Paclitaxel nanoemulsion inhalation preparation for targeted therapy of lung cancer and preparation method of paclitaxel nanoemulsion inhalation preparation
A technology for targeted therapy and inhalation preparations, which is applied in the field of preparation of paclitaxel nano-preparations, can solve problems such as toxic side effects, blood drug concentration approaching or exceeding the poisoning level, etc., achieve simple preparation methods, increase encapsulation efficiency and drug loading, Reduce the effect of the initial burst
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
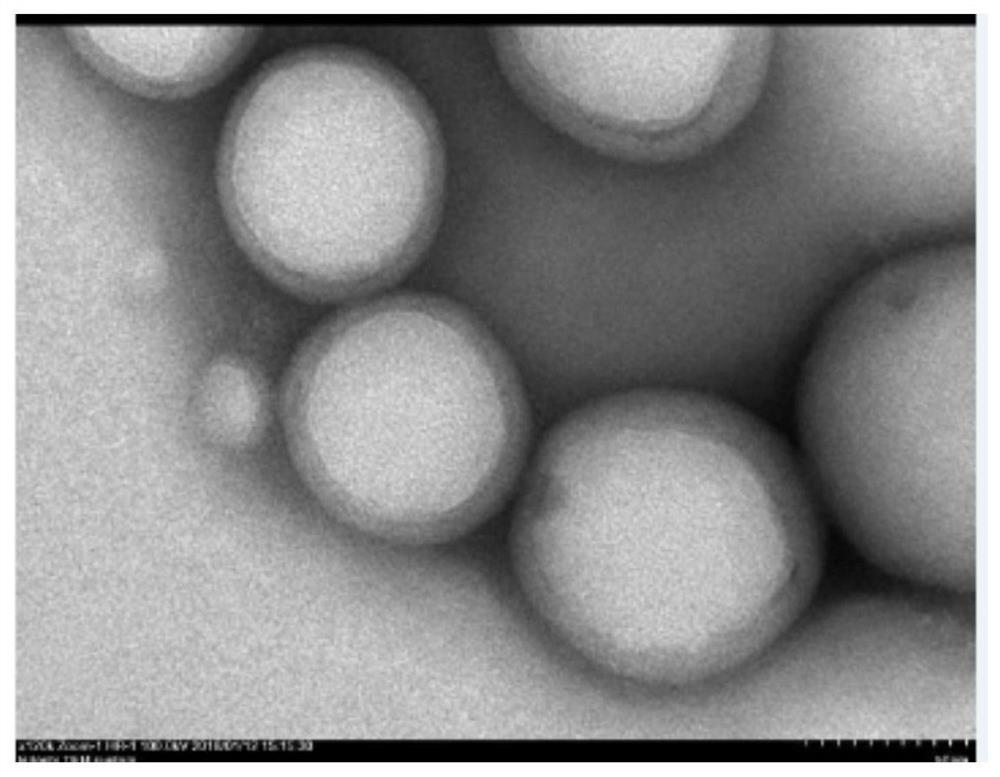
[0034] Weigh about 1 mg of paclitaxel and 0.800 g of PLGA and dissolve in 2 mL of dichloromethane as the organic phase; 250 μL of 1.0% poloxamer and 250 μL of water are mixed as the inner aqueous phase. After emulsification, inject the mixed solution (10 mL of 0.5% PVA+0.5 mL of 2% chitosan solution), stir at room temperature to evaporate the organic solvent, stir at low speed at 5000 rpm for 20 min to remove insoluble matter, and wash with water 3 times.
Embodiment 2
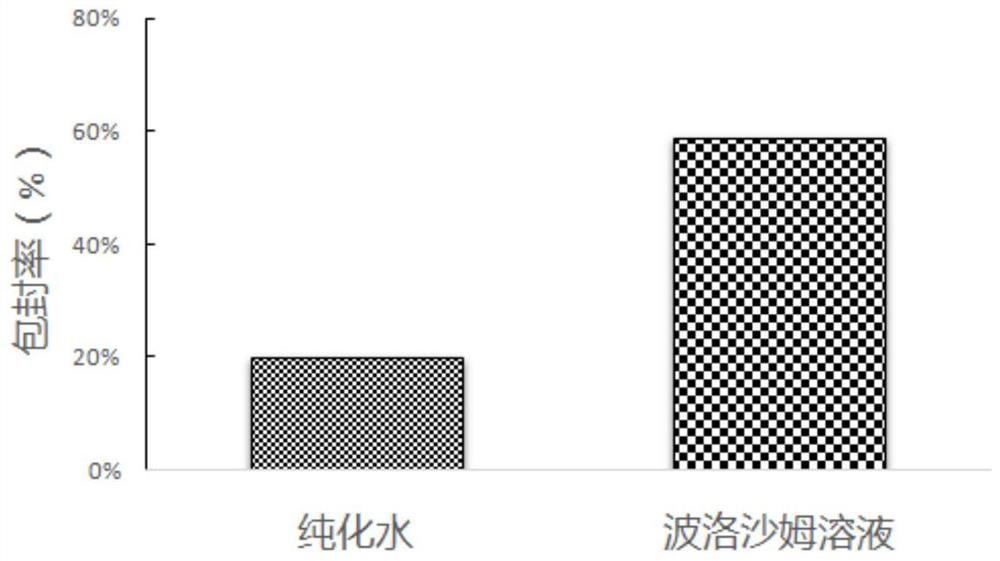
[0036] Comparison of encapsulation efficiency of chitosan-modified PLGANA nanoemulsion in poloxamer inner aqueous phase and PLGA nanoemulsion with water as inner aqueous phase.
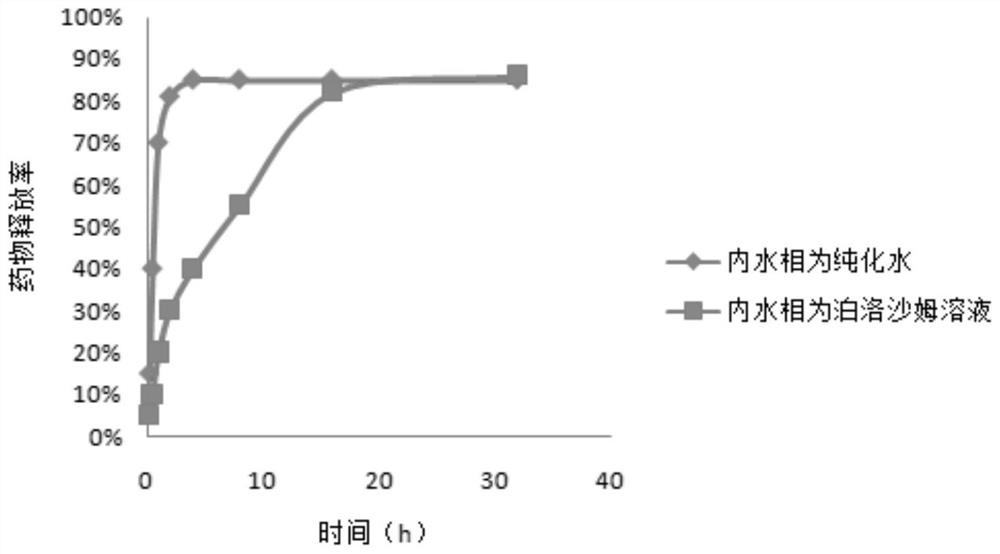
[0037] Precisely weigh 10 mg of nanoemulsion lyophilized powder, dissolve in PBS, re-disperse by ultrasonic treatment for 100w 3min, and transfer the PLGA nanoemulsion into an ultrafiltration tube. High-speed refrigerated centrifugation at 7000rpm for 30 minutes at 4°C to separate nanoparticles and supernatant. The content of the drug in the ultrafiltrate was determined by high performance liquid chromatography, and then the encapsulation rate and release rate were calculated. The encapsulation rate results are shown in figure 2 , the release rate results see image 3 .
Embodiment 3
[0039] The curative effect of the inhalation injection of the present invention was compared with the mouse model transplanted with mouse-derived Lewis lung cancer cells. The tumor-receiving mice were divided into three groups, and one group was given conventional paclitaxel injection (45 mg / kg) through the tail vein, once every two weeks and twice. One group was administered with a self-made inhalation applicator (10 mg / kg), once every two weeks, twice. The positive control group was not administered by any means. Compared the results, it was found that the survival time of the mice in the intravenous administration group and the inhalation administration group was not much different, about 21-23 days, and the mice in the non-administration group only survived for 11.5 days. The dosage of the inhalation preparation of the present invention is small, and the administration effect of the inhalation preparation is equivalent to that of the injection in a large dosage.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com