Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Carpometacarpal joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
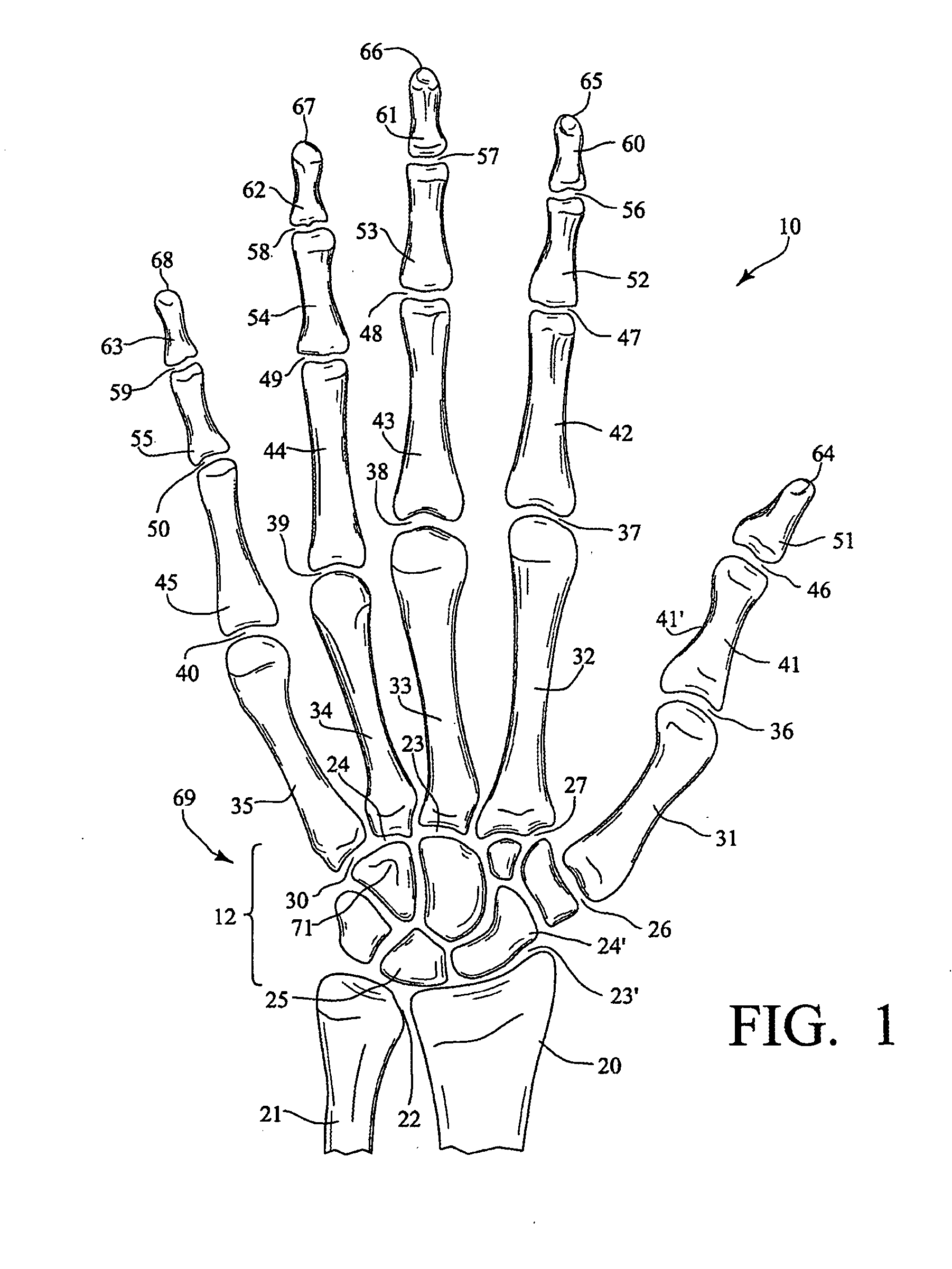
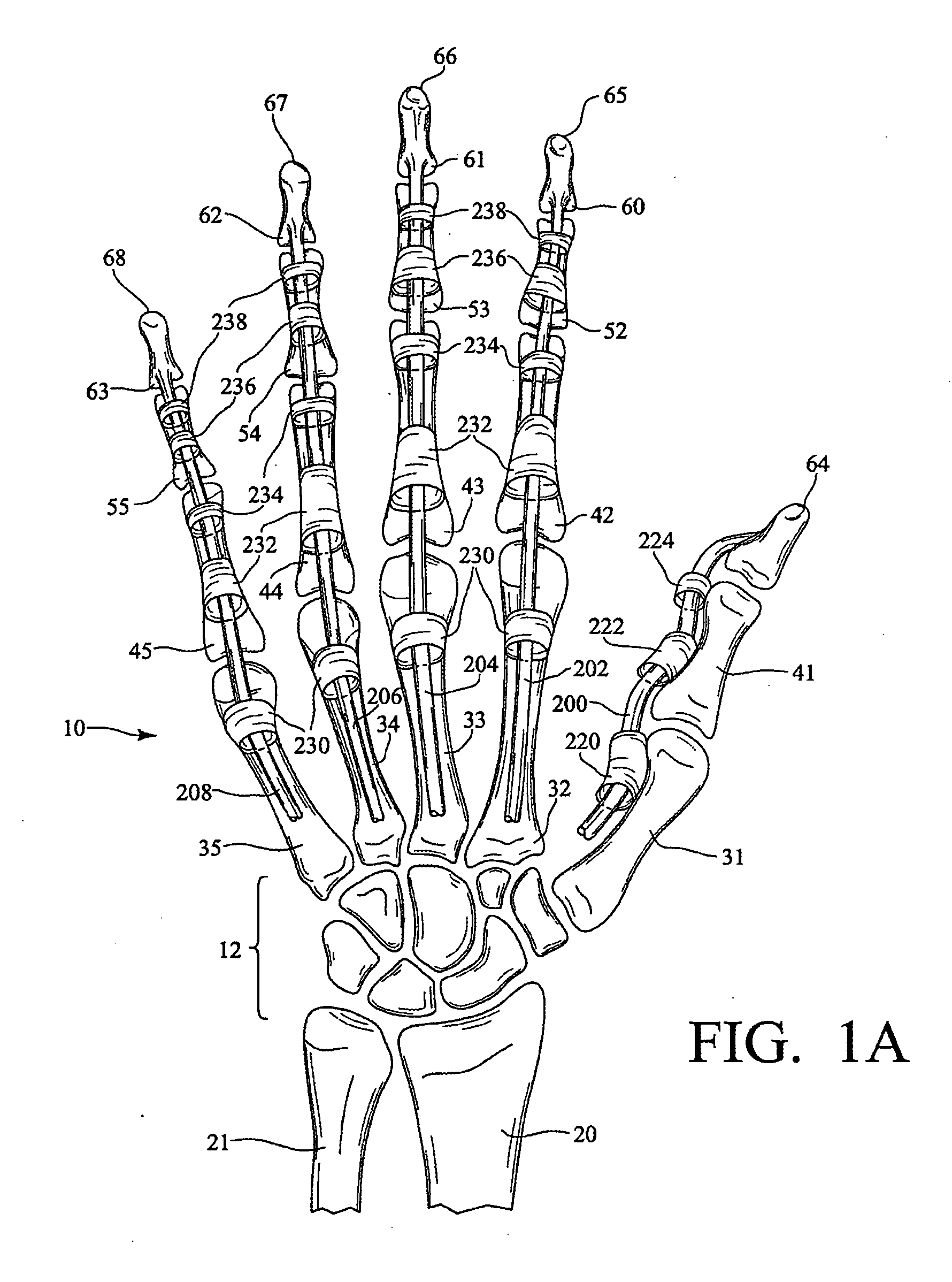
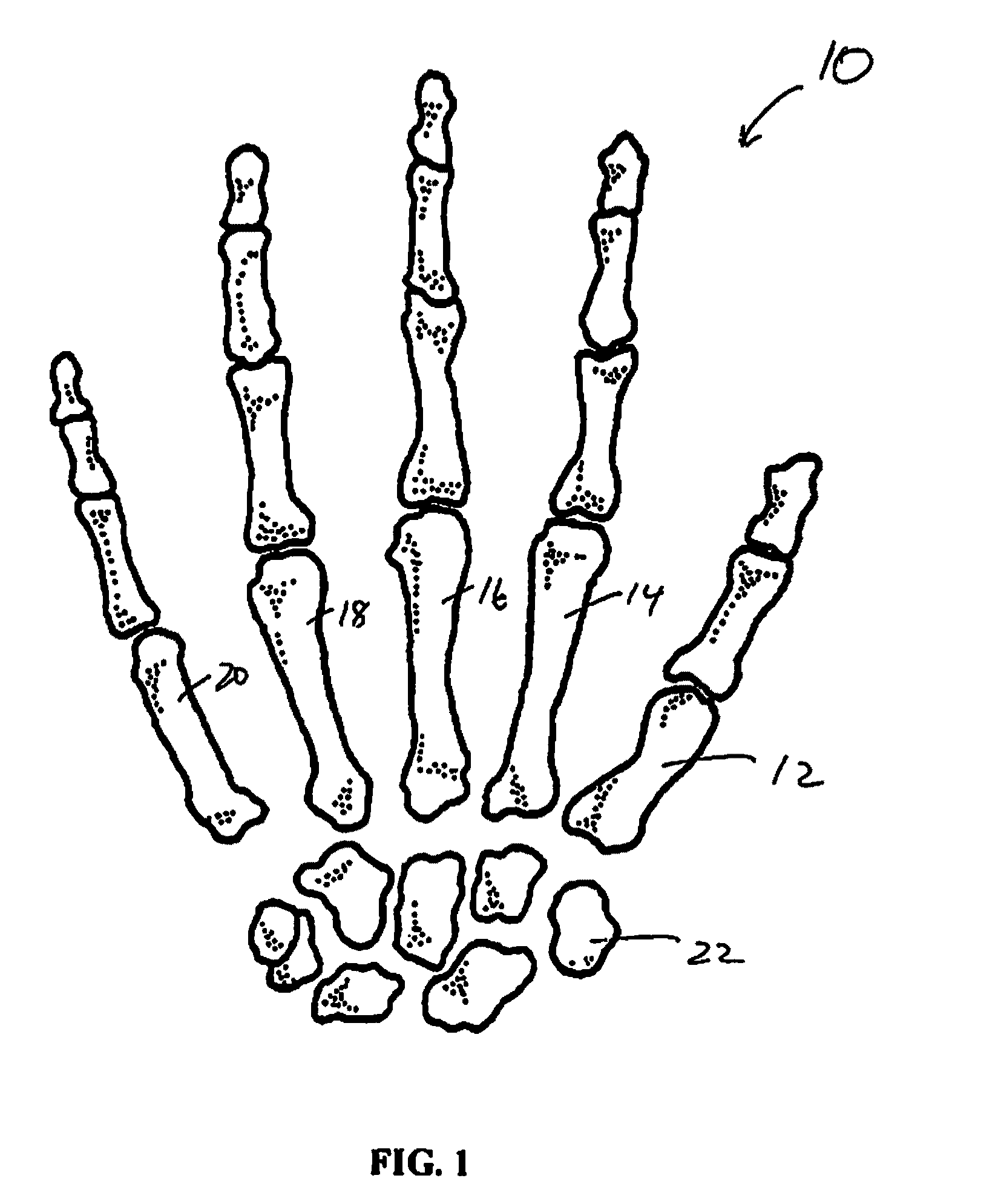
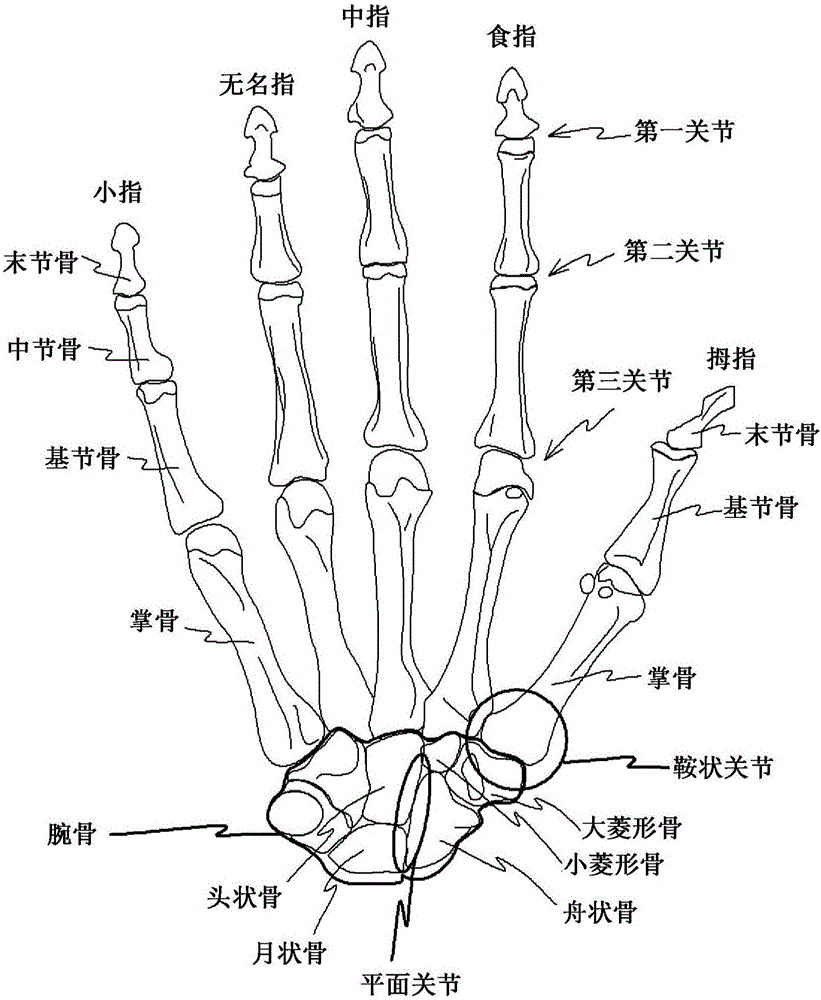
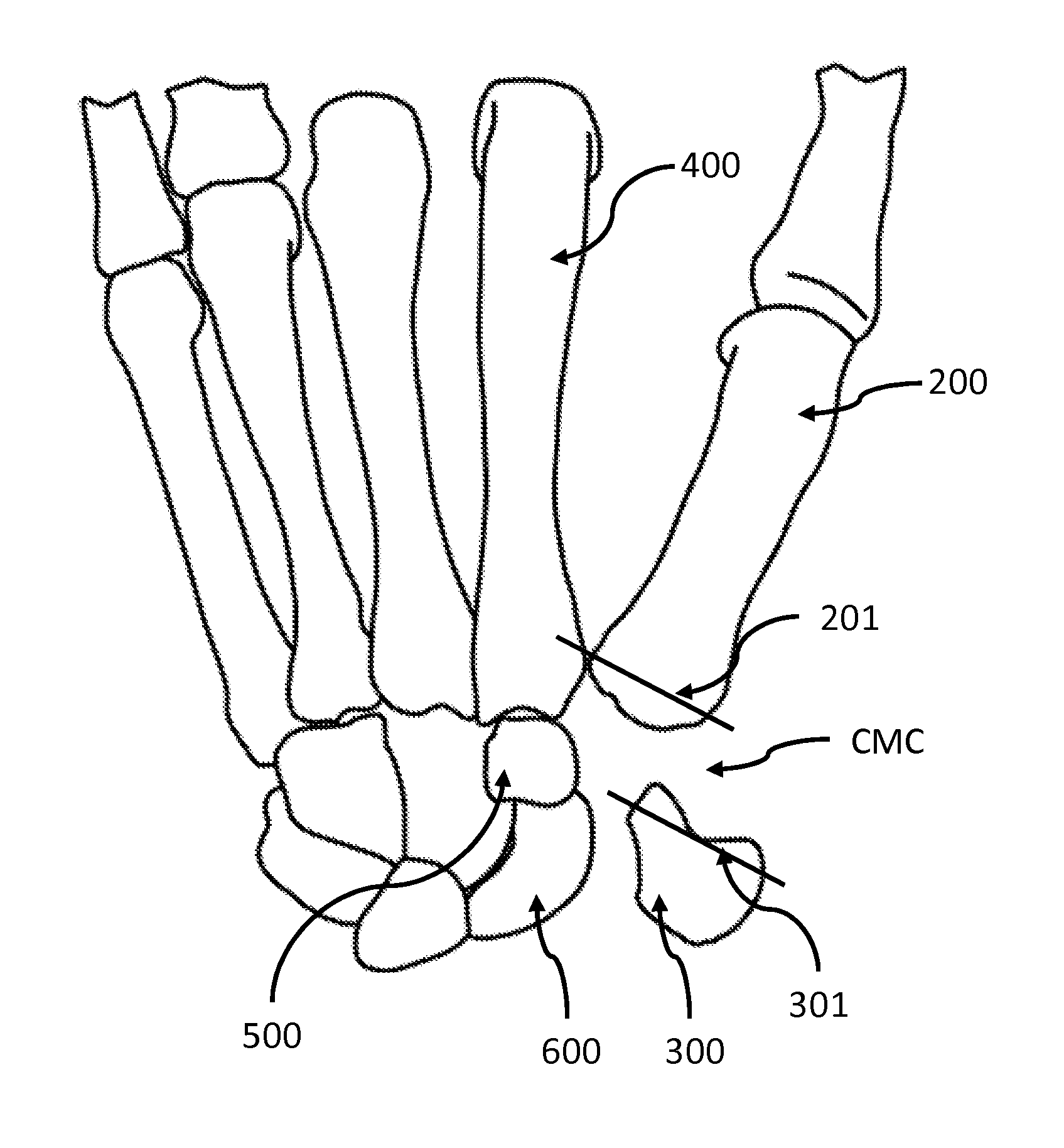
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones. The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometacarpal (TMC) joint, differs significantly from the other four CMC joints and is therefore described separately.
Surgical technique using a contoured allograft cartilage as a spacer of the carpo-metacarpal joint of the thumb or tarso-metatarsal joint of the toe
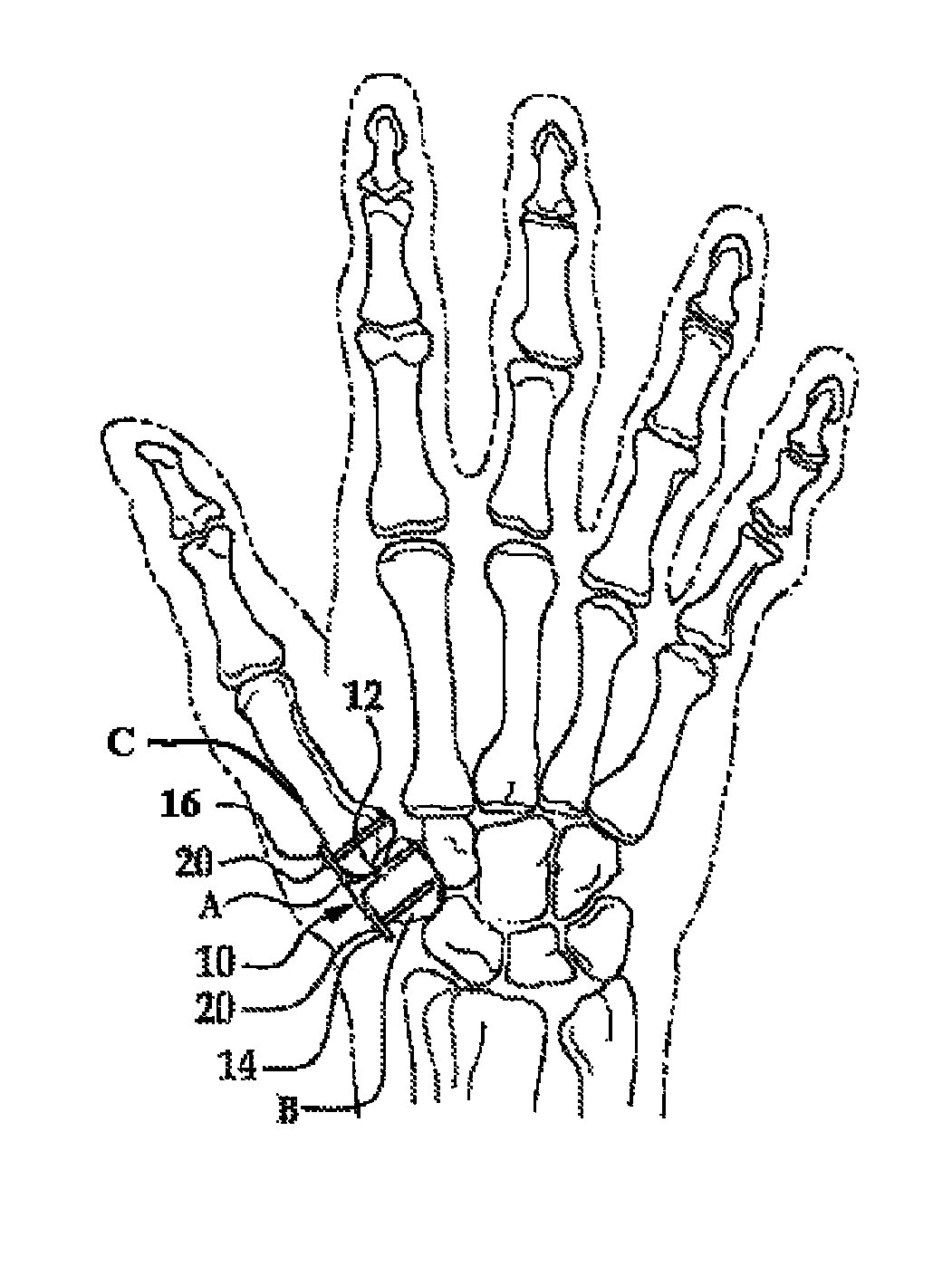
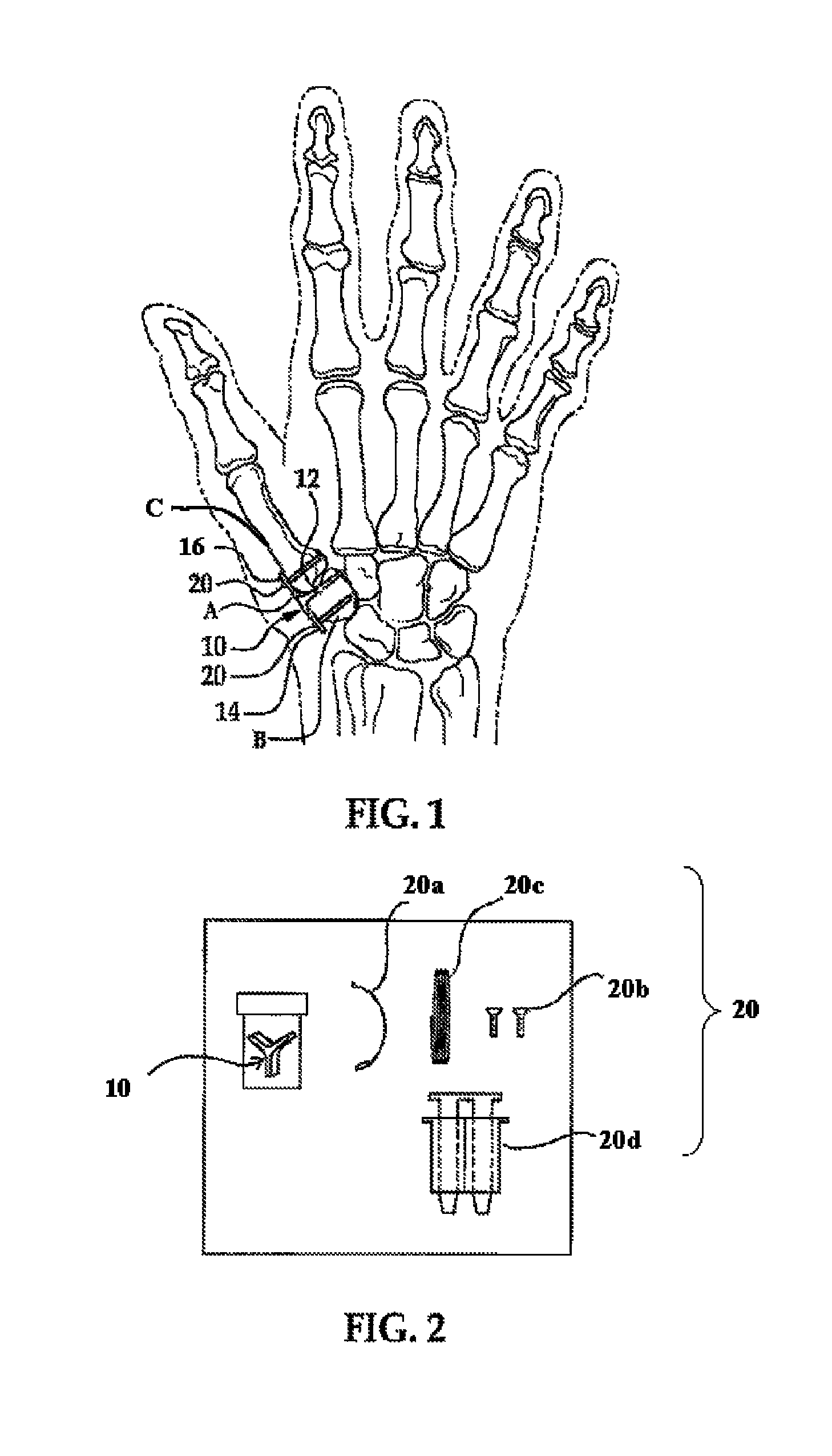
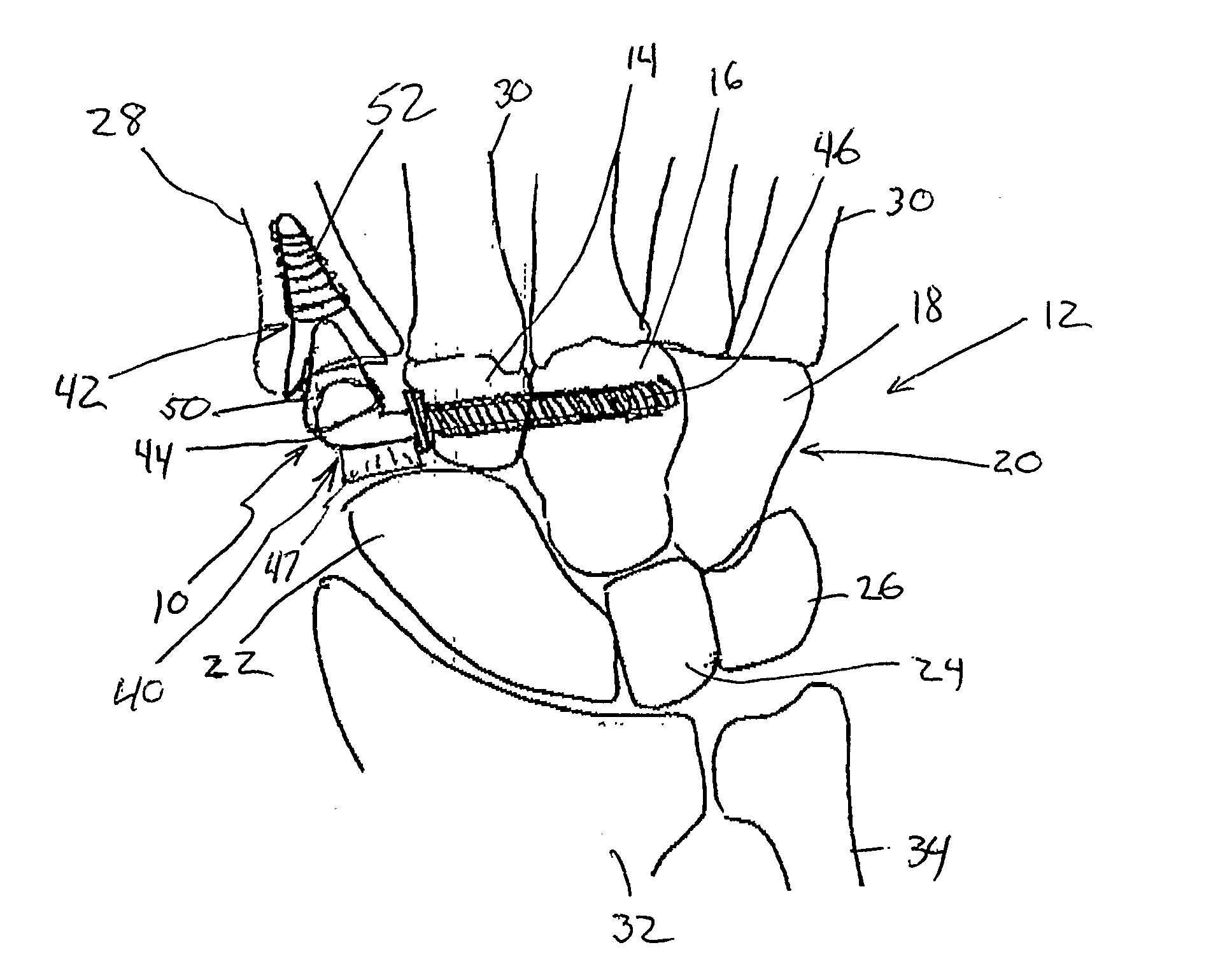
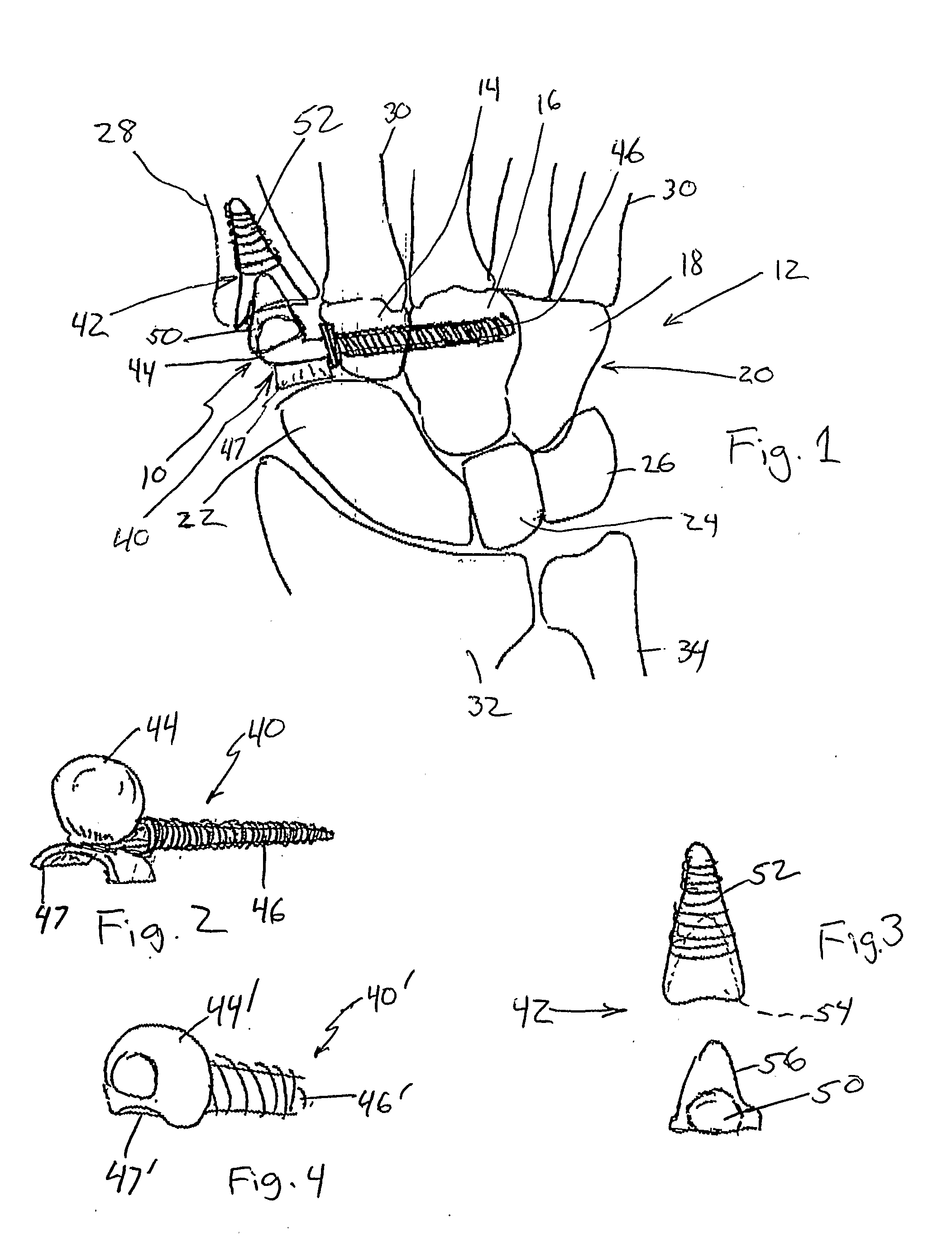
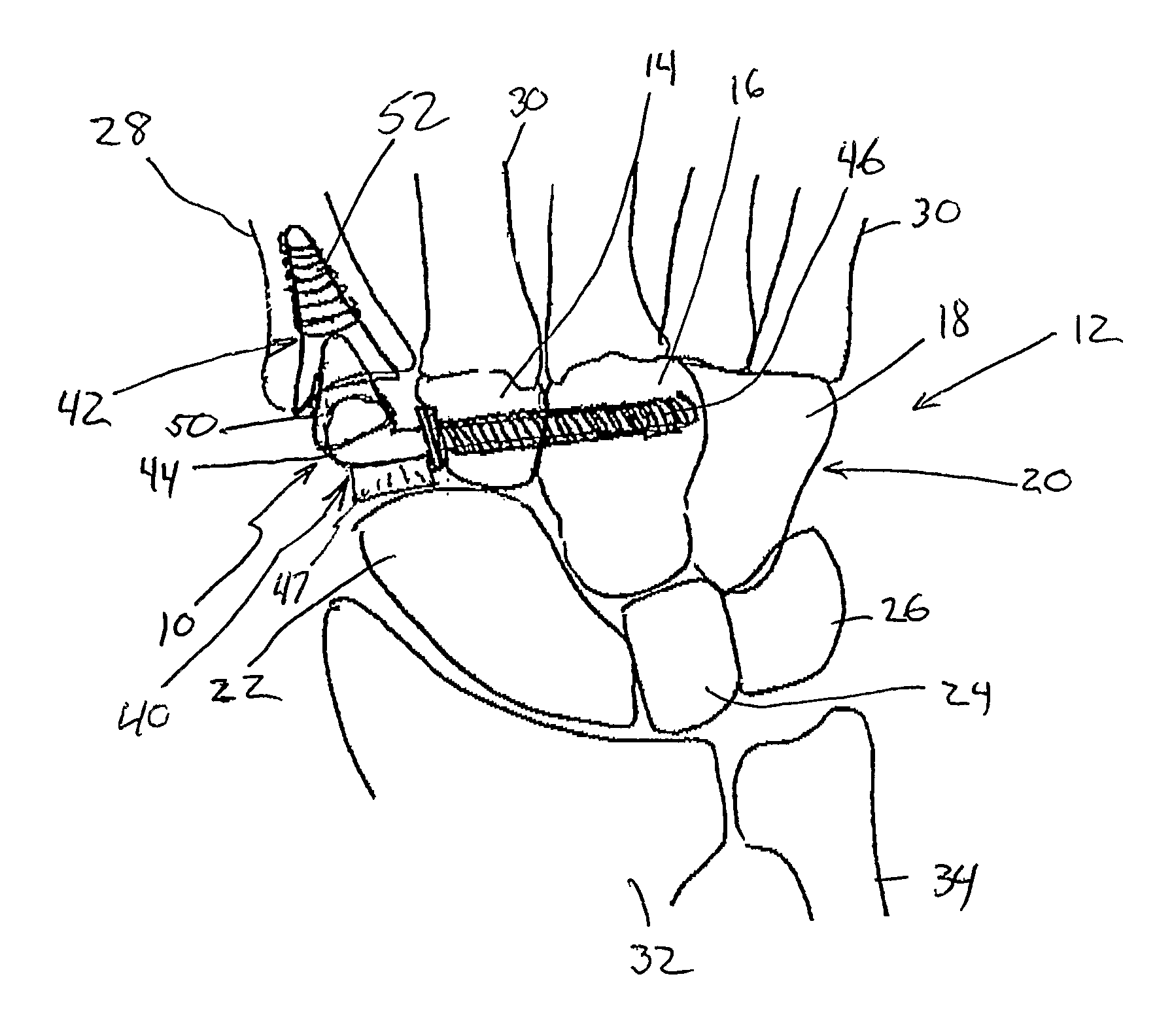
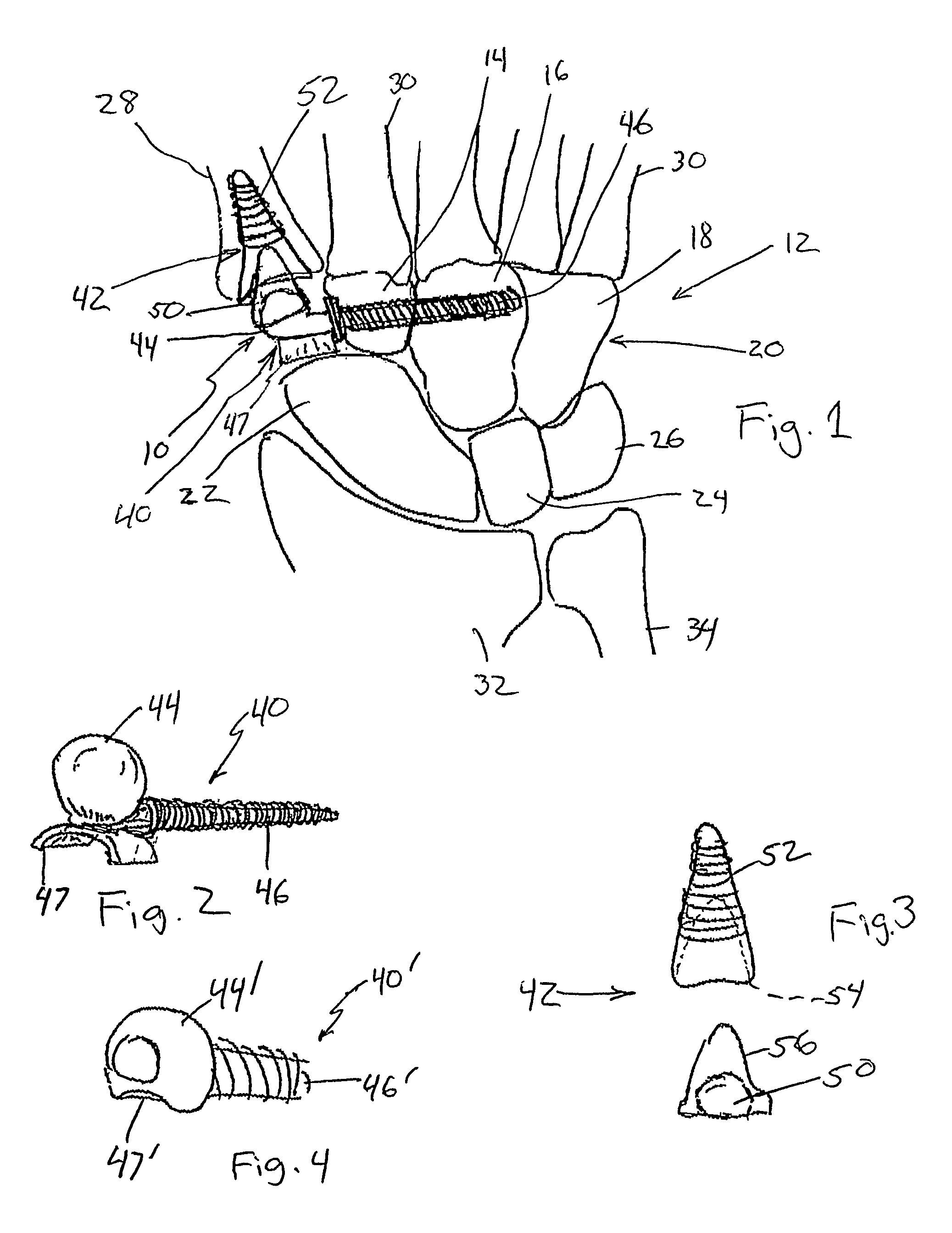
A spacer for implantation into a subject is provided that includes a sterilized piece of cartilaginous allograft tissue. The piece forms a Y-shape with a base adapted to insert within a first carpo-metacarpal joint or carpo-metatarsal joint of the subject, and has a first arm adapted to secure to a trapezium bone adjoining the joint, and a second arm adapted to secure to a proximal metacarpal or metatarsal bone adjoining the joint. A procedure for implanting the spacer includes exposing a target joint and abrading a bone surface interior to the joint to induce surface bleeding. The spacer base is then inserted into the joint. The spacer first arm is adhered to the first bone of the joint and the spacer second arm is adhered to the second bone of the joint. A kit is also provided for surgical implantation of the spacer.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL S
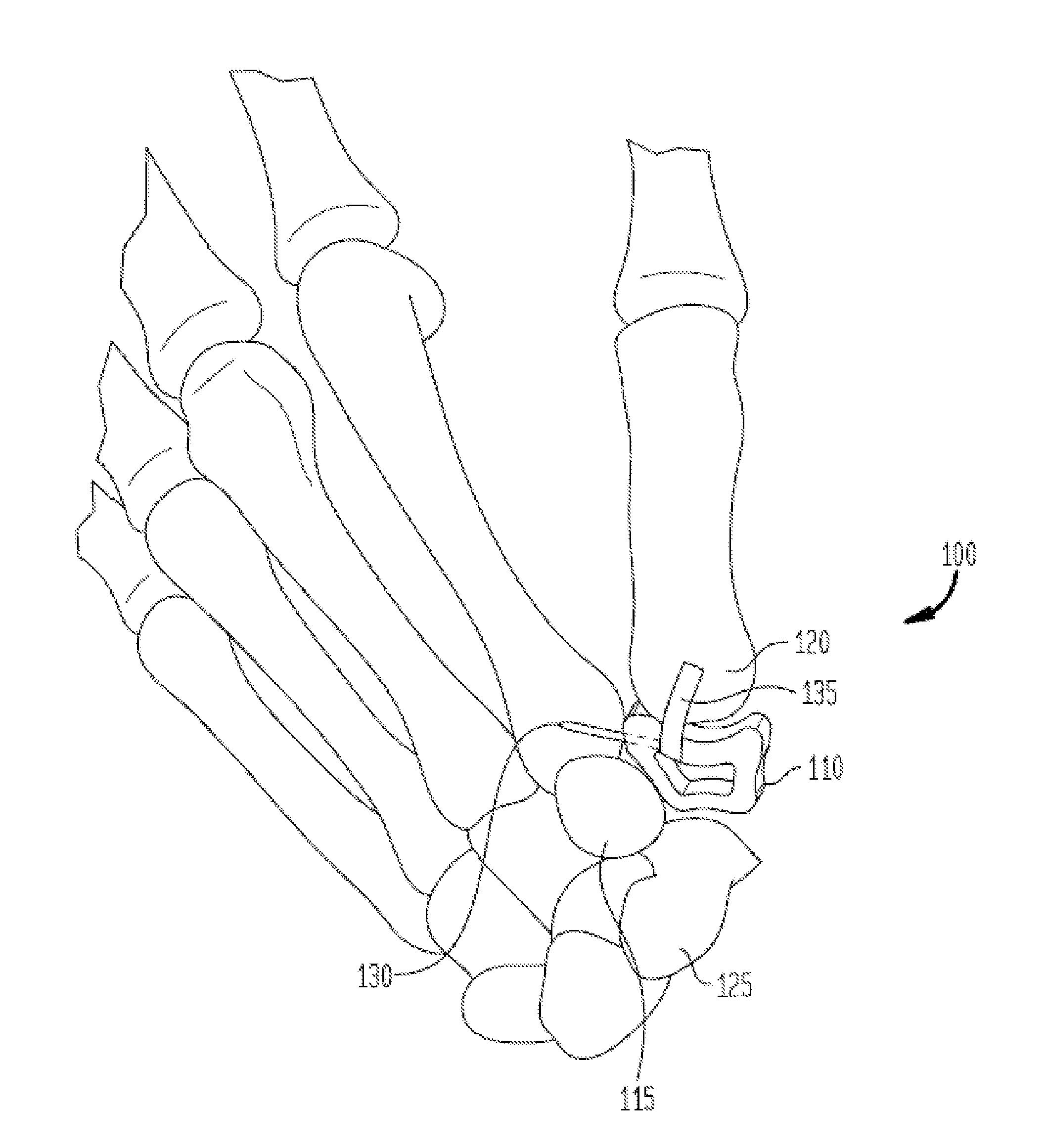
System and method for trapezium bone replacement
ActiveUS20090254190A1Efficiently distribute forceEffective forceSuture equipmentsFinger jointsTrapezium BoneProsthesis
A carpometacarpal joint replacement system for replacing the trapezium bone in the hand is provided. The system includes a trapezial implant for the carpometacarpal joint resulting in replacement of the carpal trapezium bone with a prosthesis having the same anatomical configuration as the trapezium bone. The implant device comprises a plurality of concave surfaces, with the plurality of concave surfaces articulating with the carpal and metacarpal bones.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
Semi-Constrained 1st Carpometacarpal Implant Arthroplasty
A first carpometacarpal joint implant. One embodiment of the invention includes proximal and distal components. The proximal component includes a fixation portion for attachment to one or more elements of a patient's distal carpal row, a ball-type joint portion cantilevered off the fixation portion, and a skid having a concave surface opposite the ball-type joint for engaging a patient's scaphoid bone. The distal component has a fixation portion for attachment to a patient's thumb metacarpal, and a socket-type joint portion that cooperates with the ball-type joint portion of the proximal component.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Batting glove
InactiveUS20060026738A1Increase flexibilityPromote respirationGlovesBall sportsLittle fingerEngineering
A batting glove particularly for baseball and softball includes padding along the palmar side of at least the proximal ends of the metacarpals of the ring finger and the small finger. Padding is absent over the hook of the hamate and preferably the carpometacarpal joints of the ring finger and the small finger.
Owner:HILLERICH & BRADSBY COMPANY KENTUCKY
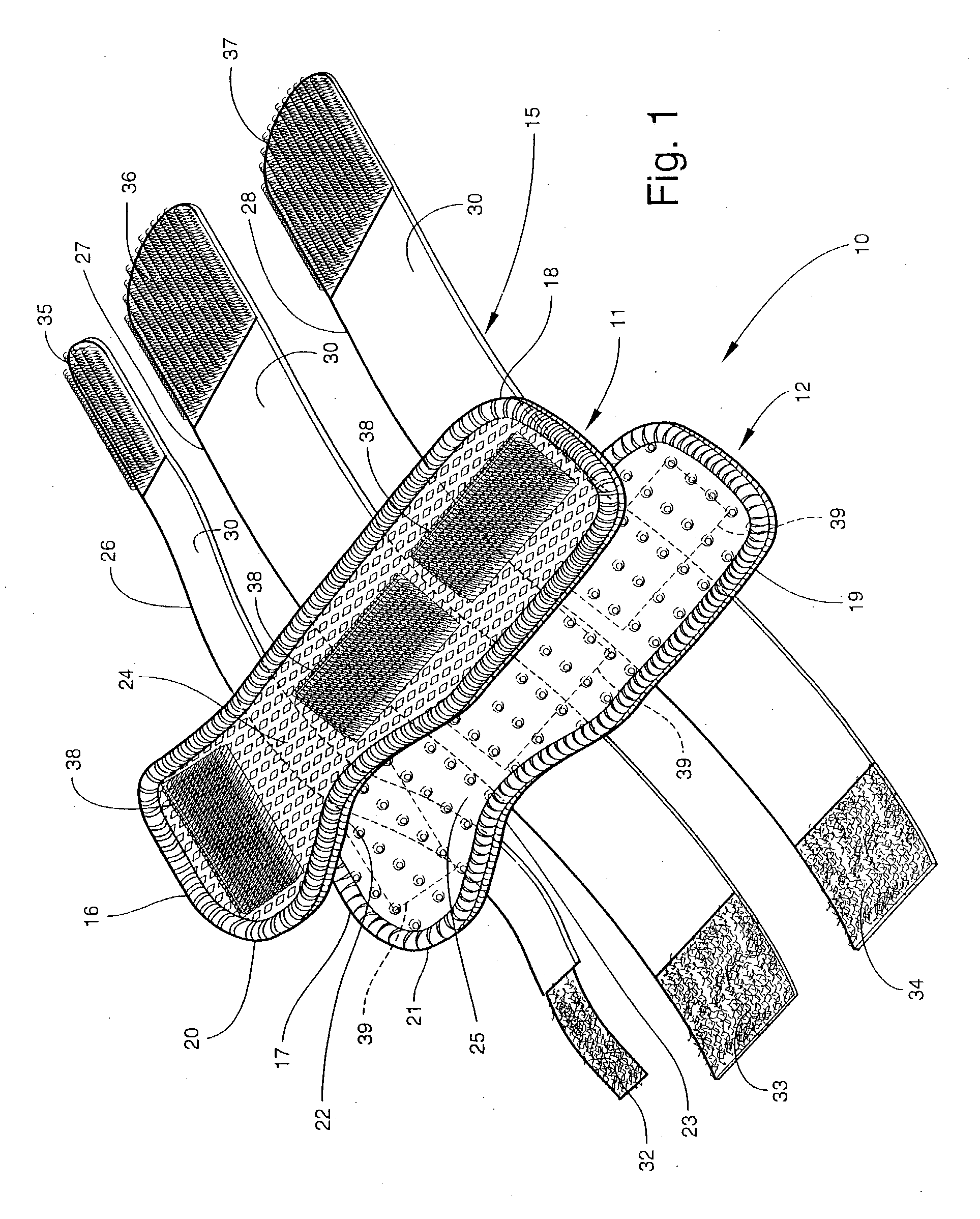
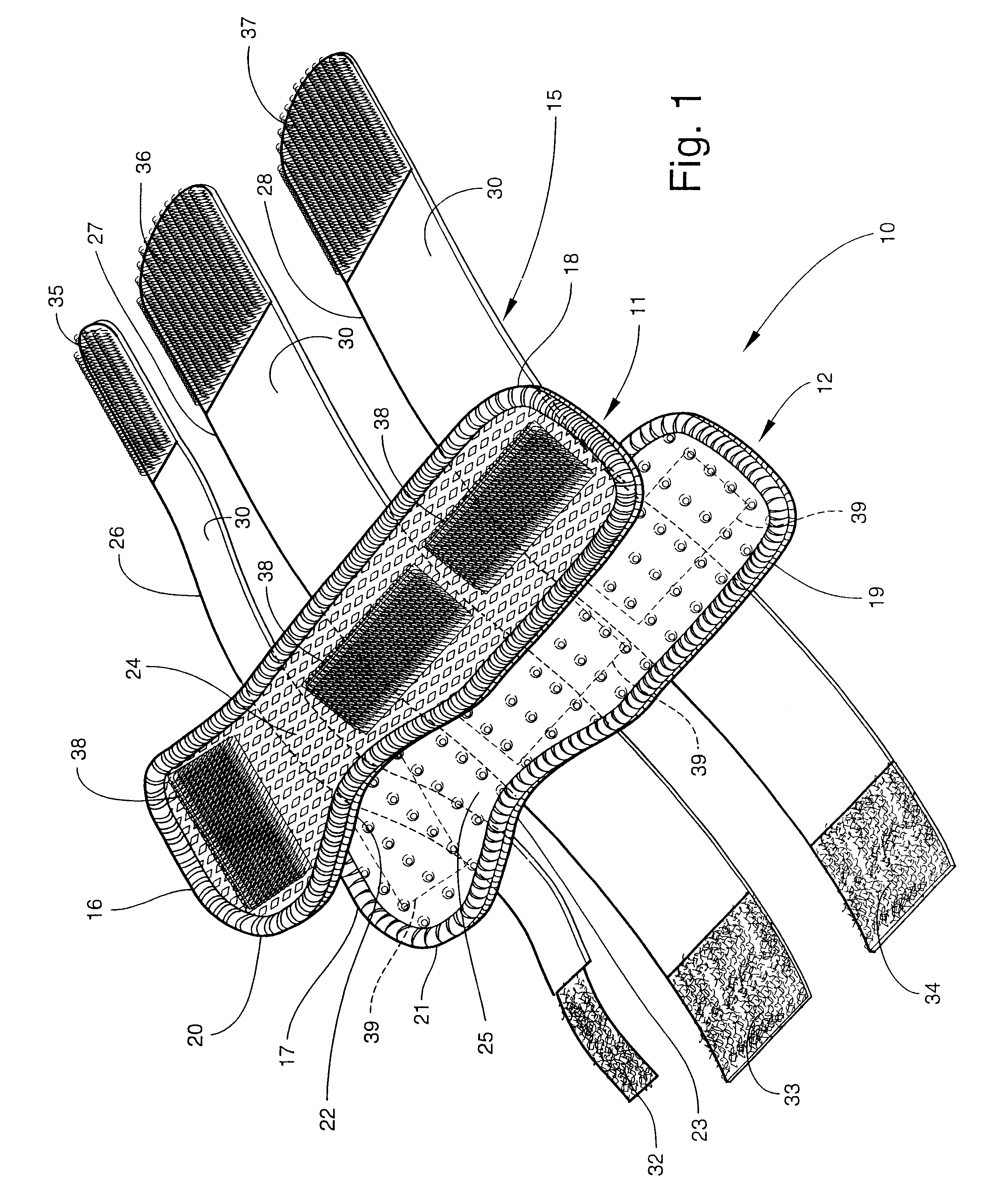
Custom-moldable wrist splint
InactiveUS20040176714A1Easy to disassembleRestraining devicesFracturePhysical medicine and rehabilitationWrist splint
A wrist splint assembly for being custom-fitted to a hand and wrist to be supported. The wrist splint assembly includes a first splint for being positioned against and formed to the volar aspect of the hand and wrist, and a second splint for being positioned against and formed to the dorsal aspect of the hand and wrist. Each of the first and second splints defines a concave side edge extending inwardly toward the longitudinal axis of the splint for permitting ease of movement of the thumb and associated carpometacarpal joint of the hand against which the splint is positioned. Each splint also includes an inner cushion layer, an initially flexible intermediate layer overlying the inner cushion layer, and a flexible outer layer. The intermediate layer is a substrate impregnated with a moisture-curable resin that hardens upon curing to form a rigid structure of the substrate that retains a shape into which it is molded during curing for maintaining the flexible inner cushion layer in a conforming shape against the hand and wrist. A support retains the first and second splints in position on the hand and wrist during use of the splint assembly.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL INC
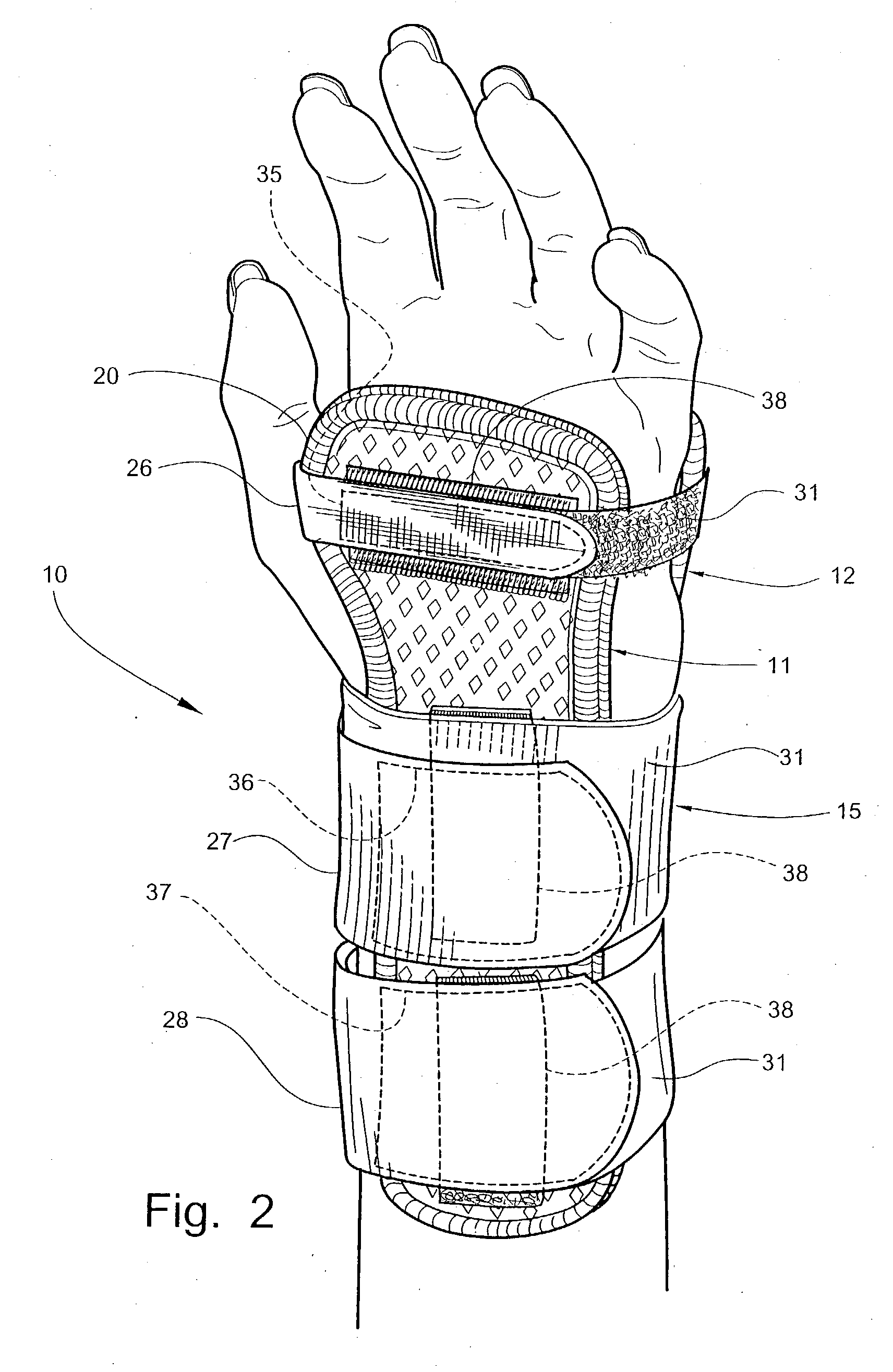
Custom-moldable wrist splint
A wrist splint assembly for being custom-fitted to a hand and wrist to be supported. The wrist splint assembly includes a first splint for being positioned against and formed to the volar aspect of the hand and wrist, and a second splint for being positioned against and formed to the dorsal aspect of the hand and wrist. Each of the first and second splints defines a concave side edge extending inwardly toward the longitudinal axis of the splint for permitting ease of movement of the thumb and associated carpometacarpal joint of the hand against which the splint is positioned. Each splint also includes an inner cushion layer, an initially flexible intermediate layer overlying the inner cushion layer, and a flexible outer layer. The intermediate layer is a substrate impregnated with a moisture-curable resin that hardens upon curing to form a rigid structure of the substrate that retains a shape into which it is molded during curing for maintaining the flexible inner cushion layer in a conforming shape against the hand and wrist. A support retains the first and second splints in position on the hand and wrist during use of the splint assembly.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL INC
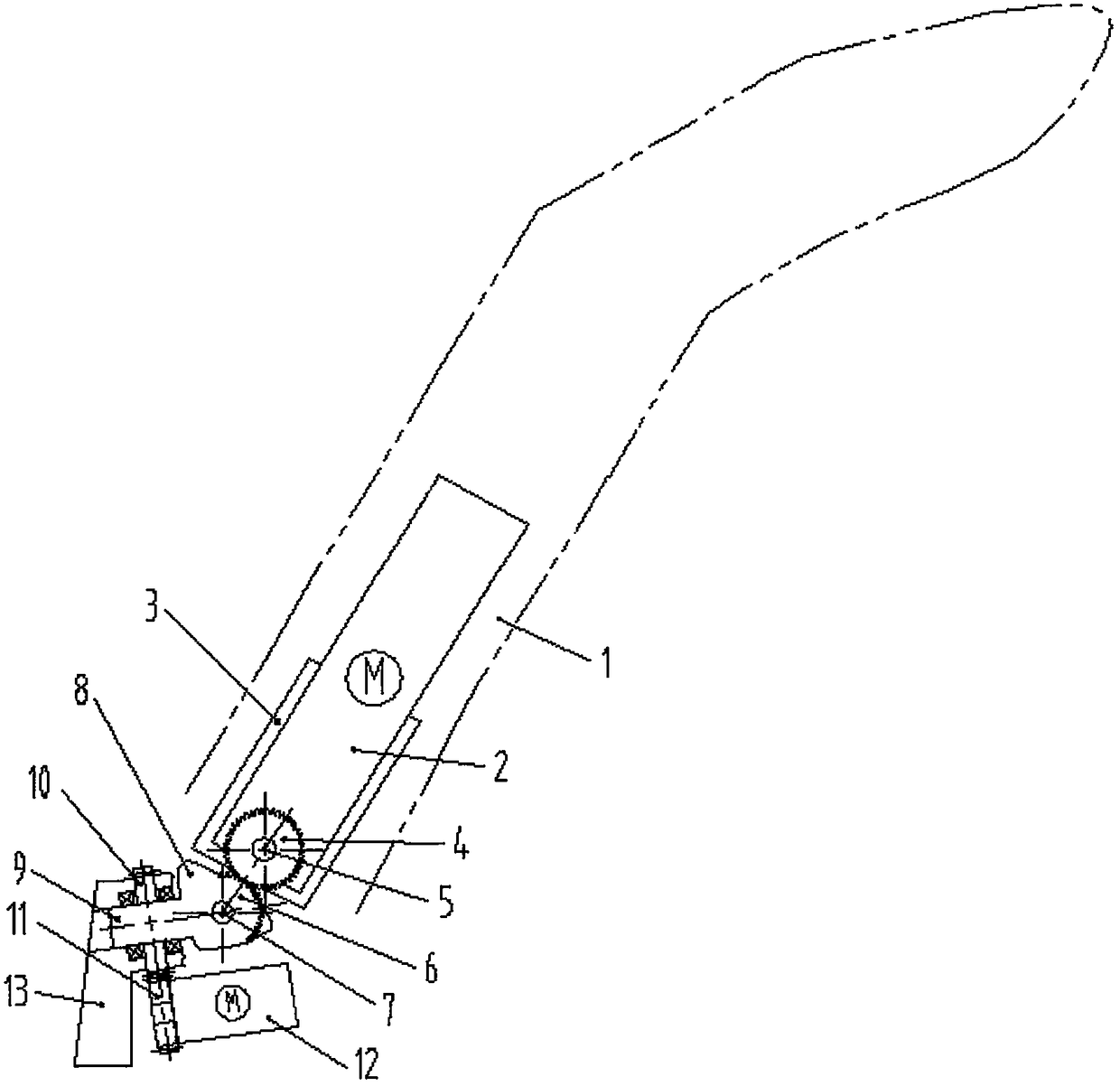
Exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN102319162ASolve the problem of bad wearingSuitable for wearingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesDrive shaftEngineering
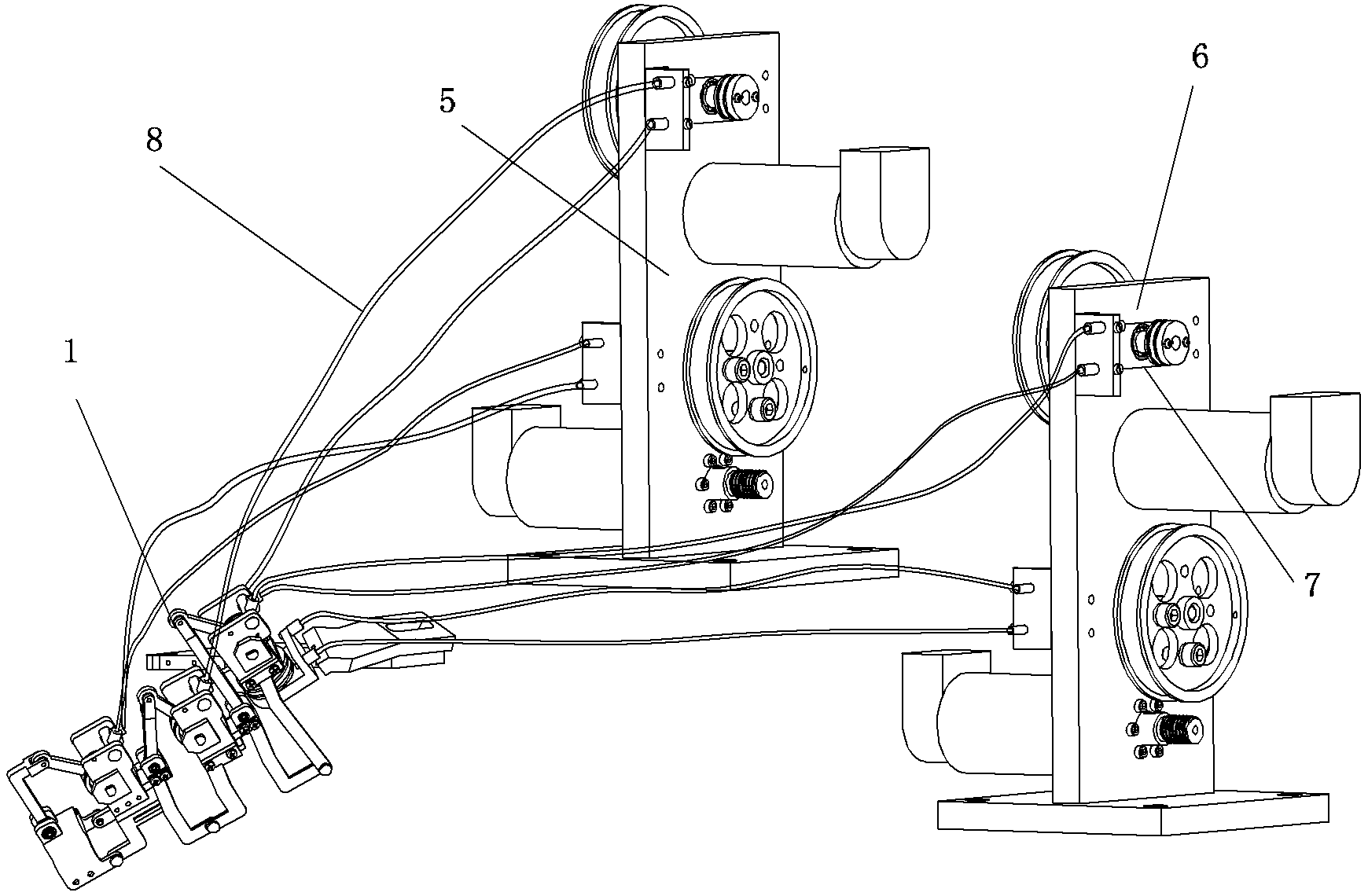
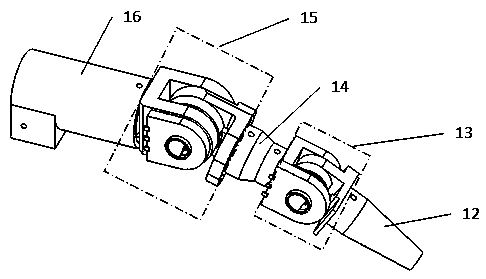
The invention relates to an exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot. The robot comprises an execution part, a transmission part and a drive part, wherein the execution part is divided into an interphalangeal joint module, a metacarpophalangeal joint module and a carpometacarpal joint module; in the carpometacarpal joint module, a metacarpal seat is fixed on the palm and wrist of a patient; the metacarpal seat and a metacarpal seat connector form a dip angle of 30 degrees, and the metacarpal seat connector has an angle of 45 degrees; an angle sensor is fixedly connected to a joint horizontal rotor, and is fixedly connected with an abduction / adduction coil; an adjustable bearing block is fixedly connected with a size adjusting jack; one end of a palm driven rod and the adjusting bearing block form a rotating pair, and the other end of the palm driven rod and a palm drive rod form a rotating pair; and the palm drive rod is fixed on a palm drive shaft, and the drive shaft and a palm drive bearing block form a rotating pair. According to the exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot, four degrees of freedom active and passive rehabilitation of the thumb can be realized, and the problem that the robot is difficult to wear due to the difference between the physiological structure of the thumb and the other four fingers can be solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Semi-constrained 1st carpometacarpal implant arthroplasty and method
A first carpometacarpal joint implant. One embodiment of the invention includes proximal and distal components. The proximal component includes a fixation portion for attachment to one or more elements of a patient's distal carpal row, a ball-type joint portion cantilevered off the fixation portion, and a skid having a concave surface opposite the ball-type joint for engaging a patient's scaphoid bone. The distal component has a fixation portion for attachment to a patient's thumb metacarpal, and a socket-type joint portion that cooperates with the ball-type joint portion of the proximal component.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Carpometacarpal (CMC) implants and methods
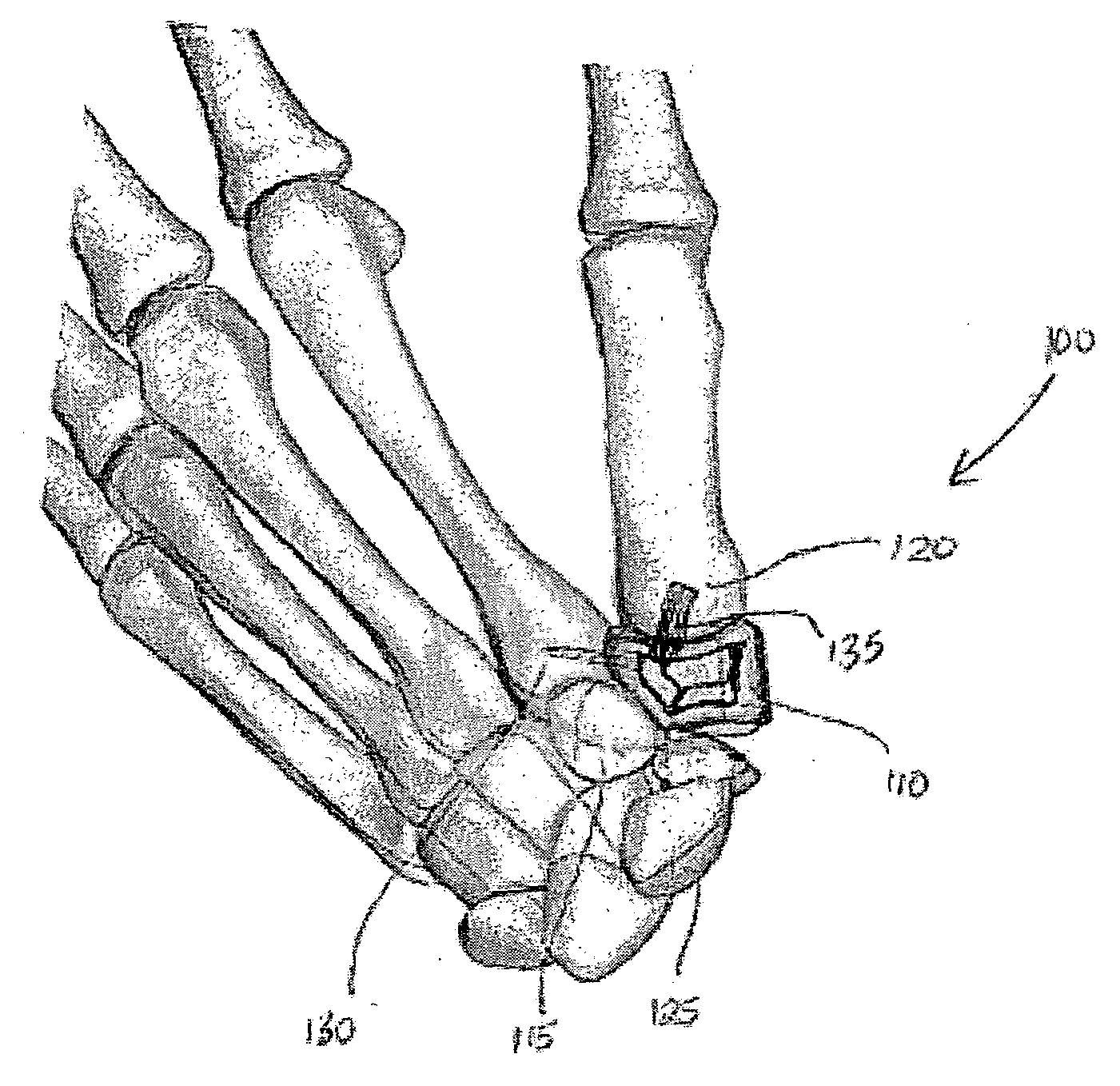
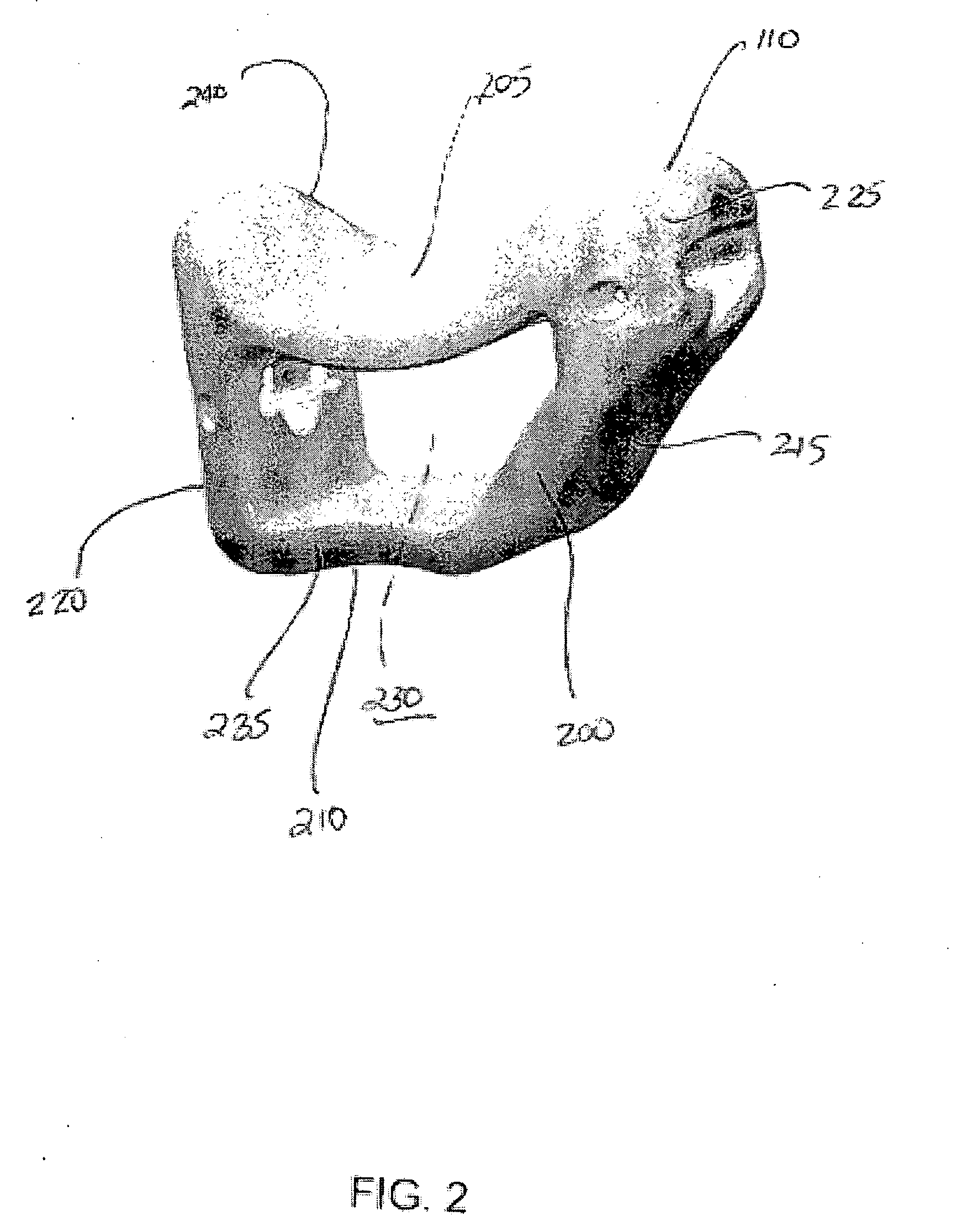
Implants suitable for use in a carpometacarpal joint includes an upper surface, a lower surface, and sidewalls extending between the upper surface and the lower surface. The implant includes hydrogel material such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel. Kits can include systems for preparing an implantation site, creating a cavity, and / or deploying the implant. Methods of treating a carpometacarpal joint include deploying an implant in a recess in a carpometacarpal bone.
Owner:CARTIVA INC
32-degree-of-freedom bionic compliant internal skeleton dexterous hand
ActiveCN110842962AIncrease production capacityEasy maintenanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsLittle fingerTendon sheath
The invention discloses a 32-degree-of-freedom bionic compliant internal skeleton dexterous hand. The dexterous hand uses an anatomy structure of a human hand for reference, a hand portion is of an inner skeleton type, and the outer surface is suitable for being covered with a flexible bionic skin layer with a certain thickness; a joint adopts double-driver antagonistic type drive, so that the compliance operation and the robustness are both taken into account; a tendon coupling piece and a tendon sheath fixing piece are adopted, so that the hand portion and a wrist portion can be easily disassembled and assembled; metacarpophalangeal joints of five fingers all have convolution degrees of freedom so that the fingers can automatically and compliantly adapt to a complex curved surface; a carpometacarpal joint of a thumb has two degrees of freedom of bending-stretching and annular rotation, a metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb has the degree of freedom of side sway, carpometacarpal joints of a ring finger and a small finger have degrees of freedom of bending-stretching and inward retracting-outward stretching, an opposing action can be performed so that complex pinching operationcan be executed; the axes of all the degrees of freedom of the multi-degree-of-freedom joint are orthogonal, so that control and motion planning calculation is facilitated; and the dexterous hand is very suitable for compliantly operating objects of complex shapes, so that production, disassembly, assembly and maintenance are facilitated.
Owner:NEUROCEAN TECH INC
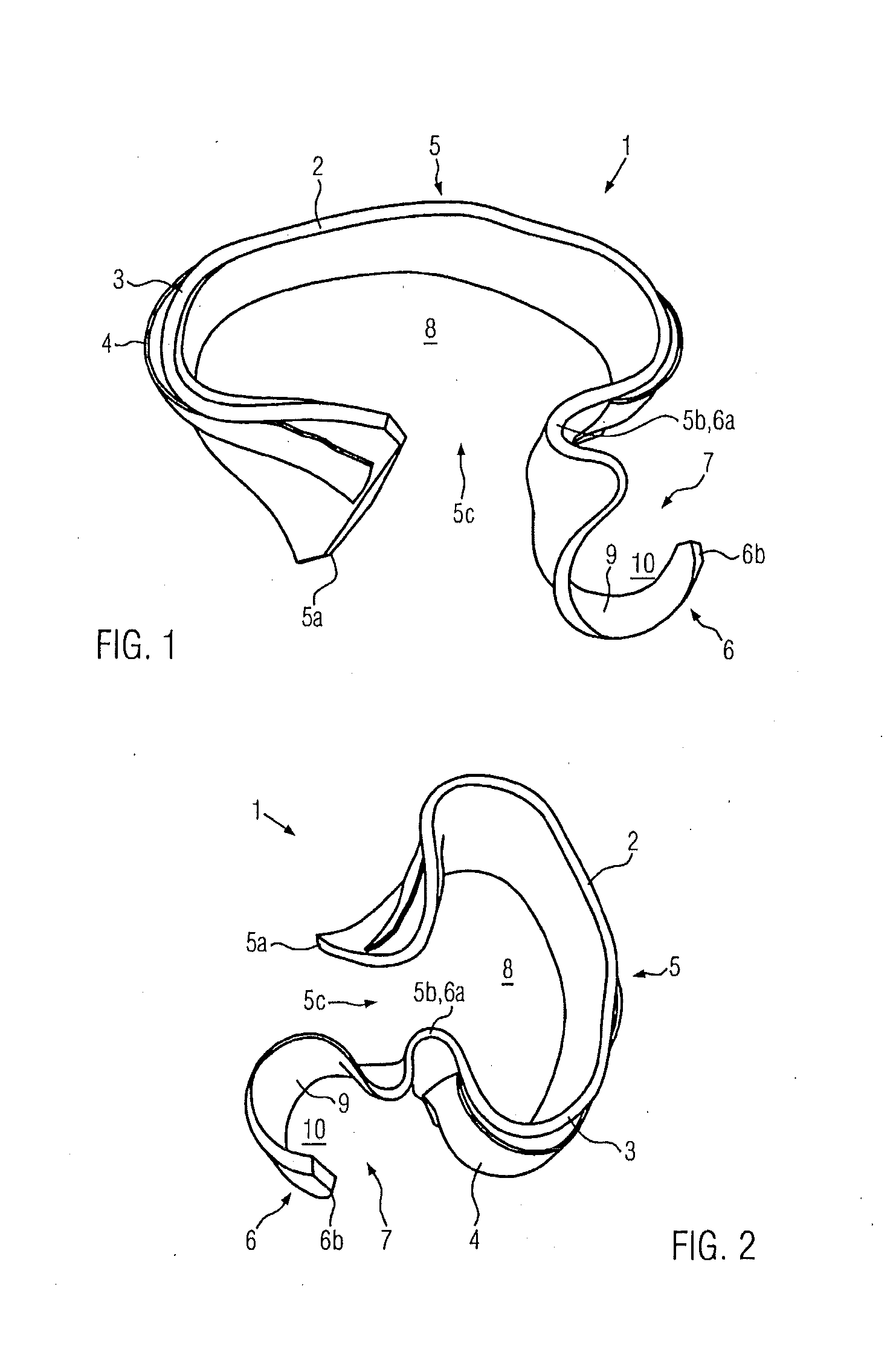
Carpometacarpal joint spacer
InactiveUS20100324693A1Stable positionRestore separationFinger jointsAnkle jointsJoint spacerPositive pressure
A swellable, resilient, flexible carpometacarpal (CMC) joint spacer is provided that is made of a swellable fluid absorbing polymeric medium, the spacer being dimensioned and configured to fit into the space between a natural or replacement trapezium and adjacent metacarpal bones and restore separation therebetween. In embodiments, the spacer has a cylindrical shape. In embodiments, the polymeric medium is a hydrogel. In embodiments, the spacer contains an internal reinforcement member. In embodiments, the spacer is delivered to a target site in at least a partially dehydrated state, whereupon it hydrates and expands to create positive pressure against opposing surfaces, thereby causing separation of the joint.
Owner:HARDENBROOK FREDERICK H
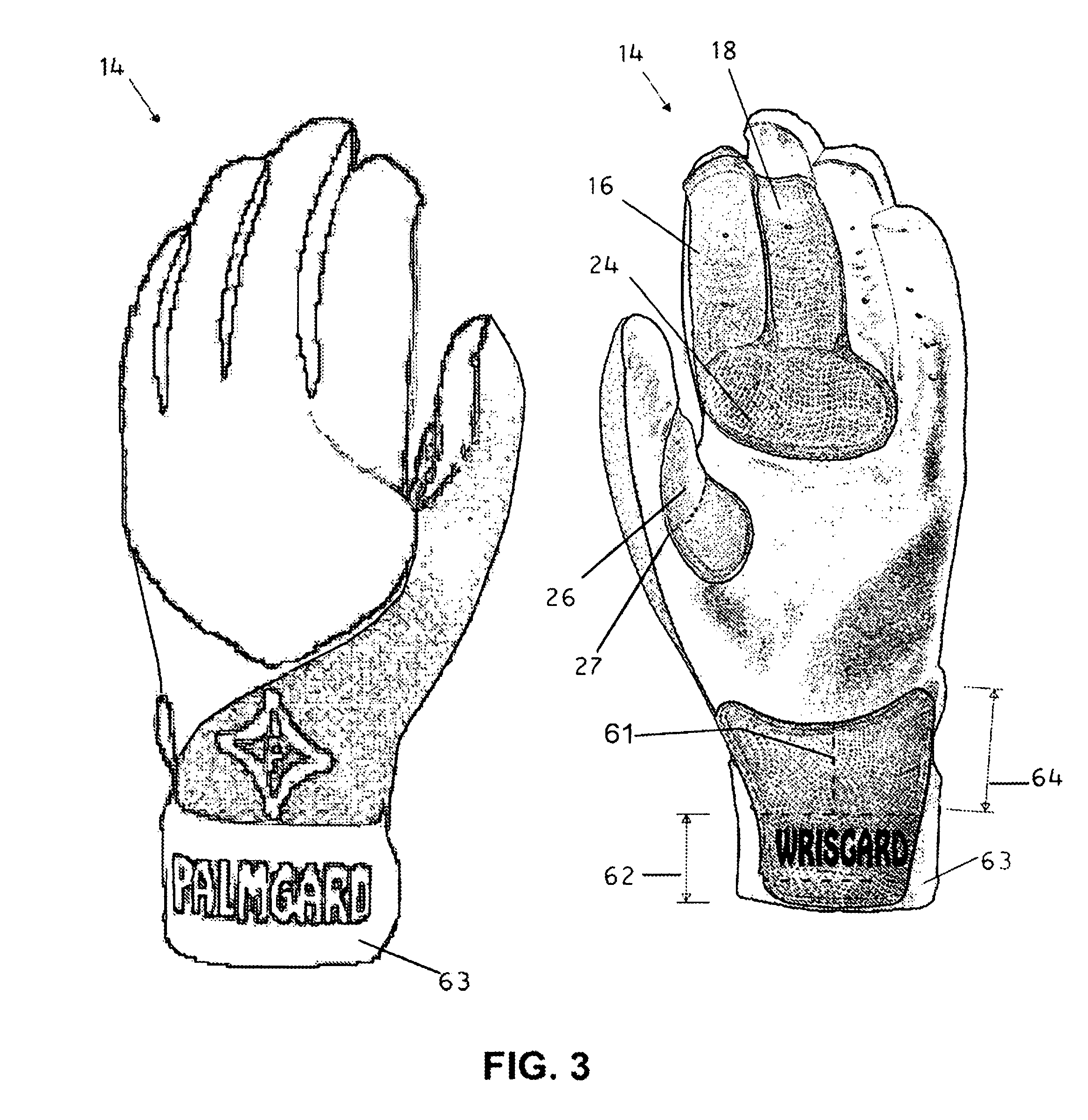
Sports glove for arthritic thumb carpometacarpal joint
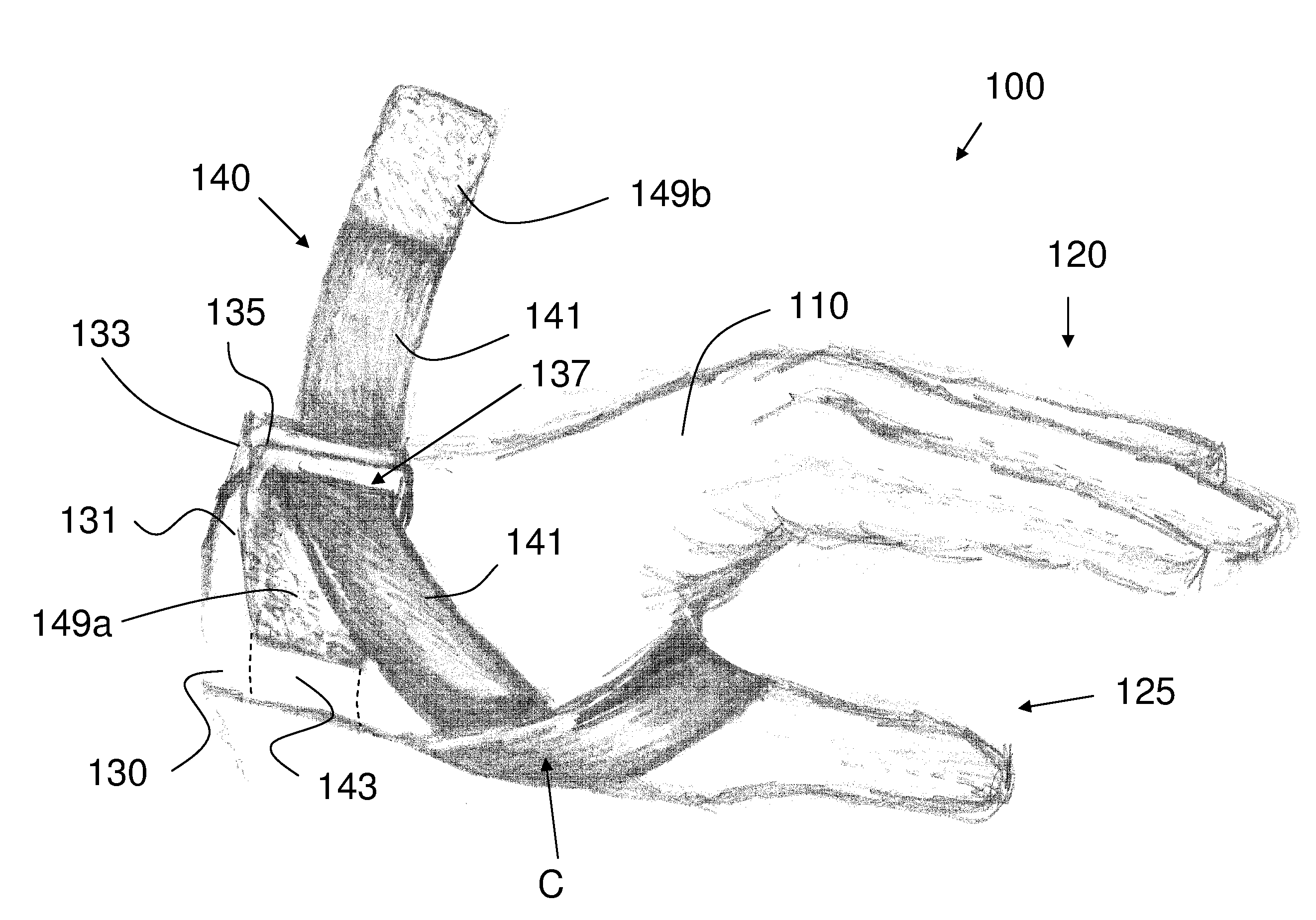
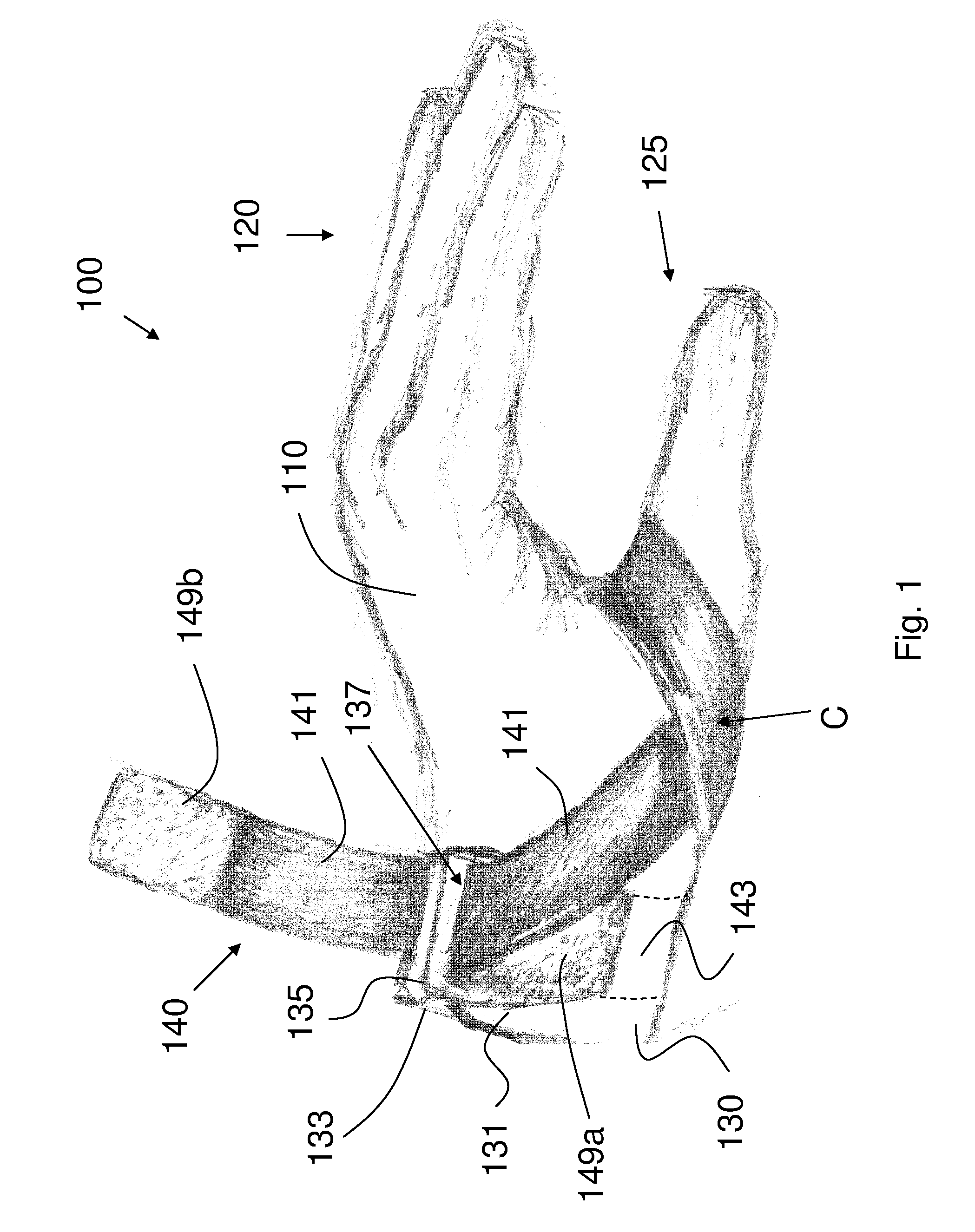
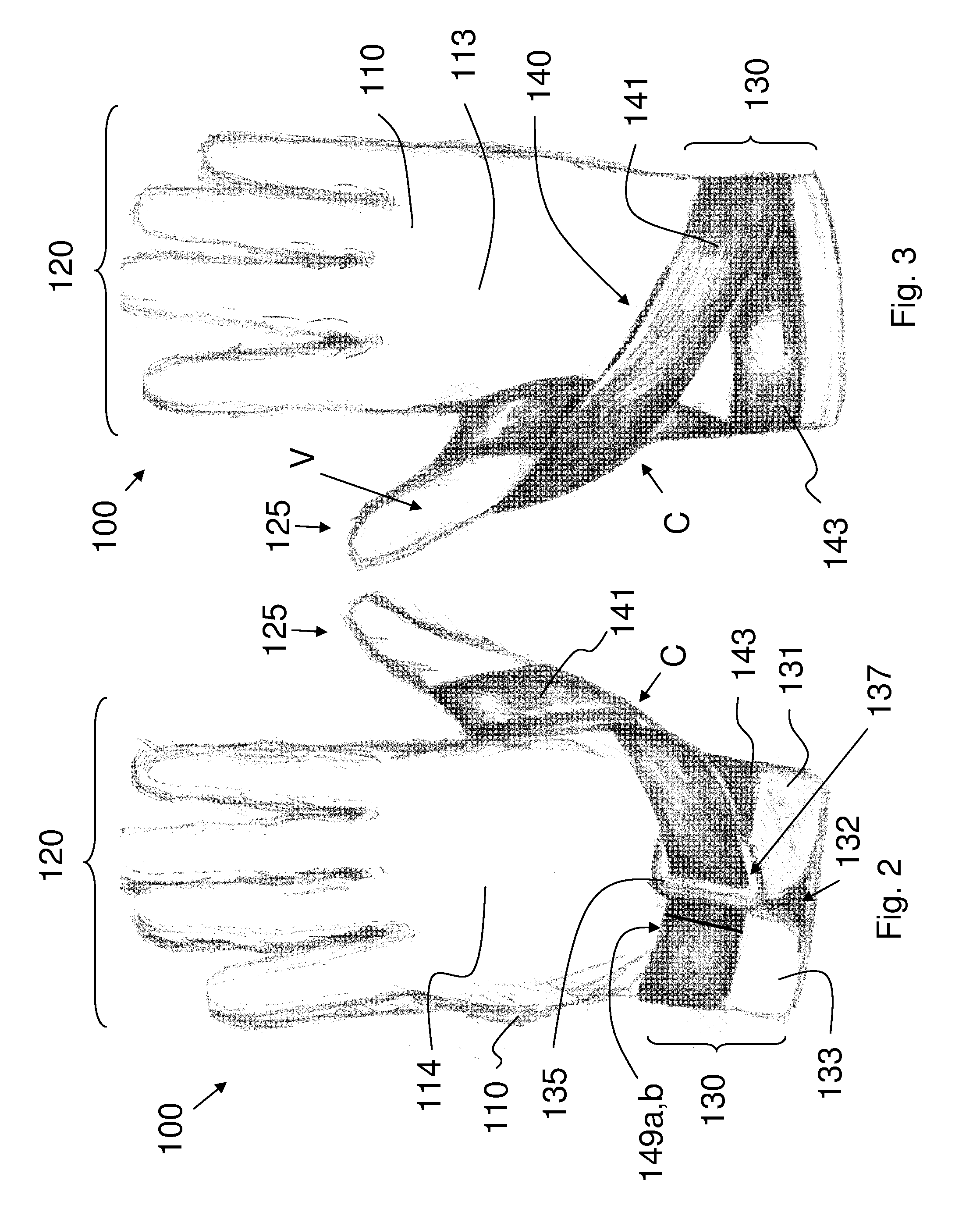
A glove for reducing lateral subluxation of the first carpometacarpal joint that includes a glove body, and a strap portion carried by the glove body. The strap portion extends from a proximal end portion of the glove, and has a length sufficient to allow the strap to be looped around the thumb, to provide dorsal-radial tension on the thumb near the distal end of the first metacarpal in order to reduce lateral subluxation at the first carpometacarpal joint. An attachment element is also provided for securing a distal end of the strap portion to a mutually engaging attachment element secured to the glove body.
Owner:ELKOWITZ STUART
Artificial implant for carpometacarpal joint
InactiveCN103815989AIncrease success rateEasy to fixFinger jointsAnkle jointsFirst metacarpal boneExoskeleton
The invention discloses an artificial implant for the carpometacarpal joint. The artificial implant is used for arthroplasty of the carpometacarpal joint surface of the first metacarpal bone and comprises an insert portion, an arthroplasty portion and an attached flange. The insert portion is provided with an insert end and a front end, the insert end is inserted into a marrow cavity exposed in an incision of the first metacarpal bone. The arthroplasty portion is connected to the front end of the insert portion and arranged outside the incision of the first metacarpal bone and is provided with a joint profile surface so as to substitute for the carpometacarpal joint surface of the first metacarpal bone. The attached flange is convexly arranged at a rim of the arthroplasty portion and used for flatly attaching to an exoskeleton surface of the incision adjacent to the first metacarpal bone. Besides, the attached flange is provided with at least one suture through hole for at least one suture to pass, so that abductor pollicis longus can be assisted in being fixed to the surface of the exoskeleton.
Owner:苏芳庆
Mobile apparatus
ActiveUS9742902B2Input/output for user-computer interactionElectrocardiographyTouchscreenMobile device
A smart phone includes photoelectric pulse wave sensing units that obtain photoelectric pulse wave signals from hands holding the smart phone, a touch screen on which a plurality of operation switches that accept operations performed by thumbs are displayed, and a switch arrangement changing unit that changes the arrangement of the displayed plurality of operation switches. The switch arrangement changing unit, when photoelectric pulse wave signals are obtained by the photoelectric pulse wave sensing units, changes the arrangement of the operation switches displayed on the touch screen in such a manner that the operation switches are arranged along a circular arc of a virtual circle whose center is located at a carpometacarpal joint of the thumb of a right hand performing operations and whose radius is the distance from the carpometacarpal joint to the tip of the thumb.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Prosthetic thumb mechanism
ActiveCN109620487ASolve the function of multi-directional and multi-modal graspingRealize multi-directional and multi-modal grasping functionArtificial handsProsthesisSecond carpometacarpal joint
The invention discloses a prosthetic thumb mechanism, and relates to the field of prosthesis. The mechanism comprises a first carpometacarpal joint mechanism, a second carpometacarpal joint mechanismand a thumb device. The second carpometacarpal joint mechanism and the first carpometacarpal joint mechanism are fixedly connected, the thumb device is connected with the second carpometacarpal jointmechanism, the first carpometacarpal mechanism achieves adduction and abduction, the second carpometacarpal joint mechanism achieves flexion and extension, and the thumb device achieves underactuationof first and second joints. The prosthetic thumb mechanism can be interchanged between the left hand and the right hand. The second carpometacarpal joint mechanism and the thumb device simultaneouslyachieve coupling movement by a worm wheel and linear transmission. The prosthetic thumb mechanism has the functions of simple structure, multiple degrees of freedom and light weight, so that the prosthetic thumb can achieve the multi-directional multi-modal grasping function.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for trapezium bone replacement
A carpometacarpal joint replacement system for replacing the trapezium bone in the hand is provided. The system includes a trapezial implant for the carpometacarpal joint resulting in replacement of the carpal trapezium bone with a prosthesis having the same anatomical configuration as the trapezium bone. The implant device comprises a plurality of concave surfaces, with the plurality of concave surfaces articulating with the carpal and metacarpal bones.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
Thumb orthosis
ActiveUS20150157483A1Low mobilityReduced functionalityNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisEngineering
An orthosis for fastening to a human hand for immobilizing the carpometacarpal joint and metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb of the hand has a stiff body which can be of multi-piece or single-piece design. The rigidity of the body enables the latter to support, to stabilize and to immobilize the hand and dimensional stability is provided such that the body can be placed in a simple manner with a defined shape onto the hand.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL GMBH & CO KG
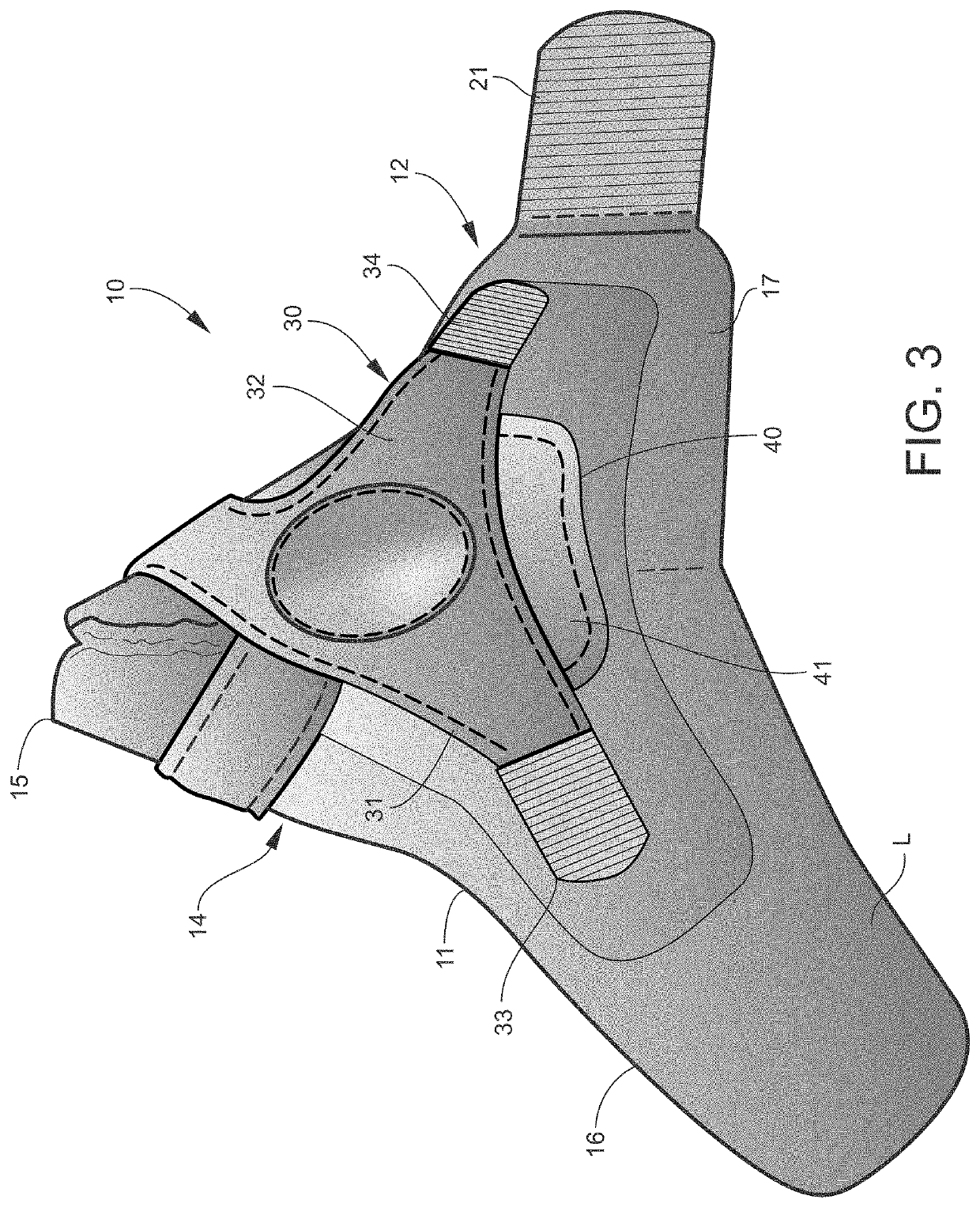
Orthopedic thumb splint and method for stabilizing the trapeziometacarpal joint of a user
An orthopedic thumb splint is adapted for stabilizing a carpometacarpal joint of a user. The exemplary thumb splint includes a flexible fabric splint body having a wrist portion and a generally funnel-shaped thumb portion. The thumb portion defines a narrowed opening for receiving a thumb of the user. A thumb-abducting flexible X-strap is secured to the splint body adjacent the narrowed opening of the thumb portion. The X-strap has first and second diverging distal ends having respective inside surfaces. The inside surface of each distal end includes touch fasteners designed to releasably mate with complementary touch fasteners located on an outside surface of the splint body.
Owner:MEDICAL SPECIALTIES
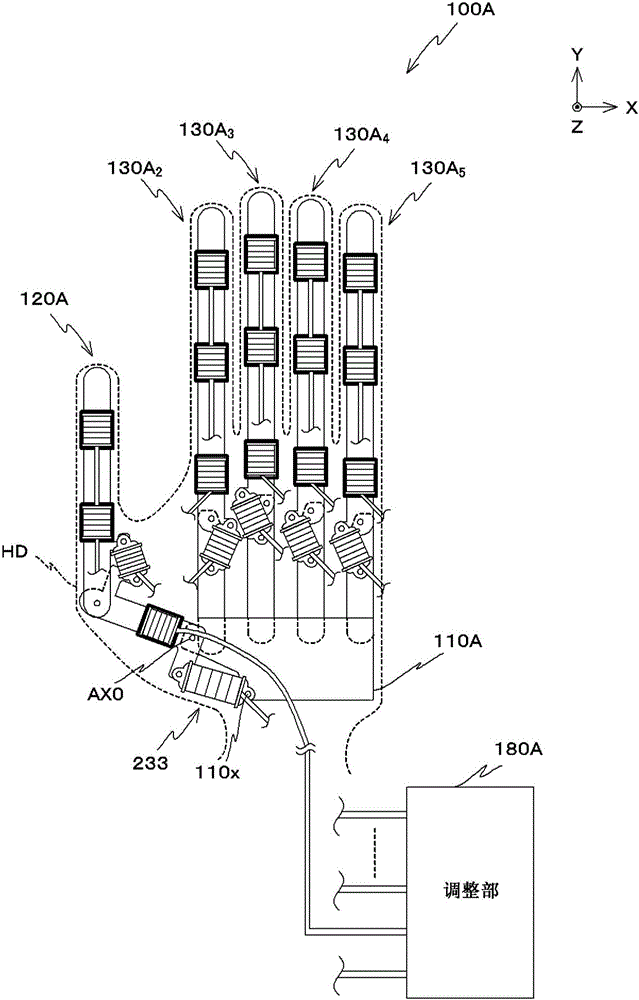
Joint movement assist device
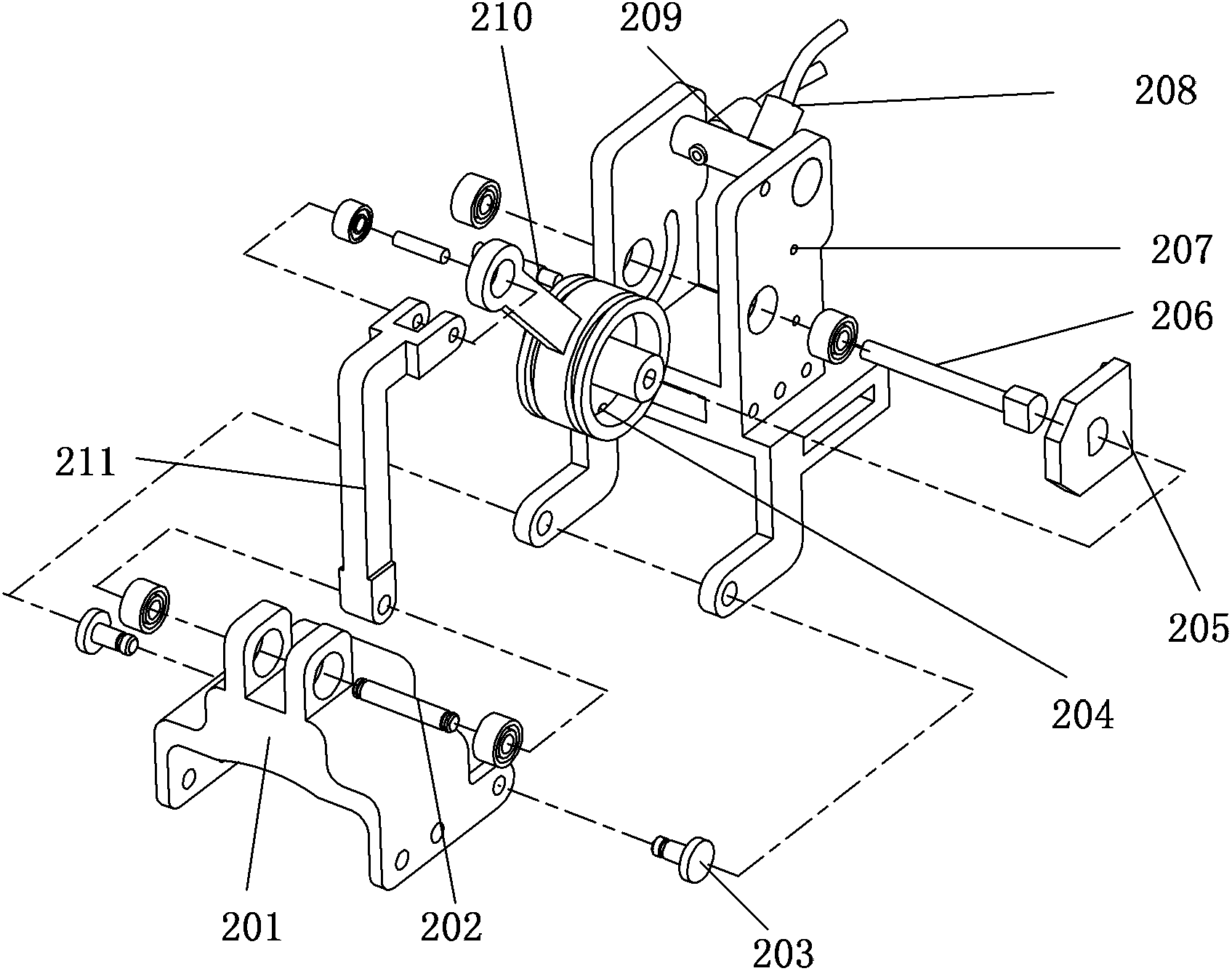
When the joint movement assist device according to the present invention is worn on a hand, and a first bellows (231) is expanded or contracted, a second thumb metacarpal scaffold member (212) rotates with respect to a first thumb metacarpal scaffold member (211A), about an axis of rotation which is a first axis that is "one joint axis" of a biaxial saddle joint. An elastic member (251) elastically restrains the part of the first bellows (231) that faces the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb so as to allow expansion and contraction between the portions connected to the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, and as to enable the distance between one end section of the first thumb metacarpal scaffold member (211A) and one end section of the second thumb metacarpal scaffold member (212) to change smoothly. The expansion and contraction of a second bellows (232a) causes a third thumb metacarpal scaffold member (213) to rotate with respect to the second thumb metacarpal scaffold member (212), about a central axis which is a second axial member (AX2) that perpendicularly intersects the first axis. Thus, appropriate assistance can be provided for joint movements similar to the joint movements of the hand of a healthy person.
Owner:山本 圭治郎 +2
Hand joint supporter
ActiveCN102724891APrevent tenosynovitisReduce loadFinger bandagesWeft knittingSacroiliac jointBiomedical engineering
Provided is a hand joint supporter which can reduce the load on the hand joints and prevent hand tenosynovitis. The hand joint supporter (10) comprises a first anchor section (2) for tightening the wearer's forearm with a tubular knitted fabric, a second anchor section (3) for tightening the palm and back of the wearer's hand with the tubular knitted fabric, a hole anchor section (11) being formed as a roughly circular through-hole in the vicinity of the second anchor section (3) in the tubular knitted fabric to insert the wearer's thumb therethrough, and a supporting section (4) extending in the front side and / or back side of the tubular knitted fabric, along the lengthwise direction of the tubular knitted fabric, across the part covering the caprometacarpal joint and being joined to the first anchor section (2) and the hole anchor section (11) so as to support the wearer's hand joints, wherein the stretch resistance, in the circumferential direction of the tubular knitted fabric, of the first anchor part (2) is larger than the stretch resistance, in the circumferential direction of the tubular knitted fabric, of a base fabric section (1), and the stretch resistance, in the length width direction of the tubular knitted fabric, of the supporting section (4) is larger than the stretch resistance, in the length width direction of the tubular knitted fabric, of the base fabric section (1).
Owner:KOWA CO LTD +1
Protective glove for use in athletics
A glove worn within a conventional baseball mitt to protect the wrist and hand. The glove generally comprises a fitted glove of soft leather with a plurality of attached non-springy, shock absorbing cushions including a radioulnar cushion extending proximally one to three inches up the forearm from a first end at the wrist crease to a second end and in width a distance sufficient to cover the palmar side of the wrist, and a carpal cushion extending distally from the wrist crease a distance sufficient to cover the carpometacarpal joint of the hand and in width a distance sufficient to cover the carpometacarpal joint of all five digits, including the carpal cushion including a line of reduced padding, typically compressive stitching, extending from the first wrist crease edge to the distal edge which edge may be arcuate to provide additional protection and conform to the shape of the ball glove.
Owner:MARKWORT SPORTING GOODS
Postoperative fixing device for mallet finger
InactiveCN103845140AImprove comfortLittle side effectsFractureTreatment demandPostoperative recovery
The invention relates to the field of treatment of mallet fingers, and in particularly relates to a postoperative fixing device for a mallet finger. The device comprises a fixing plate and a fixing belt, wherein the fixing plate is a sheet body provided with a groove on the lower surface, the fixing plate is spoon-shaped from side-looking, and the fixing plate comprises a carpometacarpal joint fixing sheet, a finger hill section fixing section, a finger median segment fixing section and a distal finger fixing section from the front end to the tail end. The distal finger fixing section extends upward from the tail end of the finger median segment fixing section, and the finger hill section fixing section and the finger median segment fixing section as well as the finger median segment fixing section and the distal finger fixing section are in circular arc transition. According to the treatment demand, angles among the three sections are designed to facilitate postoperative recovery. The fixing belt is designed in sections and the carpometacarpal joint fixing sheet is additionally arranged, so that the fixing effect is good. The comfort level of the patient is improved due to arc shapes at transition of three sections, the groove and the cushion layer.
Owner:王众
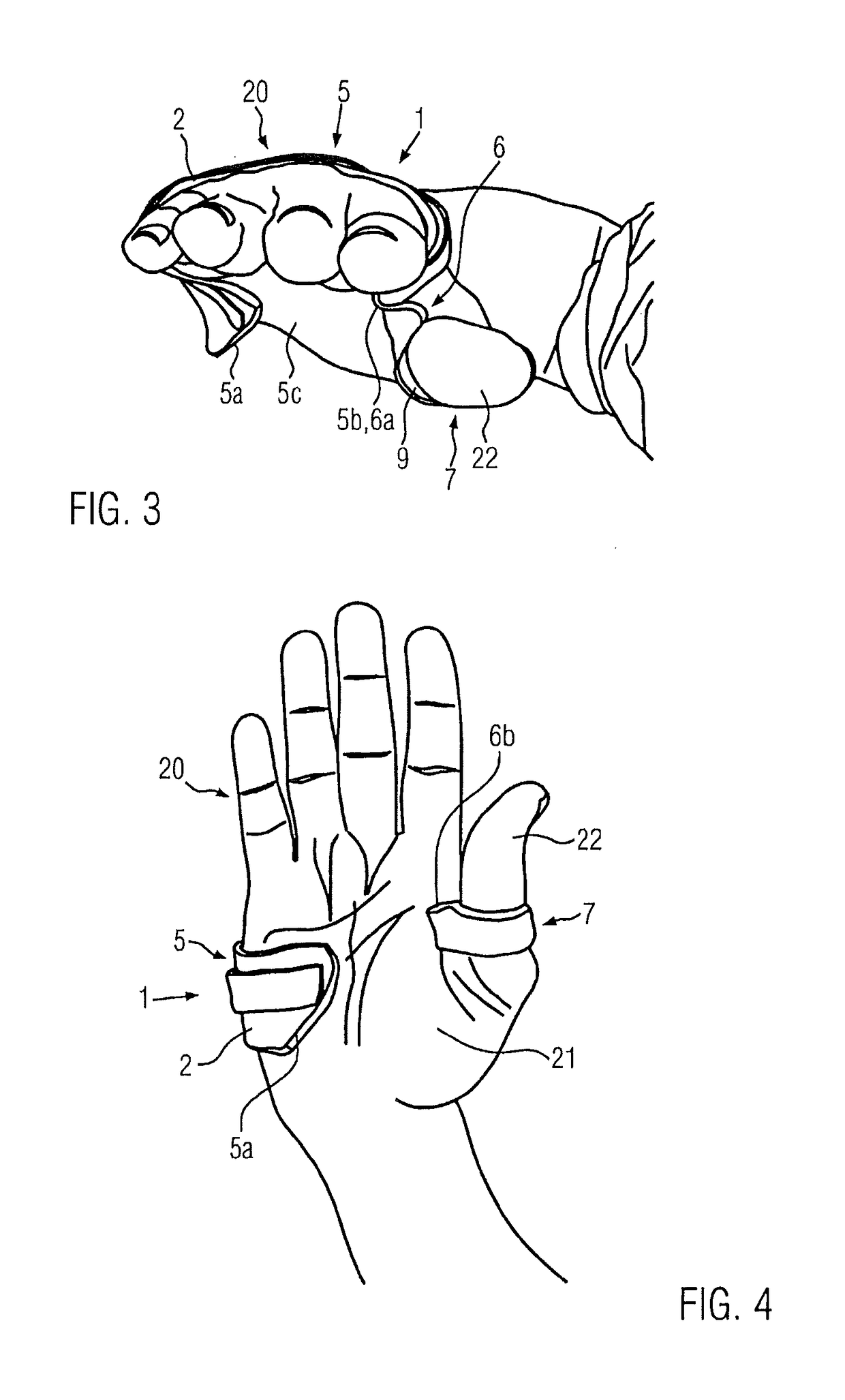
Carpometacarpal joint of bionic hand
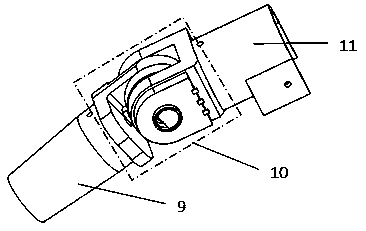
The invention relates to a carpometacarpal joint of the thumb of a bionic artificial hand. The carpometacarpal joint of the thumb of the bionic artificial hand is provided with a joint gear 6, and the axis position of the gear is made to correspond to the movement axis of a thumb carpometacarpal joint of a human hand. The thumb is driven by a micromotor 2 to rotate around the axis of the joint gear 6, so that the actions of opening and closing of the thumb are completed. A lateral rotating shaft 9 of the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb is fixed to the joint gear 6, and the axis of the lateral rotating shaft 9 and the axis of a thumb opening-closing shaft 7 perpendicularly intersect at the axis of the joint gear 6. The thumb is driven by another micromotor 12 to rotate in the side direction of the axis of the joint gear. The elevation angle of the lateral rotating shaft 9 of the thumb relative to a palm is equivalent to the elevation angle of the thumb relative to the palm when the human hand is relaxed. The functions, actions and appearance of the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb are closer to those of the human thumb, and the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb is simple and reliable in structure and good in practical effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI KESHENG PROSTHESES
Exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN102319162BSolve the problem of bad wearingSuitable for wearingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesDrive shaftEngineering
The invention relates to an exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot. The robot comprises an execution part, a transmission part and a drive part, wherein the execution part is divided into an interphalangeal joint module, a metacarpophalangeal joint module and a carpometacarpal joint module; in the carpometacarpal joint module, a metacarpal seat is fixed on the palm and wrist of a patient; the metacarpal seat and a metacarpal seat connector form a dip angle of 30 degrees, and the metacarpal seat connector has an angle of 45 degrees; an angle sensor is fixedly connected to a joint horizontal rotor, and is fixedly connected with an abduction / adduction coil; an adjustable bearing block is fixedly connected with a size adjusting jack; one end of a palm driven rod and the adjusting bearing block form a rotating pair, and the other end of the palm driven rod and a palm drive rod form a rotating pair; and the palm drive rod is fixed on a palm drive shaft, and the drive shaft and a palm drive bearing block form a rotating pair. According to the exoskeletal thumb moving function rehabilitation robot, four degrees of freedom active and passive rehabilitation of the thumb can be realized, and the problem that the robot is difficult to wear due to the difference between the physiological structure of the thumb and the other four fingers can be solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Thumb orthosis
ActiveUS10080679B2Low mobilityReduced functionalityNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEngineeringOrthotic device
An orthosis for fastening to a human hand for immobilizing the carpometacarpal joint and metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb of the hand has a stiff body which can be of multi-piece or single-piece design. The rigidity of the body enables the latter to support, to stabilize and to immobilize the hand and dimensional stability is provided such that the body can be placed in a simple manner with a defined shape onto the hand.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL GMBH & CO KG
Venipuncture practice glove
A venipuncture practice glove is mainly formed by nesting an inner anti-leakage layer provided with a simulation blood vessel and a blood storage bag in an outer simulation human skin layer, wherein the blood storage bag mainly comprises a first blood storage bag body and a second blood storage bag which are arranged on the inner anti-leakage layer; the blood storage bag bodies are communicated with each other through the simulation blood vessel; the first blood storage bag body is located at the carpometacarpal joint of the glove; the second blood storage bag body is located at the tail end of the glove; simulation blood is perfused into the venipuncture practice glove, then the venipuncture practice glove is put on an arm of a simulation patient, the first blood storage bag body can be squeezed through bending of finger joints when the simulation patient makes a fist, and the simulation blood vessel between the first blood storage bag body and the second blood storage bag body is full of the simulation blood with certain pressure. A student can make puncture practice as on a true patient's body, and the training effect is fully realized.
Owner:TIANJIN TELLYES SCI
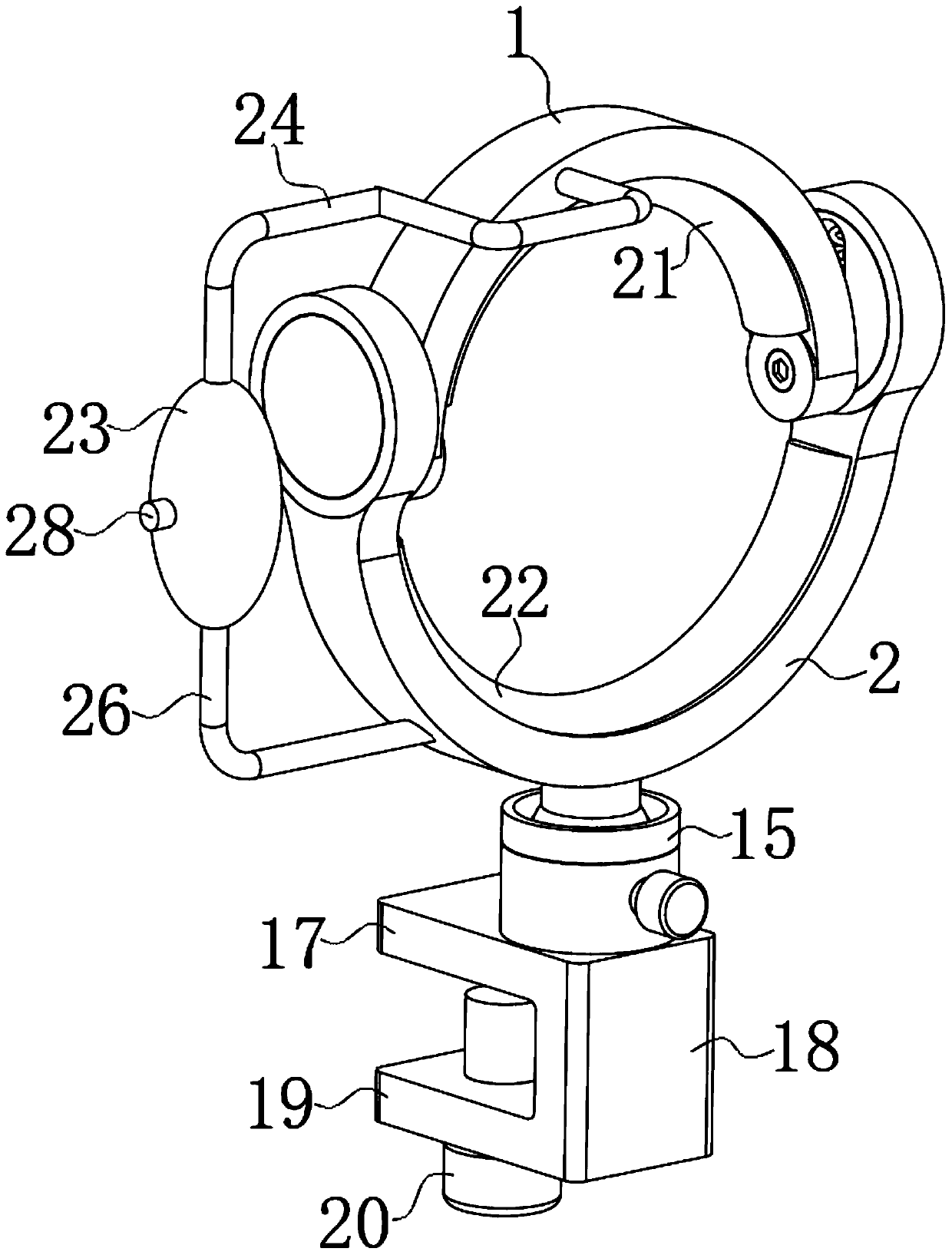
Traditional Chinese medicine plintlet carpometacarpal joint external fixation device
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine plintlet carpometacarpal joint external fixation device which comprises an upper fixing ring and a lower fixing ring. The bottom end of the upperfixing ring is fixedly connected with a fixing ring, a rotating block is rotatably mounted on the inner side of the fixing ring, the inner side of the rotating block is provided with a moving groove,the inner wall of the moving groove is provided with a sliding groove, a moving block is disposed in the moving groove, the outer wall of the moving block is fixedly connected to a sliding block, theouter wall of the sliding block is slidably connected to the inner wall of the sliding groove, the top inside a chamber of the moving groove is provided with a first fixing groove, the top surface ofthe moving block is provided with a second fixing groove, and a spring abuts between the first fixing groove and the second fixing groove. The traditional Chinese medicine plintlet carpometacarpal joint external fixation device has the advantages of being simple in structure and convenient to adjust, and the problems that an existing mode has a poor fixing effect and brings great inconvenience tothe treatment process is solved.
Owner:余利忠
Artificial implant for carpometacarpal joint
InactiveUS20150297355A1Easy to optimizeIncrease success rateSuture equipmentsFinger jointsArticular surfaceAbductor Pollicis Longus
An artificial implant for a carpometacarpal (CMC) joint used for replacing a CMC joint surface of the first metacarpal bone is provided and has: an insert portion having an inserting end for inserting into a bone marrow cavity exposed from an incision of the first metacarpal bone, and a front end; an articular replacement portion connected to the front end of the inserting portion and disposed outside the incision of the first metacarpal bone, and having an articular profile surface to replace the CMC joint surface of the first metacarpal bone; and an attached flange protruded from a peripheral of the articular replacement portion, attached to an outer bone surface of the first metacarpal bone adjacent to the incision, and having at least one suture hole, through which at least one suture passes for assisting to fix an abductor pollicis longus (APL) to the outer bone surface.
Owner:SU FONG CHIN
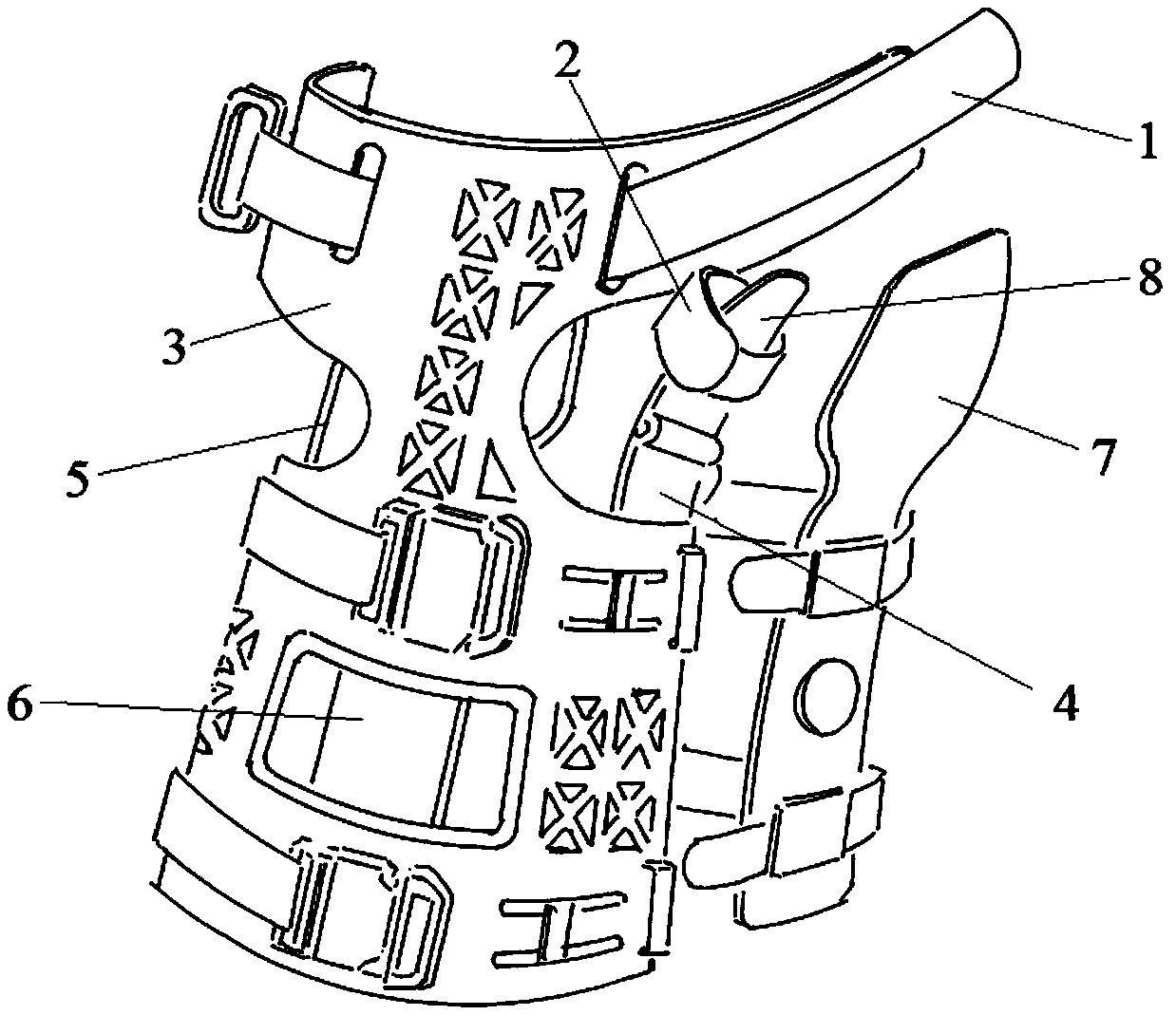
External splintage fixing device for wrist-palm joint of traditional Chinese medicine
PendingCN108652816AGood treatment effectStable mechanical properties of external fixationFractureHuman bodyTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses an external splintage fixing device for wrist-palm joint of traditional Chinese medicine, which comprises a palm plate, a radius-side splint, a ulna-side splint, a back-side splint and a palm-side splint which are used for covering the hand of a human body, a first belt used for fixing the palm plate, the radius-side splint, the ulna-side splint, the back-side splint and the palm-side splint on the hand part of the human body, and an extension splint which is arranged on the radius-side splint and is used for being fixed to the thumb of the hand of the human body. According to the invention, through the matching of the palm plate and the four splints, a whole medical device with mechanical quantitative relationship is formed, the external fixing mechanical propertyis stable, based on the principle of elastic fixing, the characteristics of the splintage of the traditional Chinese medicine are fully maintained, the external fixation is safe and reliable, the comfort and the matching properties of the wrist-palm joint of the human body are provided, and the treatment effect of external fixation treatment of the wrist-palm fracture is improved.
Owner:芜湖普敦特医疗器械有限公司
bionic hand thumb wrist metacarpal joint
ActiveCN105965535BThe overall structure is simple and reliableImprove practicalityJointsElevation angleEngineering
The invention relates to a carpometacarpal joint of the thumb of a bionic artificial hand. The carpometacarpal joint of the thumb of the bionic artificial hand is provided with a joint gear 6, and the axis position of the gear is made to correspond to the movement axis of a thumb carpometacarpal joint of a human hand. The thumb is driven by a micromotor 2 to rotate around the axis of the joint gear 6, so that the actions of opening and closing of the thumb are completed. A lateral rotating shaft 9 of the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb is fixed to the joint gear 6, and the axis of the lateral rotating shaft 9 and the axis of a thumb opening-closing shaft 7 perpendicularly intersect at the axis of the joint gear 6. The thumb is driven by another micromotor 12 to rotate in the side direction of the axis of the joint gear. The elevation angle of the lateral rotating shaft 9 of the thumb relative to a palm is equivalent to the elevation angle of the thumb relative to the palm when the human hand is relaxed. The functions, actions and appearance of the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb are closer to those of the human thumb, and the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb is simple and reliable in structure and good in practical effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI KESHENG PROSTHESES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com