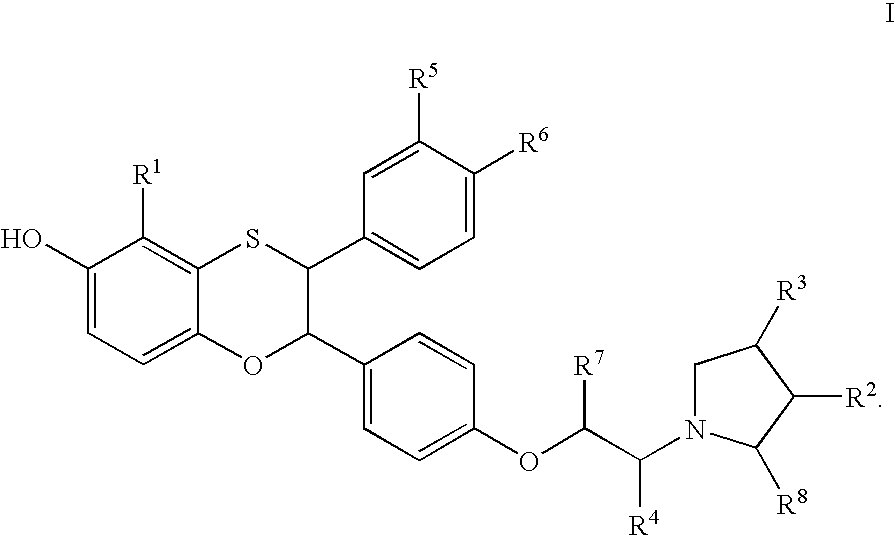
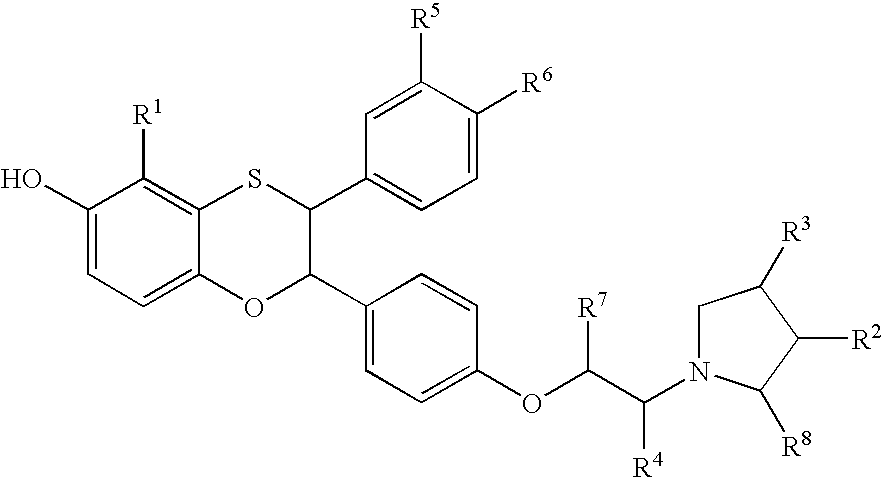
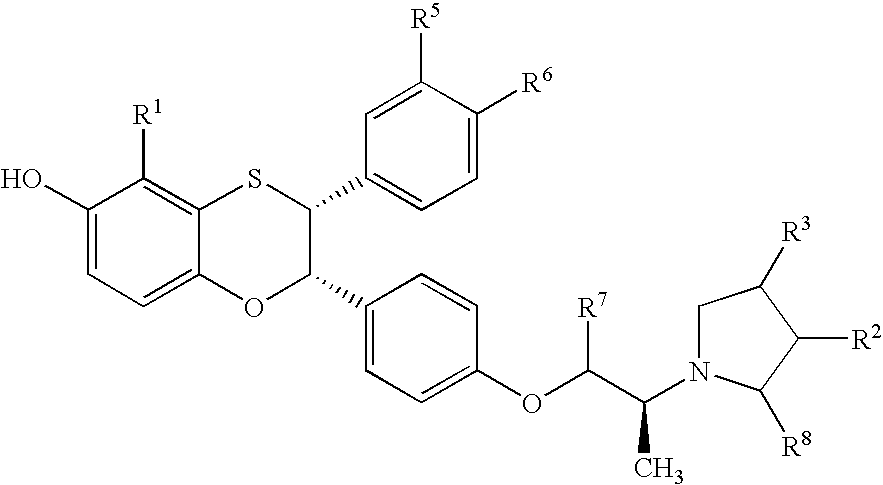
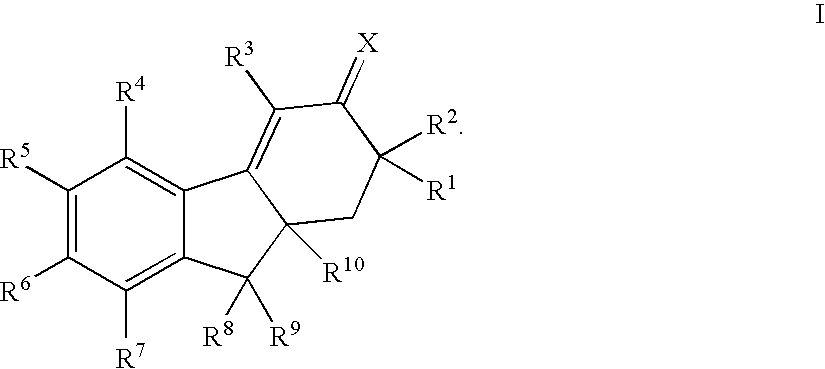
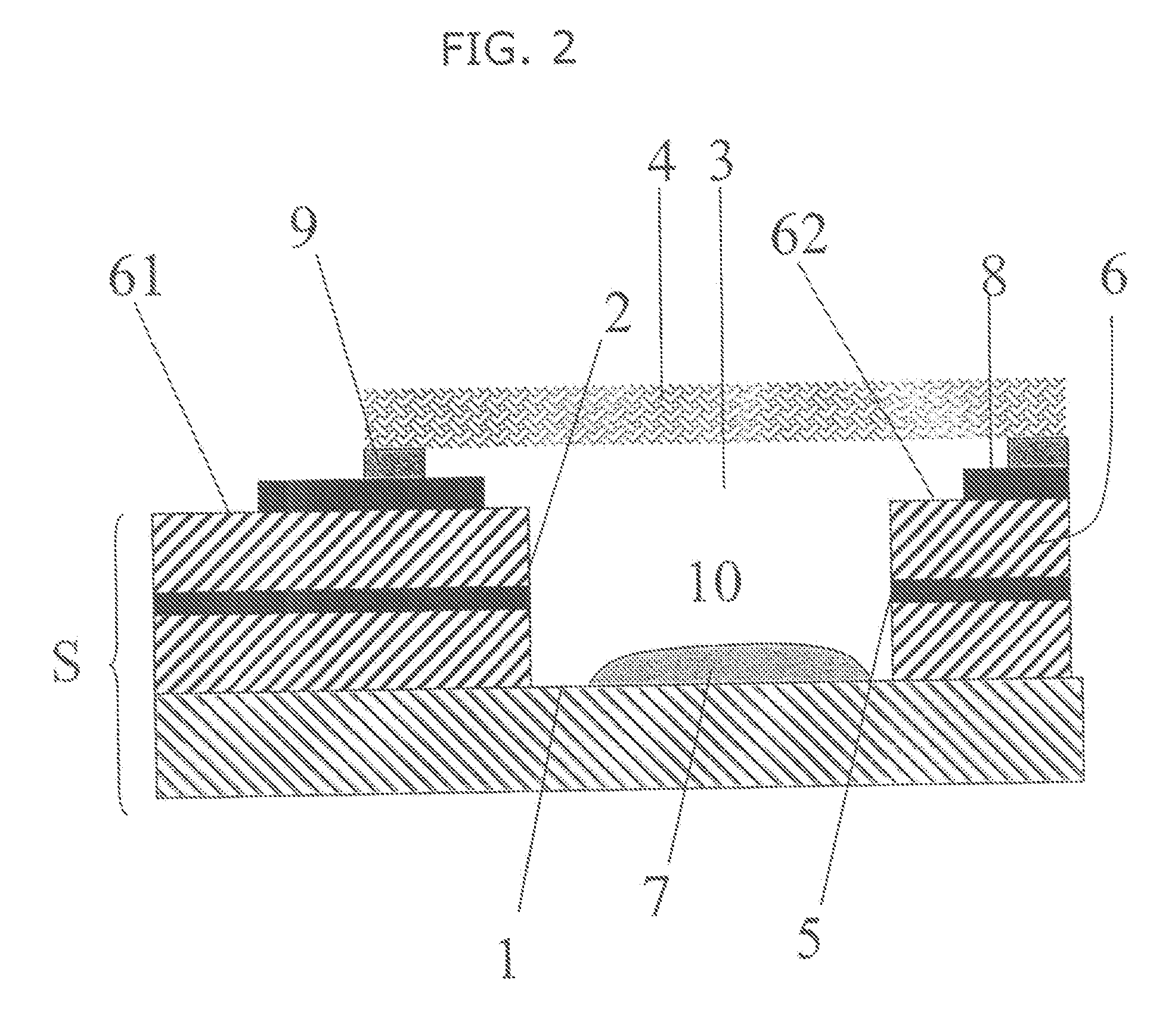
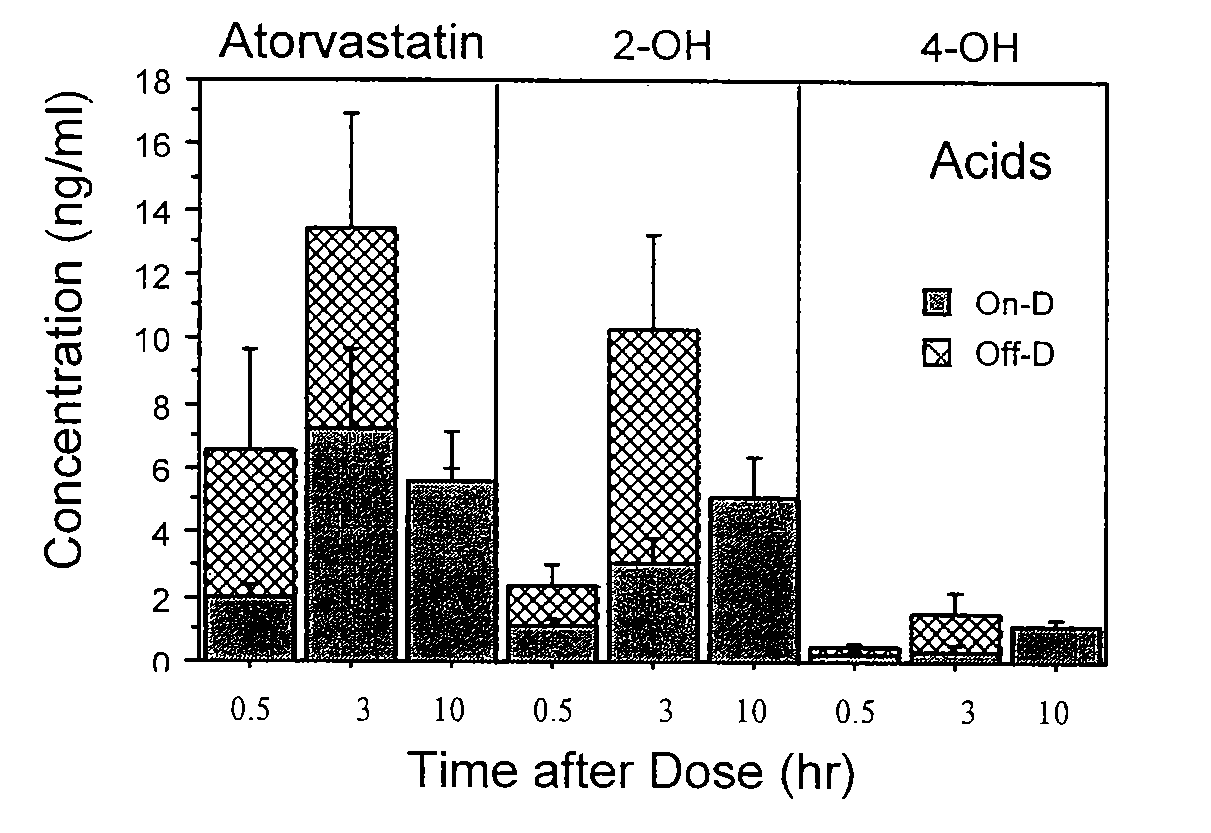
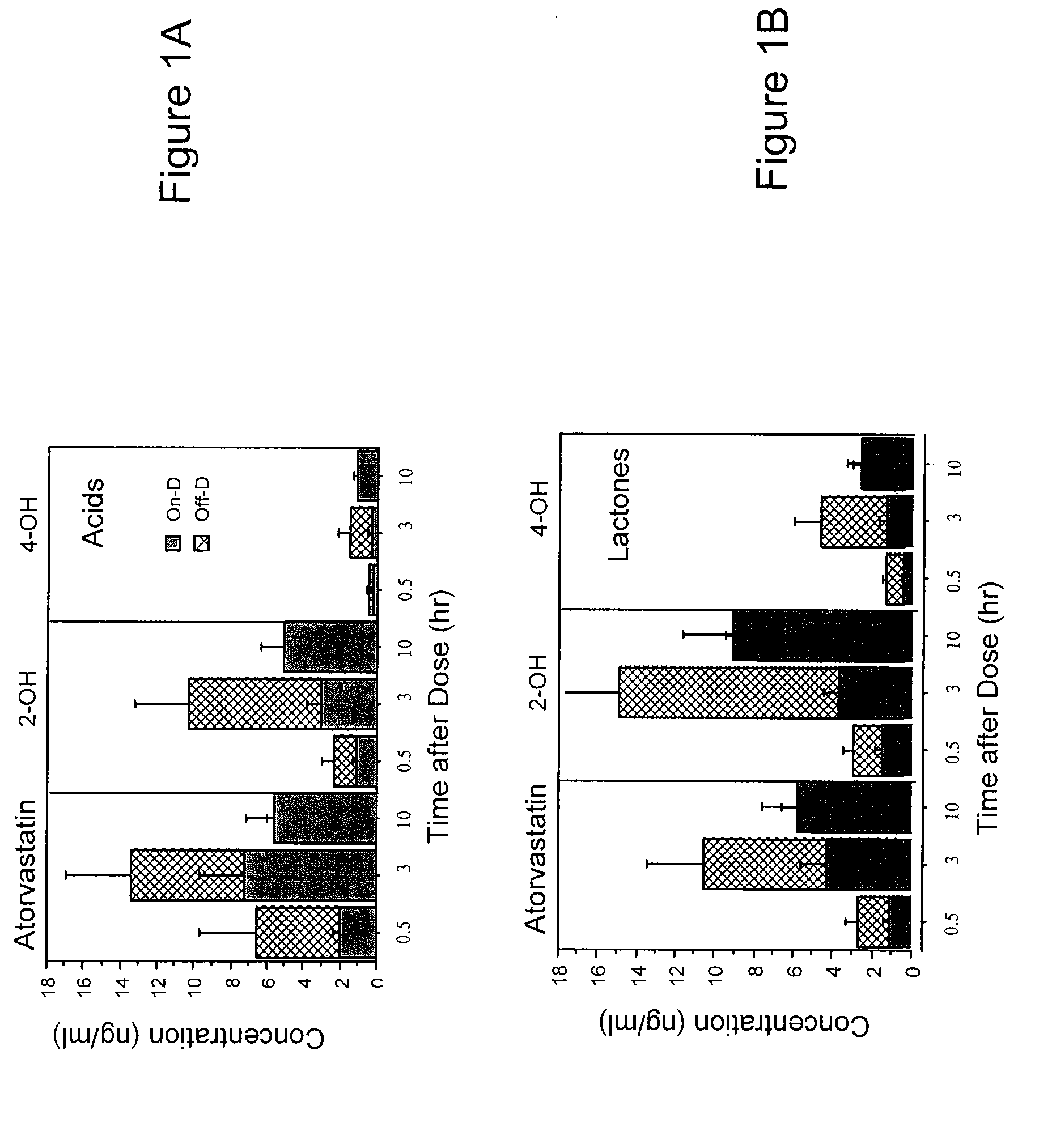
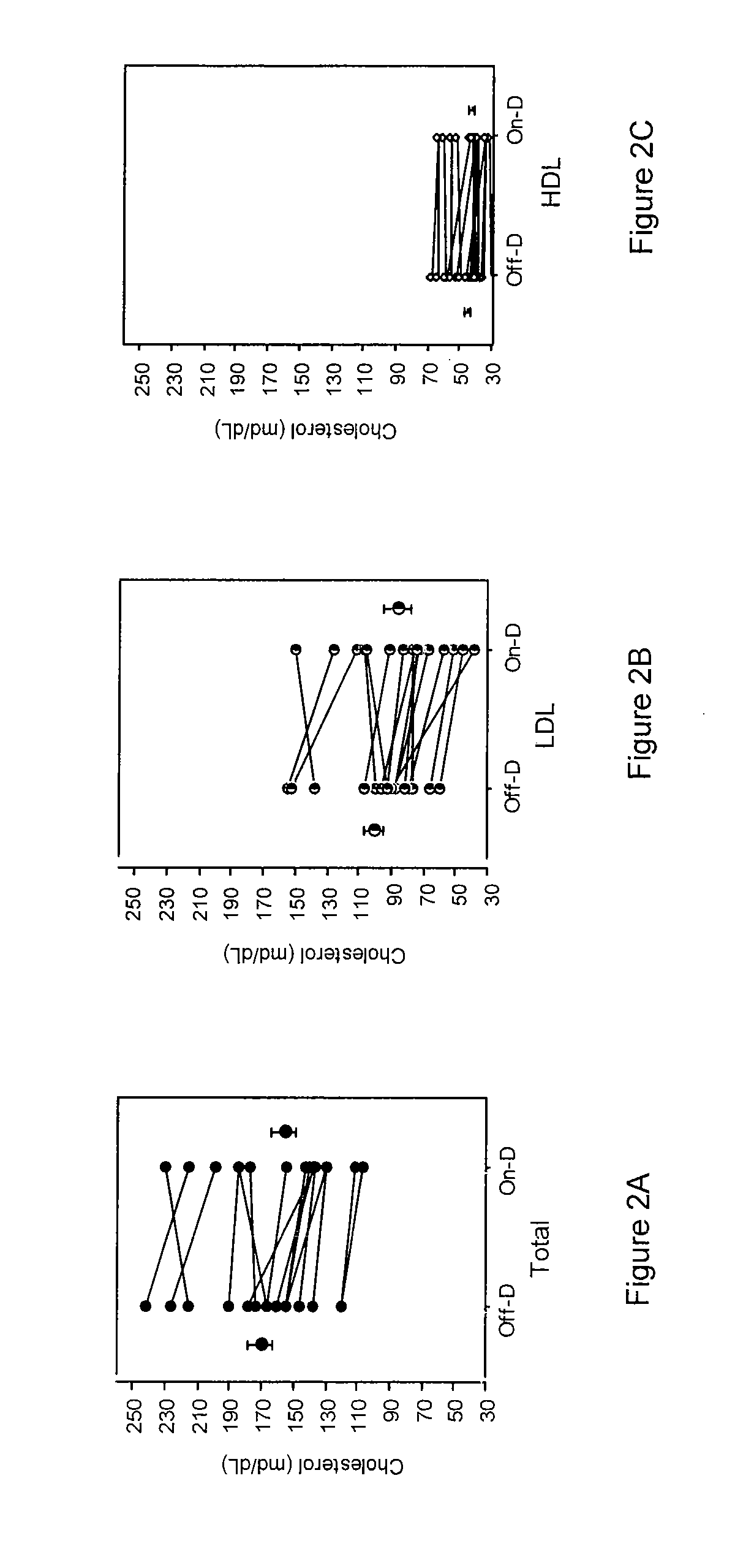
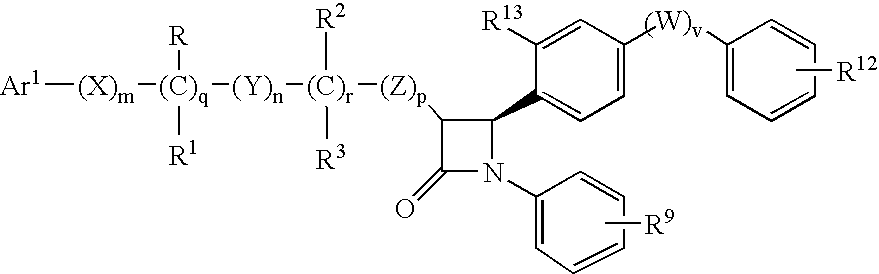
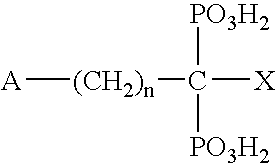Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
269 results about "Ldl cholesterol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
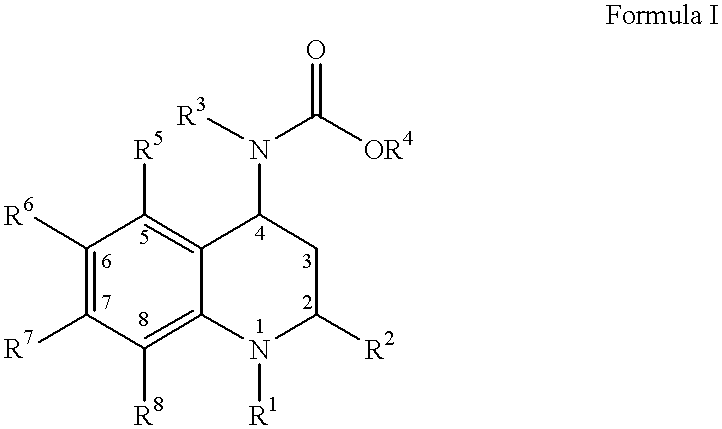
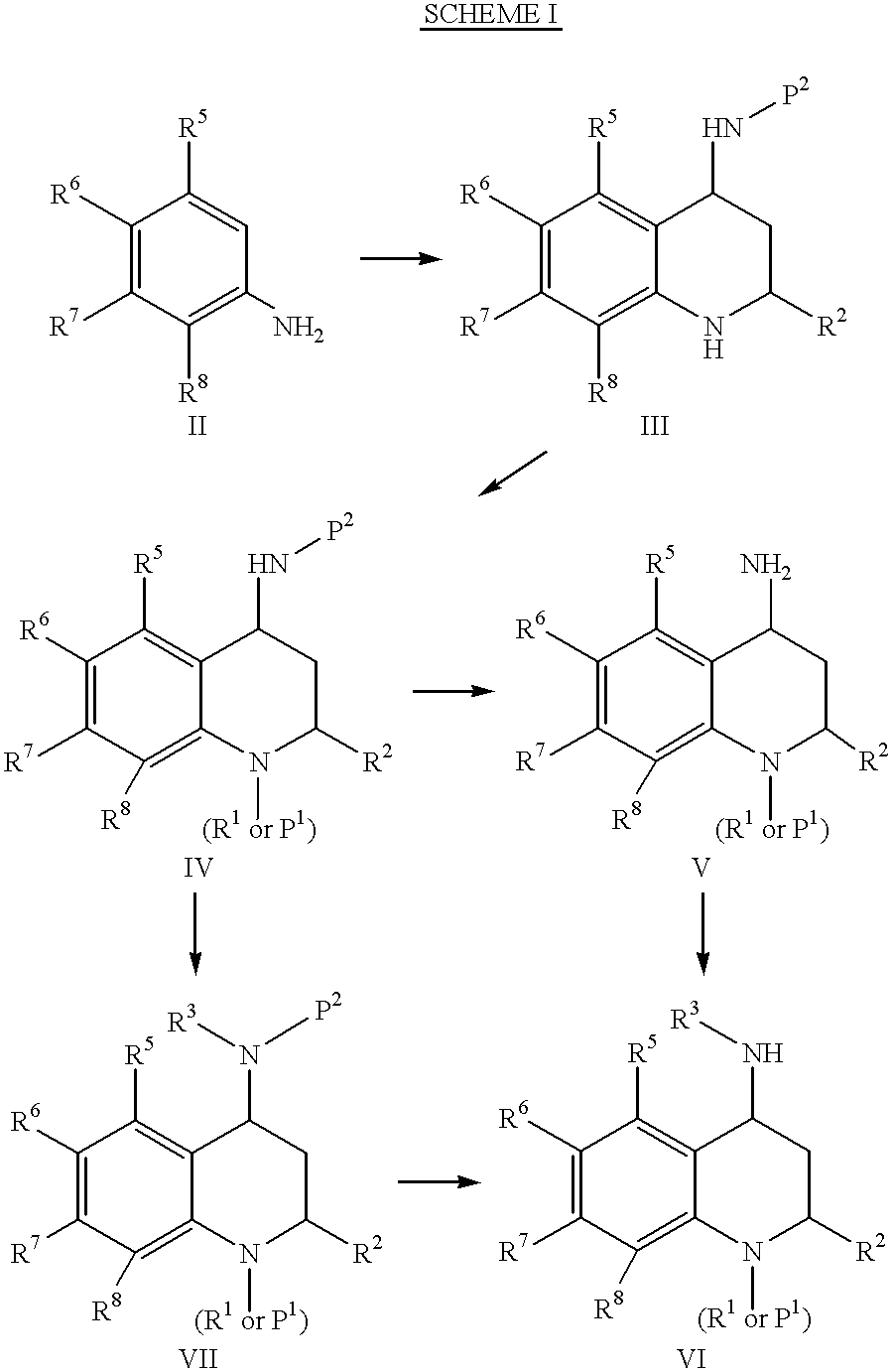
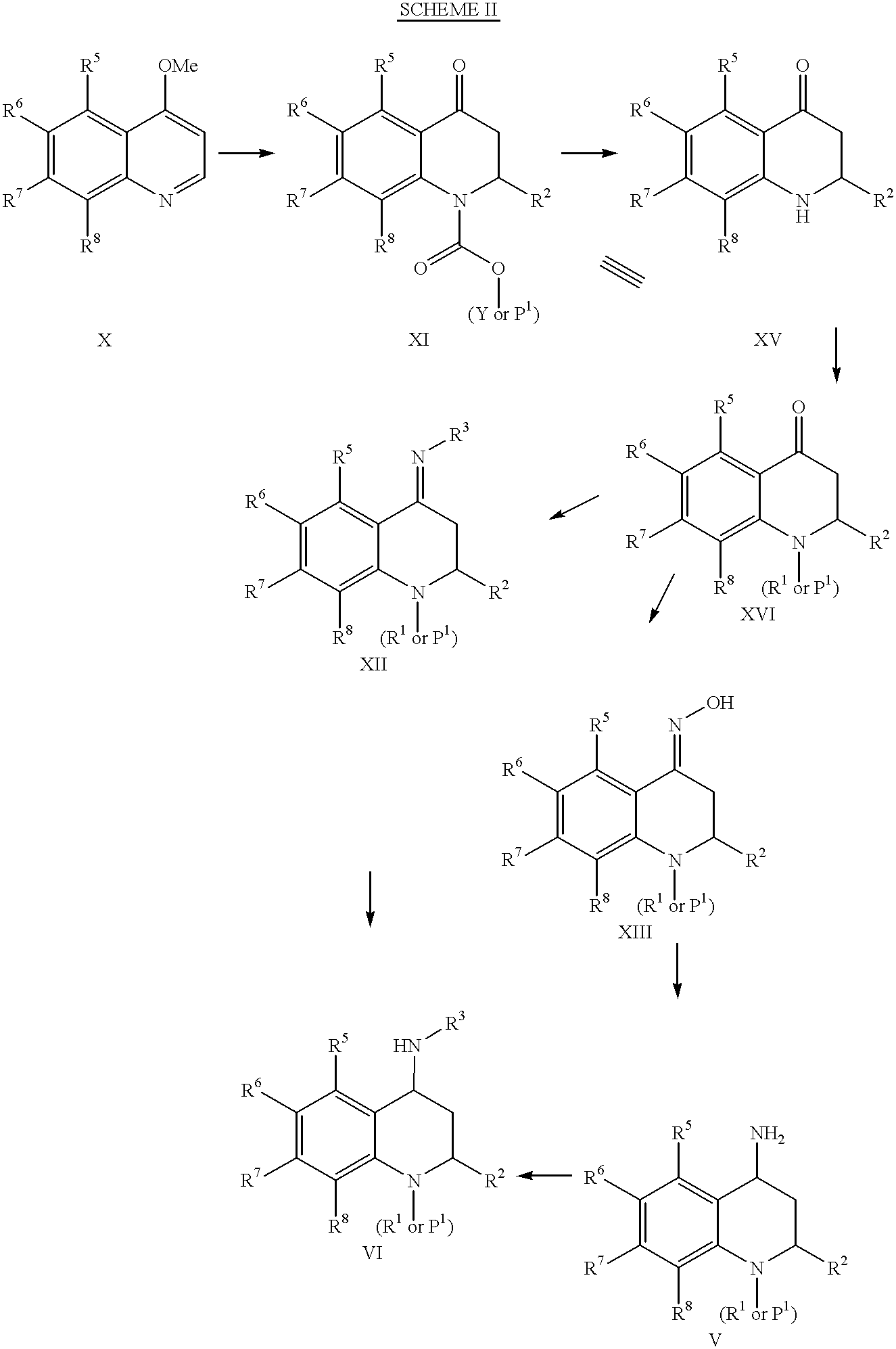
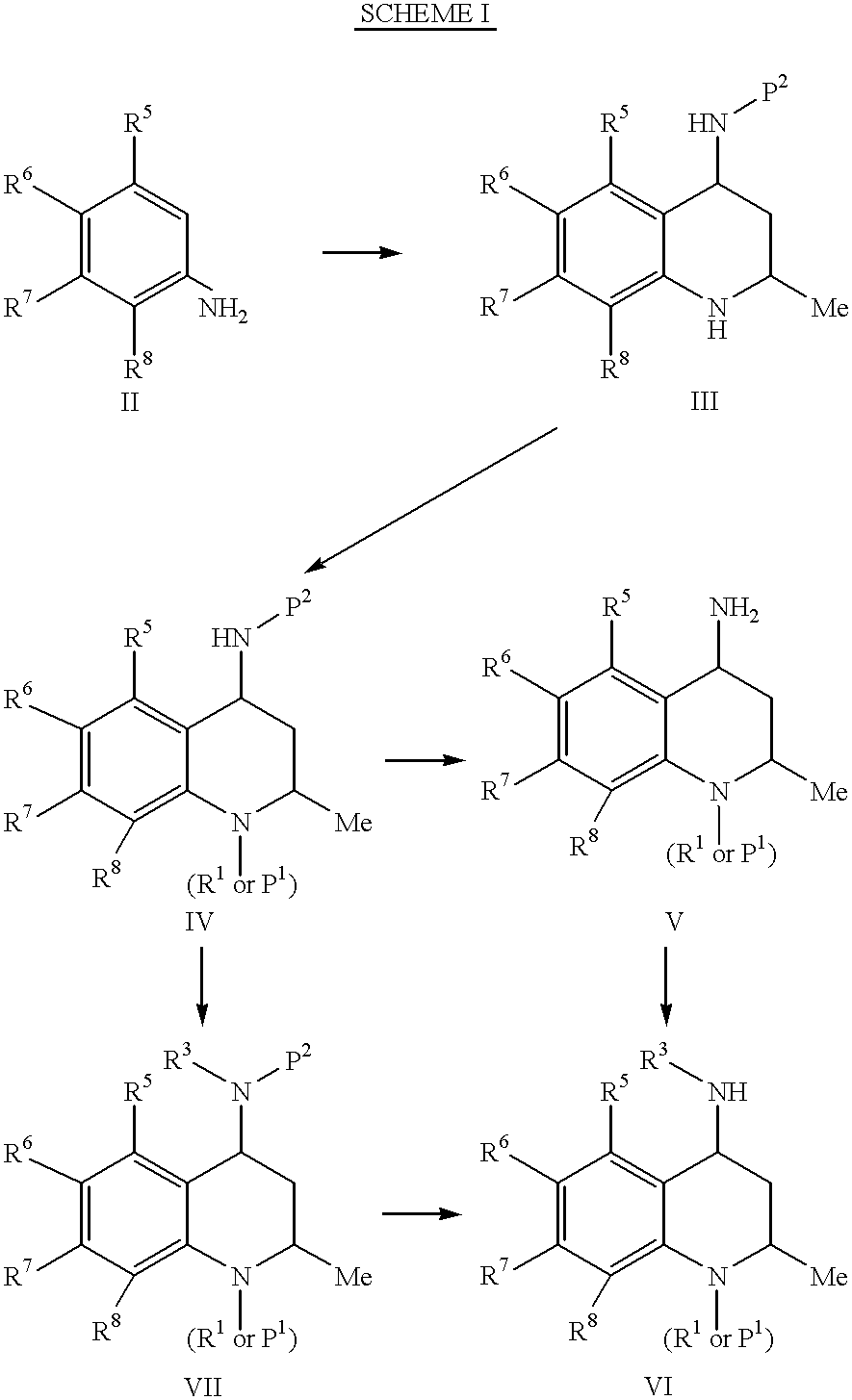
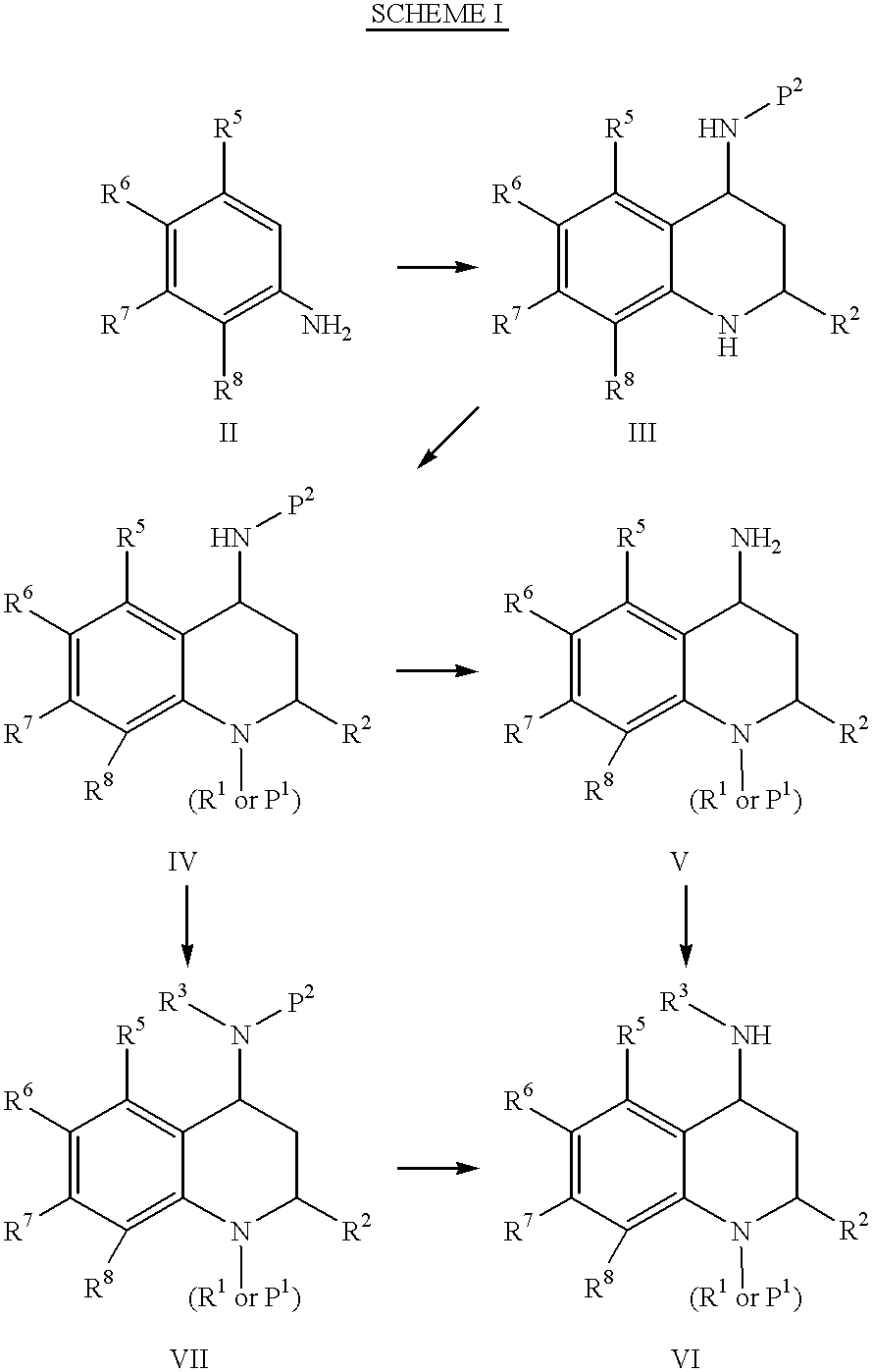
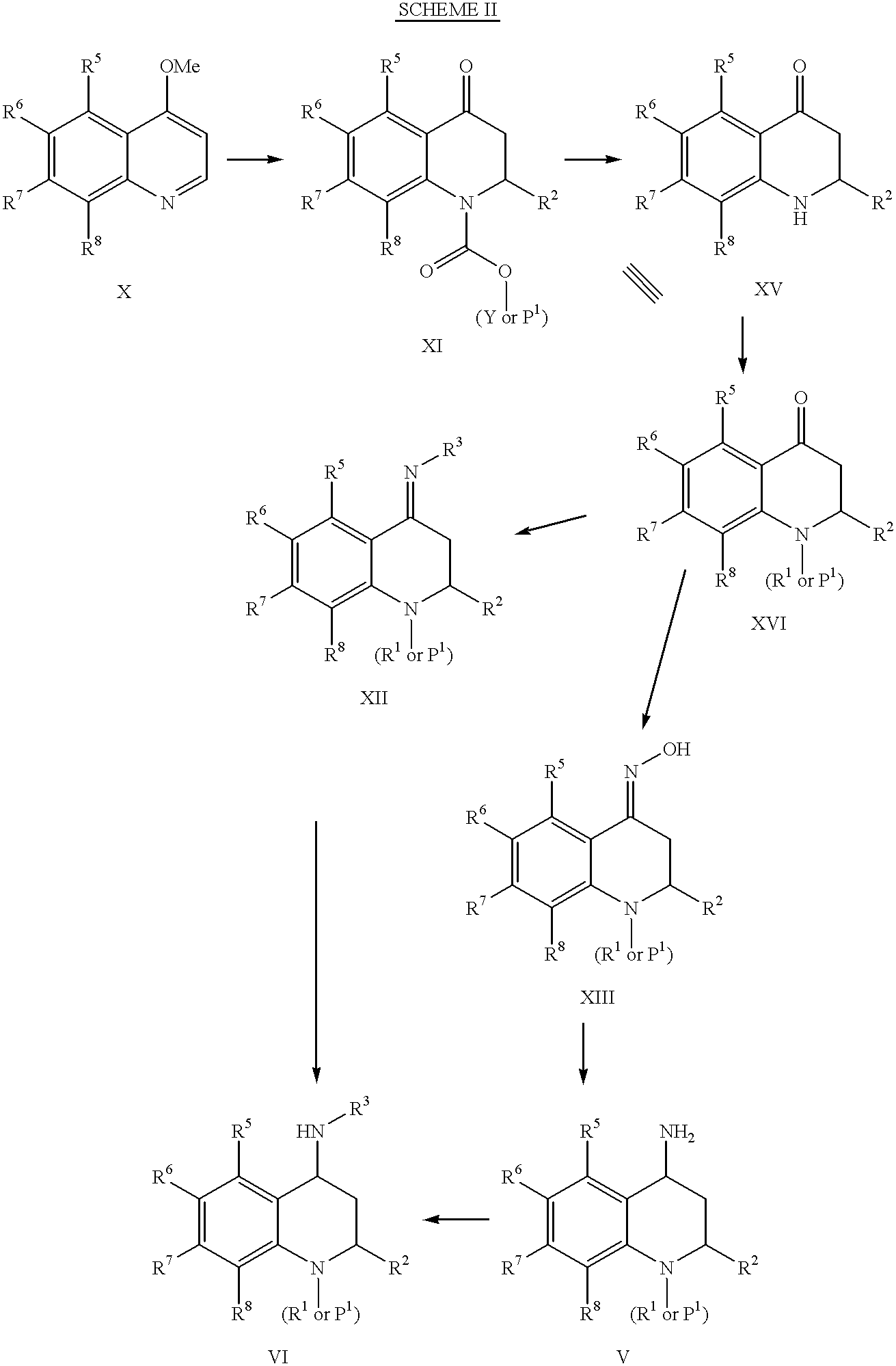
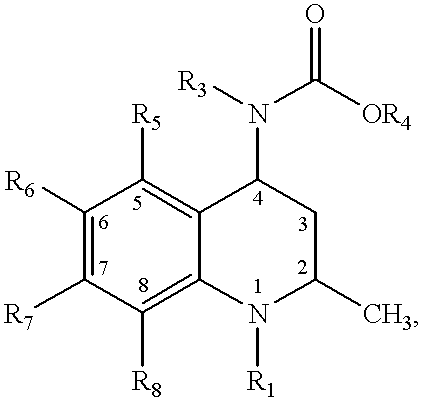
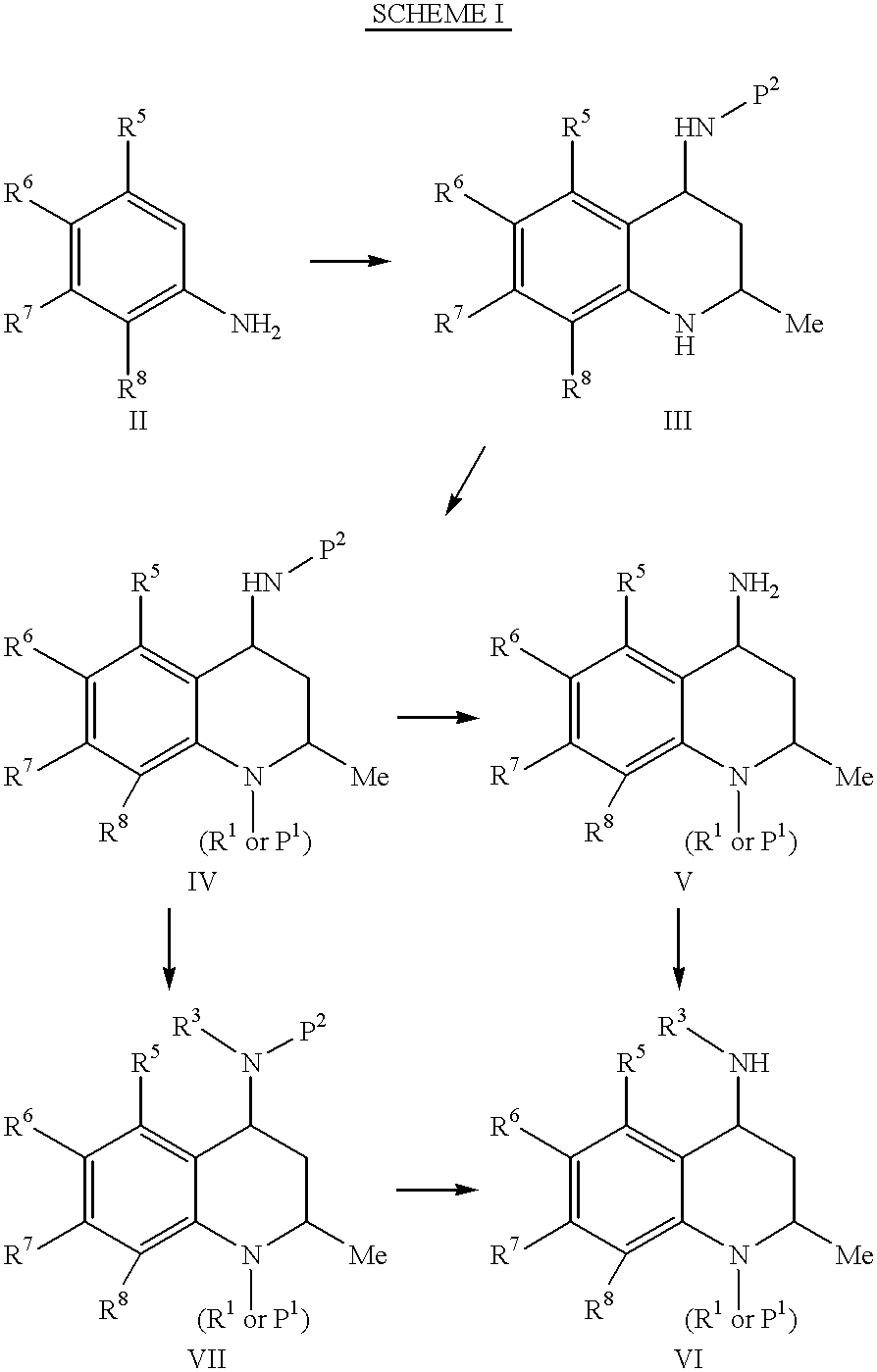
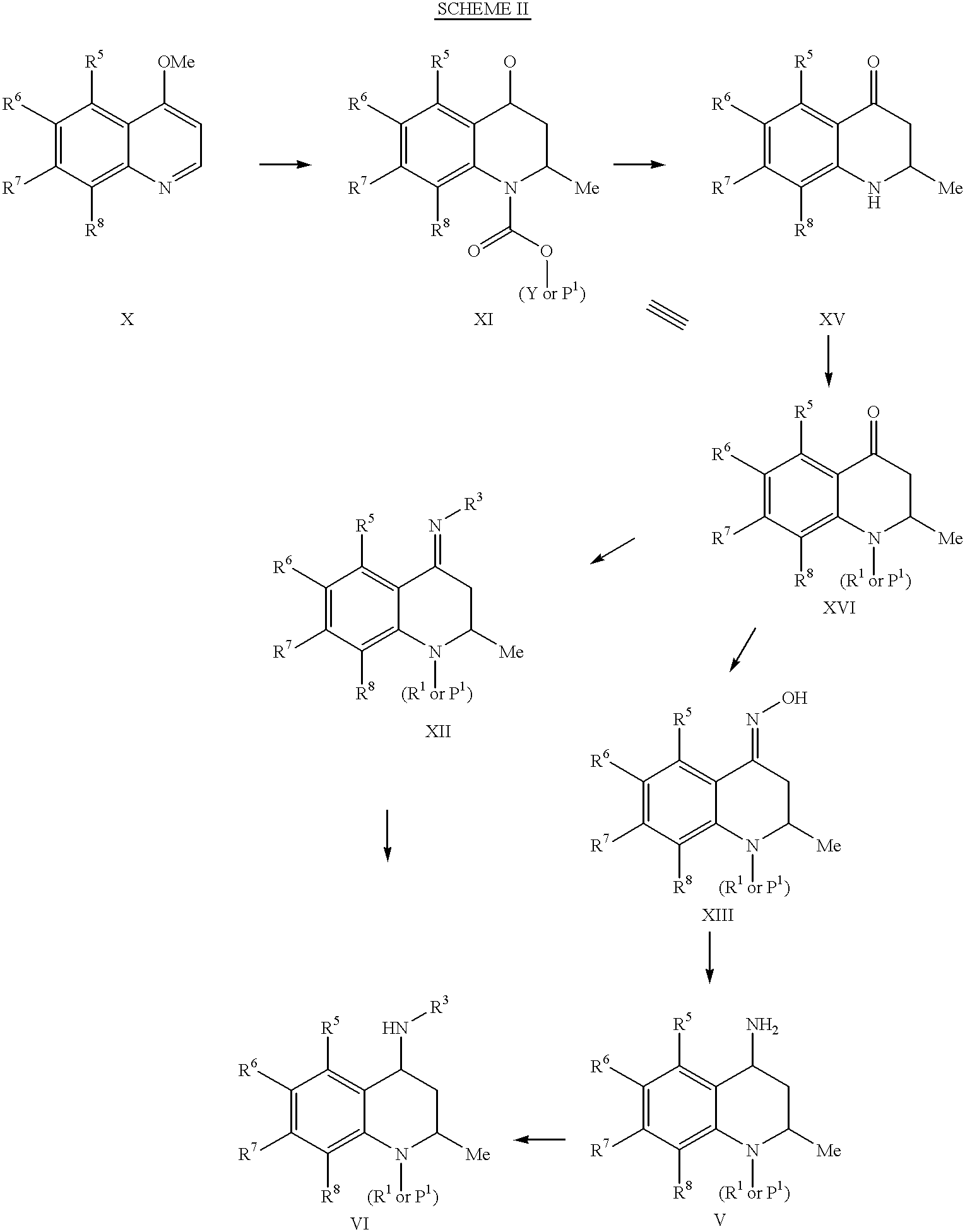
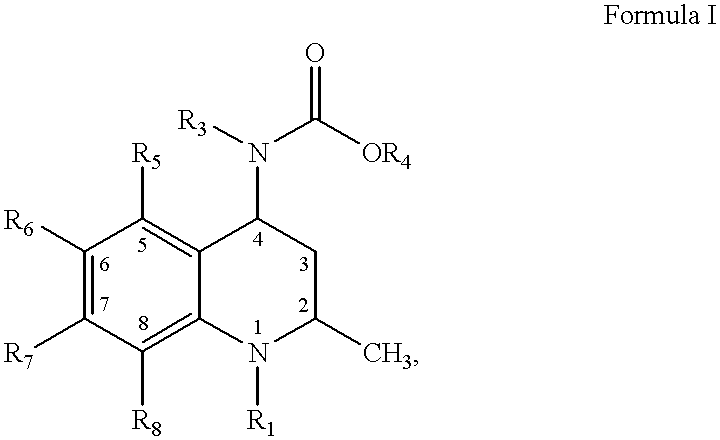
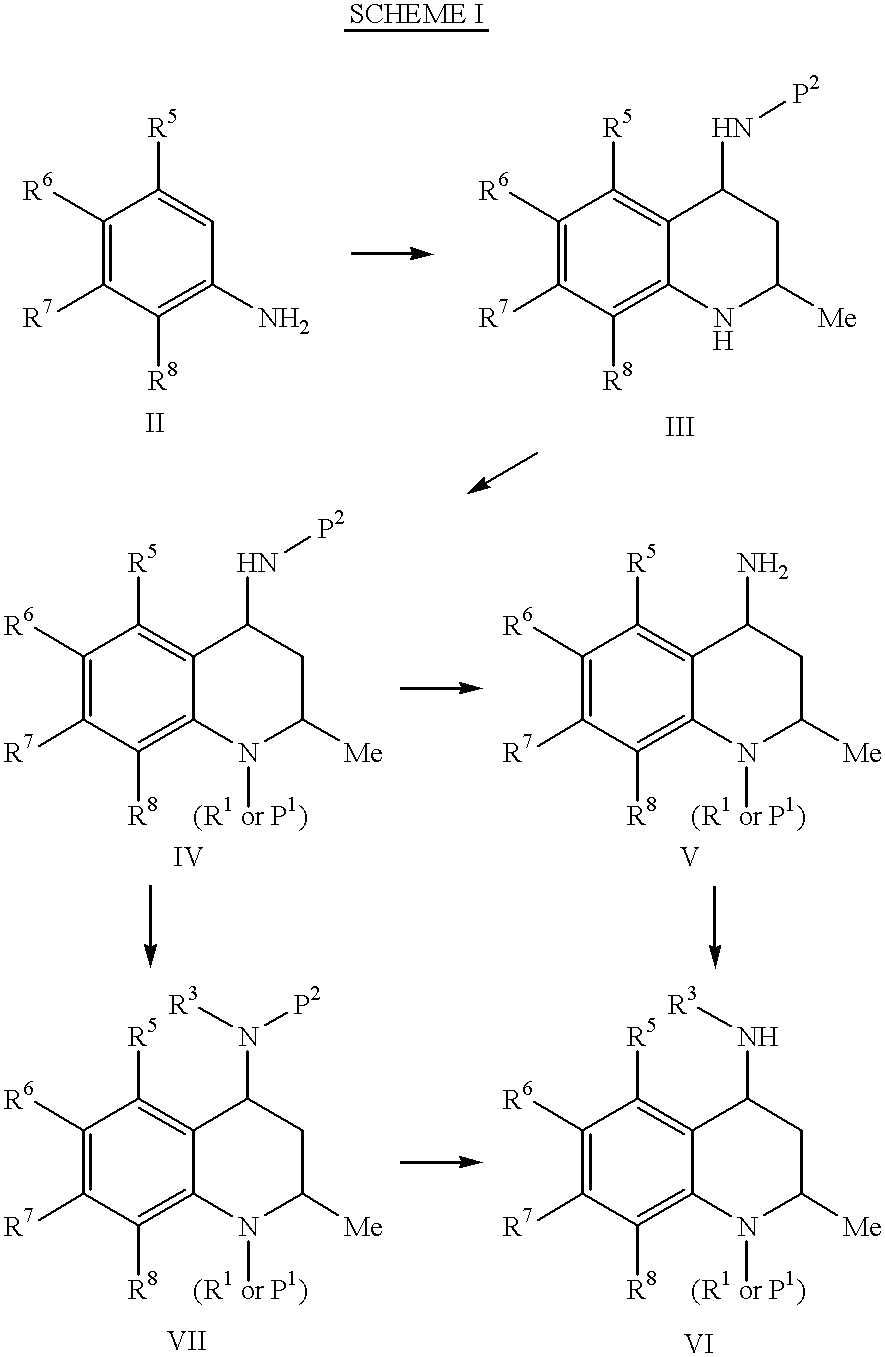
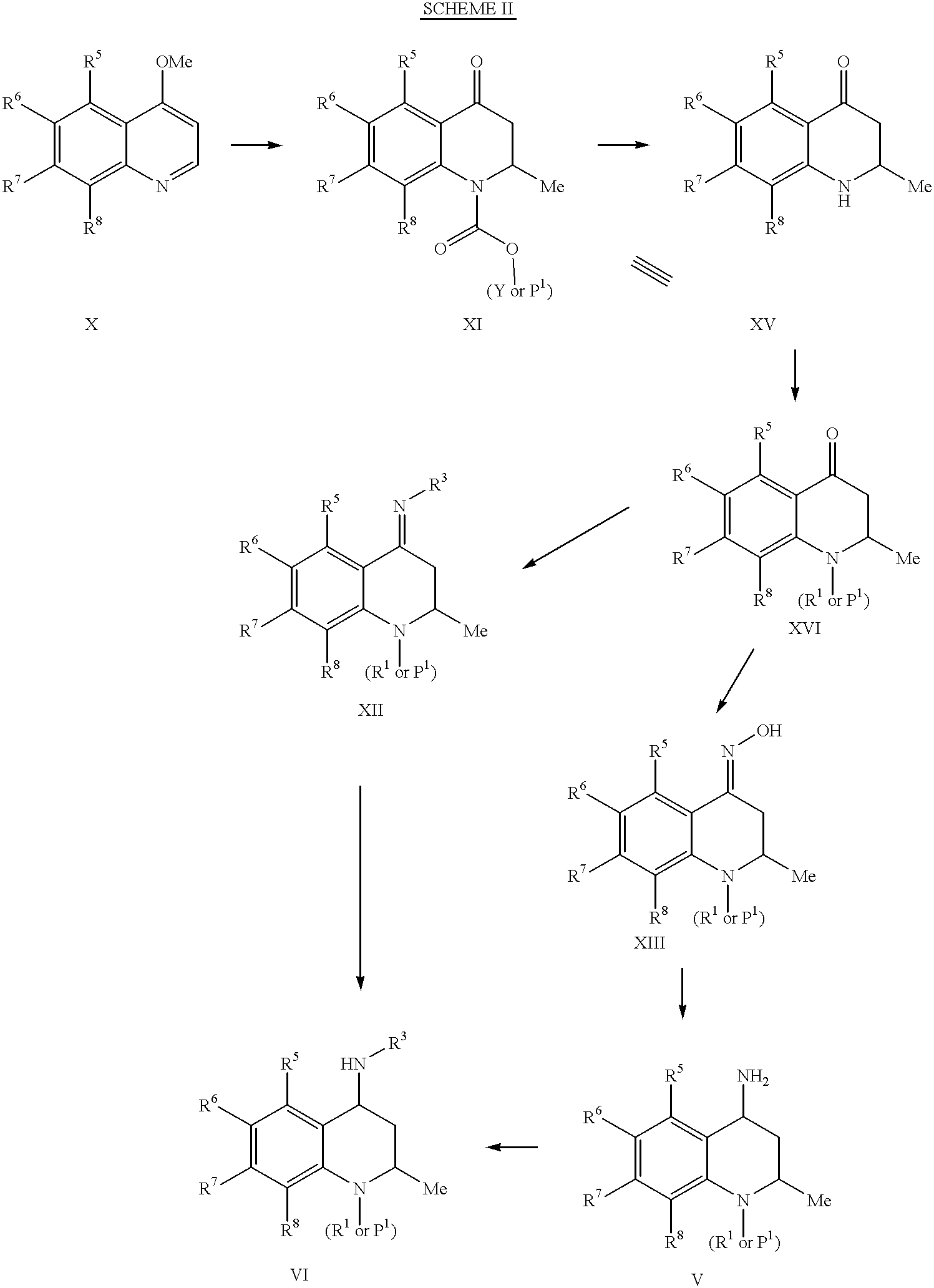
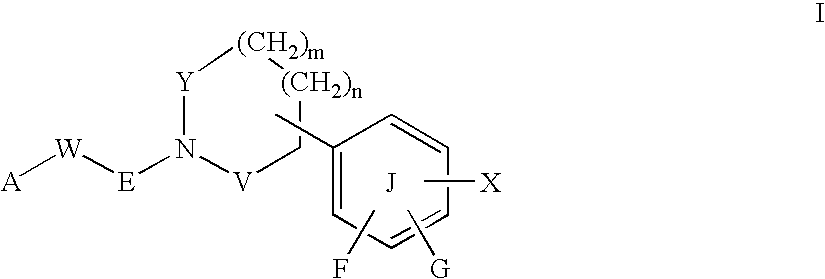
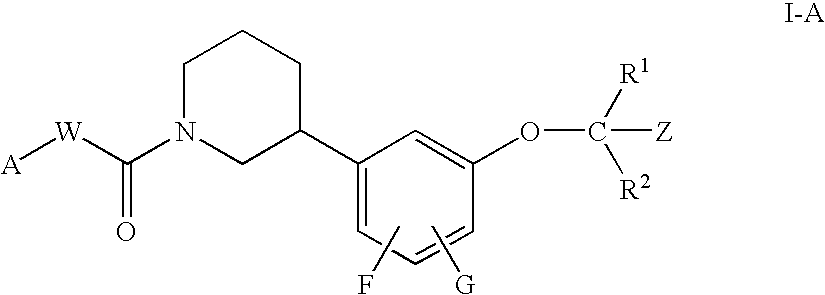
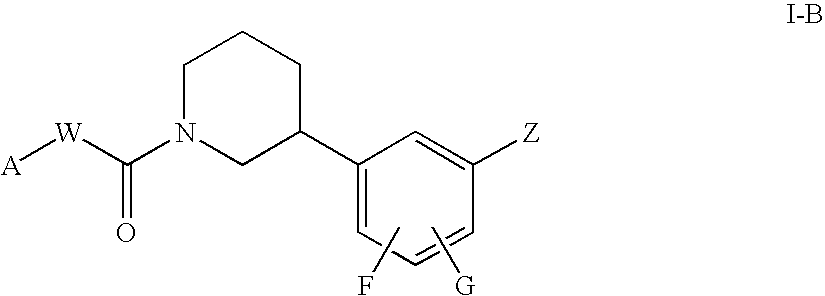
4-Carboxyamino-2-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
4-amino substituted-2-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
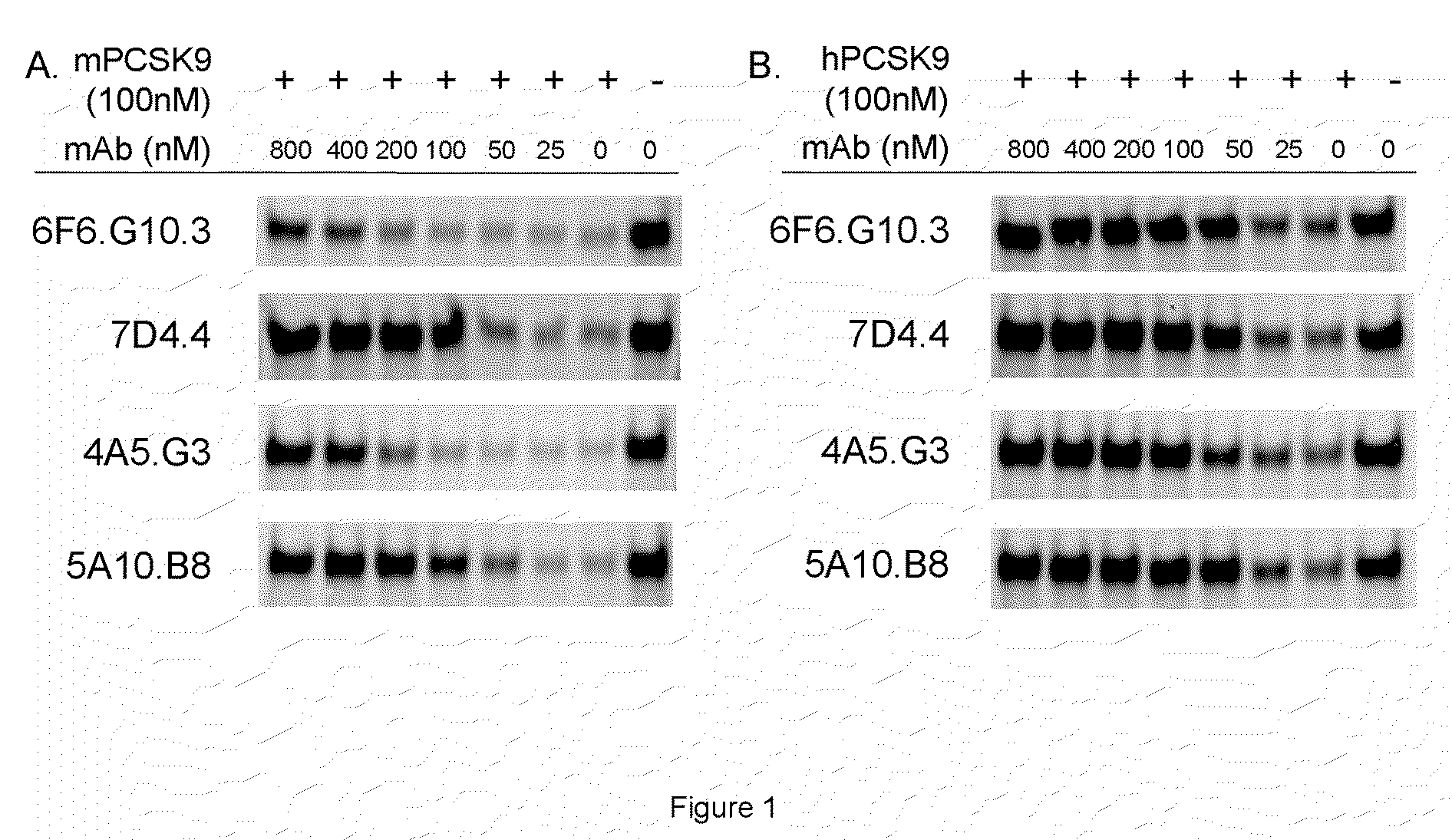
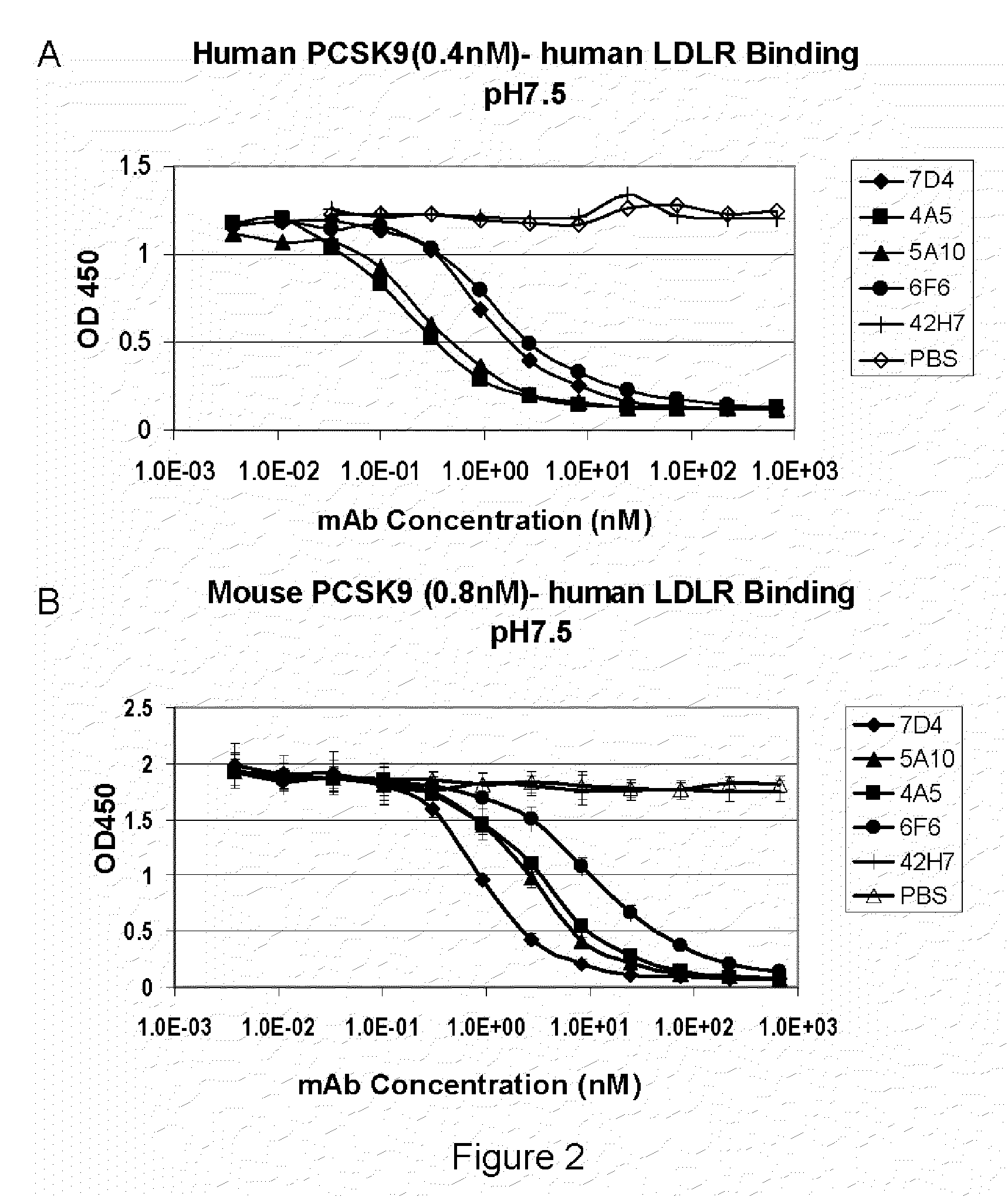
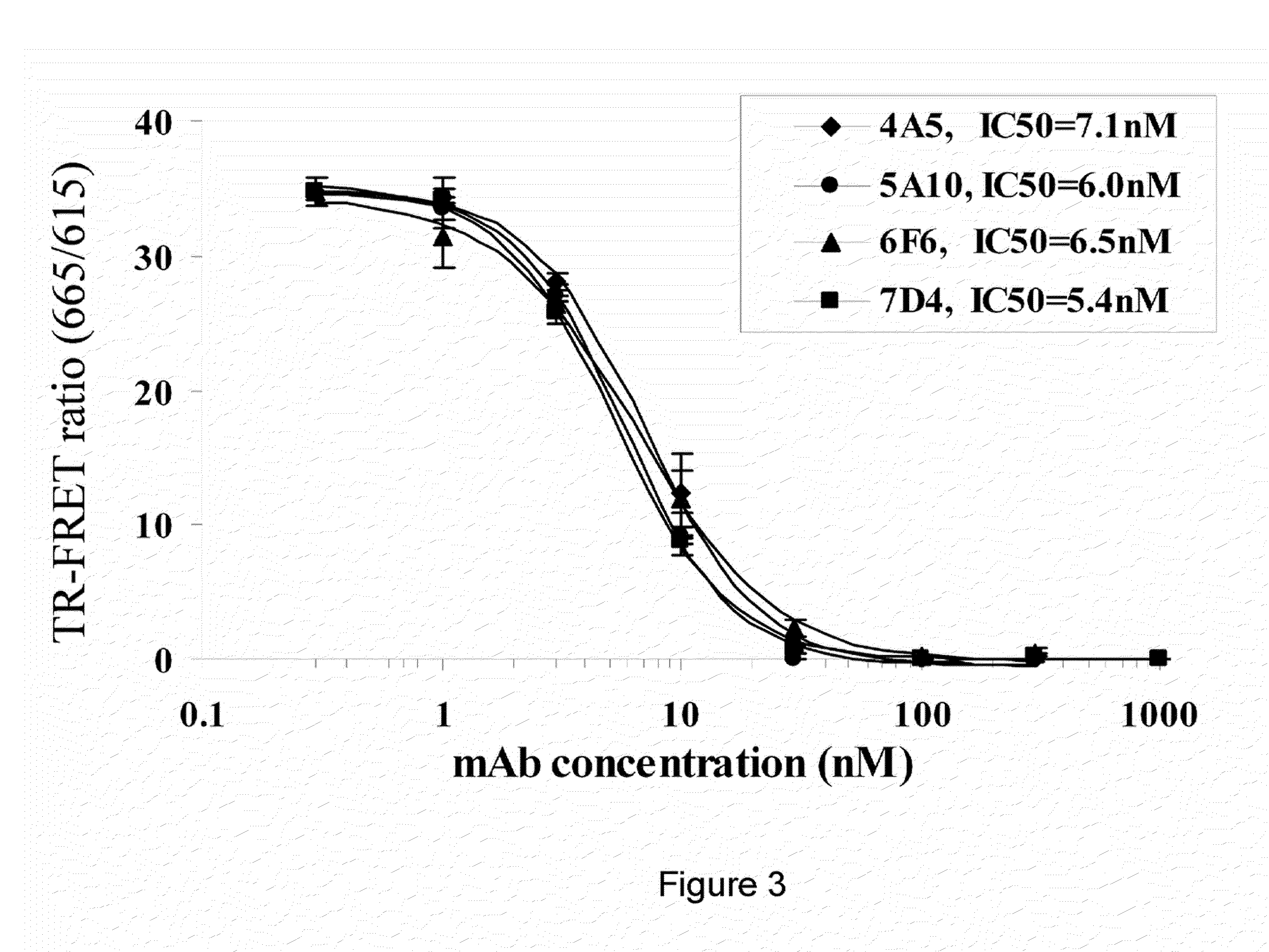
Isolated antibody which specifically binds to PCSK9
Owner:PFIZER INC RINAT NEUROSCIENCE CORP
Annulated 4-carboxyamino-2-methyl-1,2,3,4,-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
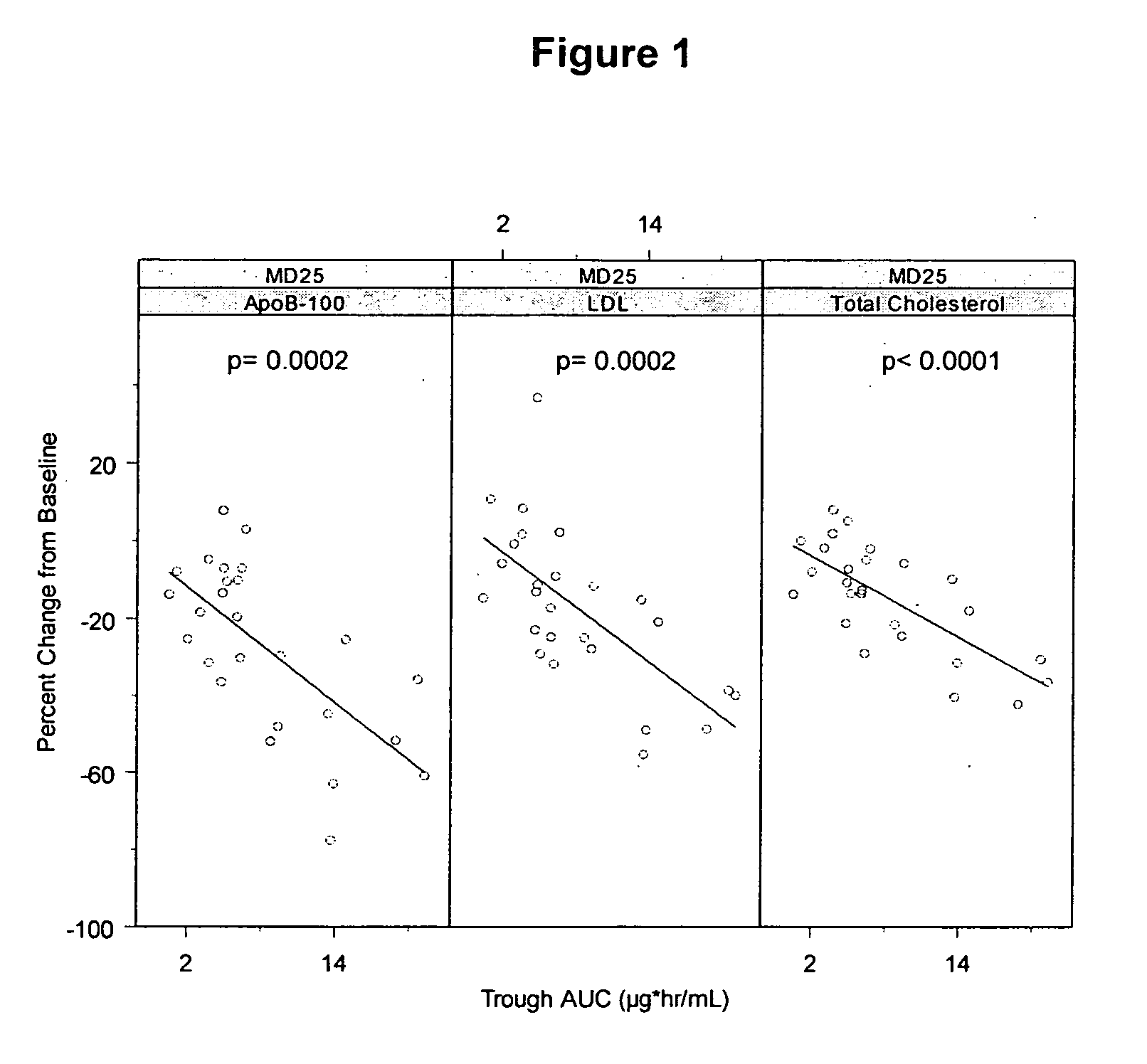
Methods for modulating lipoprotein and cholesterol levels in humans
InactiveUS20060035858A1Reduce doseMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsApolipoproteins bLipid level
Methods for the rapid and long-term lowering of lipid levels in human subjects and for the treatment of conditions associated with elevated LDL-cholesterol and elevated apolipoprotein B are provided.
Owner:KASTLE THERAPEUTICS LLC
4-amino substituted-2-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Annulated 4-carboxyamino-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
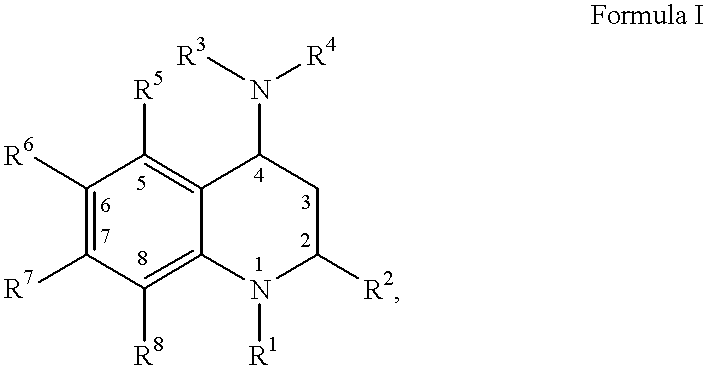
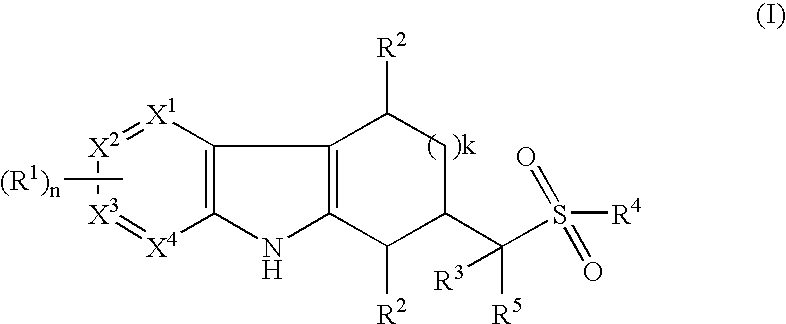
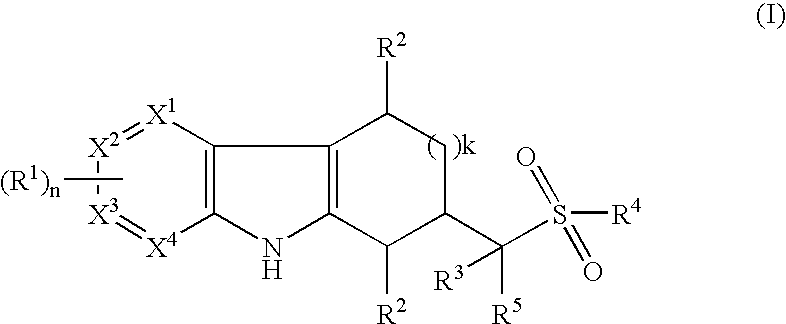
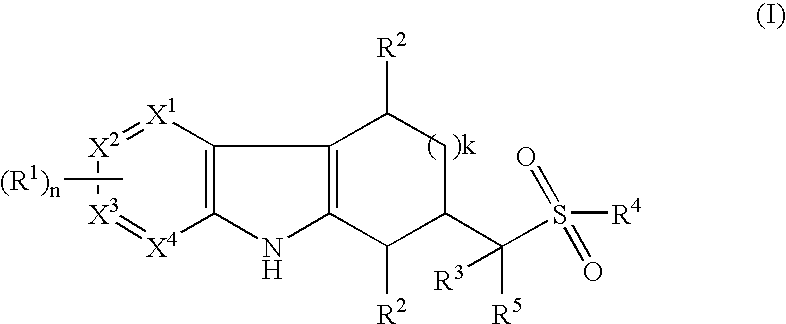
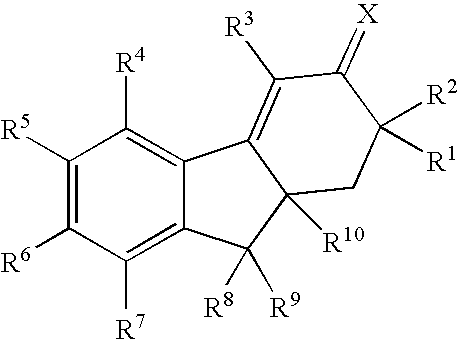
Tetrahydrocarbazoles and derivatives
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula (I) wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, X1, X2, X3, X4, n, and k are defined in the description and claims, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts and / or pharmaceutically acceptable esters thereof. The compounds are useful for in the treatment and prophylaxis of diseases which are modulated by LXRα and / or LXRβ agonists, including increased lipid and cholesterol levels, particularly low HDL-cholesterol, high LDL-cholesterol, atherosclerotic diseases, diabetes, particularly non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, Alzheimer's disease, sepsis, inflammatory diseases such as colitis, pancreatitis, cholestasis / fibrosis of the liver, and diseases that have an inflammatory component such as Alzheimer's disease or impaired / improvable cognitive function.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
4-carboxyamino-2-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Owner:PFIZER INC
Oxy substituted 4-carboxyamino-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Nutritional supplements
InactiveUS20050032757A1Reducing detectable measureReduce detectable measureBiocideFood ingredientsNutrition supplementationLow-density lipoprotein
The invention provides compositions containing one or more sterol compounds and one or more fatty acid compounds. The invention also provides methods for reducing CVD risk factors such as LDL cholesterol levels.
Owner:MELALEUCA INC
CETP inhibitors
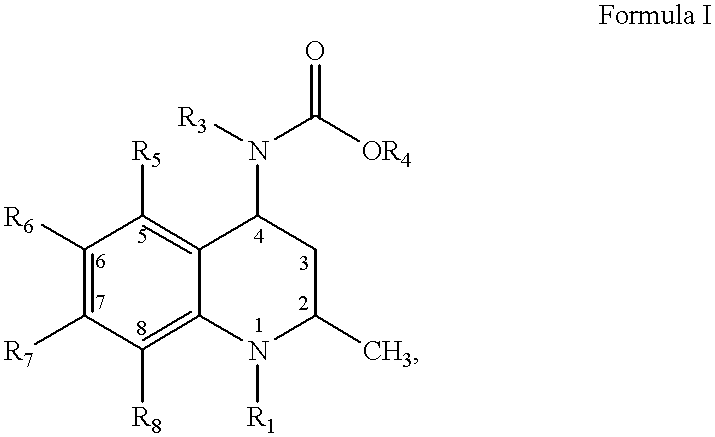
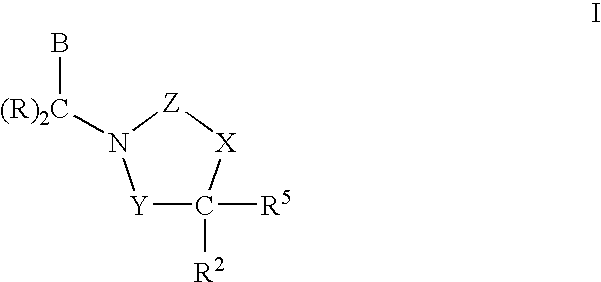
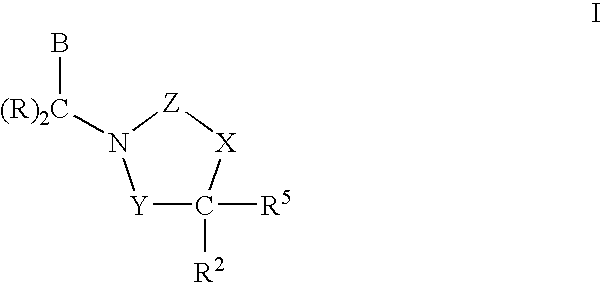
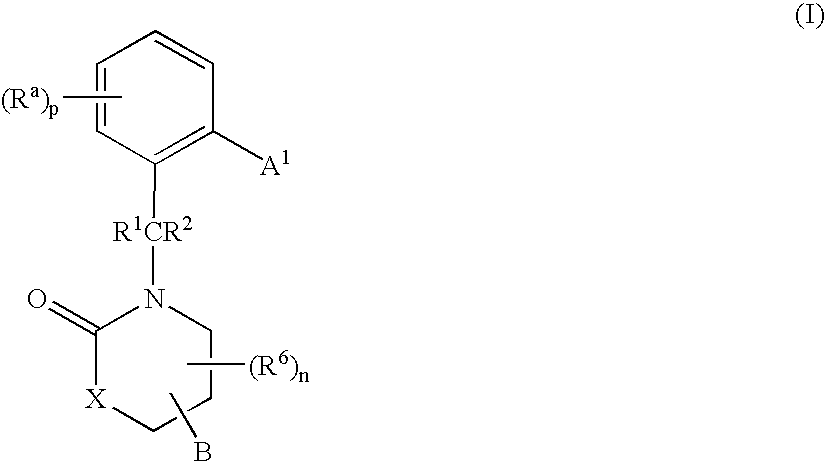
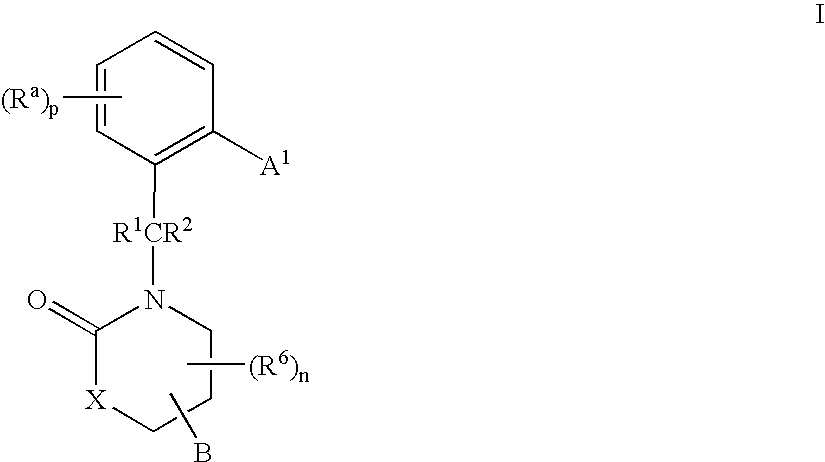
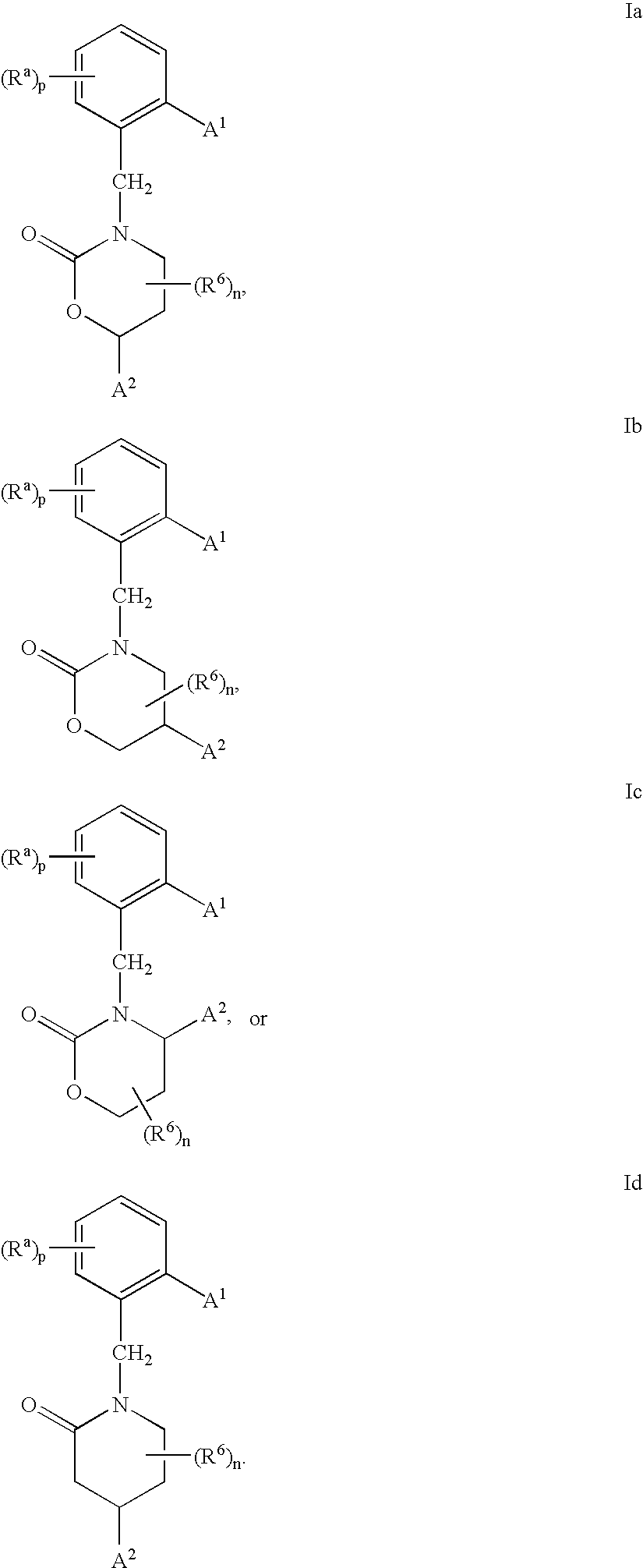
Compounds having the structures of Formula I, including pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds, are CETP inhibitors, and are useful for raising HDL-cholesterol, reducing LDL-cholesterol, and for treating or preventing atherosclerosis: In the compounds of Formula I, B or R2 is a phenyl group which has an ortho aryl, heterocyclic, benzoheterocyclic or benzocycloalkyl substituent, and one other position on the 5-membered ring has an aromatic, heterocyclic, cycloalkyl, benzoheterocyclic or benzocycloalkyl substituent connected directly to the ring or attached to the ring through a —CH2—.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
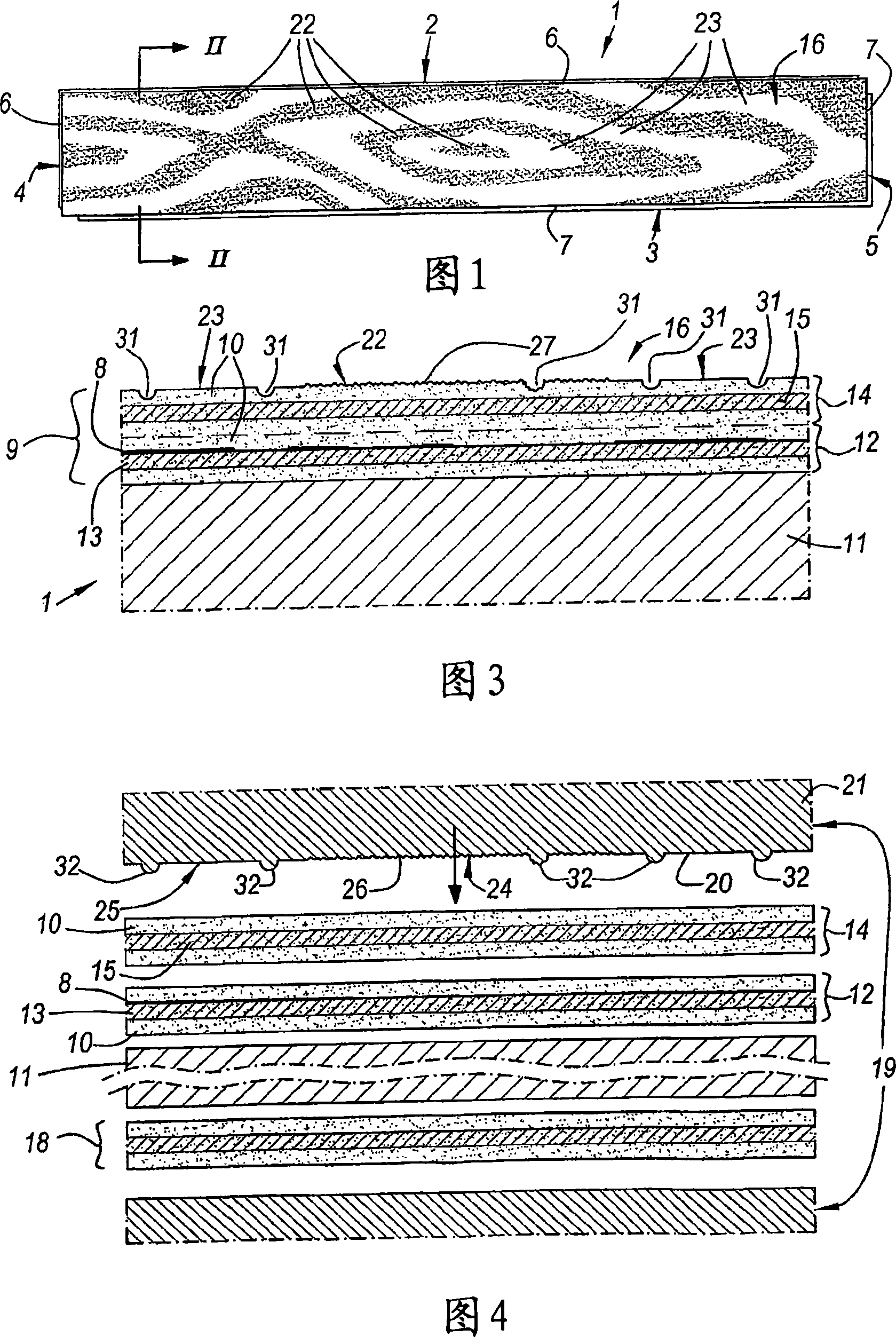
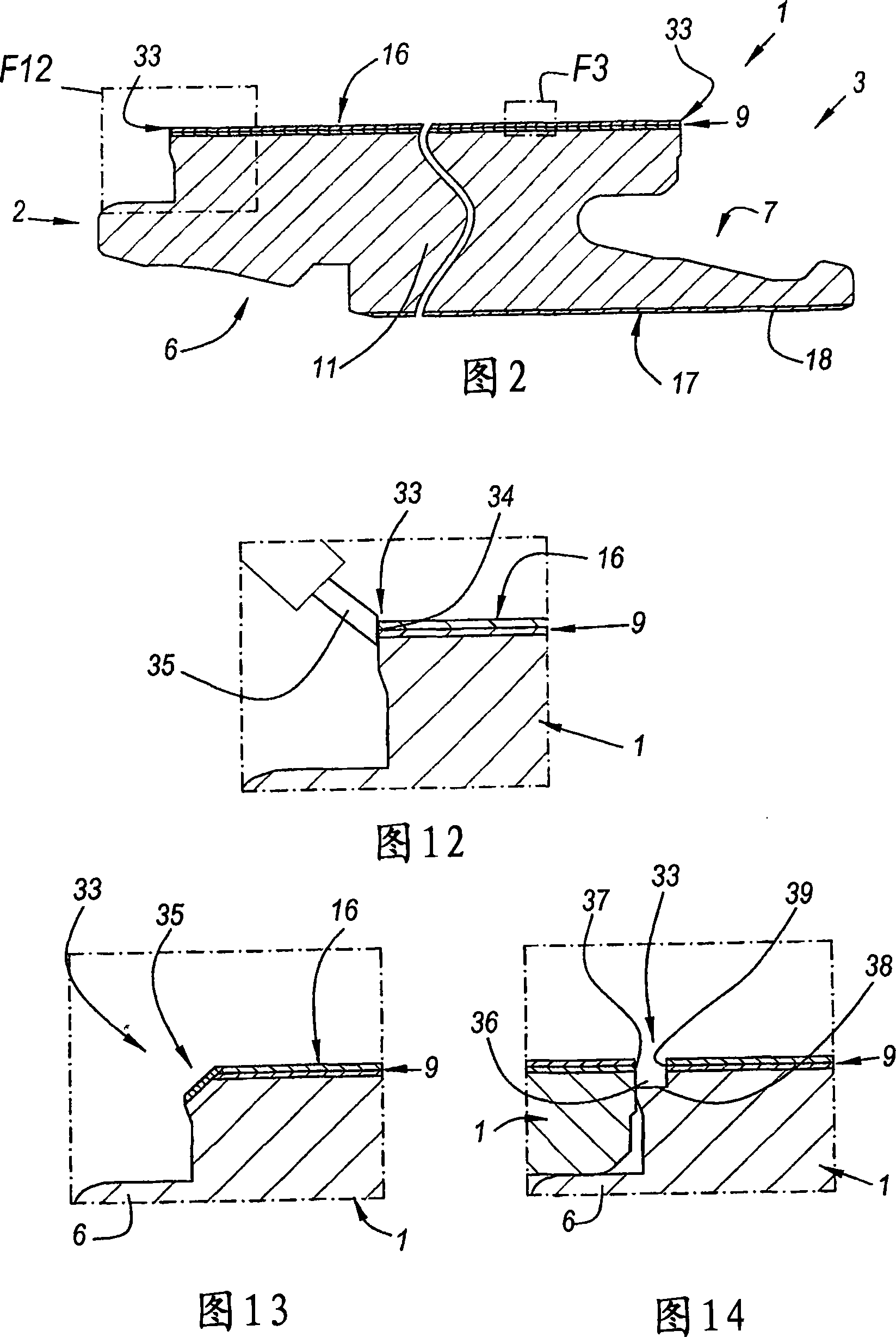
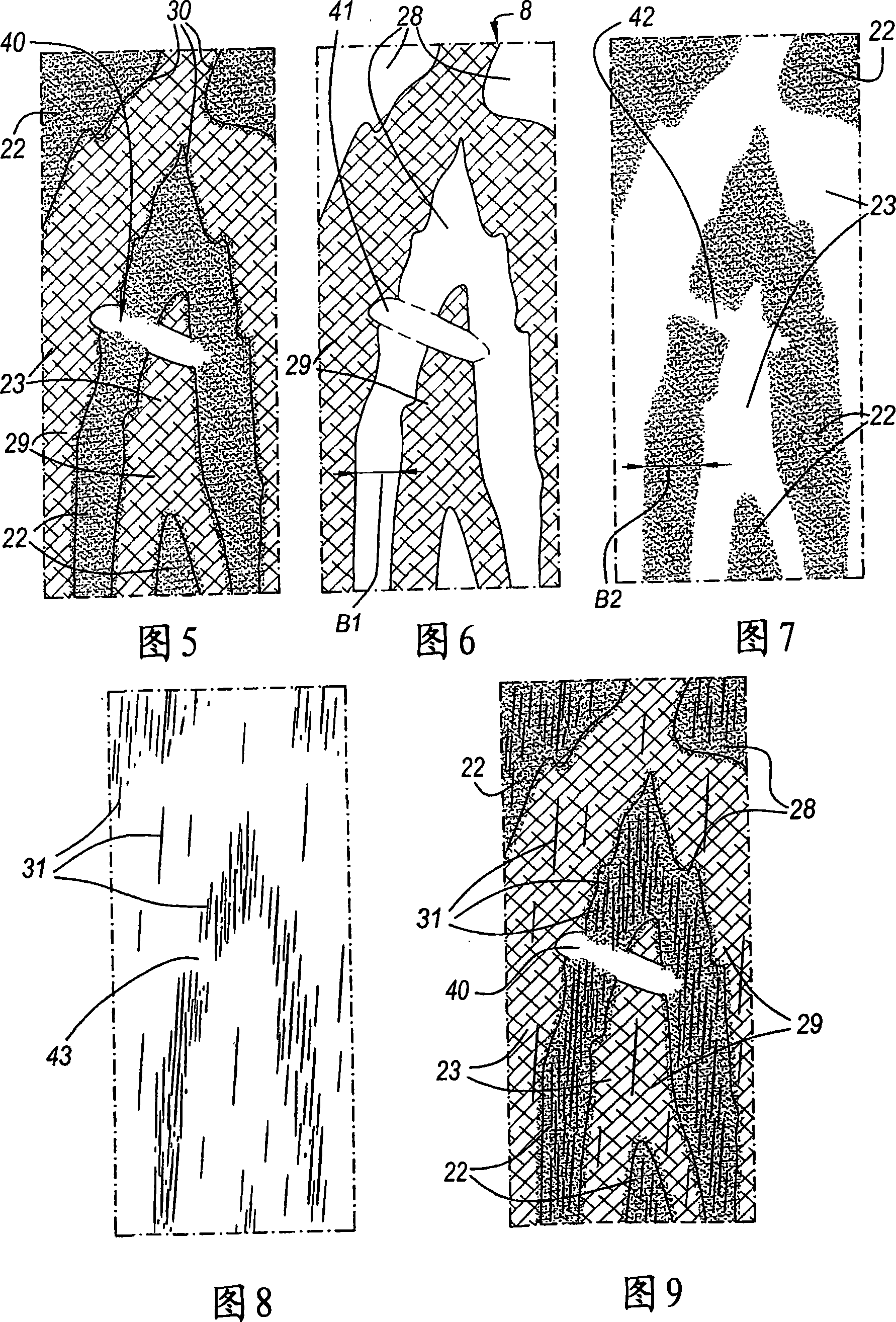
Floor panel and method for manufacturing a floor panel
ActiveCN101072691AEasy to imitateImitate improveNatural patternsSpecial ornamental structuresTriglyceridePlasma lipids
4-Amino substituted-2-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and the use of such compounds to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:FLOORING IND LTD
4-carboxyamino-2-methyl-1,2,3,4,-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Oxy substituted 4-carboxyamino-2-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolines
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions containing such inhibitors and the use of such inhibitors to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in some mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Inhibitors
Compounds of Formula (I), including pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds, are CETP inhibitors, and are useful for raising HDL-cholesterol, reducing LDL-cholesterol, and for treating or preventing atherosclerosis. In the compounds of Formula (I), A1 is a cyclic group, and B is a cyclic group which is attached to the heterocyclic ring directly or through a methylene group.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS7157604B2Urea derivatives preparationBiocideHormone Receptor ModulatorsPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Antisense modulation of apolipoprotein b expression
InactiveUS20090326040A1Organic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderApolipoproteins EApolipoproteins b
Methods for the rapid and long-term lowering of lipid levels in human subjects and for the treatment of conditions associated with elevated LDL-cholesterol and elevated apolipoprotein B are provided.
Owner:KASTLE THERAPEUTICS LLC
Compositions containing policosanol and HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor and their pharmaceutical uses
InactiveUS20050267197A1Reducing serum cholesterol levelHigh purityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsCoronary heart diseaseNeuro-degenerative disease
A composition is provided which contains policosanol and HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor and which may be used for treating and or reducing hypercholesterolemic diseases, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, coronary heart disease (heart attacks and strokes), inflammation, deep-vein thrombosis immunoregulatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and / or neurodegenerative disorders in humans and animals. The method comprises administering policosanol and HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor which together effectively lower serum cholesterol levels. Typically, the administered composition includes about 0.1-10:1 parts by weight of policosanol to HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Polymer Formulations of CETP Inhibitors
ActiveUS20100227903A1Improve bioavailabilityGood dispersionHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsBiocideChemical compoundSURFACTANT BLEND
A pharmaceutical composition comprises (a) a CETP inhibiting compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; (b) a concentration-enhancing polymer, and (c) optionally one or more surfactants; wherein the compound has the structure shown as Formula I below. The composition raises HDL-cholesterol and lowers LDL-cholesterol.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
PPAR activators
PPAR alpha activators, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and the use of such compounds to elevate certain plasma lipid levels, including high density lipoprotein-cholesterol and to lower certain other plasma lipid levels, such as LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and accordingly to treat diseases which are exacerbated by low levels of HDL cholesterol and / or high levels of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides, such as atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases, in mammals, including humans.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
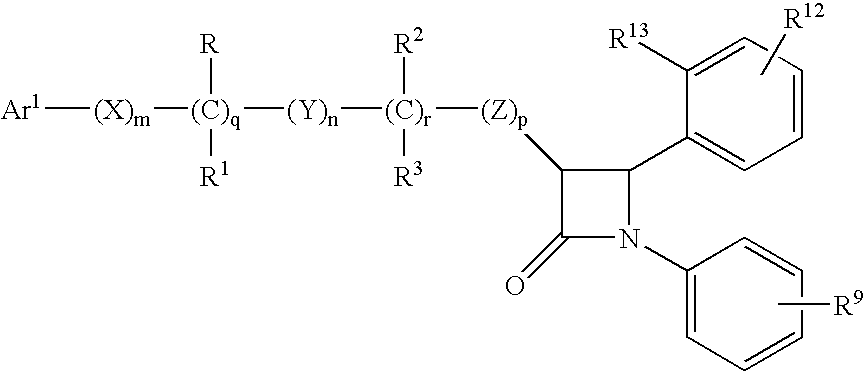
Anti-hypercholesterolemic compounds
InactiveUS20070078098A1Prevent and reduce riskShorten the progressBiocideSugar derivativesLow-density lipoproteinBlood plasma
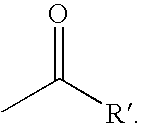
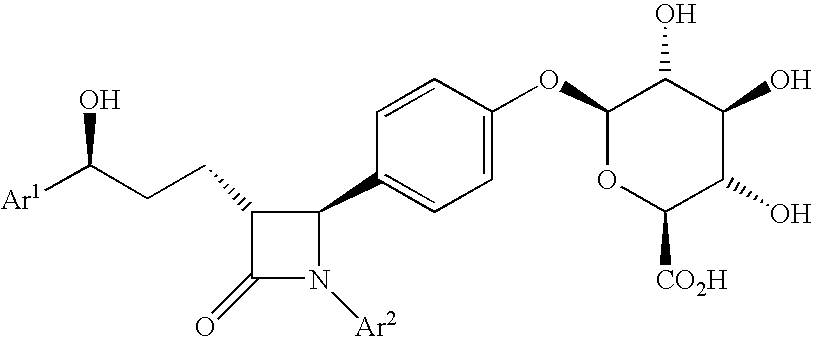
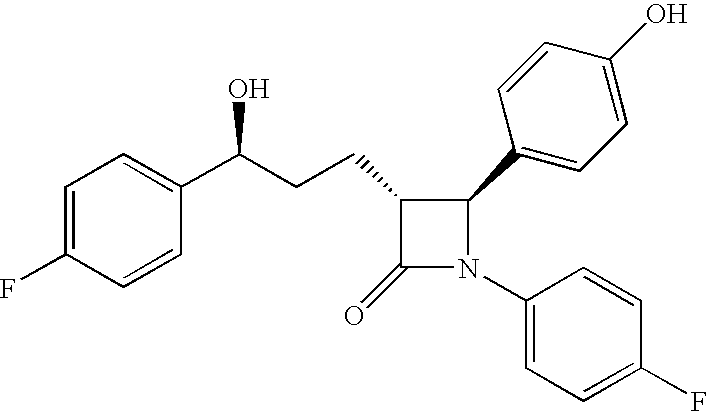
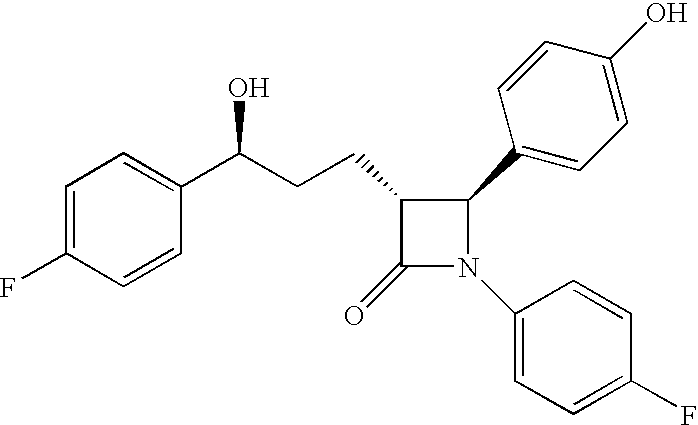
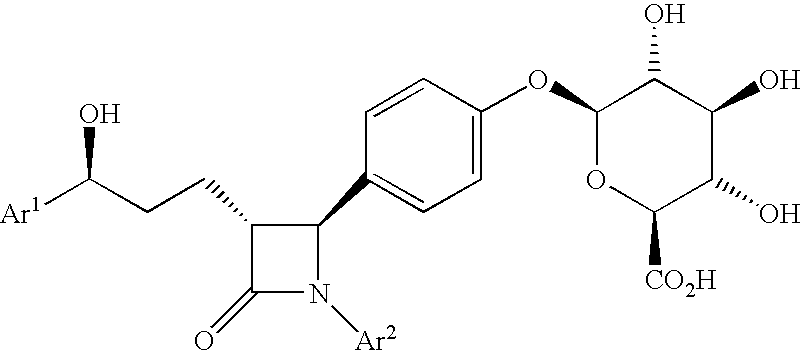
This invention provides cholesterol absorption inhibitors of Formula I: and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and esters thereof. The compounds are useful for lowering plasma cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, and for treating and preventing atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic disease events.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Anti-hypercholesterolemic compounds
ActiveUS20050267049A1Prevent and reduce riskShorten the progressBiocideSugar derivativesDepressantLow-density lipoprotein
This invention provides cholesterol absorption inhibitors of Formula I: and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts and esters thereof. The compounds are useful for lowering plasma cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, and for treating and preventing atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic disease events.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Cholesterol sensor
ActiveUS20110086373A1Rapid but detailed analysisFast test resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemistryLdl chol
A method for the determination of the amount of cholesterol in a sample is provided. The method typically provides a breakdown of the HDL and LDL cholesterol contents of the sample.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
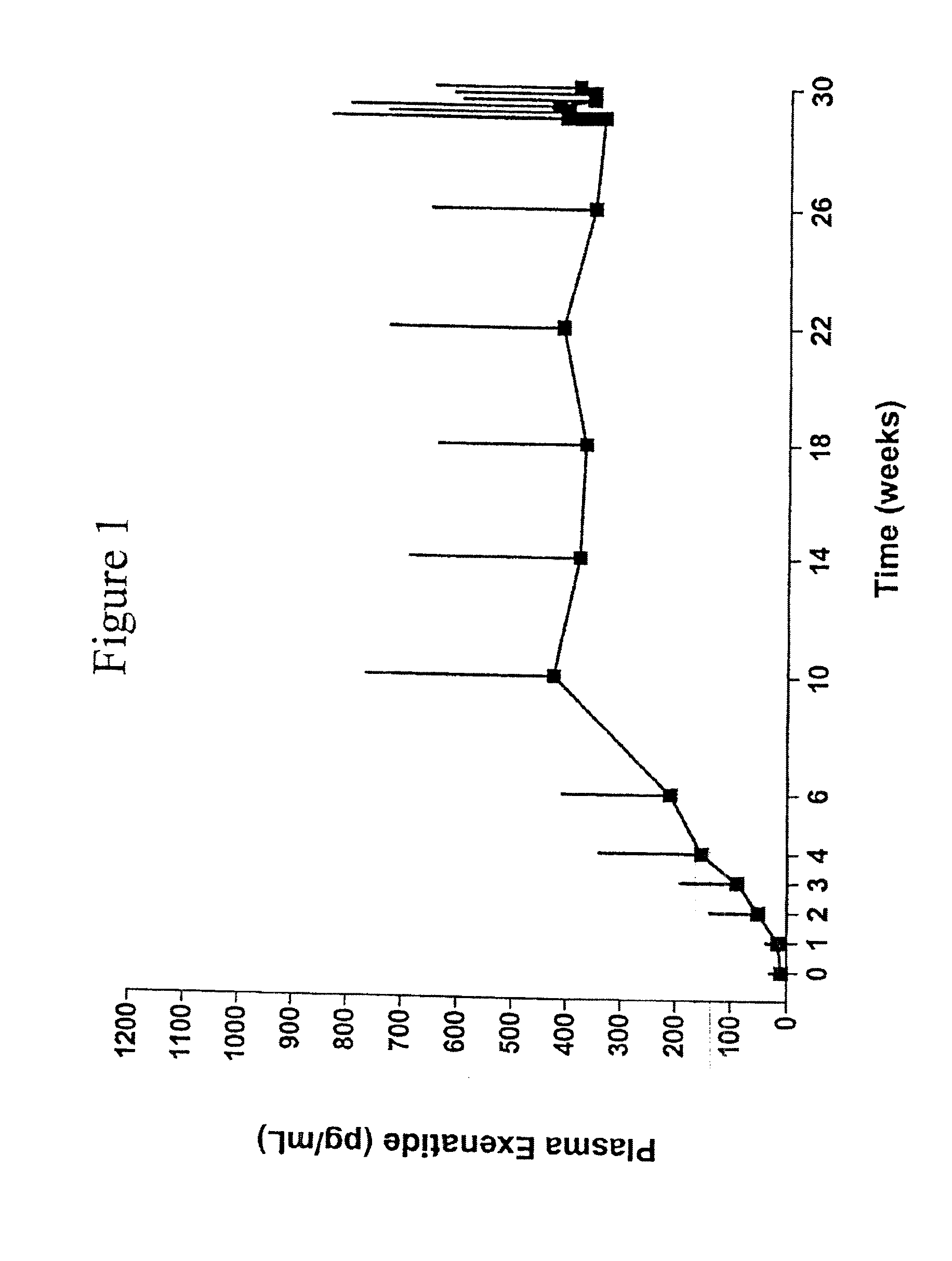
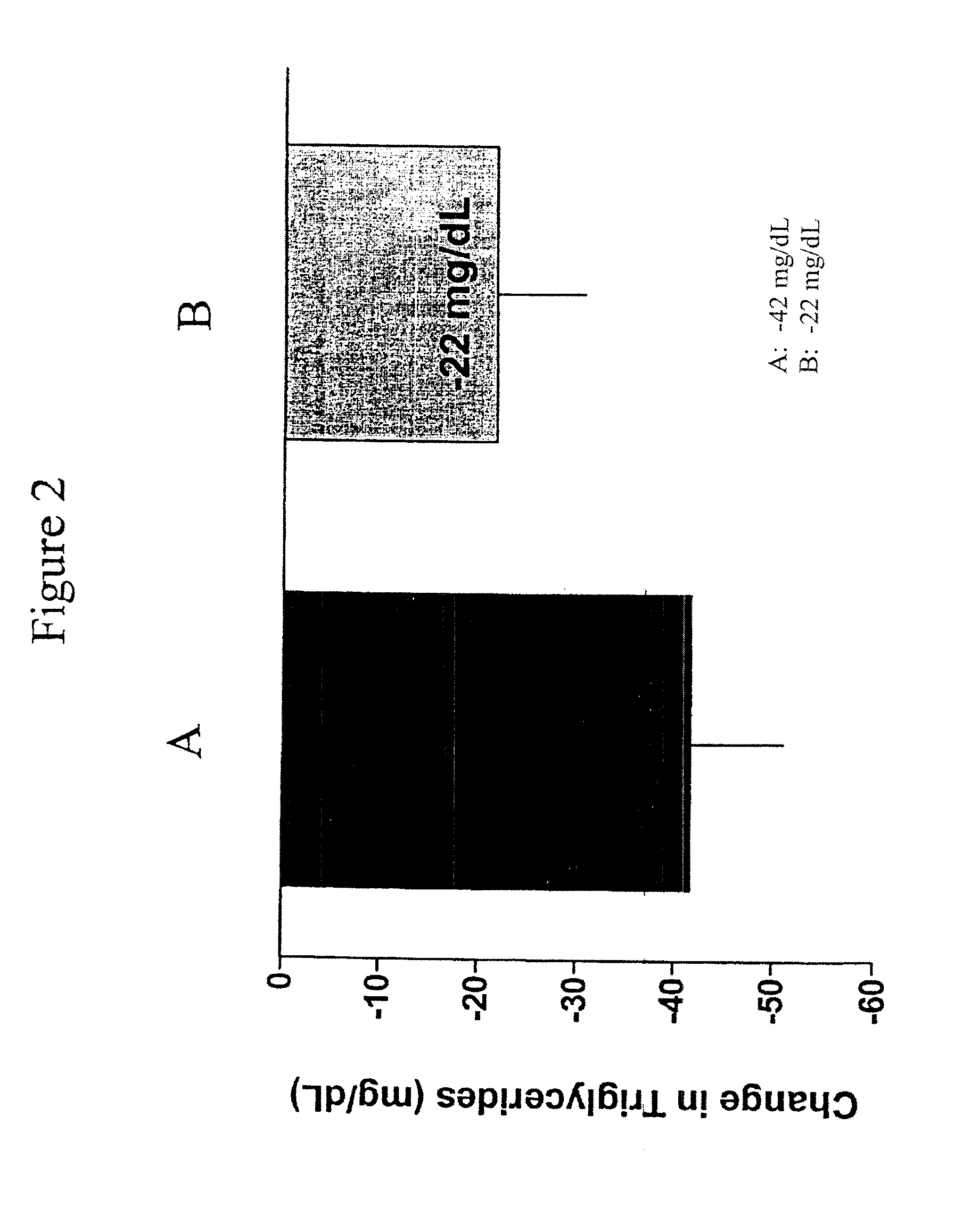
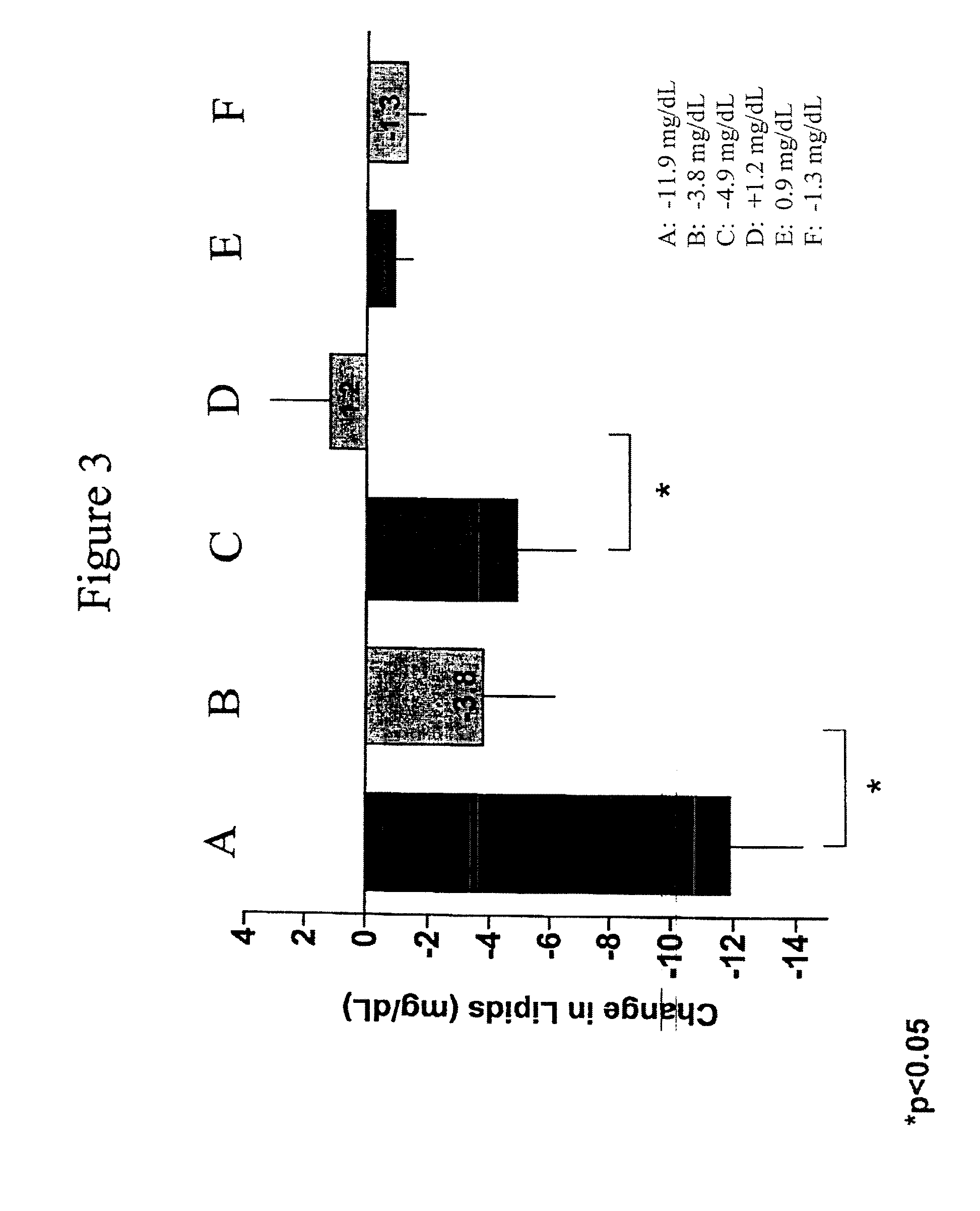
Exendins to lower cholesterol and triglycerides
InactiveUS20110263496A1Lower cholesterol levelsStable statePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDyslipidemiaSucrose
Provided herein are pharmaceutical formulations containing exendins, exendin agonists, or exendin analog agonists that are administered at therapeutic plasma concentration levels over a sustained period of time to lower total cholesterol levels; to lower LDL-cholesterol levels; to lower triglyceride levels; to treat dyslipidemia; to treat and slow the progression of atherosclerosis; and to treat, prevent, and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients. In the pharmaceutical formulations and methods of the invention, the exendin may be exendin-4, an exendin-4 agonist, or an exendin-4 analog agonist. The pharmaceutical formulations may be polymer-based pharmaceutical formulations that may be administered once weekly. An exemplary pharmaceutical formulation comprises 5% (w / w) of exenatide, about 2% (w / w) of sucrose, and about 93% (w / w) of a poly(lactide-co-glycolide) polymer, wherein the poly(lactide-co-glycolide) polymer is in the form of microshperes encapsulating the exenatide.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Compositions and methods for lowering serum cholesterol
The invention provides a method for lowering circulating LDL-cholesterol or total cholesterol in a human in need thereof, comprising: orally administering to the human a therapeutically effective amount of a statin and vitamin D daily for at least about 6 weeks, wherein the vitamin D is administered by one or more pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:GRIFFIN & SCHWARTZ
Anti-hypercholesterolemic biaryl azetidinone compounds
InactiveUS20080280836A1Prevent and reduce riskShorten the progressBiocideSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsCholesterol absorption inhibitorPlasma cholesterol
This invention provides cholesterol absorption inhibitors of Formula I:and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein R12 is an alkyl, alkeny or alkynyl group mono- or poly-substituted with —OH, —COOH or a combination of—OH and —COOH, and R9 contains an alkyl, alkeny or alkynyl group substituted with a heterocyclic ring, amino or sulfonyl. The compounds are useful for lowering plasma cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, and for treating atherosclerosis and preventing atherosclerotic disease events.
Owner:MORRIELLO GREGORI J +1
Enhanced bioavailability of nutrients, pharmaceutical agents, and other bioactive substances through laser resonant homogenization or modification of molecular shape or crystalline form
A method for improving the bioavailability of a bioactive substance includes subjecting the bioactive substance to laser radiation. The laser radiation modifies the bioactive substance to thereby modify reactions relating thereto in the body. The method enables reductions in inflammation associated with autoimmune diseases, modification of reaction by-products in the body, increased homogenization and flattening of molecular shape and improved methylation. The improved methylation can be utilized to reduce homocysteine blood levels, and to reduce anxiety, depression, paranoia, hostility, somatization (perception of bodily distress) and obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Enhanced nitric oxide generation from modified L-arginine can be used to reduce systolic and diastolic blood pressure, lower total and LDL cholesterol levels, and improve the ratio of total to HDL cholesterol. Increased depth of penetration of sparse constructive nodes of laser radiation may increase the range of photodynamic therapy applications and a wide range of in vitro and in vivo modifications of molecular shape and activity. Laser acoustic resonance can be utilized to increase the homogeneity of crystals, or favor the generation of novel or preferred crystalline forms.
Owner:OVOKAITYS TODD F +1
Cetp Inhibitors
Compounds having the structure of Formula (I), including pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds, are CETP inhibitors and are useful for raising HDL-cholesterol, reducing LDL-cholesterol, and for treating or preventing atherosclerosis. In the compounds of Formula (I), B is a cyclic group other than phenyl, and B has a cyclic substituent at a position that is ortho to the position at which B is connected to the remainder of the structure of Formula (I). The 5-membered ring of Formula (I) has a second cyclic substituent in addition to B.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com