Method for preparing graphitic carbon nanometer tube combination electrode material for lithium ion battery
A nanotube composite, lithium-ion battery technology, applied in the field of graphite electrode material preparation, can solve the problems of reduced electrode life, poor solvent compatibility, poor high current performance, etc., and achieve stable specific capacity, high specific capacity and long life. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
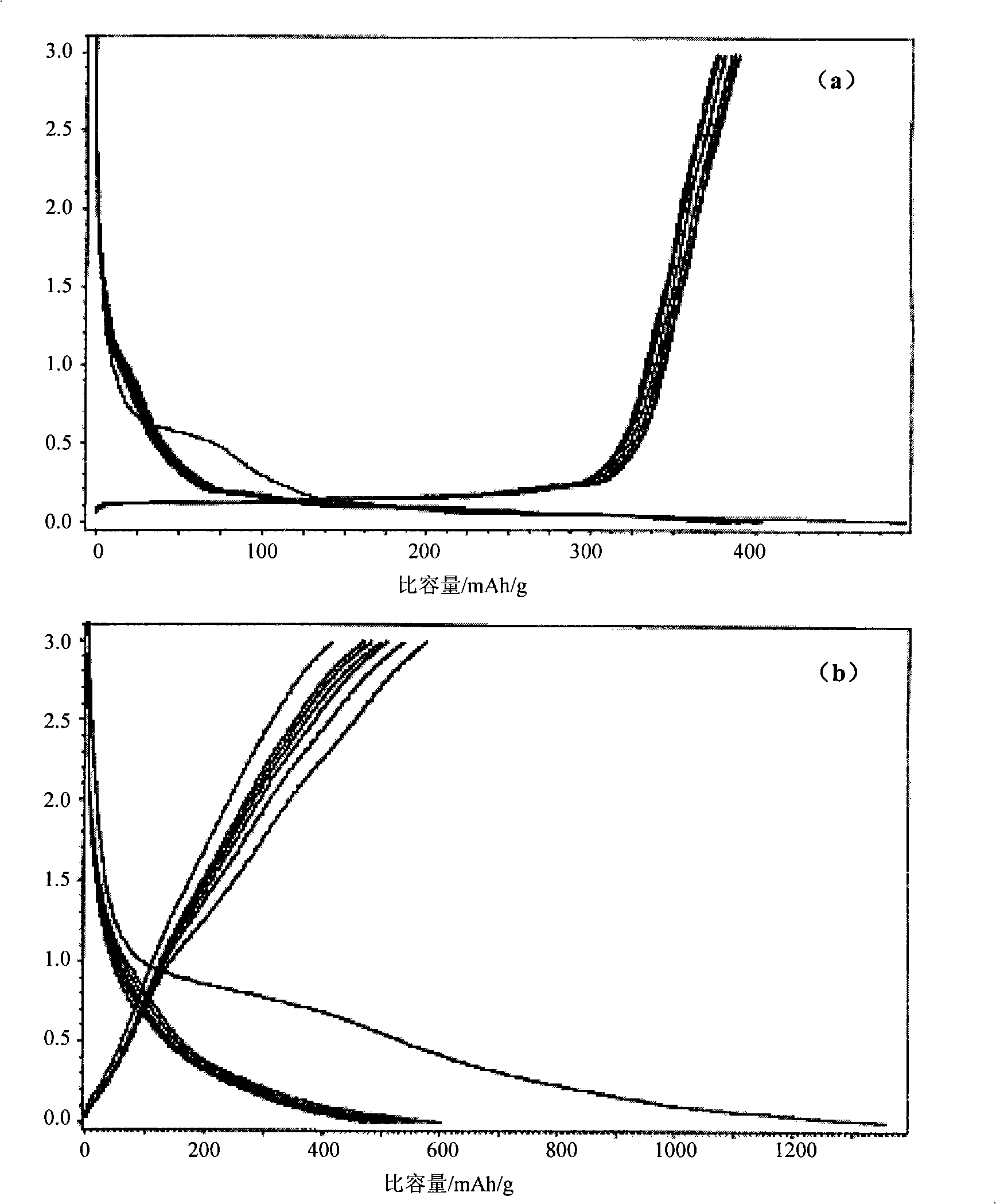
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Weigh a certain amount of Co, Ni, or Mo nitrate (catalyst) (according to the mass ratio of the catalyst and its support from 5% to 40%) to prepare a 50ml solution;
[0028] (2) Mix the corresponding amount of catalyst support graphite into the solution (1), heat it in a water bath at 90°C, and keep stirring until the solution is evaporated;
[0029] (3) Put the solid obtained in (2) into an oven at 80°C for 12 hours, then put N 2 Calcinate in a gas-protected muffle furnace at 500°C for 10 hours, take it out, grind it into powder, and put it in a desiccator for later use;
[0030] (4) Put the prepared catalyst precursor into a fixed bed-mobile gas phase device (WFSM-3011 type), at a gas flow rate of 40ml / min (Ar:H 2 =1:1; Ar is carrier gas, H 2 The temperature is linearly increased from room temperature to 500°C under the atmosphere of reducing gas, and the temperature is maintained for 60 minutes to ensure that the catalyst precursors are all reduced to active catalysts...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The main steps for the preparation of single-layer graphite in-situ modification (multilayer) graphite carbon nanotube composite electrode material:
[0035] (1) When graphite is immersed in concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated nitric acid to oxidize, a large number of functional groups will appear between the graphite layered structures, the interaction between the graphite layers and the layers will be significantly reduced, and the graphite multilayer structure will be partially converted into single Layer structure, and then reduce the graphite oxide to obtain a composite electrode material of single-layer graphite in-situ modified (multilayer) graphite;
[0036] (2) Growing carbon nanotubes in situ on the material prepared in (1) (same as Example 1) to obtain a single-layer graphite (Graphene) in-situ modified (multilayer) graphite carbon nanotube composite electrode material.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The main steps of preparing single-layer graphite modified (multi-layer) graphite carbon nanotube composite electrode material:
[0039] (1) Heat the graphite to 100-300°C and quickly immerse it in concentrated sulfuric acid or concentrated nitric acid solution below 10°C, add a surfactant (such as SDS) and ultrasonic vibration to fully oxidize and separate the graphite, and then reduce the product to form High-yield single-layer graphite, such as figure 2 (a) shown;
[0040](2) Perform chemical etching or mechanical ball milling on the prepared single-layer graphite oxide, so that many nano-scale micropores appear in the single-layer graphite, which further increases the specific surface area of the single-layer graphite and facilitates the insertion and insertion of lithium ions. De-embedding, such as figure 2 (b) Shown;
[0041] (3) Mix the prepared pure and pretreated single-layer graphite with (multilayer) graphite thoroughly and uniformly, and then grow carbon nan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com