Detection medium and preparation method thereof and diamond detector
A diamond and detector technology, which is applied in the field of semiconductor detectors, can solve the problems of increased dark current of detectors, difficulty in achieving high-dose doping, and hindering diamond sensitivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
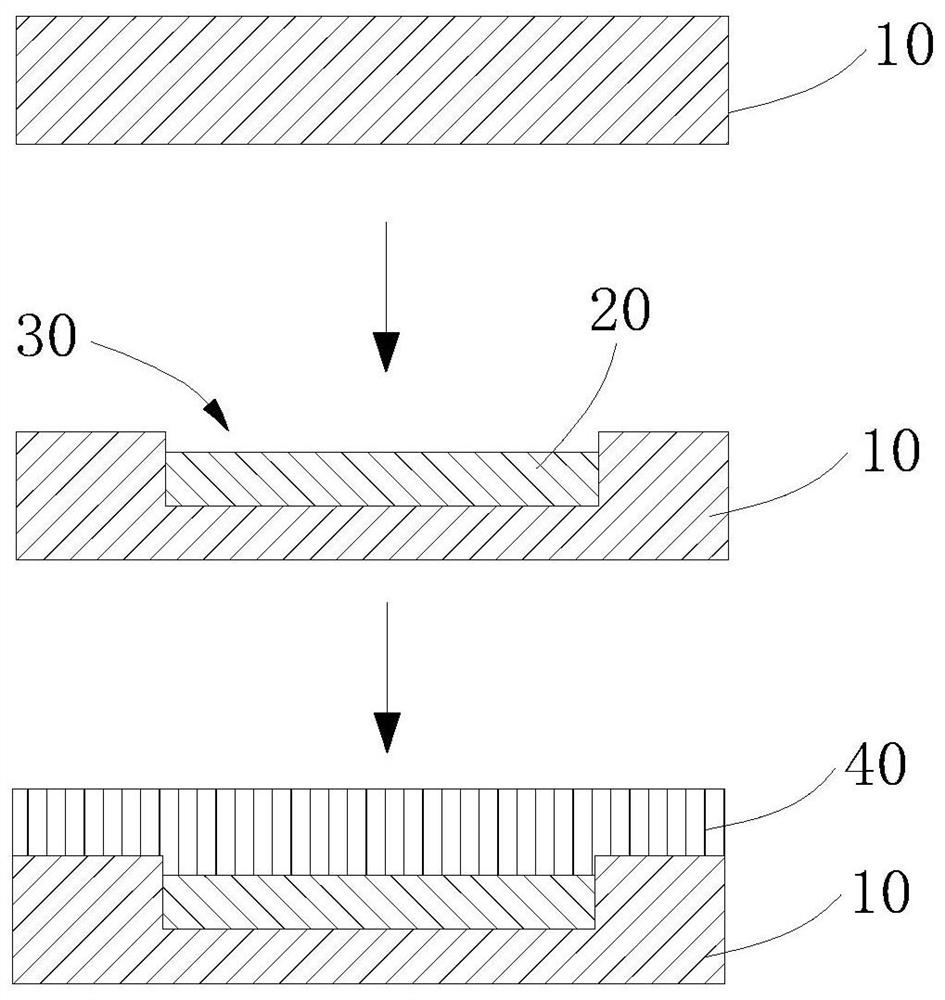
[0031] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of detection medium provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0032] S1, providing a single crystal diamond substrate 10;
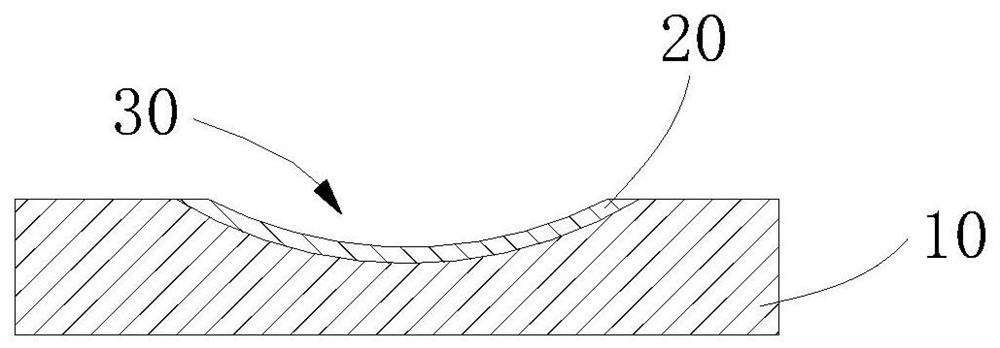
[0033] S2, using a laser to directly write the surface of the diamond substrate 10, so that the diamond is transformed into a graphite layer 20 in situ, wherein the surface of the graphite layer 20 is lower than the surface of the diamond substrate 10 and formed from the diamond substrate 10 The surface extends to the groove 30 of the graphite layer 20, the groove 30 has a width of 1 μm to 60 μm, a depth of 20 μm to 100 μm, and a length not less than 1 / 4 of the shortest dimension of the surface of the diamond substrate 10;
[0034] S3, epitaxially growing a single crystal diamond layer 40 on the diamond substrate 10, and making the single crystal diamond layer 40 cover at least the graphite layer 20 to obtain a detection medium.
[0035] In step S1, the shape of the surface o...
Embodiment 1
[0064] A groove is directly written on the upper surface of the HPHT single crystal diamond substrate with a size of 3.5mm×3.5mm×1mm. The laser beam spot diameter is 10μm, the power is 350W, and the scanning speed is 1000mm / s. The width is about 50 μm, the depth is about 20 μm, and the length is about 1.5 mm. The grooved diamond substrate was subjected to surface morphology analysis and Raman spectrum analysis, the results are as follows Figure 4 with Figure 5 shown. Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that there is a graphite layer in the groove after laser direct writing, and the graphite layer is formed by in-situ transformation of diamond. The electrical conductivity test shows that the resistance of the graphite layer is about 25Ω / cm.
[0065] Then, the diamond substrate with grooves was ultrasonicated in an ethanol solution for 10 minutes, and then placed in the growth chamber of the MPCVD equipment, vacuumed to a pressure of 0.1 Pa in the growth chamber, and preheat...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Two grooves are directly written on the upper surface of the HPHT single crystal diamond substrate with a size of 3.5mm×3.5mm×1mm. The laser beam spot diameter is 5μm, the power is 350W, and the scanning speed is 1000mm / s. The width is about 50 μm, the depth is about 40 μm, the length is about 1.5 mm, and the pitch is 1 mm. After laser direct writing, there is a graphite layer in the groove, which is formed by in-situ transformation of diamond. The electrical conductivity test shows that the resistance of the graphite layer is about 28Ω / cm.
[0069] Then, the diamond substrate with grooves was ultrasonicated in an ethanol solution for 10 minutes, and then placed in the growth chamber of the MPCVD equipment, vacuumed to a pressure of 0.1 Pa in the growth chamber, and preheated for 1 minute. Then, hydrogen gas was introduced at a flow rate of 410 sccm. Simultaneously, increase the pressure of the growth chamber and the power of the microwave synchronously until the press...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com