Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Supinations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
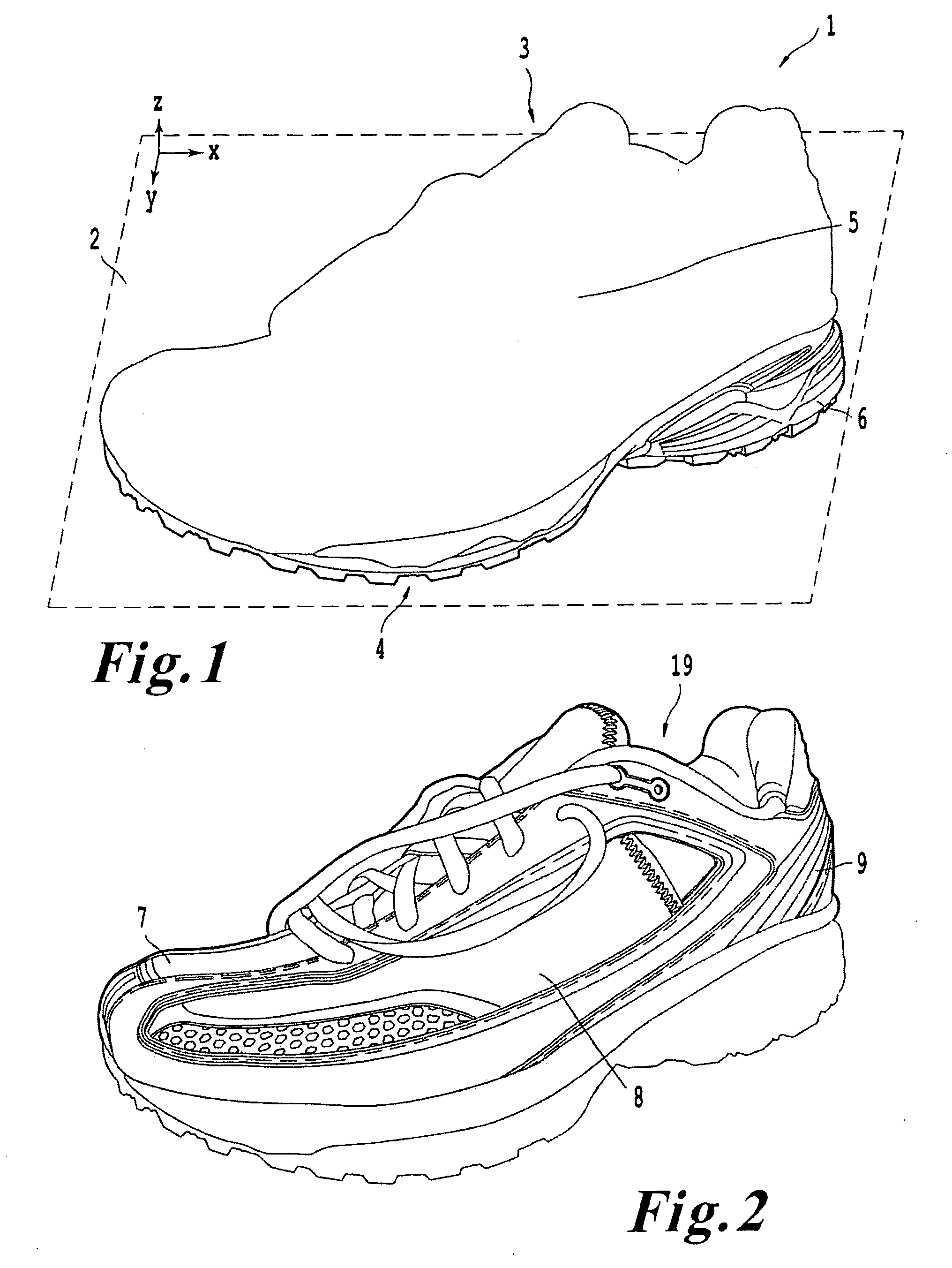
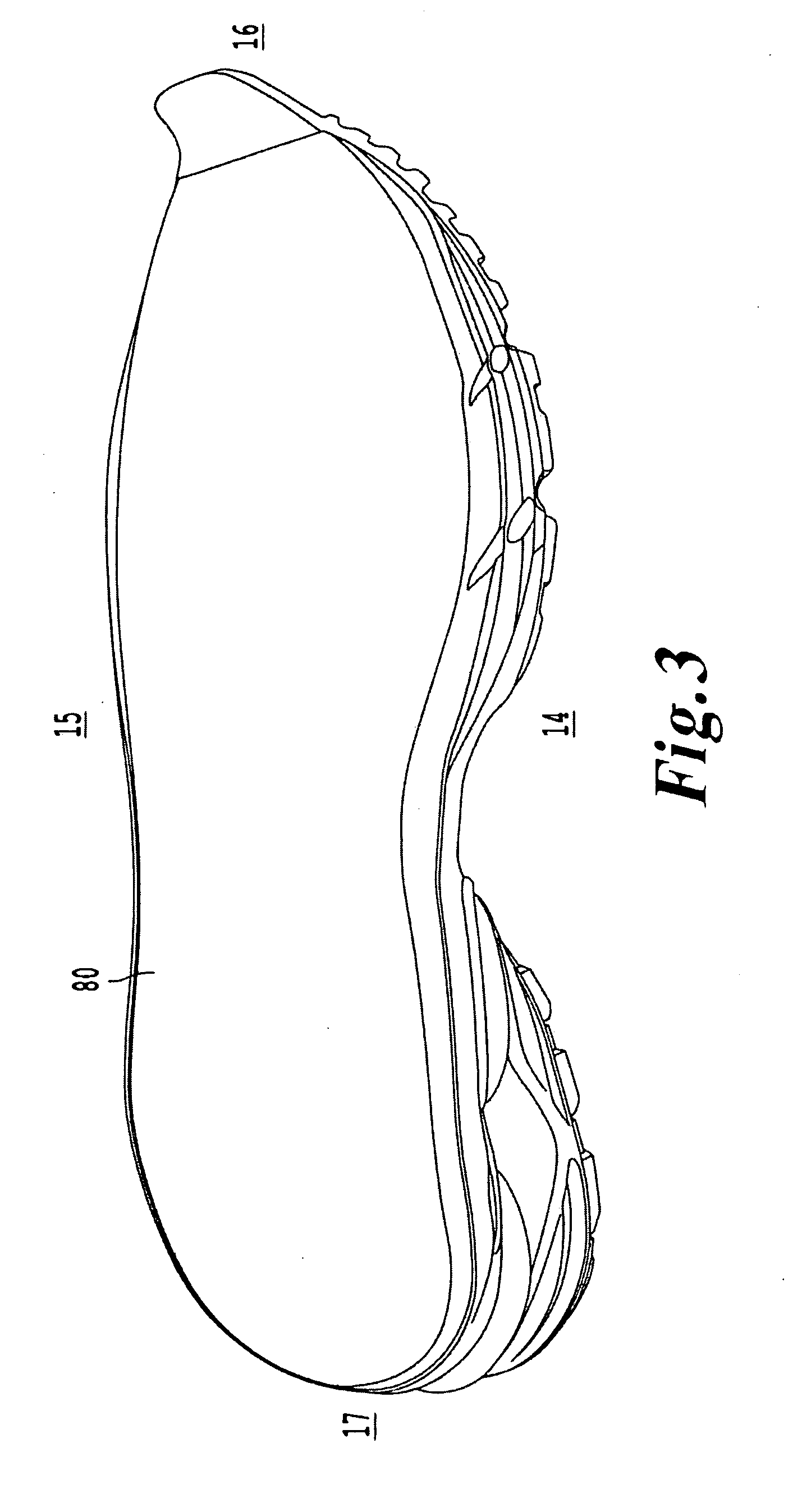
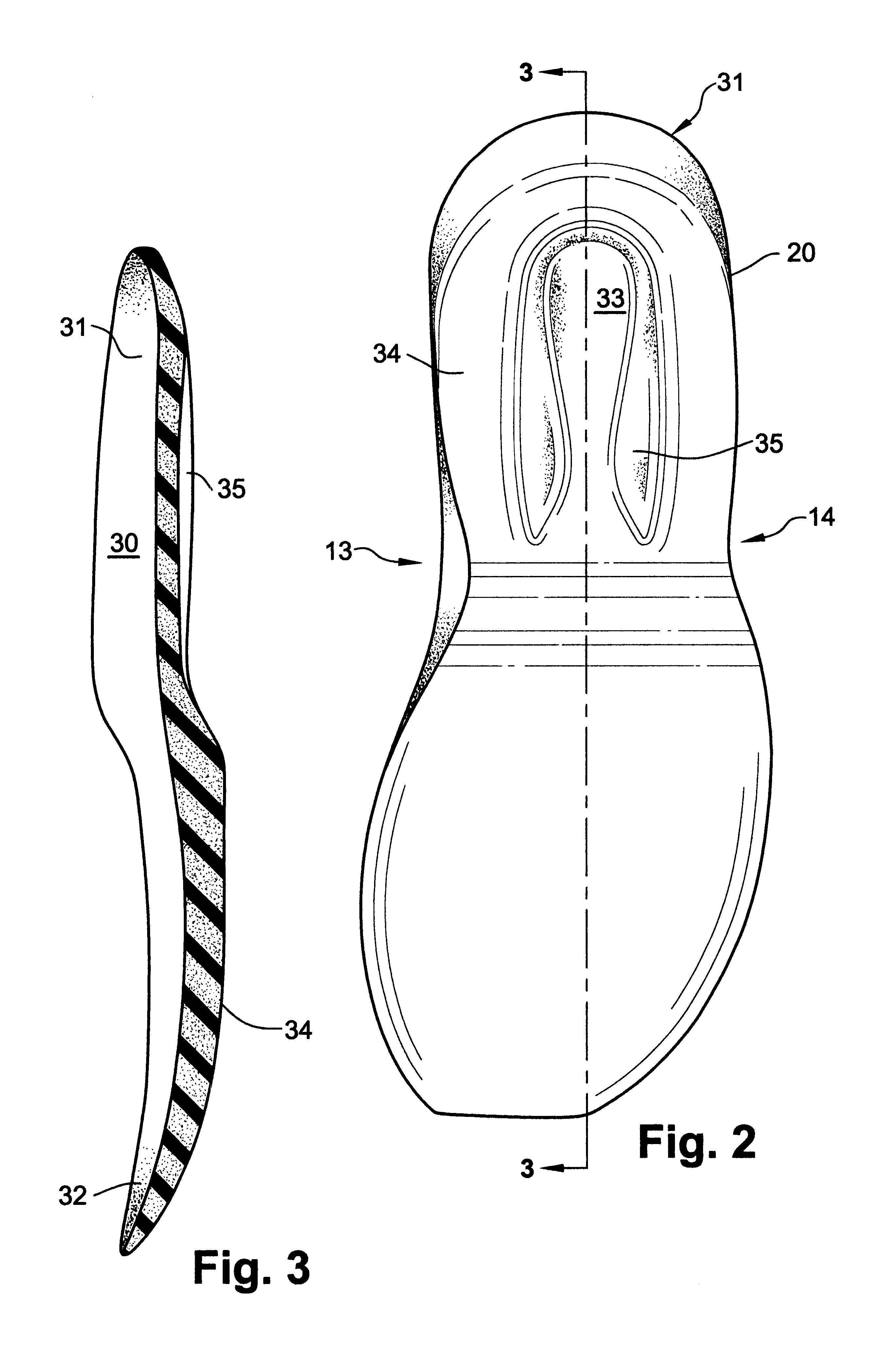
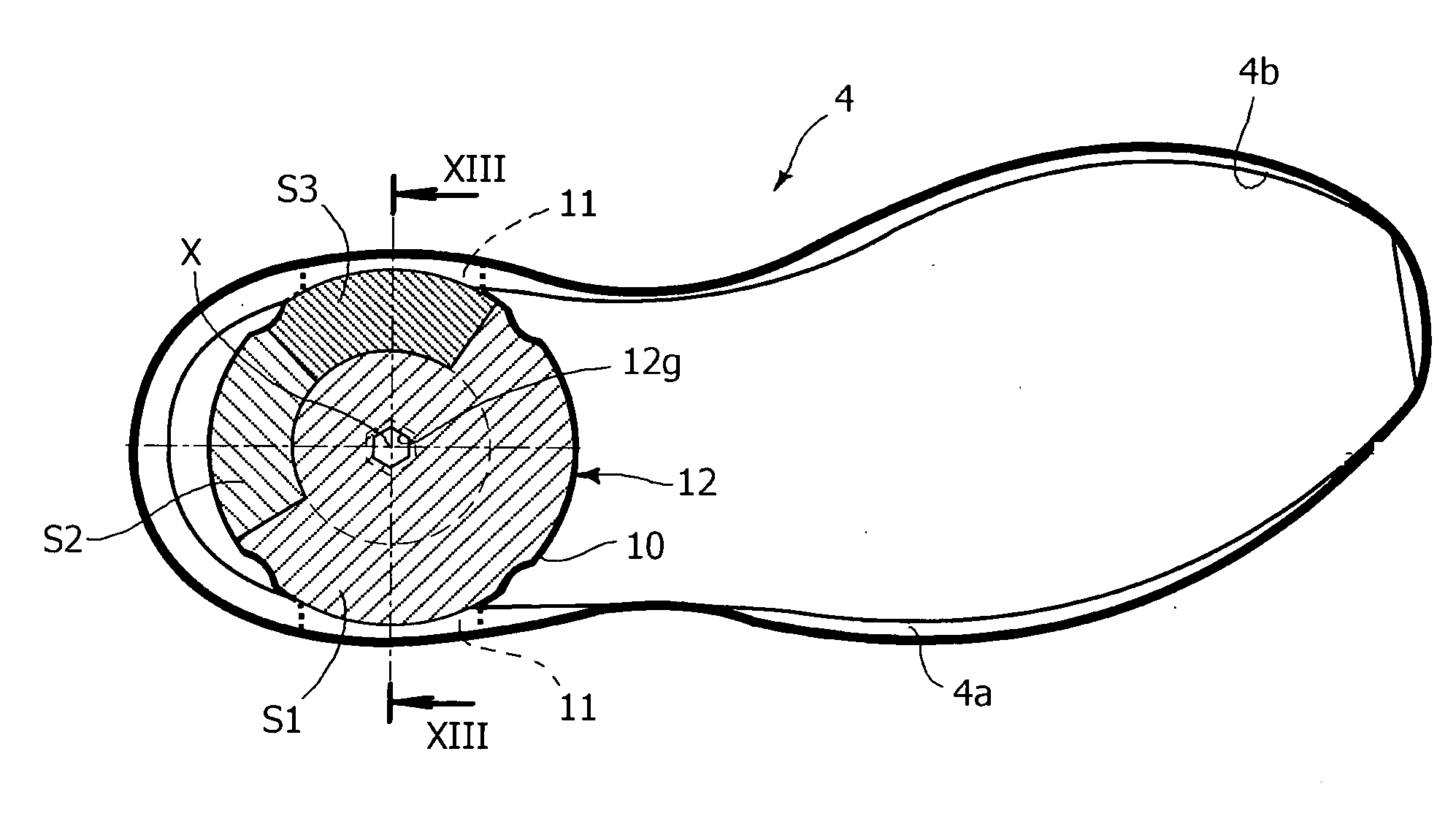
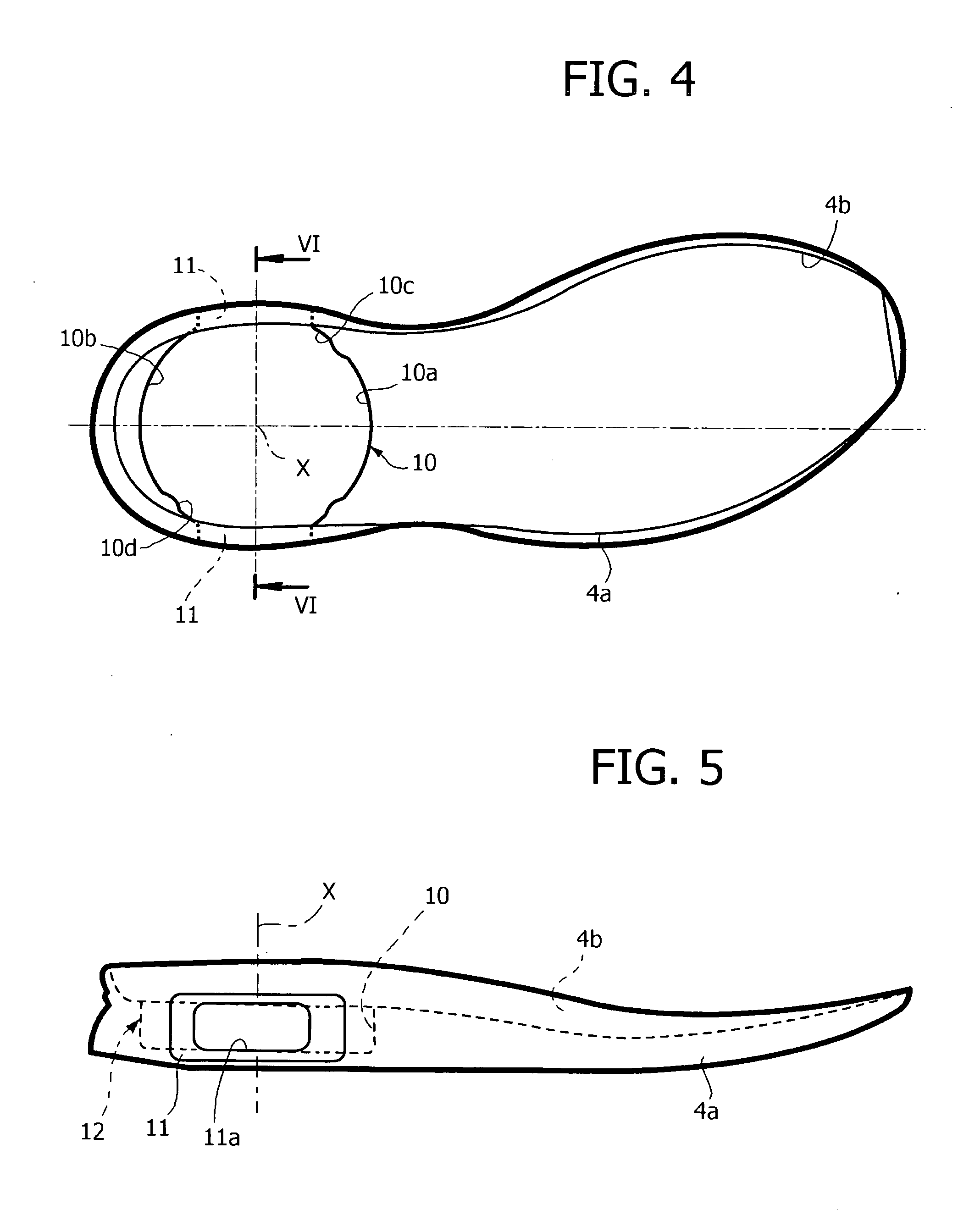
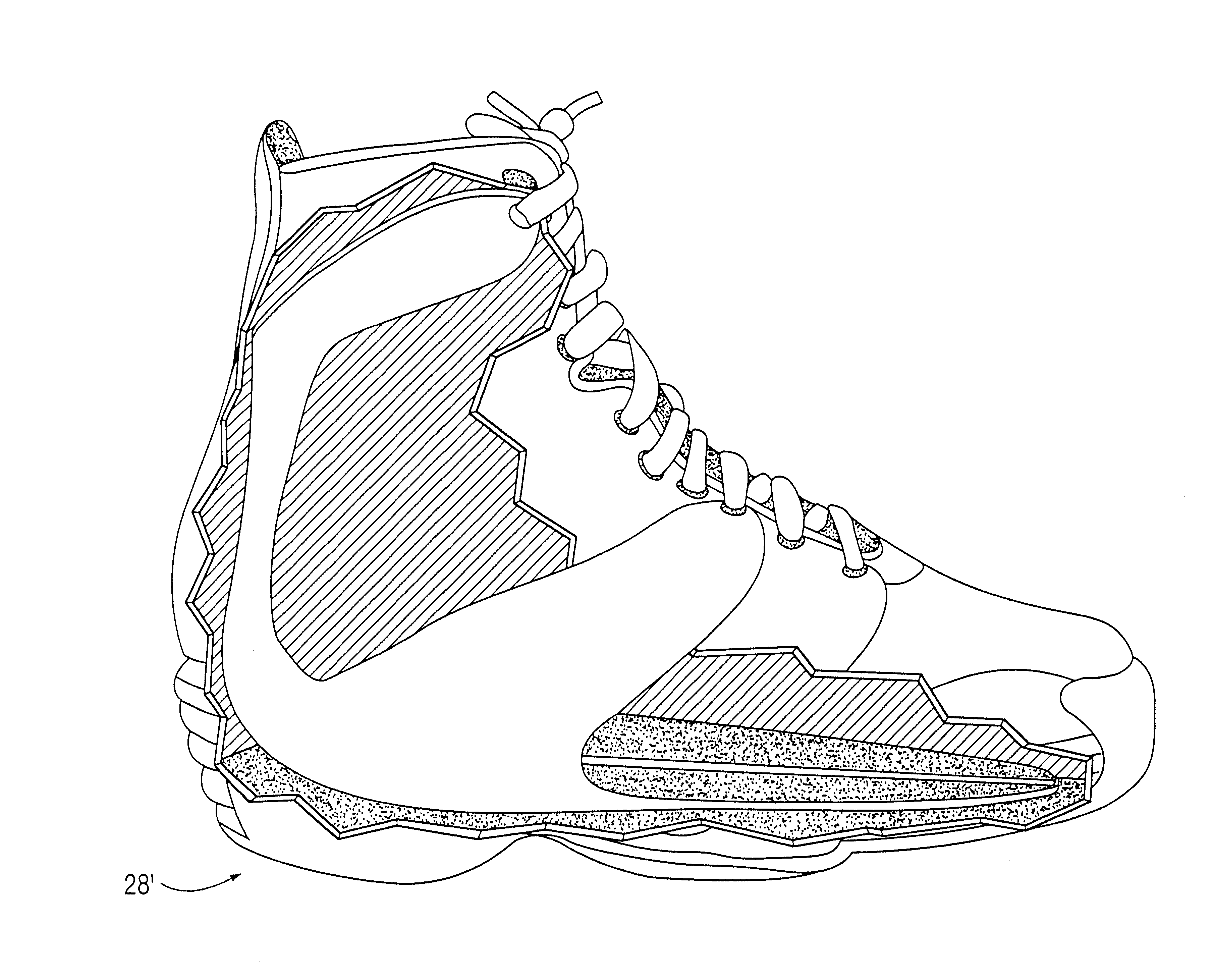
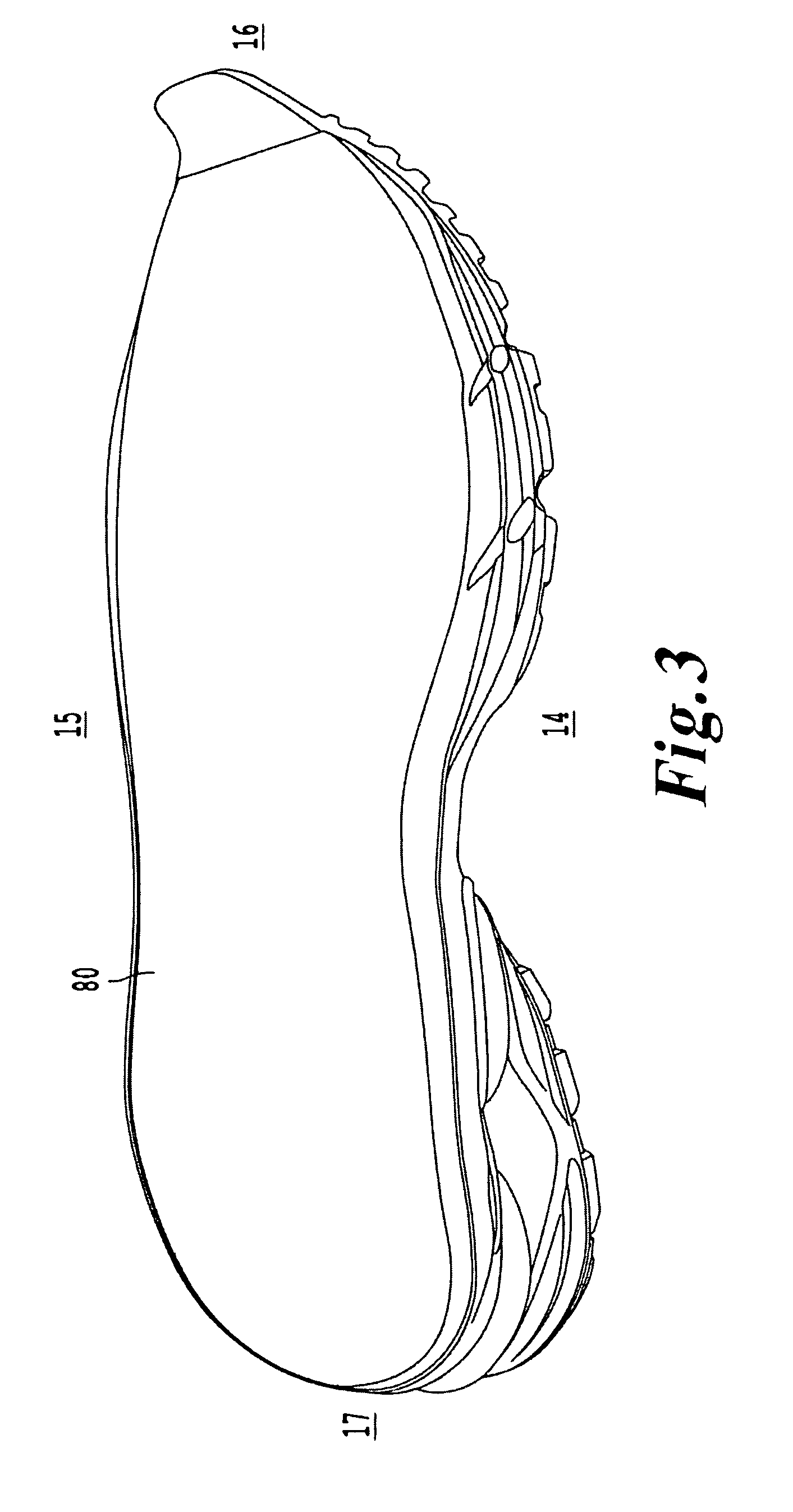
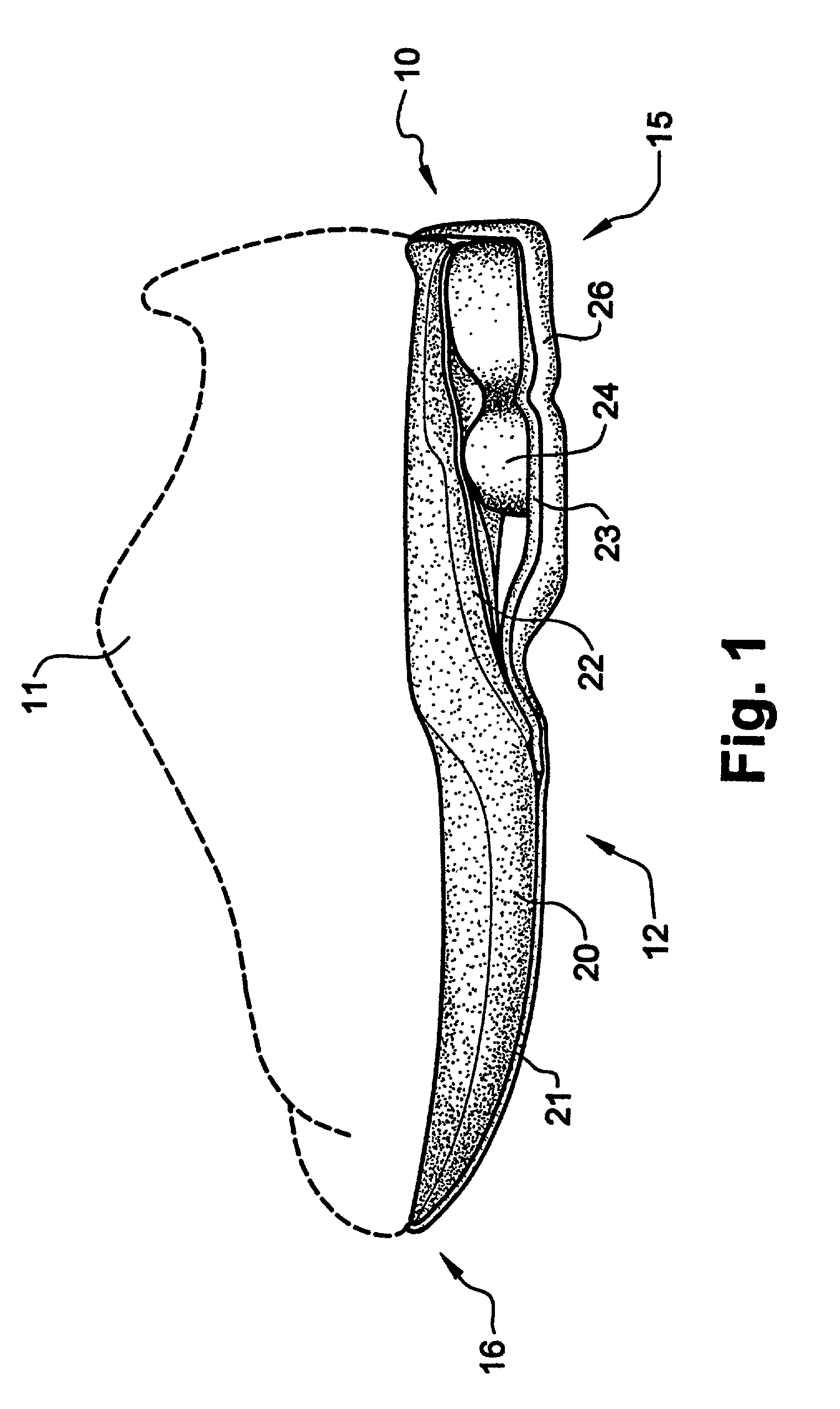
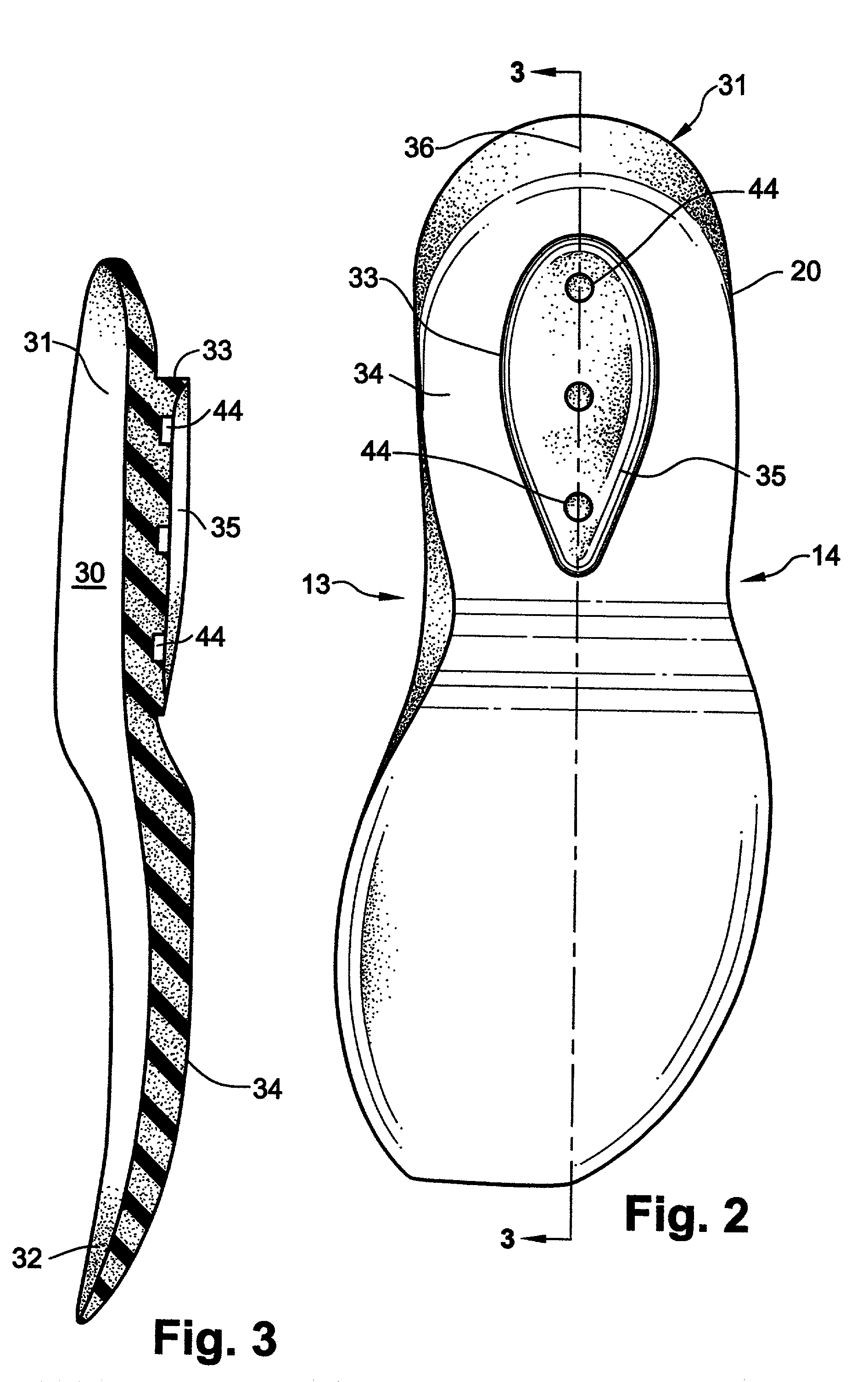
Shoe incorporating improved shock absorption and stabilizing elements
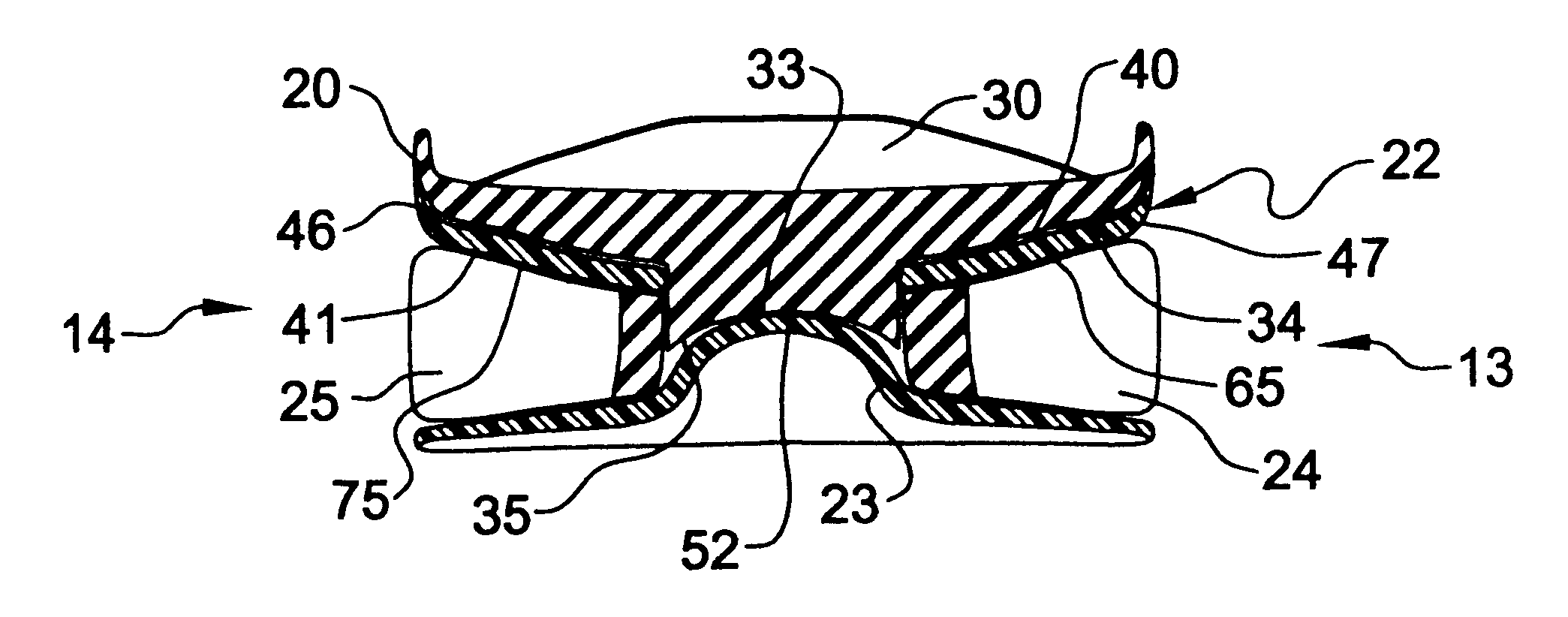
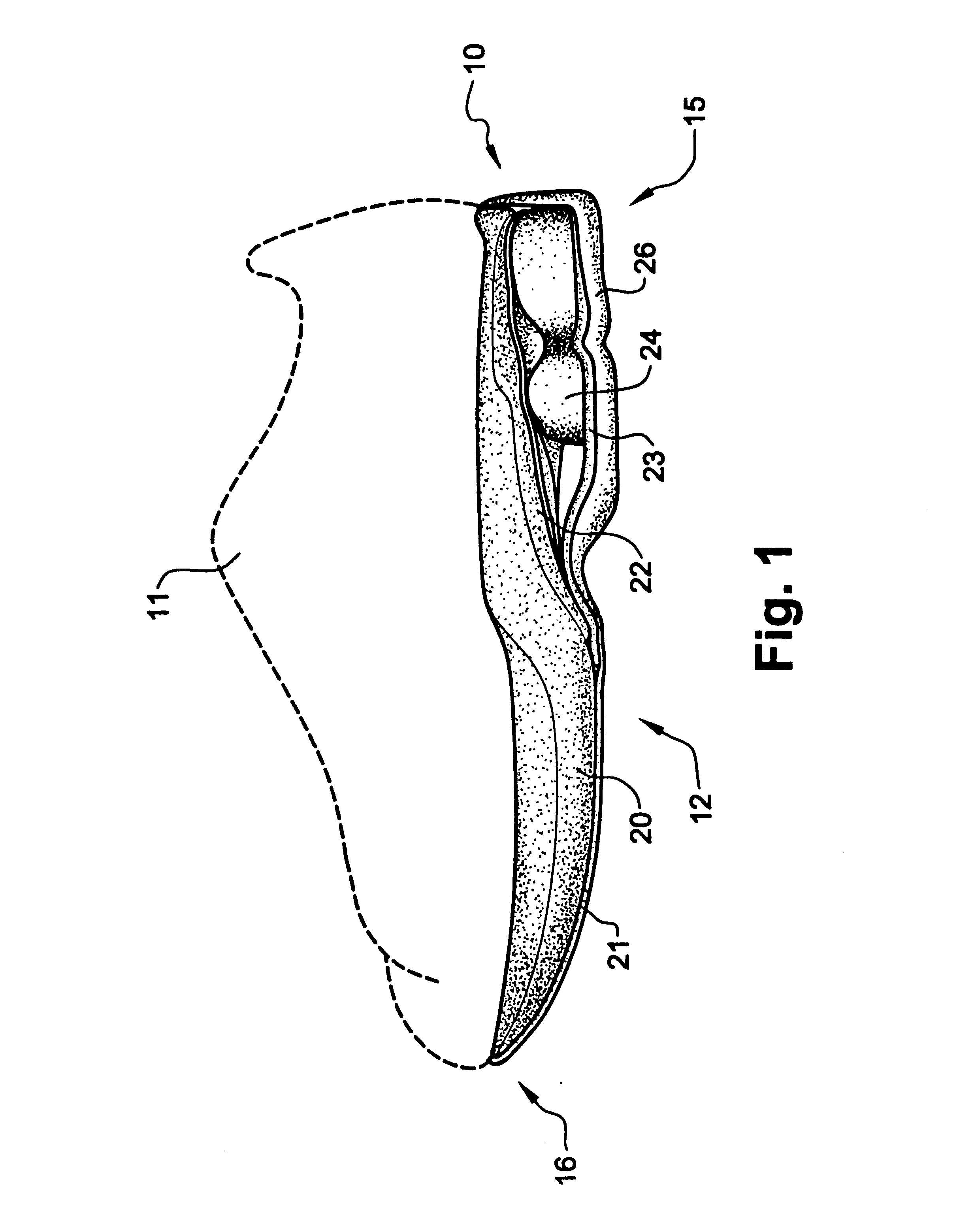
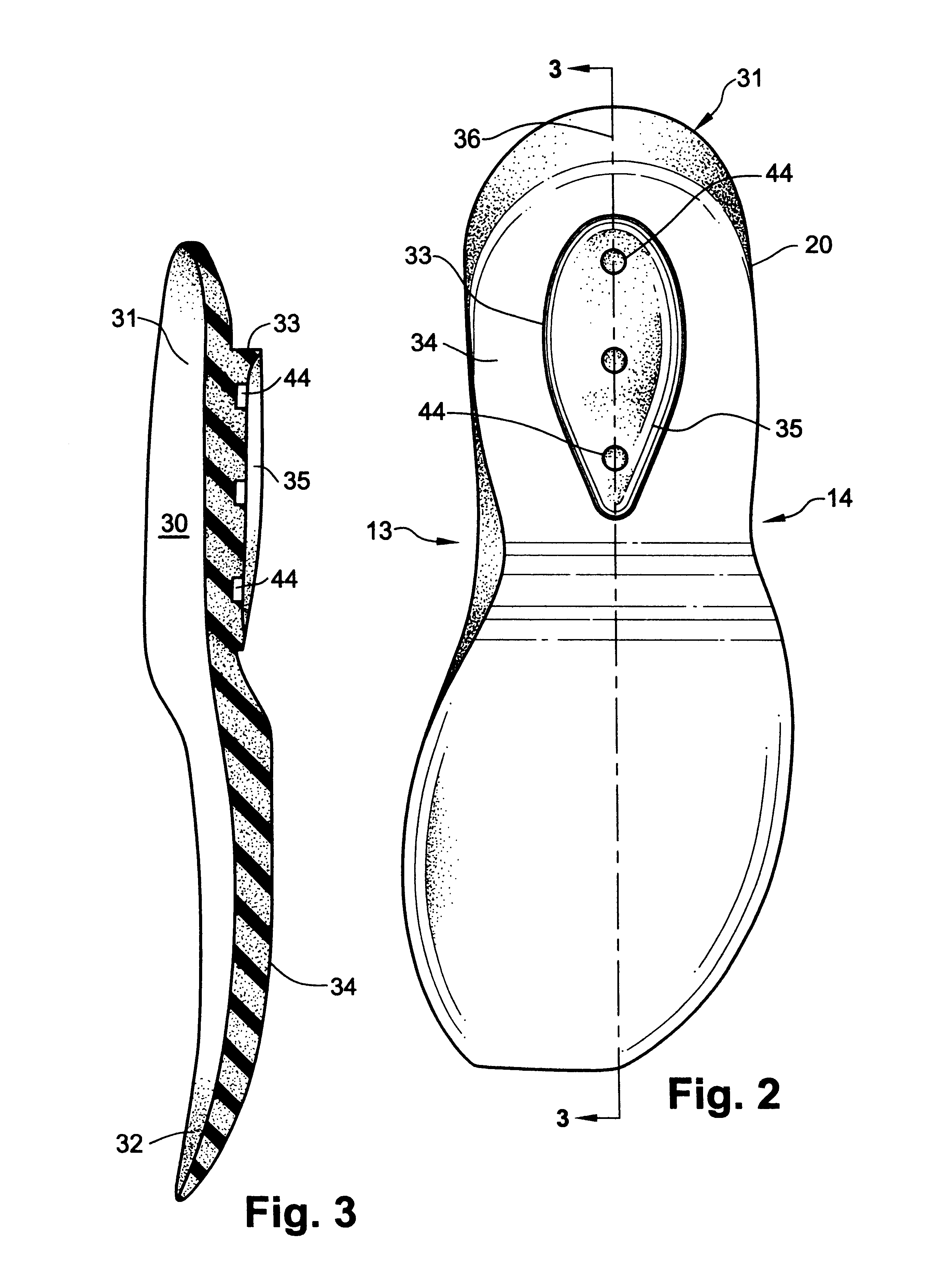
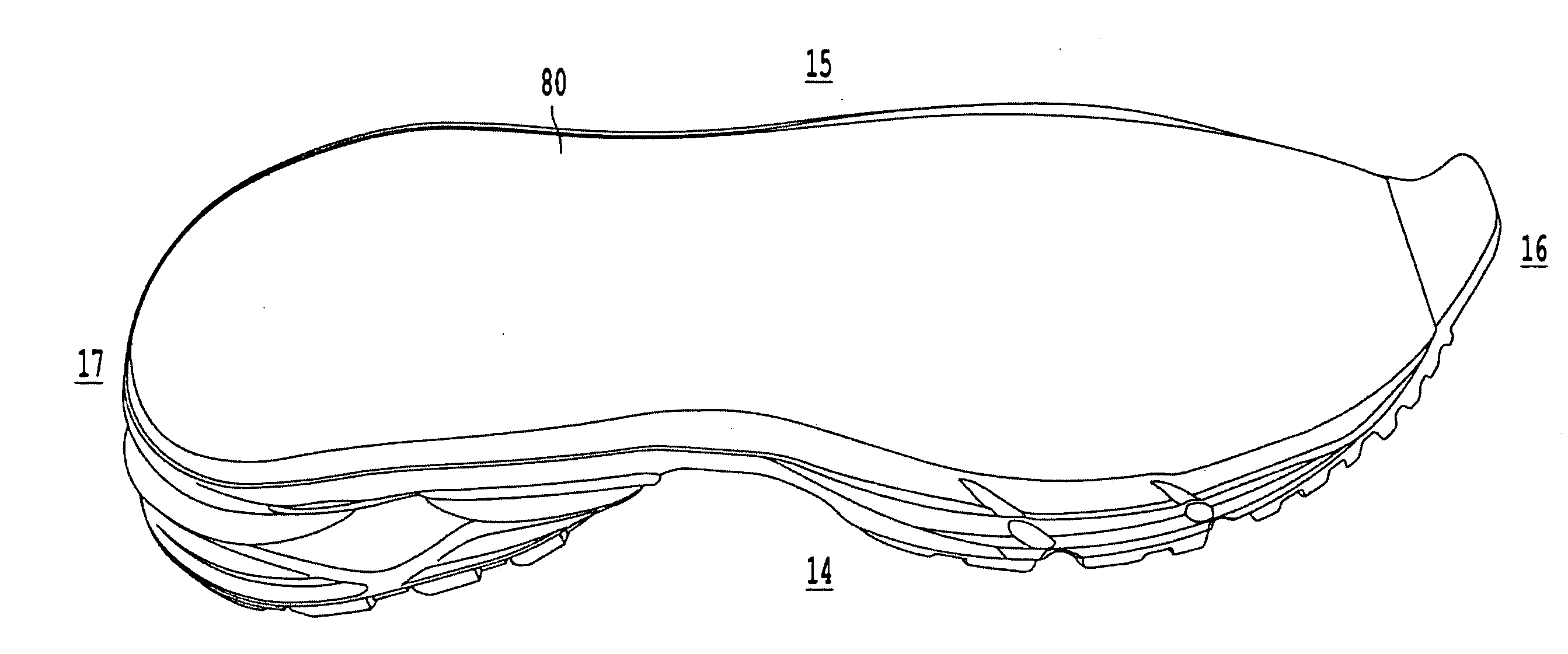
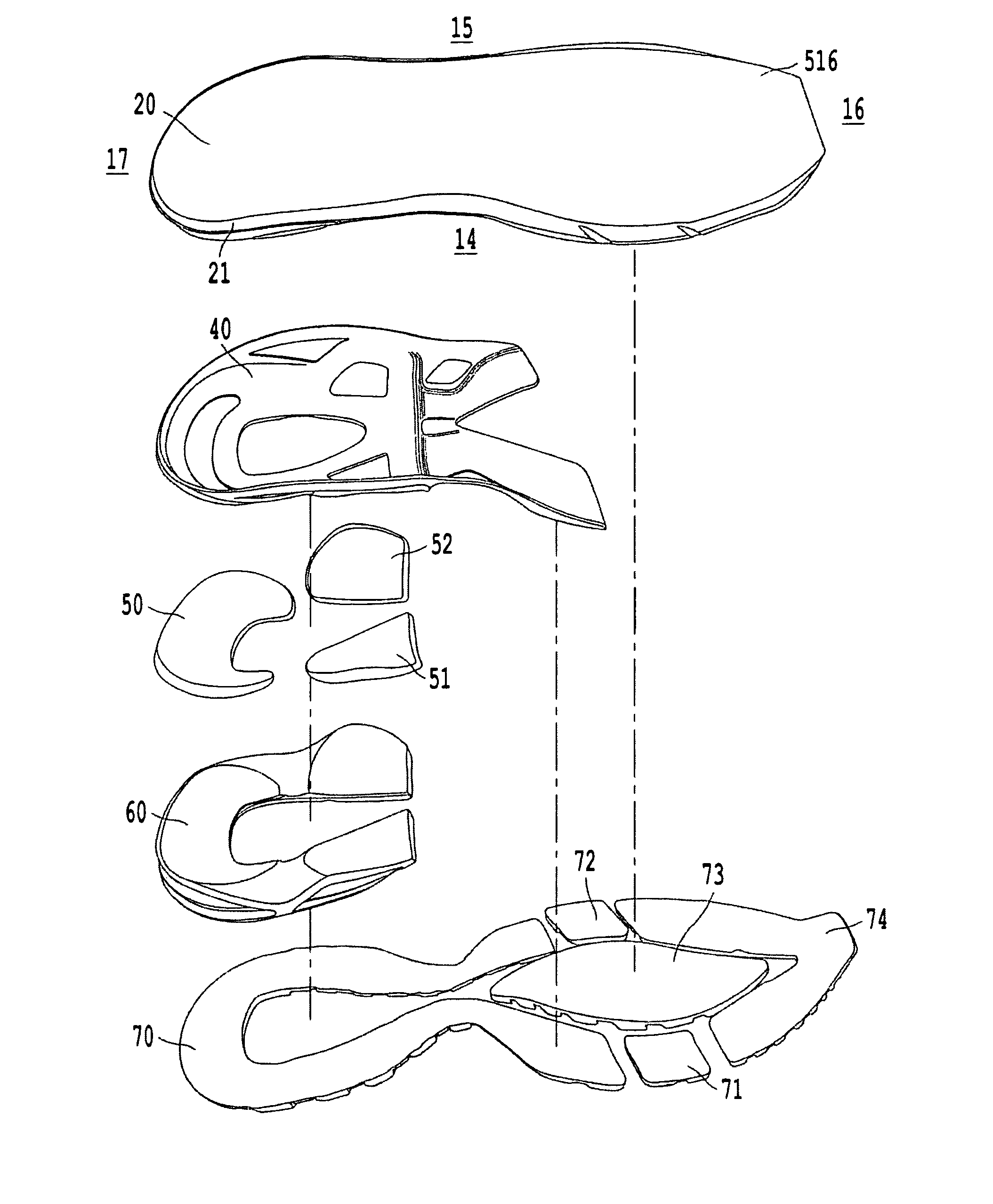
The invention is directed to a midsole assembly for footwear which includes medial and lateral unsymmetrical stabilizing pods disposed between shock absorbing upper and lower deflectable plates positioned at the heel portion of the midsole. The bottom surface of the heel portion of the midsole includes an axially aligned deflection platform defined by a concave surface. The upper shock absorption plate is disposed adjacent the bottom surface of the midsole and includes an aperture therethrough which is adapted to receive the deflection platform. The bottom plate includes a deflectable concave segment which is aligned with and adapted to engage the deflection platform of the midsole and be urged downwardly upon the imposition of force upon the midsole by the user's foot. The medial and lateral stabilizing pods are mounted between the upper and lower plates along the medial and lateral sides of the heel portion of the midsole and are respectively adapted to dynamically respond to the forces imposed on the medial and lateral sides of the heel. To control pronation and supination of the shoe and user's foot, the hardness of the medial stabilizing pod may be greater than that of the lateral stabilizing pod.
Owner:SEQUENTIAL AVIA HLDG LLC
Athletic shoe with cushion structures
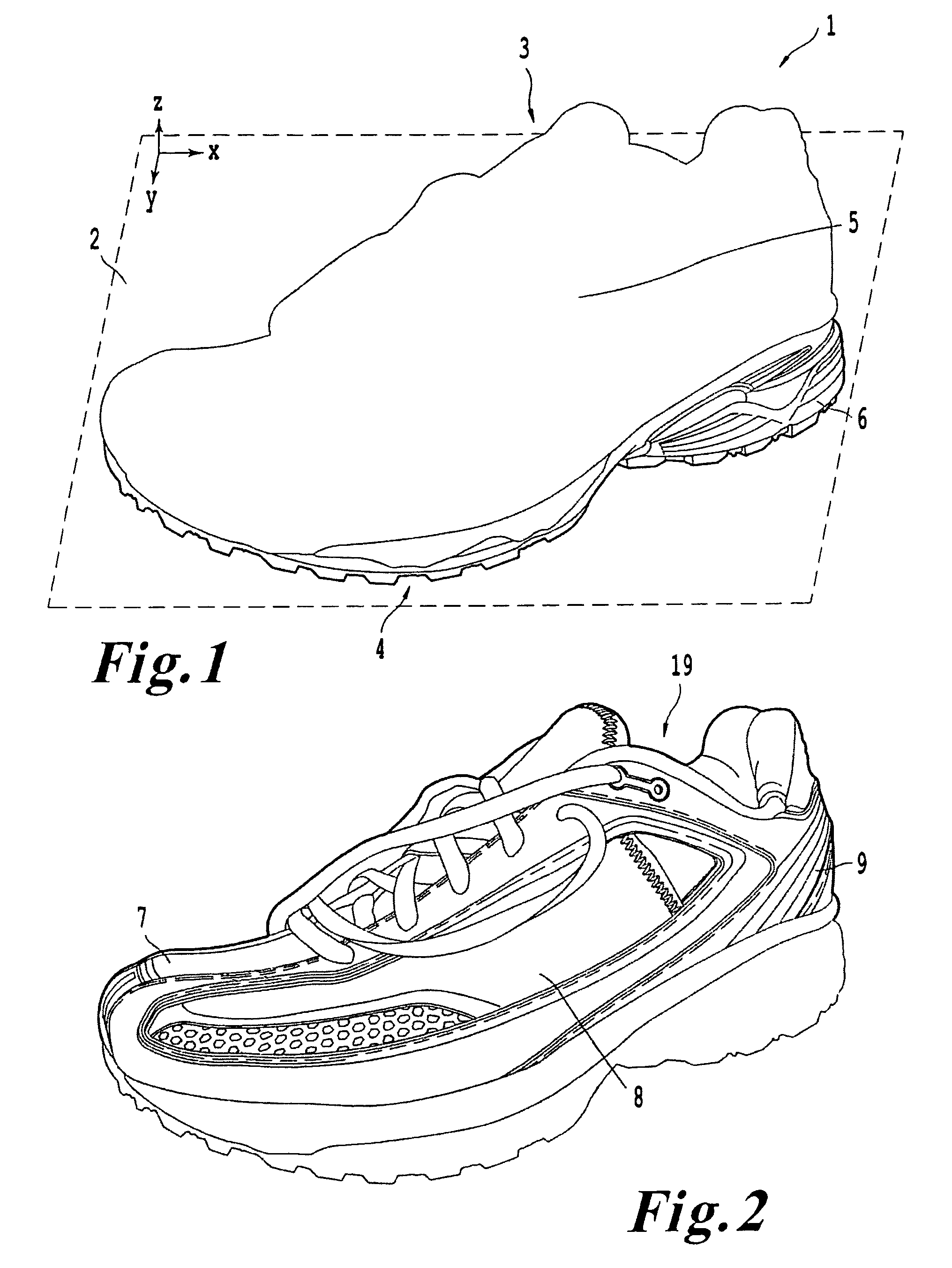
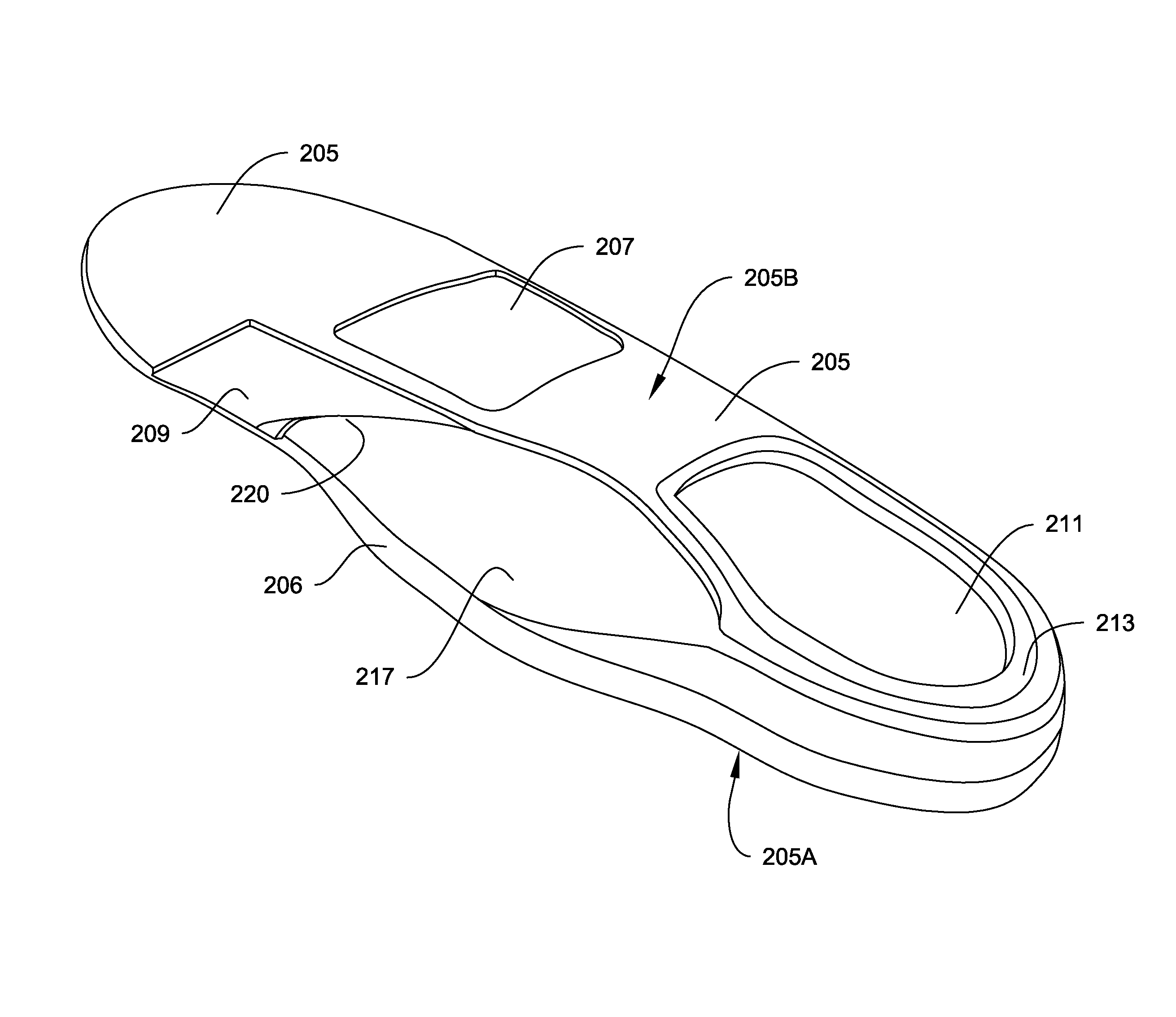
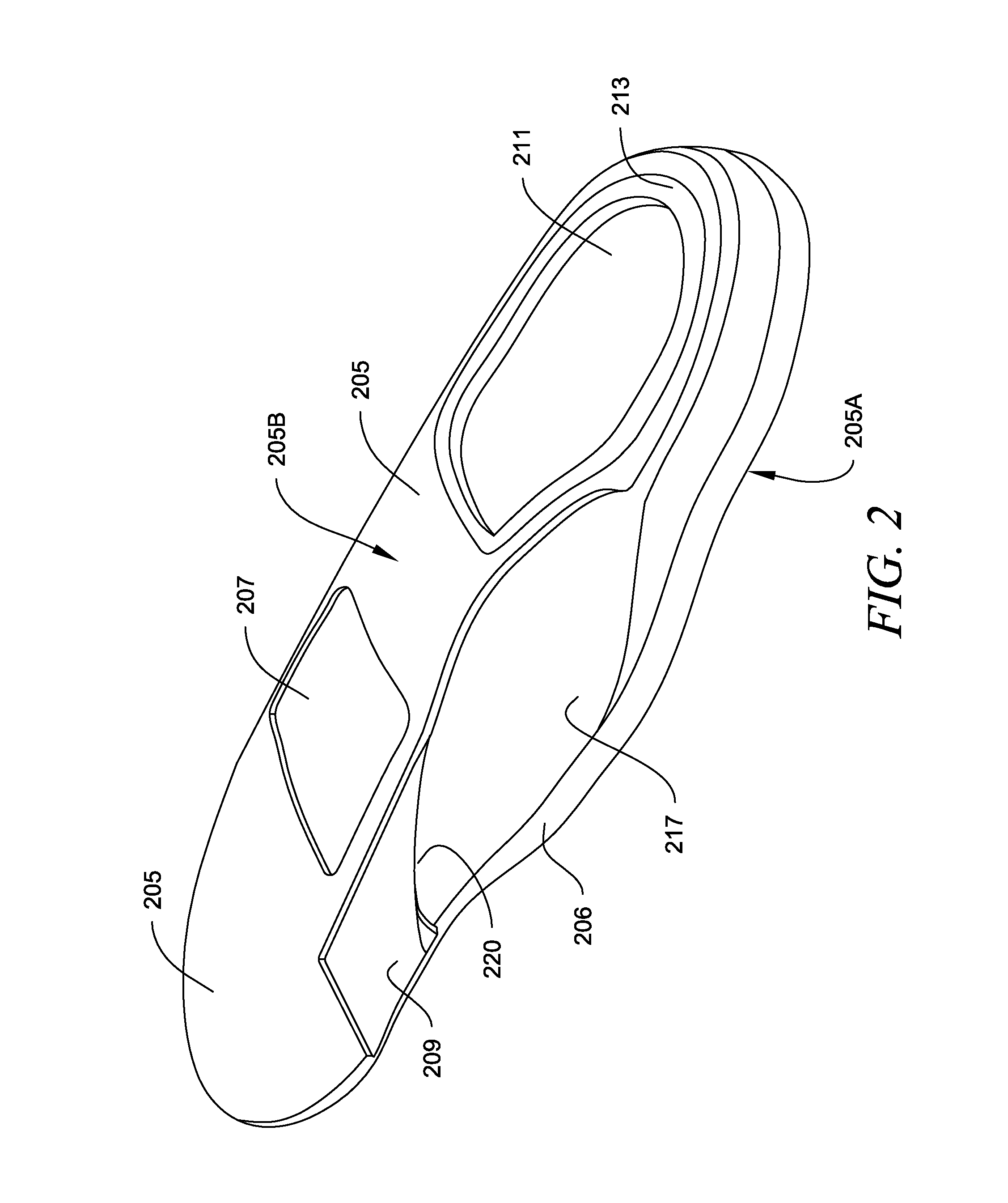
A footwear lower is presented which provides cushion support and lateral stability in a lightweight construction. The lower may include a primary midsole, cushion elements, a rear lower midsole, a directional cradle, and an outsole. The cushions may be located in the between the directional cradle and the rear lower midsole. Various embodiments of cushions are presented and may be consistent with specific types of shoes such as running trainers, trail shoes, general fitness footwear, or basketball shoes. The lower may be consistent with approaches to remediate a wearer's pronation or supination.
Owner:UNDER ARMOUR
Shoe incorporating improved shock absorption and stabilizing elements
The invention is directed to a midsole assembly for footwear which includes medial and lateral unsymmetrical stabilizing pods disposed between shock absorbing upper and lower deflectable plates positioned at the heel portion of the midsole. The upper plate is adapted to engage the bottom surface of the midsole and includes an axially aligned, concave segment which is resiliently deflected upon the imposition of force thereon by the user's foot. The bottom plate includes a deflectable concave segment which is adapted to engage the deflectable segment of the upper plate and be urged downwardly upon the imposition of force upon the upper plate by the user's foot. The medial and lateral stabilizing pods are mounted between the upper and lower plates along the medial and lateral sides of the heel portion of the midsole and are respectively adapted to dynamically respond to the forces imposed on the medial and lateral sides of the heel. To control pronation and supination of the shoe and user's foot, the hardness of the medial stabilizing pod may be greater than that of the lateral stabilizing pod.
Owner:SEQUENTIAL AVIA HLDG LLC
Cleated athletic shoe with cushion structures
A cleated shoe is presented which provides cushion support and lateral stability in a lightweight construction. The shoe includes a lower and an upper. The lower may include a primary midsole, cushion elements, and an outsole. A cleat may be connected to the outsole. At least one cushion may be located between the primary midsole and outsole. Various embodiments of cushions are presented and may be consistent with specific types of shoes associated with various types of activities such as football, baseball, lacrosse, soccer, or golf. The lower may be consistent with approaches to remediate a wearer's pronation or supination.
Owner:UNDER ARMOUR
Footwear with an adjustable stabilizing system, in particular for pronation and/or supination control
InactiveUS20060283046A1Simple and economical structureVersatile and reliable in useSolesHeelsPronationsEngineering
A footwear has a sole that comprises an adjustable stabilising system, in particular to control phenomena of pronation and / or supination. The stabilisation system comprises at least one adjustment member capable of selectively taking at least two alternative positions within a respective seat present in a component of the sole, the adjustment member having a body with at least two portions or sectors that present different degrees of compressibility.
Owner:DIADORA INVICTA SPA
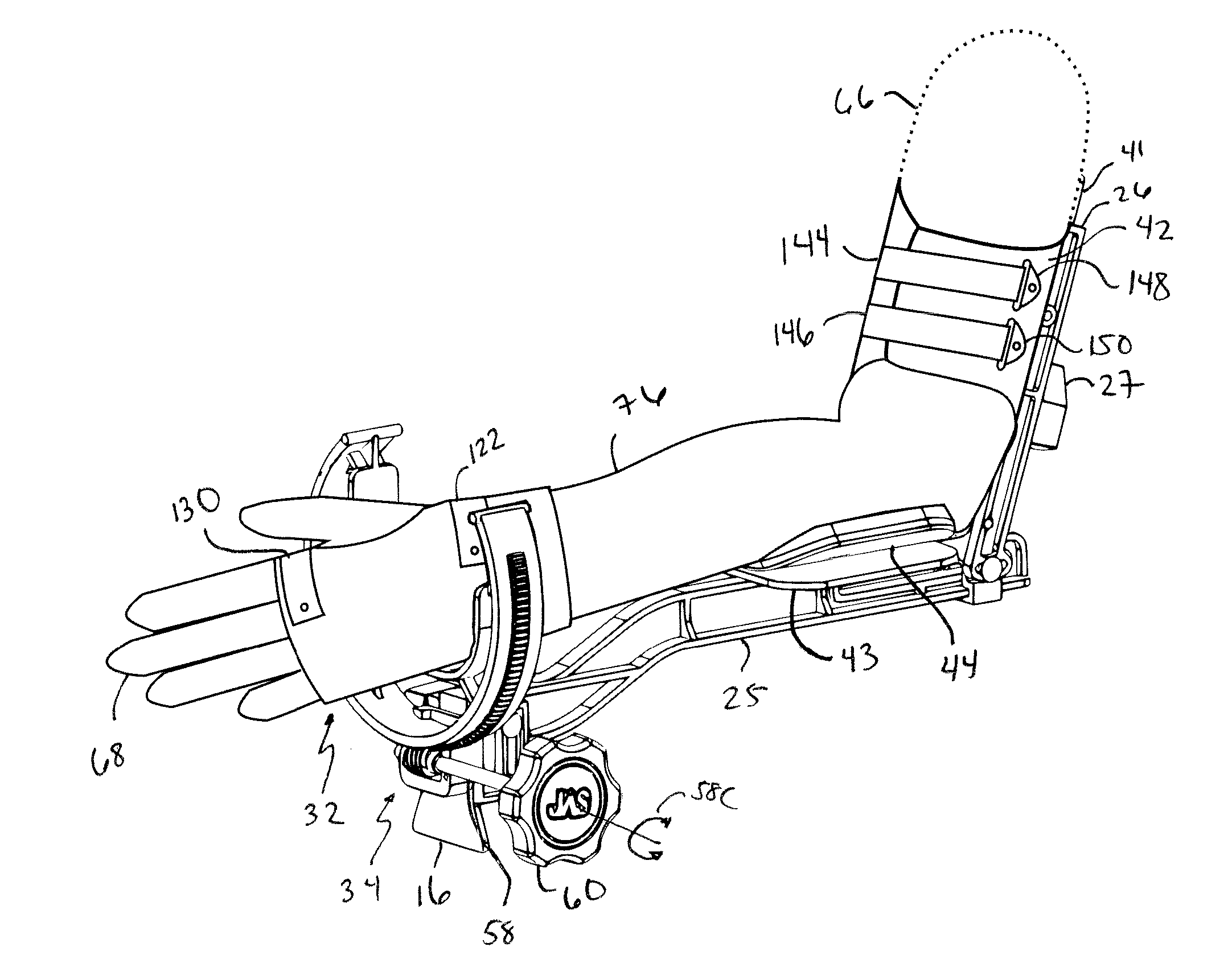
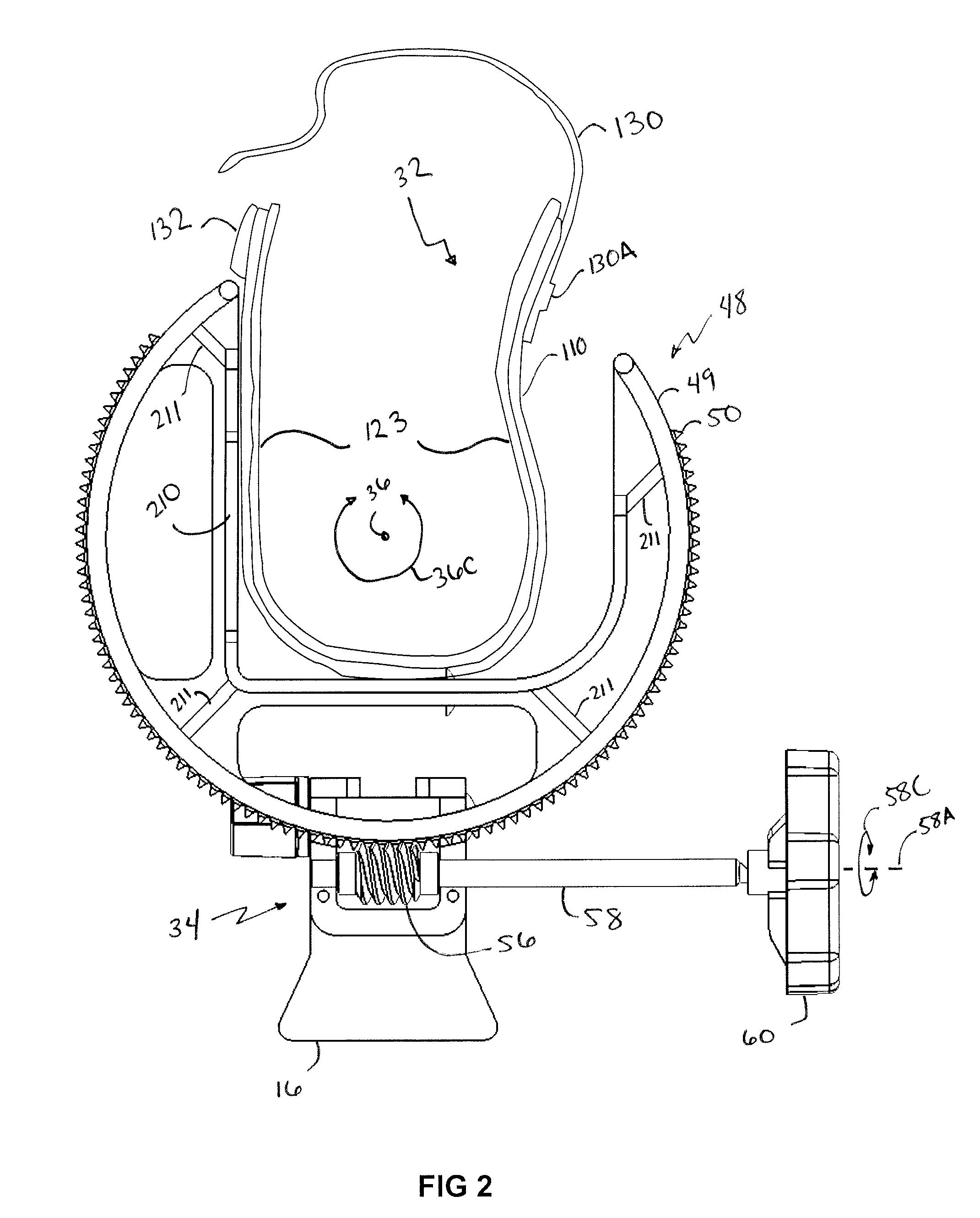
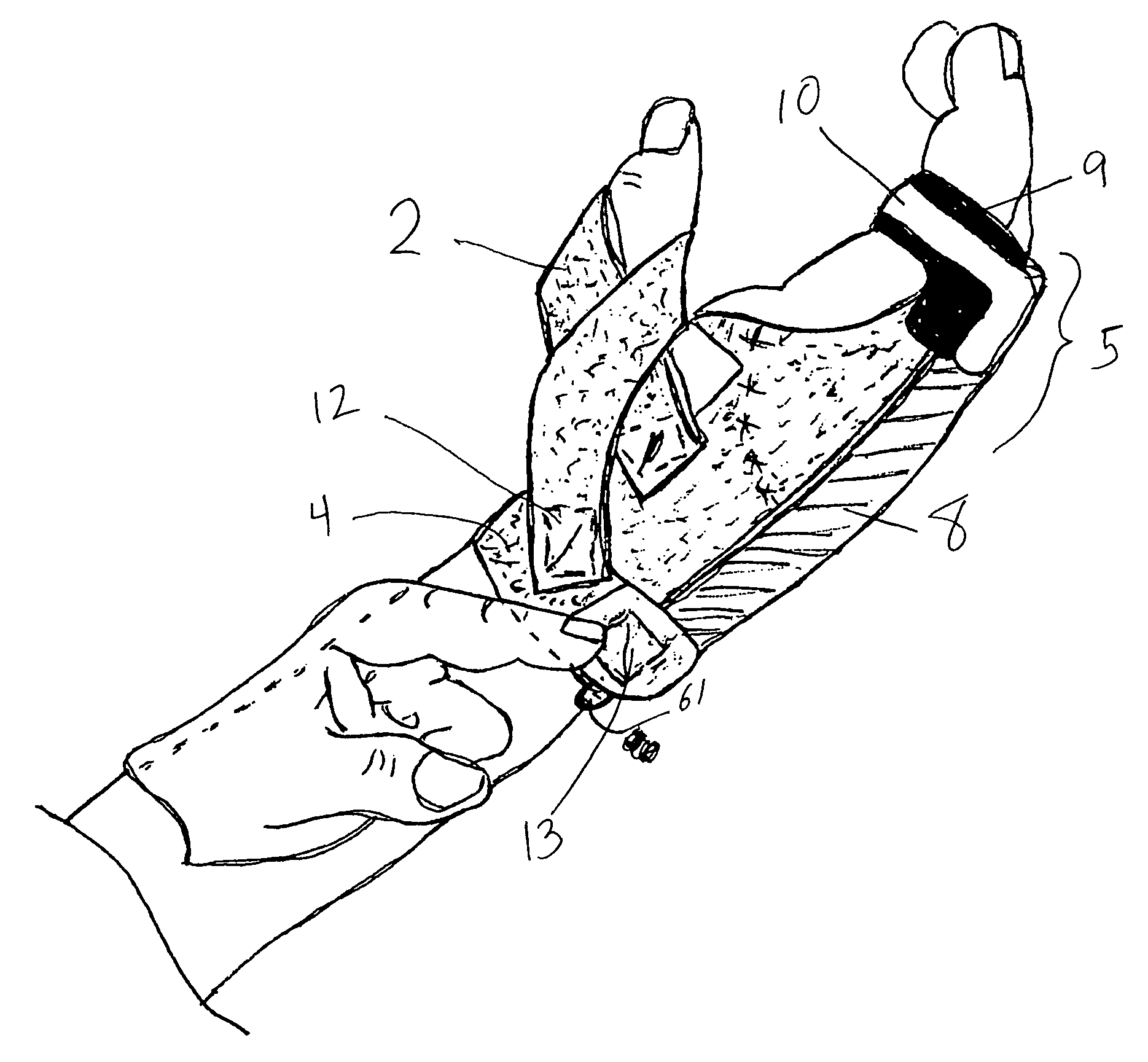
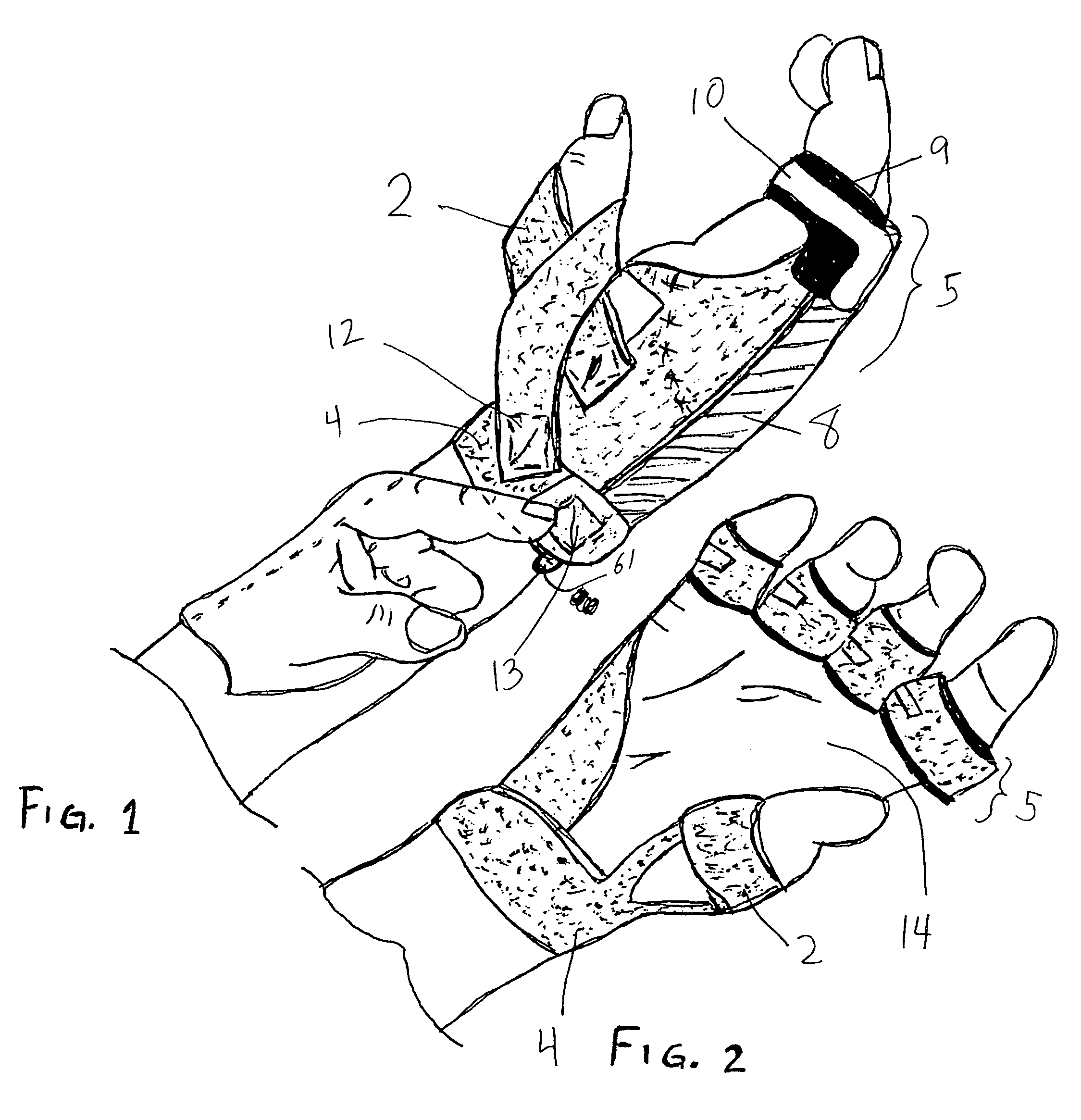
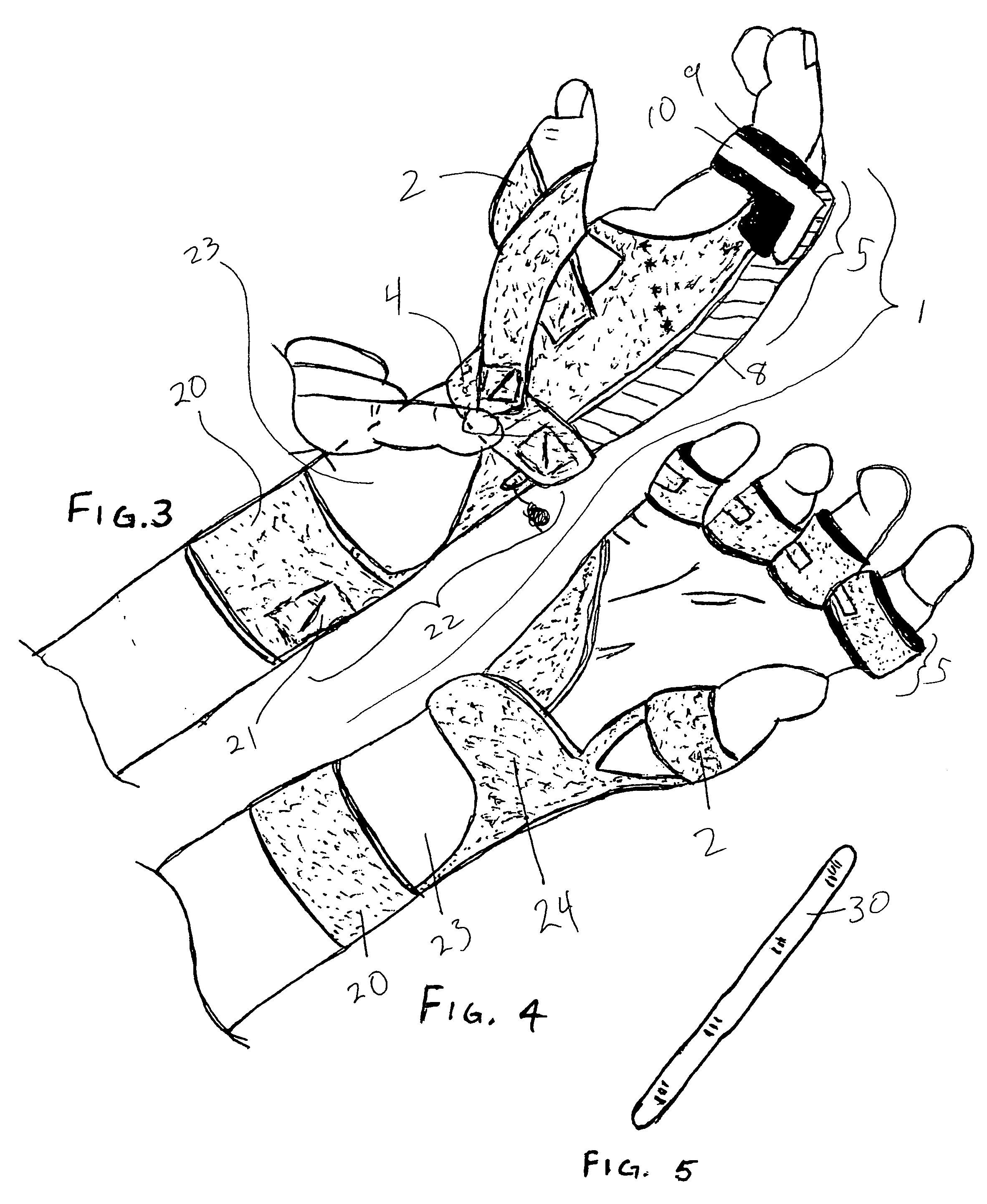
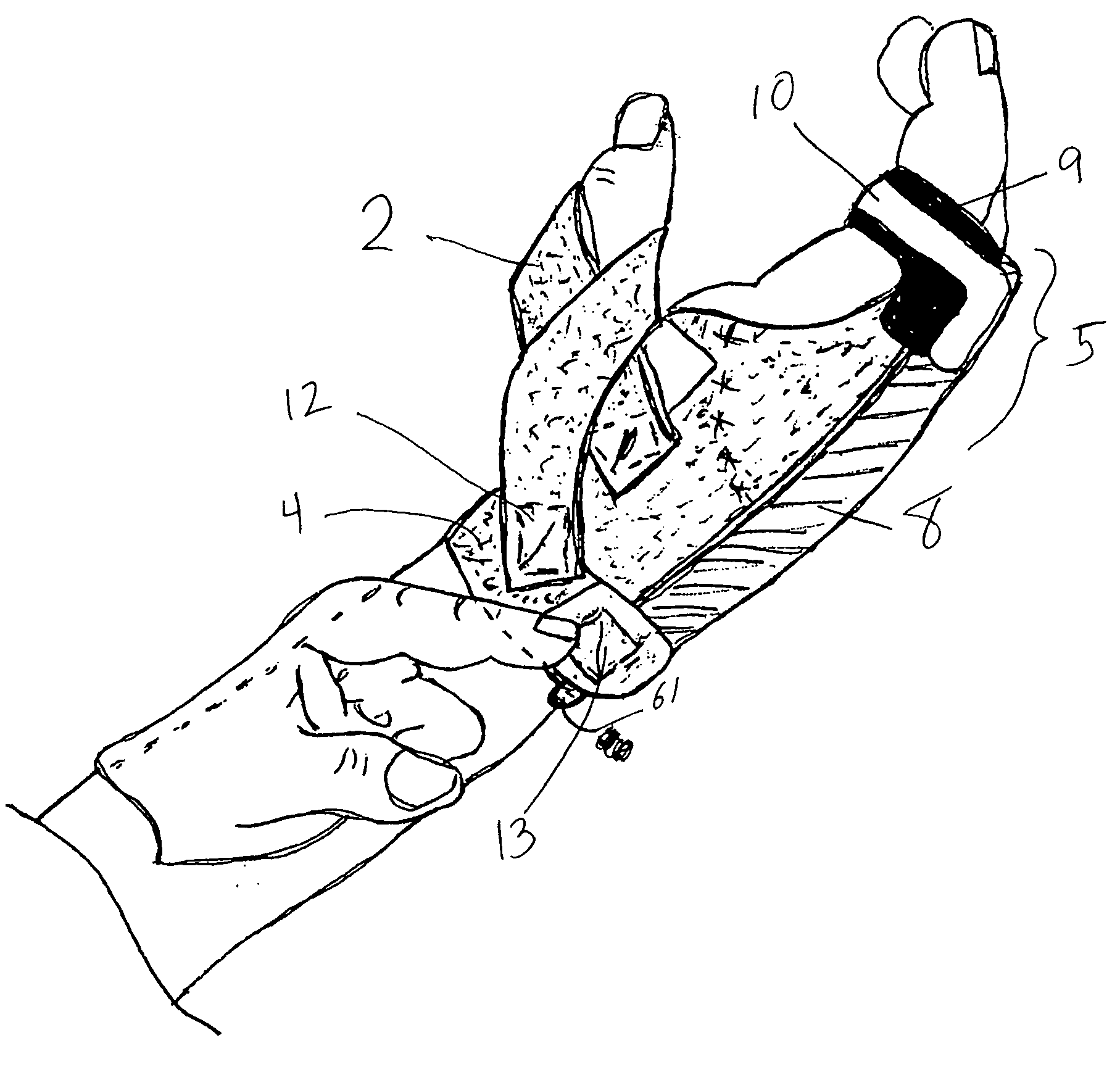
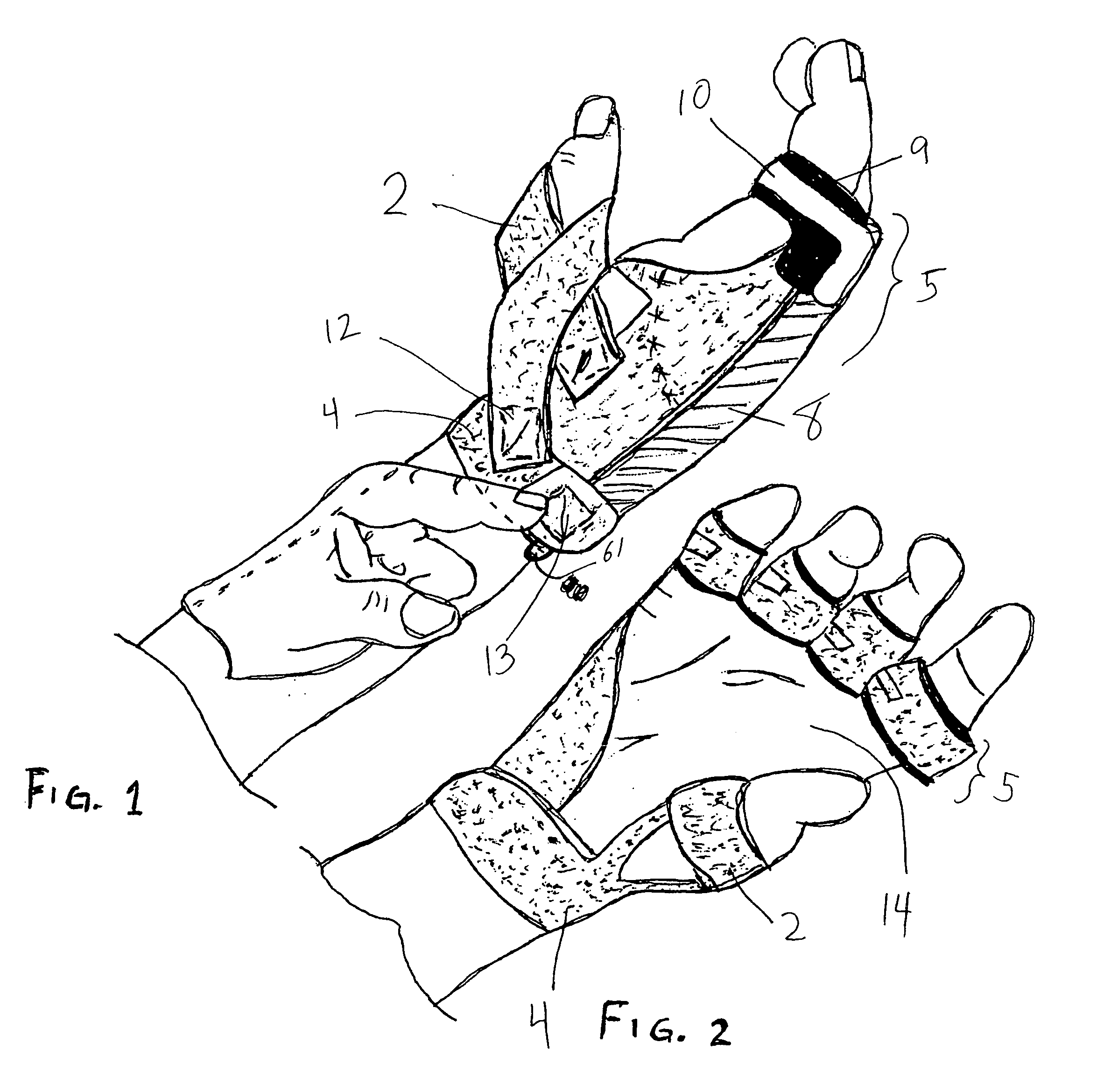
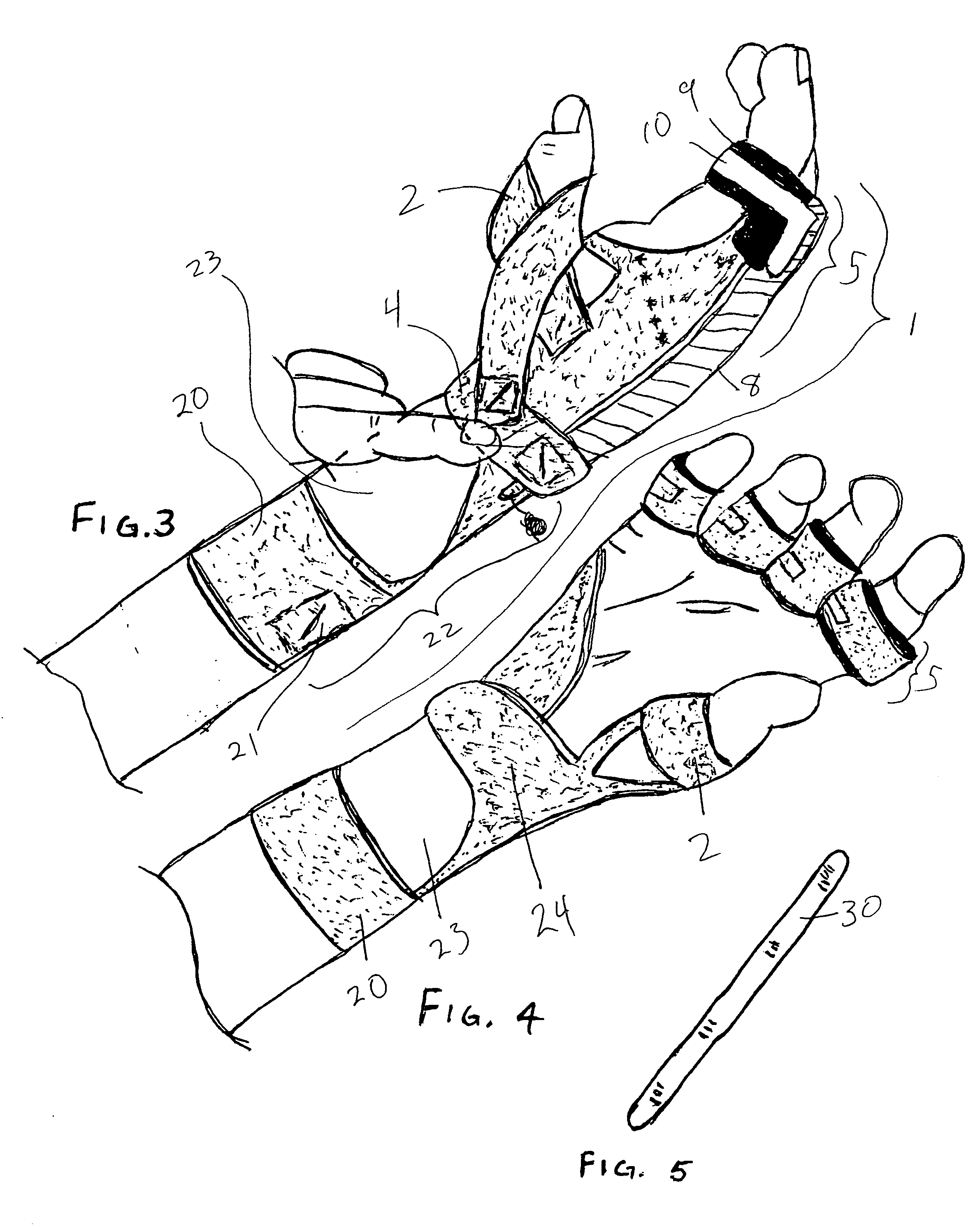
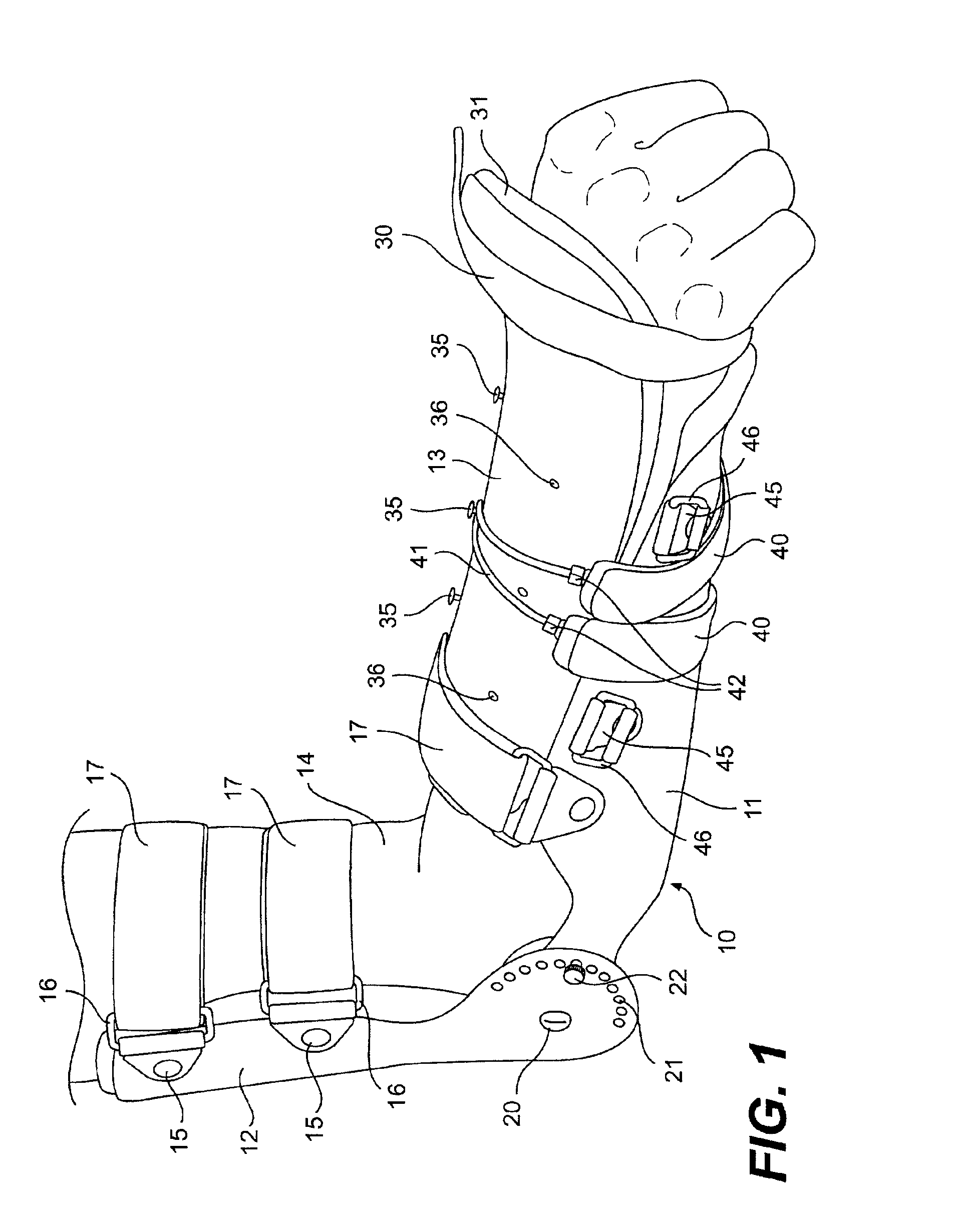
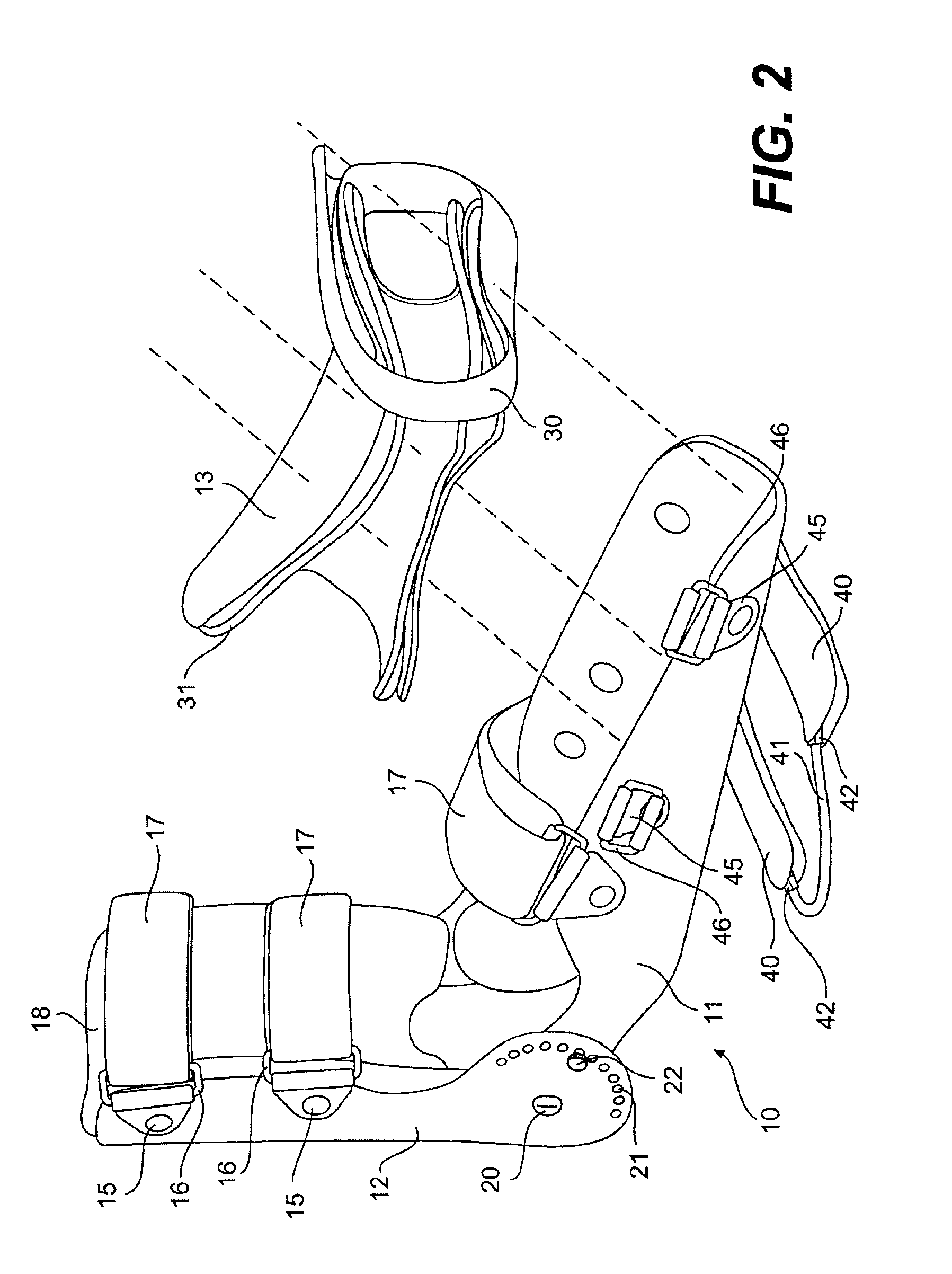
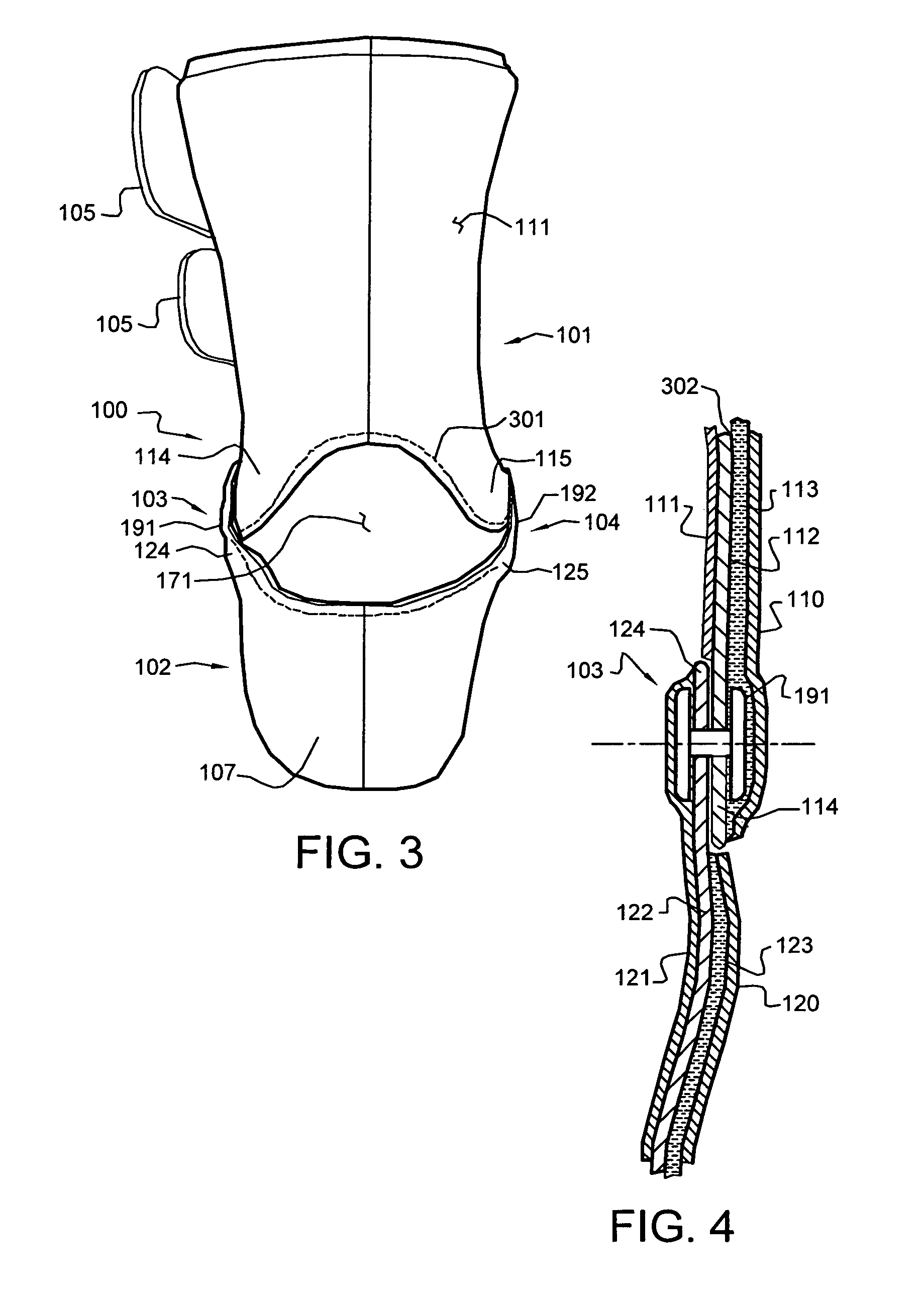
Orthosis Apparatus and Method of Using an Orthosis Apparatus
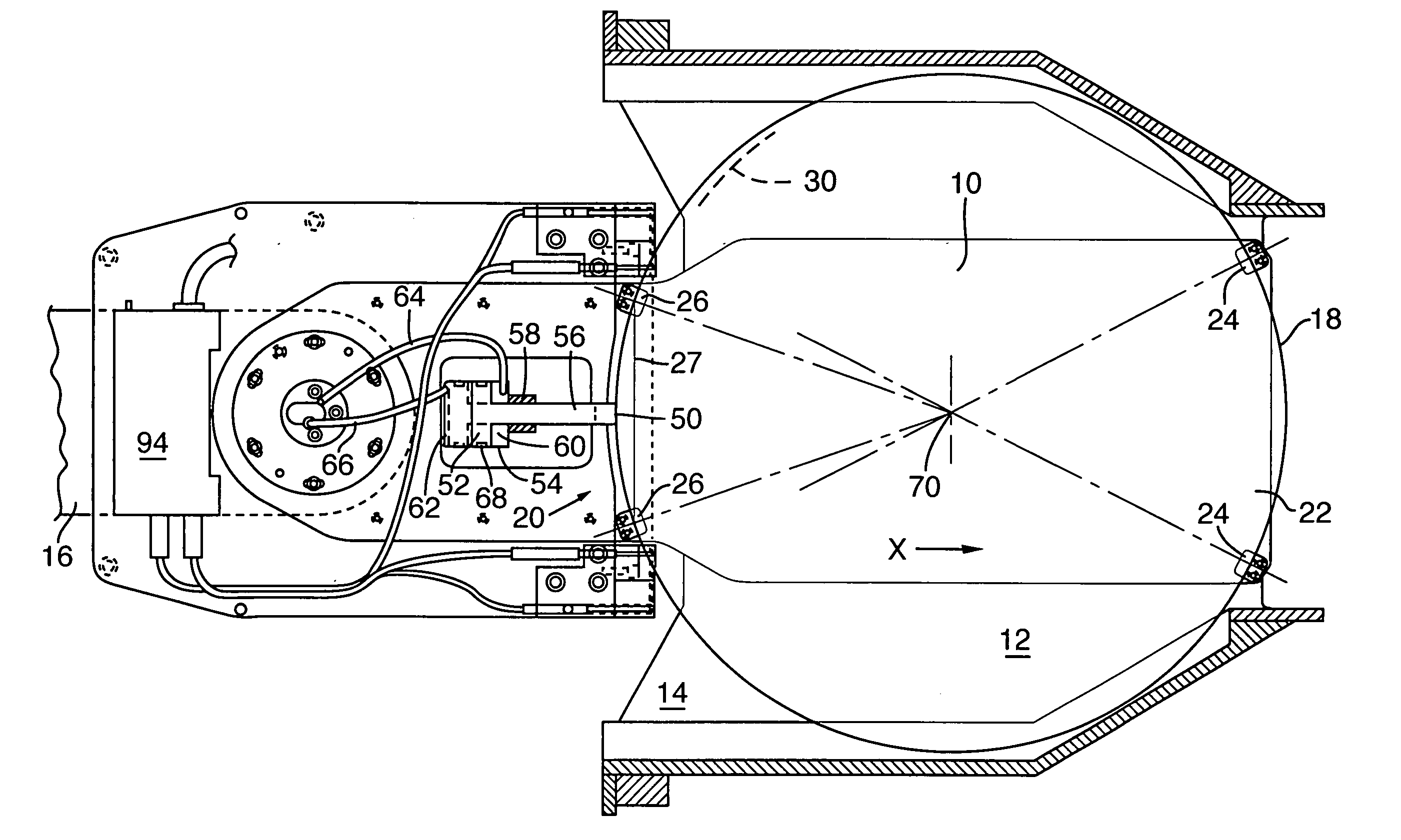
The present invention provides a new and improved orthosis for use in effecting relative movement between bones in an arm of a patient. The apparatus includes a lower cuff gripping distal bone, such as a wrist, and an upper cuff gripping a proximal bone, such as an upper arm. The lower cuff is secured in a rotatable drive assembly substantially coincident to a longitudinal axis of a medial bone, such as the forearm, during rotational distal adjustment. The angle between the forearm and the upper arm is adjustable and can be securely fixed at a desired angle. The rotation of the rotatable drive assembly effectuates the pronation and supination of the hand and wrist relative to the patient's forearm. The orthosis of the present invention can be disassembled with interchanging parts substituted depending on the patient's needs.
Owner:BONUTTI RES
Shoe, ankle orthosis and method for protecting the ankle
InactiveUS6692454B1Ankle protectionRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRolloverFoot/ankle orthoses
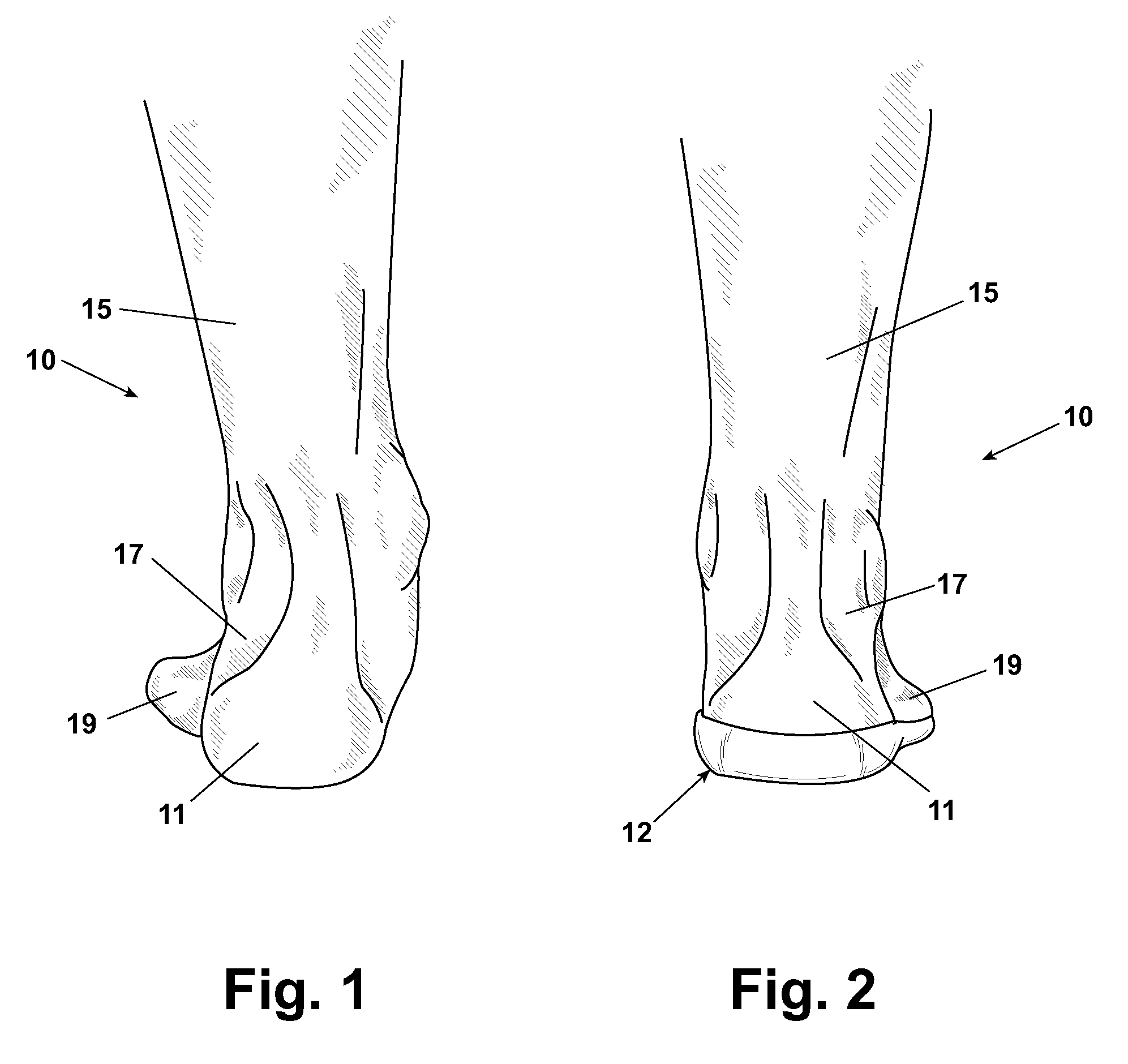
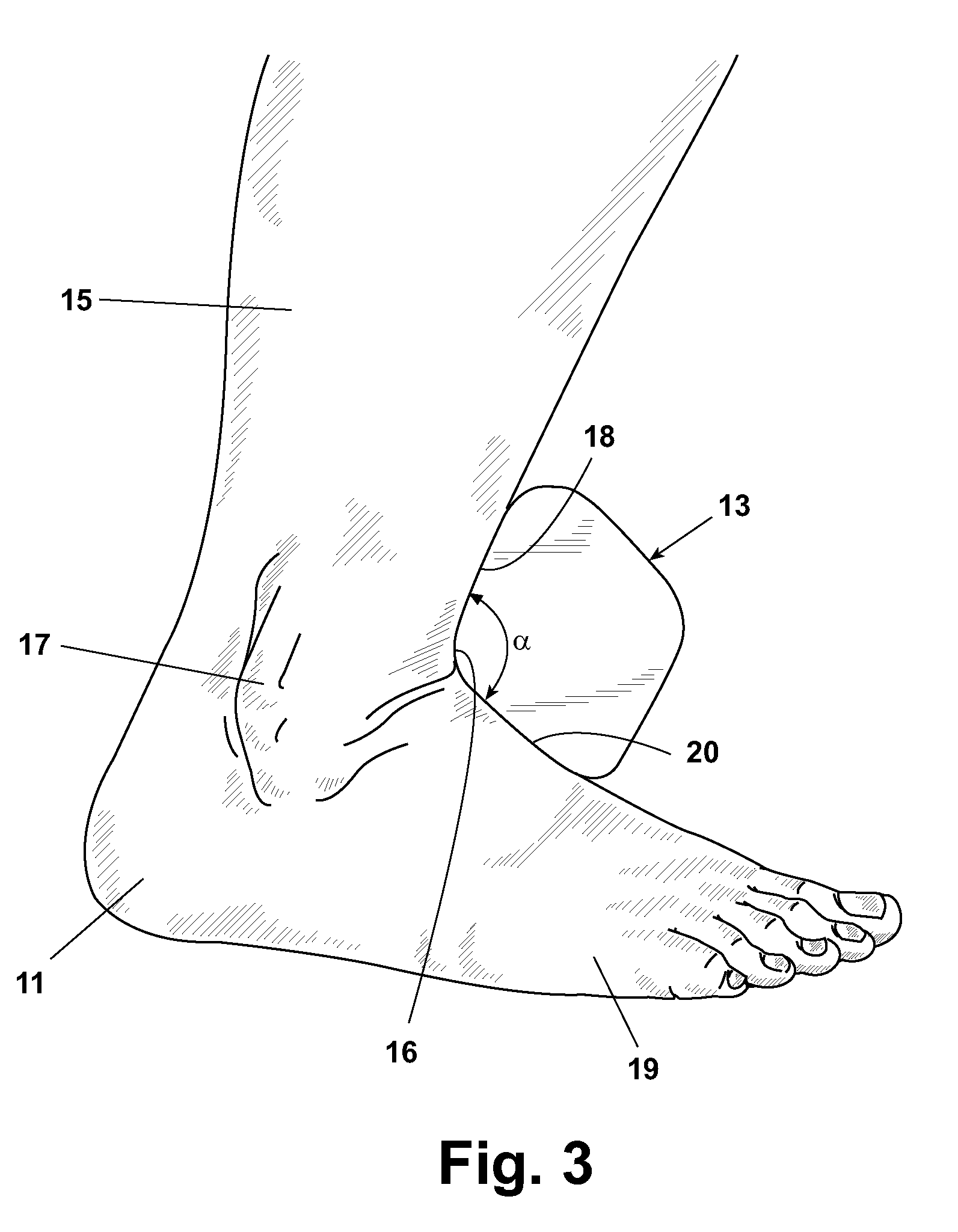
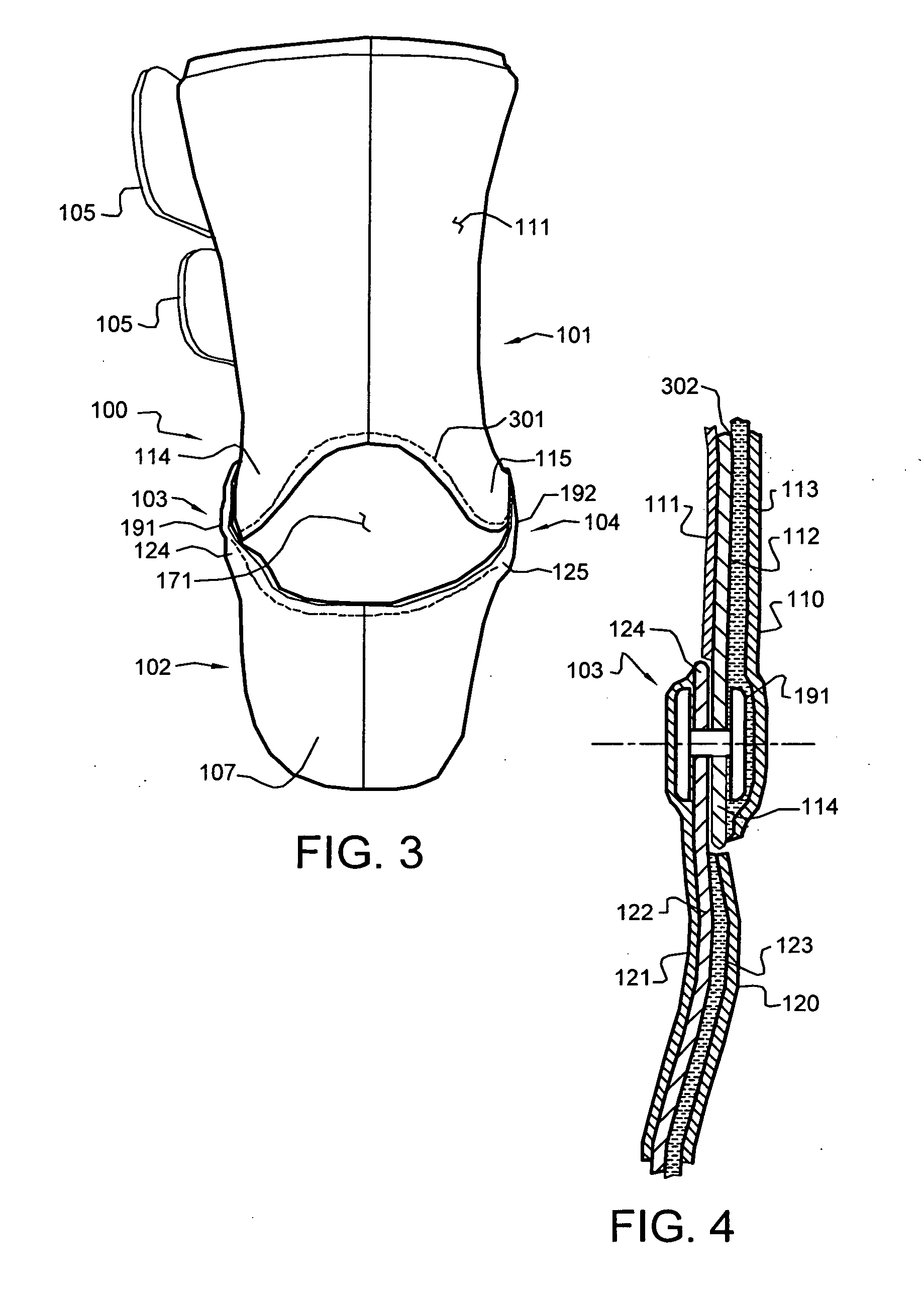
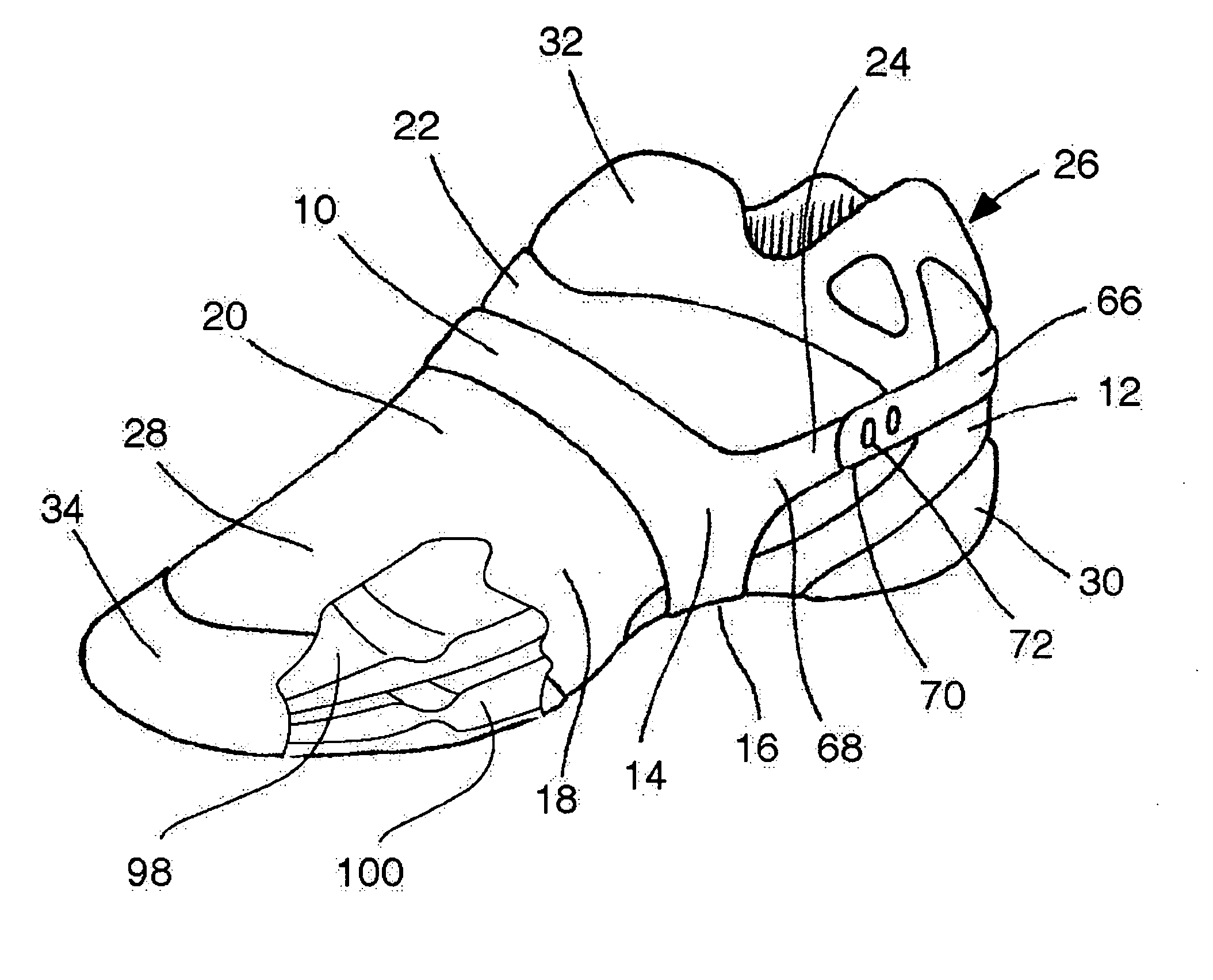
A method for protecting the ankle against injury, limit subtalar joint motion of the ankle by controlling the motions of segments of the subtalar joint fore and aft of the subtalar joint while permitting motion of the foot about the ankle joint with an improved athletic shoe, ankle orthosis. A supporting structure a part of or connected to the shoe or orthosis is preferably in the form of a heel-sole counter provided about the heel and at least a portion of the foot forward of the subtalar joint which includes a split toe sole extension. The supporting structure has a semi-rigid shape retaining character which is not collapsible vertically and which together with the shoe or orthosis limits torsional movement of the foot about the longitudinal axis of the subtalar joint as seen in a top plan view thereof by an upwardly extending portion thereof which acts as a torsion bar that is, in turn, secured to the lower leg. Preferably, the torsion bar has directional properties for resisting bending which are most rigid in a direction orthogonal or nearly orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the subtalar joint. In a disclosed embodiment of the shoe motion of the midtarsal joint is also limited by the supporting structure to aid in limiting subtalar joint motion and shoe rollover. The shoe is secured to the foot by way of a strap arrangement which applies a force to the foot in a direction which, together with the heel-sole counter opposes the subtalar joint motion in supination.
Owner:TOWNSEND BARRY W +1
Correcting foot alignment
A component system of footwear corrective alignment insoles provides adjustment of the alignment of a human foot based upon evaluation and measurement of structural anomalies in the foot. A subtalar joint goniometer measures the angular alignment of the foot with a patient's leg properly inclined with respect thereto. A database contains data with selected relationships between the degree of a patient's foot pronation and supination and a variety of corrective pads for use with an insole for correcting pronation and supination. The foot pronation and supination is corrected by first measuring a patient's foot pronation and supination, comparing the measured pronation or supination with a database that correlates degrees of pronation and supination with a variety of corrective pads for use with a corrective alignment insole, selecting corrective pads from the database that correspond to the measured pronation or supination, and mounting the selected corrective pads to a base insole.
Owner:BIOCORRECT
Athletic shoe with cushion structures
A footwear lower is presented which provides cushion support and lateral stability in a lightweight construction. The lower may include a primary midsole, cushion elements, a rear lower midsole, a directional cradle, and an outsole. The cushions may be located in the between the directional cradle and the rear lower midsole. Various embodiments of cushions are presented and may be consistent with specific types of shoes such as running trainers, trail shoes, general fitness footwear, or basketball shoes. The lower may be consistent with approaches to remediate a wearer's pronation or supination.
Owner:UNDER ARMOUR
Shoe incorporating improved shock absorption and stabilizing elements
The invention is directed to a midsole assembly for footwear which includes medial and lateral unsymmetrical stabilizing pods disposed between shock absorbing upper and lower deflectable plates positioned at the heel portion of the midsole. The bottom surface of the heel portion of the midsole includes an axially aligned deflection platform defined by a concave surface. The upper shock absorption plate is disposed adjacent the bottom surface of the midsole and includes an aperture therethrough which is adapted to receive the deflection platform. The bottom plate includes a deflectable concave segment which is aligned with and adapted to engage the deflection platform of the midsole and be urged downwardly upon the imposition of force upon the midsole by the user's foot. The medial and lateral stabilizing pods are mounted between the upper and lower plates along the medial and lateral sides of the heel portion of the midsole and are respectively adapted to dynamically respond to the forces imposed on the medial and lateral sides of the heel. To control pronation and supination of the shoe and user's foot, the hardness of the medial stabilizing pod may be greater than that of the lateral stabilizing pod.
Owner:SEQUENTIAL AVIA HLDG LLC
Articulated custom ankle-foot orthosis systems
ActiveUS20050096576A1Guaranteed wearRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPronationsEngineering
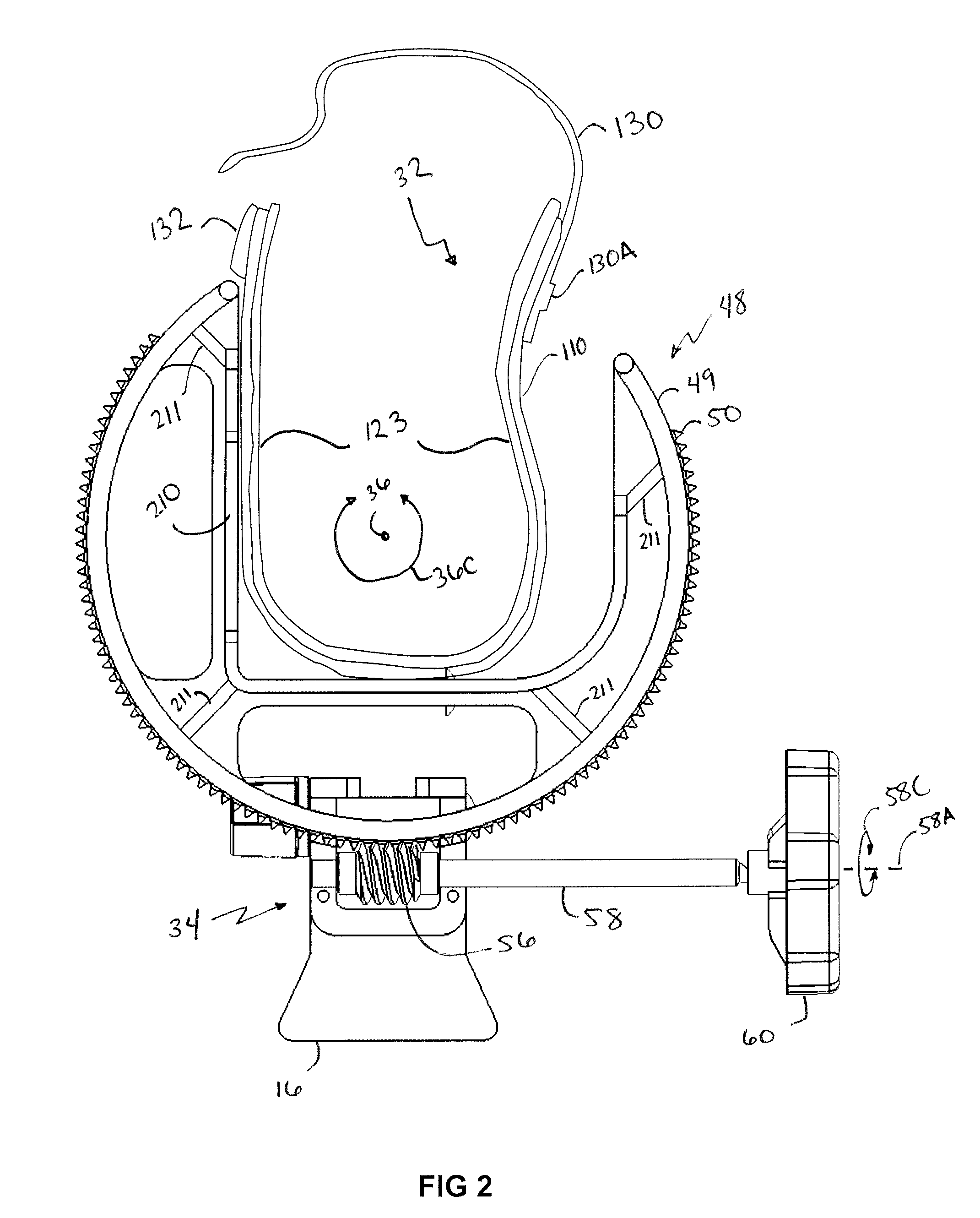
A custom articulated ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) system is disclosed that is formed on a cast of the wearer's foot. It has an adjustably tightenable calf section hingedly connected to an adjustably tightenable foot section. It is made of thermally formable plastic sheet, is lined inside and outside, and is padded inside. The brace permits dorsal / plantar flexion while supporting the ankle against supination and pronation. The apparatus and methods of manufacture are disclosed.
Owner:ARIZONA AFO INC
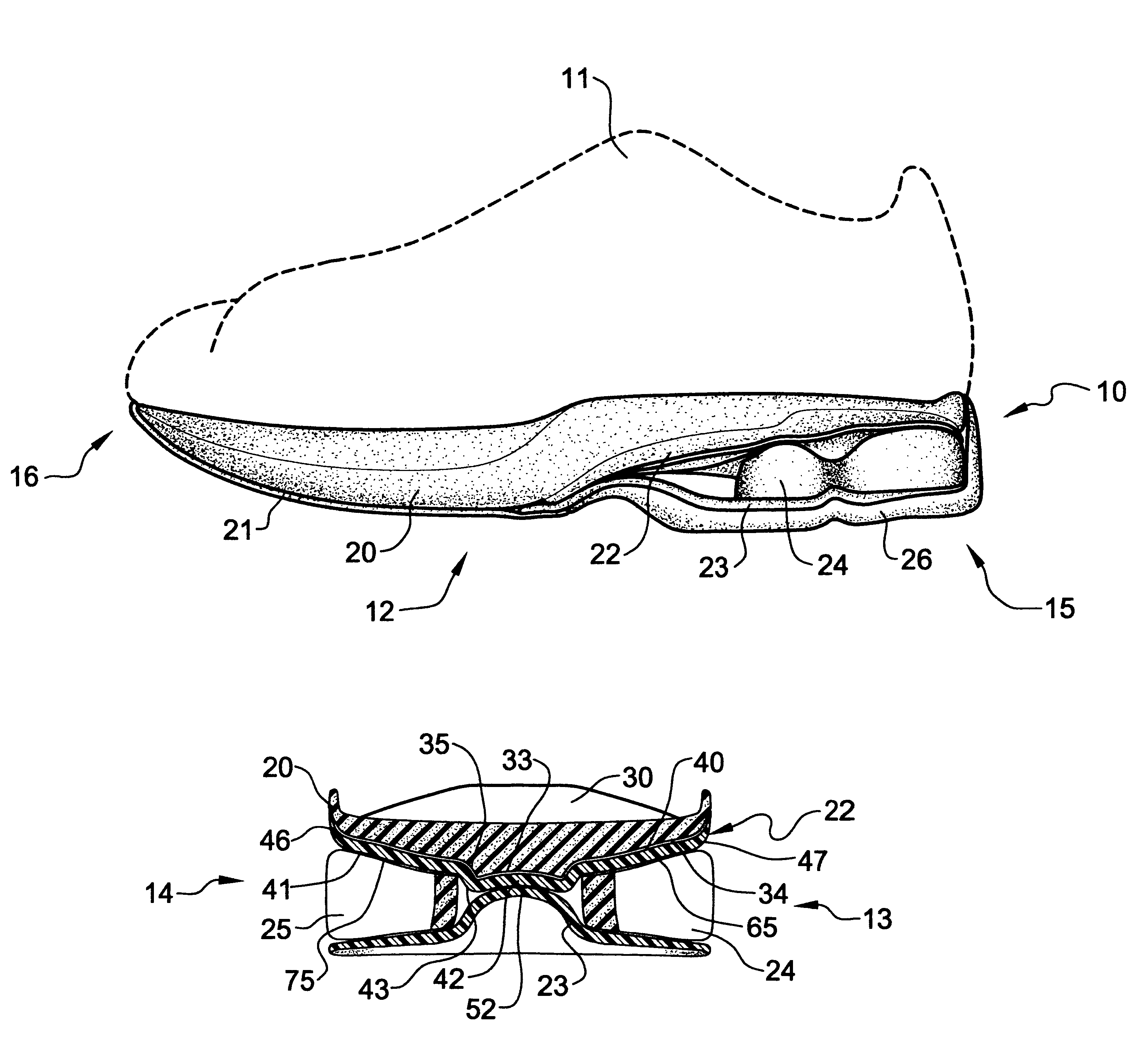
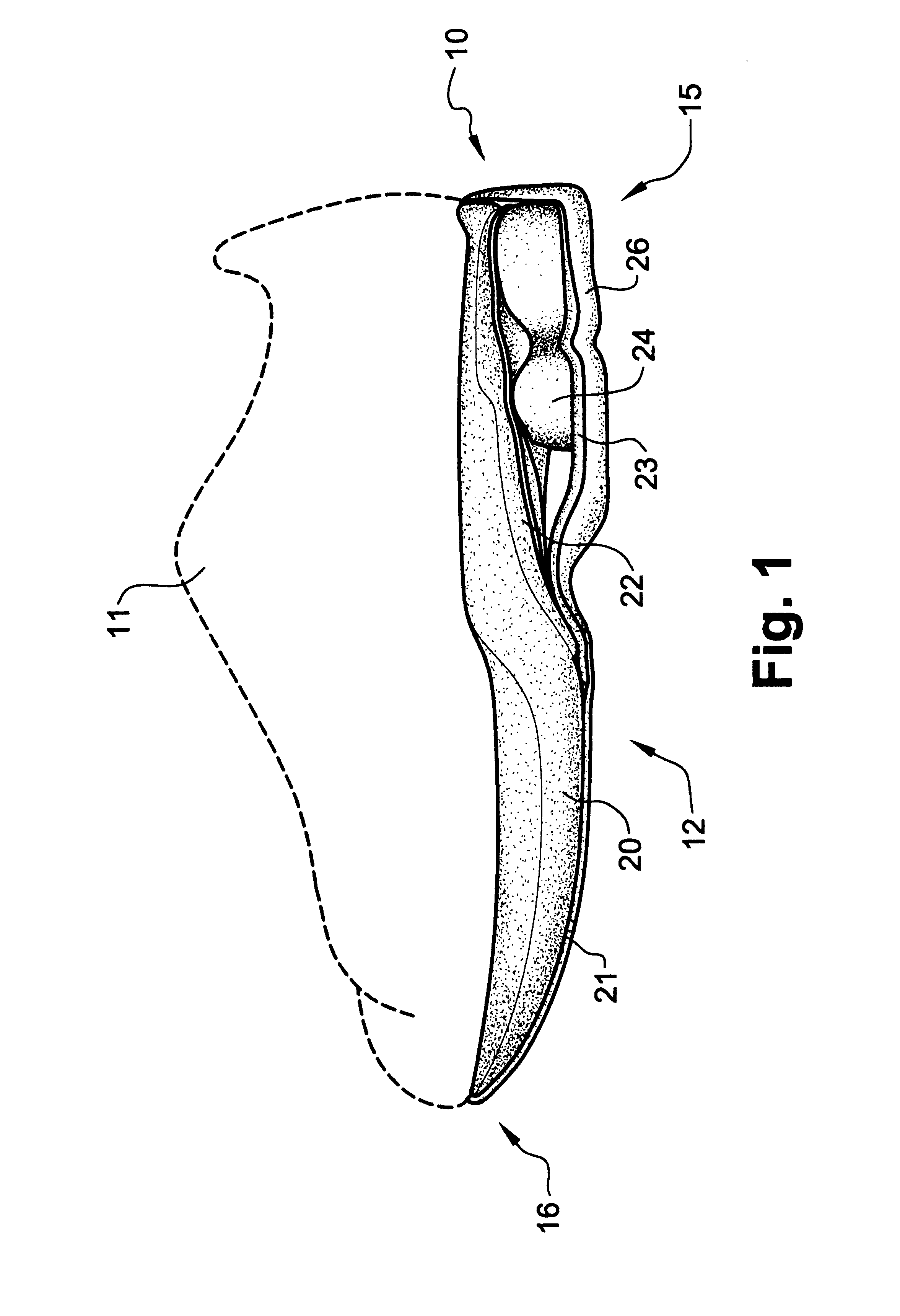
Athletic footwear and the like with integral supinator device
ActiveUS7243444B2Prevent excessive pronationAvoid injurySolesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAnkle injuryPosterior malleolus
Owner:SELNER MARC
Low-profile, radial nerve splint with interchangeable resilient digit extensor elements and supination adjustment means
Owner:PHELAN CAROLYN HOYNE +2
Low-profile, radial nerve splint with interchangeable resilient digit extensor elements and supination adjustment means
ActiveUS20060276735A1Less resiliencyReduce manufacturing costRestraining devicesGlovesThermoplasticWrist support
A low-profile, simple, orthotic glove with wrist support attachment for treating loss or impairment of extensor and / or flexor muscle function in the upper extremities, particularly in the wrist, hand and fingers, due to a peripheral neuropathy. The glove is attractive, comfortable, easy to use, and can be made with an optional wrist support attachment either built into the glove or added as an optional attachment, and can include thermoplastic to provide rigidity. The glove has channels into which interchangeable resilient digit extensor elements, or stays, of varying resiliency are placed such that stays of greater or lesser resiliency can be inserted if the degree of the patient's extensor muscle control changes, or the medical practitioner in charge decides that there is a need to change the support and exercise treatment regimens. The splint also has several improvements for thumb support, additional digit extension support, and for supination of the forearm.
Owner:PHELAN CAROLYN HOYNE +2
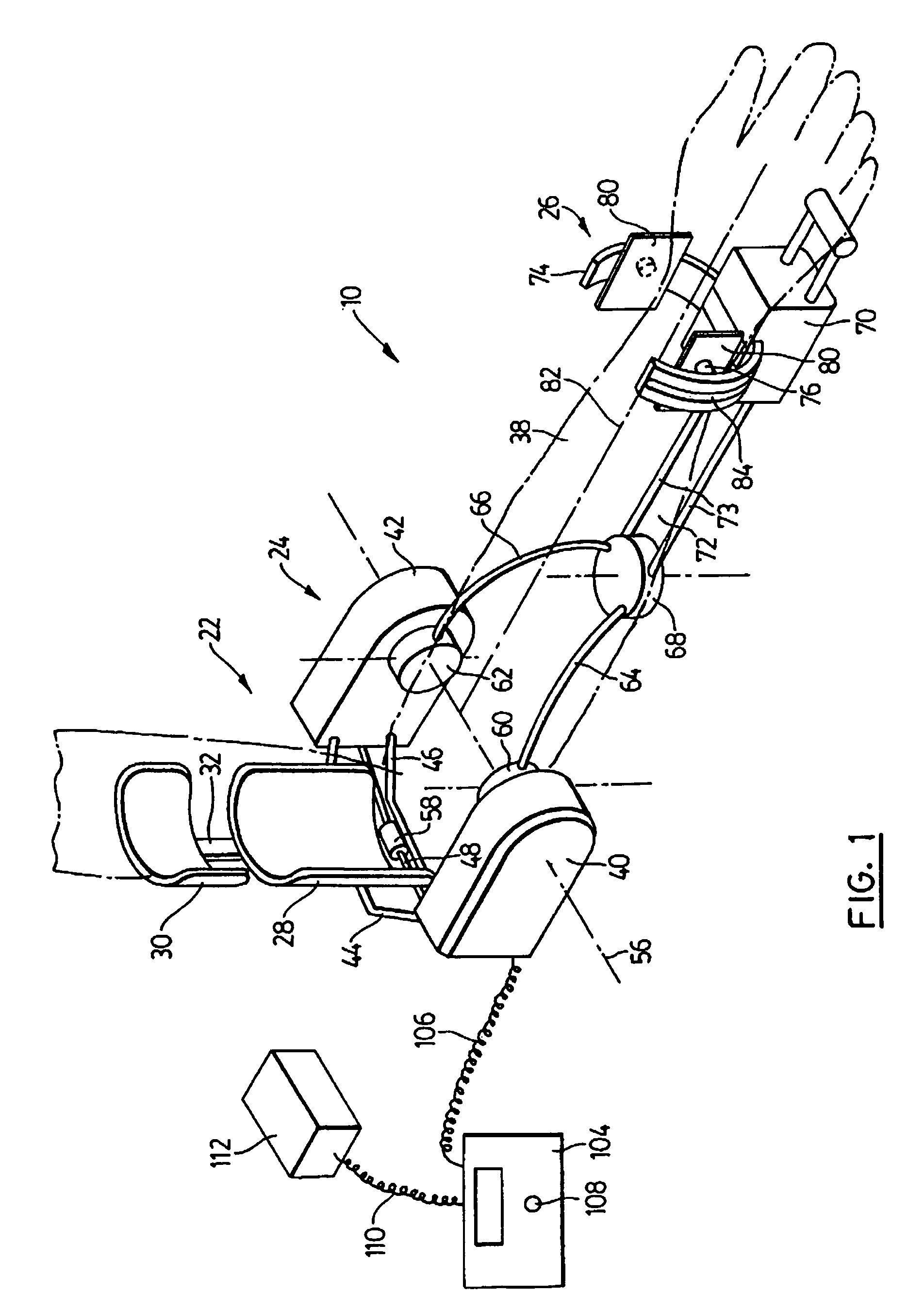
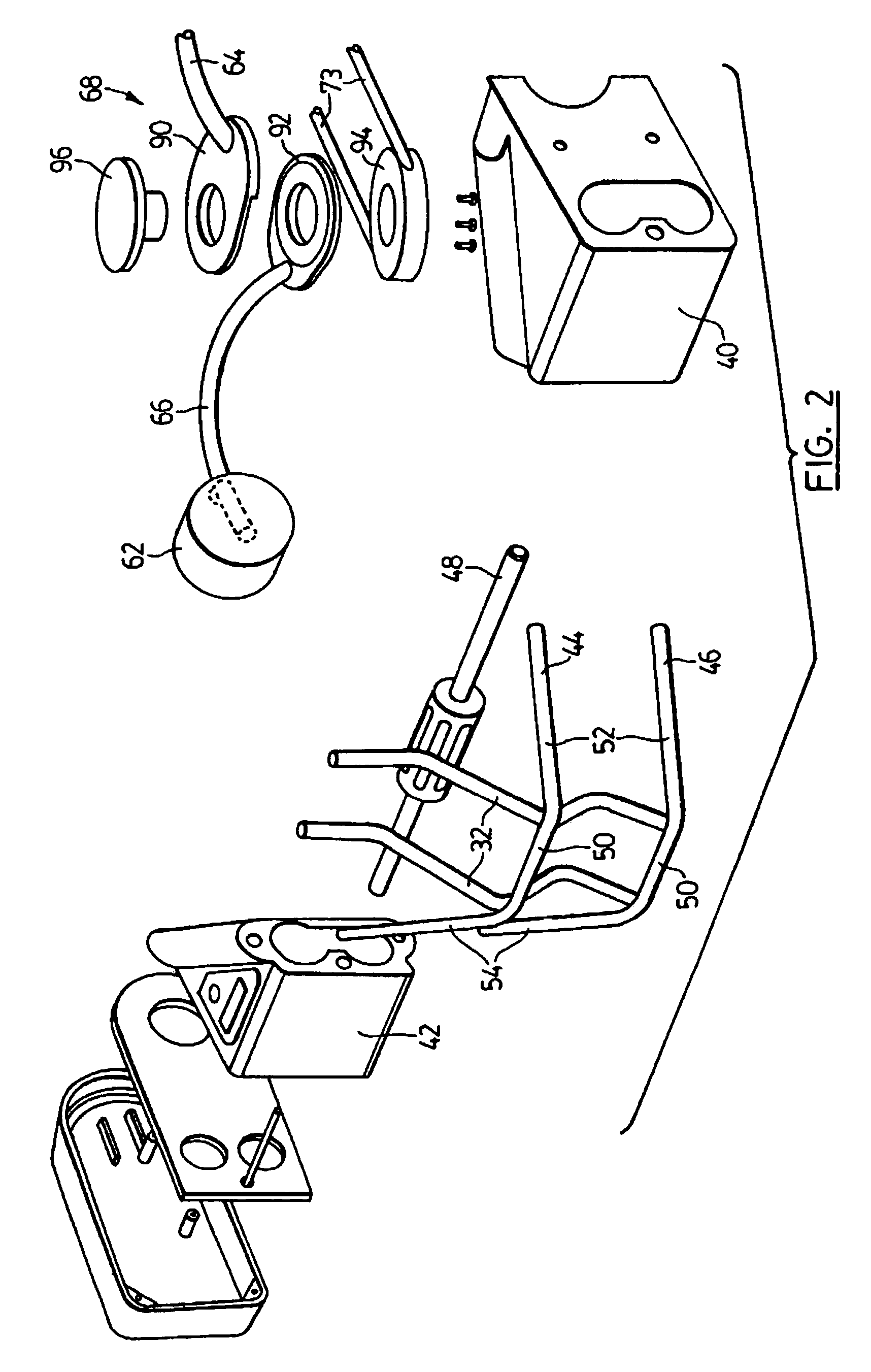
Combination pro/supination and flexion therapeutic mobilization device
InactiveUS7101347B2Control stressVariable flexionRestraining devicesChiropractic devicesEngineeringRotary actuator
A therapeutic mobilization device is disclosed. The device includes a flexion assembly, a pro / supination assembly and a valgus carrying angle compensation device. The flexion assembly has an arm attachment assembly and an elbow actuator and the elbow actuator defines and axes of rotation. The pro / supination assembly is attached to flexion assembly and has a distal forearm attachment assembly and a pro / supination actuator operably connected thereto. The valgus carrying angle compensation device is operably attached to the flexion assembly and the pro / supination assembly. Preferably the pro / supination assembly is slidably mounted on a housing shaft whereby during flexion the pro / supination assembly is free to move along the housing shaft. Further, preferably the arm attachment assembly includes an attachment ring and an adjustable clamp pivotally attached thereto whereby the attachment ring defines a pro / supination axis and the adjustable clamp pivots orthogonally to the pro / supination axis.
Owner:QAL MEDICAL LLC +2
Auxiliary training tool for comprehensive rehabilitation of cerebral palsy
The invention discloses an auxiliary training tool for comprehensive rehabilitation of cerebral palsy. The auxiliary training tool comprises a chassis, a lower limb exoskeleton device and a suspension device, wherein the chassis comprises universal casters with the locking function, a lower chassis, an upper chassis and an exoskeleton device inclination adjusting mechanism; the lower limb exoskeleton device is fixedly mounted on the chassis, and can realize rehabilitation training such as flexion / extension, adduction / abduction and pronation / supination of hip joints, flexion / extension of the knee joint, and dorsi-flexion / plantar-flexion, strephenopodia / strephexopodia and pronation ans supination of feet; the suspension device is fixedly mounted on the chassis, and plays a role in slinging, weight reduction and upper body posture correction of paitents. The auxiliary training tool can help patients with cerebral palsy to correct the abnormal posture of lower limbs, carry out the rehabilitation training on all joints of the lower limbs, promotes the development of all the joints of the lower limbs, and gradually establishes the normal standing and walking functions.
Owner:国家康复辅具研究中心
Key device to measure pronation and supination of the forearm
There is disclosed herein a method for quantifying a user's motor skills. The method comprises the steps of voluntarily moving a motion sensing member for at least a part of one cycle, the cycle comprising movement in a first direction and a return direction, measuring at least one of regularity of the movement of the member and mean angular velocity of the member. The method may be performed simultaneously with two members. Further, the members may be actuated by various body parts including a finger, a hand, or a shoulder. The data generated by the movement of the motion sensor may be stored as modulated carrier frequency in order to perform the method in locations remote from laboratories or computing facilities.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Supination/pronation therapy device
An orthotic device promotes both supination and pronation of a patient's wrist. A forearm enclosure is adapted to substantially wrap around a forearm. A forearm support member is adapted to slidably receive the forearm enclosure wherein the support member wraps partially around the forearm enclosure. A post is mountable on the forearm enclosure. An anchor is mounted on the support member. A tensioning member is connected to the anchor and on the other end to the post, wherein a rotational force of supination or pronation will be created on the forearm enclosure depending on the direction which the tensioning members extend from the anchor to the post.
Owner:R & R HLDG
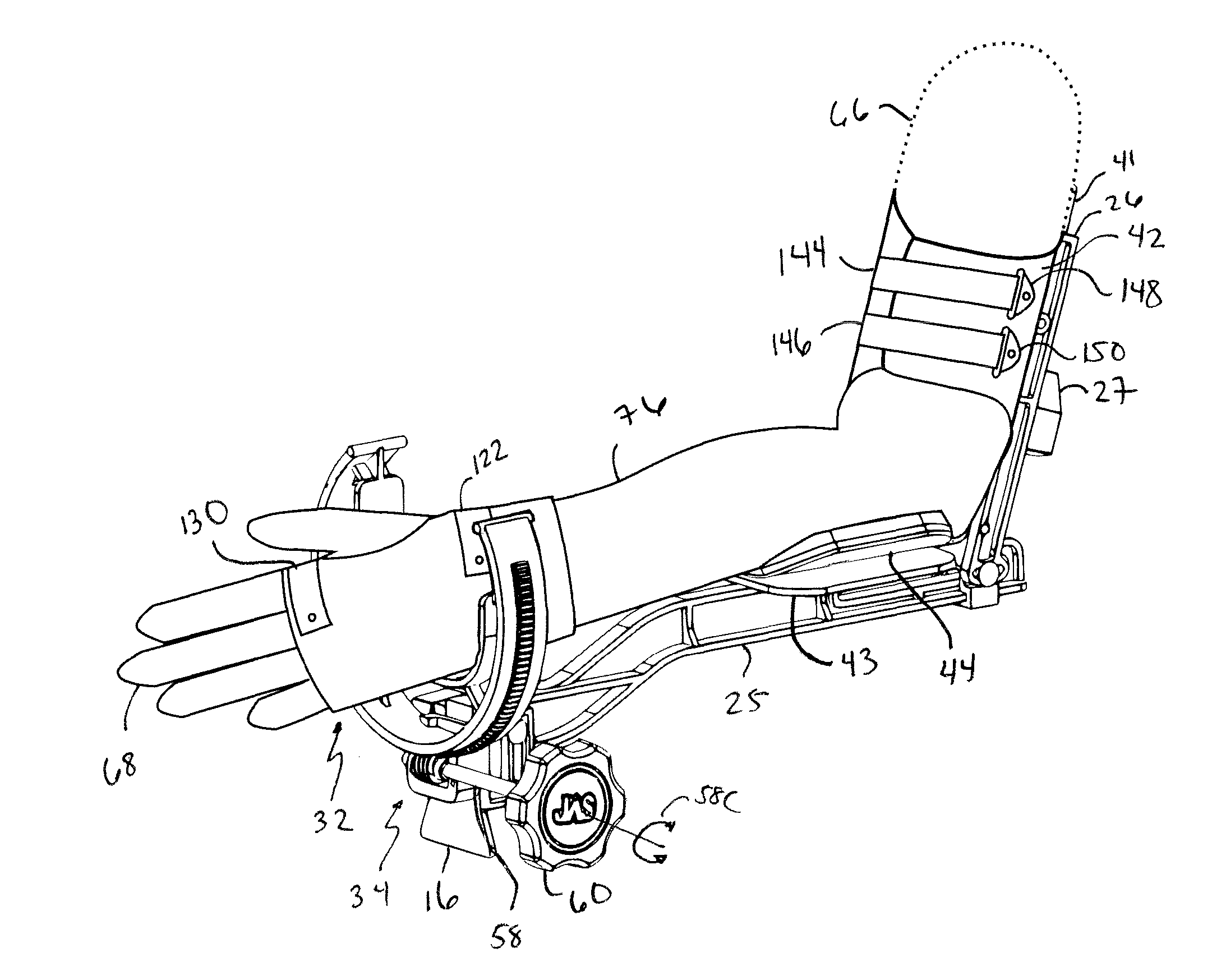
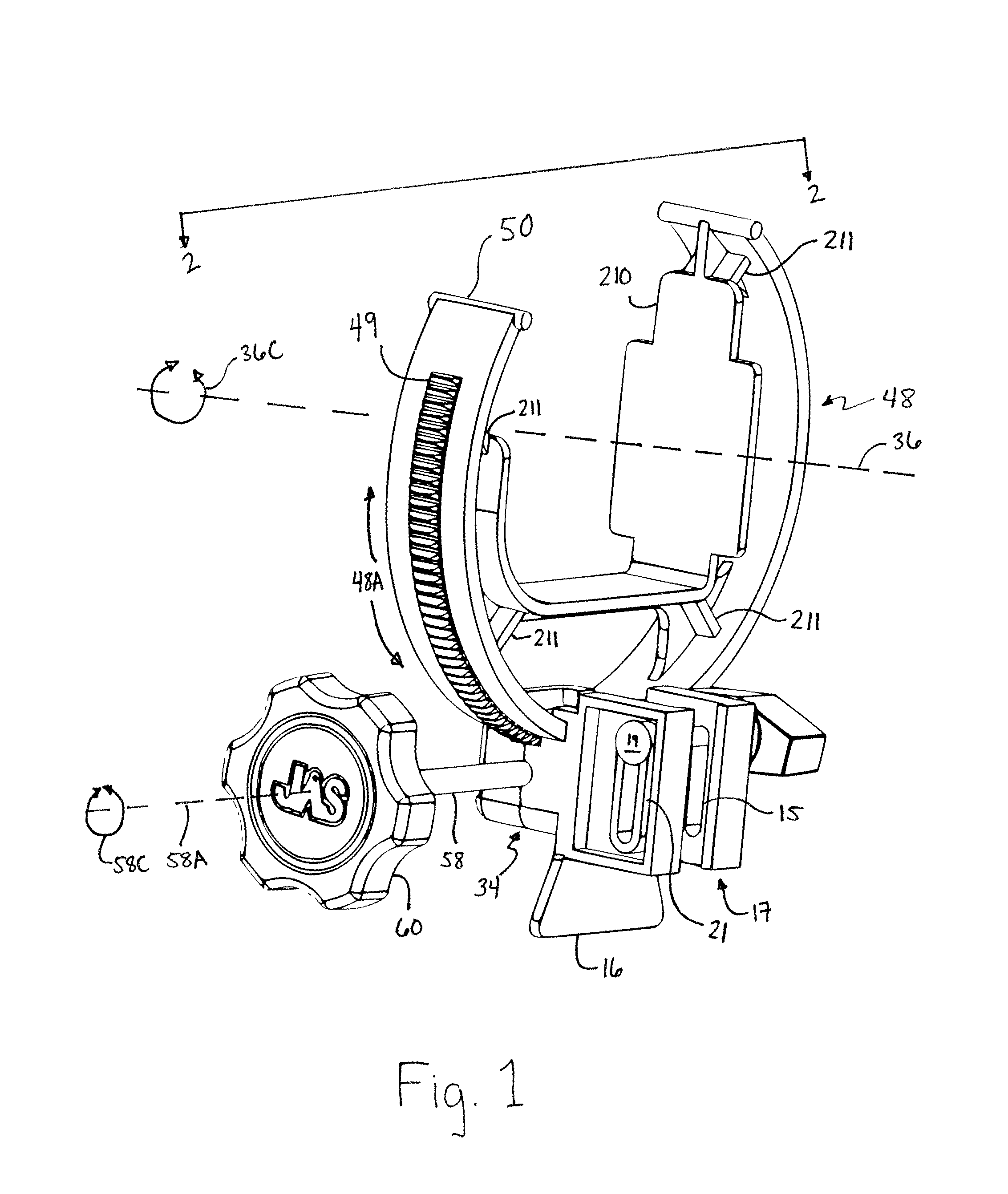
Orthosis apparatus and method of using an orthosis apparatus
The present invention provides a new and improved orthosis for use in effecting relative movement between bones in an arm of a patient. The apparatus includes a lower cuff gripping distal bone, such as a wrist, and an upper cuff gripping a proximal bone, such as an upper arm. The lower cuff is secured in a rotatable drive assembly substantially coincident to a longitudinal axis of a medial bone, such as the forearm, during rotational distal adjustment. The angle between the forearm and the upper arm is adjustable and can be securely fixed at a desired angle. The rotation of the rotatable drive assembly effectuates the pronation and supination of the hand and wrist relative to the patient's forearm. The orthosis of the present invention can be disassembled with interchanging parts substituted depending on the patient's needs.
Owner:BONUTTI RES
Customizable Component Insole System
This invention provides for individualized adjustment to a user's specific needs through the use of multiple variable size, thickness and rigidity components that can be placed or integrated into an insole. The current invention is an insole that incorporates, but is not limited to: (1) a base layer with various depressions, (2) a metatarsal dome, (3) a first metatarsal head pad, (2) a forefoot wedge to create a pronation moment around the midfoot joint, (3) a heel cushion, (4) a heel lift to raise the heel area of the foot, (5) a rearfoot wedge to increase the supination moments around the subtalar joint, and (6) an arch support of a specific stiffness or with varying stiffness.
Owner:IMPLUS FOOTCARE
Method of determining axial alignment of the centroid of an edge gripping end effector and the center of a specimen gripped by it
InactiveUS20060045719A1Minimizes specimen damage and production of contaminant particleQuickly and accurately transferMechanical apparatusData processing applicationsEngineeringActuator
A method determines axial alignment between the centroid of an end effector and the effective center of a specimen held by the end effector. The method is implemented with use of an end effector coupled to a robot arm and having a controllable supination angle. A condition in which two locations of the effective center of the specimen measured at 180° displaced supination angles do not lie on the supination axis indicates that the centroid is offset from the actual effective center of the specimen.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Seven-freedom-degree upper limb rehabilitation robot based on combination drive
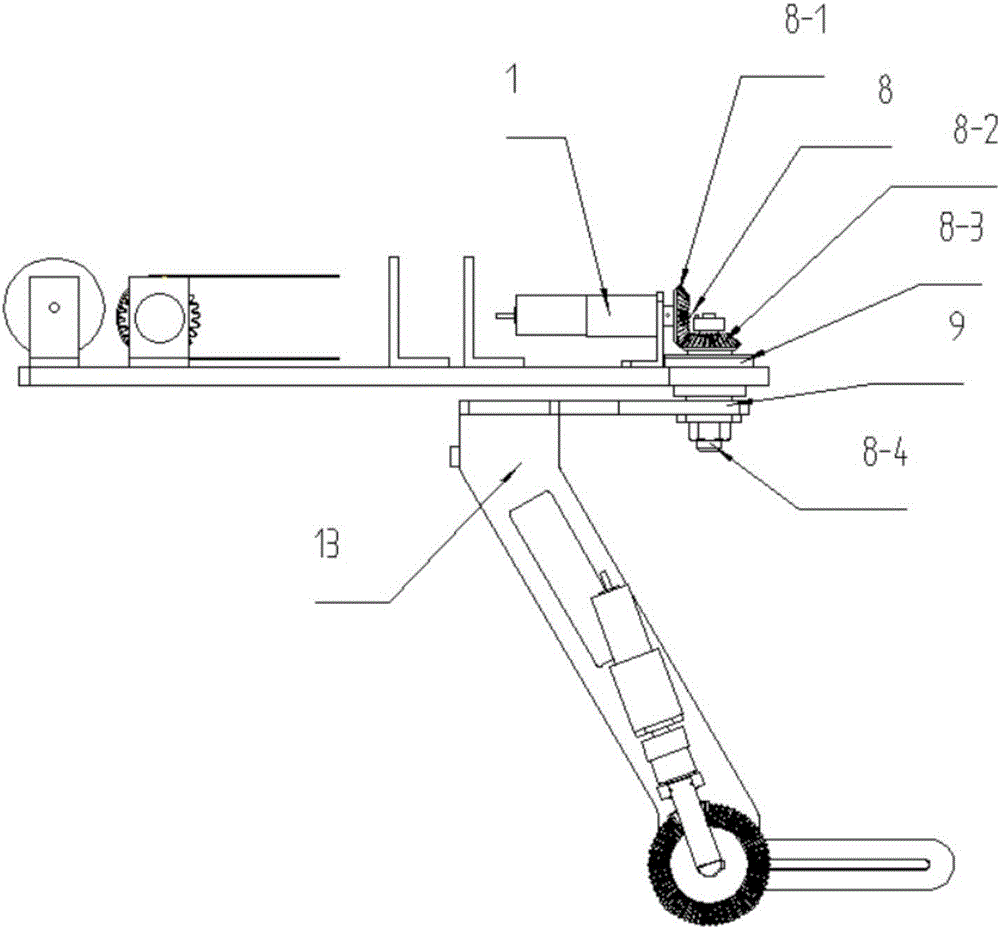
The invention discloses a seven-freedom-degree upper limb rehabilitation robot based on combination drive, and relates to the technical field of medical rehabilitation. The rehabilitation robot comprises three modules, i.e., a shoulder joint medial rotation / lateral rotation movement module, a shoulder joint extension / flexion and adduction / abduction and elbow joint extension / flexion and pronation / supination module and a wrist joint radial side flexion / ulnar side flexion and dorsal flexion / palmer flexion movement module, and the rehabilitation robot can achieve movement of seven freedom degrees. Under the coordination of the seven freedom degrees, the robot can simulate and achieve all types of movement of the upper limbs of a human body; the seven freedom degrees can singly achieve independent movement of each joint and also can achieve spatial motion through linkage motion of all the joints. The rehabilitation robot is designed to be more suitable for the structure of the human body, and the movement process of the rehabilitation robot is closer to the movement rule of human arms; a wrist joint part of the rehabilitation robot is driven by a steel wire rope, and a drive motor is moved backwards to be installed on a shoulder joint cantilever horizontal plate; thus, the weight of the wrist joint part is reduced, and the wrist joint part is more convenient to control and simpler and more compact in structure.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Counterforce brace
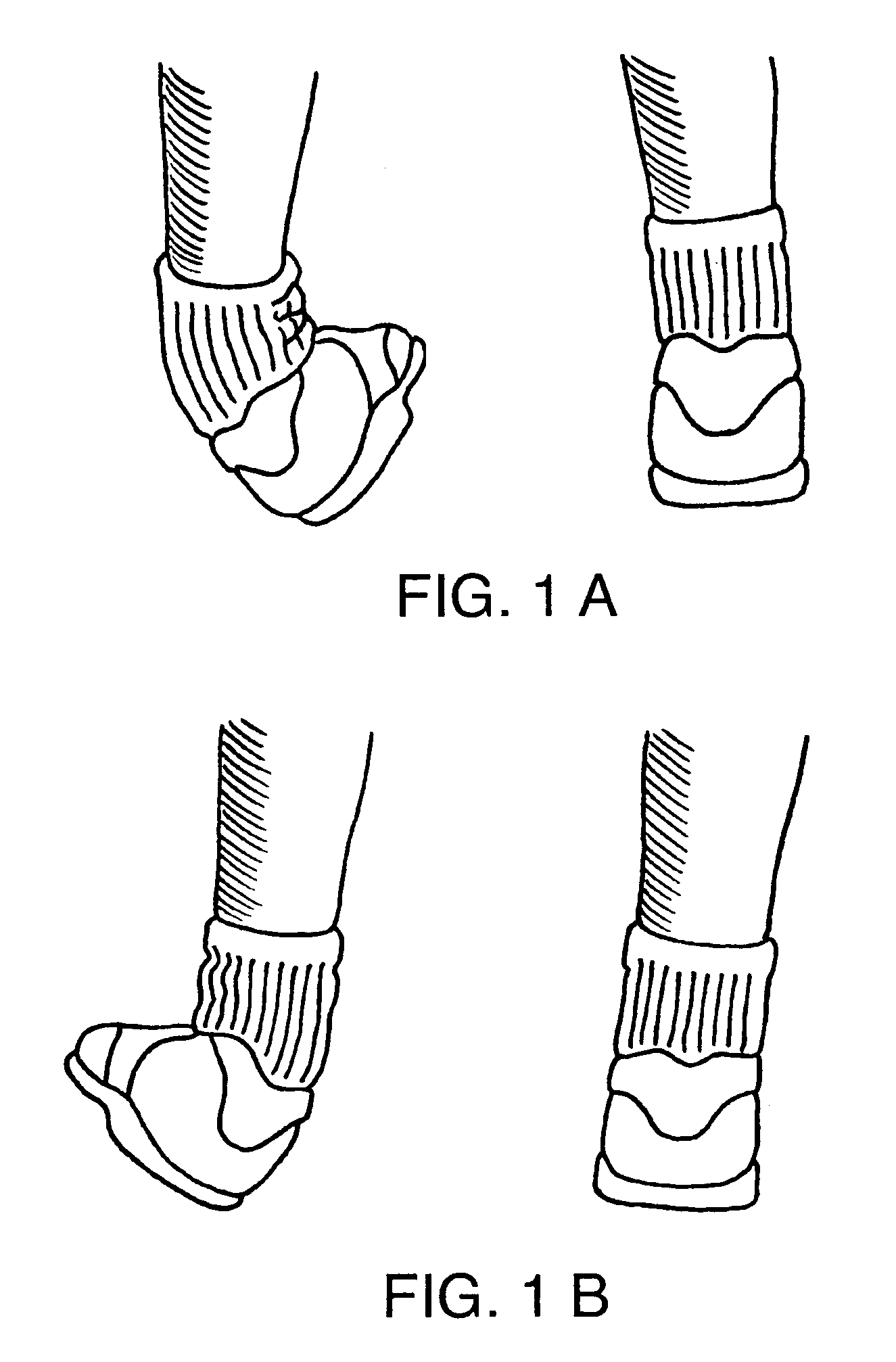
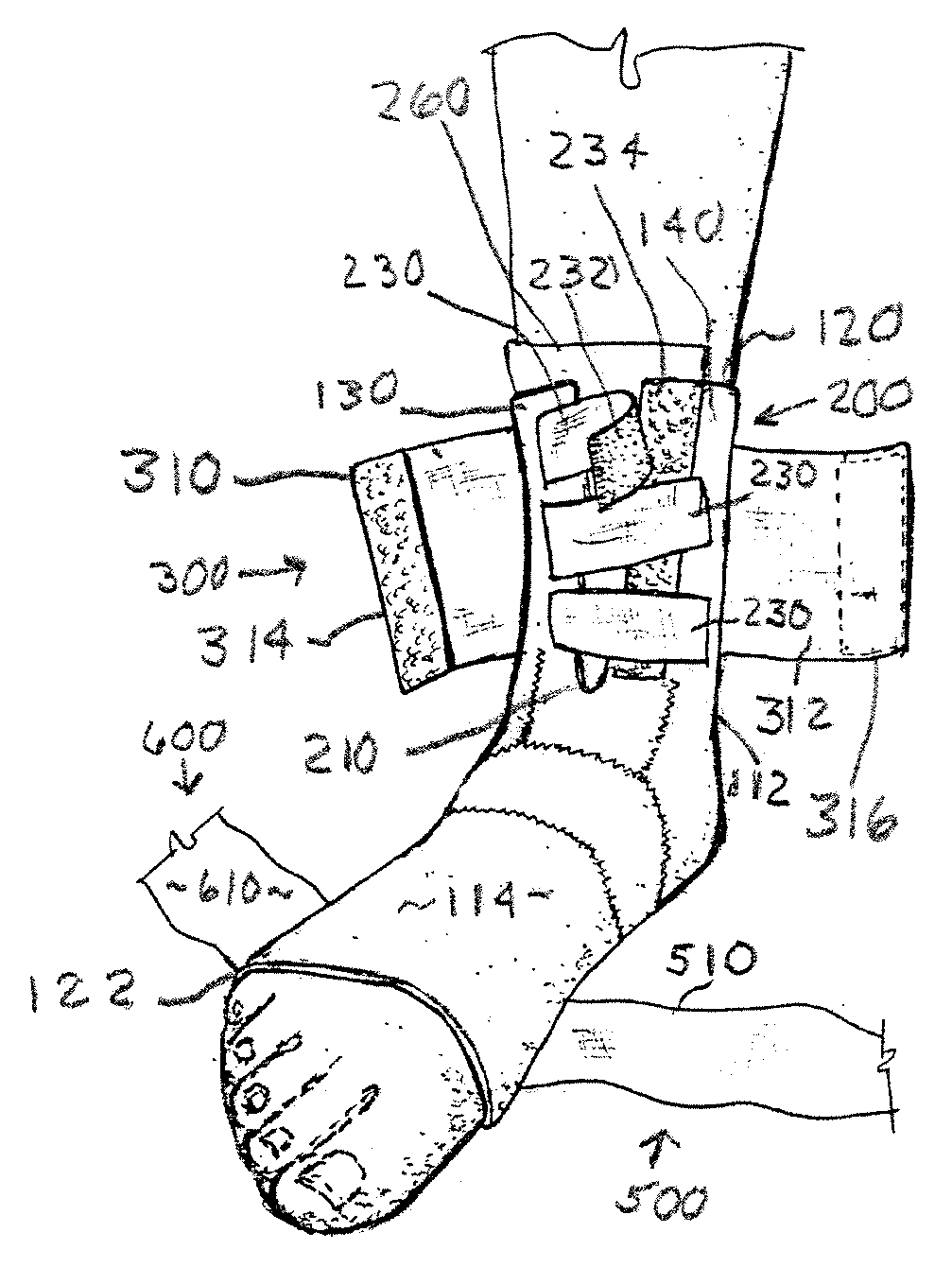
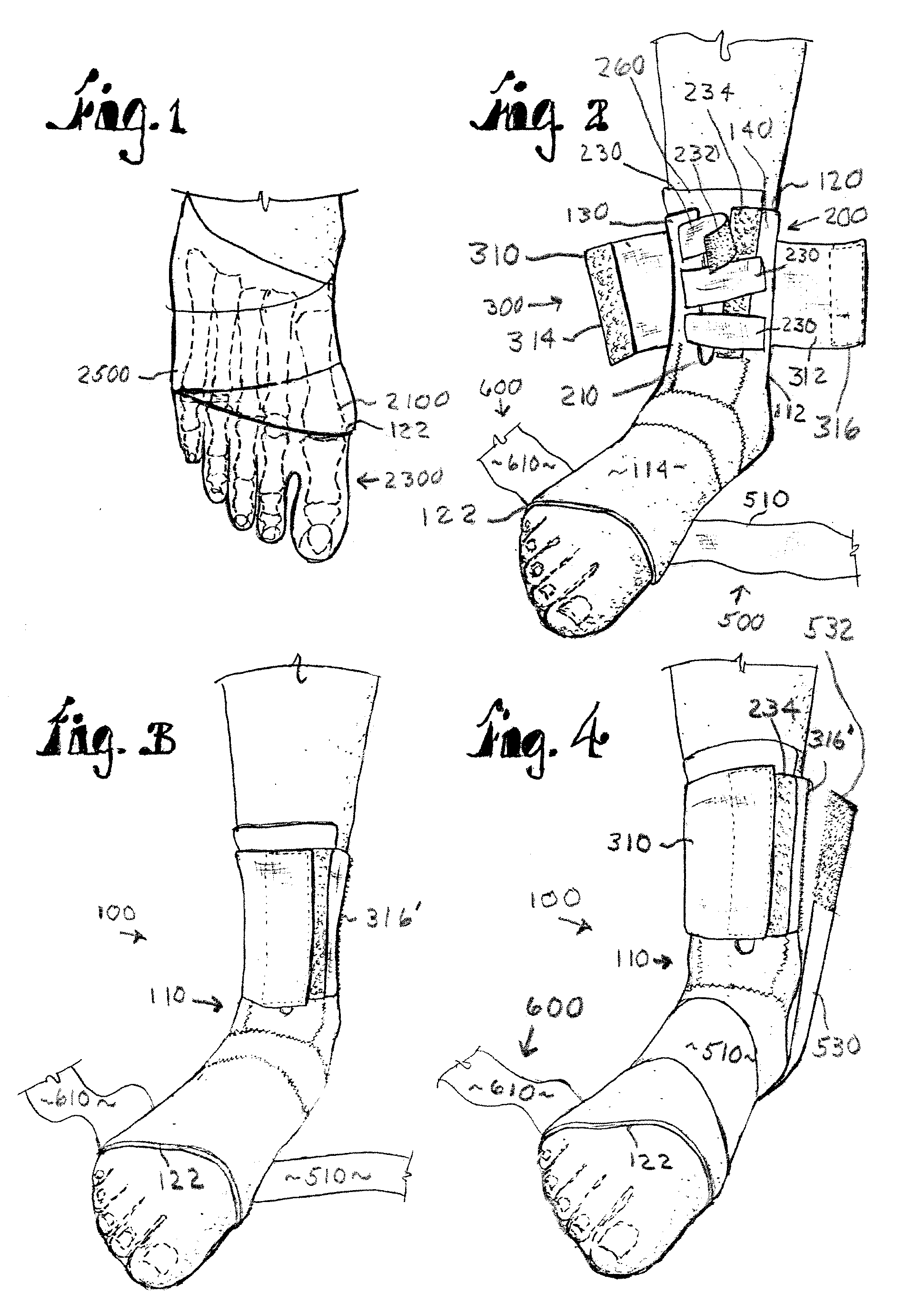
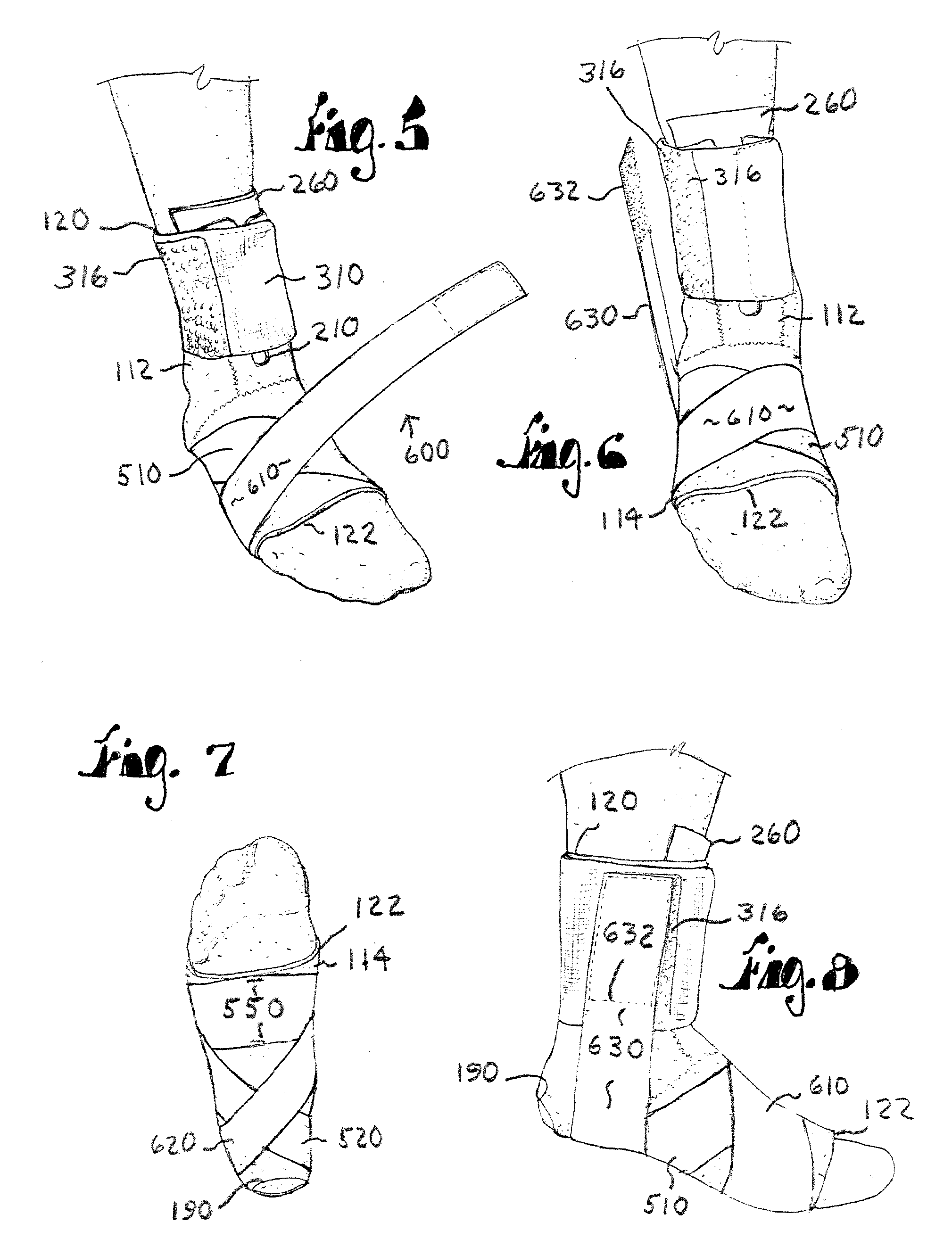
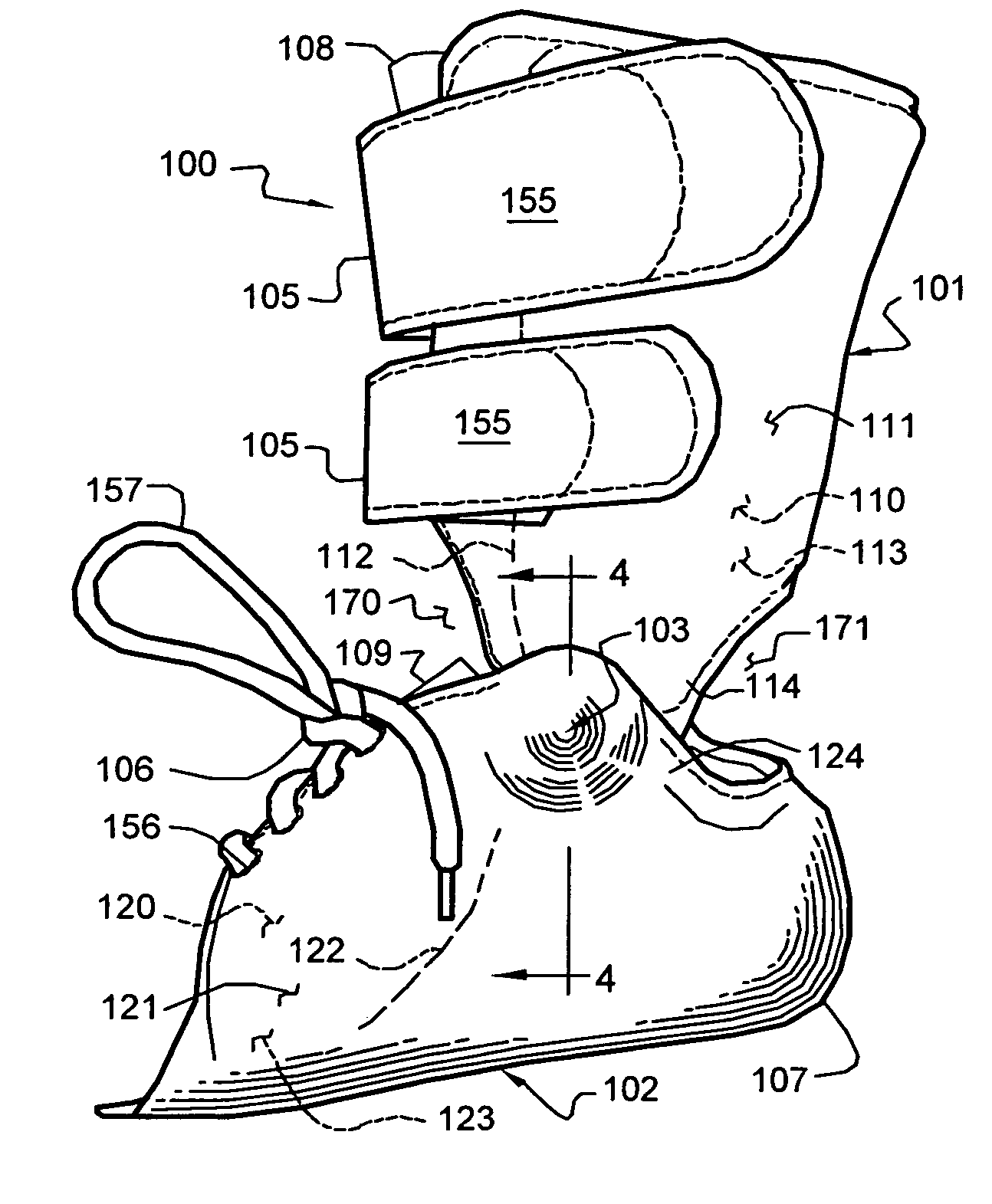
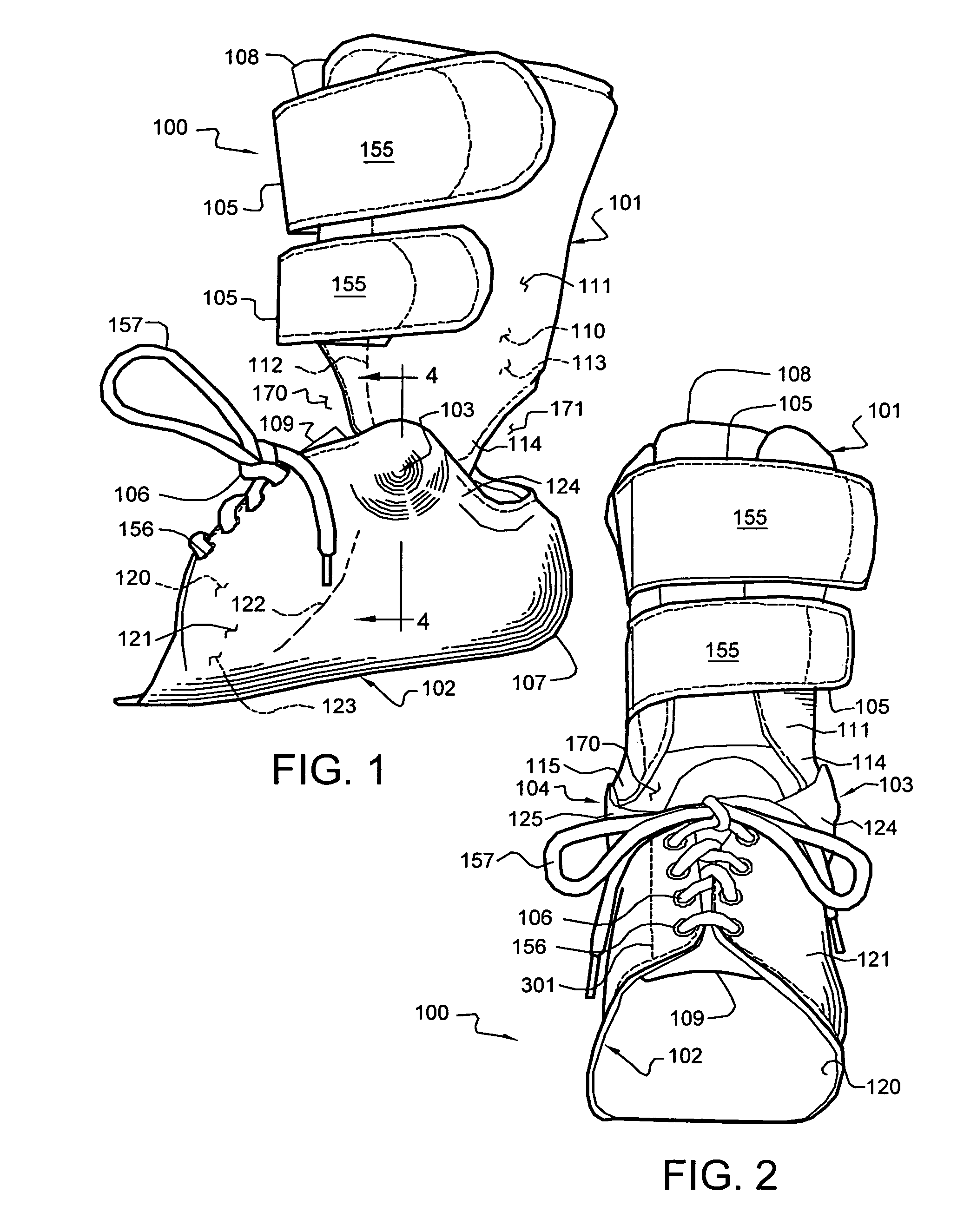
InactiveUS20090105704A1Resist excessive pronationResist supinationDiagnosticsFeet bandagesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLocking mechanism
A stabilization brace presents a compressive, sock-like body for a compressive fit about the ankle joint and forefoot. A pair of force straps extends from the metatarsal heads and is wound in a preferred manner along opposed regions of the foot and ankle to offer countervailing forces therealong. First and second closure systems secure the body to the foot and offer circumferential support thereto. The brace resists excessive supination and pronation of the foot, ankle joint and underlying structures. Three embodiments of the brace are shown wherein one end of the force straps are attached to a zone adjacent the metatarsals as well as bifurcated ends attached to the metatarsal zone and a second zone spaced therefrom. A third embodiment presents bifurcated ends attached at one zone adjacent the metatarsals and another zone of the rear of the Achilles which presents an enhanced heel locking mechanism.
Owner:GORDON JR HOWARD A
Methods and devices for preventing ankle sprain injuries
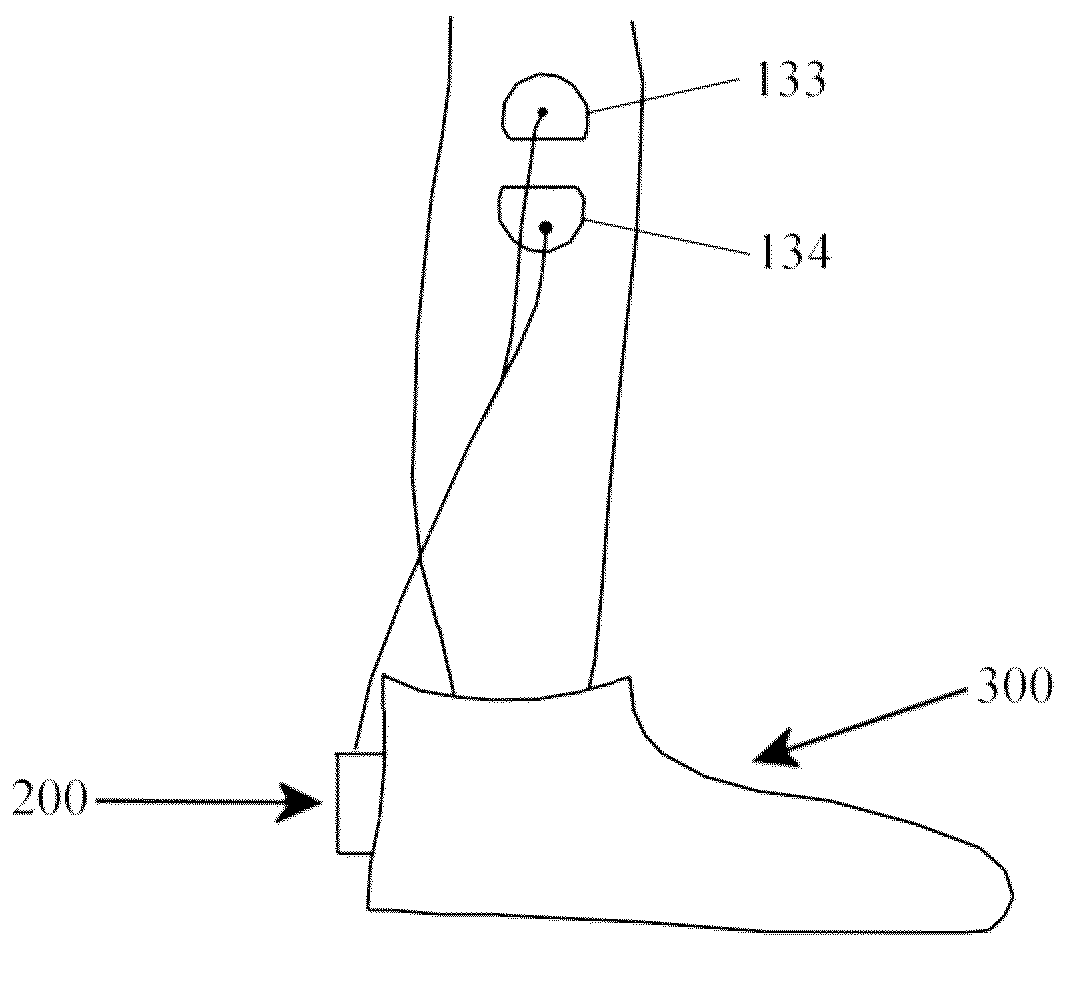
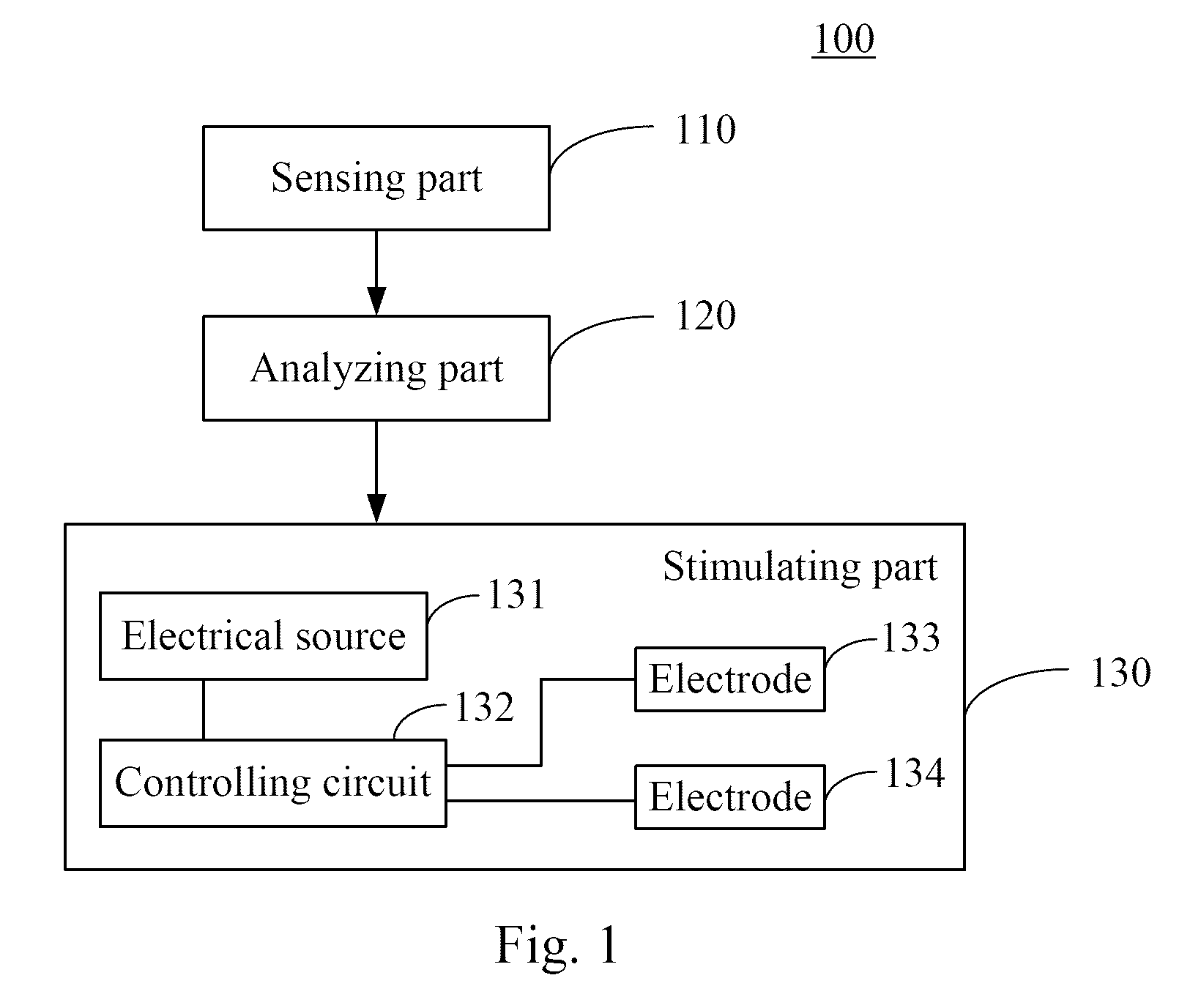
ActiveUS20100042182A1Avoid injuryElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensing dataAnkle motion
Devices and methods for preventing ankle sprain injuries. To protect the ankle joint from acute ankle supination or inversion sprain injuries, the device comprises a sensing part configured to sense data of an ankle motion; an analyzing part configured to analyze the data to judge whether the motion is a sprain motion; and a stimulating part configured to stimulate one or more lower limb muscles against the motion in light of a result of the analyzing. The method also involves sensing data of an ankle motion; analyzing the data to judge whether the motion is a sprain motion; and stimulating one or more lower limb muscles against the motion if the motion is a sprain motion.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Counterforce brace
InactiveUS20060211968A1Resist excessive pronationResist supinationFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPronation of the foot
A stabilization brace presents a compressive, sock-like body for a compressive fit about the ankle joint and forefoot. A pair of force straps extend from the metatarsal heads and along the opposed lateral and medial regions of the foot and ankle to offer countervailing forces therealong. First and second closure systems secure the body to the foot and offer circumferential support thereto. The brace resists excessive supination and pronation of the foot, ankle joint and underlying structures.
Owner:GORDON HOWARD A JR
Athletic footwear and the like with integral supinator device
ActiveUS20050274045A1Avoid feetPrevent ankle injuriesSolesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAnkle injuryPosterior malleolus
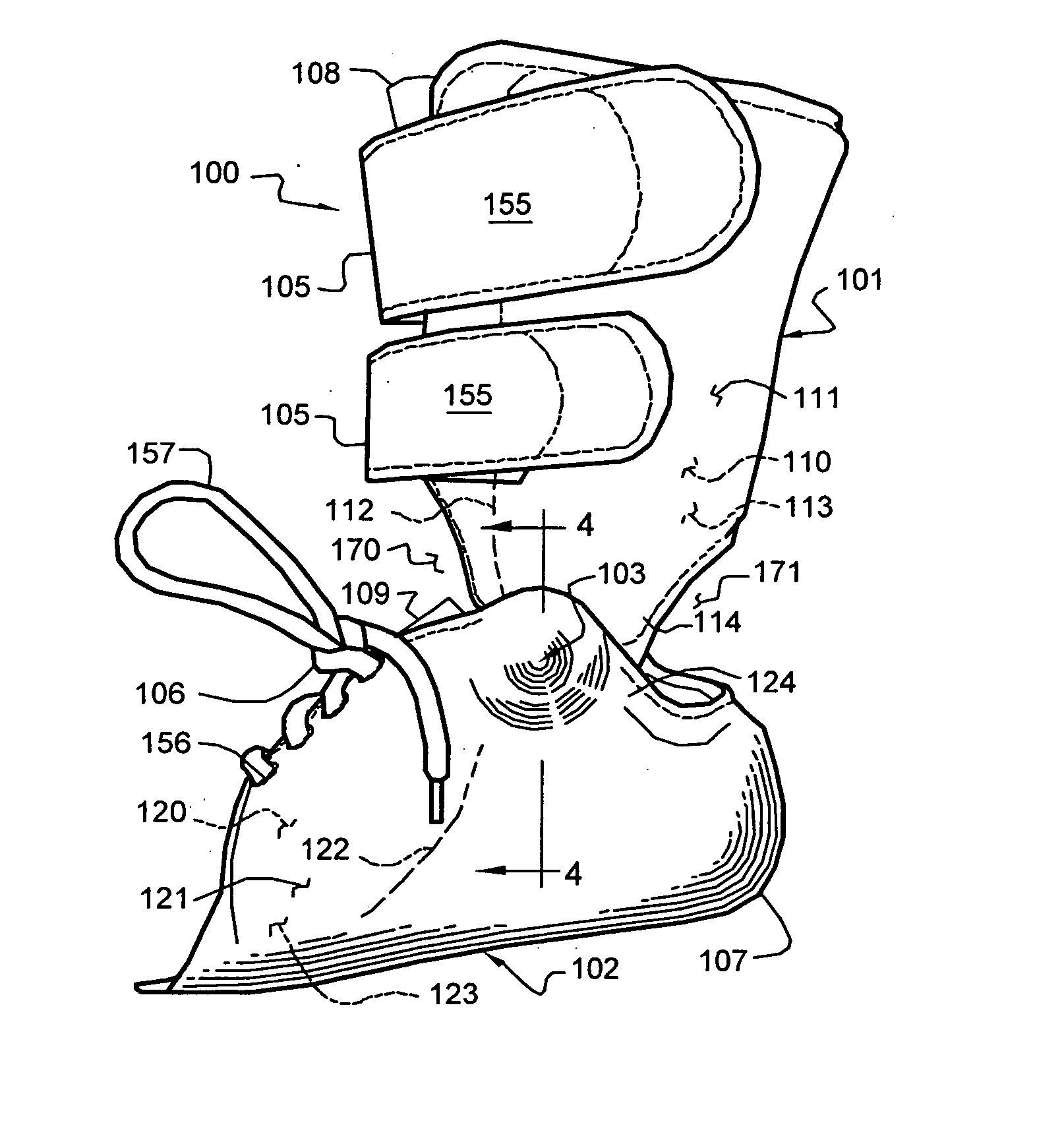
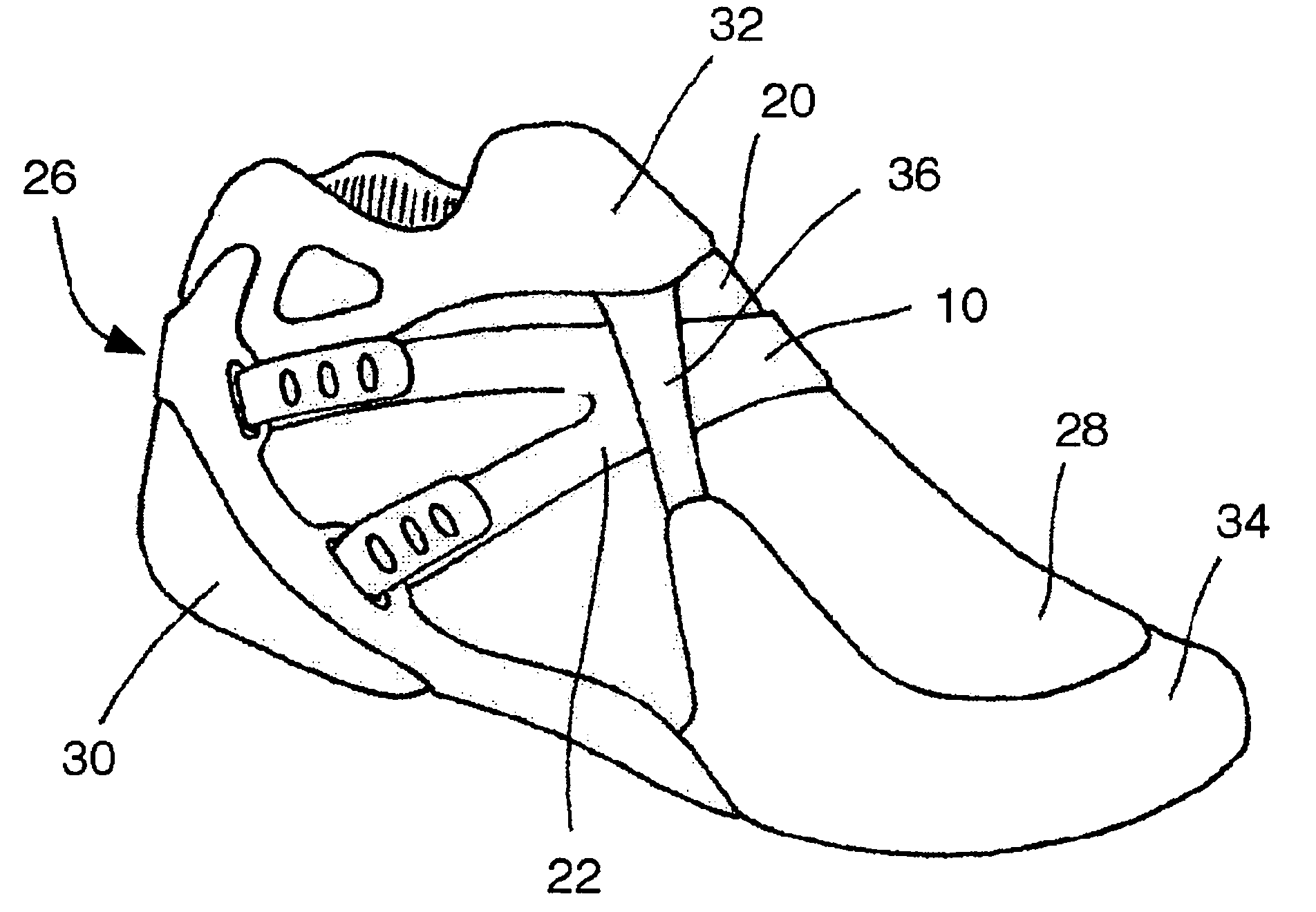
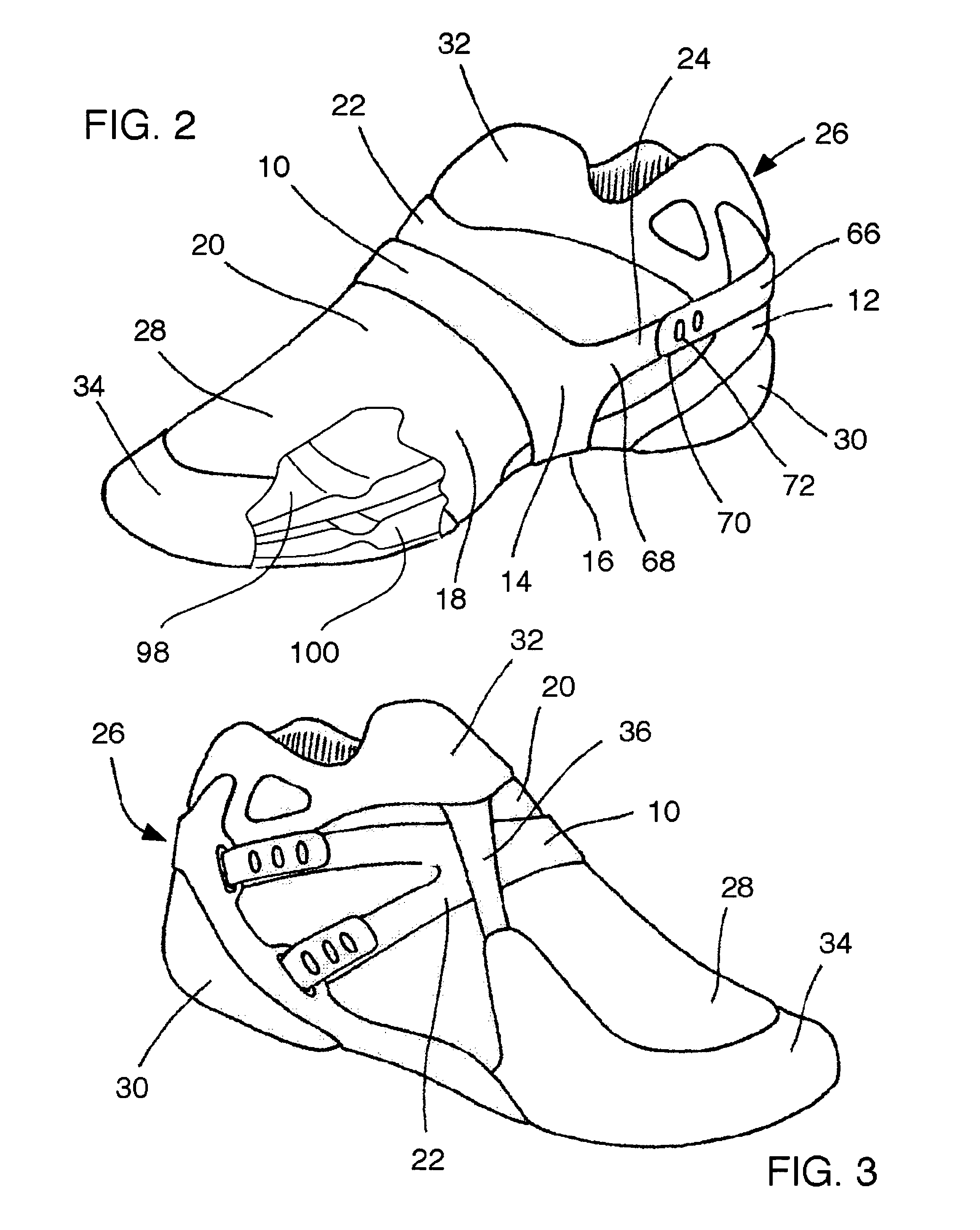
A supinator strap integrated with an athletic shoe, sock, or brace for reventing foot and ankle injuries. In the shoe, the supinator strap includes an arch support band that extends from the bottom of the shoe, just under the arch area, around the inner side of the shoe and over the top of the shoe, toward the outer side of the shoe. The supinator strap further includes a rear ankle support band that extends laterally from the arch support band and wraps from the inner side of the shoe, around the rear ankle / heel and toward the outer side of the shoe. In a preferred embodiment, both the foot and rear ankle support band and the arch support band are fully adjustable. The supinator strap provides additional support and stability to the foot and ankle when the shoe is worn, thereby helping to prevent injuries caused by excessive supination or pronation of the foot and ankle. A bridge support helps cushion the foot. An ankle stabilizing strap helps prevent ankle injuries by stabilizing the forefoot, heel, and ankle. In the sock and the brace, the supinator strap operates in a similar manner.
Owner:SELNER MARC
Articulated custom ankle-foot orthosis systems
ActiveUS7691076B2Guaranteed wearRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPronationsEngineering
Owner:ARIZONA AFO INC
Wrist and forearm exoskeleton
InactiveUS20150359697A1Large range of motionMuscle strengthChiropractic devicesEye exercisersPronationsEngineering
An exoskeleton device and method of using the same is provided that helps rehabilitate limbs such has the lower arm. Embodiments of the exoskeleton device have multiple degrees of freedom so that a limb such as the lower arm may flex or rotate in multiple directions to establish or re-establish neural connections in the brain. With the lower arm example, a person may grasp a handle in the exoskeleton and then flex the lower arm about a pronation / supination axis, a flexion / extension axis, and / or an abductor / adductor axis. The exoskeleton device has several modes of operation where actuators can aid the person's motion, resist the person's motion, or passively allow free motion of the person's limb.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
Non-sleep-interference sleeping posture and sleeping behavior testing identification method
ActiveCN104732250AAchieve non-distractionProtection of privacyCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringSupport vector machinePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A non-sleep-interference sleeping posture and sleeping behavior testing identification method includes the steps of extraction of human-bed interface compression shapes, classification and identification of sleeping postures, classification and identification of sleeping motion behaviors and analysis of sleeping behavior modes. A support vector machine is used for classification and identification of the sleeping postures, and the four sleeping postures of supination, left lateral decubitus, right lateral decubitus and prostration are identified on the basis of finite sample supervised training identification through classification of human-bed interface compression quantity matrixes; identification of the sleeping motion behaviors is achieved in the mode that logarithmic potential sensors synchronizing with human-bed interface compression quantity changes are used for outputting variation of voltage signals and obtaining signals generated when sleeper motion behavior accidents occur. According to the method, a technical support is provided for monitoring and evaluation of intellectualized design of a bed system or a mattress and healthy sleeping.
Owner:KEESON TECH CORP LTD
Electrical stimulation method for reduction of joint compression
InactiveUS8473064B2Reduce compressionDecreased co-contractionExternal electrodesElectricityPronations
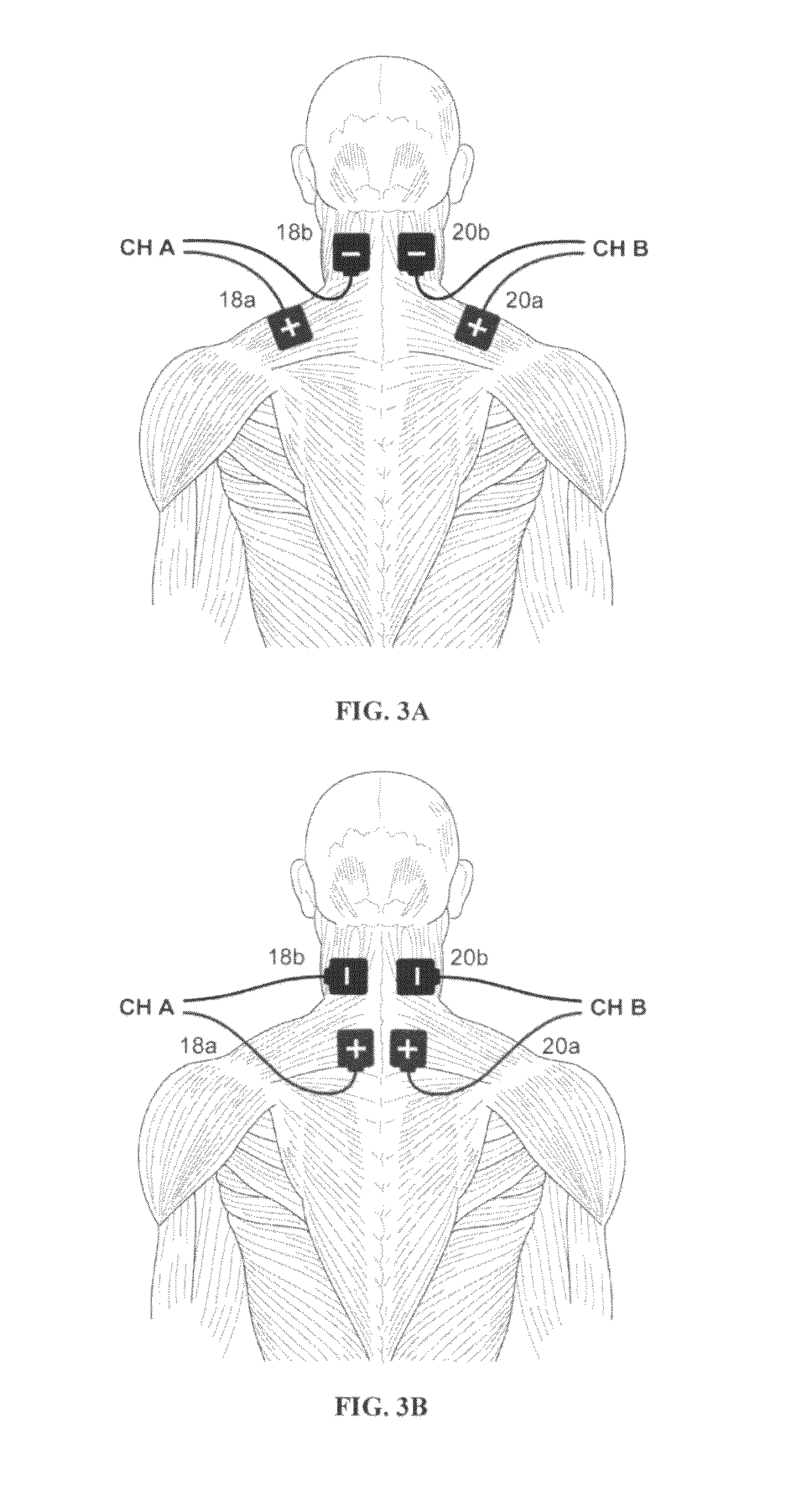
An electrical stimulation method for the reduction of joint compression utilizes an electrical stimulation device that includes a plurality of channels of electrodes each of which includes at least a first and second electrode positioned in electrical contact with tissue of at least two muscles crossing a joint. Agonist / antagonist muscles involved in abduction / adduction, flexion / extension, supination / pronation, protraction / retraction, and / or eversion / inversion of body regions via joint movement are stimulated with a patterned series of electrical pulses through channels of electrodes in accordance with a procedure for reducing joint compression. The patterned series of electrical pulses may comprise: a plurality of cycles of a biphasic sequential pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a biphasic overlapping pulse train pattern; a plurality of cycles of a triphasic sequential pulse train pattern; and a plurality of cycles of a triphasic overlapping pulse train pattern.
Owner:ACCELERATED CARE PLUS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com