible image on an optical disk recordable by means of an optical pickup which irradiates an optical beam onto the optical disk through an objective lens of the optical pickup. The method is carried out by the steps pf rotating the optical disk having a target layer on which the drawing is to be performed, applying an oscillation signal to a focus actuator of the optical pickup to thereby vibrate the objective lens in an optical-axis direction thereof so that a focus point of the optical beam recurrently passes through the target layer of the optical disk, and controlling a power of the optical beam to form a recording spot on the target layer each time the focus point of the optical beam passes through the target layer so that a visible light property of the target layer is changed to thereby perform the drawing on the target layer.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
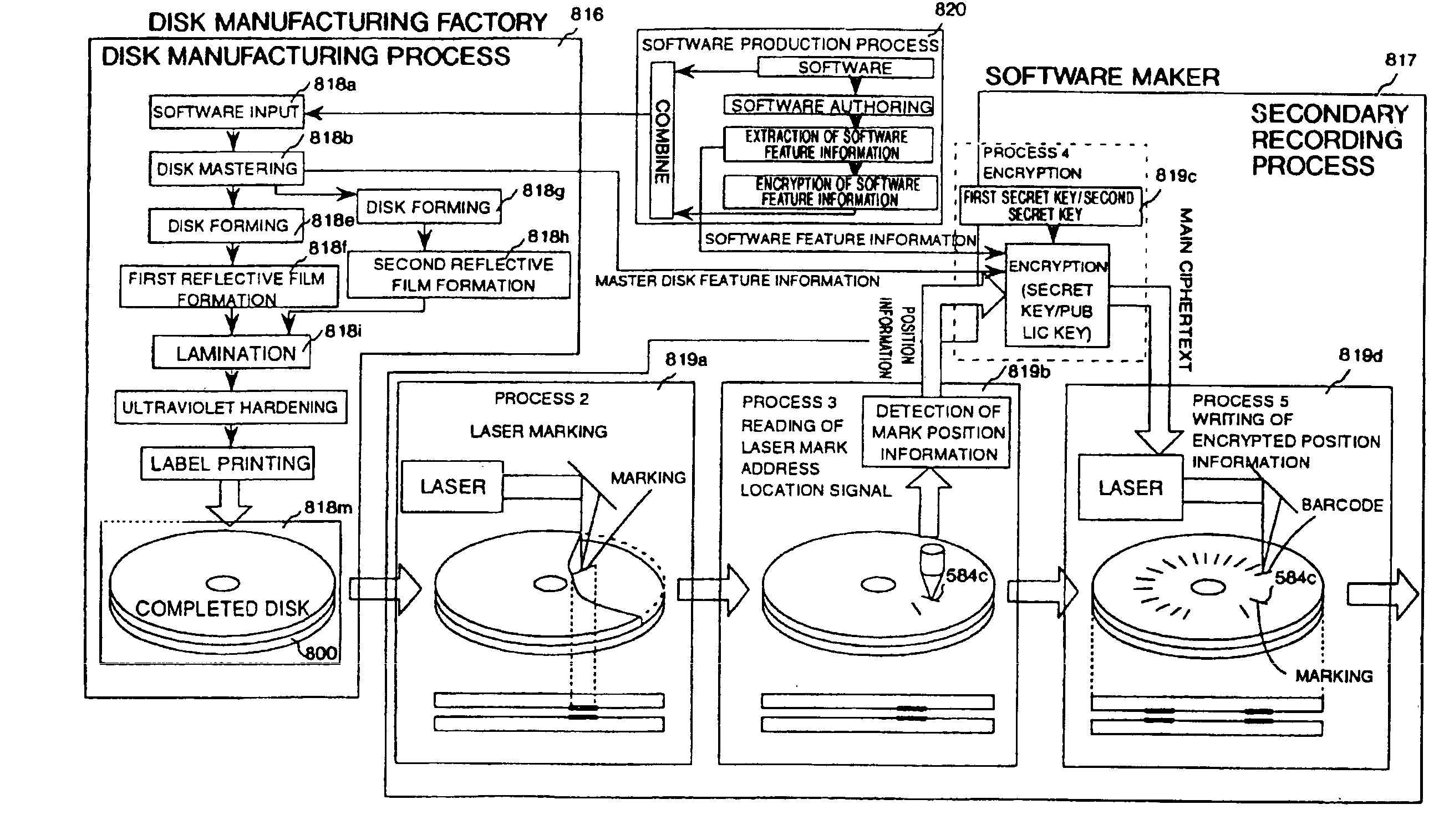
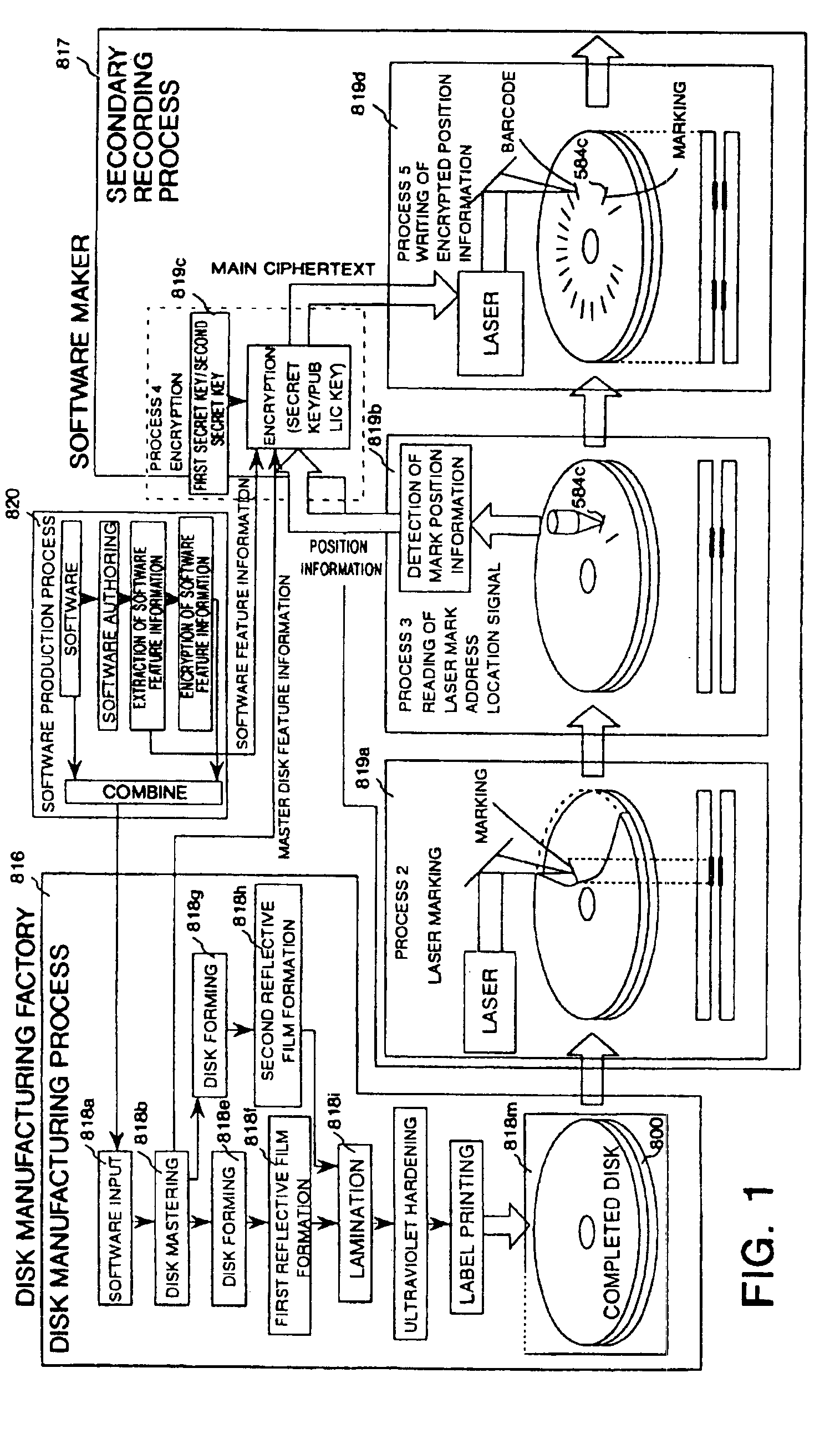
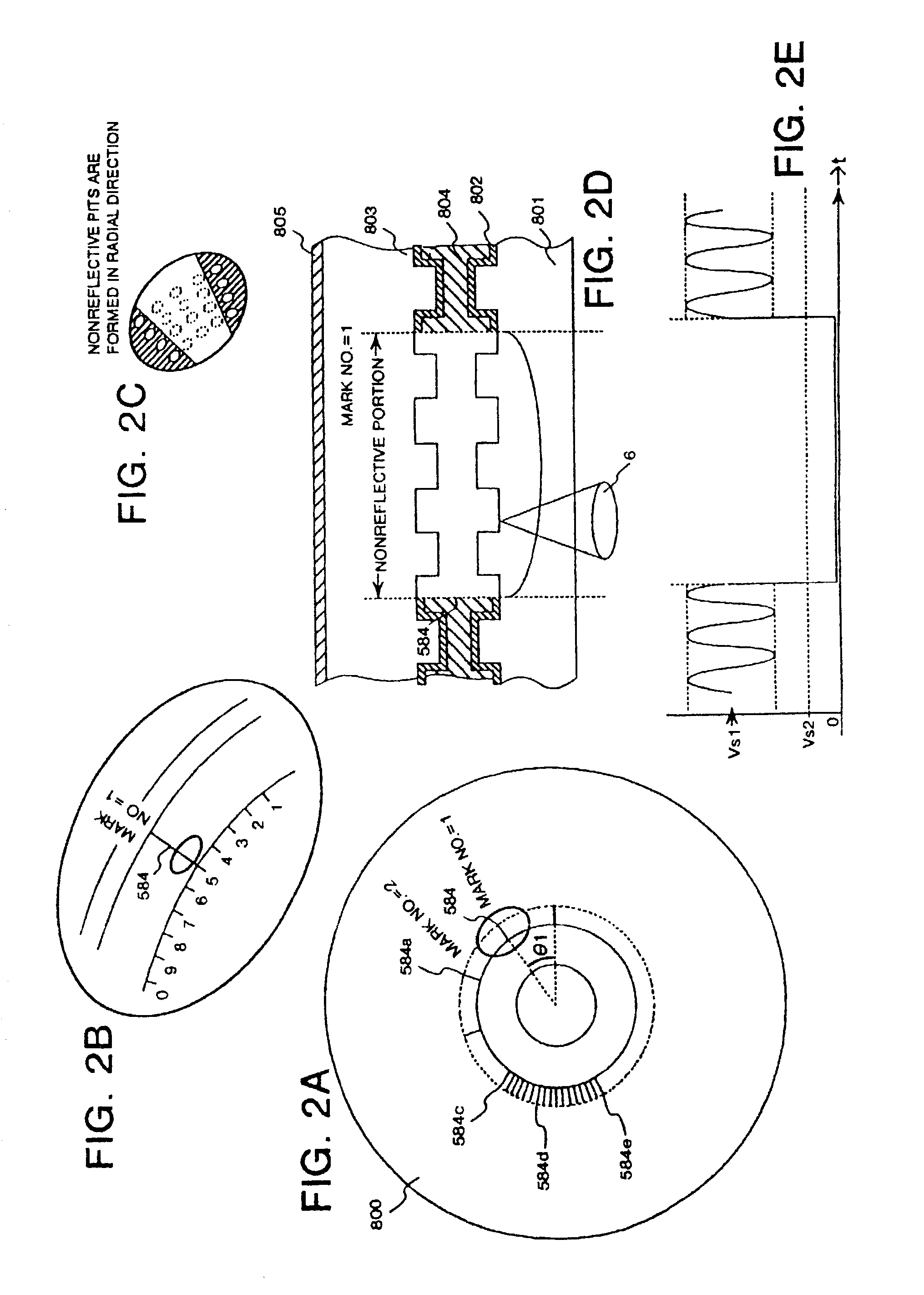
Mark forming apparatus, method of forming laser mark on optical disk, reproducing apparatus, optical disk and method of producing optical disk
InactiveUSRE39297E1Inhibit productionInformation obtainedFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageDigital signatureComputer science
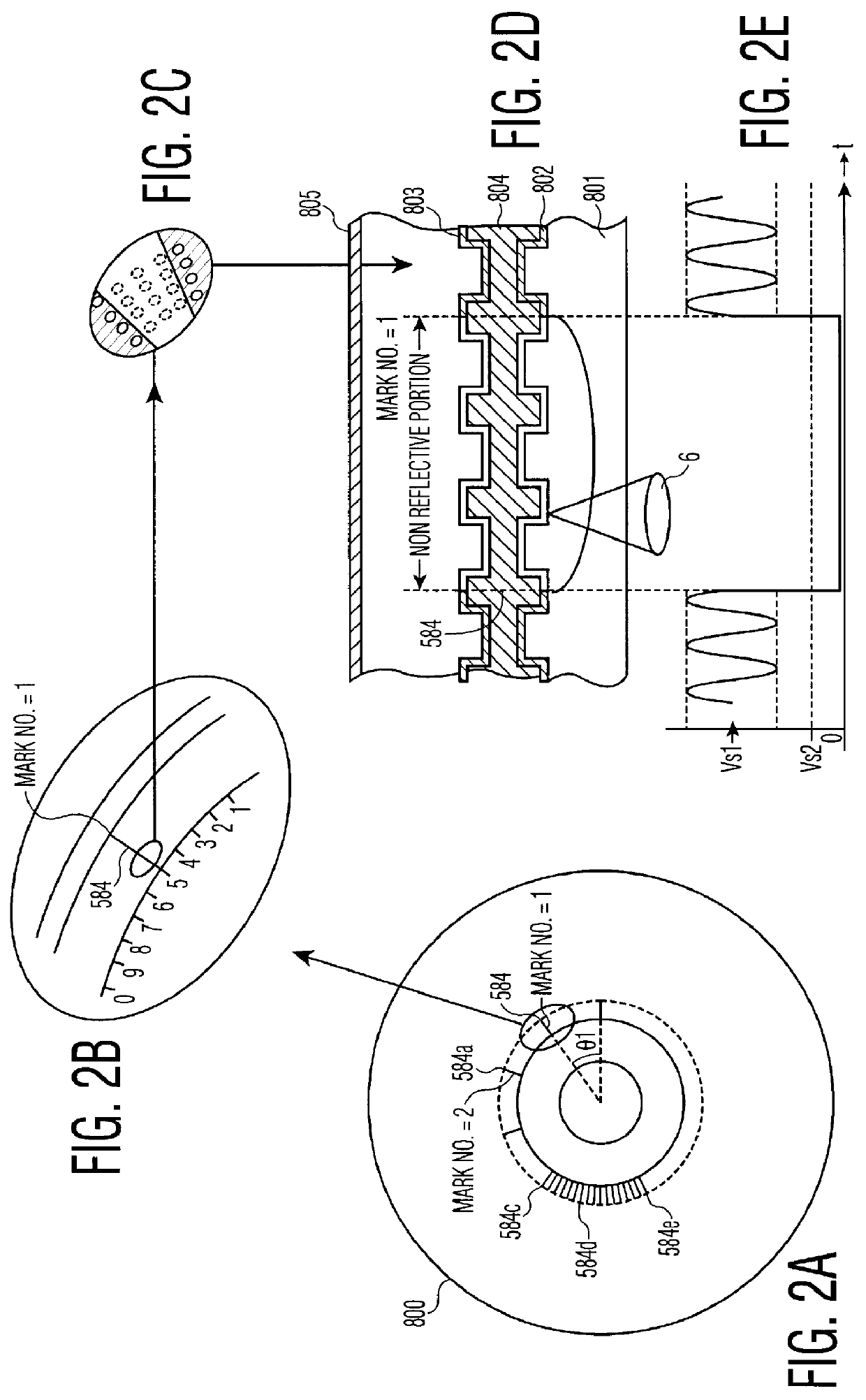
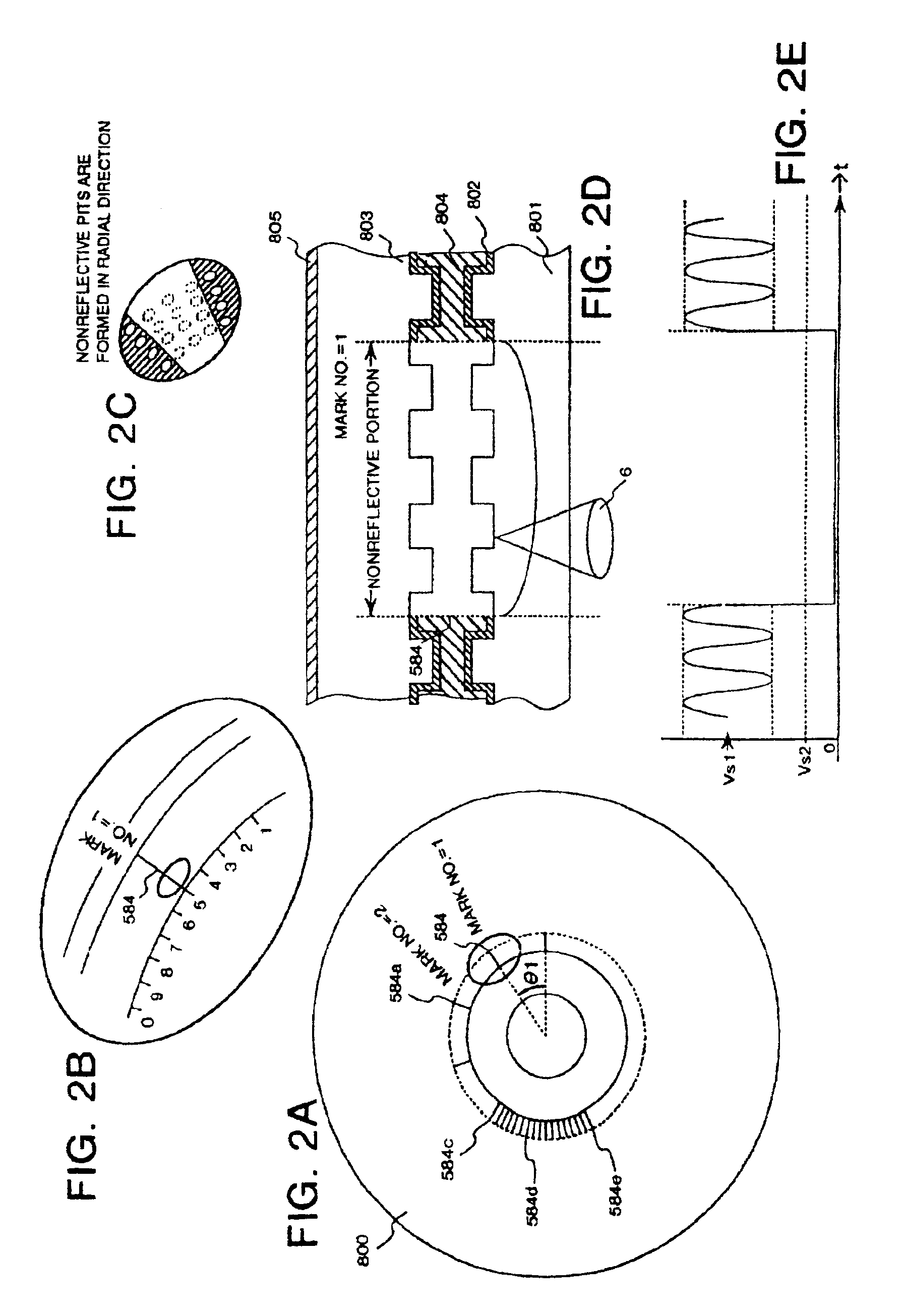
An object of the present invention is to provide a marking forming apparatus, a method of forming a laser marking on an optical disk, a reproduction apparatus, an optical disk, and a method of manufacturing an optical disk, capable of providing a greatly improved copy prevention capability as compared to prior known construction. To achieve this object, in the optical disk of the invention, for example, a marking is formed by a laser on a reflective film of a disk holding data written thereon and at least position information of the marking or information concerning the position information is written on the disk in an encrypted form or with a digital signature appended thereto.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for taking back optical disk through disk grabbing device with double layers of insertion pieces in optical disk library
ActiveCN104240734AReduce computing loadImprove stabilityRecord information storageManipulatorManagement systemSerial code
The invention discloses a method for taking back an optical disk through a disk grabbing device with double layers of insertion pieces in an optical disk library. According to the method, position sorting is carried out on optical disks in an optical disk box, the relationship between the position serial numbers of the optical disks in the optical disk box and the serial numbers of target trays where the optical disks are located is built, the position serial number of one optical disk is obtained automatically through matching according to the serial number of the corresponding target tray, the number of optical disks which need to be moved for placing the optical disk back to the original physical position is obtained through calculation, and thus the optical disk is placed back to the original position. According to the method, the stacking sequence of the optical disks in the optical disk box is not changed, database information does not need to be updated after disk replacement operation is carried out, the stability of a database is improved, the operation load of a controller is reduced, and an optical disk library management system is optimized.
Owner:SUZHOU NETZON INFORMATION STORAGE TECH
System and method for controlling tracking in an optical drive
InactiveUS20110170391A1Combination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsOptical data diskOrbit
The present techniques provide methods and systems for alignment of a read head with data tracks on an optical data disk. In embodiments, a multi-pixel detector that is segmented into multiple areas, or detector segments, may be used to detect a pattern in the light reflected from an optical data disk. The detector system may then combine the quantized values from each of the detector segments mathematically to determine the alignment of the read head with a target data track. If the read head drifts to one side or the other, detectors to the side of a center detector may start to pick up energy from the adjacent tracks. If this energy is continuously summed for the detectors on each side, the read head may be centered by balancing the sums from the detectors on each side.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Mark forming apparatus, method of forming laser mark on optical disk, reproducing apparatus, optical disk and method of producing optical disk
InactiveUSRE39653E1Improve prevention capabilitiesInhibit productionLighting support devicesDigital data processing detailsDigital signatureComputer science
An object of the present invention is to provide a marking forming apparatus, a method of forming a laser marking on an optical disk, a reproduction apparatus, an optical disk, and a method of manufacturing an optical disk, capable of providing a greatly improved copy prevention capability as compared to prior known construction. To achieve this object, in the optical disk of the invention, for example, a marking is formed by a laser on a reflective film of a disk holding data written thereon and at least position information of the marking or information concerning the position information is written on the disk in an encrypted form or with a digital signature appended thereto.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
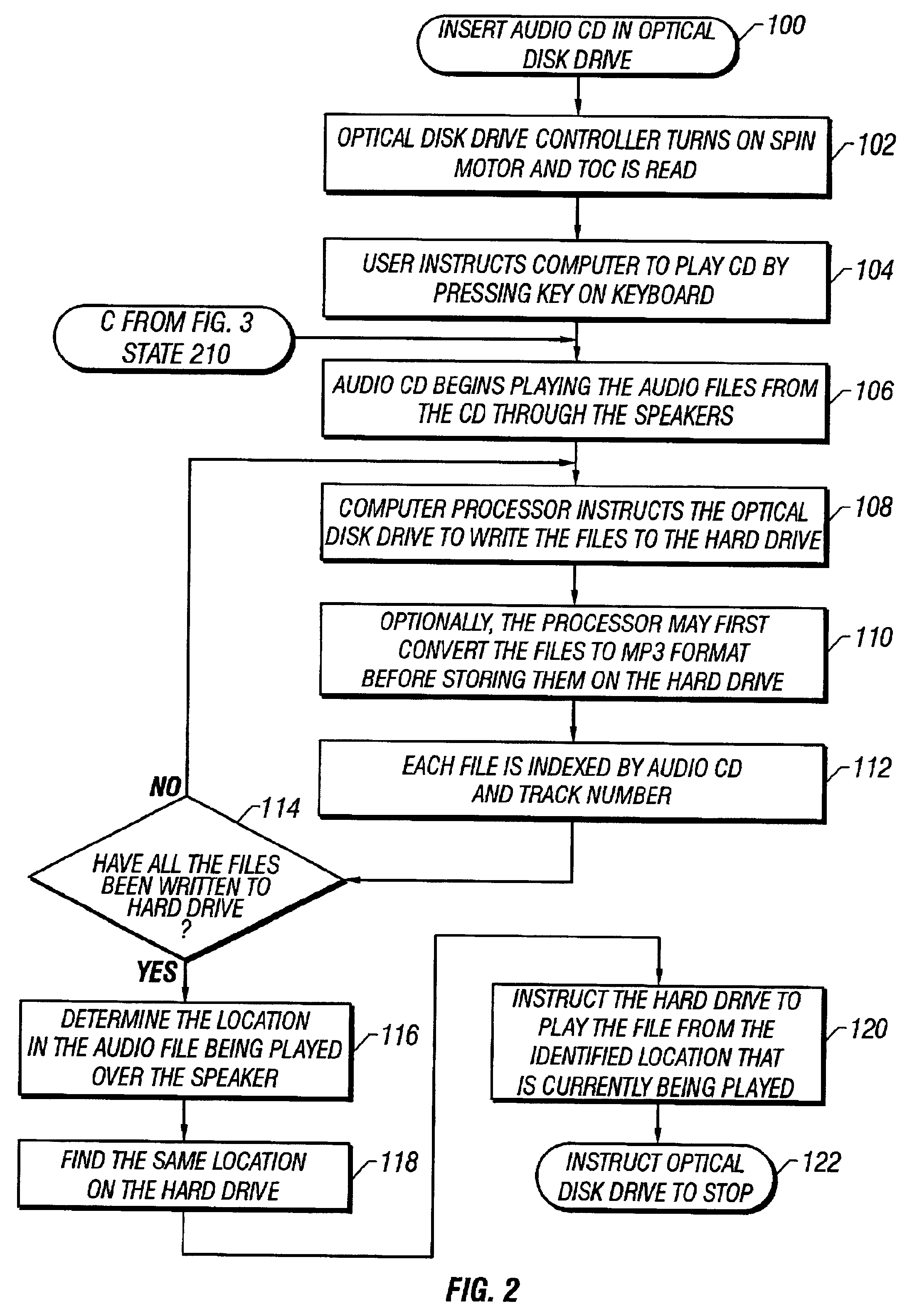
Background transfer of optical disk to hard disk
ActiveUS6931556B2Save powerIncrease powerEnergy efficient ICTData processing applicationsOutput deviceData recording
The present invention provides a method for reducing the amount of power consumed by an optical disk player. The method provides: recording at least a portion of the audio, video, or audio / video data from an optical disk onto the portable computer's hard disk while the optical disk is being played over the output device; turning the drive's spin motor off as soon as the data has been transferred to the hard disk; and then continuing to play the remaining un-played portion of the optical disk over the portable computer's speaker or other output device from the hard disk. The method further comprises recording in an index database a title of the optical disk and a title of the track written to the hard disk, and playing the data from the hard disk without re-reading the optical disk if the data has been previously written to the hard disk.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
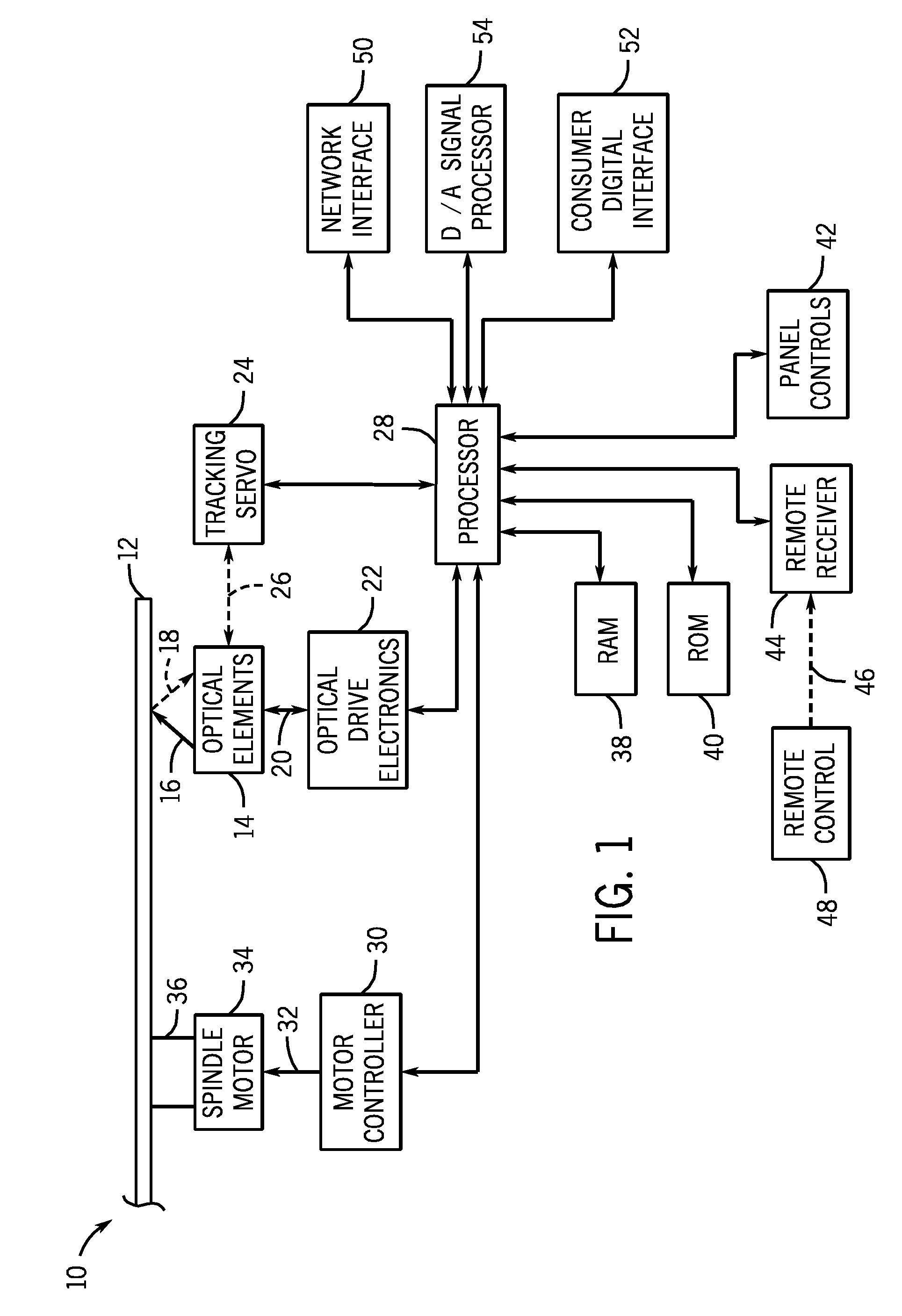
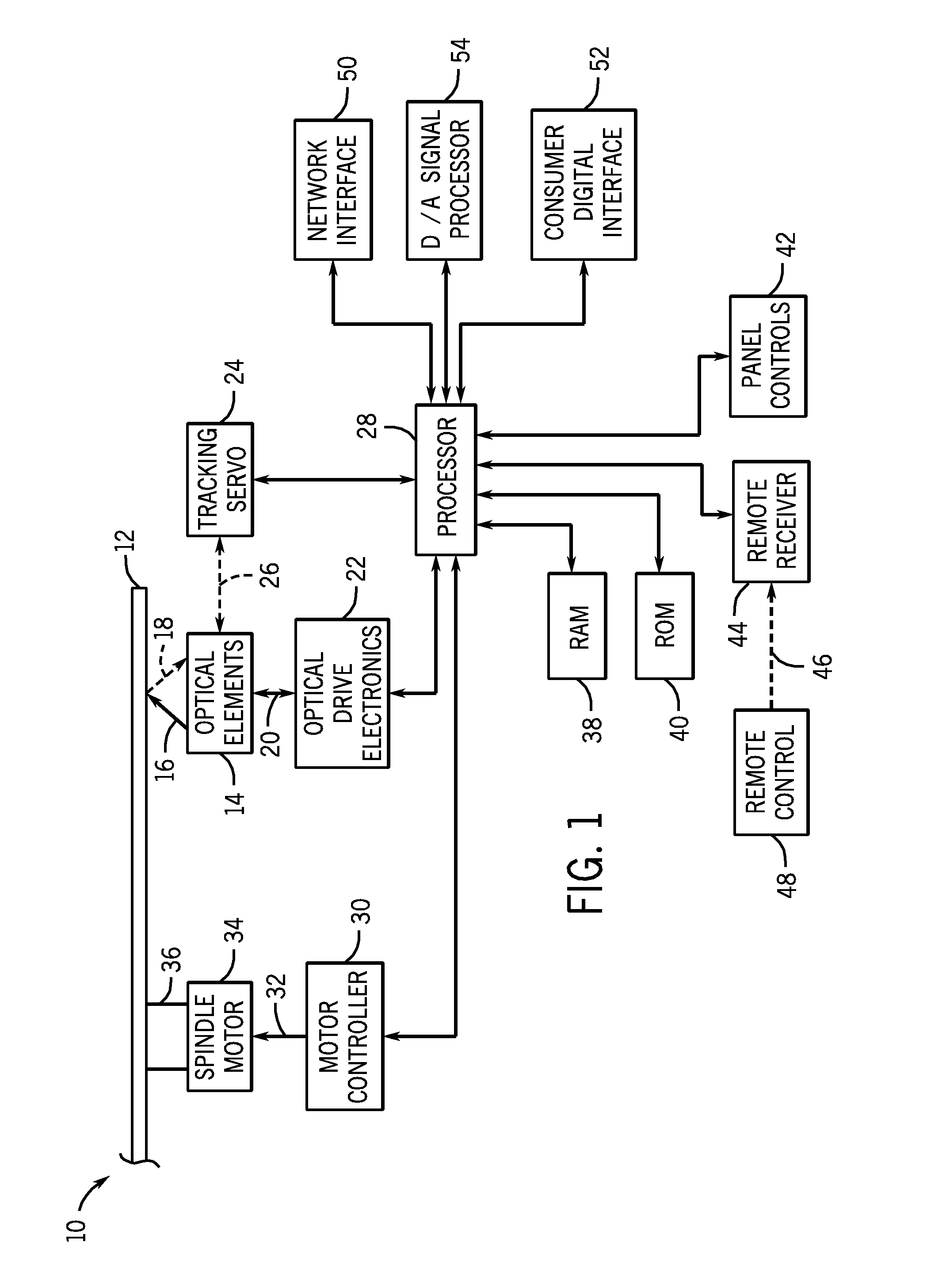
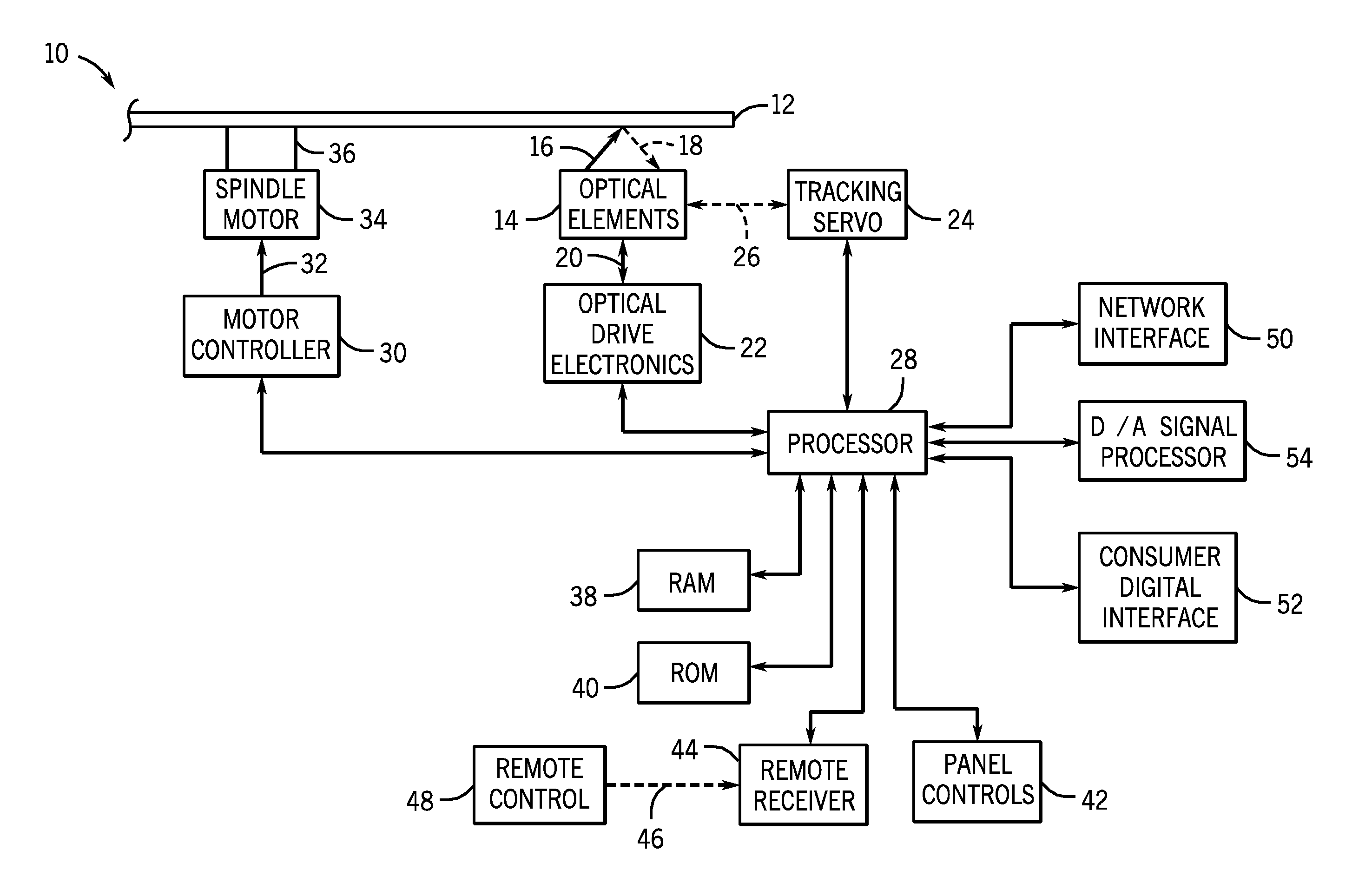
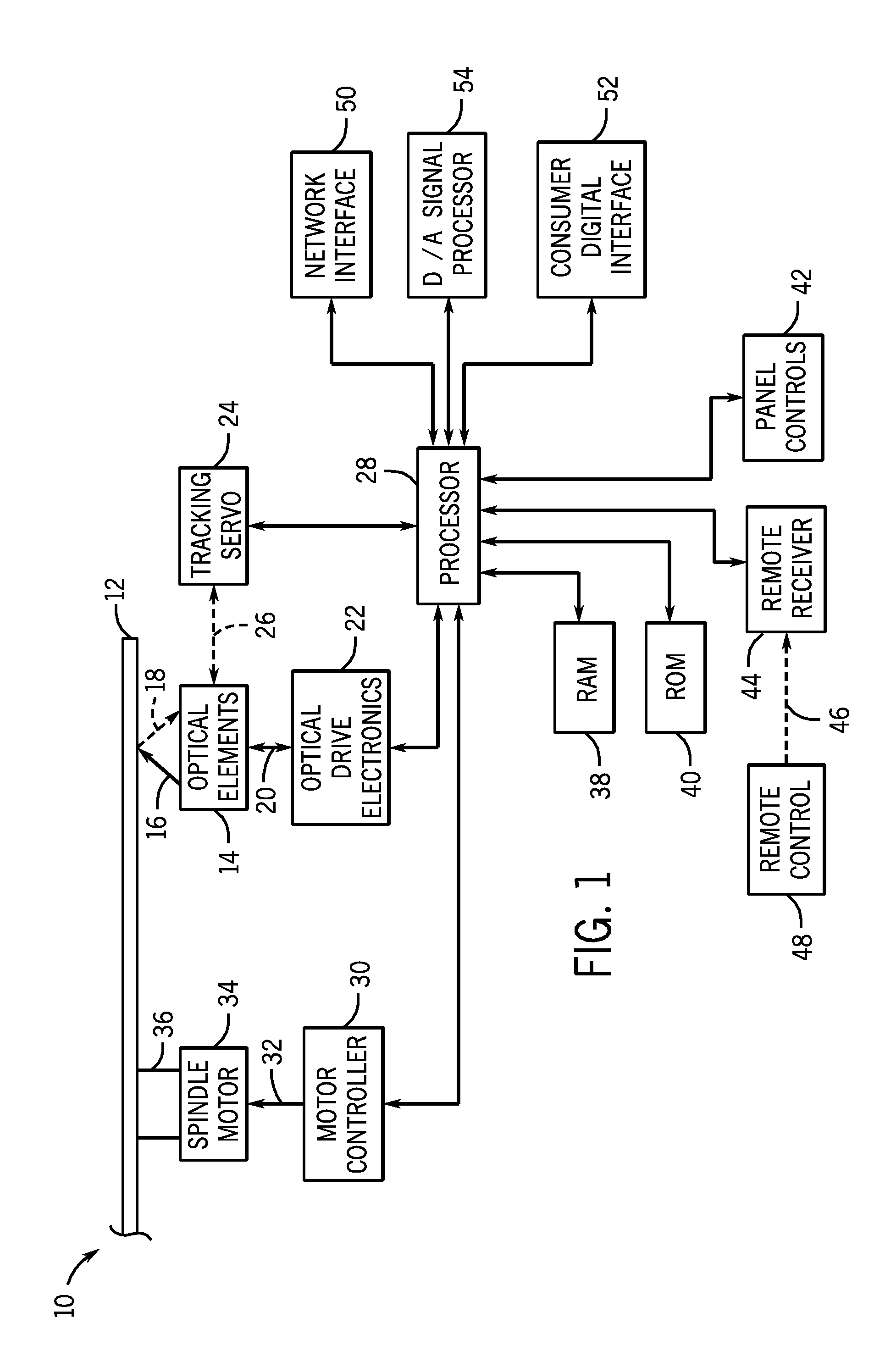
Optical Disk Drive
After an optical disk drive according to the present invention has been loaded with an optical disk and before the operation of recognizing the type of the given disk is finished, the drive presumes one of multiple types of candidate optical disks, from / on which data is readable and writable using a light beam with the shortest wavelength among the candidate disks, to be the disk being driven by the motor now and gets the beam for the presumed type of disk radiated from a light source (Step (A)). Next, the drive gets the disk spun at a rotational velocity that realizes a linear velocity equal to or higher than a standardized normal velocity when data is read from the presumed type of disk (Step (B)). Thereafter, the drive starts a focus control in a situation where the spot of the beam being formed on the disk is moving on the disk at the linear velocity equal to or higher than the normal velocity (Step (C)). And then the drive performs the operation of recognizing the type of the disk by the light beam reflected from the disk under the focus control (Step (D)).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical disk exchange and data storage separated optical disk jukebox system and data reading and writing method
ActiveCN104598164ANo human intervention requiredInput/output to record carriersRecord information storageOptical disk storageIntelligent management
The invention relates to the field of optical disk storage and provides an optical disk exchange and data storage separated optical disk jukebox system. The optical disk exchange and data storage separated optical disk jukebox system comprises a rear-end large-capacity optical disk jukebox and a front-end input-output optical disk jukebox which are connected with each other through a network bus. The rear-end large-capacity optical disk jukebox comprises a plurality of optical disk cabinets and rear-end controllers for controlling the optical disk cabinets. The optical disk cabinets are each composed of a plurality of optical disk boxes, and a plurality of optical disks are arranged in each optical disk box. The front-end input-output optical disk jukebox comprises a plurality of parallel CD drivers and front-end controllers for controlling the CD drivers. The optical disks in the CD drivers of the front-end input-output optical disk jukebox are in full-connection mapping relationship with the optical disks in the rear-end large-capacity optical disk jukebox. By means of the optical disk exchange and data storage separated optical disk jukebox system, data in the front-end input-out optical disk jukebox and data in the rear-end large-capacity optical disk jukebox are managed in a united mode, and the phenomenon that manual optical disk inserting and taking-out is low in efficiency and prone to error when data are directly read and written from the rear-end large-capacity optical disk jukebox in a data reading and writing process is avoided. Thus, efficient and intelligent management to a large optical disk jukebox is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN OPSTOR TECH LTD
Optical data disc with multiple booting points
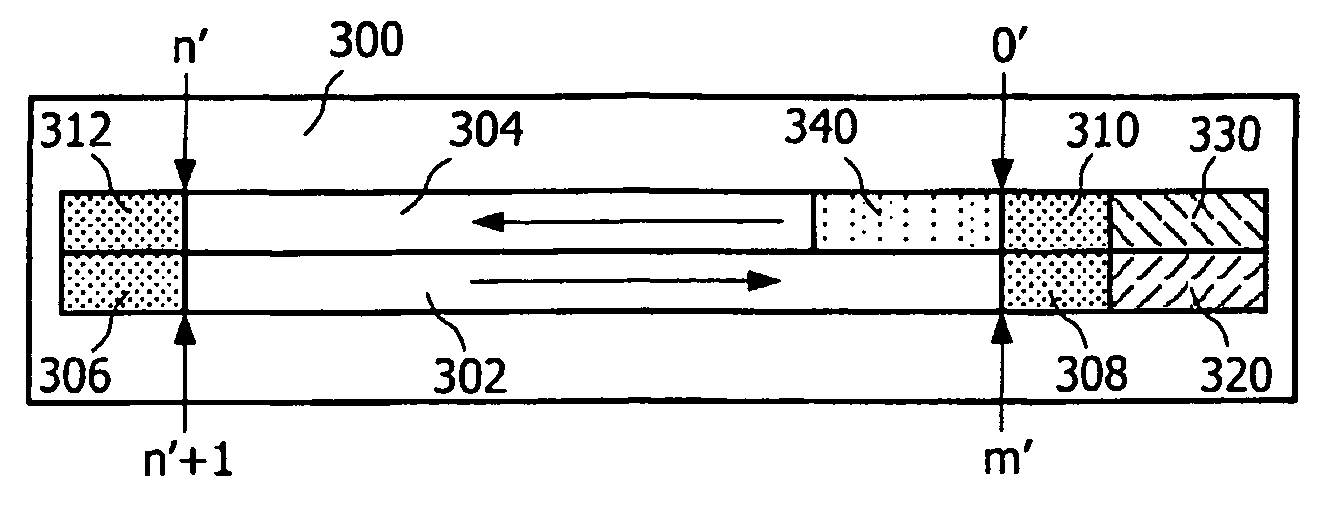
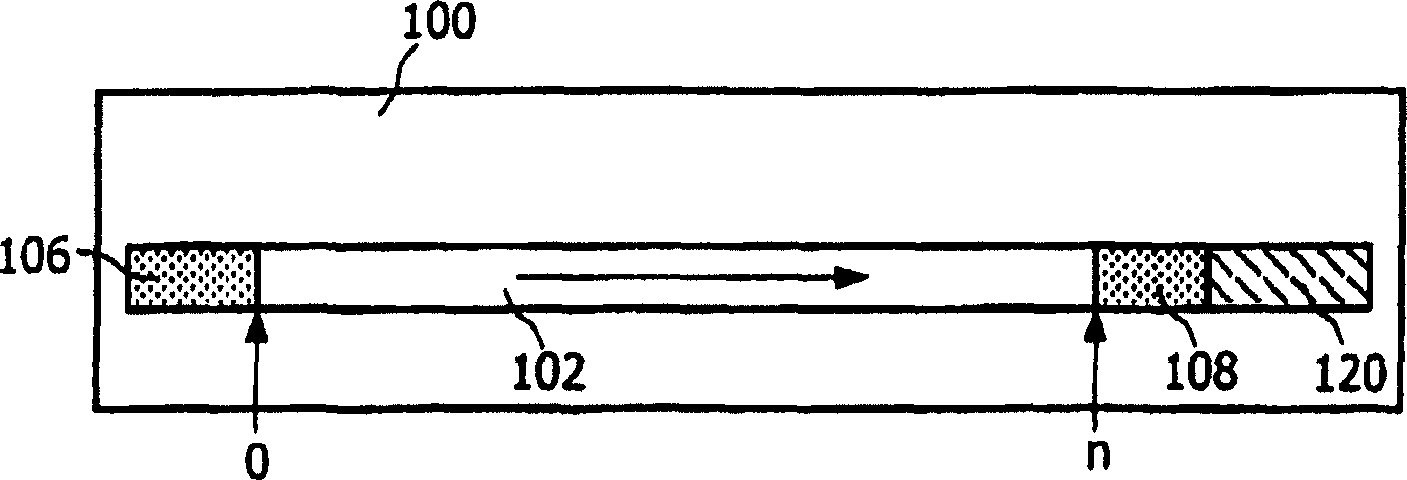
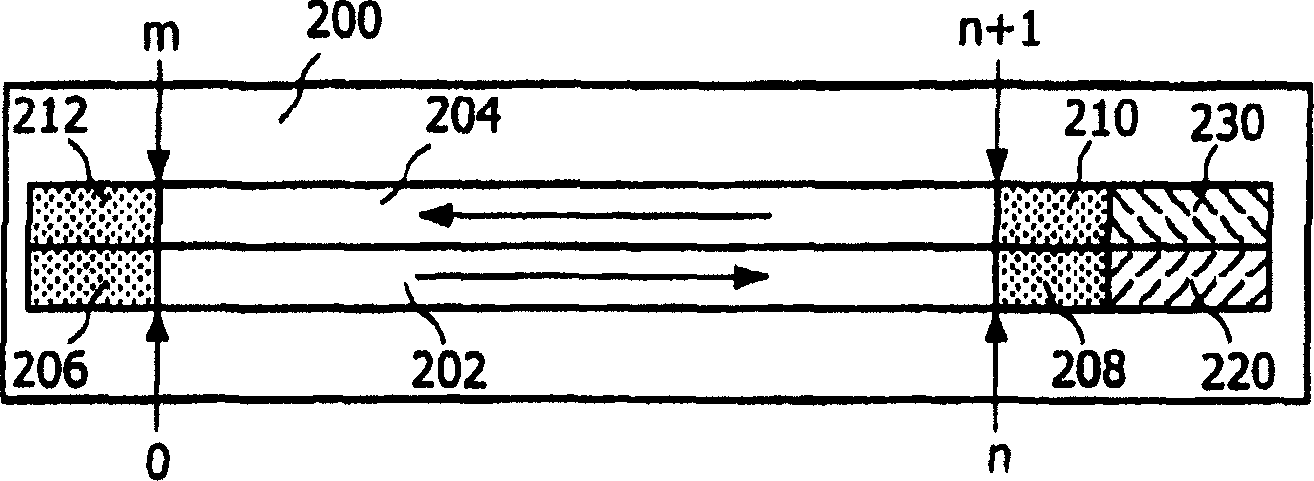
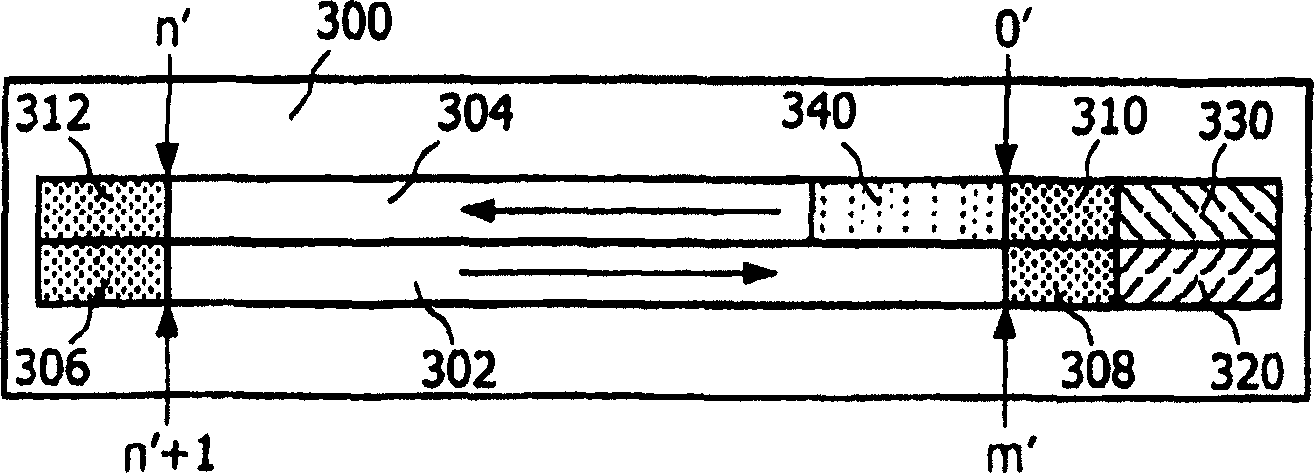
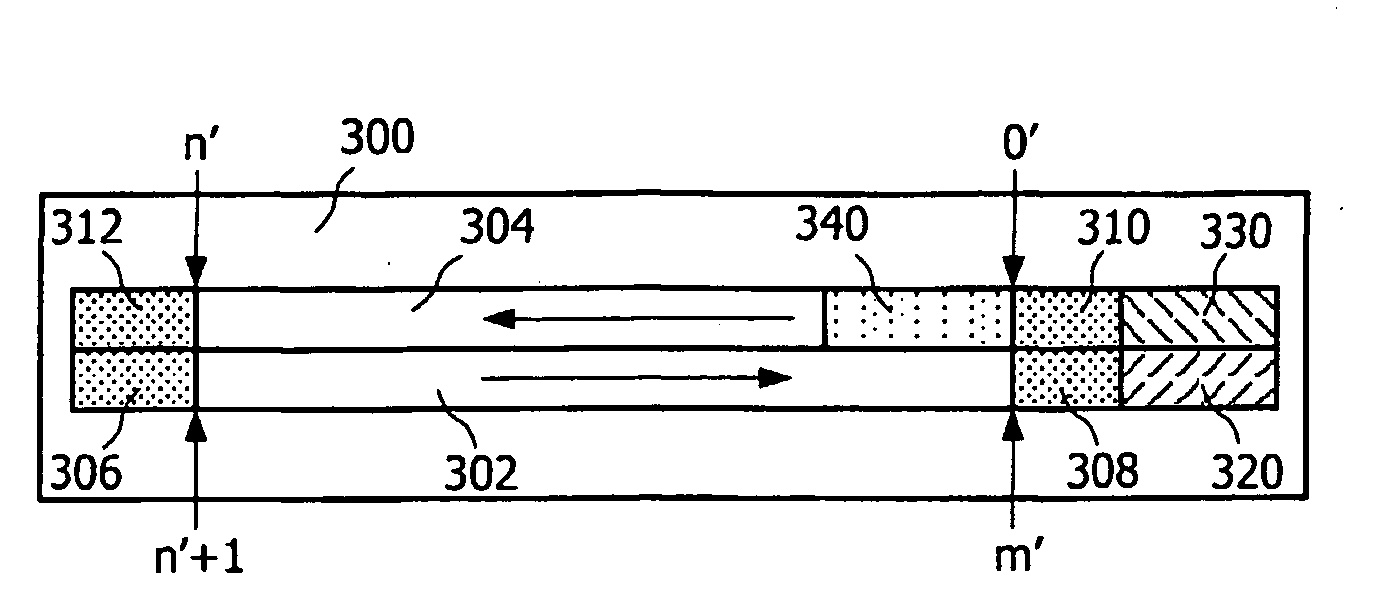
InactiveUS7882343B2Quick installationLittle overheadMultilayered discsInformation arrangementApplication program softwareEngineering
A booting procedure can take a long time and typically starts from a lead-in on a main data layer of an optical data disc. A Portable-Blue (PB) disc, a dual boot disc, includes a second data layer (304) from which application specific optical drives can boot directly. The dual boot disc still conforms to the prior art standard for PB for normal applications. The second boot (340) will cut in booting time for a specific application and will make application software small. is in particular relevant for gaming, for portable devices and relative specific applications.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for formatting and reading data disks
The present techniques present methods and systems for increasing a data reading rate on optical data disks using a single reading head. The methods take advantage of the difference between a mean focal distance (MFD), or minimum spacing that the detector can distinguish between bits, and the minimum separation of bits in a single track to increase the reading speed. As the bits may be more closely spaced across adjacent tracks or layers, these techniques may be used to increase the reading speed of the disk. Specifically, the data symbols that make up a single bit-stream may be stored in a pattern horizontally across adjacent tracks, or vertically across adjacent layers. Accordingly, the focal point of the detector is scanned across the disk in the same pattern to read the individual data symbols.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
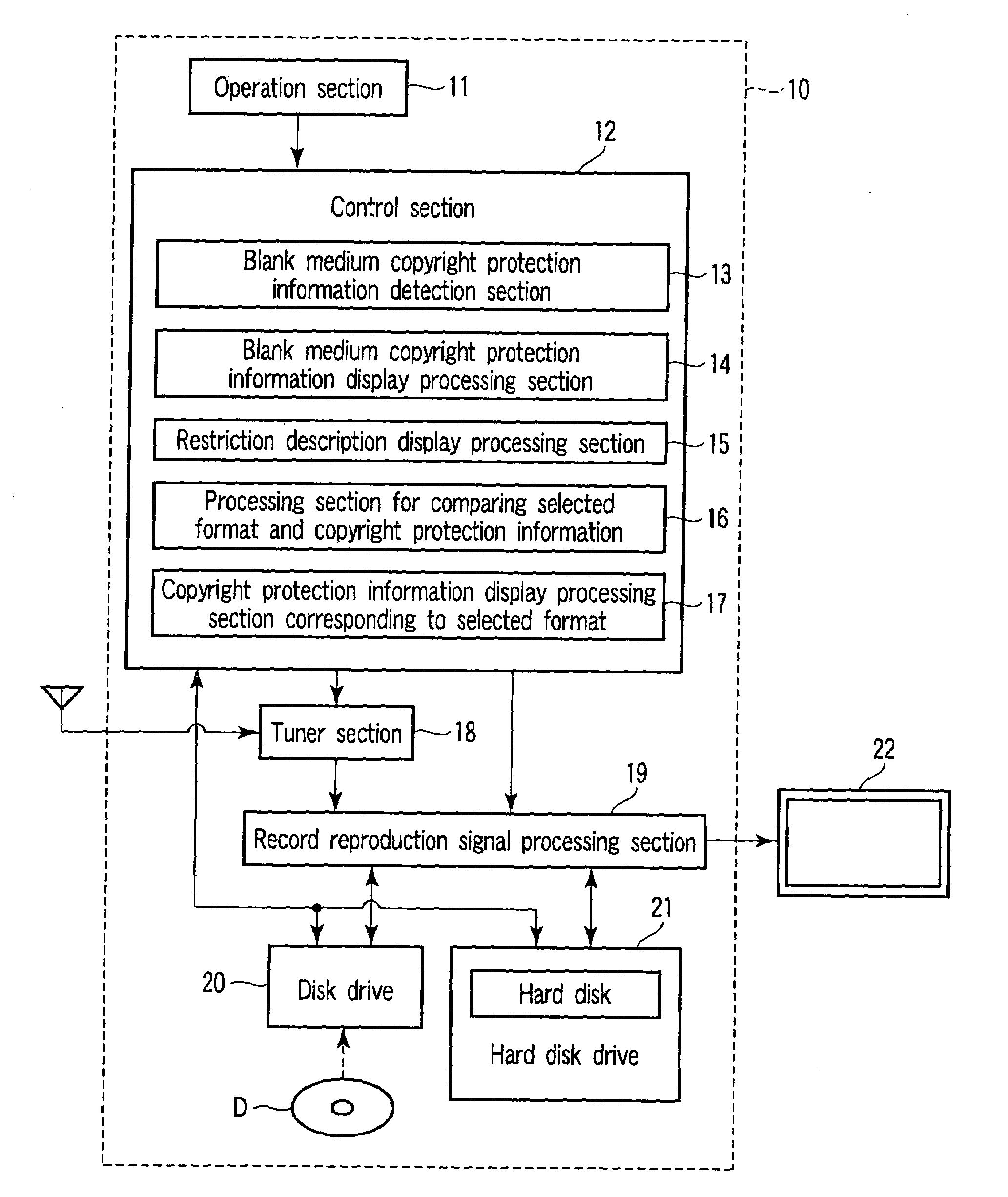
Optical disk device and method for processing optical disk
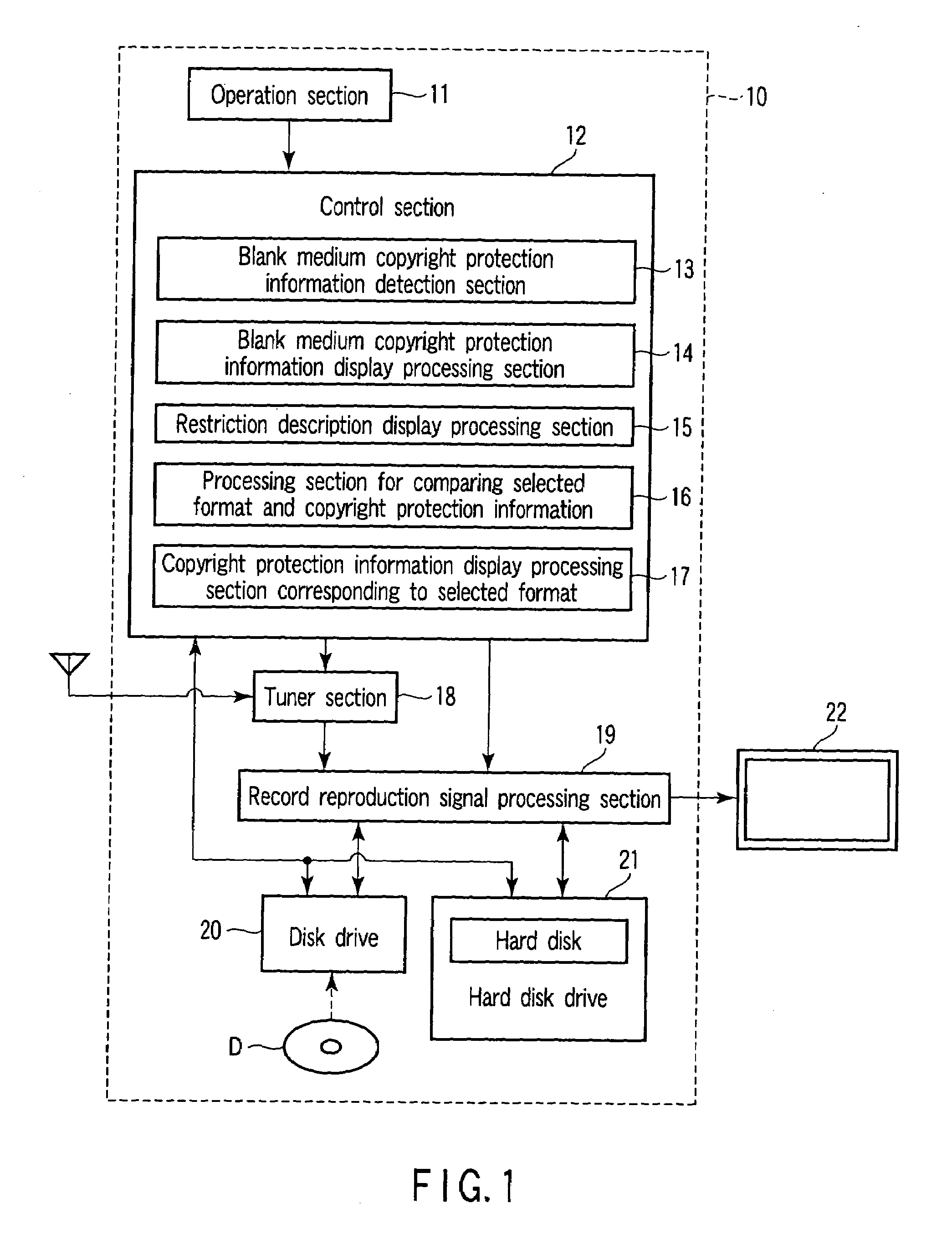
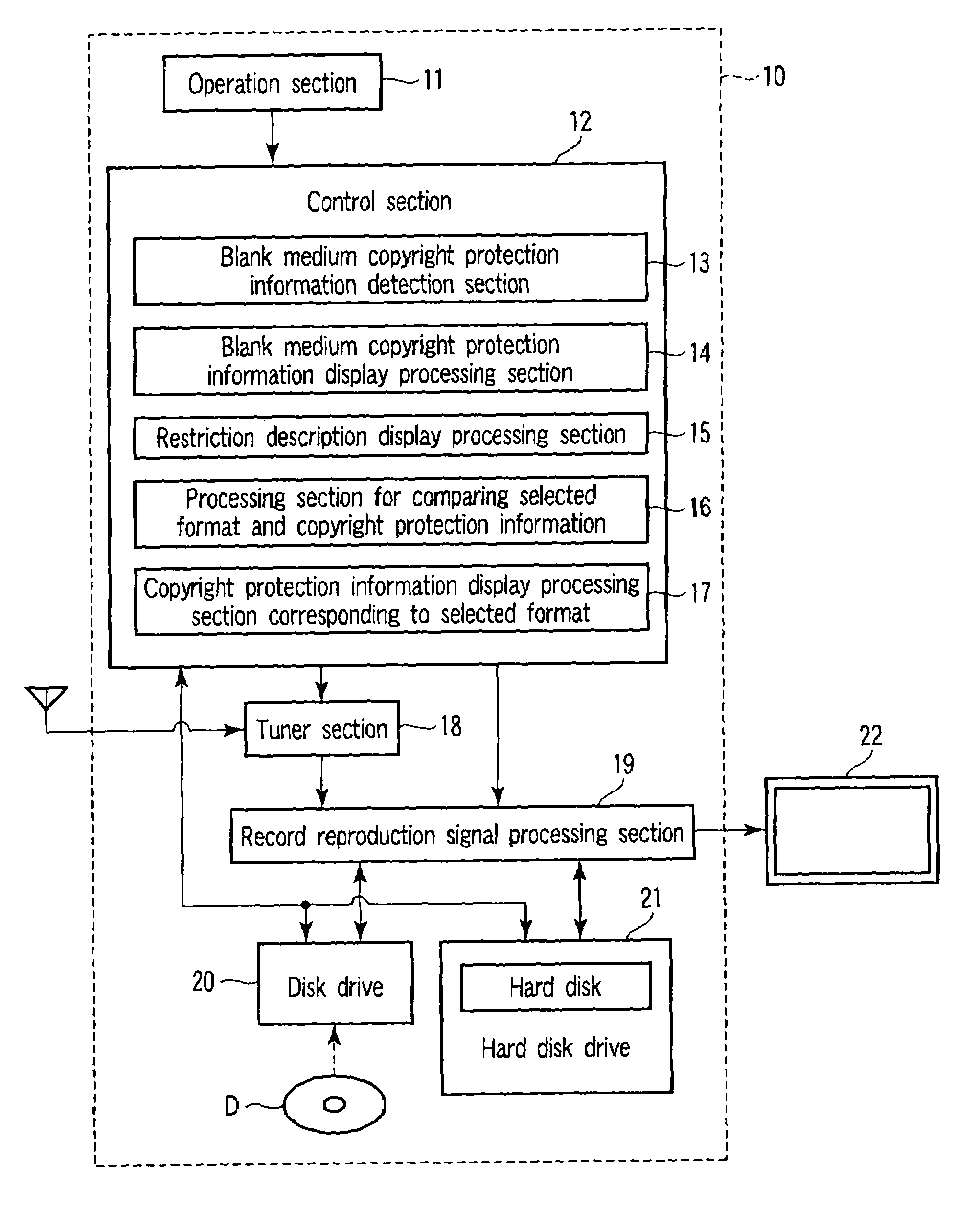
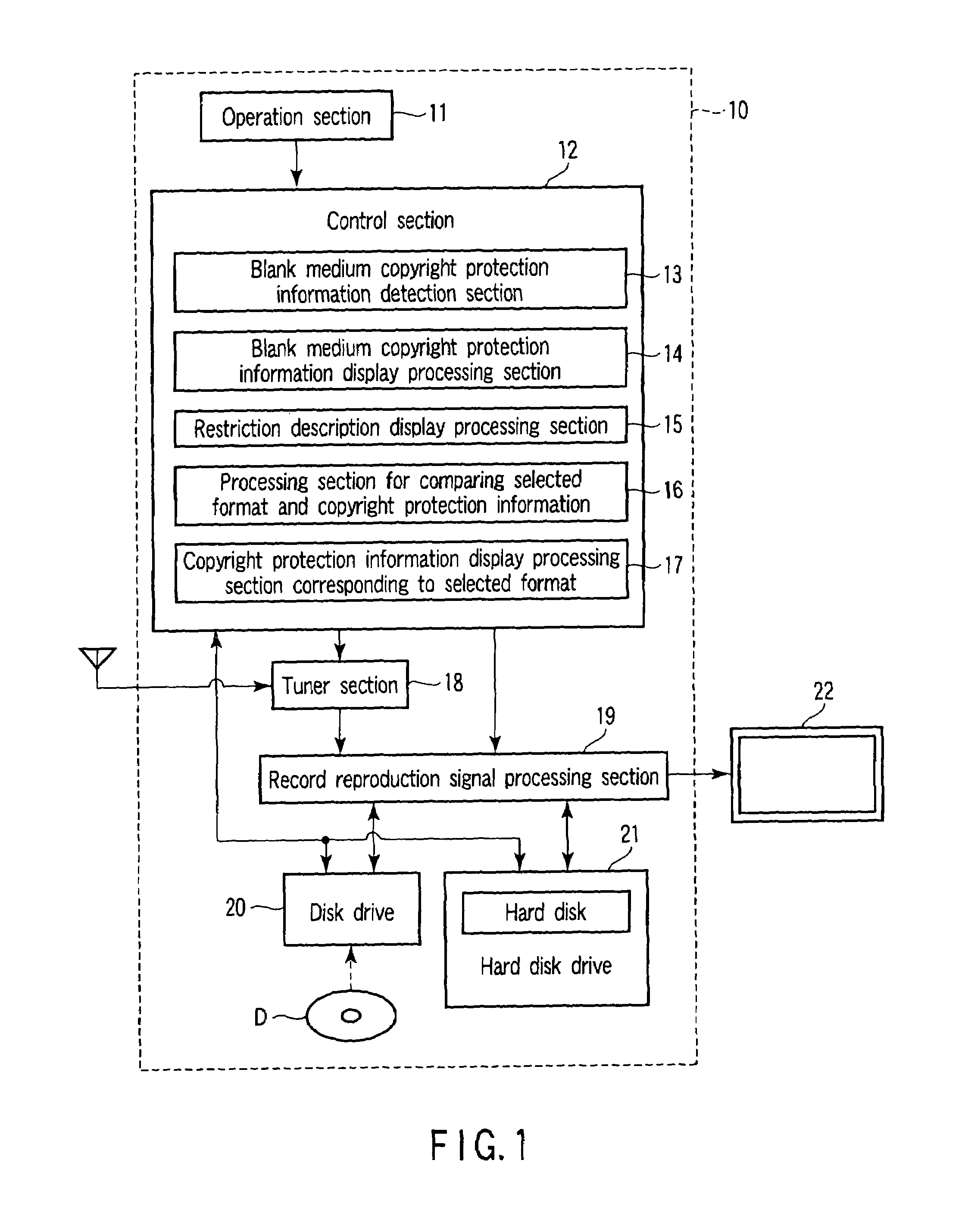
According to one embodiment, the invention provides an optical disk device having a drive and a control section. The drive applies recording processing and reproduction processing to an optical disk. When the optical disk is an unformatted blank medium, if the drive detects a medium ID and a medium key block region from the optical disk, the control section judges that there is copyright protection information and outputs display information which is used for the recording processing with respect to the optical disk together with display information showing the presence or absence of the copyright protection information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
System and method for controlling tracking in an optical drive
InactiveUS8125862B2Combination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsComputer sciencePixel detector
The present techniques provide methods and systems for alignment of a read head with data tracks on an optical data disk. In embodiments, a multi-pixel detector that is segmented into multiple areas, or detector segments, may be used to detect a pattern in the light reflected from an optical data disk. The detector system may then combine the quantized values from each of the detector segments mathematically to determine the alignment of the read head with a target data track. If the read head drifts to one side or the other, detectors to the side of a center detector may start to pick up energy from the adjacent tracks. If this energy is continuously summed for the detectors on each side, the read head may be centered by balancing the sums from the detectors on each side.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
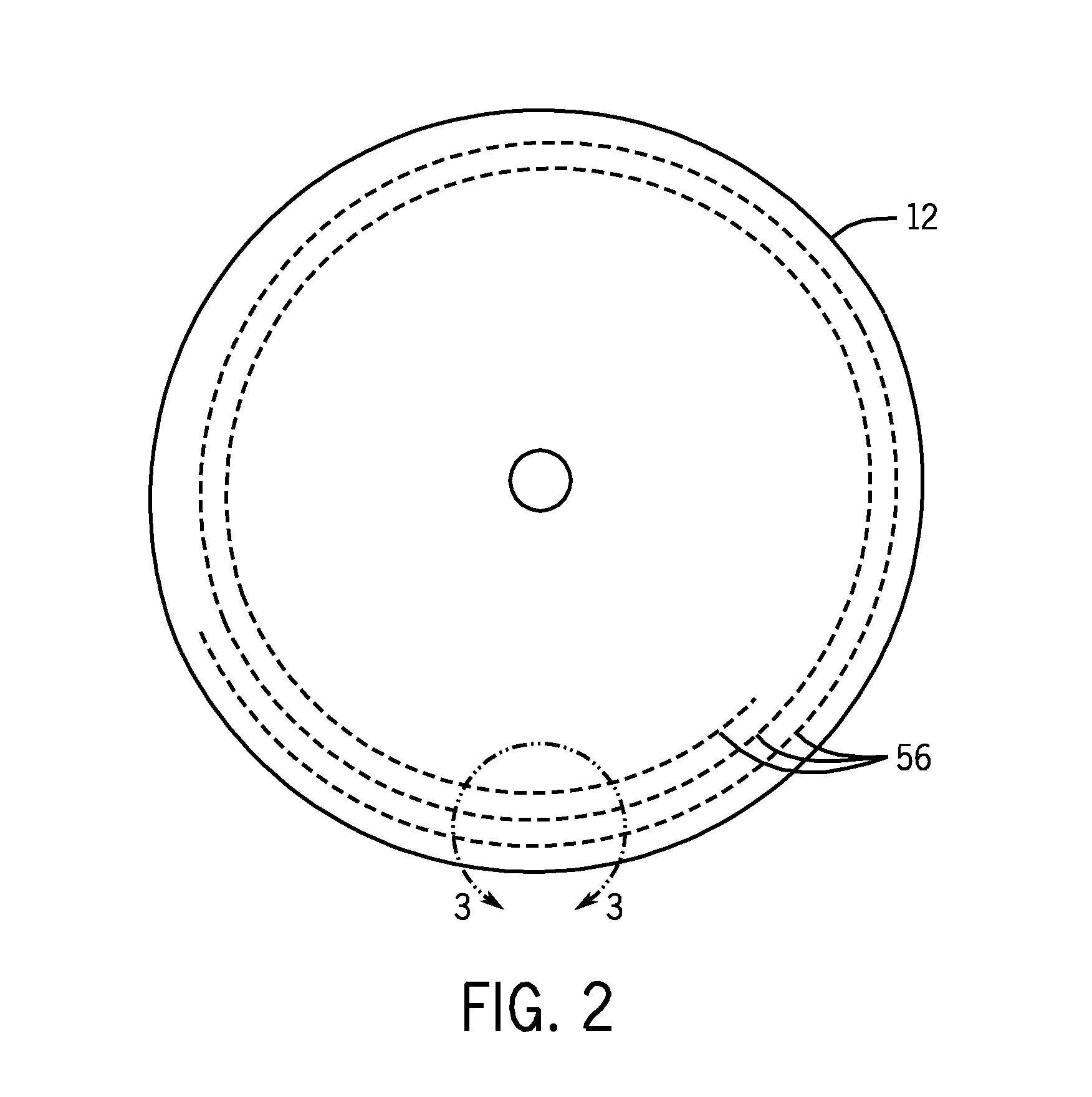
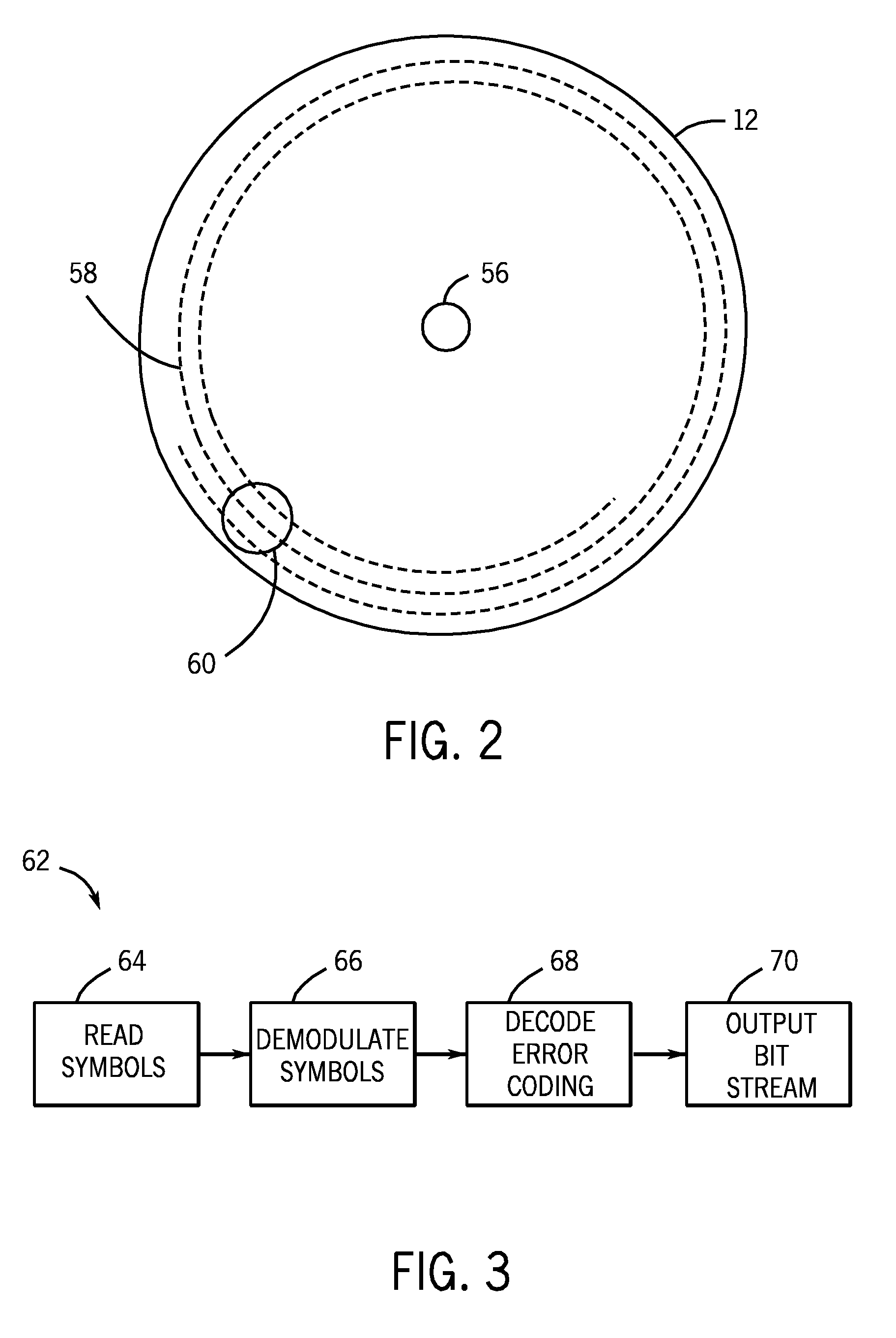
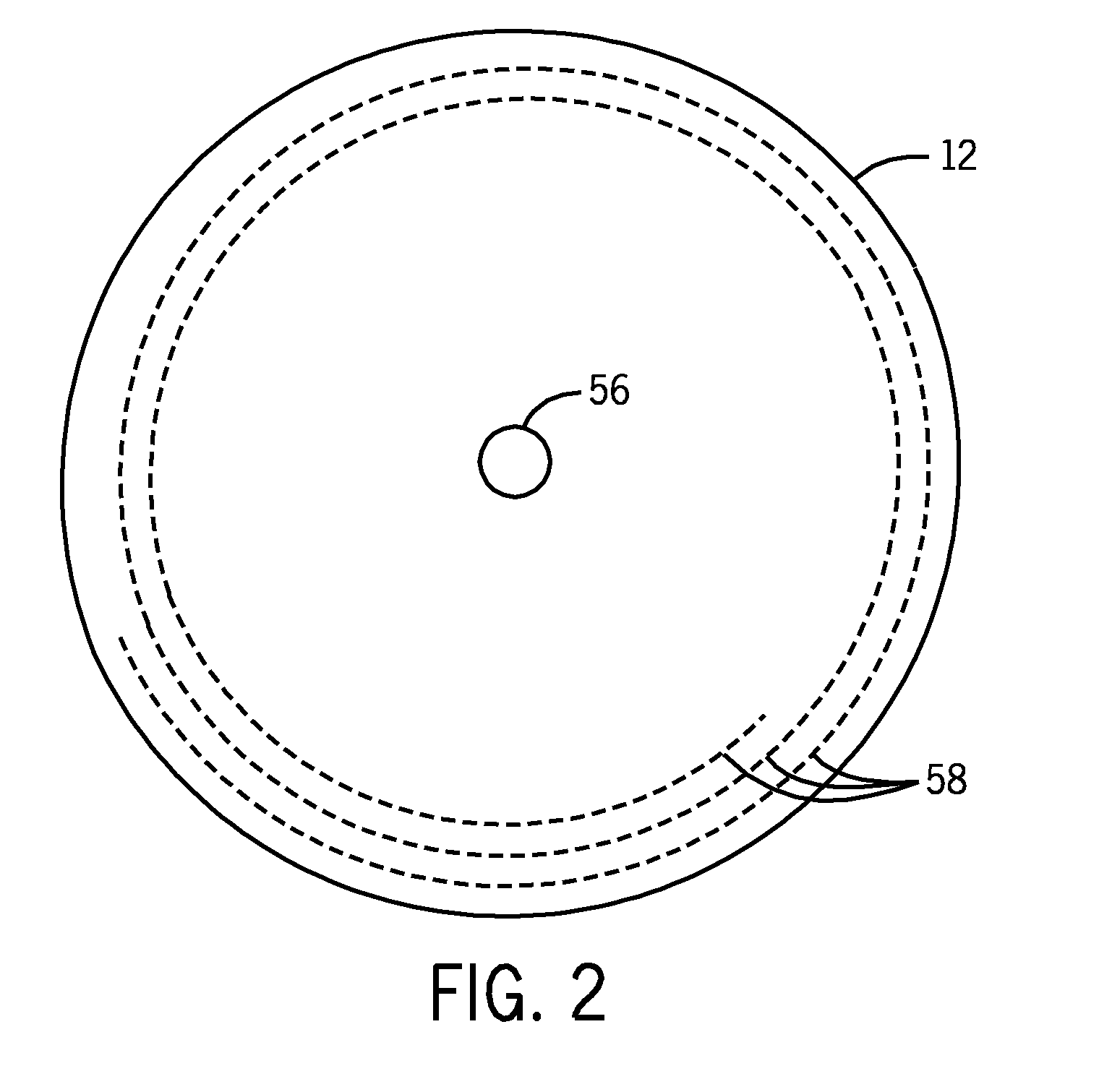
System and method for storage of data in circular data tracks on optical discs
InactiveUS20100157757A1Modification of read/write signalsFilamentary/web record carriersData signalOutput device
The present techniques provide methods and systems for reading and processing a data signal read from an optical data disc. In embodiments, an optical reader system may read data bits from a data ring in the disc. The data rings may be concentric, and a beginning of a sequence of data on the data ring may be in substantially the same position as an ending of the sequence. The reader may identify a data ring and begin the read process on the targeted data ring, and may end the read process when the reader reaches the starting point. The data sequence read from the data ring may be decoded to form a bit stream, which may be provided to various output devices. A circular trellis formed from the bit stream may enable the reading of a targeted data sequence without additional tail bits to improve data transmission efficiency.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Recording method of optical disk, optical disk recording apparatus, optical disk reproducing apparatus and optical disk
InactiveUS7061849B1Reduce generationImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsCode conversionComputer hardwareDiagonal
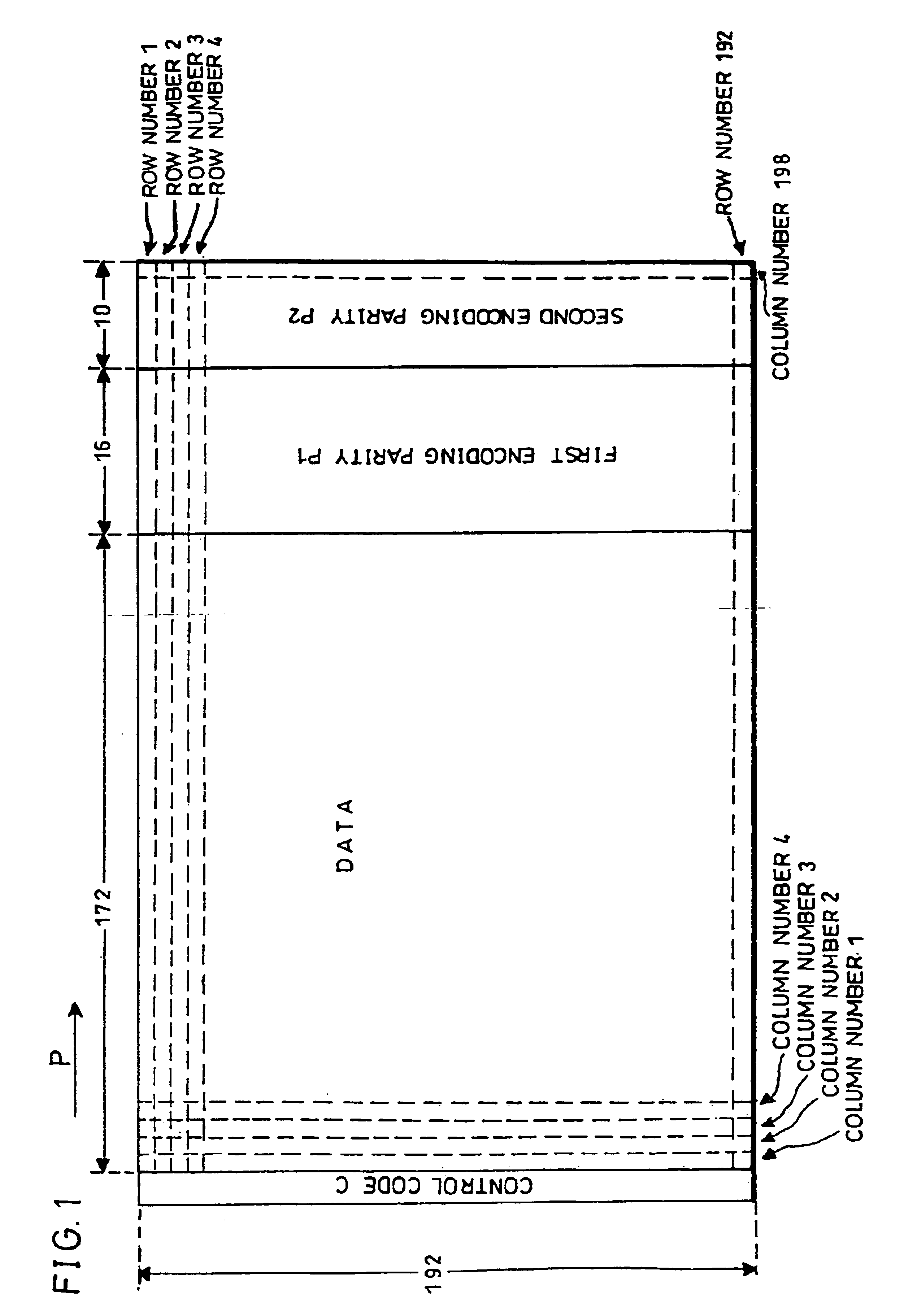
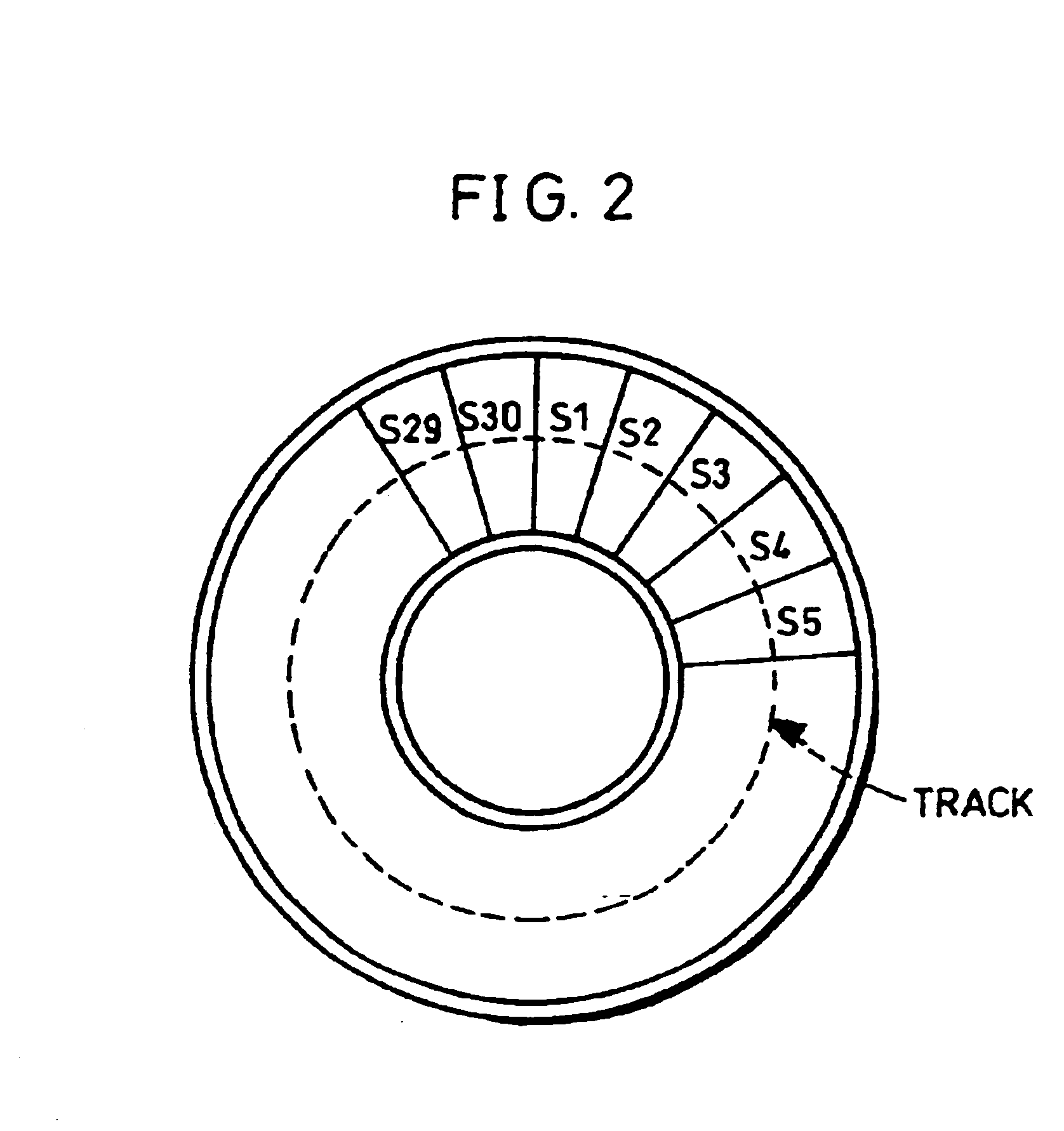
In a recording method for an optical disk, an optical disk is used, in which concave and convex areas formed as concave and convex sections on the disk substrate are arranged along a track with constant intervals and a recording area for recording data of a predetermined number of units is placed between the concave and convex areas arranged with constant intervals. Upon recording information on this optical disk, a two-dimensional array is formed by adding addition data to input data, a first encoding parity is added to the two dimensional array by carrying out a first encoding process that forms a code sequence by using a data alignment in a diagonal direction, and a second encoding parity is added to the resulting two dimensional array by carrying out a second encoding process that forms a code sequence by using a data alignment in a row direction so that a second two dimensional array is formed. Then, data is successively recorded in the row direction. With this arrangement, it is possible to reduce the occurrence of an incorrectable error in the optical disk in which the recording areas are placed along the track with constant intervals.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical disk device and method for processing optical disk
According to one embodiment, the invention provides an optical disk device having a drive and a control section. The drive applies recording processing and reproduction processing to an optical disk. When the optical disk is an unformatted blank medium, if the drive detects a medium ID and a medium key block region from the optical disk, the control section judges that there is copyright protection information and outputs display information which is used for the recording processing with respect to the optical disk together with display information showing the presence or absence of the copyright protection information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical disk, format processing method for the same, recording method for the same, and optical disk device
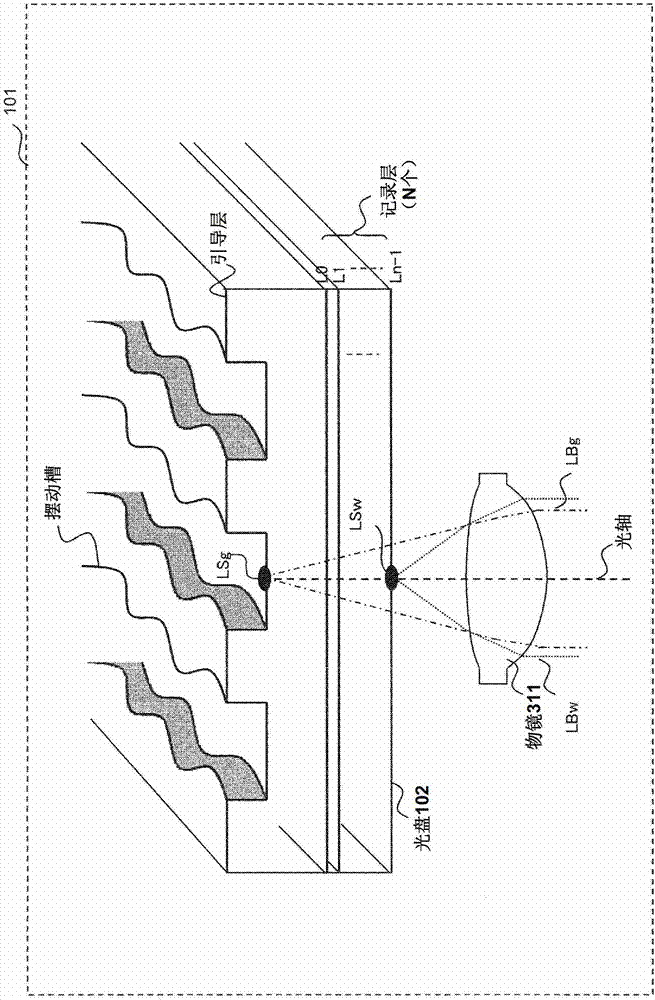
InactiveCN103325394AInformation arrangementRecord information storageComputer hardwareRecording layer
An optical disk that enables a laser beam to be focused on an object track without making mistakes, an optical disk device, a format processing method, and a recording method. The optical disk shall be configured to has a guiding layer with a physical groove structure containing address information and a single or multiple recording layers with no groove structure, in which the guide areas for recording the address information thereon are formed along a track of the guide layer at fixed intervals in a user data area of each recording layer. An address for the recording layer is generated based on information obtained from the guide layer, and the address for the recording layer is recorded in the guide area.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Additional information recording method on optical disk, and optical disk recording apparatus
InactiveUS7057979B2Easy to editIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer hardwareOptical data disk
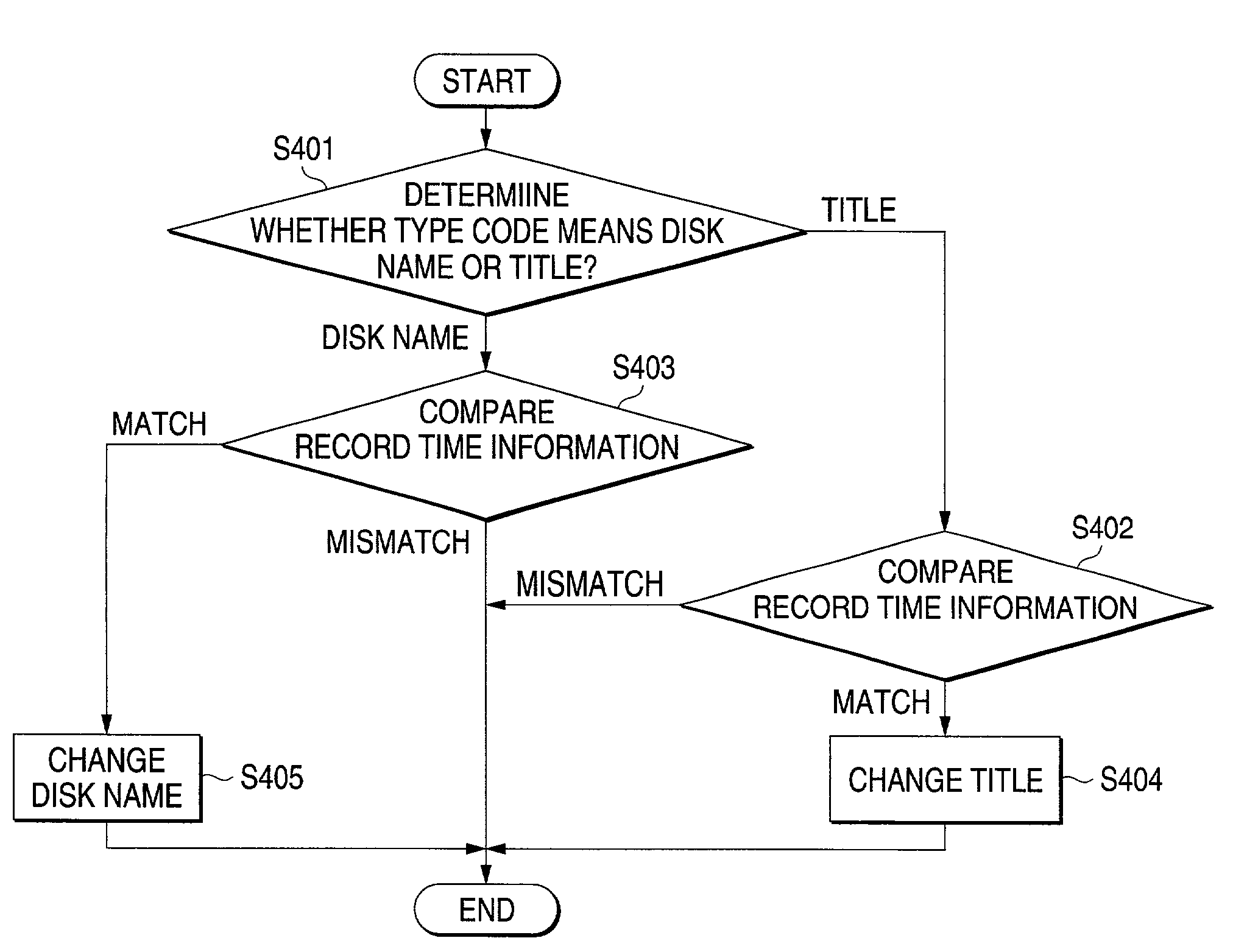
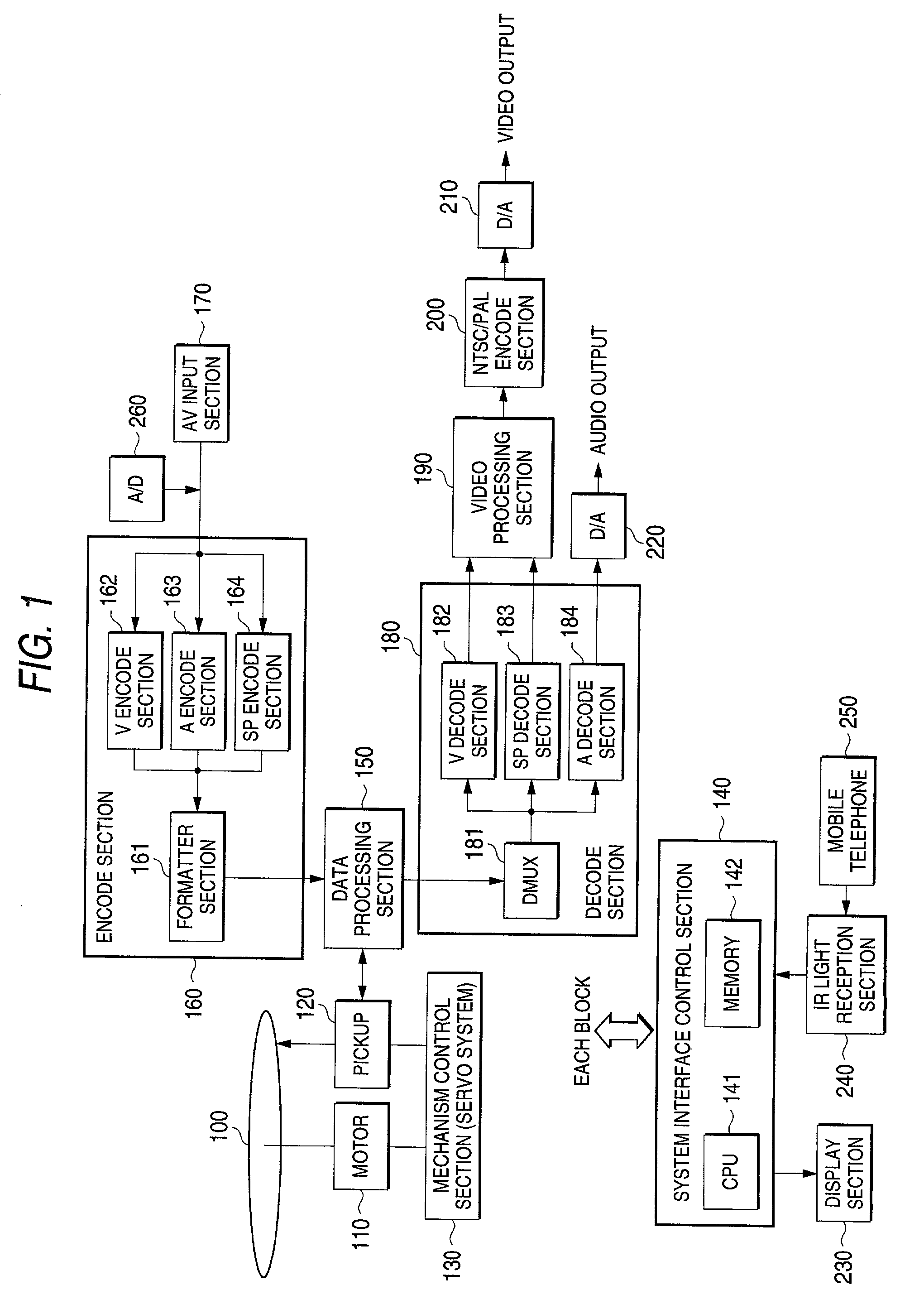
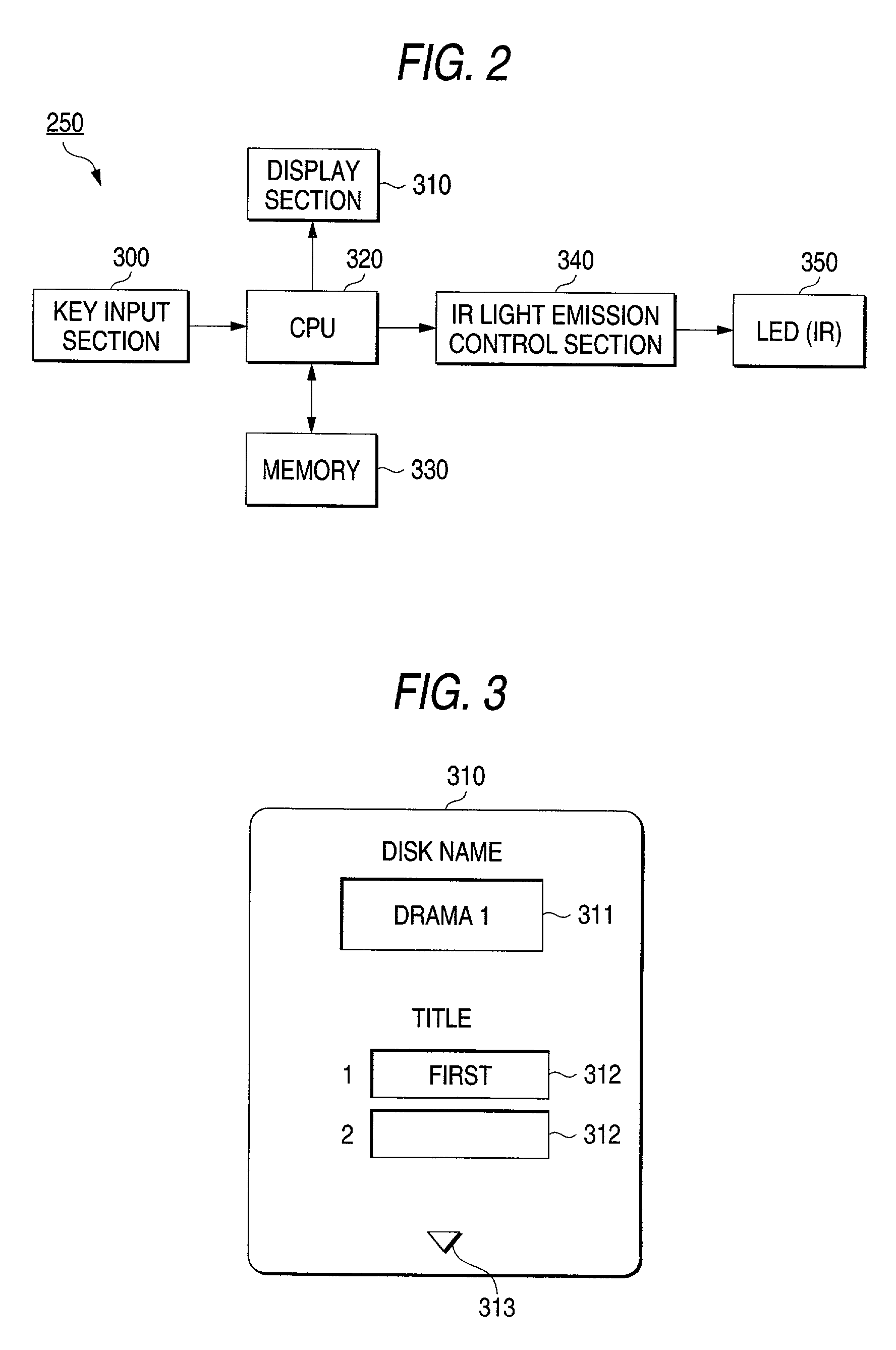
A method of recording additional information of a disk name of an optical disk, title information of a recorded program, etc., on the optical disk. Communication data containing edit data entered through a portable electronic machine capable of conducting wireless communications with an optical disk recording apparatus is transmitted by the portable electronic machine to the optical disk recording apparatus using the wireless communications and the edit data is recorded on the optical disk as additional information.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
CD, DVD disc protector
Owner:BROWN JOHNNY L +1
Method and system for bit prediction using a multi-pixel detector
InactiveUS8233368B2Combination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersData Coding SchemeData encoding
The present techniques provide methods and systems for more reliable reading of optical data disks. In embodiments, a multi-pixel detector that is segmented into multiple areas, or detector segments, may be used to detect a pattern in the light reflected from an optical data disk. The pattern may include light scattered from a single bit that may be under a center detector, as well as light scattered from proximate bits. The detector system may then combine the quantized values from each of the detector segments mathematically to determine the presence or absence of a bit or bits of data. The mathematical combination may also use data that is known about the status of adjacent data bits (such as previously read bits, or bit patterns which are allowed or not allowed by specific data encoding schemes) to improve the accuracy of the bit prediction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
An optical data disc with multiple booting points
InactiveCN1910695ASimple and fast loading processMultilayered discsInformation arrangementEngineeringApplication specific
The boot process can take a long time, and it usually starts with the lead-in area of the main data layer of an optical data disc. A Portable Blu-ray (PB) disc as a dual-boot disc includes a second data layer (304) from which an application-specific optical drive can boot directly. The dual boot disk still complies with PB prior art standards for conventional applications. This second boot (340) will shorten the boot time for certain applications and will make the application software smaller, which is especially relevant for gaming, portable devices and related certain applications.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for formatting and reading data disks
InactiveUS8891343B2Filamentary/web record carriersRecord information storagePresent methodComputer science
The present techniques present methods and systems for increasing a data reading rate on optical data disks using a single reading head. The methods take advantage of the difference between a mean focal distance (MFD), or minimum spacing that the detector can distinguish between bits, and the minimum separation of bits in a single track to increase the reading speed. As the bits may be more closely spaced across adjacent tracks or layers, these techniques may be used to increase the reading speed of the disk. Specifically, the data symbols that make up a single bit-stream may be stored in a pattern horizontally across adjacent tracks, or vertically across adjacent layers. Accordingly, the focal point of the detector is scanned across the disk in the same pattern to read the individual data symbols.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical disc library system and data reading and writing method for separating optical disc exchange and data storage
ActiveCN104598164BNo human intervention requiredInput/output to record carriersRecord information storageOptical disk storageIntelligent management
Owner:WUHAN OPSTOR TECH LTD
Optical disk including a barcode pattern formed by a laser using pulse width modulation
InactiveUSRE43230E1Improve prevention capabilitiesInhibit productionDigitally marking record carriersDigital data processing detailsDigital signaturePulse-code modulation
An object of the present invention is to provide a marking forming apparatus, a method of forming a laser marking on an optical disk, a reproduction apparatus, an optical disk, and a method of manufacturing an optical disk, capable of providing a greatly improved copy prevention capability as compared to prior known construction. To achieve this object, in the optical disk of the invention, for example, a marking is formed by a laser on a reflective film of a disk holding data written thereon and at least position information of the marking or information concerning the position information is written on the disk in an encrypted form or with a digital signature appended thereto.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for reading micro-holograms with reduced error rates
ActiveUS20100246354A1Good estimateReduce errorsRecord information storageSystems characterised by carrier structureCircular discDeterministic noise
The present techniques provide methods and systems reading a data bit of interest on an optical data disc with a reduced error rate. The data bit estimation may be improved by reducing deterministic noise resulting from an optical reader system and / or the optical data disc. The reader may adjust the position of a detector to detect light scattered from the disc based on parameters of known noise sources. In one embodiment, the detector may be moved vertically in relation to the data bit of interest on the optical disc. In another embodiment, more than one detector may be used to detect light scattered from a data bit of interest. In embodiments, the positioning of the detector(s) may be based on system or disc parameters, and the detected scatterings may provide a data reading, improved for an optical return from a present micro-hologram.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical Data Disc With Multiple Booting Points
InactiveUS20080253270A1Quick installationLittle overheadMultilayered discsInformation arrangementApplication program softwareEngineering
A booting procedure can take a long time and typically starts from a lead-in on a main data layer of an optical data disc. A Portable-Blue (PB) disc of the invention, a dual boot disc, includes a second data layer from which application specific optical drives can boot directly. The dual boot disc still conforms to the prior art standard for PB for normal applications. The second boot will cut in booting time for a specific application and will make application software small. The invention is in particular relevant for gaming, for portable devices and relative specific applications.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
CD, DVD disc protector
Owner:BROWN JOHNNY L +1
Optical disk and optical disk apparatus
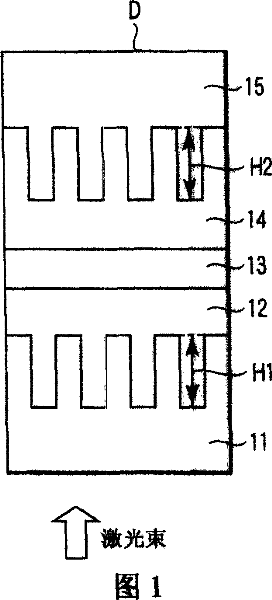
InactiveCN101038763AImprove operational reliabilityRecord information storageRecord carrier materialsInformation layerOrganic dye
An optical disk has transparent substrate layer (11) provided at light incidence side, first information layer (12) which has first groove of first depth (H1), adhesive layer (13) provided on the first information layer, and second information layer (14) which has second groove of second depth (H2) that is deeper than the first depth, and irreversibly records information therein, wherein the first depth and the second depth are lambda / 2n or less, the width of the first and second grooves is 0.3 [mu]m or less, the track pitch of the first and second grooves is 0.45 [mu]m or less, the first and second information layers include organic dye material having light absorption in the range of the wavelength of laser beam for use in recording and reproducing information from 390 nm to 420 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com