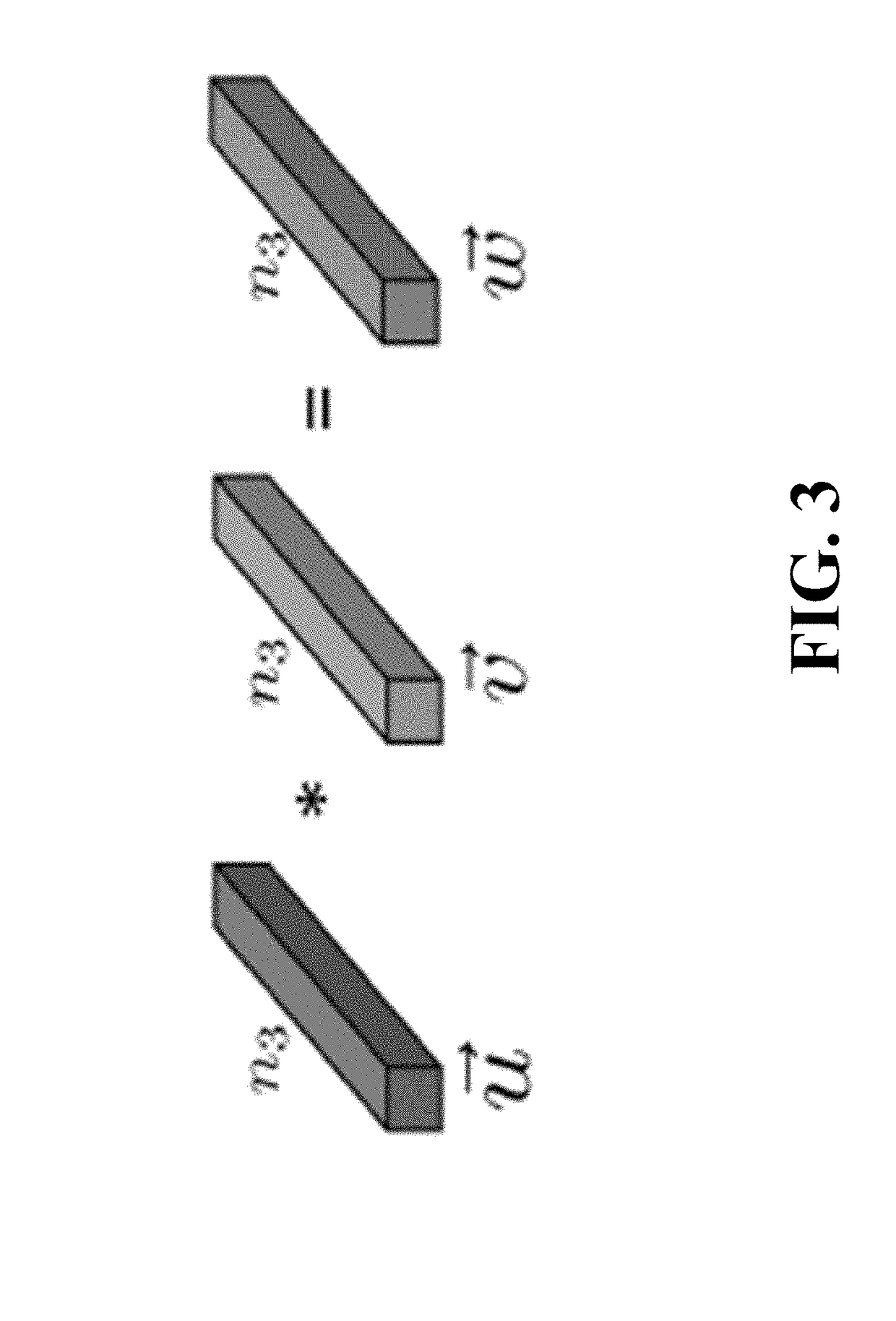
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Sparse image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sparse image is a type of disk image file used on macOS that grows in size as the user adds data to the image, taking up only as much disk space as stored in it. Encrypted sparse image files are used to secure a user's home directory by the FileVault feature in Mac OS X Snow Leopard and earlier. Sparse images can be created using Disk Utility.
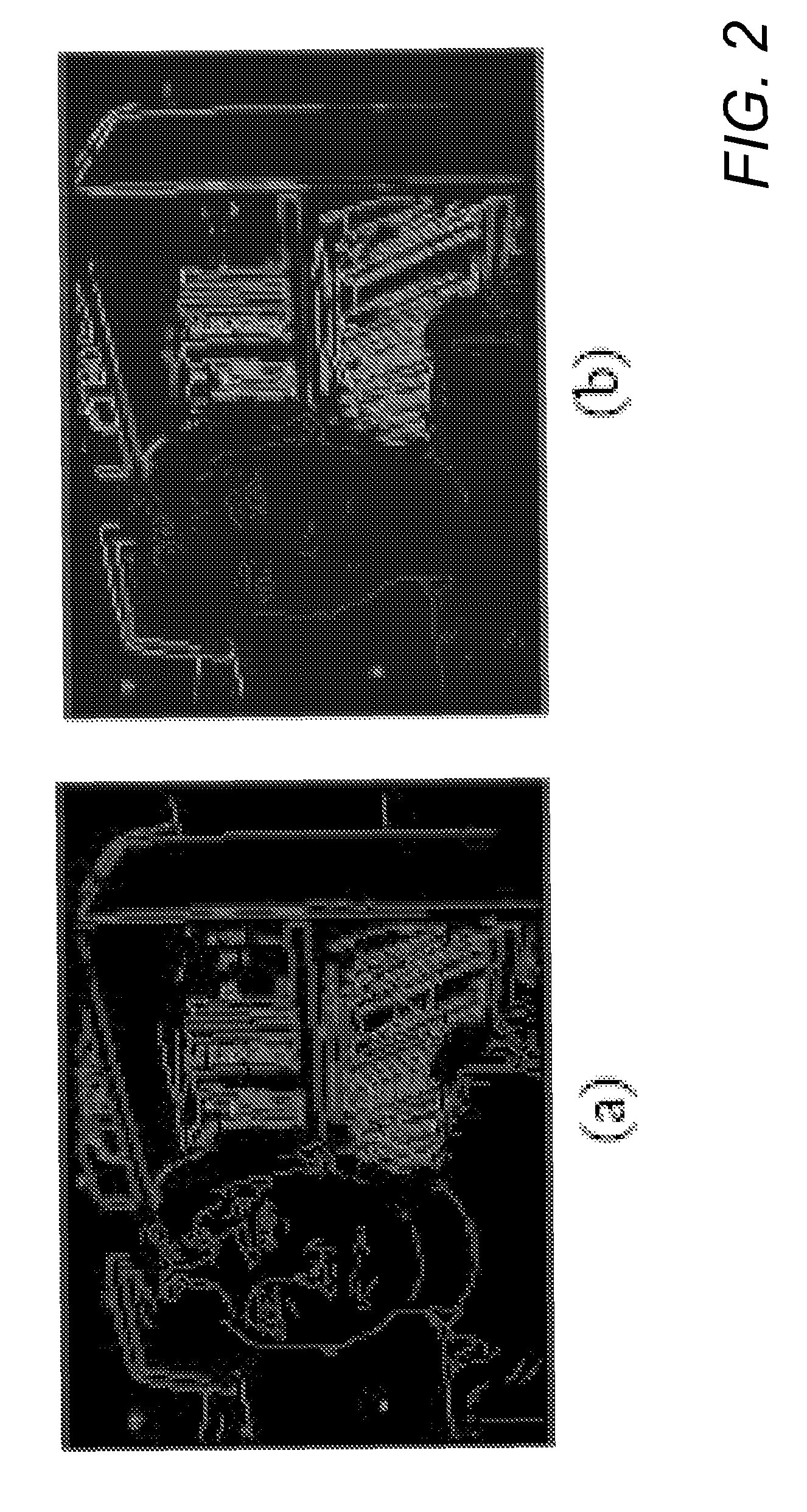
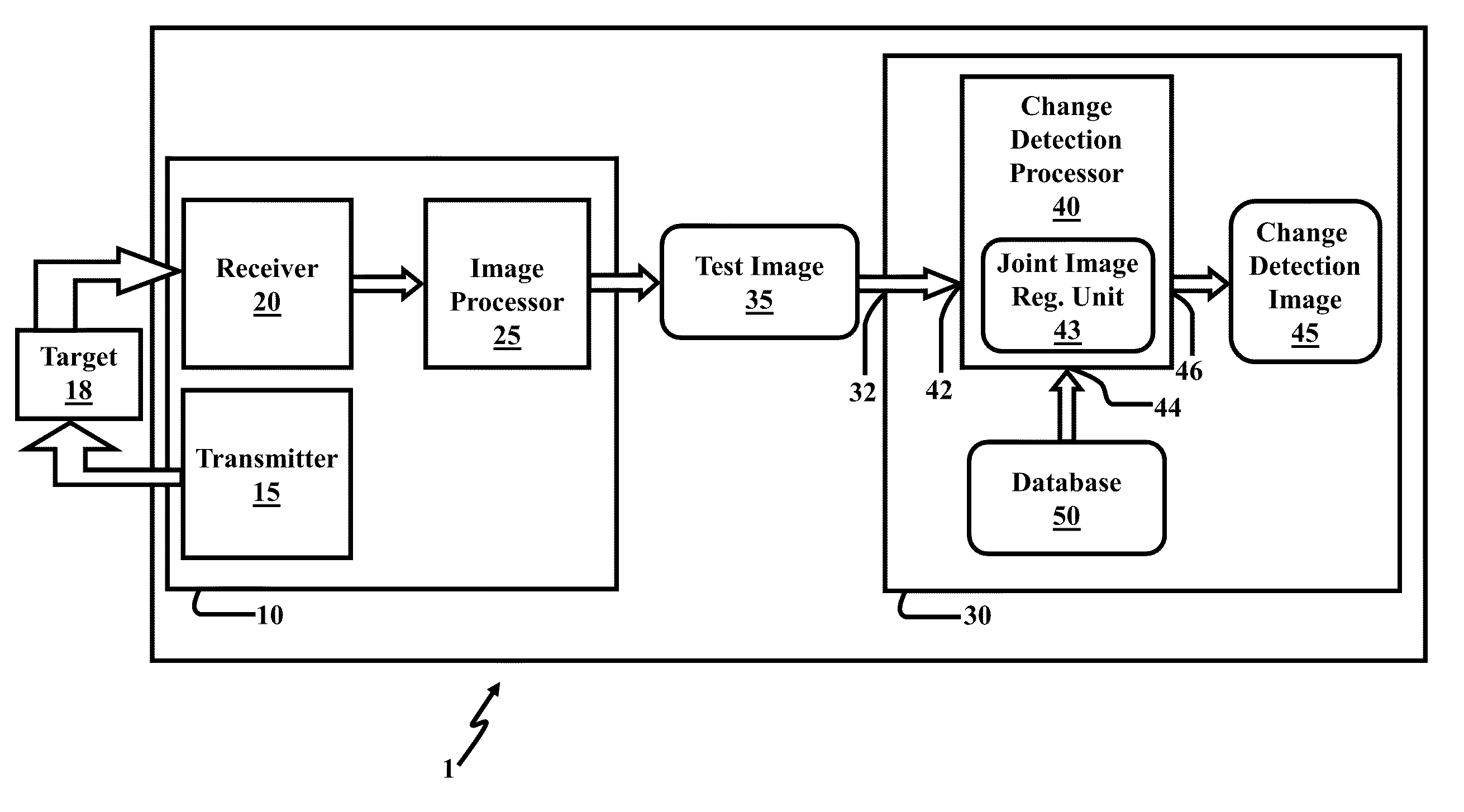
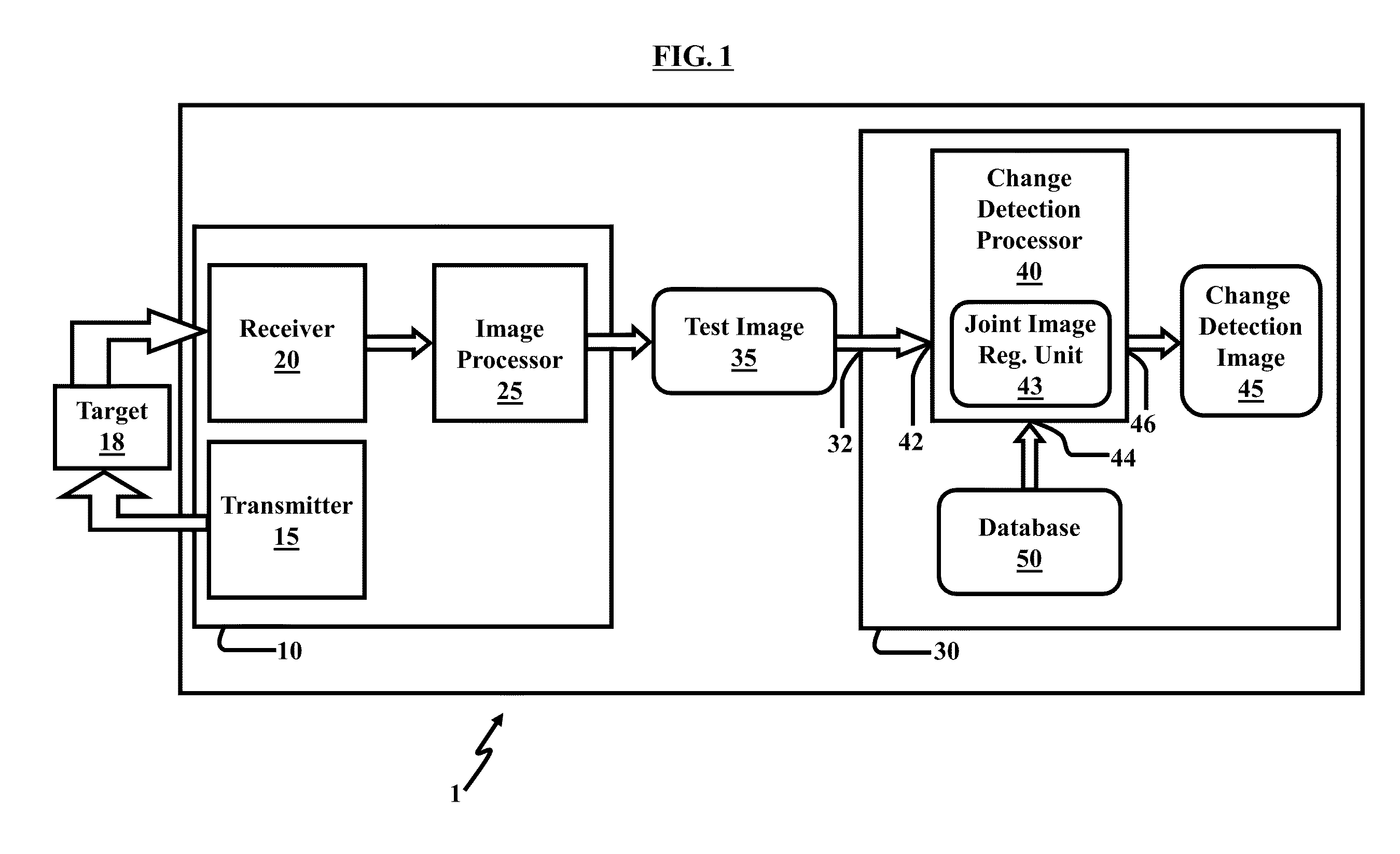
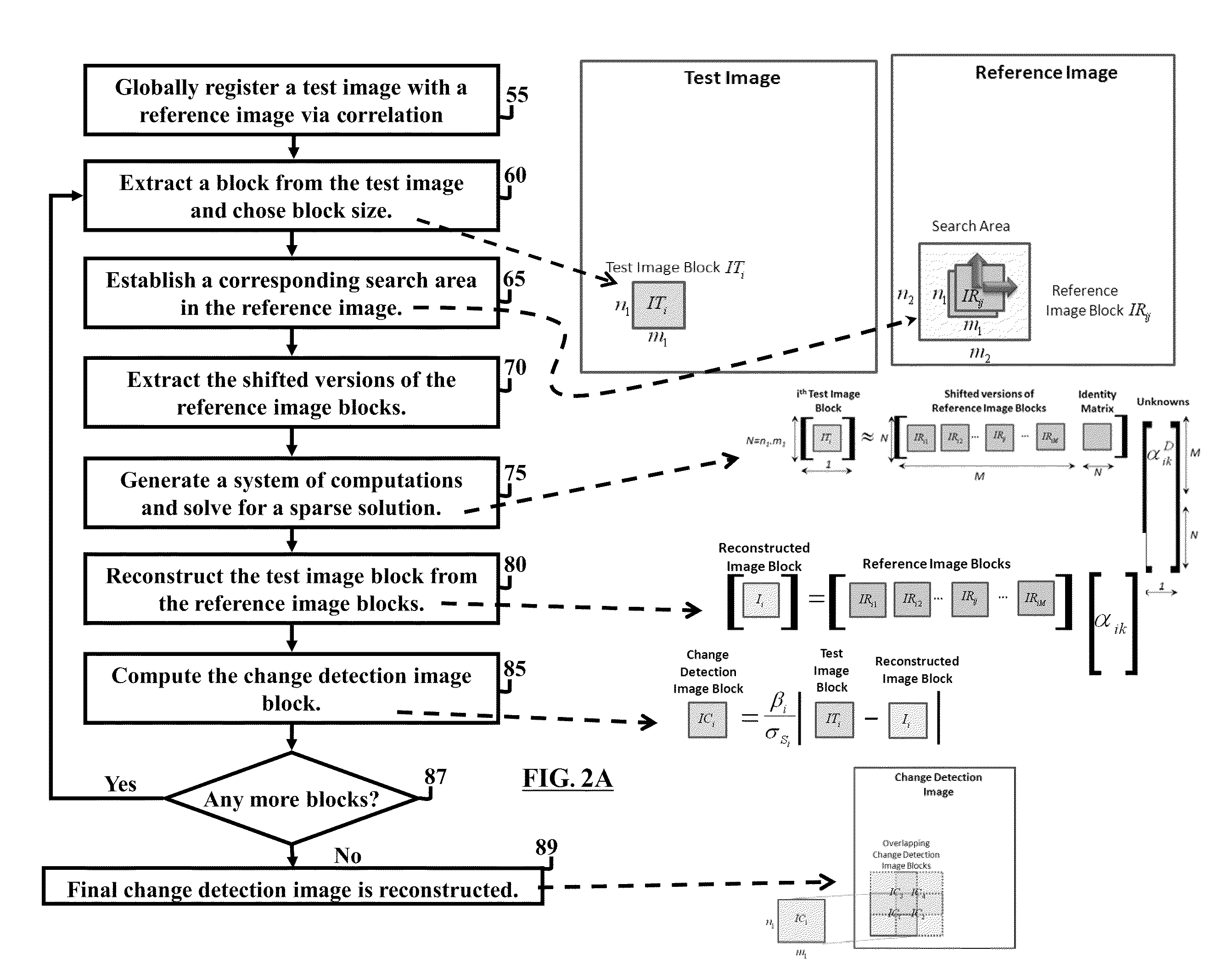
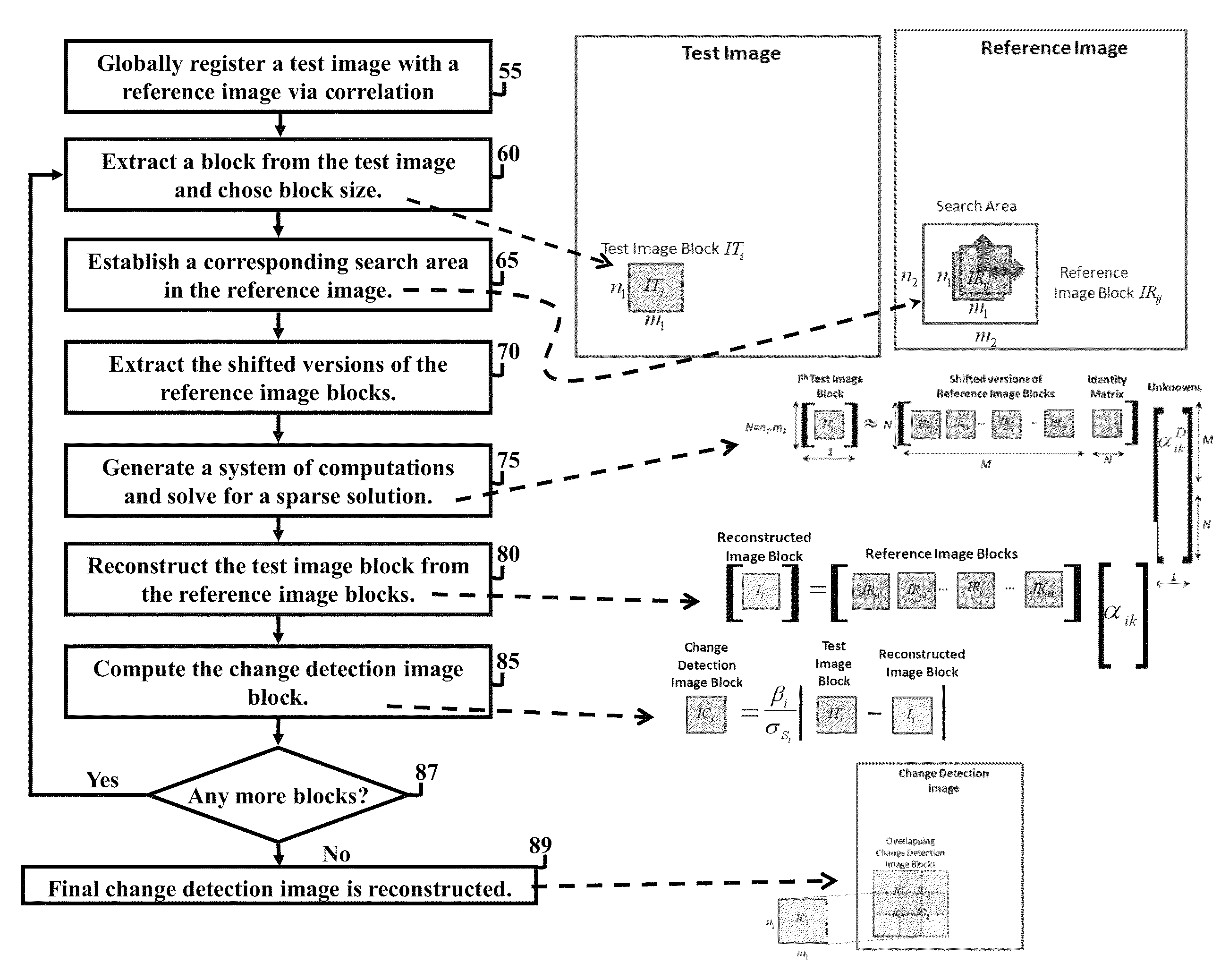
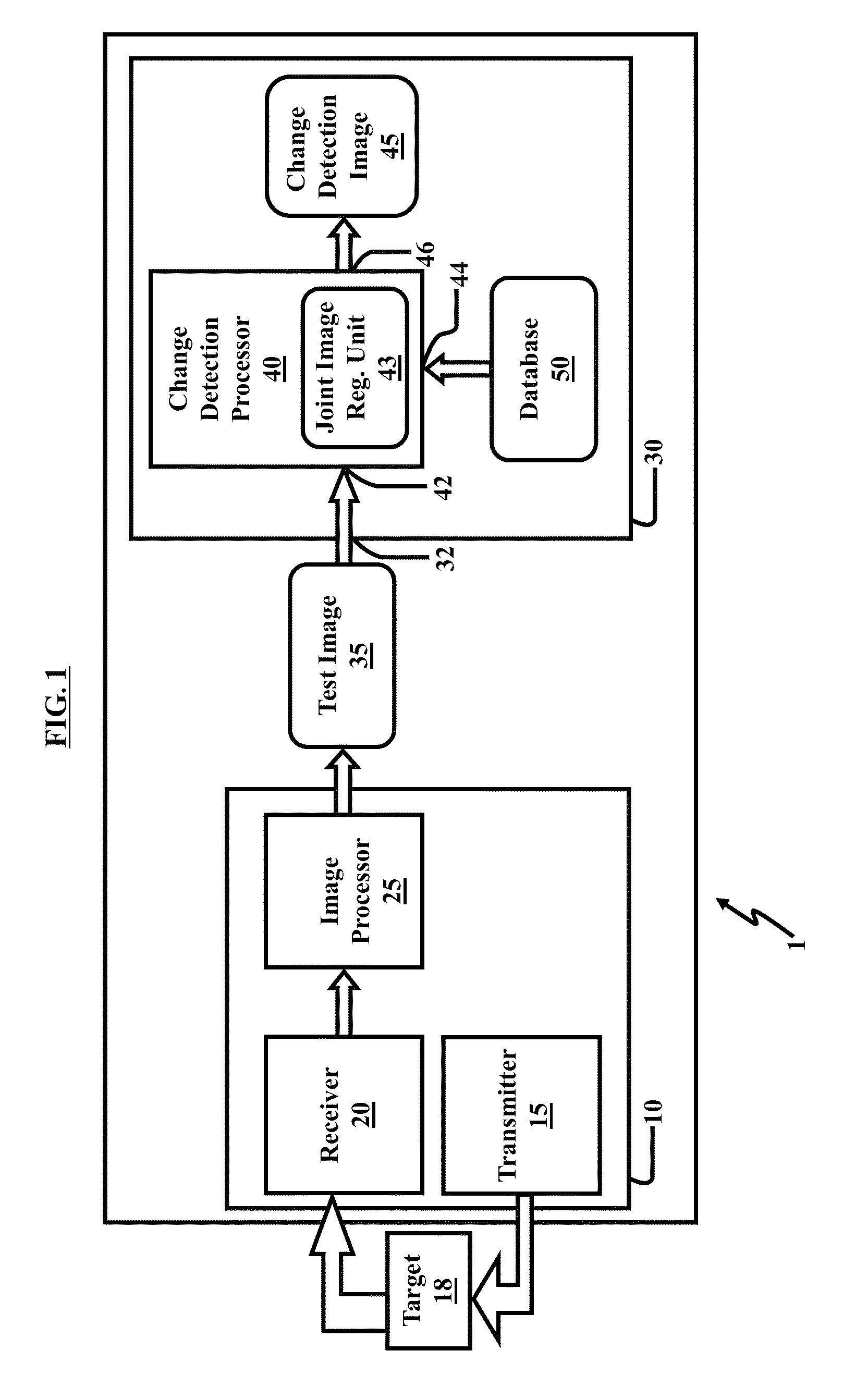
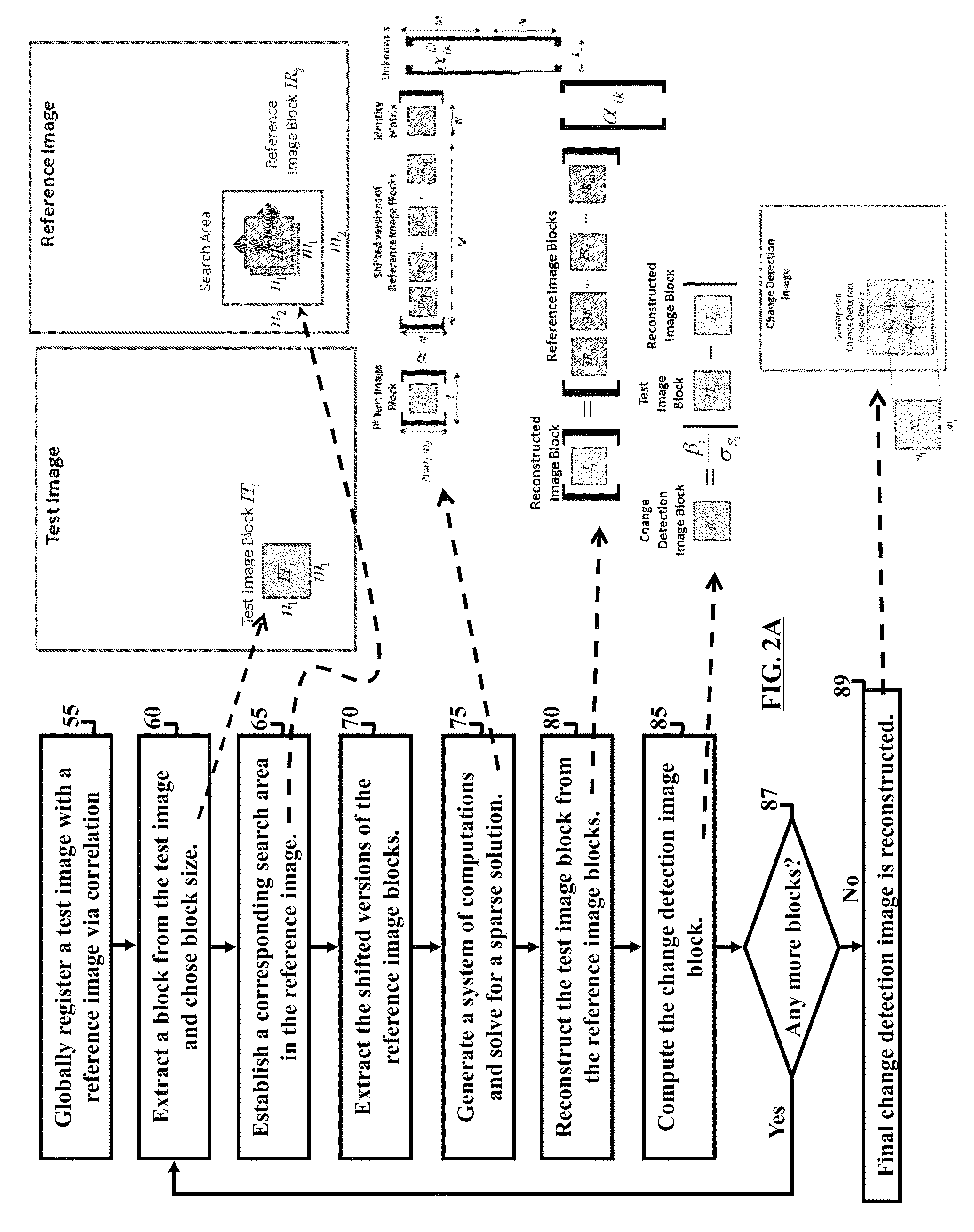
Method and system for image registration and change detection
InactiveUS20110222781A1Maximize correlationMinimize the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisLinearityImage registration
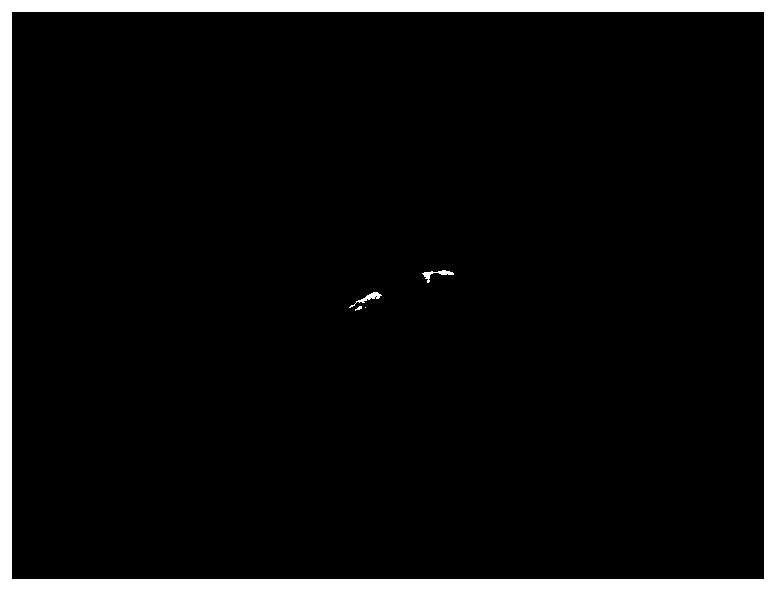
A system and method for detecting changes by comparing images which cover the same physical area but are collected at different times, the system comprising: at least one input for inputting an image of a target area; the image of the target area having signatures representing outstanding features; at least one processor operating to divide the image of a target area into a plurality of target subimages; at least one memory comprising reference data comprising reference subimages taken at or near the target area at various times, the at least one processor operating to determine a sparse image representation from the reference data; the sparse image representation of the target data being a linear combination of reference data from corresponding reference subimages stored in the at least one memory; the at least one processor operating to compare the target image to the sparse image representation and to match signatures from the target image to the sparse image representation to register the images and perform change detection.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Video foreground segmentation method
A fully automatic, computationally efficient segmentation method of video employing sequential clustering of sparse image features. Both edge and corner features of a video scene are employed to capture an outline of foreground objects and the feature clustering is built on motion models which work on any type of object and moving / static camera in which two motion layers are assumed due to camera and / or foreground and the depth difference between the foreground and background. Sequential linear regression is applied to the sequences and the instantaneous replacements of image features in order to compute affine motion parameters for foreground and background layers and consider temporal smoothness simultaneously. The Foreground layer is then extracted based upon sparse feature clustering which is time efficient and refined incrementally using Kalman filtering.
Owner:NEC CORP
Video foreground segmentation method
A fully automatic, computationally efficient segmentation method of video employing sequential clustering of sparse image features. Both edge and corner features of a video scene are employed to capture an outline of foreground objects and the feature clustering is built on motion models which work on any type of object and moving / static camera in which two motion layers are assumed due to camera and / or foreground and the depth difference between the foreground and background. Sequential linear regression is applied to the sequences and the instantaneous replacements of image features in order to compute affine motion parameters for foreground and background layers and consider temporal smoothness simultaneously. The Foreground layer is then extracted based upon sparse feature clustering which is time efficient and refined incrementally using Kalman filtering.
Owner:NEC CORP
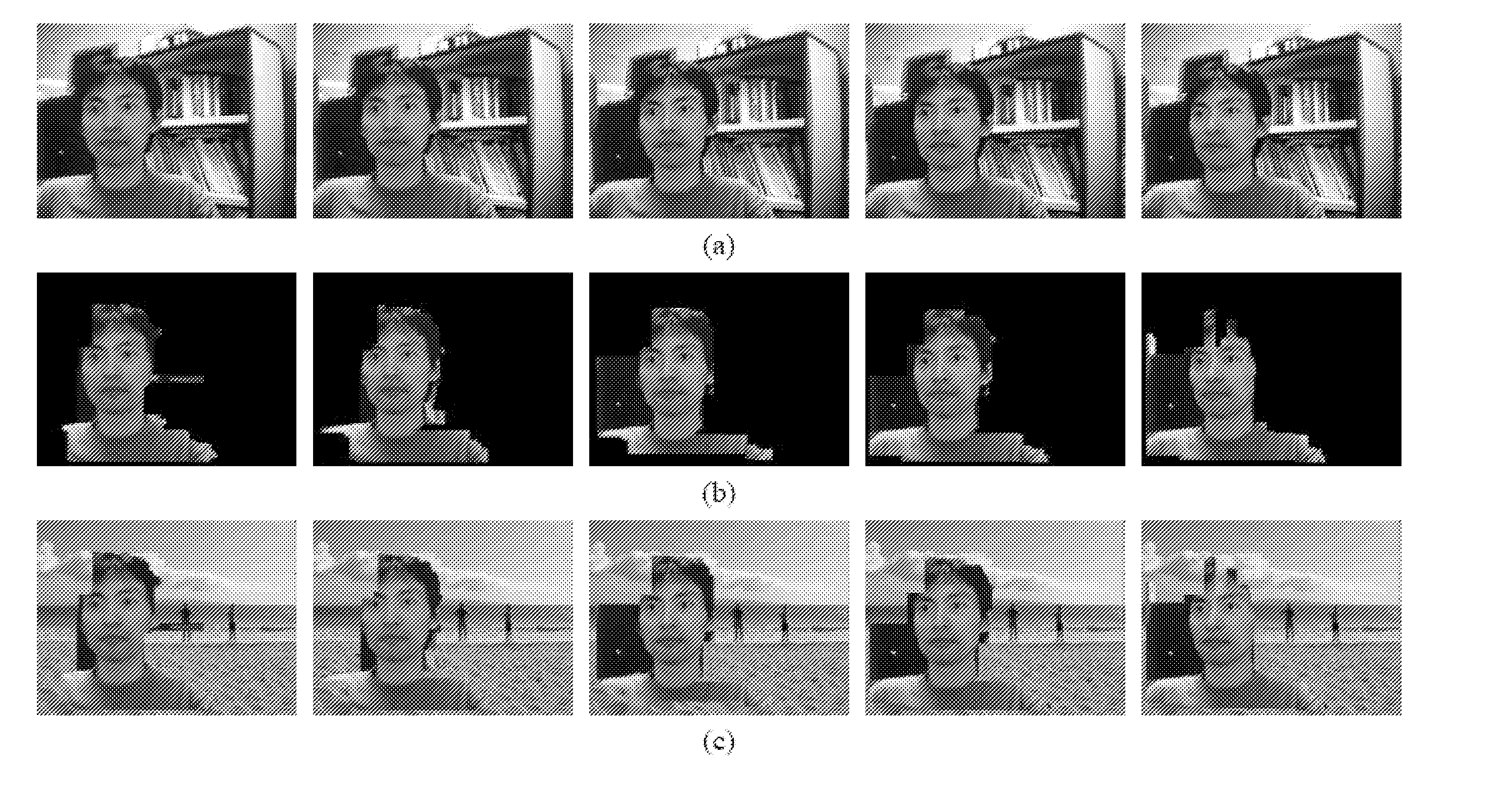
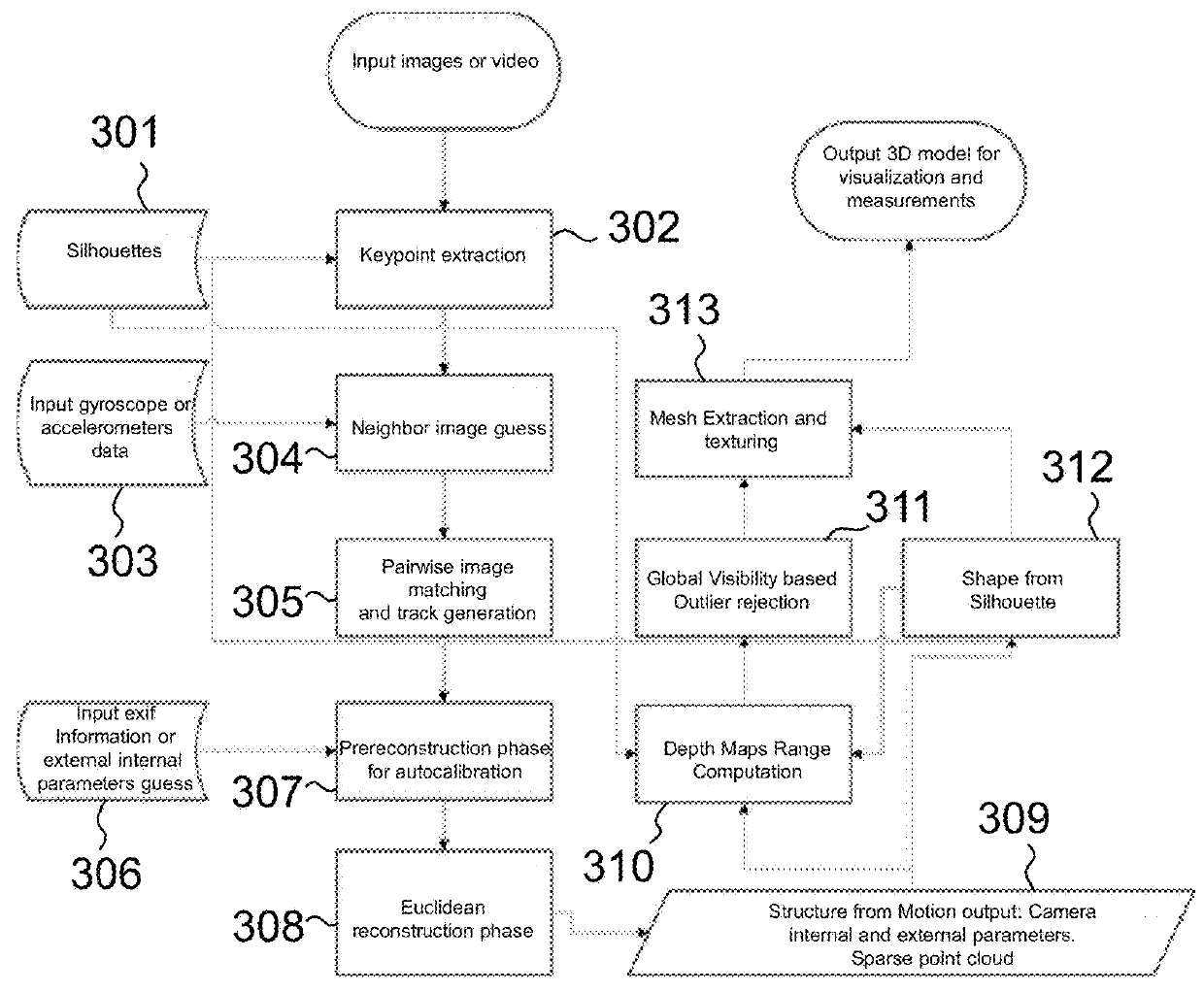
Method for 3D modelling based on structure from motion processing of sparse 2D images
ActiveUS20180276885A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCluster algorithmStructure from motion
A method based on Structure from Motion for processing a plurality of sparse images acquired by one or more acquisition devices to generate a sparse 3D points cloud and of a plurality of internal and external parameters of the acquisition devices includes the steps of collecting the images; extracting keypoints therefrom and generating keypoint descriptors; organizing the images in a proximity graph; pairwise image matching and generating keypoints connecting tracks according maximum proximity between keypoints; performing an autocalibration between image clusters to extract internal and external parameters of the acquisition devices, wherein calibration groups are defined that contain a plurality of image clusters and wherein a clustering algorithm iteratively merges the clusters in a model expressed in a common local reference system starting from clusters belonging to the same calibration group; and performing a Euclidean reconstruction of the object as a sparse 3D point cloud based on the extracted parameters.
Owner:3DFLOW SRL
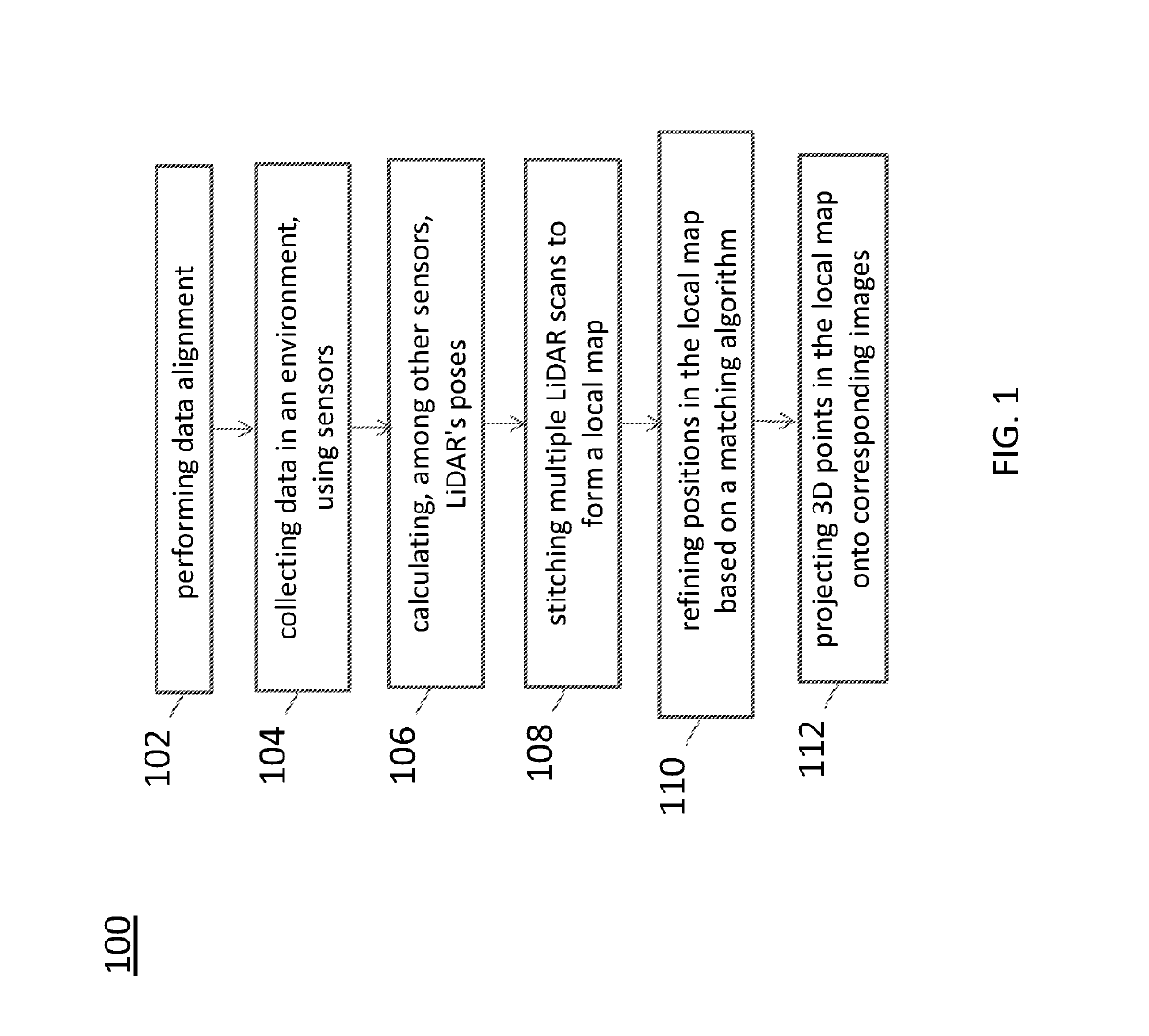
Sensor calibration and time system for ground truth static scene sparse flow generation
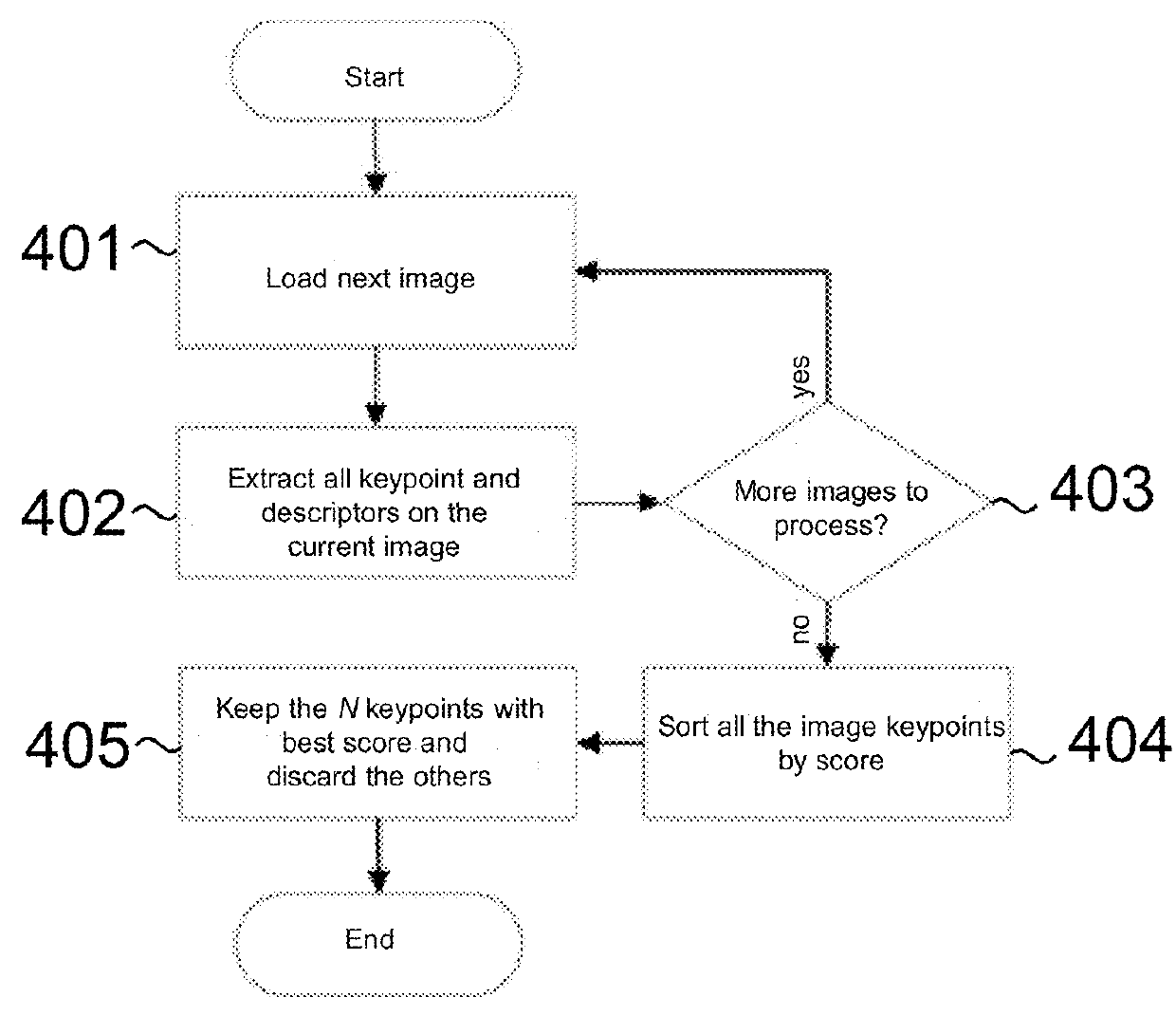
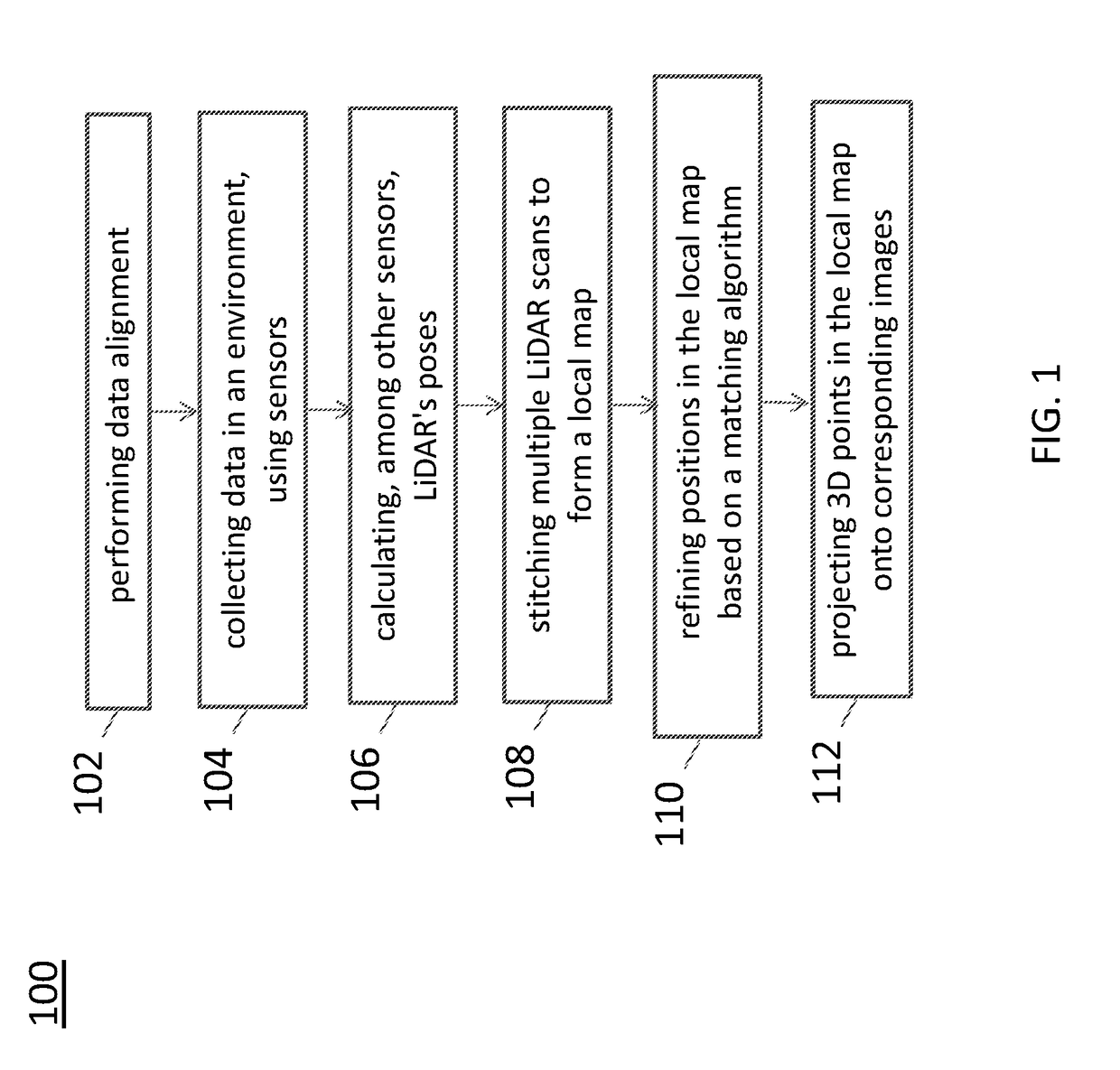
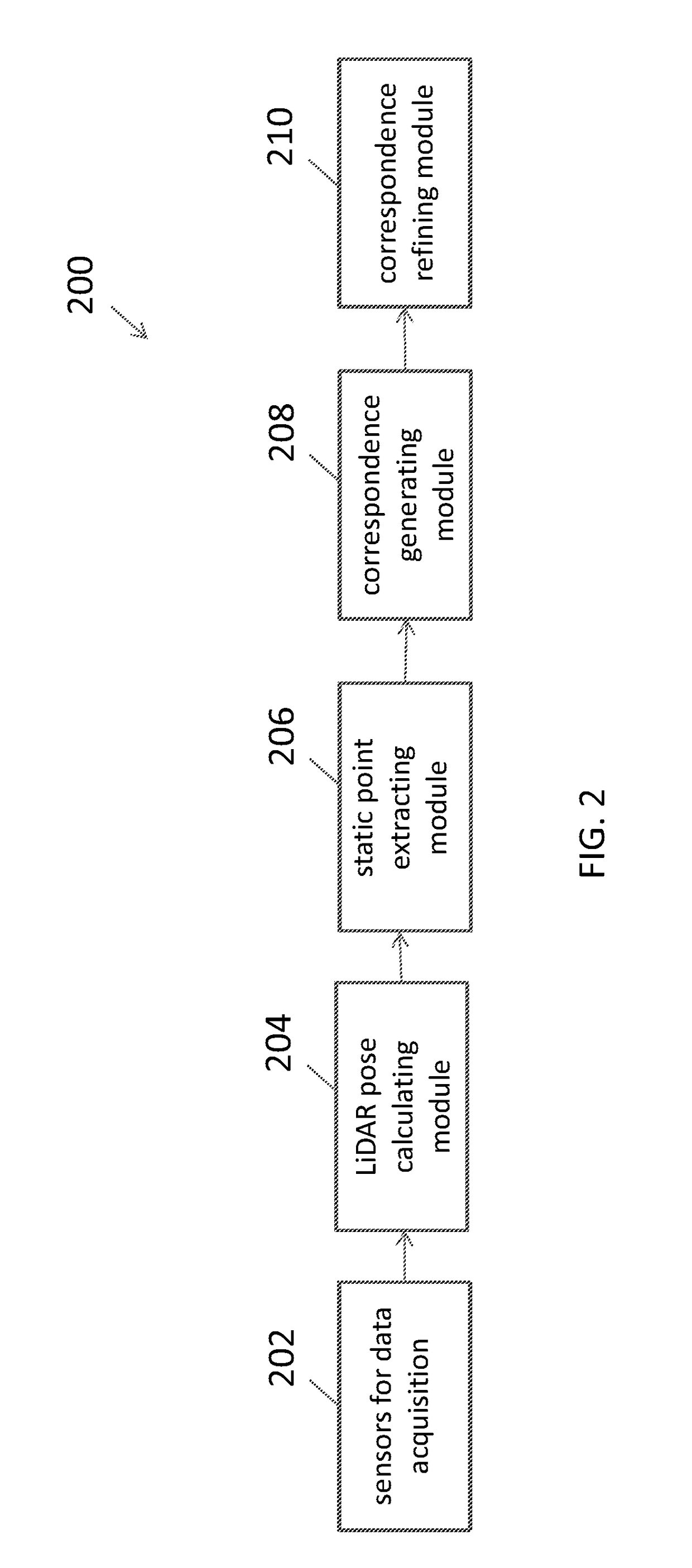
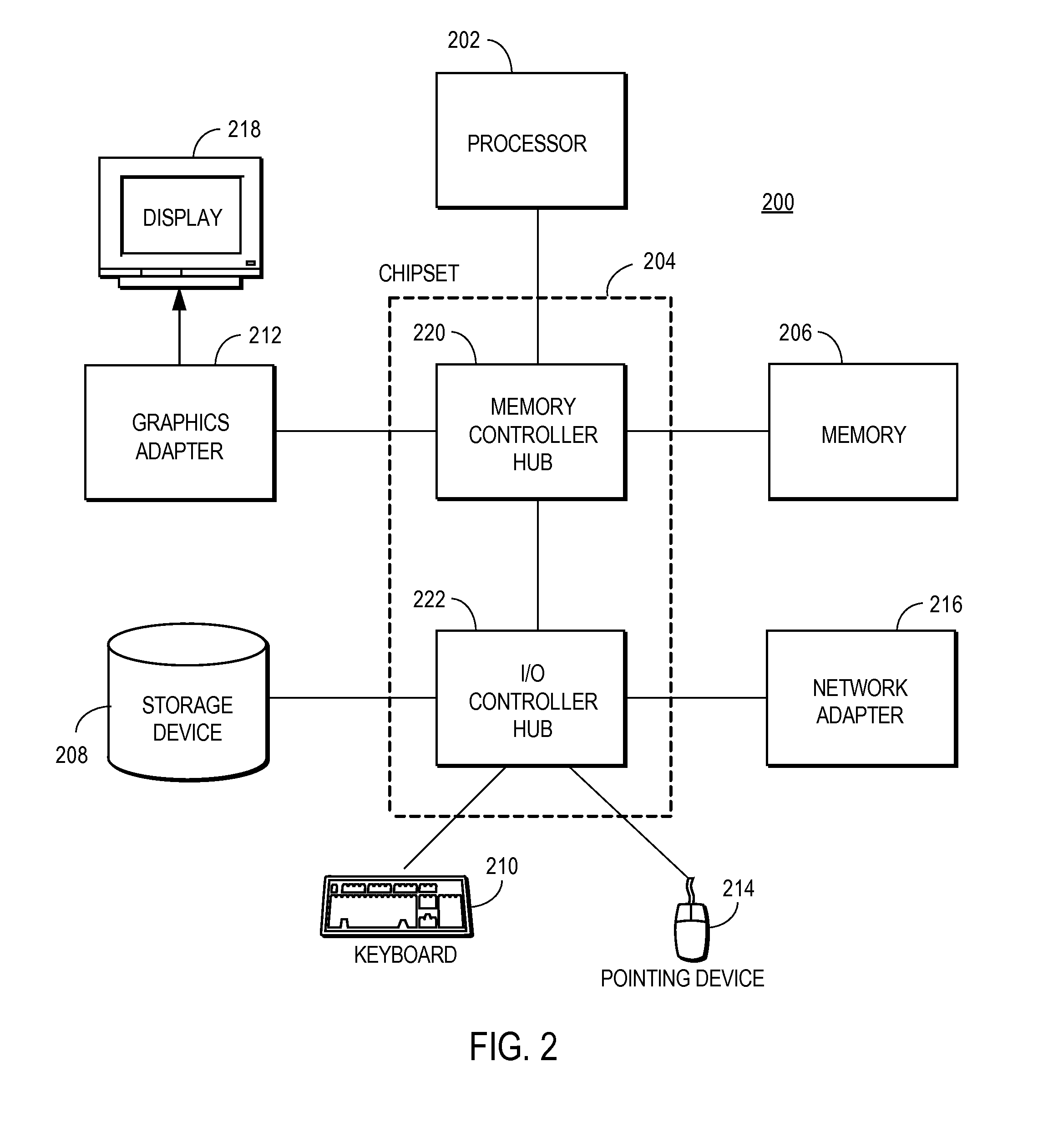
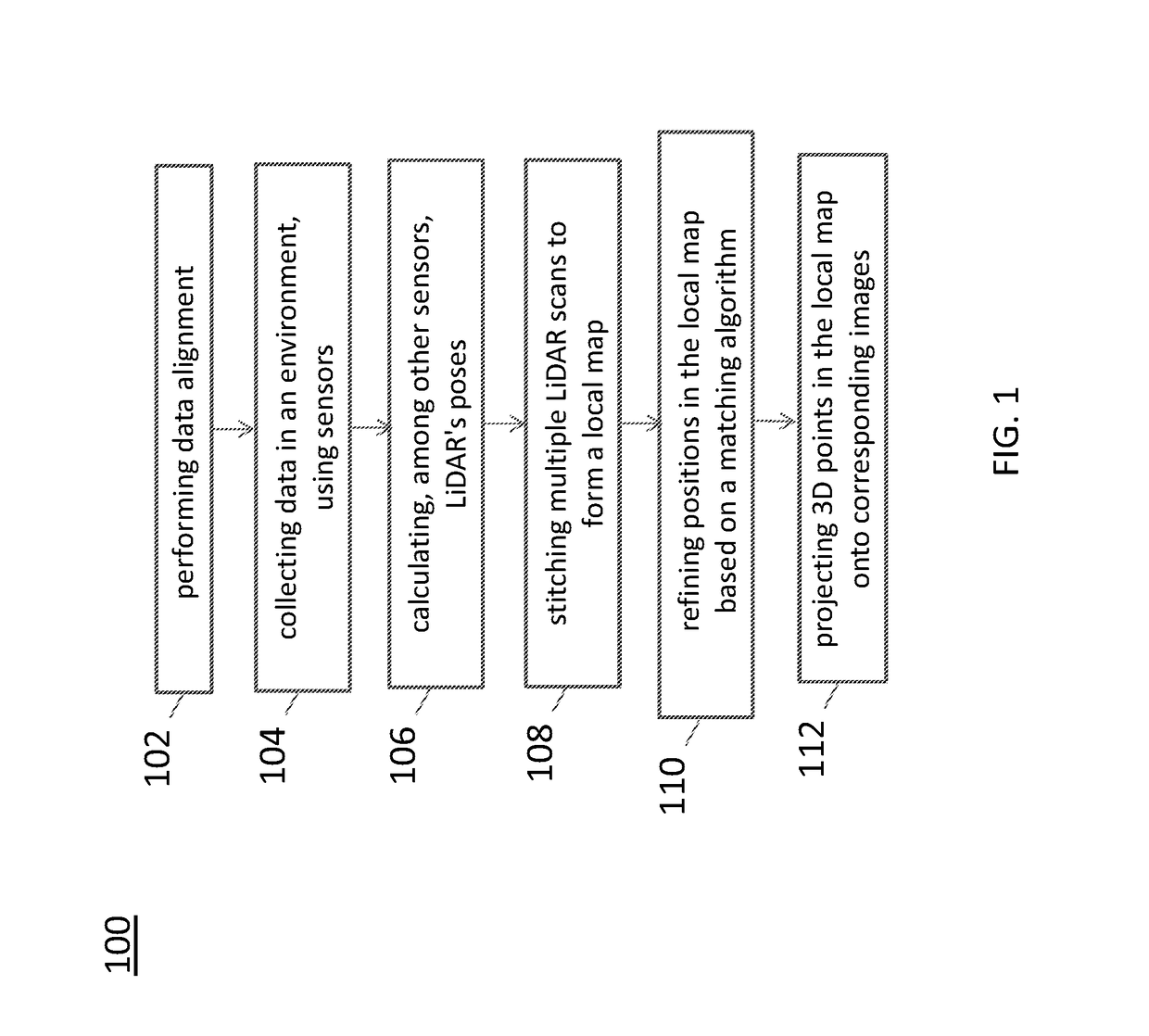
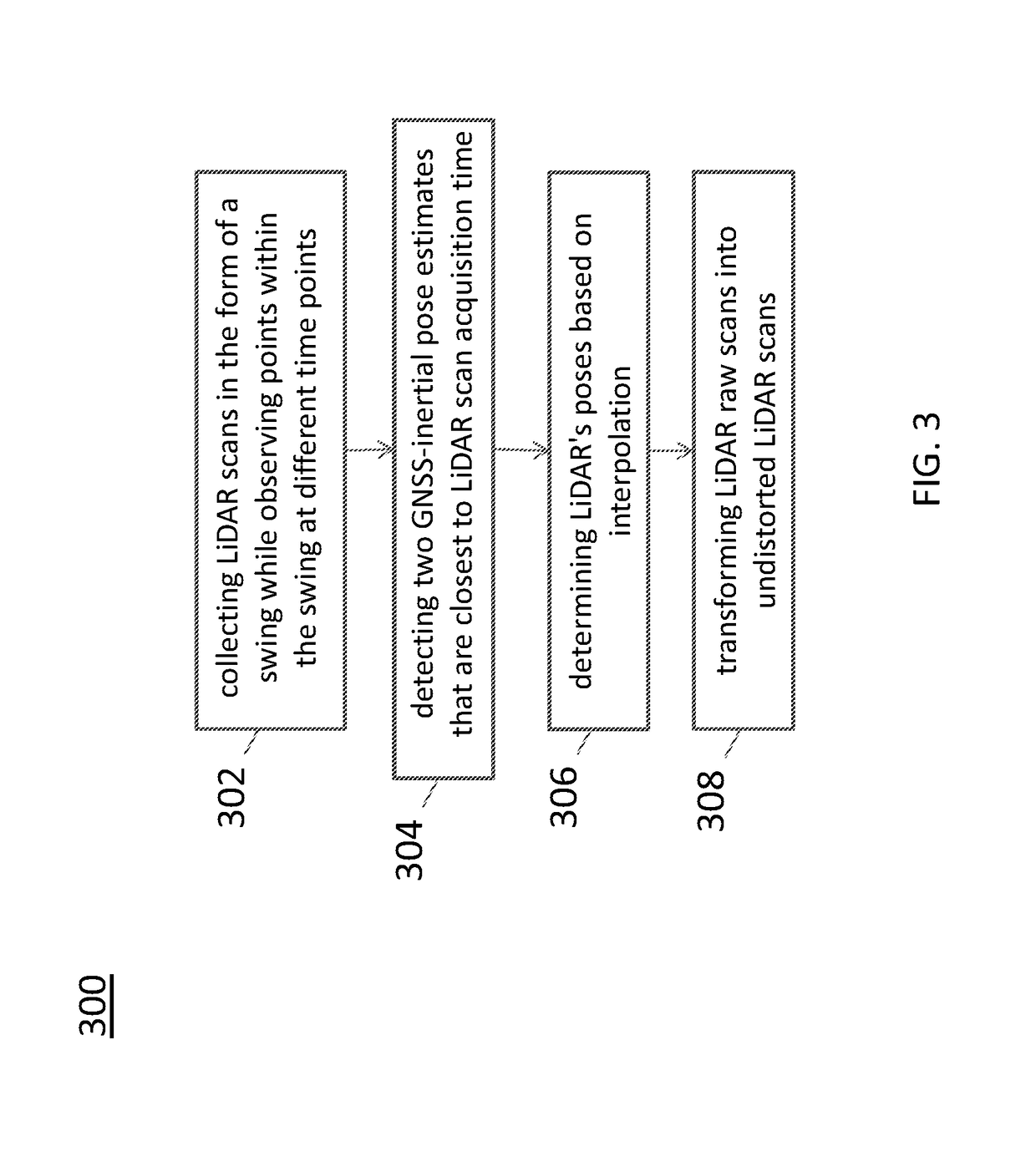
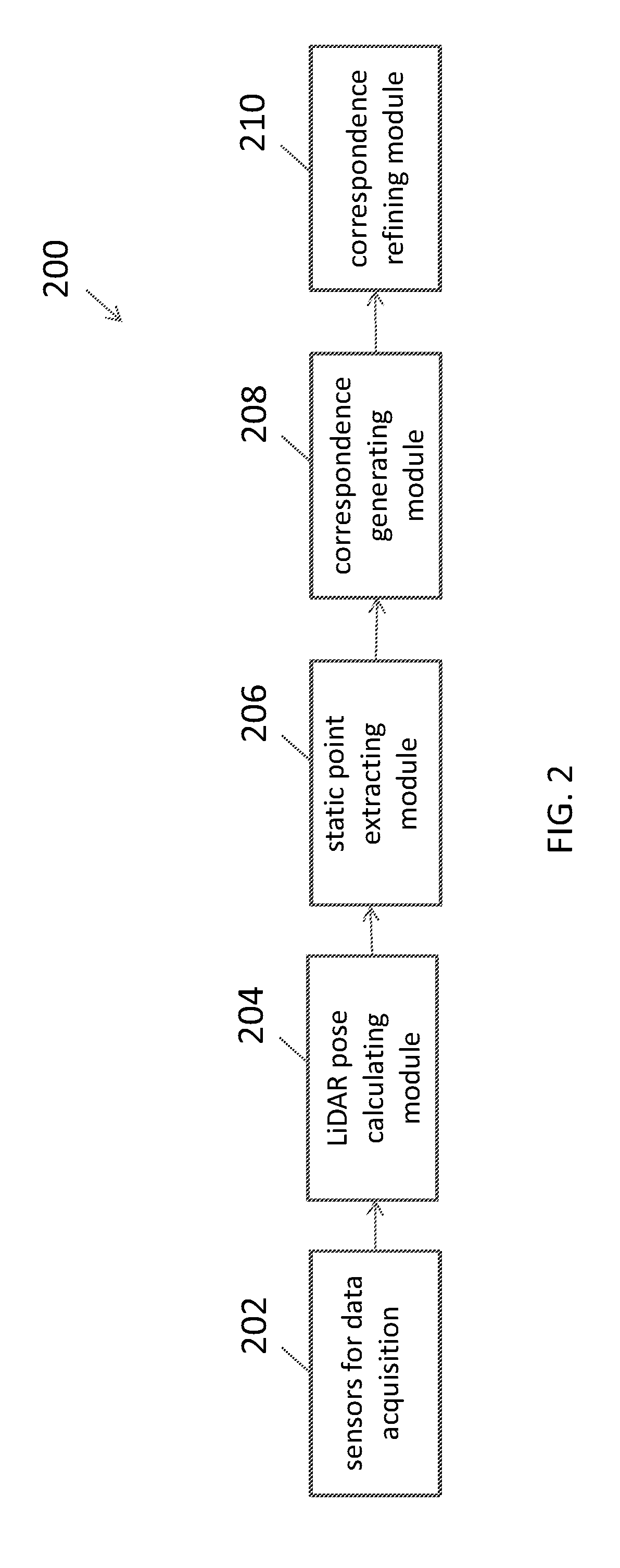
A system for generating a ground truth dataset for motion planning is disclosed. The system includes sensors for data acquisition for motion planning of a vehicle, the sensors including a LiDAR; a calculating module configured to calculate LiDAR poses in response to data from the sensors and generate undistorted LiDAR scans; an extracting module configured to extract static points from a target undistorted LiDAR scan and generate a LiDAR static-scene point cloud; and a generating module configured to generate sparse image point correspondences for each pair of images, using the LiDAR static-scene point cloud.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Apparatus and methods for microscopy having resolution beyond the Abbe limit
InactiveUS20130286179A1High inhibition rateReduce areaColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsFluorescenceImage resolution
Microscope apparatus and methods for imaging an object with a resolution beyond the Abbe limit are disclosed. The apparatus employs an object selectively patterned with a fluorescing material that is induced to fluoresce with one wavelength and inhibited from fluorescing with a second wavelength. Two orthogonal interference-fringe patterns are generated from four diffracted light beams of an inhibiting wavelength and superimposed on the object along with light that induces fluorescence. The interference-pattern image allows only sub-resolution-sized emission areas of the object to fluoresce. Multiple images of the fluorescing object are obtained, each corresponding to a slightly different position of the fringe patterns on the substrate. Each image is processed to yield a sparsely sampled super-resolution image. Multiple sparse images are interwoven to form a complete super-resolution image of the object.
Owner:PERIODIC STRUCTURES
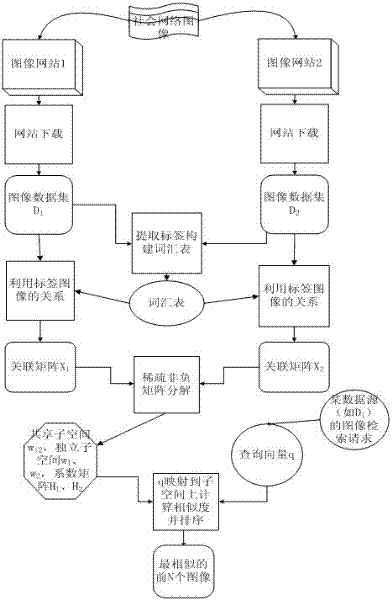
Image Retrieval Method Based on Sparse Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
InactiveCN102270241AImproving Image Retrieval PerformanceImplement transfer learningSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalSource image
The invention discloses an image retrieval method based on sparse non-negative matrix decomposition. It includes the following steps: 1) Query and extract the image and accompanying text of the retrieval results under two different image data sources; 2) Extract the tags in the accompanying text, and filter the results according to word frequency to form a vocabulary; 3) For each Image set, using the association relationship between labels and images to form an association matrix between labels and images; 4) Using sparse non-negative matrix decomposition to analyze the association matrix obtained in step 3), to obtain the shared subspaces of different sources of data and their corresponding independent subspaces Subspace; 5) The user sends a retrieval request for images on a data source, forms a query vector and maps it to the corresponding subspace of the data source, calculates the similarity with all images and sorts them, and returns the top N most similar images. The present invention makes full use of the associated knowledge of tags and images under multiple data sources, performs migration learning through sparse non-negative matrix decomposition, and improves the accuracy of image retrieval on target data sources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hard threshold OMP (orthogonal matching pursuit)-based linear array SAR (synthetic aperture radar) sparse imaging method
ActiveCN103698763AImproving Sparse Imaging PerformanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarRadar
The invention provides a hard threshold OMP (orthogonal matching pursuit)-based linear array SAR (synthetic aperture radar) sparse imaging method. A linear measurement matrix of original echo signals of a linear array SAR and scattering coefficients in a target space of an observed scene is established for the characteristic that main scattering targets are spatially sparse in the target space of the observed scene of the linear array SAR, and contrast between maximum and minimum target scattering coefficients and a target scattering coefficient change rate are used as iteration ending conditions for the iteration processing of a hard threshold OMP algorithm, so that the dependence of a conventional OMP algorithm on the number of the main scattering targets in linear array SAR sparse imaging is overcome. Compared with a conventional OMP algorithm-based linear array SAR sparse imaging method, so that the method has the advantages that the number of the main scattering targets in the target space of the observed scene is not required to be known, and the method is more applicable to the linear array SAR sparse imaging when the number of the main scattering targets is unknown under actual conditions; the imaging accuracy of the linear array SAR is improved. The method can be applied to the fields of SAR imaging, earth remote sensing and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for image registration and change detection
InactiveUS8620093B2Maximize correlationMinimize the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisImage registrationSparse image
A system and method for detecting changes by comparing images which cover the same physical area but are collected at different times, the system comprising: at least one input for inputting an image of a target area; the image of the target area having signatures representing outstanding features; at least one processor operating to divide the image of a target area into a plurality of target subimages; at least one memory comprising reference data comprising reference subimages taken at or near the target area at various times, the at least one processor operating to determine a sparse image representation from the reference data; the sparse image representation of the target data being a linear combination of reference data from corresponding reference subimages stored in the at least one memory; the at least one processor operating to compare the target image to the sparse image representation and to match signatures from the target image to the sparse image representation to register the images and perform change detection.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
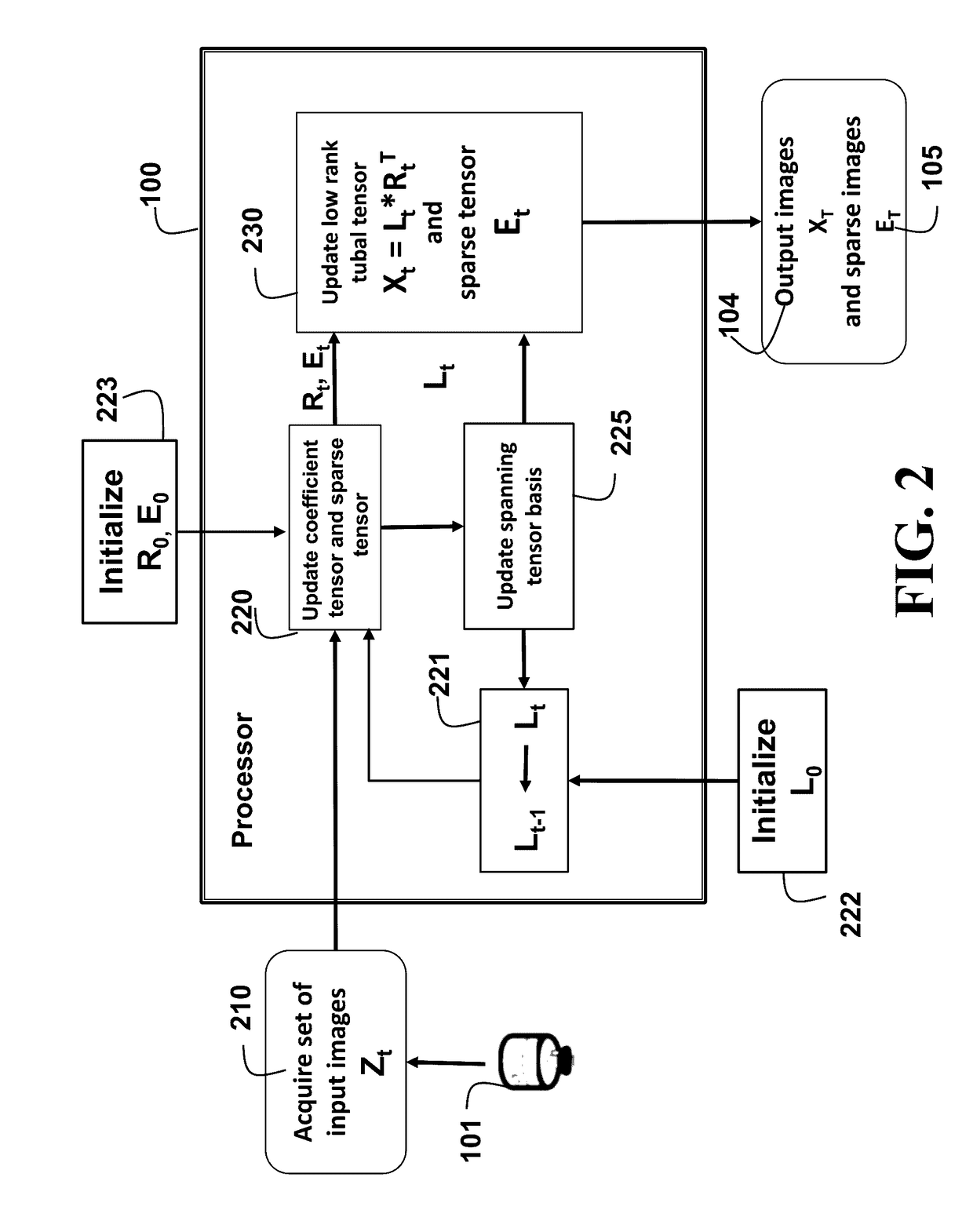
System and Method for Processing Images using Online Tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis
ActiveUS20170076180A1Reduce in quantityImprove computing efficiencyScene recognitionAlgorithmSparse image
A set of input images are acquired sequentially as image tensors. A low-tubal rank tensor and a sparse tensor are initialized using the image tensor, wherein the low-tubal rank tensor is a tensor product of a low-rank spanning tensor basis and corresponding tensor coefficients, and for each image, updating iteratively the image tensor, the tensor coefficients, and the sparse tensor using the image tensor and the low-rank spanning basis from a previous iteration. The spanning tensor basis is updated using the tensor coefficients, the sparse tensor, and the low rank tubal tensor, wherein the low rank tubal tensor represents a set of output images and the sparse tensor representing a set of sparse images.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
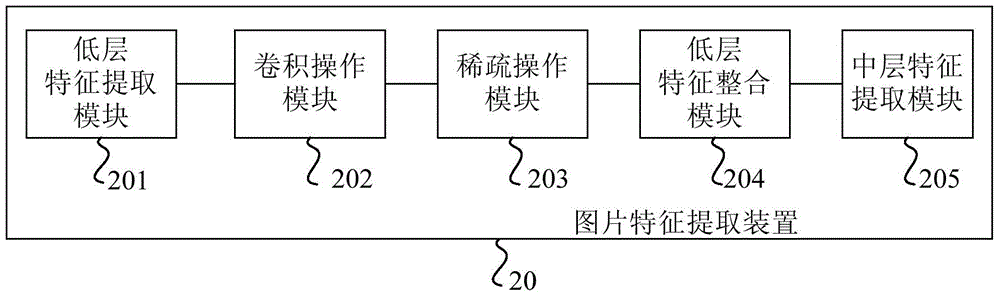
Method and apparatus for extracting image features
ActiveCN105095902AImprove extraction efficiencySolve the characteristicsCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmData set
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and an apparatus for extracting image features. The method for extracting image features comprises the steps of: acquiring a plurality of cluster centers from an image data set to be classified to serve as low-level feature extractors by using a clustering algorithm; performing convolution for each image in the image data set by using the plurality of low-level feature extractors, and generating a plurality of convolution images for each image, wherein the number of the convolution images is the same as the number of the low-level feature extractors; respectively performing threshold processing for the plurality of convolution images to obtain a plurality of sparse images; performing low-level feature integration for the plurality of sparse images to obtain a plurality of integrated images; and performing middle-level feature extraction for the plurality of integrated images to obtain middle-level features. The method in the embodiments of the present invention can adaptively extract image features and can achieve high extraction efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
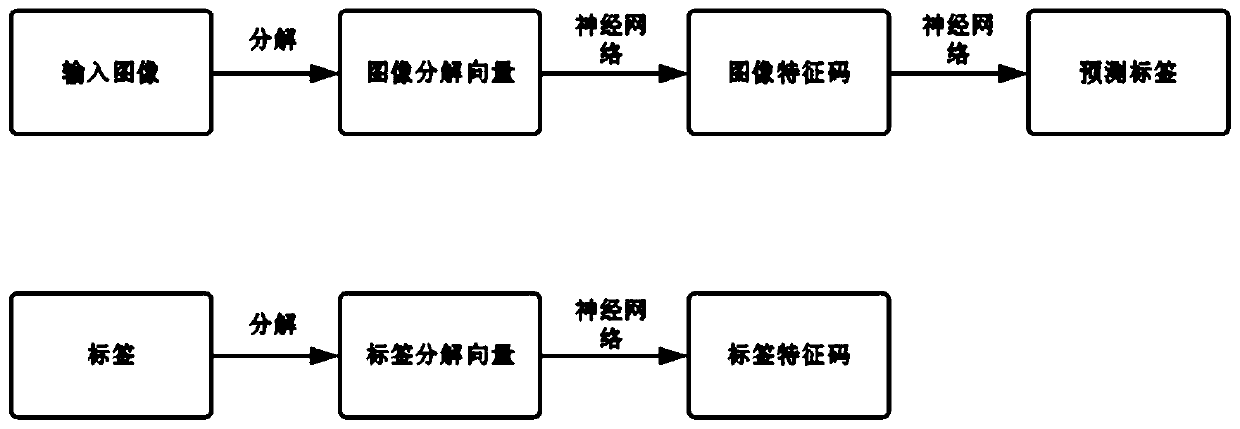
Image data multi-label classification method
ActiveCN110210515AEasy to predictReduce the difficulty of forecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionStochastic gradient descentMulti-label classification
The invention discloses an image data multi-label classification method. The method comprises the following steps: decomposing an input image, extracting high-order correlation of features by utilizing a neural network, decomposing tag data, extracting high-order correlation of tags by utilizing the neural network, and decoding a feature code of the input image from an input space to a tag space by adopting the neural network comprising multiple layers of full connection layers; constructing a loss function, initializing a training parameter, adopting a random gradient descent method to minimize a final loss function as a target, and training and solving to obtain an optimal training parameter; and inputting to-be-tested image data into the trained model for prediction, and outputting to obtain a label result to realize multi-label classification. According to the method, the problem that the secondary correlation and the multi-correlation of the labels cannot be extracted at the sametime when a person works in front of the image data is solved, the prediction difficulty caused by too sparse image data is reduced, and the accuracy of multi-label classification is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
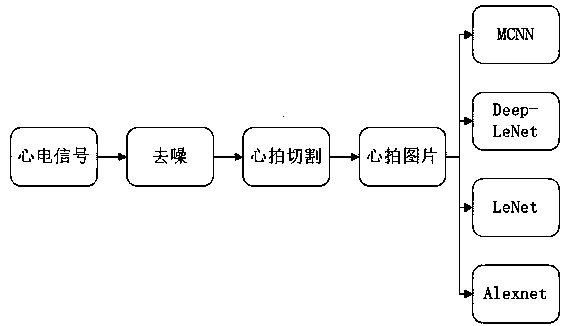
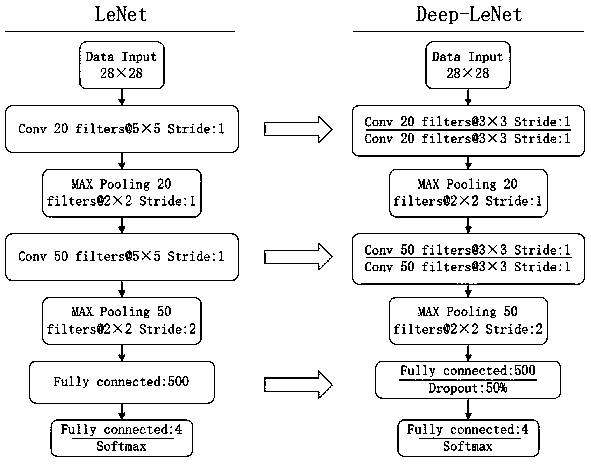
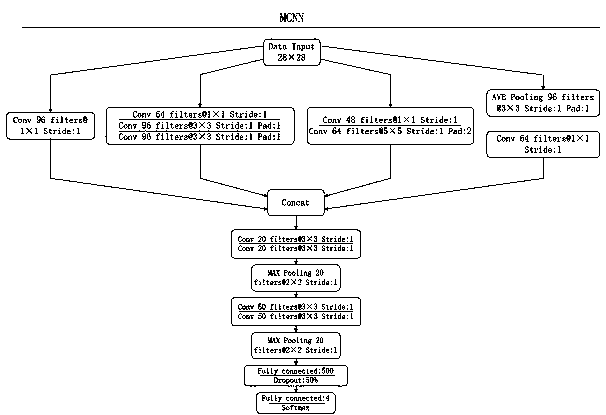
Cardiac arrythmias classification algorithm based on convolutional neural network
InactiveCN110313894AShort timeImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalCardiac arrhythmia
The invention discloses a cardiac arrythmias classification algorithm based on a convolutional neural network. The cardiac arrythmias classification algorithm comprises a small-scale Deep-LeNet network suitable for a sparse image of electrocardiosignals. According to the characteristics of a small convolutional core, the time consumed for network classification is shorter, and the accuracy is improved. Then, the convolutional neural network is put forward. The width of the network can be increased, the adaptability of the network to the scale is increased, the network is more suitable for recognizing the sparse image. Under the condition of quite slightly increasing the network time consumption, the classification accuracy of the network can be greatly increased; due to the integrated recognition and classification process, the cardiac arrythmias classification algorithm can be better used for family-practice-level diagnosis and has great significance in accurate recognition of cardiacarrythmias.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
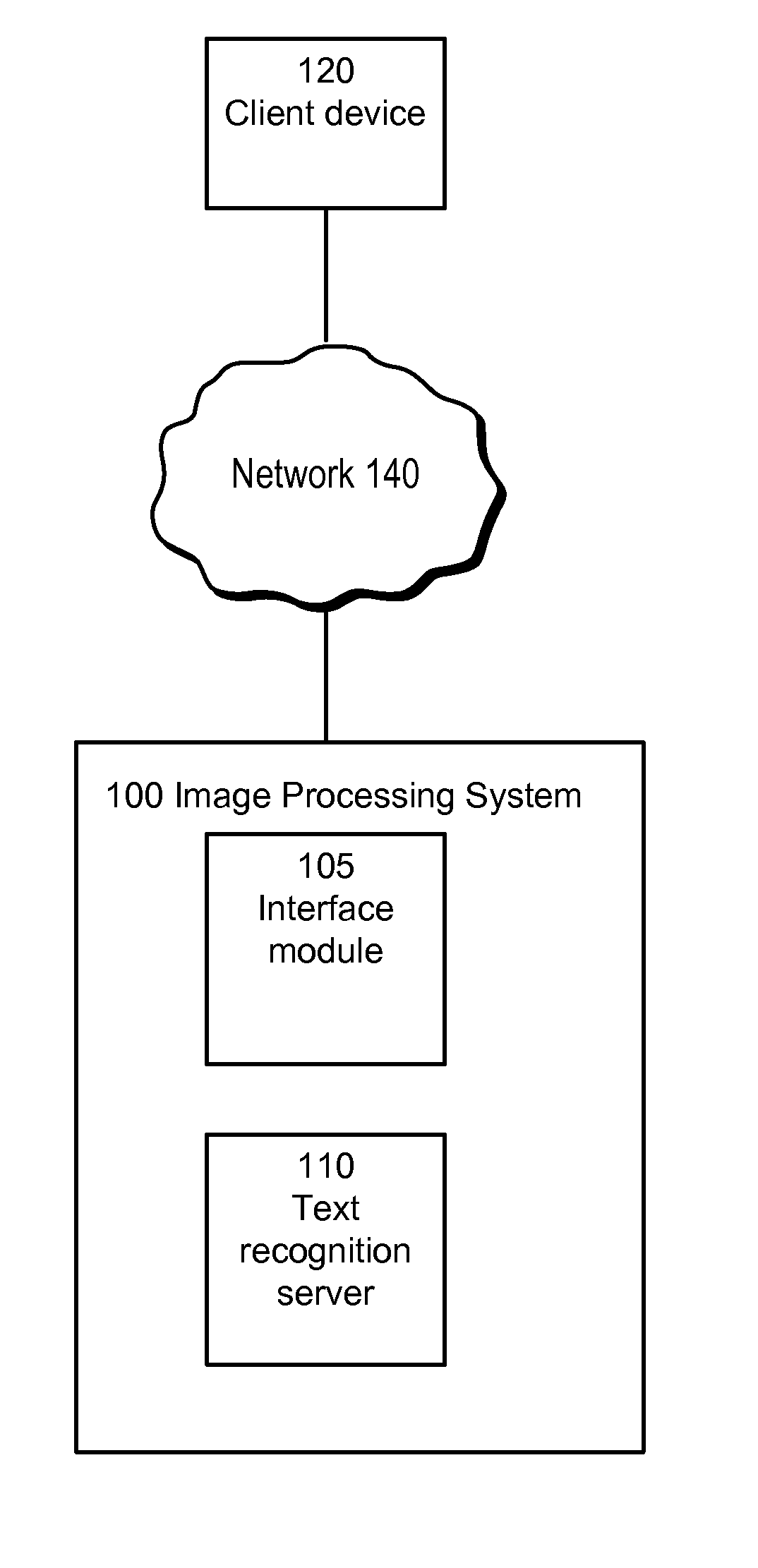
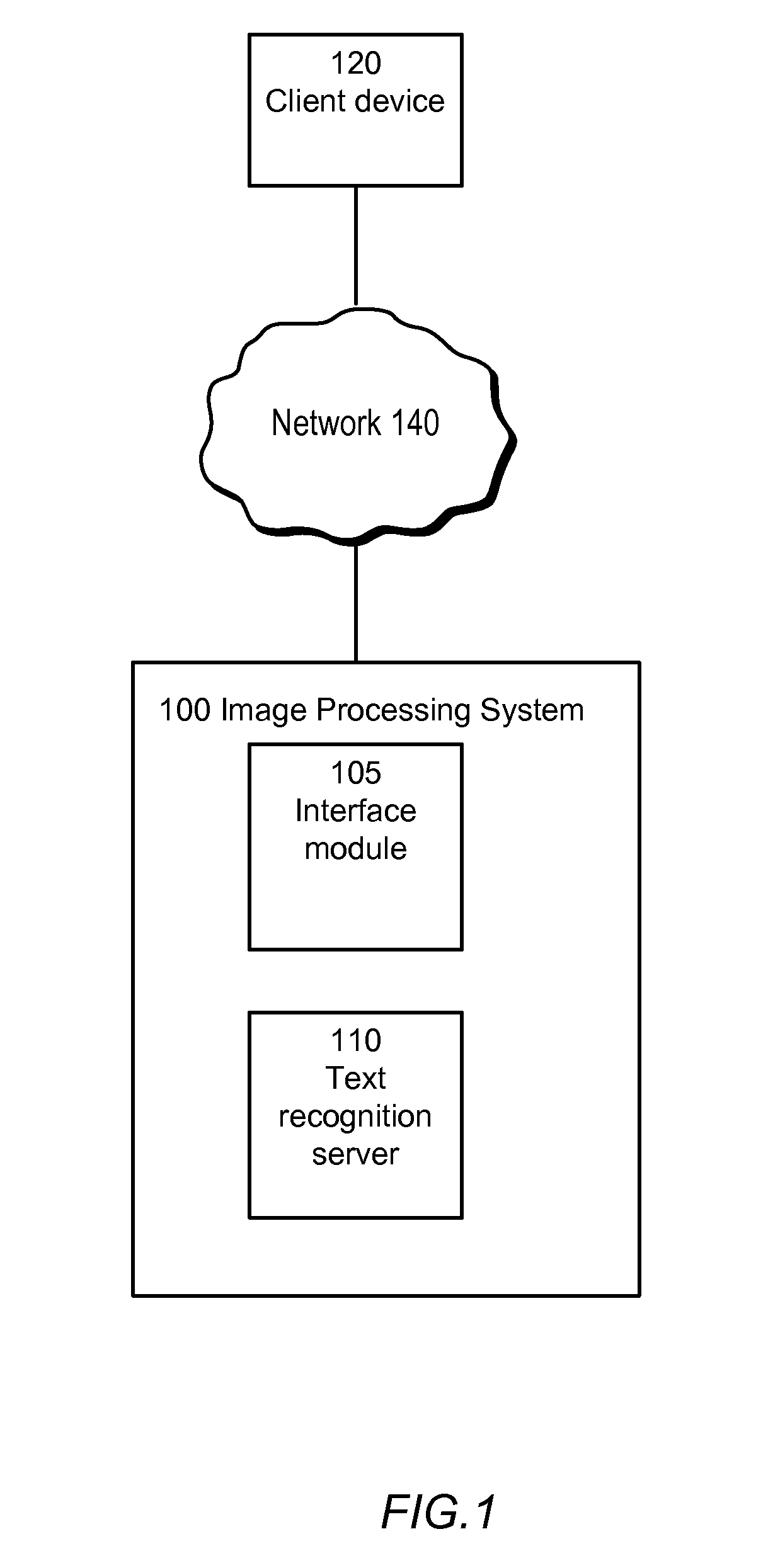
Text recognition for textually sparse images
A text recognition server is configured to recognize text in a sparse text image. Specifically, given an image, the server specifies a plurality of “patches” (blocks of pixels within the image). The system applies a text detection algorithm to the patches to determine a number of the patches that contain text. This application of the text detection algorithm is used both to estimate the orientation of the image and to determine whether the image is textually sparse or textually dense. If the image is determined to be textually sparse, textual patches are identified and grouped into text regions, each of which is then separately processed by an OCR algorithm, and the recognized text for each region is combined into a result for the image as a whole.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Image compression secure coding method based on multidirectional sparse representation
InactiveCN101848390AIncrease the number of directionsIncrease flexibilityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationObjective qualityNoise shaping
The invention discloses an image compression secure coding method based on multidirectional sparse representation, comprising the following steps of: performing discrete dual-tree wavelet transform on an image and then performing directional filtering on each obtained high-frequency sub-band to obtain fine image directional sparse representation; performing rarefaction process on an obtained directional sub-band coefficient by using a noise shaping technology; interleaving the coefficients of each layer to ensure that the sub-band coefficients of neighbor layers have a parent child relation, and then performing quantitative coding on the coefficients by using SPIHT (Set Partitioning in Hierarchical Trees); and finally encrypting the coefficient symbols in a code stream in an XOR (Exclusive OR) manner and encrypting other partial code streams by using random arithmetic coding. As the code stream obtained by coding is encrypted by using the random arithmetic coding, the encryption efficiency is high, the effect is good, the security is high and no influence is brought to the image compression performance. The high-frequency components of the image are decomposed by using a directional filter, and therefore the directional representation is more flexible, sparser image representation is obtained, the image coding compression process is favored and the decoded image has better objective quality and subjective effect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
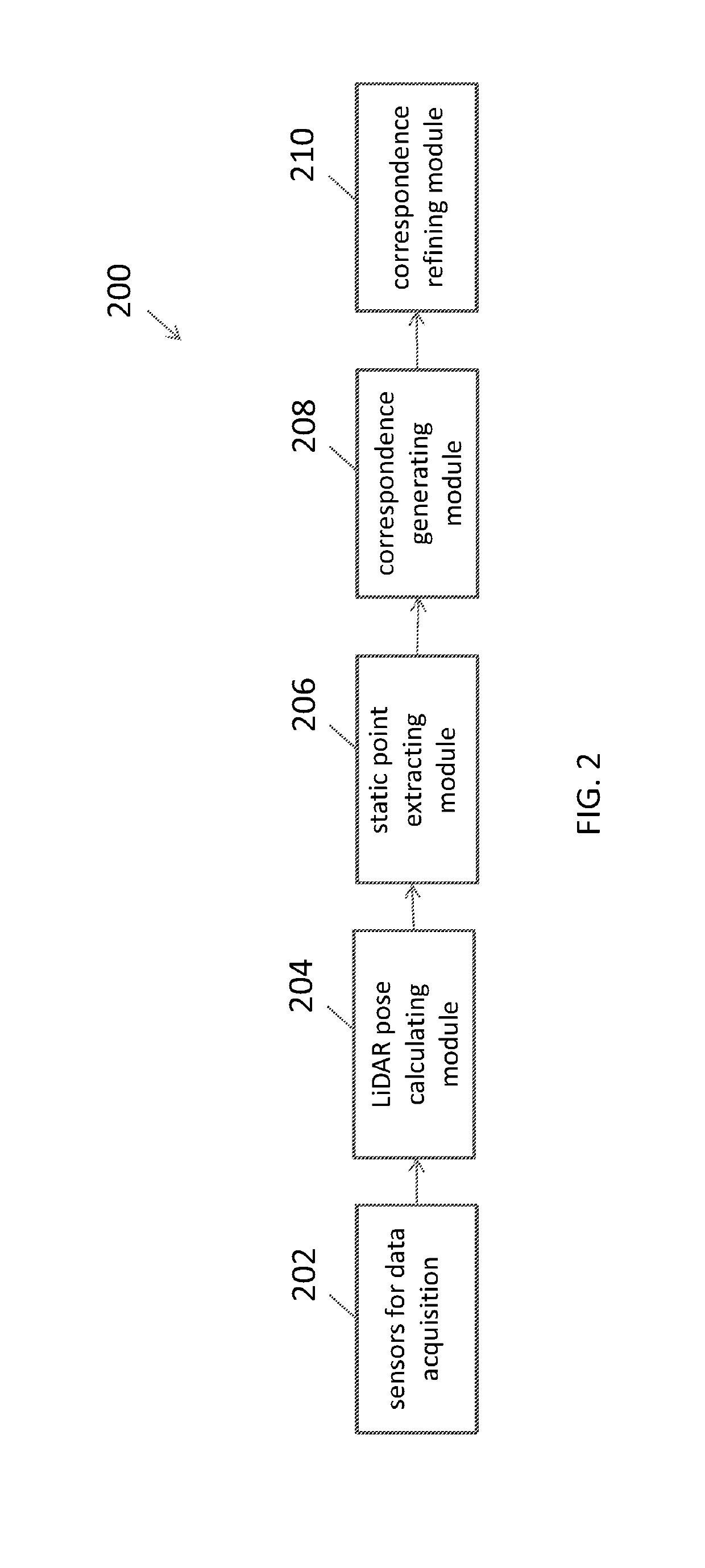
Sparse image point correspondences generation and correspondences refinement system for ground truth static scene sparse flow generation
A system for generating a ground truth dataset for motion planning of a vehicle is disclosed. The system includes an internet server that further includes an I / O port, configured to transmit and receive electrical signals to and from a client device; a memory; one or more processing units; and one or more programs stored in the memory and configured for execution by the one or more processing units, the one or more programs including instructions for: a corresponding module configured to correspond, for each pair of images, a first image of the pair to a LiDAR static-scene point cloud; and a computing module configured to compute a camera pose associated with the pair of images in the coordinate of the point cloud.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
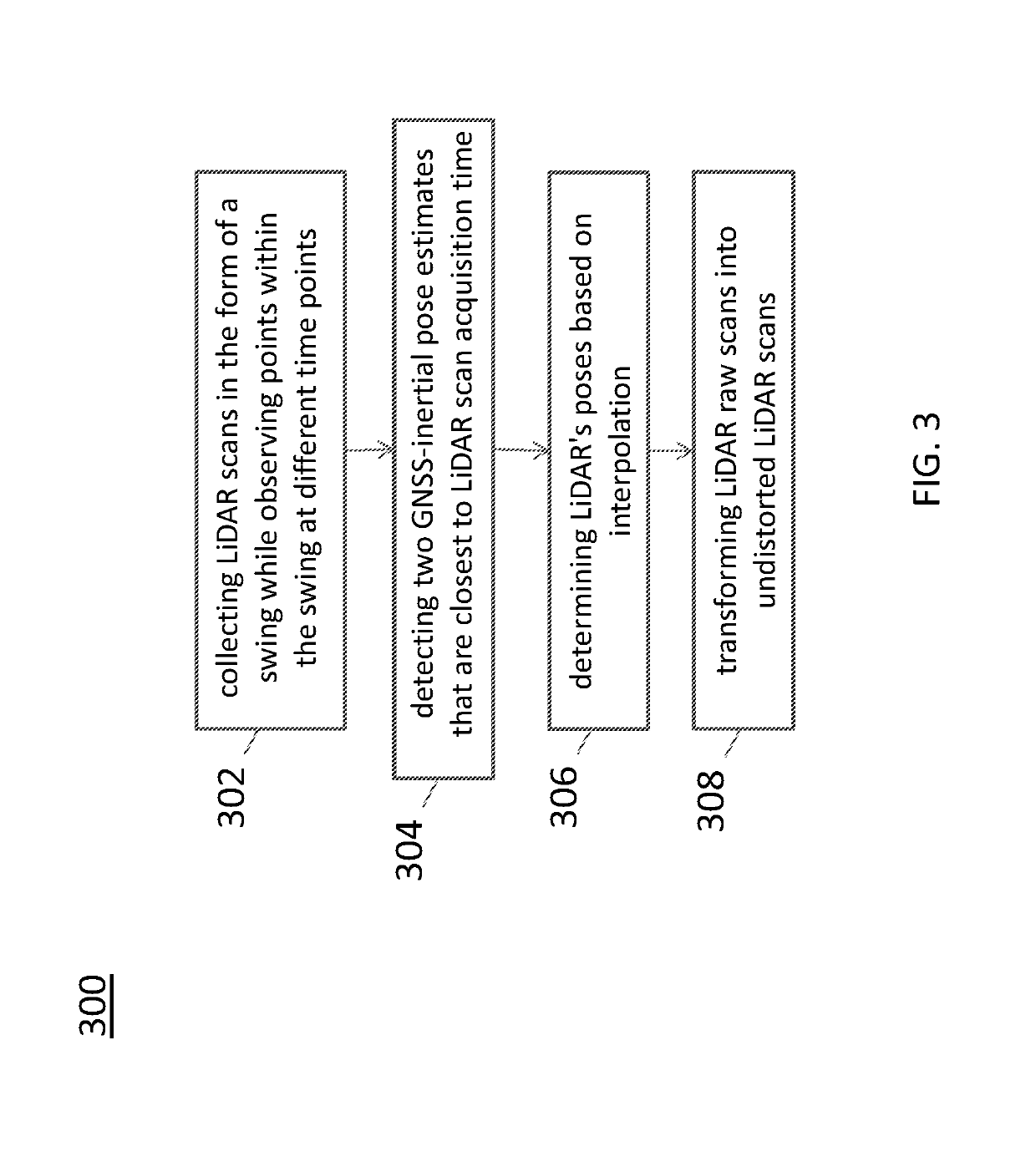
Sparse image point correspondences generation and correspondences refinement method for ground truth static scene sparse flow generation
A method of generating a ground truth dataset for motion planning of a vehicle is disclosed. The method includes: corresponding, for each pair of images, a first image of the pair to a LiDAR static-scene point cloud; and computing a camera pose associated with the pair of images in the coordinate of the point cloud.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
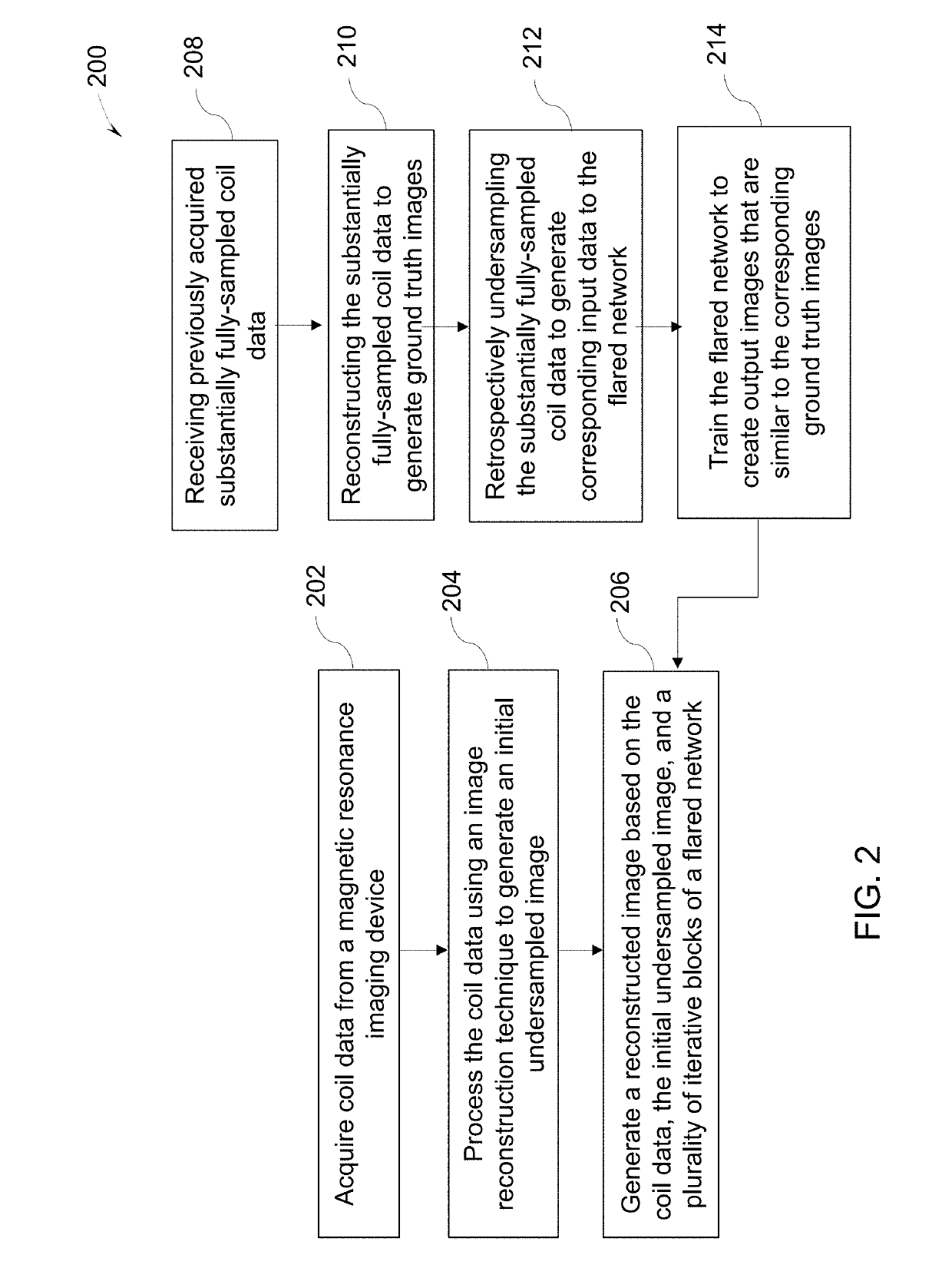
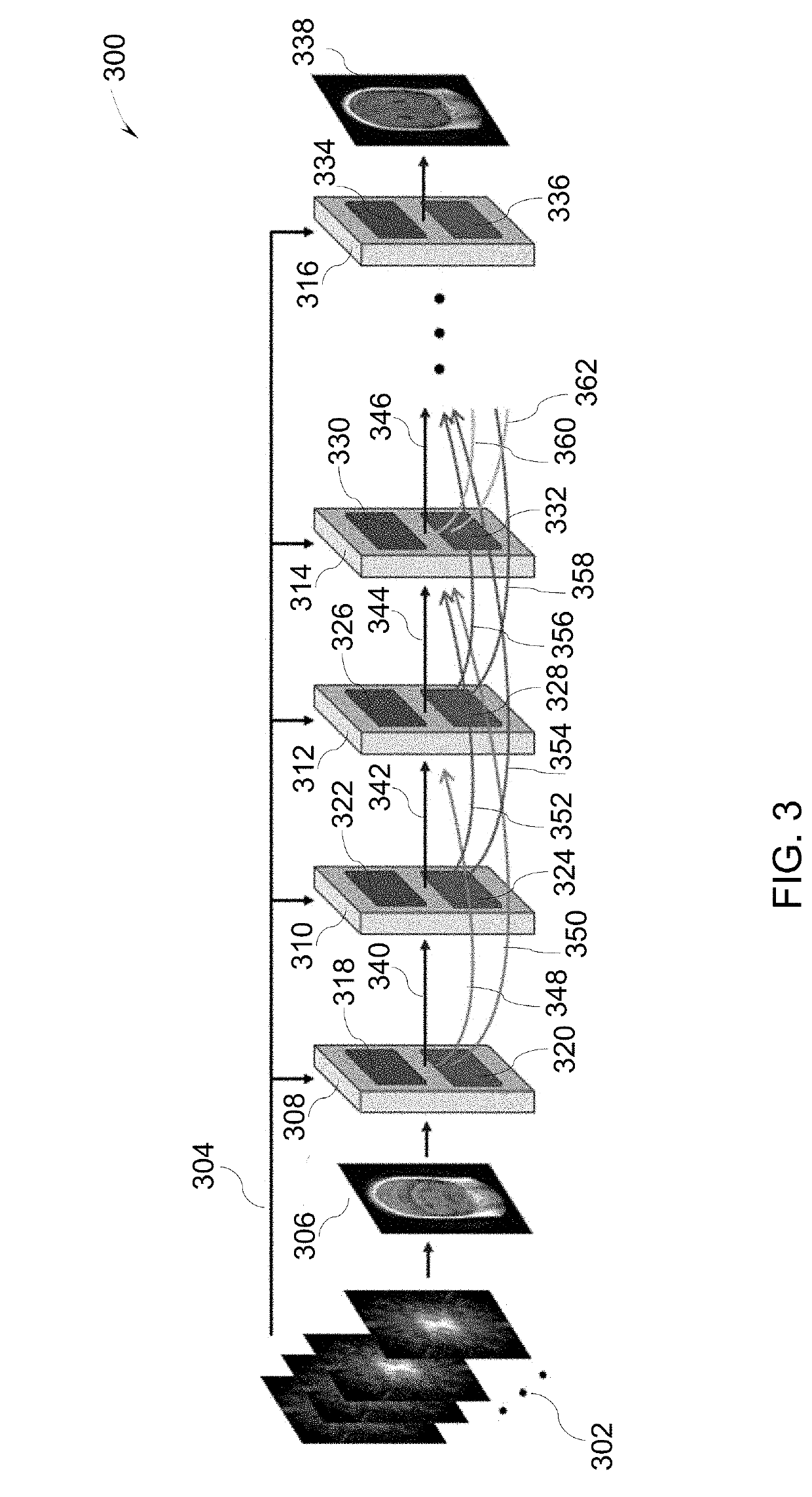
System and method for sparse image reconstruction
A method for sparse image reconstruction includes acquiring coil data from a magnetic resonance imaging device. The coil data includes undersampled k-space data corresponding to a subject. The method further includes processing the coil data using an image reconstruction technique to generate an initial undersampled image. The method also includes generating a reconstructed image based on the coil data, the initial undersampled image, and a plurality of iterative blocks of a flared network. A first iterative block of the flared network receives the initial undersampled image. Each of the plurality of iterative blocks includes a data consistency unit and a regularization unit and the iterative blocks are connected both by direct connections from one iterative block to the following iterative block and by a plurality of dense skip connections to non-adjacent iterative blocks. The flared network is based on a neural network trained using previously acquired coil data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Terahertz time-domain spectral sparse imaging method
InactiveCN106441575AImprove sparsityInhibition effectSpectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansTime domainWavelet transform
The invention discloses a terahertz time-domain spectral sparse imaging method. Shift-invariant wavelet transformation is used to decompose a terahertz image; and the sparsity of wavelet transformation coefficients of the terahertz image is enhanced, namely, high coefficient values in the wavelet transformation coefficients are obtained in an enhanced manner, and influence of low coefficient values is inhibited. The wavelet coefficients obtained after shift-invariant wavelet transformation are used to implement nonlinear transformation by utilizing an exponential function; a split iteration algorithm is used to split an optimized cost function of terahertz time-domain spectral sparse imaging into a series of subproblems, and iteration optimization is carried out on the subproblems; and the reconstruction quality is improved, and a terahertz time-domain spectral sparse imaging result can be obtained rapidly.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Colorful digital image repairing method based on compressed sensing
InactiveCN102609920AEliminate the effects ofGuaranteed recovery effectImage enhancementDigital imageBarrier function
The invention provides a colorful digital image repairing method based on compressed sensing, comprising the following steps: step 1, pre-treating an original damaged image and assigning a value of a damaged part of the image to be 0; step 2, dividing the image into blocks and analyzing to generate a singular matrix of the damaged part of each image block; step 3, multiplying the image blocks obtained in step 2 by the singular matrix to obtain a signal to be collected; then, representing the signal to be collected by using a CS sparse base to obtain a corresponding sparse signal; and finally, multiplying the sparse image by a randomly-generated Gaussian measurement matrix to obtain an observation signal; and step 4, utilizing a logarithm barrier function method based on total variation to recover a CS observation signal obtained in step 3 to obtain a recovered image. According to the colorful digital image repairing method based on compressed sensing, a specific structure which is not attached to the image has a similar recovering effect aiming to different images and can be used in different environments.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
System and method for processing images using online tensor robust principal component analysis
ActiveUS10217018B2Reduce in quantitySuperior in convergence speed and performanceScene recognitionAlgorithmTensor representation
A set of input images are acquired sequentially as image tensors. A low-tubal rank tensor and a sparse tensor are initialized using the image tensor, wherein the low-tubal rank tensor is a tensor product of a low-rank spanning tensor basis and corresponding tensor coefficients, and for each image, updating iteratively the image tensor, the tensor coefficients, and the sparse tensor using the image tensor and the low-rank spanning basis from a previous iteration. The spanning tensor basis is updated using the tensor coefficients, the sparse tensor, and the low rank tubal tensor, wherein the low rank tubal tensor represents a set of output images and the sparse tensor representing a set of sparse images.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
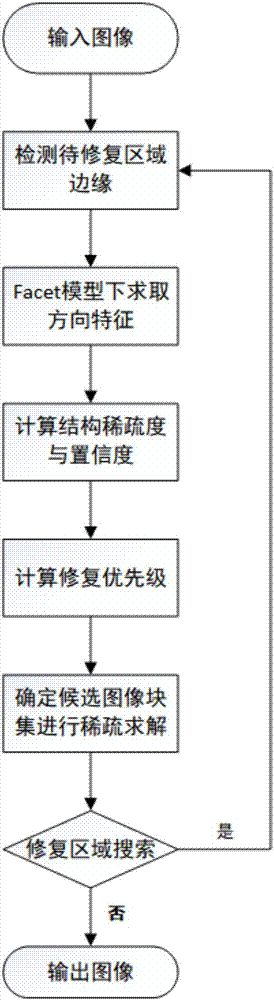
Sample double sparse image inpainting method based on features of Facet directional derivative
ActiveCN107507139AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove universalityImage enhancementDependabilitySpatial consistency
The invention relates to a sample double sparse image inpainting method based on the features of Facet directional derivative, which includes the following steps: S1, acquiring directional feature information of an image in different directions under a Facet model; S2, using an improved inpainting priority calculation function to sort image blocks to be inpainted; and S3, inpainting the damaged region with the highest inpainting priority determined in S2 through sparse representation of candidate image blocks. Directional features are fully utilized in the method. A new image block distance calculation function is constructed, and the space consistency and continuity constraints of the directional features are added in the sparse solving link. Meanwhile, the inpainting priority calculation function is adjusted and improved, and the confidence values of the image blocks are controlled within a reasonable range, in order to ensure the reliability of the priority calculation result. Both the color information and directional feature information of the image are considered, and all kinds of image damage situations can be dealt with. The method has good universality and wide market prospect and application value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
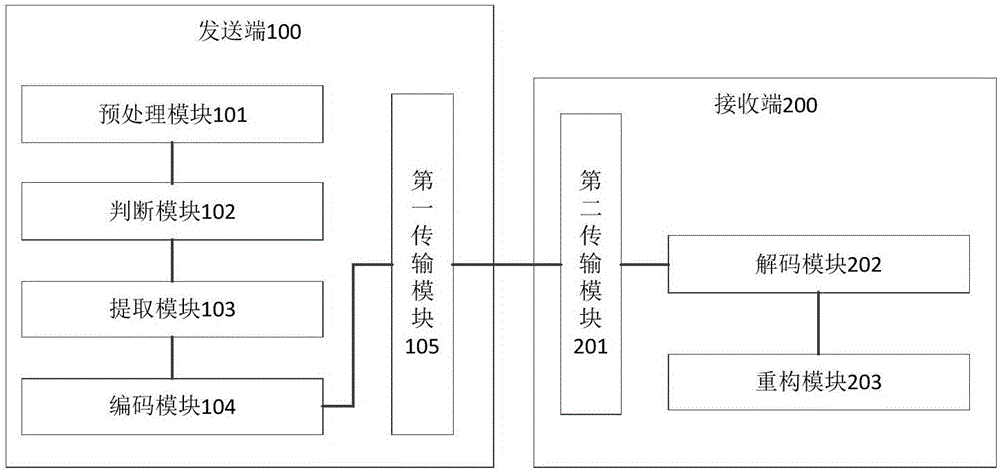
Image transmission method and system based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN105898302AImprove transmission efficiencyReduce wasteDigital video signal modificationHigh probabilityImage transfer
The invention discloses an image transmission method based on compressed sensing, and the method is used by a transmitting end for transmitting an image to a receiving end. The method comprises the steps that S1, the transmitting end carries out the preprocessing of an original image, and generates a one-dimensional signal of the original image; S2, the transmitting end judges whether the original image is a sparse image or not according to the one-dimensional signal; S3, the transmitting end extracts the main feature information of the one-dimensional signal when the transmitting end judges that the original image is the sparse image; S4, the transmitting end codes the main feature information, generates first information, and transmits the first information to the receiving end; S5, the receiving end receives and analyzes the first information, and obtains the main feature information; S6, the receiving end carries out the reconstruction of the main feature information, and obtains the original image through restoration. The system enables a high-dimensional image signal to be converted into low-dimensional image signals through a conversion matrix, and finally carries out the high-probability reconstruction of a few of low-dimensional image signals through an optimization method to obtain the original signal.
Owner:宁夏智慧宫文化传媒有限公司
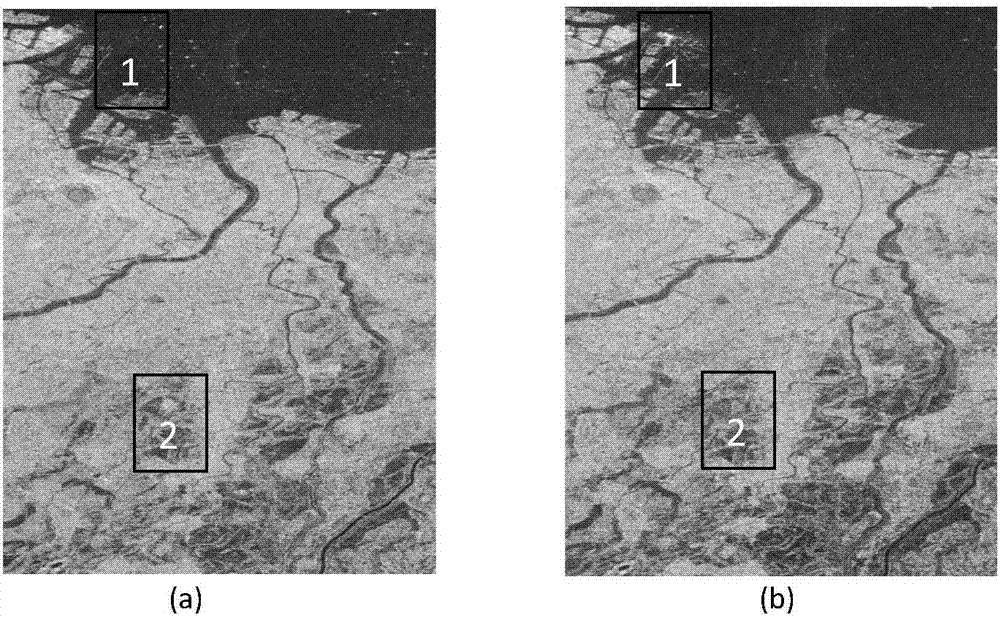
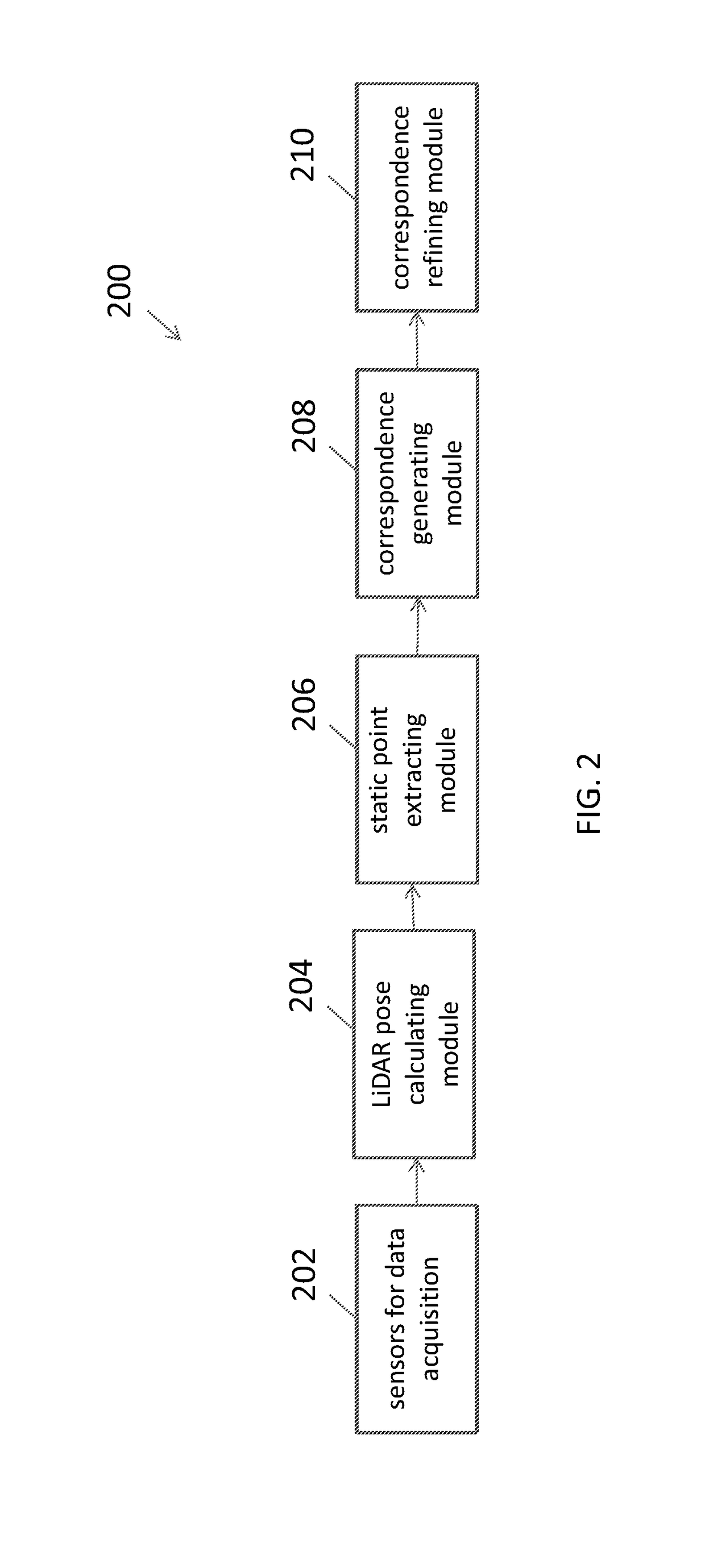
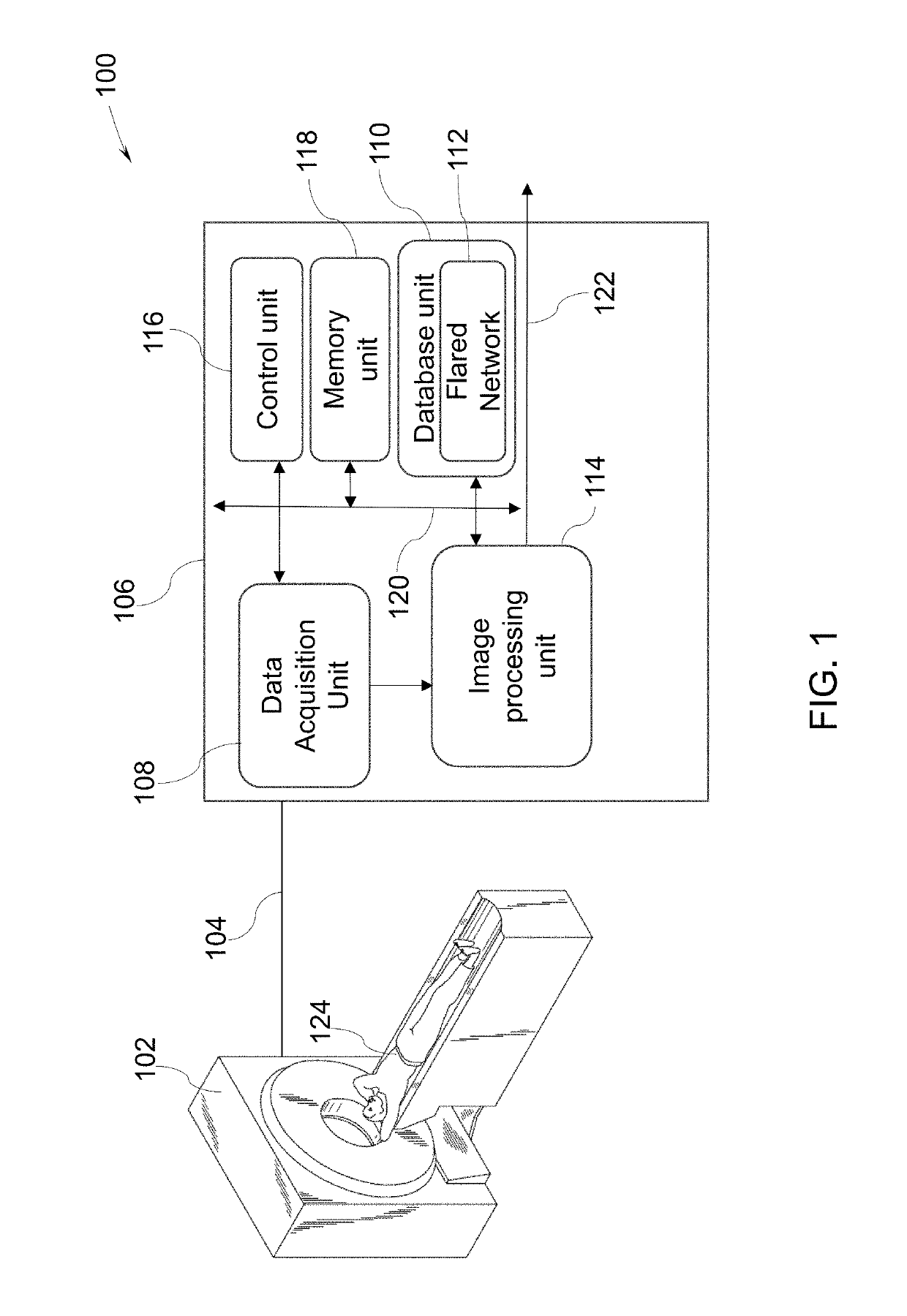
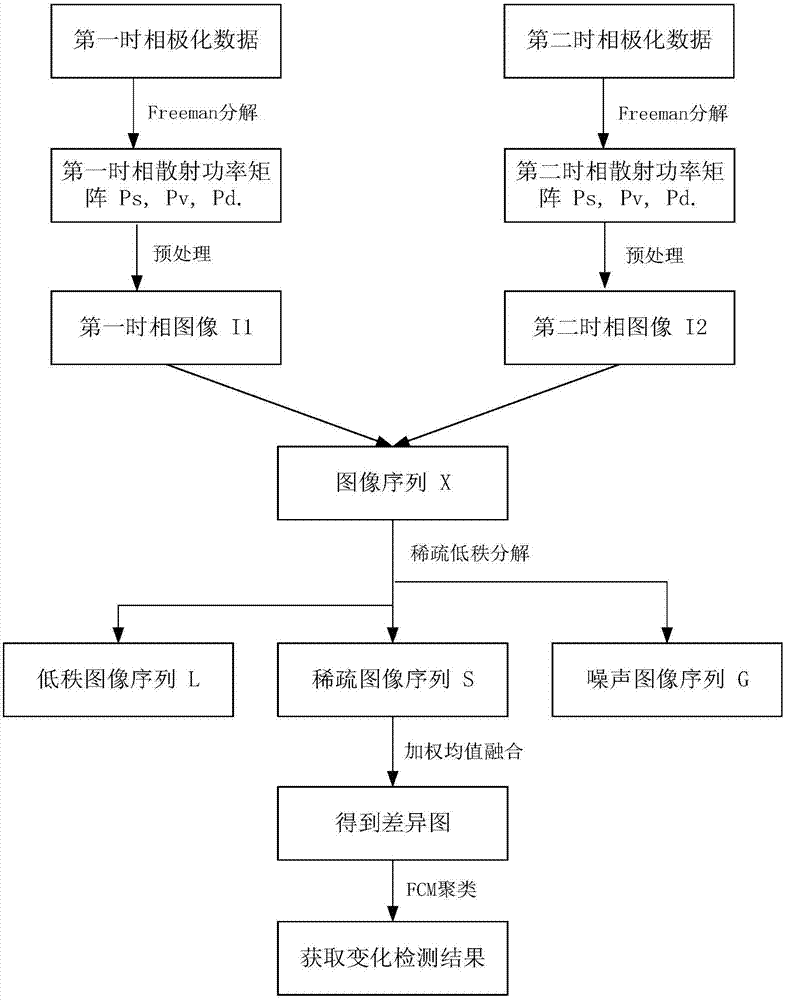
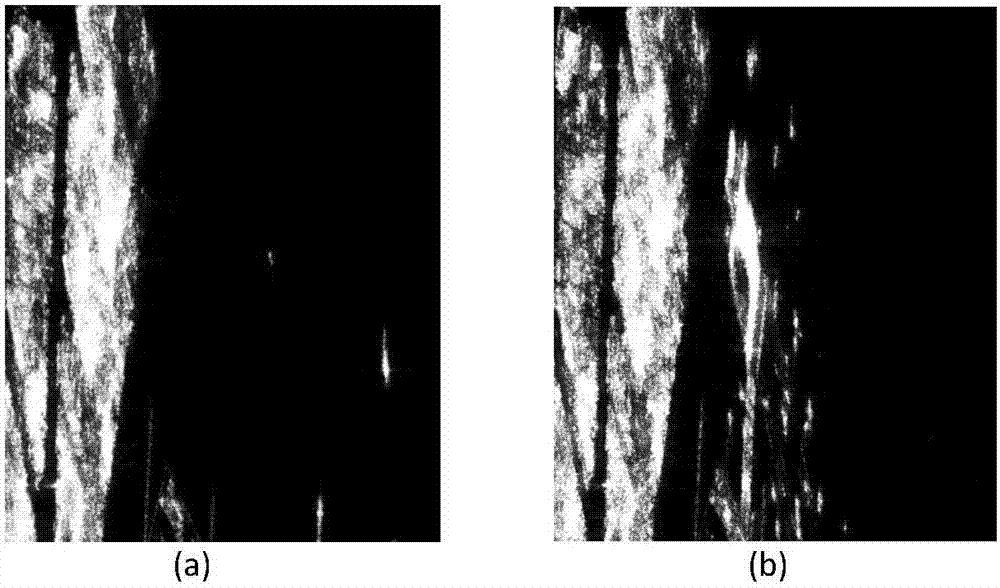
Polarimetric SAR (synthetic aperture radar) change detection method based on scattering features and low-rank sparse model
InactiveCN107123125AImprove accuracyReduce missed detection rateImage enhancementImage analysisDecompositionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a polarimetric SAR (synthetic aperture radar) change detection method based on scattering power features and a low-rank sparse model. The invention aims to solve the problems of high missing detection rate and low separability of difference images in the prior art. The process of the method of the invention includes the following steps that: 1) a first time phase coherence matrix T1 and a second phase coherence matrix T2 are extracted: 2) Freeman decomposition and registration are performed on T1 and T2, so that an input image I1 of a first time phase and an input image I2 of a second time are obtained; (3) I1 and I2 are adopted to construct a change image sequence I; (4) a low-rank sparse decomposition method is adopted to decompose the change image sequence I into the sum of three sub image sequences, namely, a low-rank image sequence L, a sparse image sequence S and a noise image sequence G; (5) the sparse image sequence S is fused, so that difference images are obtained; and 6) a fuzzy C-means method is adopted to cluster the difference images, so that the result image of change detection is obtained. The method of the invention has the advantages of strong noise resistance, low missing detection rate and high detection precision, and can be applied to urban planning, natural disaster assessment and climate change monitoring.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for imaging and identification integration based on compressed sensing and target prior information
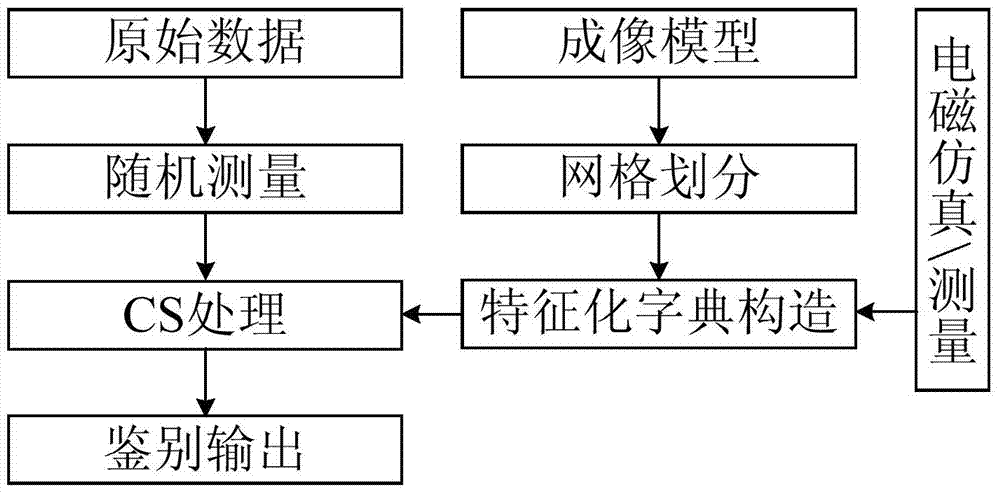
InactiveCN103941246AImprove identification efficiencyGood identification robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPrior informationComputer science
The invention belongs to the field of compressed sensing reconstruction based on target prior information and particularly relates to a method for imaging and identification integration based on compressed sensing and the target prior information. The method comprises the steps of obtaining electromagnetic scattering characteristics of targets; performing sparse imaging grid division on an imaging area and utilizing the obtained electromagnetic scattering characteristics to construct a characterization dictionary; obtaining echo data of the imaging area and working out observed data through a construction measurement matrix; utilizing the characterization dictionary in the steps and a CS algorithm to perform sparse reconstruction treatment on the observed data in the steps to obtain a sparse coefficient; enabling every element in the sparse coefficient to be in one-to-one correspondence with imaging area grids, and when the elements are nonzero values, judging that the targets exist at the corresponding positions of the imaging area grids; and if the elements are zero, judging that no target exists at the corresponding positions of the imaging area grids. Target discrimination is finished while sparse imaging on the targets is achieved, and the method is good in discrimination robustness and consistency.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Image deblurring method based on redundant dictionary pair joint optimization
The invention discloses an image deblurring method based on a redundant dictionary pair joint optimization, which is used for solving the technical problem that the recovery image in the dual-dictionary sparse image deblurring method under the existing sparse theory framework has strong ring effect at the strong edge. According to the method, a joint optimization function, an iteration solution point spread function and a clear image are established on the basis of the characteristic that the sparse coefficient of a fuzzy image under a fuzzy redundant dictionary is consistent with the sparse coefficient of a clear image under a clear redundant dictionary. The method enhances the robustness against noise, avoids the ill condition in the deconvolution process, reduces the ring effect of the recovery image at the strong edge, and obtains a clearer and more detailed image.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
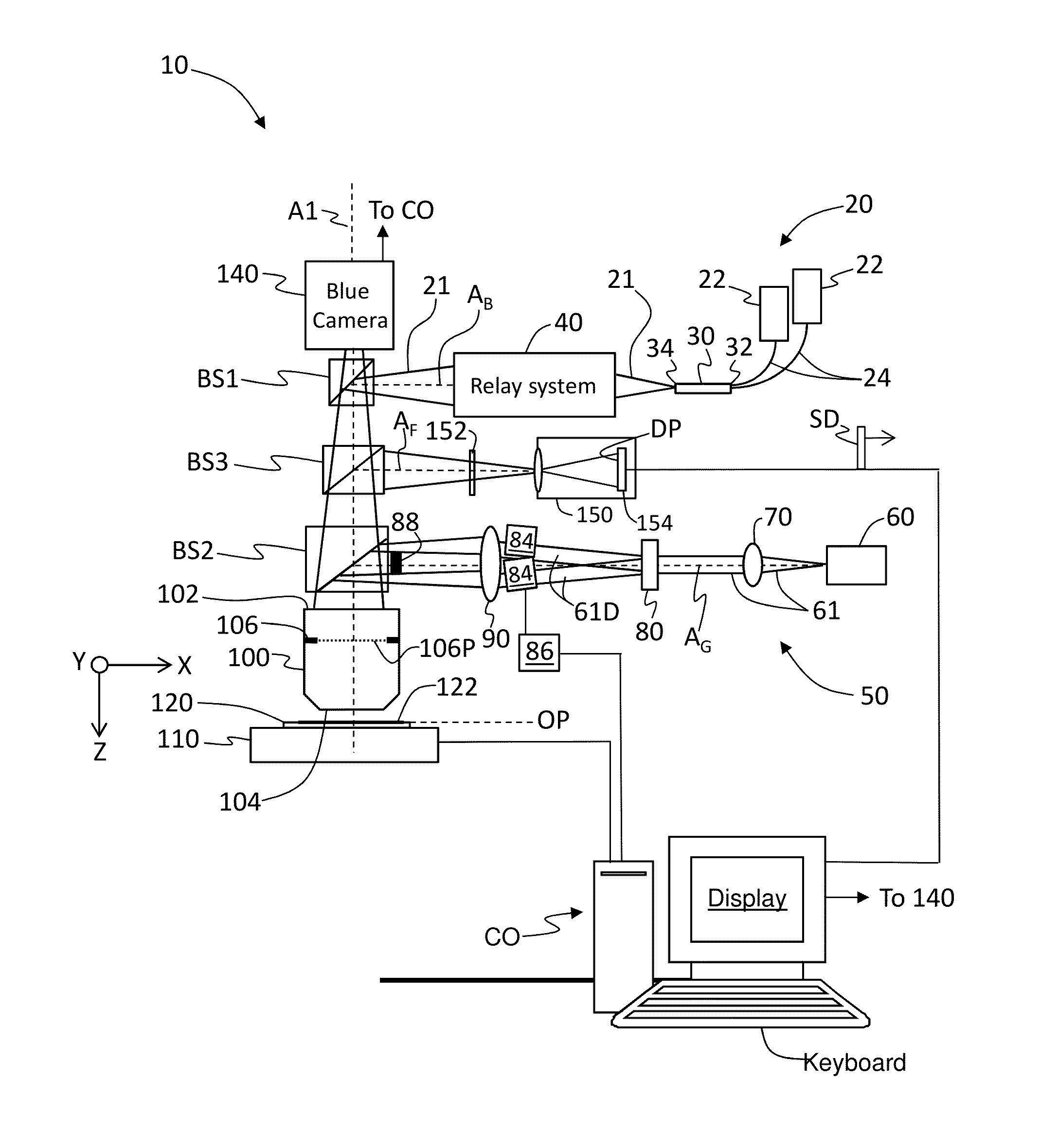
Apparatus and method for generating a camera model for an imaging system
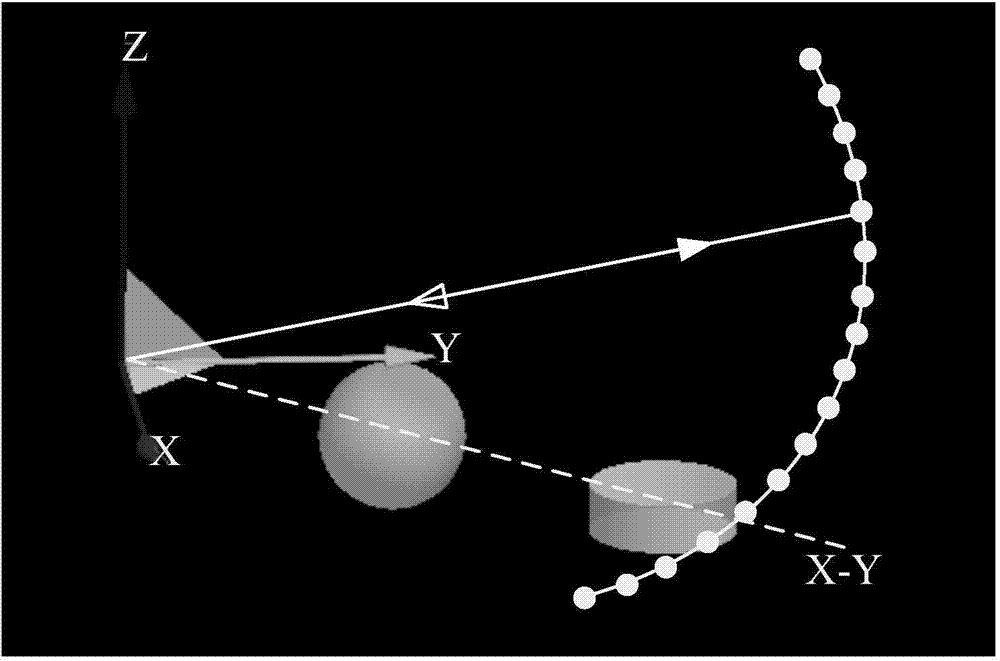
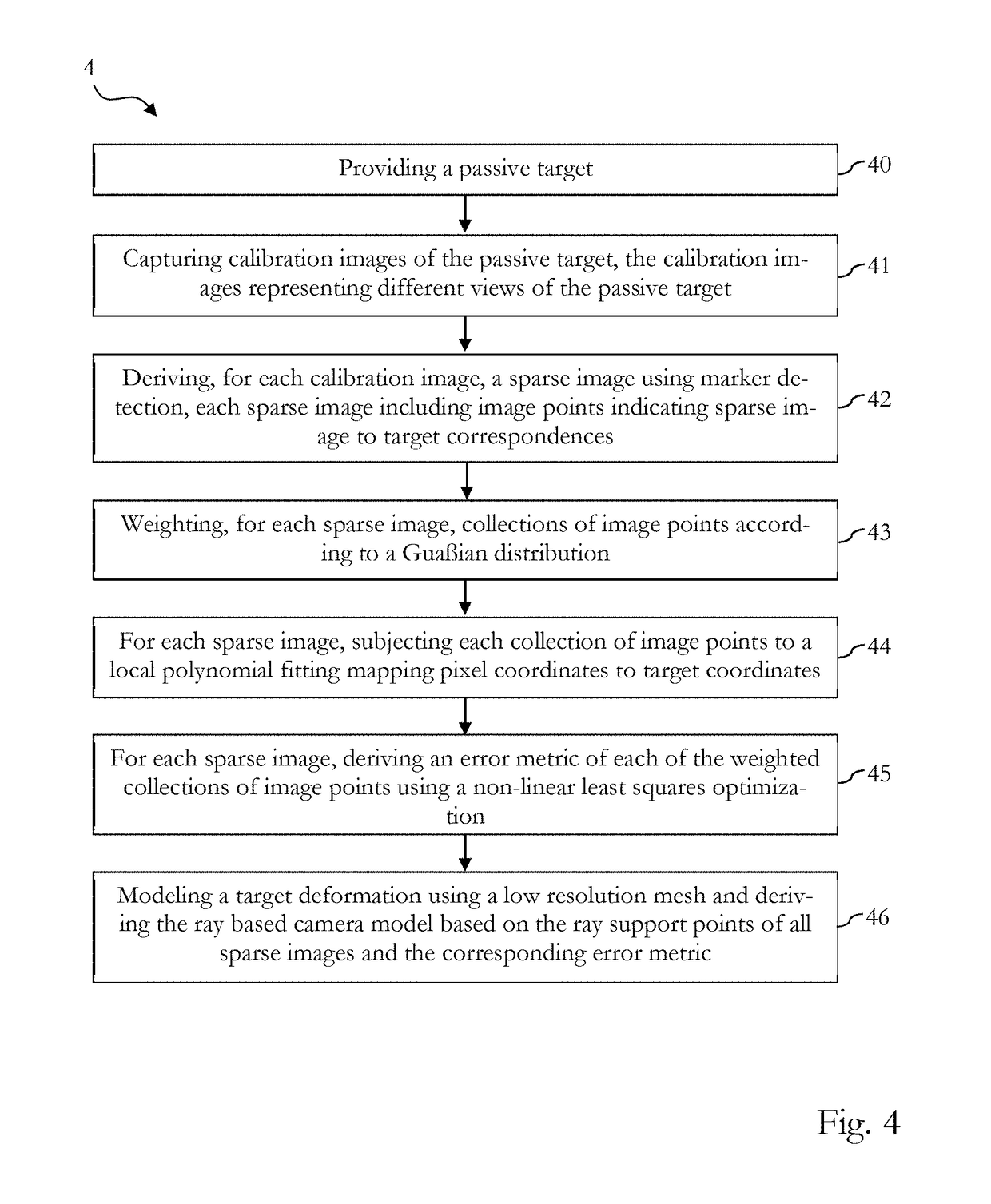
The disclosure pertains to an apparatus comprising a circuitry. The circuitry is configured to obtain a calibration image of a target, to derive a sparse image based on the calibration image, wherein the sparse image includes image points, to derive ray support points based on the image points by performing an image to target mapping of the image points based on a polynomial function, wherein the ray support points being indicative of light rays reflected by the target and incidenting on an image sensor, and to generate a camera model based on the derived ray support points.
Owner:SONY CORP
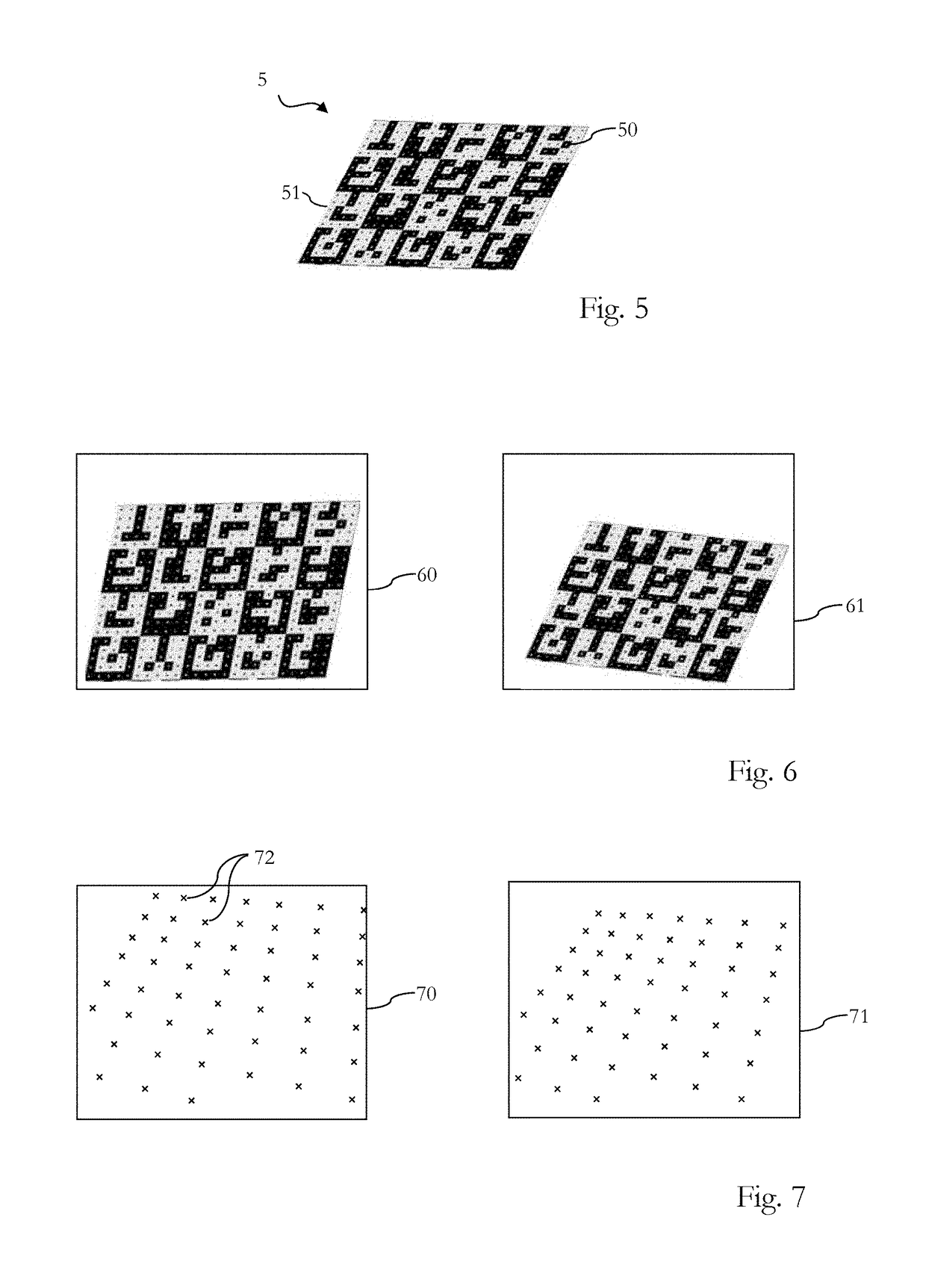
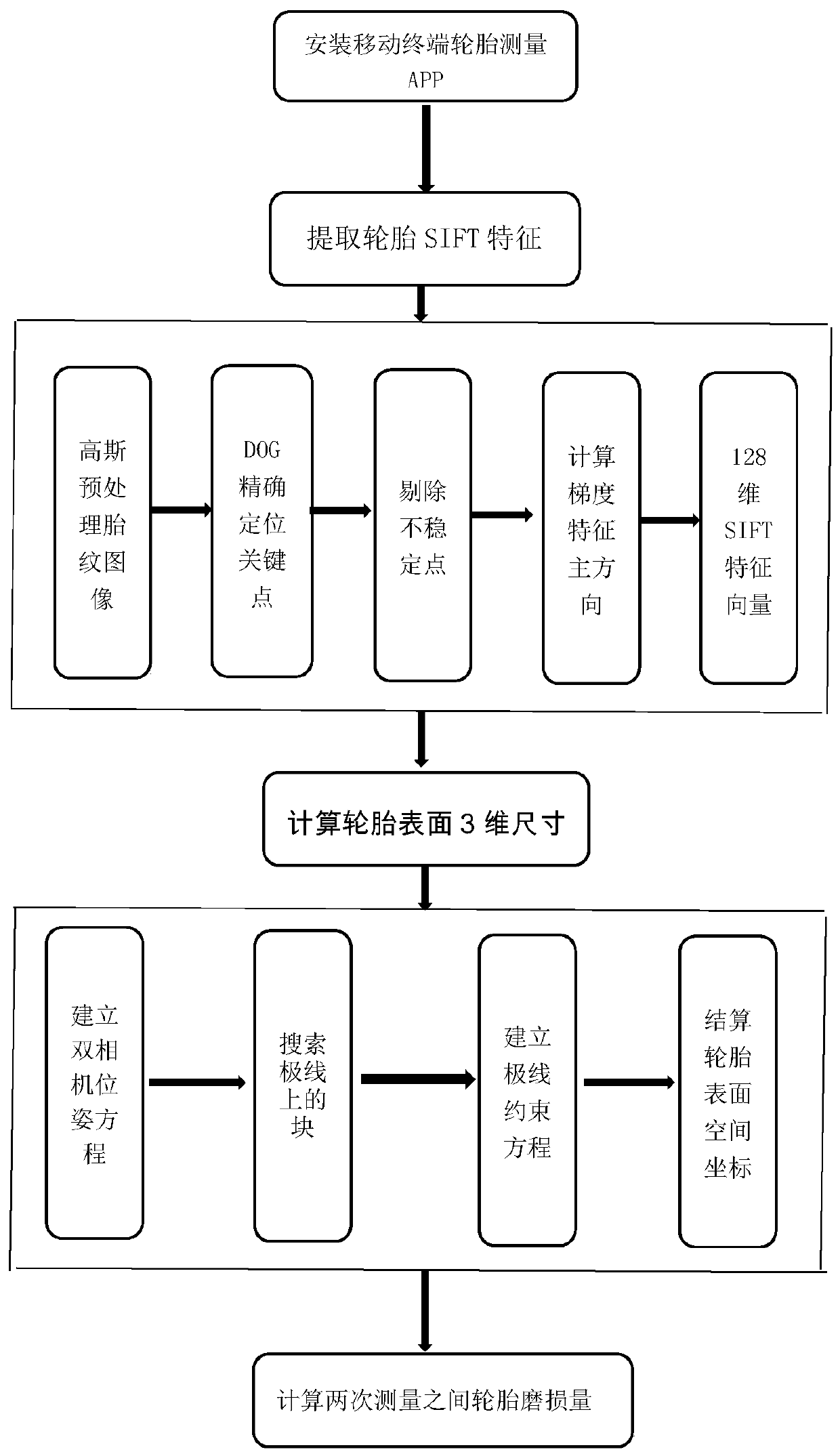
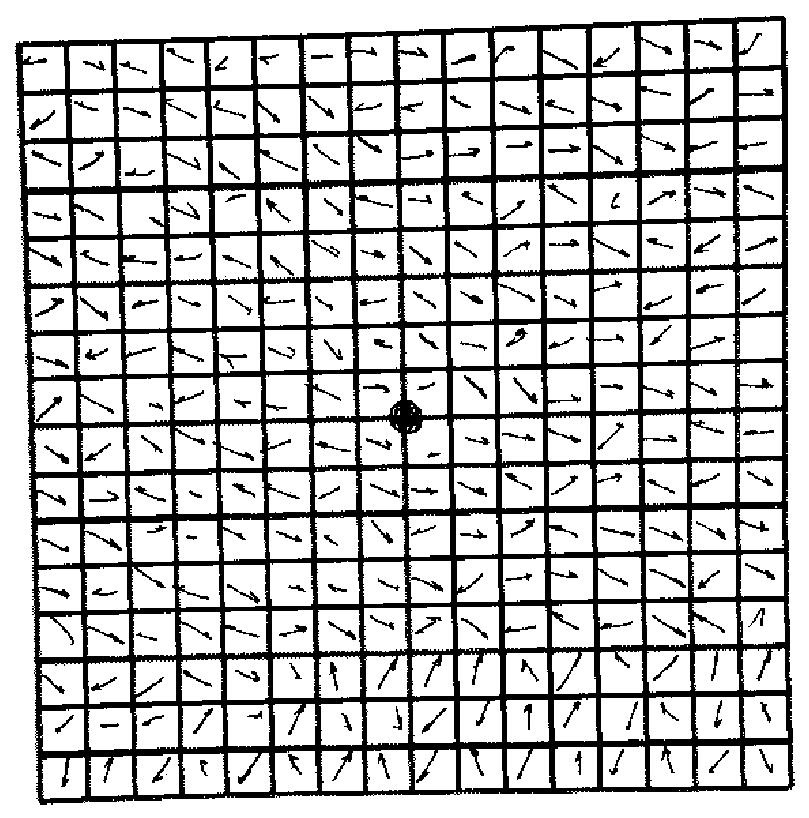
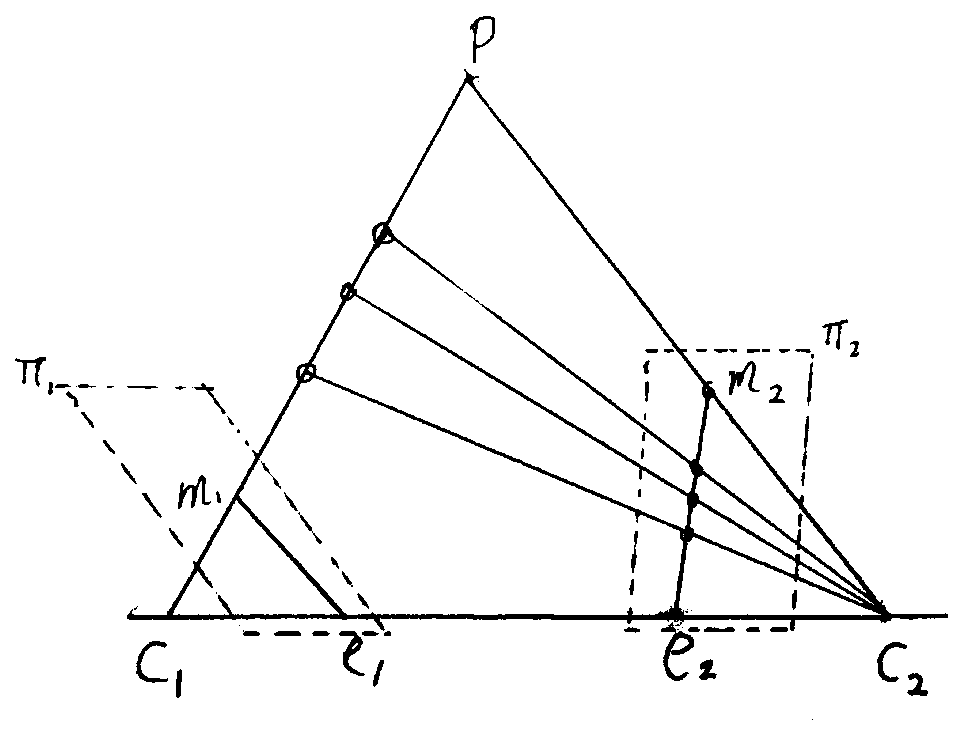
Tire contour measurement method based on camera shooting
The invention discloses a tire contour measurement method based on camera shooting, and the method comprises the steps: firstly, carrying out the shooting of the same tire tread pattern image at different positions, and extracting a tire tread pattern contour sparse image and a key point feature value from a single two-dimensional image; secondly, establishing a change rate and a change directionkey point characteristic matrix of an image pixel gray value according to the tire tread, and calculating a plurality of same key point characteristic values in two and a plurality of tire tread sparse images; then, comparing and calculating a camera internal parameter and a three-dimensional space camera pose external parameter change prediction value with two or more actual observation values oftwo or more two-dimensional space pixel values, and fitting a three-dimensional tire tread contour space curve; and finally, comparing the actual three-dimensional spatial change data of the tread pattern obtained in any time period, and calculating the use abrasion loss of the tire in the time period. According to the tire tread measurement feedback method provided by the invention, a calculation basis is provided for the tire according to use payment while safe driving of the tire is ensured.
Owner:南京链和科技有限公司
Sparse image point correspondences generation and correspondences refinement system for ground truth static scene sparse flow generation
A system for generating a ground truth dataset for motion planning of a vehicle is disclosed. The system includes an internet server that further includes an I / O port, configured to transmit and receive electrical signals to and from a client device; a memory; one or more processing units; and one or more programs stored in the memory and configured for execution by the one or more processing units, the one or more programs including instructions for: a corresponding module configured to correspond, for each pair of images, a first image of the pair to a LiDAR static-scene point cloud; and a computing module configured to compute a camera pose associated with the pair of images in the coordinate of the point cloud.
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
Text recognition for textually sparse images
A text recognition server is configured to recognize text in a sparse text image. Specifically, given an image, the server specifies a plurality of “patches” (blocks of pixels within the image). The system applies a text detection algorithm to the patches to determine a number of the patches that contain text. This application of the text detection algorithm is used both to estimate the orientation of the image and to determine whether the image is textually sparse or textually dense. If the image is determined to be textually sparse, textual patches are identified and grouped into text regions, each of which is then separately processed by an OCR algorithm, and the recognized text for each region is combined into a result for the image as a whole.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com