Variable gain audio-frequency amplifier
An audio amplifier, a variable technology, applied in audio amplifiers, amplifiers, power amplifiers, etc., can solve the problems of narrow frequency band and poor frequency characteristics of audio amplifiers, and achieve the effect of wide frequency bandwidth and good frequency characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
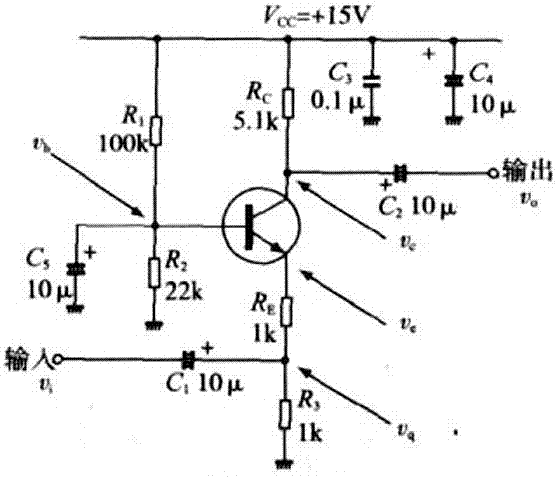
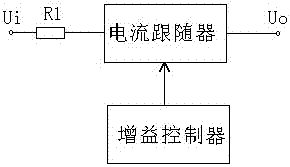
[0067] A variable gain audio amplifier is provided, including a resistor R1, a current follower and a gain controller; the resistor R1 is used to increase the input impedance of the current follower;
[0068] The current follower is a transistor common base amplifier;
[0069] The gain controller includes an input impedance controller, an input current controller and an output impedance controller;
[0070] The input impedance controller includes a potentiometer RP1;
[0071] The input current controller includes a potentiometer RP2 and a resistor R2, wherein one end of the potentiometer RP2 is connected to the input end of the input current controller, and the other end of the potentiometer RP2 is grounded; one end of the resistor R2 is connected to the input terminal of the input current controller. The input terminal is connected, and the other end of the resistor R2 is connected to the input terminal of the current follower;
[0072] The output impedance controller inclu...
Embodiment 2
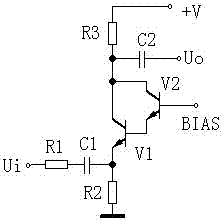
[0082] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the output stage of this embodiment is followed by a voltage follower to further increase the output power, as Figure 5b As shown, in order to ensure the output power, large-capacity capacitors should be used for the output DC blocking capacitors C4 and C5, and capacitors with different capacities can be connected in parallel to make them have very low impedance in the passband to ensure good frequency characteristics of the amplifier. J1 is the loudspeaker protection relay. J1 is disconnected when starting up. If the output potential of the amplifier deviates from the midpoint potential of capacitors C4 and C5, it will be charged and discharged through the resistor R9. When the two are equal, J1 will pull in and the amplifier will work normally.
Embodiment 3
[0084] The differences between this embodiment and embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 are: Figure 5b The withstand voltage of medium capacitors C4, C5, and C6 is higher than the power supply voltage. Figure 5c In the circuit form, the withstand voltage of capacitors C4, C5, and C6 only needs to be greater than half of the power supply voltage, but dual power supplies are used, and the negative terminals of the power supply are grounded. Capacitor C4 uses two electrolytic capacitor negative terminals connected together as a non-polar capacitor. , Capacitors C4, C5, and C6 all use large-capacity capacitors, and capacitors with different capacities can be connected in parallel to make them have very low impedance in the passband to ensure that the amplifier has good frequency characteristics.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com