Method for processing waste copper/iron-based diamond tool bit
A processing method and fund technology, which is applied in the field of effectively processing waste copper-iron-based diamond cutter heads, to achieve the effect of low labor intensity and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
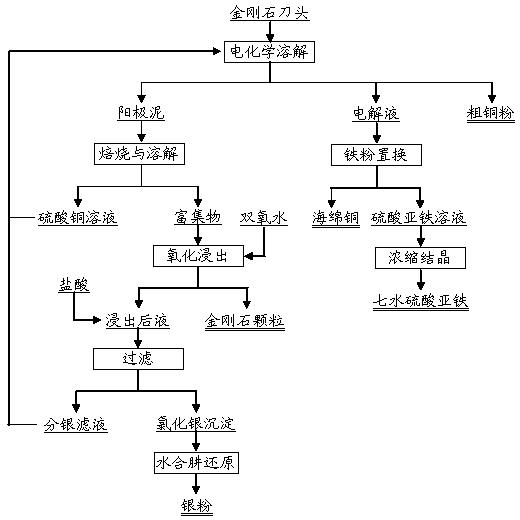
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The main components of the diamond segment are (%) by mass percentage: Cu 26.80, Fe 69.97, Ag 0.60, and synthetic diamond 1.08. Industrial grade sulfuric acid, where H 2 SO 4 ≥98%; industrial grade iron powder, of which Fe≥98%; industrial grade hydrochloric acid, of which HCl≥36%; industrial grade hydrogen peroxide, of which H 2 o 2 ≥35%; industrial grade hydrazine hydrate, where N- 2 h 4 ·H 2 O≥40%.
[0033] When the copper ion concentration is 5g / L, H 2 SO 4 In the 19.50L electrolyte with a concentration of 1.75mol / L, place the anode frame and the stainless steel cathode respectively. Weigh 1808.0g of waste diamond cutter head and place it in the anode frame, connect it to direct current electrolysis, control the temperature of the electrolyte to 50°C, the distance between the cathode and the anode is 10mm, and control the cathode current density to 120A / m according to the effective area of the cathode 2 . After 130 hours of electrolysis, the anode frame w...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The main components of the diamond segment are (%) by mass percentage: Cu 66.50, Fe 25.20, Ag 0.92, and synthetic diamond 1.25. Industrial grade sulfuric acid, where H 2 SO 4 ≥98%; industrial grade iron powder, of which Fe≥98%; industrial grade hydrochloric acid, of which HCl≥36%; industrial grade hydrogen peroxide, of which H 2 o 2 ≥35%; industrial grade hydrazine hydrate, where N- 2 h 4 ·H 2 O≥40%.
[0039] When the copper ion concentration is 10g / L, H 2 SO 4 In the 19.50L electrolyte with a concentration of 1.70mol / L, place the anode frame and the stainless steel cathode respectively. Weigh 2000.0g of waste diamond cutter head and place it in the anode frame, connect it to direct current electrolysis, control the temperature of the electrolyte to 50°C, the distance between the cathode and the anode is 10mm, and control the cathode current density to 120A / m according to the effective area of the cathode 2 . After 142 hours of electrolysis, the anode frame ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com