Method for improving corrosion resistance of sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet phosphating film
A technology of neodymium iron boron and phosphating film, which is applied in the direction of metal material coating process, etc., can solve the problems of coarse crystallization of phosphating film, poor continuity of phosphating film, and lag in film formation in the anode area, and achieve low production cost and high production efficiency. High efficiency and the effect of reducing pollution emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
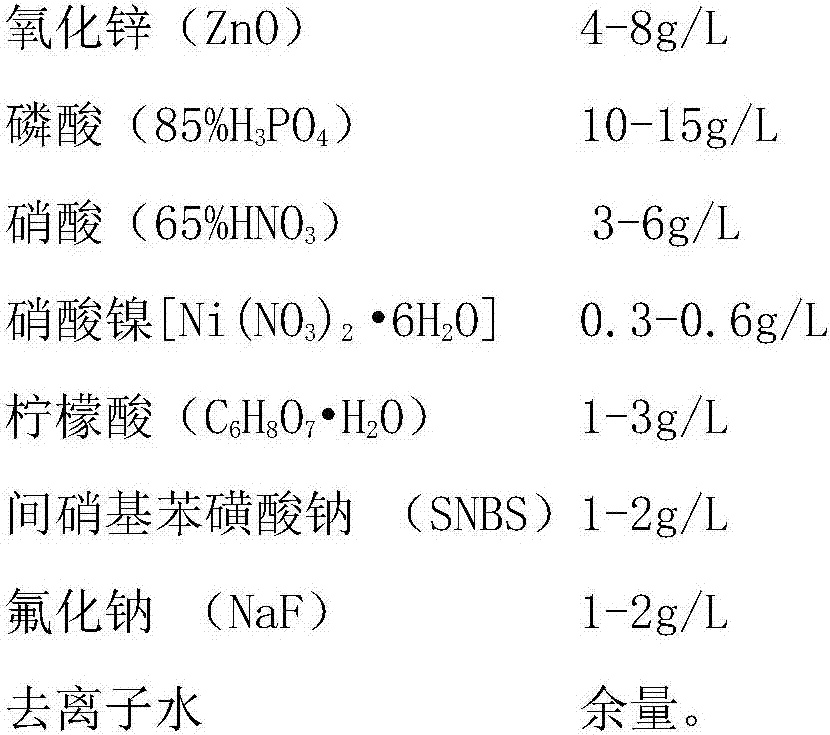
[0028] (1) Take a number of sintered NdFeB magnets with a specification of 25×12×4 and use corundum abrasives to chamfer on a spiral vibration finishing machine. After chamfering, the R angle of the product is controlled at 0.5mm;
[0029] (2) Wash the chamfered product with clean water, put it into a degreasing solution at a temperature of 40°C, turn on the ultrasonic wave, take it out after 15 minutes of degreasing, and then clean it with hot water at 50°C;
[0030] (3) The product washed with hot water is washed countercurrently by two channels of tap water for 10 seconds; then it is pickled in nitric acid with a concentration of 3g / L for 40 seconds;
[0031] (4) Wash the product after pickling by two channels of running water countercurrently for 10 seconds; then put it into an ultrasonic cleaning machine filled with flowing water and clean it for 40 seconds;
[0032] (5) After the product washed by ultrasonic water is cleaned by two deionized water, it is immediately put ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Take a number of sintered NdFeB magnets with a specification of φ10.5×2 and chamfer them on a horizontal drum finishing machine with corundum abrasives. After chamfering, the R angle of the product is controlled at 0.2mm;
[0042] (2) Wash the chamfered product with clean water and put it into a degreasing solution at a temperature of 50°C, turn on the ultrasonic wave, take it out after 30 minutes of degreasing, and then clean it with hot water at 60°C;
[0043] (3) Wash the product after hot water washing by two countercurrent tap water for 20s; then put it into nitric acid with a concentration of 4.5g / L for pickling for 70s;
[0044] (3) Wash the product after pickling by two channels of running water countercurrently for 20s; then put it into an ultrasonic cleaning machine filled with running water and clean it for 110s;
[0045] (4) After the product washed by ultrasonic water is cleaned by two deionized water, it is immediately put into the surface conditioning...
Embodiment 3
[0057] (1) Take a number of sintered NdFeB magnets with a specification of φ36-φ24×10.5 and use corundum abrasives to chamfer on a spiral vibration finishing machine. After chamfering, the R angle of the product is controlled at 0.8mm;
[0058] (2) Wash the chamfered product with clean water and put it into a degreasing solution at a temperature of 50°C, turn on the ultrasonic wave, take it out after 30 minutes of degreasing, and then clean it with hot water at 60°C;
[0059] (3) The product washed with hot water is washed countercurrently by two channels of tap water for 10 seconds; then it is pickled in nitric acid with a concentration of 5 g / L for 80 seconds;
[0060] (4) Wash the product after pickling by two channels of running water countercurrently for 15 seconds; then put it into an ultrasonic cleaning machine filled with running water and clean it for 100 seconds;
[0061] (5) After the product washed by ultrasonic water is washed with deionized water twice, it is imm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bronsted acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com