Method for detecting trace impurity elements in tungsten carbide powder
A technology for trace impurities and impurity elements, applied in the field of trace impurity element analysis of high-purity materials, can solve the problems of inability to completely dissolve tungsten carbide, inaccurate determination of elements, inability to digest free carbon, etc. The effect of removing the inhibitory effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
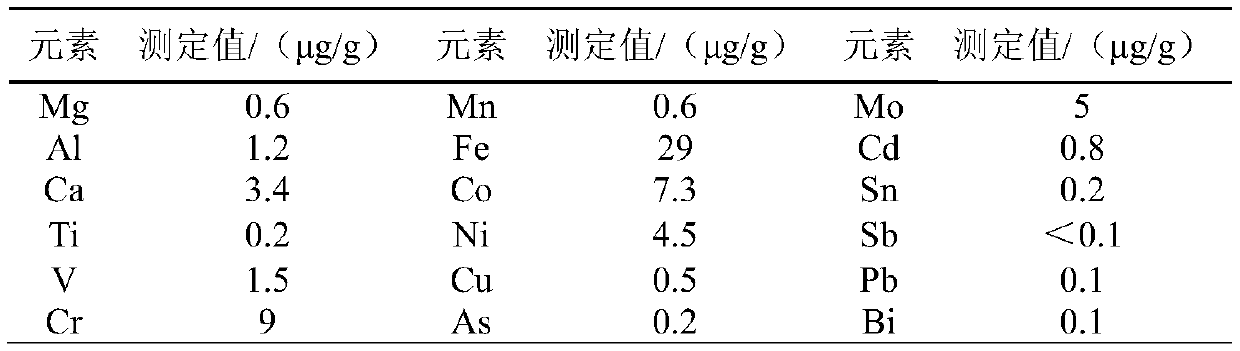
[0050] Determination of eighteen kinds of impurities such as magnesium, aluminum, calcium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, arsenic, molybdenum, cadmium, tin, antimony, lead, bismuth in 02 type ultrafine tungsten carbide powder samples amount of elements.
[0051] (1) Preparation of reagents and standard solutions
[0052] Ammonia water (ρ0.90g / mL), MOS grade;
[0053] Analysis water is ultrapure water (≥18.3MΩ cm);
[0054] Single-element standard storage solution of 18 impurity elements: 1000μg / mL, prepared with reference substances respectively.
[0055] Mixed standard solution A: containing calcium, molybdenum and lead, the mass volume concentration is 50 μg / mL, and the medium is 2.5% nitric acid (volume fraction).
[0056] Mixed standard solution 1: Contains calcium, molybdenum, lead 1μg / mL, medium is 2.5% nitric acid, and is prepared by diluting mixed standard solution A.
[0057] Mixed standard solution B: containing aluminum, a...
Embodiment 2
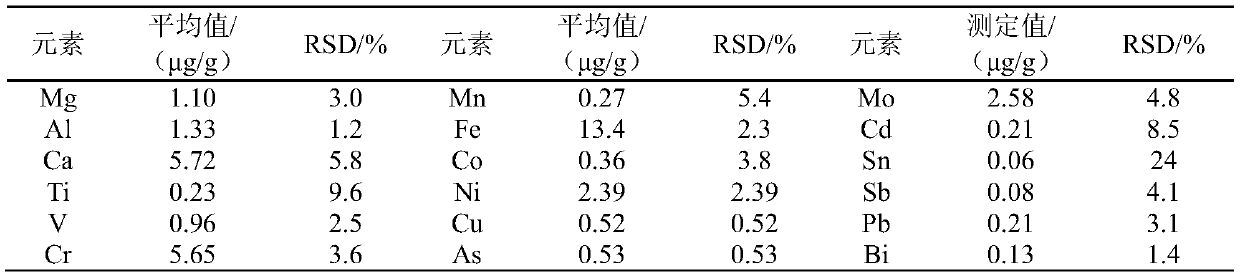
[0074] Determination of 18 kinds of impurity elements such as magnesium, aluminum, calcium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, arsenic, molybdenum, cadmium, tin, antimony, lead, bismuth in 06 type tungsten carbide powder samples , and measure the precision.
[0075] (1) Preparation of reagents and standard solutions
[0076] Ammonia water (ρ0.90g / mL), high purity;
[0077] Analysis water double distilled water (≥18.3MΩ cm);
[0078] Below with embodiment 1.
[0079] (2) Digestion of samples
[0080] Weigh 0.5g tungsten carbide sample, place it in a 100mL beaker, and oxidize it in a muffle furnace at 700°C for 12min. After cooling, add 10mL of water and 10mL of ammonia water, and heat to dissolve on a 150°C electric heating plate. Take it out and cool it slightly, then transfer it into a volumetric flask, dilute the solution to 20mL with water, and mix well. Pipette 1000μL of the test solution into a volumetric flask, dilute to 50mL wit...
Embodiment 3
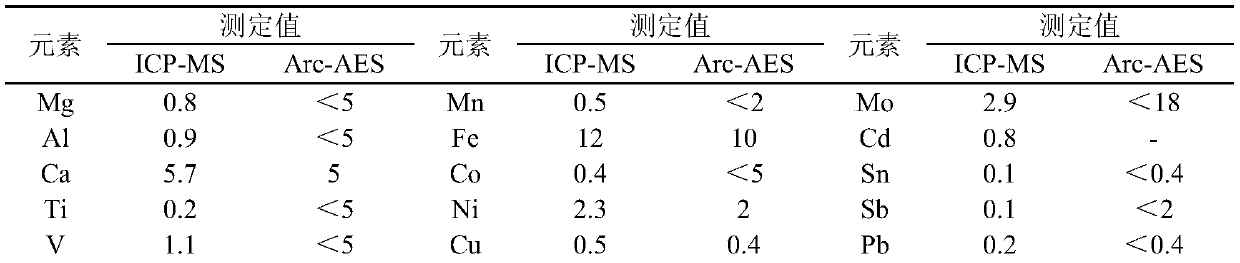
[0090] Determination of 18 kinds of impurity elements such as magnesium, aluminum, calcium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, arsenic, molybdenum, cadmium, tin, antimony, lead, bismuth in 02 type tungsten carbide powder samples , and compared with the results determined by DC arc atomic emission spectrometry (AES).
[0091] (1) Preparation of reagents and standard solutions
[0092] With embodiment 1.
[0093] (2) Digestion of samples
[0094]Weigh 0.1g tungsten carbide sample, place it in a crucible, and oxidize it in a muffle furnace at 800°C for 15min. After cooling, add 10 mL of water and 1 mL of ammonia water, and heat to dissolve on a 100°C electric heating plate. Take it out and cool it slightly, then transfer it into a volumetric flask, dilute the solution to 20mL with water, and mix well. Pipette 10mL of the test solution into a volumetric flask, dilute to 100mL with water, mix well, and test. Make a reagent blank along with t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com