Method for preparing secondary platycodins capable of improving permeability of cell membranes
A technology of permeability and cell membrane, which is applied in the field of preparation of Platycodon grandiflora secondary saponins, can solve problems that do not involve the preparation process and method of Platycodon grandiflorum secondary saponins, the active ingredient of Platycodon grandiflora
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Separation and preparation of Platycodon grandiflorum total saponins
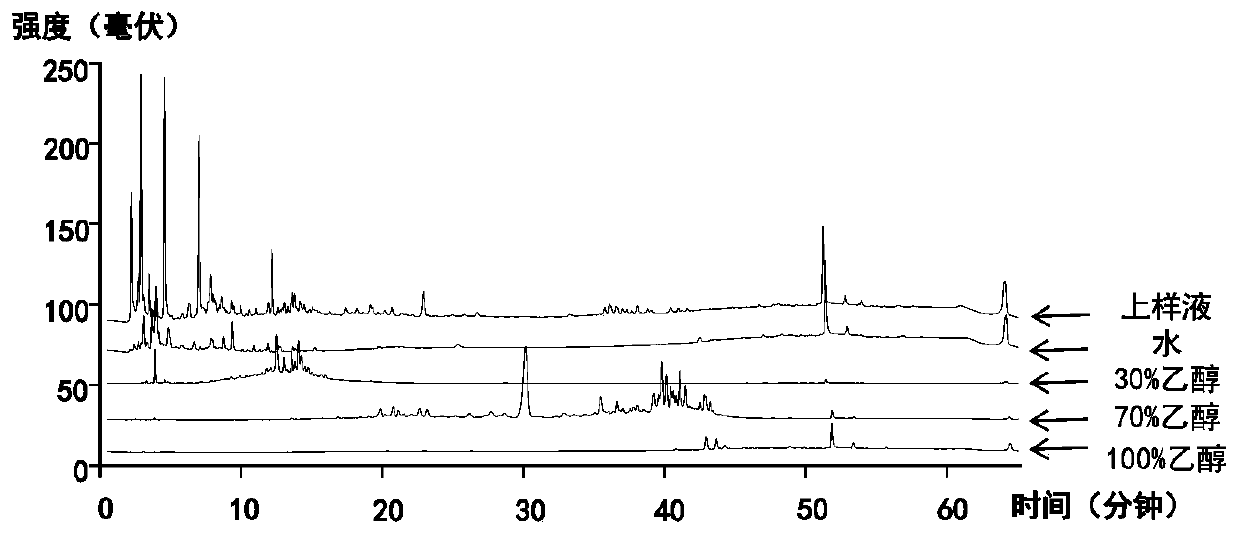
[0030] Take 2.5 kg of Platycodon grandiflora decoction pieces (purchased from Xi'an Tianrui Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number TR-170810), add 25 liters of 10 times the amount of distilled water, and heat and reflux for extraction for 2 hours. Filtrate while hot, and concentrate the filtrate under reduced pressure to about 500 ml. After cooling, add absolute ethanol to 1500 ml to make the ethanol ratio reach 70%, mix well and let stand overnight. The supernatant was collected by filtration, concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain 210 grams of platycodon saponin crude extract. Take 200 grams of it and add 20 liters of distilled water to dissolve it, configure it into a 1% solution, and load it on AB-8 macroporous adsorption resin (diameter: 5.5 cm; column height: 30 cm), and use ethanol solutions of different concentrations (0 % → 30% → 70% → 100% ethanol) gradient elution, ea...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: Analysis of Platycodon grandiflorum total saponins
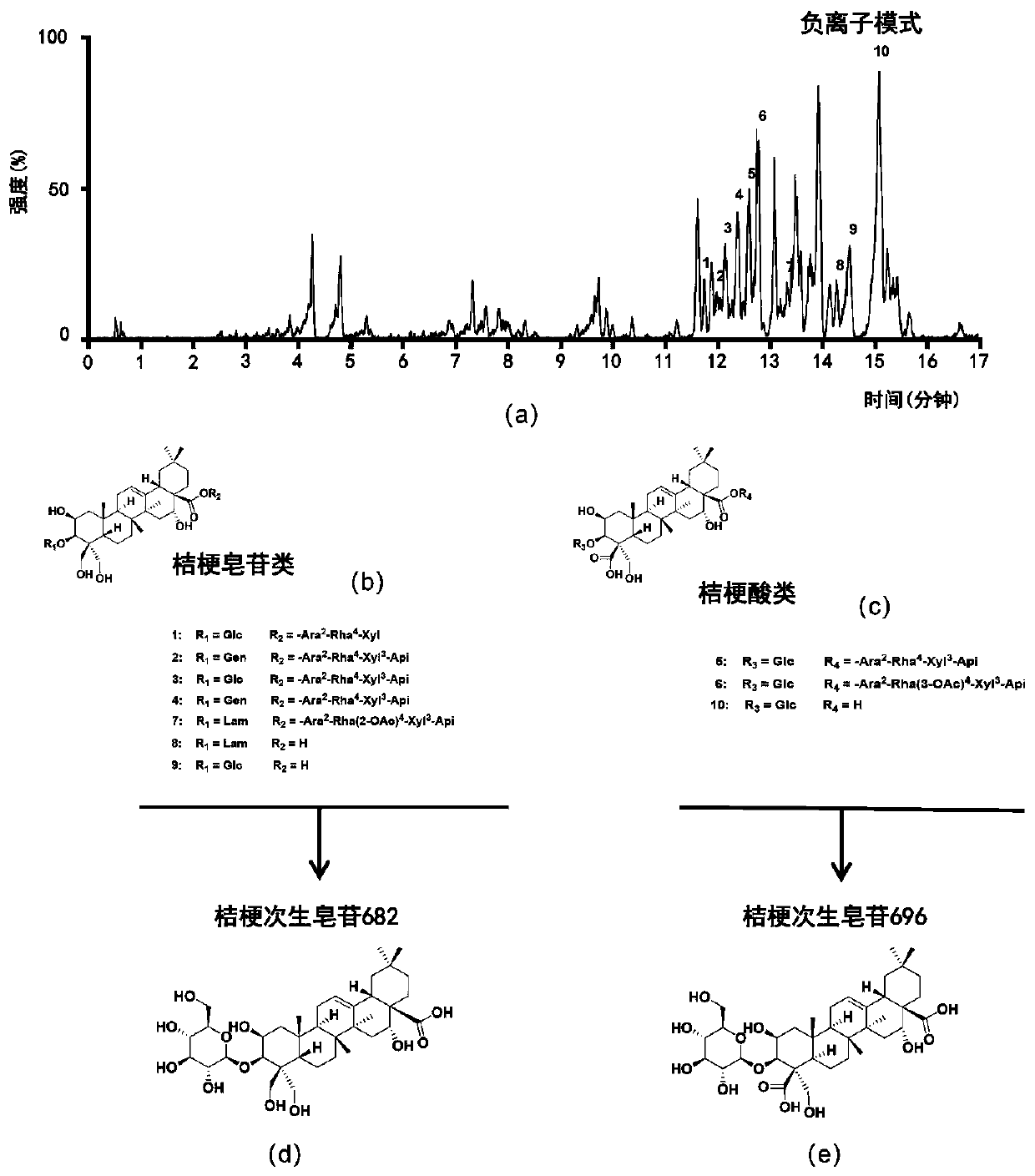
[0034] Platycodon saponins are mainly pentacyclic triterpenoid saponins, which mainly include platycodon saponin and platycodon acid saponin. Adopt UPLC-Q / TOF to analyze the platycodon total saponins of embodiment 1 and find that it mainly contains 10 platycodon saponins (see figure 2 ). It is speculated that the secondary saponins platycodon saponin 682 and platycodon saponin 696 that enter the blood are derived from the in vivo metabolites of platycodon saponins and platycodon acid saponins, respectively.
[0035] UPLC-Q / TOF experimental conditions:
[0036] 1) Liquid chromatography conditions:
[0037] ColumnWaters ACQUITY BEH C18 chromatographic column (2.1×100mm, 1.7μm); flow rate 0.4ml / min; PDA detector, detection wavelength 210nm; sample injection volume: 5.0μl; column temperature 30℃; mobile phase: A is 0.1% formic acid- Aqueous solution, B is acetonitrile; binary gradient elution: 0~2 min...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: the investigation of the hydrolysis condition of Platycodon grandiflora secondary saponin
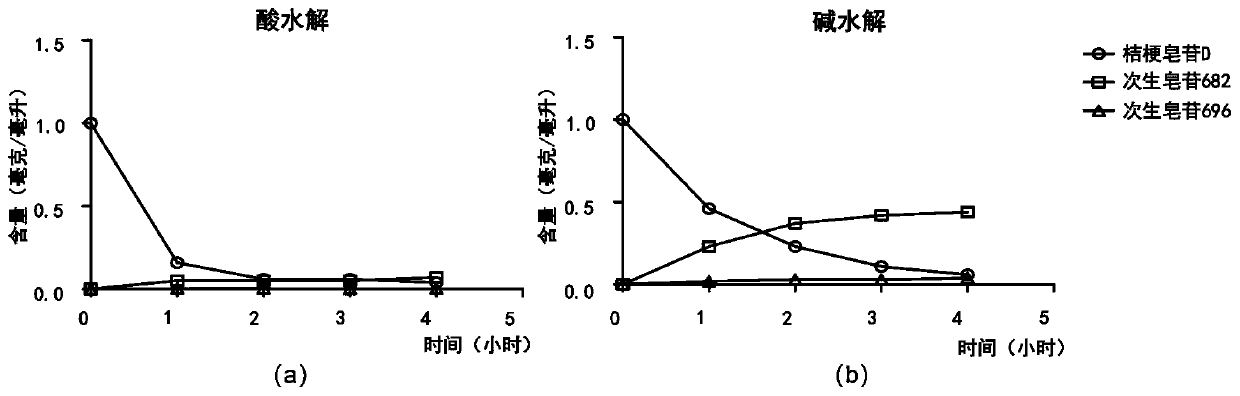
[0045] Using platycodon saponin D (Shanghai Boka Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., batch number: J-013-161216) as the reaction substrate (1 mg / ml), the hydrolysis conditions were investigated in a water bath at 85°C. The effects of acid (pH=1) and alkali (pH=14) on the hydrolysis efficiency were discussed respectively. And by the HPLC method of Example 1, the formation of Platycodon grandiflora secondary saponins 682 and 696 was investigated. The result is as image 3 As shown, the yield of secondary saponin 682 by alkali hydrolysis is significantly better than the effect of acid hydrolysis, so it is determined to use the method of alkali hydrolysis to optimize the hydrolysis conditions in the next step.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com