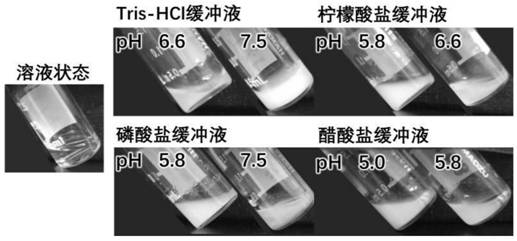
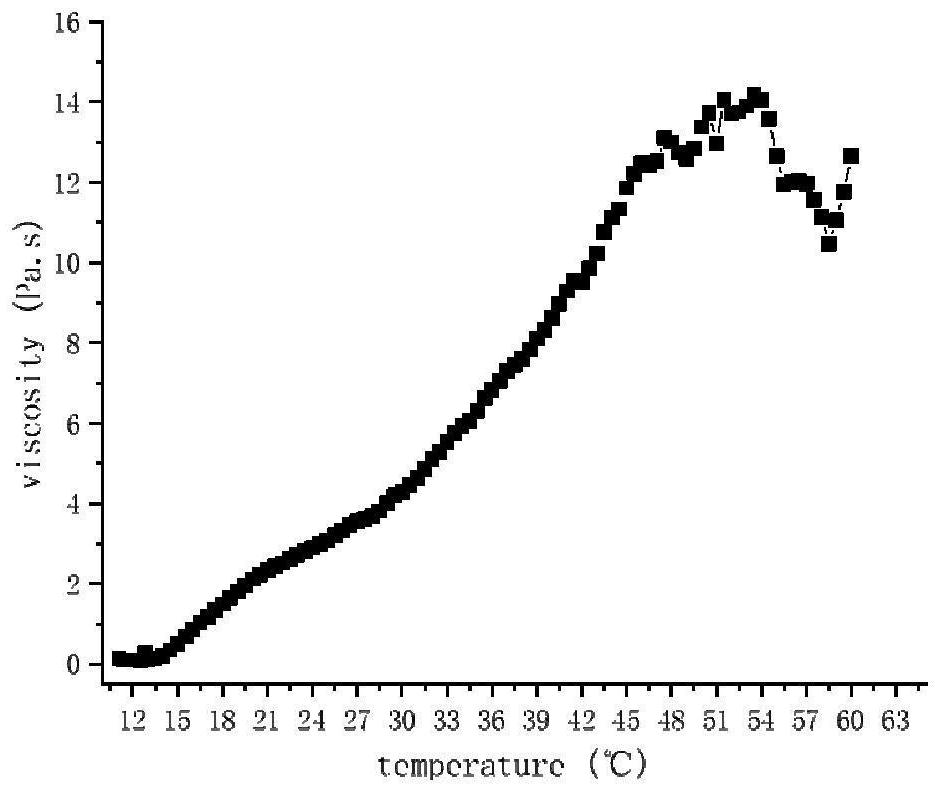
Intelligent hydrogel formed from single protein
A hydrogel and intelligent technology, which is applied in the direction of resisting vector-borne diseases, non-active ingredients of polymer compounds, prostheses, etc., to achieve the effects of sensitive temperature response, avoiding use and residue, and simple and mature preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0050] In this example, an expression vector of the target protein was constructed by cloning the target gene shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and the expression vector was introduced into E. coli to realize expression production. The specific operation of this embodiment includes: obtaining the target gene sequence from NCBI, inserting the NcoI restriction enzyme site at the N end of the target sequence, and inserting the XhoI restriction enzyme site at the C end to perform in vitro gene synthesis. Using two restriction enzyme sites, NcoI and XhoI, it is connected to the pET28a expression vector by means of restriction enzyme linkage. Then, the successfully constructed pET28a-LplA expression vector was transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells to construct recombinant Escherichia coli engineering bacteria.
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2 Fermentation of genetically engineered bacteria
[0052] The successfully constructed Escherichia coli engineering bacteria were cultured in 4mL LB medium containing kanamycin (50μg / mL) at 37℃, 220r / min to OD 600 When it is 1.8 to 2.0, prepare seed liquid. The seed solution was transferred to 200mL LB medium containing kanamycin (50μg / mL) with 1% inoculum, and cultivated to OD at 37℃, 220r / min 600 At 0.7, add 0.2mM IPTG at 30℃ to induce the expression of the target protein, and collect the bacteria after 12h.
[0053] The components of the LB medium are: tryptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L and yeast powder 5g / L.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Preparation of LPLA protein
[0055] The preparation method of LPLA protein is as follows:
[0056] (1) After resuspending the collected bacteria with 10 mL of Tris-HCl (50 mM, pH 7.5) buffer solution, use a homogenizer to disrupt the cells;
[0057] (2) Centrifuge the cell lysis solution at 10000×g for 30 min. After centrifugation, the supernatant was filtered through a 0.45μM filter membrane, and then loaded on a column filled with Ni-Sepharose, and used Buffer containing different imidazole concentrations. Gradient elution
[0058] a. Buffer A and Buffer B wash away non-specifically bound proteins;
[0059] b. Use Buffer C to elute the target protein;
[0060] (3) Collect the target protein, and use an ultrafiltration tube with a cut-off volume of 30kDa to concentrate the volume of the target protein solution to less than 1 mL;
[0061] (4) Add Tris-HCl (50mM, pH 7.5) buffer solution in batches, change the target protein solution system to 50mM, pH 7.5 Tris-HCl buffer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com