Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Vergence movement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
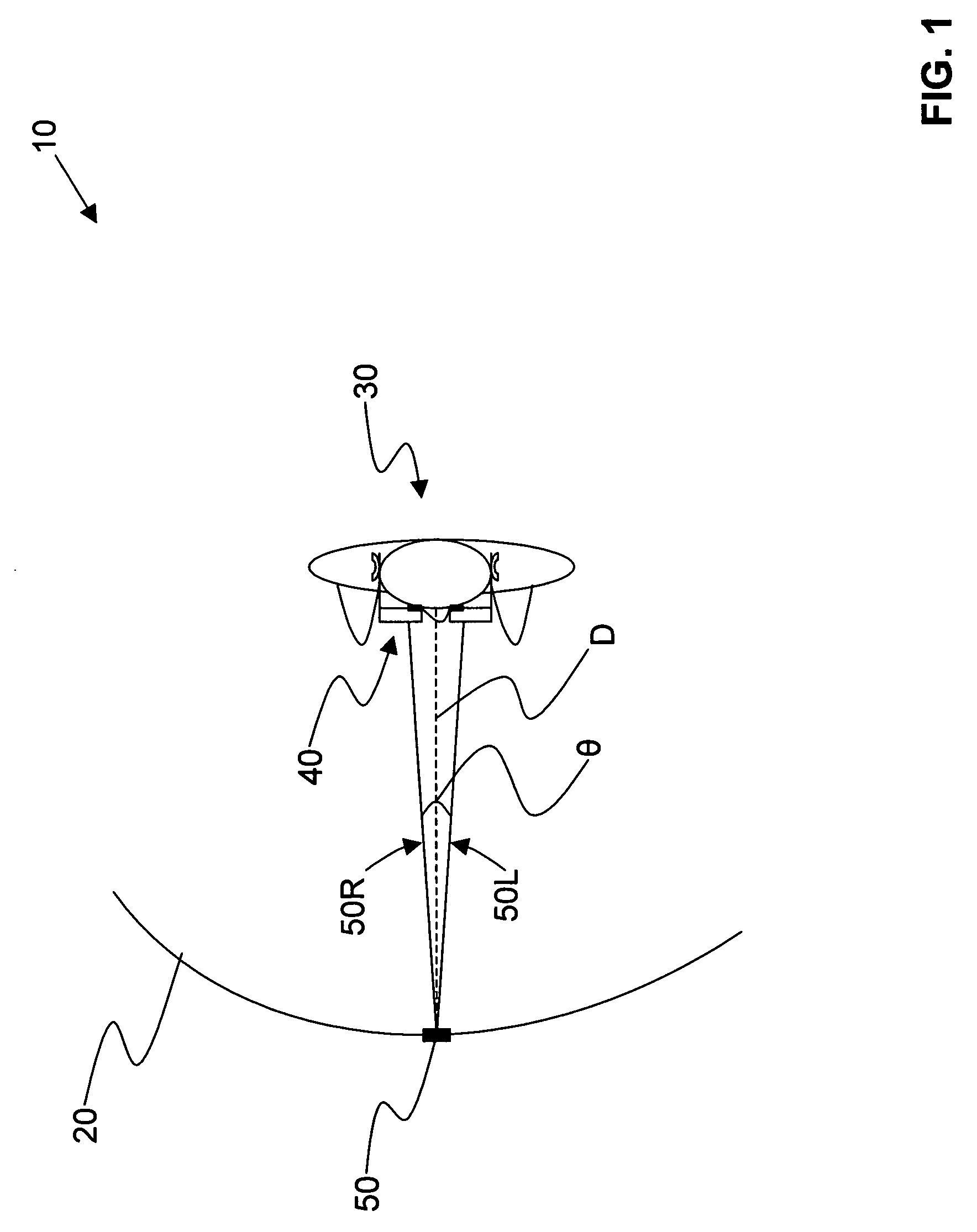
In ophthalmology, divergence is the simultaneous outward movement of both eyes away from each other, usually in an effort to maintain single binocular vision when viewing an object. It is a type of vergence eye movement.
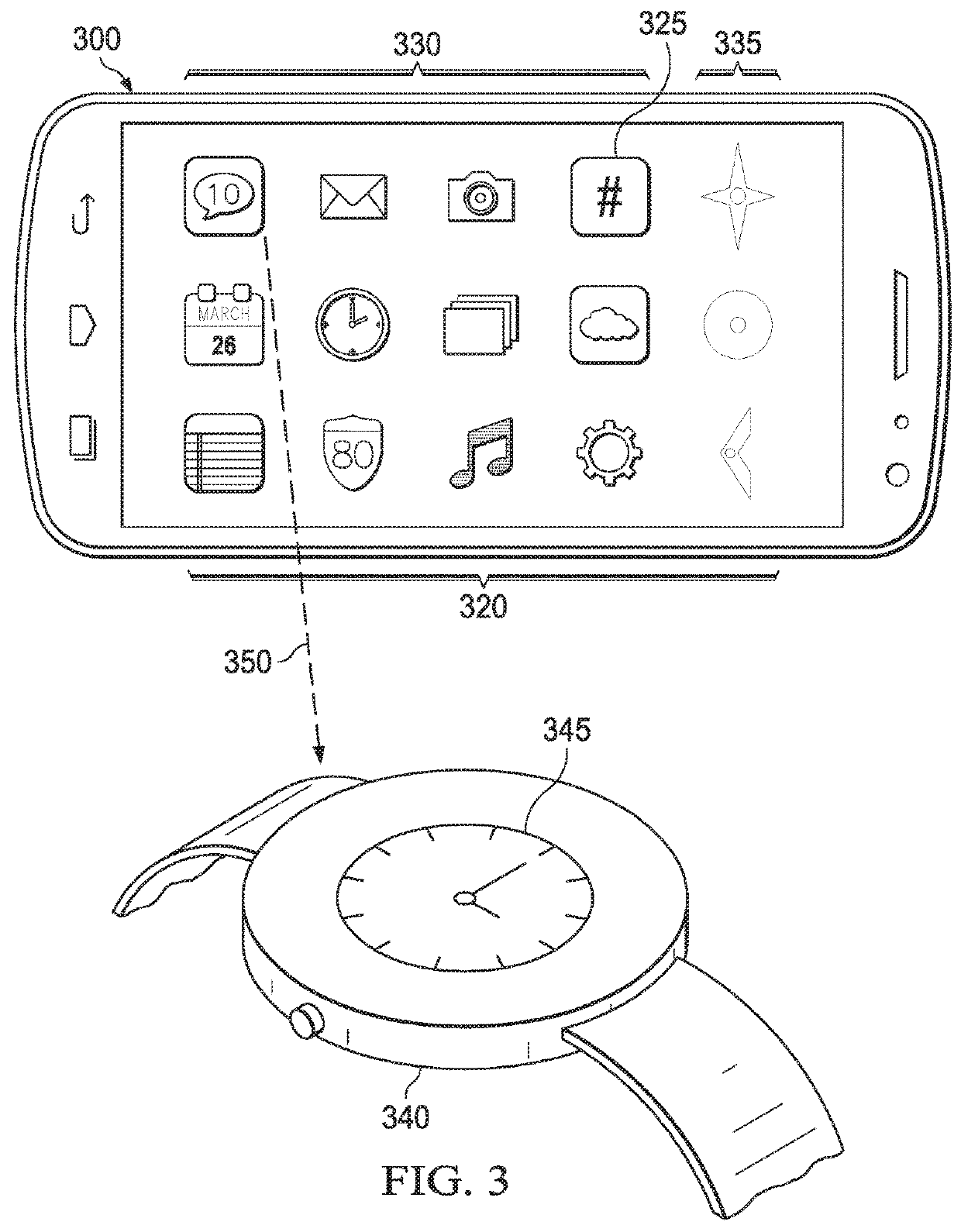
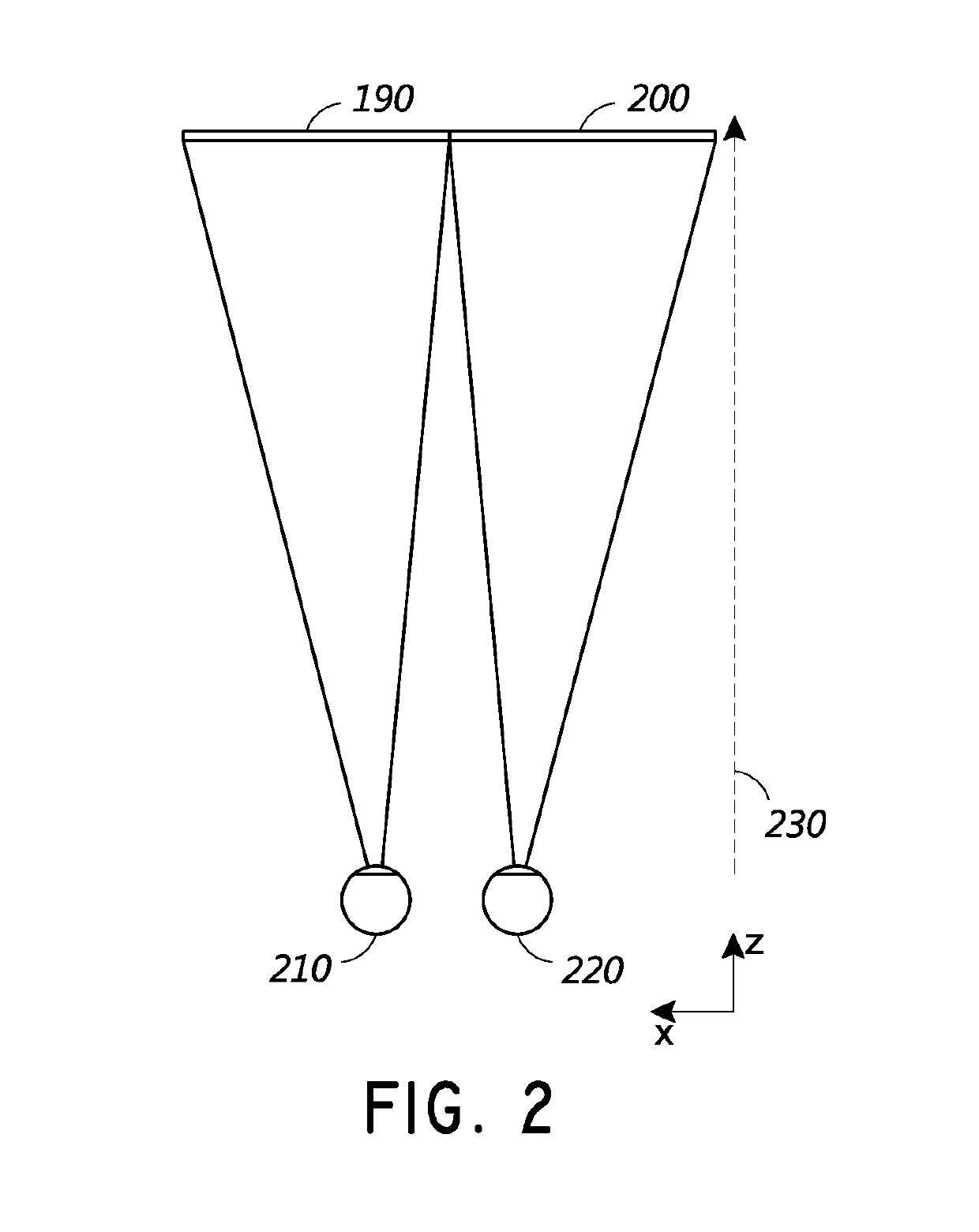
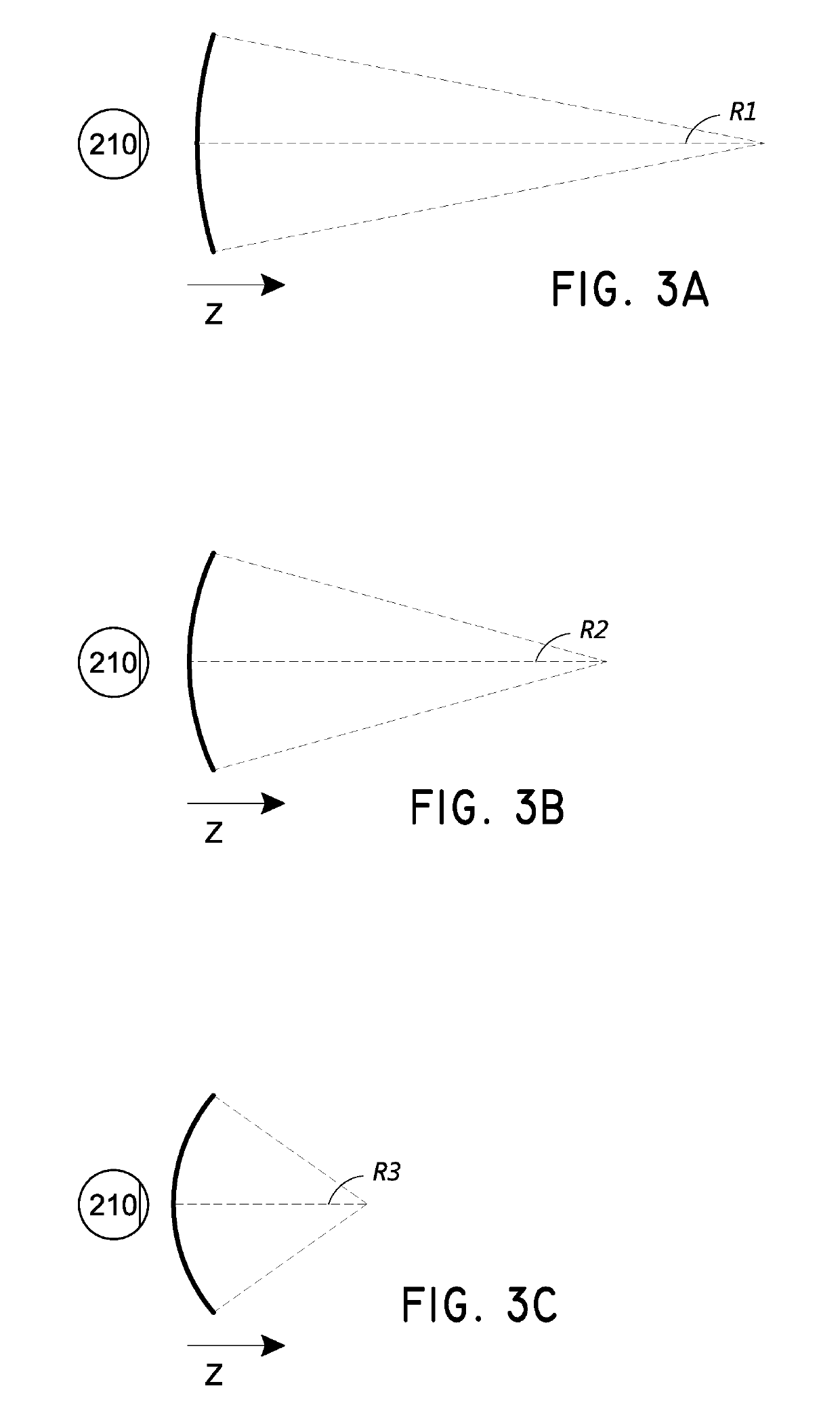
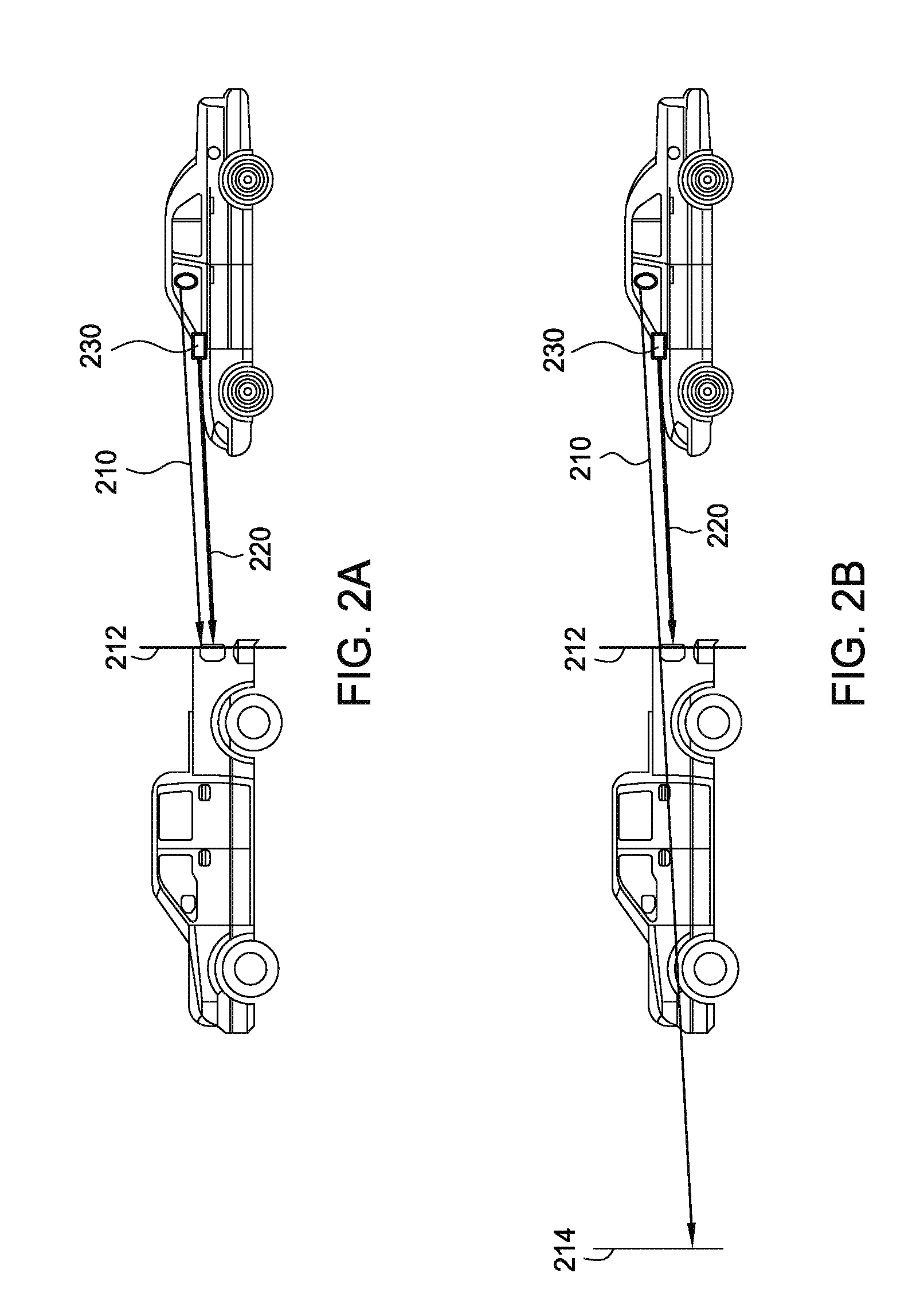
Dynamic vergence and focus control for head-mounted displays
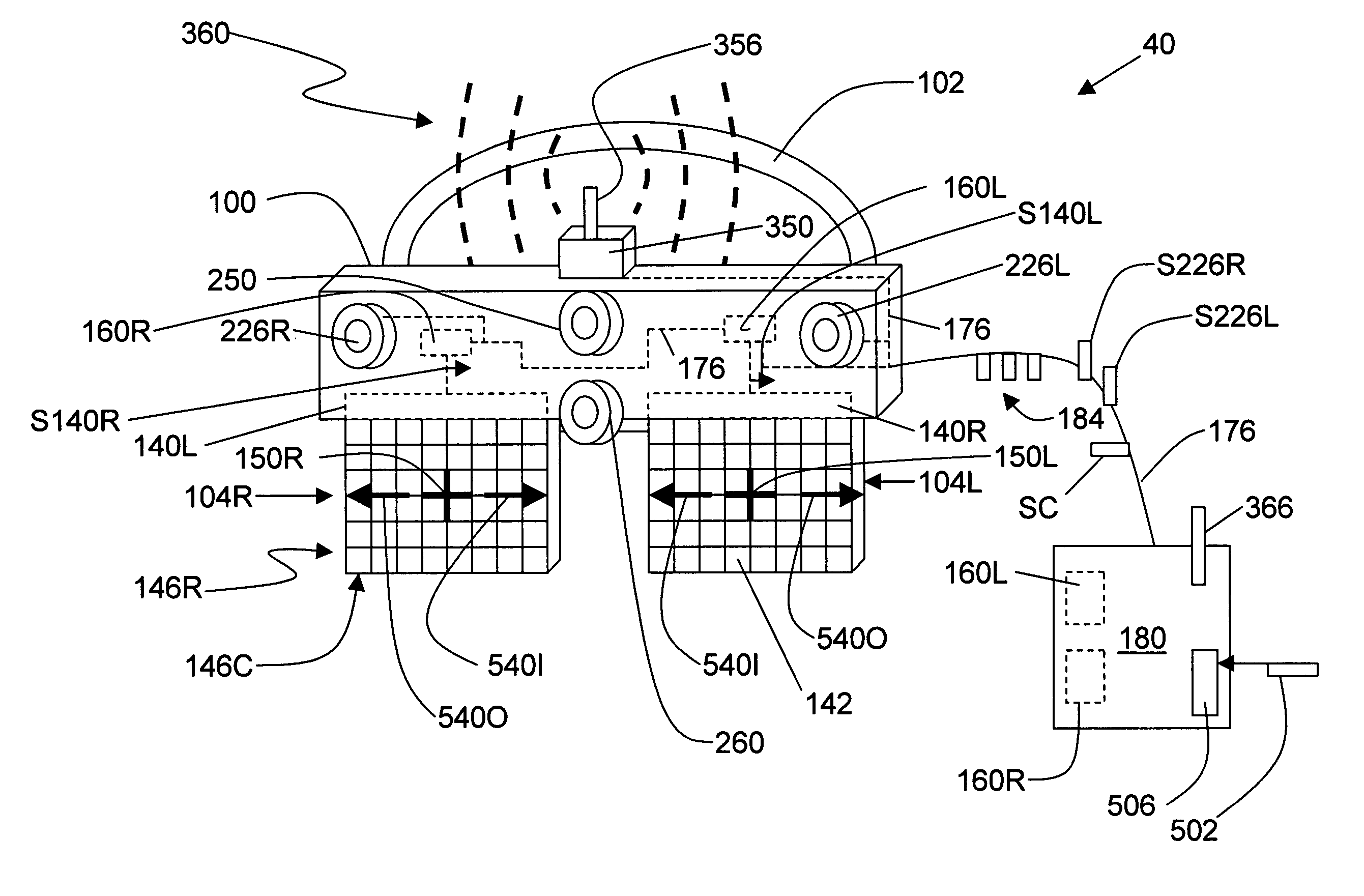
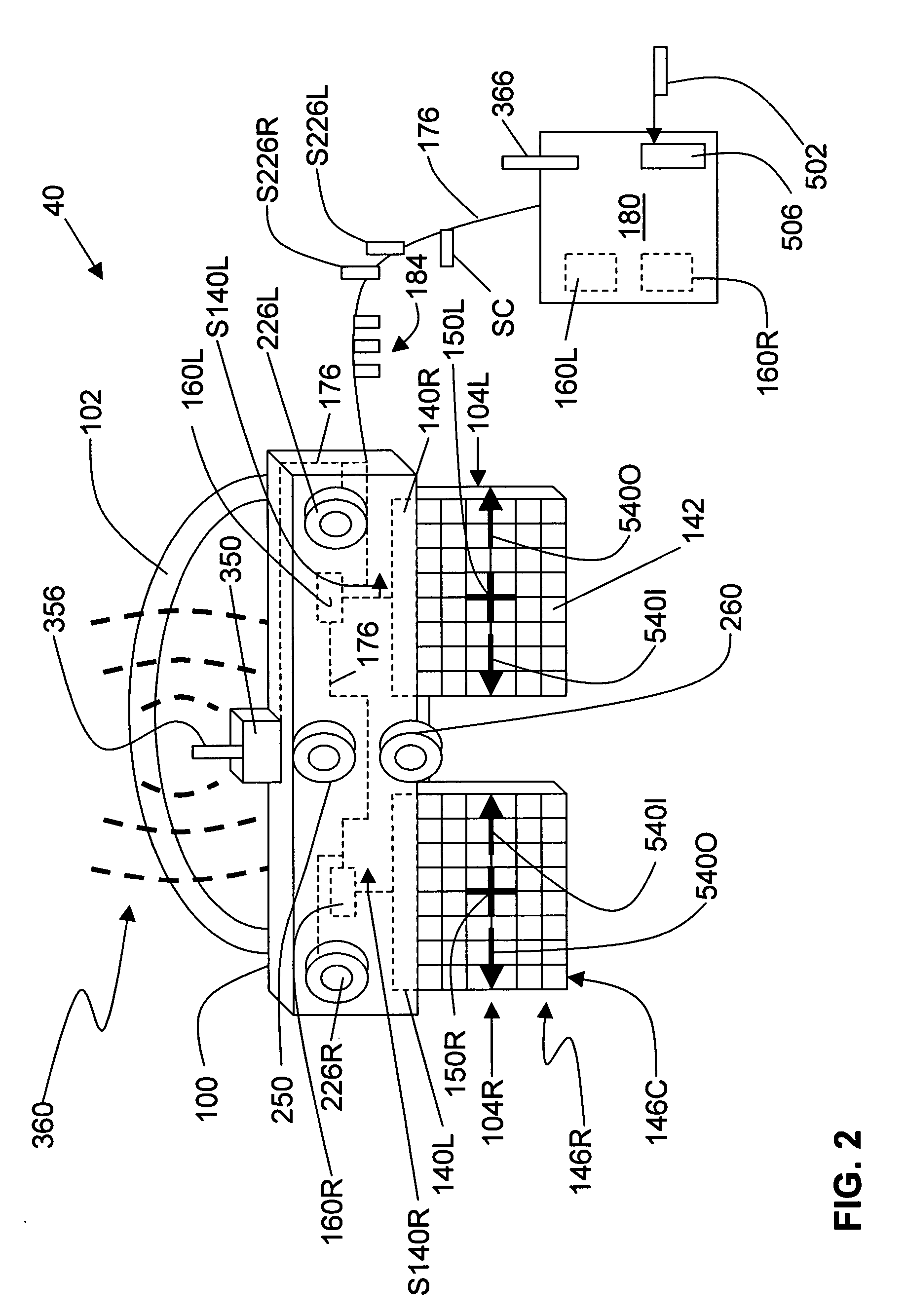
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling vergence and focus for a see-through head-mounted display (ST-HMD) used as part of an augmented reality (AR) system are disclosed. The ST-HMD (40) allows a user (30) to view left and right images (150L, 150R) through corresponding left and right eyepieces (104L, 104R) so that a single virtual object (150V) based on the right and left images as seen at a real object such as a screen (20). When the user moves relative to the real object, however, the vergence changes and the virtual object does not appear in focus at the real object. Changes in the vergence are compensated by tracking the user's head position with a tracking unit (350) and providing the tracking data to a controller (180). Based on the tracking data and the interpupilary distance (IPD) of the user, the controller calculates the offset (H) needed to be imparted to the images formed in the eyepieces to maintain the vergence of the virtual object at the real object even when the user's position changes relative to the real object.
Owner:OPTICS 1
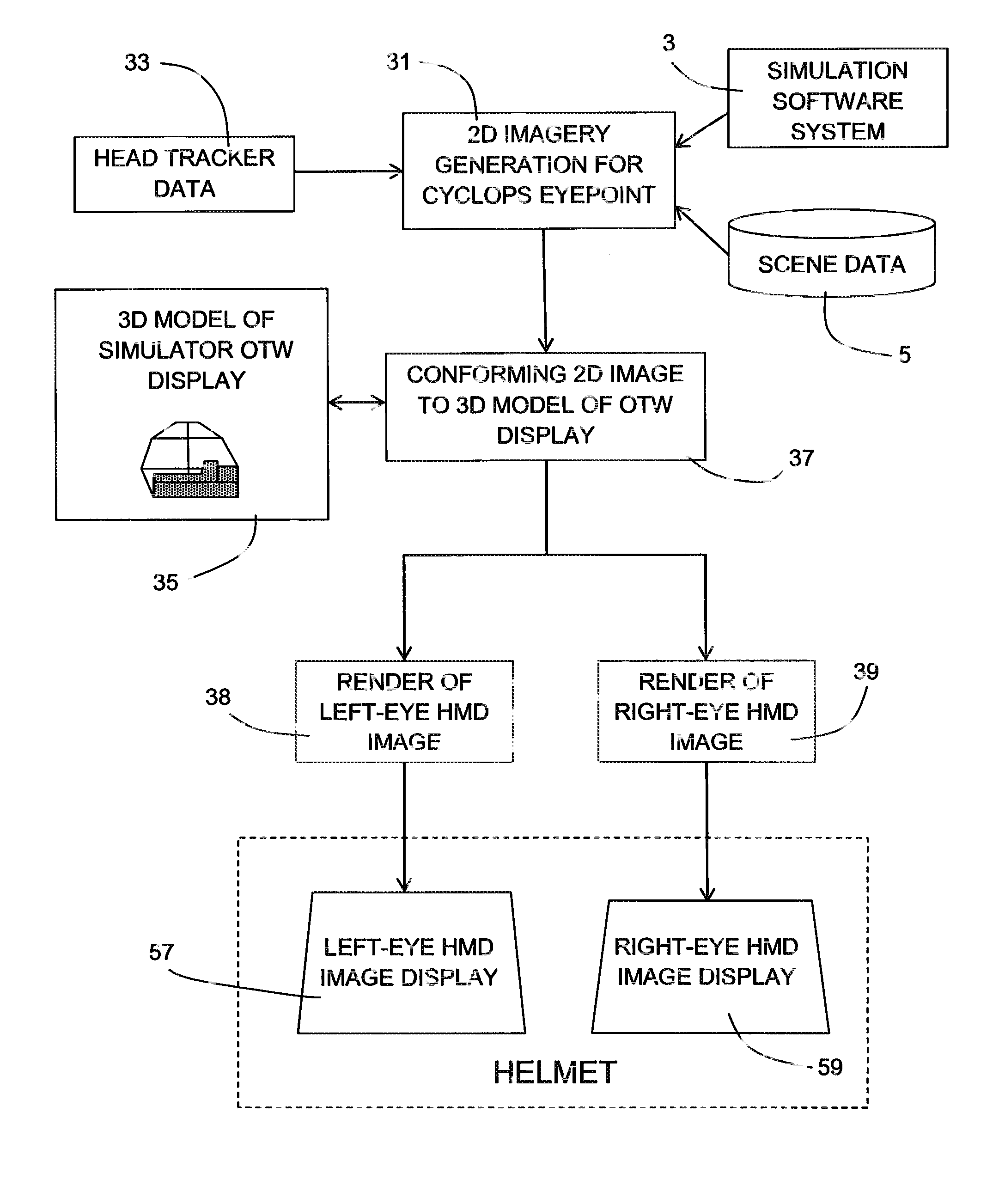
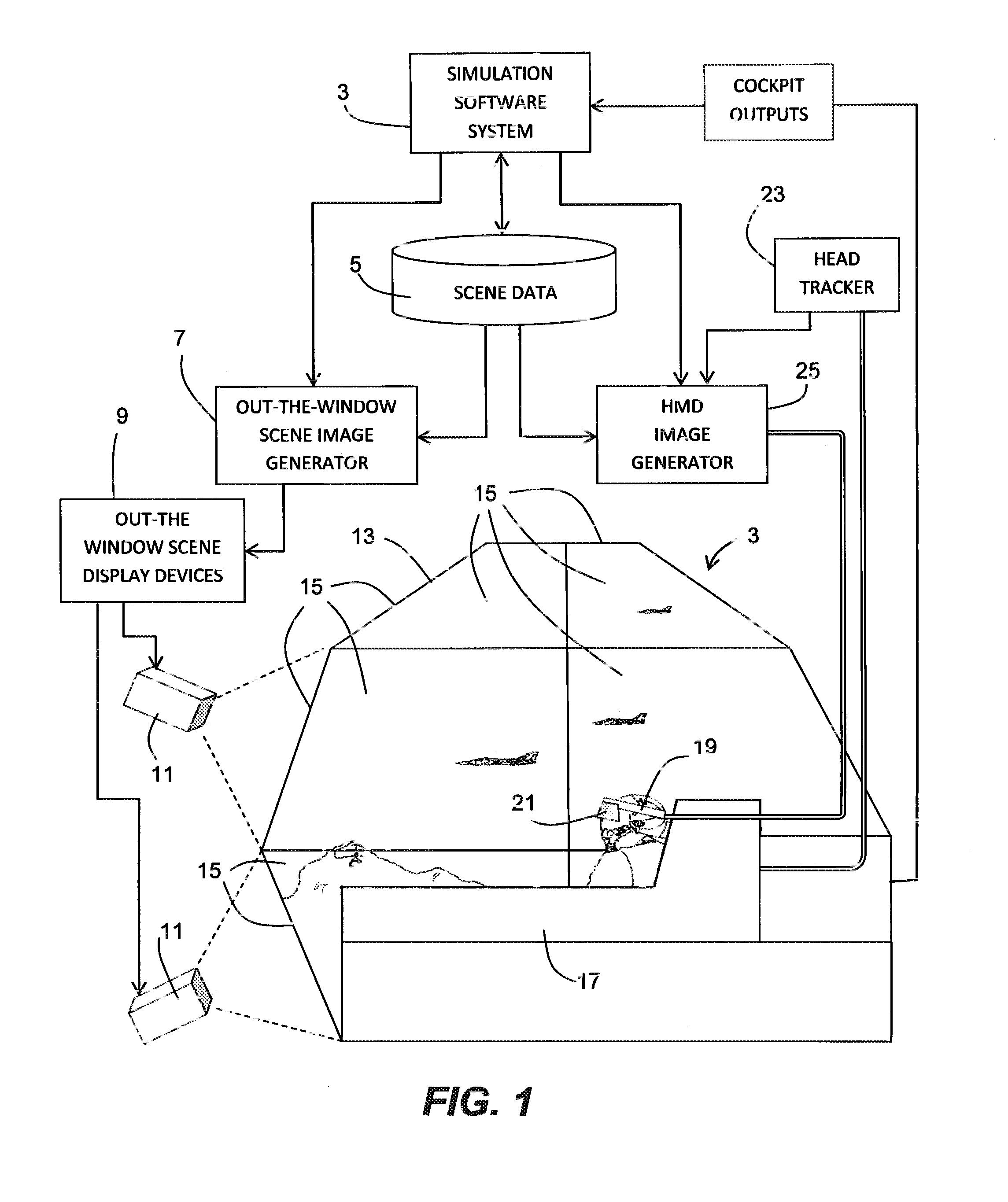
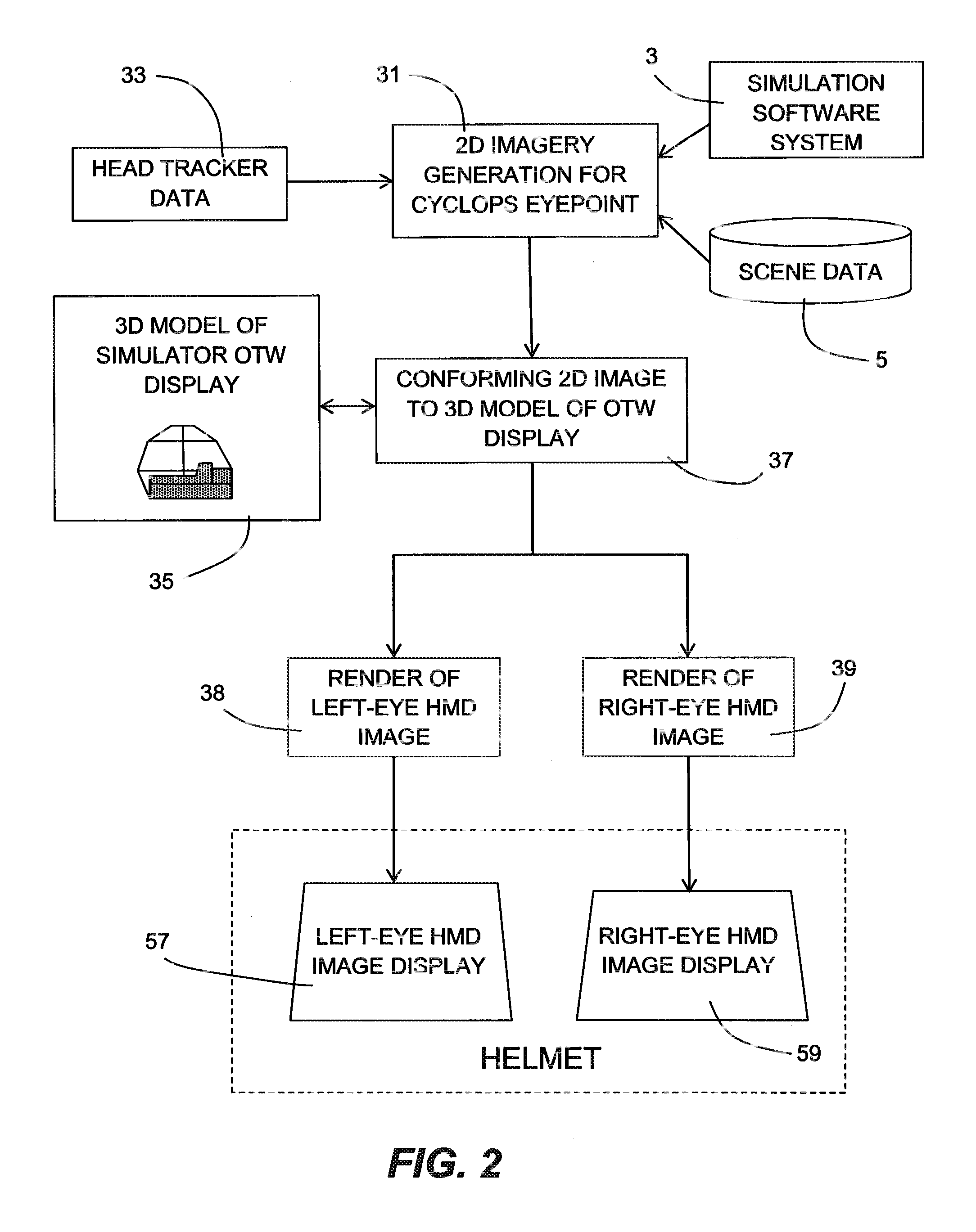
Simulated head mounted display system and method
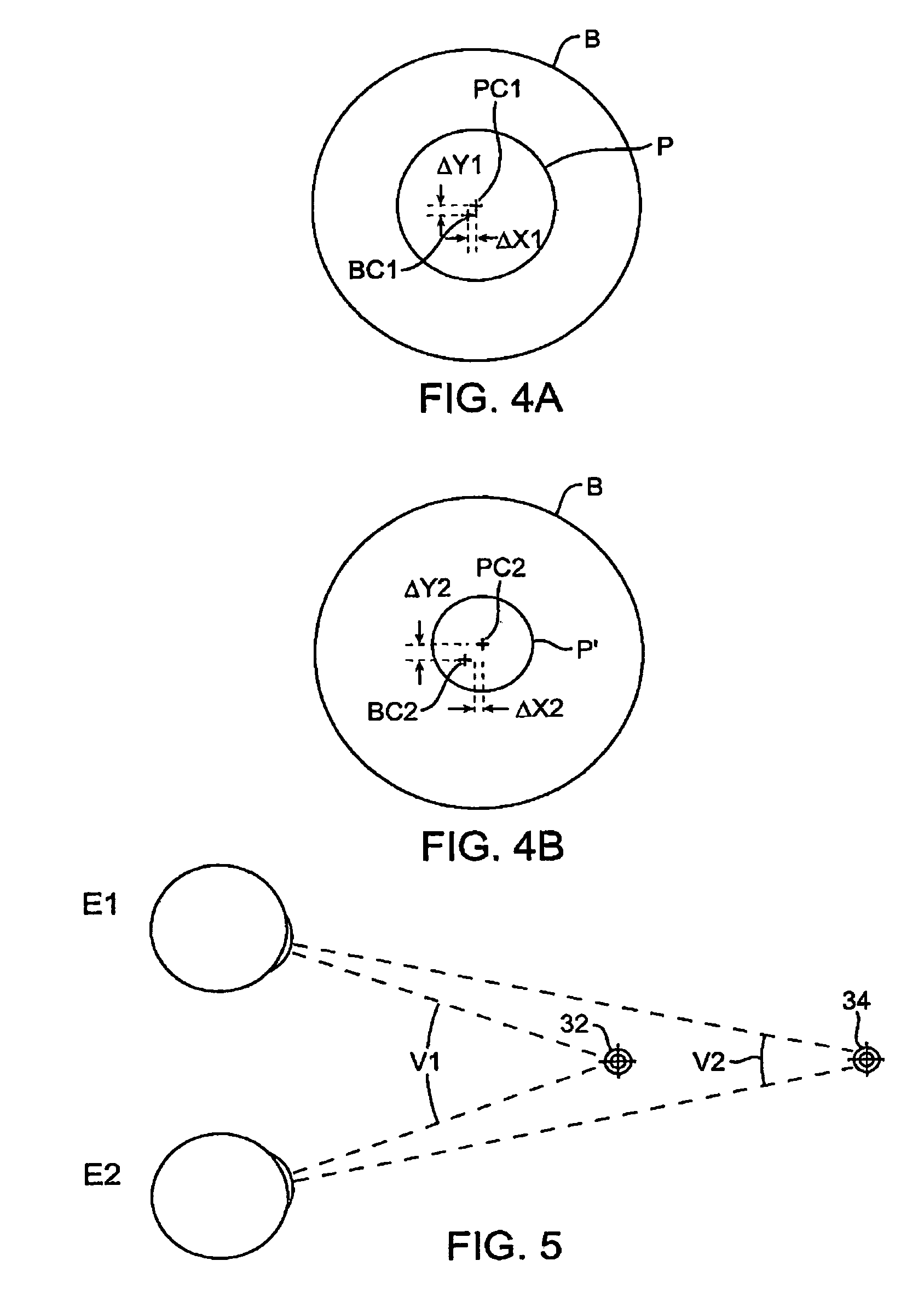
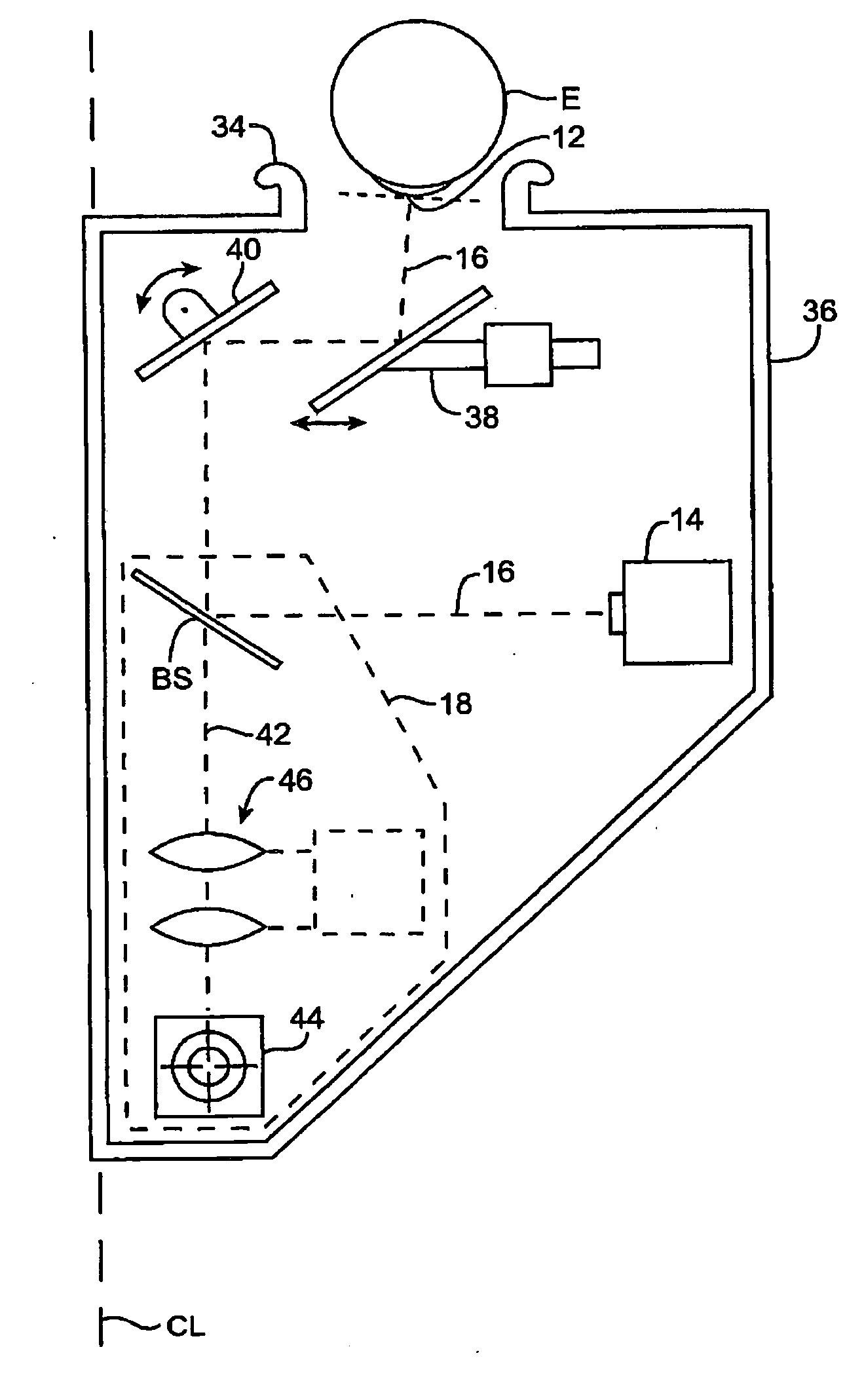
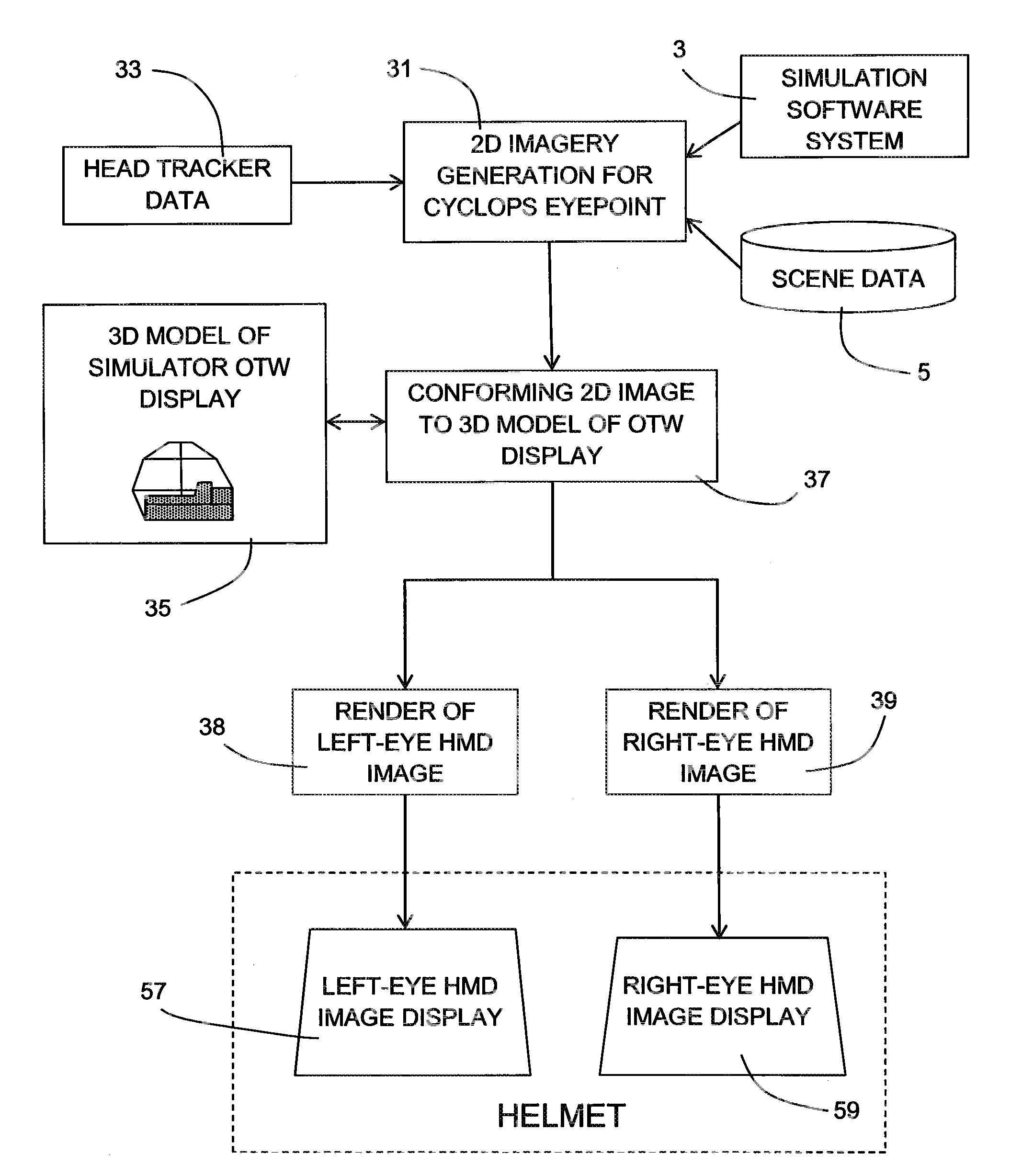
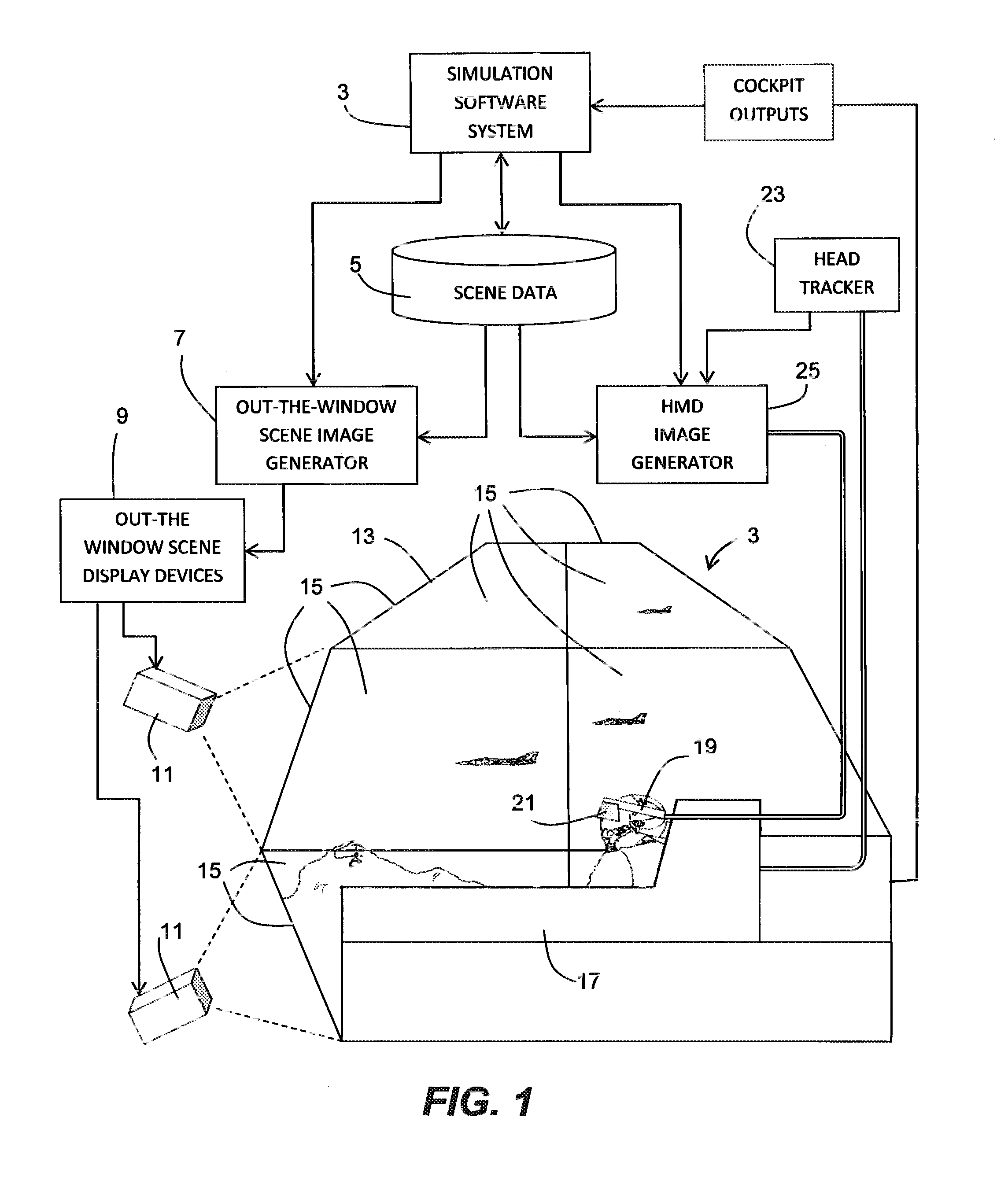
InactiveUS8704882B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsColor television detailsVergence movementViewpoints
To overcome problems with vergence, a binocular head mounted display (HMD) is used in a simulator in which an out-the-window scene is displayed in real time on a screen arrangement. Imagery for the left and right eyes of the HMD is derived by generating a starting HMD image for a Cyclops viewpoint between the user's eves, and then rendering respective views for each eve from the position of the eye in a virtual 3D model of the screen arrangement, wherein the starting HMD image is frustum projected against the screen arrangement of the 3D model.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
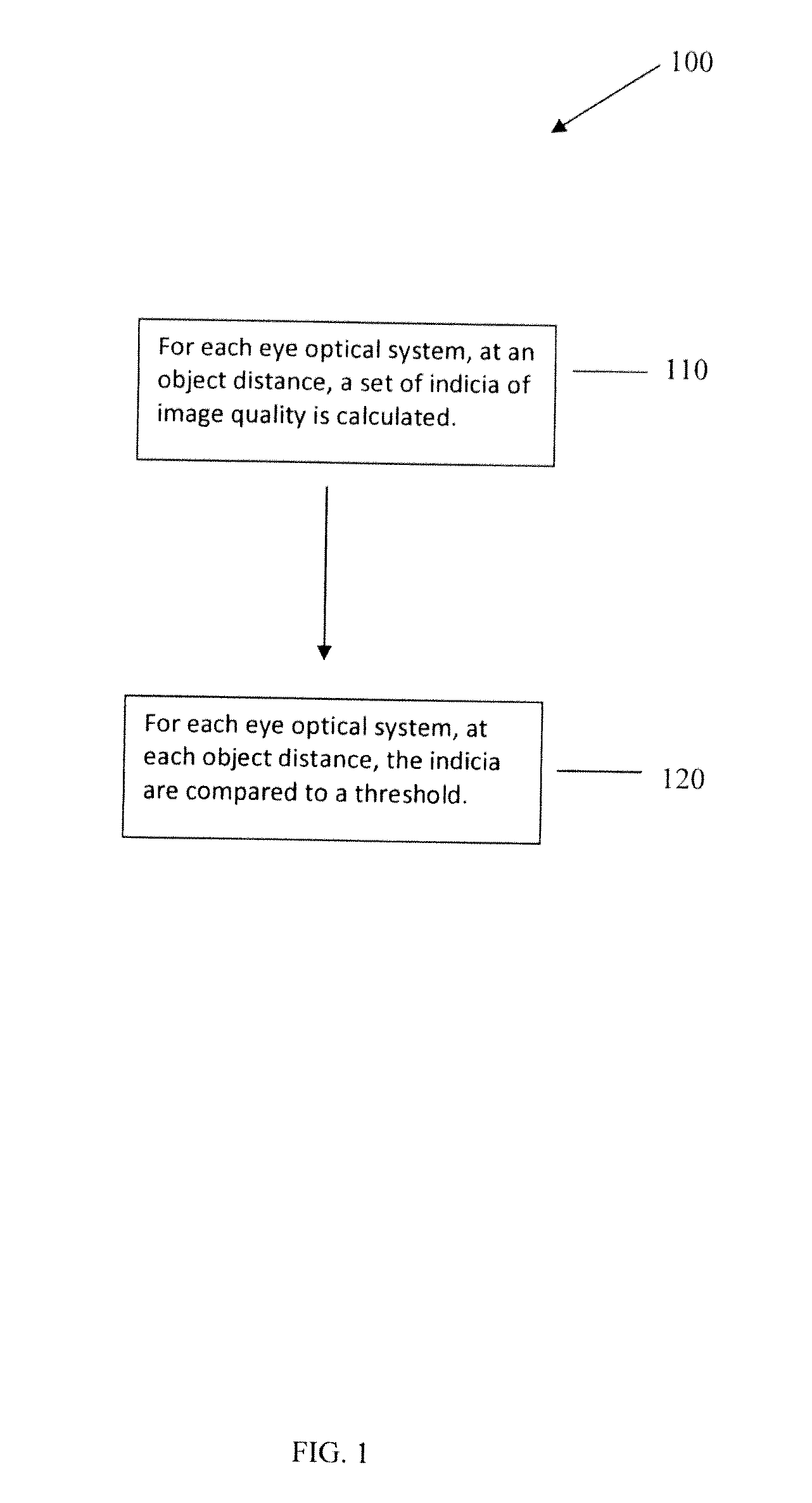
Use of an optical system simulating behavior of human eye to generate retinal images and an image quality metric to evaluate same
A method of predicting clinical performance of an ophthalmic optical correction using simulation by imaging a series of objects of different sizes by each of a plurality of eye optical systems, each of the eye optical systems including the ophthalmic optical correction, the method providing an output value representing the resolution and contrast performance of the optical design at that vergence for the eye optical systems.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
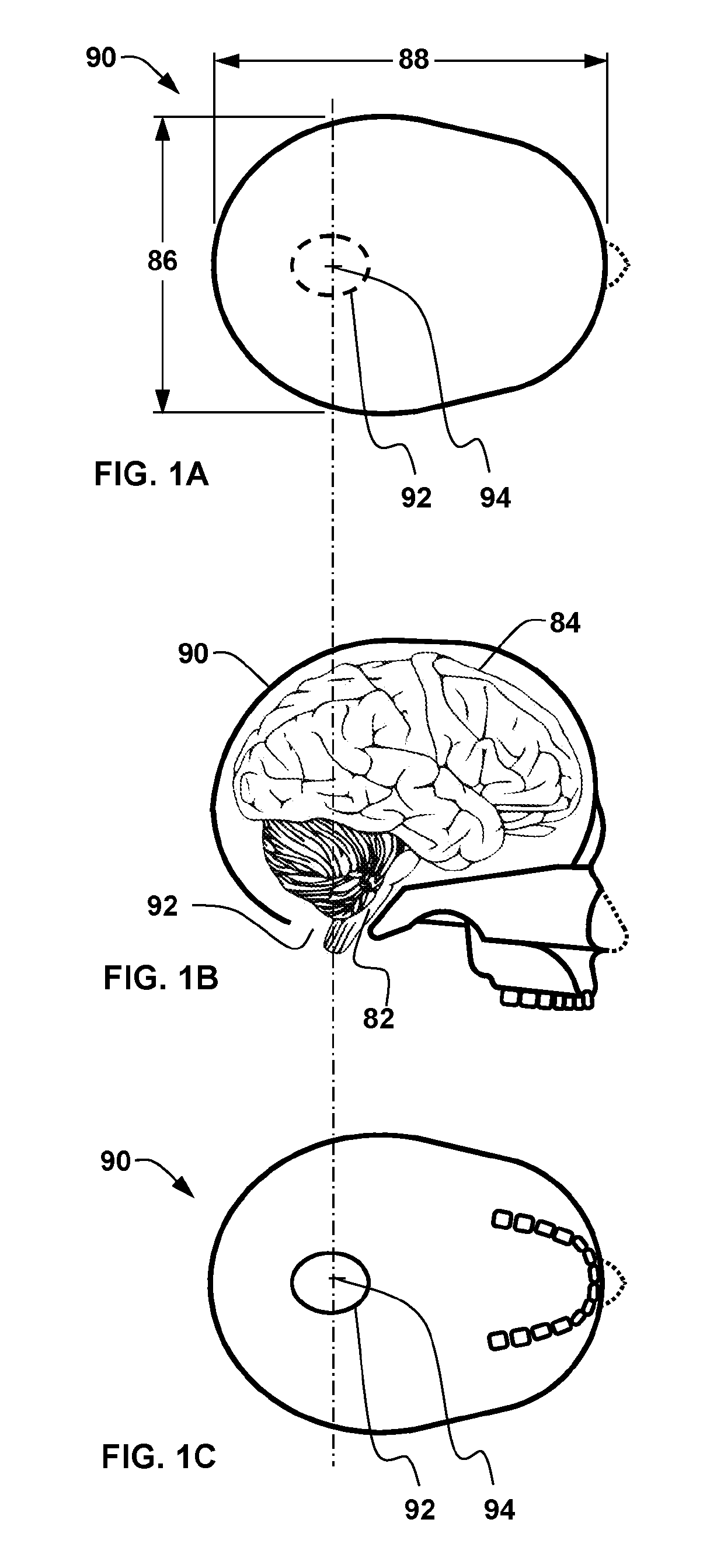
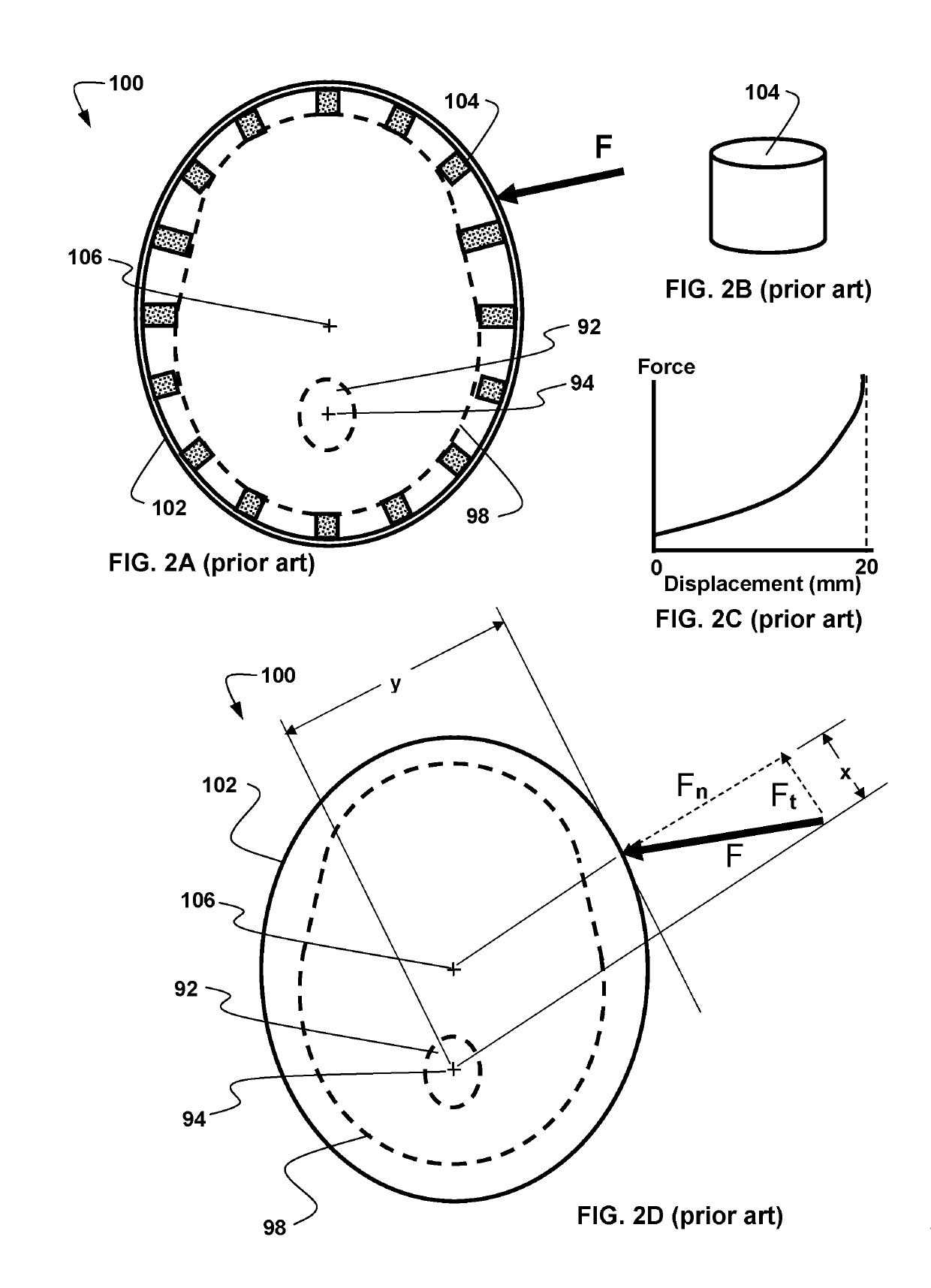
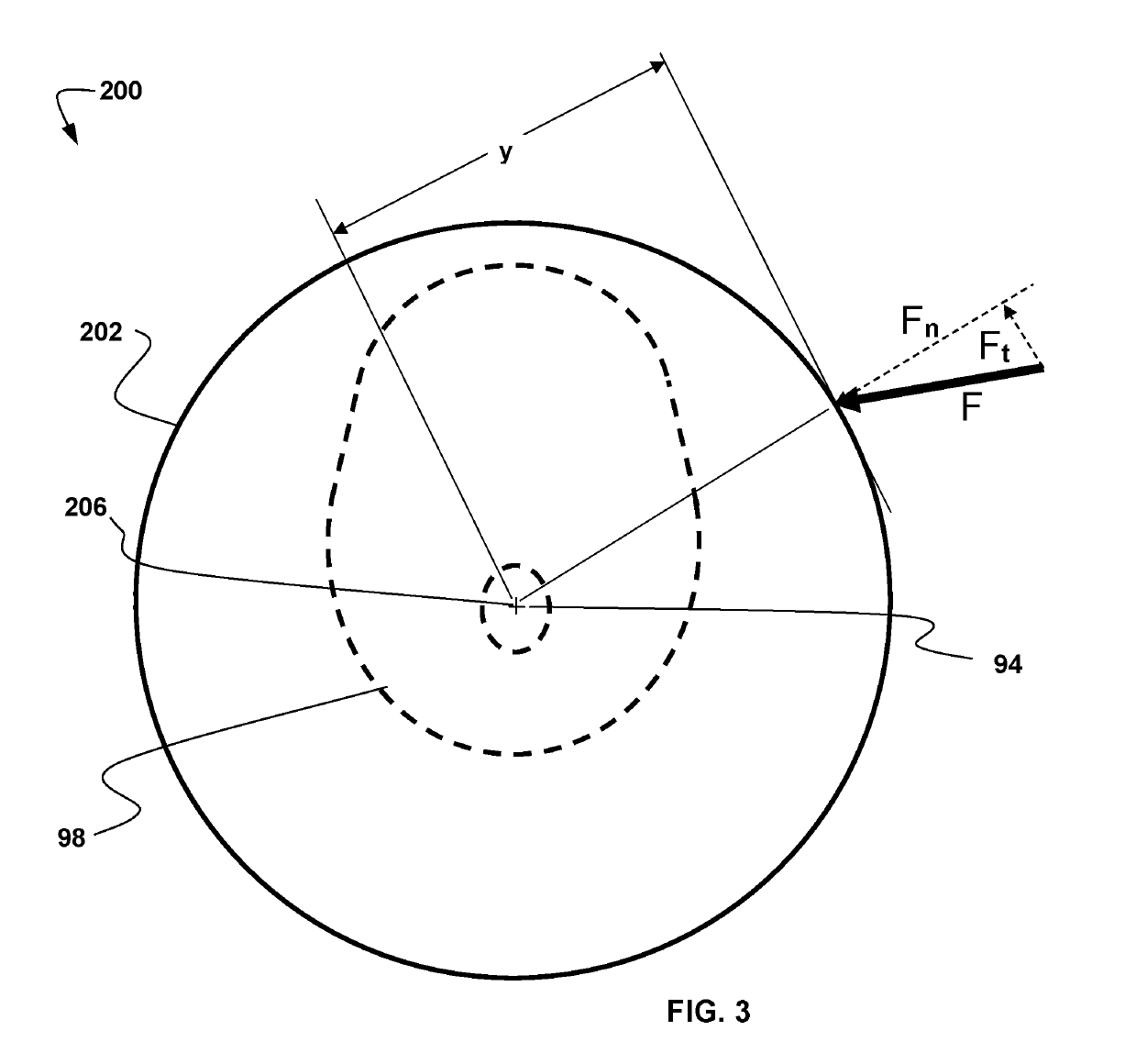
Ocular-performance-based head impact measurement applied to rotationally-centered impact mitigation systems and methods
ActiveUS20190167095A1Reduce chanceDiagnostic recording/measuringEye diagnosticsHertzVisual perception
A system or method for measuring human ocular performance can be implemented using an eye sensor, a head orientation sensor, and an electronic circuit. The device is configured for measuring vestibulo-ocular reflex, pupillometry, saccades, visual pursuit tracking, vergence, eyelid closure, dynamic visual acuity, retinal image stability, foveal fixation stability, focused position of the eyes or visual fixation of the eyes at any given moment and nystagmus. The eye sensor comprises a video camera that senses vertical movement and horizontal movement of at least one eye. The head orientation sensor senses pitch and yaw in the range of frequencies between 0.01 Hertz and 15 Hertz. The system is implemented as part of an impact reduction helmet that comprises an inner frame having interior pads configured to rest against a person's head and one or more shock absorption elements attached between the inner frame and the spherical shell that couple the spherical shell to the inner frame. The spherical shell has a circular geometry, that when viewed horizontally at its horizontal midplane, includes a center point that is the rotational center of the spherical shell. The one or more shock absorption elements are sized to provide greater spacing between the inner frame and the spherical shell at the sides and rear of the spherical shell than at the front of the spherical shell. The one or more shock absorption elements are sized to configure the alignment of the rotational center of the spherical shell with the proximate rotational center of the wearer's head.
Owner:NOVUTZ LLC
Training method for accommodative and vergence systems, and multifocal lenses therefor
ActiveUS20120019775A1Simple and inexpensiveSpectales/gogglesChiropractic devicesEye lensVisual perception
Accommodative and vergence systems training method and multifocal ophthalmic lenses of Horizontal periodic or quasi-periodic Optical Power Stepless Alternating (HOPSA-lenses) therefor are proposed. Reading the text with HOPSA-lenses worn, while the head is stationary, provides a continuous alternating of accommodation and vergence strain / relaxation and, therefore, provides dynamic training of both systems. The method is applicable for human visual system therapy, eye diseases treatment / prevention and ophthalmology researches. The method enables combining the effective visual trainings with documents reading / processing, visual target examining, watching TV / video, playing computer games, etc., as well as combining the training with conventional vision correction. Several embodiments of HOPSA-lenses are disclosed, such as multi- and mono-cyclic, multi-layer, splitting the basic correction and training functions between lens' sides or layers, having left and right lenses' surfaces individually configured to provide the congruence of optical power for fixation, and / or the convergence invariability for fixation during the training.
Owner:TYRIN ALBERT +1
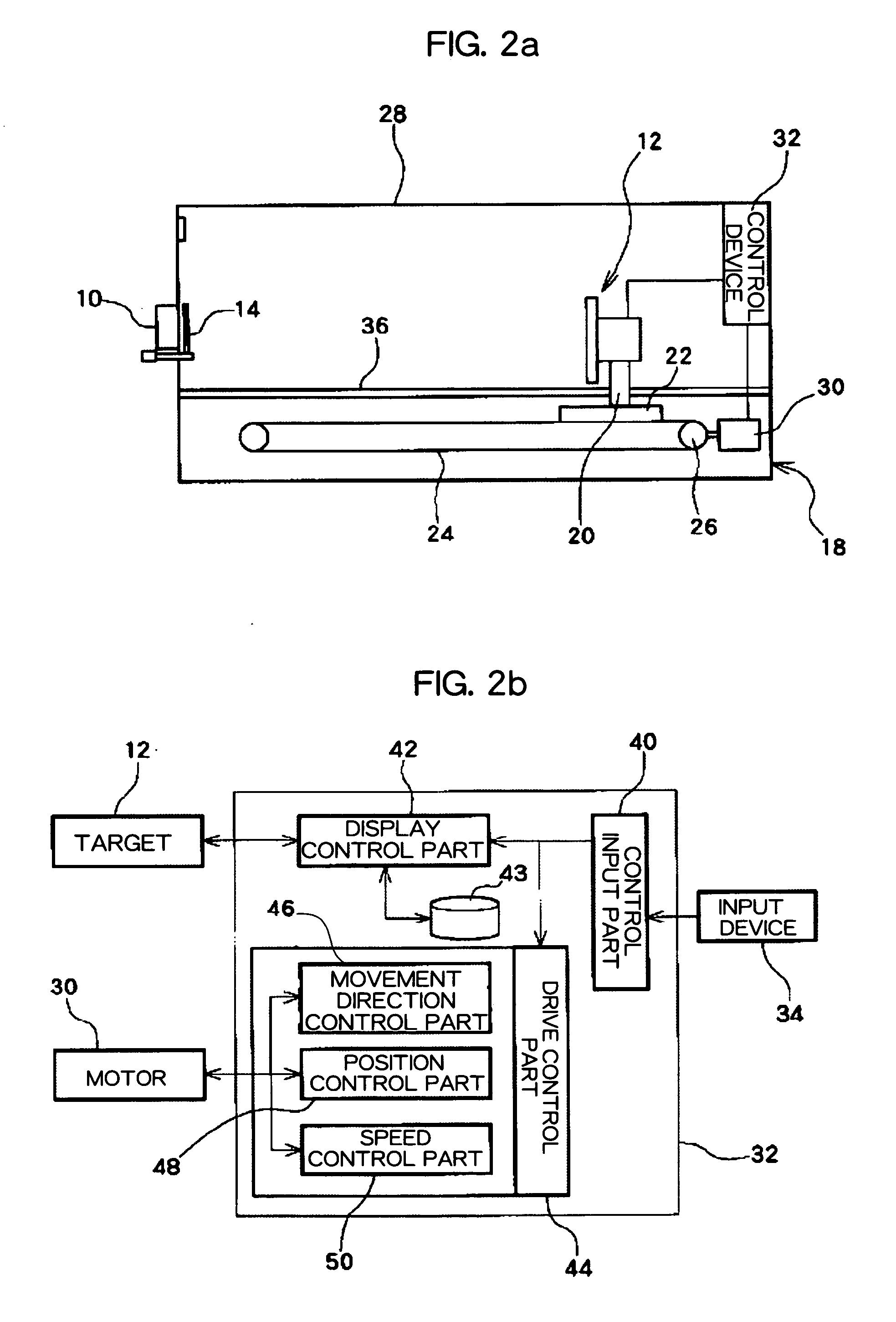
Eyesight improving device
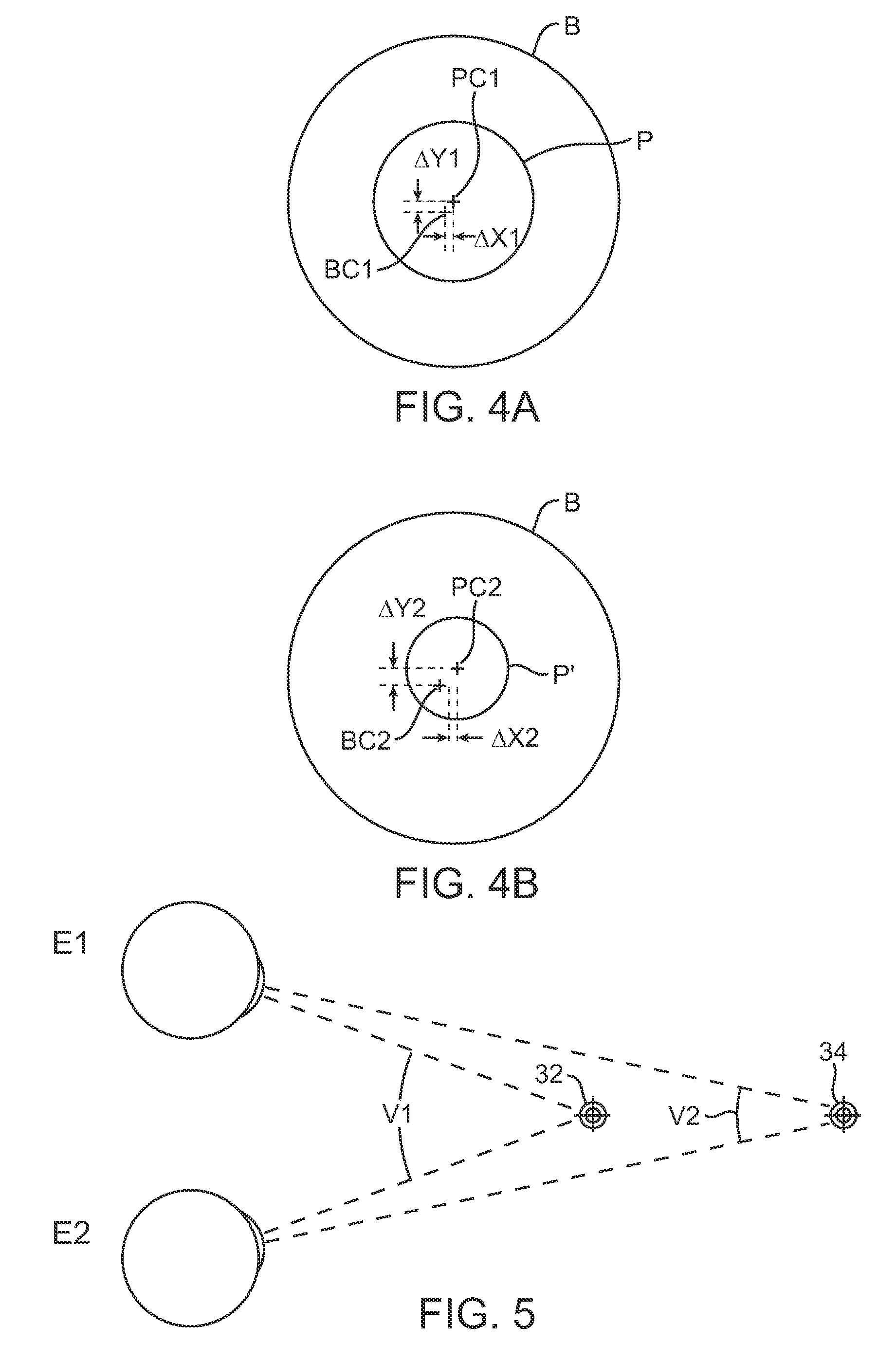
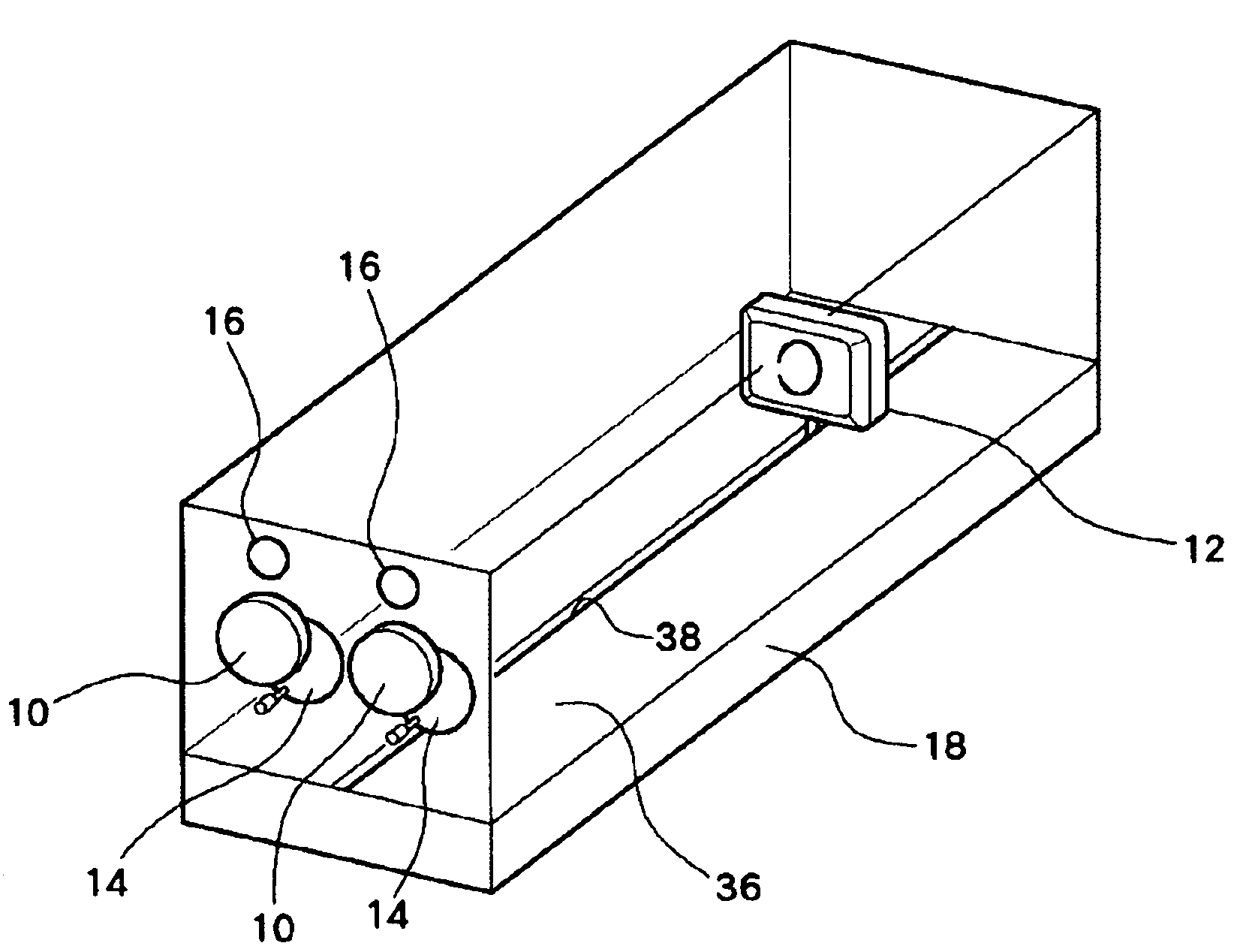
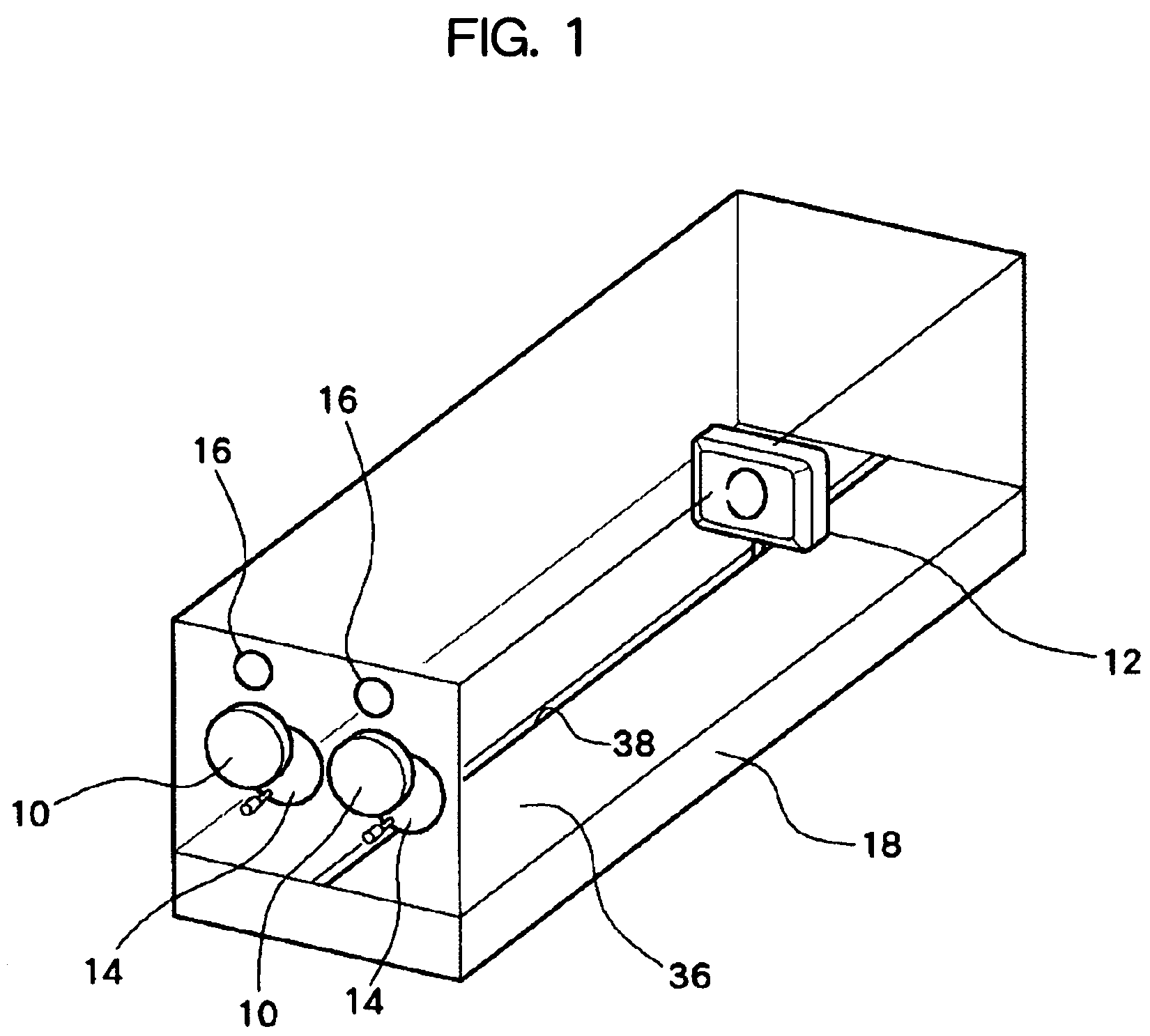
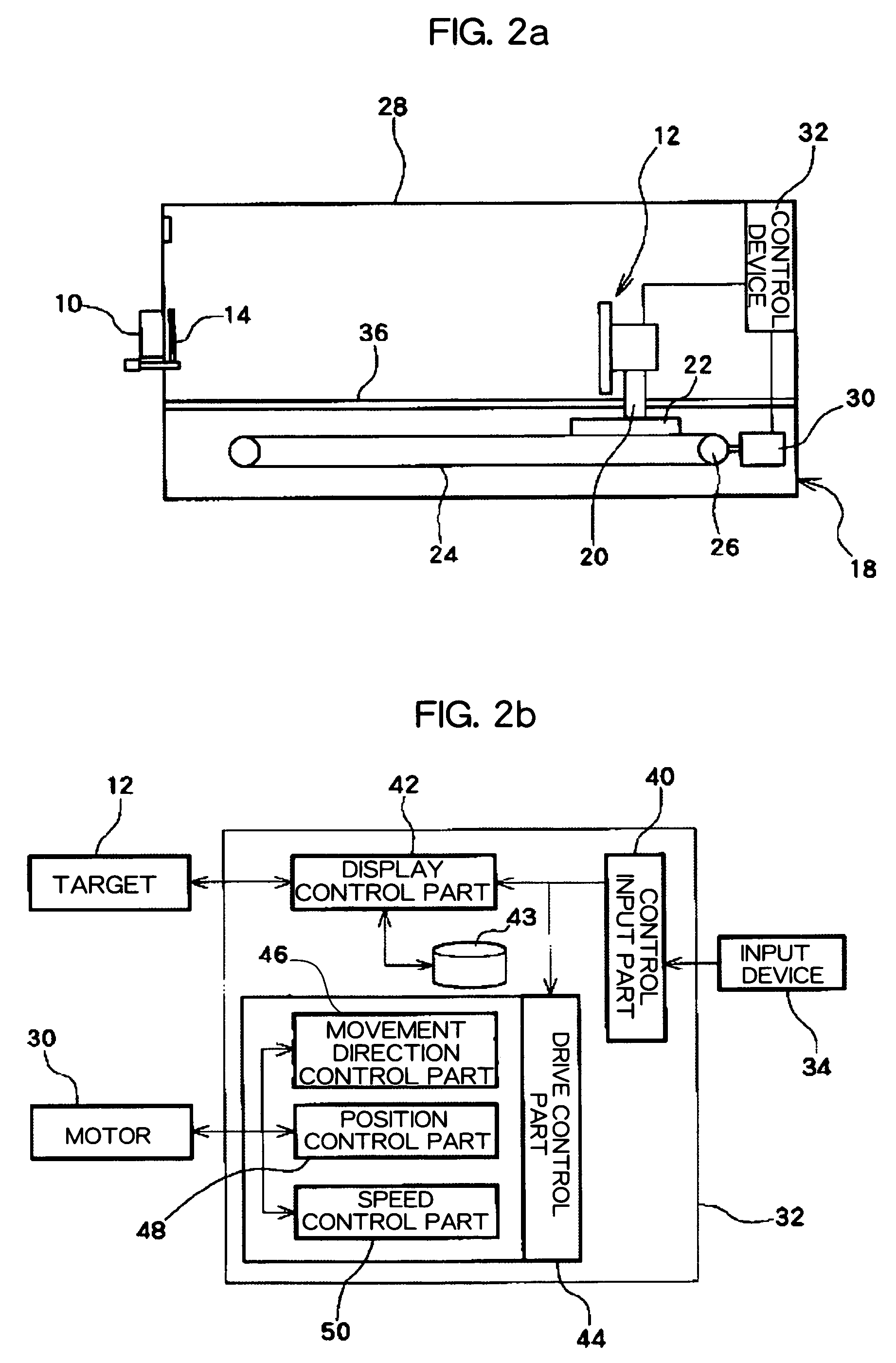
This patent provides an eyesight improving device which improves ocular imaging adjustment functions and is easy to use. A user puts the eyes on eyepiece parts 10, and sees a figure displayed on a target 12 by both eyes or one eye by opening or closing blocking device 14. In a state where the user focuses the eye on the figure, the target 12 is moved from a far point to a near point by target movement device 18 and is next moved from the near point to the far point, and this is repeated. In this case, the size of the figure is controlled to be changed in proportion to the distance between the eyepiecepart 10 and the target 12. The user can easily concentrate to focus the eye on the figure during the movement of the target 12. This training activates the ocular imaging adjustment functions of a ciliary muscle, a pupil, vergences and the like resulting with their improvement.
Owner:HORIE HIDENORI
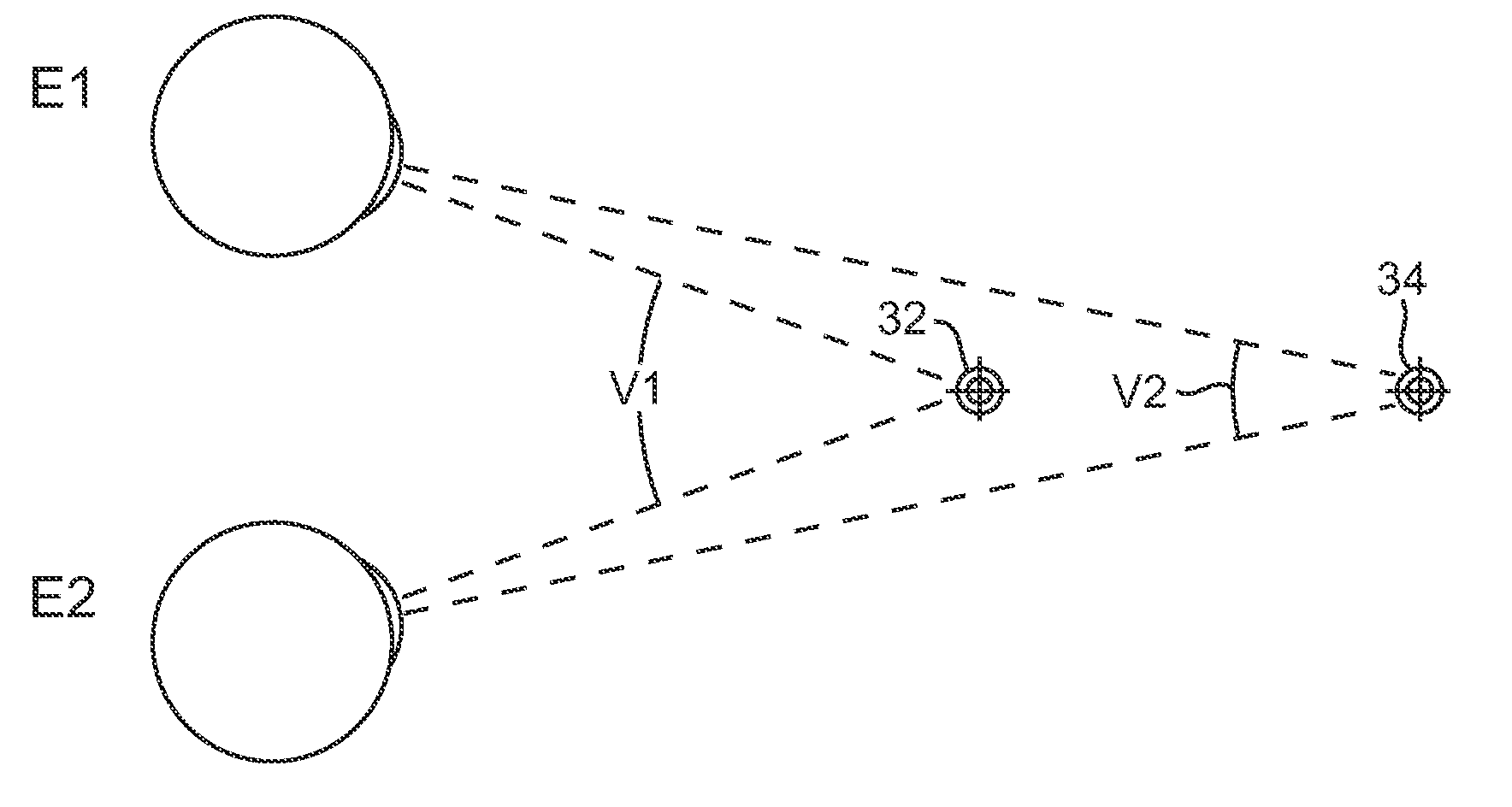
Detecting visual inattention based on eye convergence
ActiveUS20150193664A1Simple technologyImprove securityScene recognitionSensorsVergence movementVisual inattention
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for detecting when a user is not being attentive based on eye convergence. The technique includes determining a first distance from the user to a first object. The first distance may be determined using a depth sensor. The technique further includes determining a first vergence angle associated with a left eye of the user and determining a second vergence angle associated with a right eye of the user. The technique further includes determining a first eye convergence distance based on the first vergence angle, the second vergence angle, and an interocular distance between the left eye and the right eye. The technique further includes comparing the first distance to the first eye convergence distance to generate a first result. An inattention alert may be generated based on the first result.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
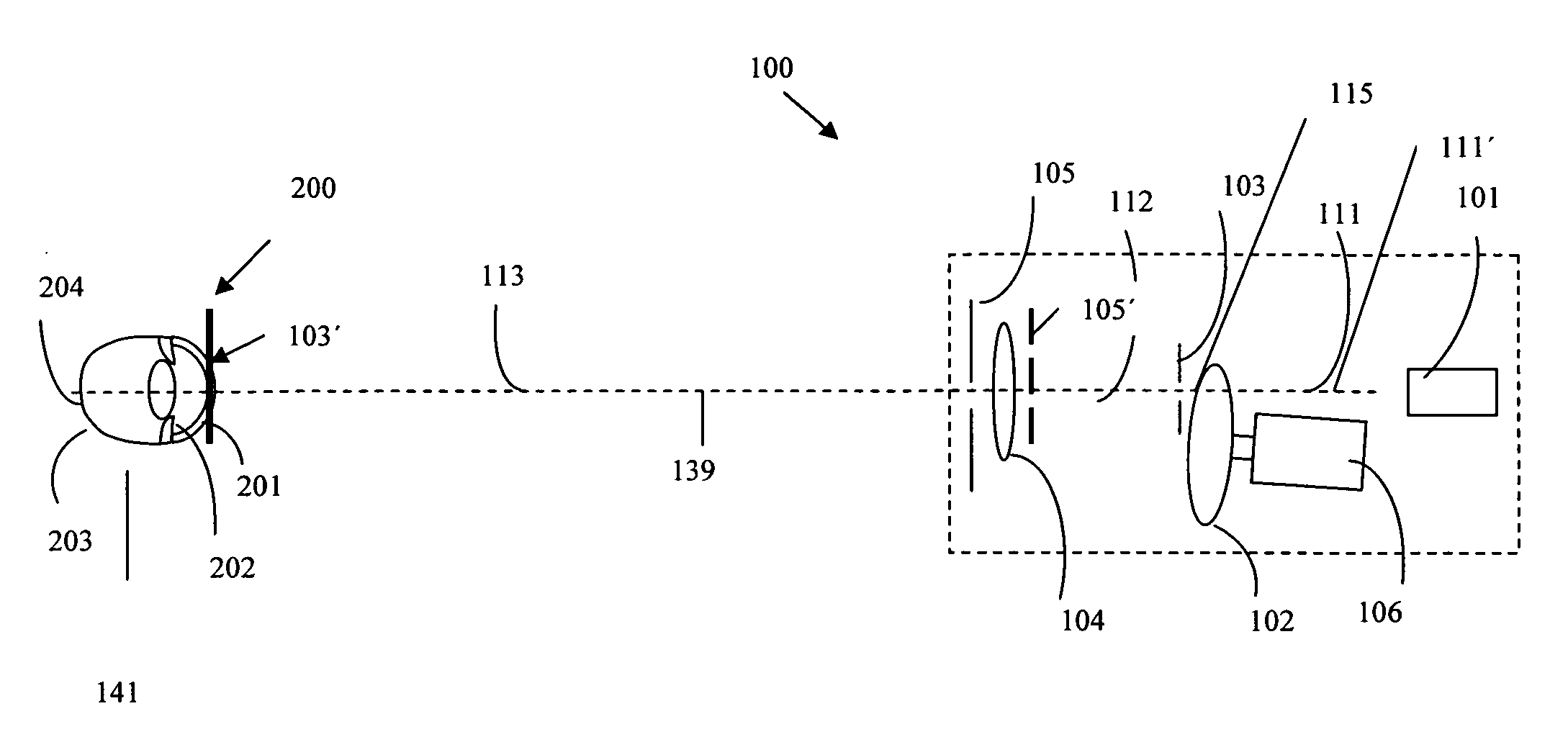
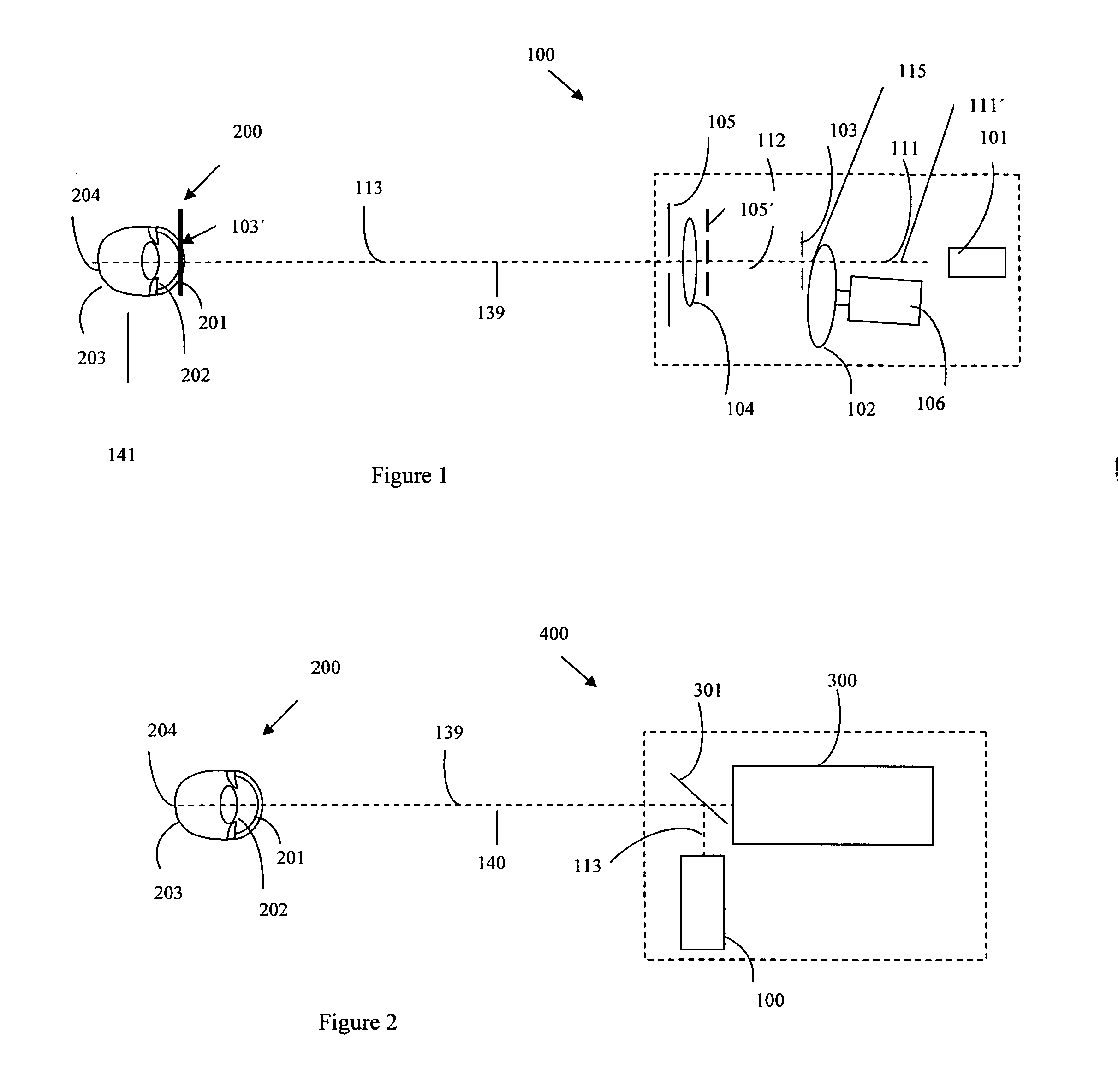
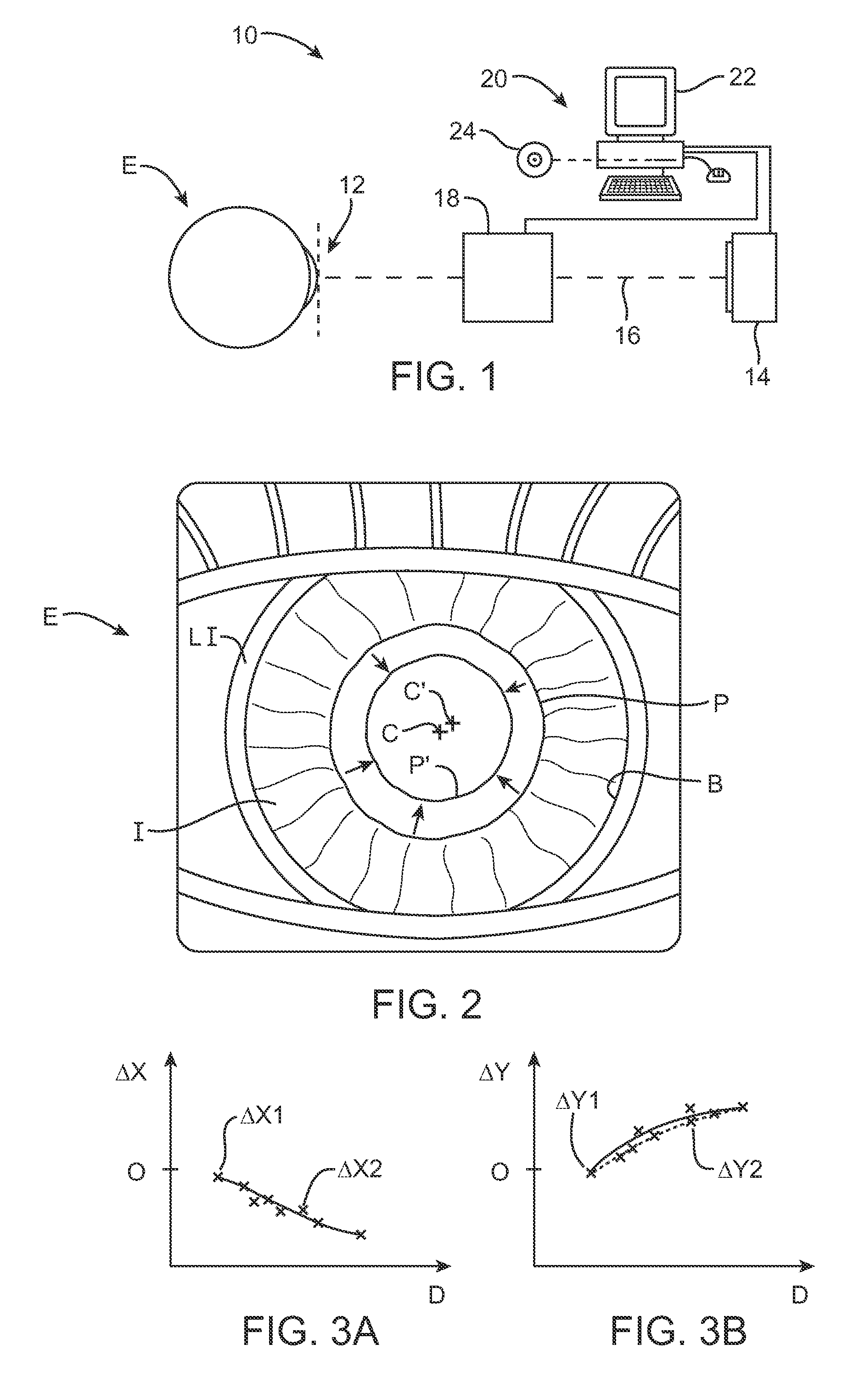
Pupilometer for pupil center drift and pupil size measurements at differing viewing distances
The present invention generally provides improved devices, systems, and methods for measuring characteristics of at least one eye, and particularly for measuring the physiological changes in eyes under different viewing conditions. An exemplary embodiment provides a pupilometer which measures any changes in location of a pupil center with changes in viewing distances. As the eye often moves significantly during viewing, the pupil center location will often be measured relative to a convenient reference of the eye such as an outer iris boundary. Pupil size may also be recorded, and the measurements from both eyes of a patient may be taken simultaneously. Exemplary embodiments may be configured so as to allow the vergence angle between the eyes to vary with differing viewing distances, regardless of whether one or both eyes are being measured.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Pupilometer for pupil center drift and pupil size measurements at differing viewing distances
InactiveUS20060215113A1Enhance pupil size pupilEnhance pupil pupil drift measurementEye diagnosticsVergence movementPupilometer
The present invention generally provides improved devices, systems, and methods for measuring characteristics of at least one eye, and particularly for measuring the physiological changes in eyes under different viewing conditions. An exemplary embodiment provides a pupilometer which measures any changes in location of a pupil center with changes in viewing distances. As the eye often moves significantly during viewing, the pupil center location will often be measured relative to a convenient reference of the eye such as an outer iris boundary. Pupil size may also be recorded, and the measurements from both eyes of a patient may be taken simultaneously. Exemplary embodiments may be configured so as to allow the vergence angle between the eyes to vary with differing viewing distances, regardless of whether one or both eyes are being measured.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Simulated head mounted display system and method
To overcome problems with vergence, a binocular head mounted display (HMD) is used in a simulator in which an out-the-window scene is displayed in real time on a screen arrangement. Imagery for the left and right eyes of the HMD is derived by generating a starting HMD image for a Cyclops viewpoint between the user's eves, and then rendering respective views for each eve from the position of the eye in a virtual 3D model of the screen arrangement, wherein the starting HMD image is frustum projected against the screen arrangement of the 3D model.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Ophthalmic system and method
InactiveUS20080084541A1Eliminates focusedMinimizing speckleEye diagnosticsVergence movementLaser probe
Ophthalmic system and method particularly suited to providing a laser probe beam for a Hartmann-Shack ophthalmic aberrometer. The laser probe beam produced by the system and method has a confined image spot at both the cornea and the retina. The probe beam can be generated with a laser beam passing through a moving holographic diffuser and two pinhole apertures. The holographic diffuser randomizes the spatial phase across the laser probe beam to substantially eliminate laser speckle from the Hartmann-Shack images. An imaging lens forms the probe beam and a first pinhole aperture image on the cornea, which eliminates beam size variation due to laser parameters and misalignment. A second-pinhole aperture is used to control the vergence of the probe beam and the probe beam spot size on the retina. The spot size on the retina is thus insensitive to the defocus power range of various subjects' eyes. The confined image spot on the retina substantially eliminates the possibility of an over-tight laser focal spot and allows the injection of higher laser power into the eye.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Training method for accommodative and vergence systems, and multifocal lenses therefor
Accommodative and vergence systems training method and multifocal ophthalmic lenses of Horizontal periodic or quasi-periodic Optical Power Stepless Alternating (HOPSA-lenses) therefor are proposed. Reading the text with HOPSA-lenses worn, while the head is stationary, provides a continuous alternating of accommodation and vergence strain / relaxation and, therefore, provides dynamic training of both systems. The method is applicable for human visual system therapy, eye diseases treatment / prevention and ophthalmology researches. The method enables combining the effective visual trainings with documents reading / processing, visual target examining, watching TV / video, playing computer games, etc., as well as combining the training with conventional vision correction. Several embodiments of HOPSA-lenses are disclosed, such as multi- and mono-cyclic, multi-layer, splitting the basic correction and training functions between lens' sides or layers, having left and right lenses' surfaces individually configured to provide the congruence of optical power for fixation, and / or the convergence invariability for fixation during the training.
Owner:TYRIN ALBERT +1
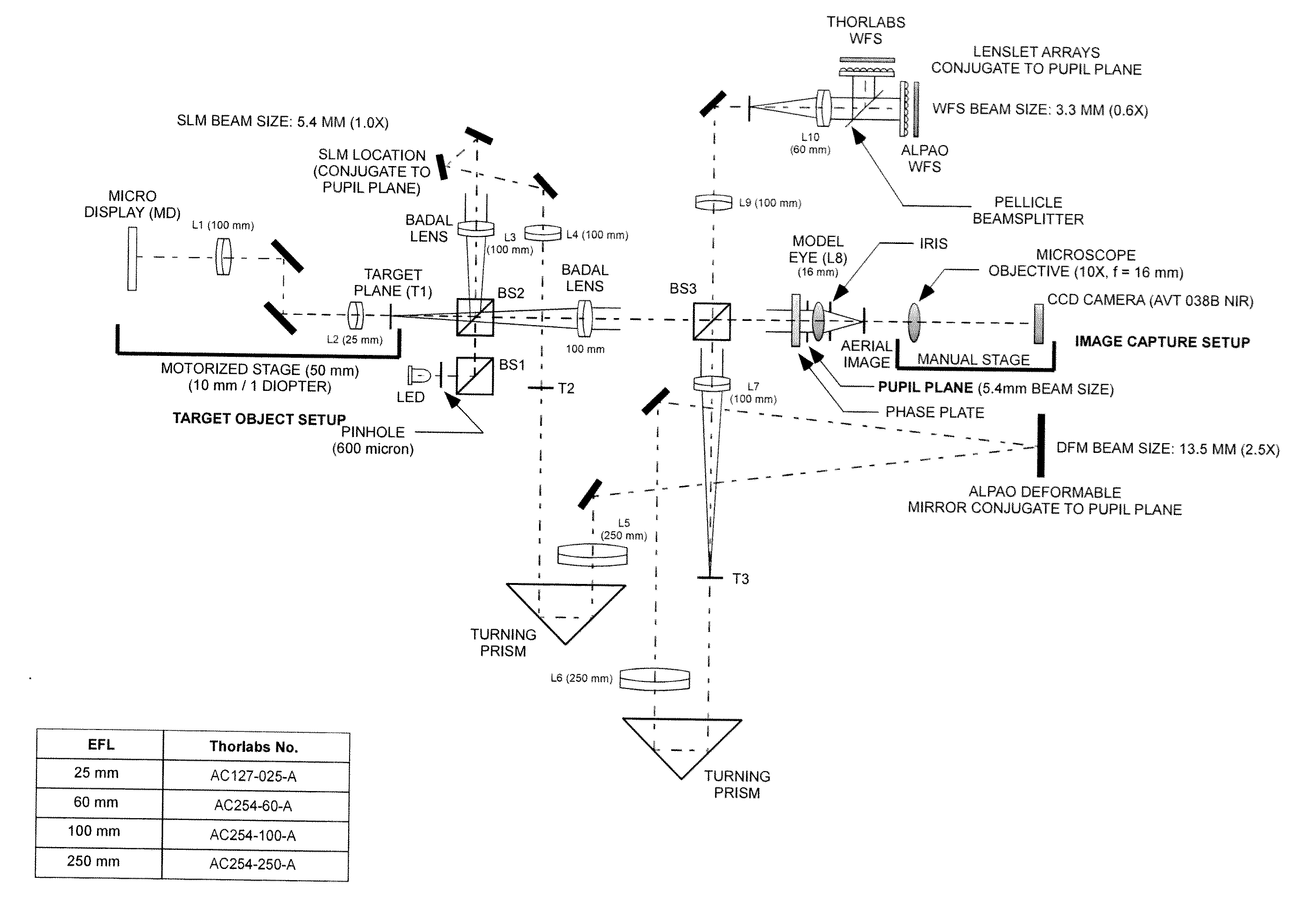
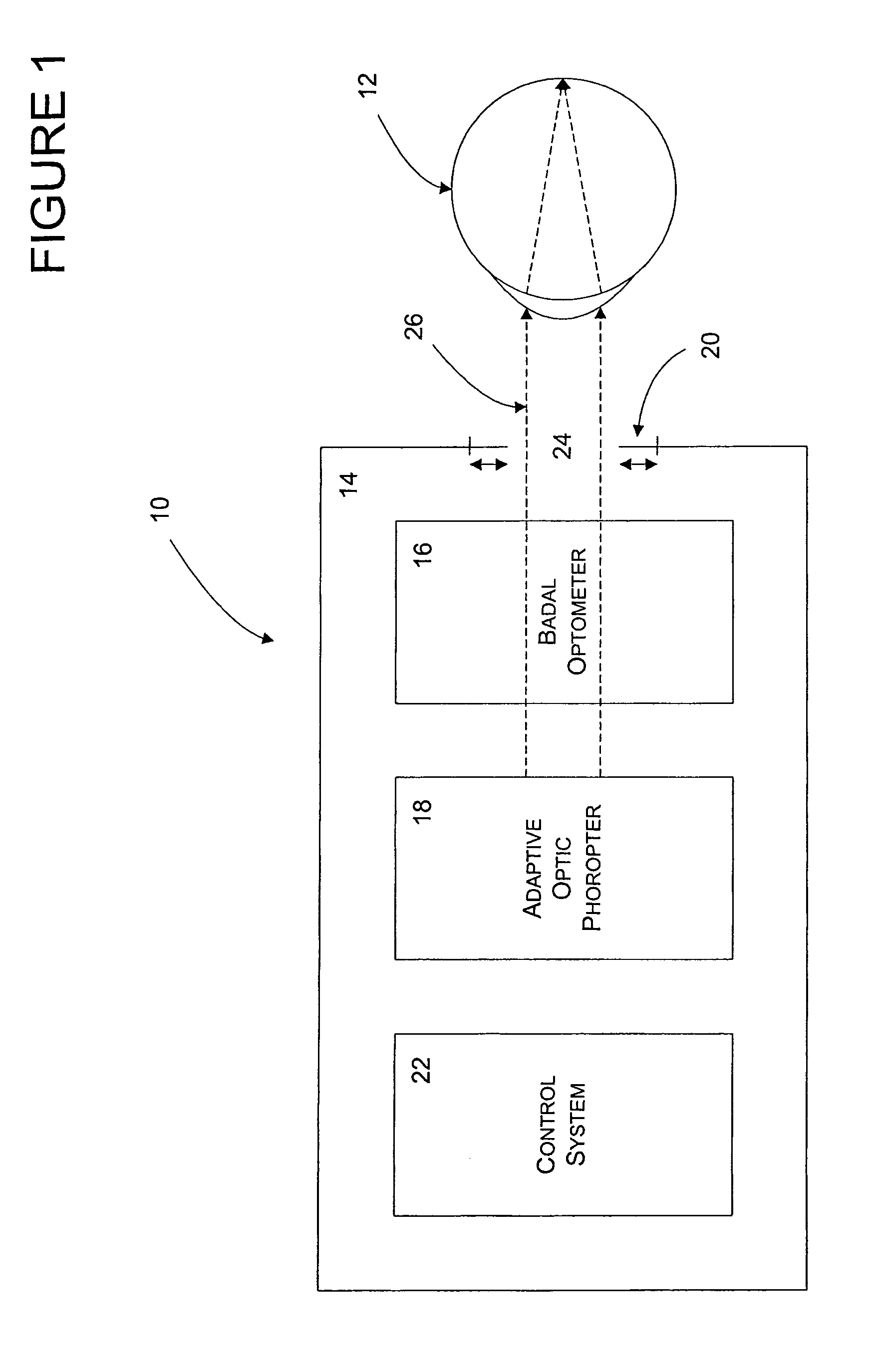
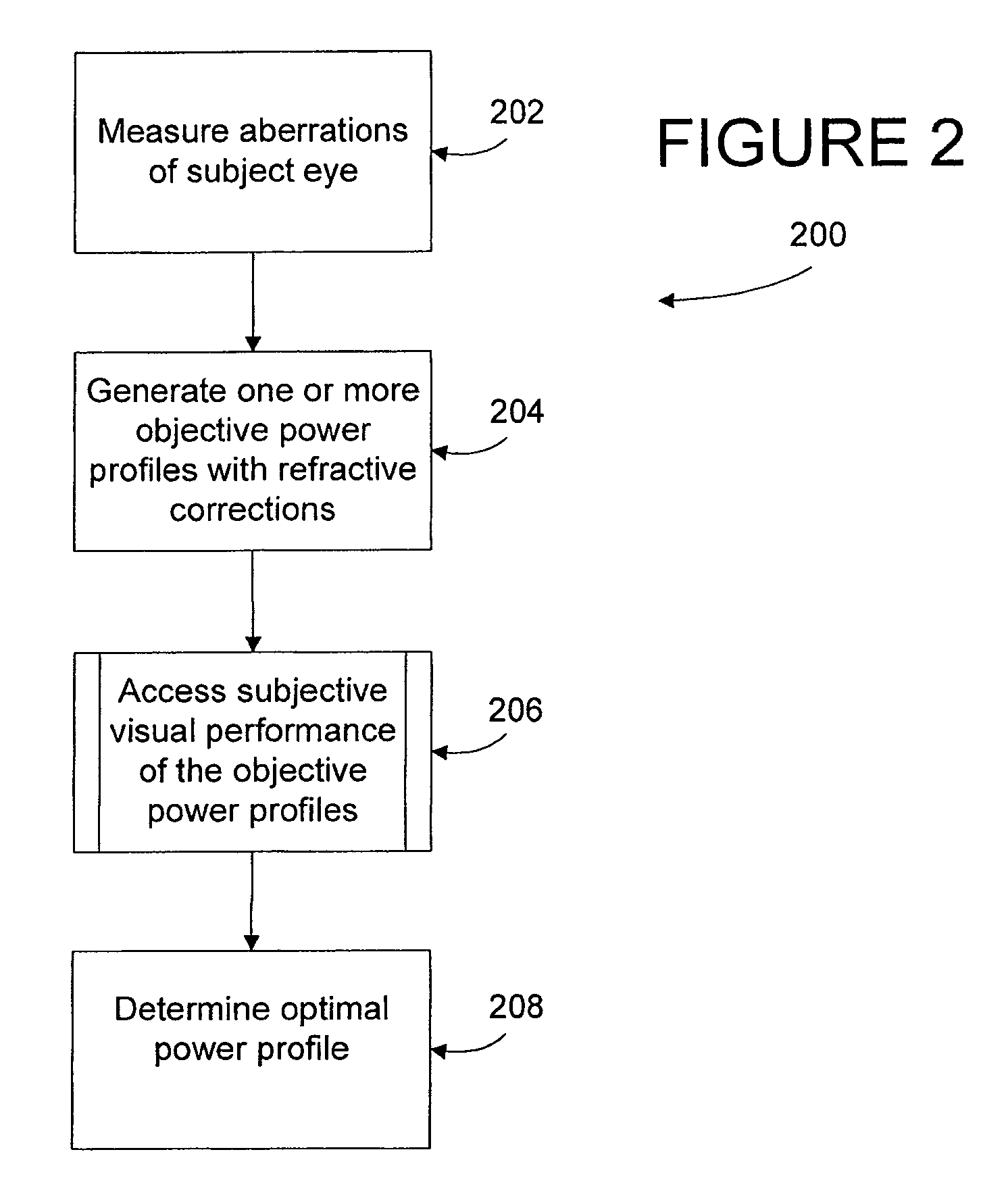
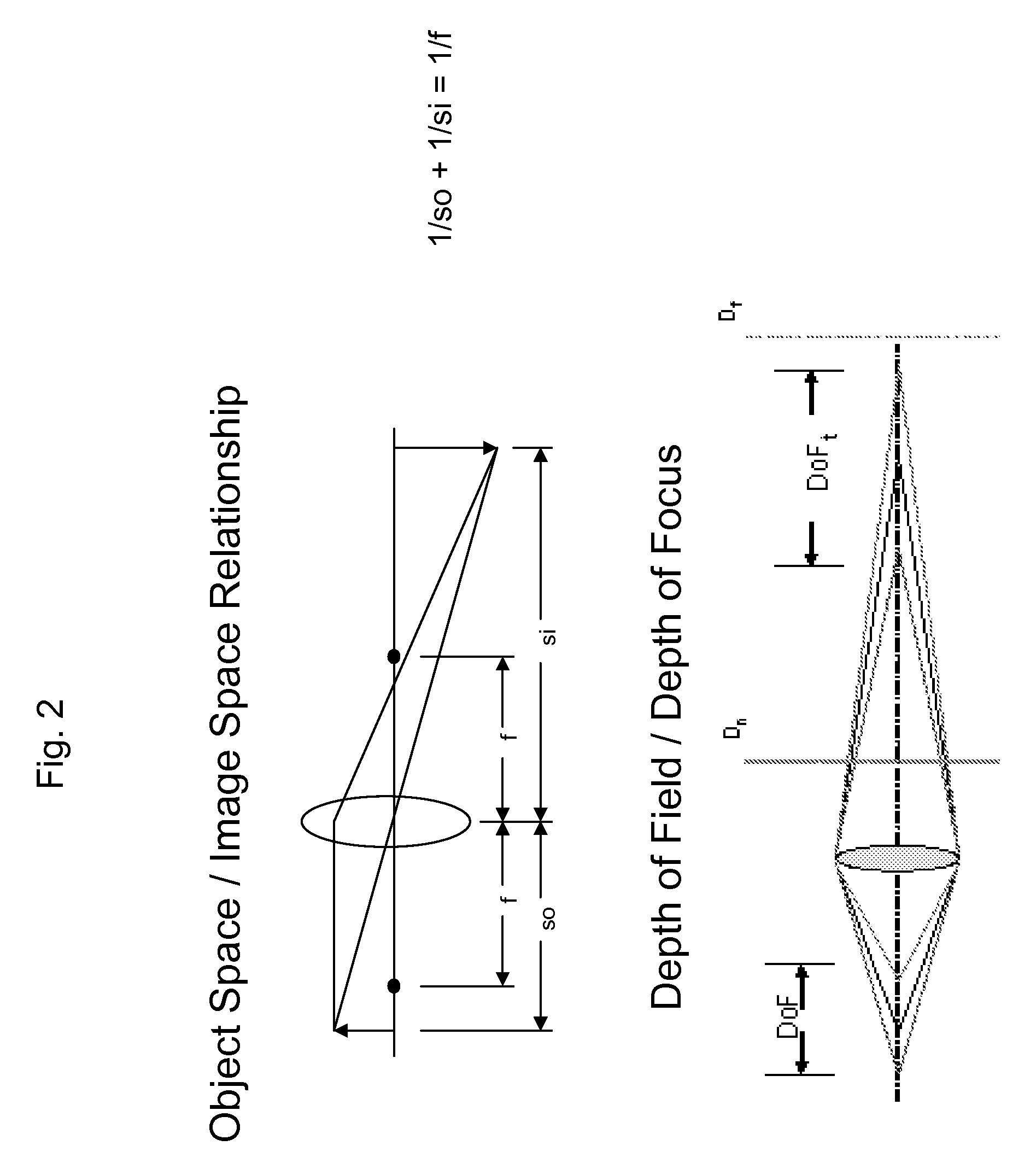
Generalized presbyopic correction methodology
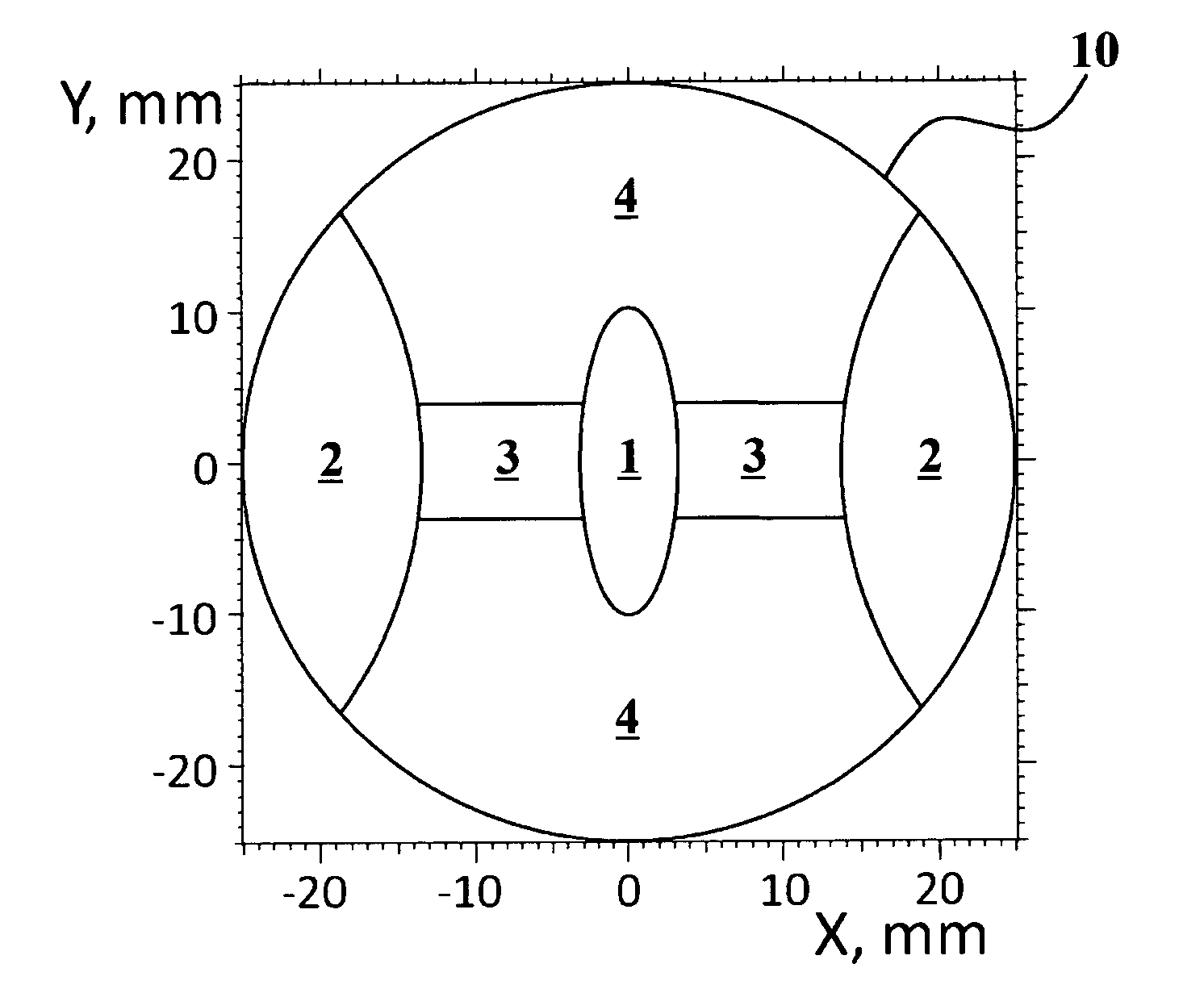
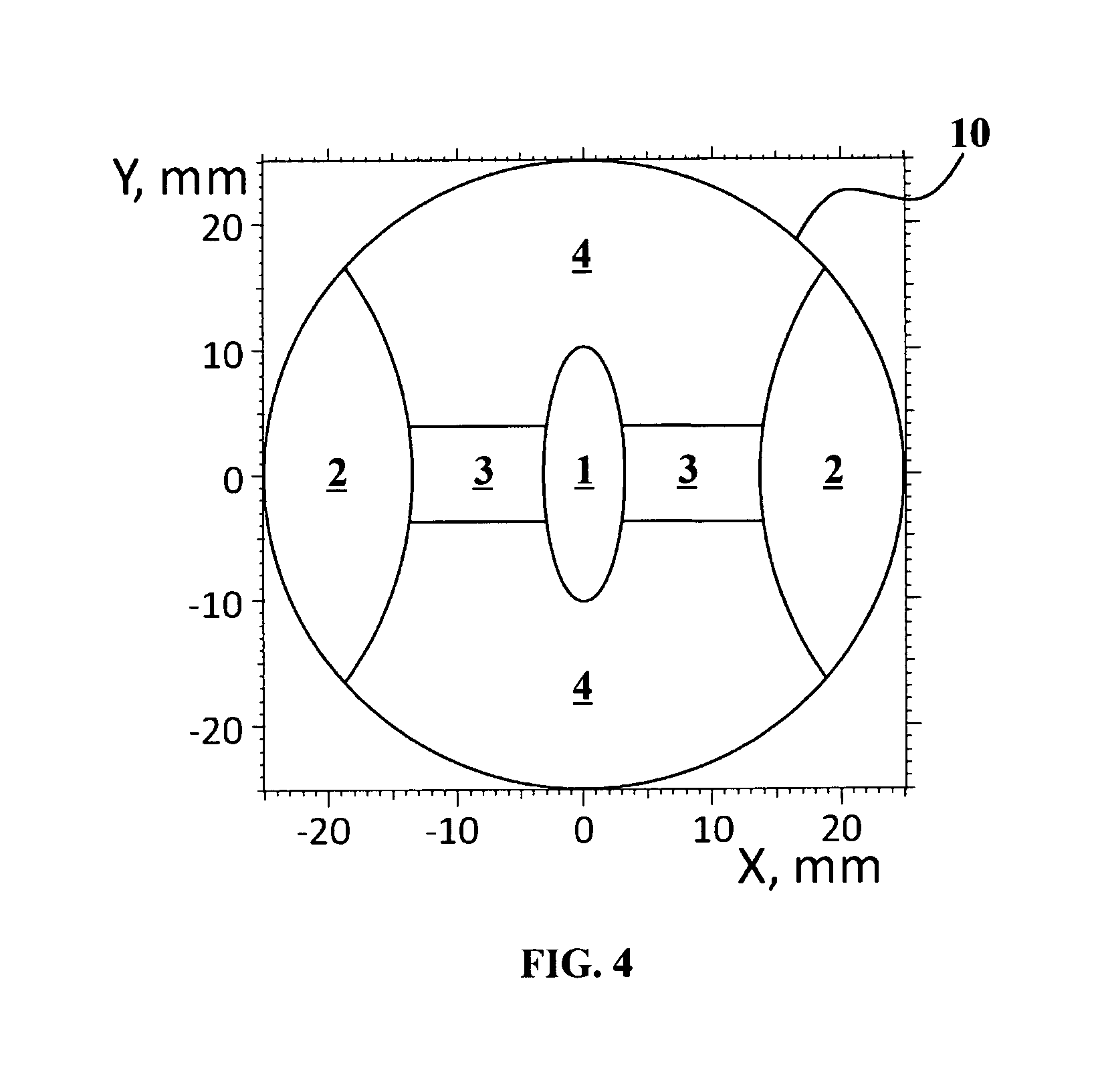
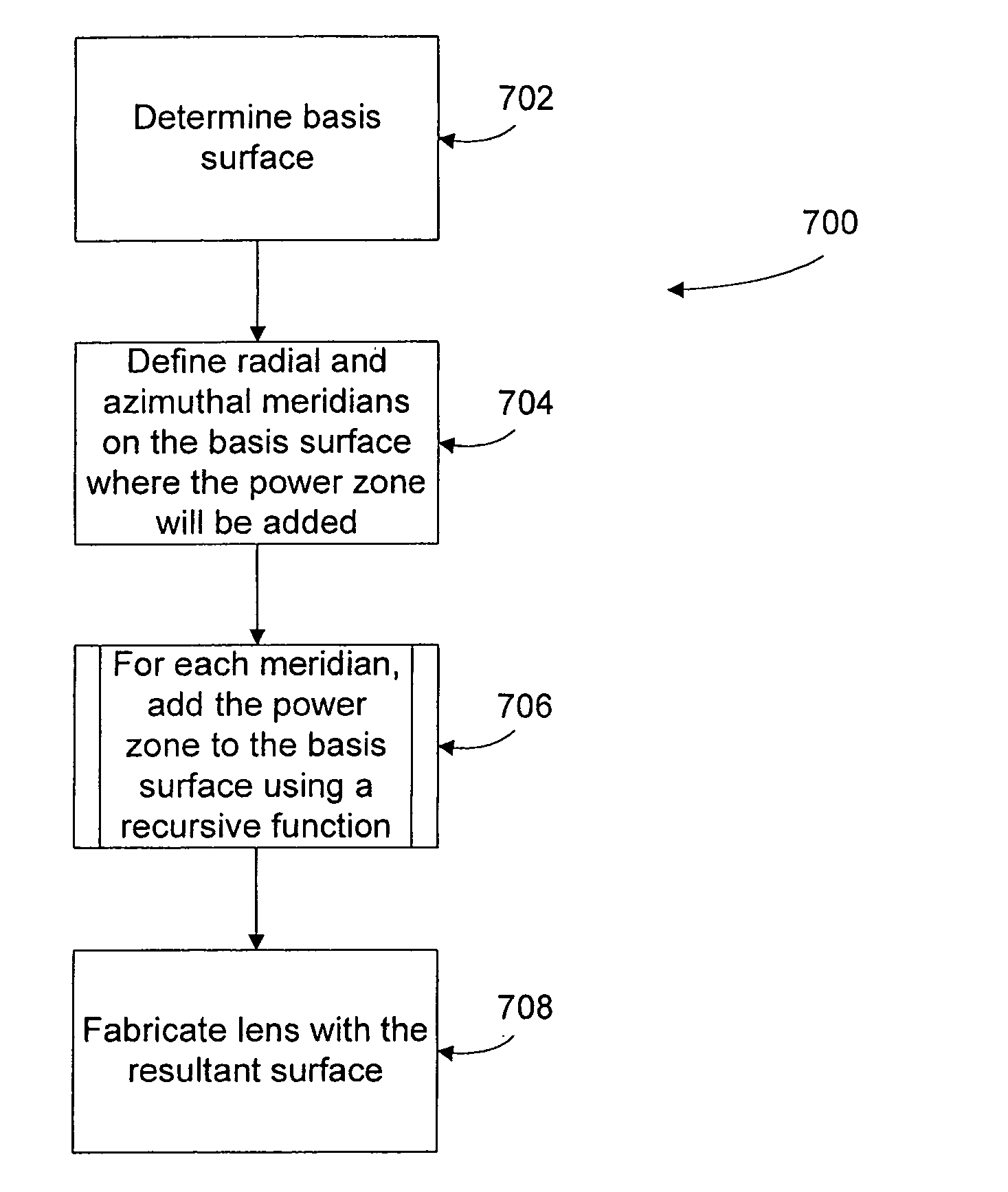
An adaptive optics phoropter is aligned with a Badal optometer and an adjustable aperture component to subjectively determine an optimal vision correction as a power profile for an ophthalmic lens or ablating a cornea. The optimal power profile is preferably determined in an iterative process by adjusting the vergence of the Badal optometer and aperture size of the adjustable aperture component for power profiles with presbyopic power zones having different amplitudes, shapes, widths, and / or de-centering. Also included is a method of recursively computing a refractive surface with a regular presbyopic power zone (e.g., according to the optimal power profile) and adding it onto an underlying irregular Zernike-basis-set aberration-corrected surface in a linear fashion for fabricating an ophthalmic lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
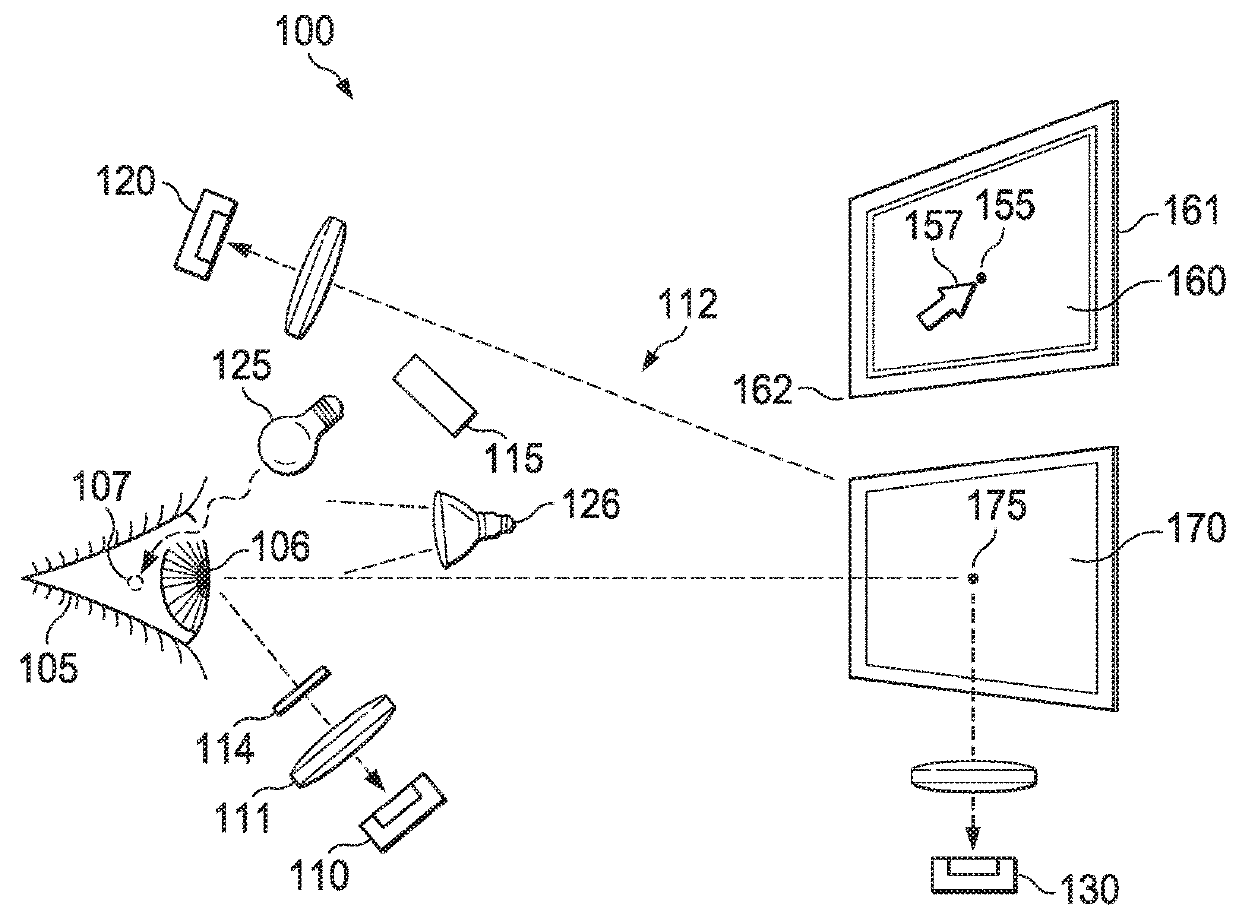
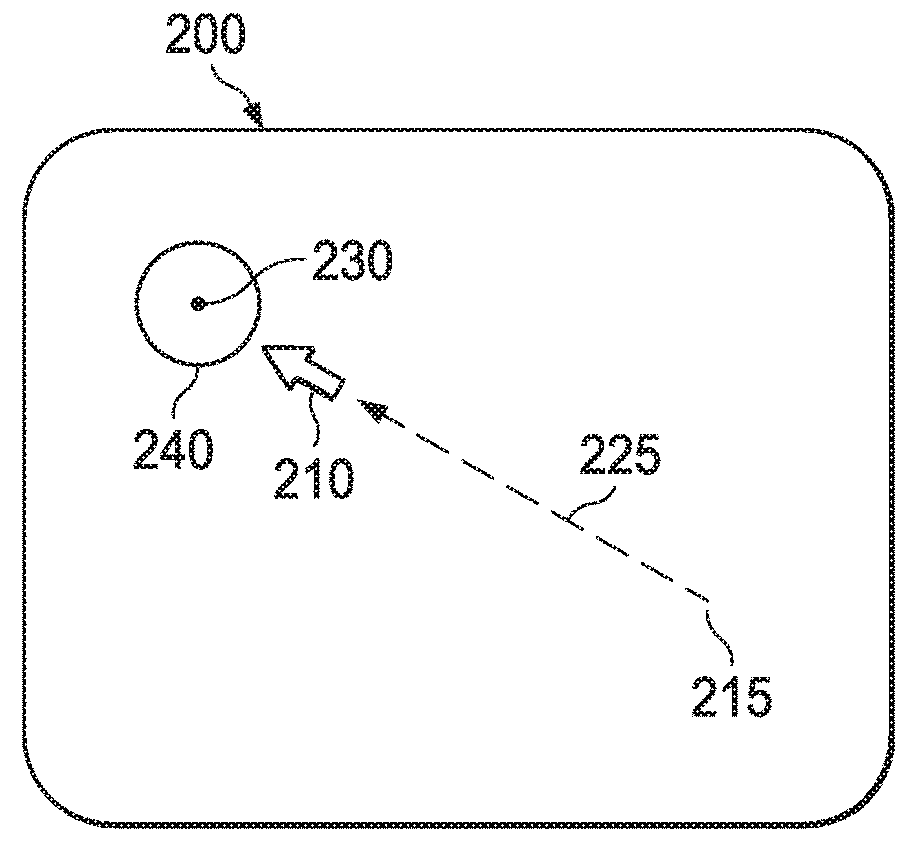
Eye-signal augmented control
ActiveUS20180275753A1Input/output for user-computer interactionAcquiring/recognising eyesVergence movementElectronic systems
An electronic system tracks a user's gaze to rapidly transport a cursor to a location within a focal region of the user's eye. The electronic system transports the cursor from an initial location across one or more displays to a new location in response to detecting one or more saccadic and / or vergence movements of the user's eye or in response to a signal indicating that the user desires to move the cursor to a new location within a focal region of the user's eye or eyes. In some embodiments, the electronic system moves the cursor to the new location along a trajectory wherein the cursor is visible along at least a portion of the trajectory, enabling the user to find the cursor more easily.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Retroreflective light field display
A projected head mounted display system is disclosed that projects images onto a retroreflective screen, which are then reflected back for view by a user. The projected head mounted display system displays computer generated images at multiple focal distances to simulate a light field so as to match eye accommodation to vergence.
Owner:TILT FIVE INC
Stereoscopic display
InactiveUS20170329402A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage data processingViewpointsDisplay device
A direct interaction stereoscopic display system that produces an augmented or virtual reality environment. The system comprises one or more displays, a beam combiner, and a mirrored surface to virtually project high-resolution flicker-free stereoscopic 3D imagery into a graphics volume in an open region. Viewpoint tracking is provided enabling motion parallax cues. A user interaction volume co-inhabits the graphics volume and a precise low-latency sensor allows users to directly interact with 3D virtual objects or interfaces without occluding the graphics. An adjustable support frame permits the 3D imagery to be readily positioned in situ with real environments for augmented reality applications. Individual display components may be adjusted to precisely align the 3D imagery with components of real environments for high-precision applications and also to match accommodation-vergence distances to prevent eye strain. The system's modular design and adjustability allows display panel pairs of various sizes and models to be installed.
Owner:SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE LLC
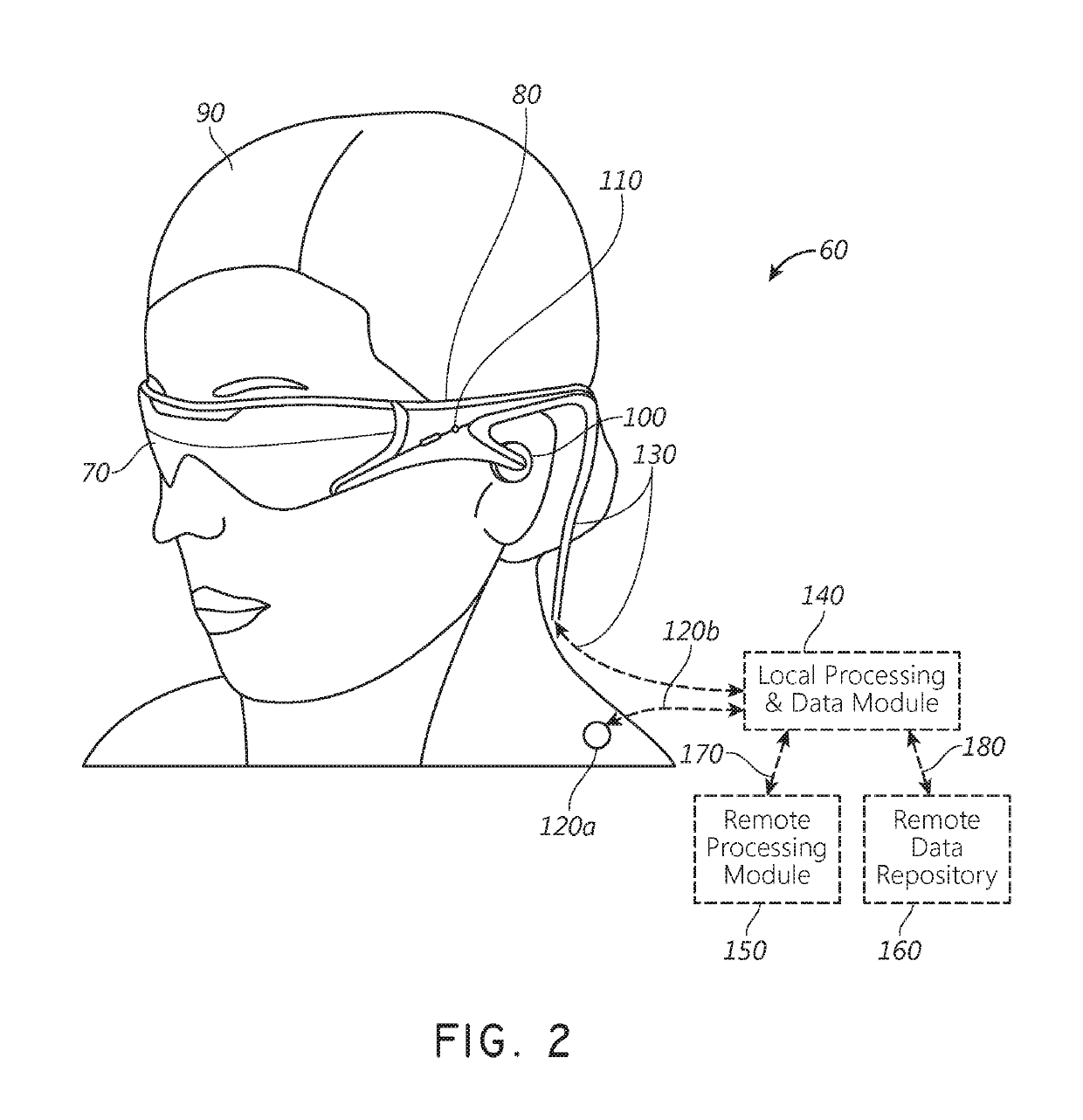
Augmented reality display system for evaluation and modification of neurological conditions, including visual processing and perception conditions
ActiveUS10332315B2Improve plasticityImprove abilitiesMedical automated diagnosisMental therapiesVergence movementWavefront
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Augmented reality systems and methods with variable focus lens elements
ActiveUS10459231B2Input/output for user-computer interactionNon-optical adjunctsRefractive errorVergence movement
An augmented reality display system includes a pair of variable focus lens elements that sandwich a waveguide stack. One of the lens elements is positioned between the waveguide stack and a user's eye to correct for refractive errors in the focusing of light projected from the waveguide stack to that eye. The lens elements may also be configured to provide appropriate optical power to place displayed virtual content on a desired depth plane. The other lens element is between the ambient environment and the waveguide stack, and is configured to provide optical power to compensate for aberrations in the transmission of ambient light through the waveguide stack and the lens element closest to the eye. In addition, an eye-tracking system monitors the vergence of the user's eyes and automatically and continuously adjusts the optical powers of the pair of lens elements based on the determined vergence of those eyes.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Stereoscopic microscope
InactiveUS20140267632A1Easy to separateIncrease investmentMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsVergence movementAngular degrees
Stereoscopic instruments for viewing stereoscopic images of objects at a range of magnifications are described. The stereoscopic instruments are arranged to provide an optical beam comprising light received from an object over a given angular range, and to split the optical beam into left and right optical beams each traversing a respective optical path. The left and right optical paths each transmit a sub-beam over a respective angular range, the respective angular ranges thereby defining a first angular relationship between the respective sub-beams. Each optical path comprises a first angle adjustment means for adjusting the first angular relationship. Some embodiments also include a means for transmitting images formed from the left and right sub-beams, the images having a second angular relationship related to a vergence angle at which a user's eyes view the object. By controlling the relative angles defined by first and second angular relationships, a degree of stereoscopy with which the user can view the object can be varied.
Owner:WARD JOHN
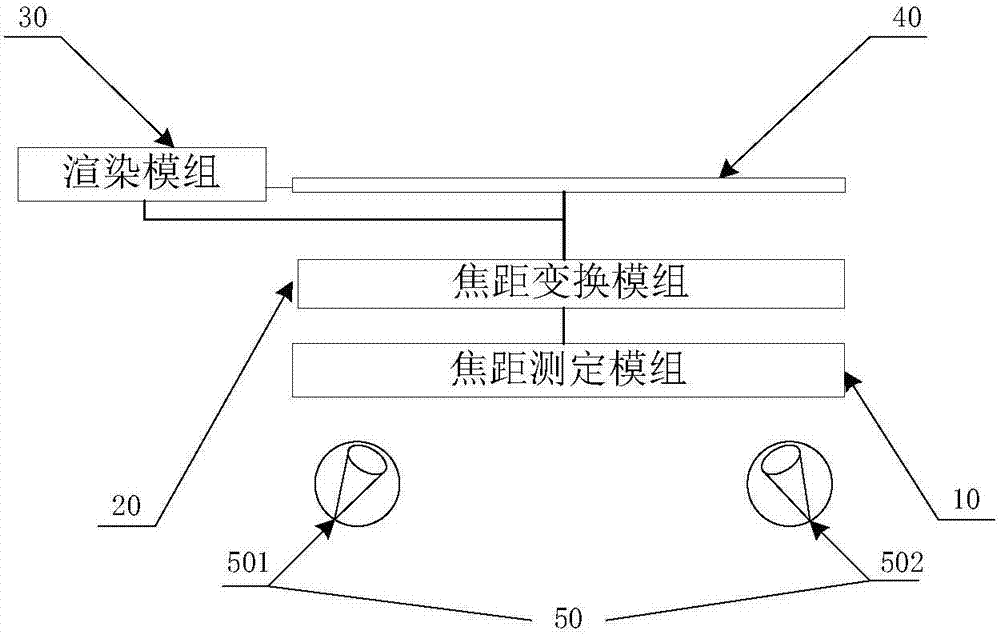
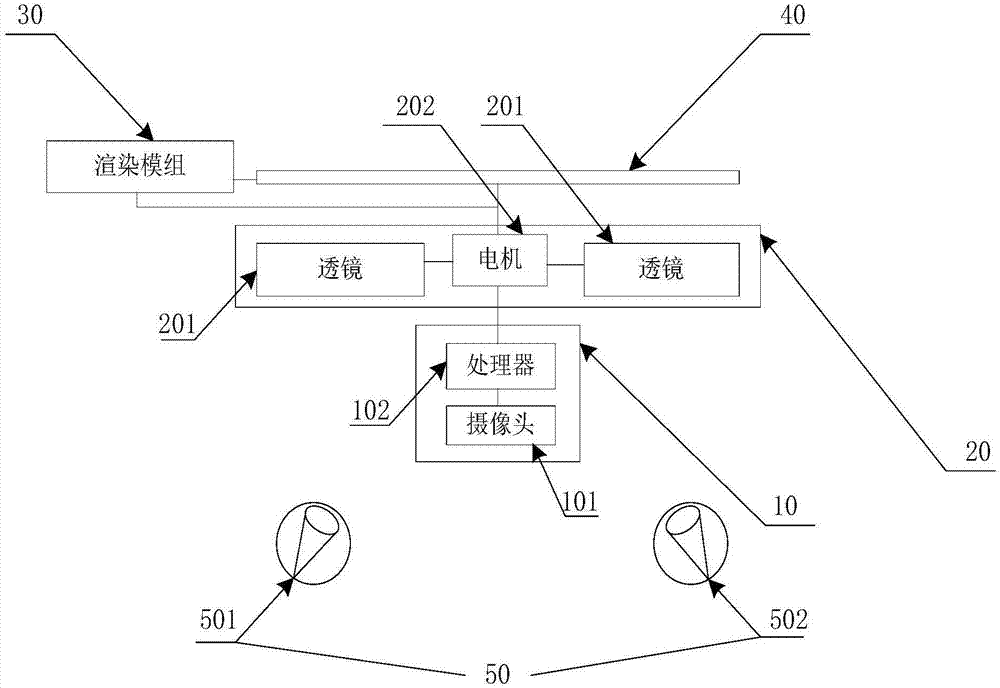
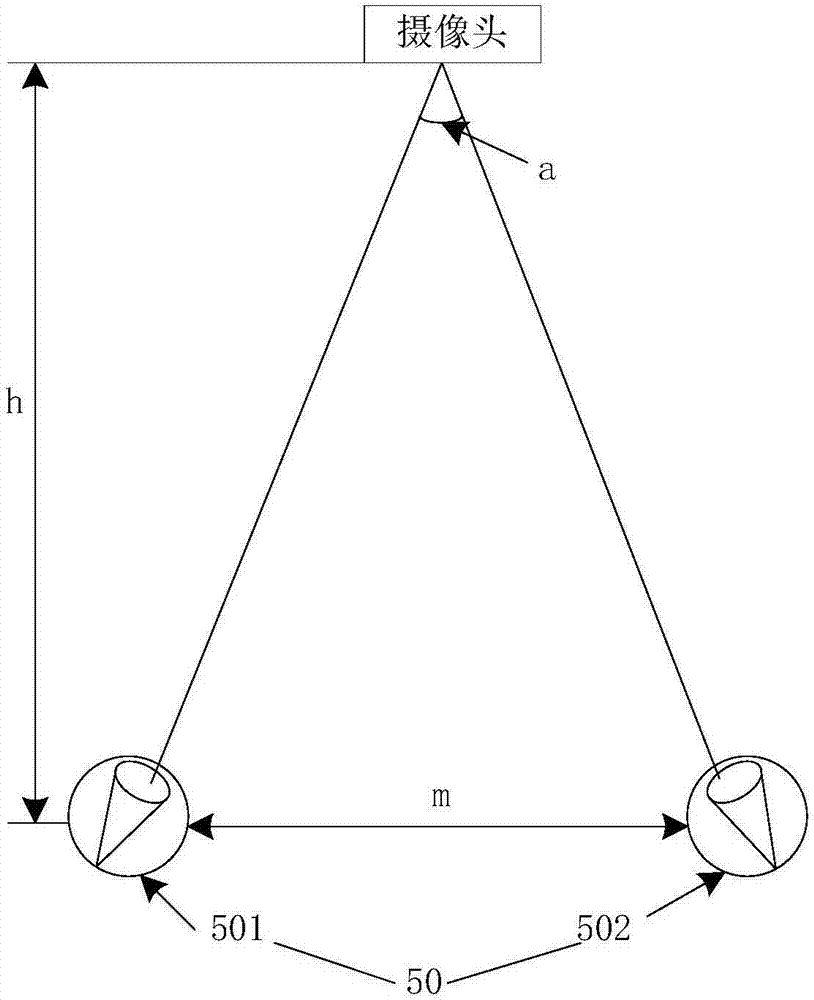
Focal length control device and method and VR glasses
Embodiments of the invention provide a focal length control device and method and VR glasses. The device includes a focal length measuring module, a focal length changing module and a rendering module. The focal length control device measures the focal length value of human eyes through the focal length measuring module, and sends the focal length value to the focal length changing module and the rendering module. The focal length changing module controls the focal length of the device according to the received focal length value of the human eyes. The rendering module is used to perform fuzzy processing on a display image according to the received focal length value of the human eyes. The focal length control device uses the focal length measuring module, the focal length changing module and the rendering module to put the human eyes' focal length, a 3D screen and a display in the same plane and create a depth-of-field effect, so that the display screen is more in line with the actual scene seen by the human eyes, and the dizziness due to the vergence-accommodation conflict of human eyes is alleviated.
Owner:CHONGQING IQIYI INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
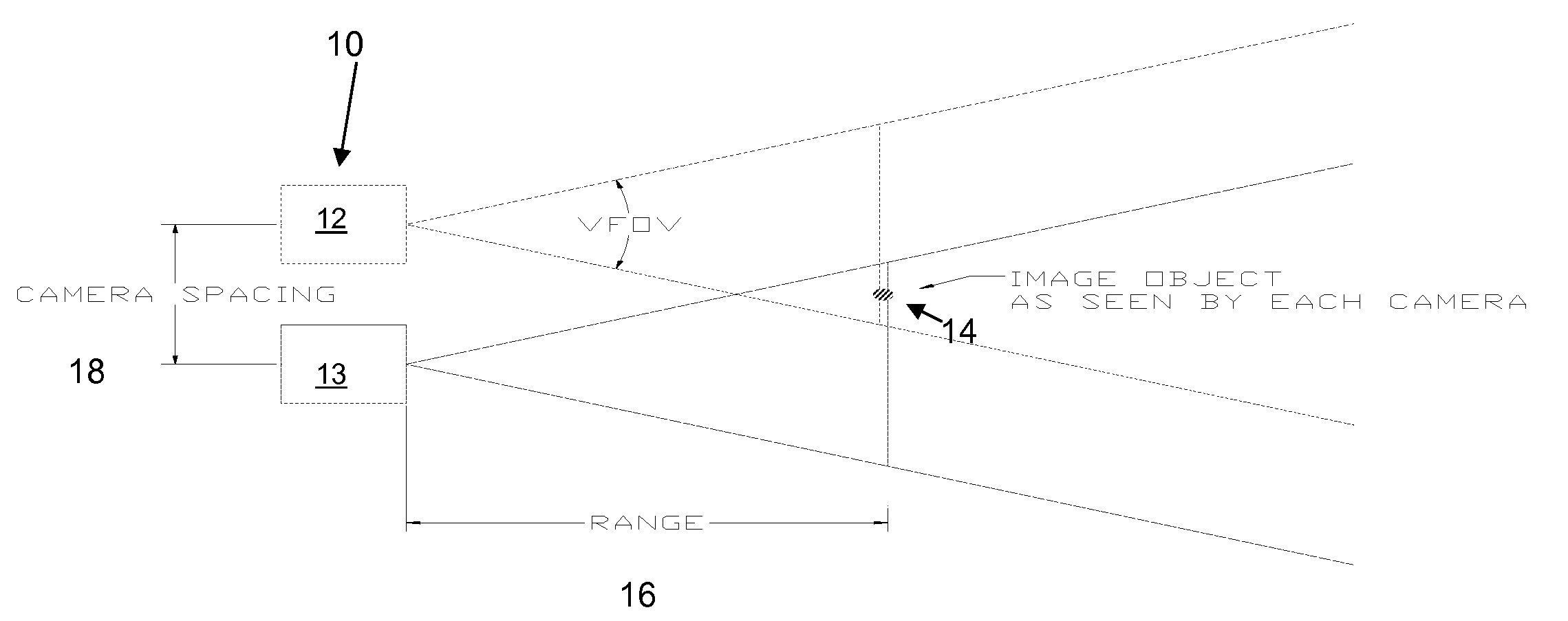
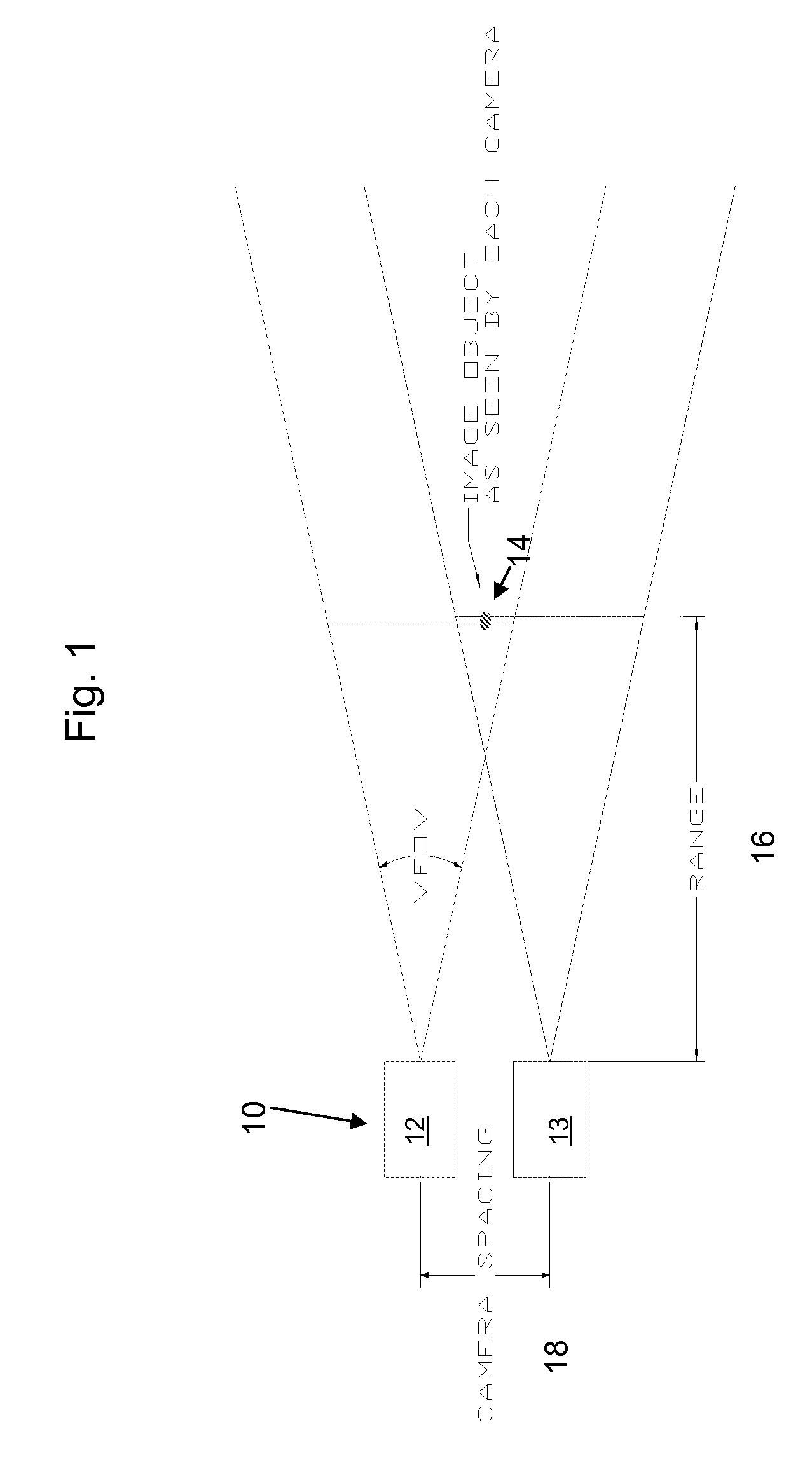
Focus actuated vergence
A system is disclosed for the vergence of images from a plurality of cameras, the system having: an first camera; a second camera disposed at some distance from that first camera; a focus adjustment whereby the focus of the first camera can be adjusted by a user; the focus adjustment being configured with a range finder whereby the distance from the first camera to a target is ascertained; a look up chart wherein divergence distance of images generated from the first camera from images of the second camera are provided for pre-calculated ranges; a processor whereby said images generated by the first camera are superimposed on the images generated by the second camera by the divergence distance determined from the lookup.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Pupilometer for pupil center drift and pupil size measurements at differing viewing distances
The present invention generally provides improved devices, systems, and methods for measuring characteristics of at least one eye, and particularly for measuring the physiological changes in eyes under different viewing conditions. An exemplary embodiment provides a pupilometer which measures any changes in location of a pupil center with changes in viewing distances. As the eye often moves significantly during viewing, the pupil center location will often be measured relative to a convenient reference of the eye such as an outer iris boundary. Pupil size may also be recorded, and the measurements from both eyes of a patient may be taken simultaneously. Exemplary embodiments may be configured so as to allow the vergence angle between the eyes to vary with differing viewing distances, regardless of whether one or both eyes are being measured.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Eyesight improving device
This patent provides an eyesight improving device which improves ocular imaging adjustment functions and is easy to use. A user puts the eyes on eyepiece parts 10, and sees a figure displayed on a target 12 by both eyes or one eye by opening or closing blocking device 14. In a state where the user focuses the eye on the figure, the target 12 is moved from a far point to a near point by target movement device 18 and is next moved from the near point to the far point, and this is repeated. In this case, the size of the figure is controlled to be changed in proportion to the distance between the eyepiecepart 10 and the target 12. The user can easily concentrate to focus the eye on the figure during the movement of the target 12. This training activates the ocular imaging adjustment functions of a ciliary muscle, a pupil, vergences and the like resulting with their improvement.
Owner:HORIE HIDENORI
Image depth display technology
InactiveCN106101691AReduce adverse effectsNatural relaxationSteroscopic systemsBeam splitterDisplay device
An image depth display technology. By adding a lens and a beam splitter to the display system, the beam splitter is used to make the light emitted by each point on the display interface of the display screen reach the first focal plane of the lens. One point on the display interface is shortened or extended along the other point, and the plane image information from the display screen can be converted into a set of image information with depth. As long as the video signal processed by the corresponding image processing technology is used during use, it can be displayed. For a picture with a certain depth, the present invention can create a sense of depth in a relatively simple and low-cost way to improve the visual experience and reduce the adverse effects on the user caused by the visual vergence adjustment conflict caused by the user using the head-mounted display. The effect is to avoid the ciliary muscle being kept tense for a long time in the process of using the head-mounted display or the traditional 2D display, which leads to the decrease of its elasticity and the loss of the ability of self-regulation, resulting in myopia.
Owner:吴考寅
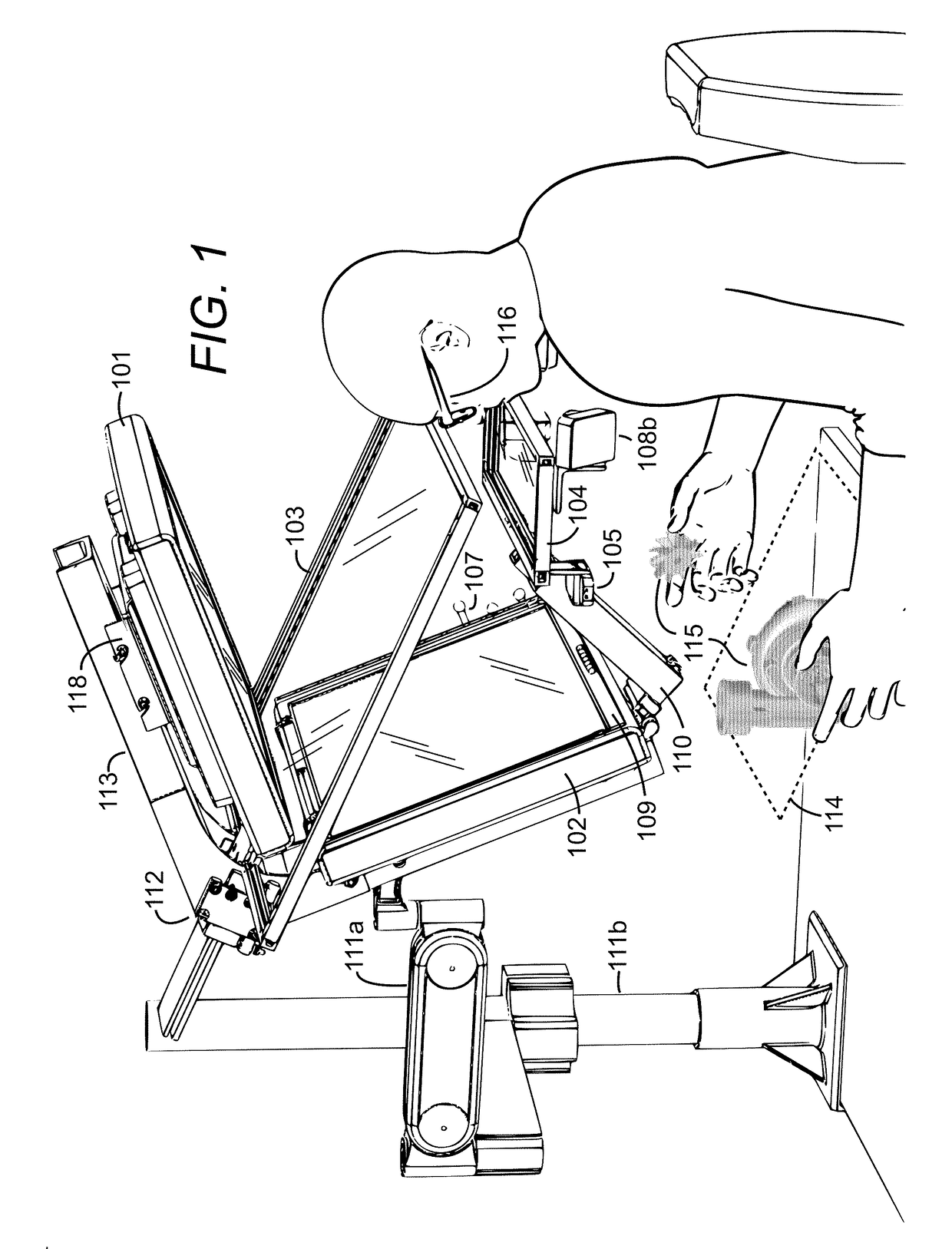
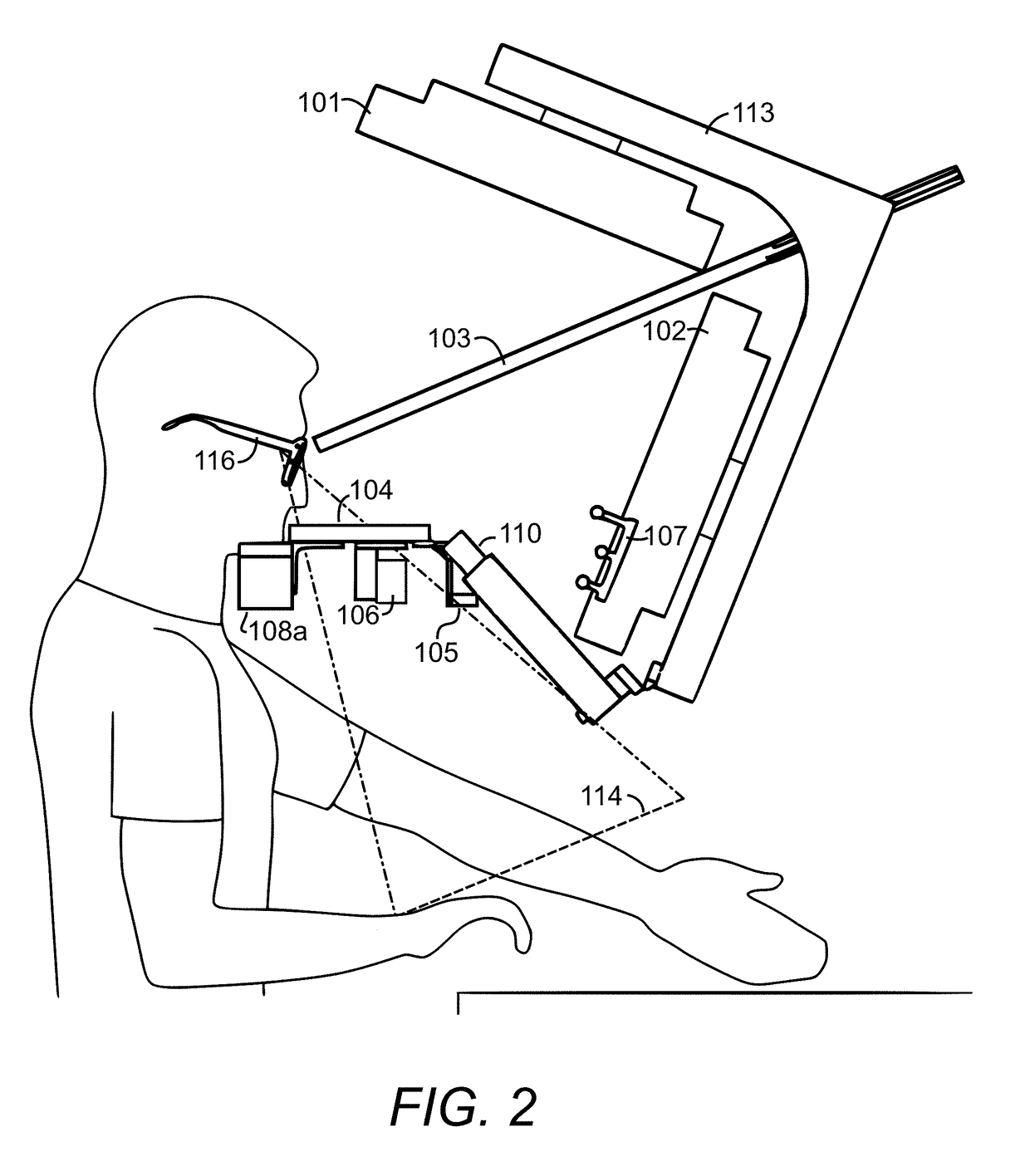
Stereoscopic video see-through augmented reality device with vergence control and gaze stabilization, head-mounted display and method for near-field augmented reality application
InactiveUS20180205932A1Television system detailsColor television detailsStereoscopic videoMicrocontroller
The present invention provides a see-through augmented reality device coupled to a head-mounted display, the device comprises: a camera configured to capture an image; a 2-axis gimbal coupled to the camera and configured to stabilize the camera; a servo motor coupled to the camera and configured to control the rotations of the camera; a microcontroller coupled to the servo motor and configured to control the servo motor; a multiplexer coupled to the microcontroller and configured to decode signals received from the microcontroller; and an augmented reality image processor coupled to the camera and configured to combine a virtual object with the image captured by the camera to create a virtual-real image and transfer the virtual-real image to the head-mounted display.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
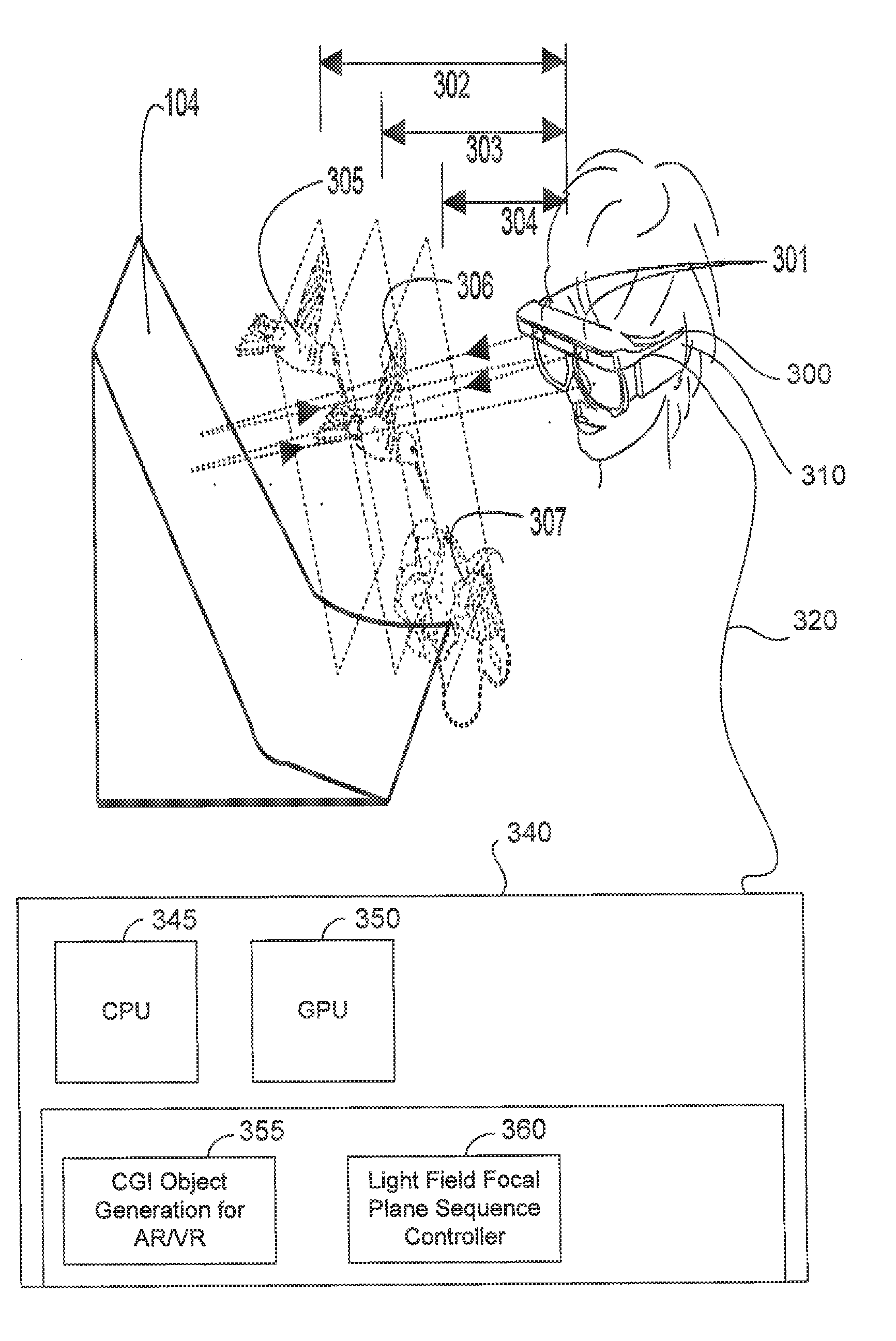
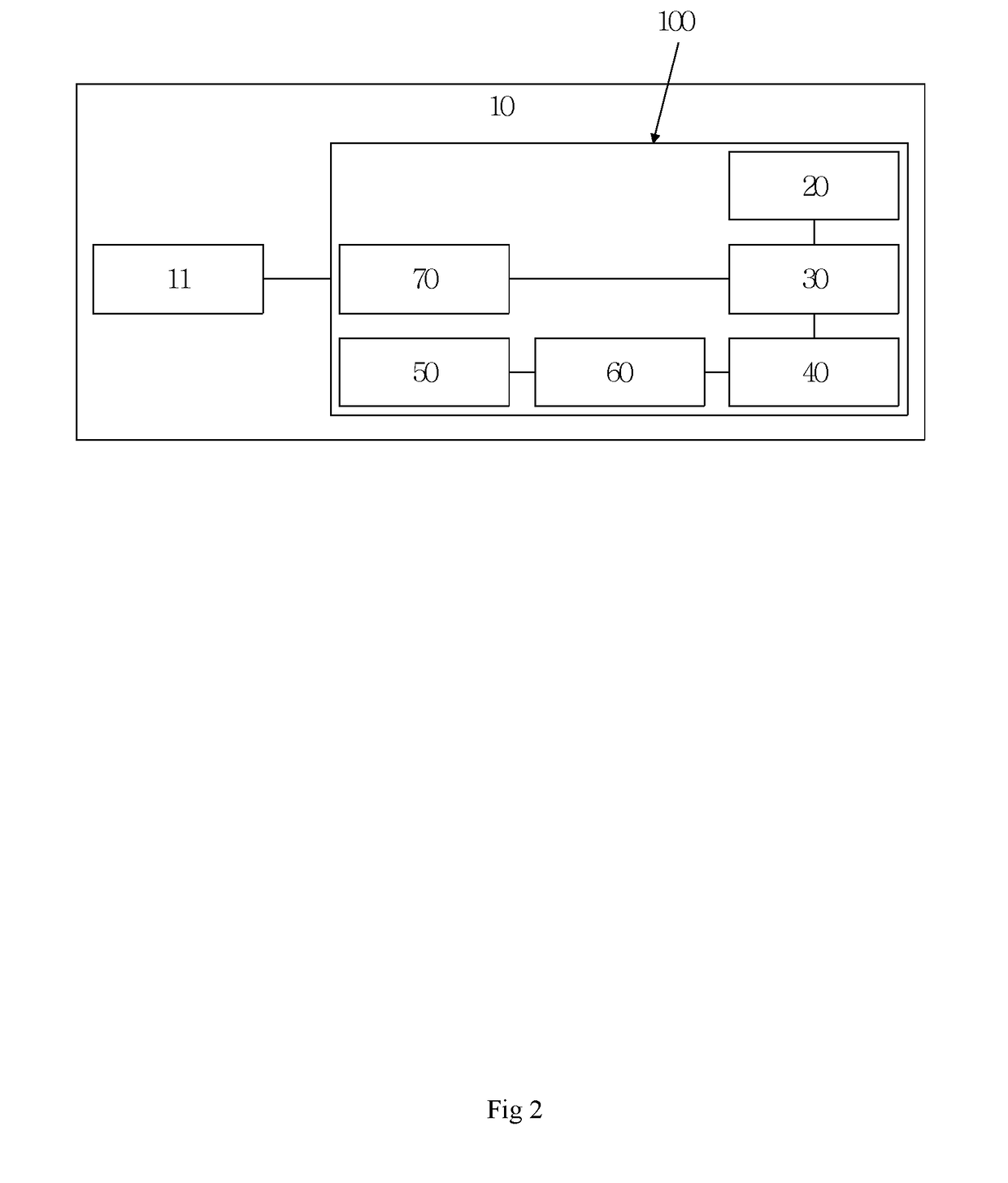
Systems and methods to provide an interactive space over an expanded field-of-view with focal distance tuning
ActiveUS10282912B1Reduce capacityEase of use and comfortStatic indicating devicesImage data processingVergence movementImage formation
Systems and methods to provide an interactive space over an expanded field-of-view with focal distance tuning are presented herein. The system may include one or more of a headset, a first image forming component, a second image forming component, a set of tuning components, one or more physical processors, and / or other components. The first image forming component may be configured to generate light rays to form a first set of images presented over a first angular portion of a user's field-of-view. The second image forming component may be configured to generate light rays to form a second set of images of virtual content presented over a second angular portion of the user's field-of-view. A vergence distance of a gaze of a user may be determined. A focal distance of the images may be adjusted to match the vergence distance.
Owner:META VIEW INC +1
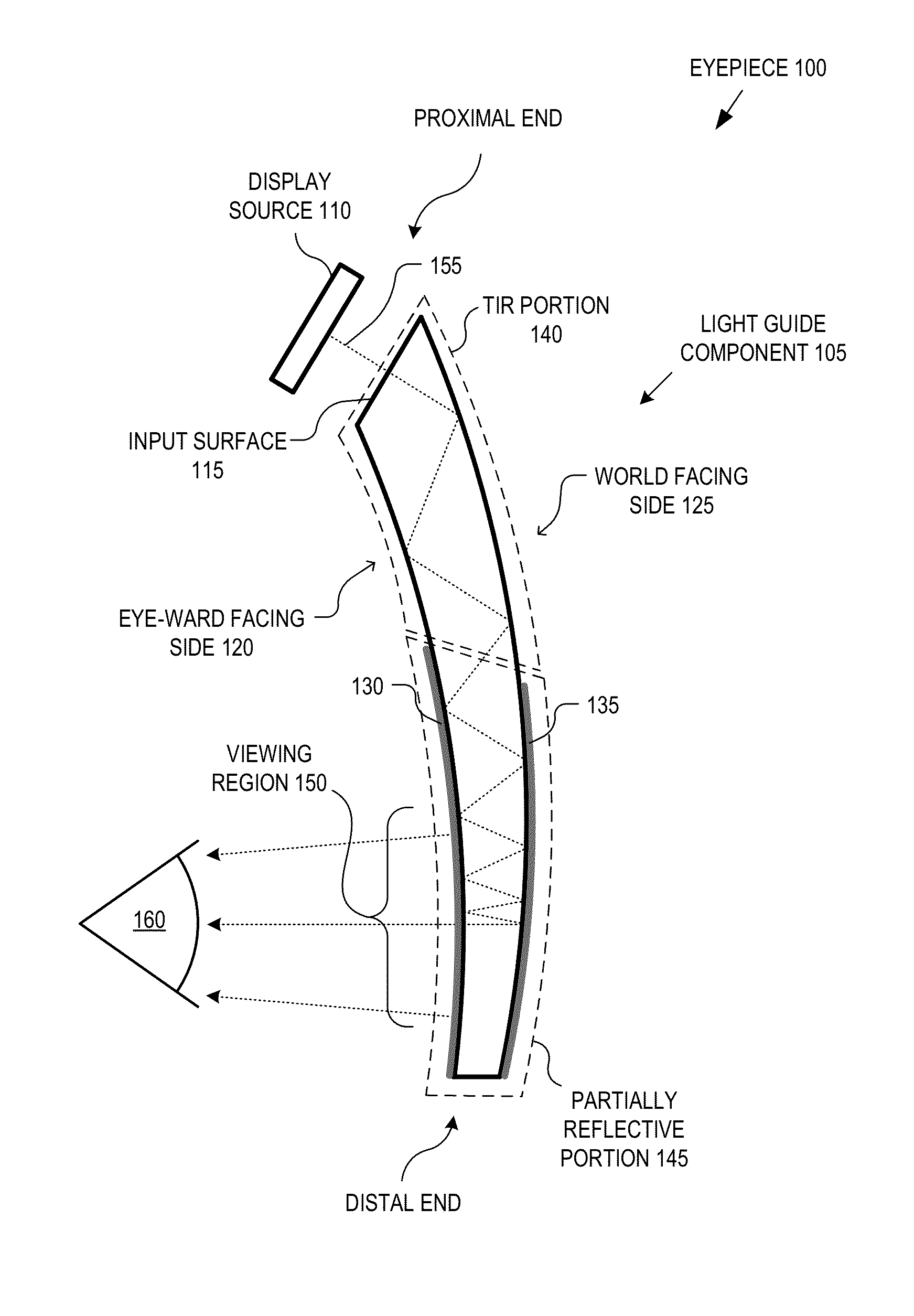
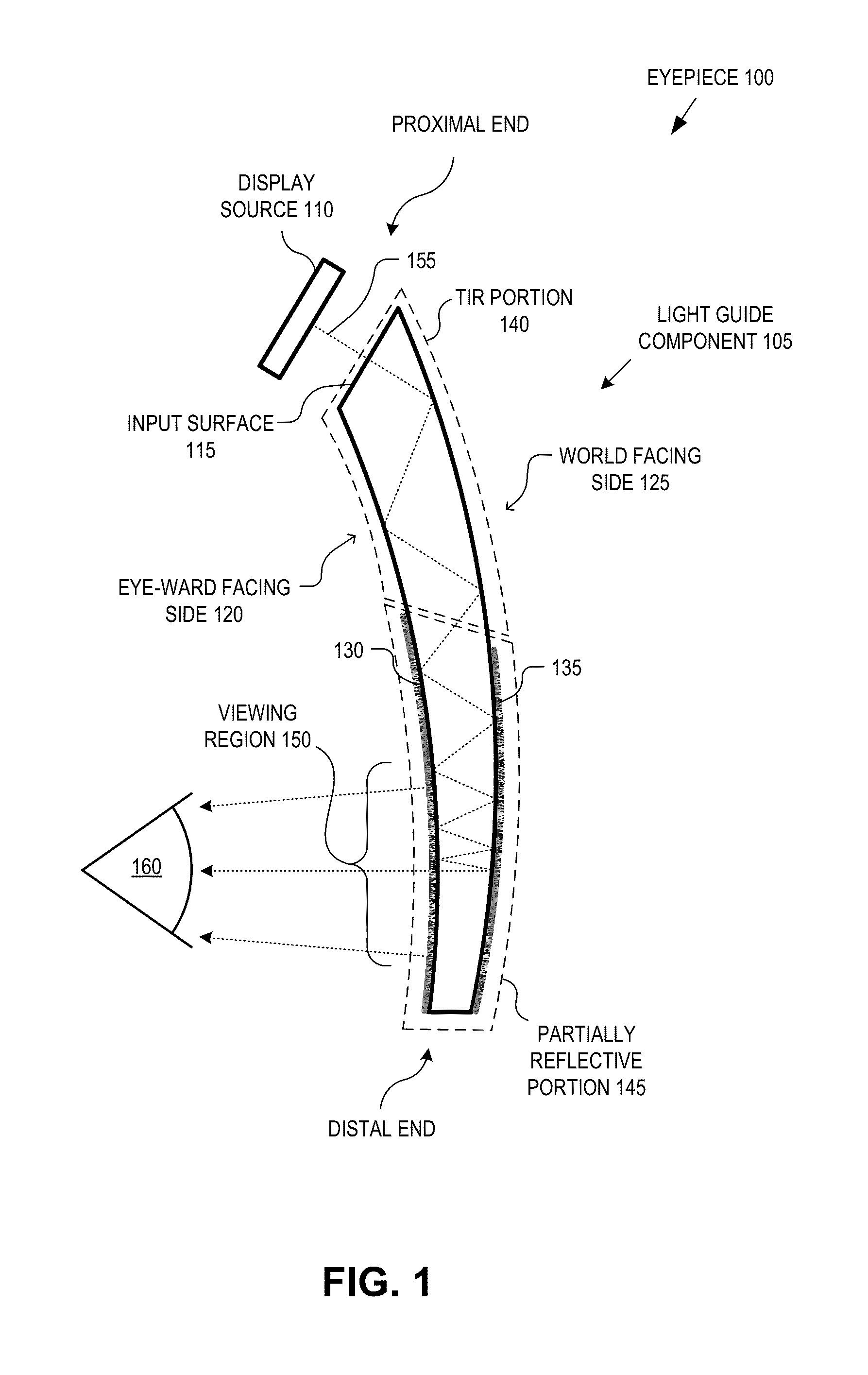
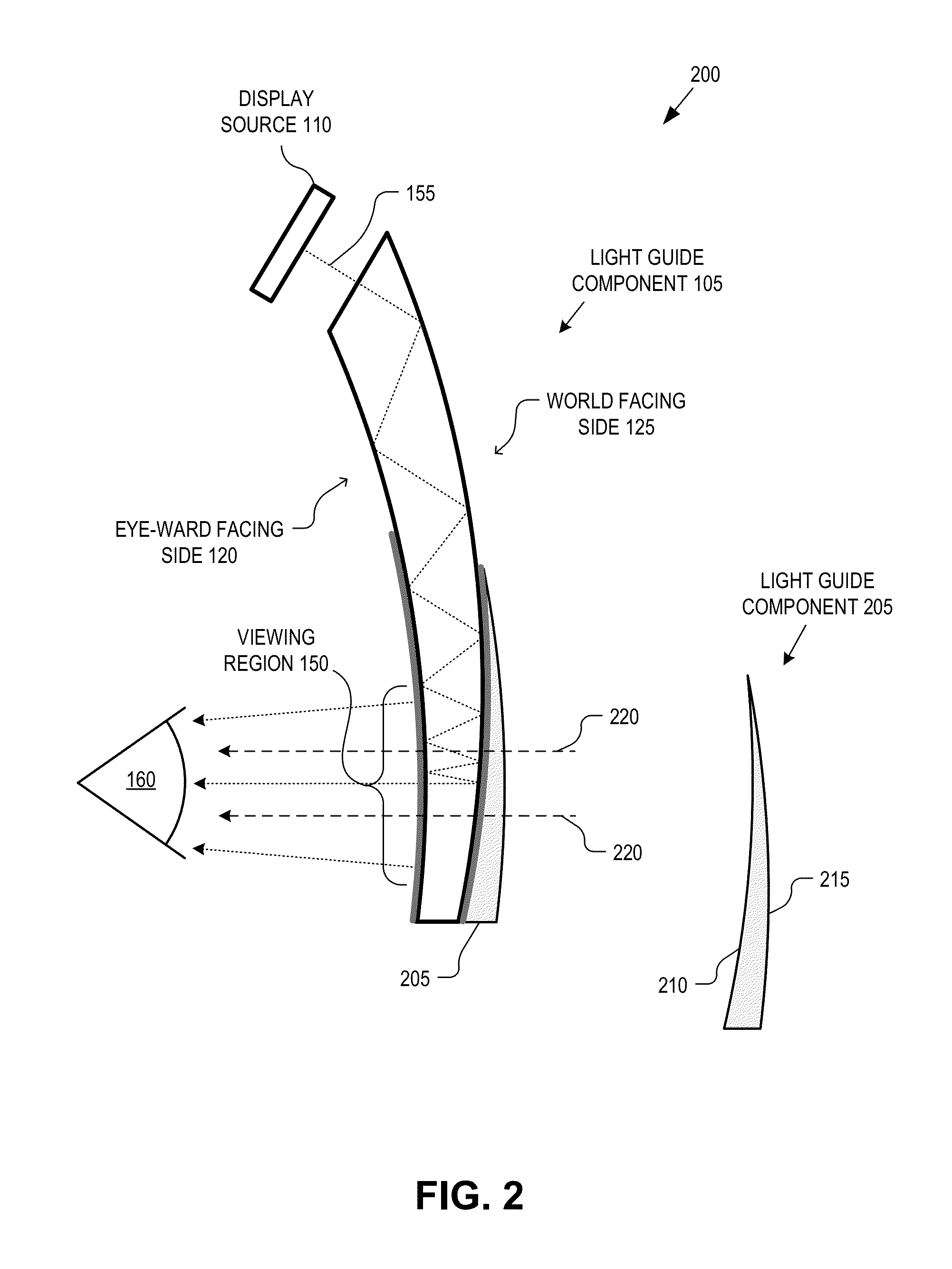
Eyepiece for head wearable display using partial and total internal reflections
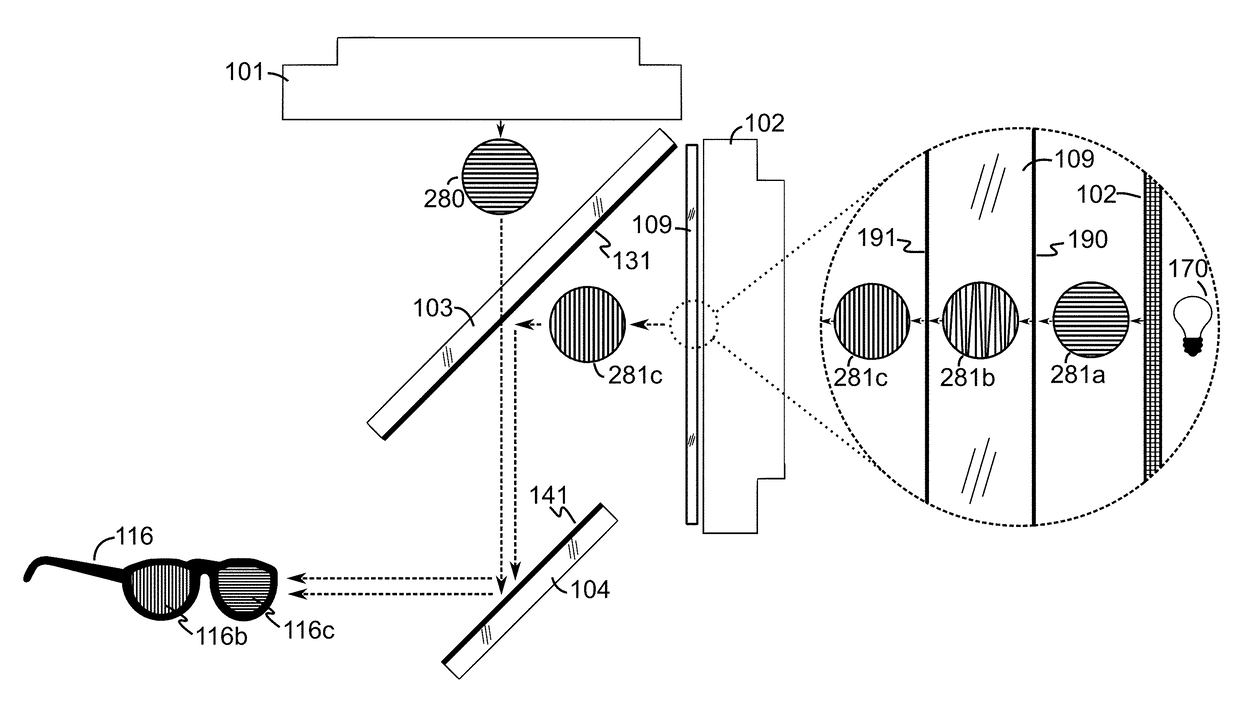
An eyepiece for a head wearable display includes a light guide component for guiding display light received at a peripheral location offset from a viewing region and emitting the display light in the viewing region. The light guide component includes an input surface oriented to receive the display light into the light guide component, an eye-ward facing side having a first curvature, a world facing side having a second curvature, a total internal reflection (“TIR”) portion disposed proximal to the input surface to guide the display light using TIR, and a partially reflective portion disposed distal to the input surface to receive the display light from the TIR portion and guide the display light to the viewing region using partial reflections. The first and second curvatures of the eye-ward and world facing sides together operate to adjust the vergence of the display light to virtually displace an image.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Detecting visual inattention based on eye convergence
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for detecting when a user is not being attentive based on eye convergence. The technique includes determining a first distance from the user to a first object. The first distance may be determined using a depth sensor. The technique further includes determining a first vergence angle associated with a left eye of the user and determining a second vergence angle associated with a right eye of the user. The technique further includes determining a first eye convergence distance based on the first vergence angle, the second vergence angle, and an interocular distance between the left eye and the right eye. The technique further includes comparing the first distance to the first eye convergence distance to generate a first result. An inattention alert may be generated based on the first result.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Parallel axis stereoscopic camera
InactiveUS20130093855A1Prevent image lossAvoid lostStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsParallaxVergence movement
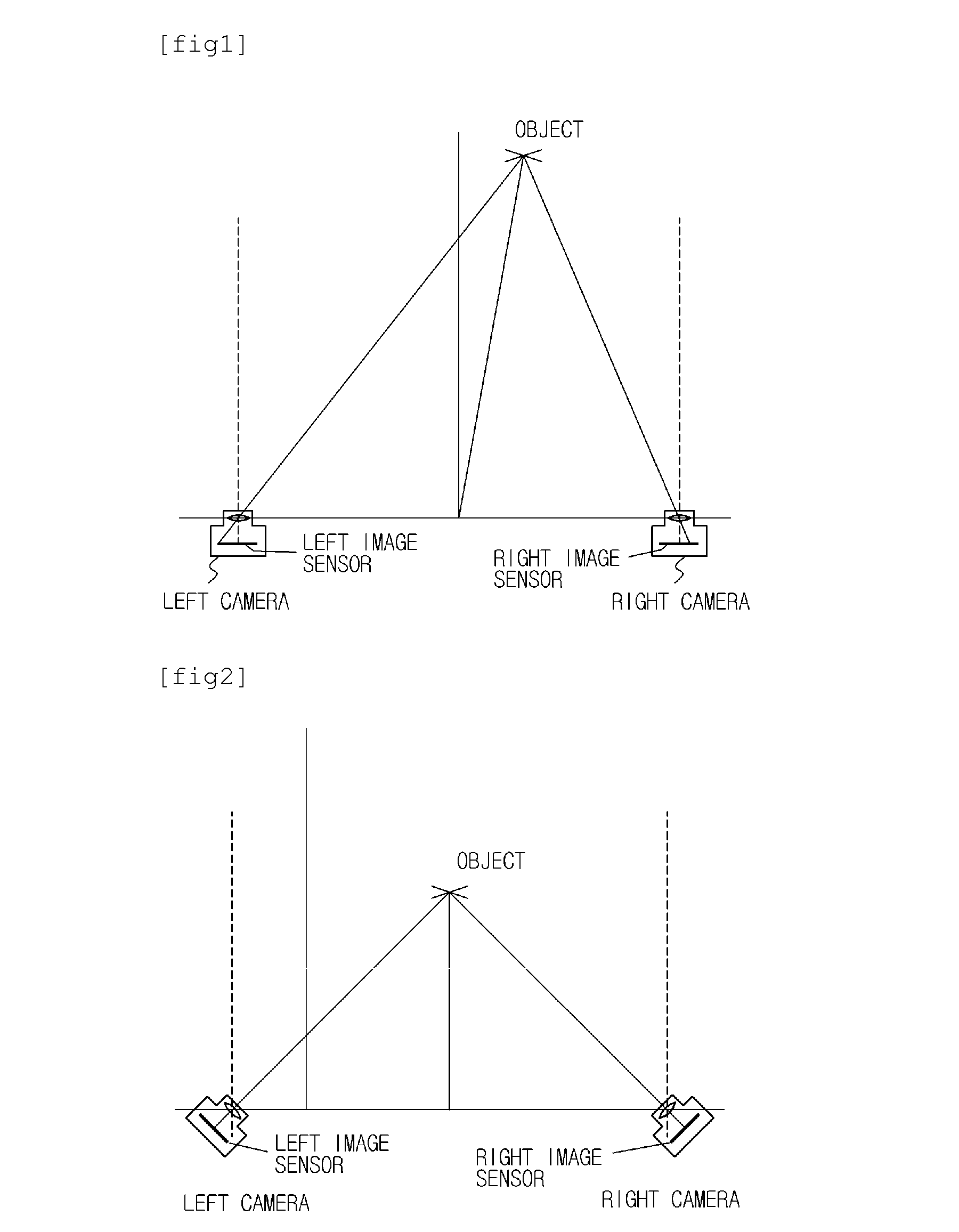
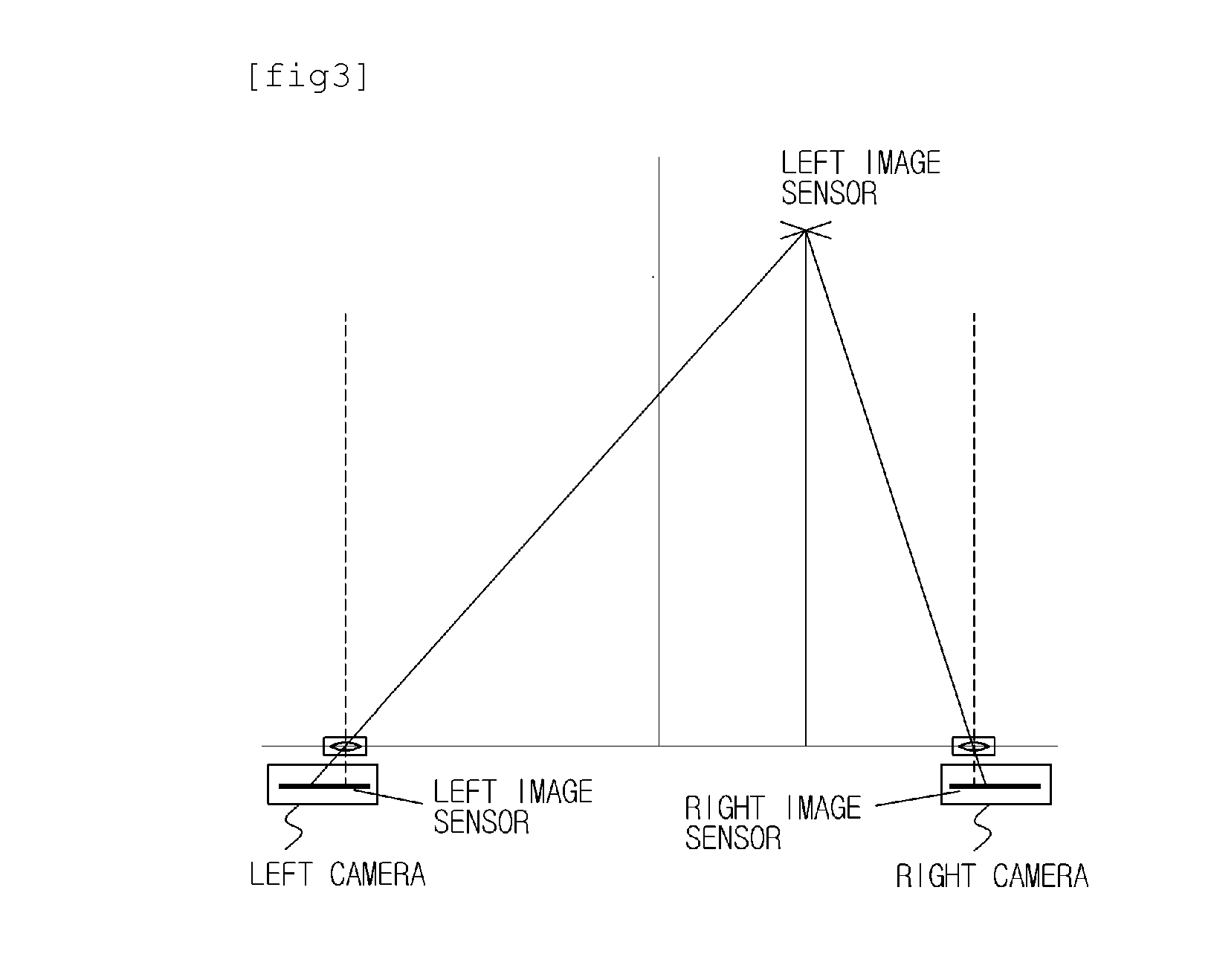
A parallel axis stereoscopic camera comprising: a camera unit which includes left and right image sensors each of which has a higher resolution than an output image, the camera unit outputting RGB data having the same resolution as the output image; a vergence controller which performs an electronic control for eliminating a binocular disparity of an object by changing a read-out starting point in the horizontal direction, of at least one of the left and right image sensors; an image processor including a left image processing unit which processes an image of left RGB data to output a left luminance / chrominance signal and a right image processing unit which processes an image of right RGB data to outputs a right luminance / chrominance signal under the control of the vergence controller; and a stereoscopic image synthesizer which synthesizes the left and right luminance / chrominance signals to produce a stereoscopic image.
Owner:ASIC BANK CO LTD
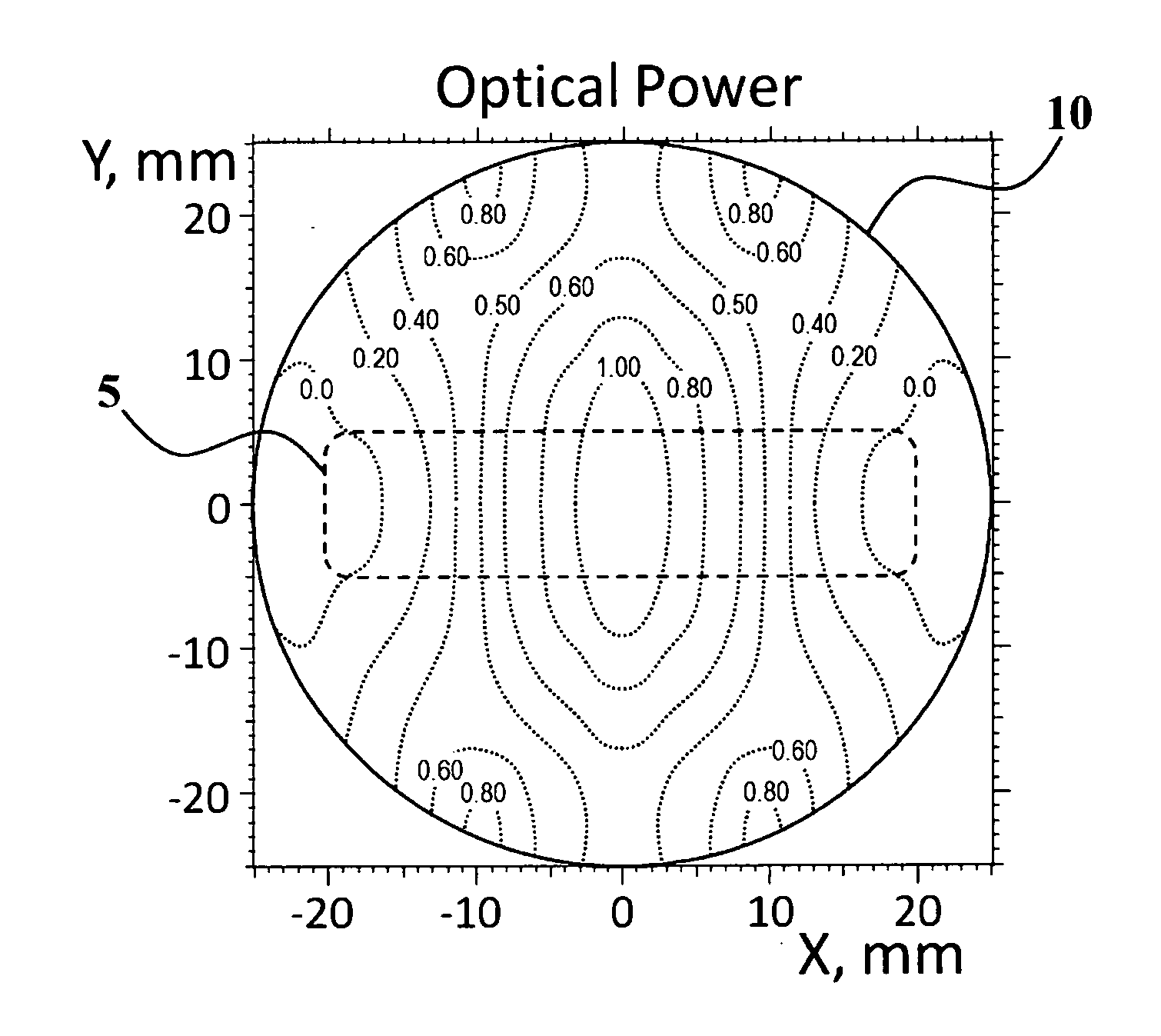
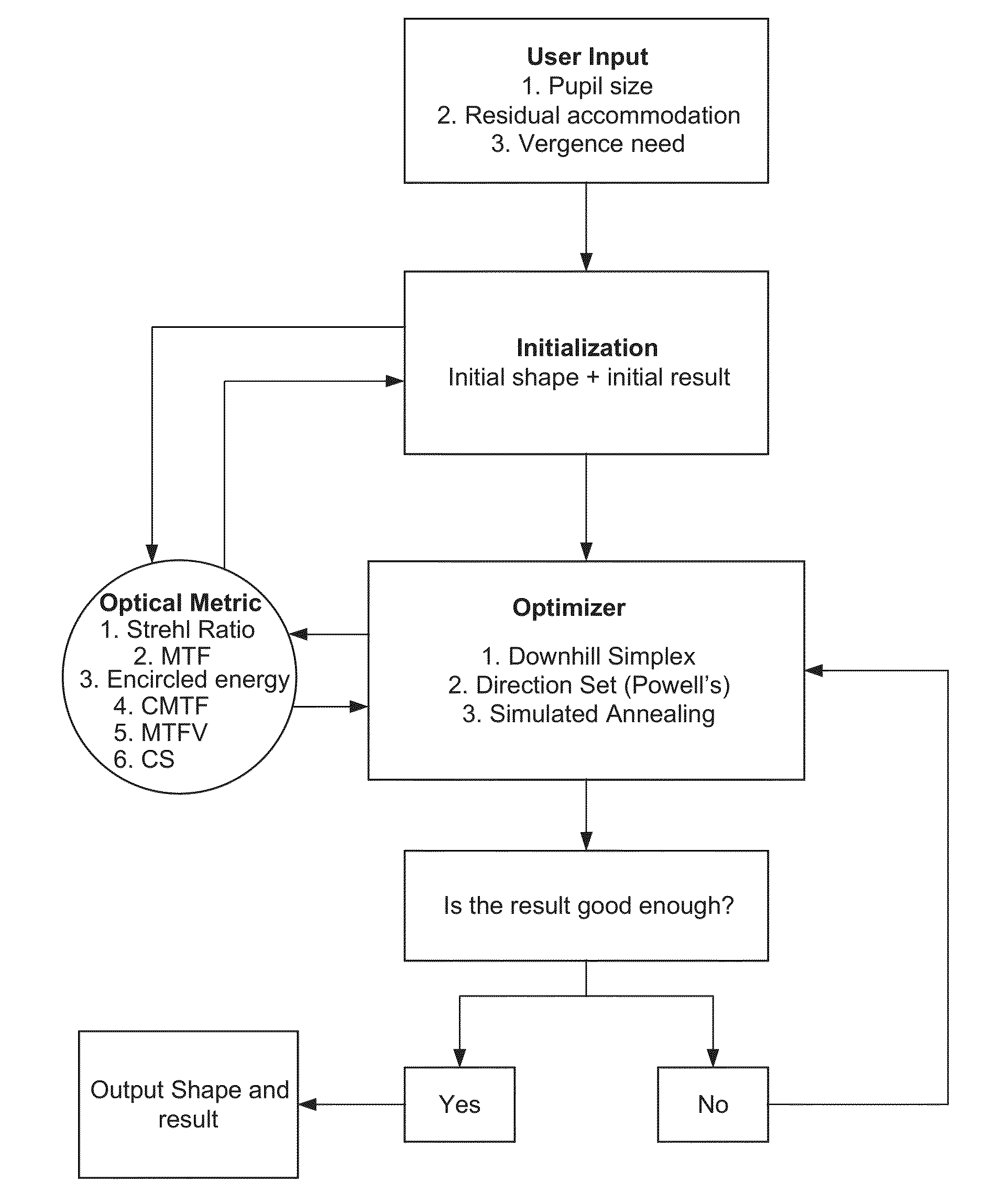
Vergence weighting systems and methods for treatment of presbyopia and other vision conditions
Methods, devices, and systems establish an optical surface shape that mitigates or treats a vision condition in a patient. An optical surface shape for a particular patient can be determined using a set of patient parameters for the specific patient by using an optical metric such as a compound modulation transfer function (CMTF).
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com