Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Cricothyroid membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cricothyroid ligament (also known as the cricothyroid membrane or Cricovocal membrane ) is composed of two parts: . the median cricothyroid ligament along the midline (a thickening of the cricothyroid membrane) and; the lateral cricothyroid ligaments on each side (these are also called conus elasticus).; The median cricothyroid ligament is a flat band of white connective tissue that ...
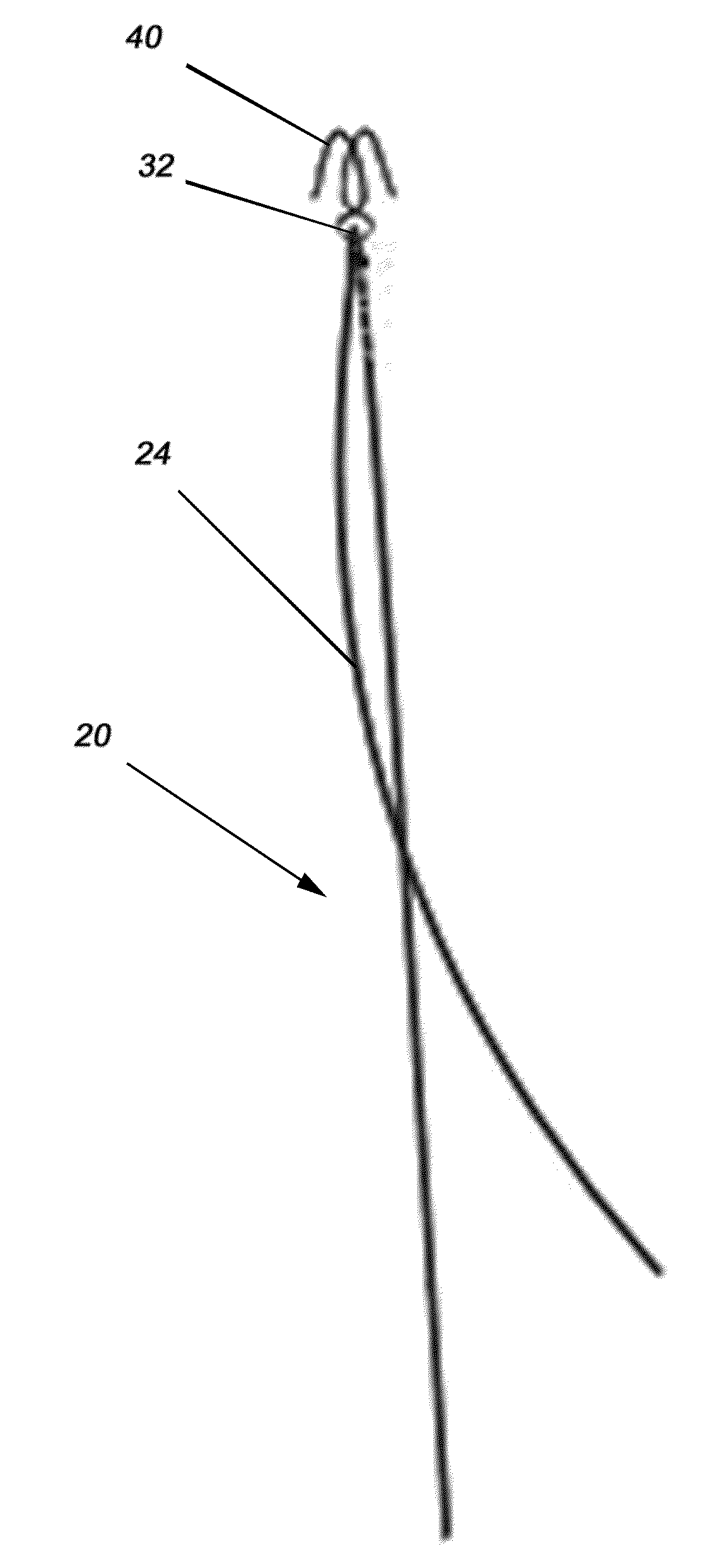
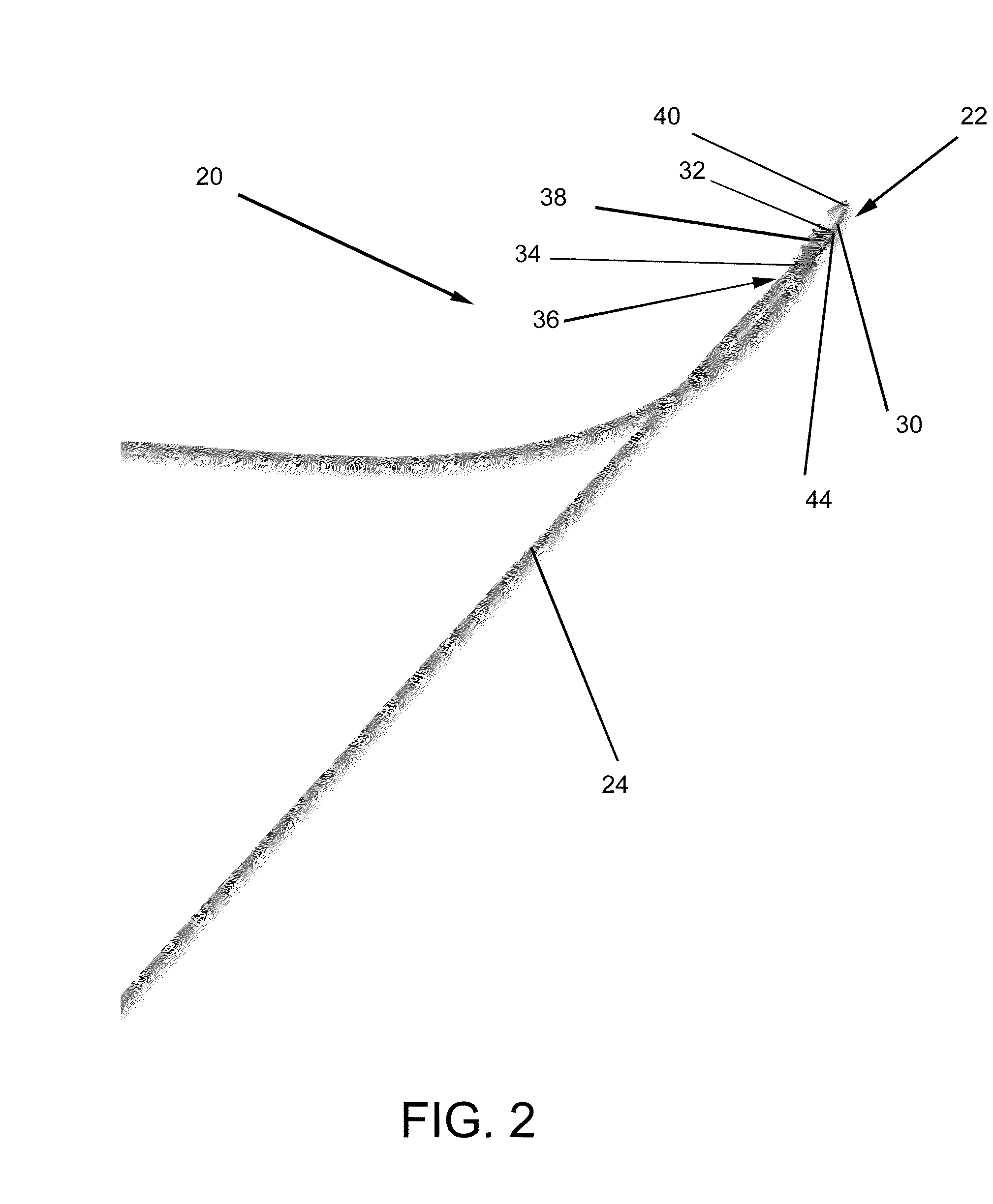
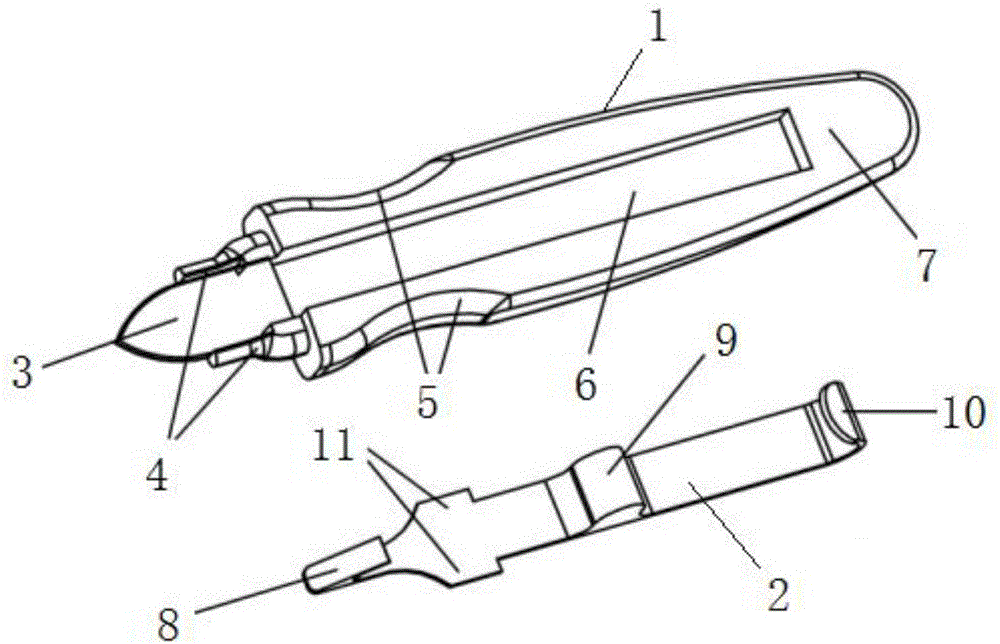
Devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction
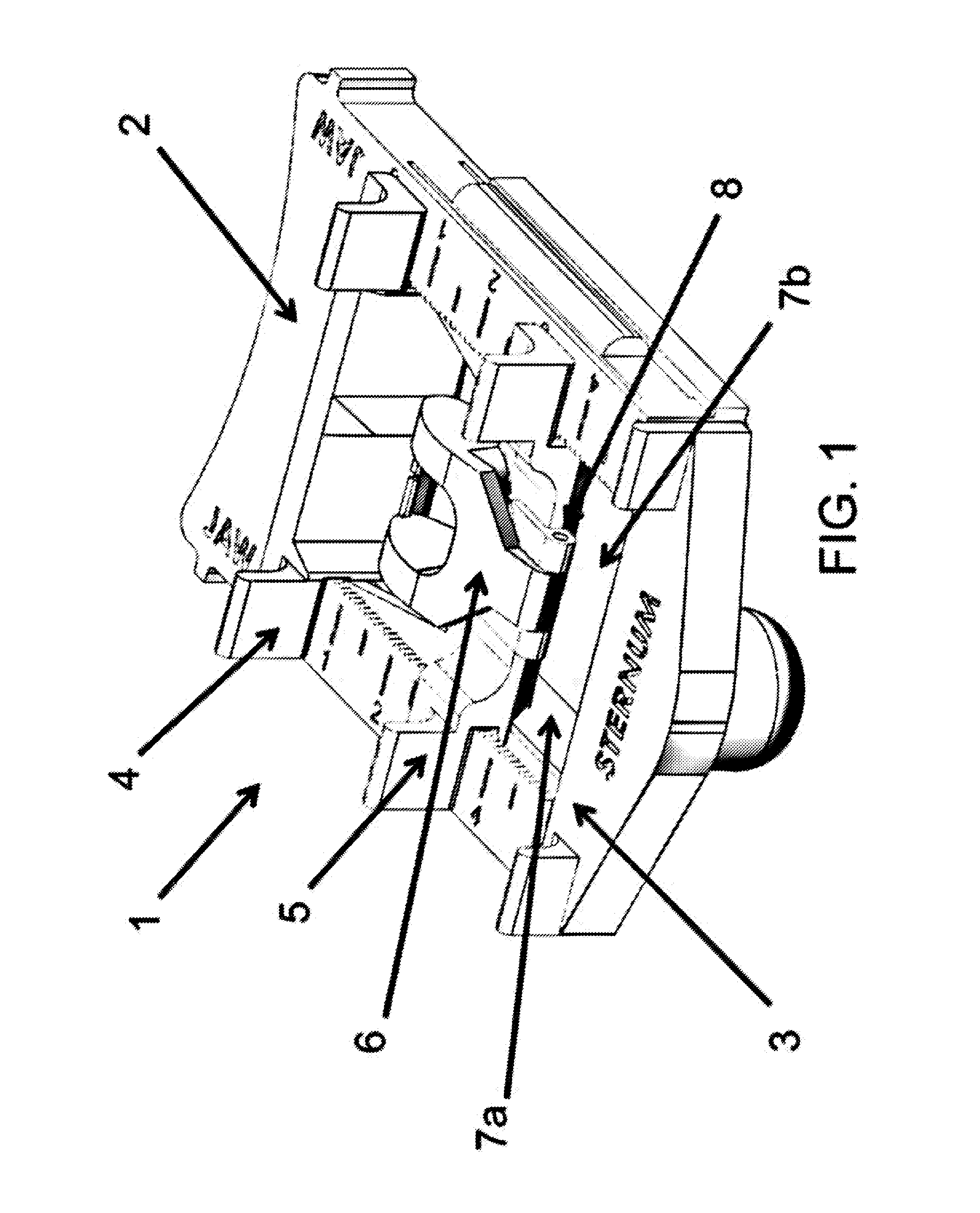
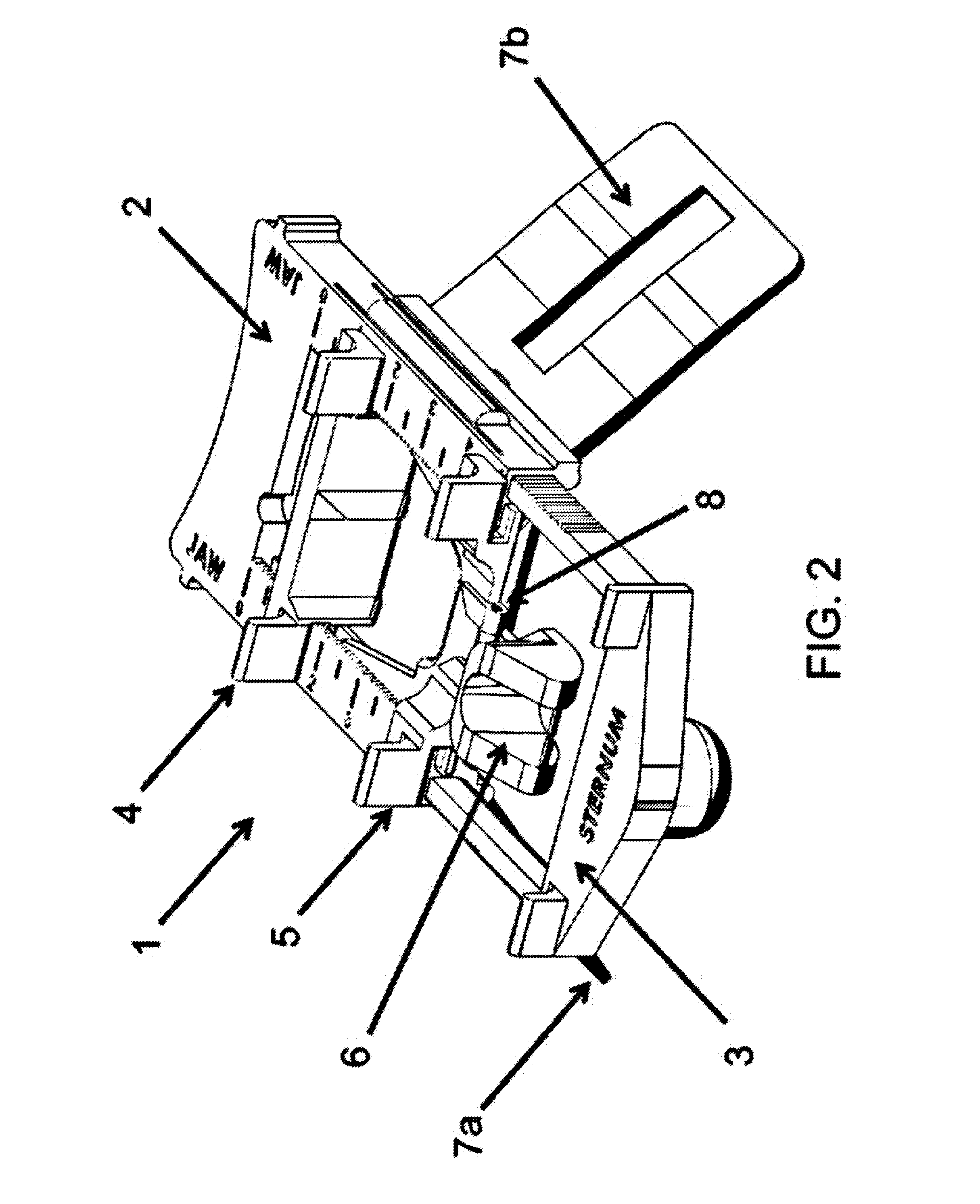
Provided herein are devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction. The device may comprise a wire having a first end and a second end at opposite ends of a longitudinal axis, the wire forming a spiral along the longitudinal axis and having a double hook at the first end, a suture threaded through the spiral of the wire from the second end to the first end, the suture forming a turn at the first end and passing exterior to the spiral to the second end. The method may comprise advancing a suture and hook from the subject's anterior thyroid cartilage or cricothyroid membrane to the muscular process of the subject's arytenoid, attaching the hook to the muscular process, and applying tension to the suture to rotate the muscular process and adduct the arytenoid.
Owner:MCCULLOCH TIMOTHY M +1
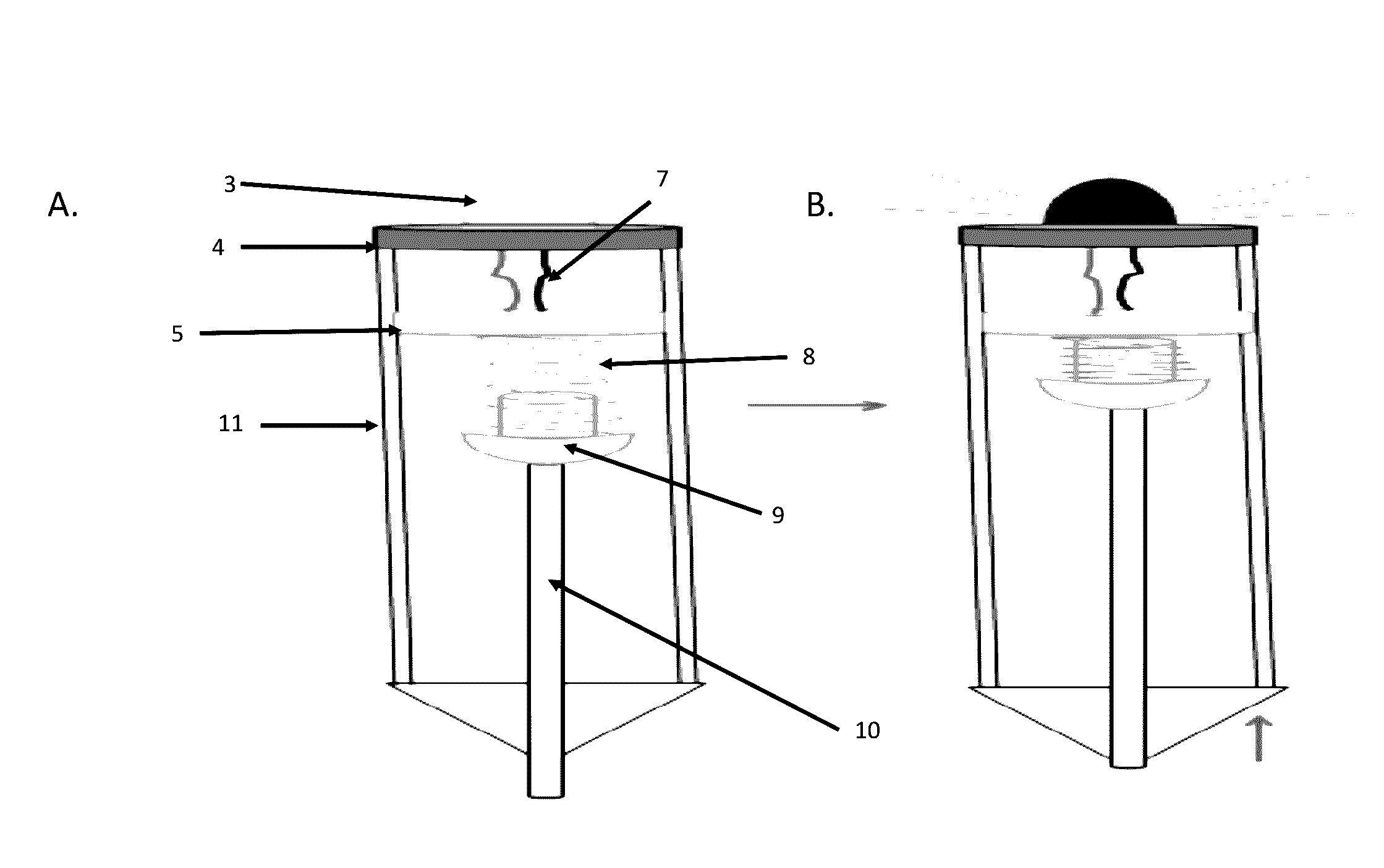
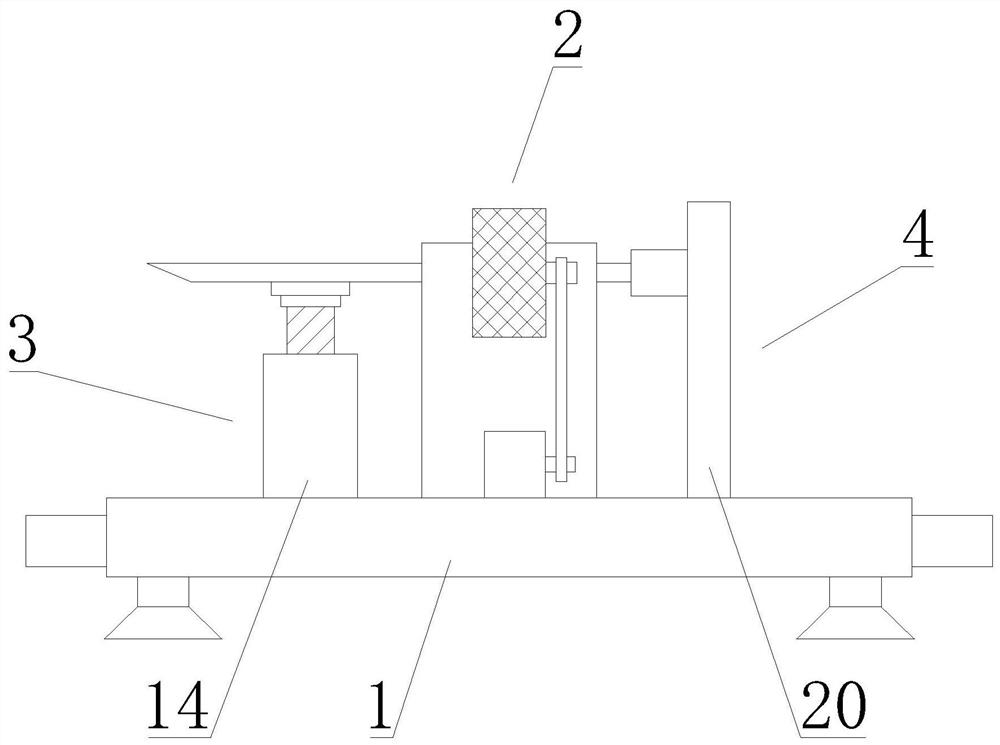
Device for the Mechanical Detection of Underlying Tissues
ActiveUS20160310006A1Fast, accurate, portable, cost-effective and user-friendlyConfidenceDiagnostics using pressurePressure sensorsElectricityMedicine
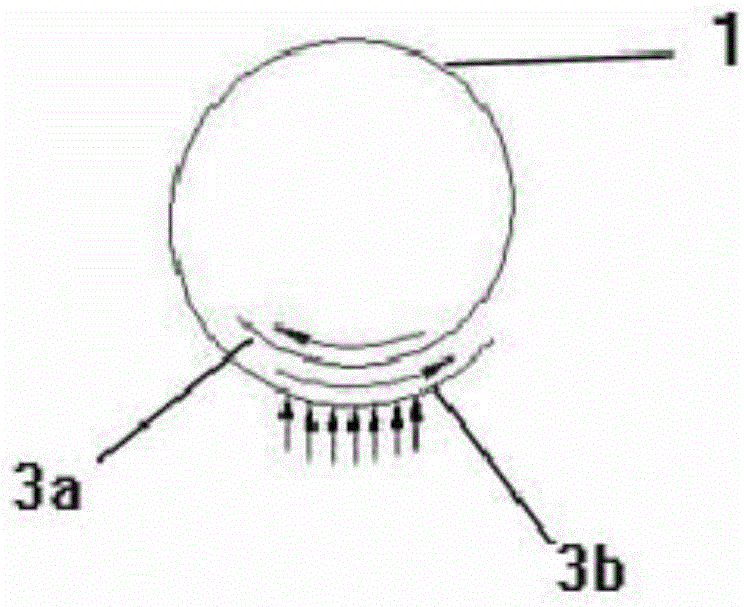
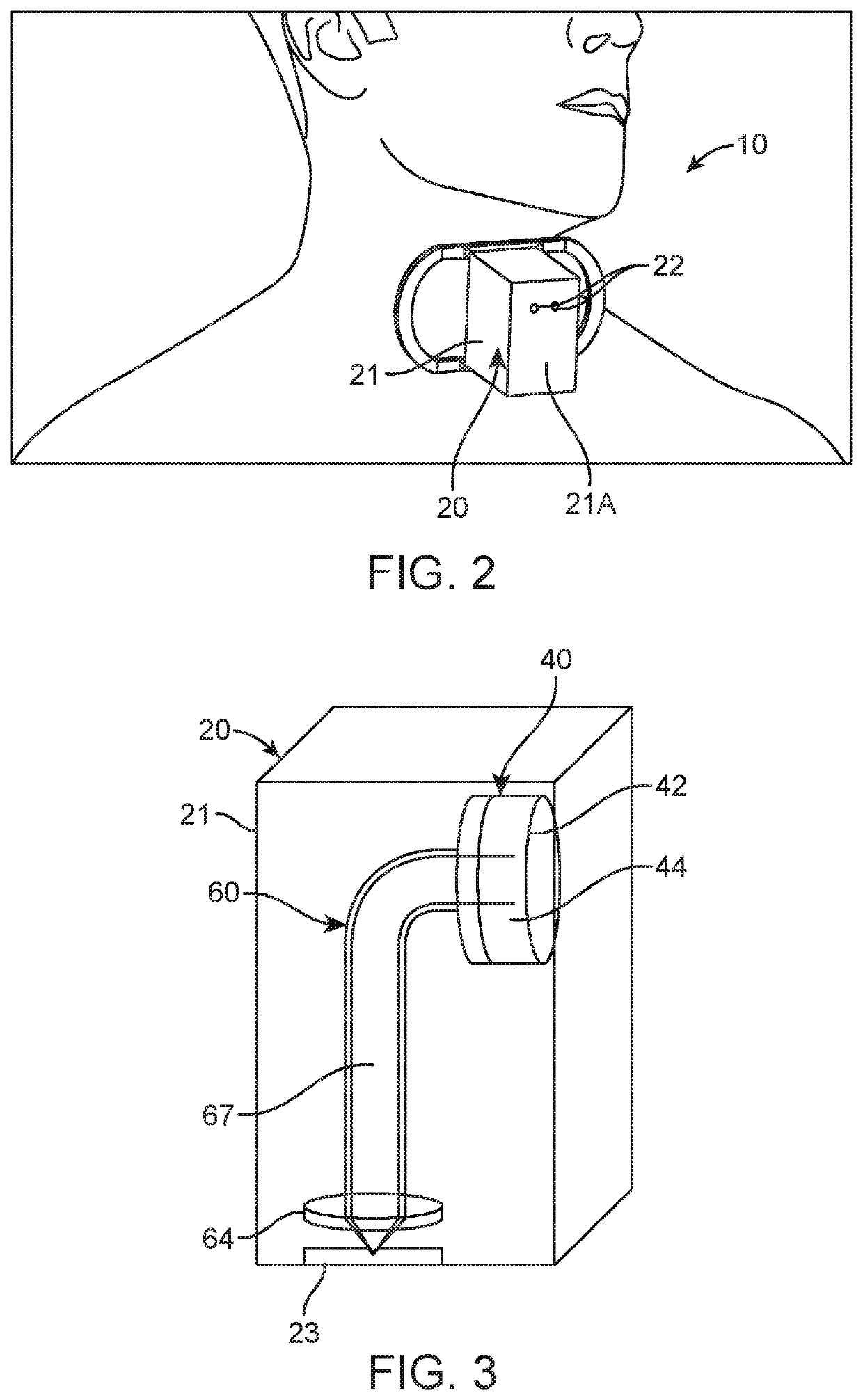
The invention provides a device for the mechanical detection of a specific underlying tissue in a subject, comprising a container, wherein the container comprises a probe, spring, sensor, and signal indicator, wherein when a mechanical force is applied to the probe, it is transmitted to the sensor, whereby the sensor provides the signal indicator with a signal and the signal indicator indicates to the user an indication of detection of the specific underlying tissue in the subject. The sensor of the invention can be an electrical sensor such as a piezoelectric force transducer or a balloon. The invention also provides a method of performing a cricothyrotomy using the device.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Novel emergency first-aid unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN106081137AEasy rescueQuick rescueAircraft componentsFirst-aid kitsCricothyroid membraneEmergency rescue
The invention discloses a novel emergency first-aid unmanned aerial vehicle. The novel emergency first-aid unmanned aerial vehicle comprises an unmanned aerial vehicle body and a modular combined first-aid case. The unmanned aerial vehicle body is composed of a remote control aircraft, a remote control unit, a battery, a voice warning indicator, an LED warming flashing illuminating lamp, a GPS navigator, an aerial photography camera and a walkie talkie. The remote control unit comprises an operation handle, a player and a walkie talkie. The modular combined first-aid case comprises a case body, a prefilled syringe, a marrow cavity injection device, a cardio-pulmonary resuscitation pressing plate and a cricothyroid membrane puncture needle. The novel emergency first-aid unmanned aerial vehicle has the advantages that a method of combining multiple functions and multiple disciplinary fields is applied in emergency medical rescue work, and the maneuverability of the unmanned aerial vehicle body is combined with the multifunctionality of the modular combined first-aid case with combination functions; and rescuers and the modular combined first-aid case containing emergency rescue equipment can be conveyed to a site rapidly, effectively and synchronously, on-site first-aid work can be commanded remotely, and the work of rescuing patients and wounded persons is carried out rapidly.
Owner:锦州医科大学骨外科学研究所 +2
Portable pen type thyrocricoid puncture device
InactiveCN101292893AEasy to carryEasy to useRespiratorsSurgical needlesRespiratorCricothyroid membrane
The present invention discloses a portable pen type cricothyroid membrane puncture outfit which comprises a puncture needle, a puncture needle guard tube, a sealing ring, a handle, a respirator or a resuscitator joint, etc. The puncture needle comprises a needle core, a sleeve and a puncture needle base. The puncture needle is arranged inside a cavity of the puncture needle guard tube. The needle core is fixed at the front end of the handle. The handle is a cavity structure. The sealing ring is arranged at the connected part of the puncture needle guard tube and the handle. The back end of the handle is equipped with the respirator or the resuscitator joint which is spliced with the puncture needle base. The puncture outfit of the present invention has the advantage that the equipments required by cricothyroid membrane puncture are combined together and are designed in the form of a pen, which is convenient for carrying and is easy to use.
Owner:SHANDONG YIHE MEDICAL TECH
Assist device for medical procedures
ActiveUS20160220772A1Avoid damageEasily and safely removableTracheal tubesWound drainsAnatomical landmarkMedicine
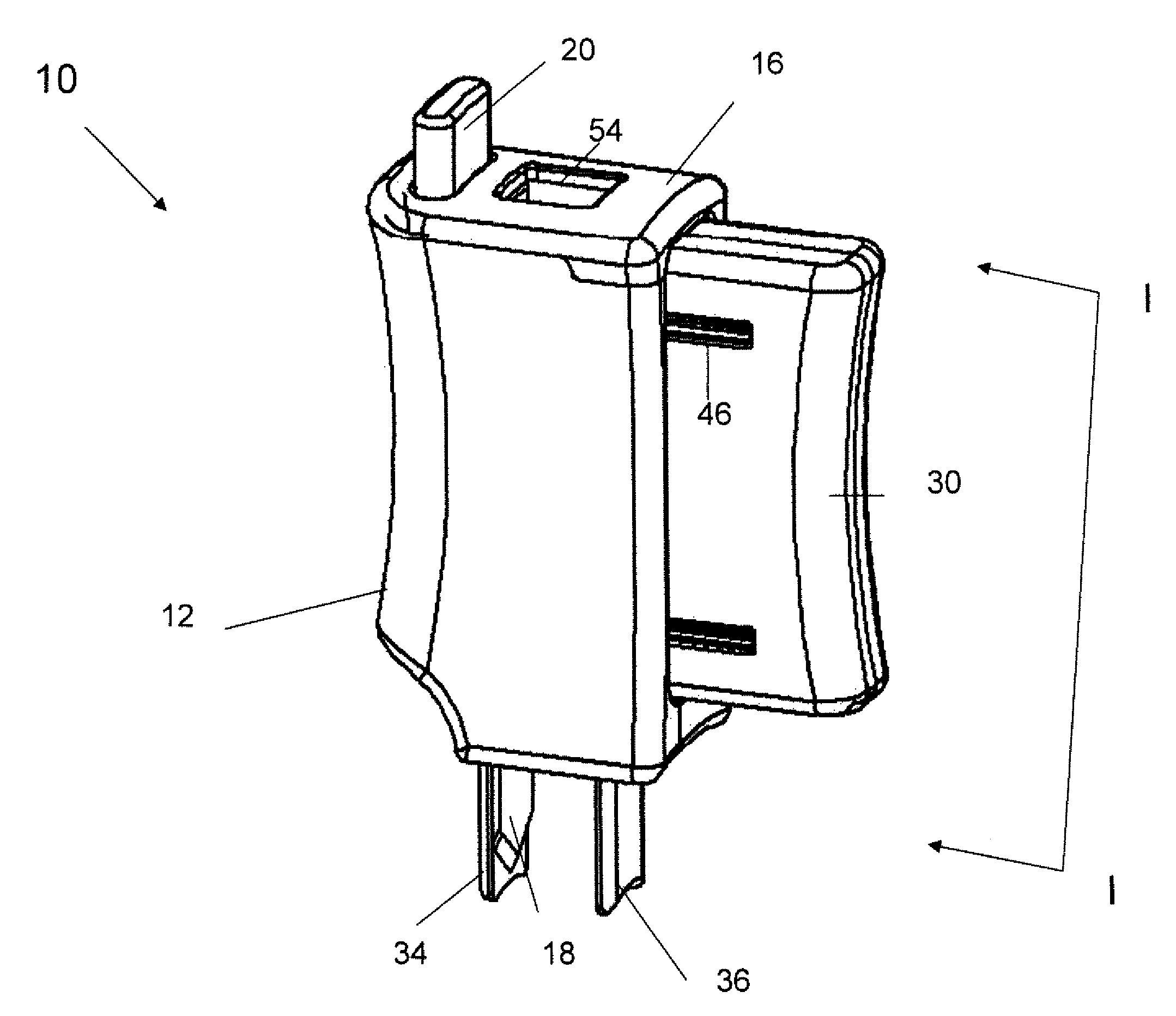
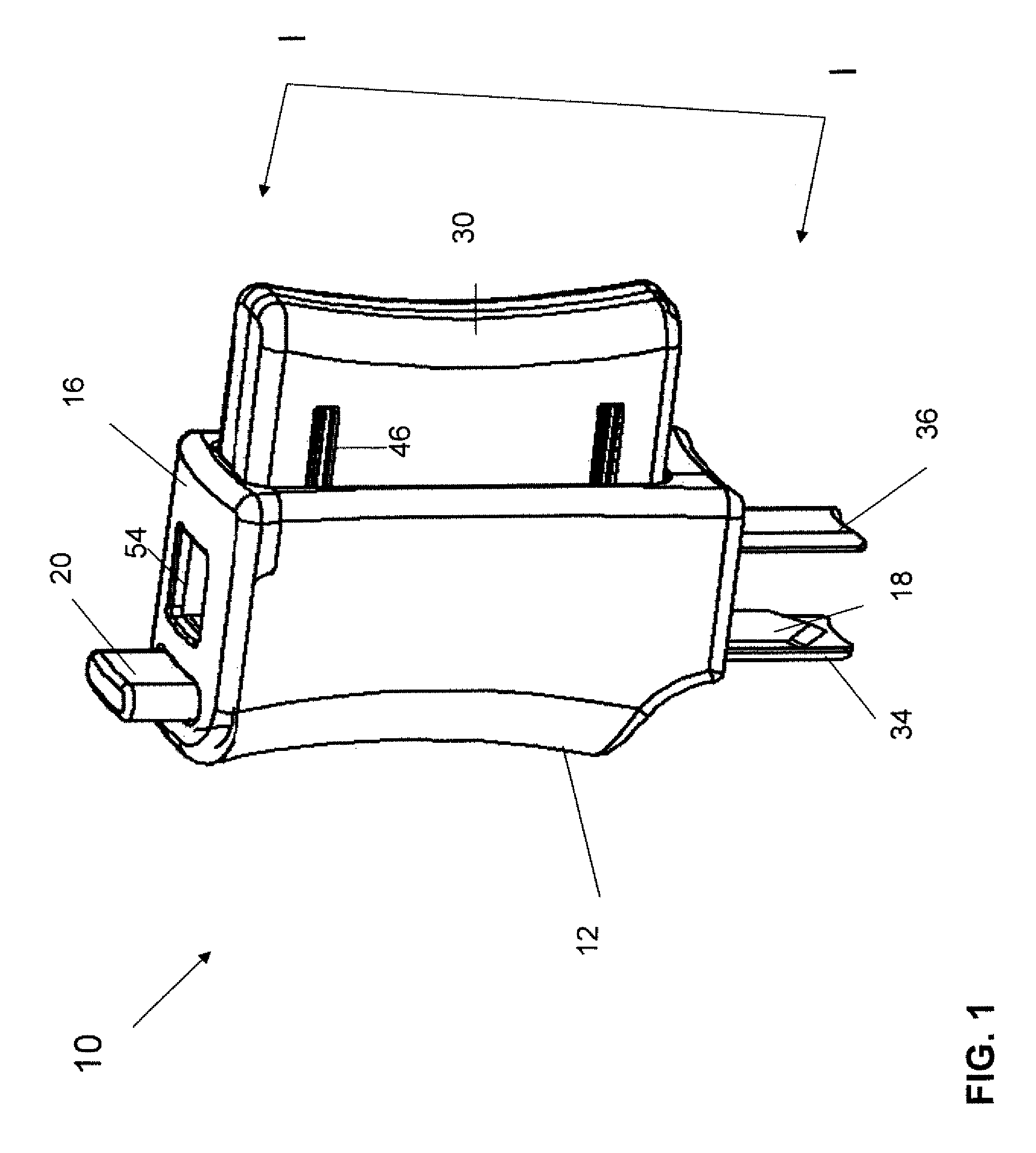
A device to assist performing medical procedures that references anatomical landmarks through adjustable components to identify and stabilize a procedure site and provide guidance in performing the procedure. In one embodiment, an airway creation assist device (ACAD) can be dimensionally adjusted for different patient sizes and properly aligned using anatomical landmarks. The ACAD provides an adjustable template that enables accurate identification of the airway creation site, including but not limited to the cricothyroid membrane. The ACAD uses an insertion guide to guide the obturator and airway tube safely and consistently into the trachea, with a mechanical stop to prevent damaging the posterior trachea wall. The ACAD improves efficacy of the procedure, and makes perforating an incorrect airway creation procedure difficult. In another embodiment, a chest decompression assist device (DAD) Is disclosed for decompression treatment of air and / or fluid in the chest.
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC
Portable pen type thyrocricoid puncture device
InactiveCN101292893BEasy to carryEasy to useRespiratorsSurgical needlesCricothyroid membraneRespirator
The present invention discloses a portable pen type cricothyroid membrane puncture outfit which comprises a puncture needle, a puncture needle guard tube, a sealing ring, a handle, a respirator or a resuscitator joint, etc. The puncture needle comprises a needle core, a sleeve and a puncture needle base. The puncture needle is arranged inside a cavity of the puncture needle guard tube. The needlecore is fixed at the front end of the handle. The handle is a cavity structure. The sealing ring is arranged at the connected part of the puncture needle guard tube and the handle. The back end of the handle is equipped with the respirator or the resuscitator joint which is spliced with the puncture needle base. The puncture outfit of the present invention has the advantage that the equipments required by cricothyroid membrane puncture are combined together and are designed in the form of a pen, which is convenient for carrying and is easy to use.
Owner:SHANDONG YIHE MEDICAL TECH
Bionic tracheal stent mounted in trachea
ActiveCN104434351AReduce fatigue fractureLimit diameter changeStentsCricothyroid membraneSoft materials
The invention discloses a bionic tracheal stent mounted in a trachea. The bionic tracheal stent comprises a stent body. The portion, corresponding to a cricothyroid membrane of the trachea, of the stent body is of a non-closed structure. The bionic tracheal stent has the advantages that the non-closed structure is arranged at the portion, corresponding to the cricothyroid membrane of the trachea of a human body, of the stent body, an arc-shaped structure made of a soft material is produced or two ends of the stent body extend in a staggered mode to enable the tracheal stent to form a helical structure, and the arc-shaped structure or the helical stent bends towards the interior of the stent body to reduce stress effect when the trachea is squeezed to contract, so that diameter change of the tracheal stent is limited, fatigue breakage of the stent due to stress contraction is reduced, and service life of the tracheal stent is prolonged.
Owner:MICRO TECH (NANJING) CO LTD
Percutaneous emergent cricothyroidotomy airway device
InactiveUS8215309B2Avoiding potentially serious complicationReduce chippingRespiratorsIncision instrumentsCricothyroid membraneCricothyrotomy
Owner:UNION COLLEGE
Automatic tracheotomy device
ActiveUS20220088334A1Easy to operateAccurate pressureTracheal tubesAntisepticsTracheotomyCricothyroid membrane
An automatic tracheotomy / cricothyrotomy device is disclosed herein. This device includes a hand-held apparatus having a box shaped center apparatus (box) with a removable attached handlebar (handlebar). The handlebar includes two handles and top and bottom center bars. The handlebar contains four receiver clips. The box contains clip locks that secure the box onto the handlebar. Additionally, the box contains a capacitance measuring system for locating specific portions of the trachea, a peel-off cover that exposes a cleansing pad and adhesive backed flange. The flange has ribbons for securing the tube in a patient's neck. The box also contains pressure and locator sensors with corresponding indicator lights / sounds. The center box also contains a mechanism for penetrating the tracheal cartilage or medial cricothyroid membrane while simultaneously inserting a tube member. The mechanism retracts the puncture obturator back into the box leaving the tube inserted. Securing ribbons are exposed then placed around a patient's neck.
Owner:CROCKETT KATHY
Devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction
Provided herein are devices and methods for anterior arytenoid adduction. The device may comprise a wire having a first end and a second end at opposite ends of a longitudinal axis, the wire forming a spiral along the longitudinal axis and having a double hook at the first end, a suture threaded through the spiral of the wire from the second end to the first end, the suture forming a turn at the first end and passing exterior to the spiral to the second end. The method may comprise advancing a suture and hook from the subject's anterior thyroid cartilage or cricothyroid membrane to the muscular process of the subject's arytenoid, attaching the hook to the muscular process, and applying tension to the suture to rotate the muscular process and adduct the arytenoid.
Owner:MCCULLOCH TIMOTHY M +1
Cricotherotomy apparatus and method
ActiveUS20180008792A1Reduces error in location of incisionTracheal tubesIncision instrumentsCricothyroid membraneEngineering
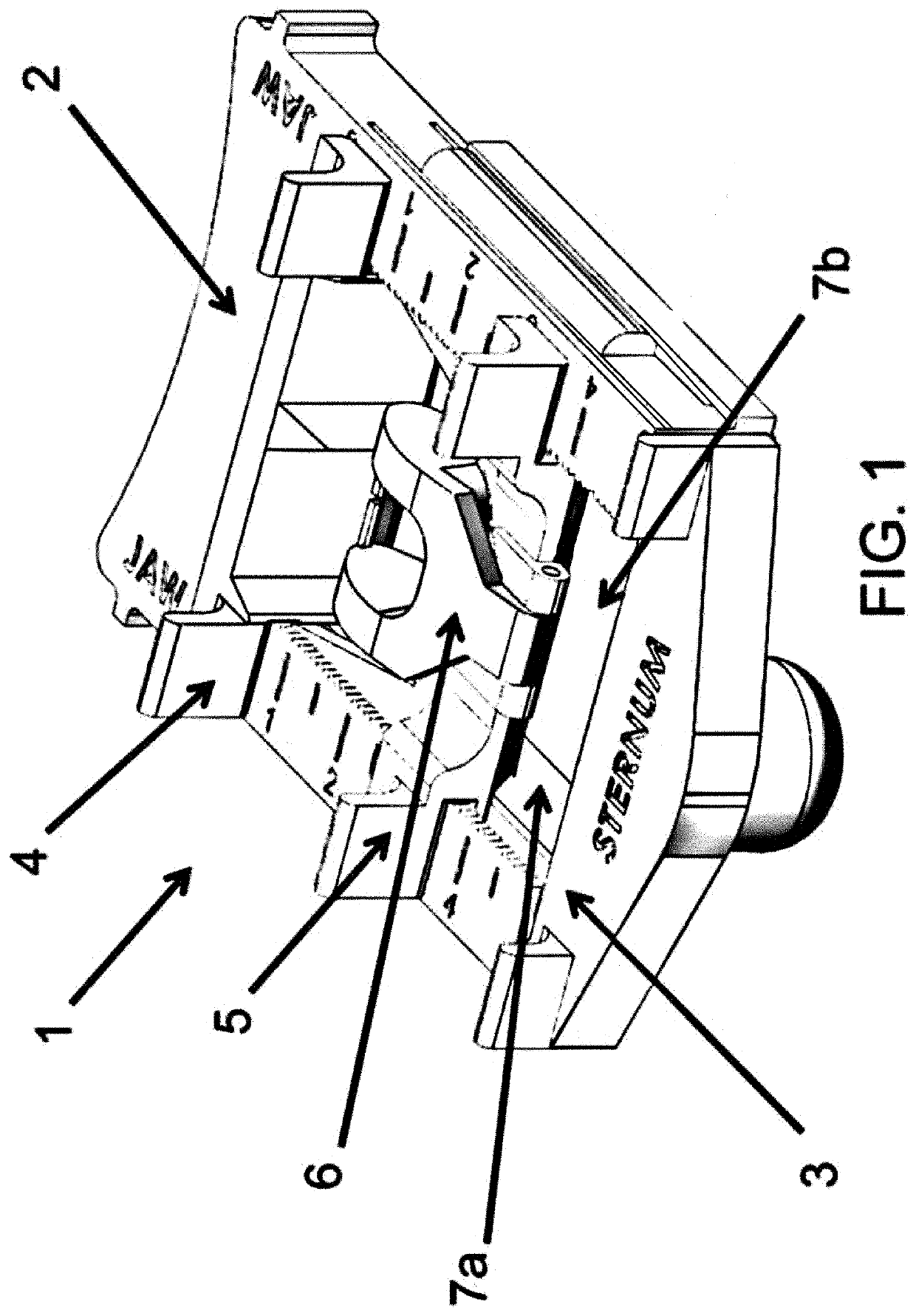
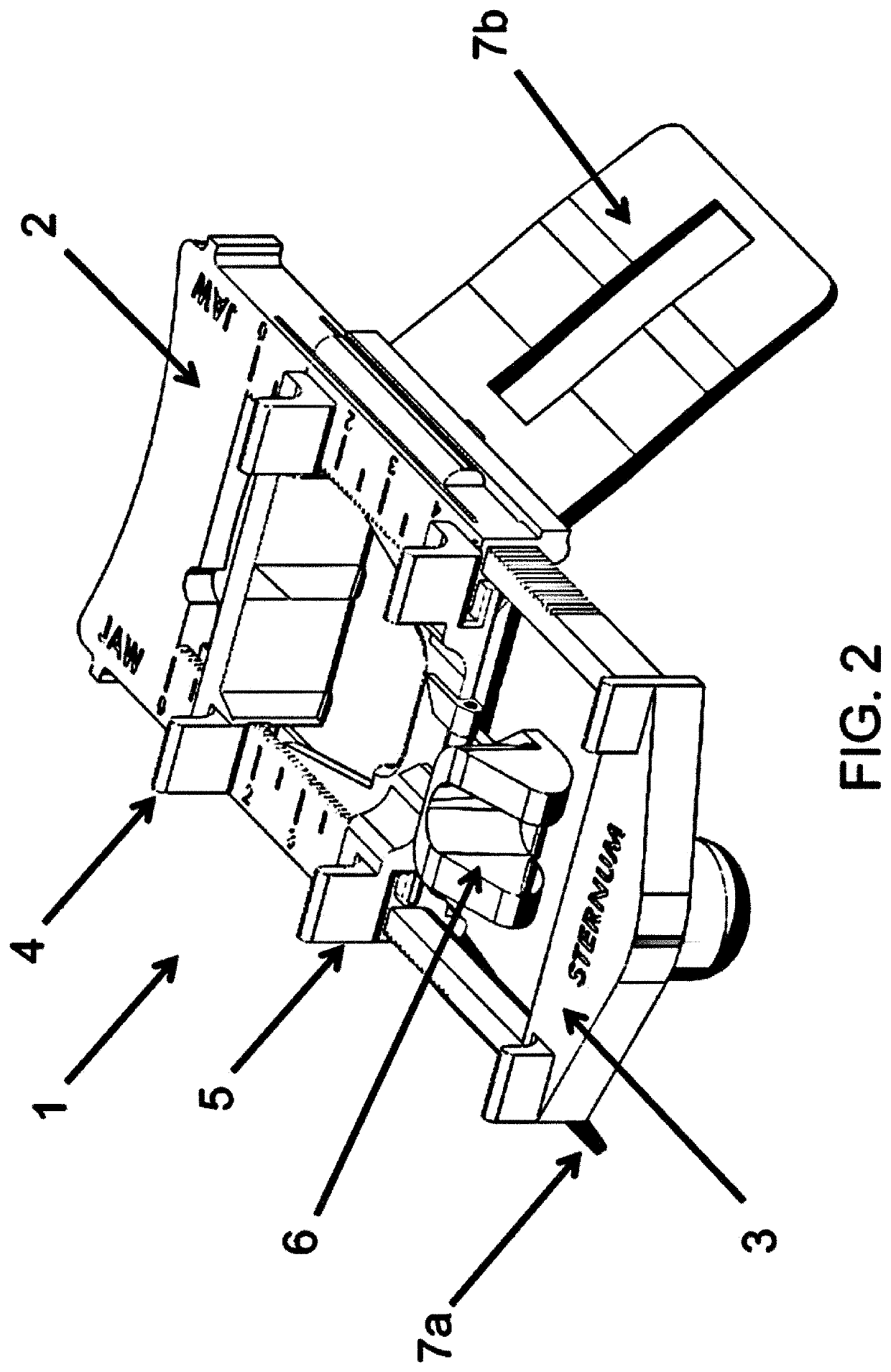
A cricothyrotomy apparatus includes a frame, a protuberance, and a blade member. The frame includes a blade guide. The protuberance extends in a first direction from the frame, and is located at a distance from the blade guide that corresponds to the distance between a sternal notch of an adult human and an anterior cricothyroid membrane of the adult human. The protuberance is sized and configured to be at least partly received by a sternal notch of an adult human. The blade member is slideably disposed in the blade guide.
Owner:WOLF TECHN SERVICES
Puncture cricothyrotomy set
PendingUS20210220593A1Undesired jerky movementThe method is simple and reliableTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheal tubeCricothyroid membrane
A puncture cricothyrotomy set includes a tracheal tube and a puncture cannula arranged therein, which has a rotary actuating device with a handle. By moving the handle about its rotational axis, the puncture cannula can be moved from its puncture position into the tracheal tube far enough that the tip section is arranged completely within the tracheal tube.
Owner:VBM MEDIZINTECHN
Portable cricothyroid membrane puncture needle assembly for thyrocricocentesis
ActiveCN113081189ACompact structureEasy to carryCannulasSurgical needlesPuncture procedureParacentesis
The invention provides a portable cricothyroid membrane puncture needle assembly for thyrocricocentesis. The portable cricothyroid membrane puncture needle assembly comprises a hollow puncture needle tube and a translation driving mechanism, wherein the head end of the puncture needle tube is provided with a puncture needle head; the head end of a puncture catheter of the puncture needle assembly is also provided with a structure which is used for wrapping the puncture needle head and is used for buffering and preventing the puncture needle head from further puncturing a trachea after the puncture needle head punctures a cricothyroid membrane; the translation driving mechanism comprises a rotating handle and is used for driving the structure and the puncture needle head to generate relative displacement so as to enable the puncture needle head to retract into the structure; and the tail end of the puncture needle tube is provided with a standard interface. The portable cricothyroid membrane puncture needle assembly is small in size, convenient to carry, remarkable in effect, more reliable in puncture operation, not prone to injuring a patient after puncture, convenient to carry in a standby state, easy to operate in a using state, capable of being operated by non-medical staff and more portable for medical staff, and the rescue success rate of a patient with ventilation disorder caused by airway obstruction is greatly increased.
Owner:万新知识产权服务(安徽)有限公司
Novel rapid cricothyroid membrane incision distractor
PendingCN113040866AAvoid harmEasy to adjust the angleIncision instrumentsCricothyroid membraneThreaded pipe
The invention discloses a novel rapid cricothyroid membrane incision distractor, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, the novel rapid cricothyroid membrane incision distractor comprises supporting arms, connectors and a handle, one end of the handle is provided with a supporting head, the supporting head is composed of two supporting arms, and the two supporting arms are in damped rotational connection with the handle through the connectors. According to the distractor, a sliding block on one supporting arm is pushed, the sliding block drives a gear to rotate through a rack when sliding, a threaded rod can be driven to rotate when the gear rotates, a cutting knife can be driven to move towards the lower end of the supporting arm through a threaded pipe when the threaded rod rotates, when the cutting knife extends out of the supporting arms, the cutting knife can be used for cutting the cricothyroid membrane of a patient, so that the cricothyroid membrane of the patient is rapidly opened, after the cricothyroid membrane is opened, the cutting knife is retracted into the supporting arms, then the two supporting arms are inserted into an incision, then the two supporting arms are opened through the handle, and the patient can be subjected to intubation treatment.
Owner:福建省南平市第一医院
Novel cricothyroid membrane puncture needle
InactiveCN101357072ANot easy to damageEasy to makeSurgical needlesTrocarCricothyroid membranePush pull
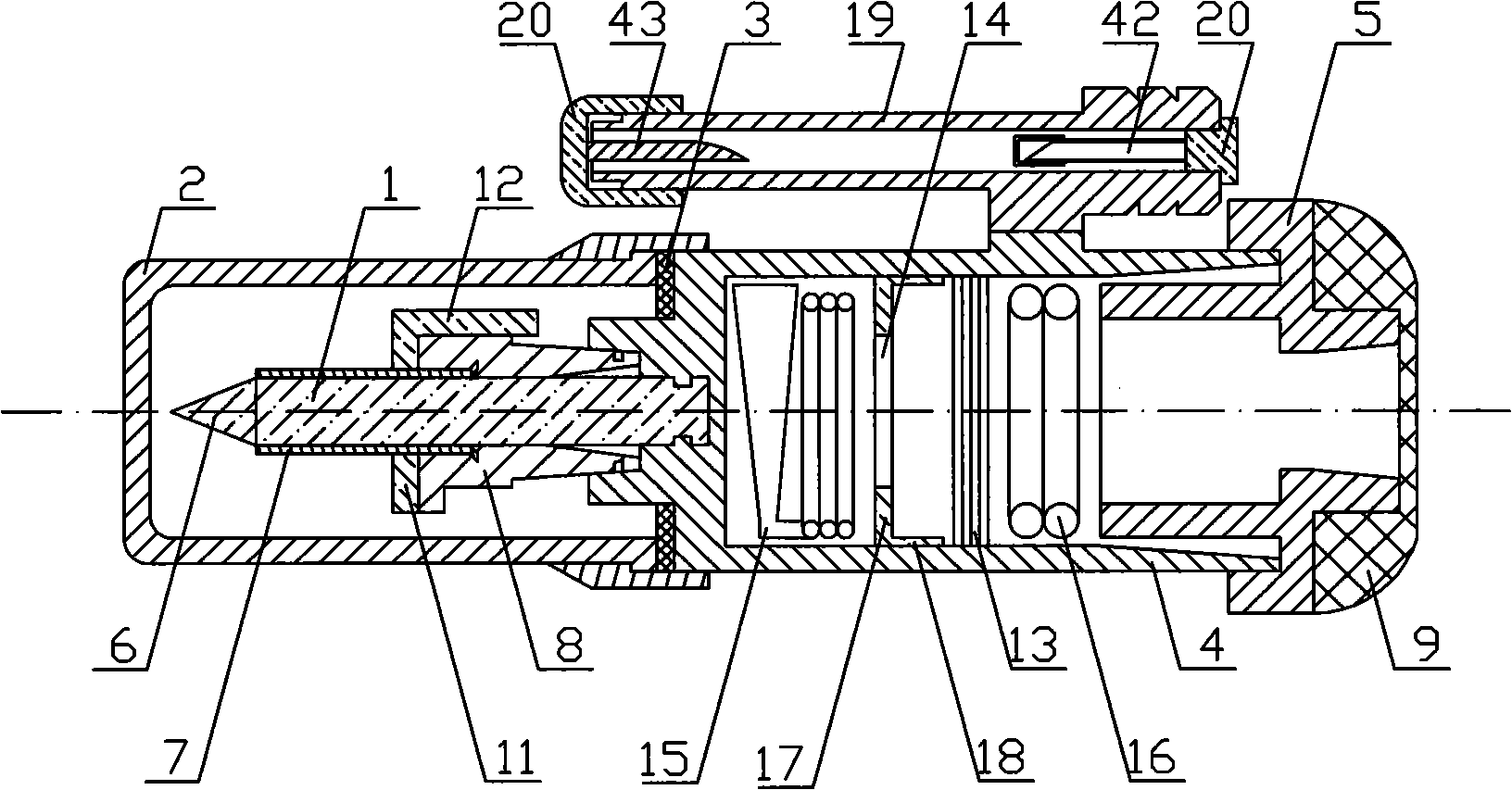
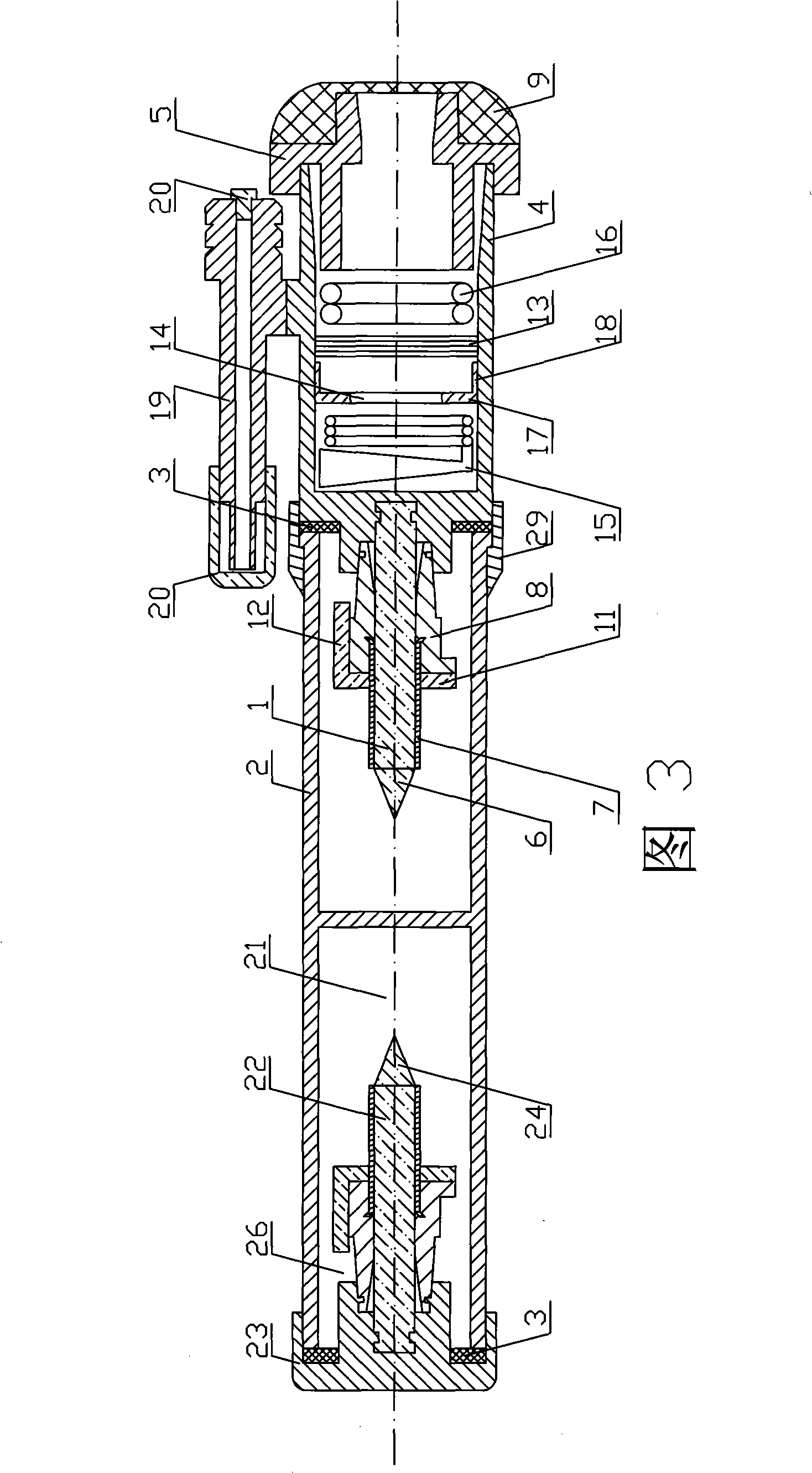
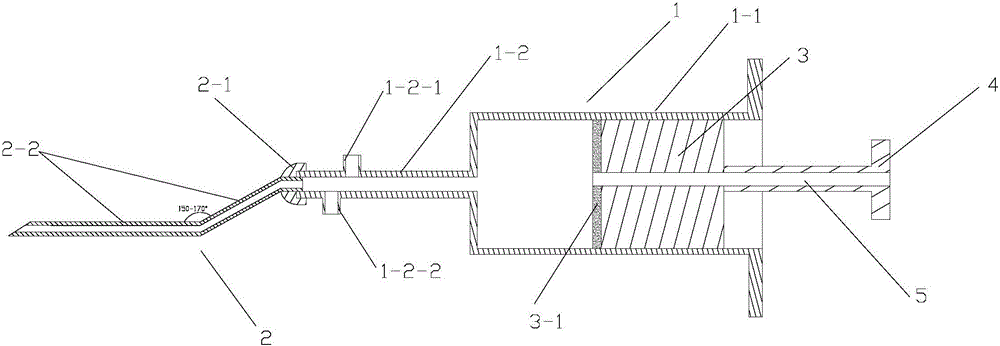
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instrument, and relates to a novel cricothyroid membrane puncture needle used for laryngeal of otorhinolaryngology. The cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is characterized in that the cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is provided with a circular pipe (1); a steel wire (2) passes through in the circular pipe (2); one end of the steel wire (2) is provided with a conical needle (3) and the other end of the steel wire (2) is provided with a handle (4); the conical needle (3) can slide inside the circular pipe (1) with the push-pull of the steel wire (2); the circular pipe (1) uses a 1 / 4 arc pipe; the pipe mouth of the circular pipe (1) is provided with a pipe handle (5); the conical needle (3) uses a triangular pyramid needle; the handle (4) can be a spherical shape or a ring shape; the novel cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is made of stainless steel and has the advantages of simple preparation, low cost, simple and convenient operation, exact piercing, being not easy to damage other normal tissues, good ventilation, being not easy to block the pipe, etc.
Owner:刘继荣
Trachea puncture cannula for cervical surgery
ActiveCN107261284AGuaranteed tightnessRelieve painTracheal tubesMedical devicesCricothyroid membraneEngineering
The invention discloses a trachea puncture cannula for cervical surgery. The trachea puncture cannula for cervical surgery comprises a plastic outer tube, an air bag, an inflation port, an air source interface, an airflow detection device, a conduit, a conduit inlet device, a puncture needle and the like, wherein the conduit inlet device is an automatic rebounding and sealing device, and the conduit inlet device is automatically sealed to prevent air leakage after the puncture needle is pulled out. The trachea puncture cannula provides oxygen for patients when applied to neck surgery on vocal cords, and is inserted into the trachea through the cricothyroid membrane of the neck, the problem that in actual surgery, a trachea cannula blocks surgical spots like the laryngopharynx to increase surgical difficulty is solved, injuries of the trachea cannula to nasopharyngeal tissue of a patient are reduced, the patient can suffer from less pain, surgical difficulty is reduced for doctors, the surgical process is accelerated, and the effect is good in laryngeal surgery and cervical surgery. The air source interface is provided with a plurality of structures to realize air source access under different conditions, such as an anaesthesia machine, a breathing machine, a center air source and an air bottle type standby air source.
Owner:烟台芝罘医院
A multifunctional rescue belt
PendingCN109157260AAchieve hemostasisRelieve painIntravenous devicesTourniquetsCricothyroid membraneTourniquet time
The invention discloses a multifunctional rescue belt which can realize hemostasis by adopting a plurality of hemostasis modes. The multifunctional ambulance belt comprises a belt body and a twistingrod which can be wound around the belt body. One end of the waist belt body is provided with a buckle device, which can be used as a cassette tourniquet; At that same time, the waist belt body is provide with a spinning device, so that the waist belt body can be use as a spinning tourniquet. The twisted rod is a detachable container, and has two safety syringes, wherein one dose of morphine injection, one dose of epinephrine injection and an insertion type cricothyroid membrane puncture needle are respectively infused into the twisted rod. The multifunctional ambulance belt can be used for various purposes and can be convenient for the user to realize self-rescue when bleeding from injury.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Cricothyroid membrane incision device
InactiveCN106562810AReduce hypoxia and even deathQuickly use the operationTracheal tubesSurgeryCricothyroid membraneMedicine
The invention discloses a cricothyroid membrane incision device. An incision device and a pull hook device form a whole; the incision of the skin, aponeurosis and cricothyroid membranes can be fast and effectively performed in the operation in one step; the pull hook device is directly put into a cut through pushing a push button and is sufficiently exposed for providing the adverse conditions for trachea cannula in a next step; the use and the operation are convenient and fast; the patient anoxia or even death due to trachea cannula delay caused by reasons of unclear cut exposure, scalpel and pull hook switching and the like is obviously reduced; and the success ratio of the cricothyroid membrane incision and trachea cannula operation is obviously improved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Cricothyroid membrane puncture needle processing device
The invention provides a cricothyroid membrane puncture needle processing device. The device comprises a base, a rotating assembly, a first limiting assembly and a second limiting assembly, wherein the rotating assembly, the first limiting assembly and the second limiting assembly are all arranged on the base; and the first limiting assembly and the second limiting assembly are correspondingly located on the front and rear sides of the rotating assembly. According to the device, the rotating assembly, the first limiting assembly and the second limiting assembly are matched with each other to fix the front ends, the middle ends and the rear ends of puncture needles, so that synchronous fixation of a large number of puncture needles is achieved, the fixed position is convenient to adjust, the fixing modes are diversified, and the fixing effect is good; and in addition, a gear is matched with a transmission chain, synchronous rotation of a large number of puncture needles is achieved, andthe processing efficiency is improved.
Owner:THE PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION
Automatic tracheotomy device
ActiveUS11406779B2Easy to operateAccurate pressureTracheal tubesAntisepticsTracheotomyCricothyroid membrane
An automatic tracheotomy / cricothyrotomy device is disclosed herein. This device includes a hand-held apparatus having a box shaped center apparatus (box) with a removable attached handlebar (handlebar). The handlebar includes two handles and top and bottom center bars. The handlebar contains four receiver clips. The box contains clip locks that secure the box onto the handlebar. Additionally, the box contains a capacitance measuring system for locating specific portions of the trachea, a peel-off cover that exposes a cleansing pad and adhesive backed flange. The flange has ribbons for securing the tube in a patient's neck. The box also contains pressure and locator sensors with corresponding indicator lights / sounds. The center box also contains a mechanism for penetrating the tracheal cartilage or medial cricothyroid membrane while simultaneously inserting a tube member. The mechanism retracts the puncture obturator back into the box leaving the tube inserted. Securing ribbons are exposed then placed around a patient's neck.
Owner:CROCKETT KATHY
Assist device for medical procedures
ActiveUS10758695B2Avoid mistakesEffective and broadly applicableTracheal tubesWound drainsAnatomical landmarkCricothyroid membrane
A device to assist performing medical procedures that references anatomical landmarks through adjustable components to identify and stabilize a procedure site and provide guidance in performing the procedure. In one embodiment, an airway creation assist device (ACAD) can be dimensionally adjusted for different patient sizes and properly aligned using anatomical landmarks. The ACAD provides an adjustable template that enables accurate identification of the airway creation site, including but not limited to the cricothyroid membrane. The ACAD uses an insertion guide to guide the obturator and airway tube safely and consistently into the trachea, with a mechanical stop to prevent damaging the posterior trachea wall. The ACAD improves efficacy of the procedure, and makes perforating an incorrect airway creation procedure difficult. In another embodiment, a chest decompression assist device (DAD) Is disclosed for decompression treatment of air and / or fluid in the chest.
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC
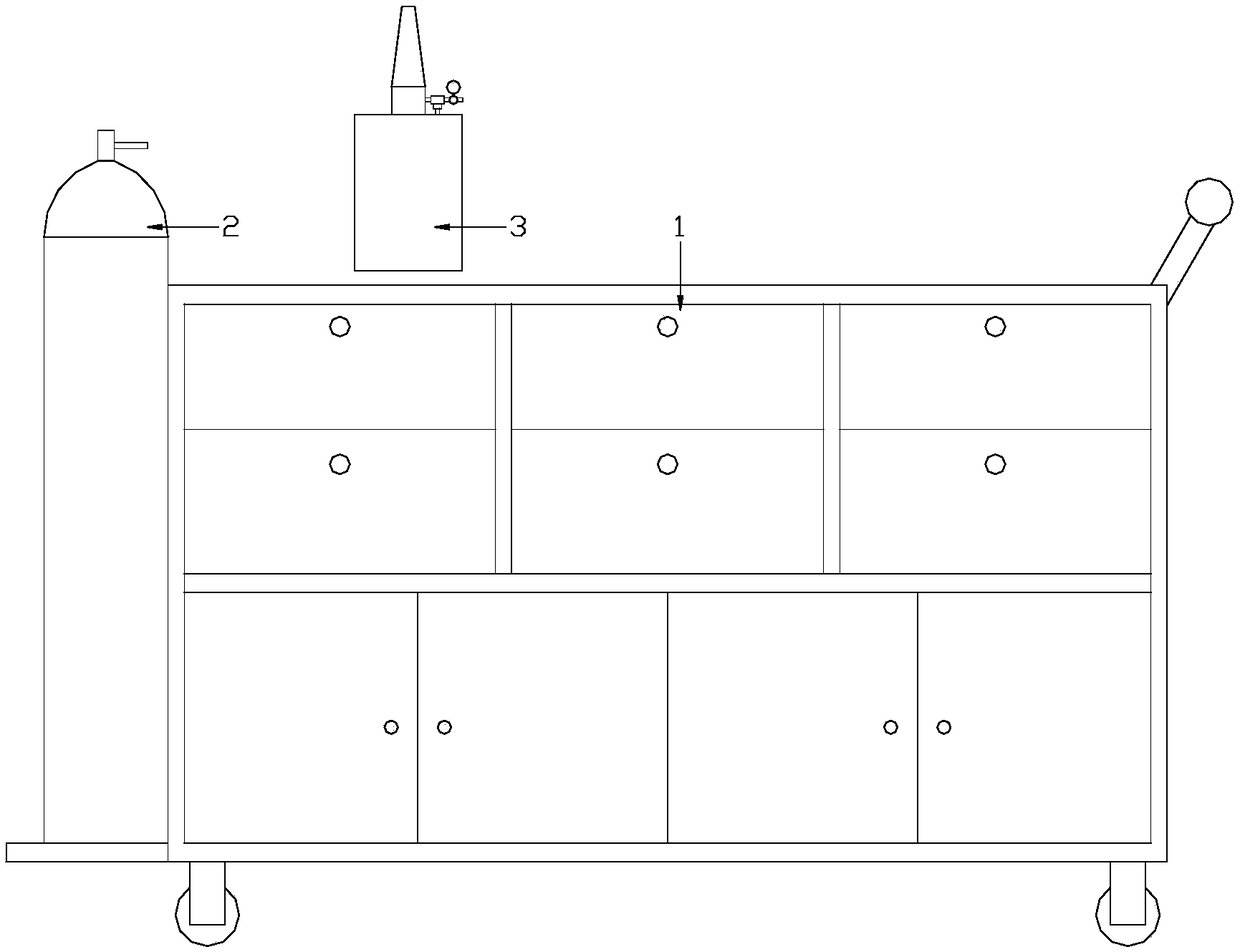
Injection oxygen supply emergency trolley
The invention discloses an injection oxygen supply emergency trolley. The injection oxygen supply emergency trolley comprises an airway trolley main body, wherein an oxygen source device is arranged on the airway trolley main body. The injection oxygen supply emergency trolley further comprises an injection oxygen supply electromagnetic valve and an injection oxygen supply controller, wherein theinjection oxygen supply controller controls the on-off of the injection oxygen supply electromagnetic valve; and an air inlet of the injection oxygen supply electromagnetic valve is connected with theoxygen source device, and an air outlet of the injection oxygen supply electromagnetic valve is connected with an oxygen supply pipe. The injection oxygen supply emergency trolley has the advantage that open type injection ventilation oxygen supply can be carried out on the basis of the conventional continuous and constant oxygen supply of a difficult airway emergency trolley, and thus differentoxygen supply modes can be selected according to disease conditions of patients; and the injection oxygen supply emergency trolley is suitable for emergency airway treatment, such as cricothyroid membrane paracentesis, emergency intubation of the difficult airway, nasopharyngeal ventilation, and ventilation oxygen supply for airway suction.
Owner:哈达
Balloon pressure indicating cricothyrotomy set
ActiveCN111407365BConvenient and quick disinfectionImprove antibacterial propertiesTracheal tubesIncision instrumentsSurgical bladeCricothyroid membrane
The invention discloses a cricothyroid membrane incision suit which comprises a surgical knife blade, a knife stem and a pincers body, wherein a knife tip is arranged at the front end of the surgicalknife blade; and arc-shaped cutting edges are arranged on both sides of the surgical knife blade. The cricothyroid membrane incision suit is made of a metallic material and further comprises a structure inner layer and an antibacterial surface layer. As the antibacterial surface layer of specific constitution is formed on the surgical knife blade of the cricothyroid membrane incision suit, the cricothyroid membrane incision suit has a good antibacterial function, and particularly has a good antibacterial function on escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Visual cricothyroid membrane puncture instrument
PendingCN114224454AWell mixedEasy to mix and handleTracheal tubesRotary stirring mixersMedicineCricothyroid membrane
The invention discloses a visual cricothyroid membrane puncture instrument, relates to the technical field of puncture instruments, and solves the technical problem that a good liquid medicine mixing effect cannot be achieved in the instrument. An external person pinches a pinching ring and drives a corresponding pulling rod to move, when the pulling rod moves up and down, a rotating disc is effectively driven to rotate through the sliding effect between a limiting block and a limiting groove, and in the rapid rotating process of the rotating disc, the corresponding limiting rod can be driven to conduct sufficient stirring in a storage bottle, so that the stirring effect is good, and the stirring effect is good. The liquid in the storage bottle is mixed through the stirring device, and meanwhile, the liquid left on the inner wall of the storage bottle can be fully scraped by abutting against the roller, so that the liquid in the storage bottle is fully mixed, a good stirring and mixing effect can be achieved, and external personnel can conveniently mix liquid medicine.
Owner:池州市人民医院
Assembly for intubation
ActiveUS10953176B2Easy to disassembleEasy to installTracheal tubesRespiratory masksCricothyroid membraneEngineering
An assembly for intubation, as provided herein, may include a cricothyroidotomy tube that can receive a malleable bougie allowing the cricothyroidotomy tube to take the shape of the bougie so that the cricothyroidotomy tube can be placed in a patient. A guide device can receive the bougie so that the bougie can be manipulated with the guide device to assist with insertion of the cricothyroidotomy tube in the patient. A bougie opening can be defined in the guide device for receiving a proximal end of the bougie to position the proximal end out of the way of a care giver to reduce interference that can be caused by the proximal end. Markings on the bougie can illustrate where to position the bougie to allow a predetermined amount of the bougie to extend from the cricothyroidotomy tube.
Owner:NORTH AMERICAN RESCUE PRODS
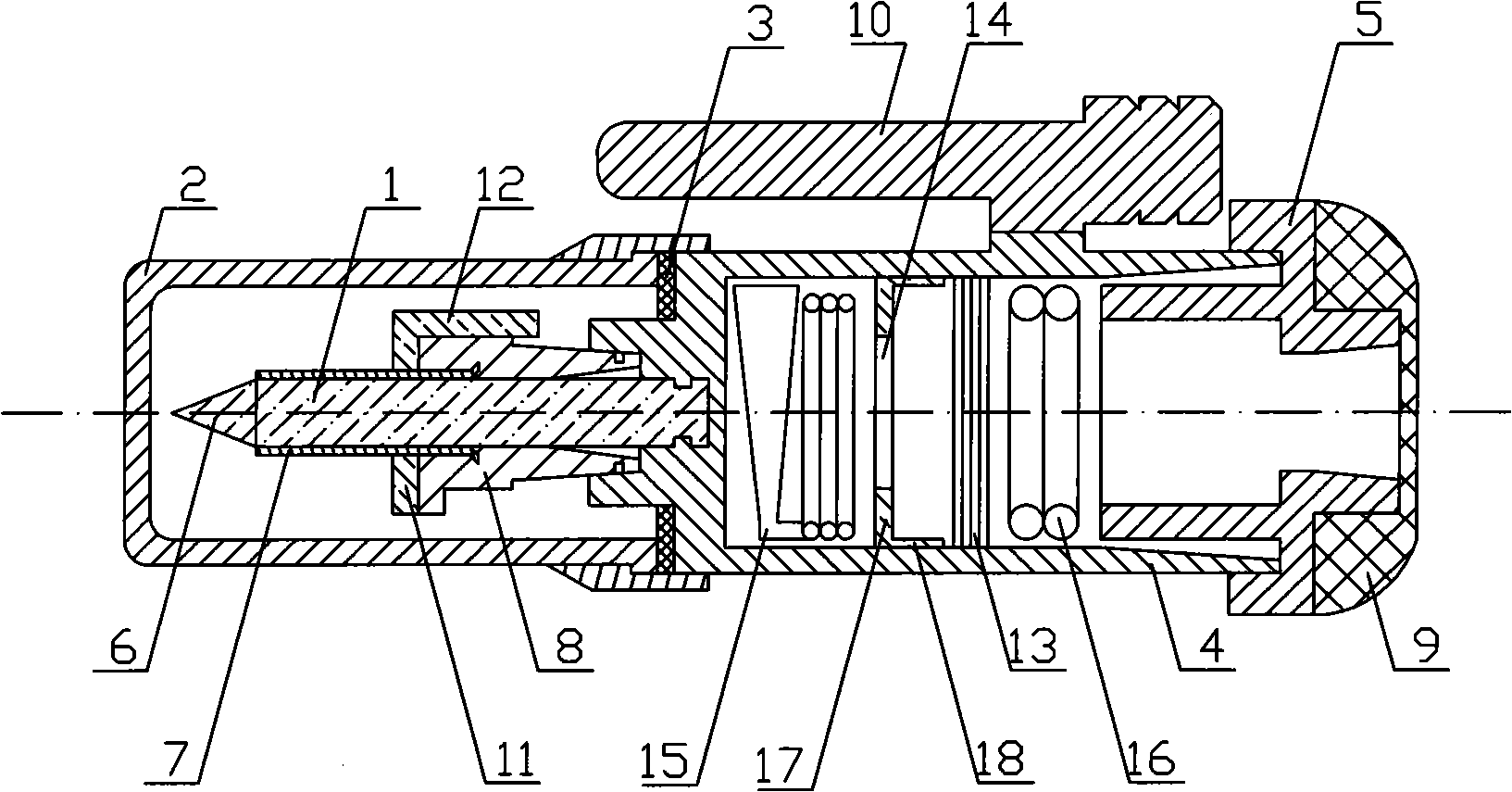
Novel cricothyroid membrane puncture needle
InactiveCN107714160ANot easy to damageEasy to absorbCannulasSurgical needlesGynecologyCricothyroid membrane
The invention relates to a novel cricothyroid membrane puncture needle. The puncture needle is characterized in that an outer tube (1) is provided with a tube body (9) which is a straight round tube,a head end tube orifice (3) is arranged at the head end of the tube body (9), a tail end tube orifice (5) is arranged at the tail end of the tube body (9), a through port (4) is arranged above the head end tube orifice (3) in a manner of being perpendicular to the tube body (9), a first tube handle (6) and a second tube handle (8) are vertically arranged on the tube body (9) parallelly, tube handle small holes (7) are formed in the left and right ends of the first tube handle (6) and used for thread ropes to penetrate, a tube core (2) is provided with a straight tube (11) which is slightly thinner than the outer tube (1), the straight tube (11) can be put into the outer tube (1), and the head end of the straight tube (11) is a triangular-pyramid-shaped head end (10) while the tail end of the same is spherical tail end (12). The puncture needle is simple and convenient to operate, accurate in puncture, capable of immediately relieve throat obstruction and less prone to causing damage toother normal tissue.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Cricothyroid membrane puncture needle breathing machine joint
The invention relates to a cricothyroid membrane puncture needle breathing machine joint. The joint comprises a breathing machine connector, a cricothyroid membrane puncture needle connector, a fixing plate and a sealing ring. The breathing machine connector is a universal connector, and the caliber can be connected with the breathing machine; the cricothyroid membrane puncture needle connector can be tightly connected with a cricothyroid membrane puncture needle; the sealing ring is arranged on one side of the cricothyroid membrane puncture needle connector; the fixing plate is arranged between the breathing machine connector and the cricothyroid membrane puncture needle connector, two symmetrically-distributed holes are formed in two wings of the fixing plate, and the cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is fixed to the neck of a patient through a small belt for penetrating and auxiliary fixing; the length of the joint is decreased to 2.5 cm from 7.5 cm. The cricothyroid membrane puncture needle breathing machine joint is small in length and is provided with the fixing plate, and the defects that an existing cricothyroid membrane puncture needle breathing machine joint is excessively long so that ventilation is blocked, is not firmly fixed and is likely to be disengaged are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
A portable cricothyroid puncture device
The invention discloses a portable cricothyroid membrane puncturer, which comprises a hollow puncturer main body, a movable cover is provided for movable sealing at one end of the puncturer main body, and a sealing cover is provided at the other end of the puncturer main body; A puncture needle is placed in the inner cavity of the main body of the puncture device. The advantages are: small overall size, good sealing, simple structure, low cost, and convenient for industrialized mass production; easy to carry, easy, fast, and fast to operate, and can save critical patients against the clock and win precious time for rescuing patients.
Owner:SHANDONG YIHE MEDICAL TECH
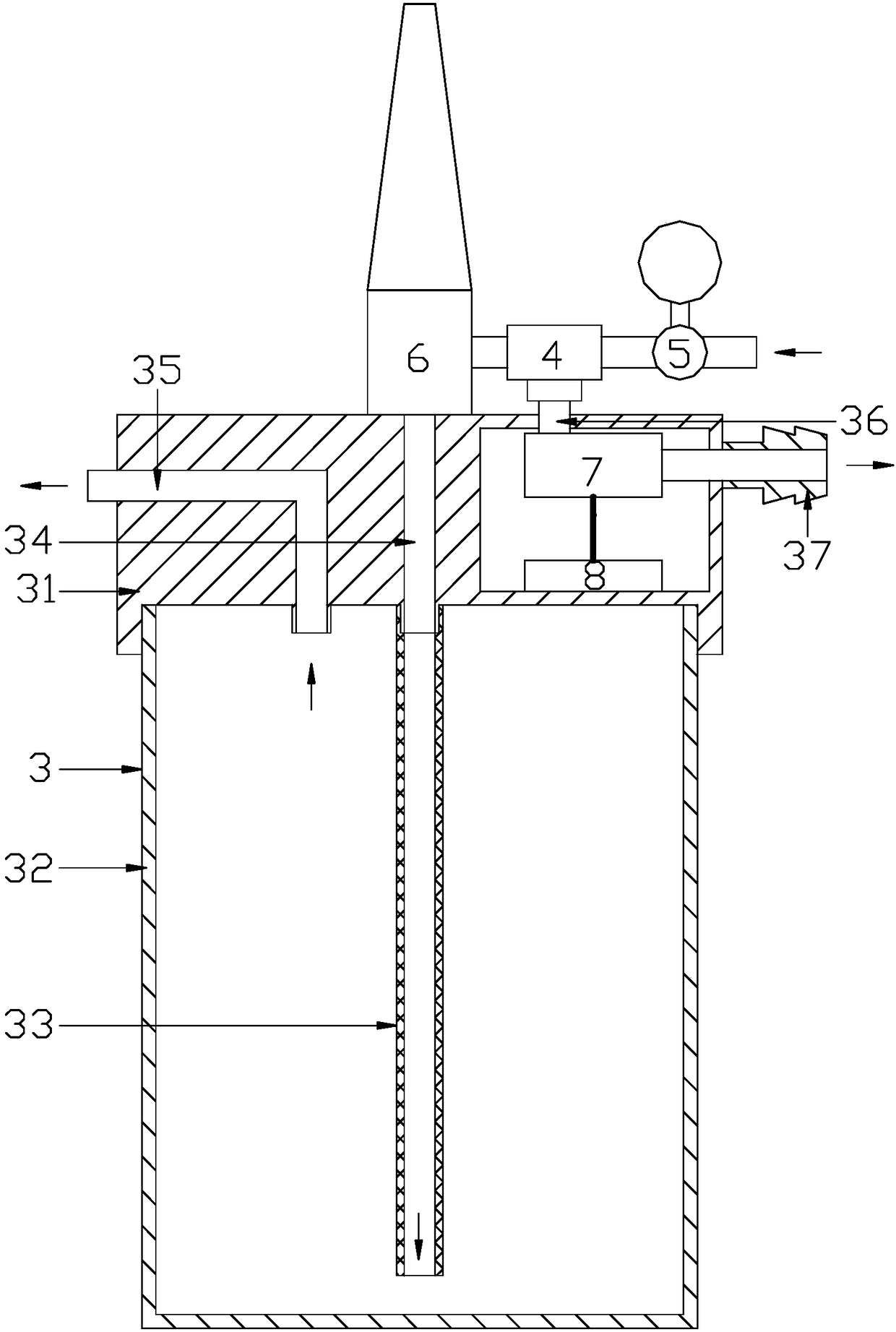
Airway high-frequency ventilation device
The invention relates to an airway high-frequency ventilation device comprising an air supply needle cylinder and a needle. The air supply needle cylinder includes a cylinder body and a connecting part which are connected with each other. An oxygen transfer mouth externally connected with an oxygen supply extends outward from the outer wall of the connecting part. A piston sized to match the inner diameter of the cylinder body is arranged inside the cylinder body. A side, away from the connecting part, of the piston is connected with a push handle which extends out of the cylinder body. The needle includes a needle cap and a needle body. When the existing cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is used to perform emergency treatment on a difficult airway through cricothyroid membrane puncture and high-frequency jet ventilation, a variety of complications can be easily caused. The existing cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is not applicable to children with small airway. Puncture may greatly damage cricothyroid membrane tissues. The existing cricothyroid membrane puncture needle is inconvenient to carry and needs to be powered by a power supply. By adopting the airway high-frequency ventilation device of the invention, the defects of the cricothyroid membrane puncture needle are overcome. The airway high-frequency ventilation device has the advantages of stable air supply, a large number of target users, small surgical injury, fewer complications, fast use, and applicability to emergency treatment on a respiratory tract through oxygen transfer in the field or other environments.
Owner:PANZHIHUA HOSPITAL OF CHINESE TRADITIONAL & WESTERN MEDICINE
Airway operation simulation device for emergency surgical operation
In one aspect of the present disclosure, an artificial anatomical model for simulating a cricothyrotomy procedure is provided. The model includes an upper body structure including a neck member having a tracheal access window covered by a membrane. Arranged beneath the intima of the neck member is an anatomically precise laryngeal-tracheal structure. The structure includes a first member of a rigid first material, the first member being shaped and dimensioned to define a cricothyroid gap covering a cuttable artificial cricothyroid membrane material of a second member received therein. The second member seals and is in fluid communication with the expandable chamber.
Owner:HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com