Micro-through-hole Cu-based CVD diamond heat sink sheet and preparation method thereof
A technology of micro-vias and diamonds, which is applied in the field of micro-vias Cu-based CVD diamond heat sink and its preparation, can solve the problems of damage to electronic components and large thermal expansion coefficients, and achieve improved adhesion, excellent heat dissipation performance, The effect of increasing the nucleation density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0053] A kind of preparation method of Cu base CVD diamond heat sink of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0054] S1, cleaning the Cu substrate surface;
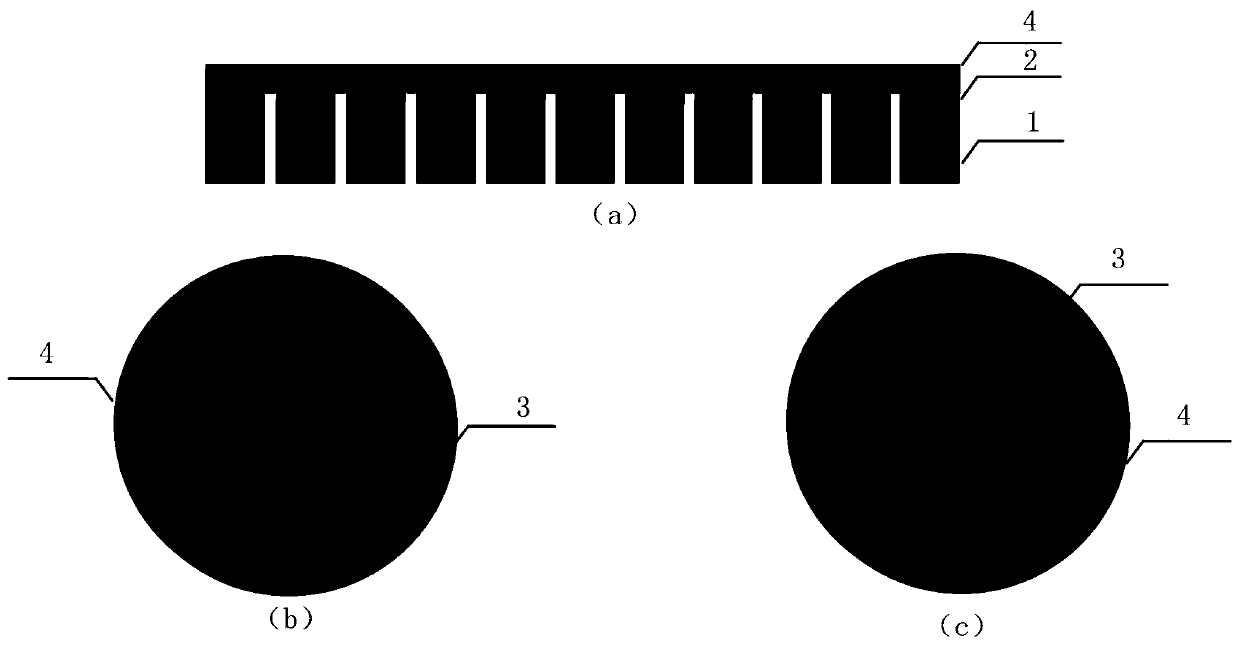
[0055] see figure 2 , the purity of 99.99% to 99.999%, the oxygen-free copper substrate wire cutting diameter of 10 to 20mm into 0.5 to 1mm copper sheet as the Cu substrate.
[0056] The Cu substrate is washed with hydrochloric acid solution, acetone, alcohol, and deionized water in sequence for 3 to 5 minutes to remove the oxide film and organic matter on the surface of the Cu substrate, and then dried with nitrogen gas.
[0057] S2. Evaporation on the surface of the Cu substrate forms a carbide metal transition layer to improve the bonding force between the Cu substrate and the diamond.
[0058] Main process parameters: sputtering power 80~100W, air pressure 1.0~1.5Pa, temperature 300~400℃, Ar gas flow 20~30sccm, time 10~15min; metal transition layer materials include tungsten, molybdenum, titanium,...
Embodiment 1
[0073] S1. Cut the oxygen-free copper matrix with a purity of 99.99% and a diameter of 10mm into 0.5mm copper sheets as the Cu substrate, and then use hydrochloric acid solution, acetone, alcohol, and deionized water to clean the Cu substrate for 3 minutes to remove the oxide film and Cu. The organic matters on the surface of the substrate are blown dry with nitrogen;
[0074] S2. Control the sputtering power to 80W, air pressure to 1.0Pa, temperature to 300°C, Ar gas flow to 20sccm, time to 10min; metal transition layer materials include tungsten, molybdenum, titanium, iron, chromium, nickel, cobalt, hafnium, zirconium, neodymium, vanadium , tantalum, yttrium or aluminum, etc., are vapor-deposited on the surface of the Cu substrate to form a carbide metal transition layer;
[0075] S3. Electrostatically assembling diamond nanoparticles on the surface of the transition metal to increase the nucleation density of diamond on the metal transition layer. The diamond nanoparticles ...
Embodiment 2
[0083] S1. Cut the oxygen-free copper matrix with a purity of 99.99% and a diameter of 14mm into 0.6mm copper sheets as the Cu substrate, and then use hydrochloric acid solution, acetone, alcohol, and deionized water to clean the Cu substrate for 4 minutes to remove the oxide film and Cu. The organic matters on the surface of the substrate are blown dry with nitrogen;
[0084] S2. Control sputtering power 80-100W, air pressure 1.2Pa, temperature 340℃, Ar gas flow 24sccm, time 12min; metal transition layer materials include tungsten, molybdenum, titanium, iron, chromium, nickel, cobalt, hafnium, zirconium, neodymium , vanadium, tantalum, yttrium or aluminum, etc., are vapor-deposited on the surface of the Cu substrate to form a carbide metal transition layer;
[0085] S3. Electrostatically assembling diamond nanoparticles on the surface of the transition metal to increase the nucleation density of diamond on the metal transition layer. The diamond nanoparticles are spherical an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com