Preparation method of iron molybdenum oxide (II) nanocube
A technology of nano-cubes and ferrous molybdate, which is applied in the direction of nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, and iron compounds, can solve the problem that monoclinic ferric molybdate materials are difficult to obtain a regular shape structure, and achieve easy-to-large Large-scale industrial production, uniform particle size distribution, and high operational controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: a kind of ferric molybdate ( ) preparation method of nano-cubic structure material, using liquid phase synthesis technology to prepare iron molybdate ( ) nanostructure comprising the steps of:
[0022] (1) The iron source is ferrous salt, selected from ferrous chloride hydrate (FeCl 2 4H 2 O), ferrous oxalate hydrate (FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 O), hydrated ferrous nitrate (Fe(NO?)? 6H?O), hydrated ferrous sulfate (Fe 2 SO 4 ·7H 2 O) or ferrous acetate hydrate (Fe(CH 3 COO) 2 4H 2 O);
[0023] Molybdenum source is hexavalent molybdenum salt, selected from sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ), ammonium molybdate ((NH 4 ) 2 Mo 2 o 7 , (NH 4 ) 2 Mo 4 o 13 , (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O, (NH 4 ) 4 Mo 8 o 26 ), or molybdic acid (H 2 MoO 4 ·H 2 o).
[0024] Add the iron source and the molybdenum source in a molar ratio (1.5-3): 1 to the alcohol-water mixture of sodium acetate and polyvinylpyrrolidone with a mass percent concentration of 0.3-2.0%,...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: iron molybdate ( ) Preparation and structural characterization of nanocubes;
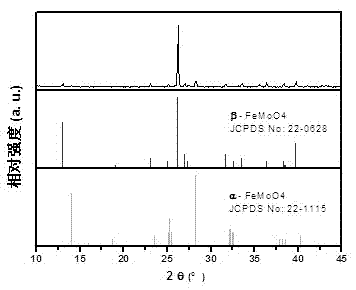
[0034] Take 0.56 g ferrous sulfate hydrate (Fe 2SO 4 ·7H 2 O) and 0.25 g sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ) into the container, add 25ml ethylene glycol and 15ml distilled water, add 0.2 g polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and 0.2 g sodium acetate, mix and stir evenly; transfer the mixed material to a closed pressure-resistant reaction vessel, and React at 200°C for 20 hours. Then cool to room temperature, open the airtight reaction vessel, filter with Buchner funnel, and wash with deionized water to obtain a dark brown powder product. The product was identified as monoclinic β-FeMoO by Bruker D8 ADVANCE X-ray powder diffractometer with Cu Kα rays (wavelength λ= 1.5418?, scanning step speed 0.08° / s). 4 ( figure 1 ), which matches the JCPDS card standard value No. 22-0628, and is mixed with a very small amount of α-FeMoO 4 (JCPDS No: 22-1115).
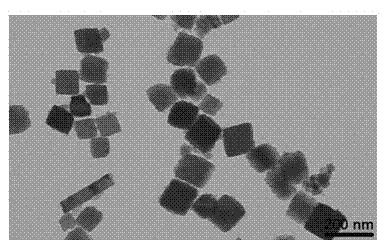
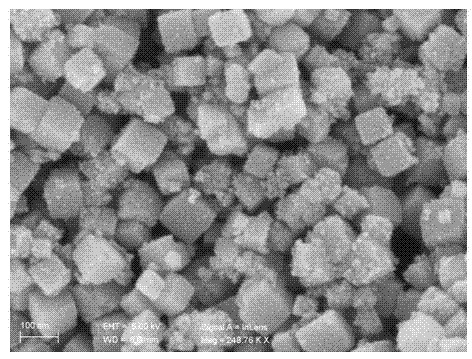
[0035] Cubic phase iron molybdate...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: get 0.36 g ferrous oxalate hydrate (FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 O) and 0.25 g sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ) into a container and add 25 ml ethylene glycol and 15 ml distilled water, add 0.2 g polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and 0.2 g sodium acetate, mix and stir evenly; transfer the mixed material to a closed pressure-resistant reaction vessel , reacted at 180°C for 20 hours. Then cool to room temperature, open the airtight reaction vessel, filter with Buchner funnel, and wash with deionized water to obtain a dark brown powder product.
[0037] The obtained ultrafine powder is monoclinic β-FeMoO 4 (JCPDS No. 22-0628), good crystallinity; composed of nanoparticles with an average particle size of about 90 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com