Method for fabricating light-emitting diode (LED) chip
A technology of light-emitting diodes and manufacturing methods, which is applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as laser burning to the GaN layer, photoelectric parameter changes, lattice mismatch, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing photoelectric parameters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The preferred embodiments of the present invention are given below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings to describe the technical solution of the present invention in detail.
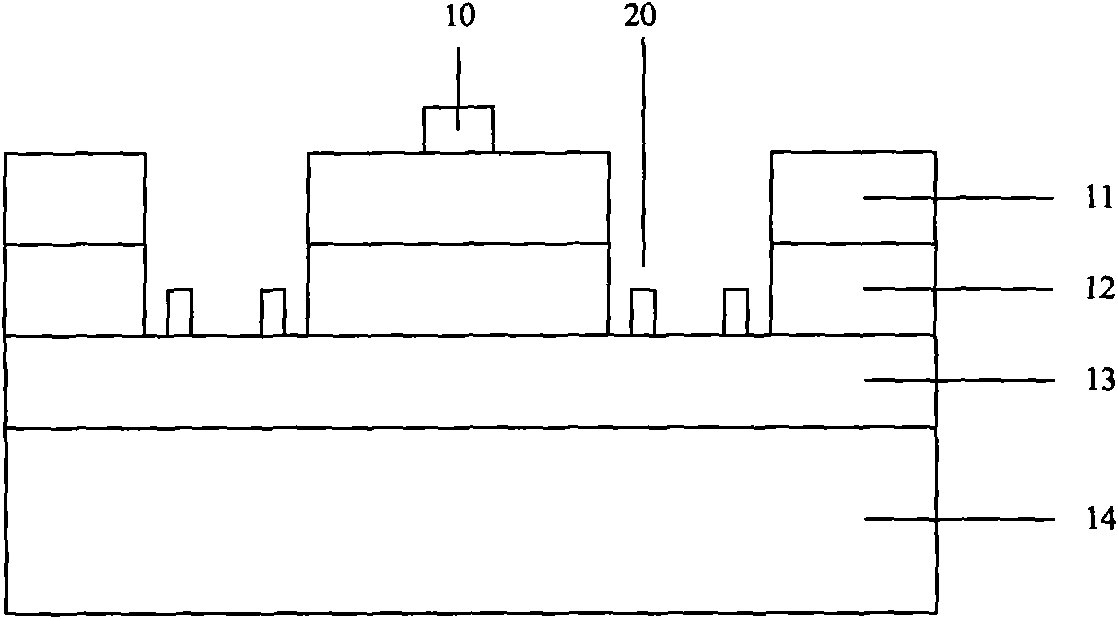
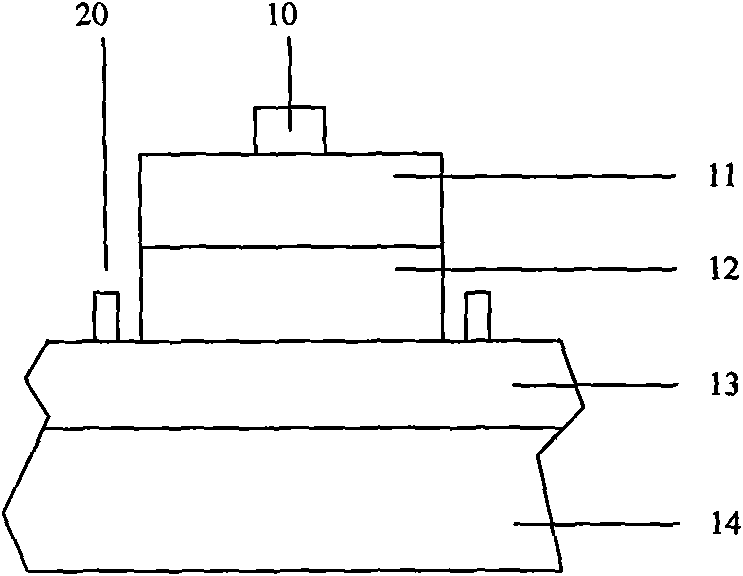
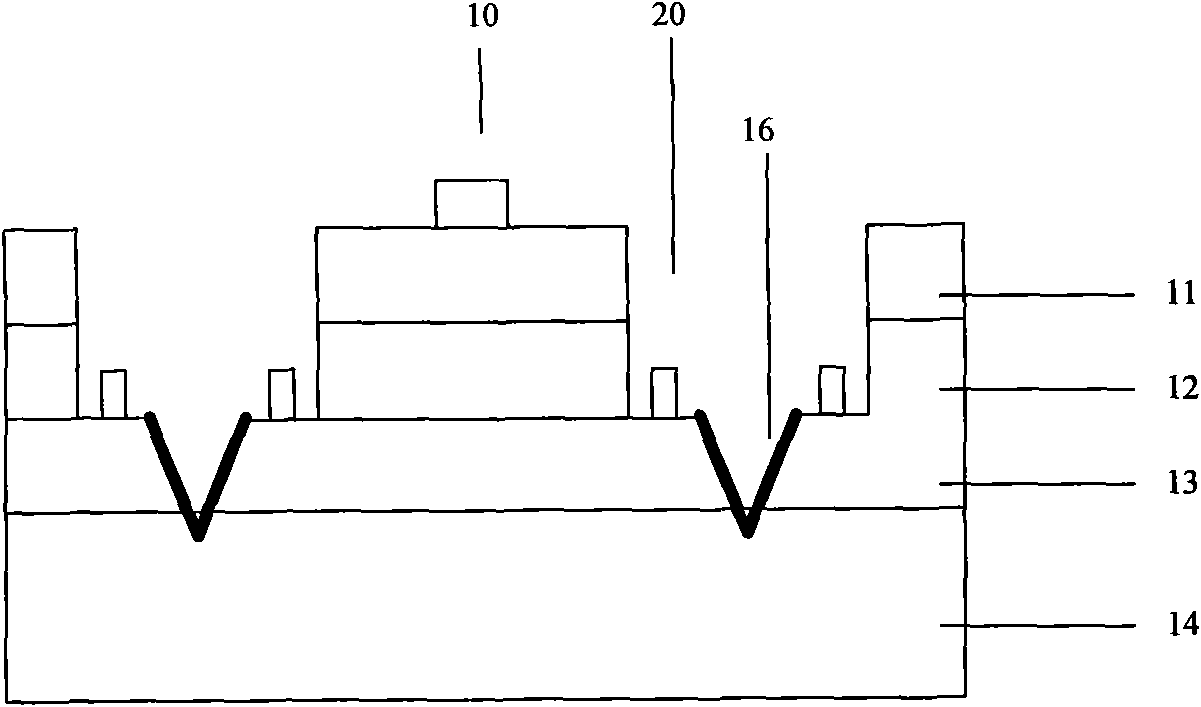
[0018] Please refer to Figure 3a , Figure 3a It is a schematic cross-sectional view of a light-emitting diode wafer in this embodiment. The light-emitting diode wafer includes a sapphire substrate 14 with a thickness of 420um-450um, and an N-type nitride layer 13 and a P-type nitride layer 11 grown on the sapphire substrate 14. And the multi-quantum well layer 12 between the N-type nitride layer 13 and the P-type nitride layer 11. Among them, the growth method of growing the nitride layer on the sapphire substrate 14 is preferably metal organic vapor phase growth method (MOCVD or MOVPE), and molecular beam epitaxy growth method (MBE), halogen vapor phase growth method (Halide VPE), liquid phase growth method can also be used. Growth method (LPE), and different growth methods can also...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com