Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
345 results about "Radiographic equipment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This is a page devoted to the basic equipment used for radiographic work, both medical and industrial.
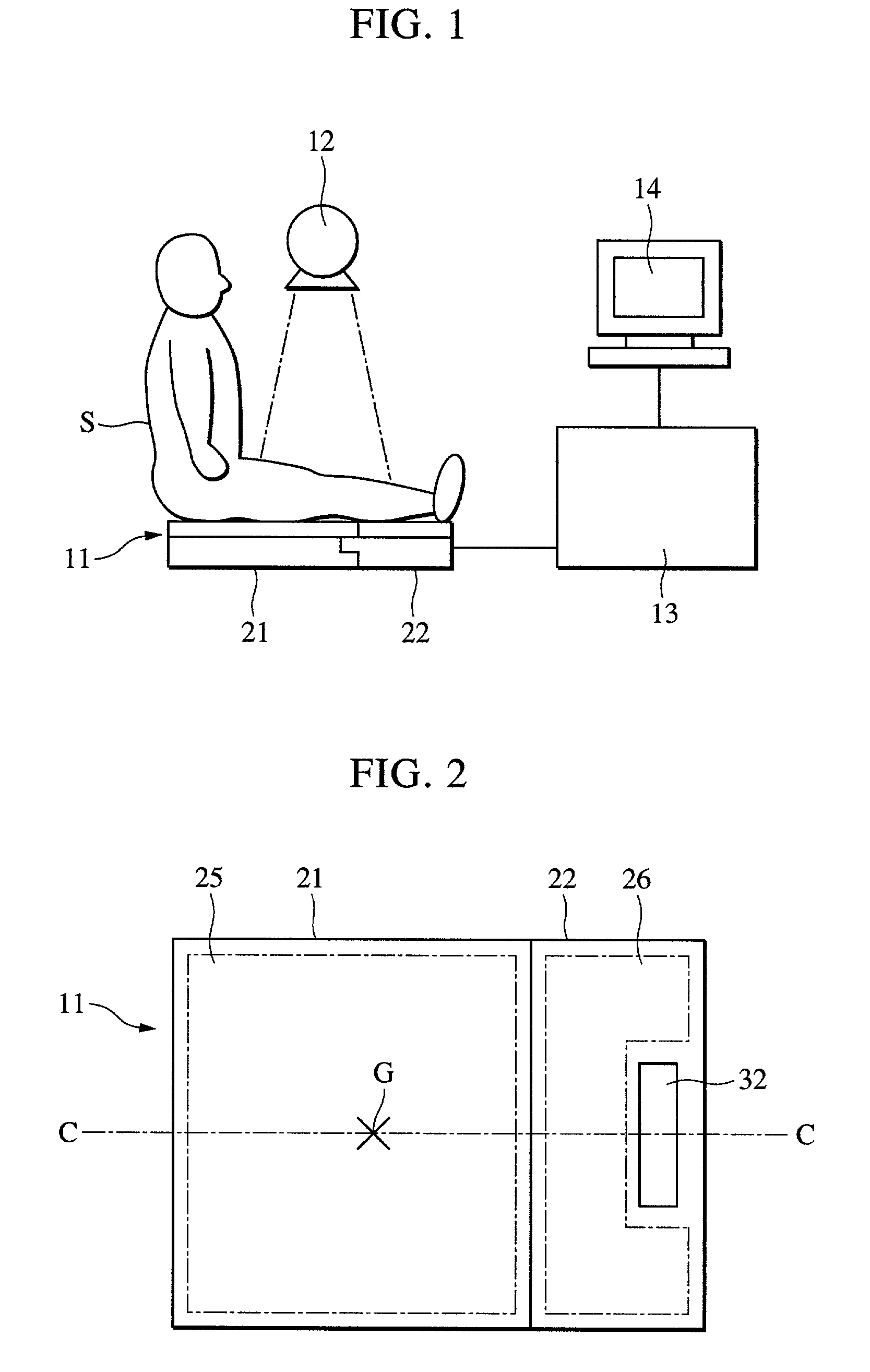
Radiographic apparatus
ActiveUS8798231B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageFluorescence
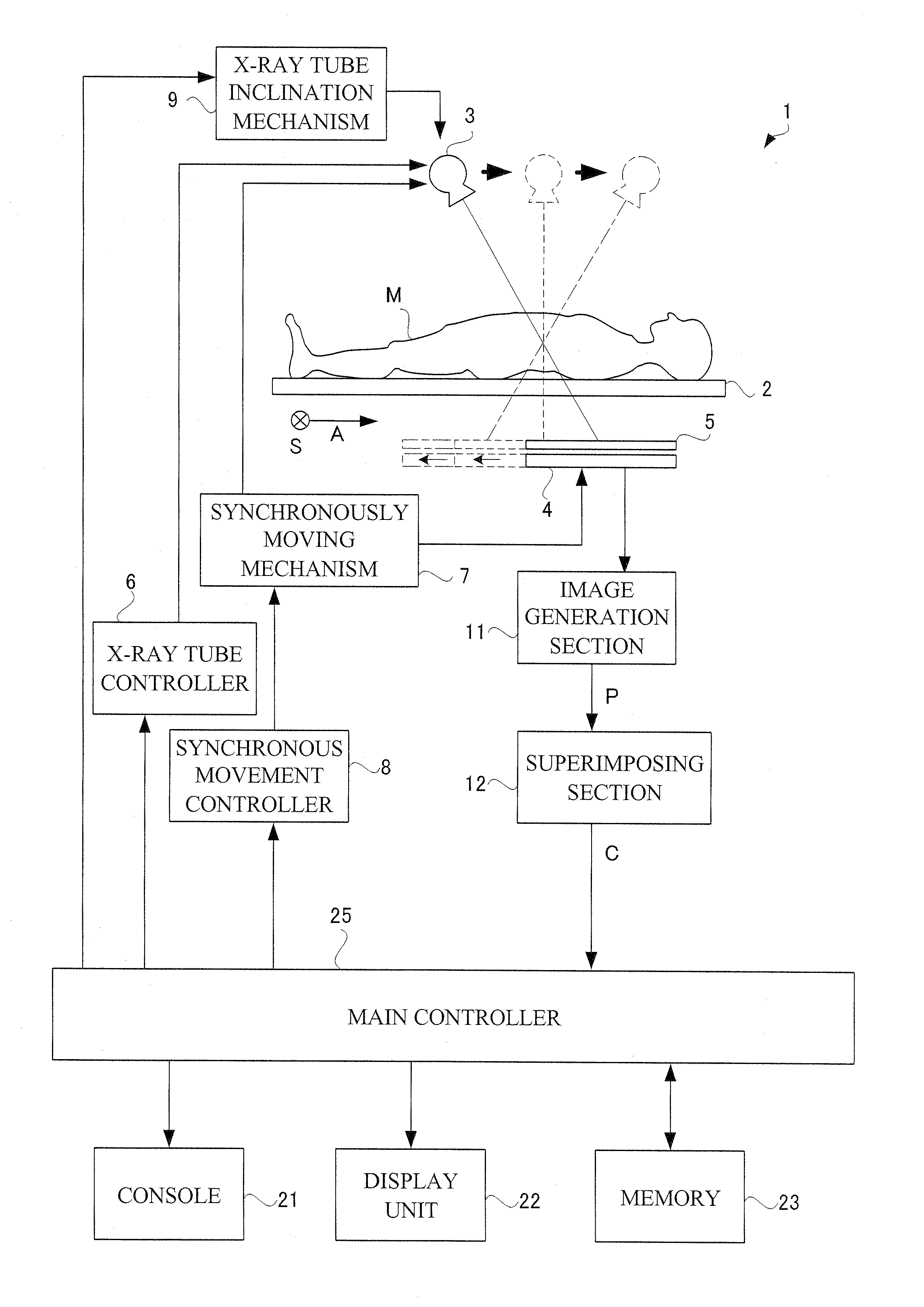
One object of this invention is to provide radiography apparatus with suppressed exposure to a subject in tomography mode. An FPD provided in X-ray apparatus according to this invention converts X-rays into electric signals, and thereafter amplifies the signals to output them to an image generation section. According to this invention, an amplification factor is higher in a tomography mode than in a spot radiography mode. A tomographic image is obtained through superimposing two or more fluoroscopic image. In comparison of the fluoroscopic images, they differ from one another in appearance of the false image. Accordingly, superimposing the images may achieve cancel of the false images. In this way, the tomographic image finally obtained has no false image.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
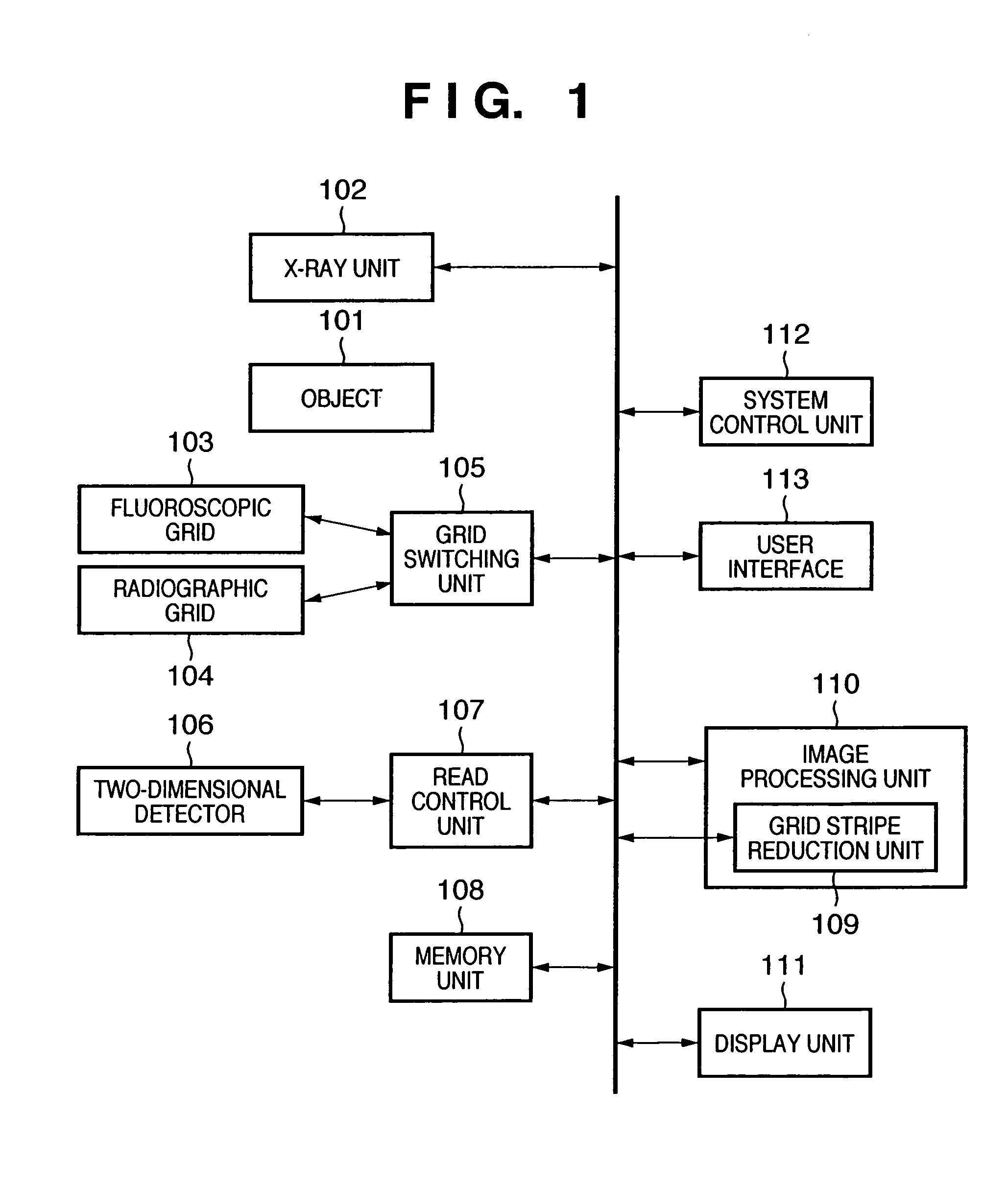
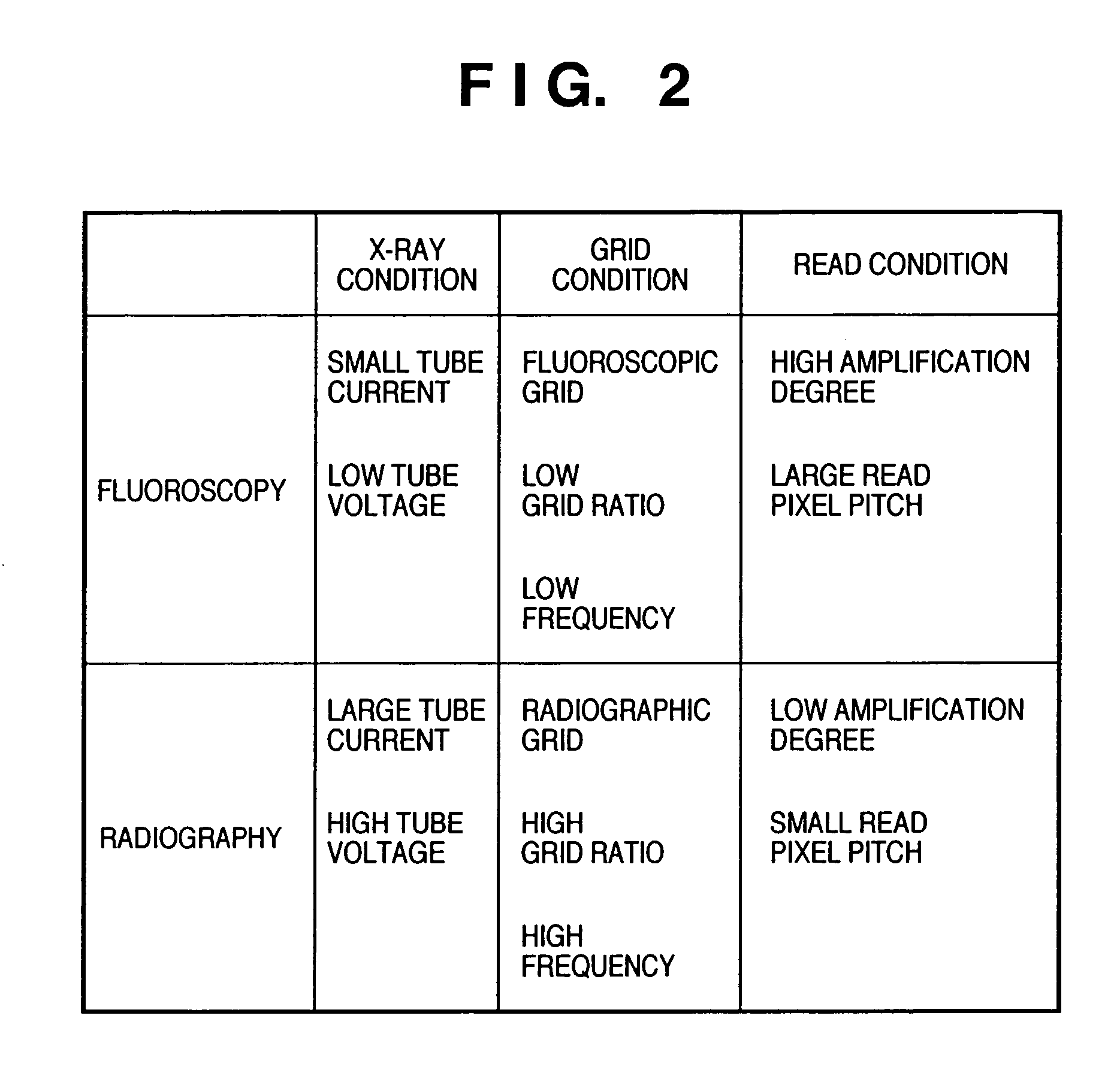
Radiographic apparatus and method for switching a grid
InactiveUS7110502B2Reducing grid stripes generatedRadiation/particle handlingTomographySoft x rayTwo dimensional detector
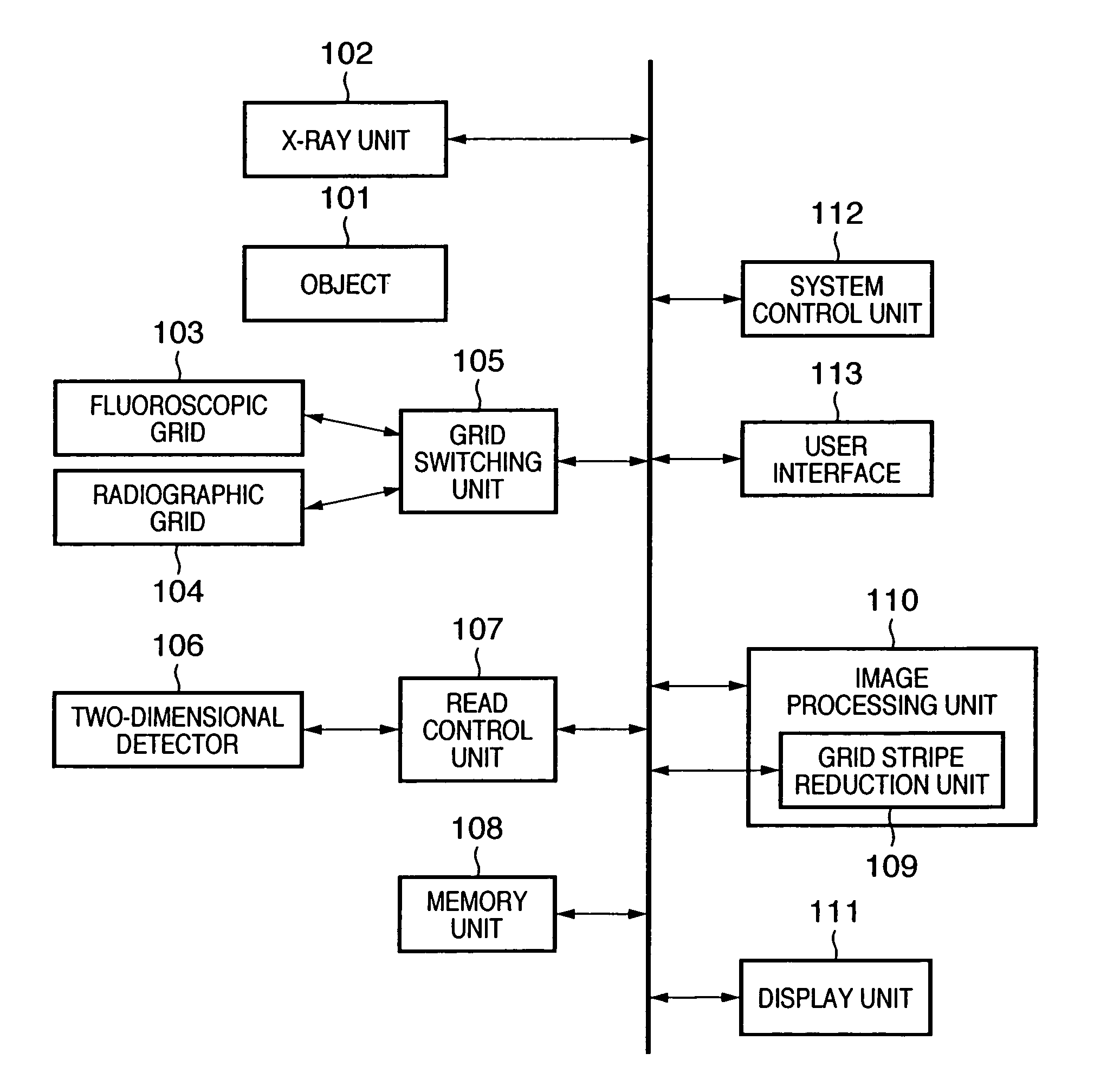
This invention provides a radiographic apparatus and method, which can suitably set a grid in radiography or fluoroscopy and execute fluoroscopy or radiography of an object under optimum imaging conditions. The radiographic apparatus includes an X-ray unit (102) which irradiates an object with radiation (X-rays), a two-dimensional detector (106) which detects, through a grid, the radiation which has passed through the object, and a read control unit (107) which acquires an image of the object from the detected X-rays. The apparatus further includes a user interface (113) capable of setting imaging conditions such as an X-ray condition, grid condition, and read condition, a grid switching unit (105) which selects one of a plurality of grids on the basis of the set imaging conditions, and a grid stripe reduction unit (109) which reduces grid stripes generated on the image by the grid.
Owner:CANON KK
Radiographic apparatus and control method therefor
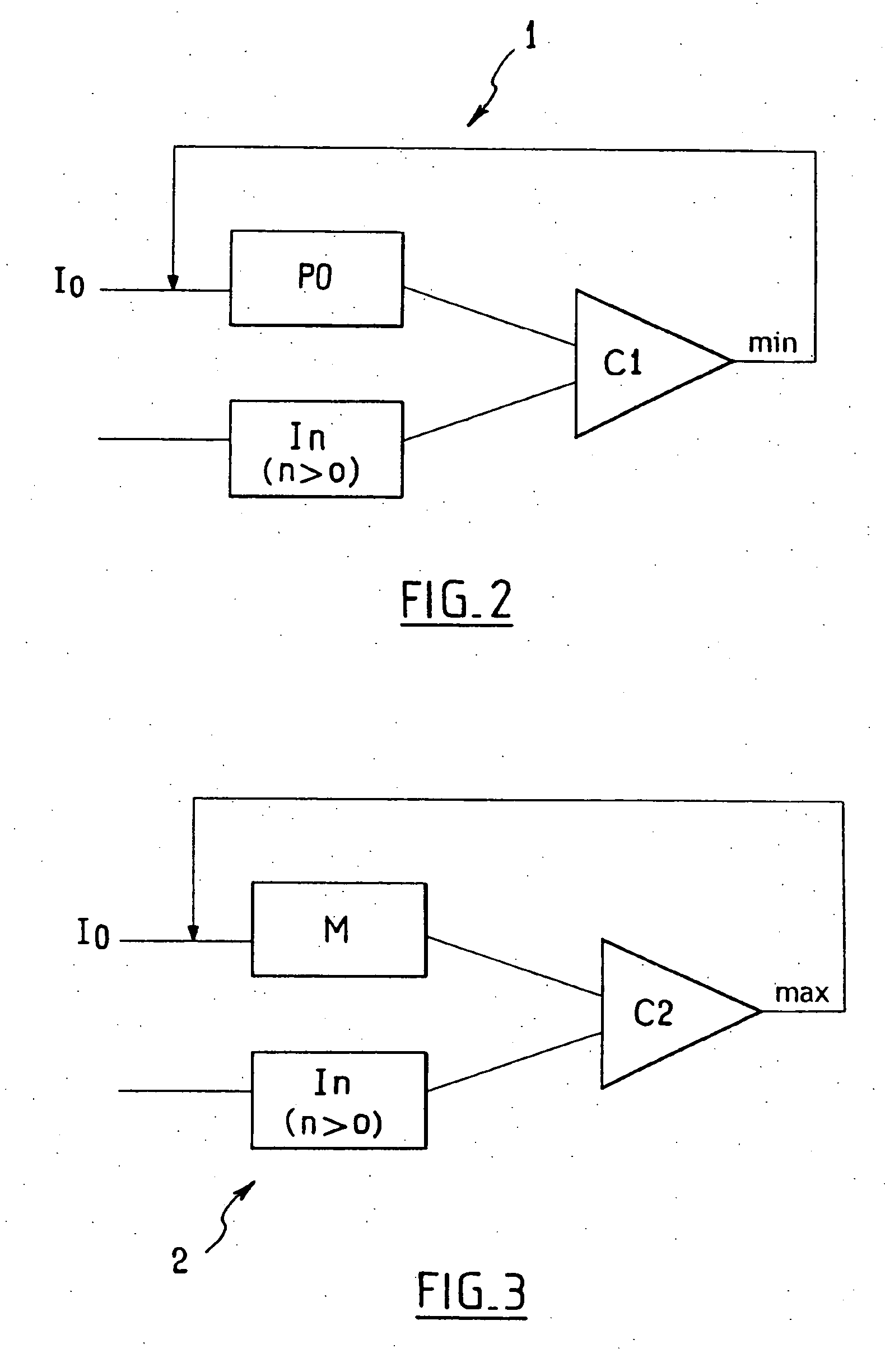
InactiveUS20050199834A1Reduce refresh timeReduce waiting timeTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesComputer scienceRadiographic equipment
If image data is input to an image processor (step S1), the image processor generates an integrated image sum (step S2). The image processor extracts a maximum output max from the integrated image sum (step S3). The image processor compares the maximum output max with a preset threshold (step S4). In this case, the threshold is set to 80% of the saturation amount. When the saturation amount is 3 V, the threshold is 2.4 V. If the maximum value max is smaller than the threshold, imaging continues. If the maximum value max is equal to or larger than the threshold, the integrated image sum is cleared to 0 (step S5), and refresh operation is performed.
Owner:CANON KK
Delivering X-ray systems to pipe installations
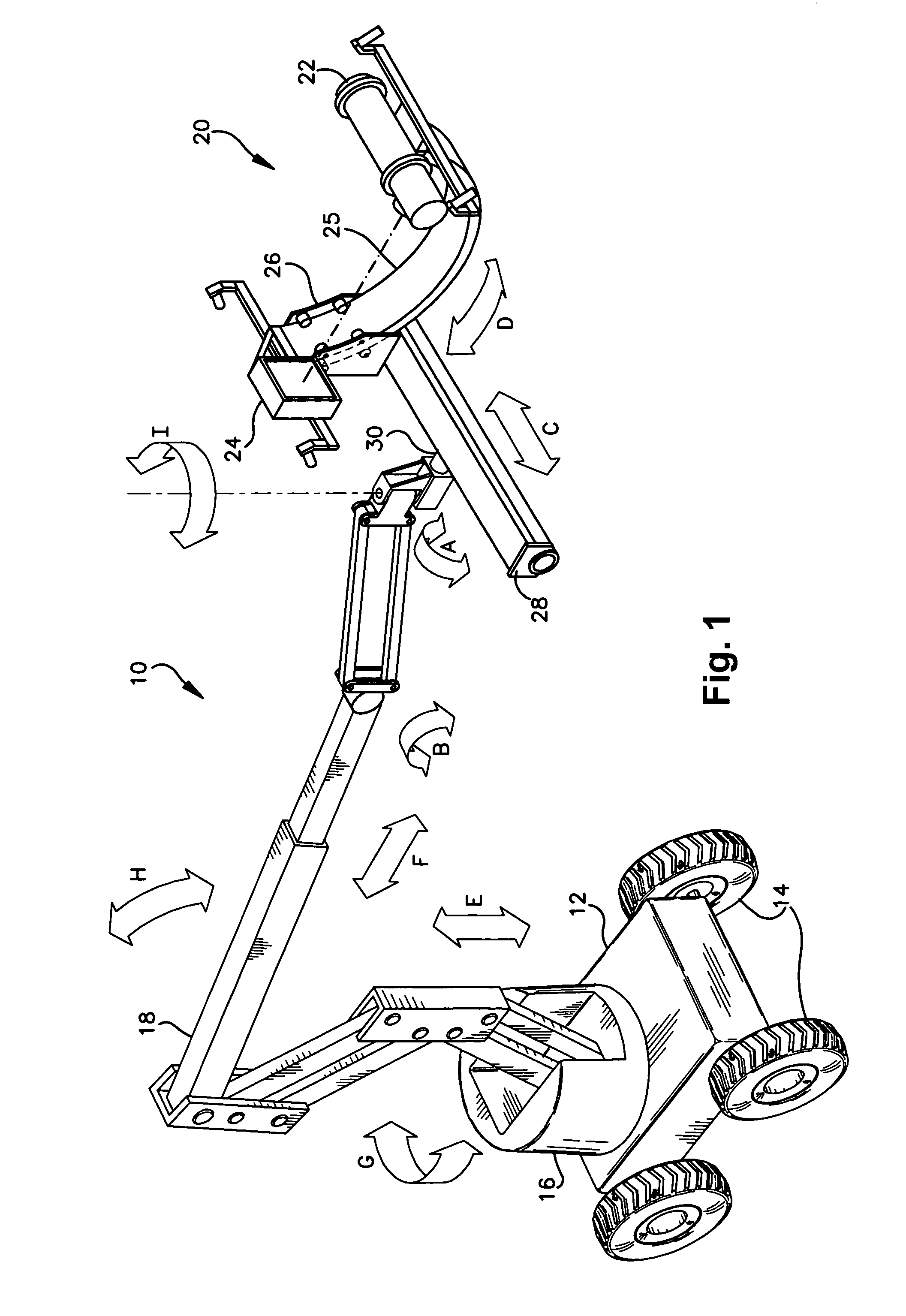
InactiveUS20060078091A1Convenient registrationSimplify mappingUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-ray apparatusX-rayEngineering
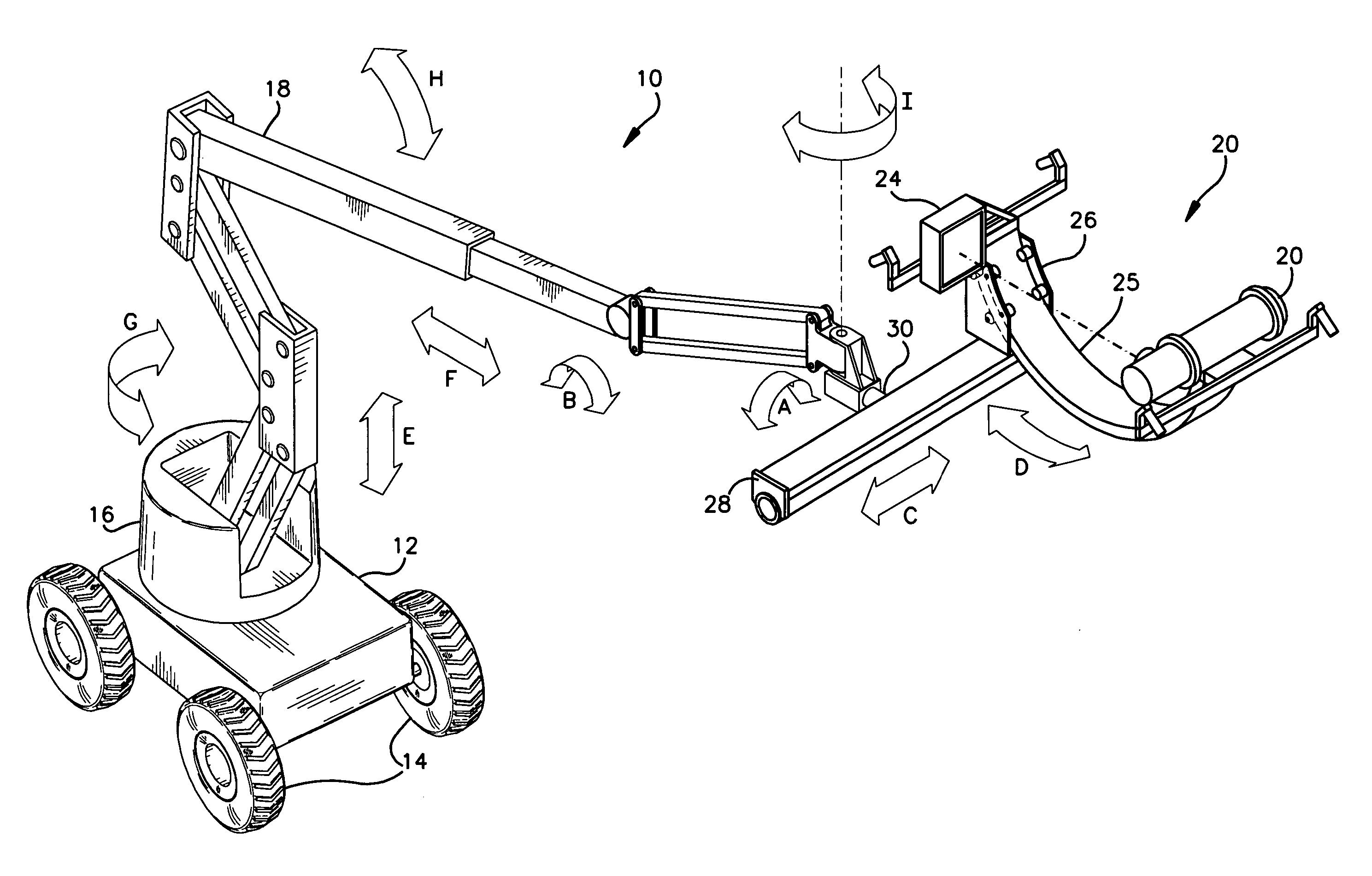
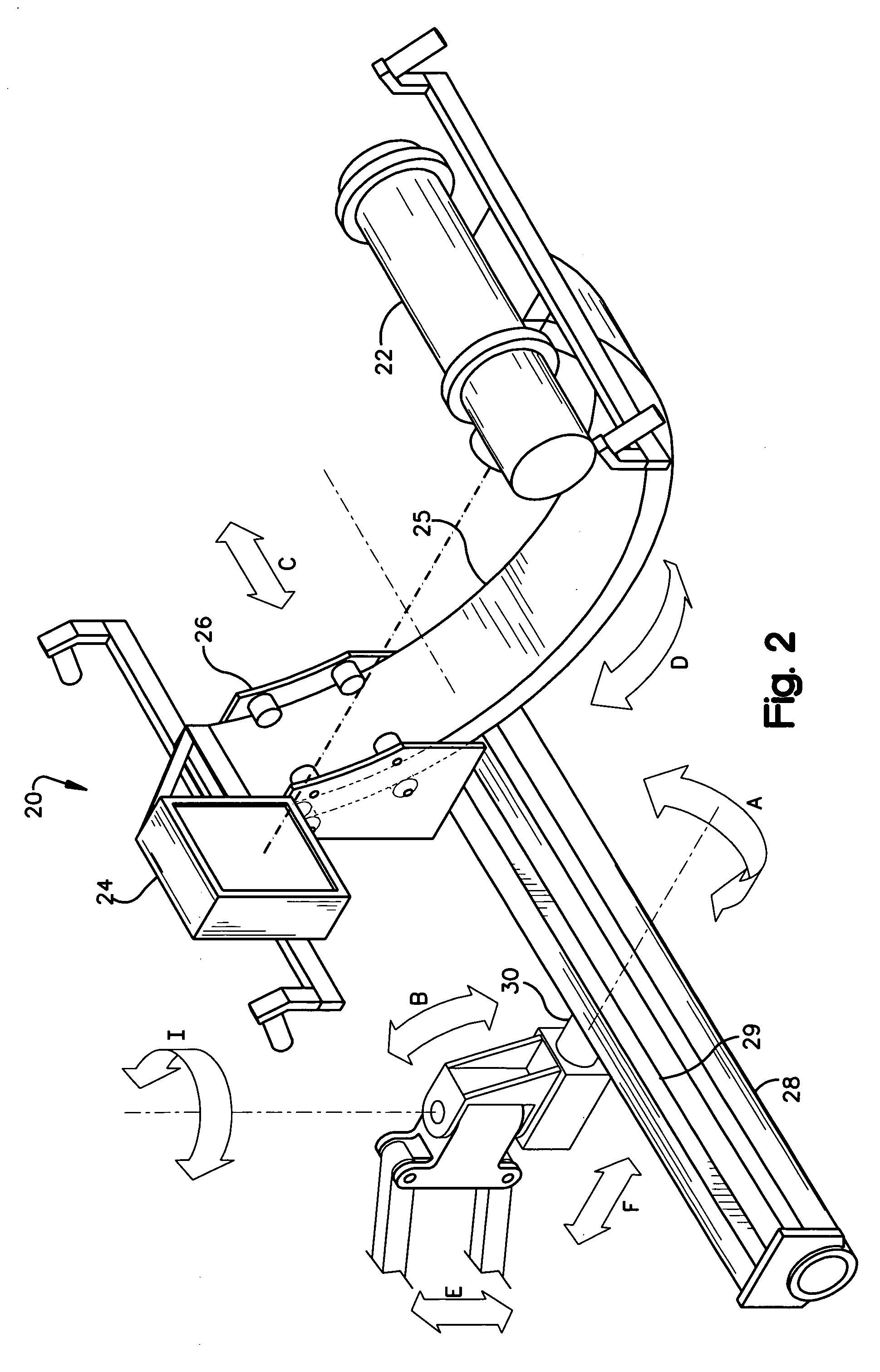
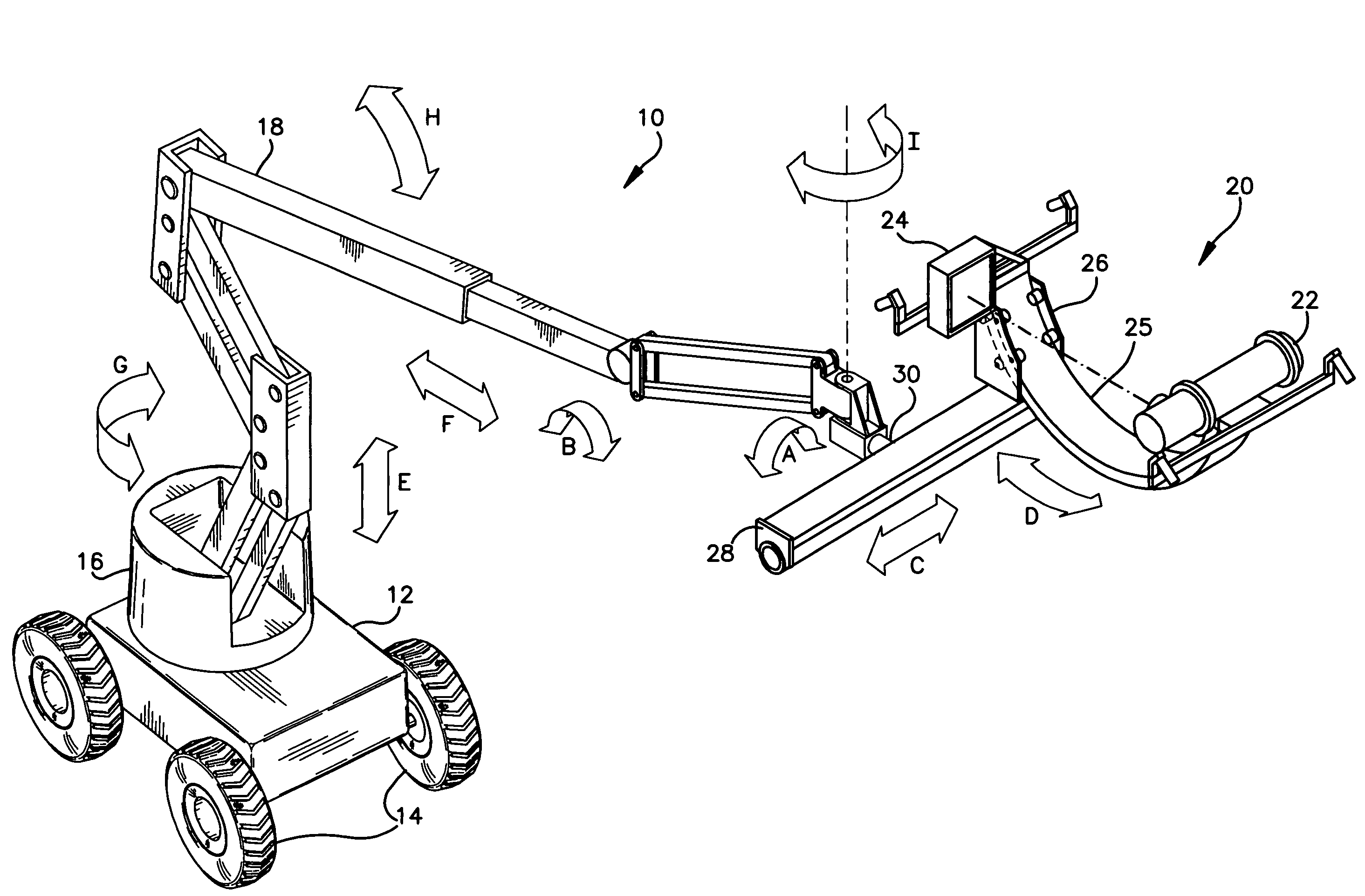
A mobile radiographic device for use in inspecting pipelines and the like, comprising an articulating aerial boom coupled to a mobile carriage vehicle. A pivot mount is rotatably coupled to the distal end of the aerial boom. A platform having a sliding rail is operatively coupled to the pivot mount. A mounting fixture is rotatably mounted to a cradle, which in turn is coupled to the sliding rail of the platform. A radiation source and a radiation detector are mounted on diametrically opposing sides of the fixture in order to illuminate the outer surface of a pipeline or other object with radiation. A first positioning means is provided for coarsely positioning the scanning apparatus relative to the pipeline. A second positioning means is provided for finely positioning the scanning apparatus relative to the pipeline. The second positioning means is operable from a remote location when the radiation source is illuminating the pipeline with radiation. The first and second positioning means provide a plurality of degrees of freedom for positioning the scanning apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Delivering X-ray systems to pipe installations
InactiveUS7319738B2Simplify registration and mappingEasy alignmentUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-ray apparatusX-rayEngineering
A mobile radiographic device for use in inspecting pipelines and the like, comprising an articulating aerial boom coupled to a mobile carriage vehicle. A pivot mount is rotatably coupled to the distal end of the aerial boom. A platform having a sliding rail is operatively coupled to the pivot mount. A mounting fixture is rotatably mounted to a cradle, which in turn is coupled to the sliding rail of the platform. A radiation source and a radiation detector are mounted on diametrically opposing sides of the fixture in order to illuminate the outer surface of a pipeline or other object with radiation. A first positioning means is provided for coarsely positioning the scanning apparatus relative to the pipeline. A second positioning means is provided for finely positioning the scanning apparatus relative to the pipeline. The second positioning means is operable from a remote location when the radiation source is illuminating the pipeline with radiation. The first and second positioning means provide a plurality of degrees of freedom for positioning the scanning apparatus.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radiographic apparatus, radiographic method, program, computer-readable storage medium, radiographic system, image diagnosis aiding method, and image diagnosis aiding system
InactiveUS7050537B2Health-index calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringImage diagnosisComputer science
A radiographic apparatus or system for imaging a dynamic state or process of an object such as a human body includes an indication unit for performing dynamic state guiding indication using a perceivable pattern corresponding to a dynamic state or motion to be engaged in by the patient, and an image acquisition unit for acquiring a plurality of radiographs of the human body. The resulting radiographs can be reviewed for diagnosis, and can be stored, either locally or at a remote location.
Owner:CANON KK
Radiographic apparatus and method, and control apparatus and method upon radiography
InactiveUS6859513B2Easy to operateImprove radiographing efficiencyTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayX ray image
A radiographic apparatus for obtaining an X-ray image on the basis of examination request information received from an externa ol apparatus, determines a radiographing condition by giving the received examination request information preference to a default radiographing condition corresponding to the received examination request information.
Owner:CANON KK
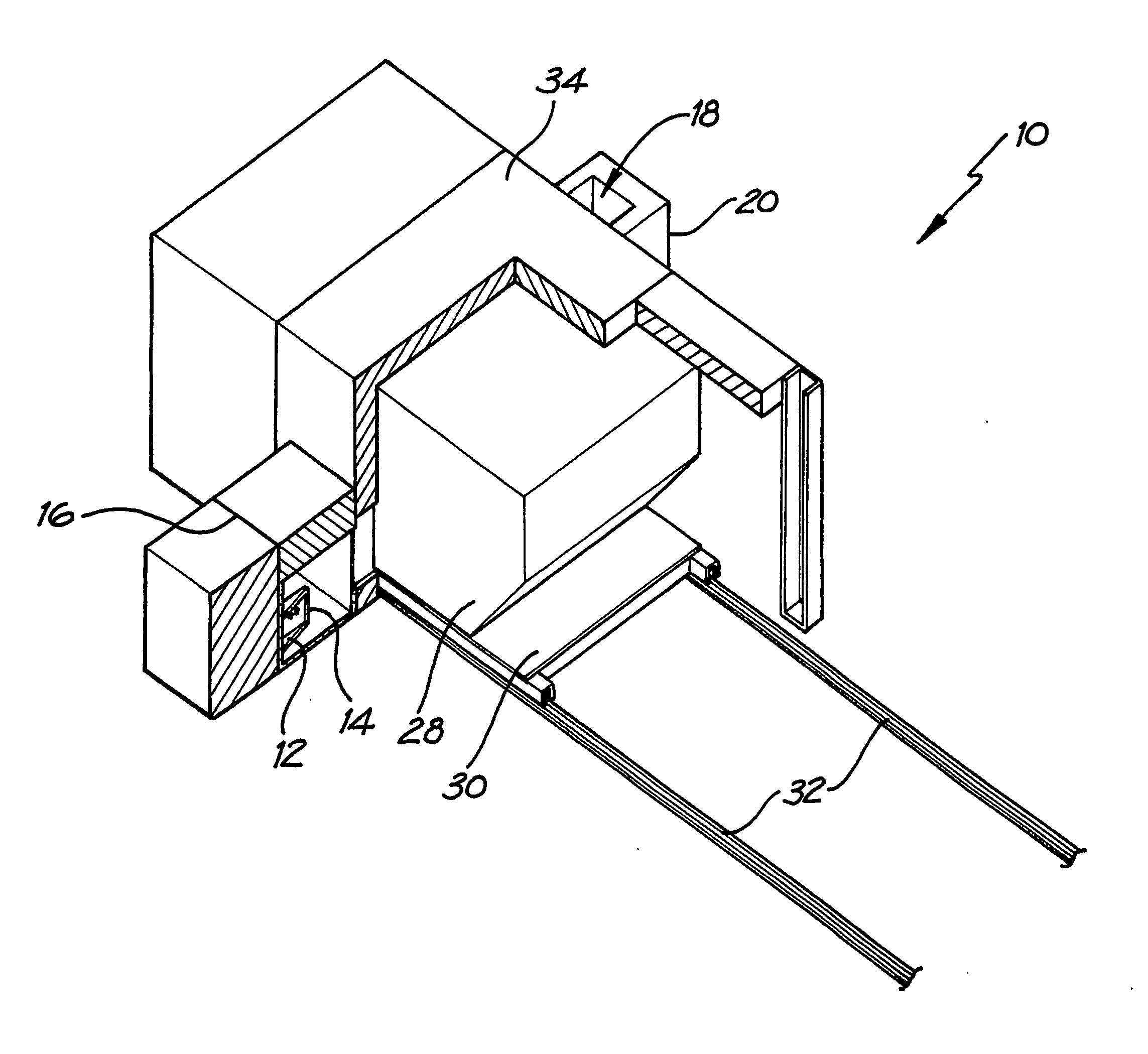
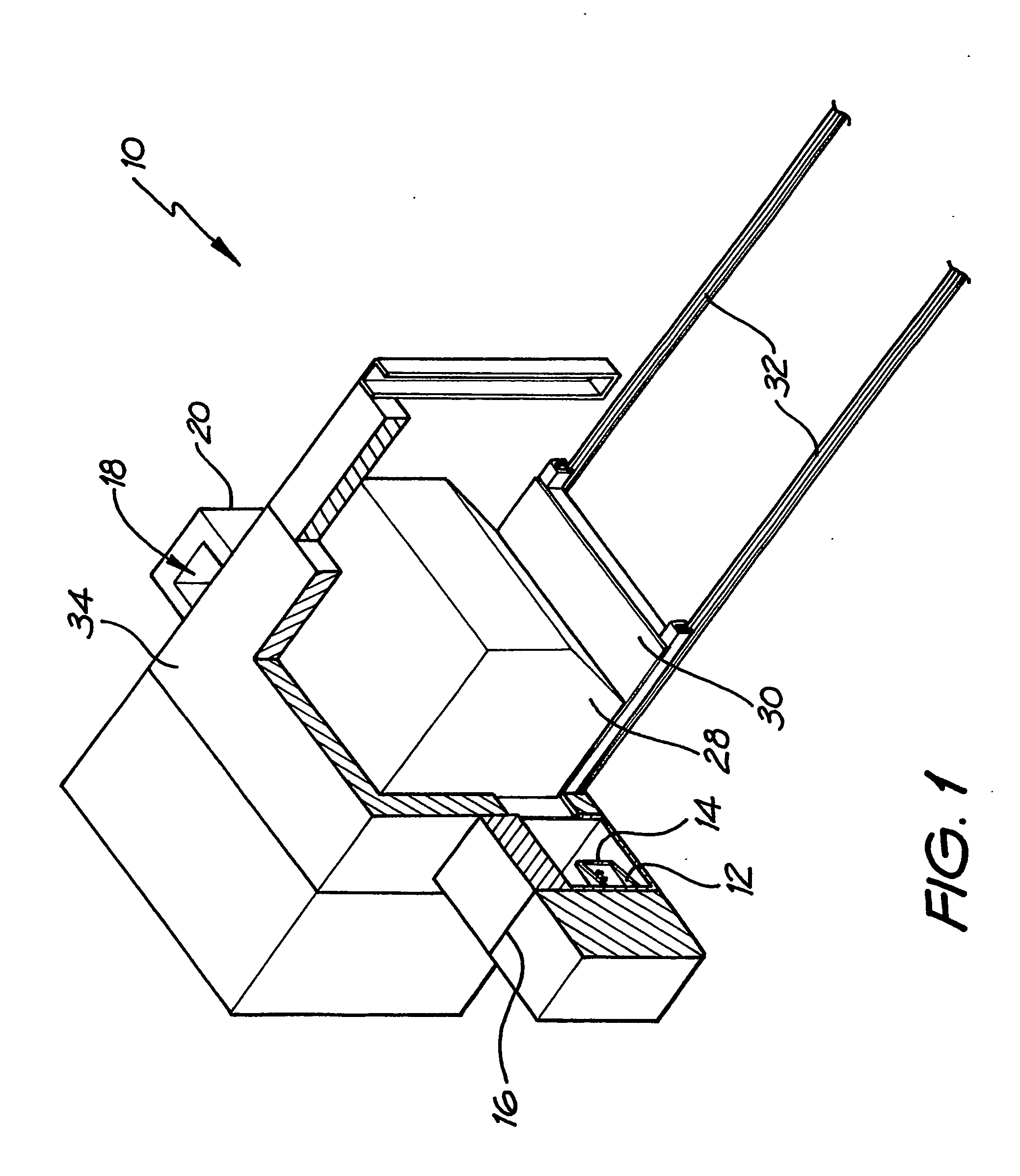
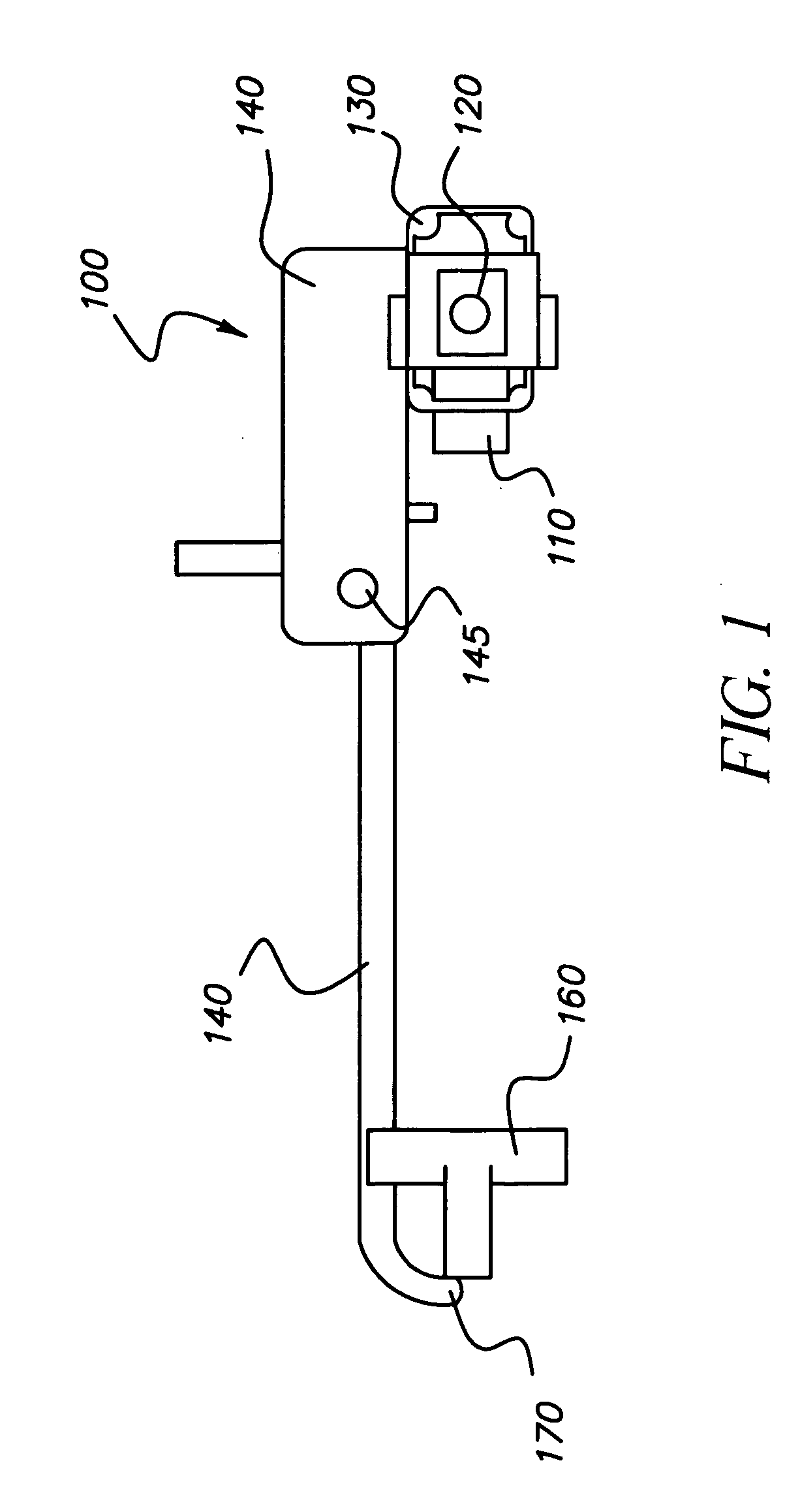
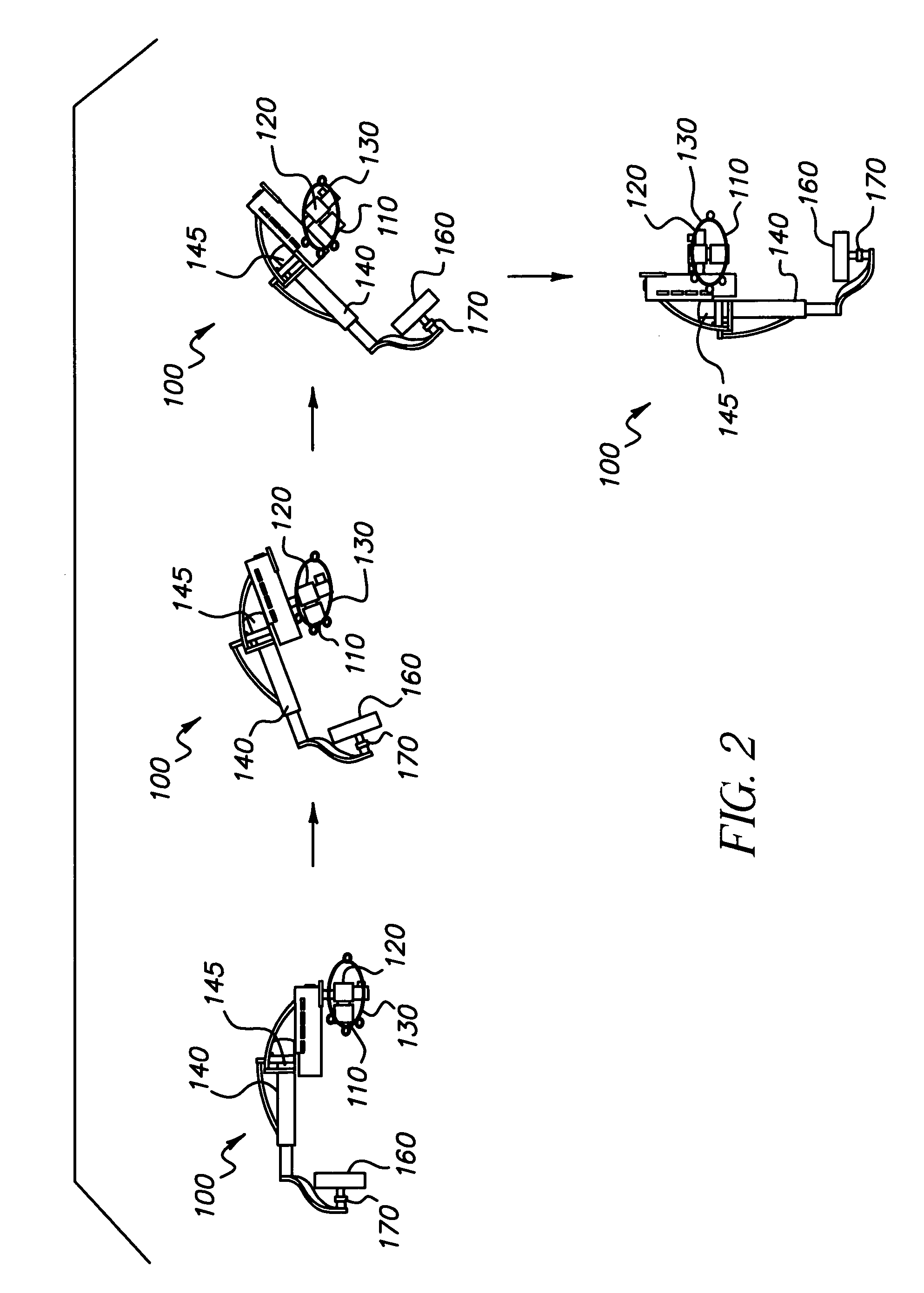
Counterweight for mobile x-ray device
A mobile radiography apparatus has a portable transport frame. A sectioned vertical column mounted on the frame defines a vertical axis and has a base section having a fixed vertical position relative to the vertical axis and at least one movable section that is translatable to a variable vertical position. A boom apparatus supports an x-ray source and extends outward from the movable section and has an adjustable height relative to the vertical axis. A counterweight is operatively coupled to the boom apparatus to support displacement of the boom apparatus to any of a plurality of vertical positions along the movable section, wherein the counterweight, in cooperation with boom apparatus movement, travels along a shaft that extends within the movable section, wherein, at one or more of the height positions of the boom apparatus, a portion of the counterweight extends upward above the shaft of the sectioned vertical column.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Radiographic equipment
ActiveUS20060093088A1Accurate informationImprove abilitiesNuclear energy generationNeutron radiation measurementX-rayDetector array
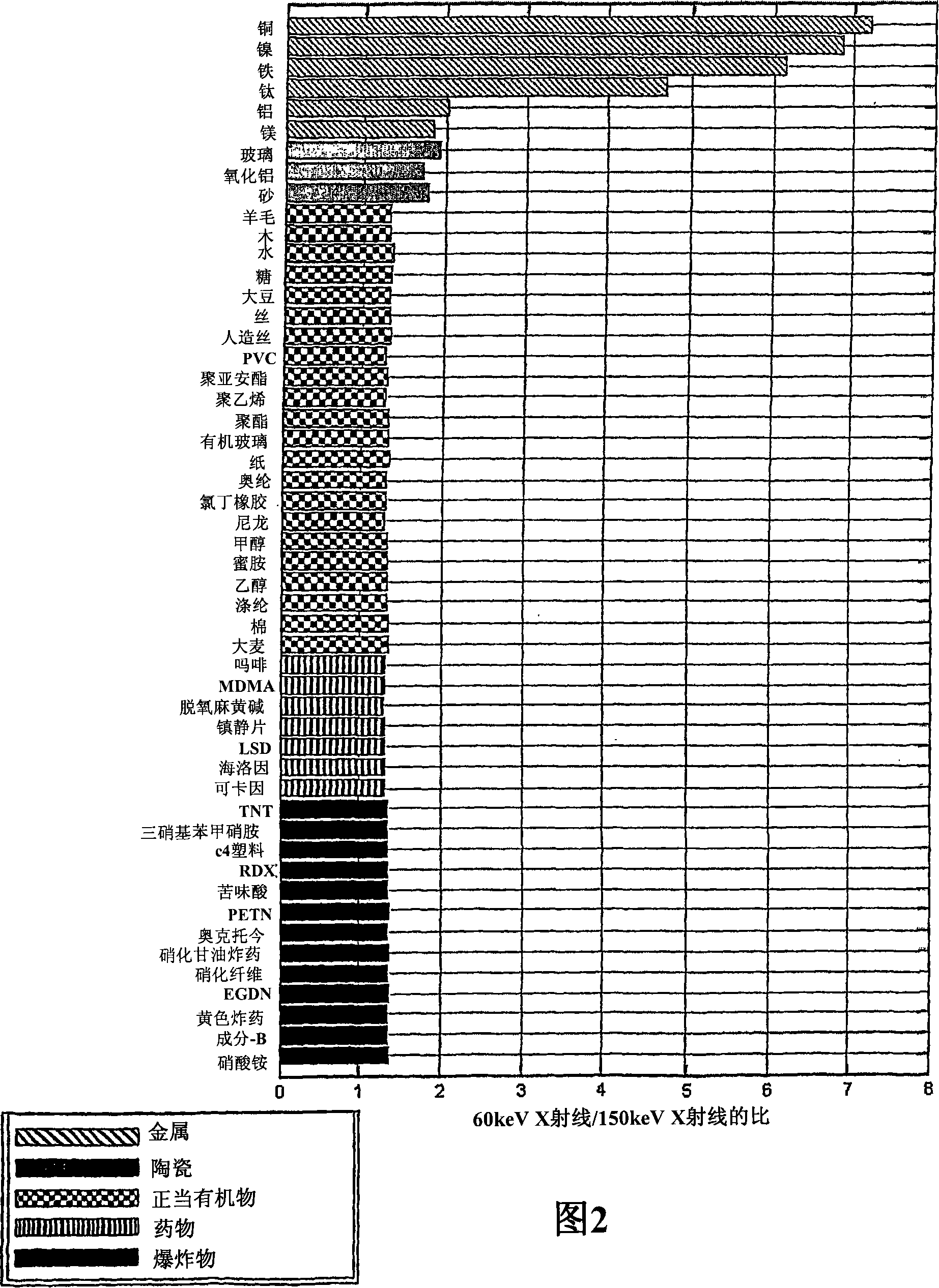
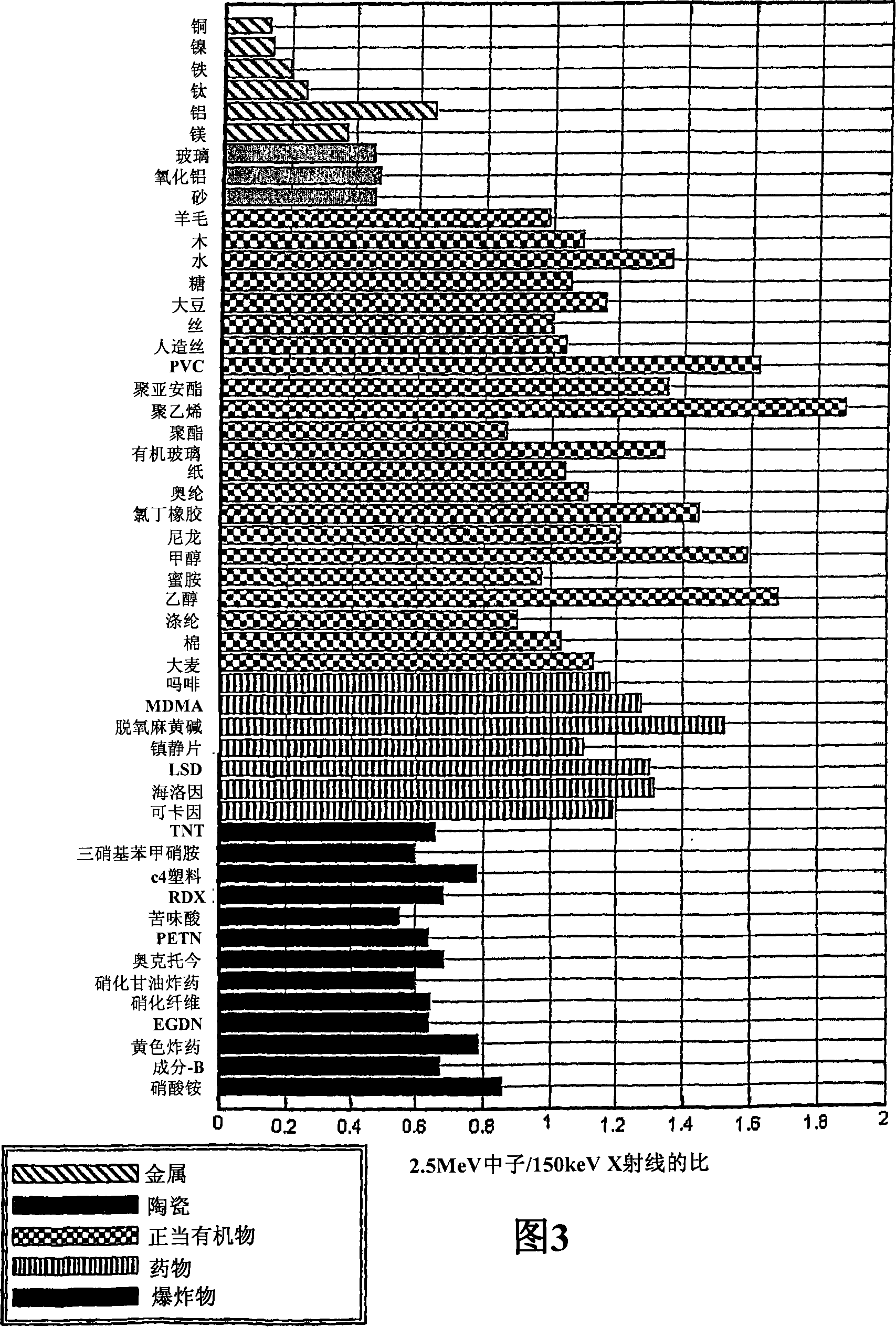
The invention concerns radiographic equipment. The equipment includes a source of substantially mono-energetic fast neutrons produced via the deuterium-tritium or deuterium-deuterium fusion reactions, comprising a sealed-tube or similar generator for producing the neutrons. The equipment further includes a source of X-rays or gamma-rays of sufficient energy to substantially penetrate an object to be imaged and a collimating block surrounding the neutron and gamma-ray sources, apart from the provision of one or more slots emitting substantially fan-shaped radiation beams. Further included is a detector array comprising a multiplicity of individual scintillator pixels to receive radiation energy from the sources and convert the received energy into light pulses, the detector array aligned with the fan-shaped beams emitted from the source collimator and collimated to substantially prevent radiation other than that directly transmitted from the sources reaching the array. Conversion means are included for converting the light pulses produced in the scintillators into electrical signals. Conveying means are included for conveying an object between the sources and the detector array. Computing means are included for determining from the electrical signals the attenuation of the neutrons and the X-ray or gamma-ray beams and to generate output representing the mass distribution and composition of the object interposed between the source and detector array. The equipment further includes a display means for displaying images based on the mass distribution and the composition of the object being scanned.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Process and device for vascular navigation
ActiveUS20060241369A1Television system detailsRadiation/particle handlingImage recordingBlood vessel
A process and radiography device for aiding vascular navigation suitable for an area of interest wherein a series of successive images In of the region of interest is acquired by a image recording. From the series of images In thus acquired a determination is made of a first mask presenting background structures and blood vessels of the region of interest, and a second mask presenting the only background structures. An image IL is acquired exhibiting at least one instrument introduced into one of the vessels of the region of interest. An image Iv is determined for visualizing by combination of the first and second masks and the image. The image to be visualized thus determined is displayed.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
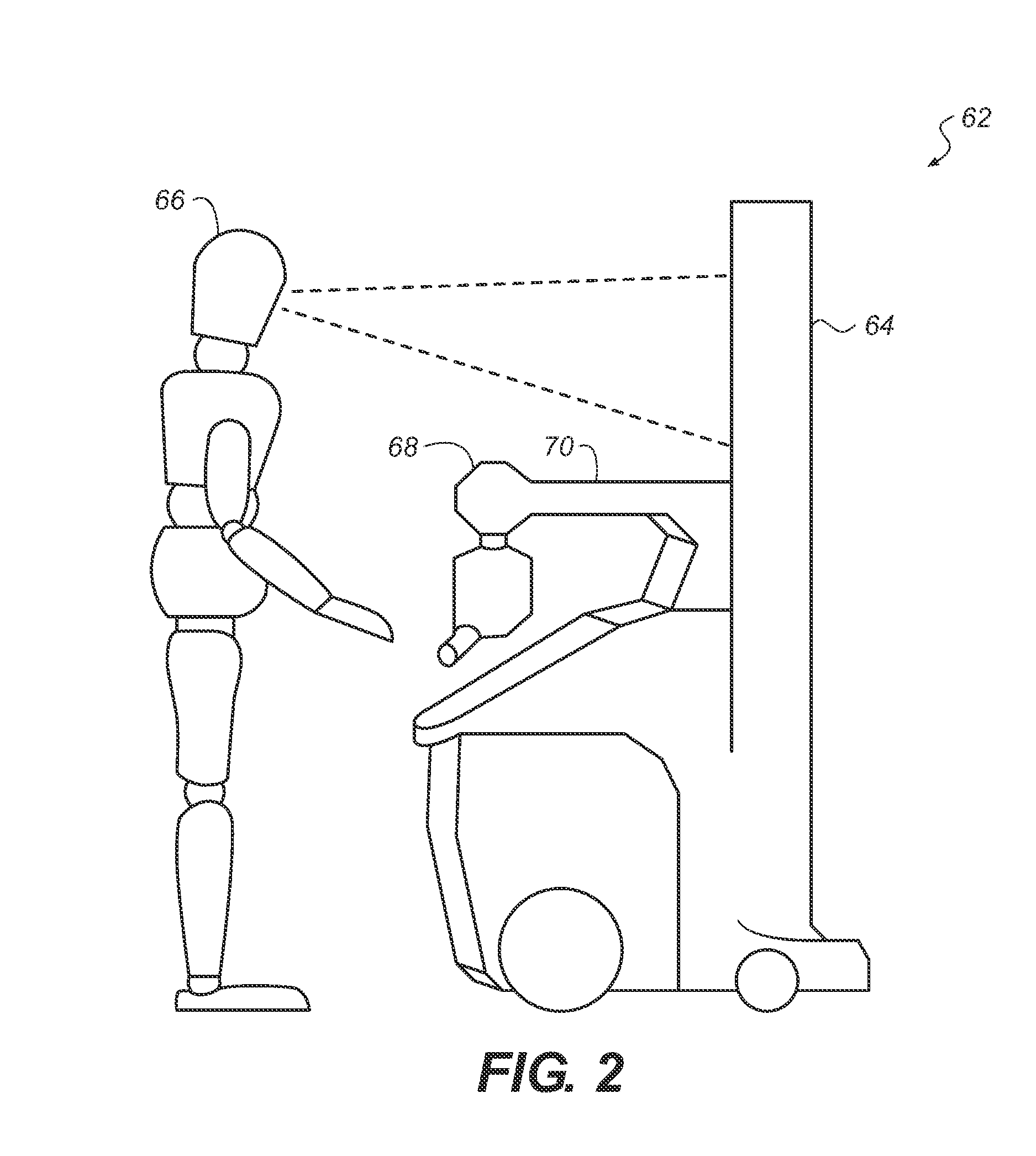
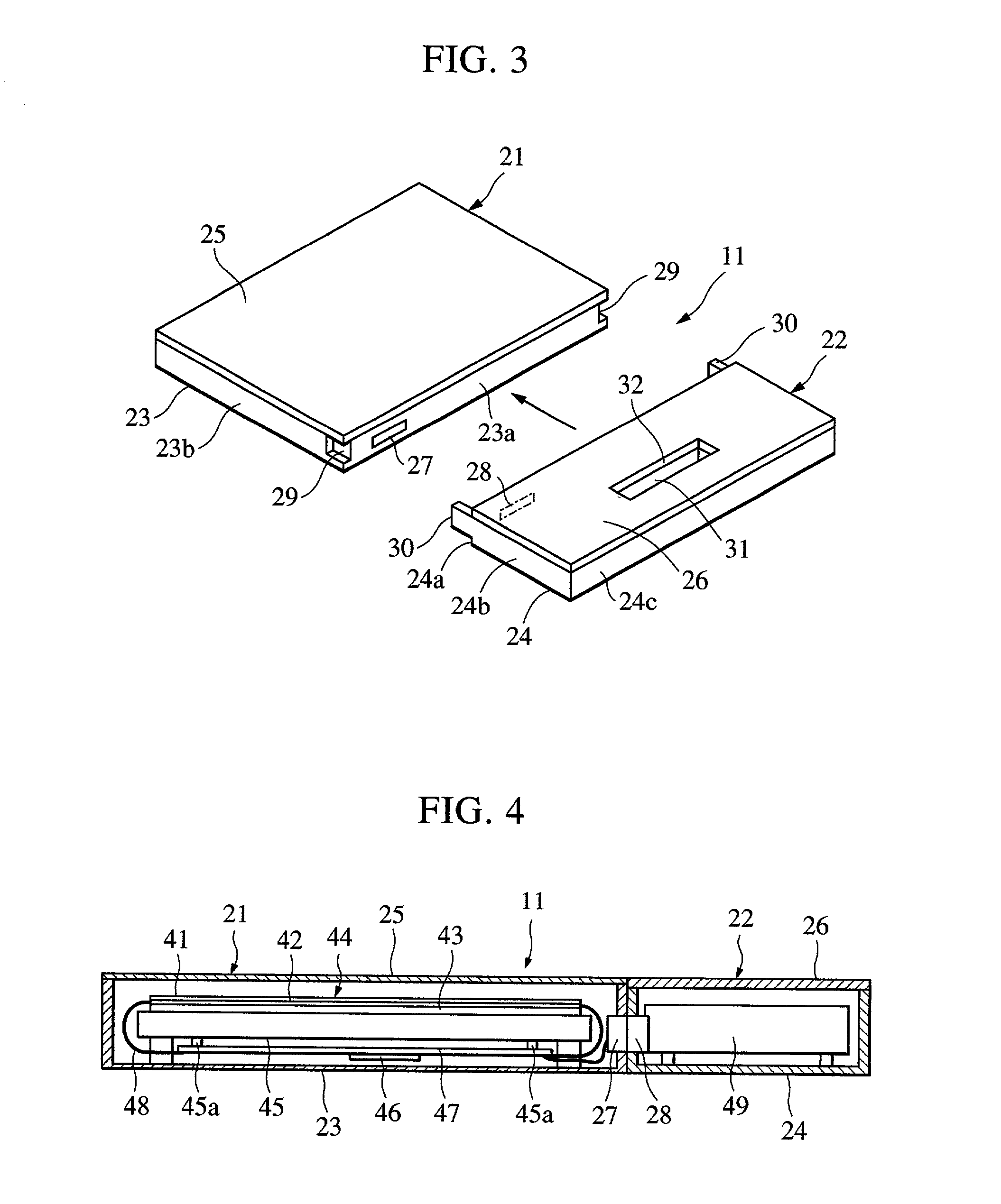
Radiographic apparatus
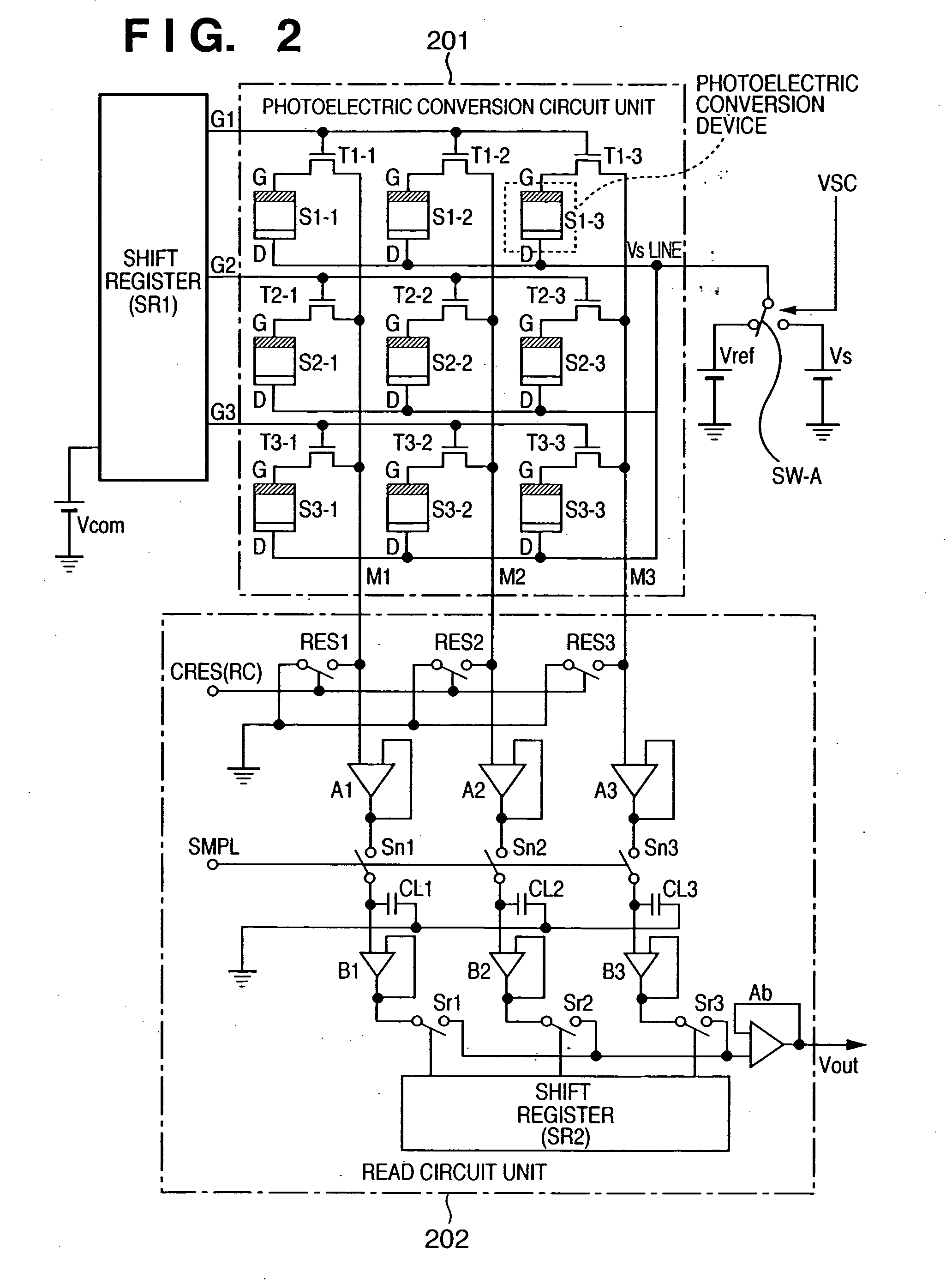
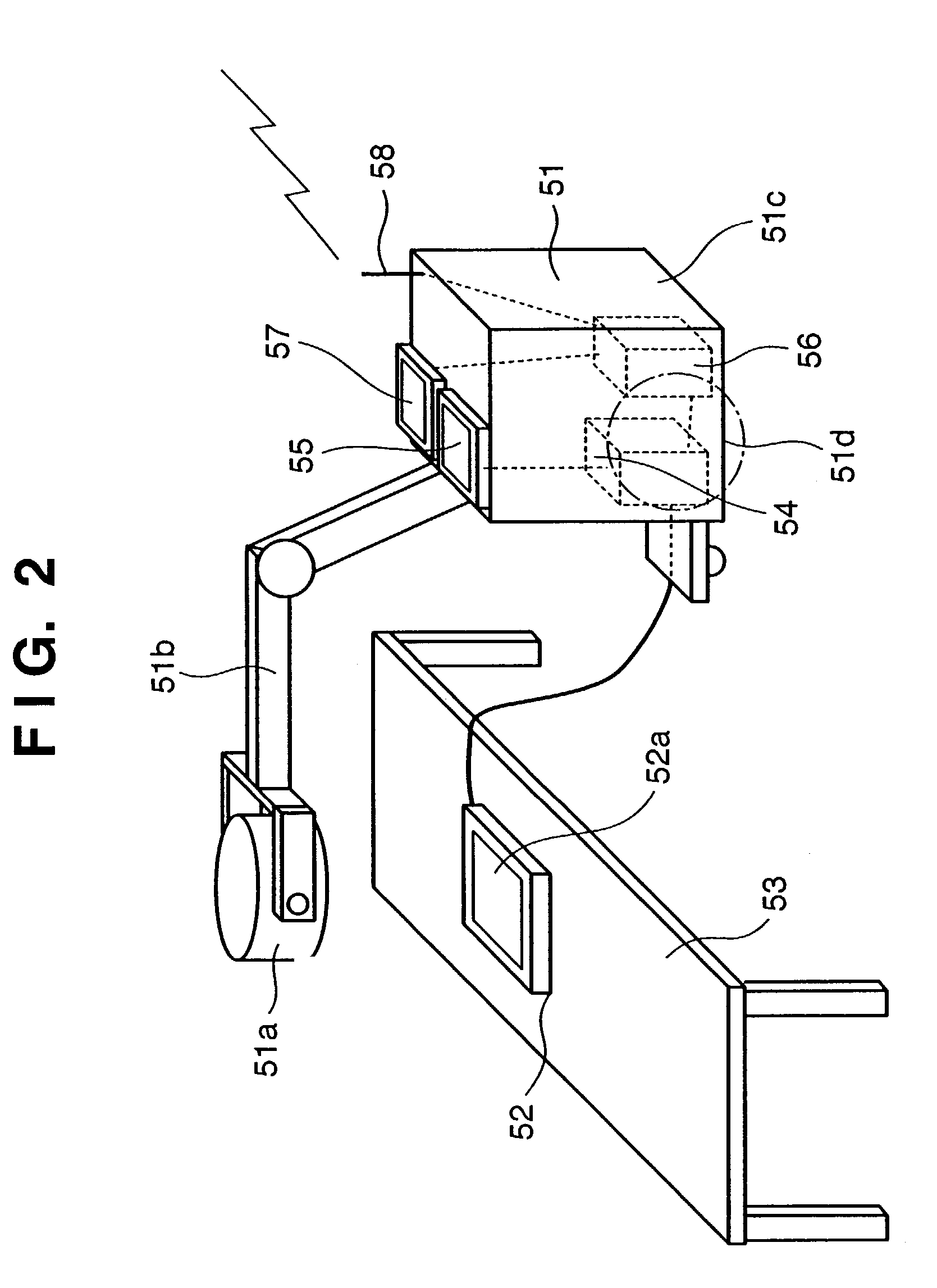
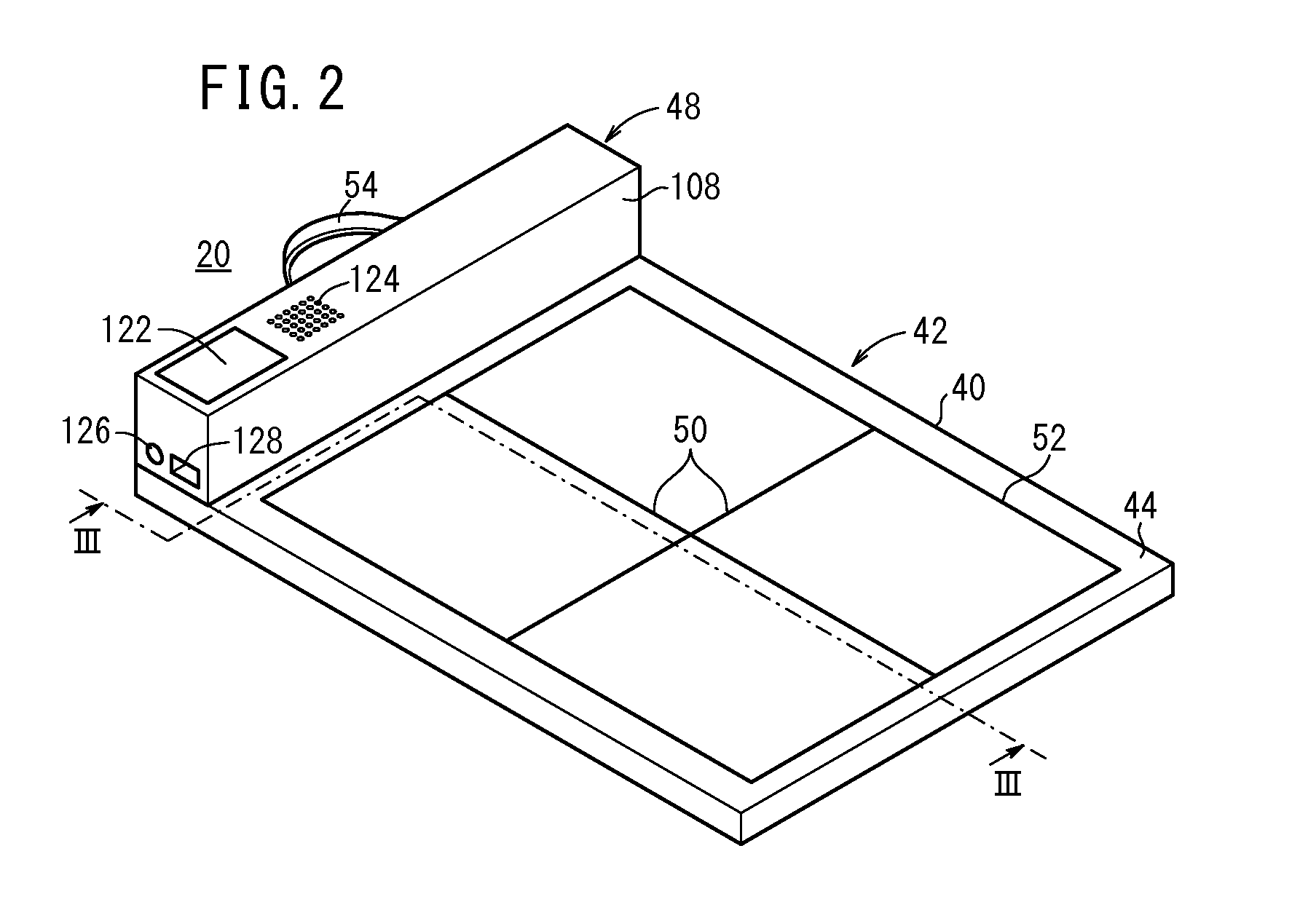
InactiveUS7104686B2Improve portabilityDecrease degree of freedom being suppressedSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
A radiographic apparatus includes a detection section including photoelectric conversion elements that detect radiation that has been transmitted through a subject. The apparatus has a substantially rectangular detection surface; and a housing that contains the detection section. The housing has a handle in an area along a longer side of the detection surface when viewed along a direction normal to the detection surface.
Owner:CANON KK
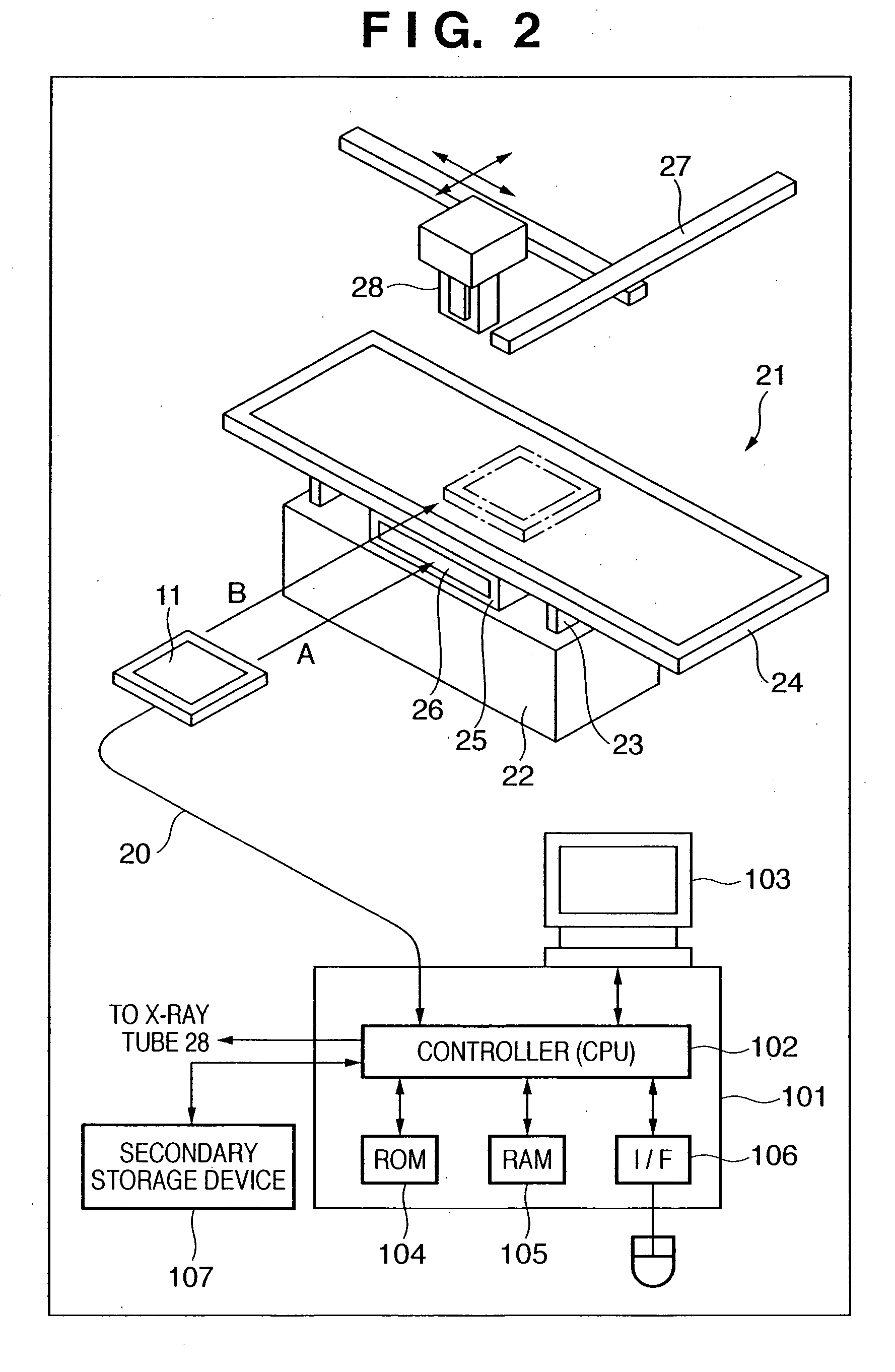
Imaging apparatus and imaging system
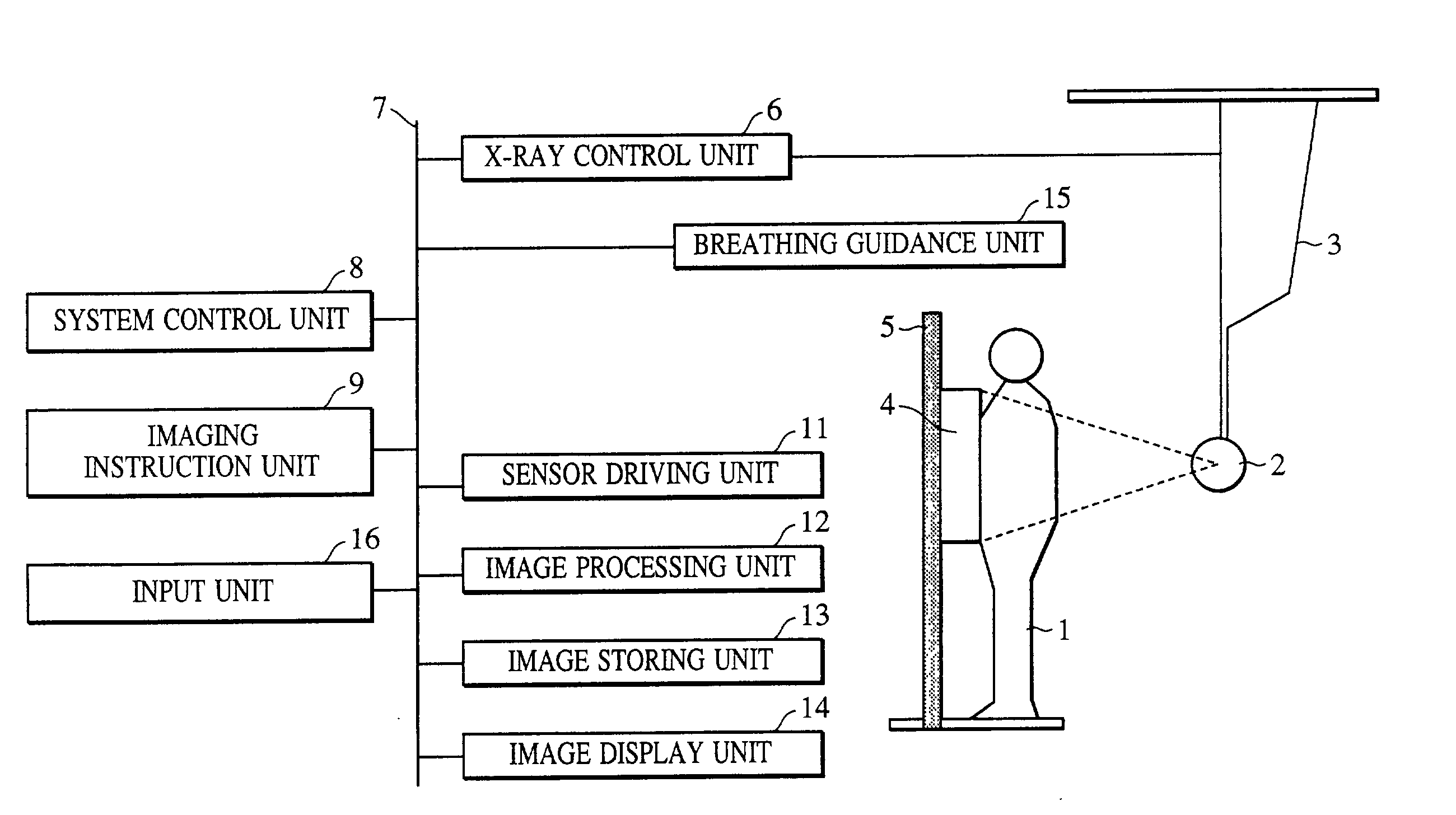
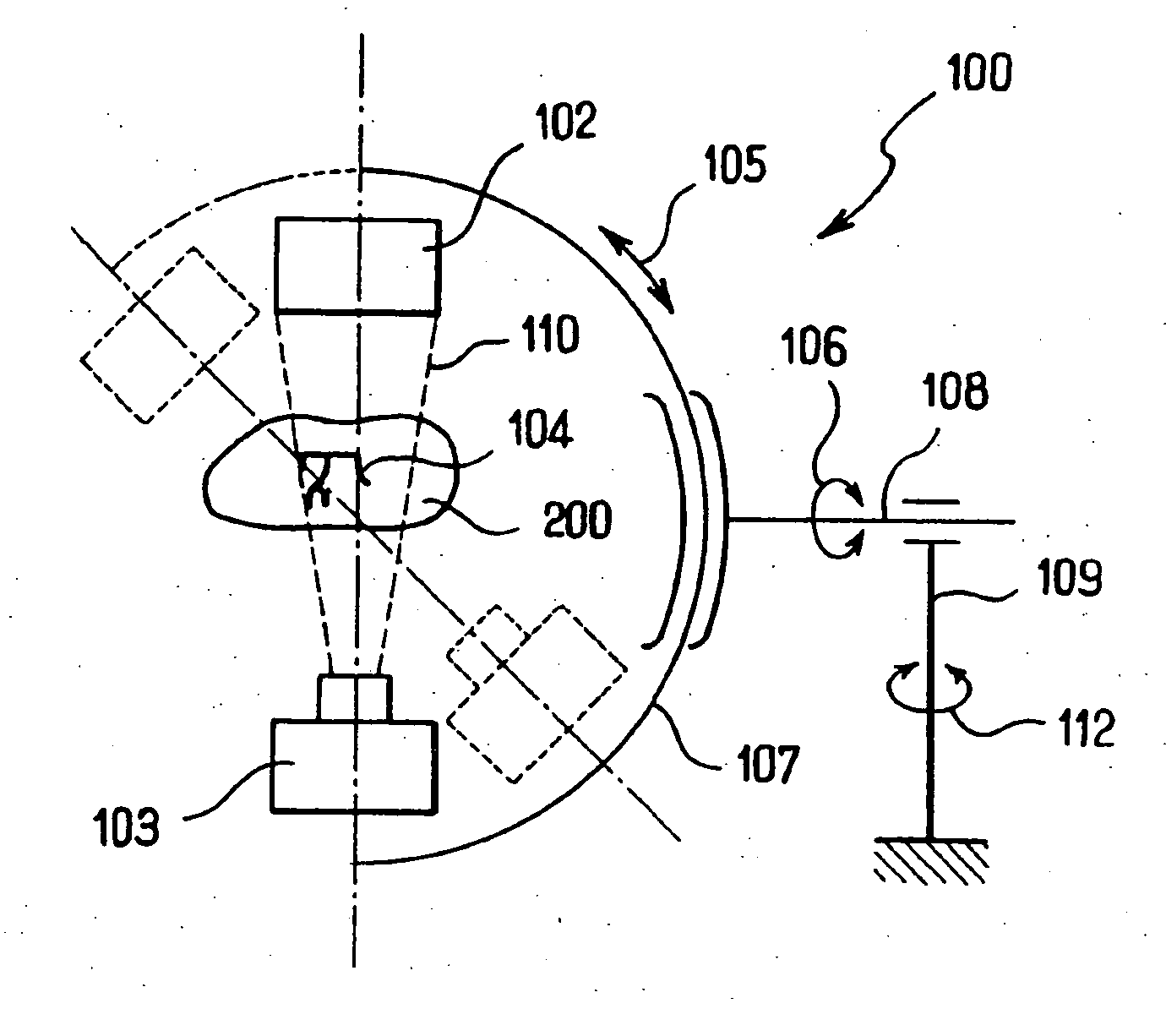
InactiveUS20050220270A1Easy to takeLess negligibly affectedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsX ray imageWorkstation
An X-ray image radiographing system according to the present invention comprises an X-ray generator 103, a detection unit 102, a correction unit 108 for performing a correction processing for the data outputted from the detection unit 102, and an output unit 115 such as a monitor for outputting data processed by the correction unit 108. Moreover, it comprises a control unit 101 for controlling the detection unit 102, the X-ray generator 103 and the correction unit 108, a radiographing condition memory 107 accessible by the control unit 101, a radiographing button 105 for making a radiographing request to the control unit 101, a radiographing mode setting unit 106 for setting a radiographing mode in the control unit 101, and a photo timer 104 having an AE function. The radiographing mode setting unit 106 may be constituted of a workstation, for example. Thereby, it is possible to provide an image radiographing apparatus and the image radiographing system capable of easily coping with a plurality of radiographing modes.
Owner:CANON KK
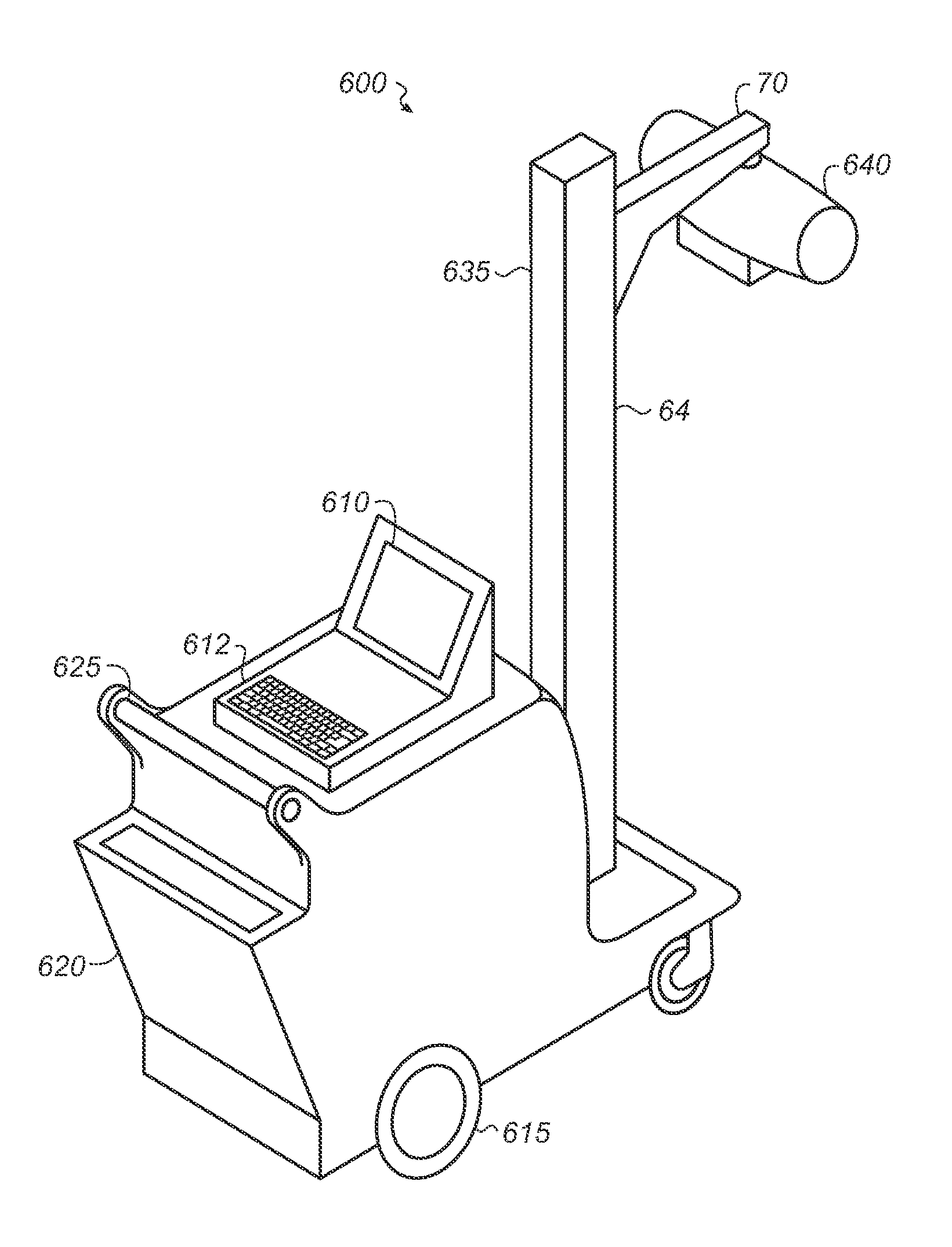
Radiography apparatus with multiple work zones
InactiveUS20080069304A1Disadvantage in costDisadvantage in reliabilityX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsDisplay deviceX-ray
A radiography apparatus having an x-ray source, an x-ray imaging detector, and a support structure coupling the source and the x-ray detector and rotatable about a predetermined axis for positioning about a subject. The apparatus includes a first operator control console with a first command entry device for entry of operator setup instructions and a first display. A second operator control console is spaced apart from the first operator control console and has a second command entry device for entry of operator setup instructions and a second display. A control logic processor is responsive to the operator setup instructions for controlling operation of the radiography apparatus. At least some of the operator setup instructions entered at the first command entry device and operator setup instructions entered at the second command entry device are the same.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
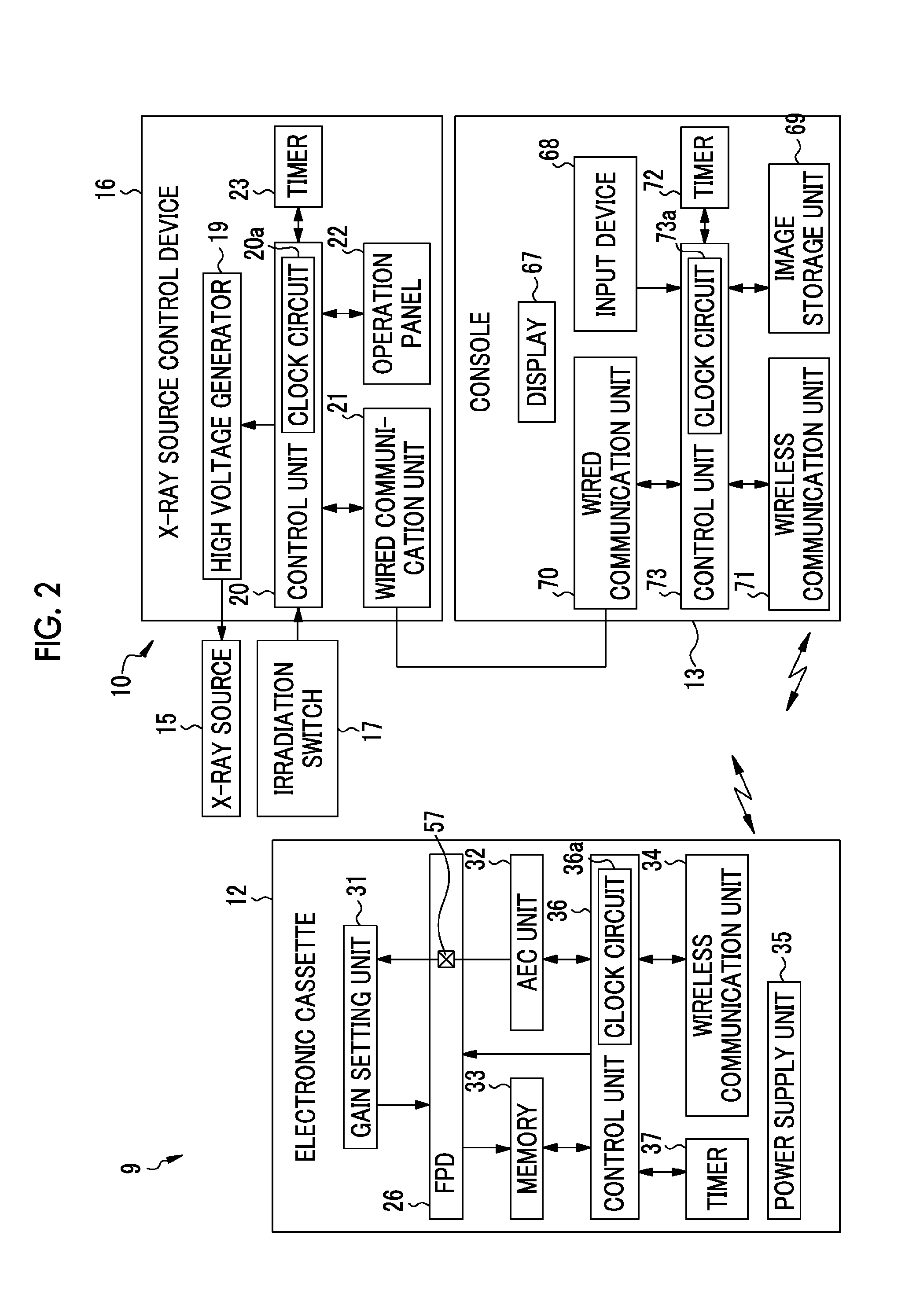
Radiographic image obtainment method and radiographic apparatus
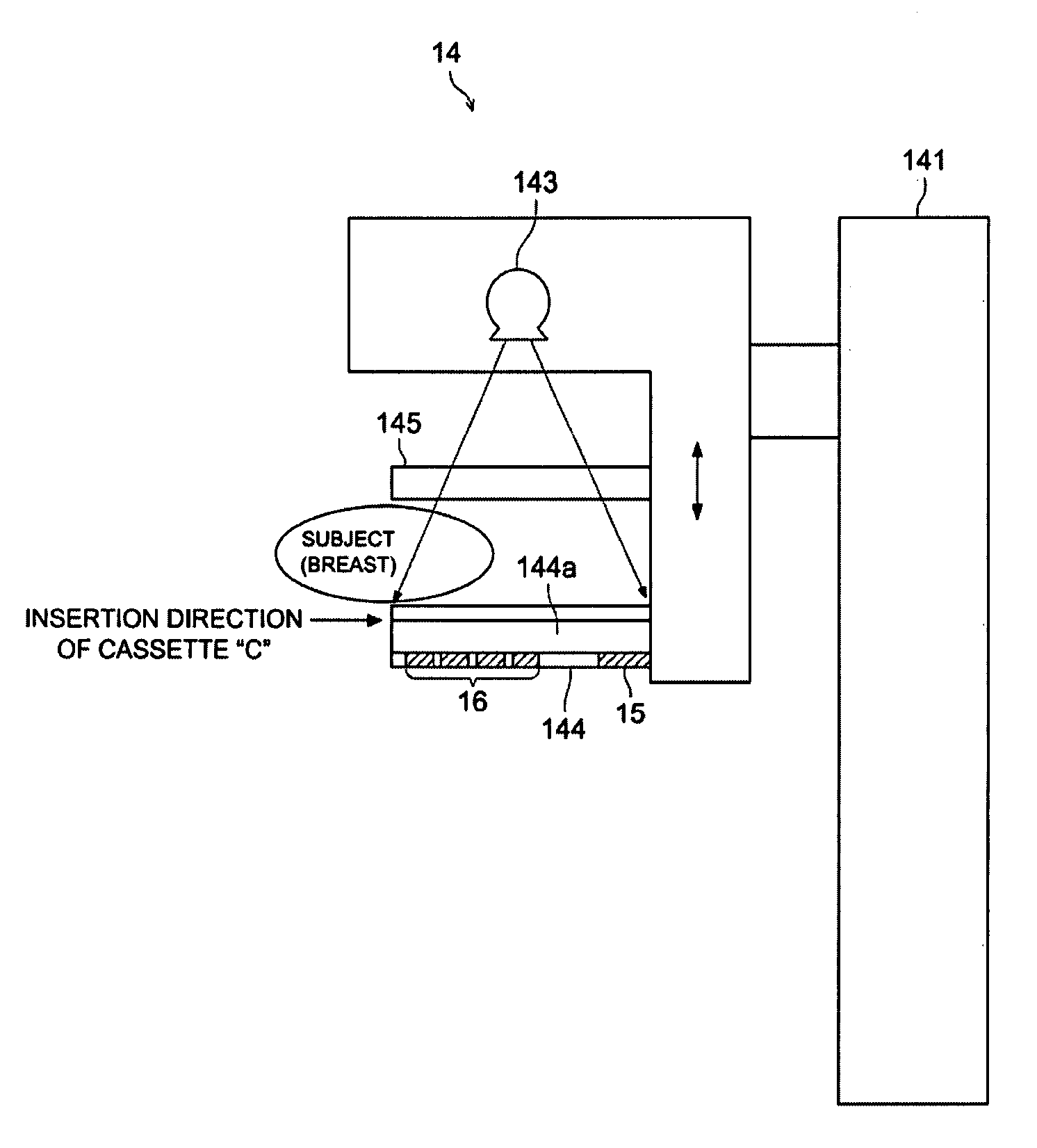
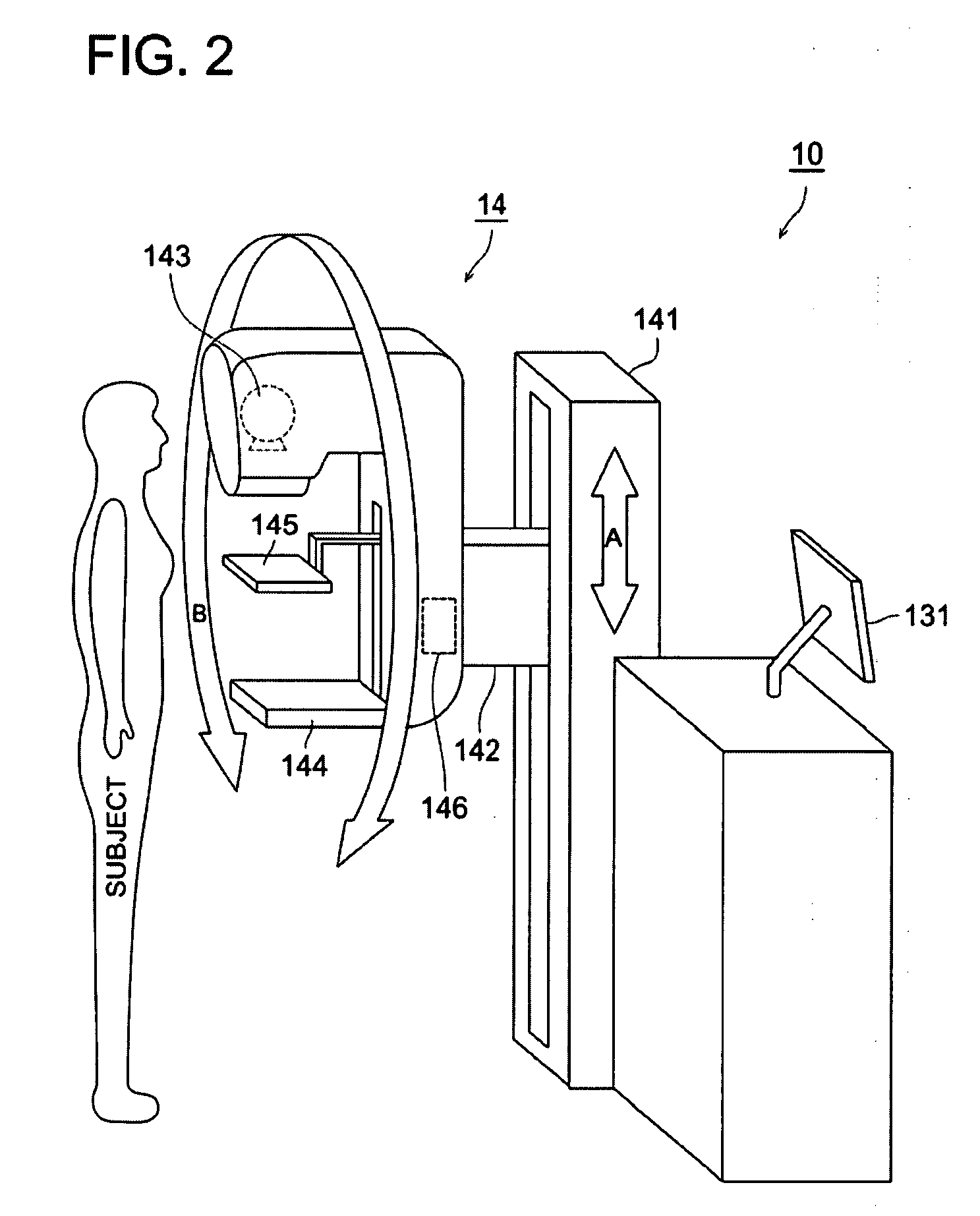
InactiveUS20120163537A1Reduce positional offsetQuality improvementMammographyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGratingRadiographic equipment
In a radiographic apparatus, a radiation image detector or first and second gratings are structured in such a manner to be attachable to the radiographic apparatus and detachable therefrom. The radiographic apparatus includes a cassette attachment / detachment detection unit that detects attachment and detachment of the radiation image detector, or a grid attachment / detachment detection unit that detects attachment and detachment of the first and second gratings. The apparatus further includes a preliminary irradiation control unit that controls a radiation source so that preliminary irradiation for detecting a relative positional deviation between the first and second gratings and the radiation image detector is performed when attachment or detachment of the radiation image detector, or the first and second gratings has been detected.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
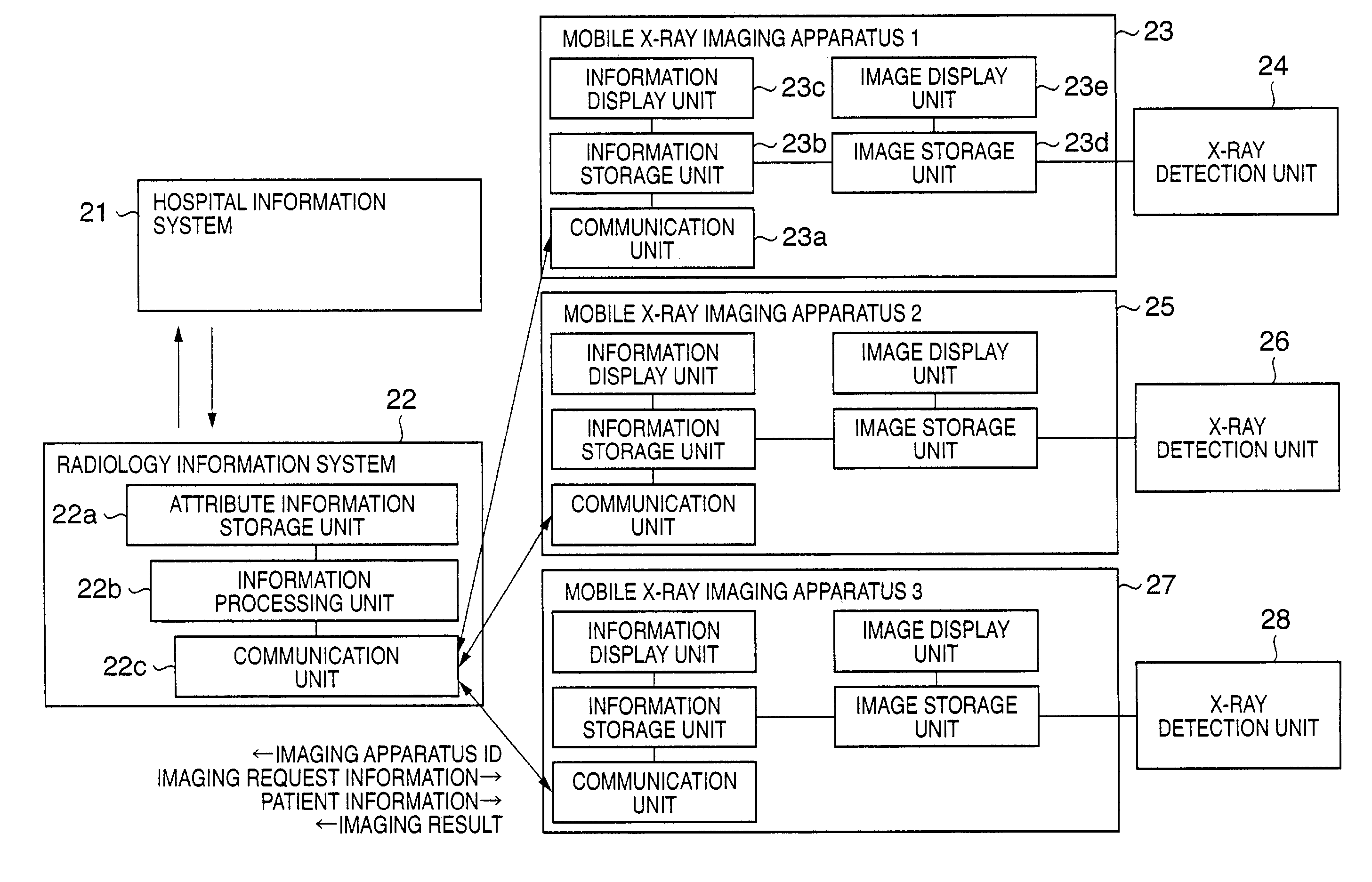
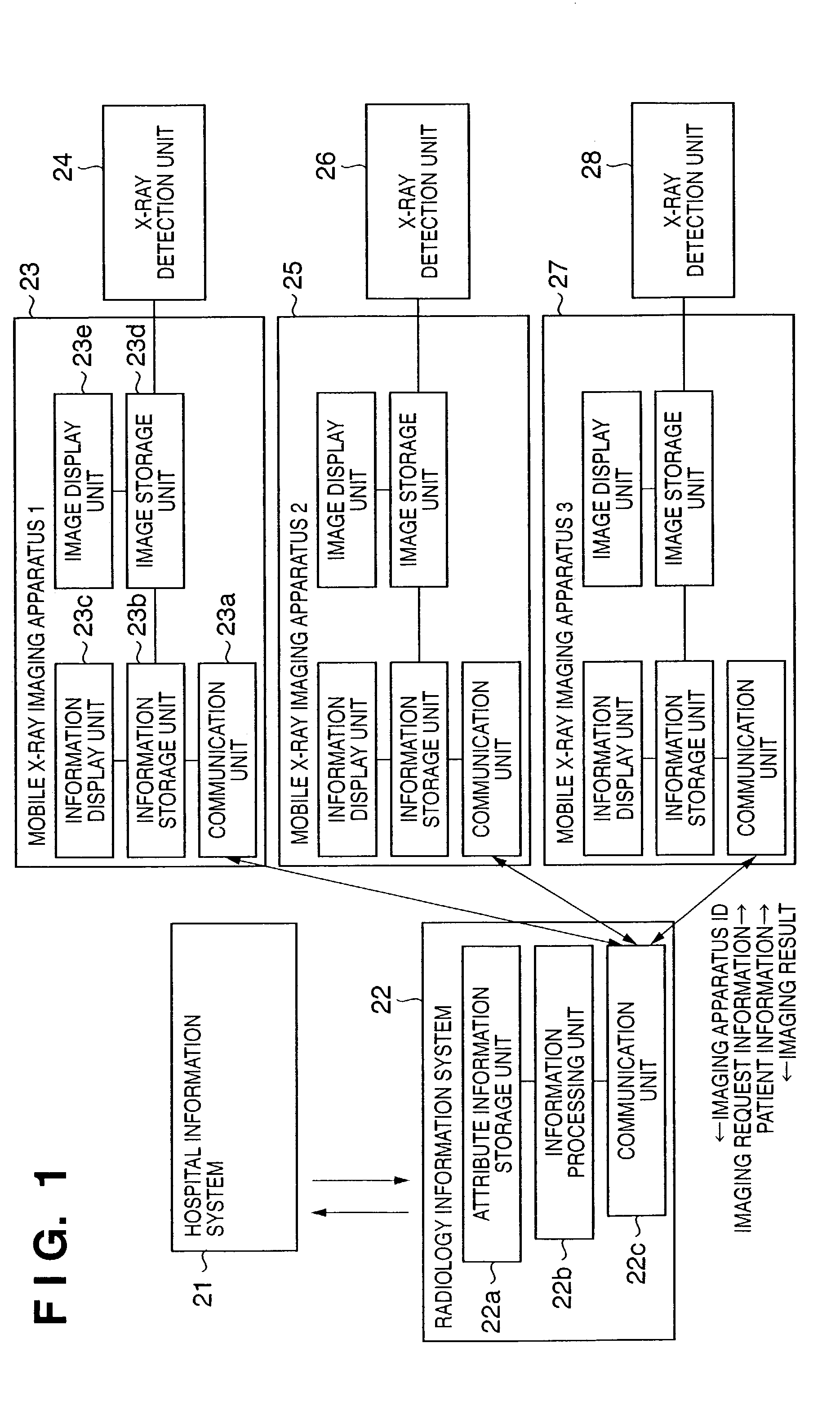
Mobile radiographic apparatus, radiographic system, radiographic method, program, computer-readable storage medium, and information system
InactiveUS6999558B2Efficient and effective work flowRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusPhotoelectric conversionComputer science
In a radiographic method using a mobile radiographic apparatus including an image generating unit which includes photoelectric conversion elements and generates radiographic image data of an object, key information for selecting radiographic request information is transmitted to an external information system having the radiographic request information. The radiographic request information transmitted from the information system is received. The operation of the image generating unit is controlled based on the received radiographic request information.
Owner:CANON KK
Radiation detector and radiological image radiographing apparatus
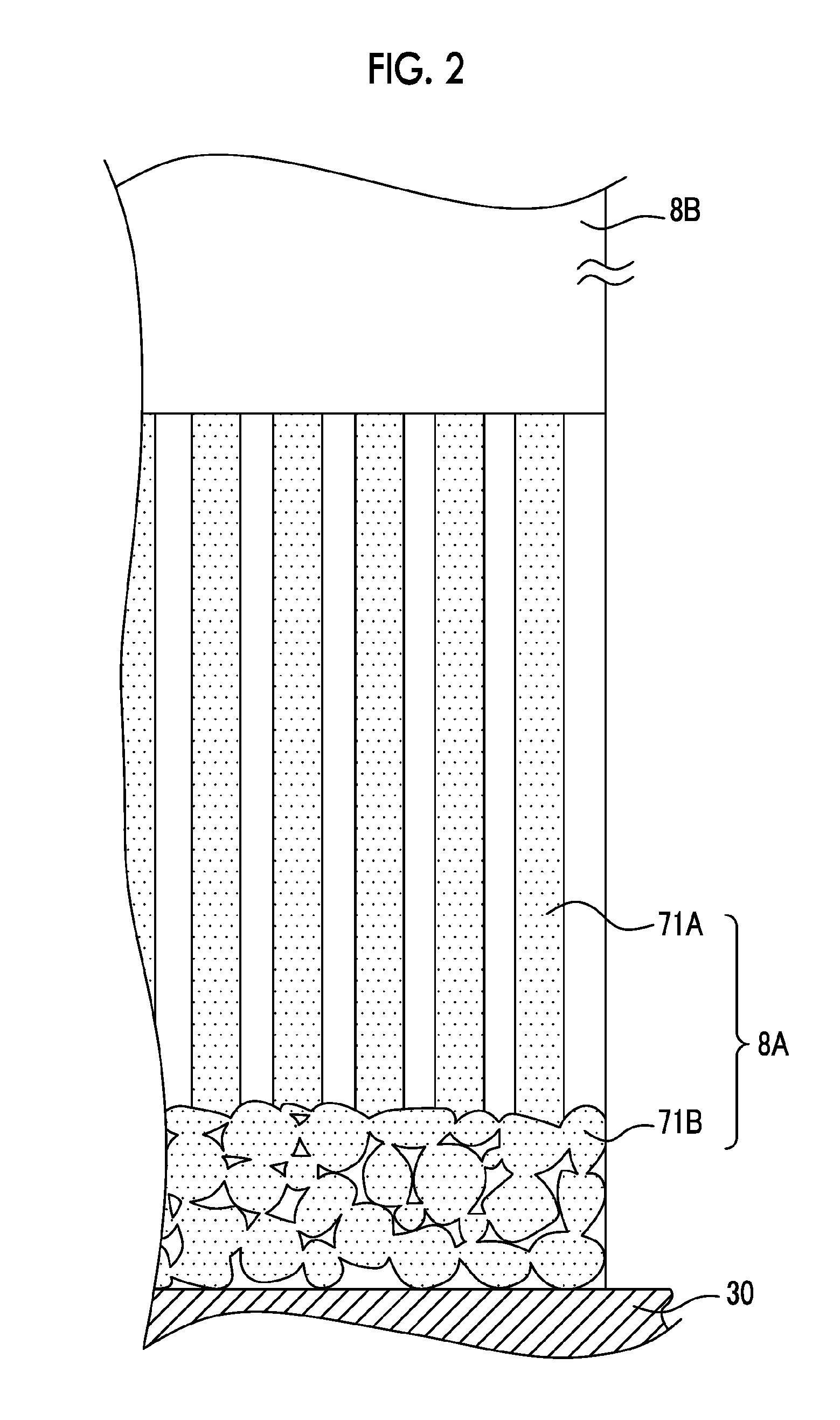
ActiveUS20130048866A1Increase costQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotoelectric conversionScintillator
A radiation detector and a radiological image radiographing apparatus capable of improving the quality of an obtained radiological image without causing an additional cost are provided. A first scintillator configured to include columnar crystals generating first light corresponding to a radiation emitted through a TFT substrate is laminated on the other surface of the TFT substrate that has a first photoelectric conversion element, which has one surface from which a radiation is emitted and the other surface from which at least one of the first light and the second light is emitted and which generates electric charges corresponding to the light, and a first switching element. A second scintillator which generates second light corresponding to a radiation emitted through the first scintillator and has different energy characteristics of absorbed radiations from the first scintillator is laminated on a surface of the first scintillator not facing the TFT substrate.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging area specifying apparatus, radiographic system, imaging area specifying method, radiographic apparatus, and imaging table
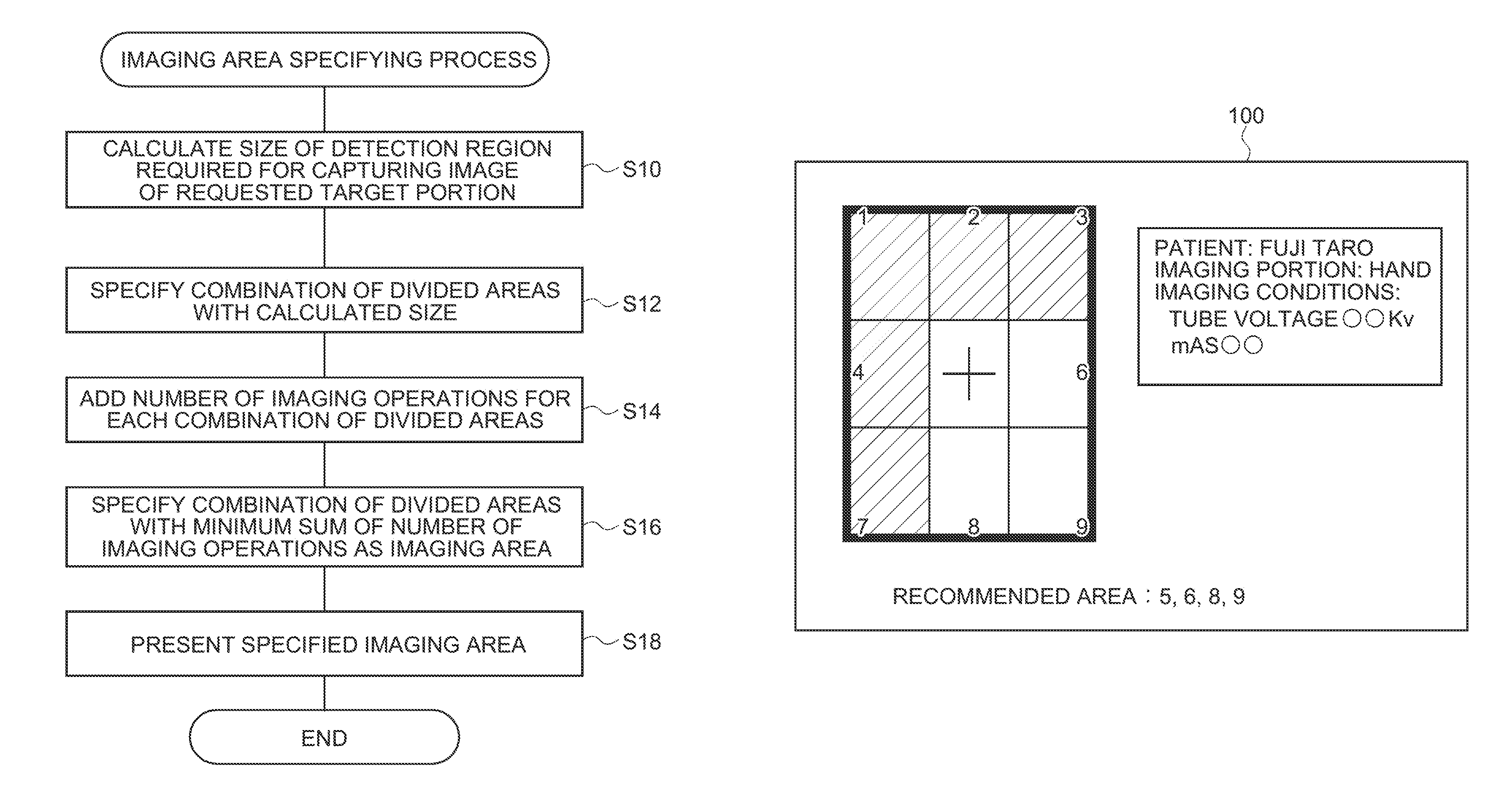
InactiveUS8550709B2Avoid problemsRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsElectric signalRadiographic equipment
An imaging area specifying apparatus that includes a storage component and a specifying component is provided. The storage component stores as correlation information a correlation value correlated with the amount of radiation emitted to each of a plurality of predetermined areas divided from a detection region of a radiation detector that outputs an electric signal indicating a radiological image represented by radiation which is emitted to the detection region for detecting the radiation. The specifying component specifies an imaging area capable of capturing the radiological image of a predetermined size while preventing variations in the amount of radiation emitted to each of the divided areas in the detection region, on the basis of the correlation information stored in the storage component.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiography device
InactiveUS20130134316A1Avoiding breakage (fracture) and crackingPerformance deteriorationMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorRadiographic equipment
In this radiography device, the radiation conversion panel side of a scintillator is formed in a convex shape towards the radiation conversion panel, the end portions of columnar crystals are formed at said side, and the end portions of the columnar crystals can contact the radiation conversion panel.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiographic apparatus and radiographic system
InactiveUS20120114098A1Fast decayAvoid configurationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsGratingPhase difference
A radiographic apparatus includes a first grating, a second grating, a scanning unit, and a radiological image detector. The second grating includes a periodic form that has a period which substantially coincides with a pattern period of a radiological image formed a radiation having passed through the first grating. The scanning unit relatively displaces the radiological image and the second grating to a plurality of relative positions at which phase differences between the radiological image and the second grating are different each other. The radiological image detector detects the radiological image masked by the second grating. The scanning unit includes a driving unit that drives one of the first grating and the second grating relatively to the other in a pattern arrangement direction of the radiological image and a plurality of elastic members that has natural frequencies different from each other.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
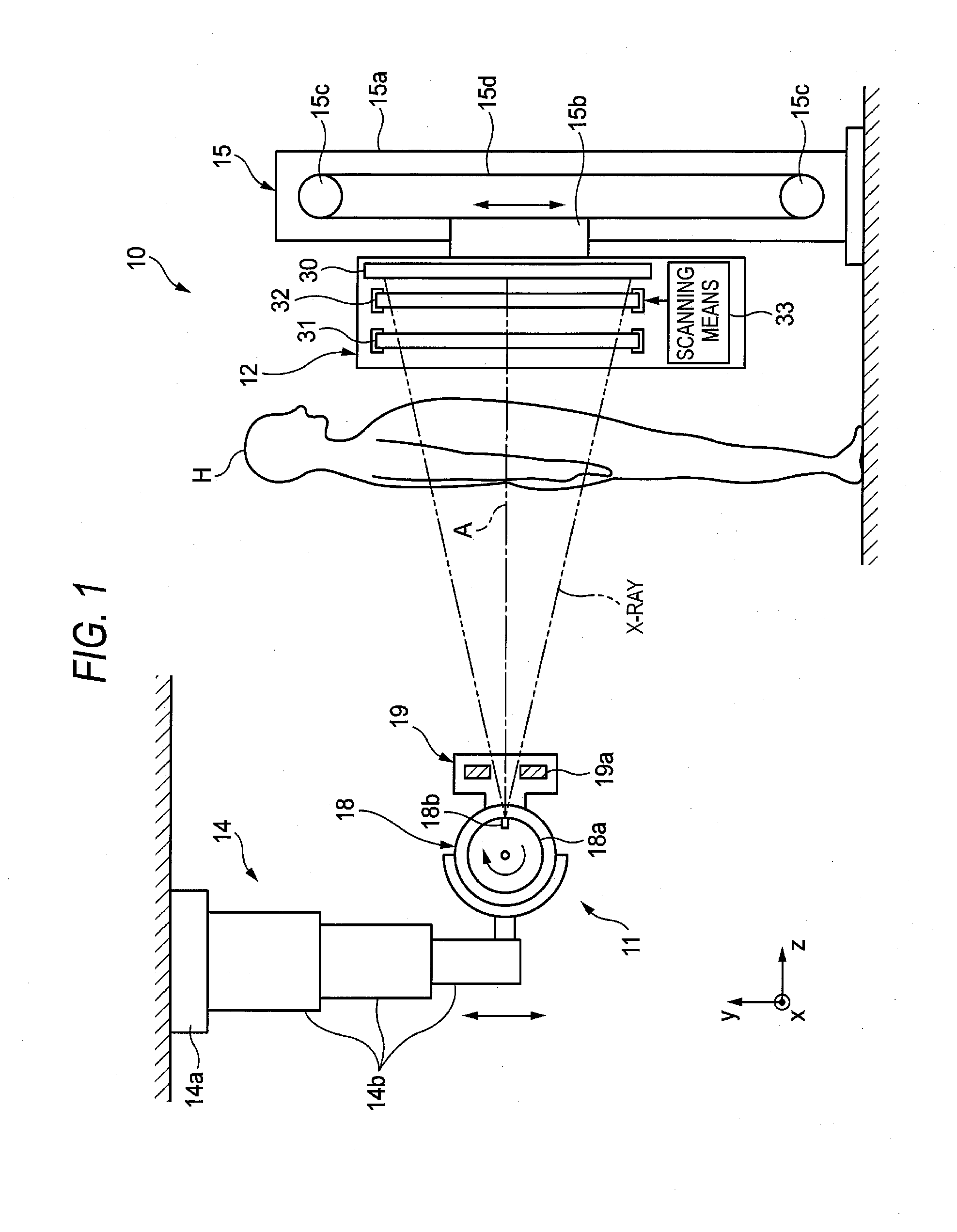
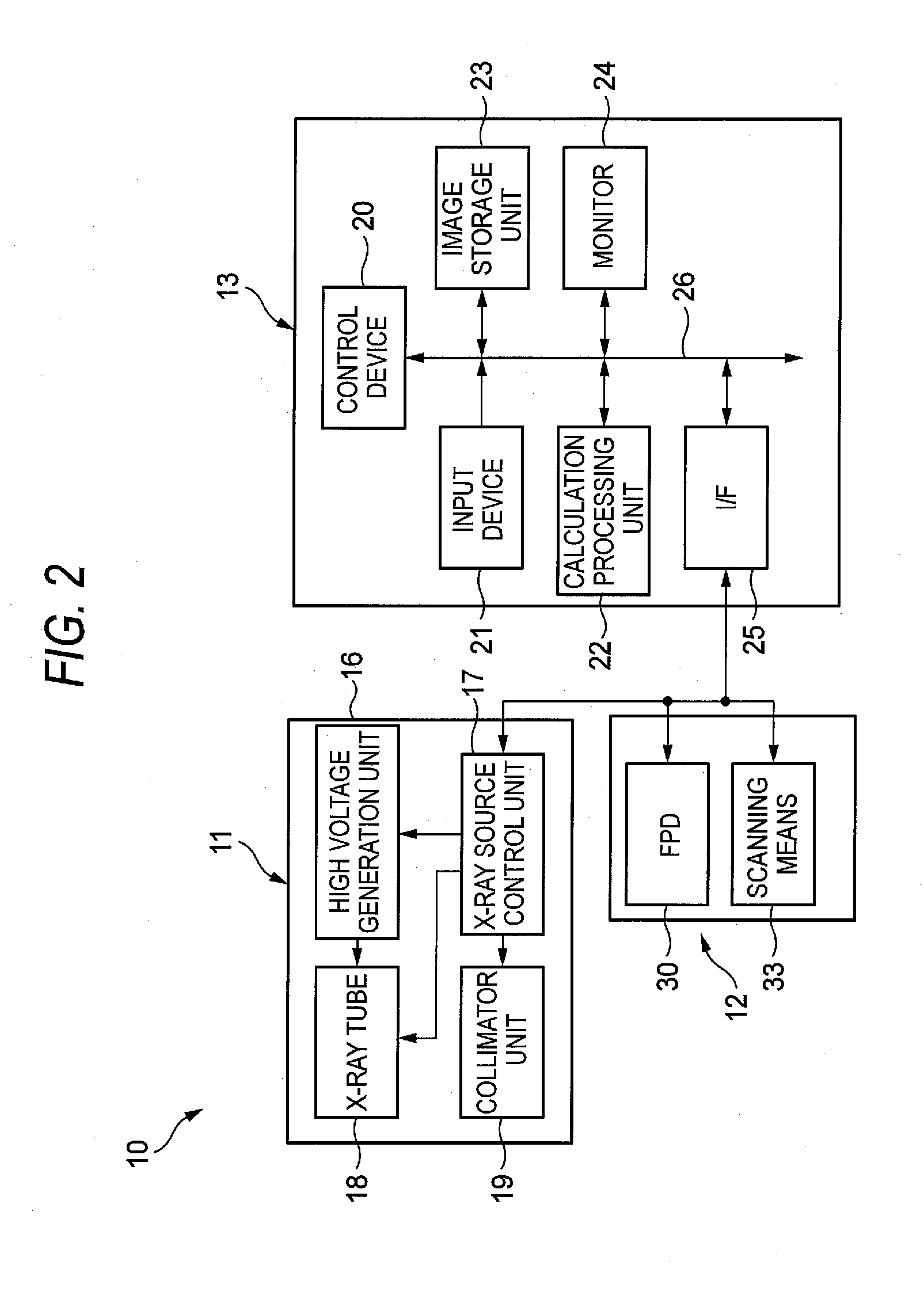
Radiographic apparatus
InactiveUS6904119B2Variation in timeLittle slippageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImage resolutionRadiographic equipment
The radiographic apparatus according to this invention has a scan frame with an X-ray tube frame and a flat panel type detector (FPD) frame arranged therein. The X-ray tube frame surrounds an X-ray tube, and the FPD frame surrounds an FPD. The X-ray tube frame and FPD frame are rotatable together about a sectional axis. Thus, the X-ray tube and FPD rotate on the respective frames together directly about the sectional axis (for a main scan). Further, the X-ray tube and FPD are rotatable together about a scan center axis (for an auxiliary scan). The main scan and auxiliary scan are combined to achieve a high-speed scan and improves resolution in the direction of the sectional axis, thereby obtaining a three-dimensional sectional image with isotropic spatial resolution.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Medical image radiographing system, method for managing medical image and method for displaying medical image
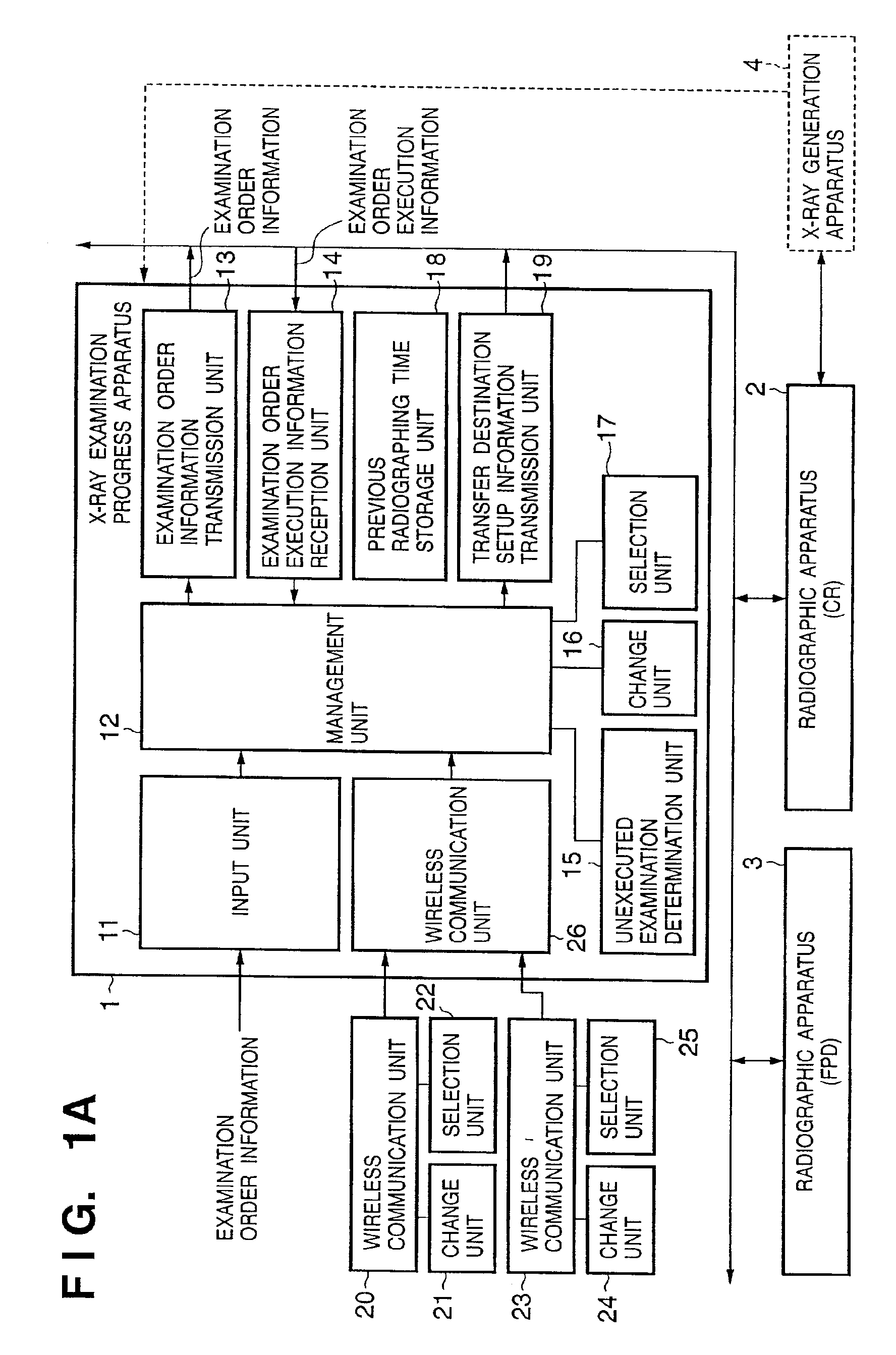
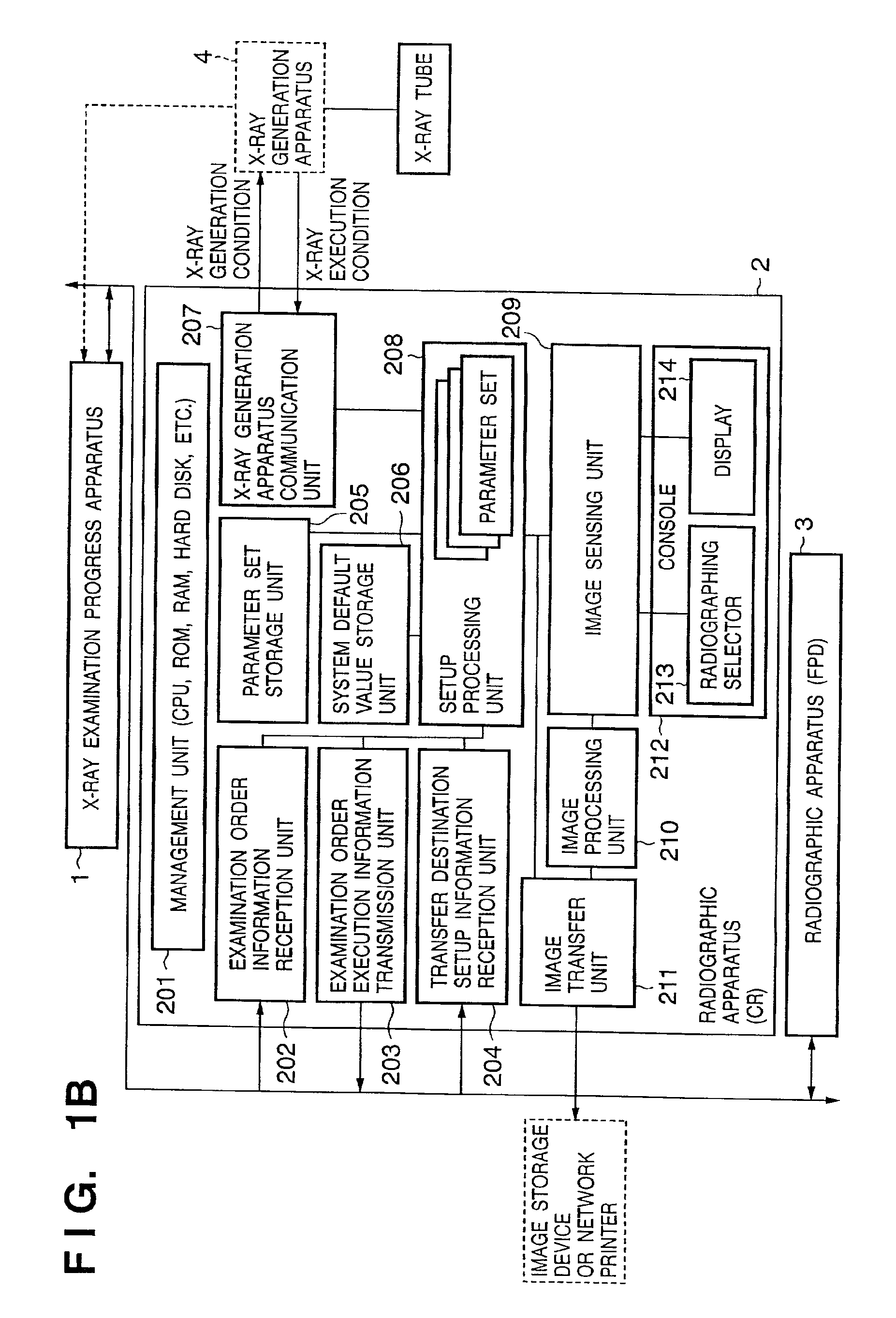
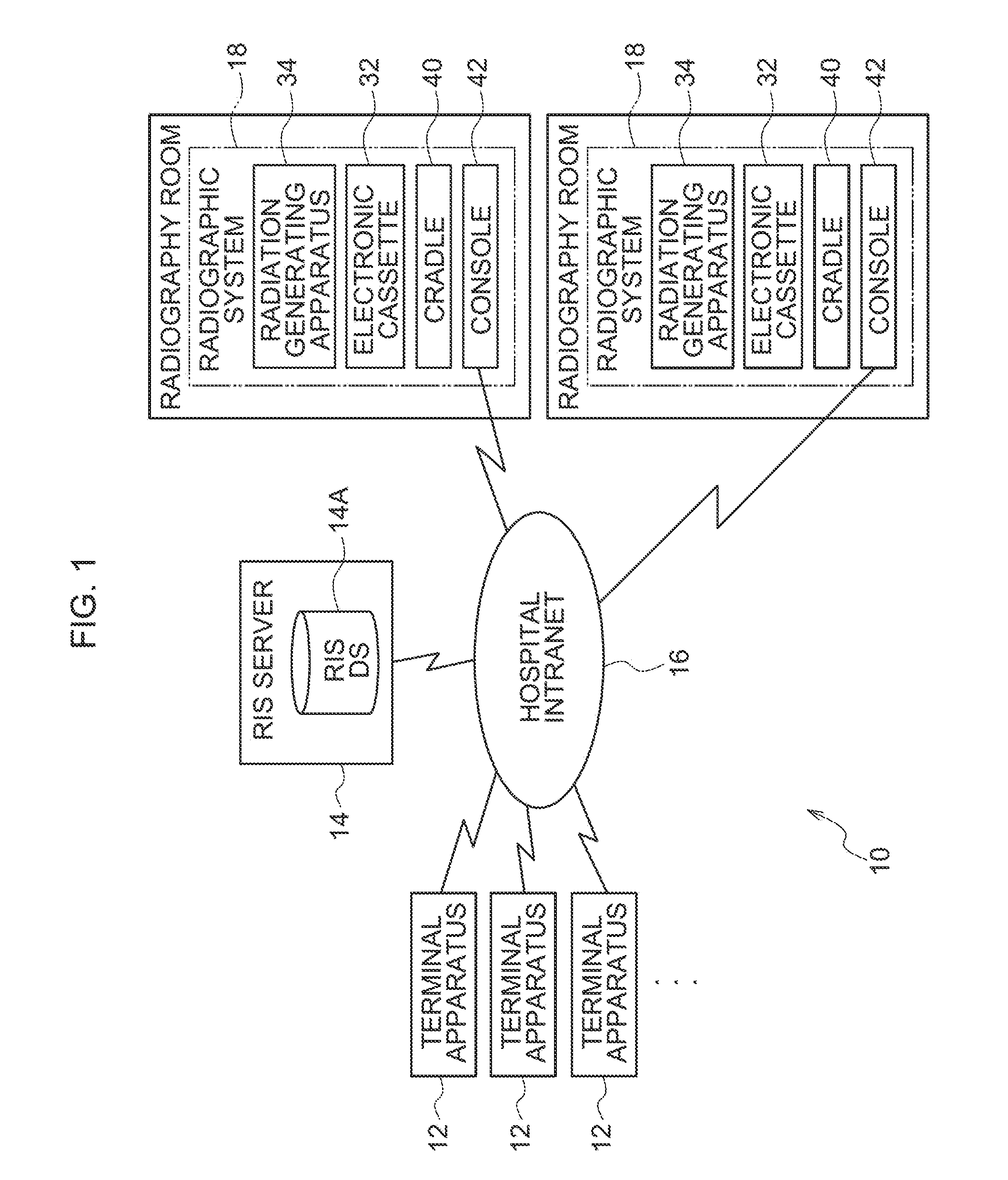
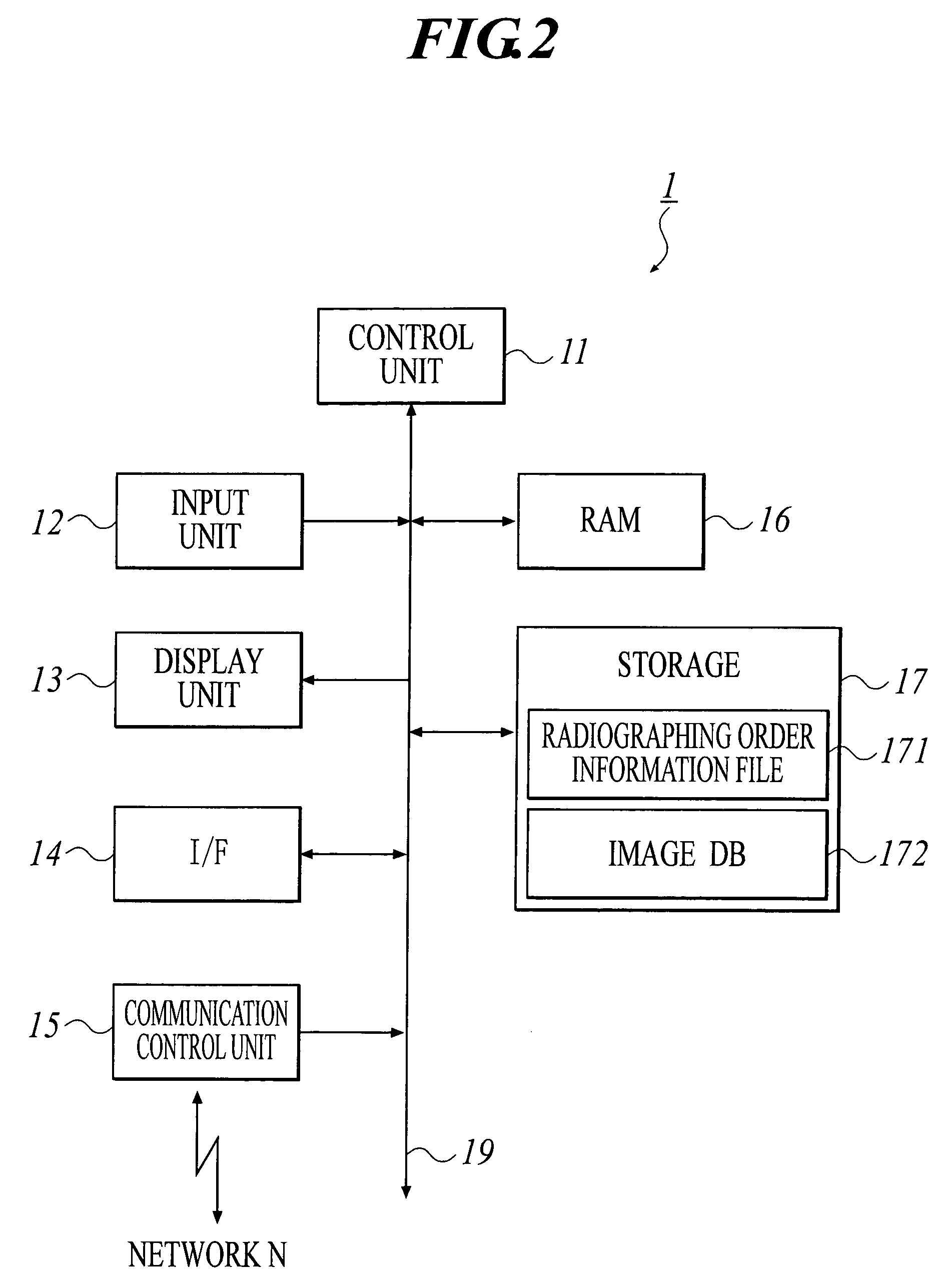
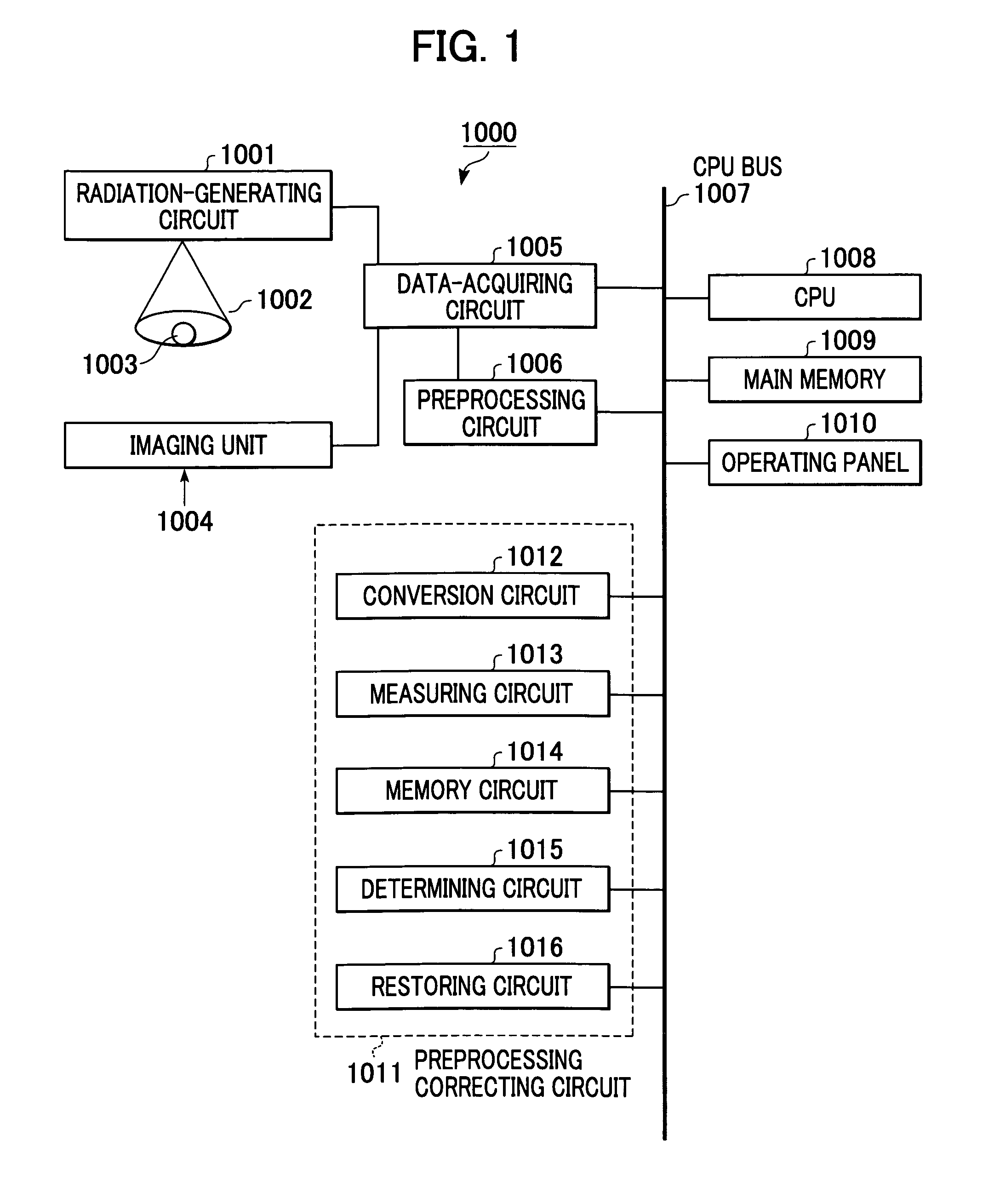
InactiveUS7092970B2Minimize input mistakeImprove visibilityCharacter and pattern recognitionOffice automationMedical radiographyComputer vision
A medical image radiographing system has: a radiographic-room-use radiographing apparatus for performing medical radiography in a radiographic room; a portable radiographing apparatus for performing medical radiography at a bedside of the patient; and a controller for displaying an input screen and for inputting information through the input screen, wherein, when radiographing order information is inputted, the controller displays a selection input screen for inputting selection of whether the radiographing order information is for one by the radiographic-room-use radiographing apparatus or one by the portable radiographing apparatus, and displays a radiographing order information input screen different according to the selection, and at input completion of the radiographing order information, the controller displays a confirmation input screen for inputting confirmation of the input completion regardless of the one by the radiographic-room-use radiographing apparatus or the one by the portable radiographing apparatus.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Radiographic apparatus
ActiveUS7889843B2Improve reliabilityImprove securityRadiation diagnostic device controlSolid-state devicesImage detectionComputer science
Owner:CANON KK
Image radiographing system
InactiveUS20080075228A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsForeign body detectionImaging processingMammary gland structure
A radiographing apparatus of an image radiographing system is equipped with plural sensors each detecting an amount of radiation transmitted through a breast in the course of radiographing, and It transmits sensor data showing an output value of each sensor to a control apparatus through a network. In the control apparatus, a mammary gland content rate corresponding to an output value of each sensor is acquired based on sensor data transmitted from the radiographing apparatus, then, a breast type is discriminated based on an average mammary gland content rate and on the state of distribution of mammary gland content rates, and image processing conditions are established based on the results of discrimination of the breast type. Then, based on the image processing conditions thus established, image processing is given to image data acquired from a reading apparatus.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
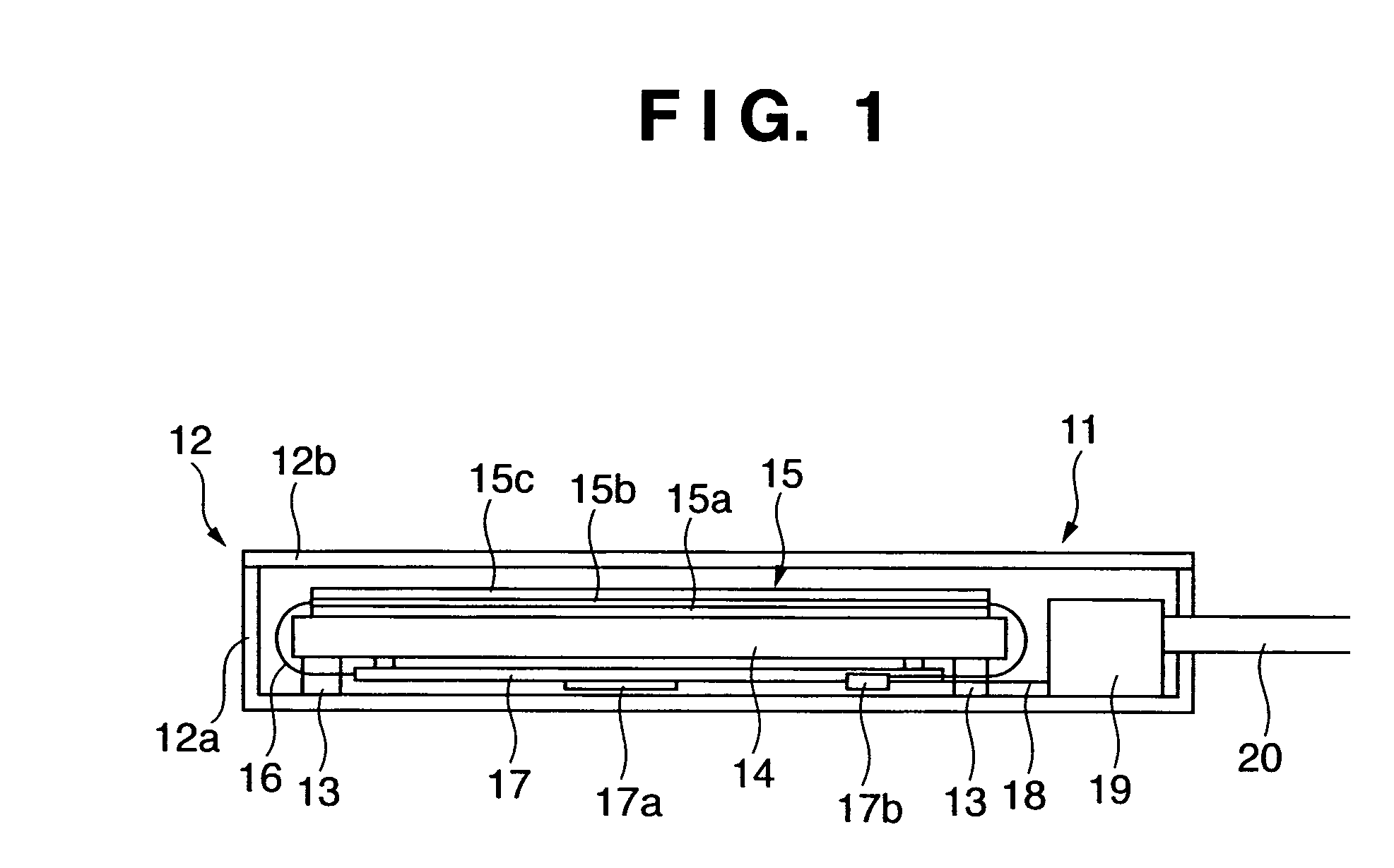
Cassette type radiographic apparatus
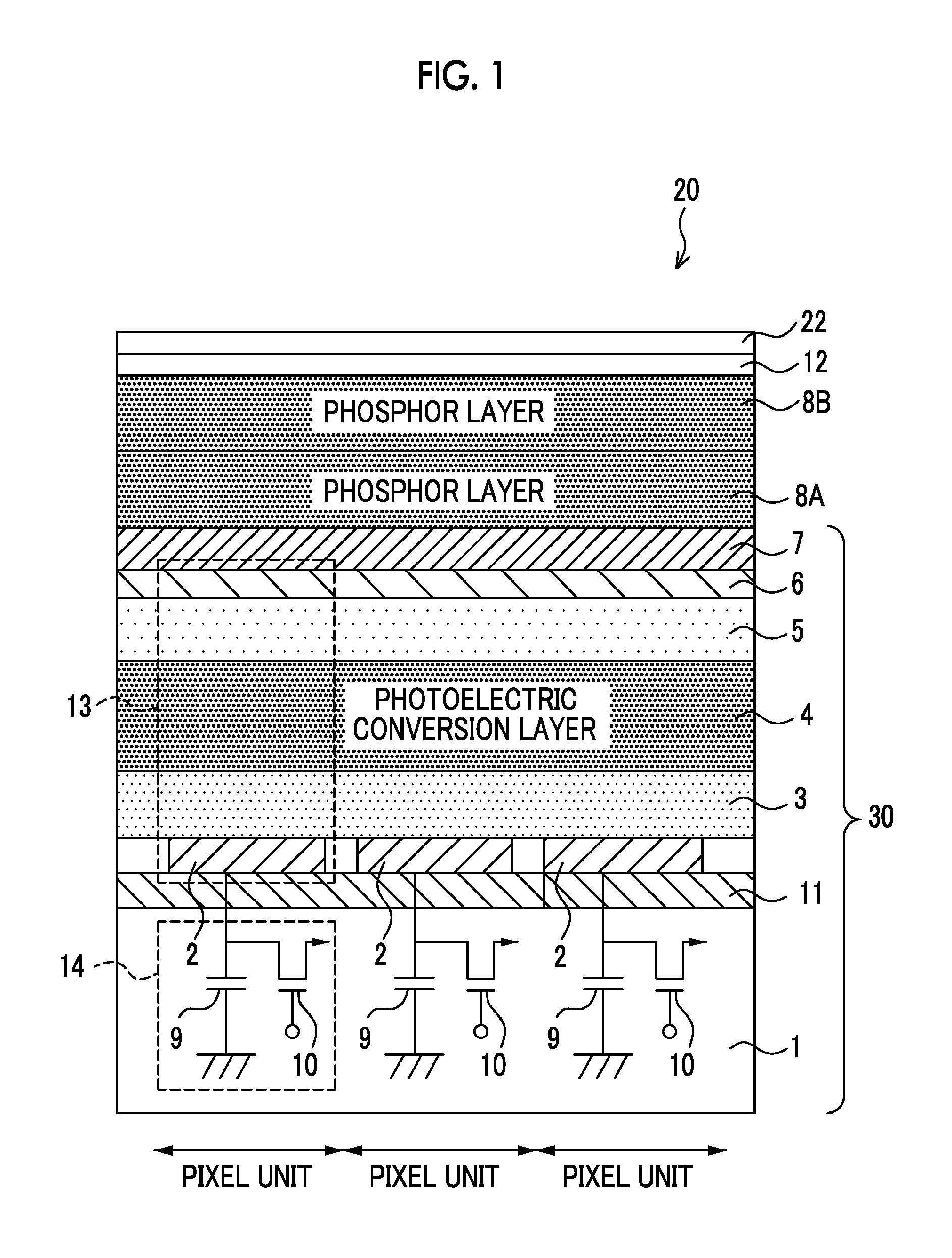
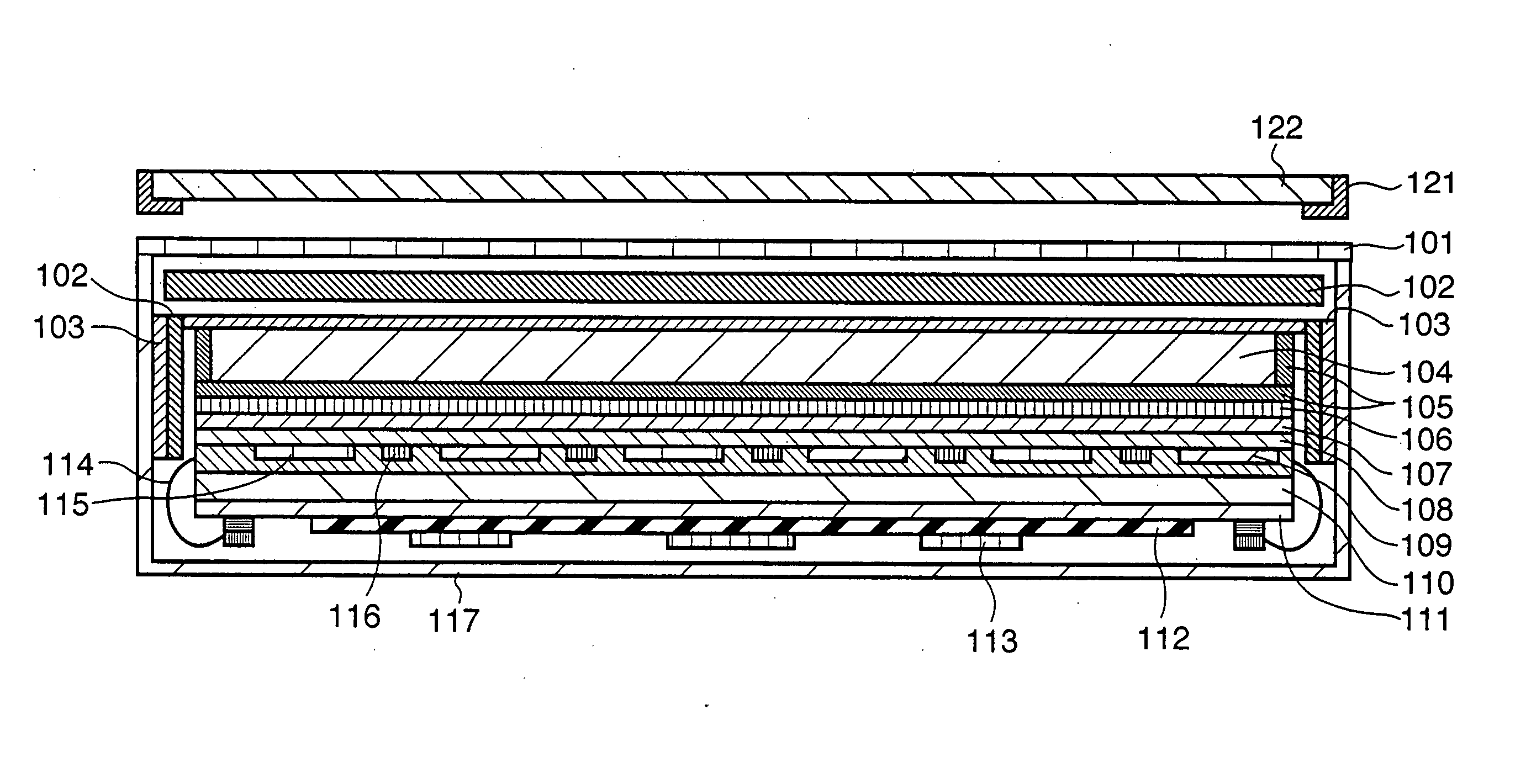
ActiveUS20060038132A1Relieve pressureReduce stressMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhosphor
A radiographic apparatus includes a columnar crystal phosphor which converts X-rays into visible light, a photodetector which converts the visible light into an electrical signal, and a case (a case lid and case main body) which houses the columnar crystal phosphor and photodetector. A buffer member which buffers a force from outside the case (the case lid and case main body) and a highly rigid member which has higher rigidity than that of the columnar crystal phosphor are arranged between the case (the case lid and case main body) and columnar crystal phosphor.
Owner:CANON KK
Gaseous-based radiation detector and apparatus for radiography
A detector for detection of ionizing radiation comprises a cathode; an anode; an ionizable gas arranged between these electrodes; a radiation entrance arranged such that ionizing radiation can enter and ionize the ionizable gas; and a readout arrangement. A voltage across the electrodes causes electrons created during ionization of the gas to drift towards the anode, where the readout arrangement detects them. To reduce the risk of occurrence of sparks, and / or to reduce the energy in occurring sparks, one of the cathode and anode has at least the surface layer facing the other electrode made of a material having a resistivity of at least 5x10-8 OMEGAm.
Owner:XCOUNTER
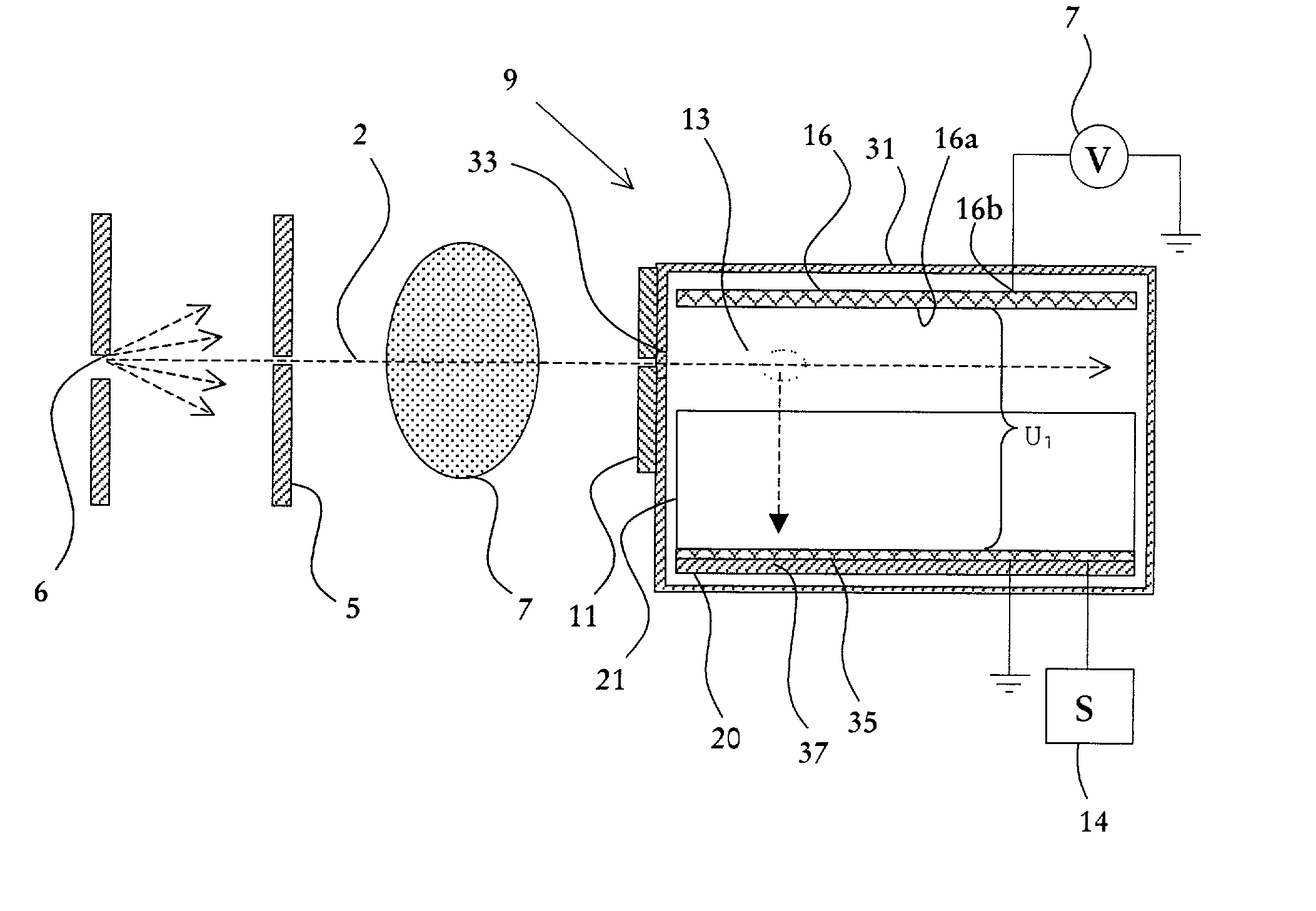
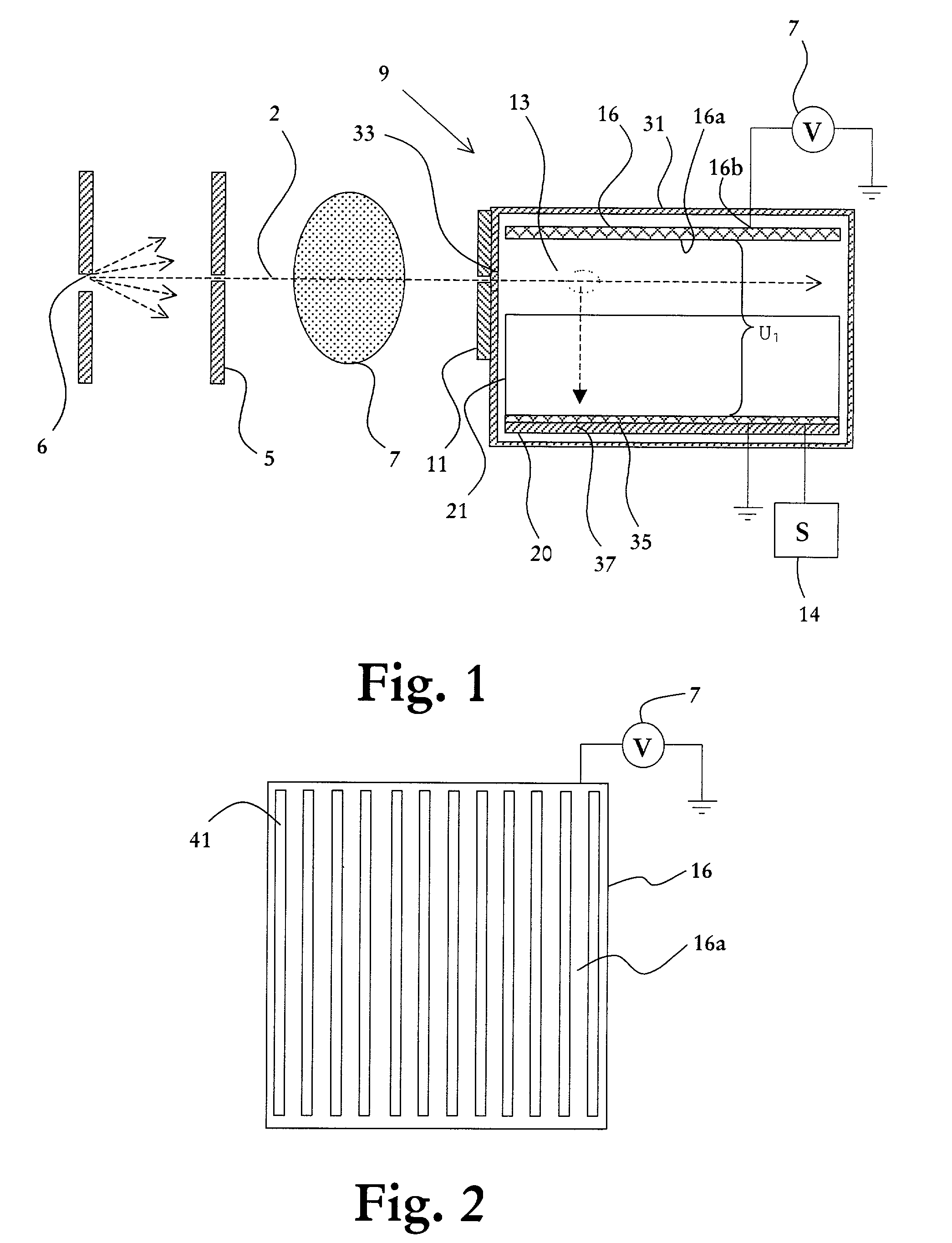
Radiography apparatus and radiography method
A radiography apparatus with a function for evaluating image quality is provided. To accomplish this, the radiography apparatus includes a radiating-generating unit for emitting radiation, an imaging unit for converting the radiation into image data, a measuring unit for measuring an image-quality evaluating value of the image data, and a determining unit for determining the image quality of the imaging unit based on a plurality of image-quality evaluating values of the image data acquired at a plurality of points in time, where each image-quality evaluating value corresponds to the image data acquired at one of the points in time.
Owner:CANON KK
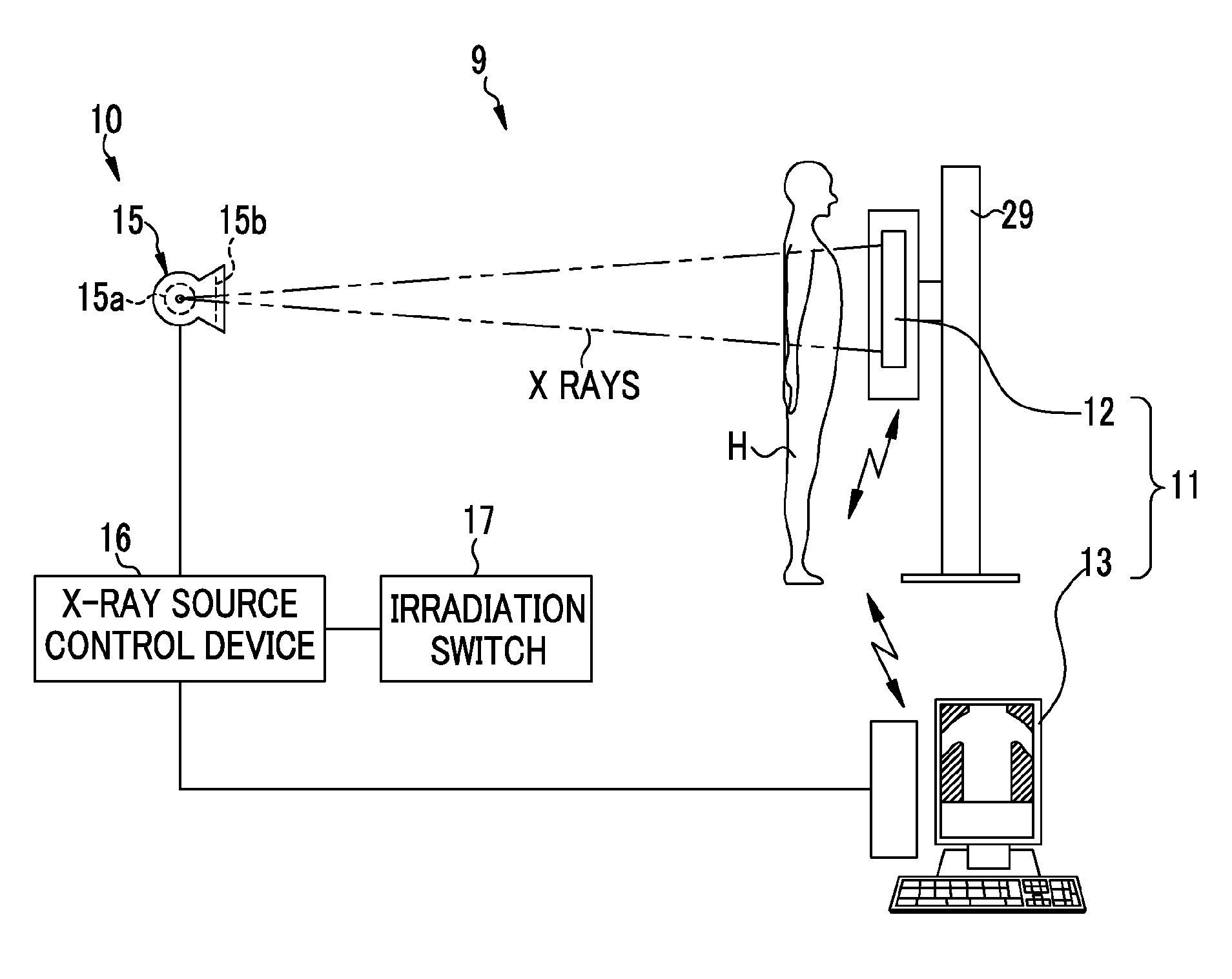
Radiographic device, radiographic system, control method and recording medium for radiographic device
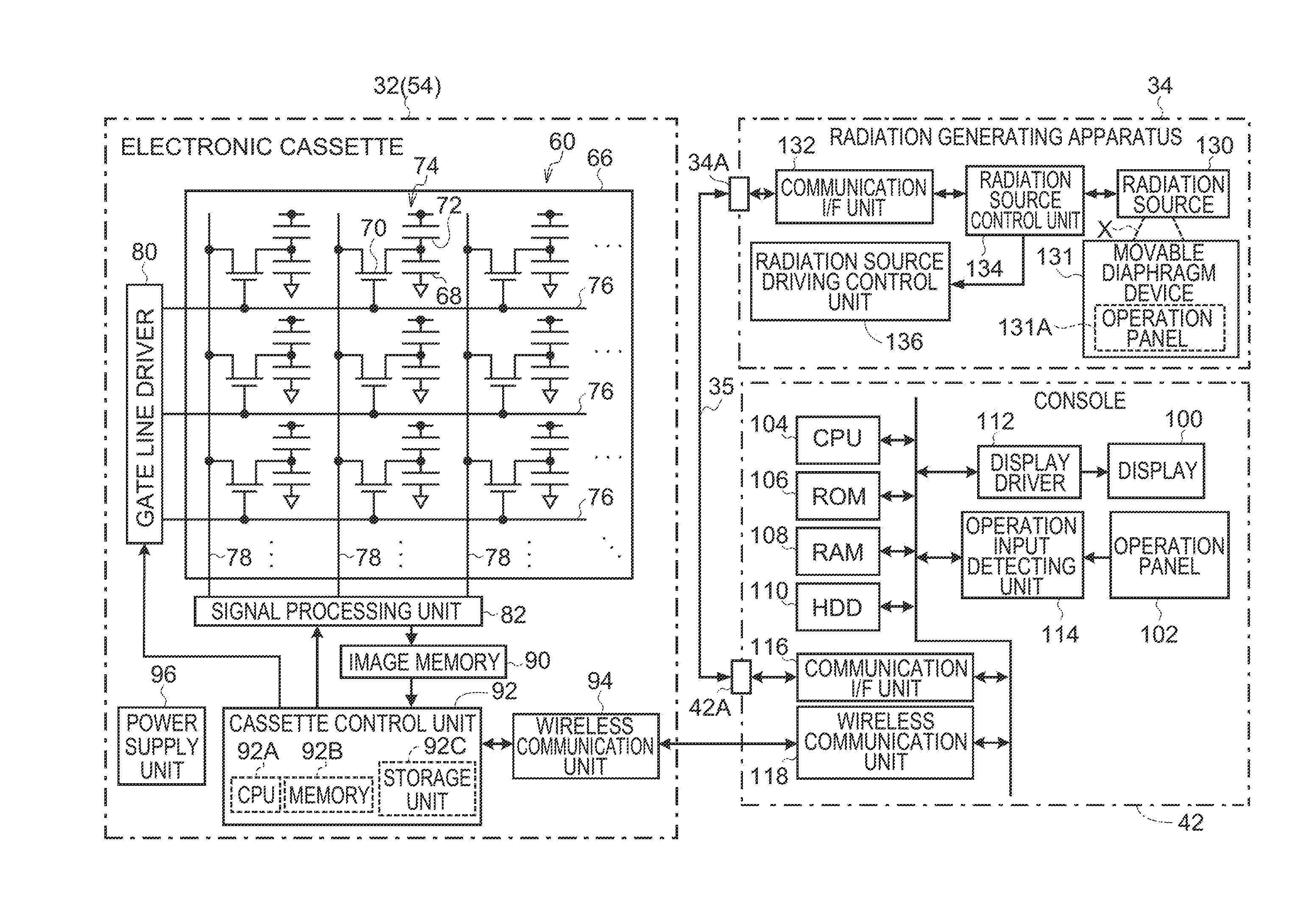
ActiveUS20130148784A1Reduce doseStopping irradiationRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusX-rayStop time
An AEC unit of an electronic cassette sets a dose target value and a short-circuited pixel used for AEC based on a radiographing condition. When a control unit of the electronic cassette detects start of irradiation of X rays, the AEC unit starts integration of a cumulative dose of X rays which are incident to a target region based on a dose detection signal output by the short-circuited pixel. The AEC unit predicts a stop timing at the time point t1, waits until the time point t2 which is a predetermined time earlier than a scheduled stop time, and sends a stop timing notification to an X-ray generation device at the time point t2. When the stop timing notification is received, a X-ray source control device immediately inputs an irradiation stop command so as to stop an operation of an X-ray source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
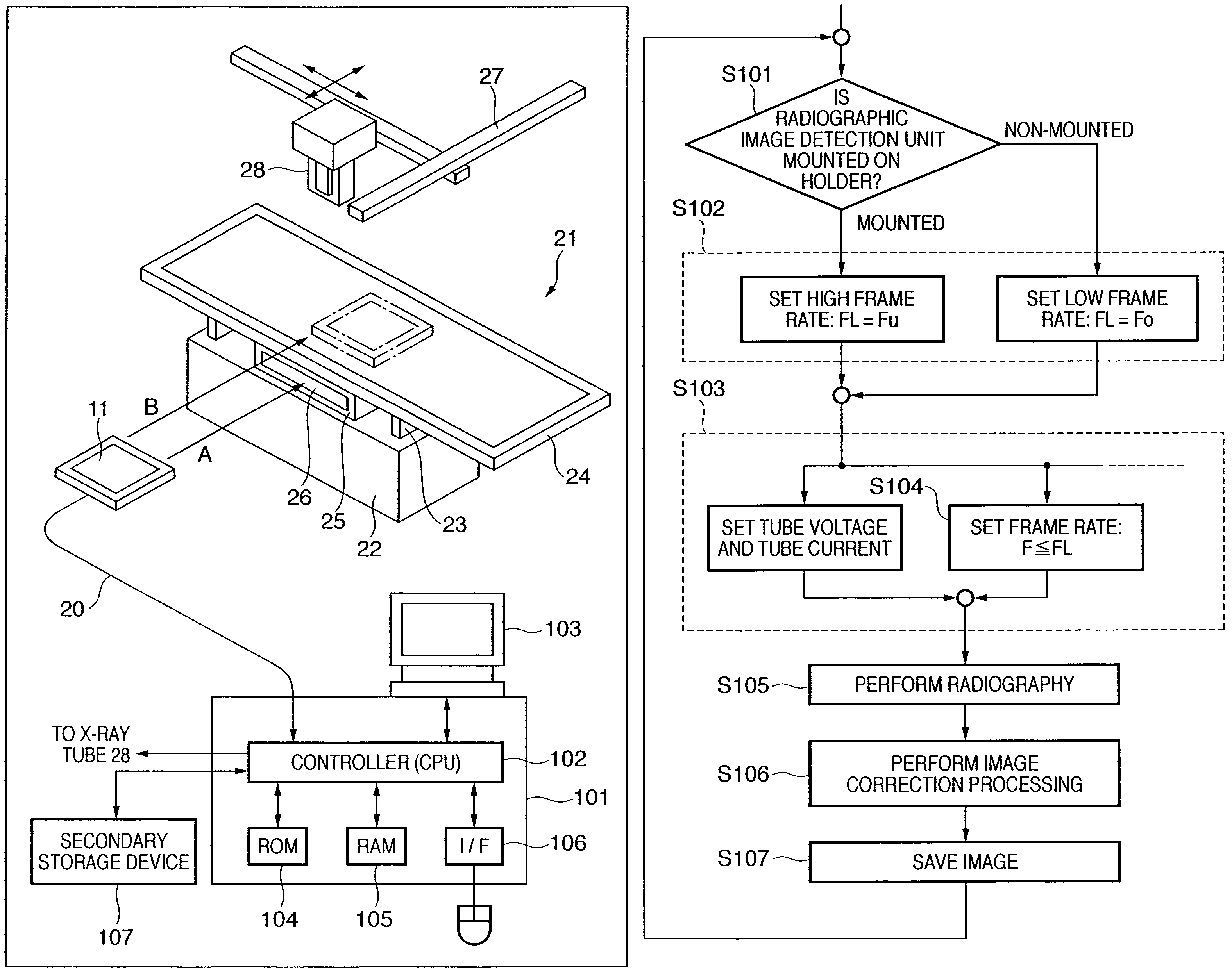
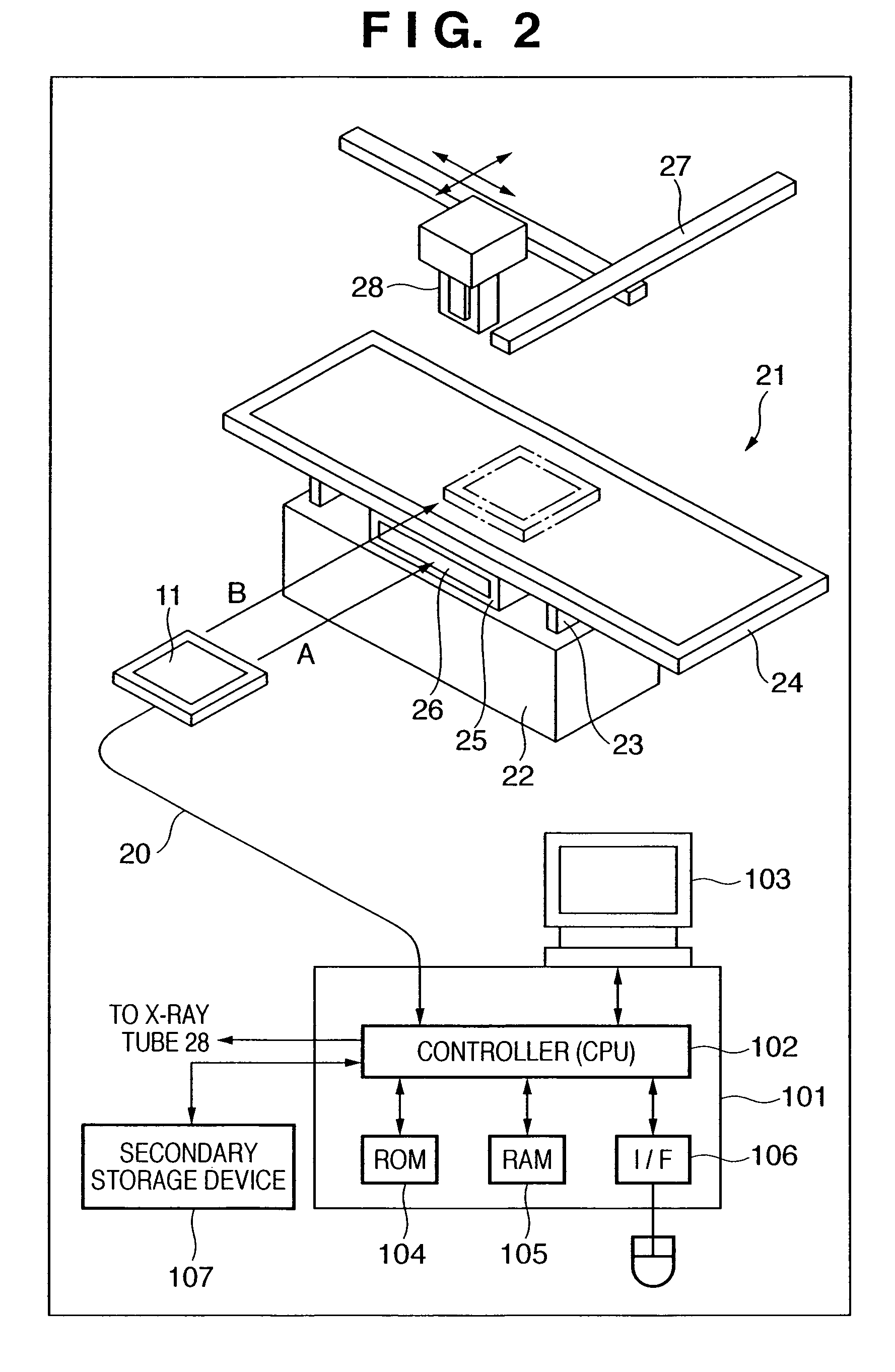
Radiographic apparatus
ActiveUS20090154648A1Process controlImprove reliabilityRadiation diagnostic device controlImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesImage detectionComputer science
In order to improve the reliability of a radiographic image detection unit and the reliability of a radiographic apparatus, when it is not detected that the radiographic image detection unit is mounted on a support portion or a cooling portion, processing for restricting radiography of a moving image is executed.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaging area specifying apparatus, radiographic system, imaging area specifying method, radiographic apparatus, and imaging table
InactiveUS20110110497A1Avoid problemsRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsElectric signalRadiographic equipment
An imaging area specifying apparatus that includes a storage component and a specifying component is provided. The storage component stores as correlation information a correlation value correlated with the amount of radiation emitted to each of a plurality of predetermined areas divided from a detection region of a radiation detector that outputs an electric signal indicating a radiological image represented by radiation which is emitted to the detection region for detecting the radiation. The specifying component specifies an imaging area capable of capturing the radiological image of a predetermined size while preventing variations in the amount of radiation emitted to each of the divided areas in the detection region, on the basis of the correlation information stored in the storage component.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiographic equipment
InactiveCN101128731AClear distinctionEasy to separateMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionUltrasound attenuationSoft x ray
The invention concerns radiographic equipment for forming an image of an interior of an object. The equipment comprises a source of X-ray or gamma-ray radiation having two or more energies and operable to irradiate an object to be scanned and a radiation source producing neutrons operable to irradiate the object. The equipment also comprises a radiation detector array having a plurality of pixels, each sensitive to and arranged with respect to the X-ray or gamma-ray radiation source and the neutron producing radiation source and operable to measure the intensity of each type of radiation transmitted through the object; means to process the intensity of each type of radiation, to determine the attenuation of each type of radiation having passed through the object, and to form an image indicative of the shape and composition of the object's interior.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com