Multi-drug-carrying targeted nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
A nanoparticle, multi-drug loading technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of prevention and treatment of acute liver failure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
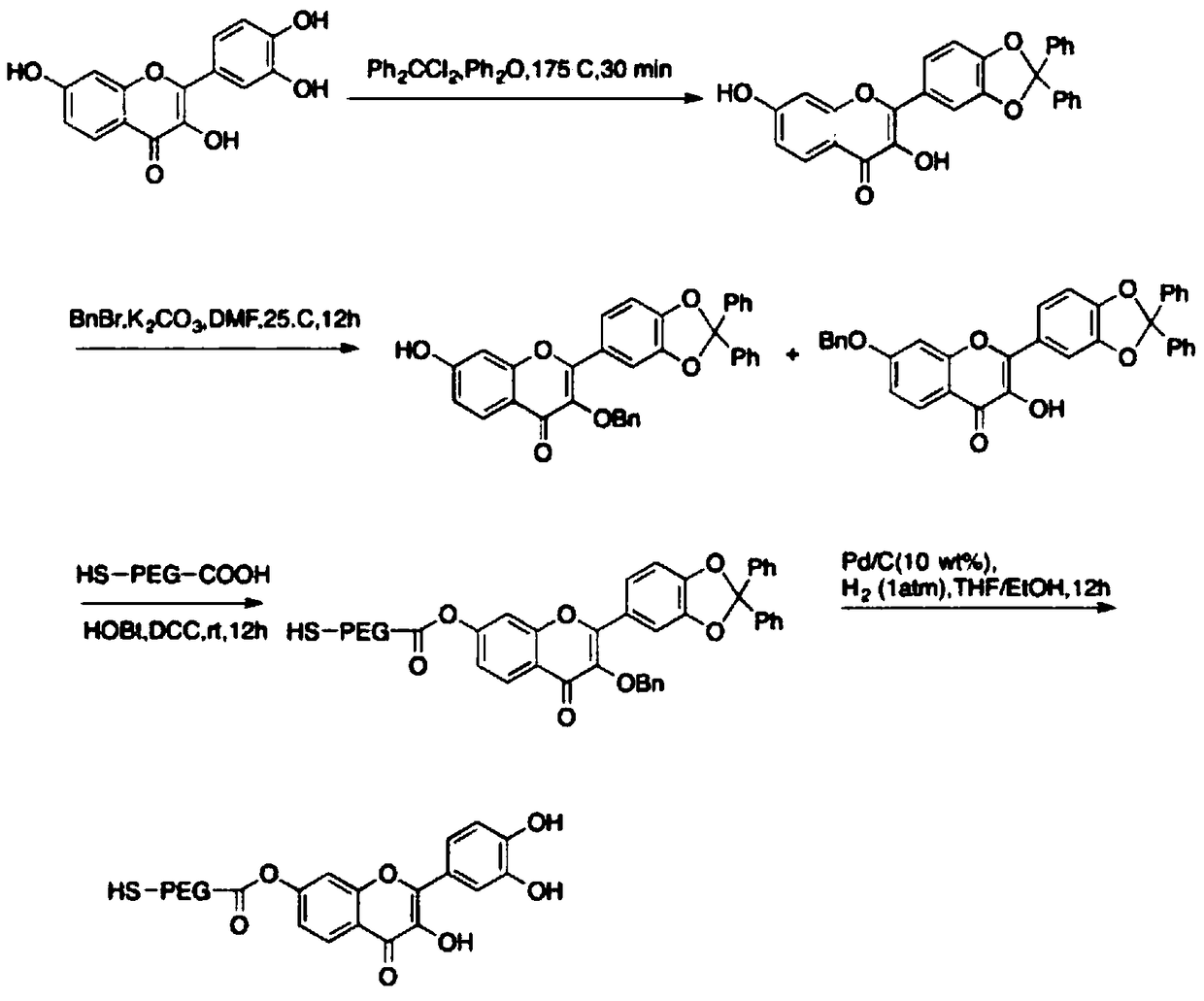
[0062] Example 1 Preparation of multidrug-loaded targeting nanoparticles
[0063] 1. Preparation of gold-coated iron oxide core-shell nanoparticles (GNPs)
[0064] 0.1M FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O aqueous solution and 0.2M FeCl 3 · 6HO was placed in 90ml solution containing 0.1M HCl. Then 80 ml of 2M sodium hydroxide were carefully added dropwise and the reaction was allowed to distribute well for 70 minutes with continuous stirring and nitrogen protection. The resulting black suspension was collected using a high power neodymium alloy magnet (2500G) and washed 3-4 times with nitrogen-treated double-steamed water. A 0.1 g / mL citrate working solution was subjected to a stable iron oxide nanoparticle suspension at pH 6.8, and the mixture was stirred continuously and heated to 80 °C for 2 h. The solution was then kept to cool down to room temperature to obtain citric acid-stabilized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. 60 mg of citric acid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles were dispersed in 15 mL of doub...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Characterization of multidrug-loaded targeting nanoparticles
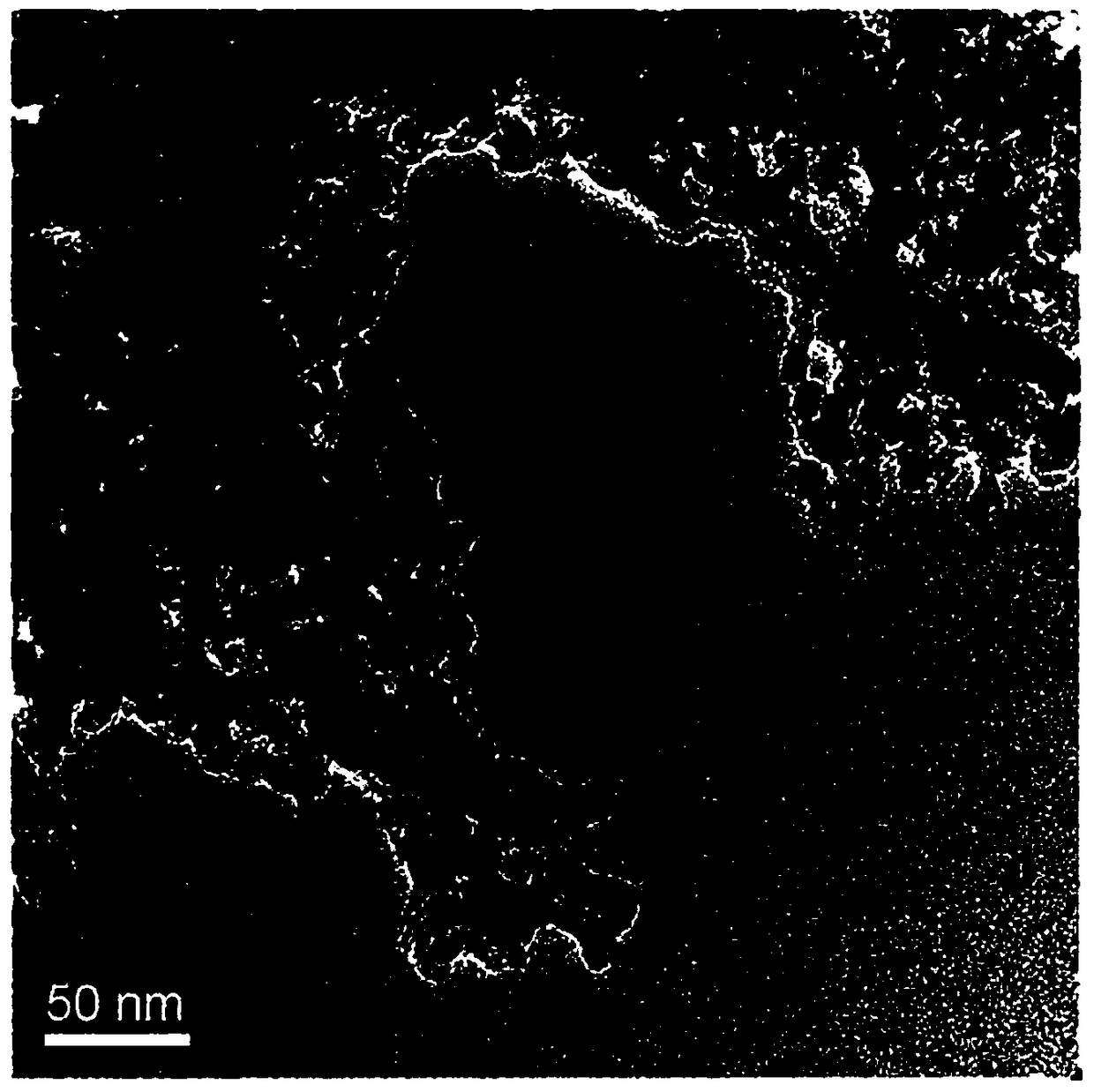
[0068] Electron micrographs of FN nanoparticles were examined using TEM (Tecnai G2 20200 kV TEM (Fei, Electron Optics)). A small drop of the sample solution in double-distilled water was dried on a carbon-coated copper grid for TEM analysis. In addition, the average size of the FN nanoparticles we obtained above was checked using dynamic light scattering (DLS) with a LB-550DLS particle size analyzer (Horiba Scientific, Edison, NJ). Magnetic properties of the nanoparticles were examined at room temperature (25°C) using a Lake Shore 735VSM.
[0069] TEM analysis of the nanoparticles showed that the nanoparticles had a spherical morphology ( image 3). Dynamic light scattering revealed that these nanoparticles had an average hydrodynamic diameter of 15 nm ( Figure 4 ). The gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles appear darker in the studied region due to the high electron density of gold. In addit...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3 Multidrug-loaded targeted nanoparticles inhibit LM-induced metabolic abnormalities and systemic inflammation in mice
[0071] To identify Listeria monocytogenes (LM)-induced lethal sepsis as the cause of metabolic system disturbance and systemic inflammatory response, and then evaluate the effect of FN nanoparticle intervention on improving the abnormal physiological state. In our study, LM administration significantly induced metabolic disorders compared with control mice. All mice in the model group died within 42 h after injection of LM. The survival rates of mice in the FN nanoparticle intervention group were 0% (25 / 25; 54h after injection; 20mg / kg FN), 36% (9 / 25; 40mg / kg FN) and 60% (15 / 25; 80mg / kg FN). kg FN)( Figure 8 A). Additionally, LM infection altered respiratory rate, blood pressure and body temperature in mice. Figure 8 B-8D shows increased respiratory rate, hypothermia and dyskinesia in LM-infected mice. However, FN nanoparticle treatment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com