Carbide-containing high-strength high-toughness bainite wear-resistant steel and preparation method thereof
A high-strength toughness and wear-resistant steel technology, applied in the field of wear-resistant steel, can solve the problems of difficulty in improving toughness and insufficient toughness reserves.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] The preparation method of the above-mentioned carbide-containing high-strength toughness bainitic wear-resistant steel disclosed by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0041] 1) Smelting and forging: use an electric furnace or a converter to smelt the molten steel of the above-mentioned bainite wear-resistant steel. The chemical composition of the bainite wear-resistant steel is: C is 0.6-1.2wt%, Si is 1.2-2.5wt%, and Mn is 0.8 ~2.0wt%, Cr is 5~10wt%, P≤0.015wt%, S≤0.01wt%, Mo is 0.3~0.7wt%, Ni is 0.3~0.7wt%, the balance is Fe and unavoidable trace impurities ;Molten steel needs to be subjected to conventional refining outside the furnace and conventional vacuum degassing treatment, and RE is added after degassing, cast into an ingot, and then the ingot is rolled or forged into a plate, which contains spherical carbide and spheroidized Pearlite structure; if the ingot is forged into a plate, the forging process is as follows: the heating temperature i...
Embodiment 1
[0045] 1. Melting: Melt high-quality steel scrap in an electric furnace, add ferrosilicon, ferrochromium, electrolytic manganese, molybdenum, and carburizers to adjust to the required composition, then transfer to a refining furnace for refining, and add rare earth to further purify the composition after degassing. Cast into ingots. The obtained ingot composition is: C is 0.9wt%, Si is 1.5wt%, Mn is 1.5wt%, Cr is 9wt%, Mo is 0.5wt%, Ni is 0.5wt%, P is 0.016wt%, S is 0.006 wt%, the balance is Fe and unavoidable trace impurities.
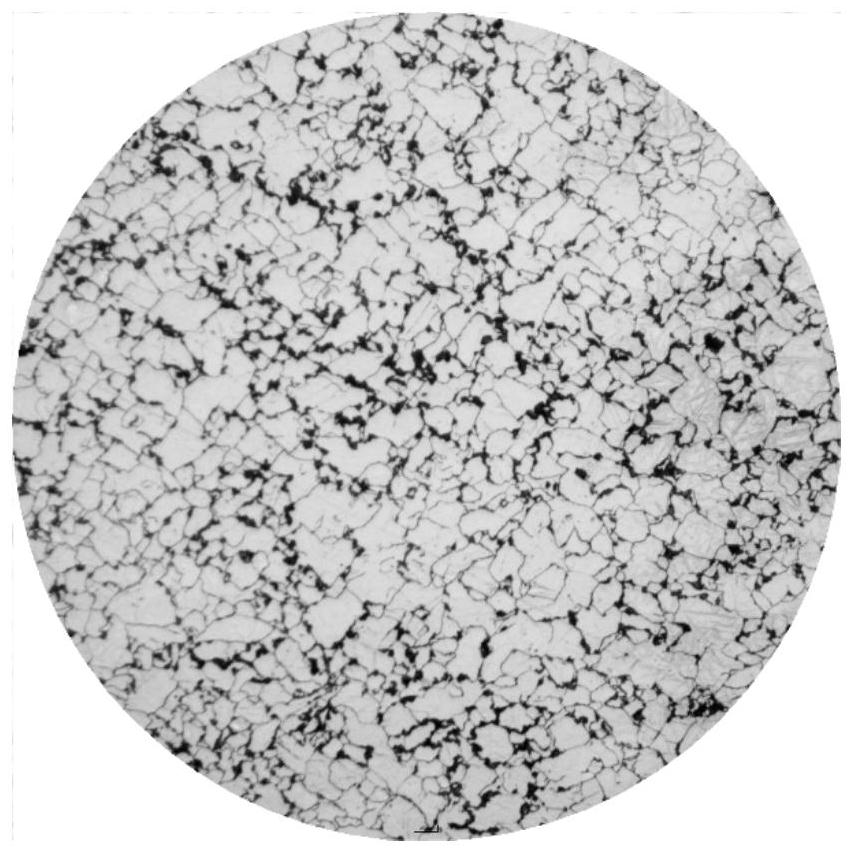
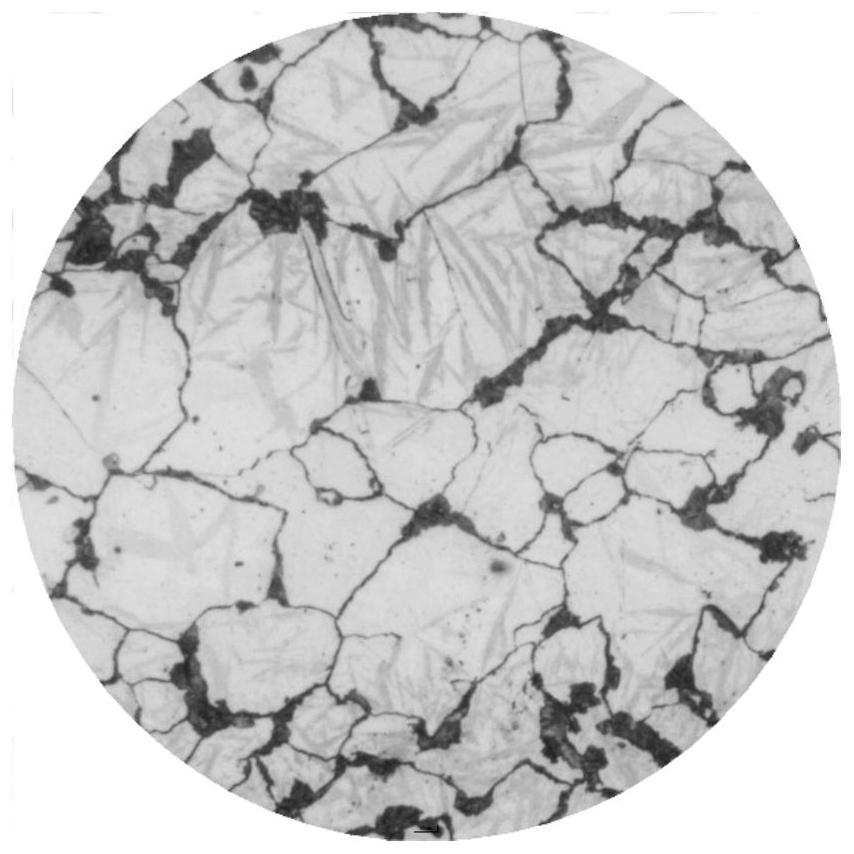
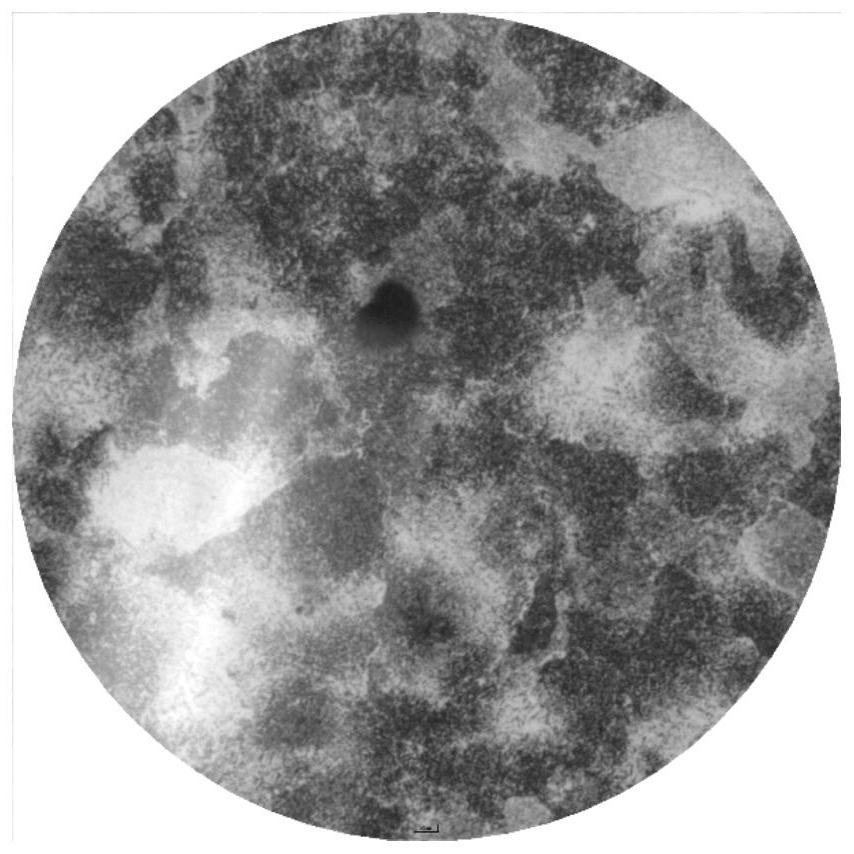
[0046] 2. Forging: Forging heating temperature is 1150-1180°C, initial forging temperature is 1120°C, final forging temperature is 950°C, forging ratio is 8, after forging a forging with a thickness of 300mm, it is slowly cooled to room temperature, and then spheroidized and annealed; the microstructure is Spheroidal carbides and pearlite matrix, such as figure 1 , figure 2 with image 3 shown. Carbide content such as Image 6 Shown, Cr 7 C 3...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1. Melting: Melt high-quality steel scrap in an electric furnace, add ferrosilicon, ferrochromium, electrolytic manganese, molybdenum, and carburizers to adjust to the required composition, then transfer to a refining furnace for refining, and add rare earth to further purify the composition after degassing. Cast into ingots. Gained ingot composition is that C is 0.75wt%, Si is 1.5wt%, Mn is 1.2wt%, Cr is 6wt%, Mo is 0.5wt%, Ni 0.6wt%, P 0.015wt%, S 0.006wt%, remaining The amount is Fe and unavoidable trace impurities.
[0051] 2. Forging: forging heating temperature 1150-1180°C, initial forging temperature 1150°C, final forging temperature 950°C forging ratio 8, after forging into a 300mm thick forging, slowly cool to room temperature, and then spheroidizing annealing; the microstructure is still spherical carbonization and pearlite matrix.
[0052] 3. Final heat treatment: first heat up to 600°C at <100 / h and hold for 2.5h, then heat to 880°C, hold for 450min, then ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com