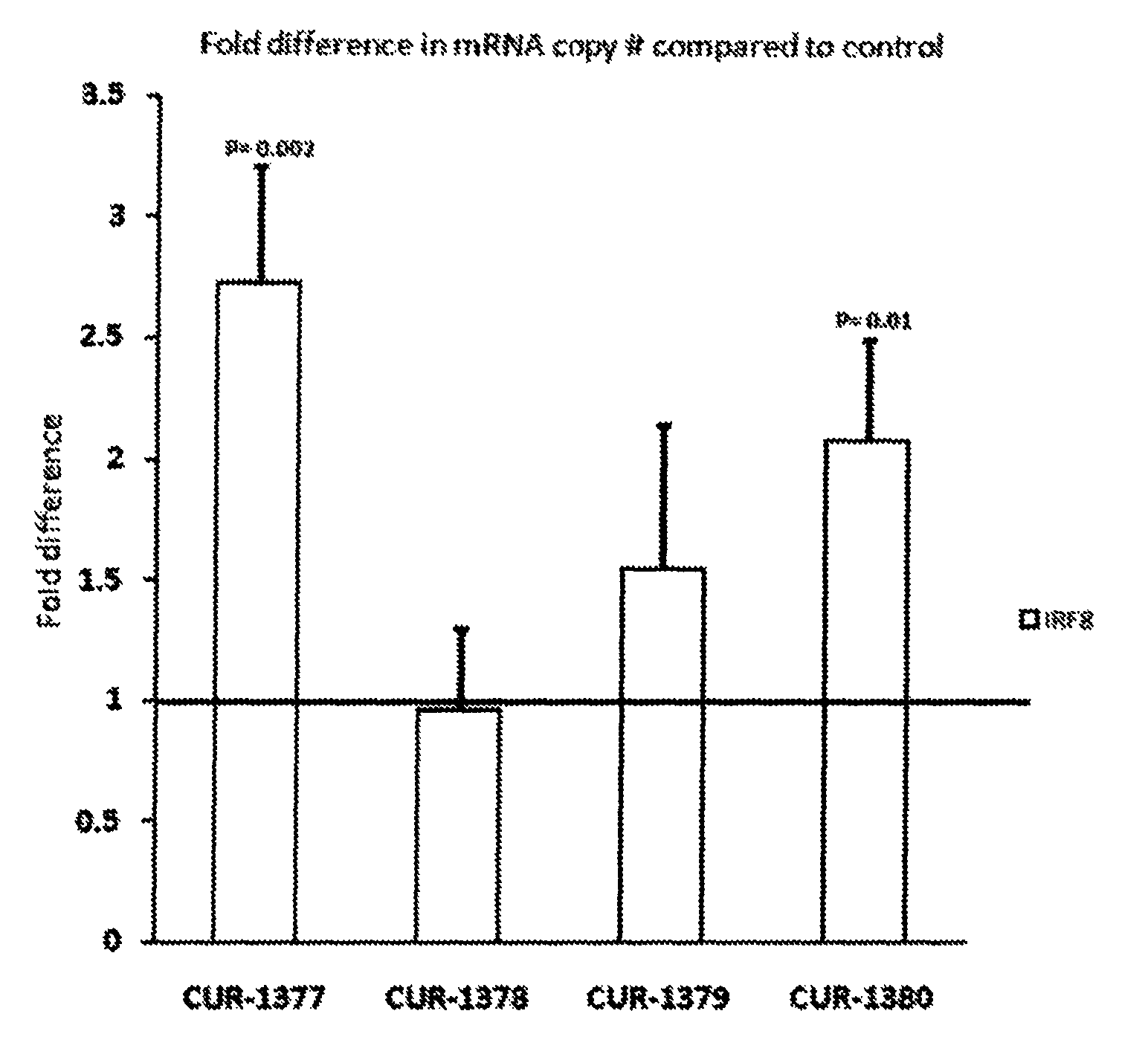
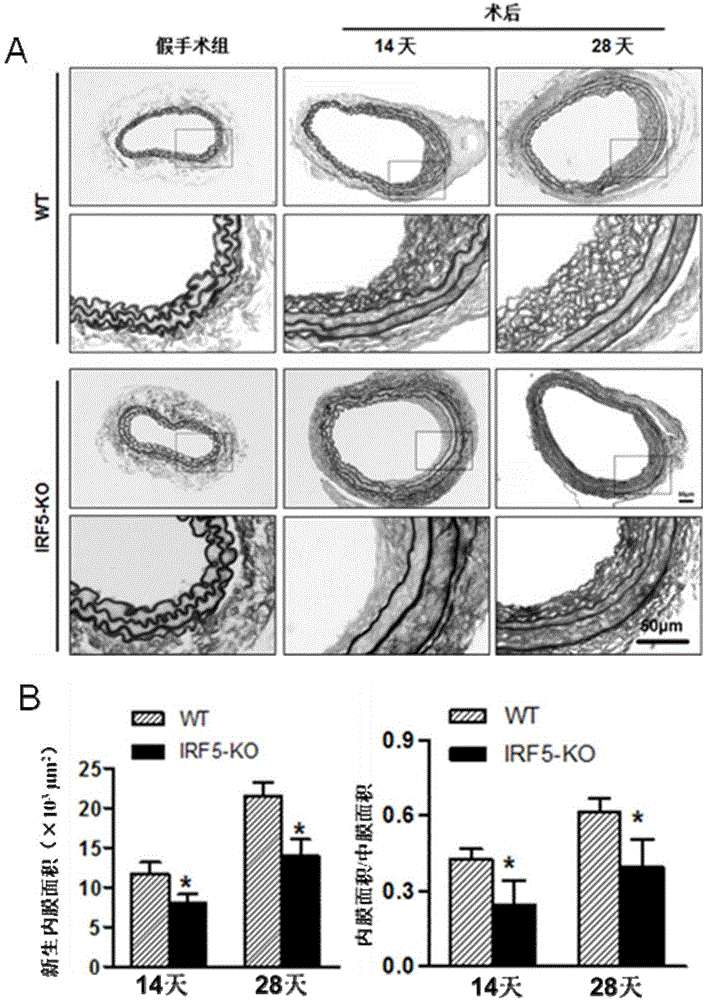
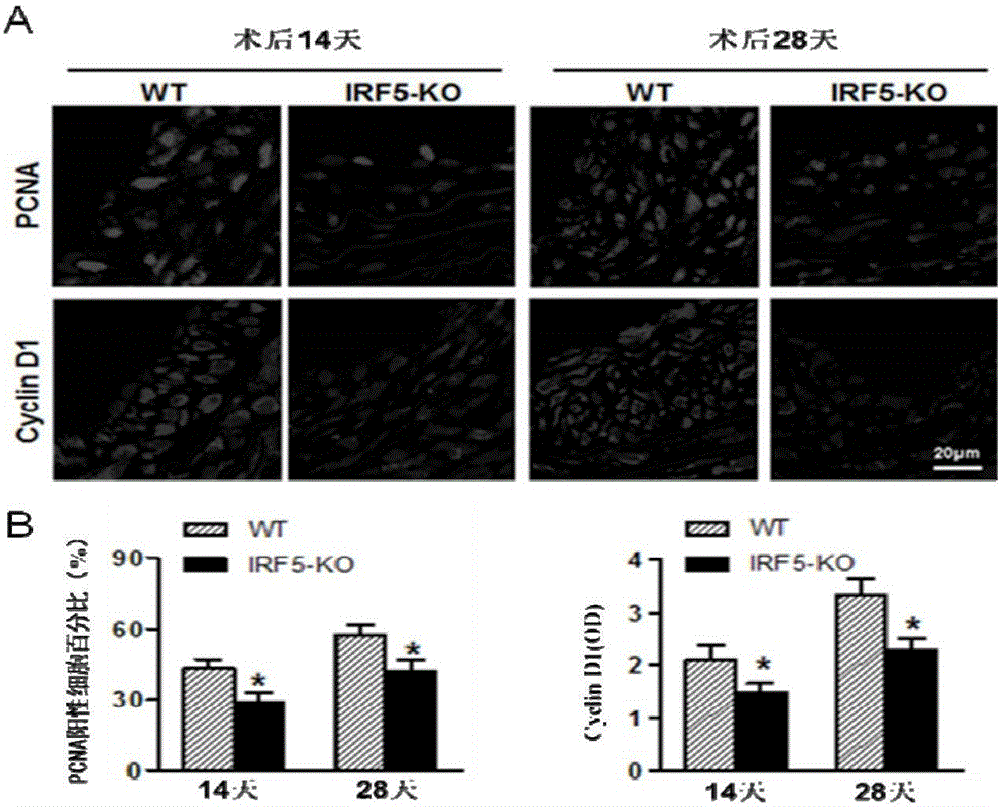
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Interferon regulatory factors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interferon regulatory factors (IRF) are proteins which regulate transcription of interferons (see regulation of gene expression). They are used in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Interferon regulatory factors contain a conserved N-terminal region of about 120 amino acids, which folds into a structure that binds specifically to the interferon consensus sequence (ICS), which is located upstream of the interferon genes. The remaining parts of the interferon regulatory factor sequence vary depending on the precise function of the protein. The Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus, KSHV, is a cancer virus that encodes four different IRF-like genes; including vIRF1, which is a transforming oncoprotein that inhibits type 1 interferon activity. In addition, the expression of IRF genes is under epigenetic regulation by promoter DNA methylation.
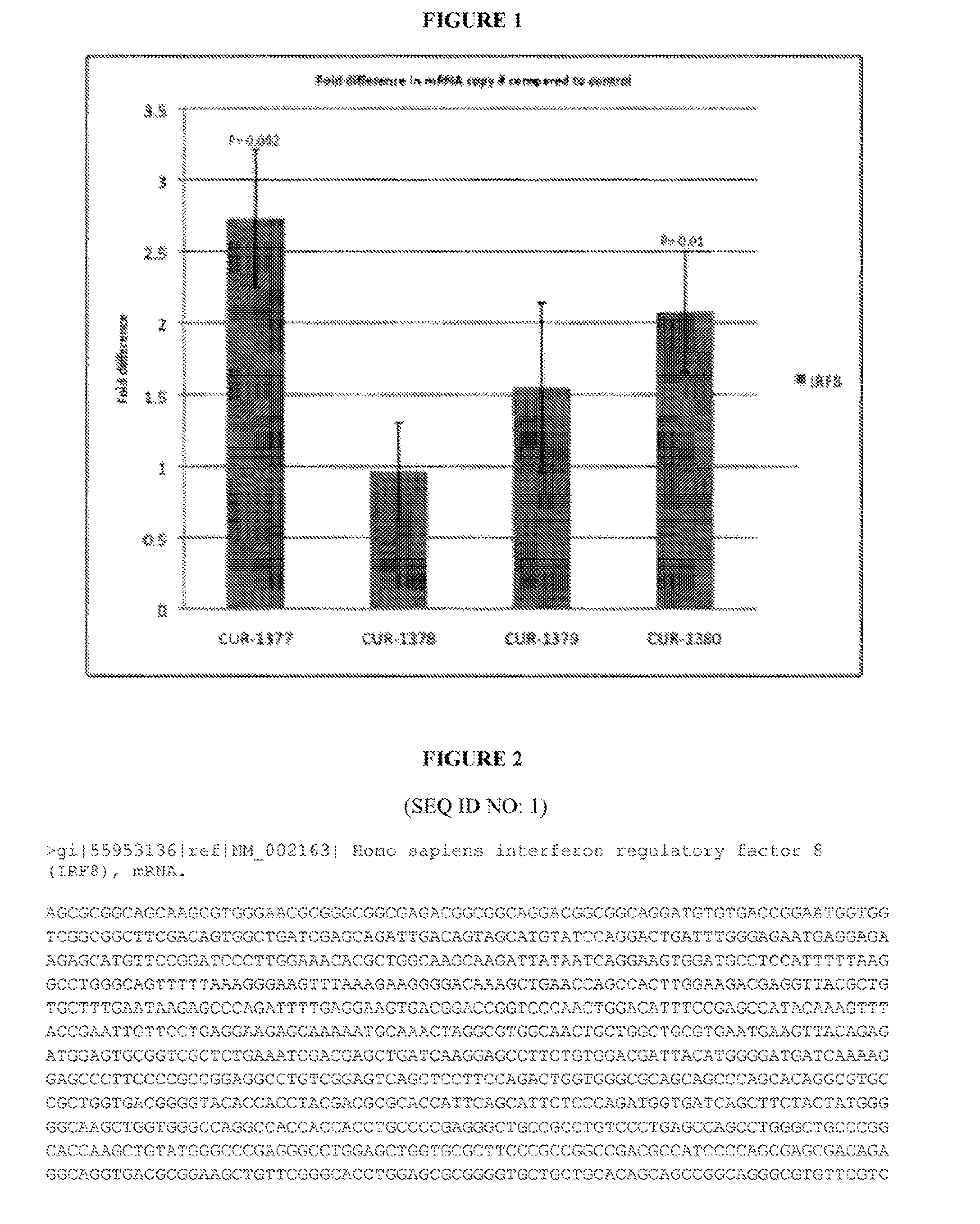
Treatment of interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to irf8
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Interferon Regulatory Factor 8 (IRF8), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Interferon Regulatory Factor 8 (IRF8). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with The expression of IRF8.
Owner:CURNA INC
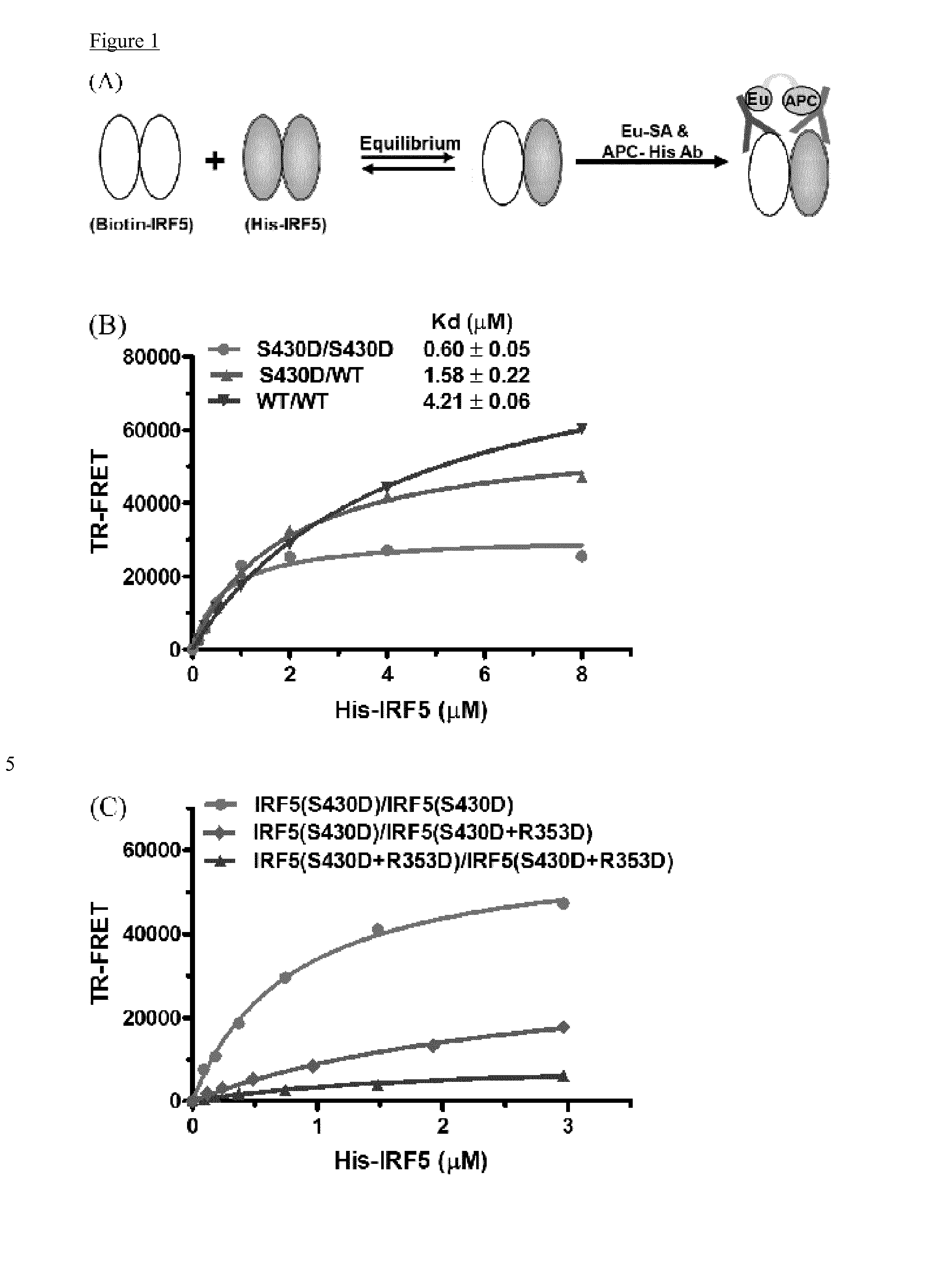
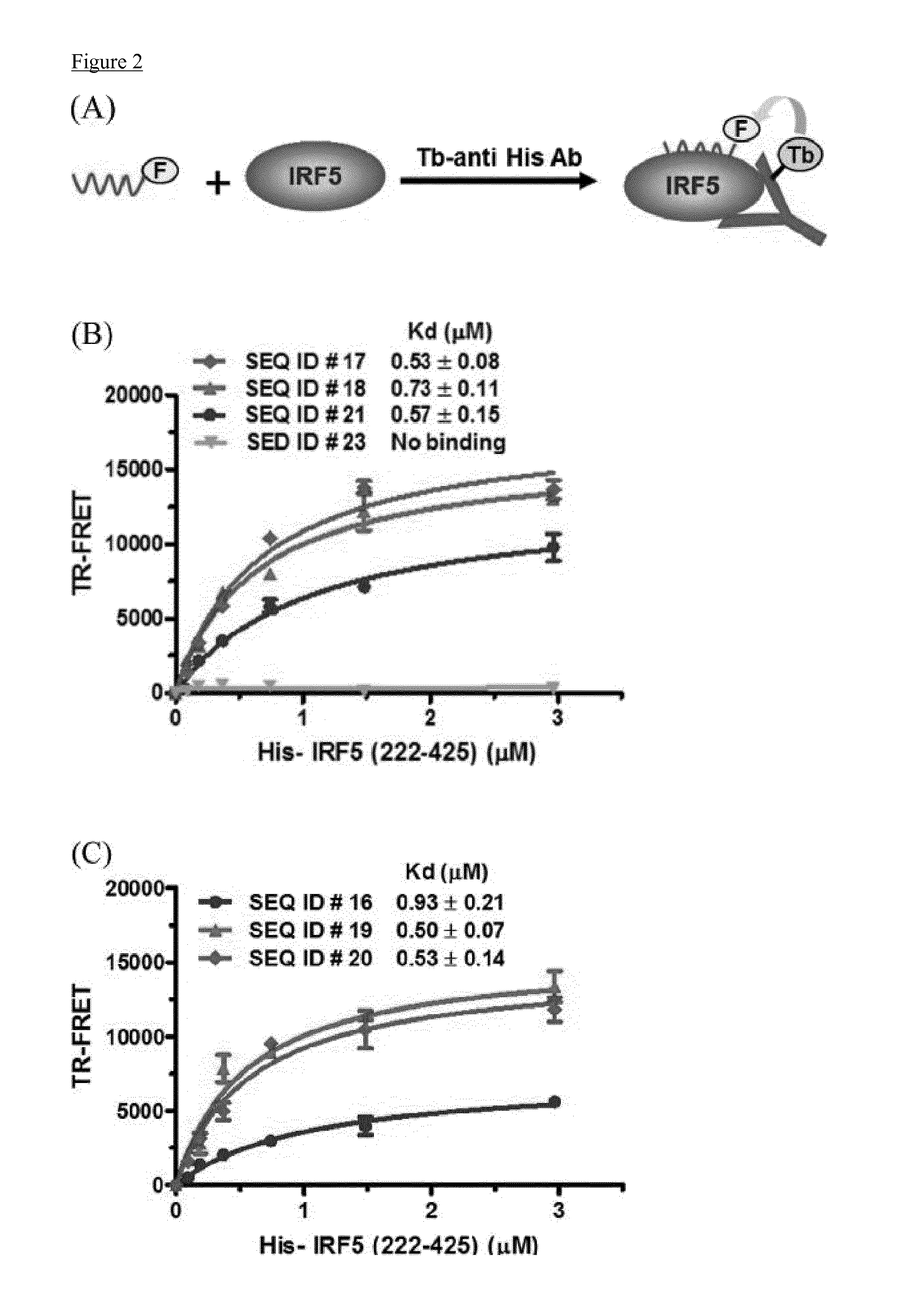
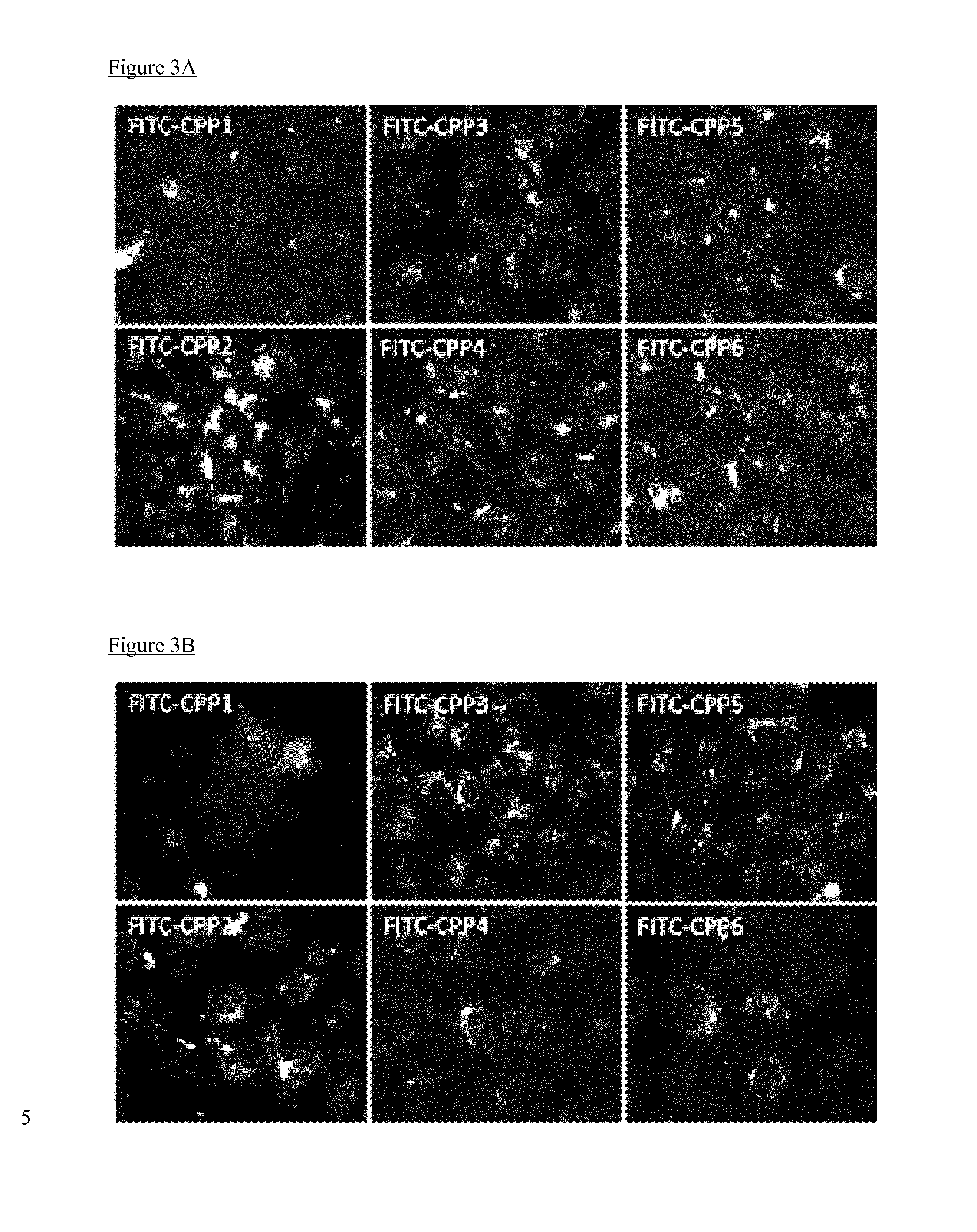
Cell penetrating peptides which bind irf5
InactiveUS20160009772A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCompound screeningBiologyInterferon regulatory factors
The present invention comprises cell penetrating peptides that bind to interferon regulatory factor IRF5 and disrupt the IRF5 homo-dimerization and / or attenuate downstream signaling, and a method for screening peptides that inhibit IRF5. Generally, the cell penetrating peptides of the invention bind human interferon regulatory factor IRF5 (CPP-IRF5).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Reducing irf4, dusp22, or flj43663 polypeptide expression
InactiveUS20100324119A1Reduce spreadReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementT cellCell biology
This document relates to the activity of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in T-cell lymphomas. For example, methods and materials involved in reducing the expression of an IRF4 polypeptide in T-cell lymphoma cells and identifying agents having the ability to reduce expression of an IRF4 polypeptide in T-cell lymphoma cells are provided. This document also relates to reducing DUSP22 or FLJ43663 polypeptide activity in T-cell lymphomas. For example, methods and materials involved in reducing the expression of DUSP22 polypeptides and / or FLJ43663 polypeptides in T-cell lymphoma cells and identifying agents having the ability to reduce expression of DUSP22 polypeptides and / or FLJ43663 polypeptides in T-cell lymphoma cells are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
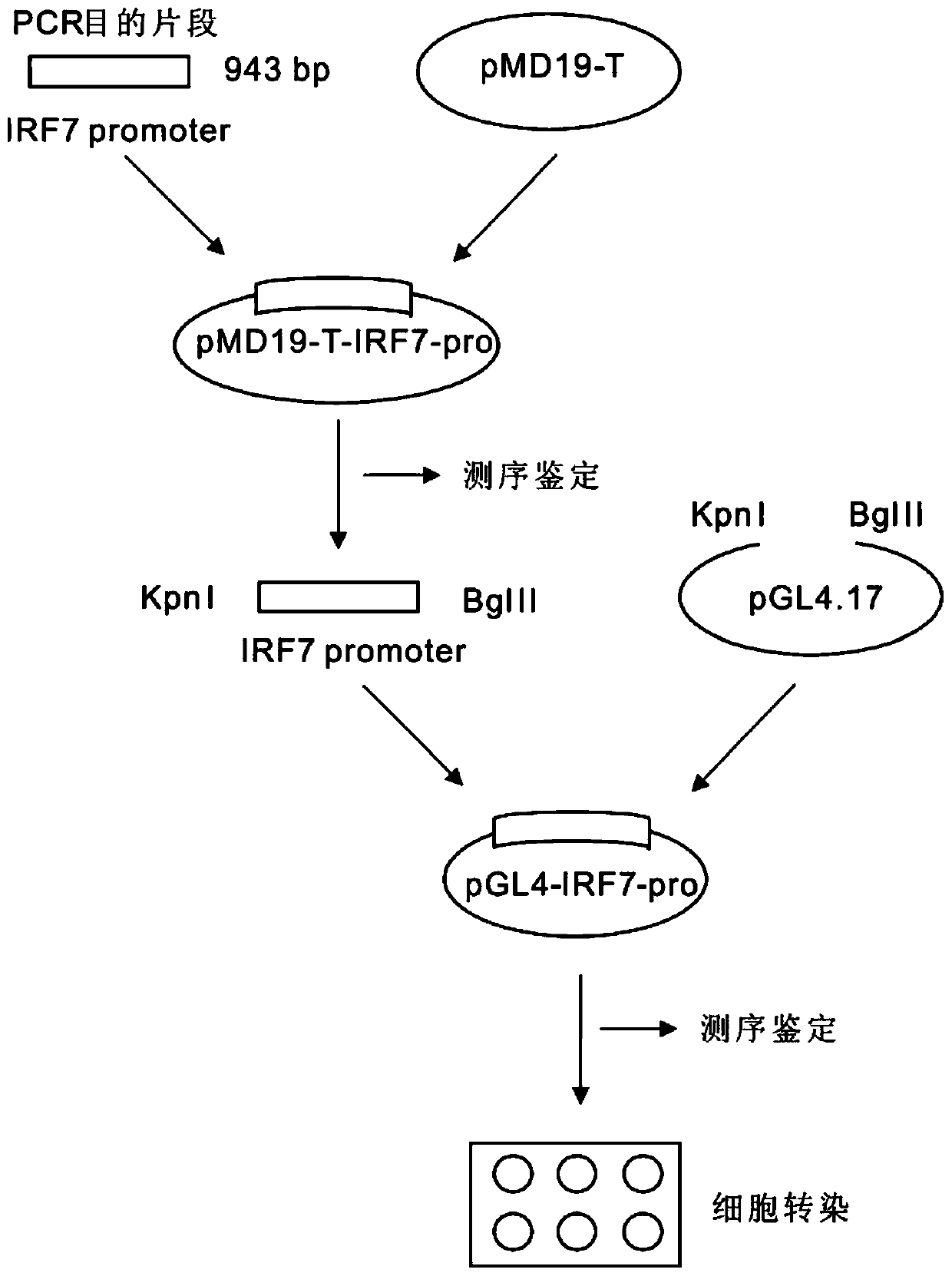
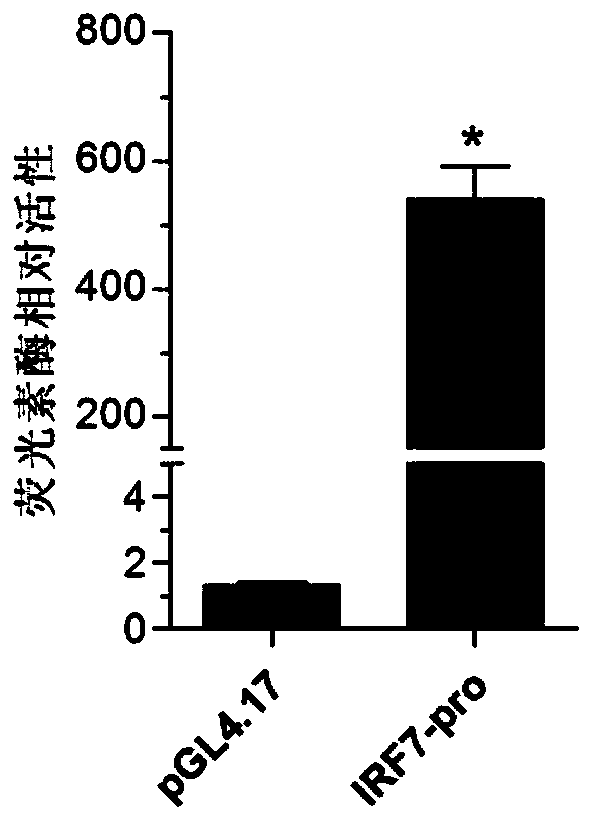
Larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter, nucleic acid builder, cell and preparing method and application of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter
ActiveCN107058325AGood experimental systemPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter, a nucleic acid builder, a cell and a preparing method and application of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter, the nucleic acid builder and the cell. The nucleotide sequence of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter is shown as Seq ID No.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to Seq ID No.1. The invention further protects application of the starter or the nucleic acid builder or a carrier or a reconstitution cell or fish or a mammal containing the starter or the nucleic acid builder or the carrier or the reconstitution cell in regulating target gene expression or transgenic fish.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV +1
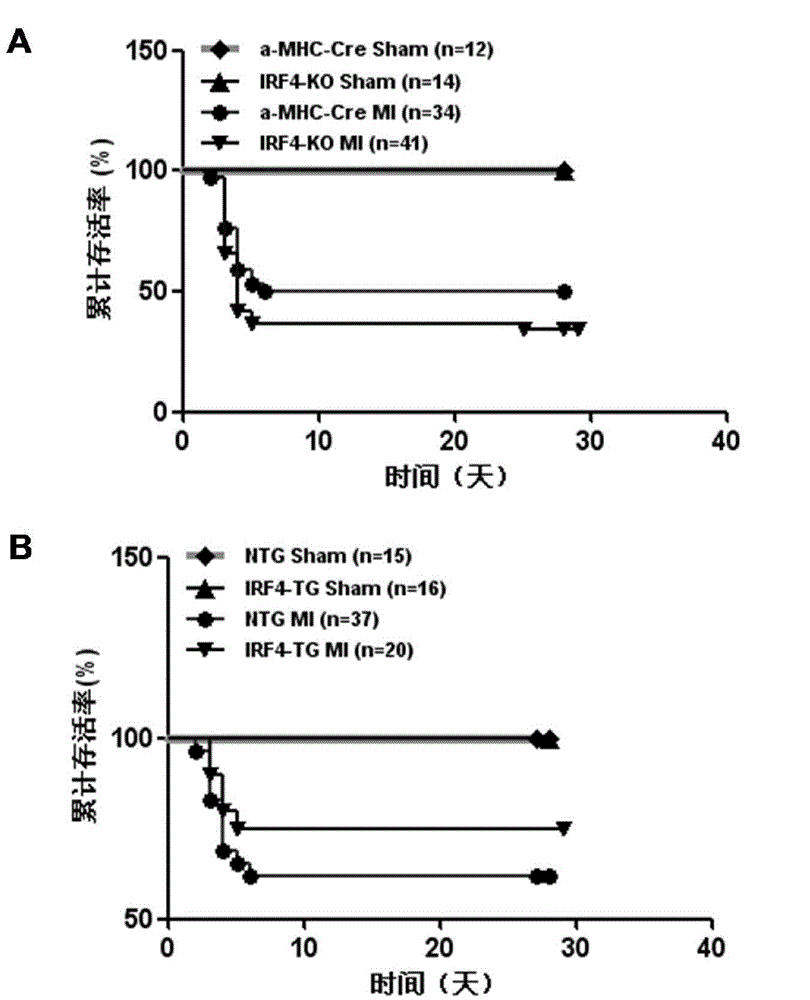
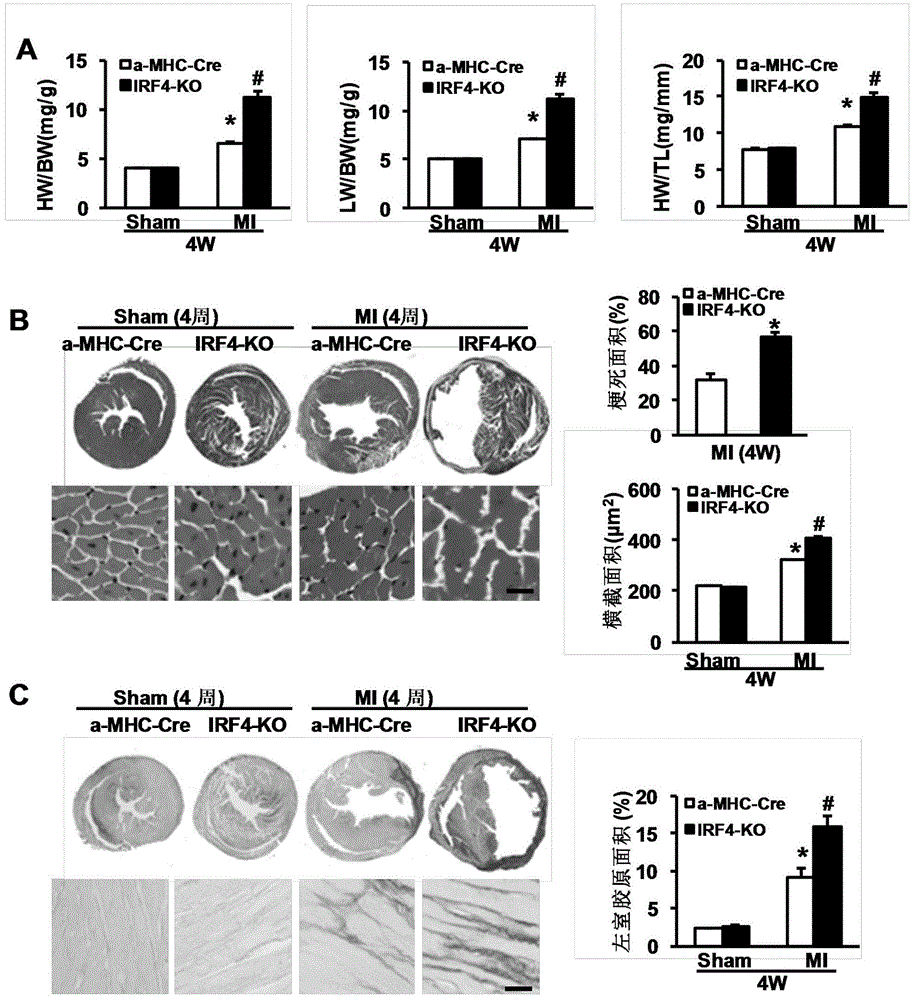
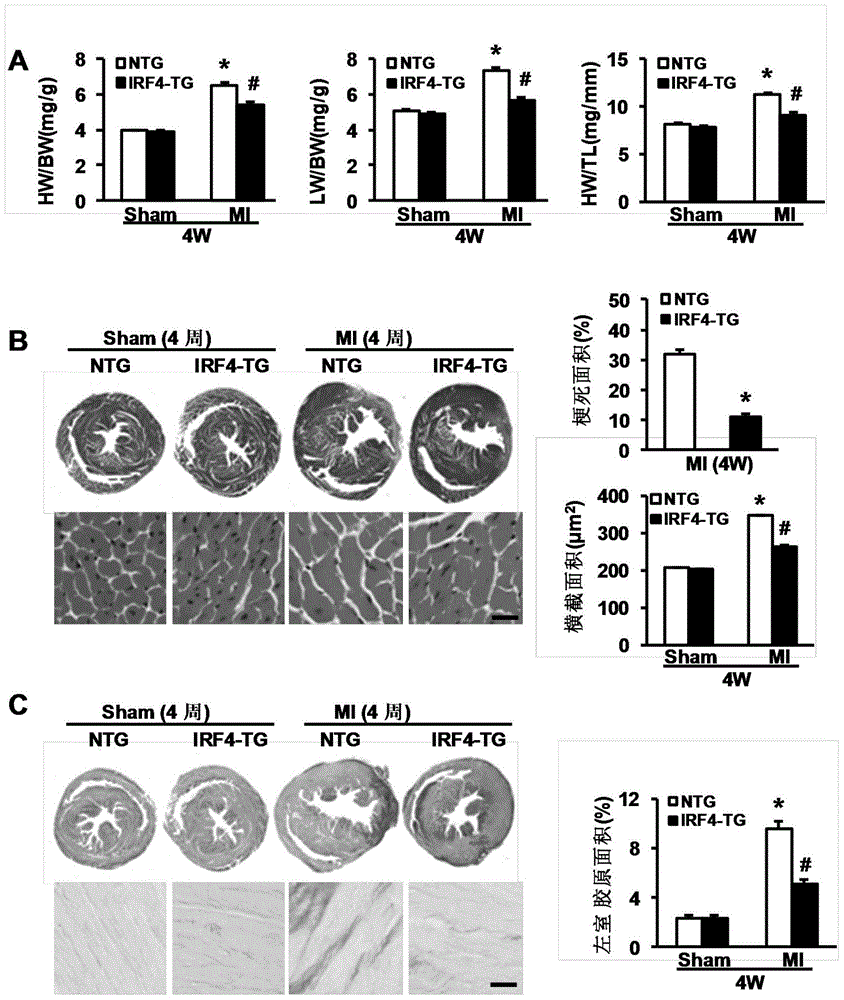
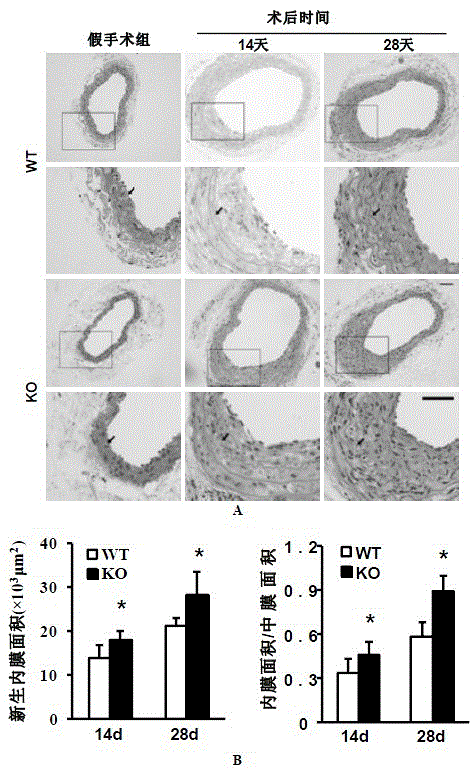
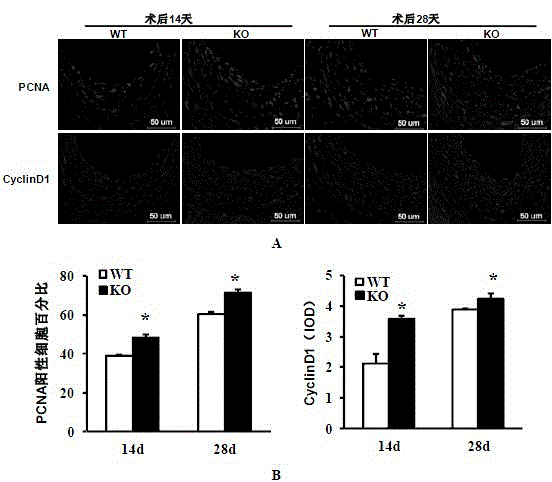
Function and application of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis
ActiveCN103784943APrevent restenosisPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderIRF4Cell phenotype
The invention discloses a function and application of an interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis, belonging to the field of gene functions and applications. According to the application disclosed by the invention, IRF4 gene knockout mice and mild C57 mice are taken as experimental subjects, and a vascular injury model is adopted to carry out neointima formation determination, vascular wall cell proliferation level detection and smooth muscle cell phenotype detection of a vascular injury model mouse; results show that compared with the mild mouse, the IRF4 gene knockout mouse has more distinct neointima formation and cell proliferation, which indicates that the function of the IRF4 gene in scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis is manifested by that the IRF4 gene has effect of inhibiting restenosis caused by vascular injury, especially protecting scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis. As for the function of IRF4, the IRF4 can be used for preparing medicaments for treating angiostenosis, especially medicaments for treating scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
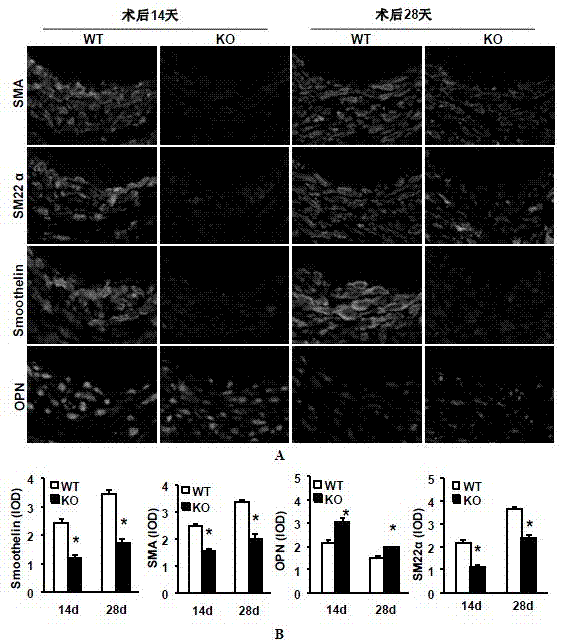
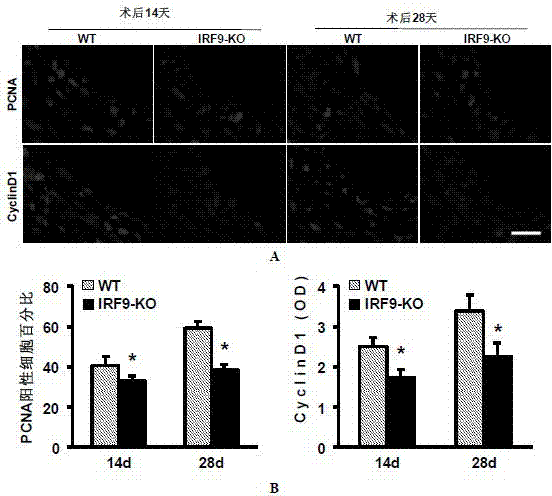
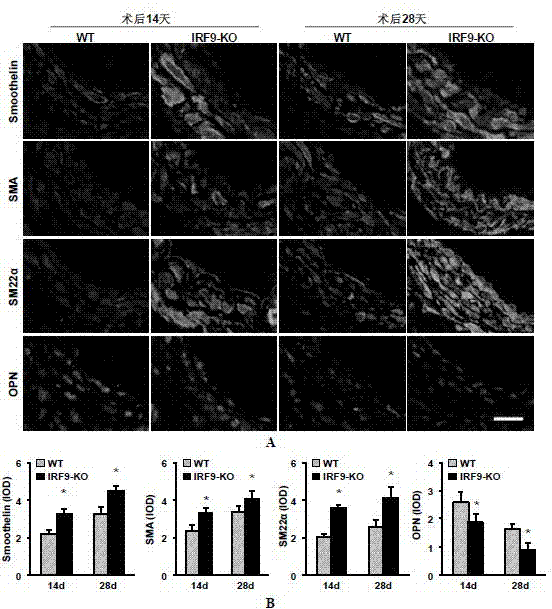
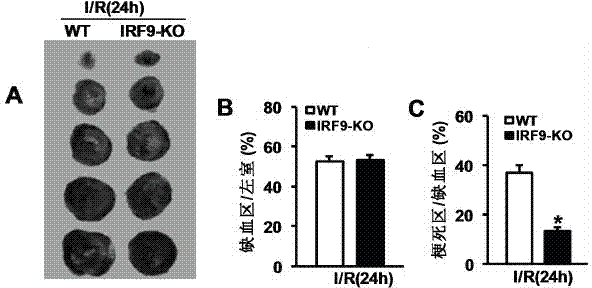
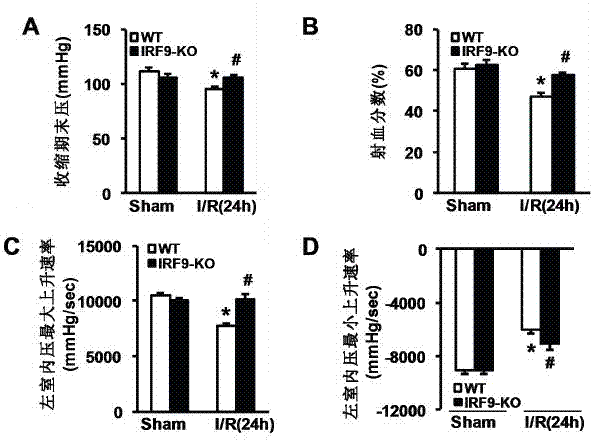
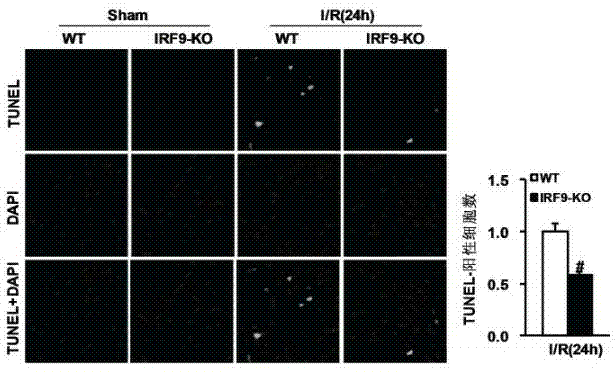
Function of IRF (Interferon Regulatory Factor) 9 in stent and carotid endarterectomy restenosis as well as application of inhibitor of IRF9
ActiveCN103784961APromote restenosisGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsCell phenotypeDisease
The invention discloses the function of IRF 9 in stent and carotid endarterectomy restenosis as well as an application of an inhibitor of IRF9, belonging to the field of the function and the application of a gene. According to the invention, IRF9 gene knockout mice and wild C57 mice are taken as experimental subjects, detection of mouse intima neogenesis, vascular wall cell proliferation level and smooth muscle cell phenotype is performed through a vascular injury model, and the results show that IRF9 gene knockout mice represents inhibited intima neogenesis and cell proliferation in comparison with the wild C57 mice. The invention discloses the function of the IRF9 gene in the stent and carotid endarterectomy restenosis, which mainly shows that the IRF9 gene has the function of promoting the intima neogenesis and cell proliferation. According to the abovementioned function, the IRF9 can be used as a drug target for screening drugs for treating hemadostenosis diseases, and the inhibitor of the IRF9 can be used for preparing the drug for treating the stent and carotid endarterectomy restenosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
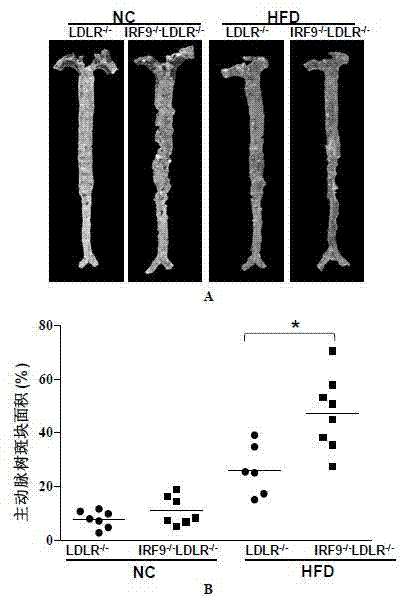
Function and application of interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) gene in atherosclerosis
ActiveCN103784973AInhibit atherosclerotic diseasePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsReceptorPlaque area
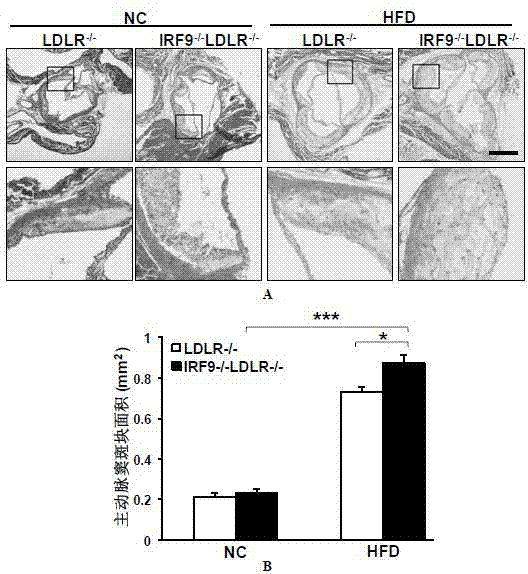
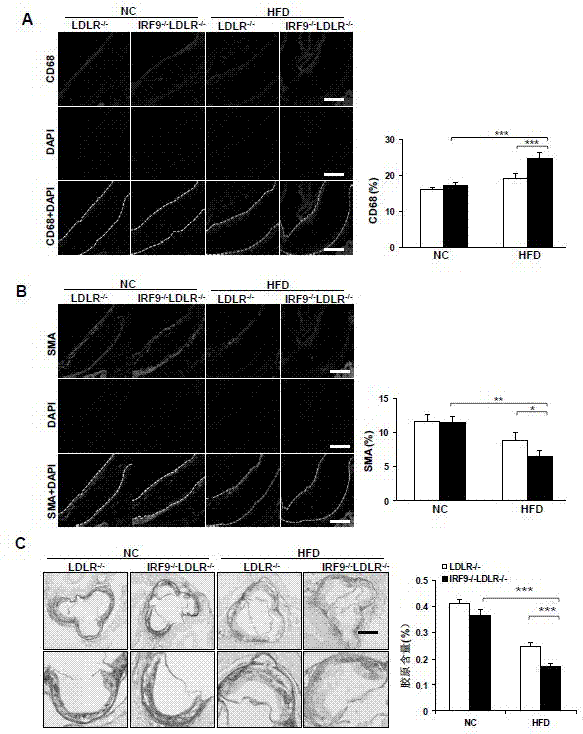
The invention discloses a function and application of an interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) gene in atherosclerosis (AS), belonging to the field of gene functions and applications. According to the function and application disclosed by the invention, LDLR (Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor)- / - mice and IRF9- / -LDLR- / - mice are taken as experimental subjects, an atherosclerosis model is obtained by high fat induction, and AS model mouse plaque area determination and inclusion analysis are carried out; results show that compared with LDLR- / - mice, the aortal plaque area of the IRF9- / -LDLR- / - mice is significantly increased. The results indicate that the function of IRF9 gene in atherosclerosis is manifested by the action in inhibiting aortal plaque formation, especially inhibiting atherosclerosis. As for the function of the IRF9 gene, IRF9 gene can be used for preparing medicaments for treating atherosclerosis.
Owner:武汉惠康基因科技有限公司
Reducing irf4, dusp22, or flj43663 polypeptide expression
InactiveUS20110306517A1Reduce spreadReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementT cellCell biology
This document relates to the activity of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in T-cell lymphomas. For example, methods and materials involved in reducing the expression of an IRF4 polypeptide in T-cell lymphoma cells and identifying agents having the ability to reduce expression of an IRF4 polypeptide in T-cell lymphoma cells are provided. This document also relates to reducing DUSP22 or FLJ43663 polypeptide activity in T-cell lymphomas. For example, methods and materials involved in reducing the expression of DUSP22 polypeptides and / or FLJ43663 polypeptides in T-cell lymphoma cells and identifying agents having the ability to reduce expression of DUSP22 polypeptides and / or FLJ43663 polypeptides in T-cell lymphoma cells are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
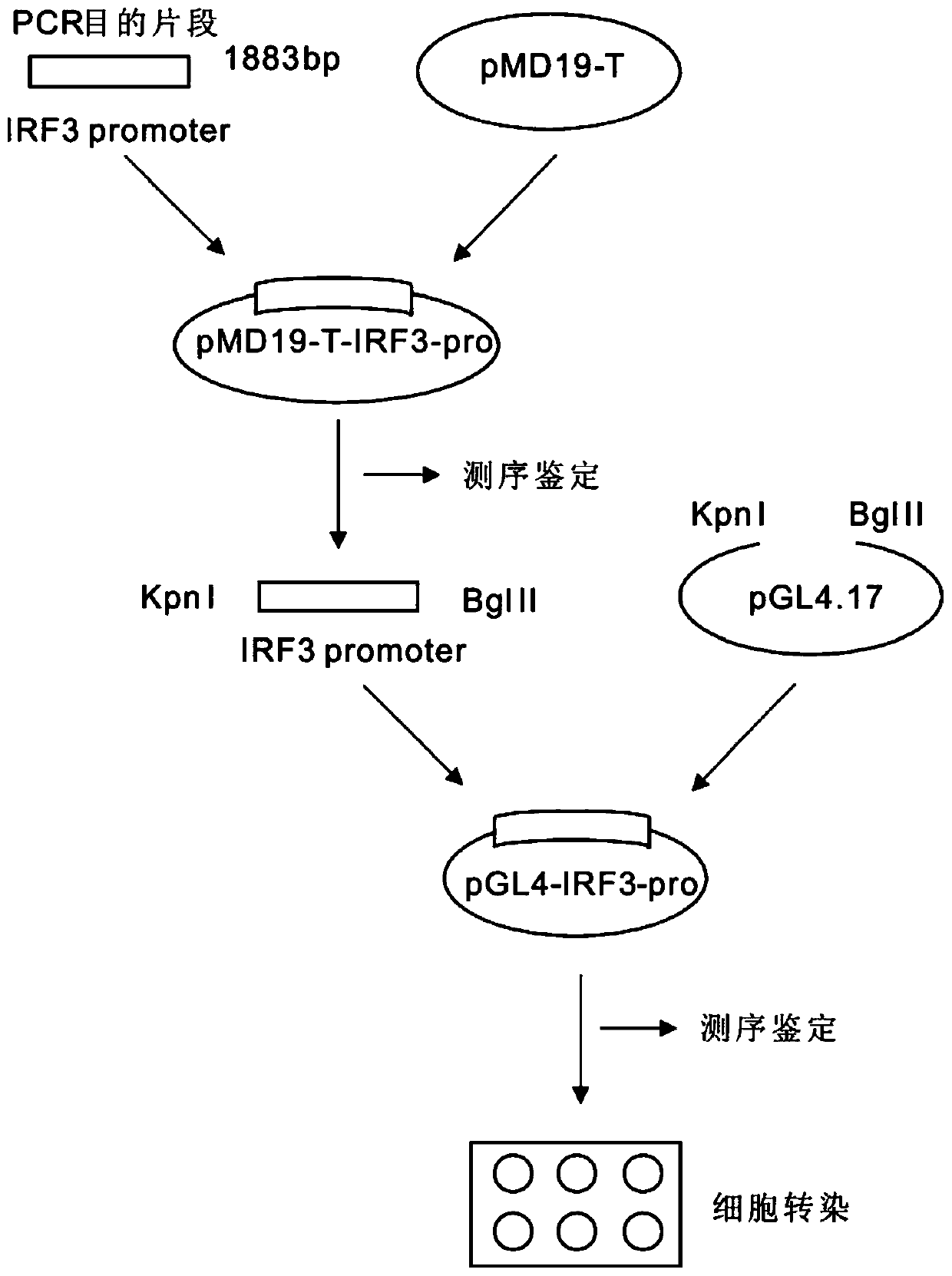
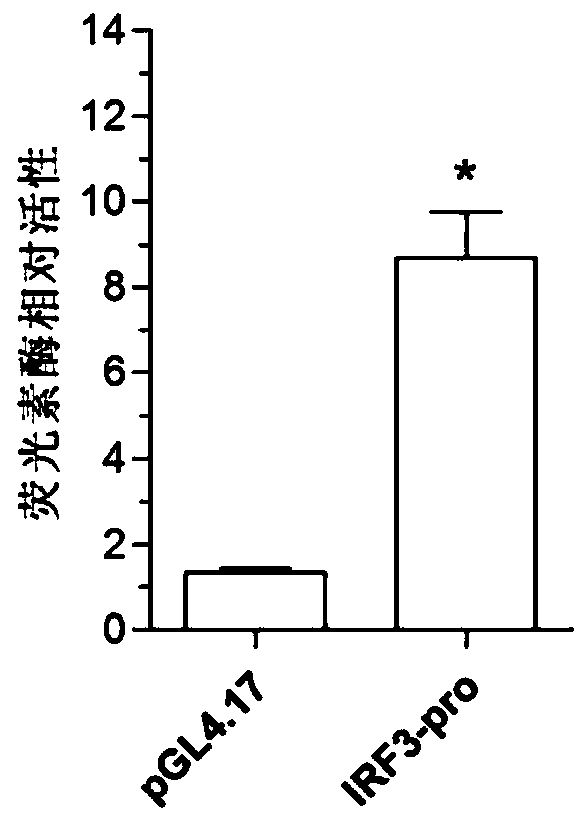
Larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter, nucleic acid builder, cell and preparing method and application of larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter
ActiveCN107058326AGood experimental systemPeptidesVector-based foreign material introductionMammalNucleotide
The invention discloses a larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter, a nucleic acid builder, a cell and a preparing method and application of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter, the nucleic acid builder and the cell. The nucleotide sequence of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter is shown as Seq ID No.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to Seq ID No.1. The invention further protects application of the starter or the nucleic acid builder or a carrier or a reconstitution cell or fish or a mammal containing the starter or the nucleic acid builder or the carrier or the reconstitution cell in regulating target gene expression or transgenic fish.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV +1
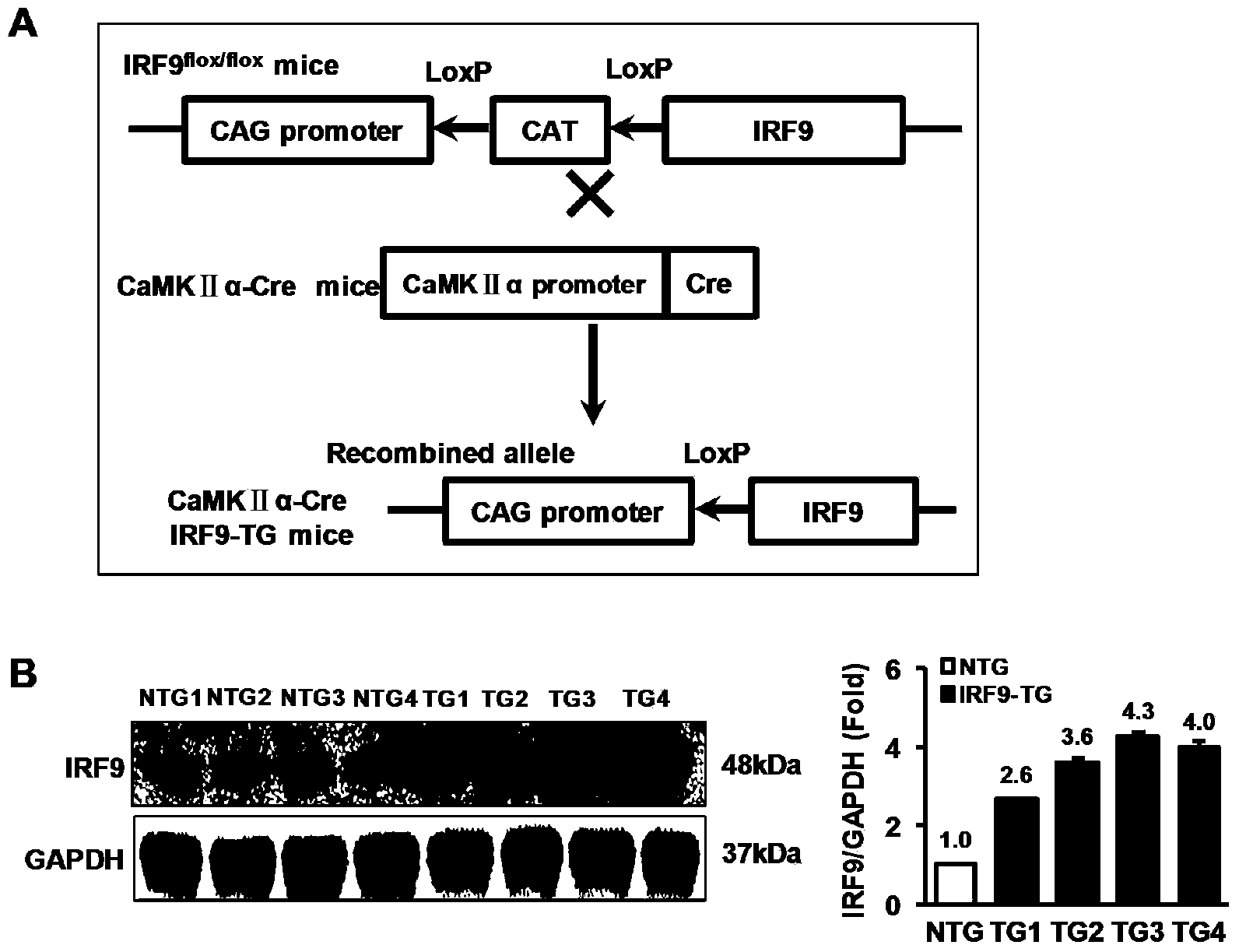
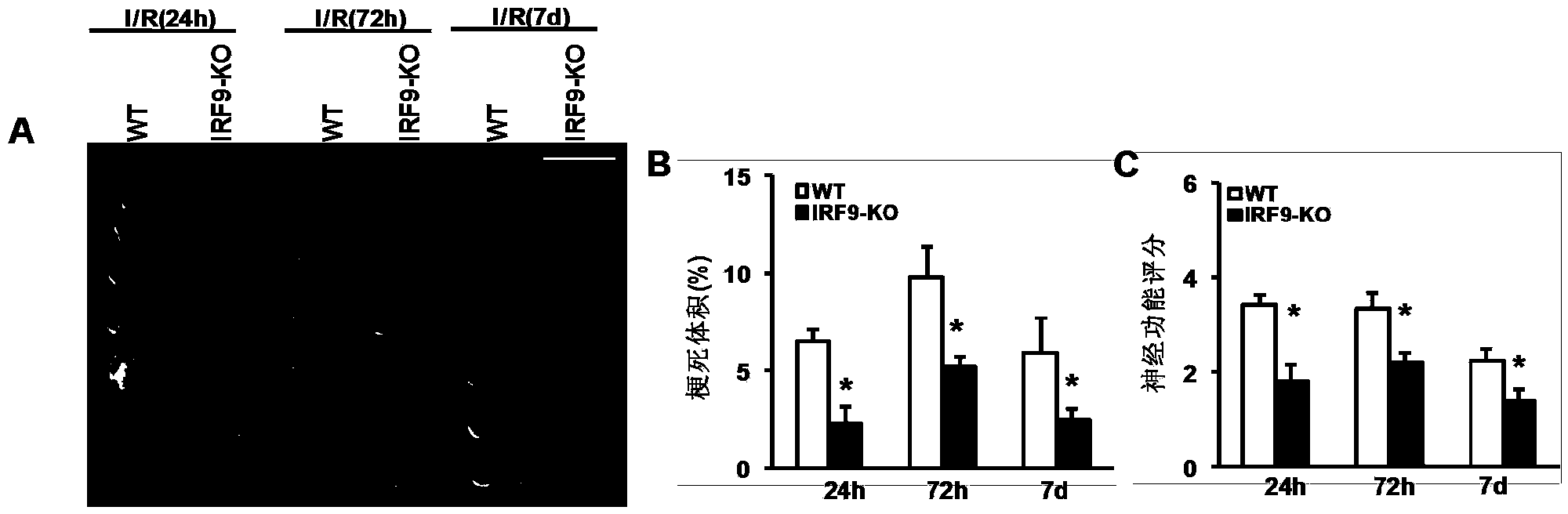
Interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) and application of inhibitor thereof in cerebral apoplexy
ActiveCN103751803AExacerbation of stroke diseaseNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The invention discloses interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) and application of an inhibitor thereof in cerebral apoplexy, belonging to the field of gene function and application. The invention uses IRF9 gene knock-out mice and brain-specific IRF9 transgenic mice as experimental subjects and adopts middle cerebral artery ischemia reperfusion model, results show that compared with mild type C57 mouse, the brain infarction volume of IRF9 gene knock-out mouse is apparently inhibited, and nerve function is improve remarkably, while the infarction volume of nerve-specific IRF9 transgenic mouse is apparently inhibited, and nerve function is deteriorated markedly. Therefore, IRF9 gene has nervous system function deterioration effect; especially, IRF9 gene can deteriorate cerebral apoplexy. As for the above function of IRF9, the invention provides application of IRF9 as drug target of cerebral apoplexy treatment in developing medicaments for treating cerebral apoplexy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
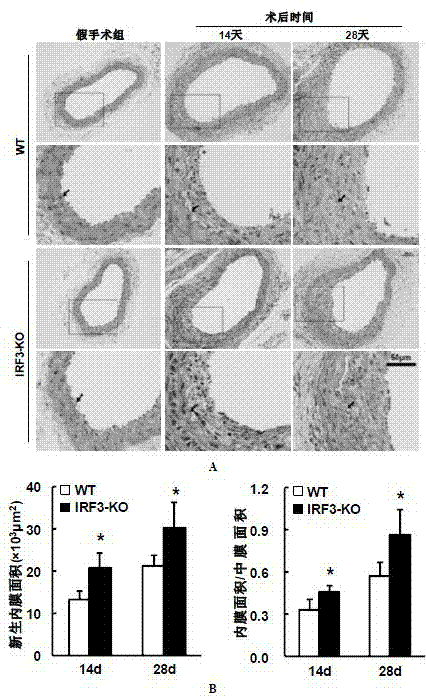
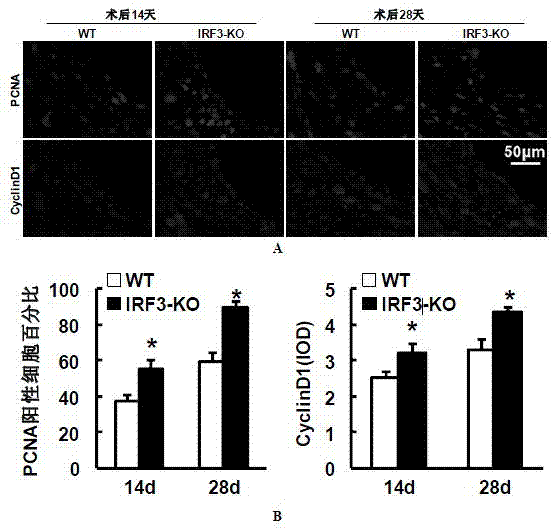
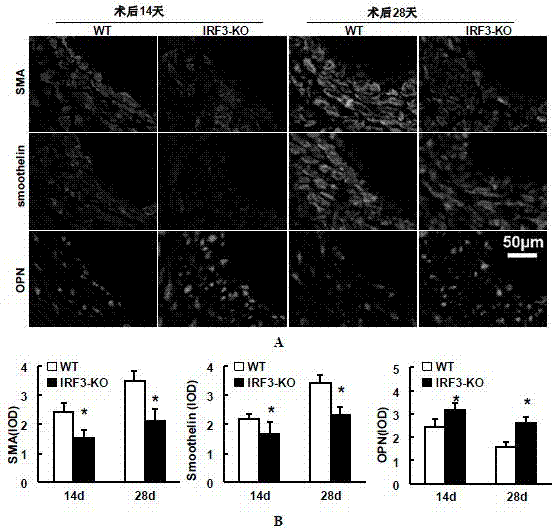
Function and application of IRF3 (Interferon Regulatory Factor 3) to restenosis after stenting and carotid endarterectomy
ActiveCN103784945APrevent restenosisPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCell phenotypeDisease
The invention discloses the function and application of an IRF3 (Interferon Regulatory Factor 3) gene to restenosis after stenting and carotid endarterectomy, belonging to the field of function and application of genes. An IRF3 gene knock-out mouse and a wild C57 mouse are taken as experimental objects, and determination of neointima formation, detection of the vascular wall cell proliferation level and detection of smooth muscle cell phenotype of a blood injury model mouse are performed through the blood injury model. As proved by a result, the neointima formation and cell proliferation of the IRF3 gene knock-out mouse are more remarkable than those of the wild mouse. The function of the IRF3 gene to restenosis after stenting and carotid endarterectomy mainly refers to the function of inhibiting restenosis caused by vascular injury of the IRF3 gene, particularly the function of inhibiting restenosis after stenting and carotid endarterectomy. Aiming at the functions of the IRF3, the IRF3 can be used for preparing medicaments for treating restenosis disease, particularly for preparing medicaments for treating restenosis after stenting and carotid endarterectomy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
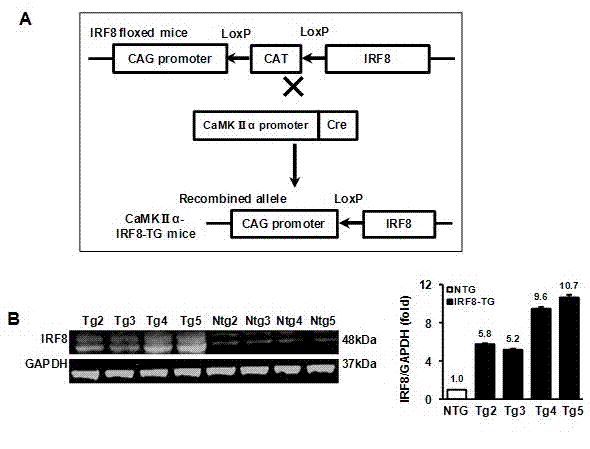
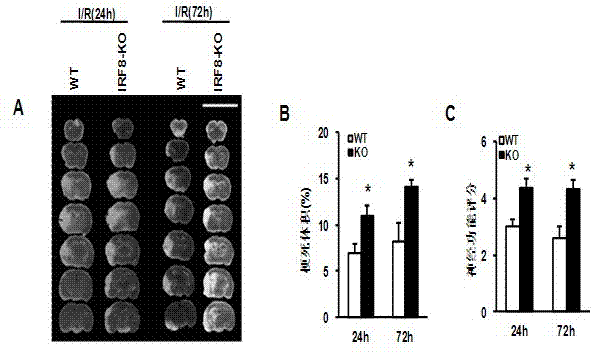
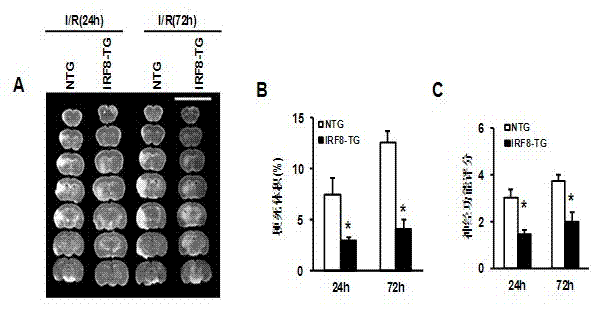
Application of interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) in cerebral apoplexy disease
The invention discloses function and application of an IRF8 gene in a cerebral apoplexy disease, belonging to the field of the function and the application of a gene. According to the invention, IRF8 gene knockout mice and neuron-specific IRF8 transgenic mice are taken as experimental subjects, a brain middle artery ischemia reperfusion model is adopted, and the results show that the cerebral infarction volume of the IRF8 gene knockout mice is obviously increased and the neurological function is obviously worsened as well in comparison with that of the wild C57 mice, the infarction volume of the IRF8 transgenic mice is obviously reduced, and the neurological function obviously gets better. The invention discloses the function of the IRF8 gene in the cerebral apoplexy disease, which mainly means that the IRF8 gene has an effect of protecting the function of a nervous system, especially an effect that the IRF8 gene can protect the cerebral apoplexy disease. According to the abovementioned function of the IRF8, the invention provides the application of the IRF8 in preparation of a drug for treating the cerebral apoplexy disease.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
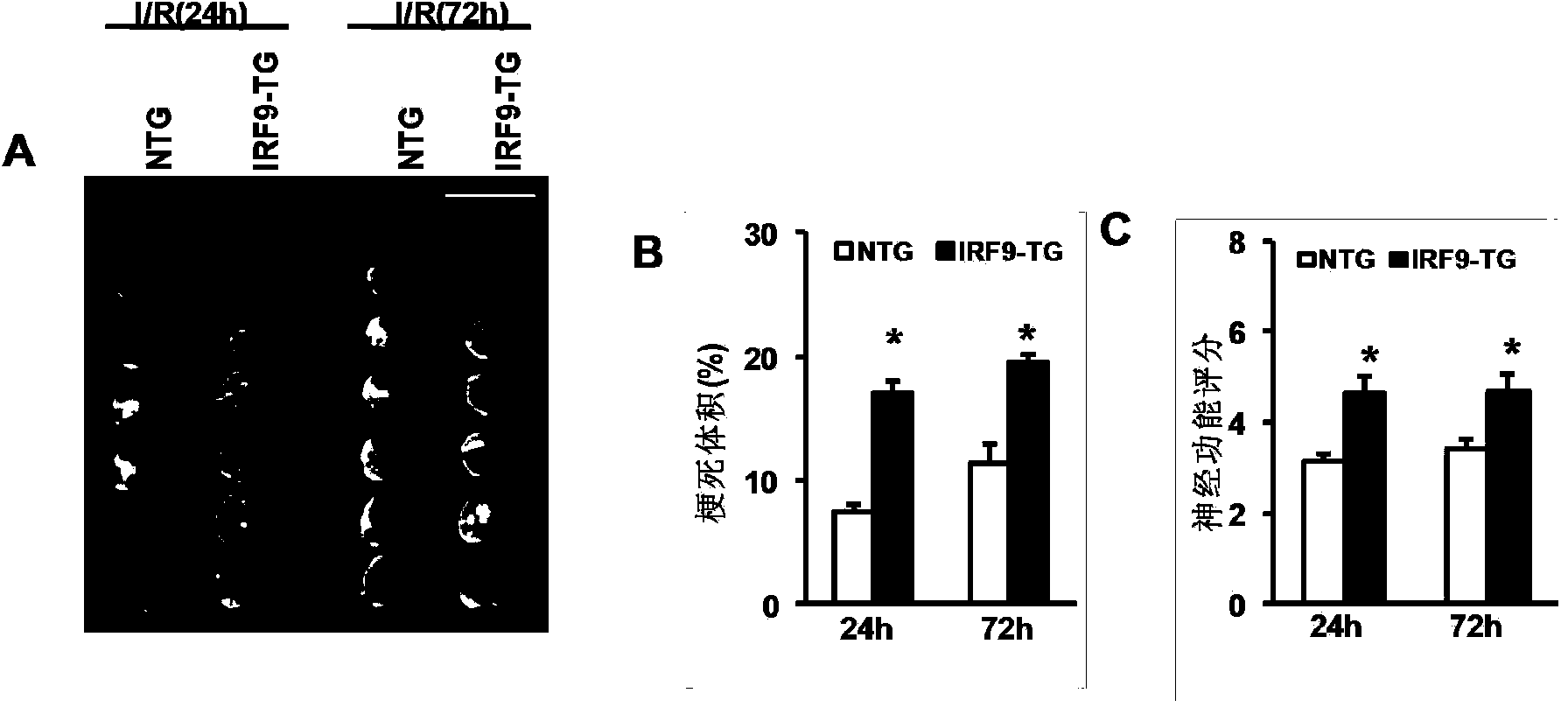
Application of interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) and inhibitor thereof in coronary arteriosclerotic heart disease
ActiveCN103784972AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnterior Descending Coronary ArteryCoronary atherosclerosis
The invention discloses an application of interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) and an inhibitor thereof in coronary arteriosclerotic heart disease, belonging to the field of gene functions and applications. According to the application disclosed by the invention, IRF9 gene knockout mice are taken as experimental subjects, and a myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury model is constructed by ligating mouse heart left anterior descending (LAD) artery; results show that compared with a wild type (WT) mouse, the IRF9 gene knockout mouse has the characteristics that the myocardial infarction area is significantly reduced, and the heart function is significantly improved. The function of the IRF9 gene in coronary arteriosclerotic heart disease is mainly manifested by that the IRF9 gene can deteriorate coronary arteriosclerotic heart disease. As for the function of IRF9, the invention provides the application of the IRF9 in developing medicaments for treating coronary arteriosclerotic heart disease as a drug target, and the application of the IRF9 inhibitor in preparing medicaments for treating coronary arteriosclerotic heart disease.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
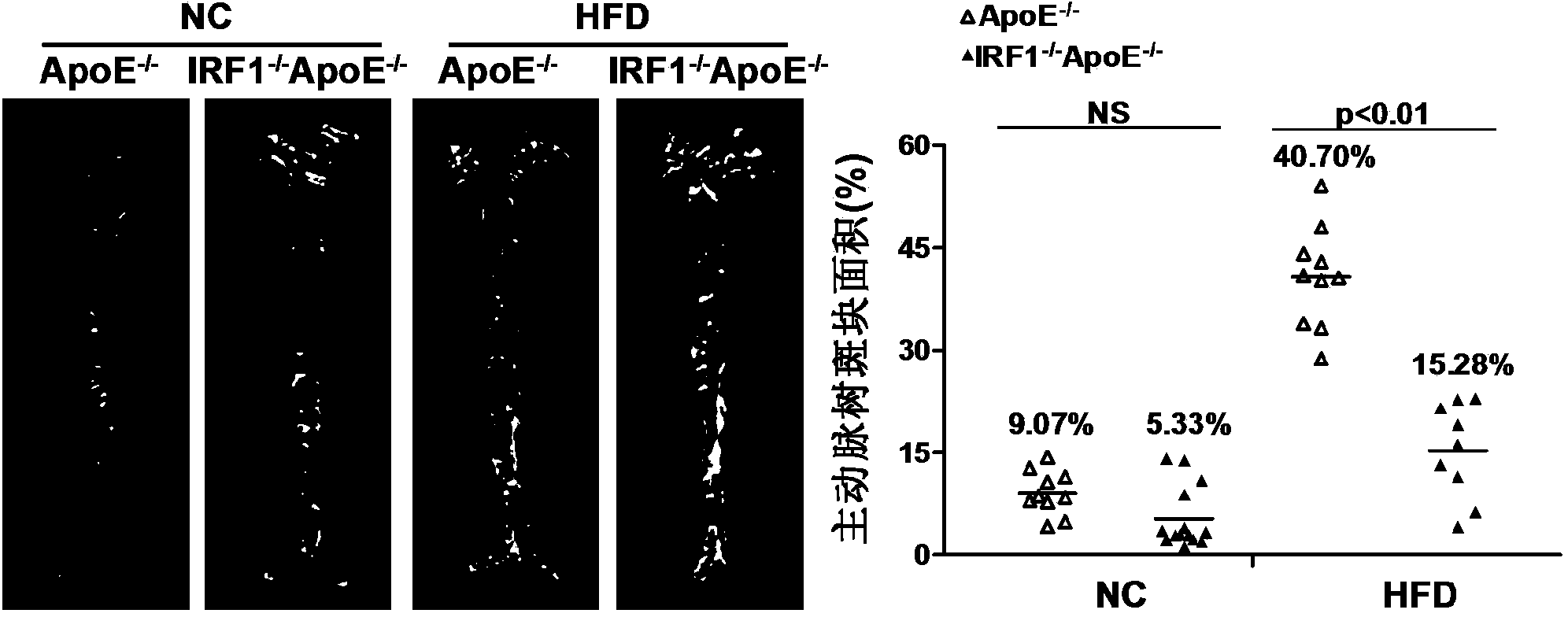
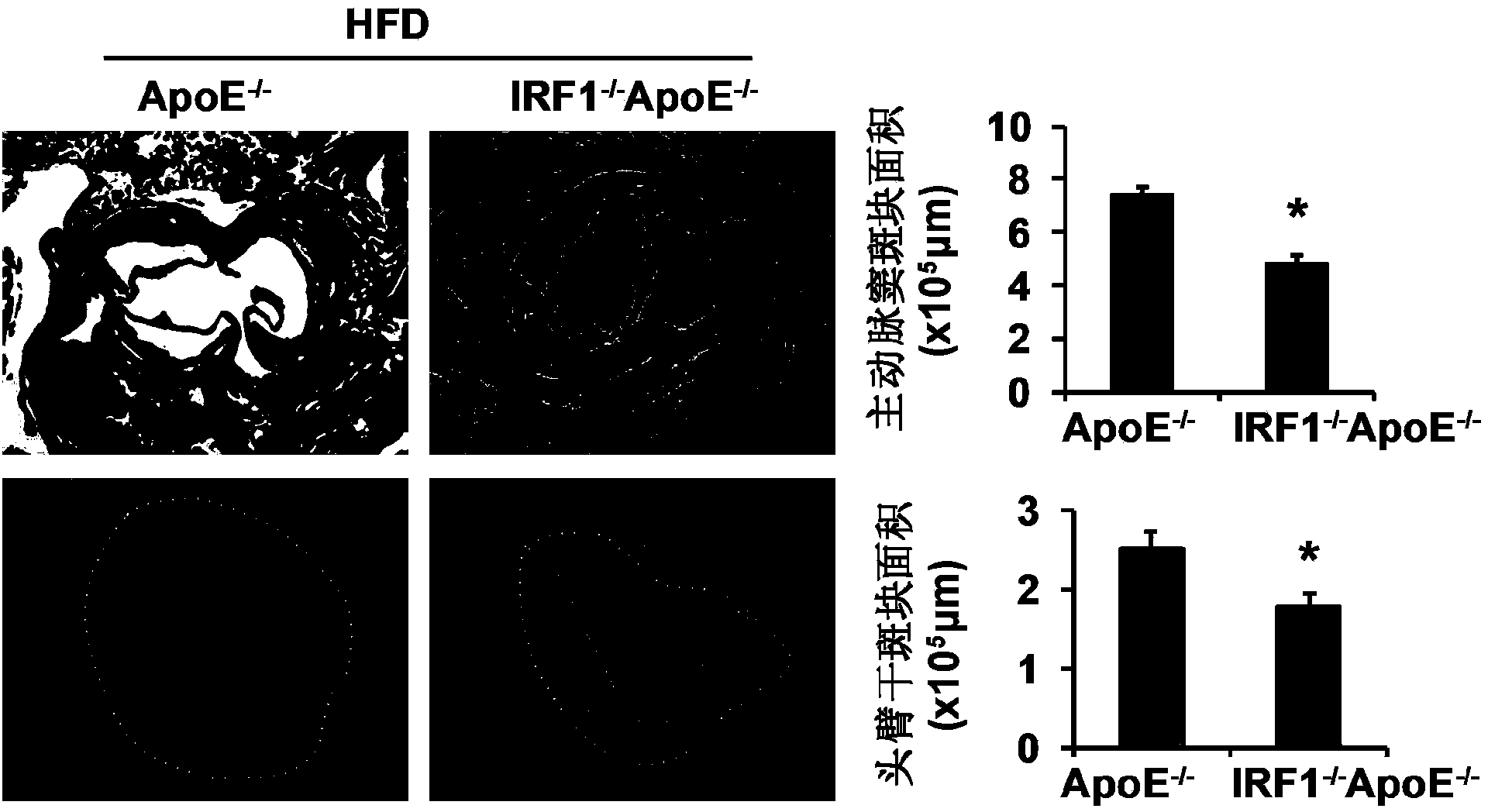
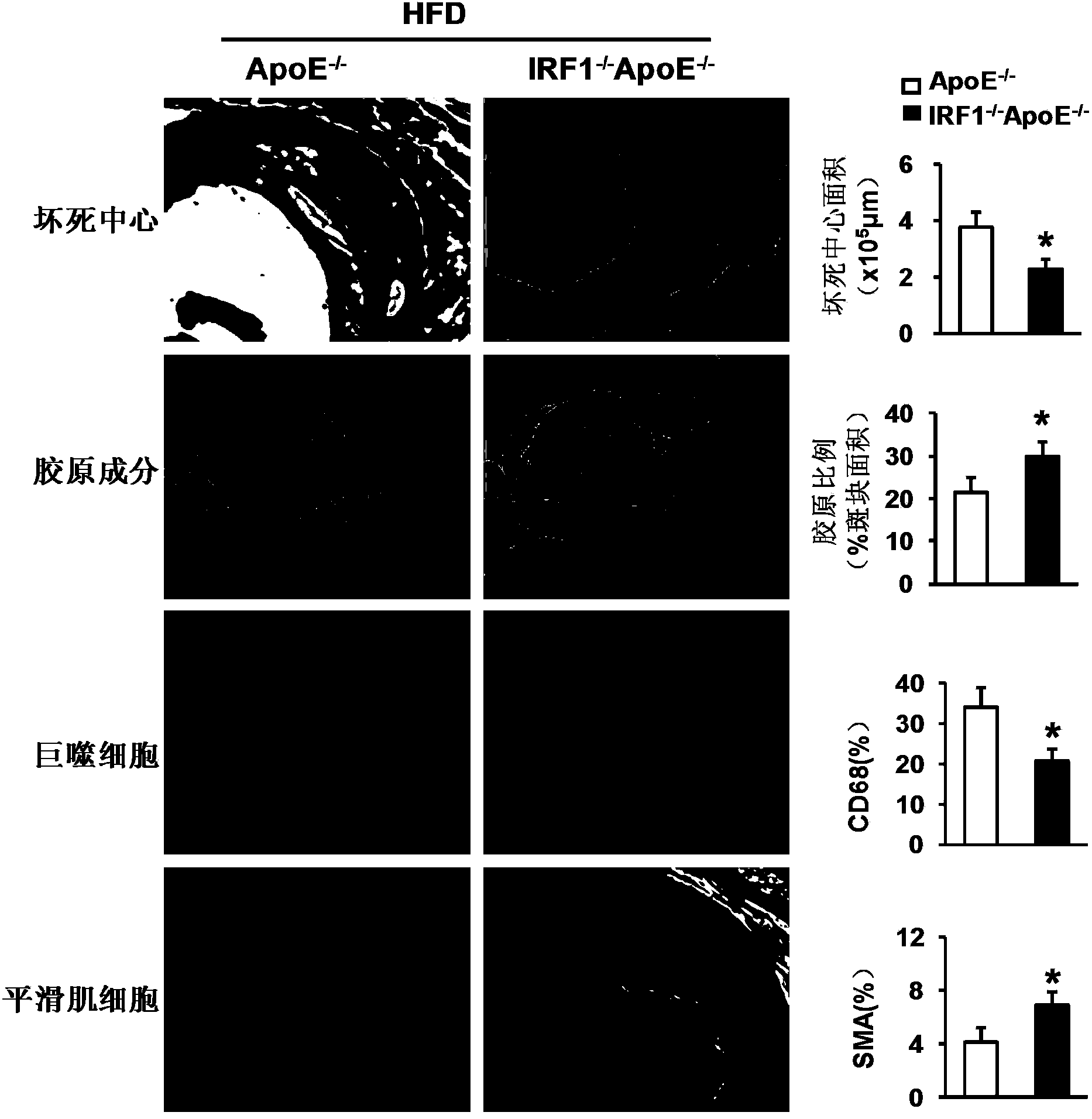
Applications of interferon regulatory factor 1 gene in treatment of atherosclerosis
InactiveCN104258419APromotes atherosclerosisAlleviate and/or treat atherosclerosisGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsFactor iiAtheroma
The invention discloses applications of an interferon regulatory factor 1 gene in treatment of atherosclerosis, belonging to the field of the functions and applications of a gene. An atherosclerosis model is obtained by taking ApoE- / -mice and IRF1- / -ApoE- / -mice as experimental objects through induction of high-fat diet, results show that the IRF1 gene defects markedly reduce the plaque area of the aorta, enhance the stability of aortic sinus plaque, and markedly lighten the inflammatory response compared with the ApoE- / -mice. The function of the IRF1 in the atherosclerosis is mainly reflected by the fact that the IRF1 achieves the effect of promoting the formation of the aortic plaque, especially the effect of promoting the atherosclerosis. Aiming to the functions of the IRF1, the IRF1 can be used as a drug target for screening drugs preventing, alleviating and / or treating atherosclerosis, and an inhibitor of the IRF1 can be used for preparing a drug for preventing, alleviating and / or treating atherosclerosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
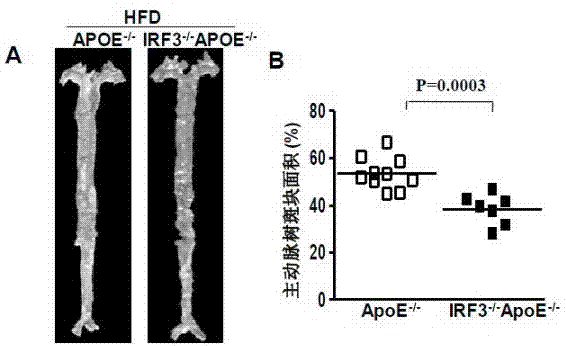
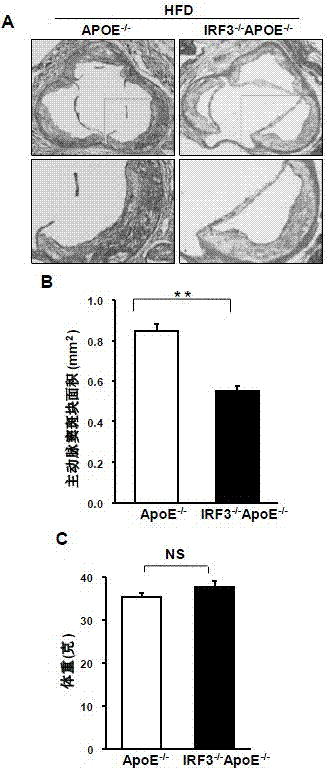
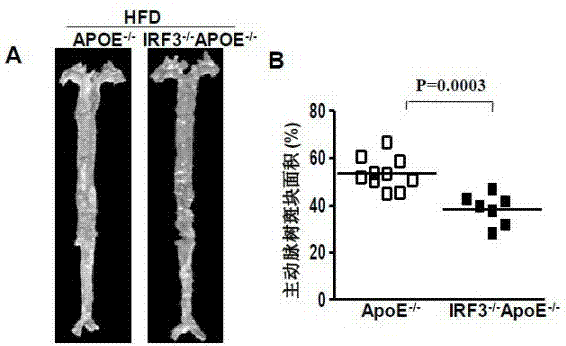
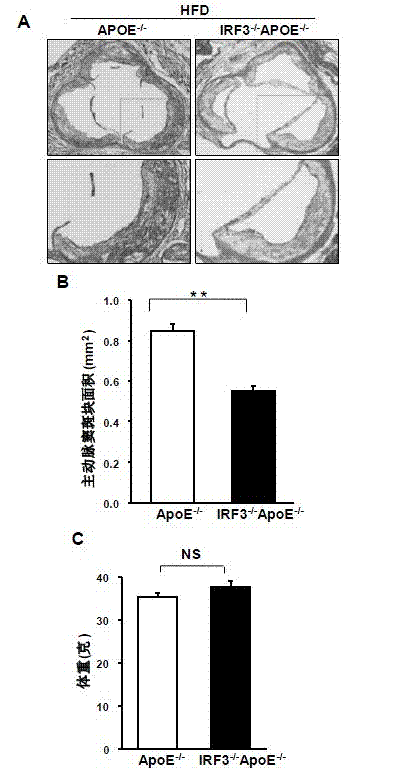
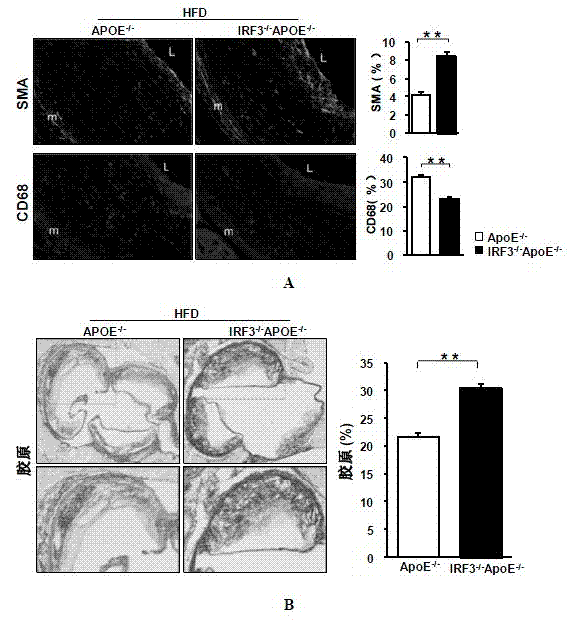
Function of IRF (Interferon Regulatory Factor) 3 gene in atherosclerosis and application of inhibitor of IRF3 gene
ActiveCN103784971BExacerbation of atherosclerotic diseaseGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseHigh fat
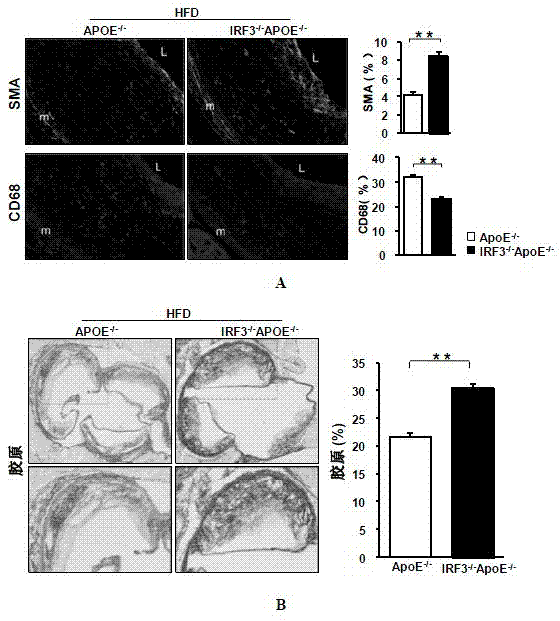
The invention discloses the function of an IRF3 gene in atherosclerosis and an application of an inhibitor of the IRF3 gene, belonging to the field of the function and the application of a gene. According to the invention, ApoE- / -mice and IRF3- / -ApoE- / -mice are taken as experimental subjects, an atherosclerosis model is obtained through high-fat induction, AS model mouse plaque area measurement and inclusion analysis are performed, and the results show that the aorta plaque area of the IRF3- / -ApoE- / -mice is remarkably reduced in comparison with that of the ApoE- / -mice. The invention discloses the function of the IRF3 gene in an atherosclerosis disease, which means that the IRF3 gene has an effect of promoting the formation of the aorta plaques, especially that the IRF3 gene can worsen the atherosclerosis. According to the abovementioned function, the IRF3 can be used as a drug target for screening drugs for treating the atherosclerosis disease. The inhibitor of the IRF3 can be used for preparing the drug for treating the atherosclerosis disease.
Owner:武汉惠康达科技有限公司
NOX2 as a Biomarker of Radiotherapy Efficiency in Cancer Patients
ActiveUS20200181714A1Improve efficiencyCytochromesMicrobiological testing/measurementAtaxia-telangiectasiaTumor response
Although tumor-associated macrophages have been extensively studied in the control of response to radiotherapy, the molecular mechanisms involved in the ionizing radiation-mediated activation of macrophages remain elusive. Here the present inventors show that ionizing radiation induces the expression of interferon-regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) promoting thus macrophage activation toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype. They reveal that the activation of the Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase is required for ionizing radiation-elicited macrophage activation, but also for macrophage reprogramming after treatments with γ-interferon, lipopolysaccharide or chemotherapeutic agent (such as cis-platin), underscoring the fact that the kinase ATM plays a central role during macrophage phenotypic switching toward a proinflammatory phenotype. They further demonstrate that NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2)-dependent ROS production is upstream to ATM activation and is essential during this process. They also report that hypoxic conditions and the inhibition of any component of this signaling pathway (NOX2, ROS and ATM) impairs pro-inflammatory activation of macrophages and predicts a poor tumor response to preoperative radiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Altogether, these results identify a novel signaling pathway involved in macrophage activation that may enhance effectiveness of radiotherapy through the re-programming of tumor infiltrating macrophages.
Owner:INSTITUT GUSTAVE ROUSSY
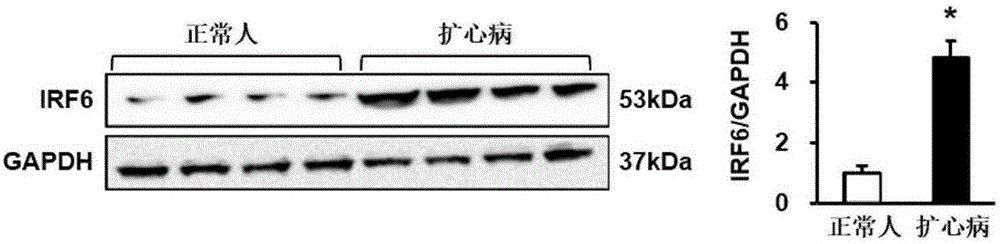
Interferon regulatory factor 6(IRF6) and application of inhibitor of factor in treatment of myocardial hypertrophy
InactiveCN106474490APromote hypertrophyPromote fibrosisCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCardiac muscle
The invention discloses an interferon regulatory factor 6(IRF6) and application of an inhibitor of the factor in treatment of myocardial hypertrophy and belongs to the fields of gene function and application. The mutual relation between IRF6 gene expression and the myocardial hypertrophy is determined, wherein the myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis are remarkably inhibited and cardiac functions are improved by inhibiting the IRF6 expression, and the myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis are remarkably promoted and the cardiac functions deteriorate by promoting the IRF6 expression. Therefore, the IRF6 can serve as a drug target for screening drugs for protecting the cardiac functions, preventing, relieving and / or treating the myocardial hypertrophy or resisting myocardial fibrosis, the inhibitor of the IRF6 can be used for preparing the drugs for protecting the cardiac functions, preventing, relieving and / or treating the myocardial hypertrophy or resisting myocardial fibrosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Function of IRF (Interferon Regulatory Factor) 3 gene in atherosclerosis and application of inhibitor of IRF3 gene
ActiveCN103784971AExacerbation of atherosclerotic diseaseGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseasePlaque area
The invention discloses the function of an IRF3 gene in atherosclerosis and an application of an inhibitor of the IRF3 gene, belonging to the field of the function and the application of a gene. According to the invention, ApoE- / -mice and IRF3- / -ApoE- / -mice are taken as experimental subjects, an atherosclerosis model is obtained through high-fat induction, AS model mouse plaque area measurement and inclusion analysis are performed, and the results show that the aorta plaque area of the IRF3- / -ApoE- / -mice is remarkably reduced in comparison with that of the ApoE- / -mice. The invention discloses the function of the IRF3 gene in an atherosclerosis disease, which means that the IRF3 gene has an effect of promoting the formation of the aorta plaques, especially that the IRF3 gene can worsen the atherosclerosis. According to the abovementioned function, the IRF3 can be used as a drug target for screening drugs for treating the atherosclerosis disease. The inhibitor of the IRF3 can be used for preparing the drug for treating the atherosclerosis disease.
Owner:武汉惠康达科技有限公司
Application of interferon regulatory factor 4 (irf4) gene in coronary atherosclerotic heart disease
ActiveCN103751804BPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIRF4Anterior Descending Coronary Artery
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
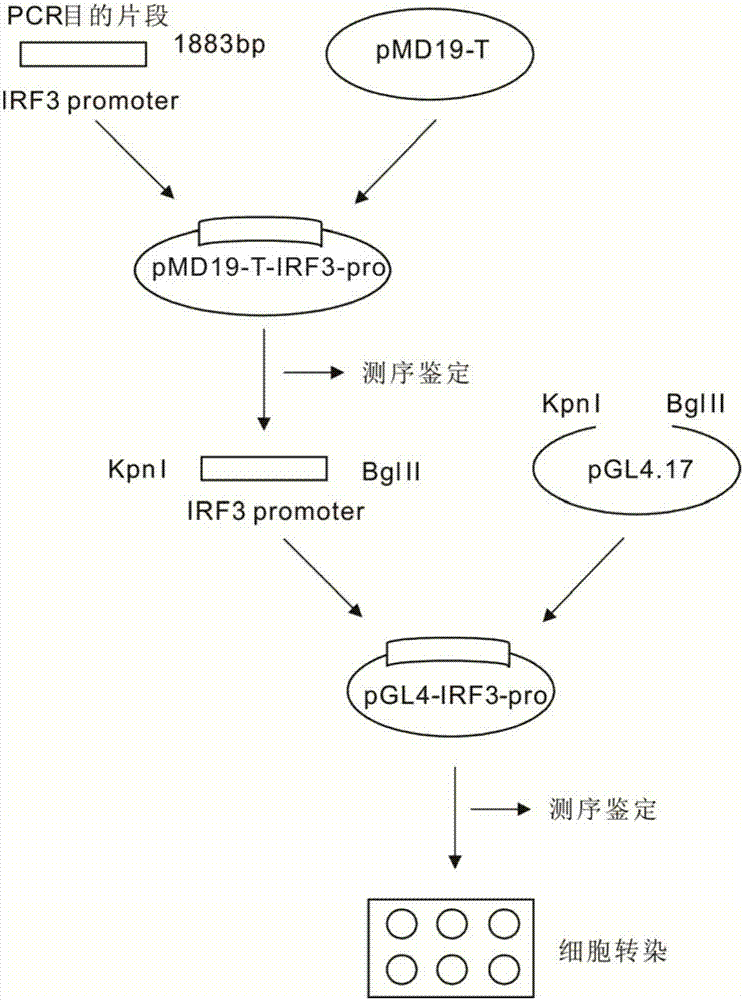
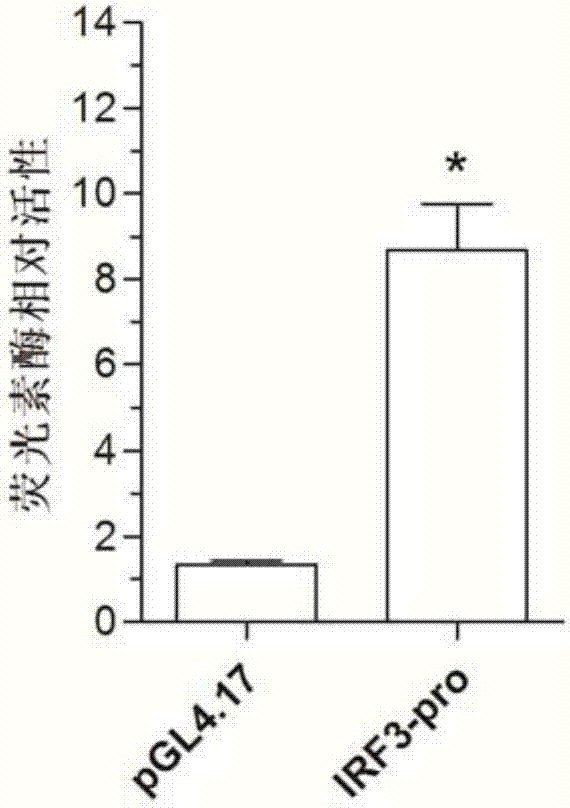
A large yellow croaker interferon regulator irf3 promoter, nucleic acid construct, cell and preparation method and use thereof
The invention discloses a larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter, a nucleic acid builder, a cell and a preparing method and application of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter, the nucleic acid builder and the cell. The nucleotide sequence of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF3 starter is shown as Seq ID No.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to Seq ID No.1. The invention further protects application of the starter or the nucleic acid builder or a carrier or a reconstitution cell or fish or a mammal containing the starter or the nucleic acid builder or the carrier or the reconstitution cell in regulating target gene expression or transgenic fish.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV +1
A large yellow croaker interferon regulatory factor irf7 promoter, nucleic acid construct, cell and its preparation method and use
The invention discloses a larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter, a nucleic acid builder, a cell and a preparing method and application of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter, the nucleic acid builder and the cell. The nucleotide sequence of the larimichthys crocea interferon regulatory factor IRF7 starter is shown as Seq ID No.1 or a nucleotide sequence complementary to Seq ID No.1. The invention further protects application of the starter or the nucleic acid builder or a carrier or a reconstitution cell or fish or a mammal containing the starter or the nucleic acid builder or the carrier or the reconstitution cell in regulating target gene expression or transgenic fish.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV +1
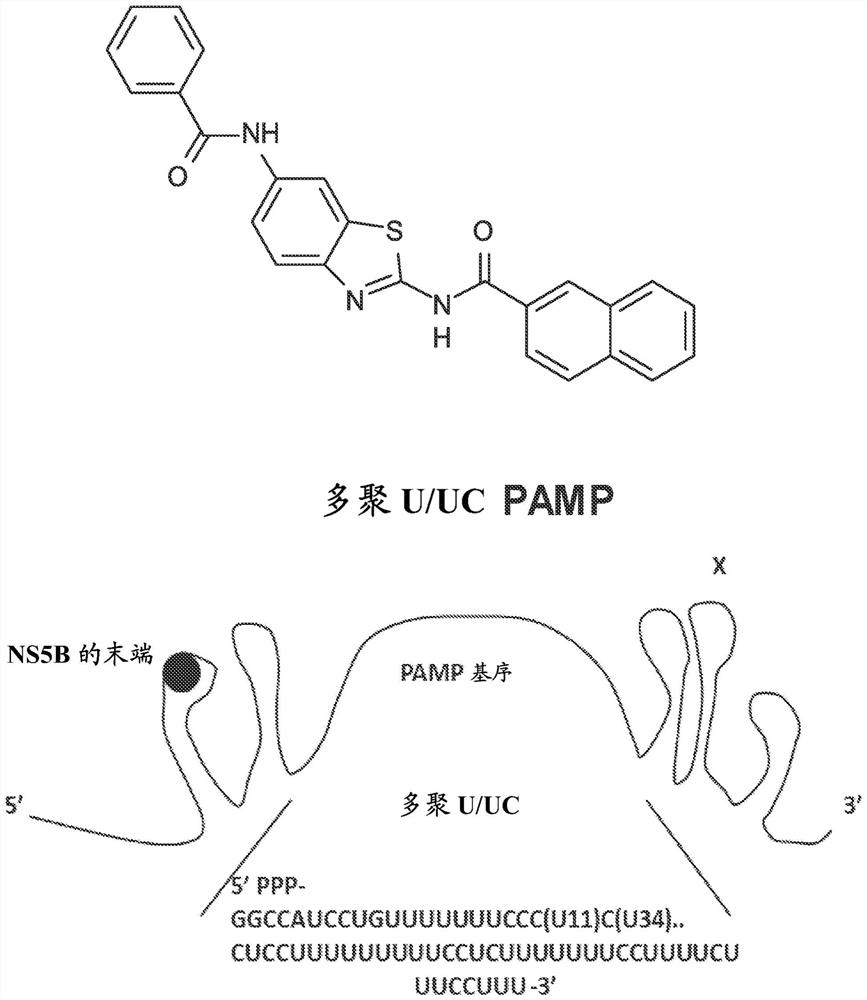
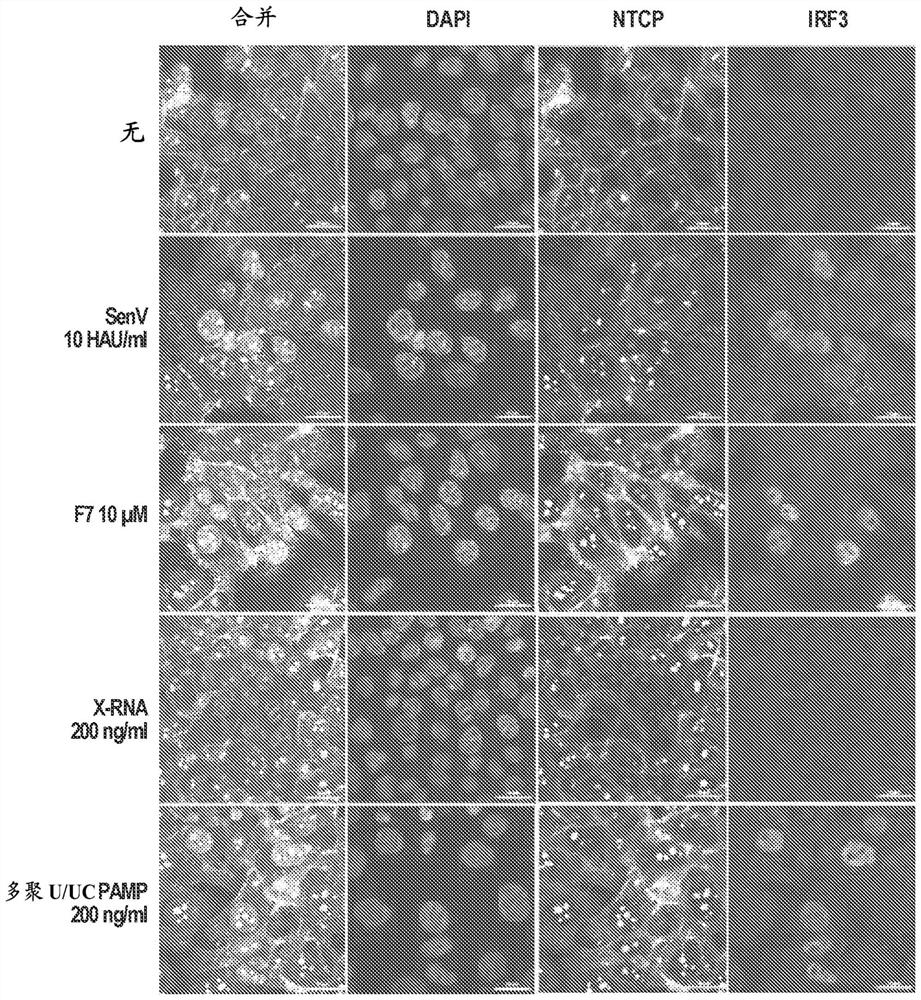
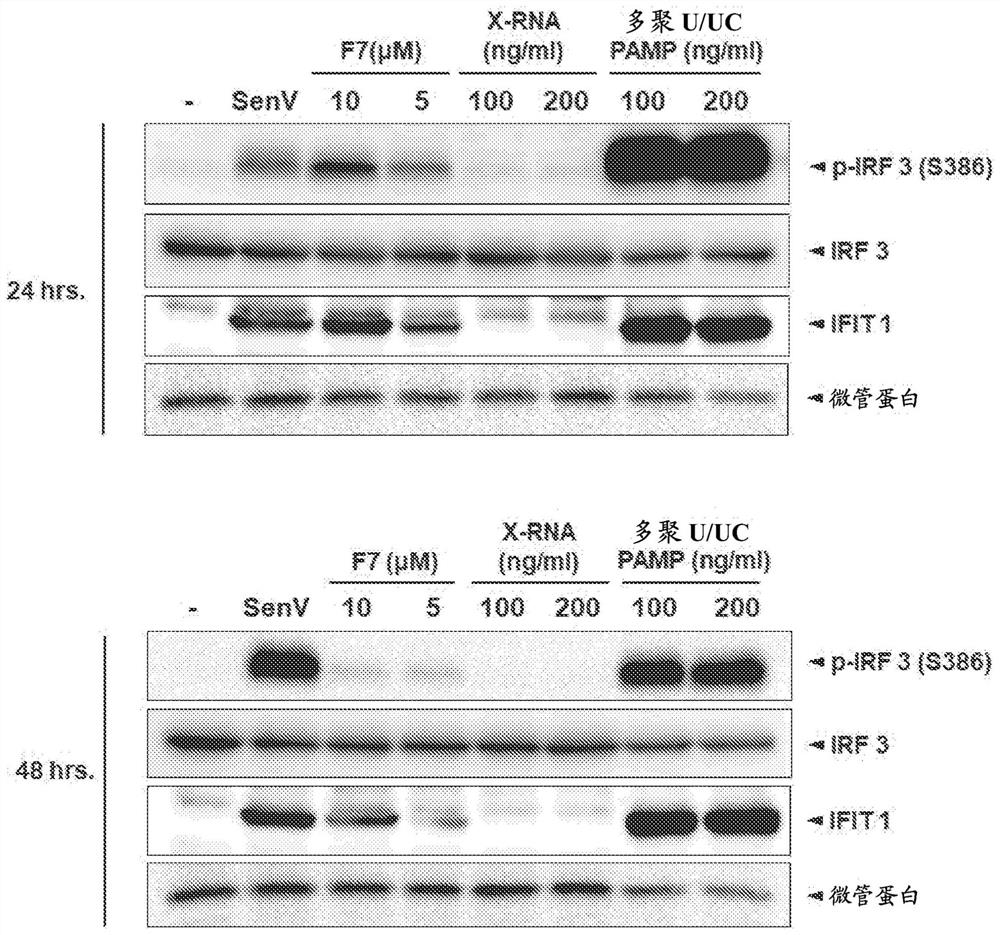
Compositions and methods for treating hepatitis b virus infection
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for inhibiting hepatitis B virus (HBV) in infected cells. Exemplary methods include contacting an infected cell with one or more agents that induce interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) activation in the infected cell. In some embodiments, one or more agents include a nucleic acid molecule comprising a pathogen-related molecular pattern (PAMP), a small molecule agent (e.g., a benzothiazole derivative molecule), or a combination thereof. In some embodiments, the method further comprises contacting the infected cells with an NRTI. The method may be an in vivo method of treating a subject suffering from HBV infection comprising administering a therapeutically related amount of one or more agents formulated in one or more therapeutically effective compositions. An exemplary composition is formulated for treating hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in a subject, comprising a RIG-I agonist, a vehicle for intracellular delivery, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Function and application of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis
ActiveCN103784943BPrevent restenosisPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseCell phenotype
The invention discloses a function and application of an interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis, belonging to the field of gene functions and applications. According to the application disclosed by the invention, IRF4 gene knockout mice and mild C57 mice are taken as experimental subjects, and a vascular injury model is adopted to carry out neointima formation determination, vascular wall cell proliferation level detection and smooth muscle cell phenotype detection of a vascular injury model mouse; results show that compared with the mild mouse, the IRF4 gene knockout mouse has more distinct neointima formation and cell proliferation, which indicates that the function of the IRF4 gene in scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis is manifested by that the IRF4 gene has effect of inhibiting restenosis caused by vascular injury, especially protecting scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis. As for the function of IRF4, the IRF4 can be used for preparing medicaments for treating angiostenosis, especially medicaments for treating scaffold and endarterectomy restenosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
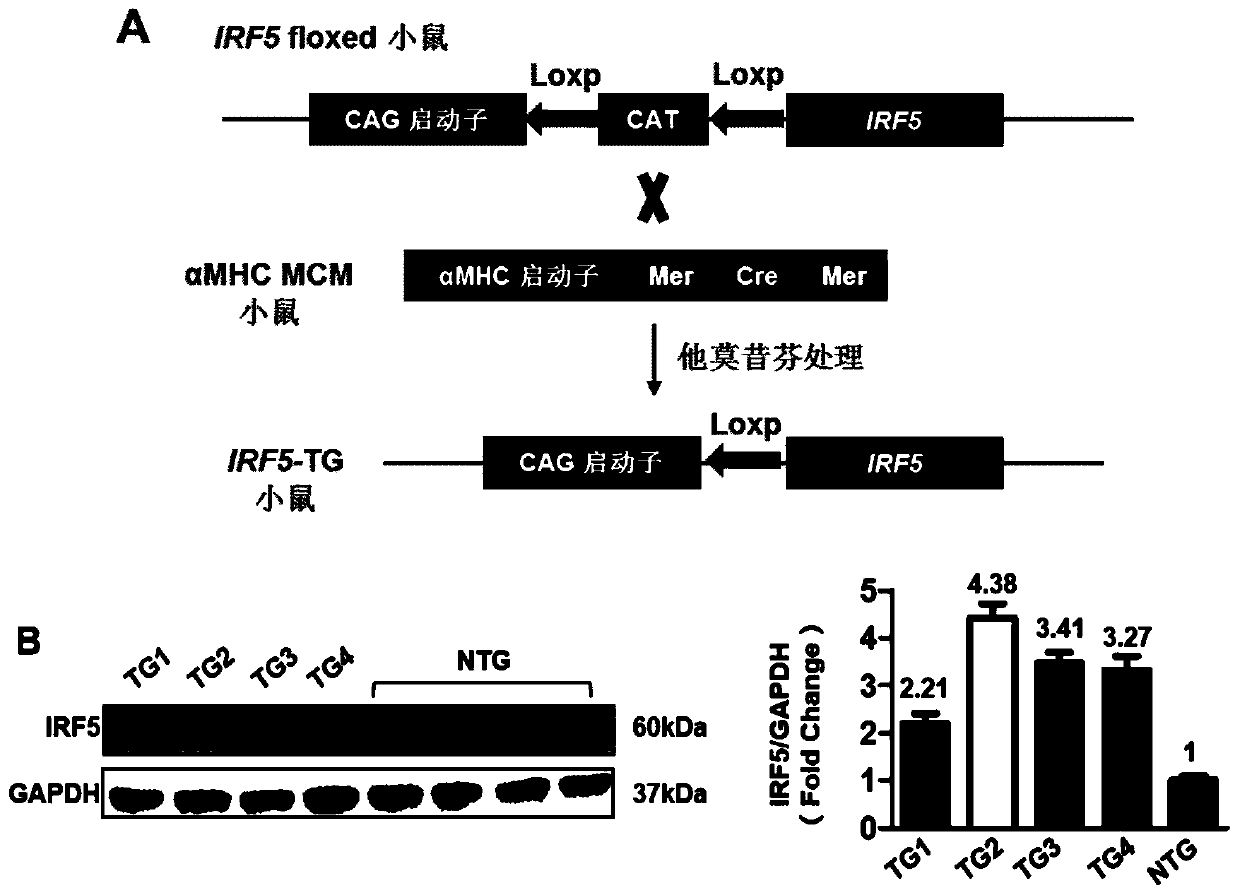
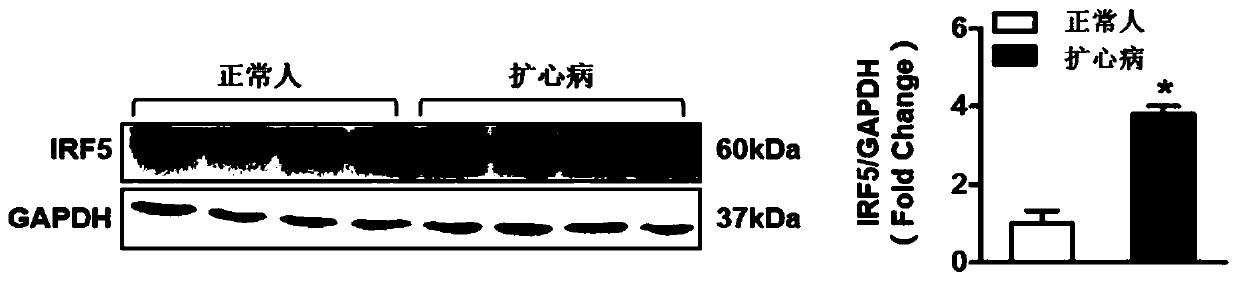
Application of interferon regulatory factor 5 (irf5) and its inhibitors in the treatment of cardiac hypertrophy
ActiveCN106512008BPromote hypertrophyWorsening heart functionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseCardiac muscle
The invention discloses an application of an interferon regulatory factor 5(IRF5) and an inhibitor thereof in treating cardiac hypertrophy, and belongs to the filed of function and application of genes. The application of the interferon regulatory factor 5(IRF5) and the inhibitor thereof in treating cardiac hypertrophy determines the relationships between the expression of IRF5 genes and cardiac hypertrophy disease. The relationships are inhibiting the expression of the IRF5 genes, accordingly remarkably inhibiting cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, and improving cardiac function; promoting the expression of the IRF5 genes, accordingly remarkably promoting cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, and deteriorating cardiac function. Thereby, IRF5 can be adopted as a drug target used for screening drugs which protect cardiac function, prevent, relieve and / or treat cardiac hypertrophy and resist myocardial fibrosis. The inhibitor of IRF5 can be used for preparing drugs which protect cardiac function, prevent, relieve and / or treat cardiac hypertrophy and resist myocardial fibrosis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
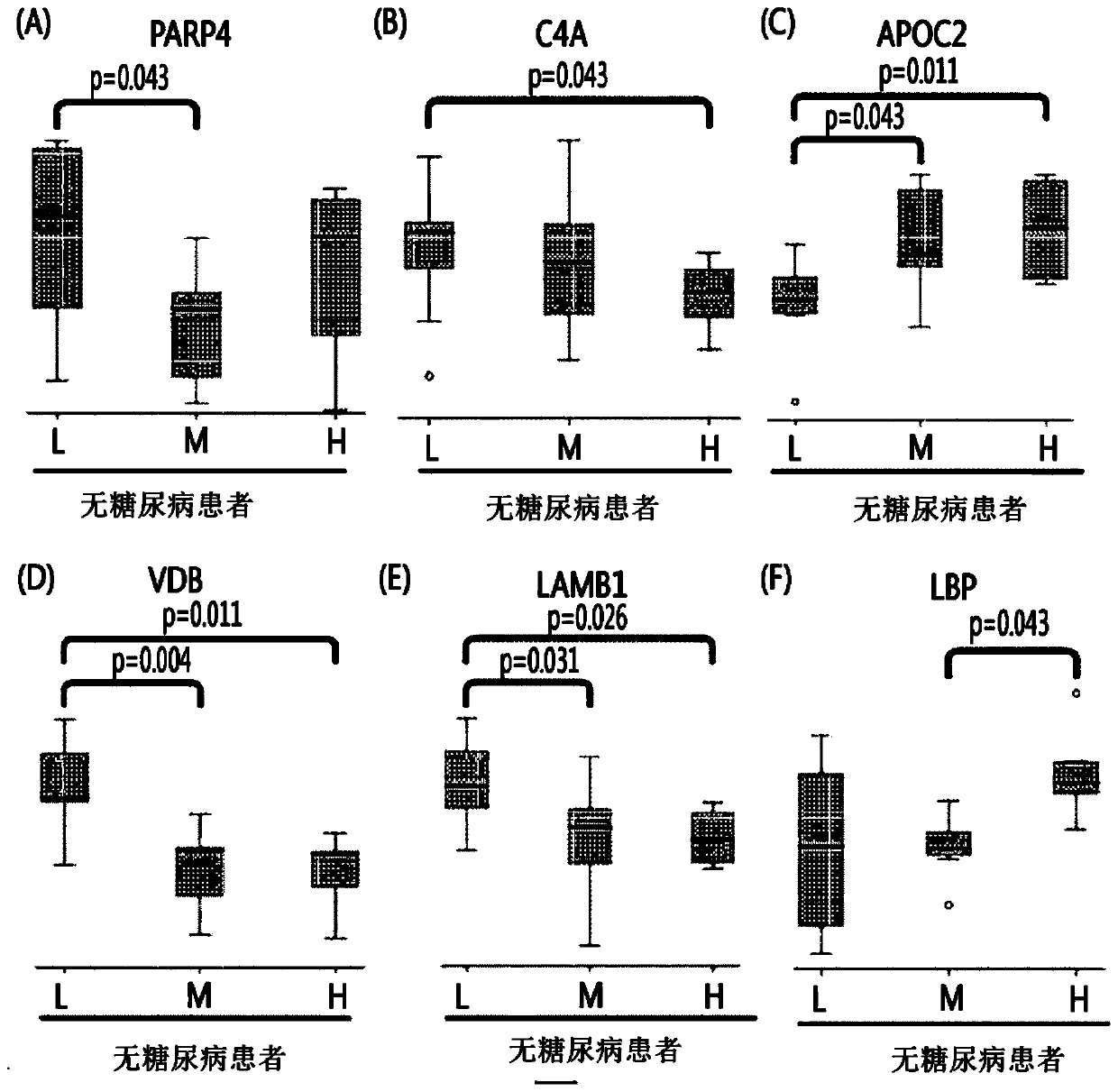
Biomarkers for diagnosing vascular stenotic diseases and their uses
ActiveCN107533064BInfer or grasp the degree of diseaseSimple and Effective Early DiagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsDiseaseCytokinesis
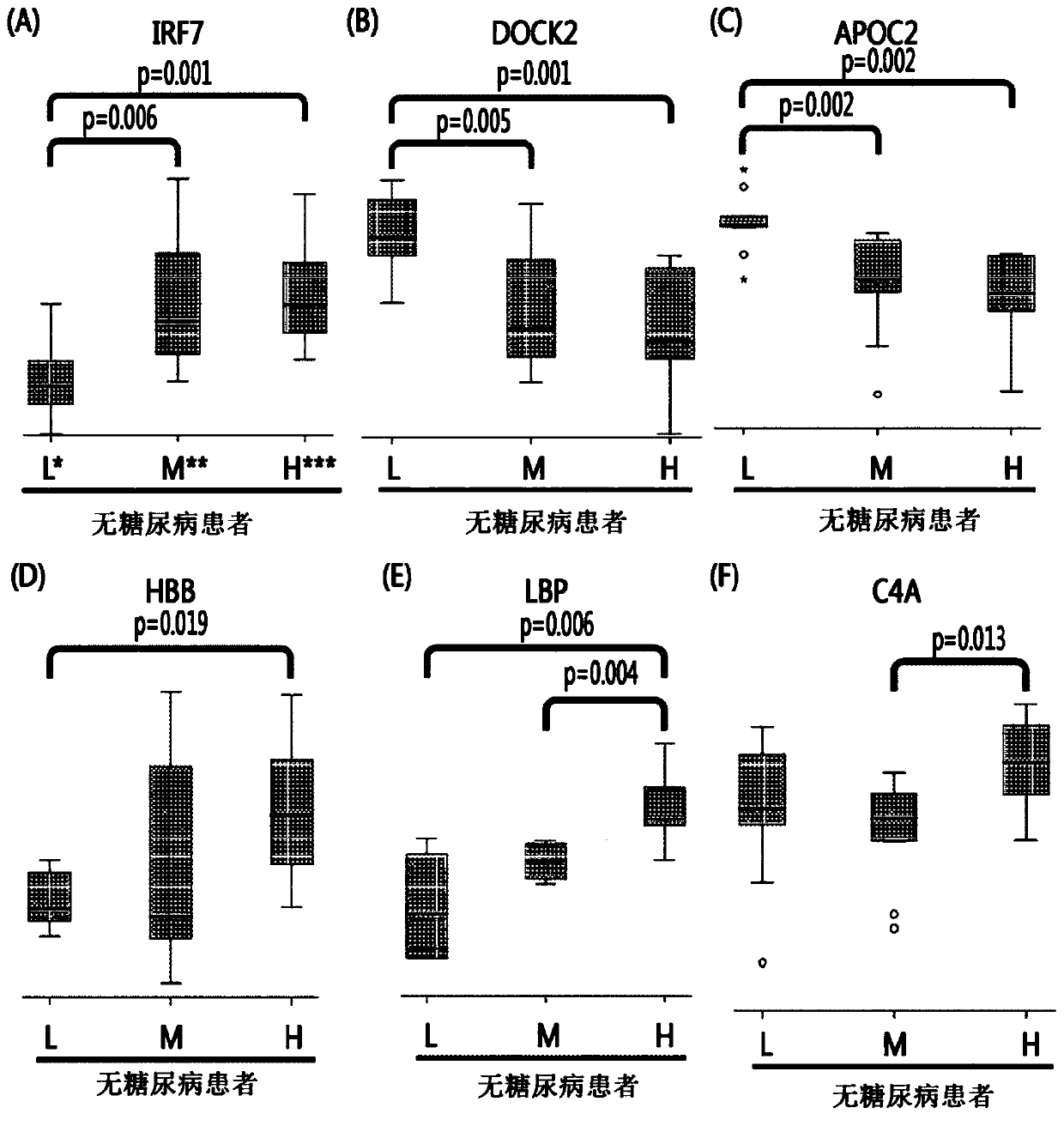
Provided are: a composition for diagnosing non-diabetic angiostenosis, containing a preparation measuring the level of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 4 (PARP4), vitamin D-binding protein (VDB), and laminin subunit beta-1 (LAMB1); a composition for diagnosing diabetic angiostenosis, containing a preparation measuring the level of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7), a dedicator of cytokinesis protein 2 (DOCK2), and a hemoglobin subunit beta (HBB); a kit for diagnosing angiostenosis, containing the composition for diagnosing diabetic angiostenosis; a method for providing information for diagnosing non-diabetic angiostenosis; and a method for providing information for diagnosing non-diabetic angiostenosis. The present invention provides a composition for diagnosing angiostenosis, so as to measure and compare the changing protein expression levels in non-diabetic or diabetic angiostenosis patients, thereby enabling early diagnosis of angiostenosis and a meaningful prediction or an identification of the degree of the disease. In addition, the diagnostic composition of the present invention enables non-invasive diagnosis, thereby enabling simple and valid early stage diagnosis of angiostenosis by using blood and urine testing and the like.
Owner:BERTIS CO LTD
A Bicistronic DNA Vaccine for Grouper Viral Neuronecrosis
ActiveCN113322276BGood immune protectionReduce mortalitySsRNA viruses positive-senseNervous disorderDiseaseNecrovirus
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Treatment of interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to IRF8
Owner:CURNA INC
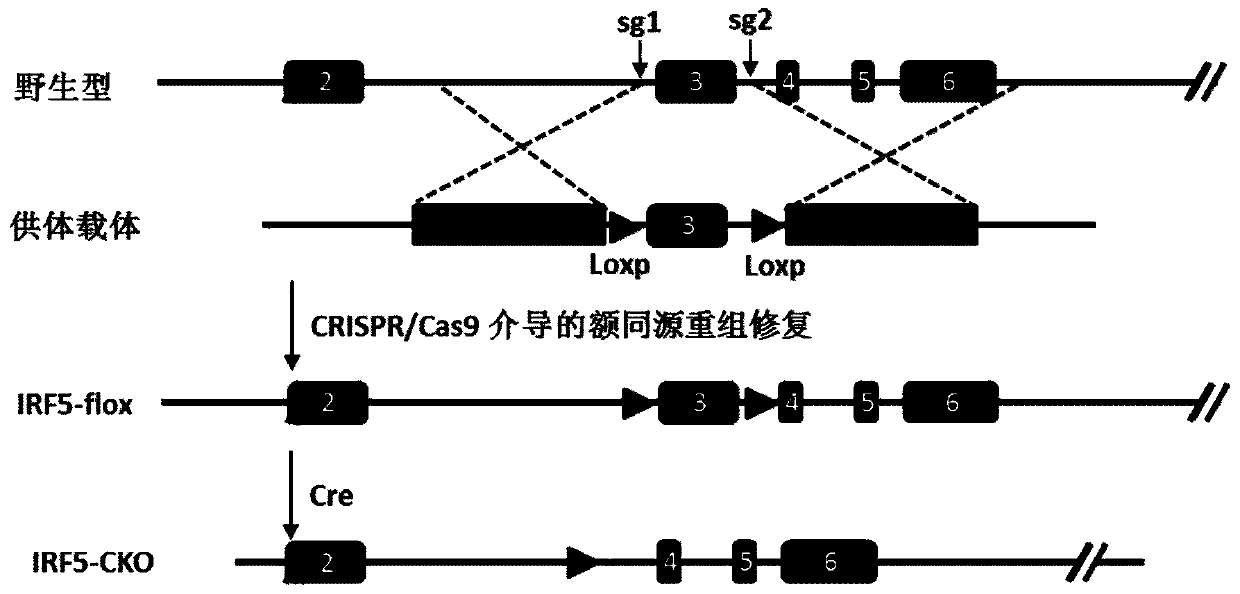
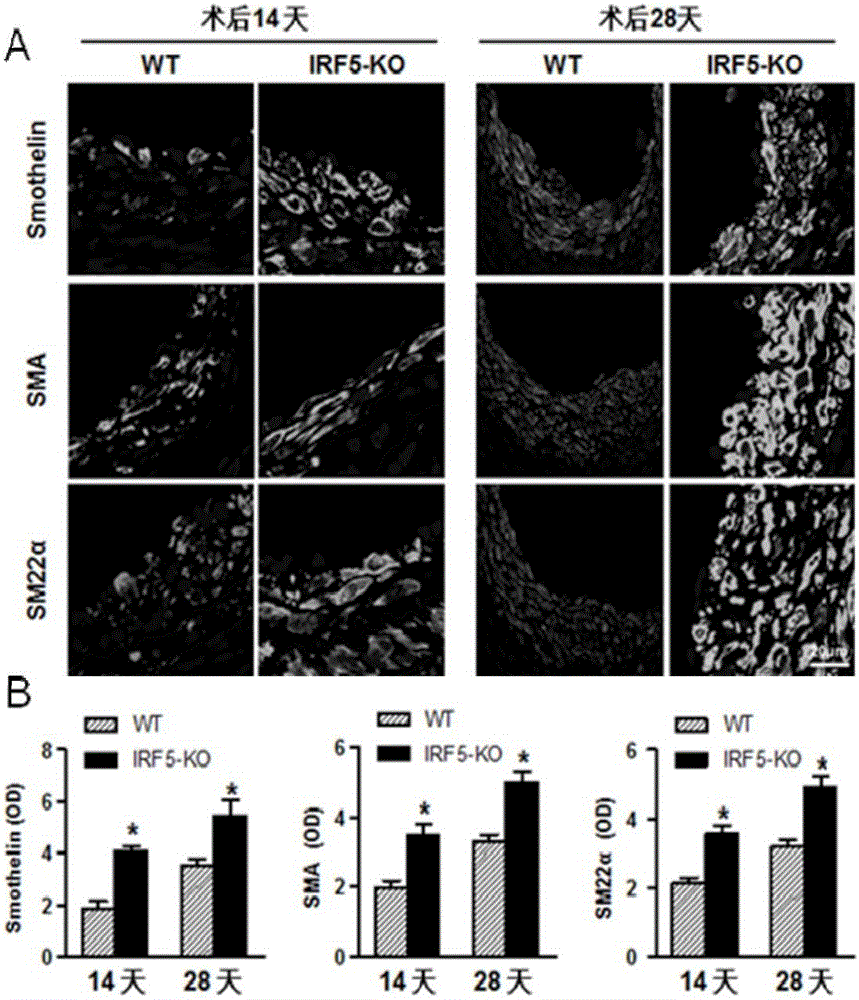
Function and application of IRF5 (interferon regulatory factor-5) and IRF5 inhibitor in treatment of restenosis after VI (vascular injury)
InactiveCN106390142AHave a restenotic effectPrevent restenosisCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCell phenotype
The invention discloses a function and an application of an IRF5 (interferon regulatory factor-5) and an IRF5 inhibitor in treatment of restenosis after VI (vascular injury). An IRF5 gene knockout mouse and a wild mouse are taken as experimental subjects, detection of intima neogenesis, vessel wall cell proliferation level and smooth muscle cell phenotype transformation of the mice are performed through a VI model, and results show that IRF5 gene knockout can obviously inhibit intima neogenesis and cell proliferation and inhibit transformation of smooth muscle cells from contractile phenotype to synthetic phenotype. Therefore, the function of the IRF5 on treatment of restenosis after VI mainly lies in promoting intima neogenesis, cell proliferation and smooth muscle cell phenotype transformation. Based on the function of the IRF5, the IRF5 can be taken as a drug target to be used for screening drugs for preventing and treating restenosis after VI, and the IRF5 inhibitor can be used for preparing a drug and an arterial stent for preventing and treating restenosis after VI.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
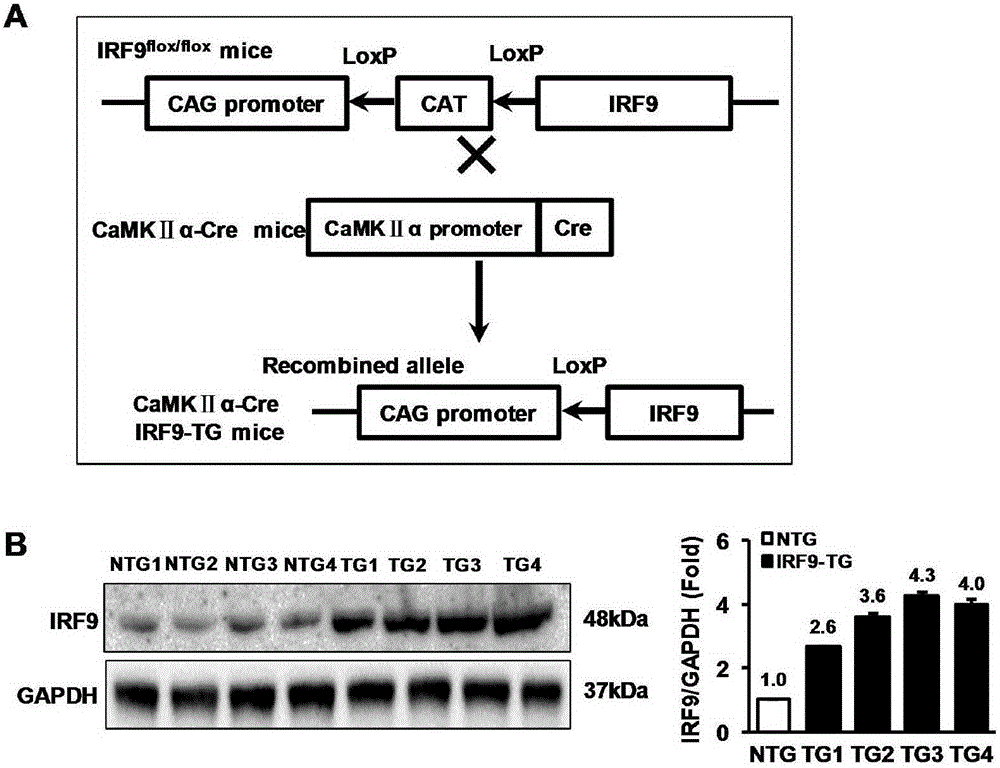
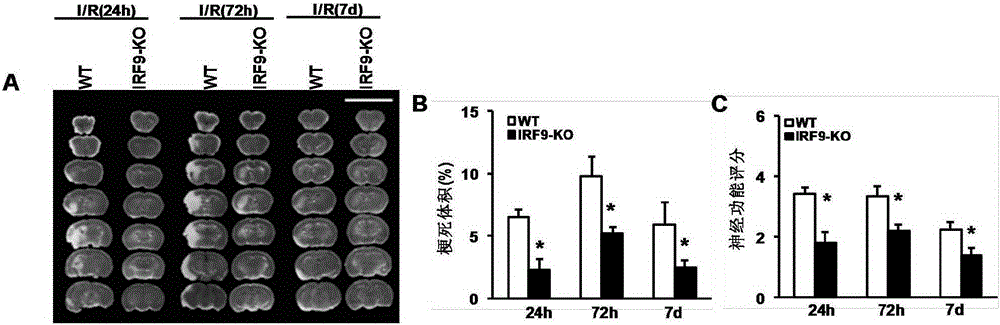
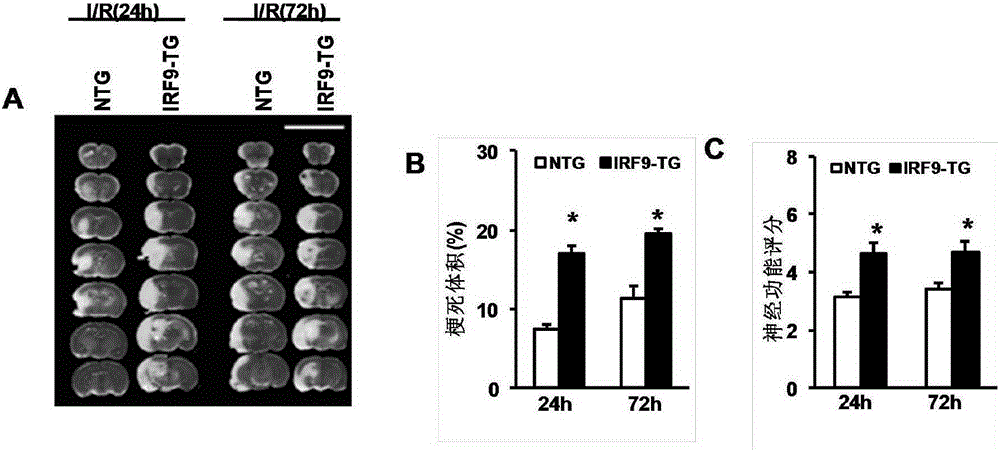
Application of interferon regulatory factor 9 (irf9) and its inhibitors in stroke diseases
ActiveCN103751803BExacerbation of stroke diseaseNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The invention discloses interferon regulatory factor 9 (IRF9) and application of an inhibitor thereof in cerebral apoplexy, belonging to the field of gene function and application. The invention uses IRF9 gene knock-out mice and brain-specific IRF9 transgenic mice as experimental subjects and adopts middle cerebral artery ischemia reperfusion model, results show that compared with mild type C57 mouse, the brain infarction volume of IRF9 gene knock-out mouse is apparently inhibited, and nerve function is improve remarkably, while the infarction volume of nerve-specific IRF9 transgenic mouse is apparently inhibited, and nerve function is deteriorated markedly. Therefore, IRF9 gene has nervous system function deterioration effect; especially, IRF9 gene can deteriorate cerebral apoplexy. As for the above function of IRF9, the invention provides application of IRF9 as drug target of cerebral apoplexy treatment in developing medicaments for treating cerebral apoplexy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Bicistronic DNA vaccine for grouper viral nervous necrosis
ActiveCN113322276AGood immune protectionReduce mortalitySsRNA viruses positive-senseNervous disorderBicistronic mrnaHumoral immune reaction
The invention provides a bicistronic DNA vaccine for grouper viral nervous necrosis, which is a recombinant eukaryotic expression vector, and the recombinant eukaryotic expression vector can simultaneously express P-domain of nervous necrosis virus capsid protein and superfamily structural domain of garrupa interferon regulatory factor 3 protein. The bicistronic DNA vaccine for resisting the nervous necrosis virus, prepared by the invention, is transfected into a fish body, so that a nervous necrosis virus capsid protein P-domain and a superfamily structural domain of interferon regulatory factor 3 protein of a host can be well expressed. The prepared nervous necrosis virus resistant bicistronic DNA vaccine enhances the nervous necrosis virus infection resistance of fish bodies, reduces the death rate of the fish bodies infected with viruses, enhances humoral immunity of the fish bodies caused by the vaccine, causes all-around immune response of the fish bodies, and provides a good immune protection effect for the fish bodies.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com