Ocular delivery of drugs
a technology for ocular delivery and drugs, applied in the field of new, can solve the problems of low ocular bioavailability of formulations, inconvenient ocular surface inflammation, and inability to optimally deliver restasis®, and achieve good stability, tolerability and bioavailability, and the effect of suitable ophthalmic compositions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0085]Materials And Methods
[0086]Polymer
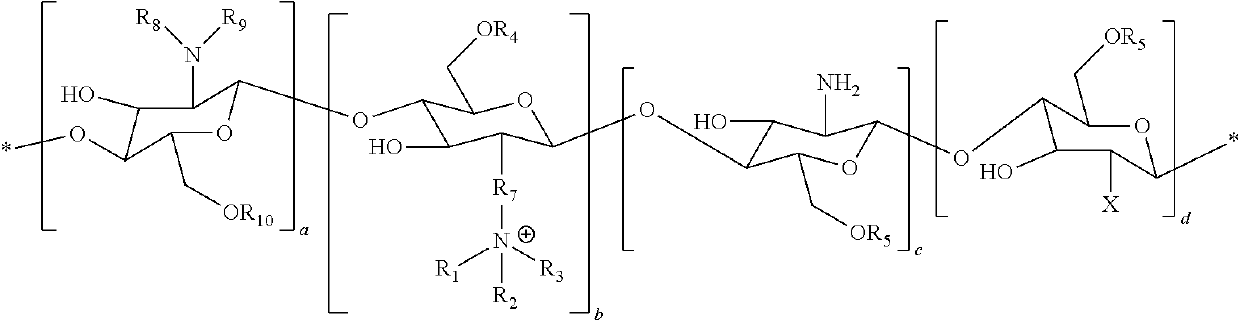
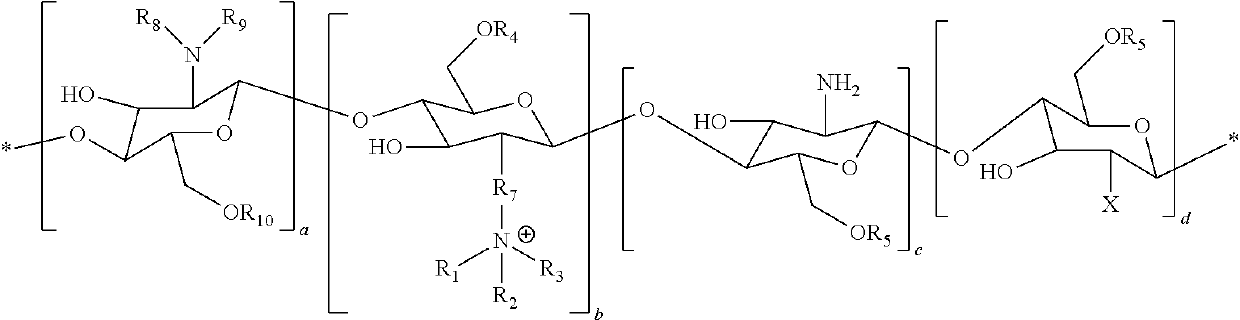
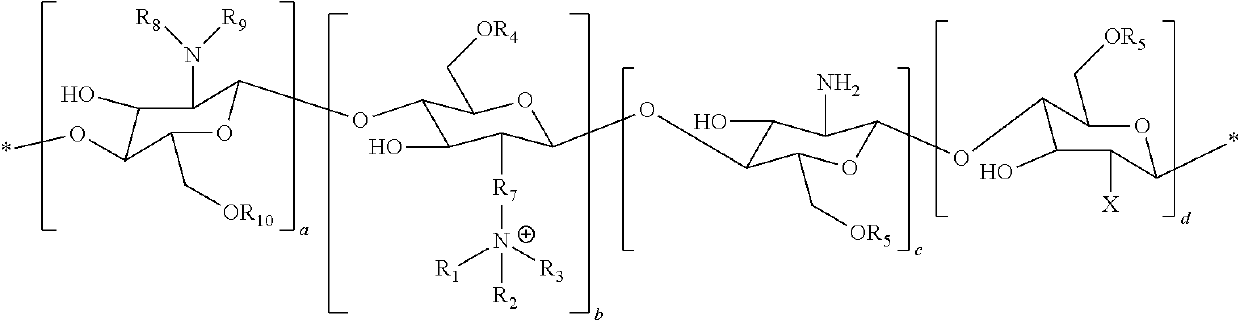
[0087]N-palmitoyl-N-monomethyl-N, Ndimethyl-N,N,N-trimethyl-6-O-glycolchitosan (GCPQ) was synthetized and characterized as previously described in I. F. Uchegbu, A. G. Schatzlein, X. Hou, Polymeric micellar clusters and their uses in formulating drugs, in, US20100159014 A1. The GCPQ used for the experiments had 20.51 Mol % of palmitoyl groups per monomer units, 11.93 Mol % of quaternary ammonium groups per monomer units, and a molecular weight of 9.13 KDa.
[0088]CsA Compositions
[0089]The composition containing CSA was prepared as follows. To a weighed sample of the polymer and weighed sample of the drug was added phosphate buffered saline (pH=7.4, 20 mL). The initial polymer, drug weight ratio was 7.5: 1 and the drug content was adjusted to give a concentration of 0.05%, 0.08% and 0.1% w / v. The liquid mixture was vortexed for two minutes to ensure complete mixing and subsequently subjected to high pressure homogenisation (Avestin Emulsiflex, GC...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com