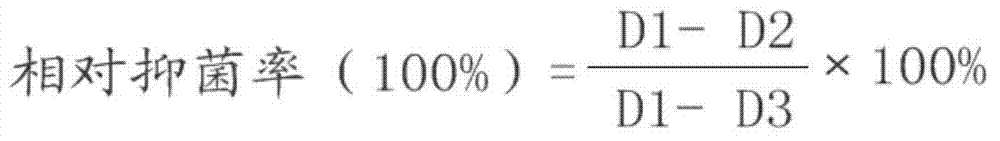Microbe, application of microbe in bio-fertilizer preparation, bio-fertilizer and application of bio-fertilizer
A bio-fertilizer, microorganism technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, chemicals for biological control, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing yield and reducing morbidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
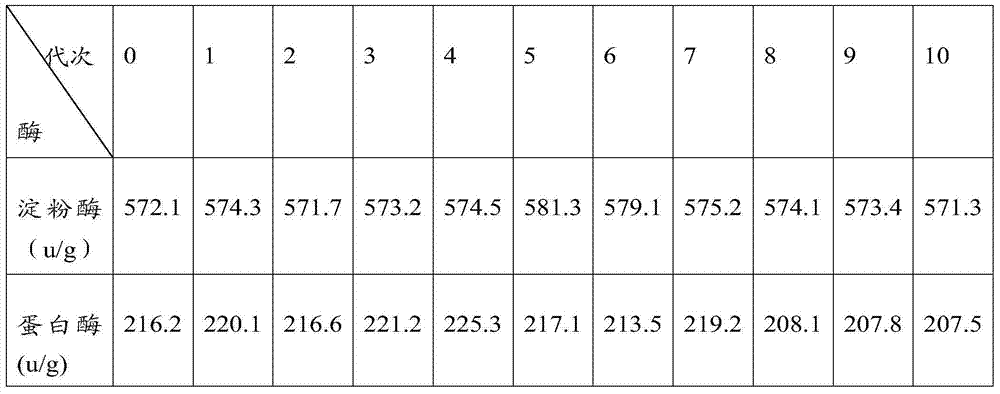
[0031] Embodiment 1, the screening of this microorganism
[0032] 1. Materials
[0033] Soil for testing: From the same continuous-cropping cucumber greenhouse in Shouguang City, Shandong Province, remove the topsoil and collect 3-15cm rhizosphere soil, about 100g per sample. The soil samples were numbered, bagged, and brought back to the laboratory for storage in a 4°C refrigerator.
[0034] Test medium: PDA medium, Bengal red medium.
[0035] 2. Preparation of soil suspension
[0036] Put the soil sample into a sterilized mortar and grind it in a sterile operating bench until the particles are uniform. Using the 10-fold ratio dilution method, first weigh 1g of the ground soil, put it into a triangular flask filled with 99mL of sterile water and shake it for 30min to make a 10-2 soil dilution, then take 1mL and add it to 9mL of sterile water. Fully oscillate in water to make a 10-3 dilution, and so on, make a 10-4 dilution for later use.
[0037] 3. Plate inoculation
...
Embodiment 2
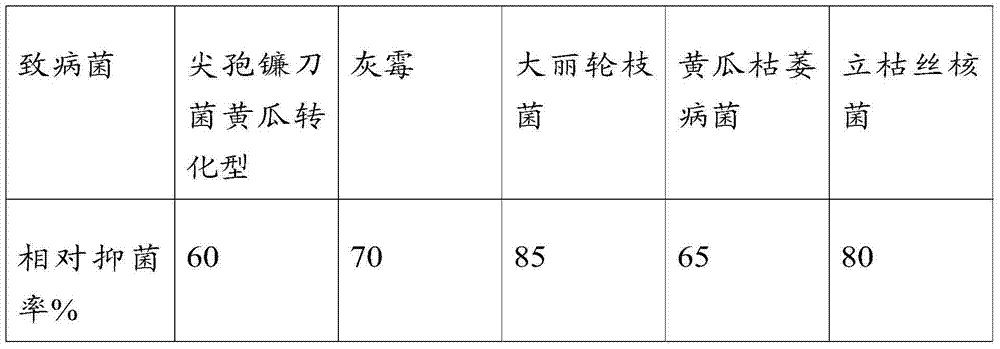
[0047] Embodiment 2, the inhibitory action of this microorganism to crop pathogen
[0048] Pathogenic bacteria for testing: Fusarium oxysporum transformation type of cucumber, Botrytis cinerea, Verticillium dahliae, Cucumber wilt fungus, Rhizoctonia solani (among them, Fusarium oxysporum transformation type of cucumber can cause cucumber wilt, Botrytis cinerea Botrytis cinerea causes foliage, Verticillium dahliae causes verticillium wilt, and Rhizoctonia solani causes sheath blight).
[0049] Test medium: PDA medium, PDB medium, Bengal red medium.
[0050] In the examples of the present invention, the microbial growth rate method was used to measure the antibacterial activity of the aseptic fermentation filtrate of the microorganisms.
[0051] The microorganisms preserved above were inoculated into PDB medium, cultured at 25° C. and 160 r / min for 8 days, and then filtered through a 0.45 μm microporous membrane to obtain a sterile fermentation filtrate. Mix the filtrate with ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3, the preparation of this microbial spore suspension
[0057] Specifically prepare as follows:
[0058] Transfer the refrigerated microbial strains to the PDA medium plate (200g potato, 20g sucrose, 18g agar, 1000mL distilled water) for 3 generations; then use an inoculation loop to pick the edge hyphae of the 3rd generation colony, and transfer to PDB In the liquid culture medium (200g of potatoes, 20g of sucrose, 1000mL of distilled water), at 25°C to 30°C, the optimum temperature is 28°C, 120rpm, cultivated for 10 days under the conditions to obtain the fermentation liquid of the microorganism. The fermented liquid obtained was filtered through a 100 μm sieve to obtain a spore suspension, and the live spore concentration was 3.0×10 10 -5.0×10 10 cfu / ml.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com