Novel polyorthoester medicinal auxiliary material and slow-release new preparation thereof
A technology for polyorthoesters and pharmaceutical excipients, which is applied in the directions of drug combinations, medical preparations without active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., which can solve moisture sensitivity, difficulty in preparation and storage, and polymer functions Problems such as difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
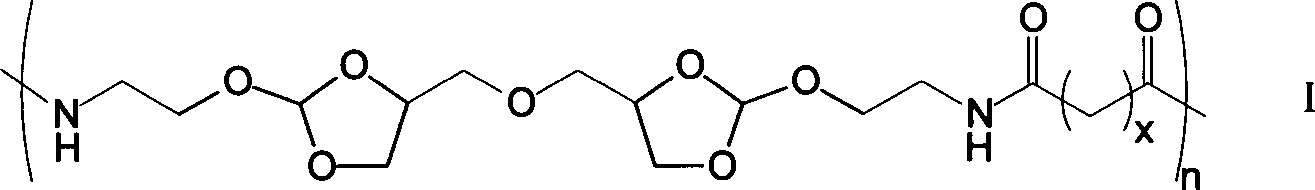
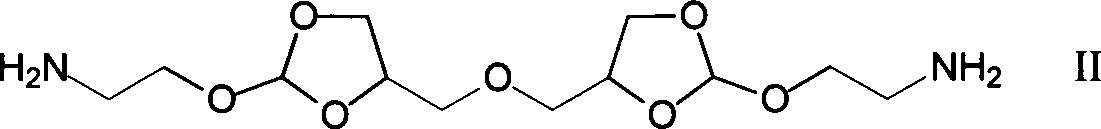
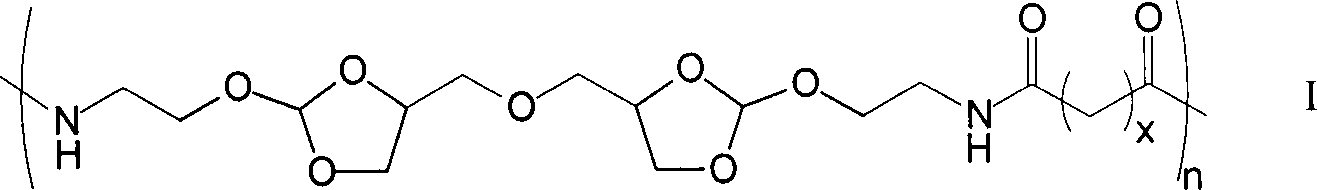
[0021] Under a nitrogen atmosphere, weigh 0.979g of diamine monomer (4,4'-dimethylene oxide-bis-(2-aminoethoxy-1,3-dioxolane) in a 50mL two-necked reaction flask Add 5mL DMF to dissolve, then add 1.36mL triethylamine, then add 1.348g succinyl heavy amido dodecanoate, then add 5mL DMF to react for 1-5 days; after the reaction is completed, add the reaction solution dropwise to 100mL containing In the ethyl acetate of triethylamine, leave standstill 10min after dropping, filter, wash 3 times with ethyl acetate, vacuum-dry to obtain 1.04g white solid powder, namely polyorthoester-polyamide copolymer (POEd-1), The yield was 65%.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Preparation of New Drug Preparations for Sustained Release
[0024] 1) Preparation method of a pharmaceutical composition using bupivacaine as an active agent: after mechanically mixing a selected amount of polyorthoester-polyamide copolymer (POEAd) with bupivacaine, heating to Dissolving at 50-90° C., and then allowing the solution to cool naturally to room temperature to obtain a uniformly mixed solid pharmaceutical composition, wherein the weight content of the active agent is 5% to 30%.
[0025] 2) Preparation method of a pharmaceutical composition using bupivacaine as an active agent: after a selected amount of polyorthoester-polyamide copolymer (POEAd), bupivacaine and polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether are mechanically mixed, Heating to 50-90°C under nitrogen atmosphere and stirring to dissolve, then allowing the solution to cool naturally to room temperature to obtain a uniformly mixed solid pharmaceutical composition, wherein the active agent has a weight con...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Release Properties of Pharmaceutical Compositions
[0032]Weigh the pharmaceutical composition of Example 2 and place it in a bottle with a lid. Add 50ml of 50mMPBS (pH7.4) into each bottle, and culture in a 37°C incubator with shaking at 60rpm. At selected time points, approximately 2 ml of culture broth was withdrawn and analyzed for active agent content by HPLC. Remove the residual medium and add the same volume of fresh buffer. Drug release rate for pharmaceutical compositions with the same active agent content and copolymer: group 3>group 2>group 1; group 6>group 5>group 4; for pharmaceutical composition 1 with the same active agent content, drug release Rate: POEAd-1>POEAd-2>POEAd-3.
[0033] The experimental results confirm that the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can adjust and control the drug release rate of the composition in various ways, such as changing the main chain affinity / hydrophobic properties of the copolymer, the type and con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com