Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
619results about "Angles/tapers measurement gauges" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
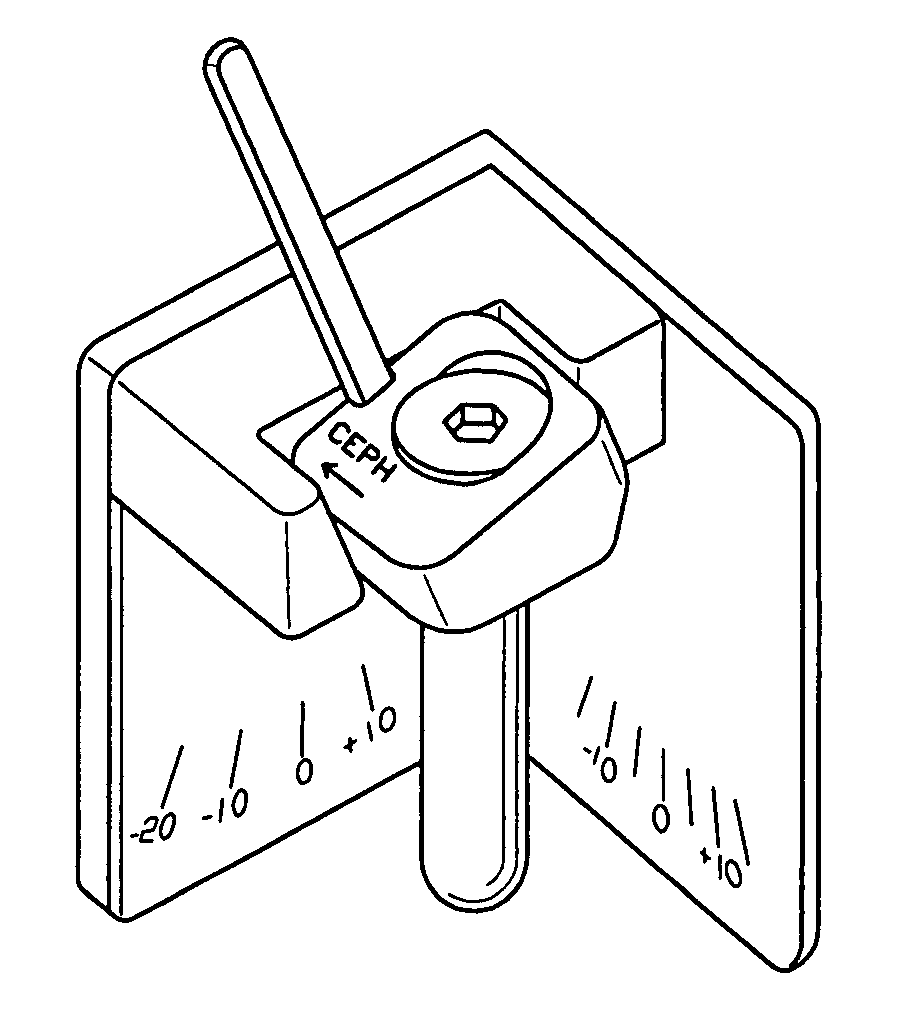
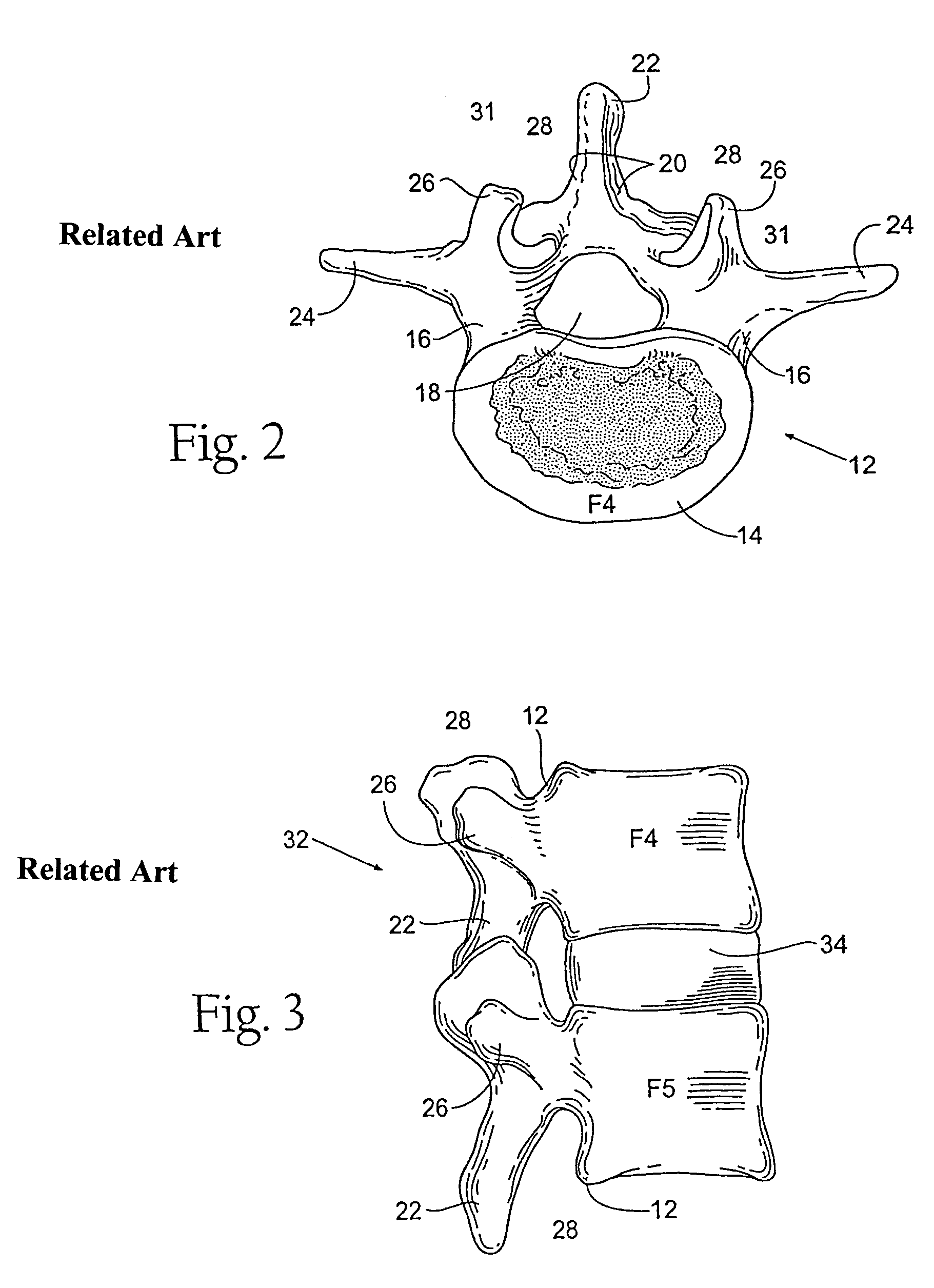
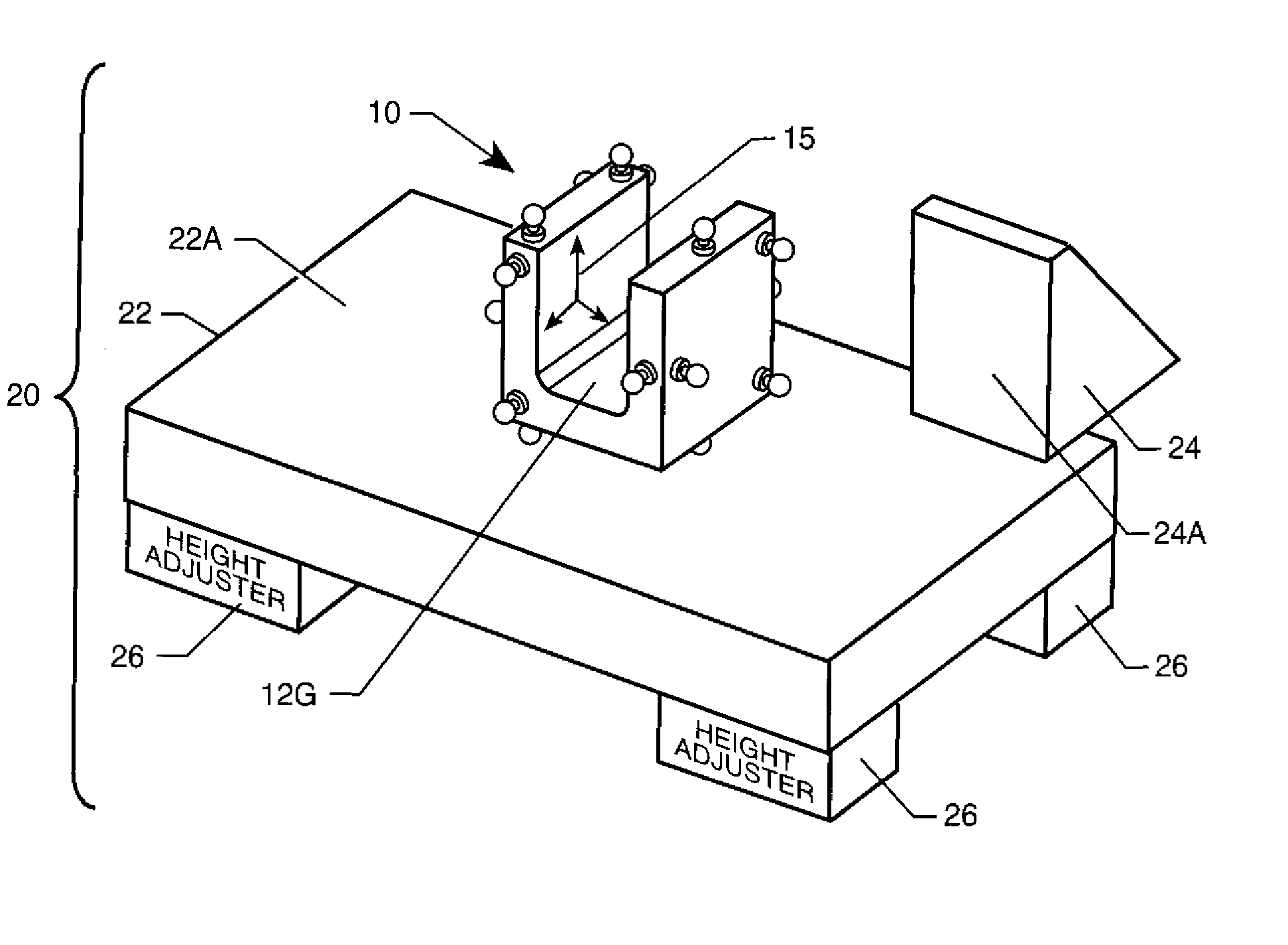
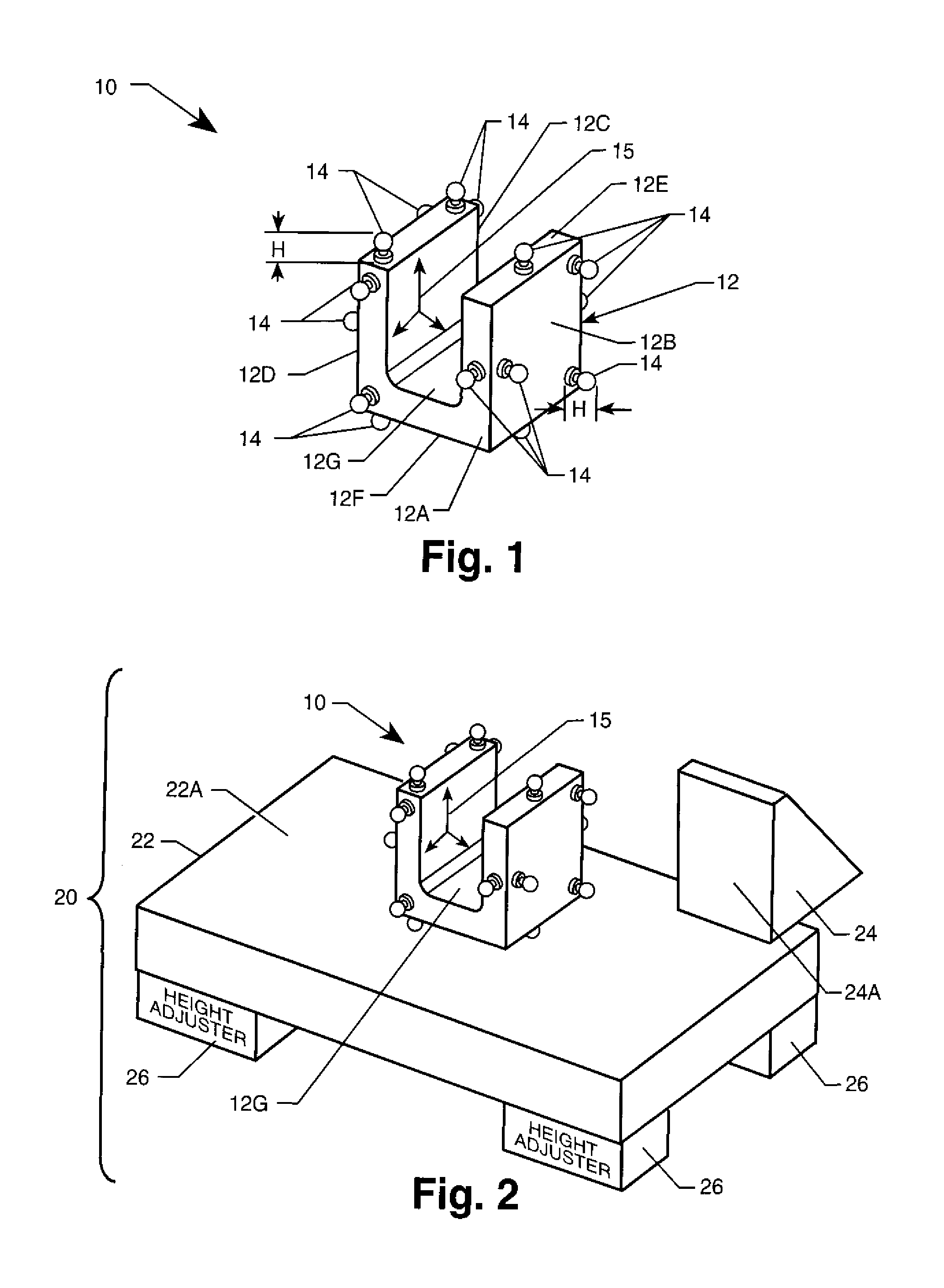
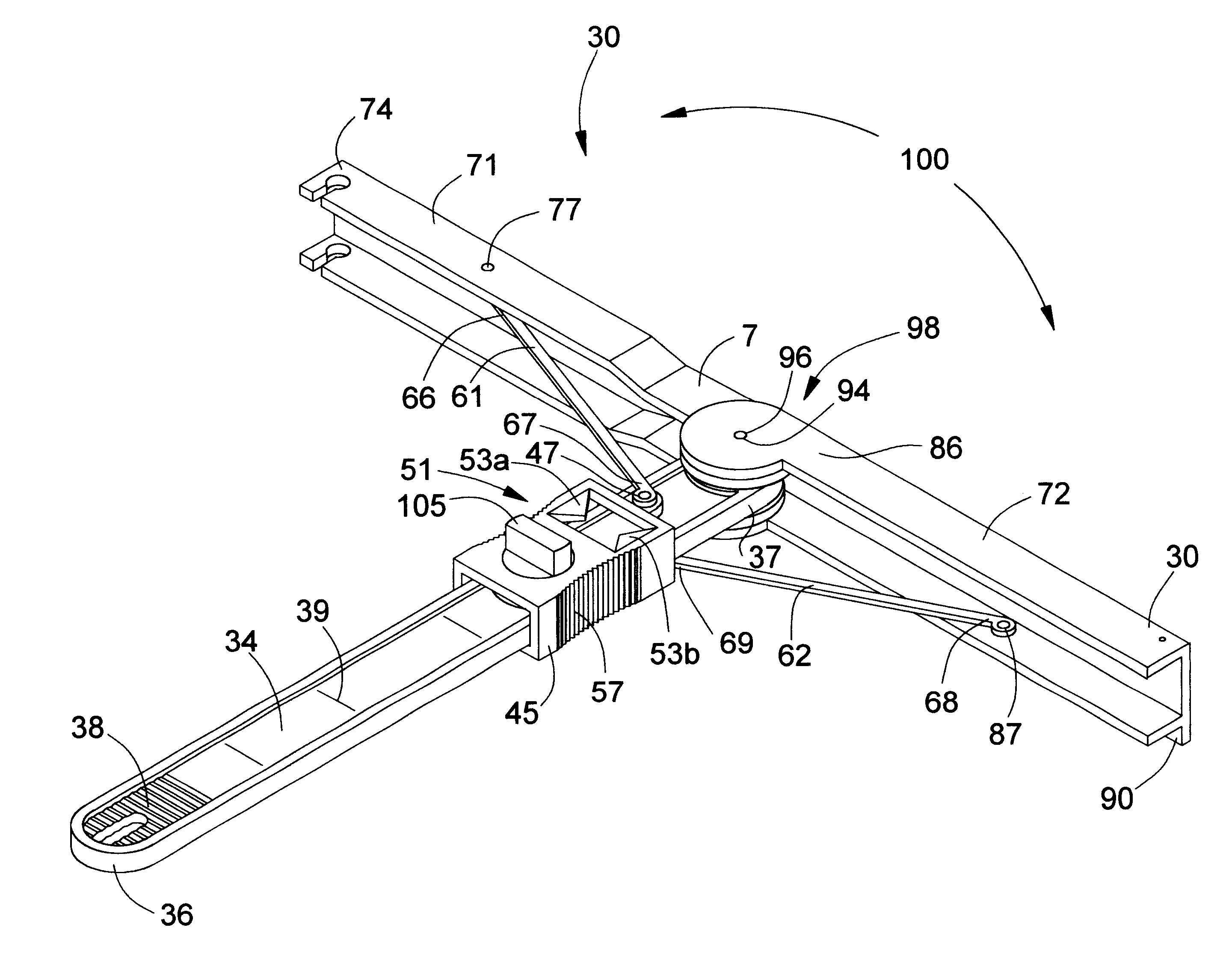
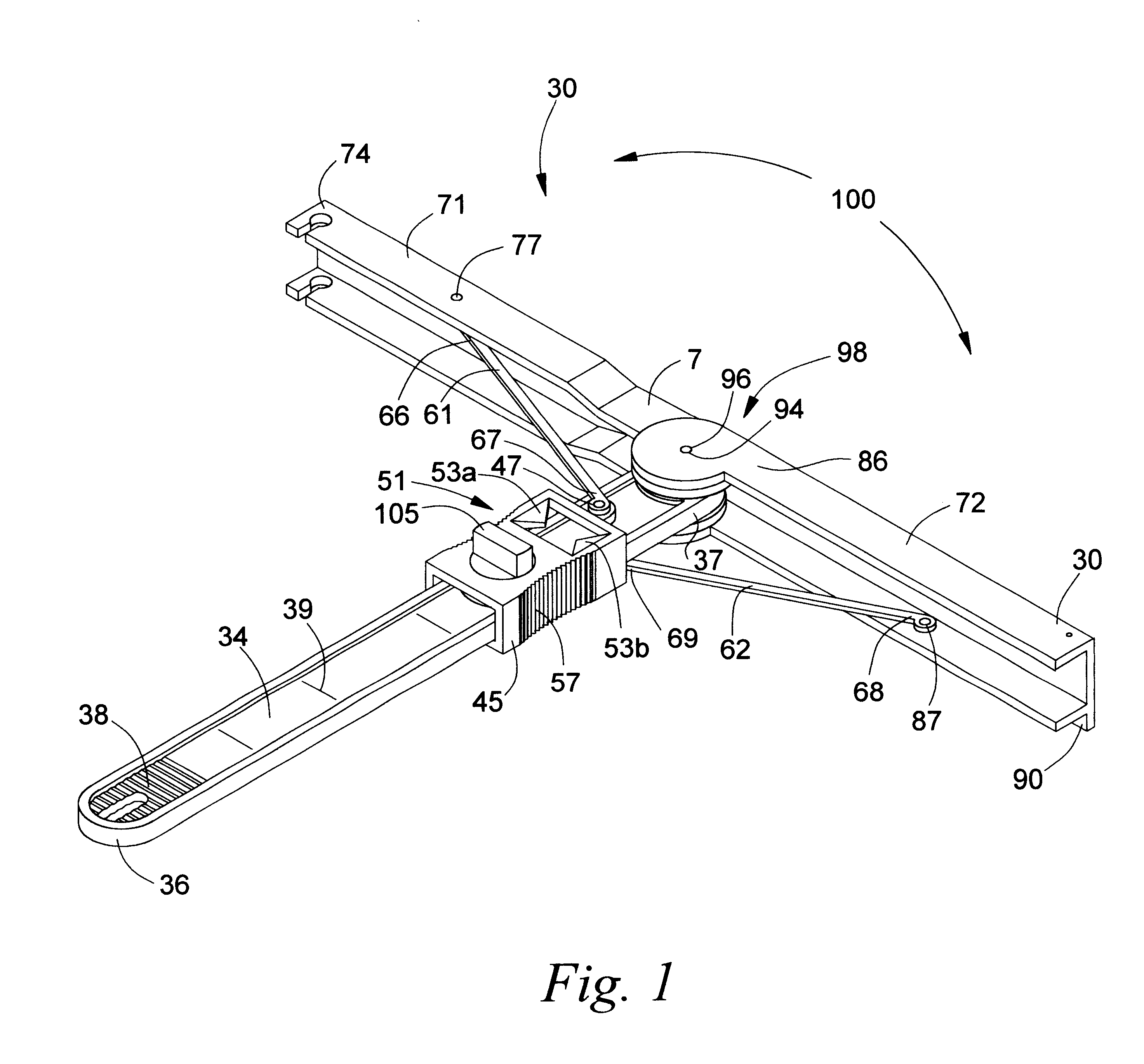
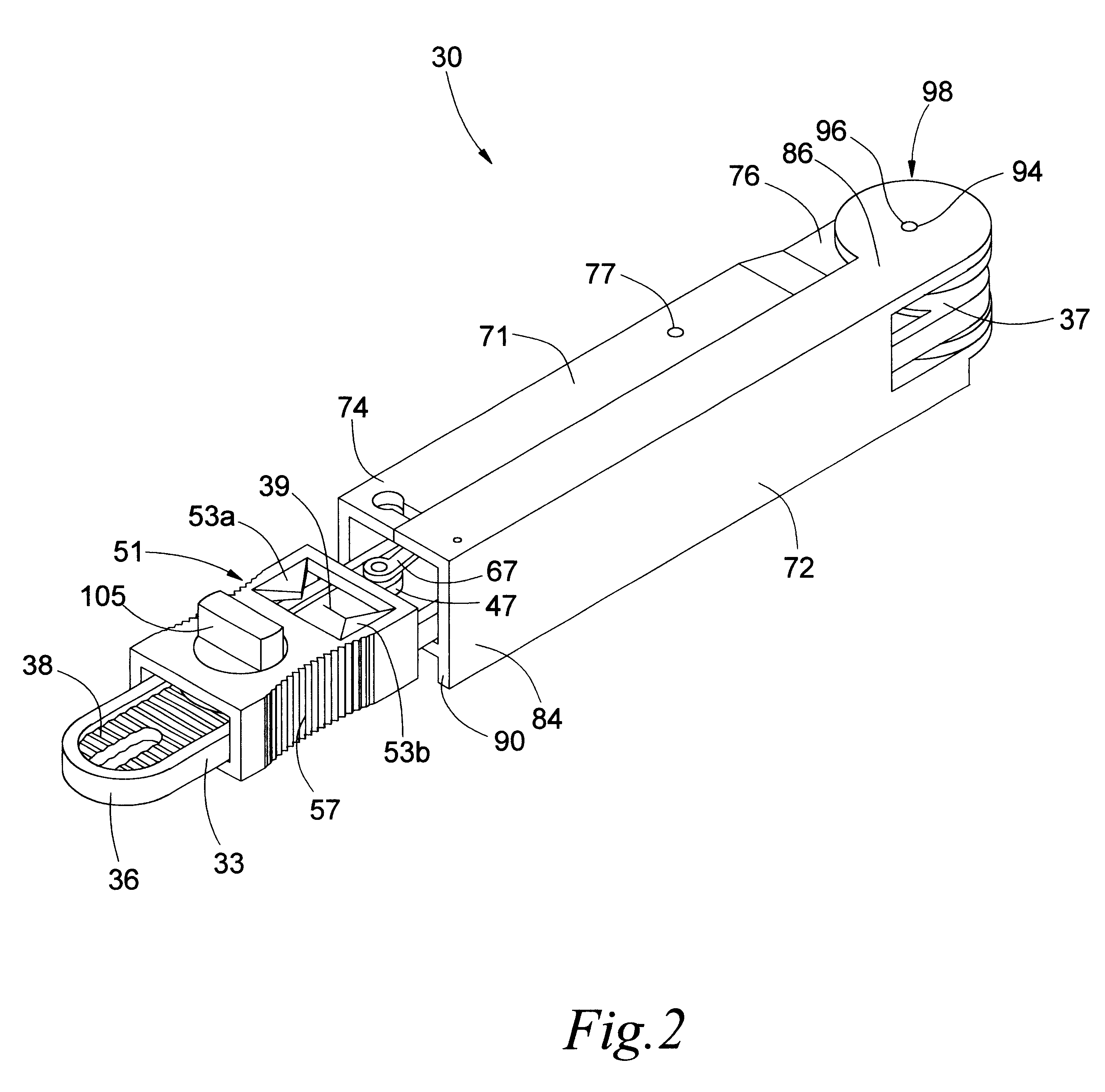
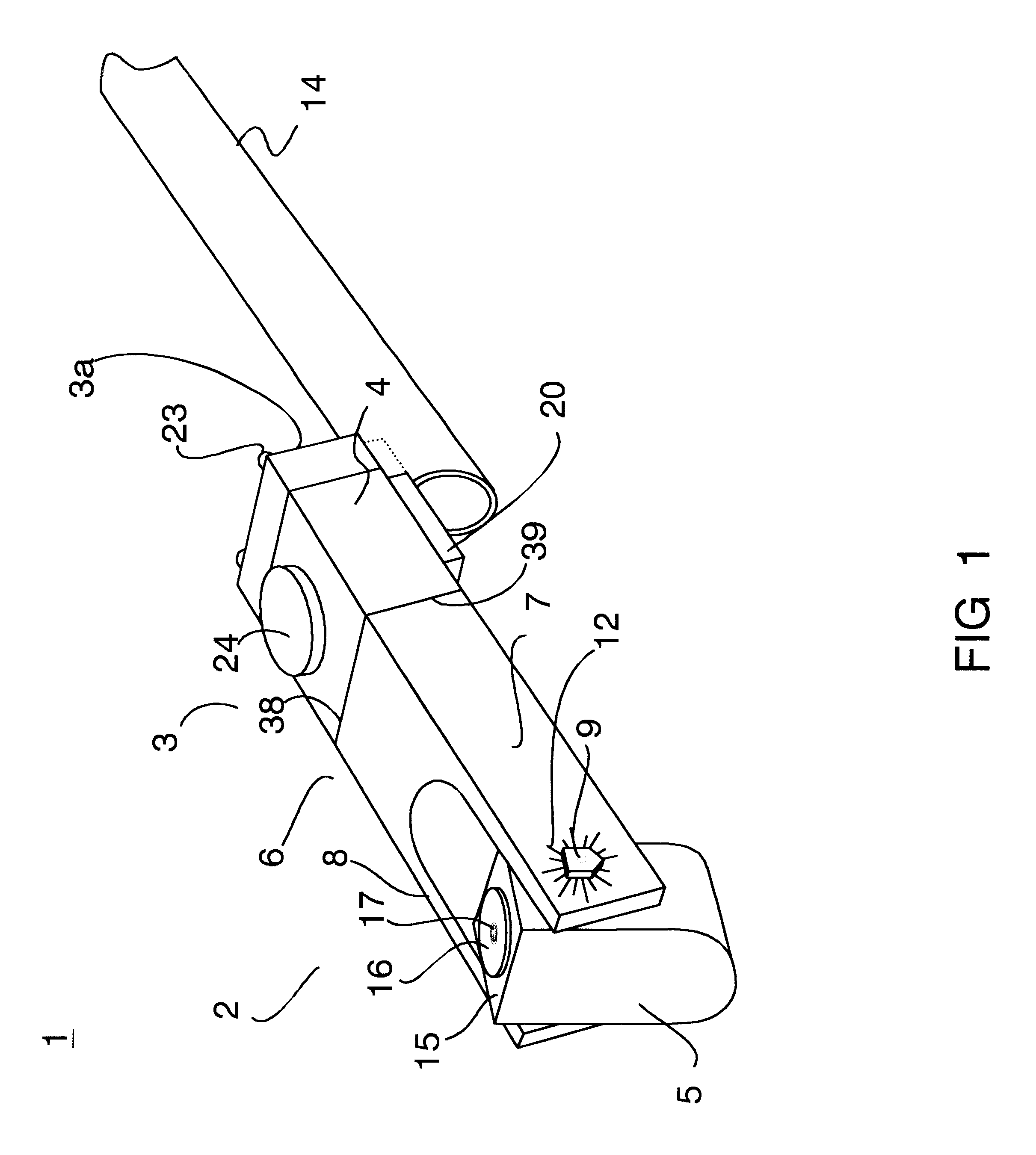
Facet joint prosthesis measurement and implant tools
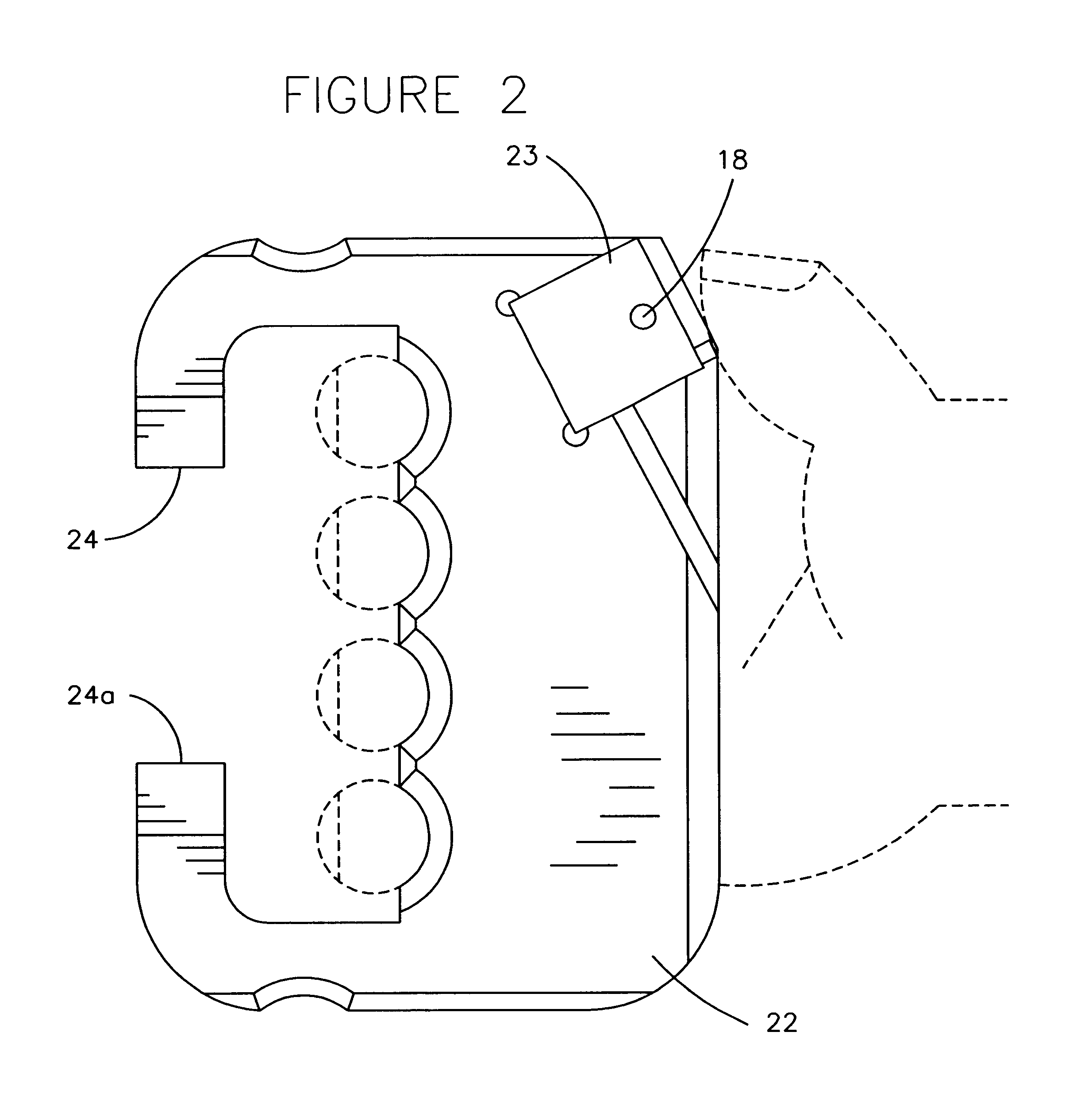
ActiveUS7051451B2Easy to measureAngles/taper measurementsInternal osteosythesisFacet joint prosthesisProsthesis
The present invention provides tools and methods designed to aid in the placement of facet joint prosthesis at virtually all spinal levels. One aspect of the present invention is a measurement tool for installing a cephalad facet joint prosthesis including a fixation measurement element and a support arm element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a cephalad facet joint prosthesis for implantation in a patient. Another aspect is a measurement tool for installing a caudal facet joint prosthesis including a stem element and a trial caudal bearing surface element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a caudal facet joint prosthesis for implantation in a patient. Yet another aspect is a measurement tool holder including a measurement surface connected to a holder element. This tool holder assists in determining the measurements obtained with the caudal facet joint prosthesis measurement tool.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
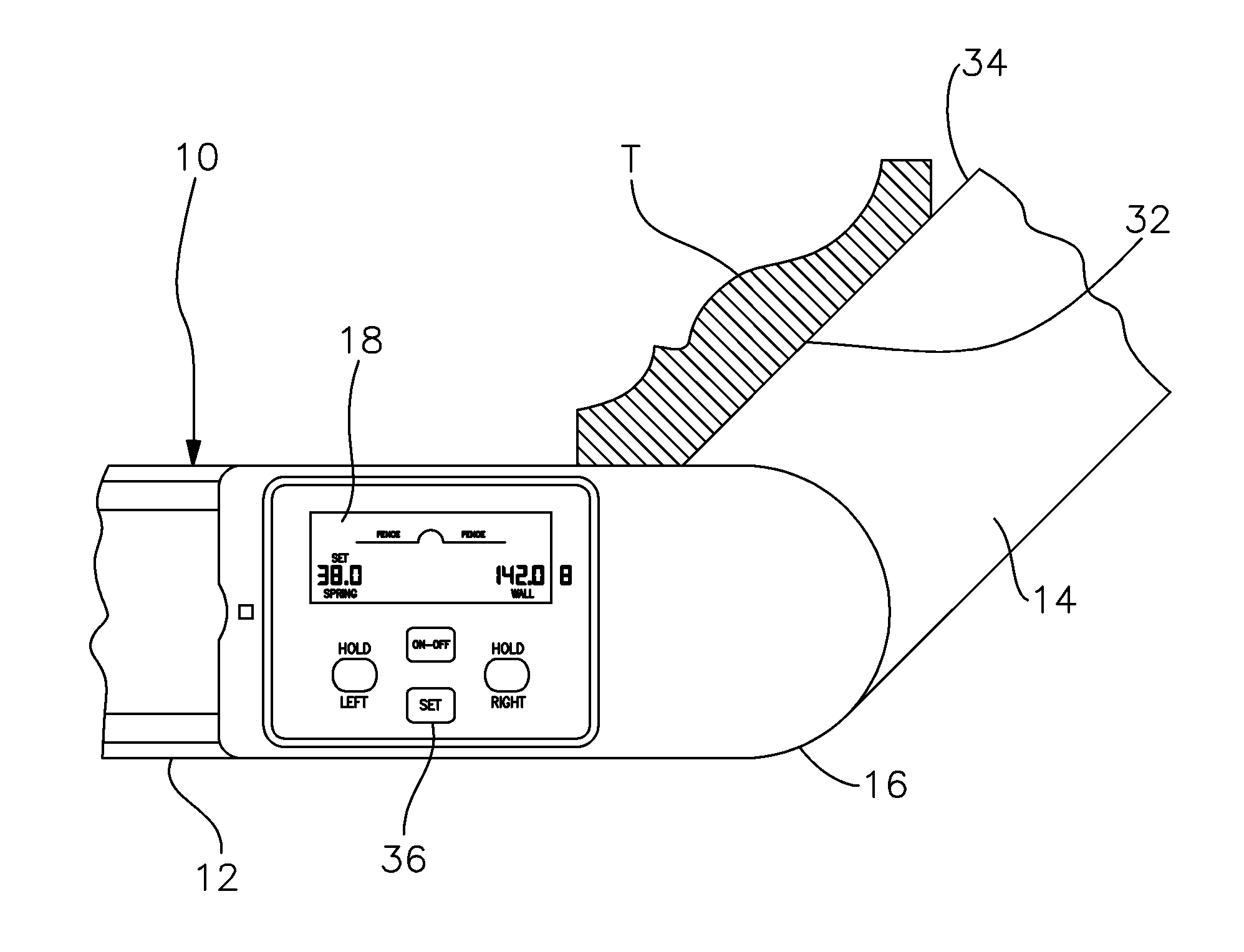
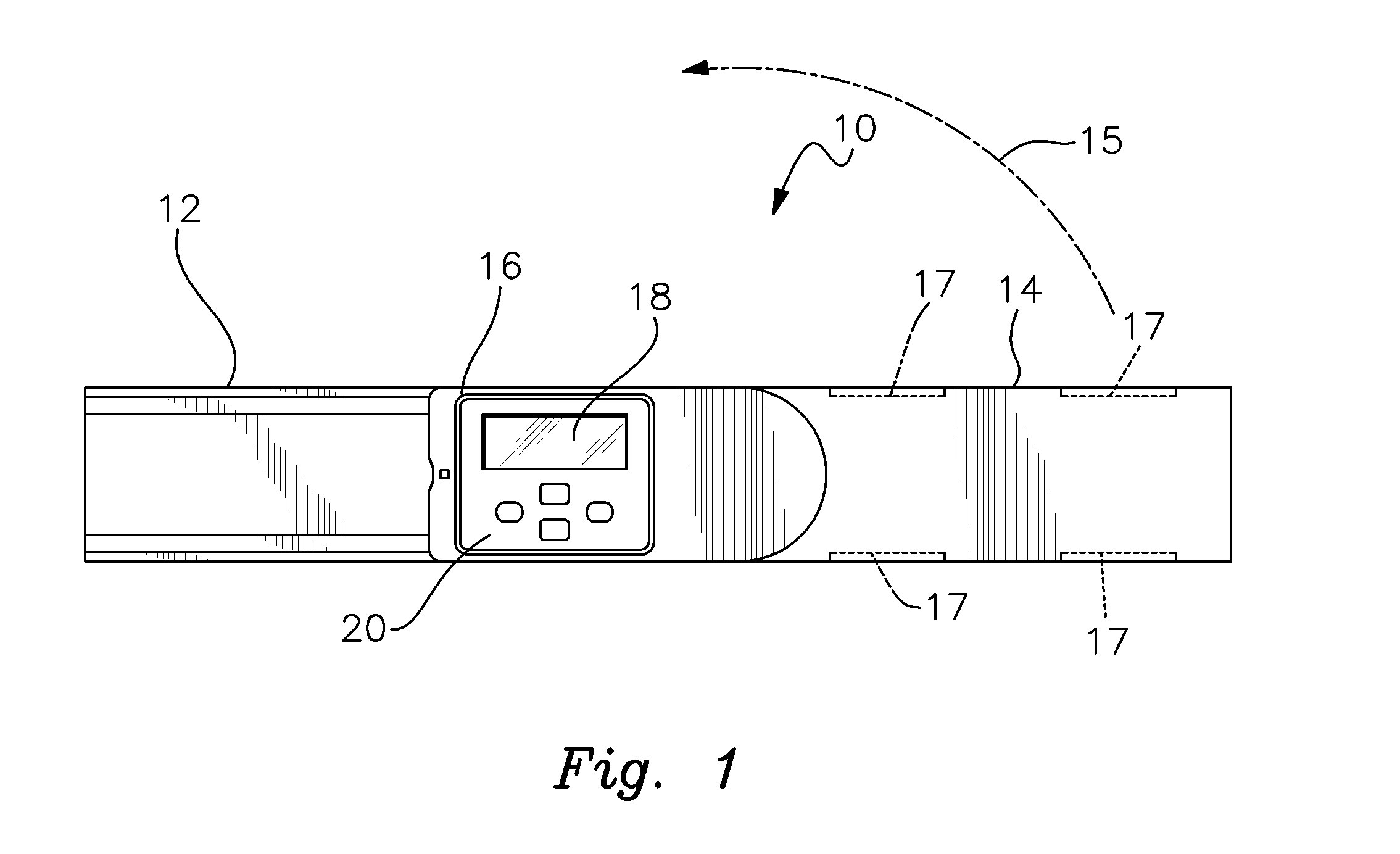
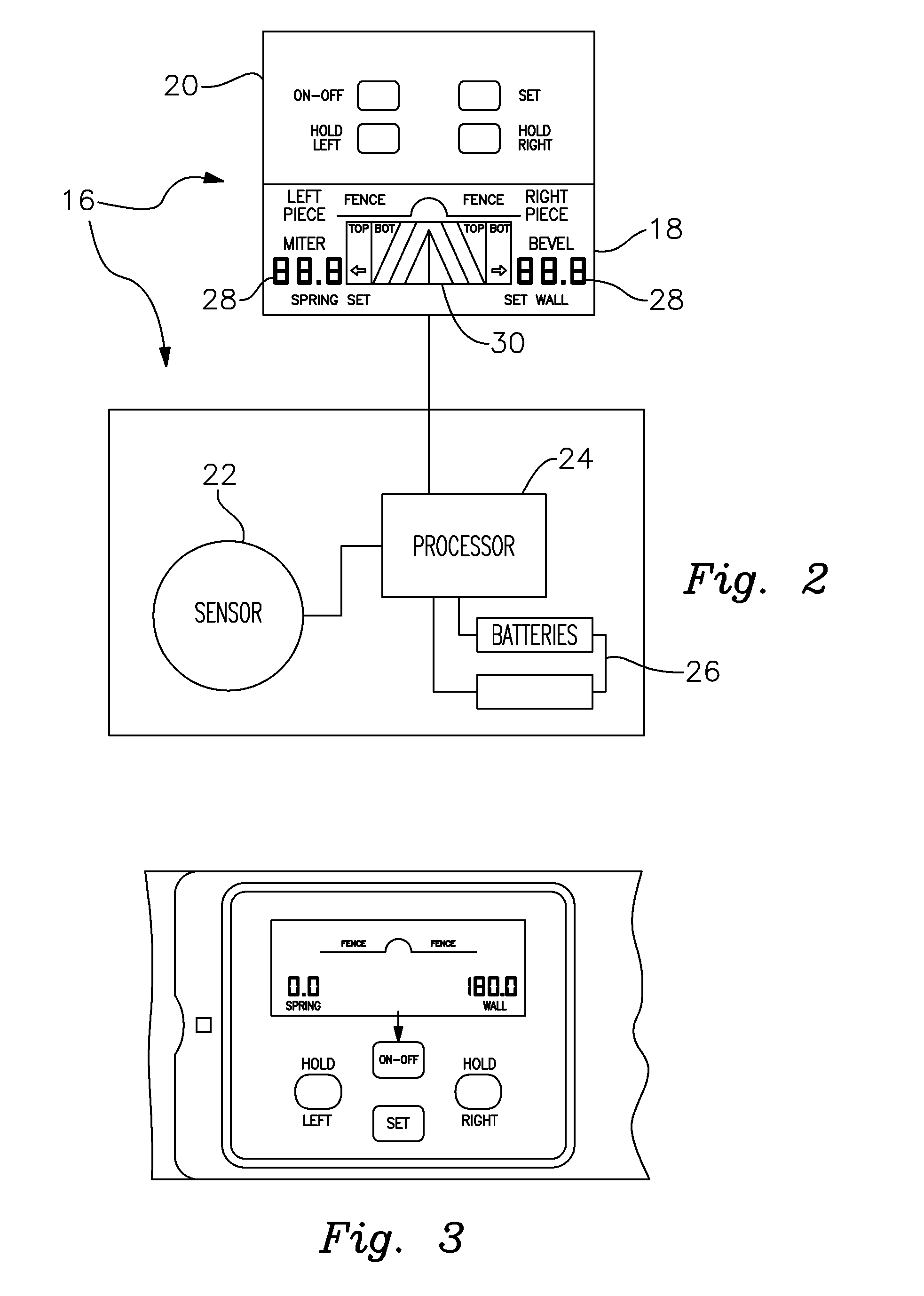
Crown Molding Protractor
InactiveUS20160238365A1Calculated quickly and accuratelyFacilitates and guides adjustmentBuilding constructionsAngles/tapers measurement gaugesProtractorCrown molding
A digital protractor is provided for measuring spring and wall angles and determining and effecting bevel and miter angle adjustments of a miter saw to adjoining pieces of trim in accordance with the measured spring and wall angles. The protractor includes a pair of pivotally interconnected arms. At least one sensor is attached to one of the arms and a digital readout is secured to the other arm. The readout includes means for determining the bevel and miter angles such that the protractor can be set to those angles to properly adjust the miter saw in accordance with the calculated angles.
Owner:WIXEY BARRY DOUGLAS +2
Portable coordinate measurement machine
InactiveUS7073271B2High abrasionHigh impactAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansStructural engineeringCoordinate-measuring machine
Owner:FARO TECH INC
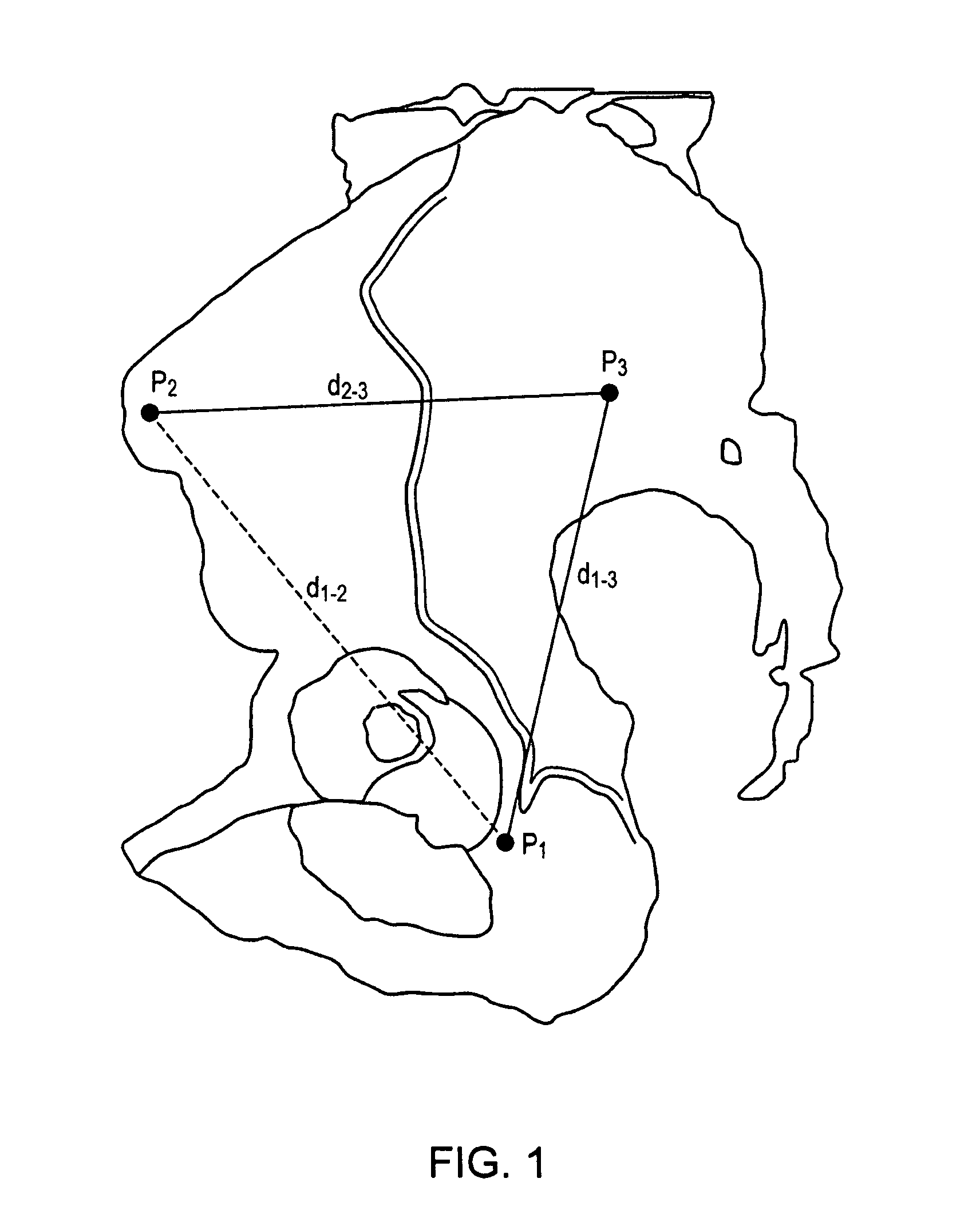
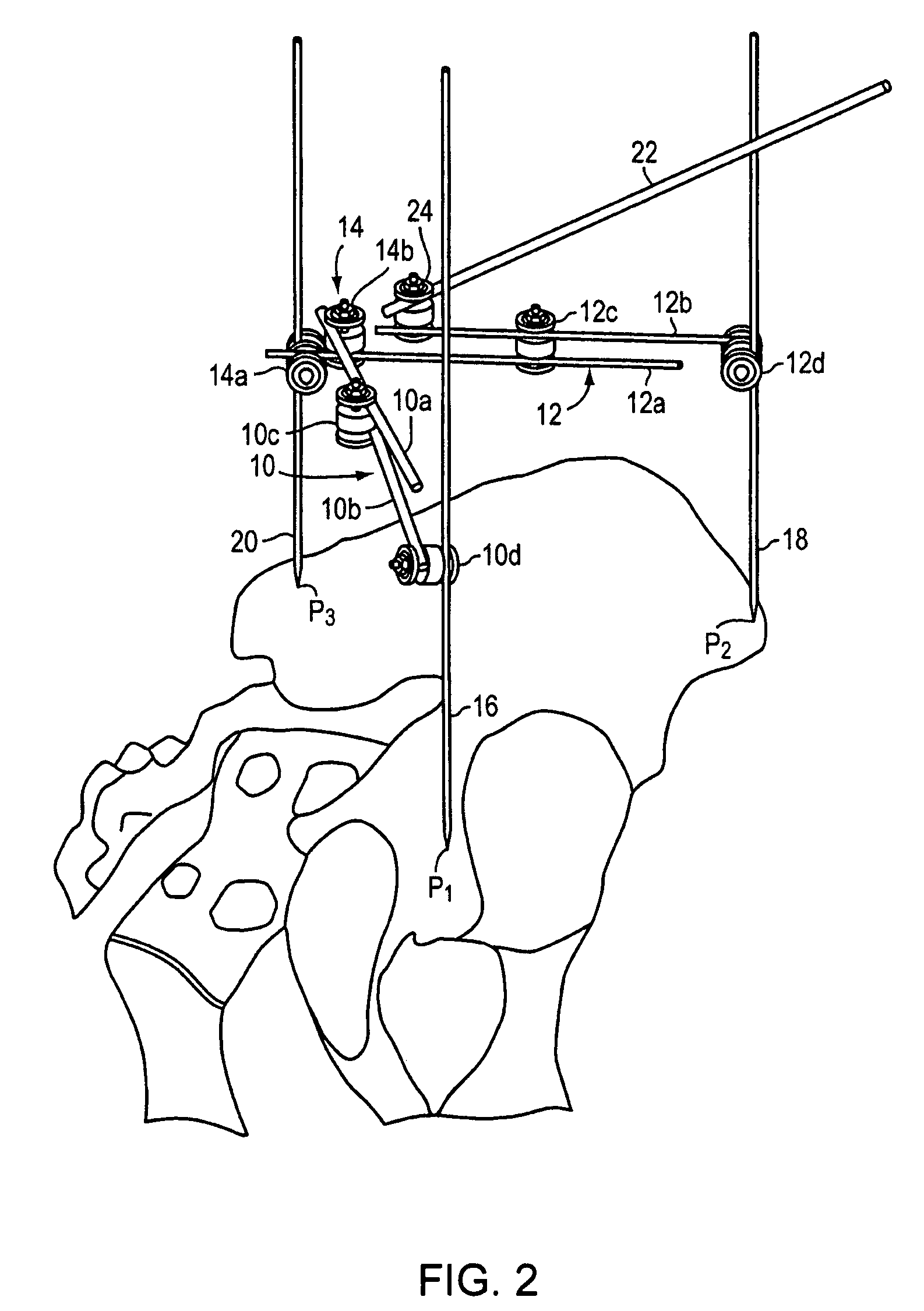
Method and apparatus for determining acetabular component positioning
ActiveUS20090306679A1Solve precise positioningError componentJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringAcetabular componentMedicine
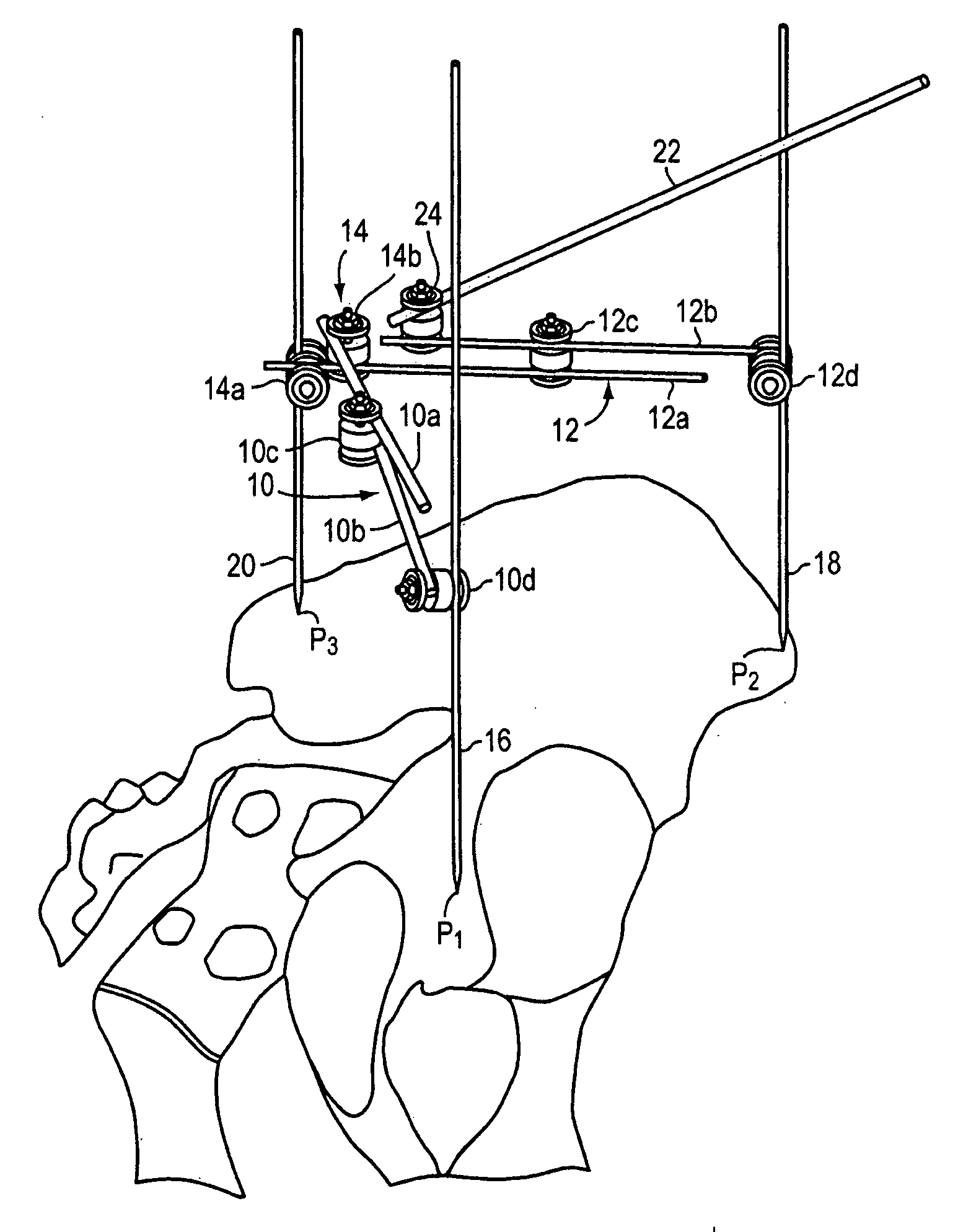
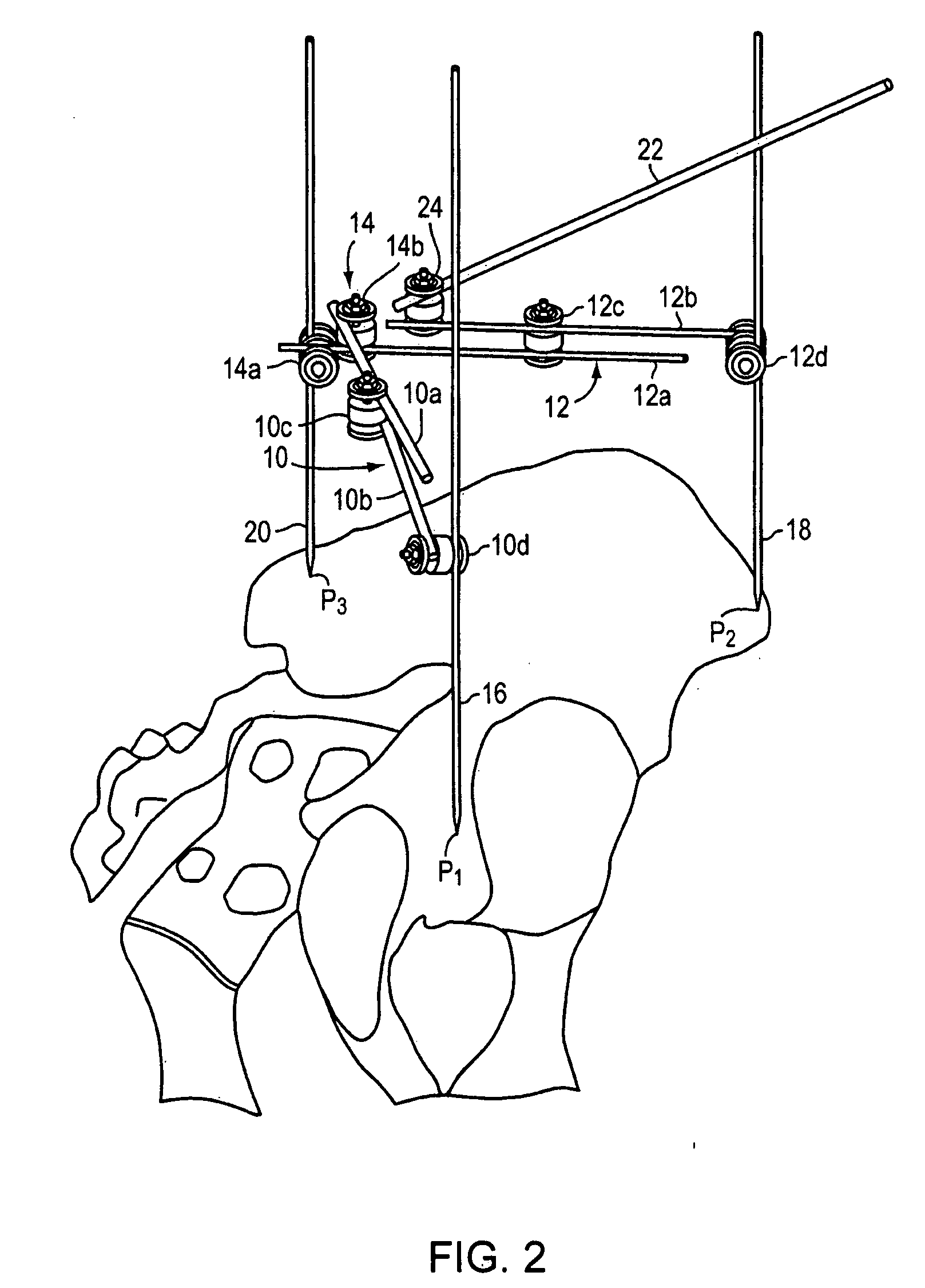
An instrument for establishing orientation of a pelvic prosthesis comprises a tri-pod having an angularly adjustable guide rod on it. The tips of the legs define a plane, and the guide rod is set by the surgeon to a defined orientation with respect to this plane on the basis of preoperative studies. In use, two of the legs of the instrument are positioned by the surgeon at defined anatomical locations on the pelvis (e.g., a point in the region of the posterior / inferior acetabulum and a point on the anterior superior iliac spine). The third leg then lands on the pelvis at a point determined by the position of the first two points, as well as by the separations between the third leg and the other two legs. The separations are adjustable, but are preferably fixed percentages of the separation between the first and second legs. The position of the guide rod then defines with respect to the actual pelvis the direction for insertion of a prosthesis.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Portable coordinate measurement machine
InactiveUS6952882B2Easy to convertEasy to distinguishProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngles/taper measurementsProximity sensorEngineering
A portable coordinate measurement machine comprises an articulated arm having jointed arm segments. The arm includes joint assemblies which include at least one read head together with one or more (preferably five) sensors (preferably proximity sensors) in communication with a periodic pattern of a measurable characteristic, the pattern and read heads being positioned within the joint so as to be rotatable with respect to each other.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for determining acetabular component positioning
ActiveUS8267938B2Solve precise positioningError componentJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringAcetabular componentMedicine
An instrument for establishing orientation of a pelvic prosthesis comprises a tri-pod having an angularly adjustable guide rod on it. The tips of the legs define a plane, and the guide rod is set by the surgeon to a defined orientation with respect to this plane on the basis of preoperative studies. In use, two of the legs of the instrument are positioned by the surgeon at defined anatomical locations on the pelvis (e.g., a point in the region of the posterior / inferior acetabulum and a point on the anterior superior iliac spine). The third leg then lands on the pelvis at a point determined by the position of the first two points, as well as by the separations between the third leg and the other two legs. The separations are adjustable, but are preferably fixed percentages of the separation between the first and second legs. The position of the guide rod then defines with respect to the actual pelvis the direction for insertion of a prosthesis.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
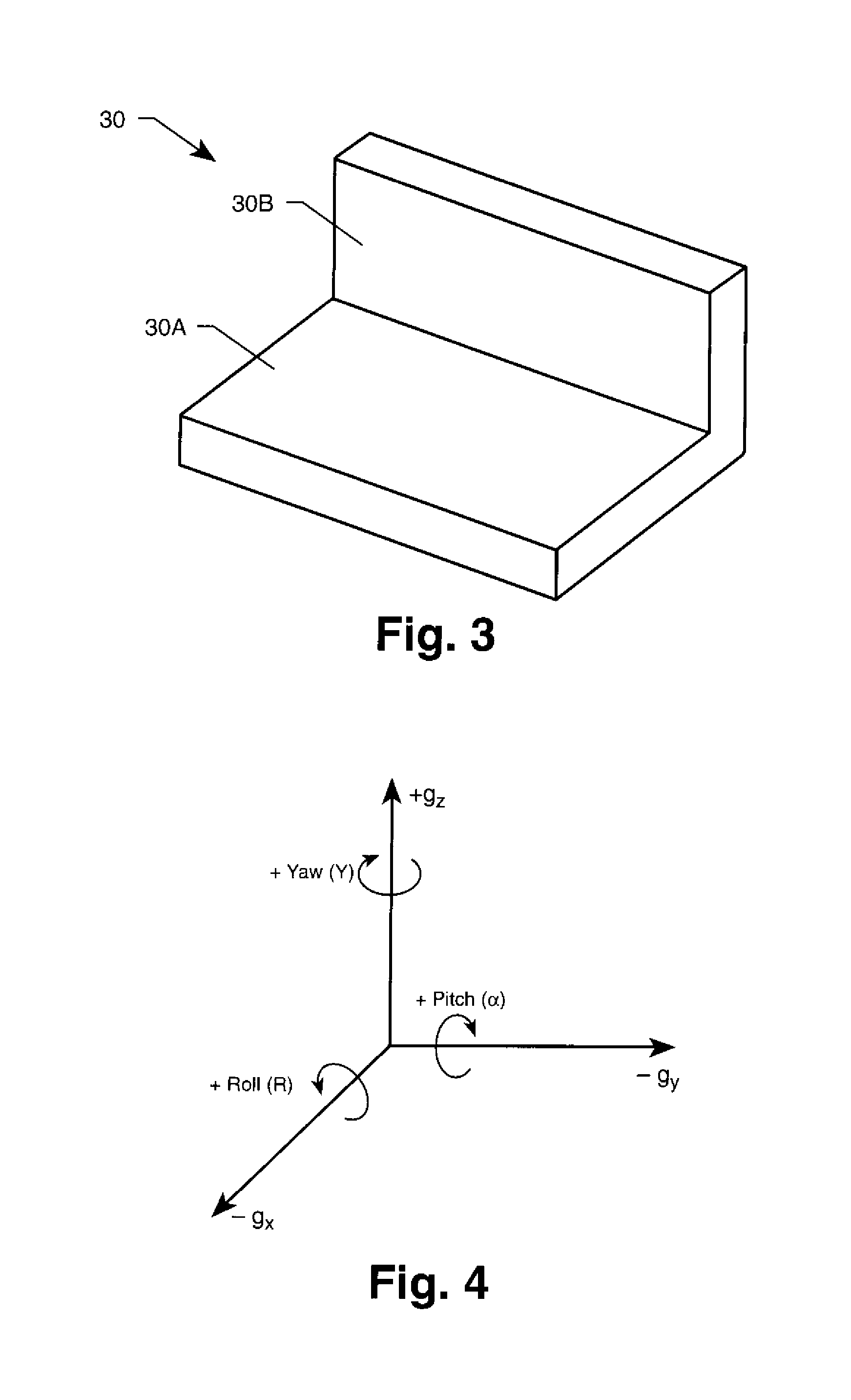
Miniaturized inclinometer for angle measurement with accurate measurement indicator
InactiveUS6871413B1Accurate measurementUnlimited 360 degree resolutionAngles/taper measurementsUsing electrical meansMultiplexerSignal conditioning
The novel miniaturized inclinometer for angle measurement with accurate measurement indicator is designed to monitor the angular motion of limbs. The device contains at least one inclinometer with signal conditioning electronics, including a microprocessor, placed within a miniature housing. A number of different sensors can be used and positioned in their housings so that their outputs vary as a function of their angle with respect to the gravity sector. The microprocessor controls a multiplexer, which controls the activities of the sensors; performs analog to digital conversions and measures the output curves from the sensor pairs to perform a conversion which results in a three hundred and sixty degree range with respect to gravity. Calibration data is stored in a read only memory and the microprocessor corrects variables to ensure accuracy and measures the difference in angle between the pairs of sensors.
Owner:LORD CORP
Method and apparatus for improving measurement accuracy of a portable coordinate measurement machine
InactiveUSRE42082E1Easy to convertEasy to distinguishProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngles/taper measurementsEngineeringMeasurement precision
A method for improving the measurement accuracy of a portable coordinate measurement machine which comprises an articulated arm having jointed arm segments is presented. This method includes sensing deformation of a portion of the articulated arm when the arm is placed under a load, this deformation causing an error in the measurement made by the CMM, and correcting such error in response to the sensed deformation.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Positioning System For Single Or Multi-Axis Sensitive Instrument Calibration And Calibration System For Use Therewith
InactiveUS20080202199A1Simple procedureWave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusReference fieldTangential contact
A positioning and calibration system are provided for use in calibrating a single or multi axis sensitive instrument, such as an inclinometer. The positioning system includes a positioner that defines six planes of tangential contact. A mounting region within the six planes is adapted to have an inclinometer coupled thereto. The positioning system also includes means for defining first and second flat surfaces that are approximately perpendicular to one another with the first surface adapted to be oriented relative to a local or induced reference field of interest to the instrument being calibrated, such as a gravitational vector. The positioner is positioned such that one of its six planes tangentially rests on the first flat surface and another of its six planes tangentially contacts the second flat surface. A calibration system is formed when the positioning system is used with a data collector and processor.
Owner:NASA
Laser line generating device with swivel base
A laser alignment device includes a laser generating device, an upper attachment portion, and a lower attachment portion. The laser generating device includes a housing and a laser generator. The upper attachment portion is disposed near a bottom of the housing, and the lower attachment portion is pivotally and / or rotationally connected to the upper attachment portion.
Owner:IRWIN IND TOOL CO
Multi-purpose measuring tool
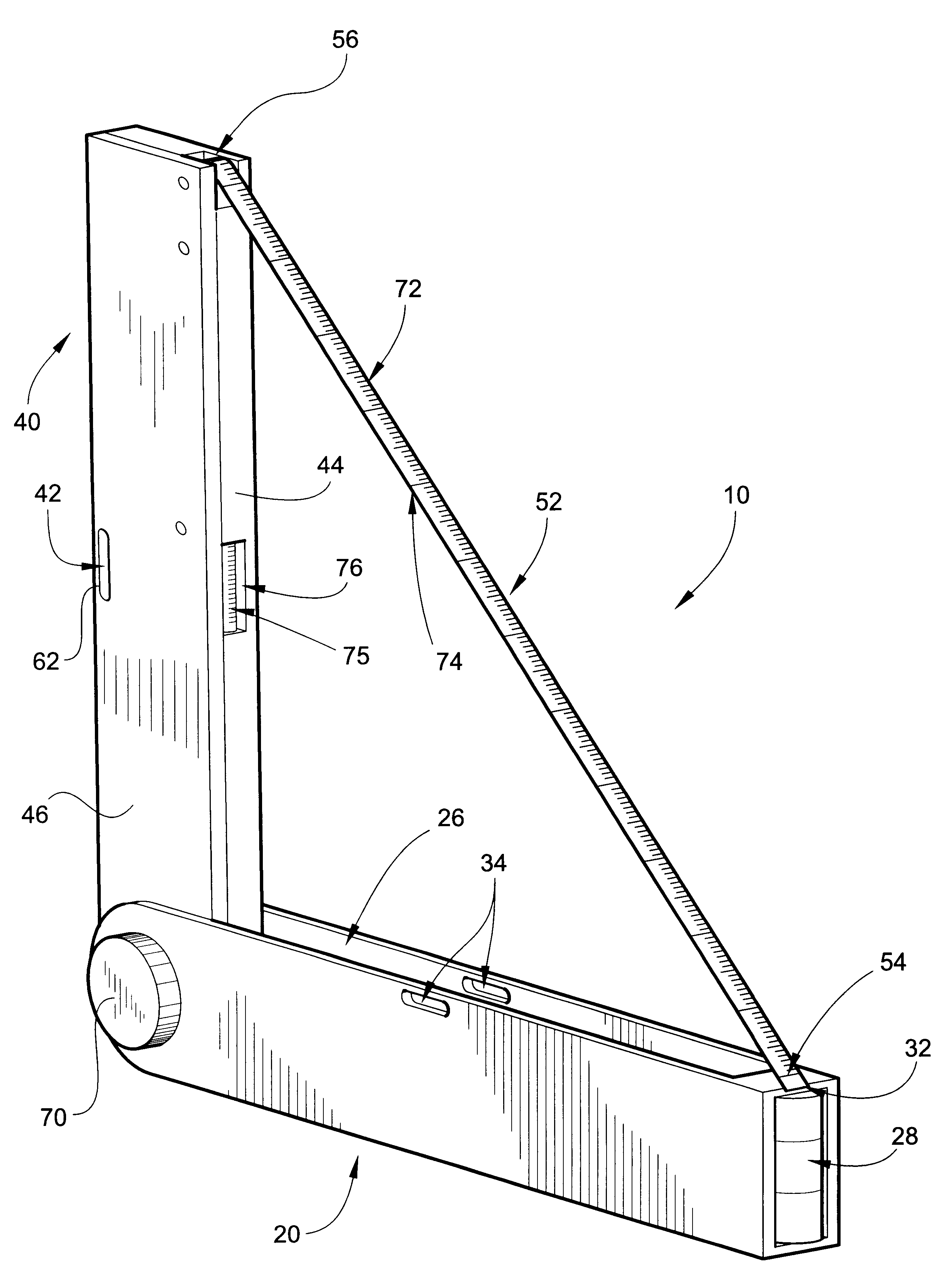
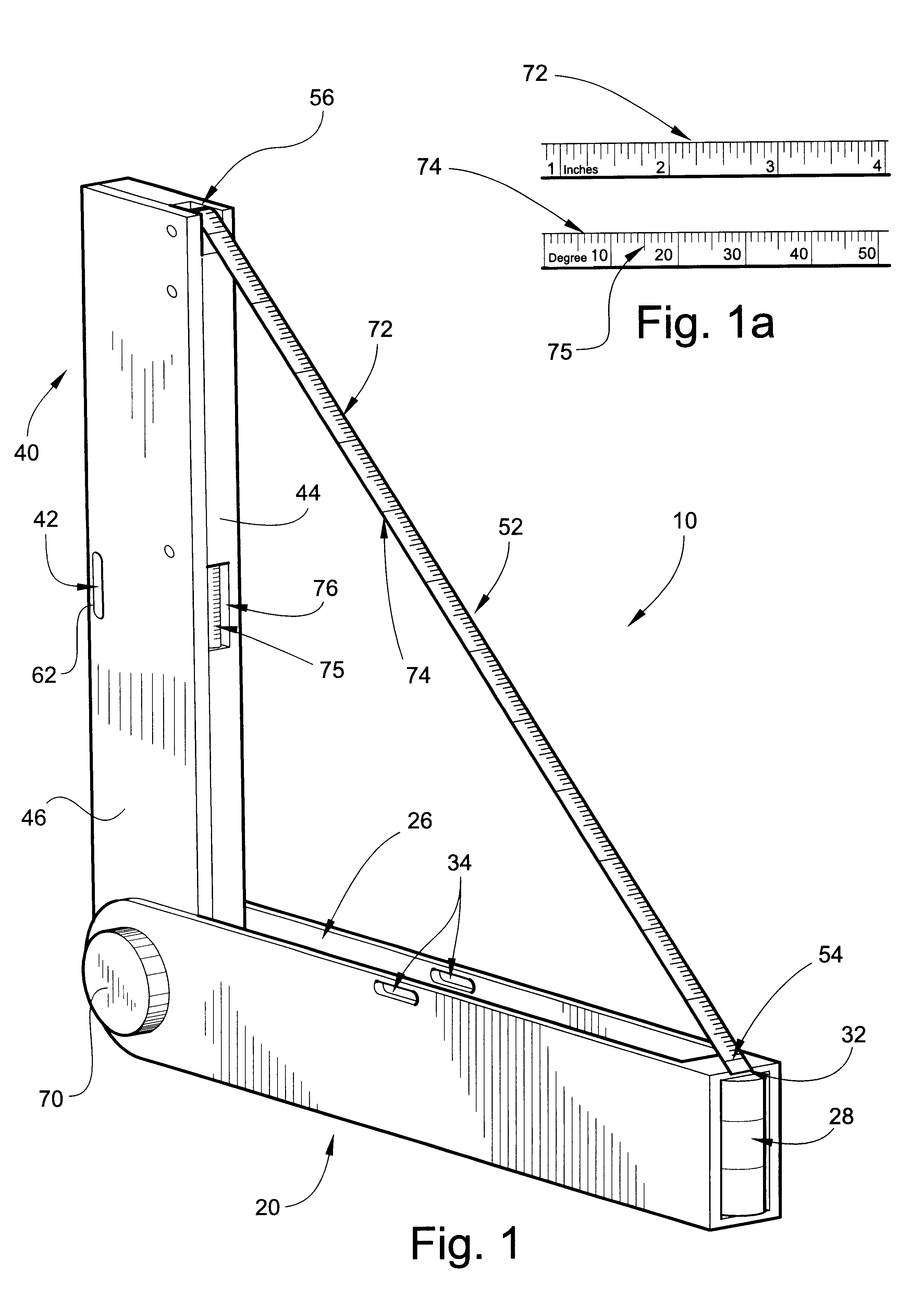
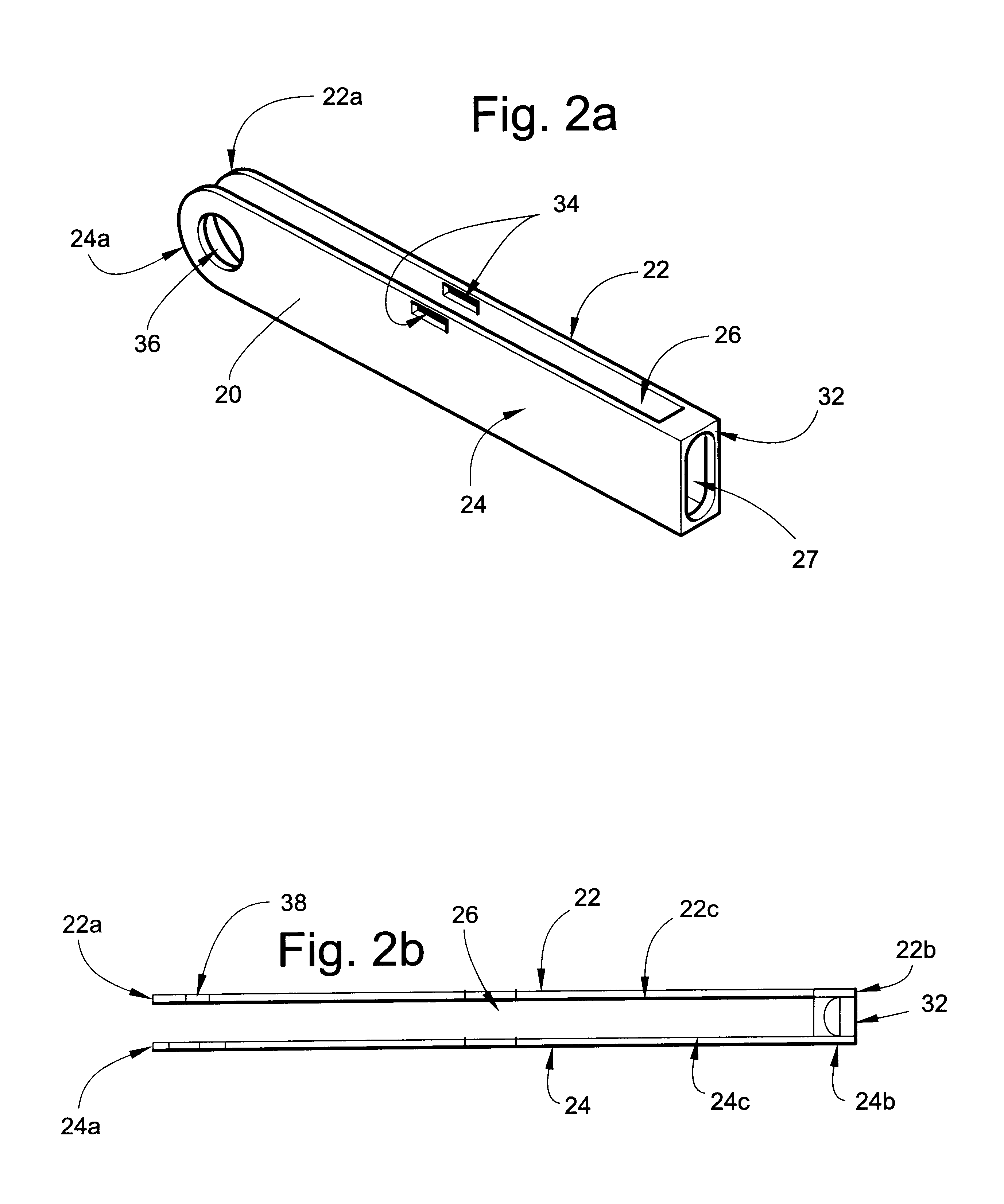
A multi-purpose measuring tool has an elongate base and arm pivotally connected at rounded ends thereof in an angularly variable relation to perform multiple functions, including measuring inclines, measuring corner angles, measuring distances, use as a square, use as a bevel gauge and use as a torpedo level. A retractable measuring tape housed within the arm has a terminal finger gripping end adapted to be pulled away from the arm and removably attached to a distal end of the base. The measuring tape is dual purpose in that one side of the tape is used for determining the angle of the arm relative to the base to perform some of the above functions, and the other side of the tape is used for traditional linear distance measurements. The tool's base includes a "vertical" bubble level and the arm includes a "horizontal" bubble level to perform some of the above functions.
Owner:MOE RICHARD J
Adjustable angle carpentry apparatus
Owner:QUICK ANGLE
Pipe-bending alignment device
InactiveUS6385856B1Accurate measurementReduce manufacturing costAngles/taper measurementsIncline measurementEngineeringAngle gauge
An economical, compact guide for introducing multiple bends in one or more planes in a pipe, conduit, or other tube-like item. The guide has a gauge section rotatably attached to a mounting section and is affixable by means of a non-deforming clamp to the end of a pipe segment to be bent. The gauge section has a bend-angle gauge and a bend-plane level. The bend-angle gauge is a plumb arm mounted so as to measure and indicate the bending of a pipe to any degree of bend. The bend-plane guide is a 360° level mounted on an upper face of the plumb arm. Multiple bends are made in the pipe segment without removing or re-aligning the guide. This ensures that the initial reference position is maintained throughout the bending process and ensures that all bends are in the proper bend-plane, thus avoiding "dogging" between successive bends. Multiple successive bend-planes also may be established without removing or re-aligning the guide on the pipe, by rotating the gauge section of the guide relative to the mounting section by the magnitude of the desired out-of-plane angle.
Owner:GODIN JEFFREY L
Snap locking angle adjustable device, in particular a carpenter's square
The invention is a snap locking angle adjustable device, particularly applicable to carpenter's squares. Carpenter's squares, being used in rough environment, must be simple to adjust while providing robust snap locking at high angle precision. Prior art attains this by protruding steel balls, attached around the pivot axis of the square's handle, pressed strongly against a hole punched area around the pivot axis of the square's blade-balls aligns to holes gives the snap locking. The problem is to simplify manufacturing. The invention comprises components with moulded alignment structures. These components are the complete pivot members (handle or blade) themselves, or are separately attached to the pivot members. The components, and optionally, are sandwiched, alignment structures against each other, and axially pressed together strongly by a spring held in compression by a press frame that also may constitute a pivot shaft for the pivot members.
Owner:LOGOSOL
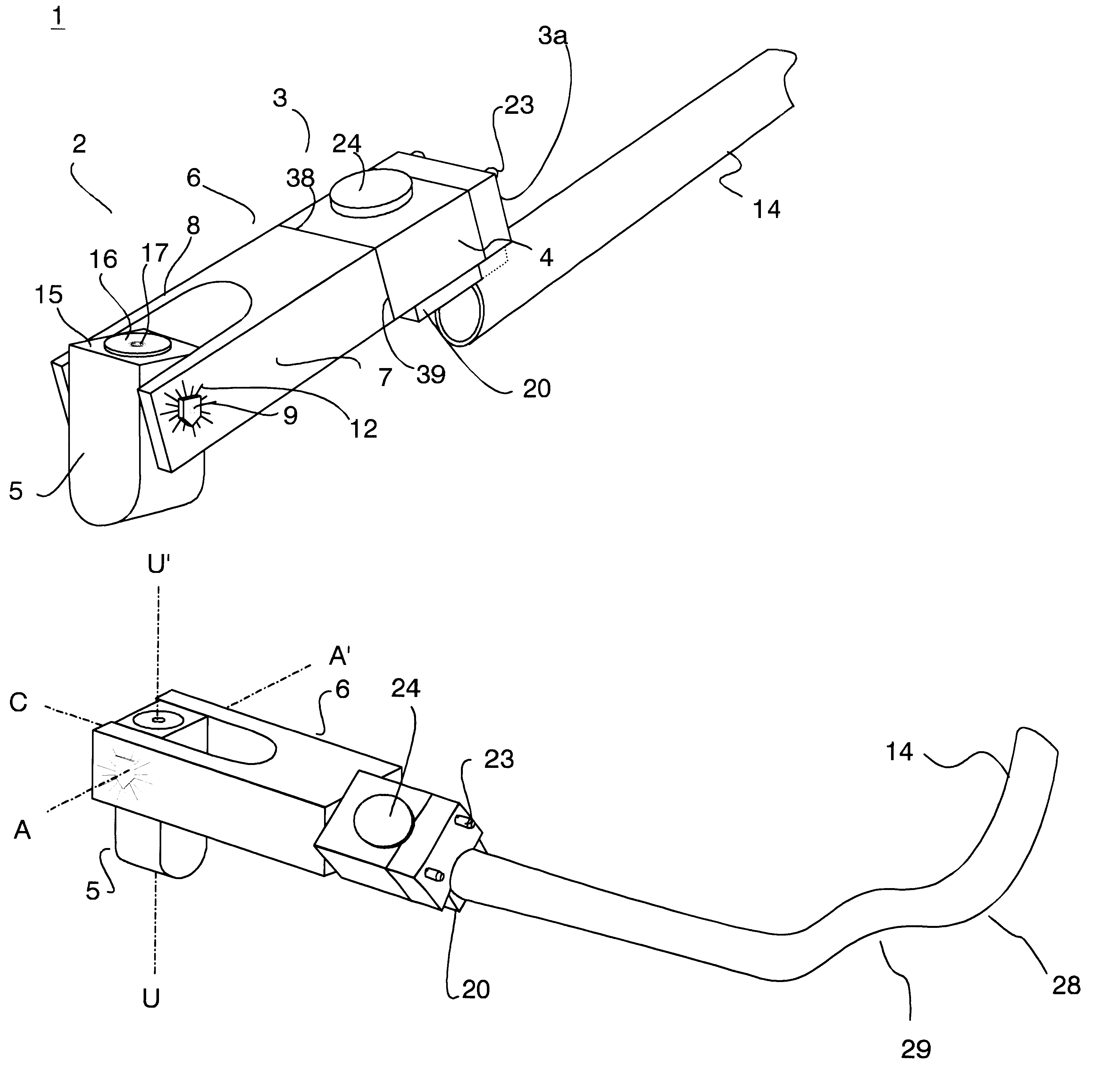
Sliding T bevel with digital readout
A digital T-bevel has a blade with a slot along a part of its length and a handle having an end that is mounted both to move along the length of the slot and to pivot with respect to the blade longitudinal axis. The handle also includes an encoder to measure the angle of the handle relative to the blade longitudinal axis and the necessary electronic circuitry to convert the measured angle into digital form to drive a display to visually display the numerical value of the measured angle.
Owner:GEN TOOLS & INSTR
Angle measuring device
InactiveUS20080208522A1Low production costMuch of lightWrenchesScrewdriversElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:EDUARD WILLE GMBH & CO KG
Locomotive/train navigation system and method
ActiveUS20060253233A1Quick fixRail switchesDigital data processing detailsEngineeringNavigation system
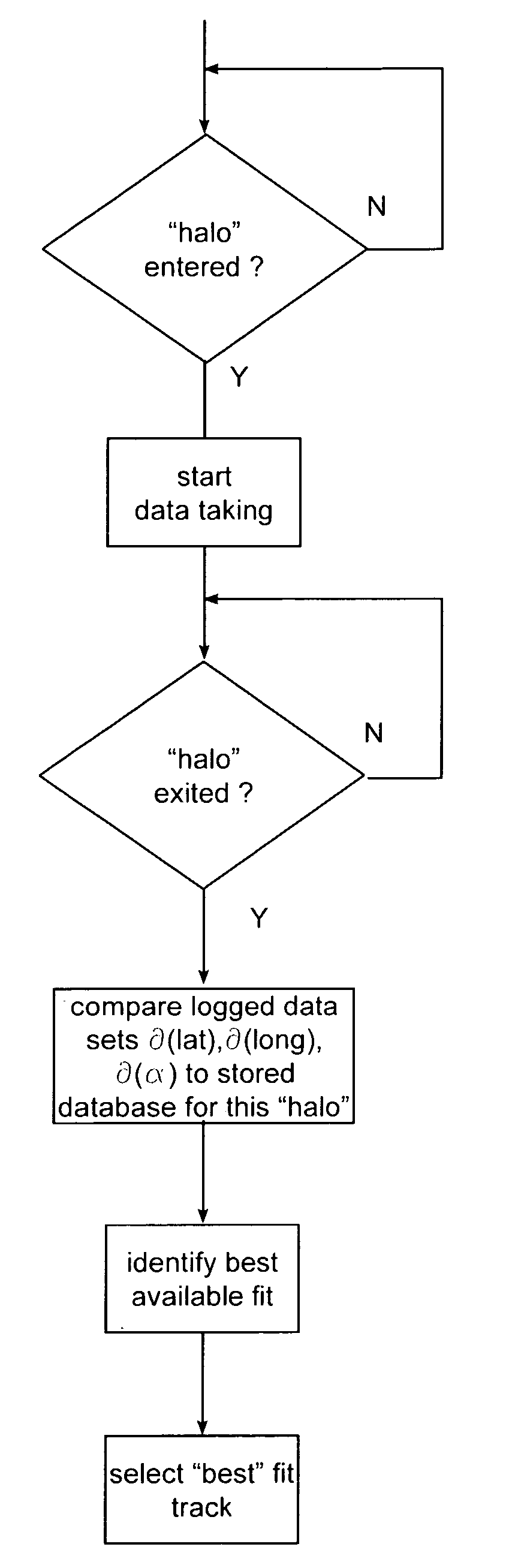
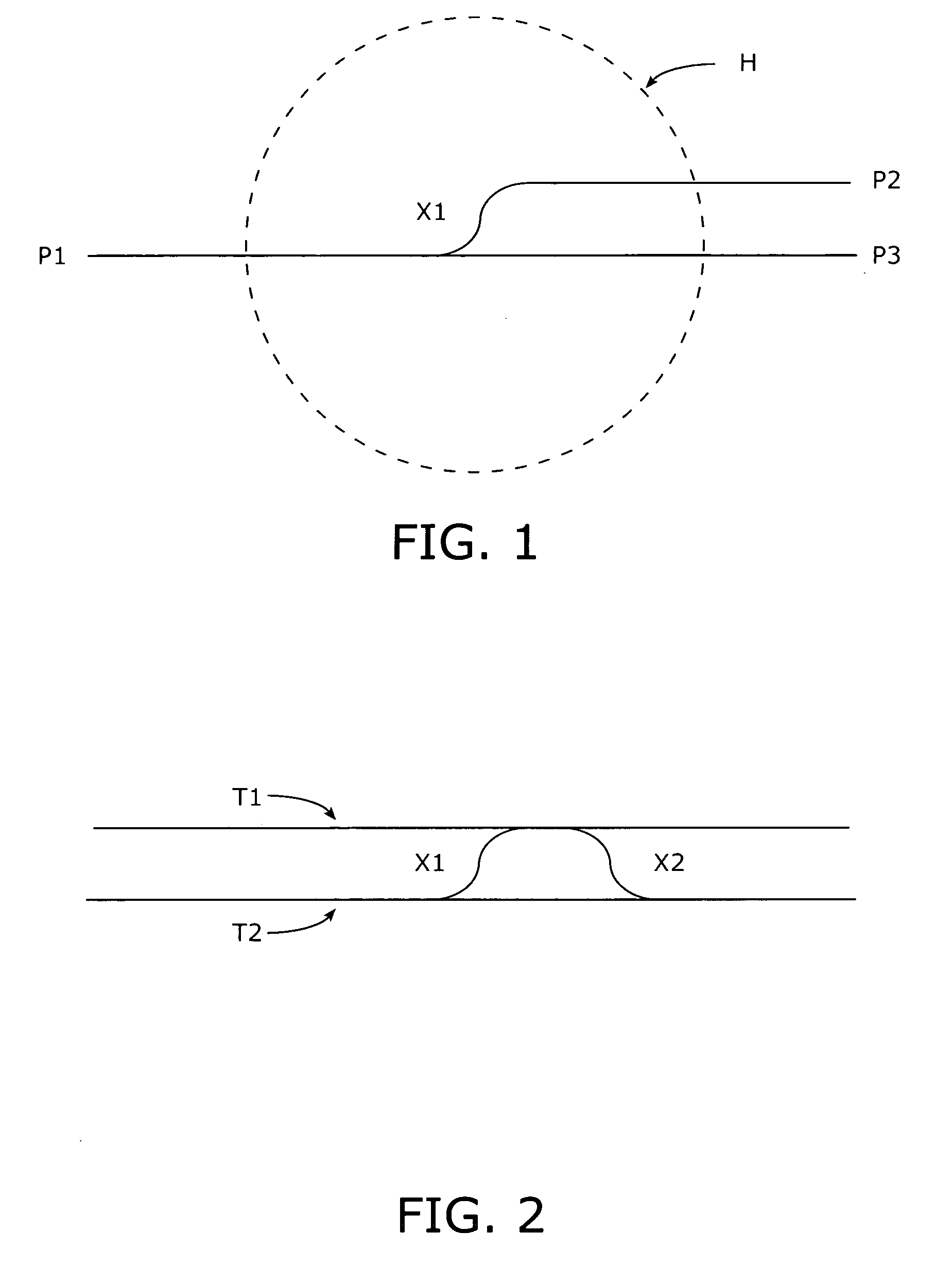
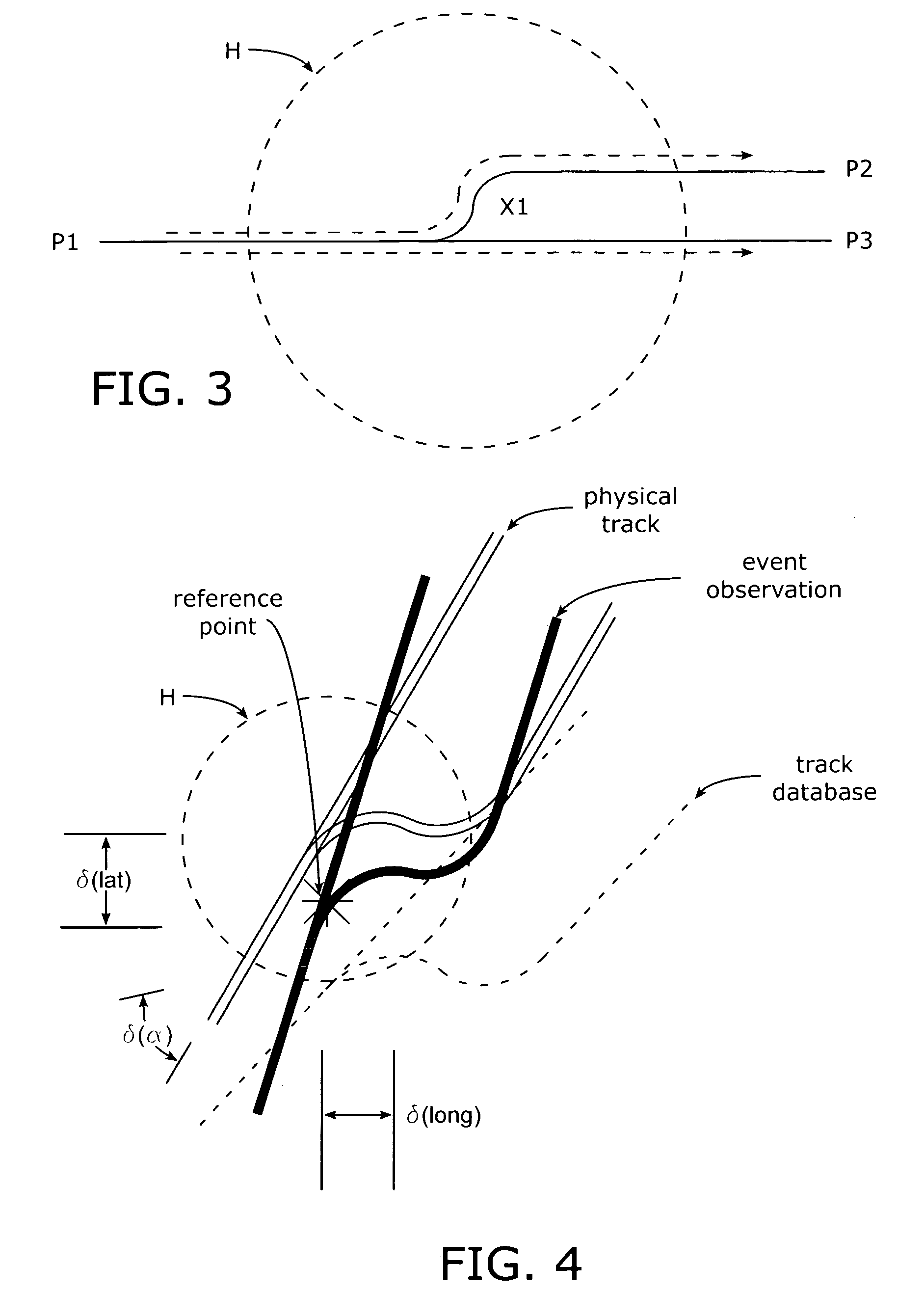
In a rail track system having transition points, a locomotive having a navigation system (such as a combined inertial / GPS location system) moves along an initially known track and enters the “halo” surrounding a track transition to begin data collection / logging to accumulate successive position information data points as the locomotive moves into, progresses through, and exits the “halo.” The collected data for movement within the “halo” is then subject to a best fit assessment relative to the data pre-stored in the track database.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Concentricity measuring apparatus and method, squareness measuring apparatus and method, and concentricity-squareness measuring apparatus and methdo
InactiveUS20070180721A1Mechanical measuring arrangementsAngles/tapers measurement gaugesBiomedical engineering
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
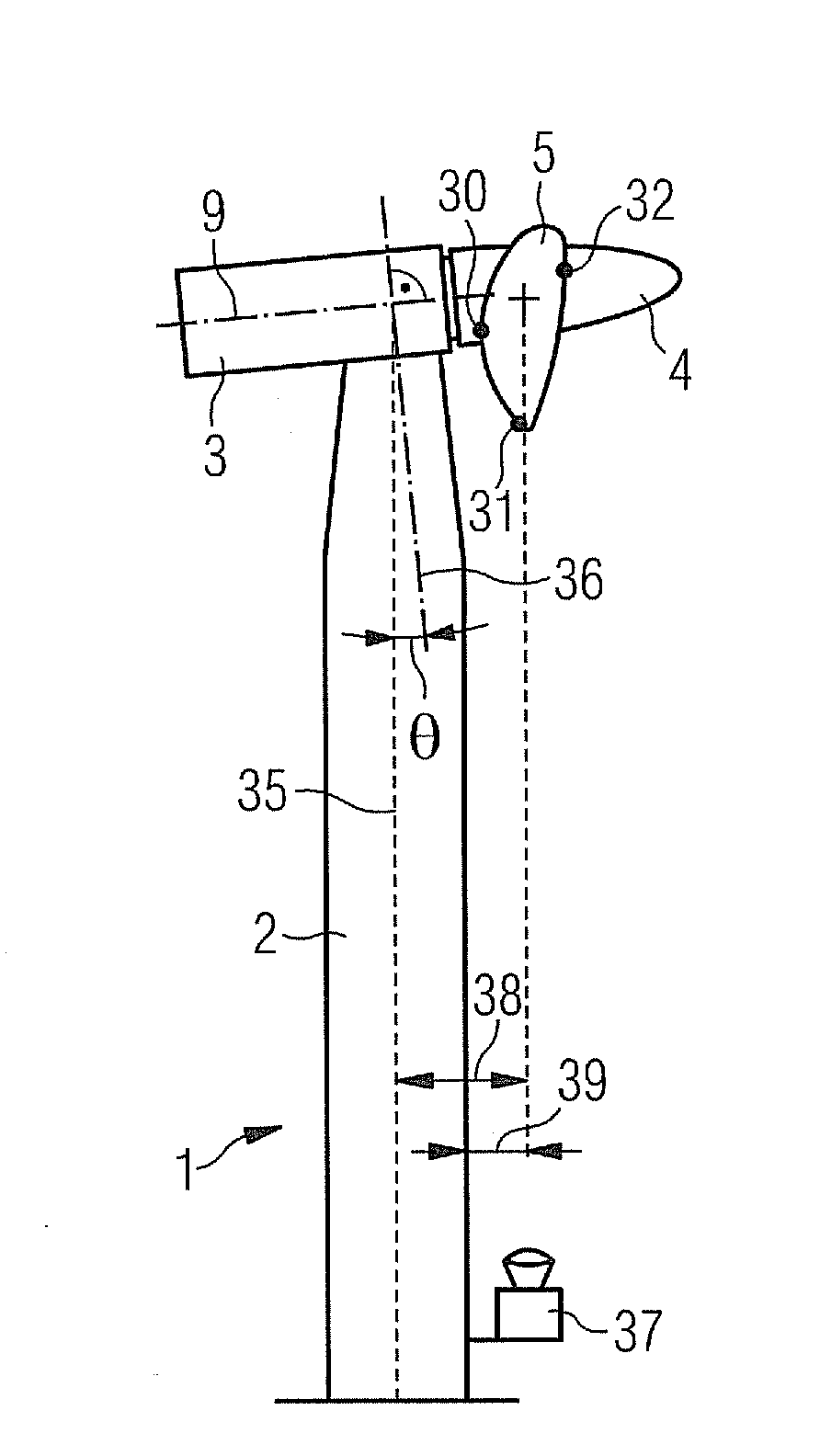
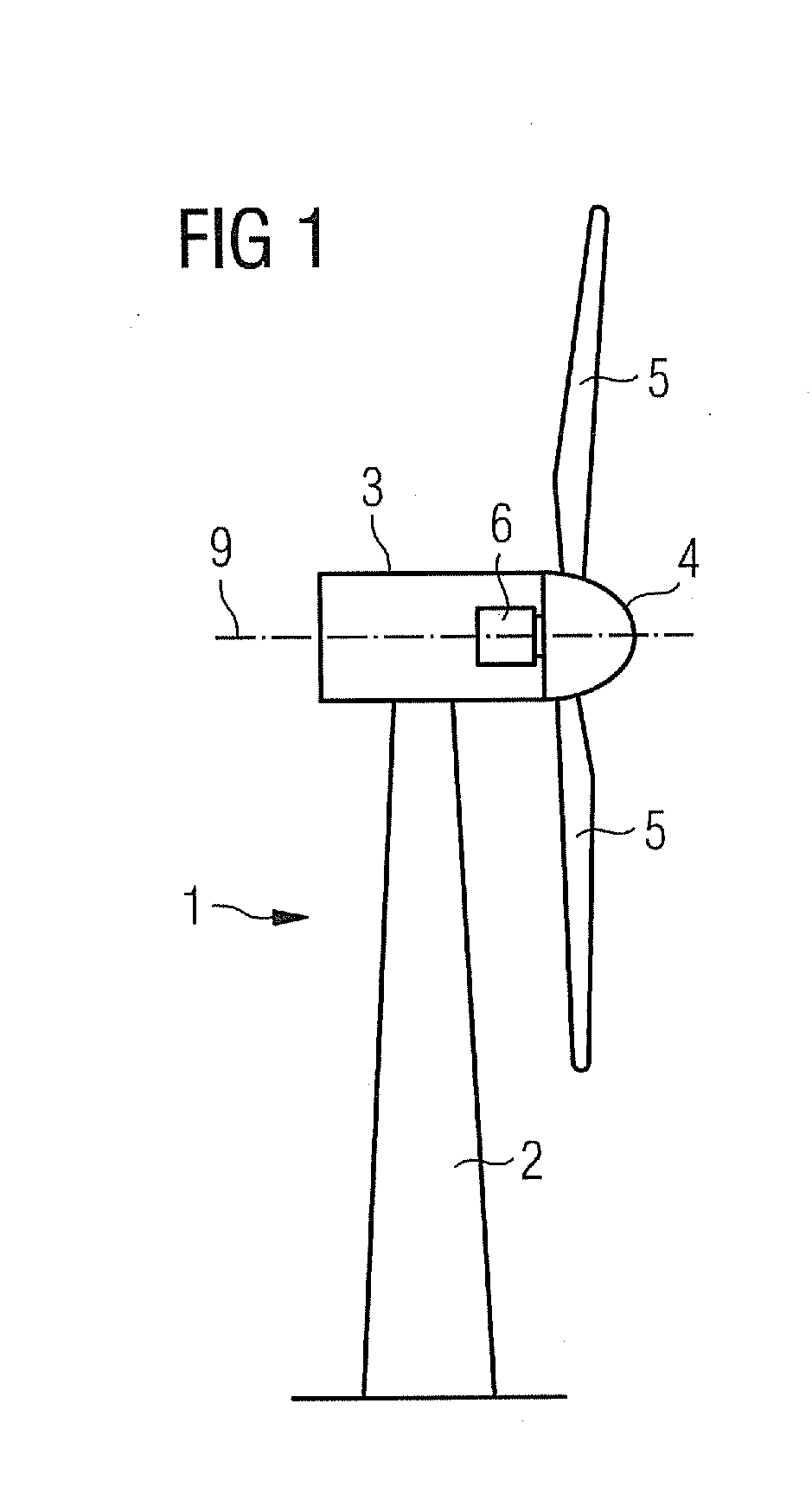
Wind turbine and method for measuring the pitch angle of a wind turbine rotor blade
InactiveUS20110206511A1Avoid loadReducing production of powerPropellersWind motor controlEngineeringWind force
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Knee joint flexure progression meter
A knee joint flexure progression meter and system. The knee joint flexure meter has an elongated progression meter bar with a major axis, an upper surface, a lower surface having a longitudinal recess therein, and a plurality of spaced apart indicia disposed on the upper surface thereof. A crossbar is disposed perpendicularly to the progression meter bar major axis. The crossbar is both adjustable and removable with respect to the progression meter bar. The crossbar is dimensioned smaller than the recess in the progression meter bar, so that the crossbar can be contained within the recess. A mechanism is provided for containing the crossbar within the progression meter bar for transportation or temporary storage.
Owner:BOYD GARY G
Miter saw for displaying angle of cutter blade cutting workpiece
ActiveUS7039548B2Reduce errorsMetal sawing devicesAngle measurementMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
Optical inclination sensor
An optical inclination sensor is provided having at least one reflective surface and at least two separate optical fibers having ends spaced from a reflective surface. As the reflective surface tilts with respect to a pre-determined reference position the gap lengths between the fiber ends and the reflective surface change and the differences in these gap lengths is used to calculate an angle of inclination with respect to a reference position. The optical inclination sensor can include at least one mass attached to a housing and moveable with respect to the housing as the mass and housing are rotated about one or more axes. Optical strain sensors are disposed a various locations between the mass and housing so that as the mass moves with respect to the housing, each one of the optical strain sensors are placed in compression or tension. The housing can be a generally u-shaped housing having two arms and a base section with the mass disposed within the housing. Alternatively, the housing includes a first beam, and the mass is a second beam arranged generally orthogonal to the first beam and pivotally attached thereto. The optical strain sensors are disposed between the first beam and the second beam. The optical strain sensors are placed in tension or compression as the second beam pivots with respect to the first beam.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Miter cutting guide apparatus
InactiveUS6401584B1Saves user time and moneyGuide fencesCross-cut reciprocating sawsEngineeringCeramic
A miter cutting guide apparatus is provided to aid in the making of miter cuts used on wood millwork as trim around floors, walls, doors, cabinets and the like and which can also be used on ceramics such as for tile cutting. Two miter arms are pivotally attached by a pivot locking means such as a screw. Each miter arm has a complementary base resting underneath and being guidably received by each miter arm, thereby allowing each miter arm to reciprocate along its complementary base.
Owner:ROWE JAMES T
Rotor clearance measurement gage
ActiveUS6886267B1Increasing precisenessIncrease rangePlug gaugesMechanical clearance measurementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Leveling assembly for setting a vertical prop
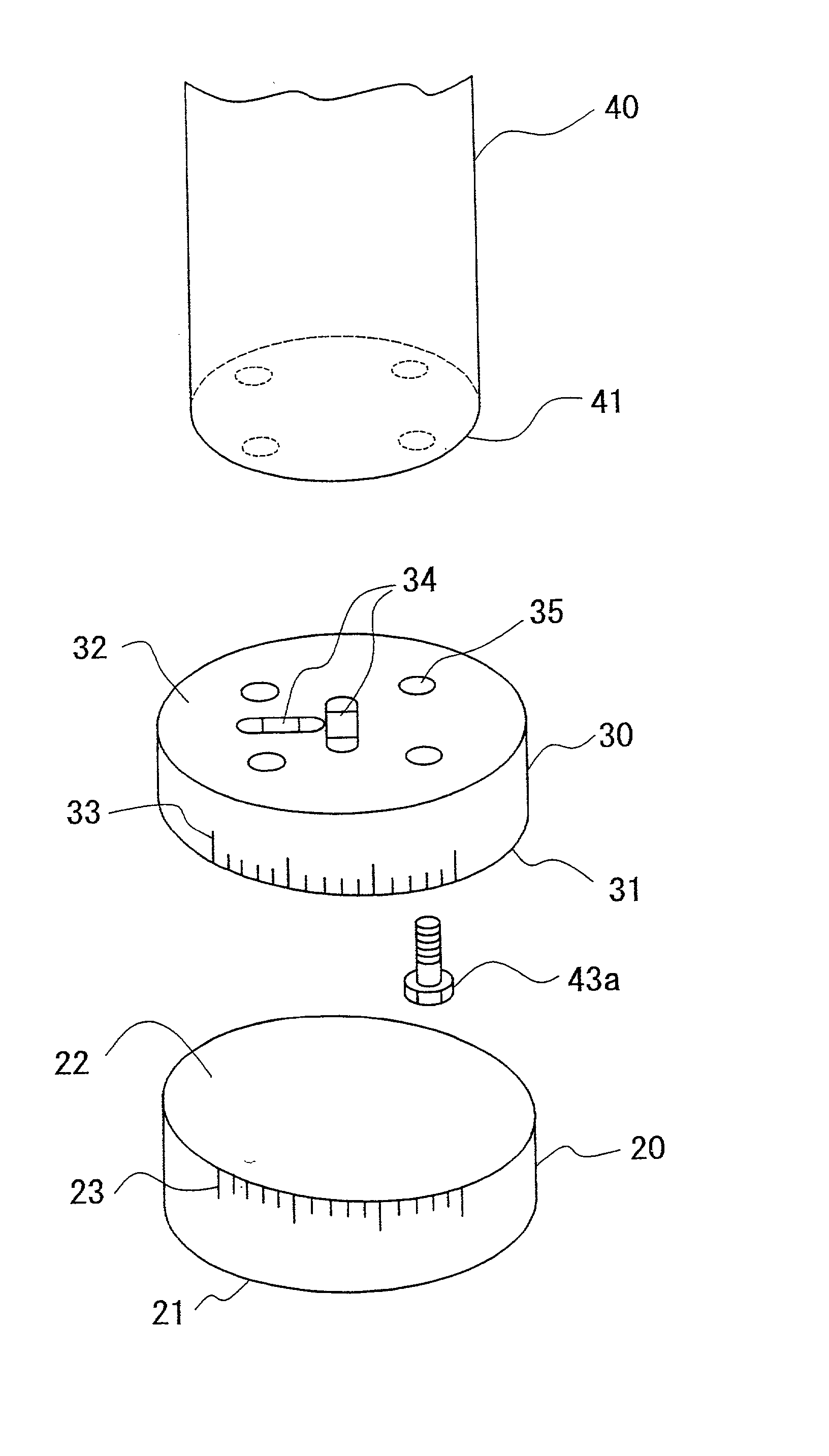
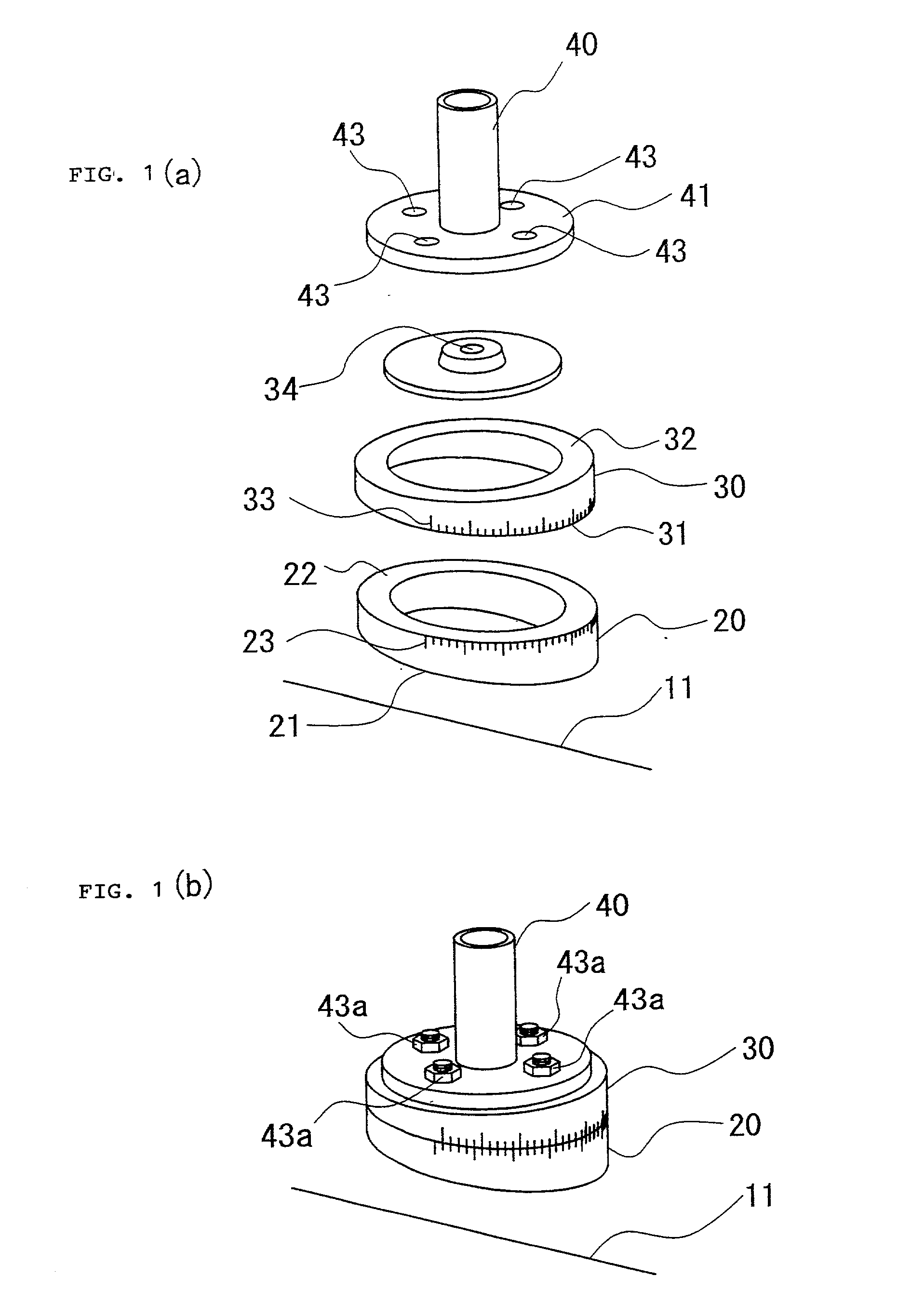
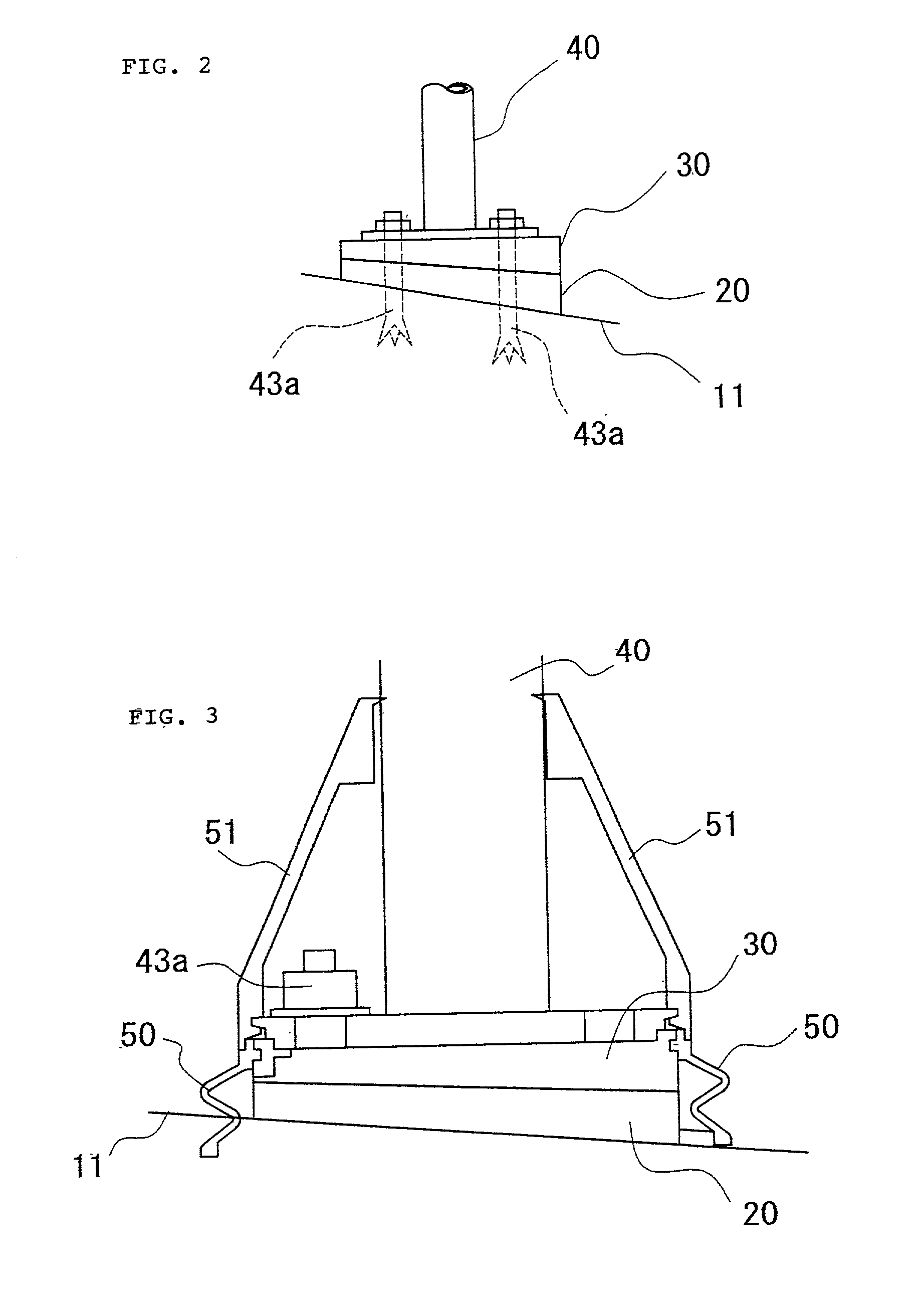
InactiveUS20030126751A1Machine framesDrilling/boring measurement devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A leveling assembly for setting a vertical prop comprised of inclined surface setting member 20 and horizontal surface forming member 30 wherein; the horizontal surface forming member 30 has a horizontal surface 32 to be adjusted as being horizontal and a first adjusting surface 31 formed by surface not parallel to horizontal surface 32, the inclined surface setting member 20 has a setting surface 21 facing a slope inclined surface 11 and a second adjusting surface 22 facing the first adjusting surface 31 formed by a surface not parallel to setting surface 21, and, the horizontal surface forming member 30 and inclined surface setting member 20 to be piled up to make the first adjusting surface 31 and the second adjusting surface 21 next to each other, and, the horizontal surface 32 to be horizontal to the slope inclined surface 11 by rotating relatively the position and changing degree between the horizontal surface 32 and the setting surface 21.
Owner:IZUMI SHUHEI
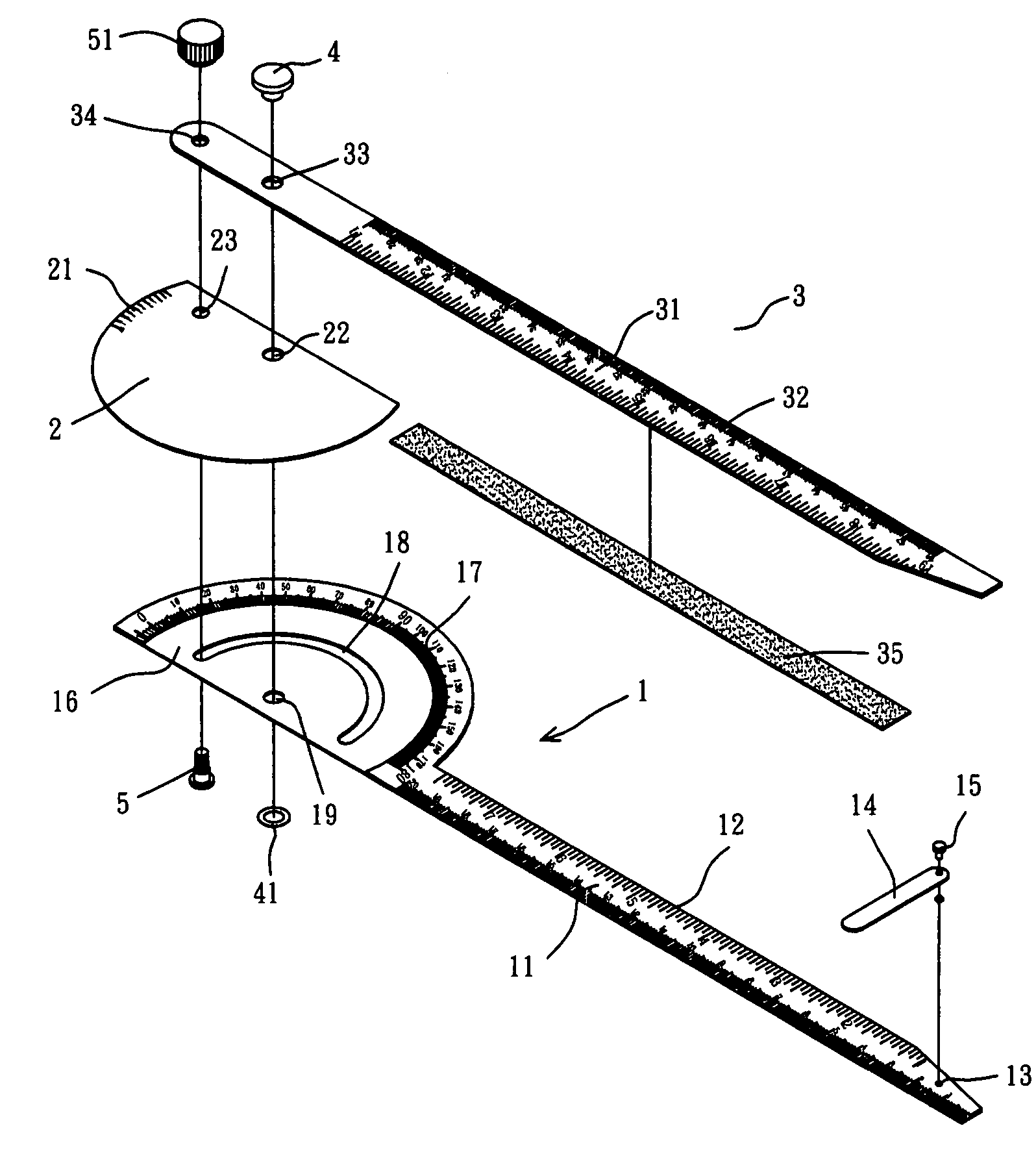
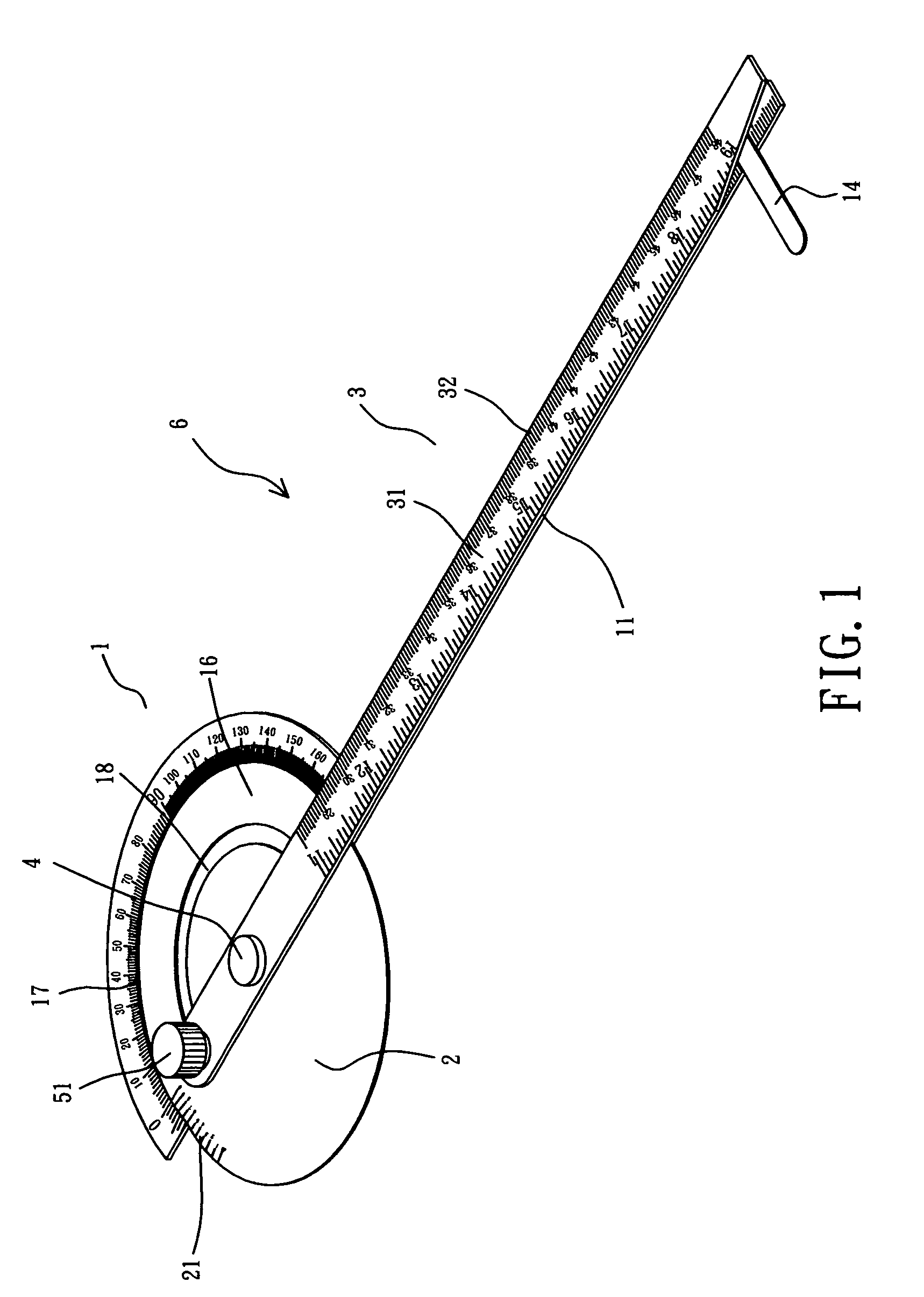
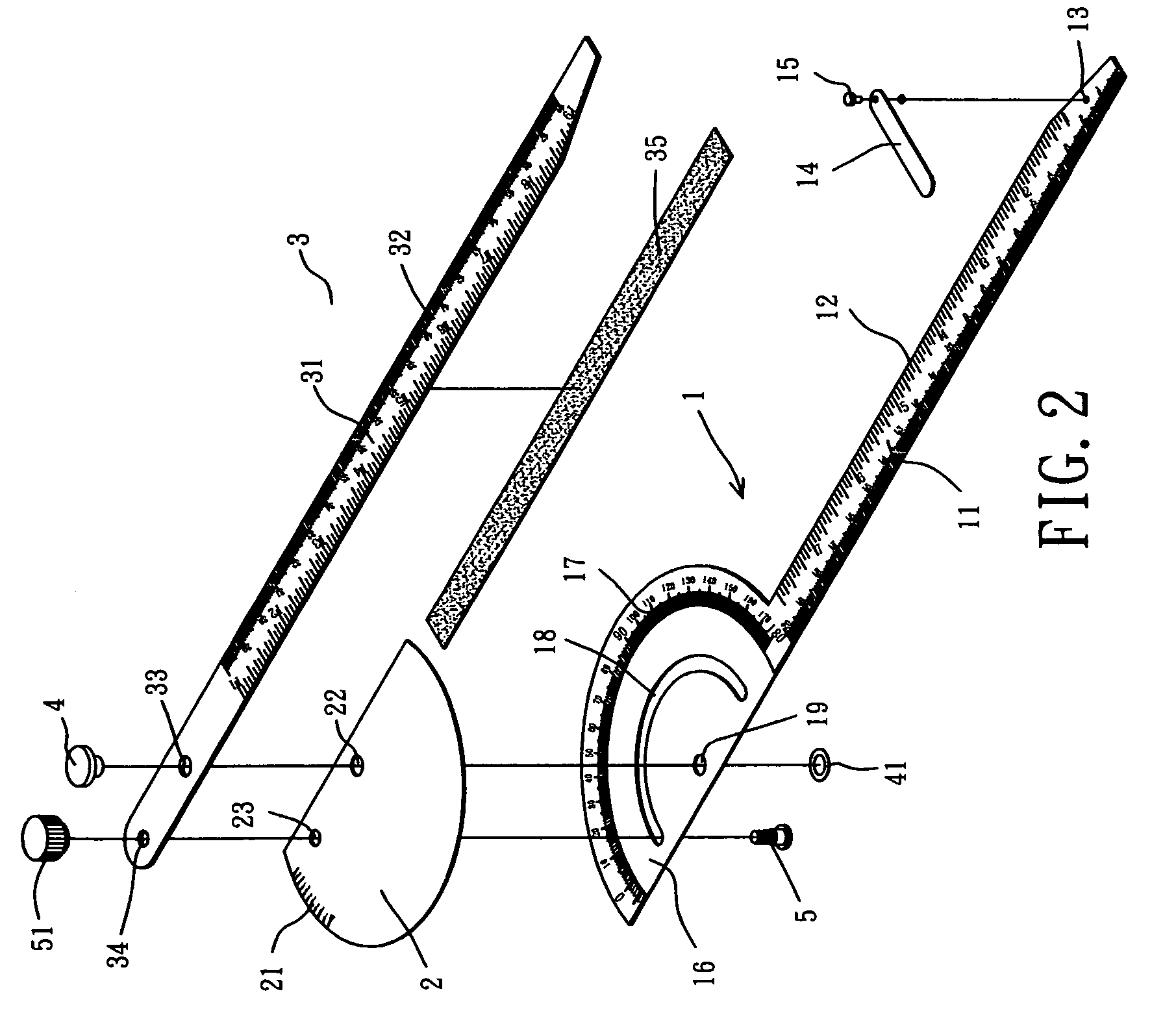
Protractor and ruler combination
InactiveUS6978550B2Facilitating operating protractorAvoid scratchesCircular curve drawing instrumentsStraightedgesProtractorEngineering management
A protractor and ruler combination includes a main ruler having a side formed with a protractor, a secondary ruler rotatably mounted on the main ruler, and an auxiliary ruler having a side secured on the secondary ruler, so that the secondary ruler is moved in concert with the auxiliary ruler on the protractor of the main ruler. Thus, the auxiliary ruler is moved relative to the main ruler, and the secondary ruler is moved in concert with the auxiliary ruler on the protractor of the main ruler, so that the included angle between the ruler section of the main ruler and the ruler section of the auxiliary ruler is measured exactly.
Owner:XIEH KUN LI
Rotational angle sensor assembly
In order to minimize change in base position from which an output representative of the angle of rotation of a rotary shaft (2) relative to a housing (1) is based, to reduce the number of component parts used, to enable a load acting on the rotary shaft (2) to be supported and to enable a rotational angle sensor assembly to be assembled with a simplified machining operation, the rotational angle sensor assembly includes a rotational angle detecting means (3) for detecting the angle of rotation between mutually opposed first and second rotational angle detectors (3A) and (3B). A housing (1) is of a cup-shaped configuration having a hollow defined therein, with the first rotational angle detector (3A) disposed at the bottom of the housing hollow. The second rotational angle detector (3B) is mounted on one end of the rotary shaft (2) that is rotatably supported by rolling bearings (4). The bearings (4) are pre-loaded at a predetermined pressure by a spring member (6). A portion of the rotary shaft (2) remote from the first rotational angle detector (3A) extends outwardly from an opening (1f) of the housing (1).
Owner:NTN CORP
System for precision miter cutting
InactiveUS6877238B2Easy to cutMetal sawing accessoriesBuilding constructionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system for modeling a recessed or protruding angle formed by convergent surfaces and transferring that modeled angle directly to a miter saw for facilitating the cutting of workpieces in conformance with the bisection of that modeled angle. This system may be manufactured with, or retrofitted onto a standard miter saw or used with a hand miter saw designed to accommodate the system.
Owner:KANAGA LAWRENCE W
Locomotive/train navigation system and method
ActiveUS7650207B2Quick fixRail switchesRoad vehicles traffic controlGps positioning systemEngineering
In a rail track system having transition points, a locomotive having a navigation system (such as a combined inertial / GPS location system) moves along an initially known track and enters the “halo” surrounding a track transition to begin data collection / logging to accumulate successive position information data points as the locomotive moves into, progresses through, and exits the “halo.” The collected data for movement within the “halo” is then subject to a best fit assessment relative to the data pre-stored in the track database.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
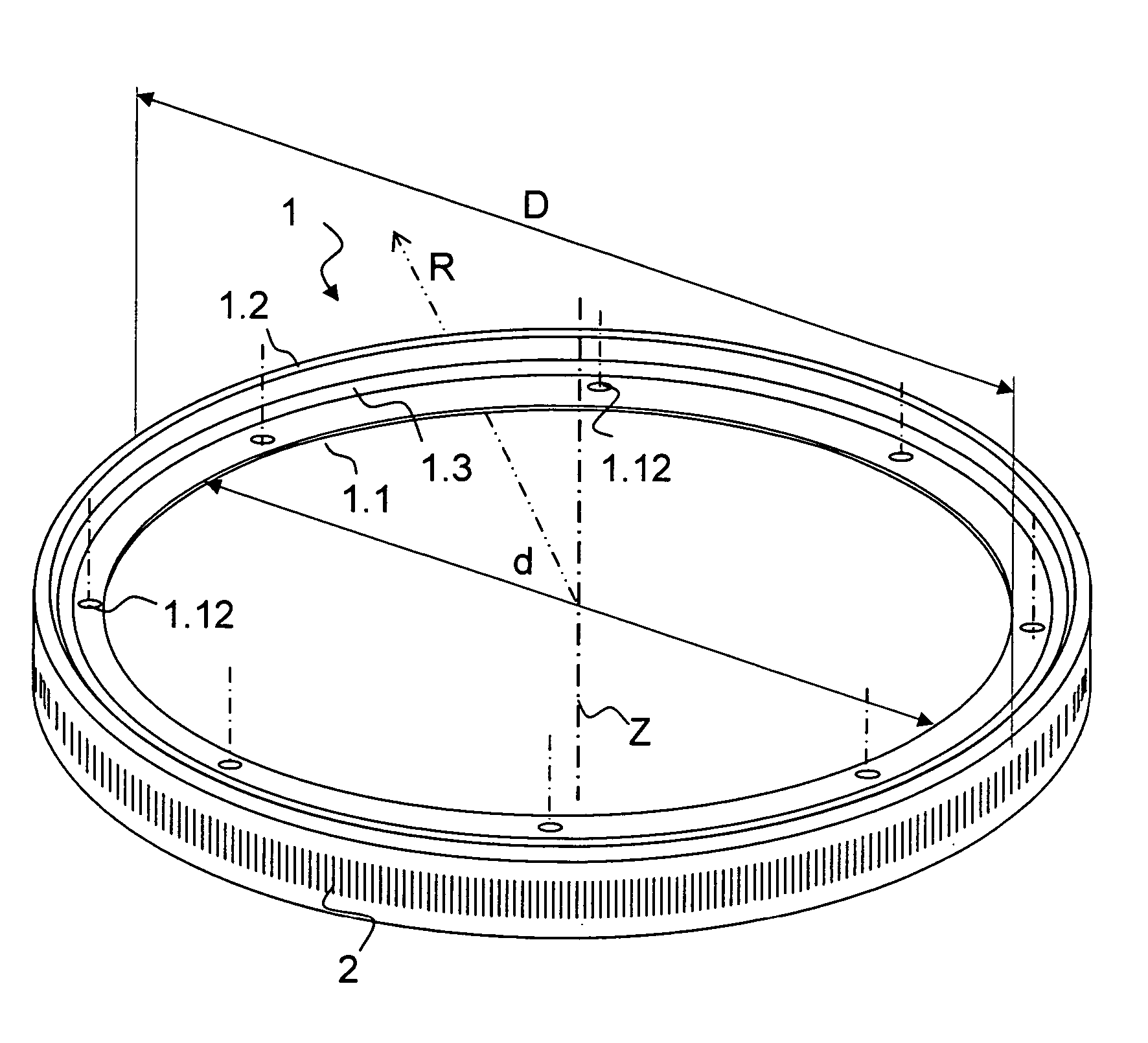
Body having angle scaling
ActiveUS7290344B2Avoid poor resultsMinimize determinative deformationAngles/taper measurementsWalking sticksMachine partsClassical mechanics
A monolithic body having angle scaling is rotatable about an axis to measure the rotational position of a machine part. The body has a first annular region which has a flange-type configuration for connection to the machine part, and a second annular region on which the angle scaling is arranged, as well as a crosspiece region. The crosspiece region is arranged between the first annular region and the second annular region. The crosspiece region has a geometrical extension in the direction of the axis which is at least three times smaller than the greatest geometrical extension of the second annular region in the direction of the axis (Z).
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com