Method for rapid determination of content of a plurality of elements in rare earth metal / alloy
A technology for rapid determination of rare earth metals, applied in measurement devices, preparation and sampling of samples for testing, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, large errors, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of improving efficiency, good linearity, and ensuring precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
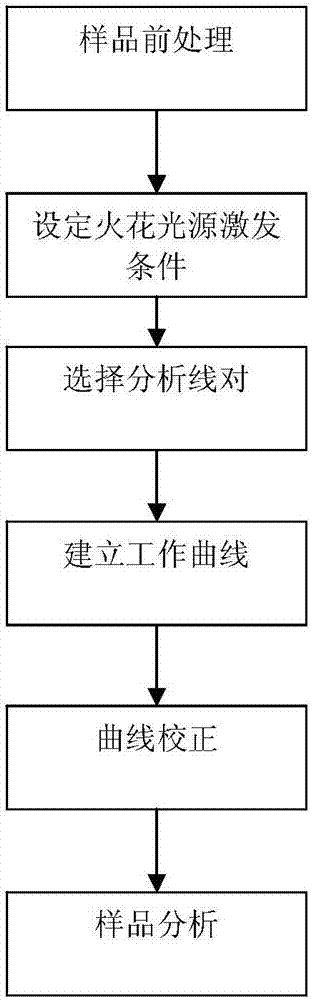
[0074] The first step, sample pretreatment
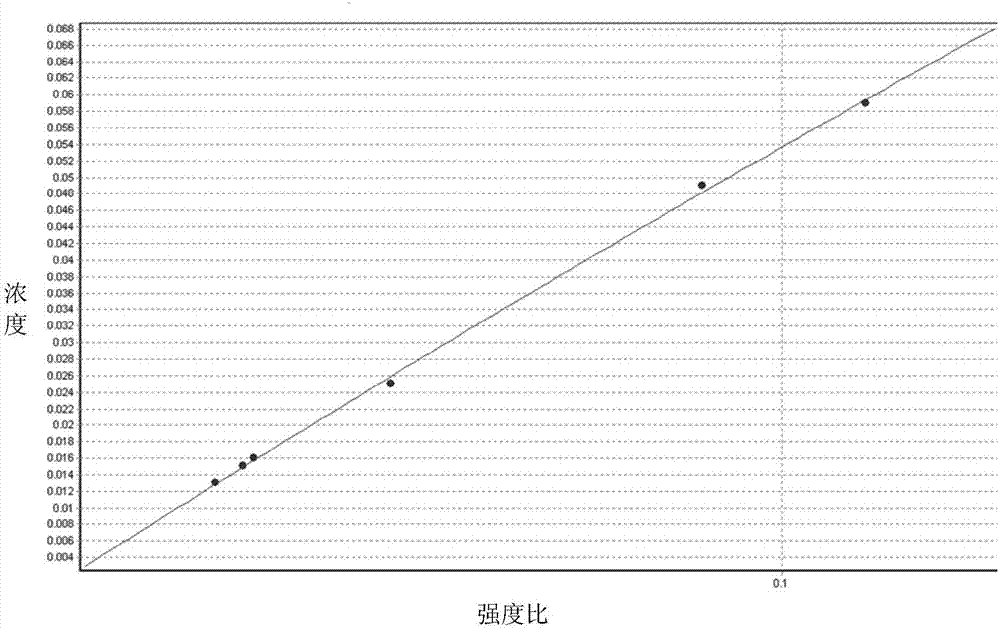
[0075] Select a PrNd alloy sample to be tested with a plane with a diameter greater than 5mm, or cut a PrNd alloy to be tested with a plane with a diameter greater than 5mm, and then use abrasive dry grinding or mechanical processing to treat the surface of the sample to be tested to a certain degree of smoothness. To ensure the tightness between the excitation platform and the sample to be tested and the repeatability of the analysis results.
[0076] The second step is to set the excitation conditions of the spark light source
[0077] Preparation of the spark emission spectrometer, start the spectrometer and turn on the constant temperature heating and vacuum pump switch. After the temperature and vacuum degree of the optical chamber are constant to the set range, turn on the excitation protection gas (argon or helium, purity ≥ 99.99%). Excite the waste sample 3 to 5 times, replace the residual air in the air path, and stabilize...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com