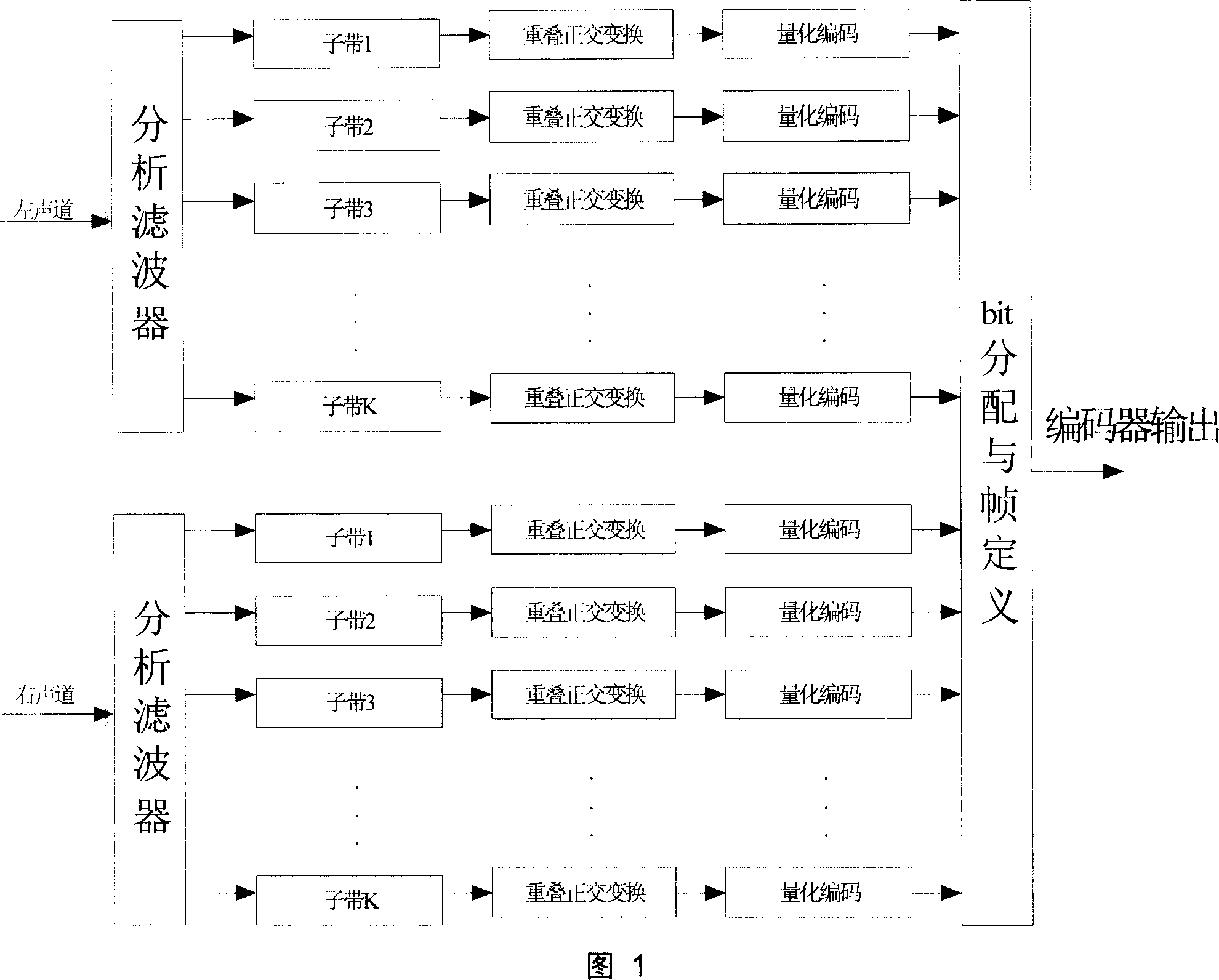
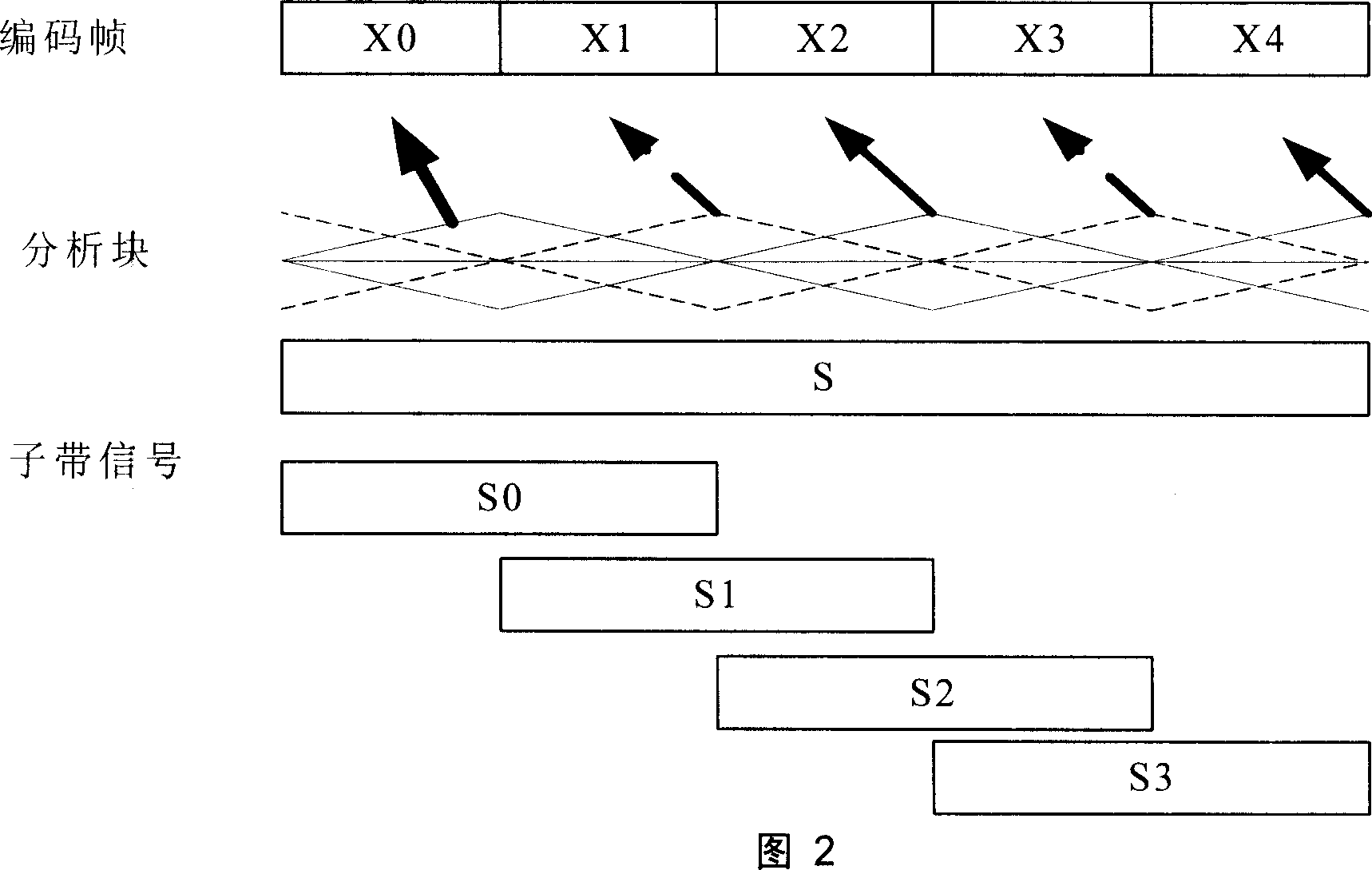
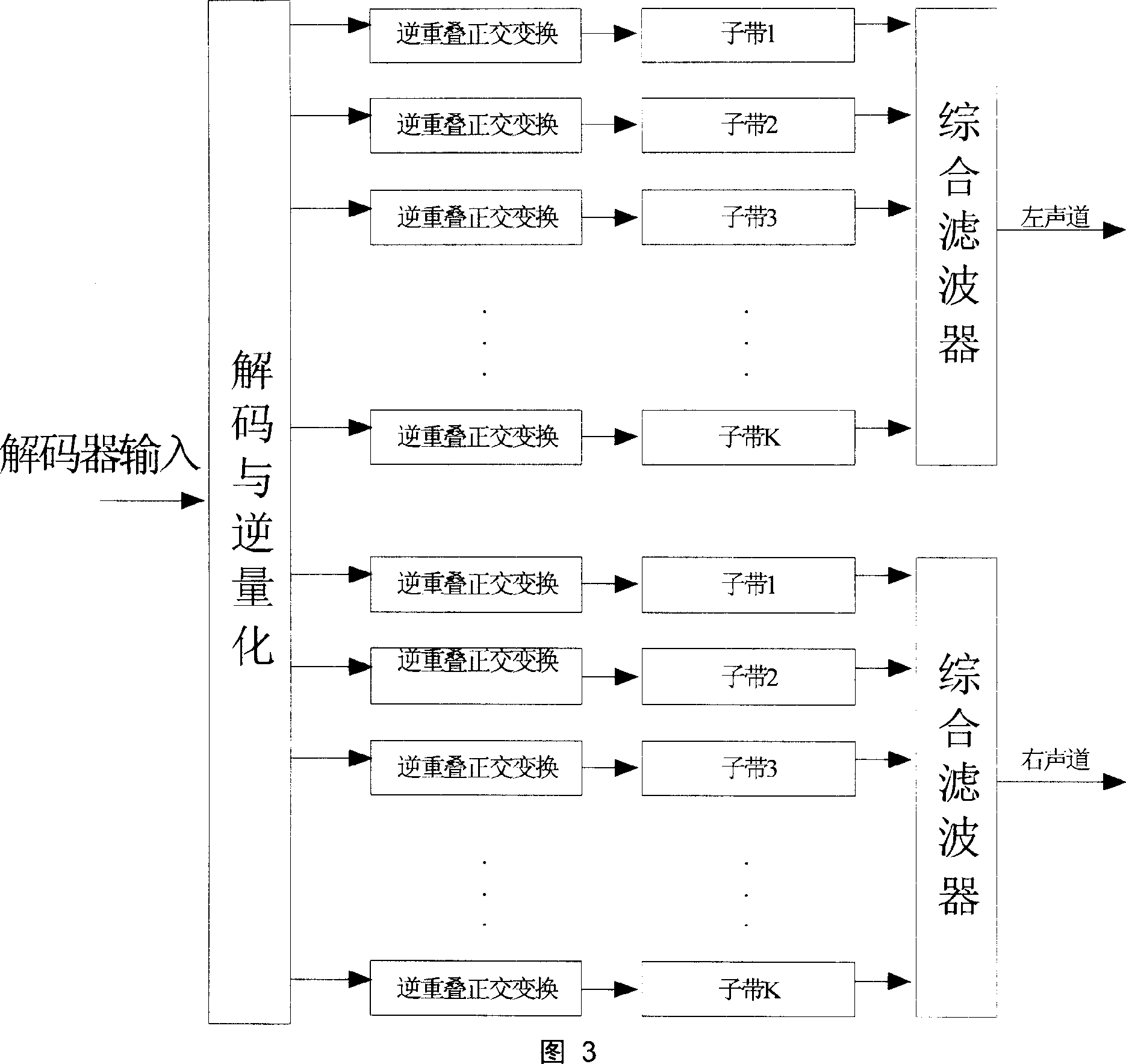
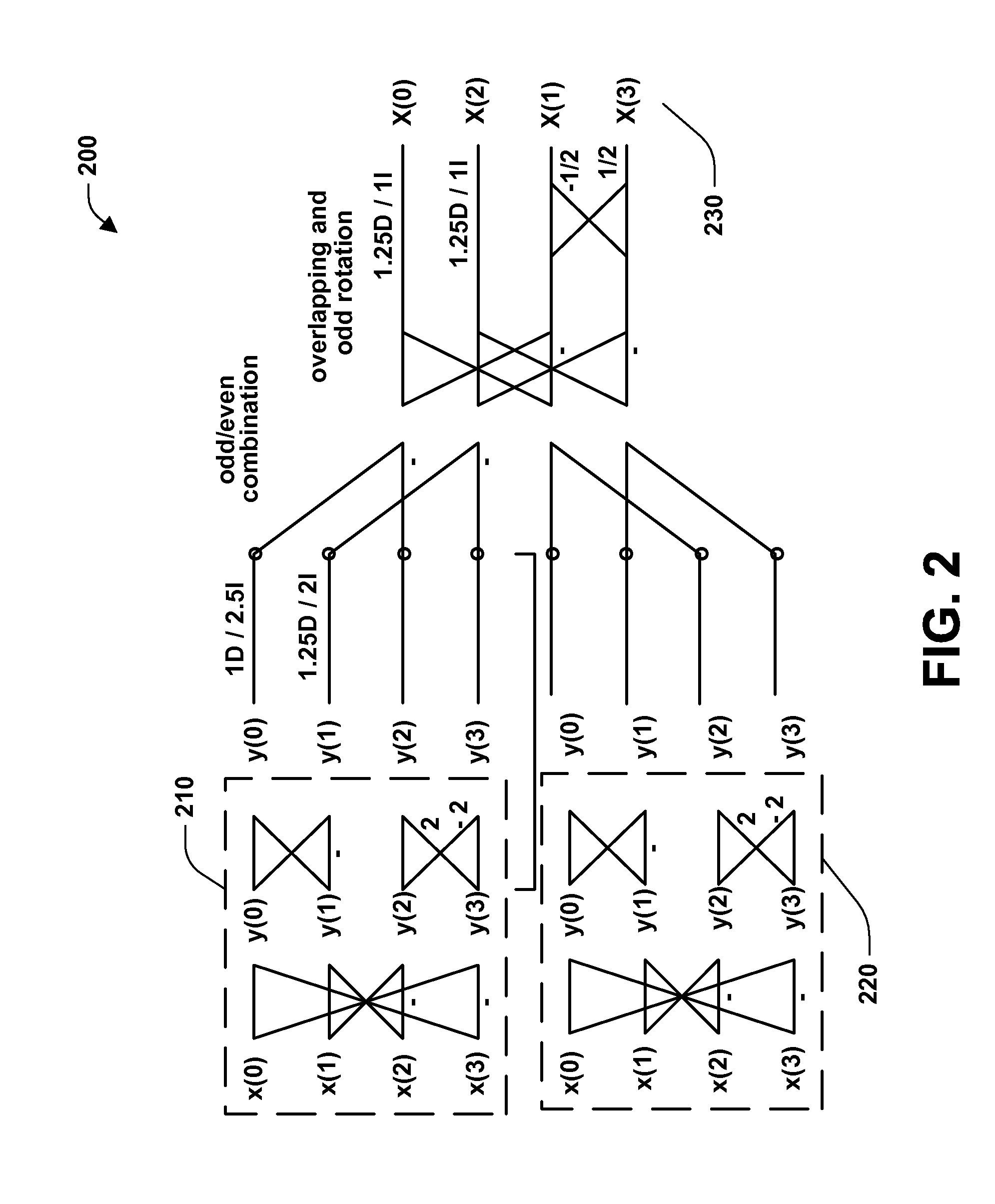
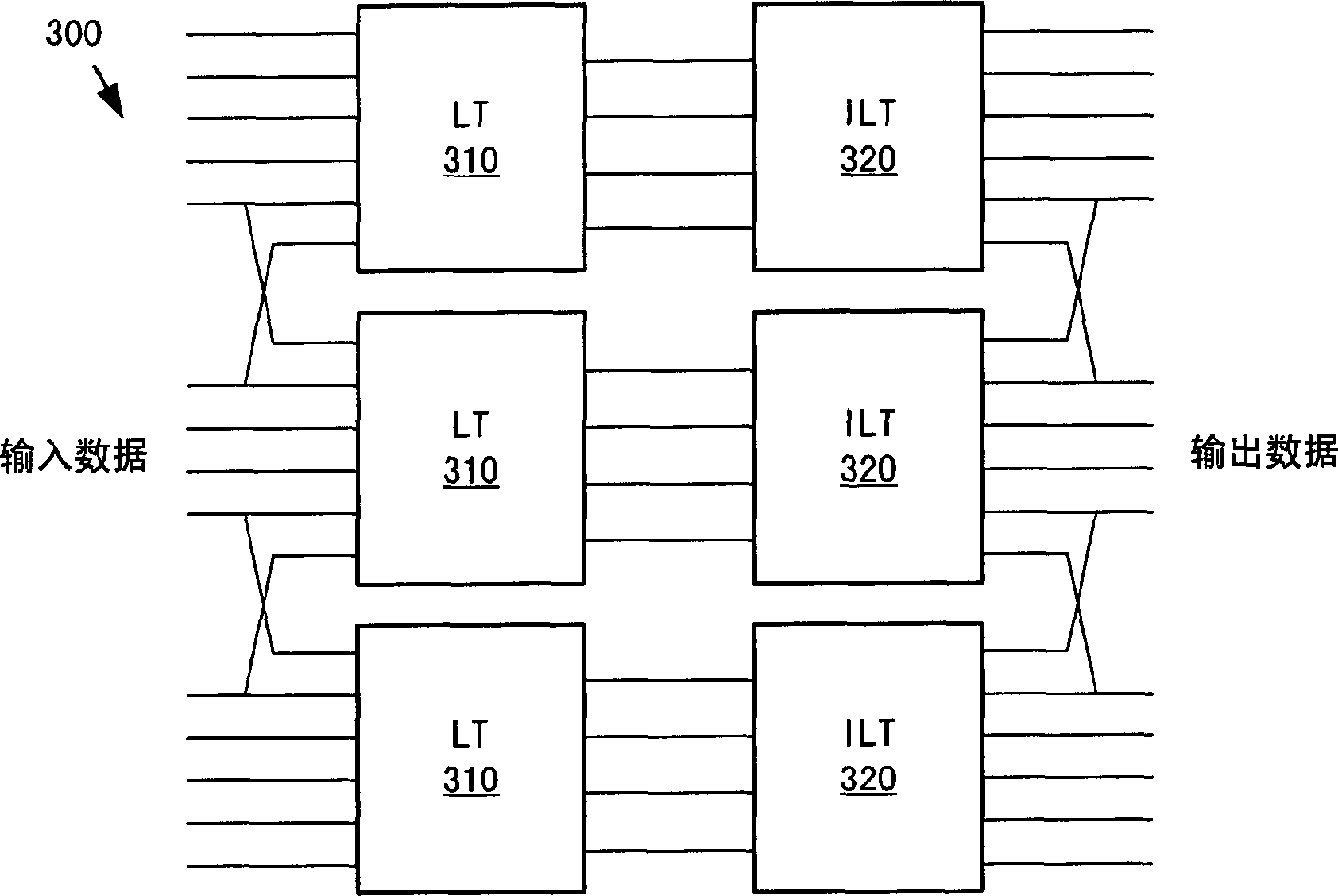
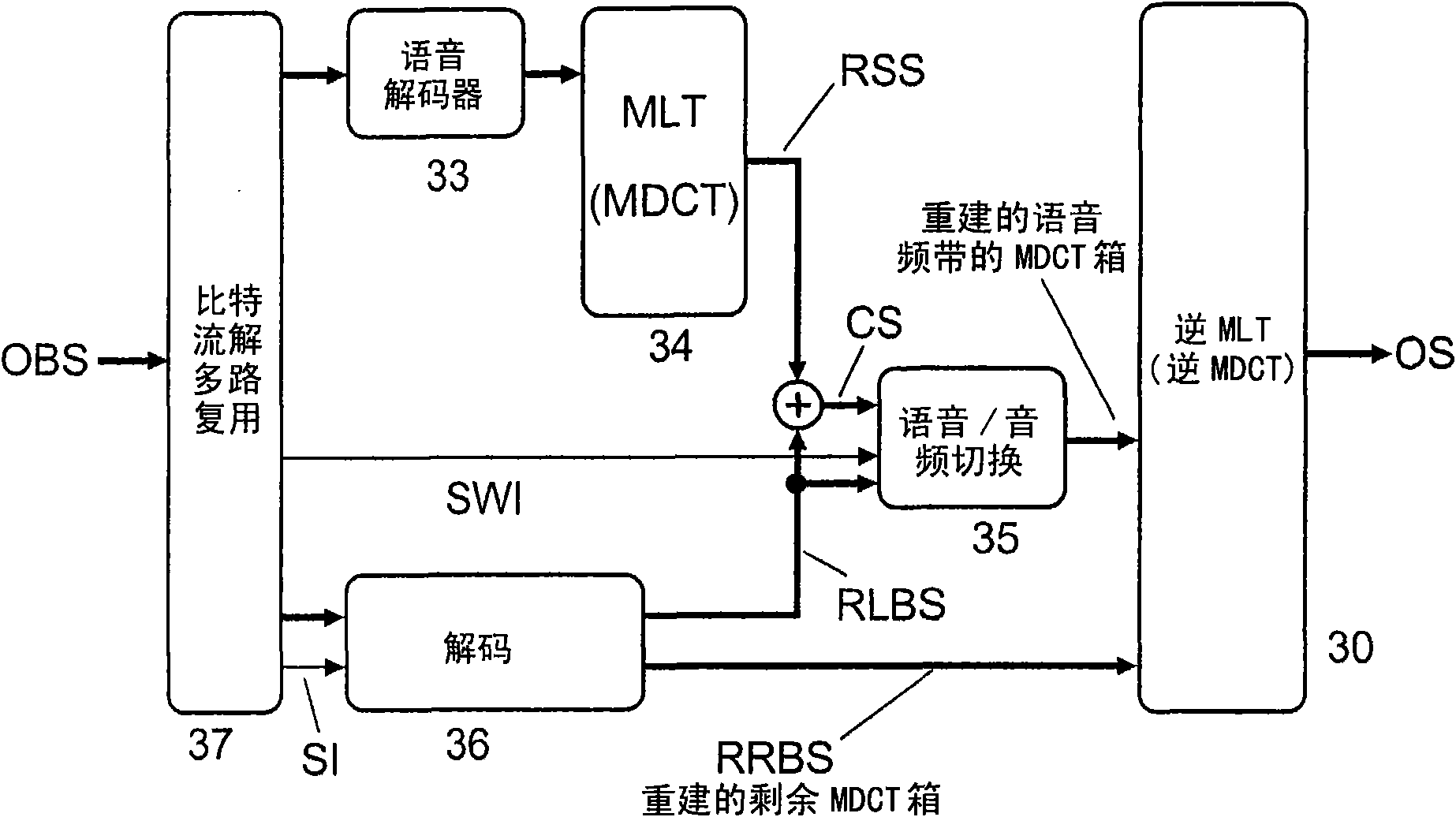
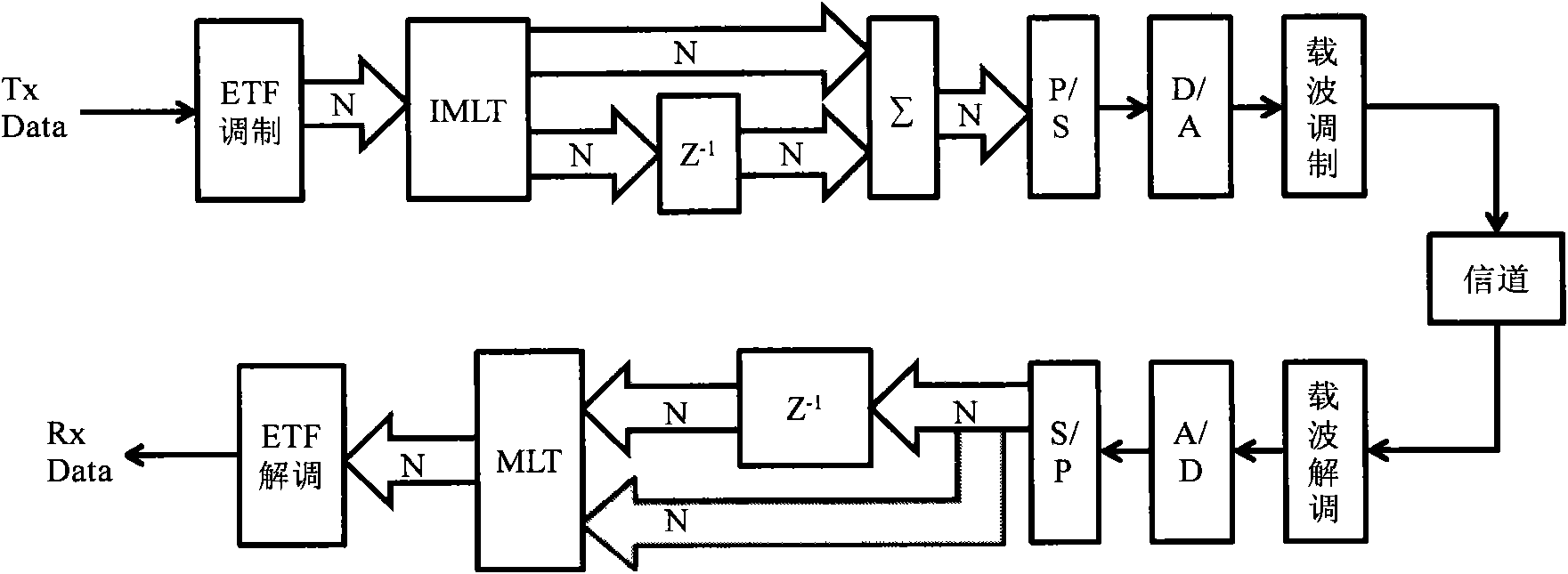
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Lapped transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal processing, a lapped transform is a type of linear discrete block transformation where the basis functions of the transformation overlap the block boundaries, yet the number of coefficients overall resulting from a series of overlapping block transforms remains the same as if a non-overlapping block transform had been used.
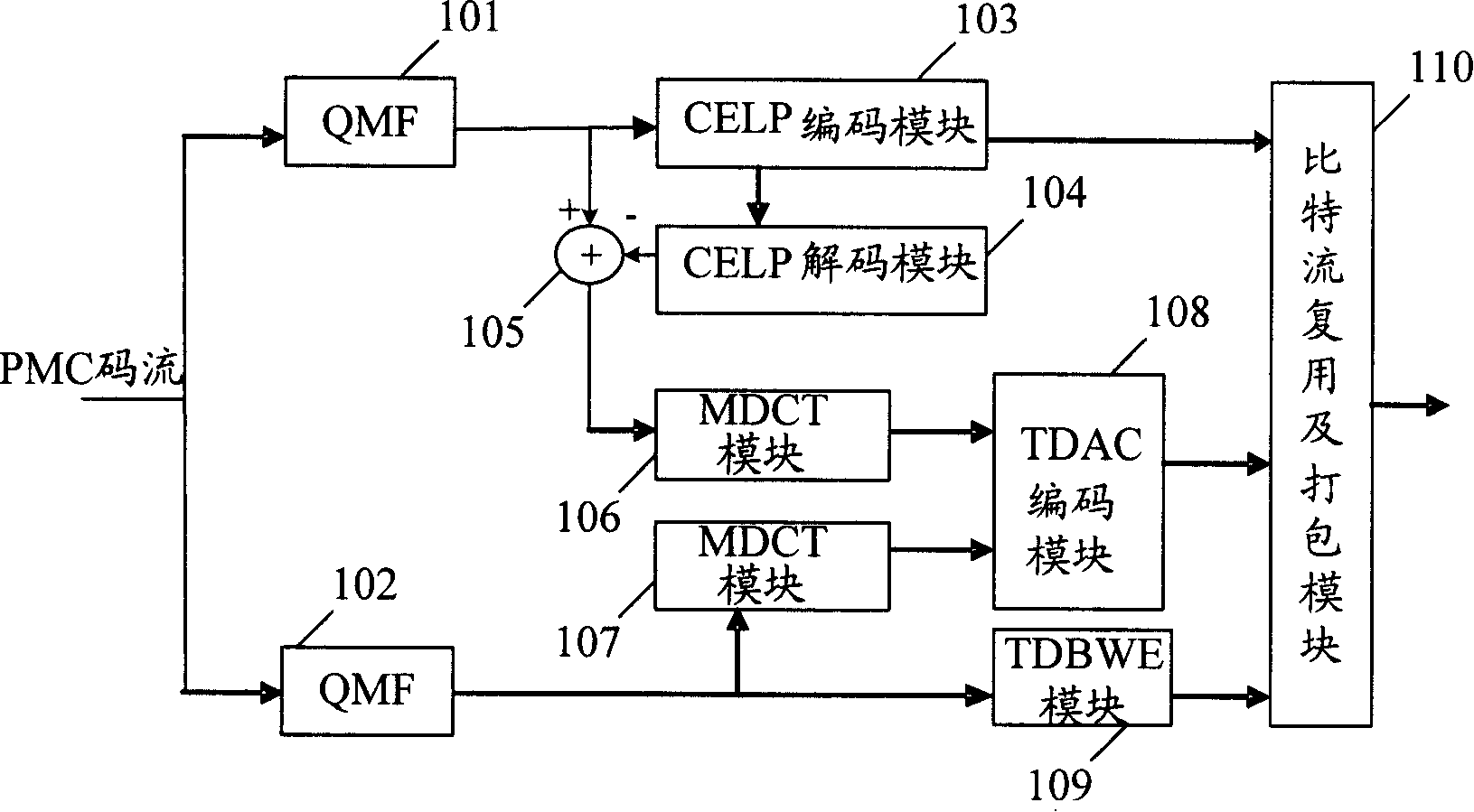
Error hidden frame reconstruction method based on overlap change compression code
The present invention belongs to the field of voice-frequency signal processing technology, it is characterized by that it successively contains the following steps: extracting time-domain transient characteristics in signal subband interior, and extracting interframe spectrum related characteristics; utilizing time-domain transient state and interframe spectrum related value to divide error frame into two stages according to the state, it contains 10 states; according to different error frame state selecting interpolation method to generate frequency spectrum coefficient and frequency domain phase of error frame, calculating time-domain signal and front and rear edge smoothing treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
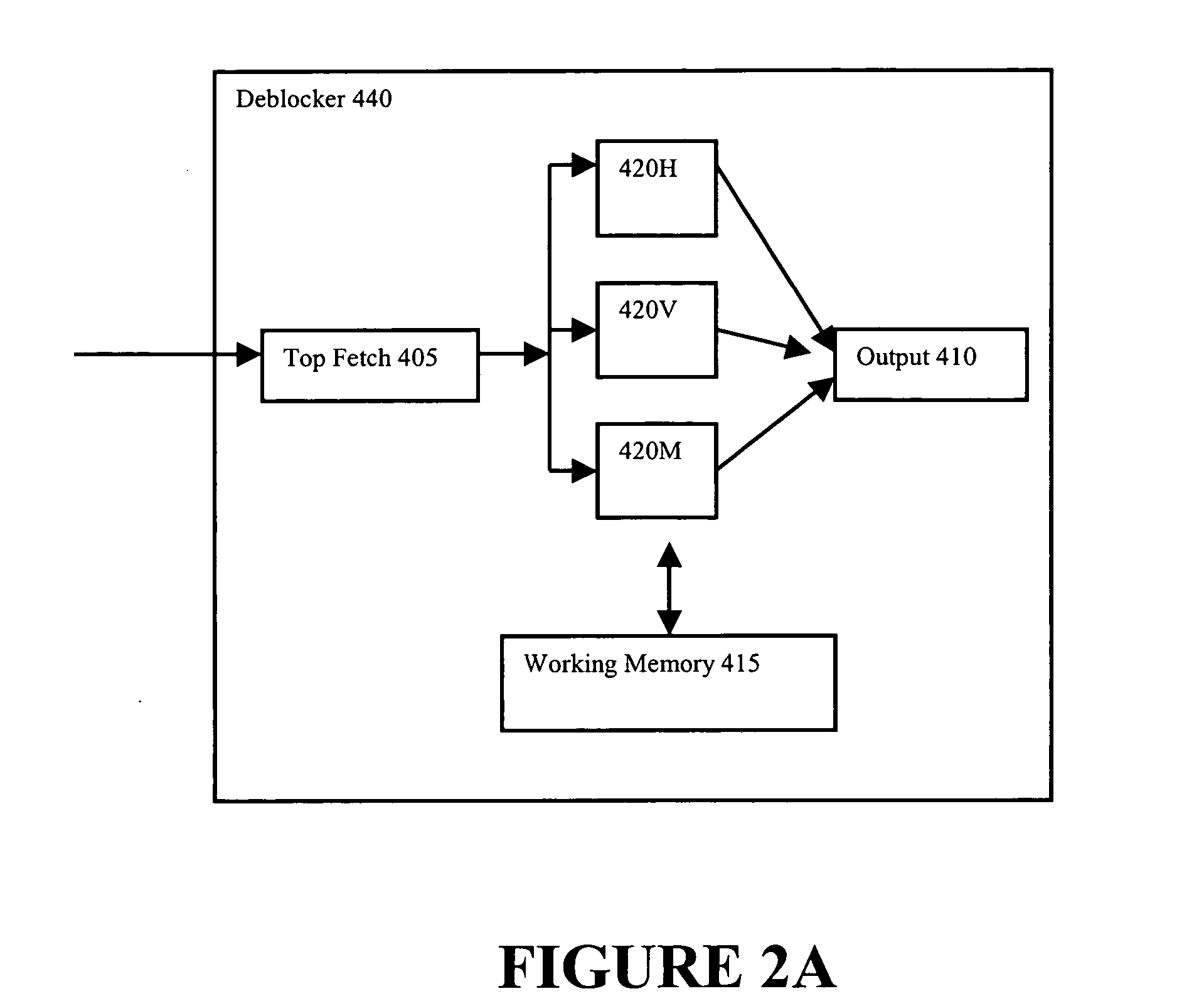
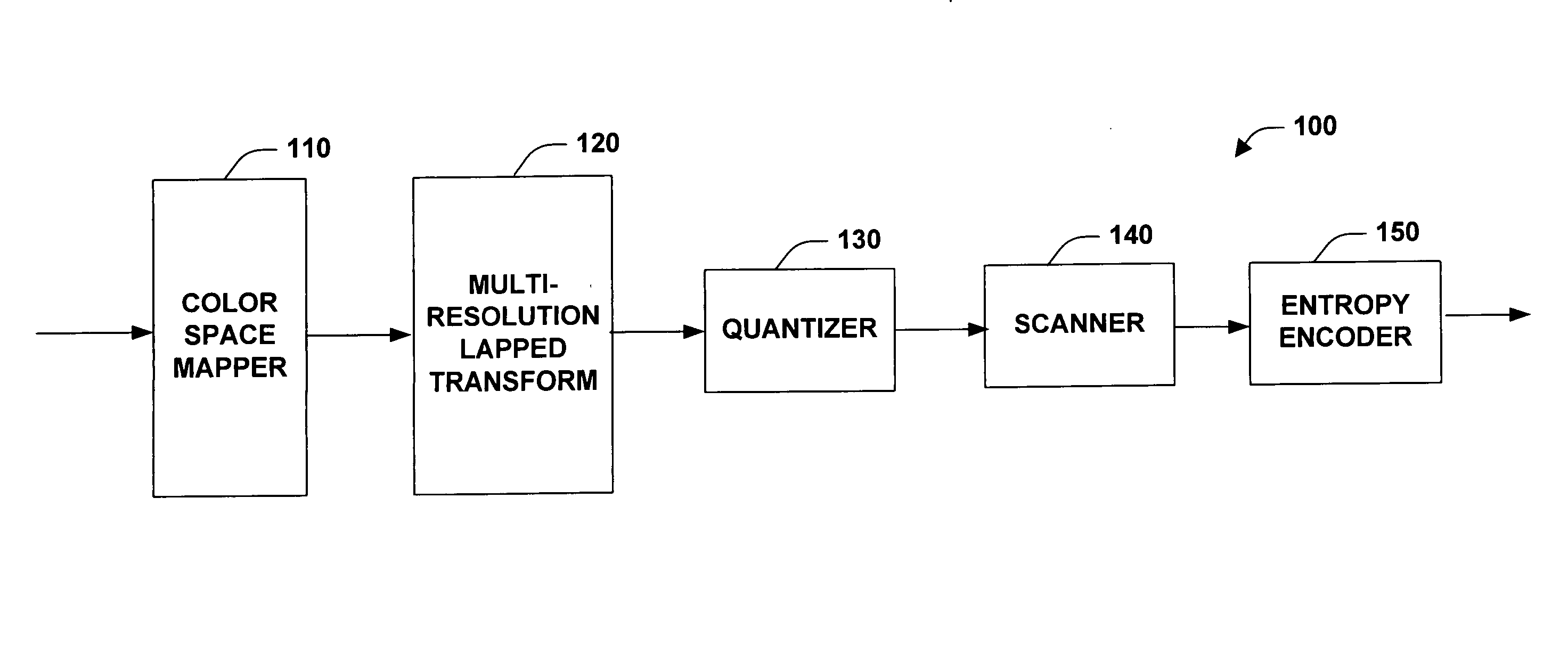
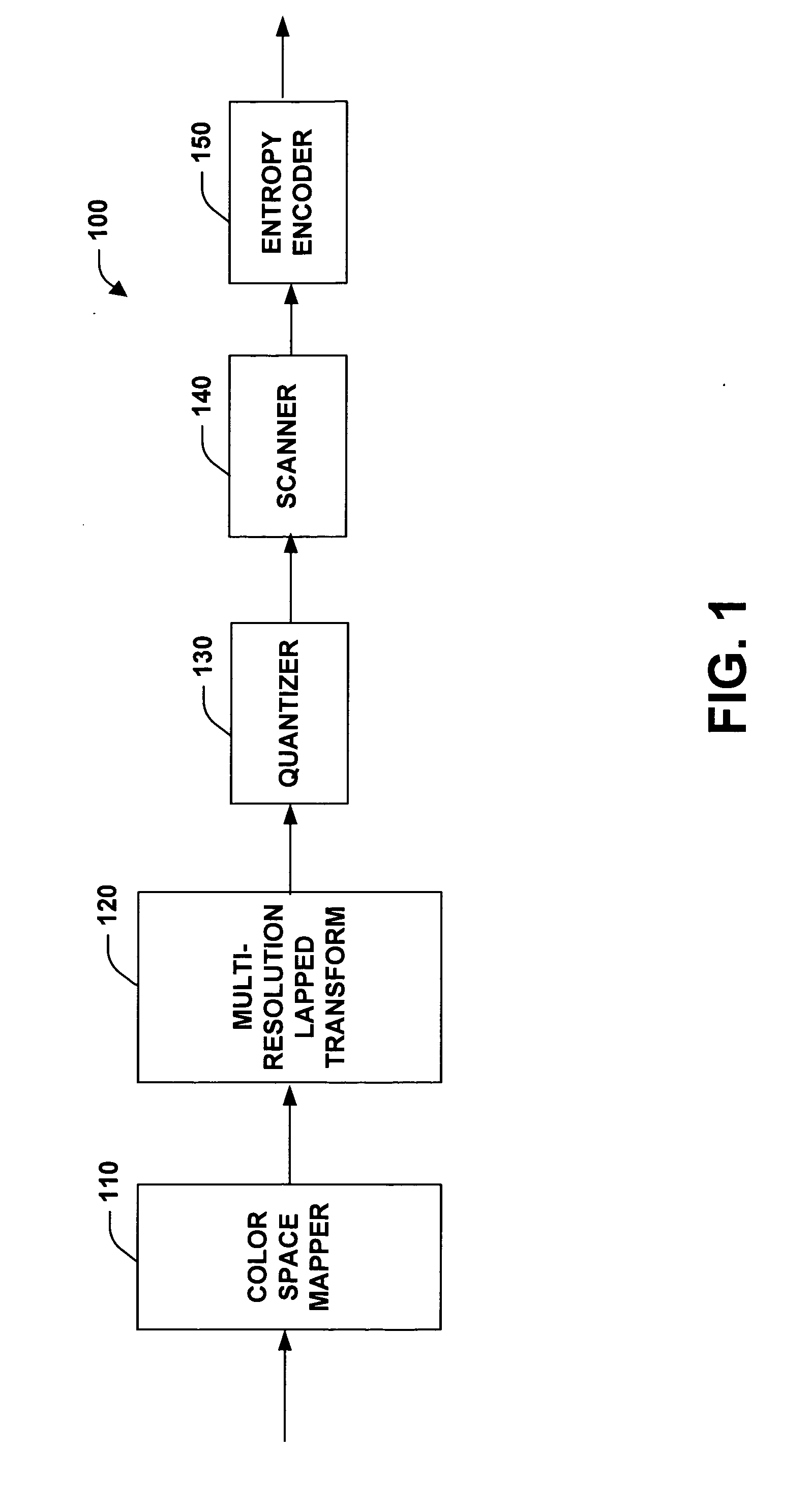
System and method for progressively transforming and coding digital data
InactiveUS20060285760A1Reduce blockinessReduced ringing artifactsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData compressionDigital data
A system and method facilitating progressively transforming and coding digital pictures is provided. The present invention via employment of a multi-resolution lapped transform provides for progressive rendering as well as mitigation of blocking artifacts and ringing artifacts as compared to many conventional compression systems. The invention includes a color space mapper, a multi-resolution lapped transform, a quantizer, a scanner and an entropy encoder. The multi-resolution lapped transform outputs transform coefficients, for example, first transform coefficients and second transform coefficients. A multi-resolution representation can be obtained utilizing second transform coefficients of the multi-resolution lapped transform. The color space mapper maps an input image to a color space representation of the input image. The color space representation of the input image is then provided to the multi-resolution lapped transform. The quantizer receives the first transform coefficients and / or the second transform coefficients and provides an output of quantized coefficients for use by the scanner and / or the entropy encoder. The scanner scans the quantized coefficients in order to produce a one-dimensional vector for use by the entropy encoder. The entropy encoder encodes the quantized coefficients received from the quantizer and / or the scanner resulting in data compression.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding layered audio
InactiveCN101206860AQuality improvementSolve the problem that it cannot effectively handle high sampling rate input signalsSpeech analysisCode conversionCoding decodingLapped transform
The invention discloses a hierarchical coding and decoding method and the device thereof. In the embodiment of the invention, the hierarchical and coding decoding proposal adopts the steps as following, after an input signal is converted into a MLT (Modulated Lapped Transform) coefficient, according to an auditory perception model, the input signal is divided into a kernel layer signal and an enhancement layer signal, and then an overlapped and packed coding data is obtained; during decoding, according to the auditory perception model, after the weighted calculation is performed to the importance of each sub-band in the enhancement layer, the reverse MLT is performed to the obtained MLT coefficient of the kernel layer and the enhancement layer, and the decoding flow is output. Compared with the prior hierarchical coding decoding art, in the invention, the MLT is performed to the input signal, the weighted calculation is performed to the importance of each sub-band in the enhancement layer according to the auditory perception model, thus, the quality of coding and decoding is enhanced, and the problem that the input signal with high sampling rate can not be effectively processed in the prior art is solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Conditional lapped transform
ActiveUS20050053150A1Decrease in code efficiencyCoding efficiency of certain areasPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionEncoder decoderComputer graphics (images)
A digital media content (e.g., image, video, audio, etc.) encoder / decoder employs a spatially varying parameter to condition the application of an overlap pre-process and post-process to adjacent transform block edges for the spatial-domain lapped transform. This conditional application of the lapped transform to sub-blocks of the digital media can be signaled on an edge, block, macro-block or other granularity. Further, a restriction on use of the conditional lapped transform based on a frame-level quantization or other bit-rate related parameter minimizes the signaling overhead impact at low bit-rates of coding.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Packet loss concealment for overlapped transform codecs
InactiveUS20060209955A1Error minimizationMinimizes a model-based energy criterionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPacket loss concealmentUnderdetermined system
Real-time packet-based audio communications over packet-based networks frequently results in the loss of one or more packets during any given communication session. The real-time nature of such communications precludes retransmission of lost packets due to the unacceptable delays that would result. Consequently, packet loss concealment methods are employed to “hide” lost packets from the listener. Unfortunately, conventional loss concealment methods, such as packet repetition or stretch / overlap methods, do not fully exploit information available from partially received samples. Therefore, when a single frame of N coefficients is lost, 2N samples are only partially reconstructed, thereby degrading the reconstructed signal. To address this problem, an optimized packet loss concealment solution is identified for particular lost packets by solving an underdetermined system of linear equations representing partially received samples while minimizing a computed error based on a model of the signal obtained from neighboring blocks or frames received by the decoder.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for progressively transforming and coding digital data
InactiveUS7155065B1Reduce blockinessReduced ringing artifactsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationDigital dataData compression
A system and method facilitating progressively transforming and coding digital pictures is provided. The present invention via employment of a multi-resolution lapped transform provides for progressive rendering as well as mitigation of blocking artifacts and ringing artifacts as compared to many conventional compression systems. The invention includes a color space mapper, a multi-resolution lapped transform, a quantizer, a scanner and an entropy encoder. The multi-resolution lapped transform outputs transform coefficients, for example, first transform coefficients and second transform coefficients. A multi-resolution representation can be obtained utilizing second transform coefficients of the multi-resolution lapped transform. The color space mapper maps an input image to a color space representation of the input image. The color space representation of the input image is then provided to the multi-resolution lapped transform. The quantizer receives the first transform coefficients and / or the second transform coefficients and provides an output of quantized coefficients for use by the scanner and / or the entropy encoder. The scanner scans the quantized coefficients in order to produce a one-dimensional vector for use by the entropy encoder. The entropy encoder encodes the quantized coefficients received from the quantizer and / or the scanner resulting in data compression.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
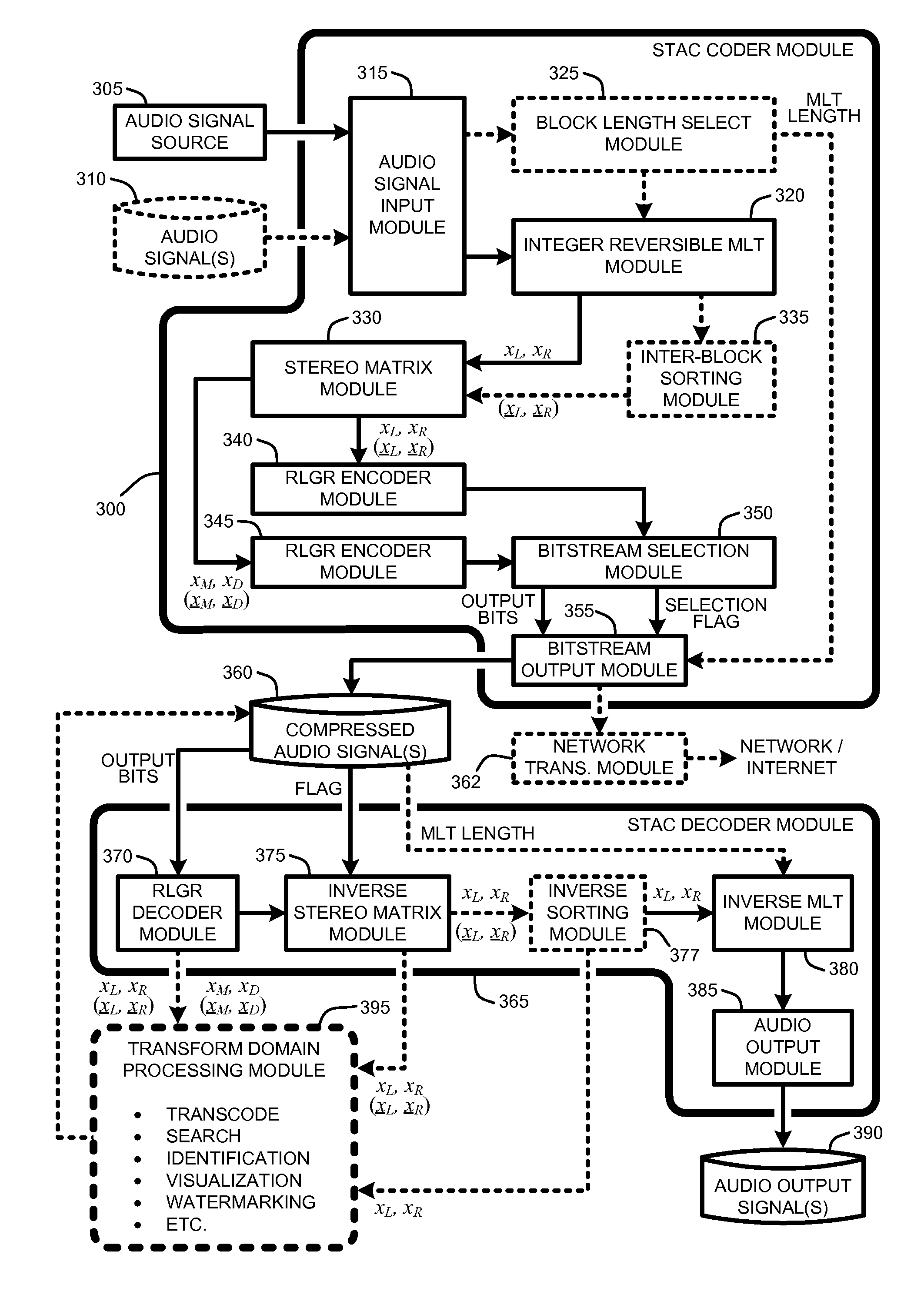
Audio compression and decompression using integer-reversible modulated lapped transforms
ActiveUS20080234845A1Further compression gainMaintaining perceptual transparencySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumLossless compression
A “STAC Codec” provides lossless audio compression and decompression by processing an audio signal using integer-reversible modulated lapped transforms (MLT) to produce transform coefficients. Transform coefficients are then encoded using a backward-adaptive run-length Golomb-Rice (RLGR) encoder to produce losslessly compressed audio signals. In additional embodiments, further compression gains are achieved via an inter-block spectral estimation and data sorting strategy. Further, compression in the transform domain allows the bitstream to be partially decoded, using the corresponding RLGR decoder, to reconstruct the frequency-domain coefficients. These frequency-domain coefficients are then directly used to speed up various transform-domain based applications such as transcoding media to lossy or other formats, search, identification, visualization, watermarking, etc. In other embodiments, near-lossless compression is achieved by right-shifting transform coefficients by some number of bits such that quantization errors are not perceived as distortion in the decoded audio signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Combined filter processing for video compression
InactiveUS20060245501A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Vertical edge
Presented herein are combined filter(s) for video compression. In one embodiment, there is presented a method for overlap transforming a block. The method comprises filtering a portion of a horizontal edge of a block; and overlap transform filtering a vertical edge of the block after filtering the portion of the horizontal edge of the block.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Information signal representation using lapped transform
ActiveUS20130064383A1Easy to useEfficiently traverseEar treatmentSpeech analysisLapped transformComputer science
An information signal reconstructor is configured to reconstruct, using aliasing cancellation, an information signal from a lapped transform representation of the information signal including, for each of consecutive, overlapping regions of the information signal, a transform of a windowed version of the respective region, wherein the information signal reconstructor is configured to reconstruct the information signal at a sample rate which changes at a border between a preceding region and a succeeding region of the information signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Adaptive down-sampling and lapped transform-based image compression method
InactiveCN101583032ASolve the problem of unsatisfactory refactoring qualityOvercome the shortcoming of poor real-time performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage compressionSelf adaptive
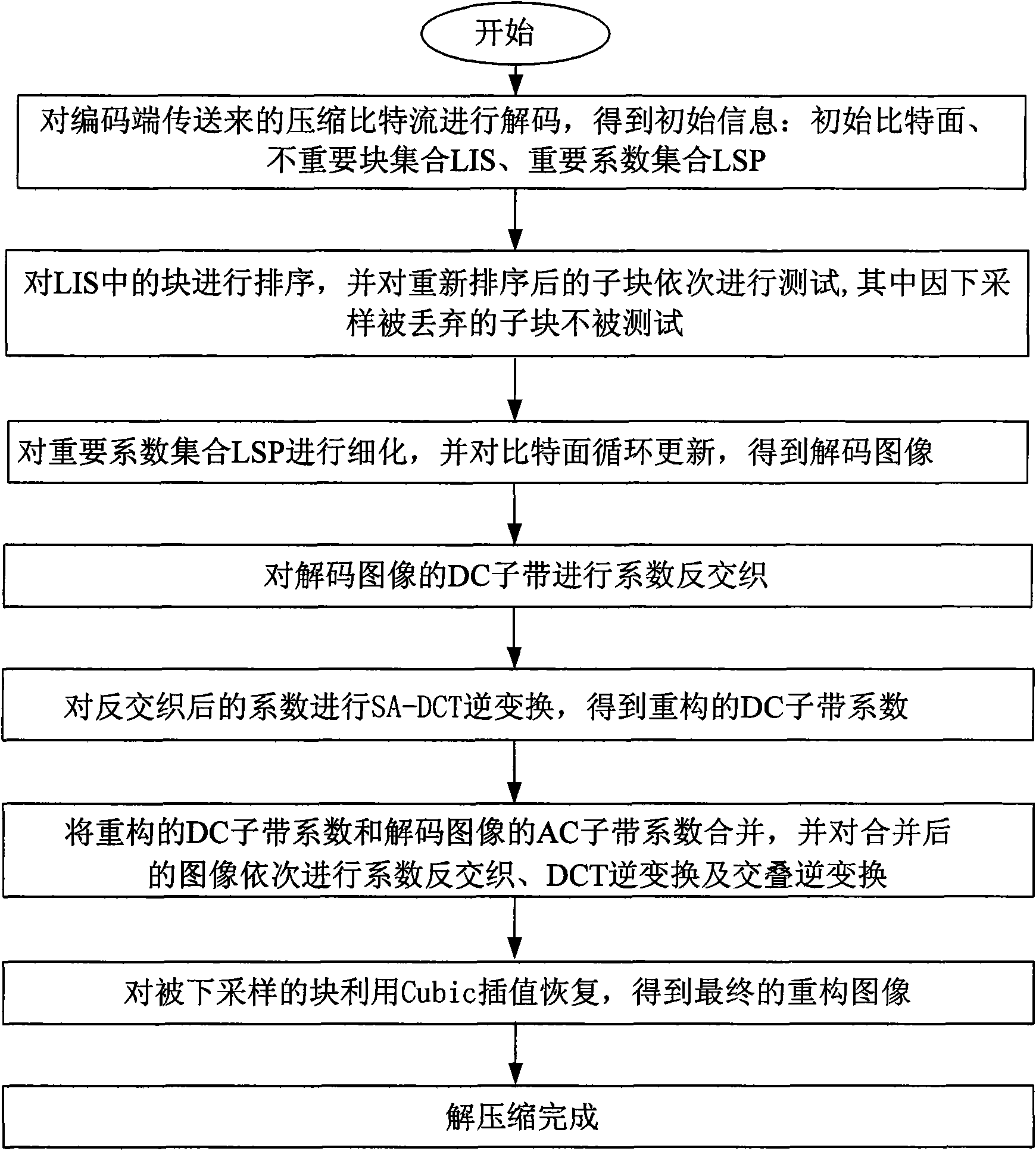
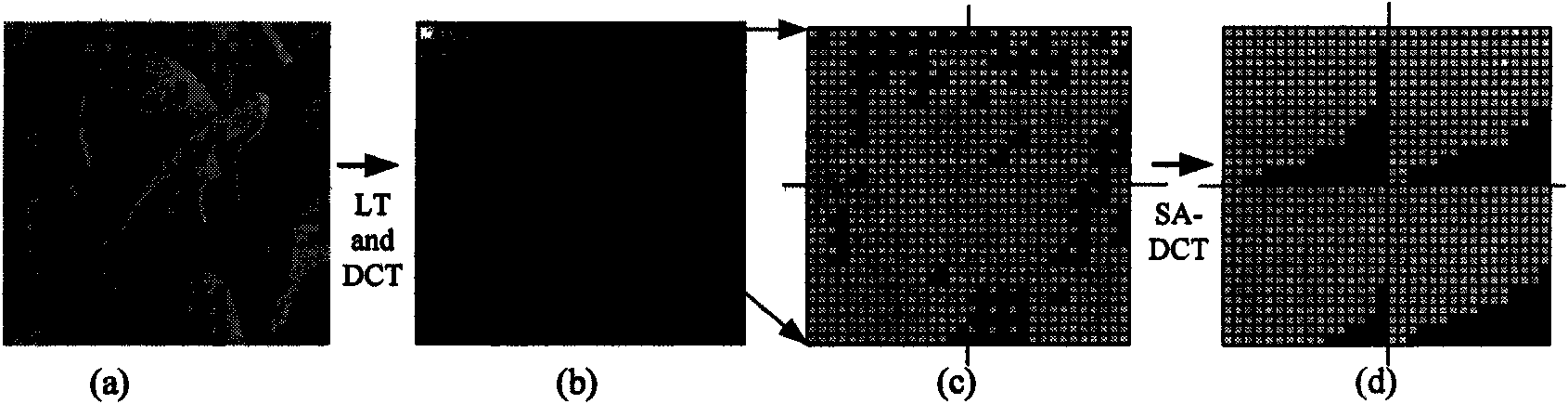
The invention provides an adaptive down-sampling and lapped transform-based image compression method, and mainly solves the problems of low performance and high complexity existing in the prior down-sampling based compression method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, adaptively down-sampling the prior image; 2, firstly performing lapped transform on the image after adaptive down-sampling between DCT blocks which are not subjected to the down-sampling, and then performing the DCT transformation on the whole image; 3, interweaving factors after transformation into a wavelet tree structure to obtain a low frequency subband DC and a high frequency subband AC; 4, performing the shape-adaptive DCT transformation on the low frequency subband DC, and interweaving the factors again; 5, by an object-oriented SPECK coding method, coding the factors with the wavelet tree structure to obtain a compressed bit stream; and 6, decompressing the bit stream transmitted to a decoding end to obtain a final re-constructed image. The method can obtain the performance higher than that of the prior image compression method under the condition of low bit rate, is low in complexity, and can be used for the low-bit-rate image coding which has strict requirements on complexity and real-time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Video edge filtering
InactiveUS20090279611A1Reduce data bandwidthEfficient executionColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Edge filter
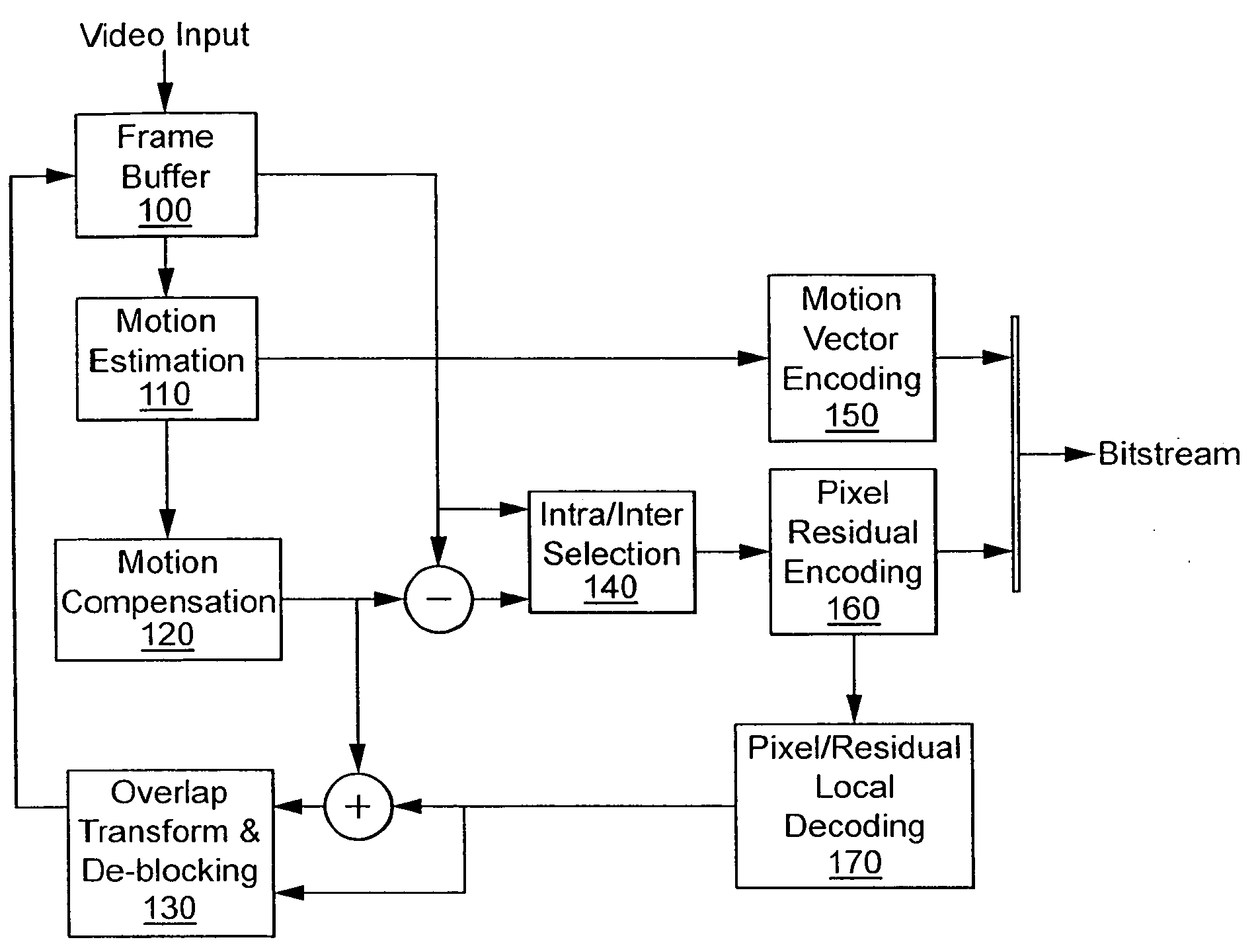
A method and apparatus are provided for performing overlap transform and deblocking of a decompressed video signal. The video image is sub-divided into a plurality of non-overlapping macroblocks, each of which comprises a plurality of smaller sub-blocks. Each macroblocks comprises two luminance partitions and one chrominance partition. Each partition is buffered and further buffering is provided for sub-blocks of each partition. Overlap transform and deblocking are performed by buffering sub-blocks from current partitions and sub-blocks from partitions from adjacent macroblocks. Overlap transform is performed in the current macroblock for buffered sub-blocks and deblocking is performed for blocks in the adjacent macroblocks.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
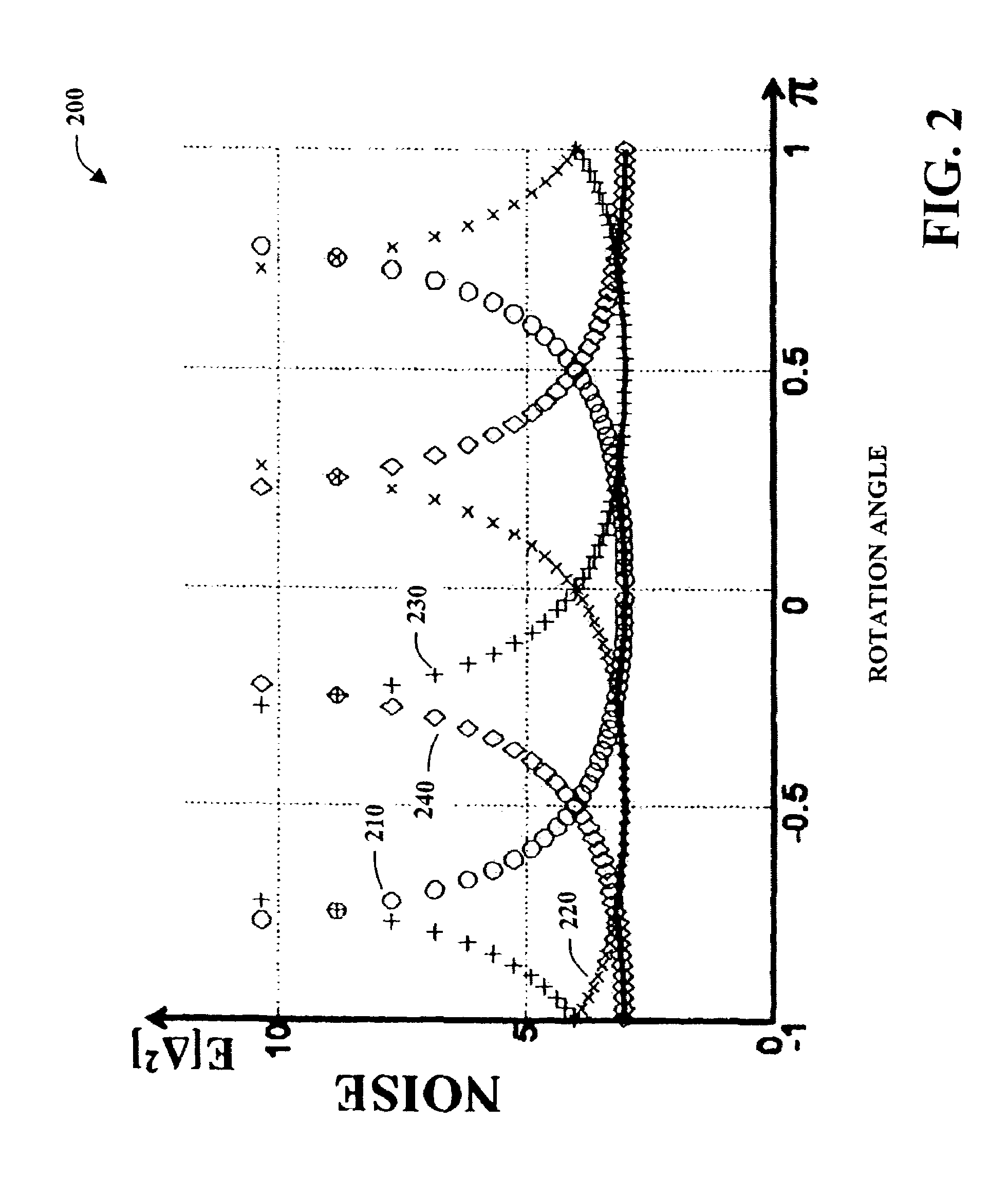
Reversible overlap operator for efficient lossless data compression
ActiveCN1805547AComputation using non-contact making devicesSpeech analysisComputer graphics (images)Lossless compression
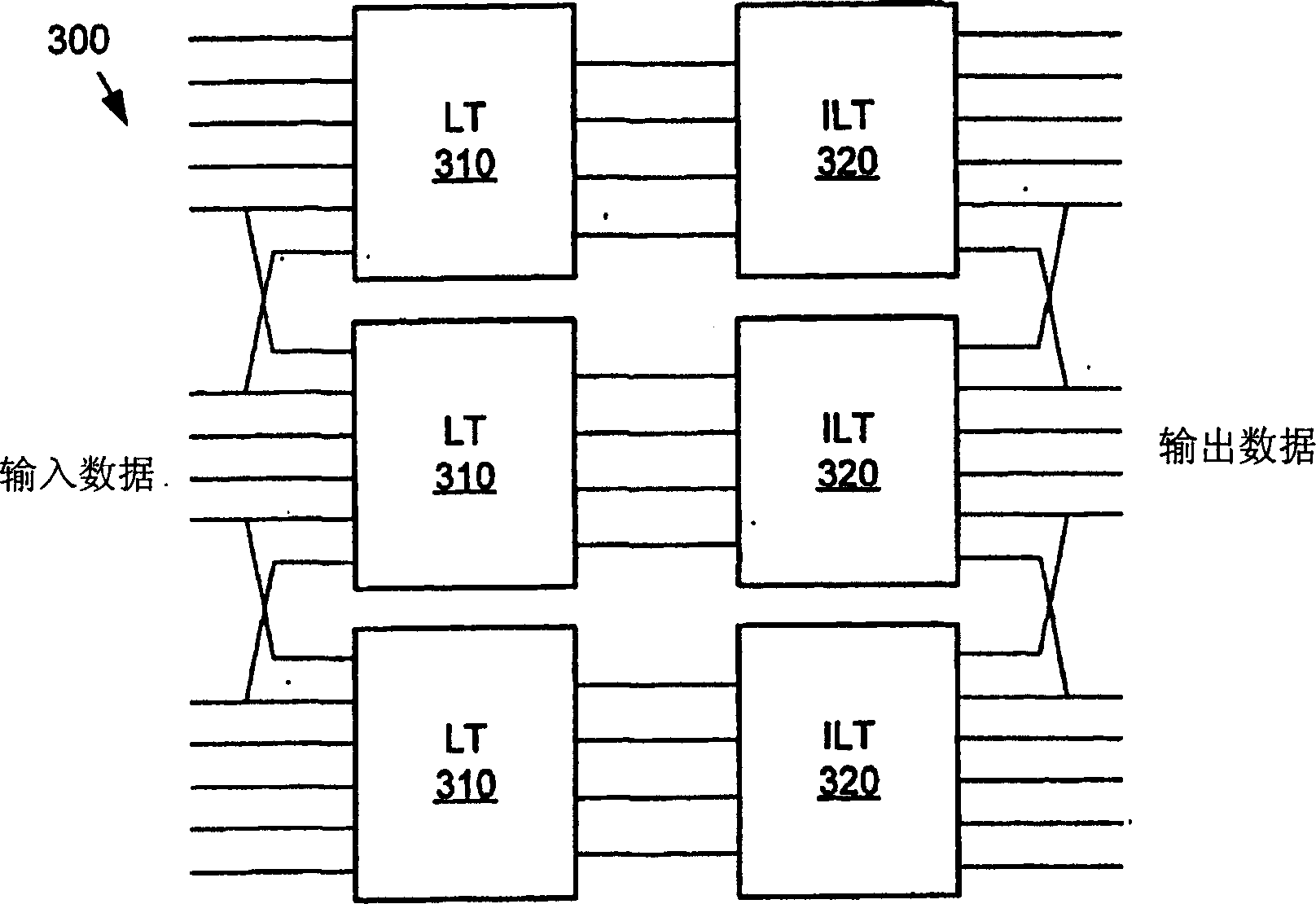
An efficient lapped transform is realized using pre- and post-filters (or reversible overlap operators) that are structured of unit determinant component matrices. The pre-and post-filters are realized as a succession of planar rotational transforms and unit determinant planar scaling transforms. The planar scaling transforms can be implemented using planar shears or lifting steps. Further, the planar rotations and planar shears have an implementation as reversible / lossless operations, giving as a result, a reversible overlap operator.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
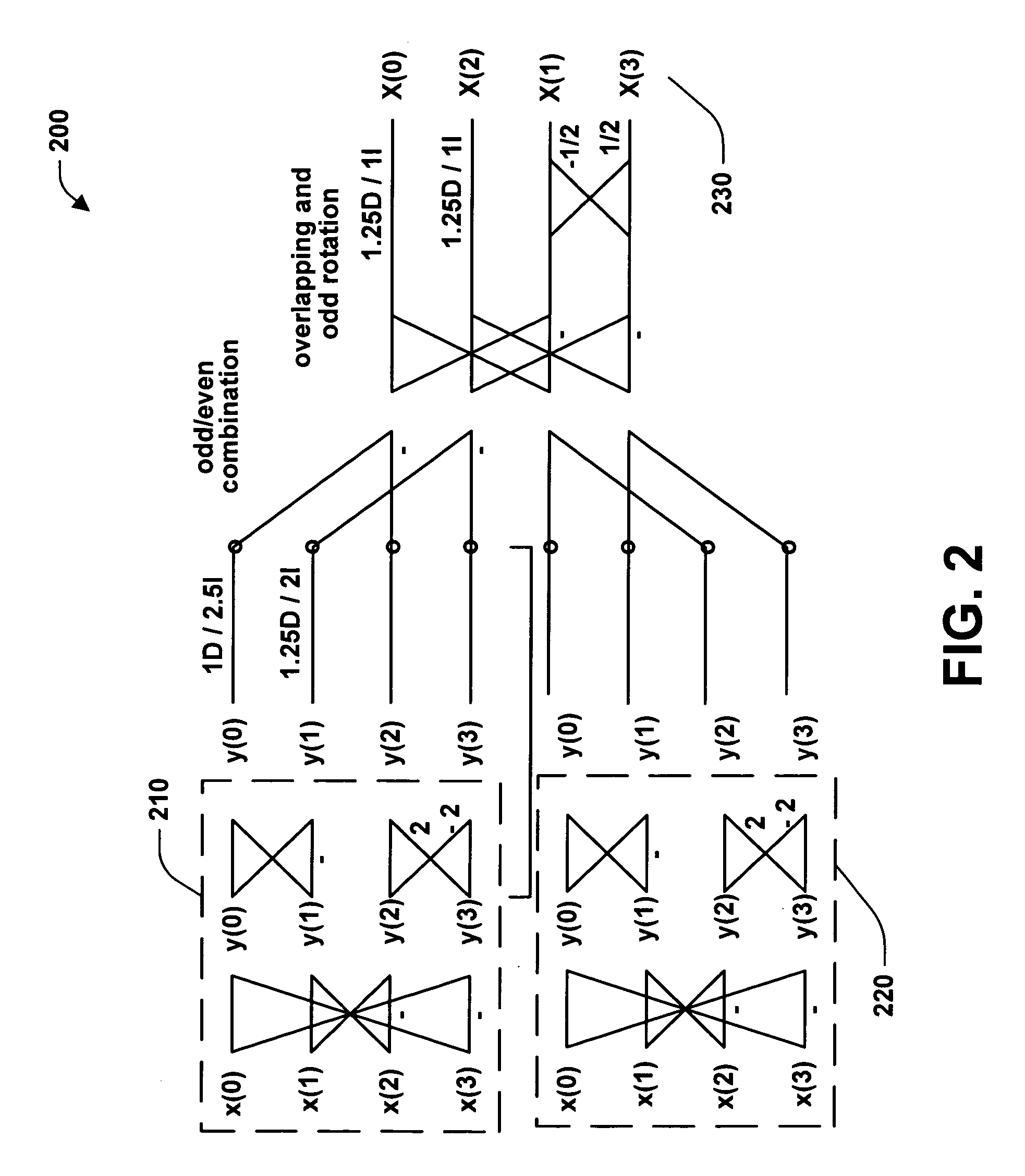
Reversible 2-dimensional pre-/post-filtering for lapped biorthogonal transform
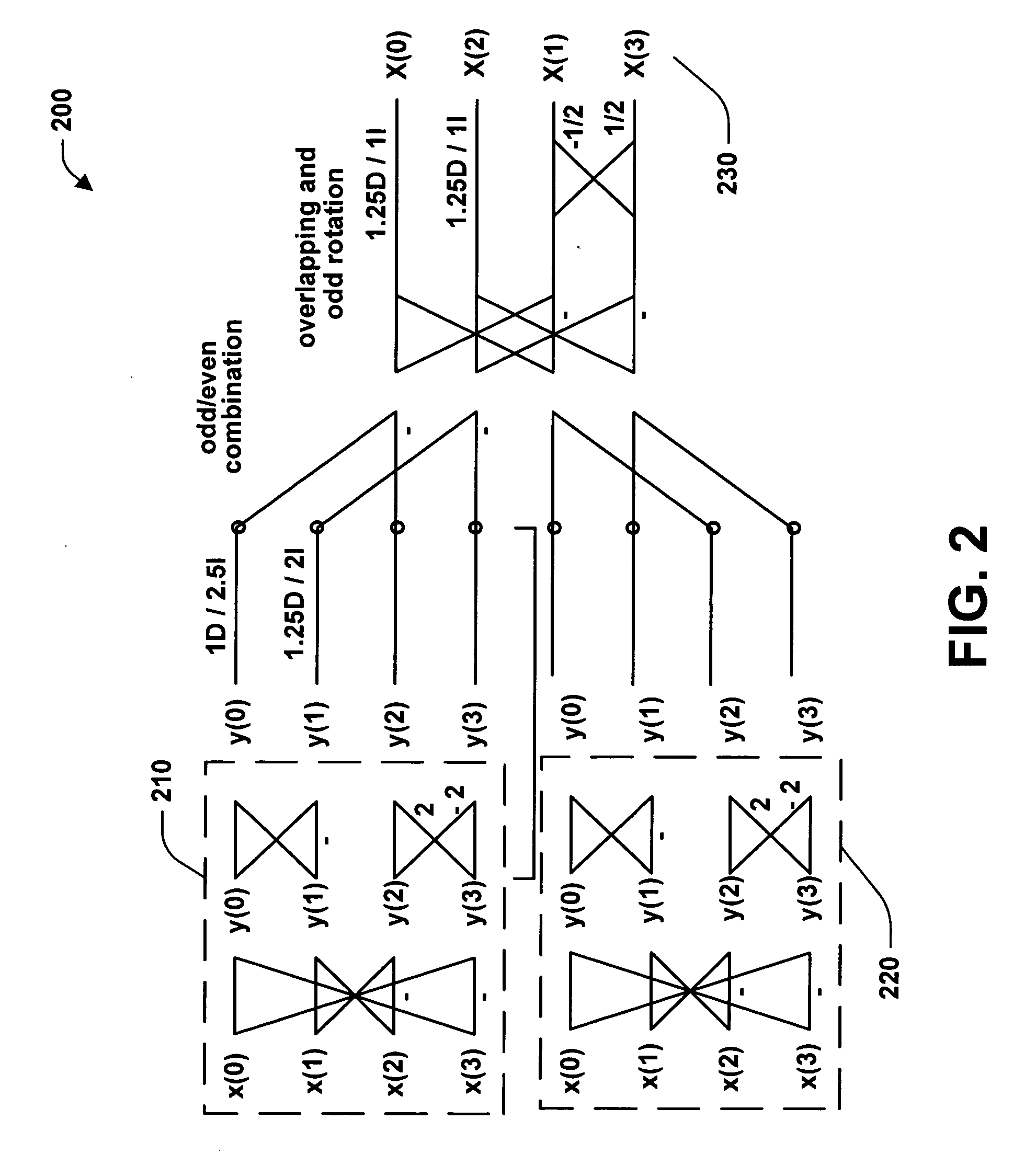
An efficient lapped transform useable in digital media codecs is realized using a reversible 2-dimensional overlap operator for pre / post filtering that is applied on a staggered grid relative to a core transform. The 2-dimensional lapped operator is based on a separably applied 1-dimensional reversible lapped operator, which is re-arranged as a sequence of elementary transforms in interleaved stages on subsets of points of the respective block and further implemented in lifting steps for computational efficiency. The interleaved stages include applying rotation and scaling stages between initial and final stages involving a normalized 2x2 Hadamard transform
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for encoding or decoding a speech and/or non-speech audio input signal
InactiveCN101615393AImprove unityExcellent codec qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumLapped transform
A disadvantage of known audio or speech codecs is a clear dependency of the coding quality on the types of content, i.e. music-like audio signals are best coded by audio codecs and speech-like audio signals are best coded by speech codecs. No known codec is holding a dominant position for mixed speech / music content. The inventive joined speech / audio codec uses speech coding processing as well as audio coding processing. Transform based audio coding processing is combined in an advantageous way with linear prediction based speech coding processing, using at the input a Modulated Lapped Transform the output spectrum of which is separated into frequency bins (low frequencies) assigned to the speech coding and the remaining frequency bins (high frequencies) are assigned to the transform-basedaudio coding. The invention achieves a uniform good codec quality for both speech-like and music-like audio signals, especially for very low bit rates but also for higher bit rates.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
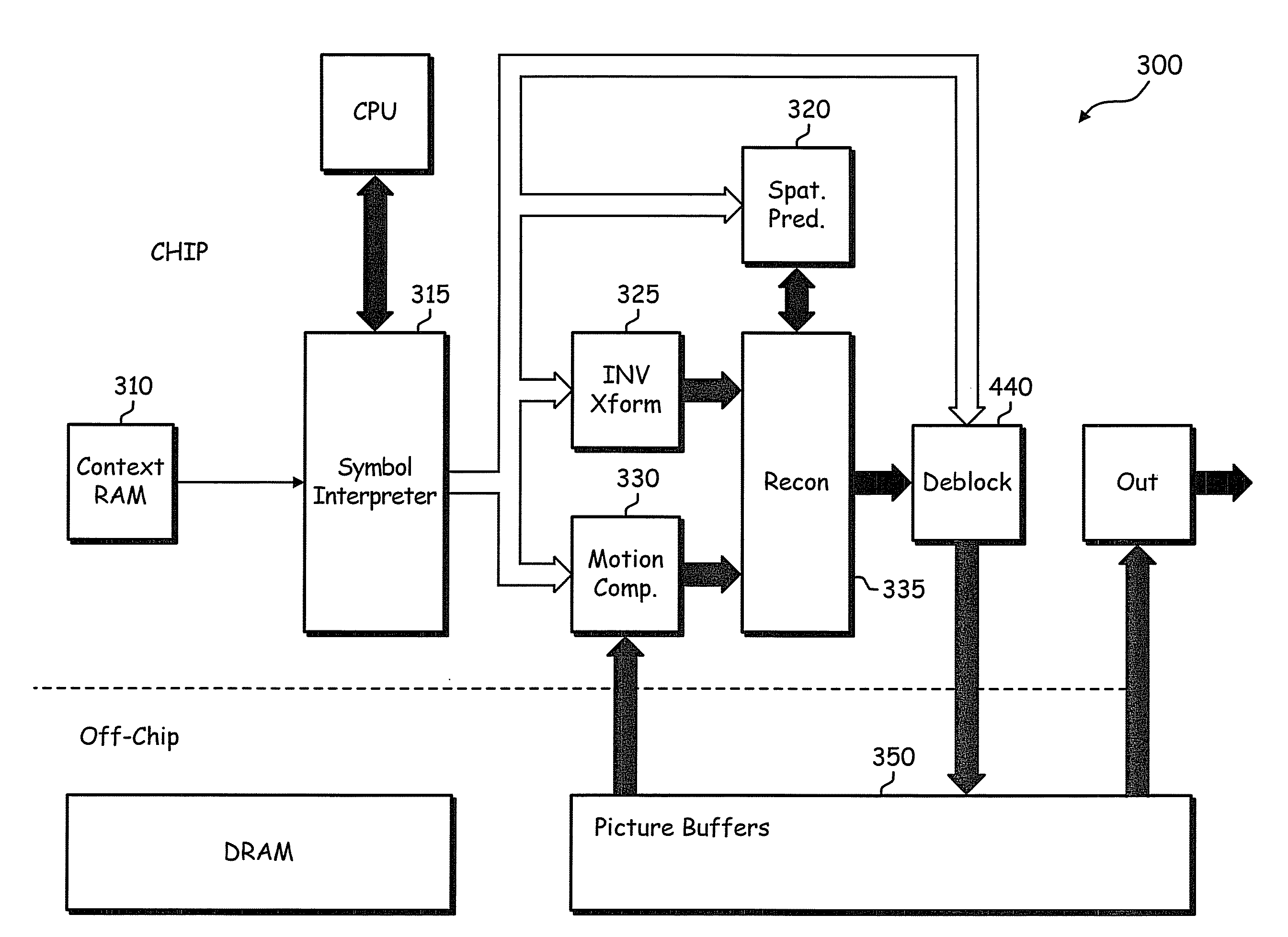
Method and apparatus for lapped transform coding and decoding
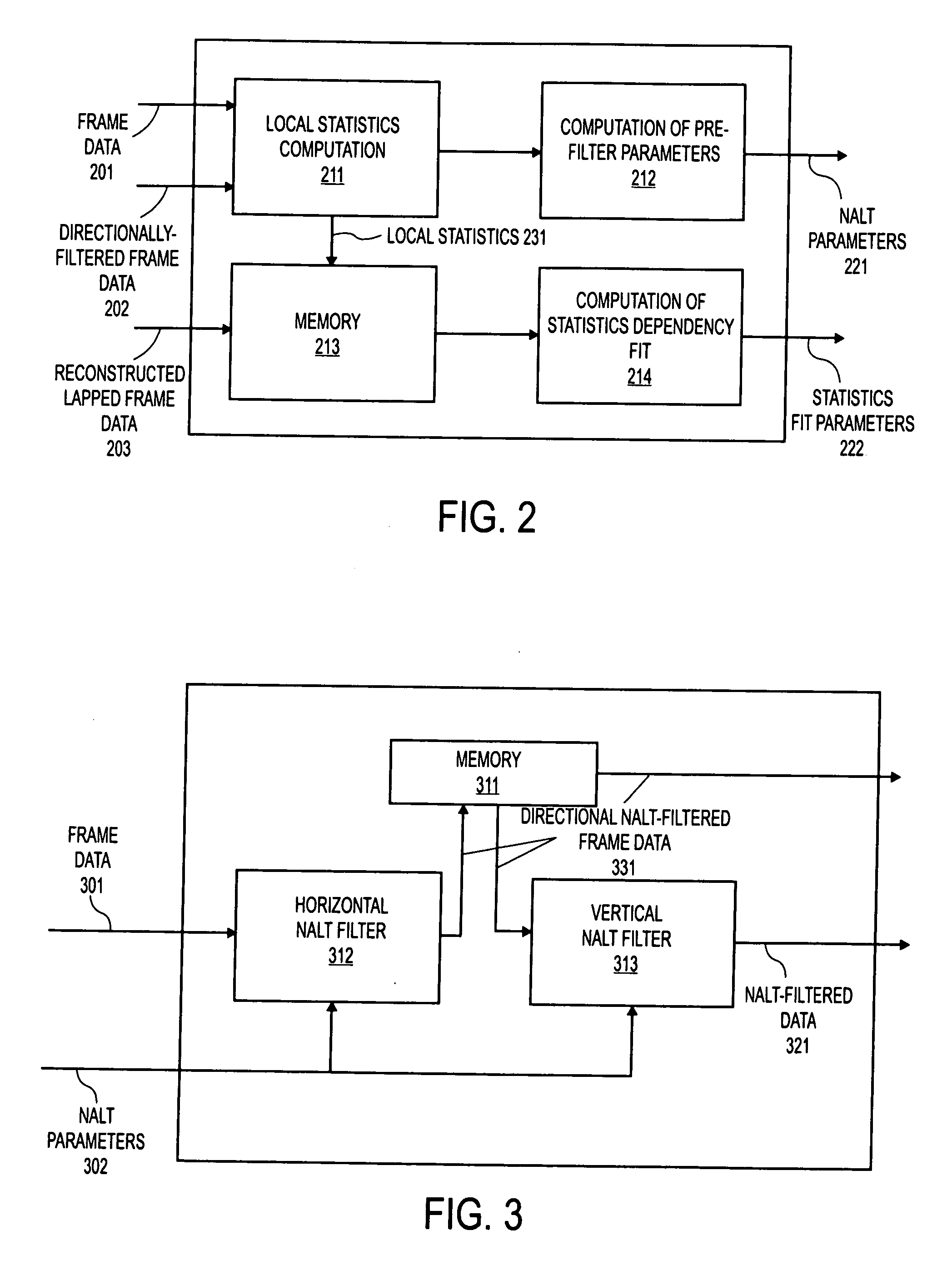
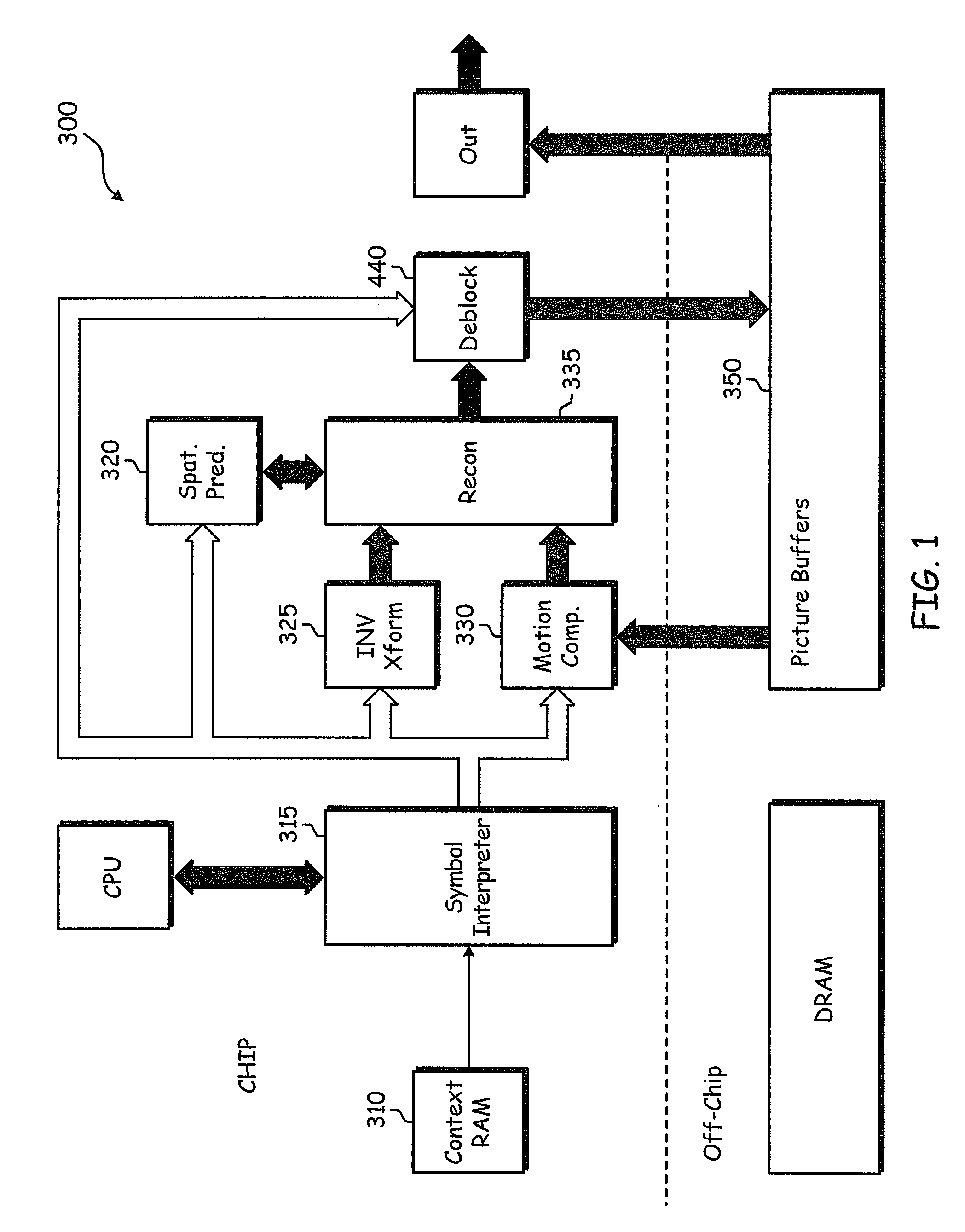
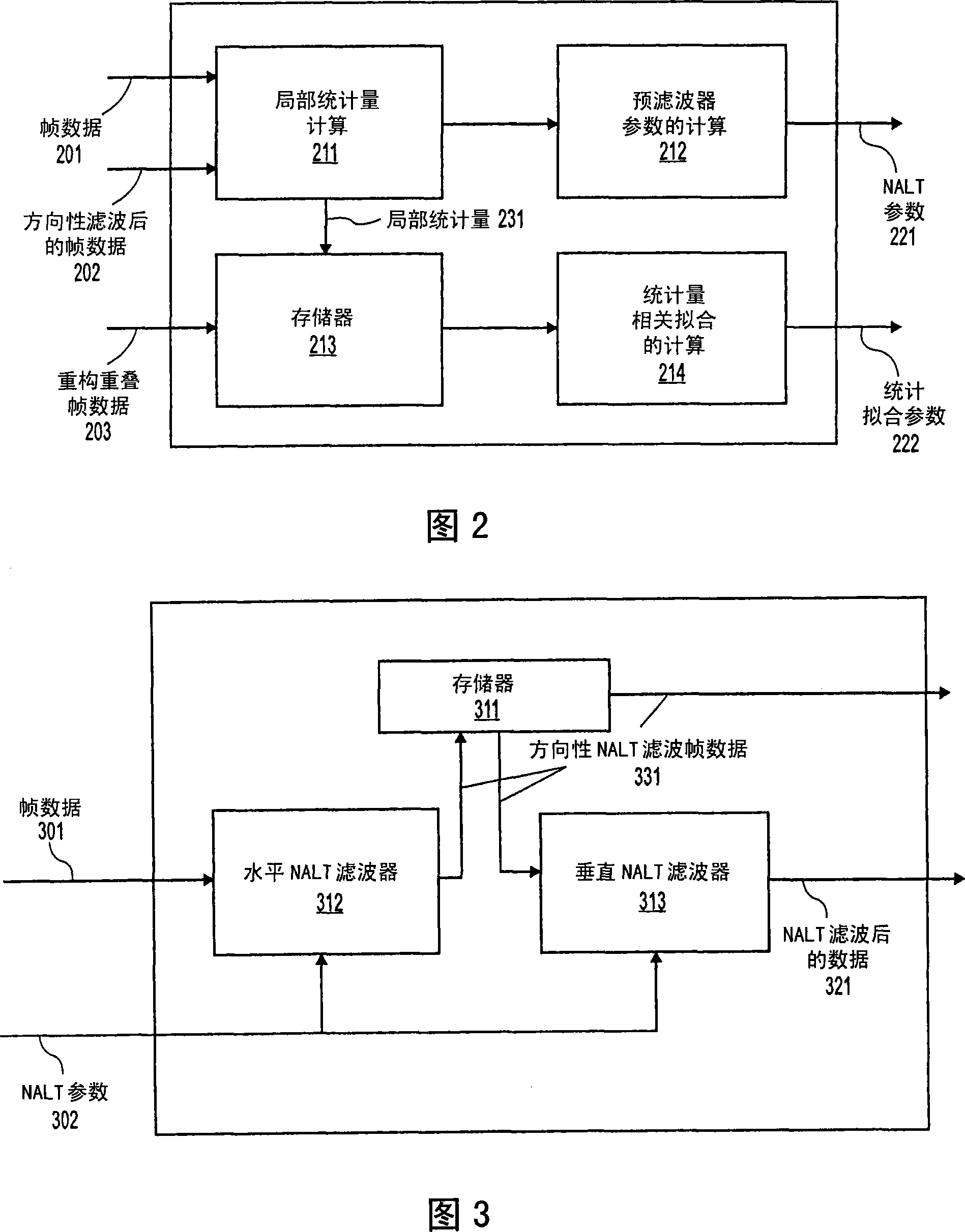
InactiveUS20060288065A1Digital video signal modificationComplex mathematical operationsLocal statisticsLapped transform
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for deriving and using non-linearly adapted lapped transforms (NALTs) In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving parameters of a statistical fit between local statistics of original and processed frame data, determining adaptation parameters for application of an inverse lapped transform to frame data, and filtering the frame data in response to filtering adaptation parameters.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Time-frequency expanding anti-jamming method, equipment and system based on lapped transformation algorithm
InactiveCN101986634AAvoid spreadingImprove anti-interference abilityMulti-frequency code systemsAnti jammingInverse discrete fourier transform
The invention discloses a time-frequency expanding anti-jamming method, equipment and system based on a lapped transformation algorithm. The method comprises a spread spectrum code chip obtaining step, a frequency domain spread spectrum step, a modulation step in which inverse overlapping transformation modulation is utilized and a demodulation step in which overlapping transformation demodulation is utilized. The invention adopts an EFT-OFDM system of lapped transformation modulation, avoids the narrow-band interference from spreading on a subcarrier caused by traditional inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) or discrete Fourier transform (DFT) through frequency schedule by a cognitive radio technology, thus the anti-jamming capability of the system is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Packet loss concealment for overlapped transform codecs
InactiveUS7627467B2Minimizes a model-based energy criterionMinimize artifactPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPacket loss concealmentUnderdetermined system
Real-time packet-based audio communications over packet-based networks frequently results in the loss of one or more packets during any given communication session. The real-time nature of such communications precludes retransmission of lost packets due to the unacceptable delays that would result. Consequently, packet loss concealment methods are employed to “hide” lost packets from the listener. Unfortunately, conventional loss concealment methods, such as packet repetition or stretch / overlap methods, do not fully exploit information available from partially received samples. Therefore, when a single frame of N coefficients is lost, 2N samples are only partially reconstructed, thereby degrading the reconstructed signal. To address this problem, an optimized packet loss concealment solution is identified for particular lost packets by solving an underdetermined system of linear equations representing partially received samples while minimizing a computed error based on a model of the signal obtained from neighboring blocks or frames received by the decoder.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for overlap transforming and deblocking
ActiveUS20060245503A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer scienceLapped transform
Presented herein are inverse quantization and transform system(s) and method(s). In one embodiment, there is presented a method for deblocking. The method comprises reconstructing a macroblock, said macroblock comprising four blocks; and completing deblocking of a first one of the four blocks, with blocks from three neighboring blocks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for progressively transforming and coding digital data
InactiveUS20050281472A1Reduce blockinessReduced ringing artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationCode conversionData compressionDigital data
A system and method facilitating progressively transforming and coding digital pictures is provided. The present invention via employment of a multi-resolution lapped transform provides for progressive rendering as well as mitigation of blocking artifacts and ringing artifacts as compared to many conventional compression systems. The invention includes a color space mapper, a multi-resolution lapped transform, a quantizer, a scanner and an entropy encoder. The multi-resolution lapped transform outputs transform coefficients, for example, first transform coefficients and second transform coefficients. A multi-resolution representation can be obtained utilizing second transform coefficients of the multi-resolution lapped transform. The color space mapper maps an input image to a color space representation of the input image. The color space representation of the input image is then provided to the multi-resolution lapped transform. The quantizer receives the first transform coefficients and / or the second transform coefficients and provides an output of quantized coefficients for use by the scanner and / or the entropy encoder. The scanner scans the quantized coefficients in order to produce a one-dimensional vector for use by the entropy encoder. The entropy encoder encodes the quantized coefficients received from the quantizer and / or the scanner resulting in data compression.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
System and method for progressively transforming and coding digital data
InactiveUS20050276494A1Reduce blockinessReduced ringing artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationCode conversionData compressionDigital data
A system and method facilitating progressively transforming and coding digital pictures is provided. The present invention via employment of a multi-resolution lapped transform provides for progressive rendering as well as mitigation of blocking artifacts and ringing artifacts as compared to many conventional compression systems. The invention includes a color space mapper, a multi-resolution lapped transform, a quantizer, a scanner and an entropy encoder. The multi-resolution lapped transform outputs transform coefficients, for example, first transform coefficients and second transform coefficients. A multi-resolution representation can be obtained utilizing second transform coefficients of the multi-resolution lapped transform. The color space mapper maps an input image to a color space representation of the input image. The color space representation of the input image is then provided to the multi-resolution lapped transform. The quantizer receives the first transform coefficients and / or the second transform coefficients and provides an output of quantized coefficients for use by the scanner and / or the entropy encoder. The scanner scans the quantized coefficients in order to produce a one-dimensional vector for use by the entropy encoder. The entropy encoder encodes the quantized coefficients received from the quantizer and / or the scanner resulting in data compression.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
System and method for progressively transforming and coding digital data
InactiveUS20050276491A1Reduce blockinessReduced ringing artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationCode conversionData compressionDigital data
A system and method facilitating progressively transforming and coding digital pictures is provided. The present invention via employment of a multi-resolution lapped transform provides for progressive rendering as well as mitigation of blocking artifacts and ringing artifacts as compared to many conventional compression systems. The invention includes a color space mapper, a multi-resolution lapped transform, a quantizer, a scanner and an entropy encoder. The multi-resolution lapped transform outputs transform coefficients, for example, first transform coefficients and second transform coefficients. A multi-resolution representation can be obtained utilizing second transform coefficients of the multi-resolution lapped transform. The color space mapper maps an input image to a color space representation of the input image. The color space representation of the input image is then provided to the multi-resolution lapped transform. The quantizer receives the first transform coefficients and / or the second transform coefficients and provides an output of quantized coefficients for use by the scanner and / or the entropy encoder. The scanner scans the quantized coefficients in order to produce a one-dimensional vector for use by the entropy encoder. The entropy encoder encodes the quantized coefficients received from the quantizer and / or the scanner resulting in data compression.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
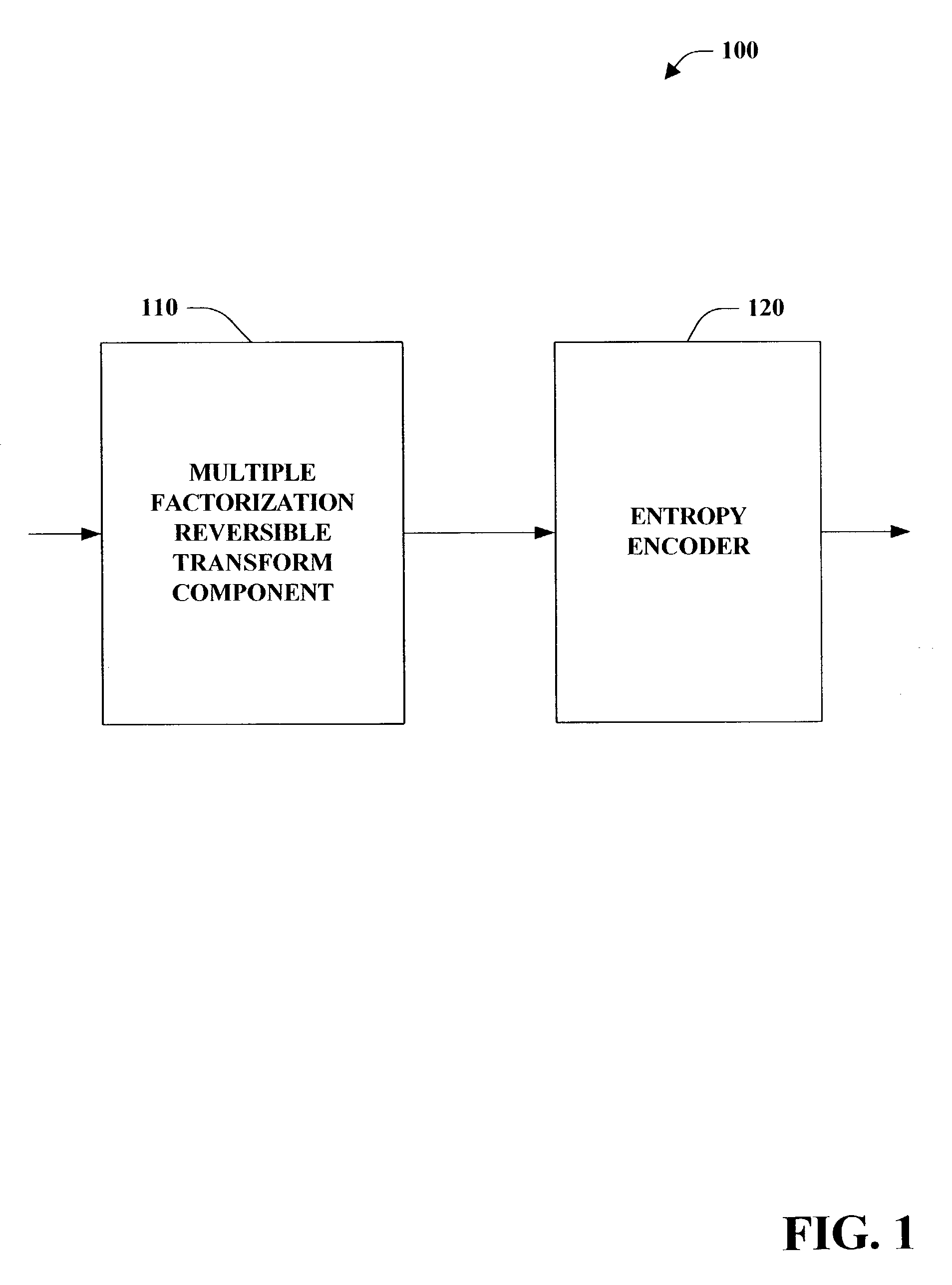
Progressive to lossless embedded audio coder (PLEAC) with multiple factorization reversible transform
InactiveUS7395210B2Facilitates lossless compressionIncrease the compression ratioSpeech analysisCode conversionLapped transformComputer science
A system and method for lossless and / or progressive to lossless data coding (e.g., audio and / or image) is provided. The system and method employ a multiple factorization reversible transform component that provides quantized coefficients based, at least in part, upon a multiple factorization reversible transform. The multiple factorization reversible transform component can employ an N-point modulated lapped transform in accordance with one aspect of the present invention. The multiple factorization reversible transform component can comprise a modulation stage, a pre-FFT rotation stage, a complex FFT stage and a post-FFT rotation stage.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
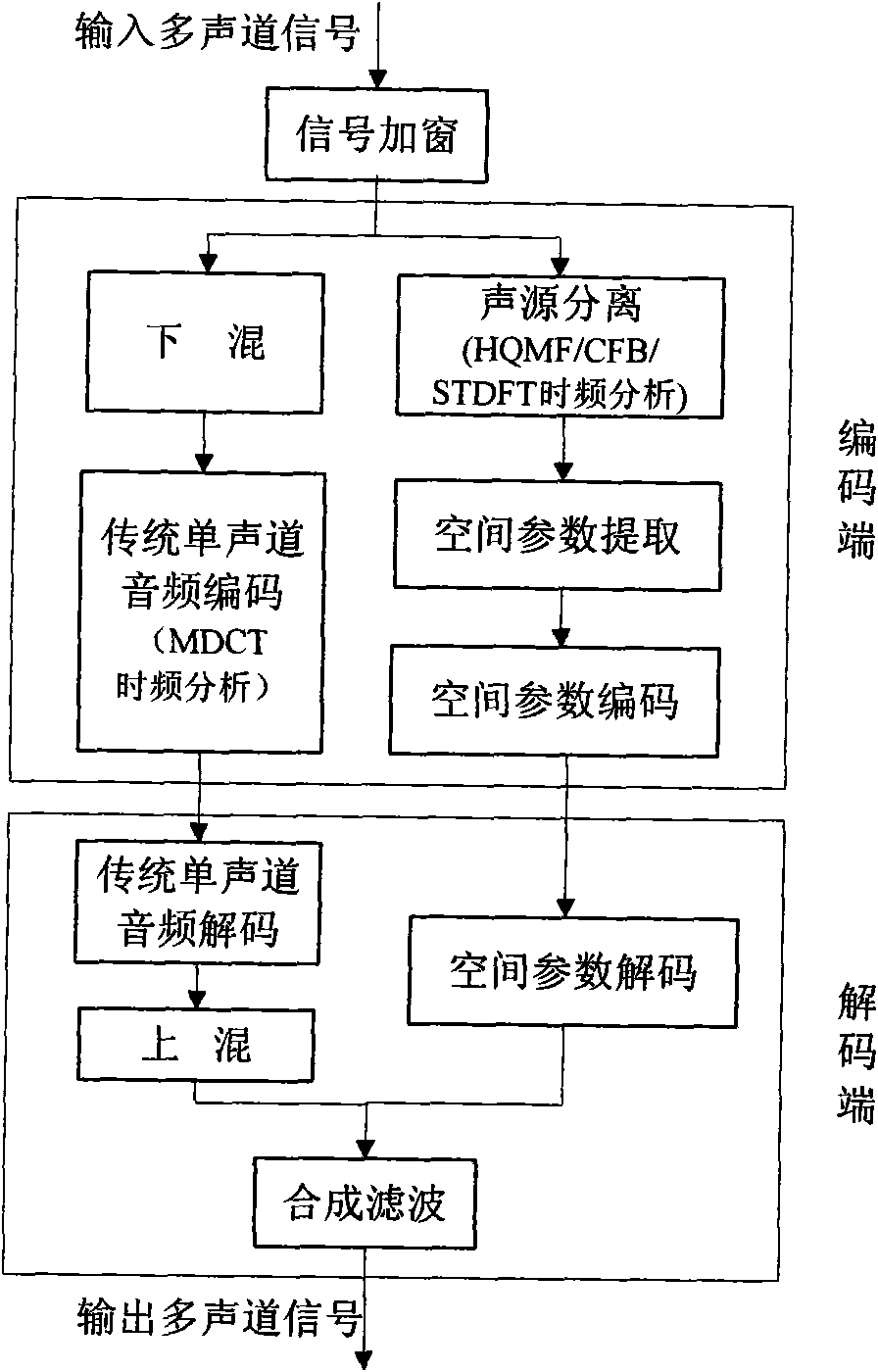
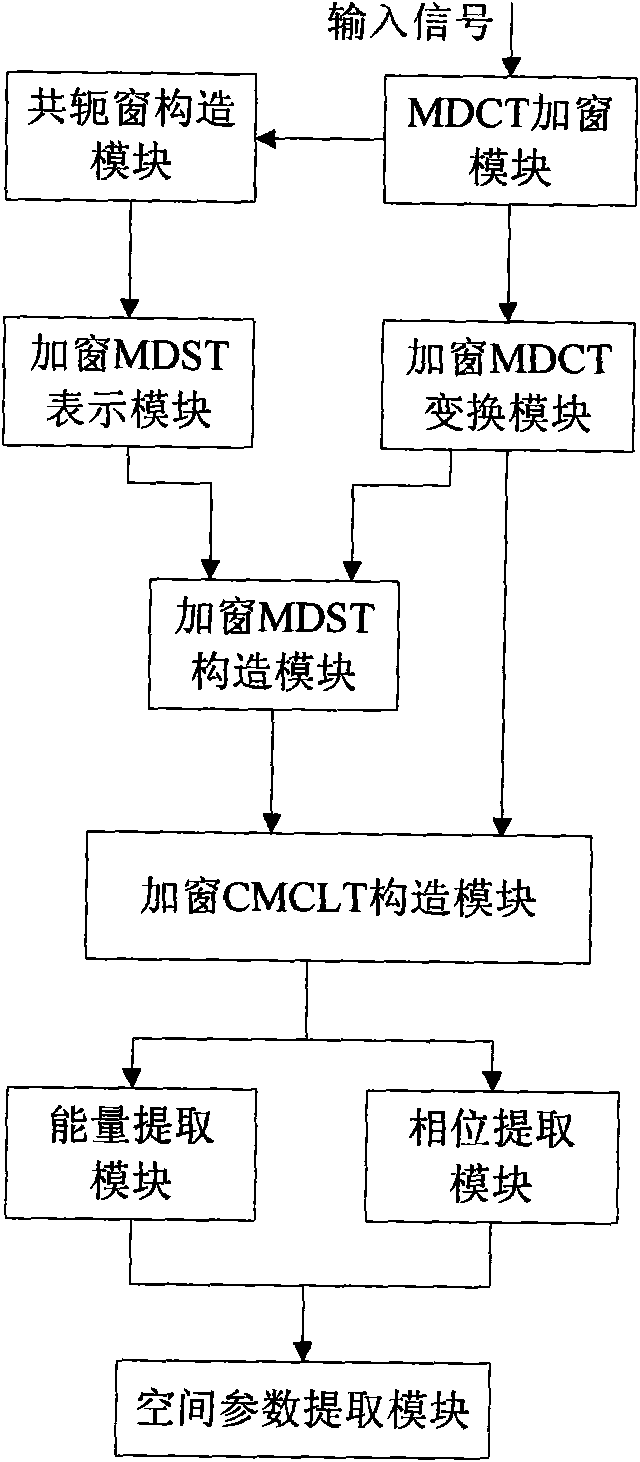
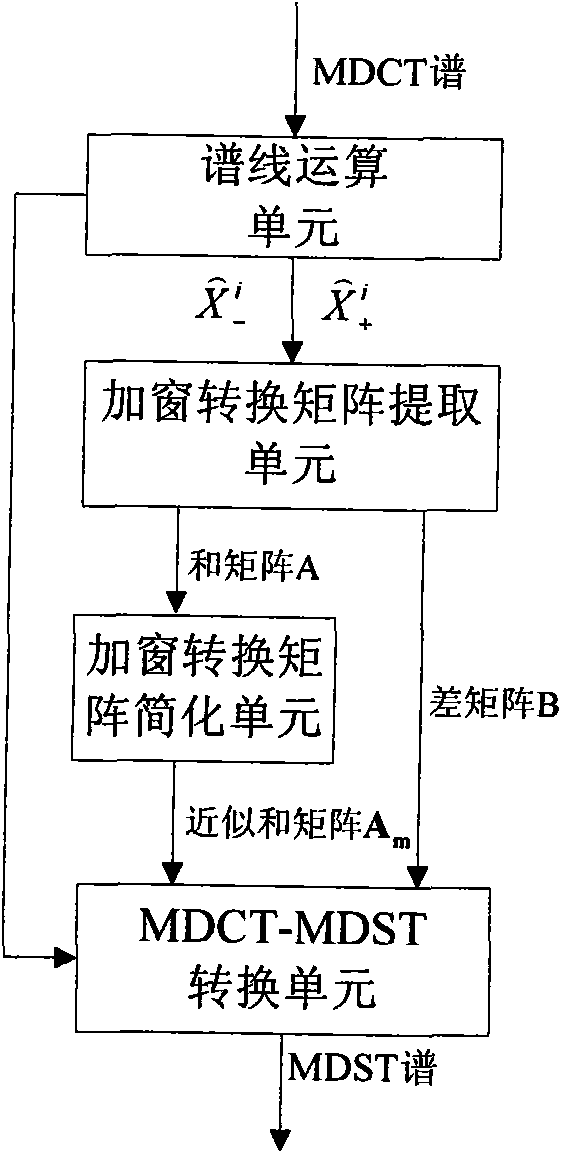
Method for adjusting windowing signal MDCT domain energy and phase and device thereof
InactiveCN101552006AReduce complexityOptimize codec workSpeech analysisSignal onFrequency conversion
The present invention provides a method for adjusting windowing signal MDCT domain energy and phase, and a device thereof. The method includes steps as follows: constructing windowing signal CMCLT spectrum according with the windowing signal MDCT spectrum and the MDST spectrum; extracting the energy information and phase information of the windowing signal on the CMCLT domain, then extracting space parameter on the MDST domain according with the obtained energy information and the phase information. The CMCLT spectrum is a conjugate concoct duplicate superpose conversion spectrum which is a complex number stretched form with the MDCT spectrum and the MDST spectrum as a real part and a imaginary part by using a window function as a conjugate window function, accordingly, defining MDCT. The method and the device can uniform a time frequency analyzing tool in a space audio encoding system, extract the space parameter of multi-acoustic channel signal. Whole encoding end only needs once time frequency conversion after uniforming the time frequency conversion tool which can reduce complicated degree of the space audio- coding and encoding system, accordingly, optimize coding and encoding work.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
System and method for progressively transforming and coding digital data
InactiveUS20050276472A1Reduce blockinessReduced ringing artifactsColor television with pulse code modulationCode conversionData compressionDigital data
A system and method facilitating progressively transforming and coding digital pictures is provided. The present invention via employment of a multi-resolution lapped transform provides for progressive rendering as well as mitigation of blocking artifacts and ringing artifacts as compared to many conventional compression systems. The invention includes a color space mapper, a multi-resolution lapped transform, a quantizer, a scanner and an entropy encoder. The multi-resolution lapped transform outputs transform coefficients, for example, first transform coefficients and second transform coefficients. A multi-resolution representation can be obtained utilizing second transform coefficients of the multi-resolution lapped transform. The color space mapper maps an input image to a color space representation of the input image. The color space representation of the input image is then provided to the multi-resolution lapped transform. The quantizer receives the first transform coefficients and / or the second transform coefficients and provides an output of quantized coefficients for use by the scanner and / or the entropy encoder. The scanner scans the quantized coefficients in order to produce a one-dimensional vector for use by the entropy encoder. The entropy encoder encodes the quantized coefficients received from the quantizer and / or the scanner resulting in data compression.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Audio compression and decompression using integer-reversible modulated lapped transforms
ActiveUS7991622B2Fast decodingFurther compression gainSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumLossless compression
A “STAC Codec” provides lossless audio compression and decompression by processing an audio signal using integer-reversible modulated lapped transforms (MLT) to produce transform coefficients. Transform coefficients are then encoded using a backward-adaptive run-length Golomb-Rice (RLGR) encoder to produce losslessly compressed audio signals. In additional embodiments, further compression gains are achieved via an inter-block spectral estimation and data sorting strategy. Further, compression in the transform domain allows the bitstream to be partially decoded, using the corresponding RLGR decoder, to reconstruct the frequency-domain coefficients. These frequency-domain coefficients are then directly used to speed up various transform-domain based applications such as transcoding media to lossy or other formats, search, identification, visualization, watermarking, etc. In other embodiments, near-lossless compression is achieved by right-shifting transform coefficients by some number of bits such that quantization errors are not perceived as distortion in the decoded audio signal.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for overlap transforming and deblocking
ActiveUS7953161B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer scienceLapped transform
Presented herein are inverse quantization and transform system(s) and method(s). In one embodiment, there is presented a method for deblocking. The method comprises reconstructing a macroblock, said macroblock comprising four blocks; and completing deblocking of a first one of the four blocks, with blocks from three neighboring blocks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
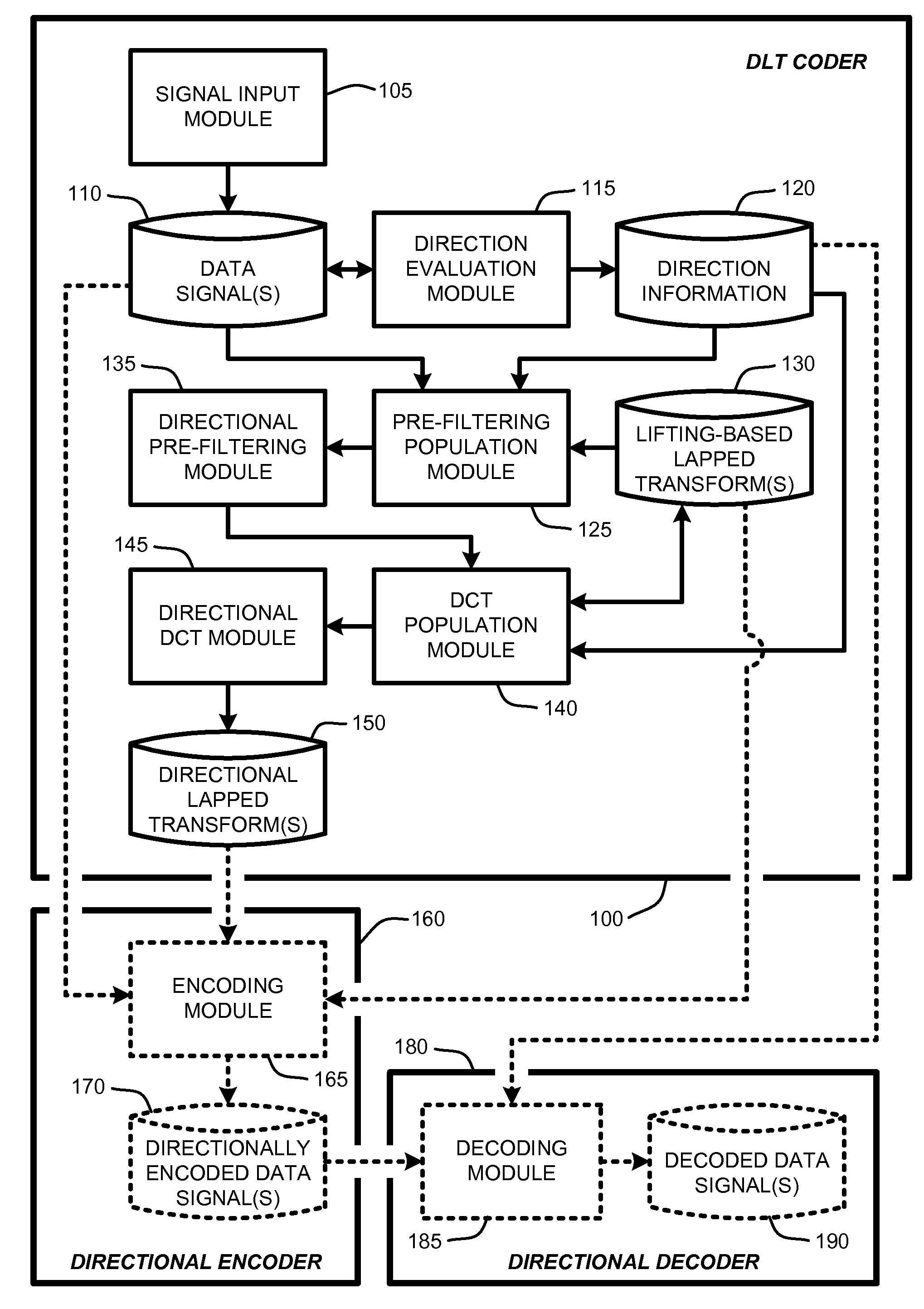
Lifting-based directional lapped transforms
InactiveUS20090238484A1Less blocking artifactImprove coding efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningBase codeData signal
A “directional lapped transform coder” (“DLT Coder”) provides various techniques for designing directional lapped transforms. In general, lapped transforms are factorized into lifting steps. A “directional operator” is then introduced into each lifting step in order to construct the directional lapped transform by selecting data elements from a data signal along a path corresponding to the directional operator. The resulting directional lapped transform preserves the advantages of conventional lapped transforms while also providing more efficient representation directional signals. In various embodiments, the resulting directional lapped transform is used to enable an image / video coding scheme that provides significant improvement over conventional state-of-the-art image lapped transform based coding schemes for images with strong directional correlations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for lapped transform coding and decoding
InactiveCN101199206ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationLocal statisticsSelf adaptive
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for deriving and using non-linearly adapted lapped transforms (NALTs) In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving parameters of a statistical fit between local statistics of original and processed frame data, determining adaptation parameters for application of an inverse lapped transform to frame data, and filtering the frame data in response to filtering adaptation parameters.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
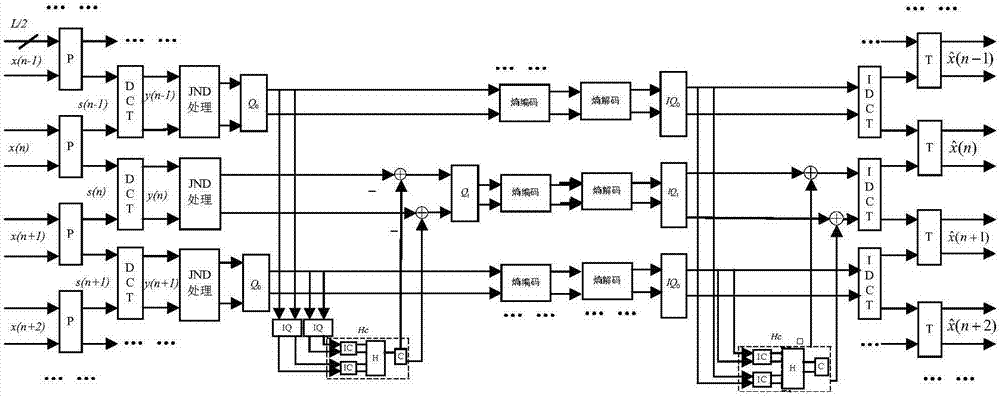
JND-based random offset quantization multiple description coding and decoding method and system
InactiveCN107027028AAvoid packet lossImprove sparsityDigital video signal modificationTime domainTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a JND-based random offset quantization multiple description coding and decoding method and system. The multiple description coding method comprises the following steps of obtaining image information, dividing the image information into two subsets, respectively taking the two subsets as a first subset and a second subset and simultaneously generating a first description and a second description, wherein the two descriptions simultaneously include the first subset and the second subset; for the first description, adopting the first subset to predict the second subset based on a multiple description method, carrying out entropy coding according to predicted values of the first subset and the second subset and outputting a first multiple description code stream; and for the second description, adopting the second subset to predict the first subset based on the multiple description method, carrying out entropy coding according to the predicted values of the first subset and the second subset and outputting a second multiple description code stream, wherein the multiple description method includes the steps of carrying out lapped transform based on a time domain, DCT transform, JND-based threshold filtering and random offset quantization processing on the two subsets in sequence.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com