Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Implant procedures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
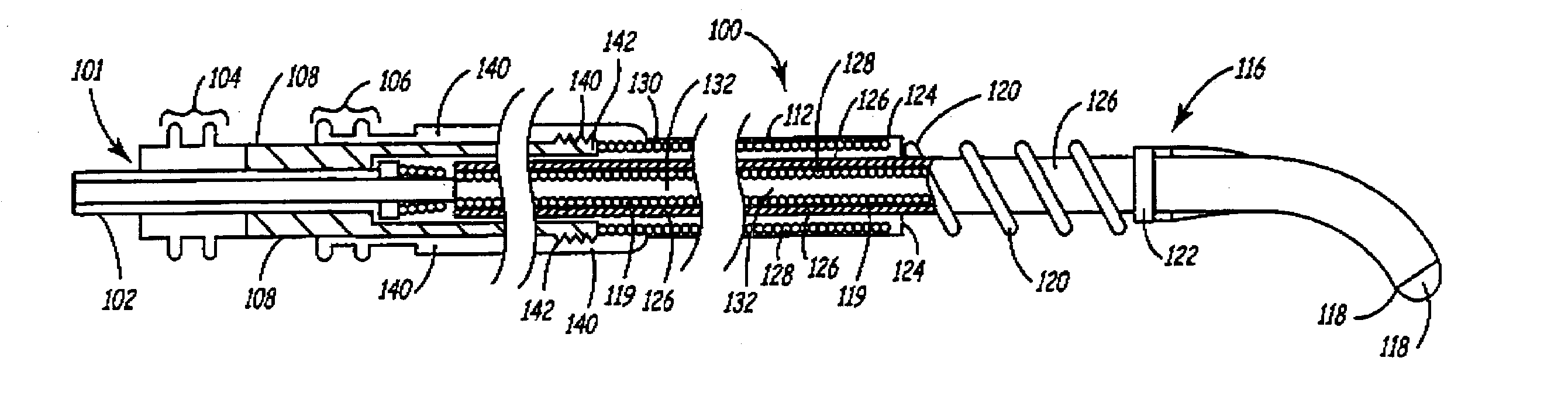
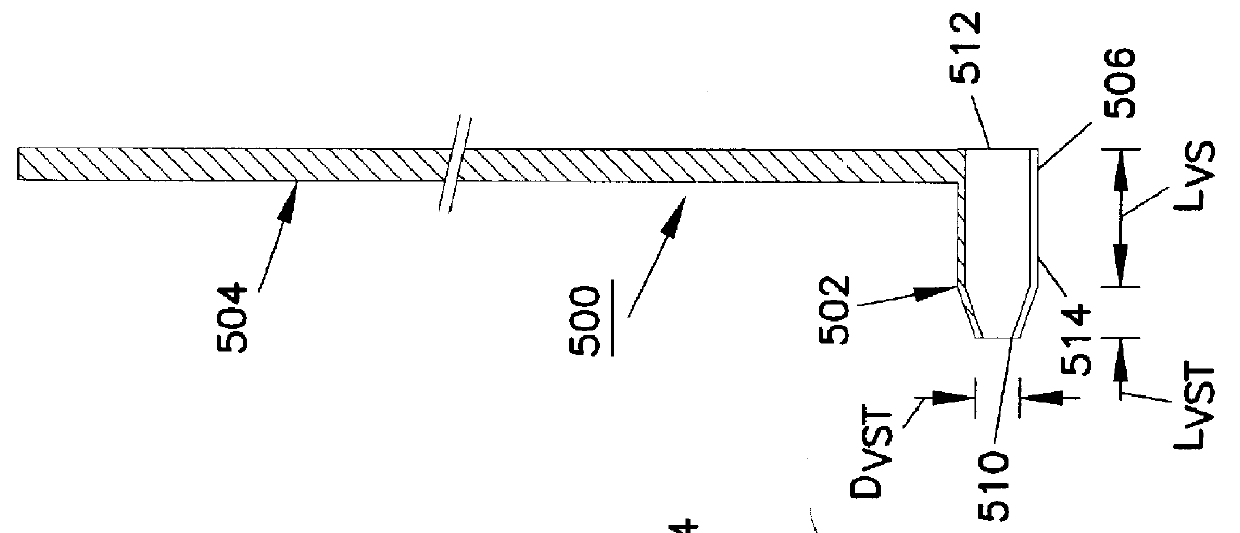
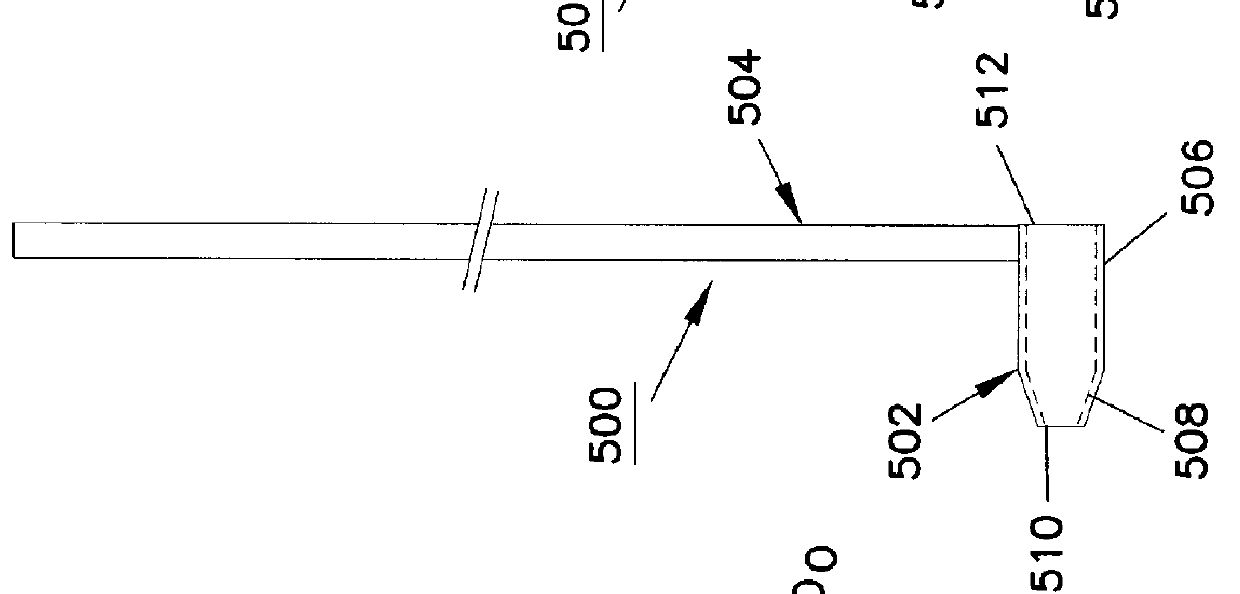
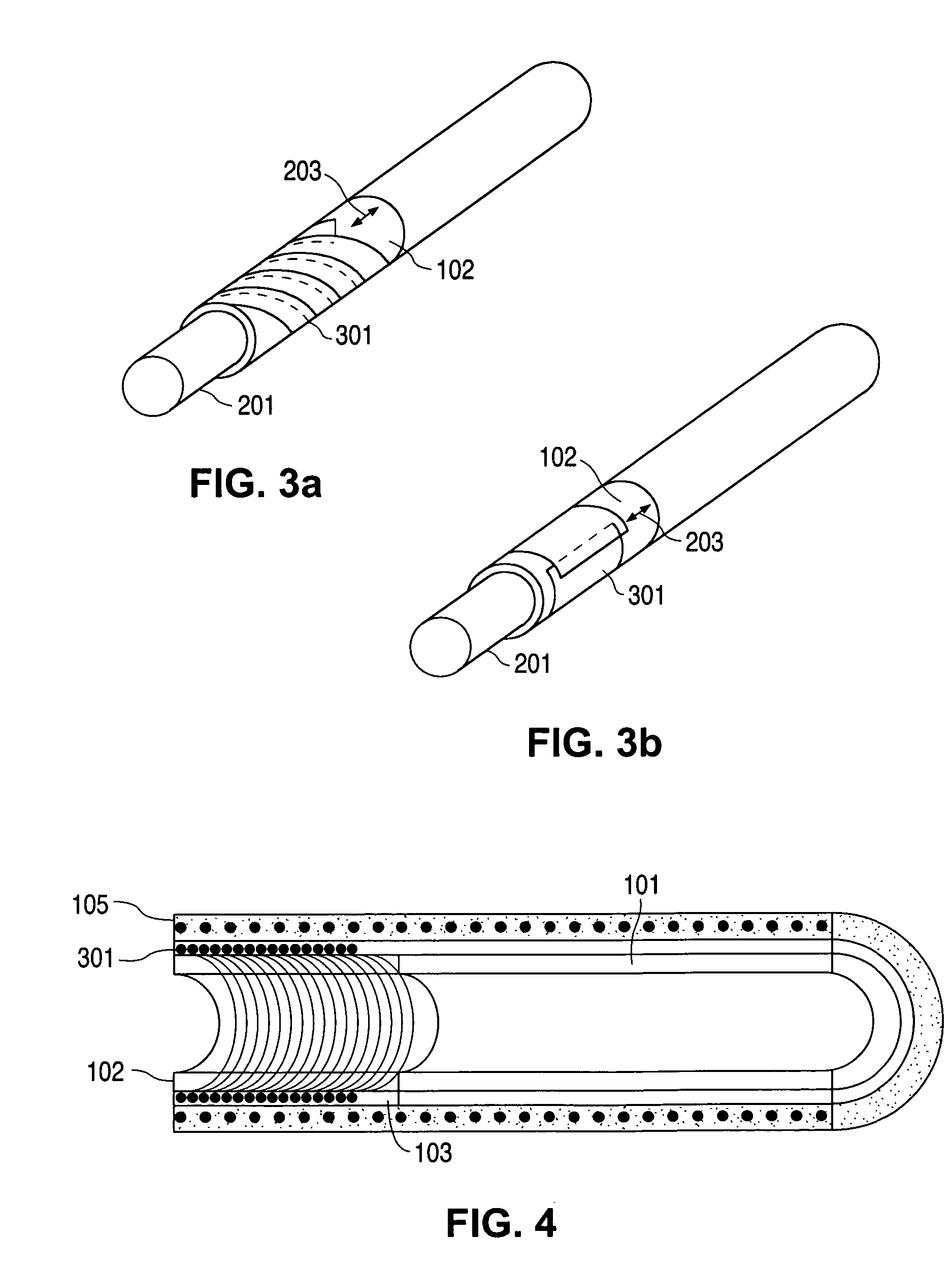
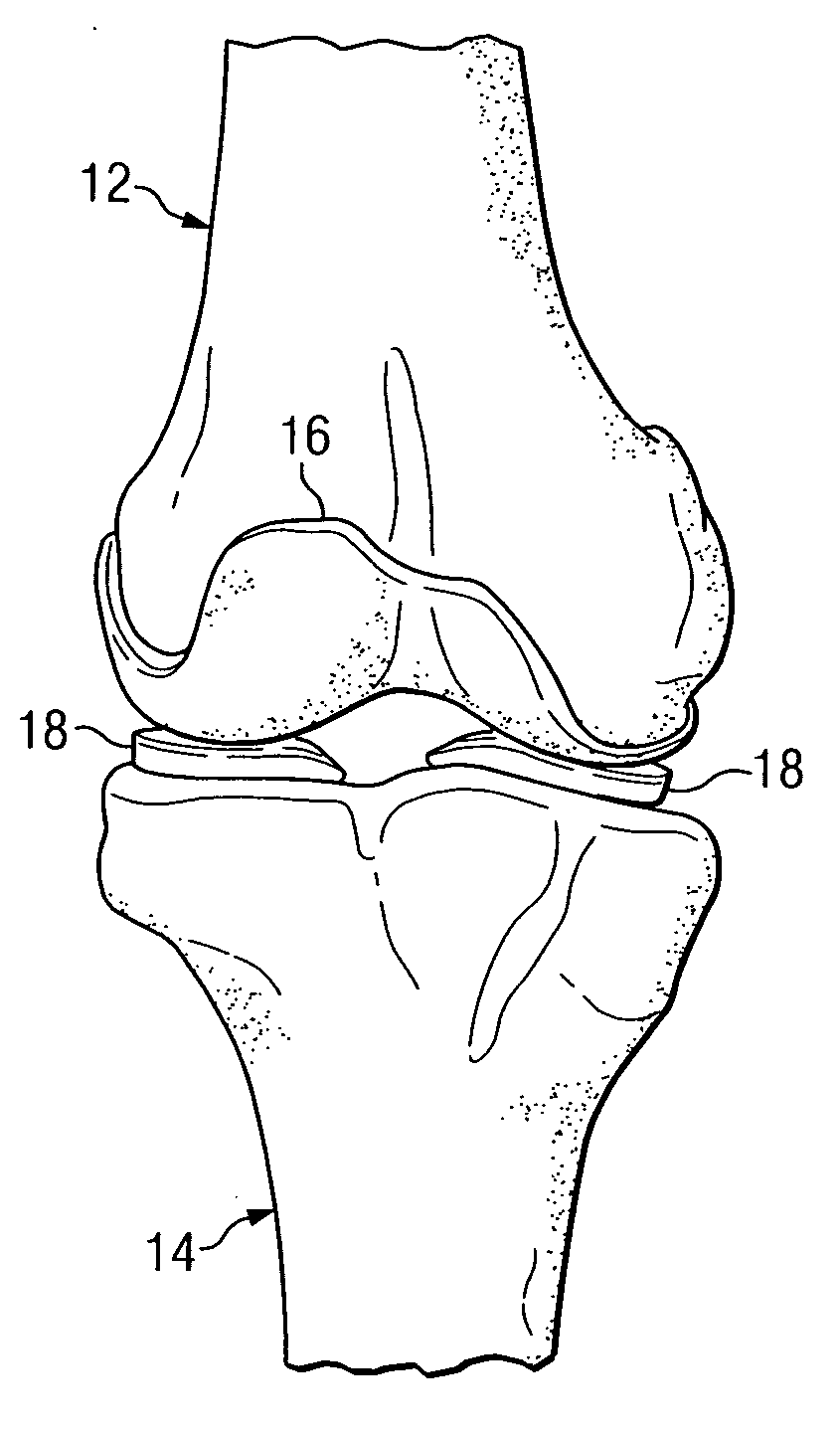
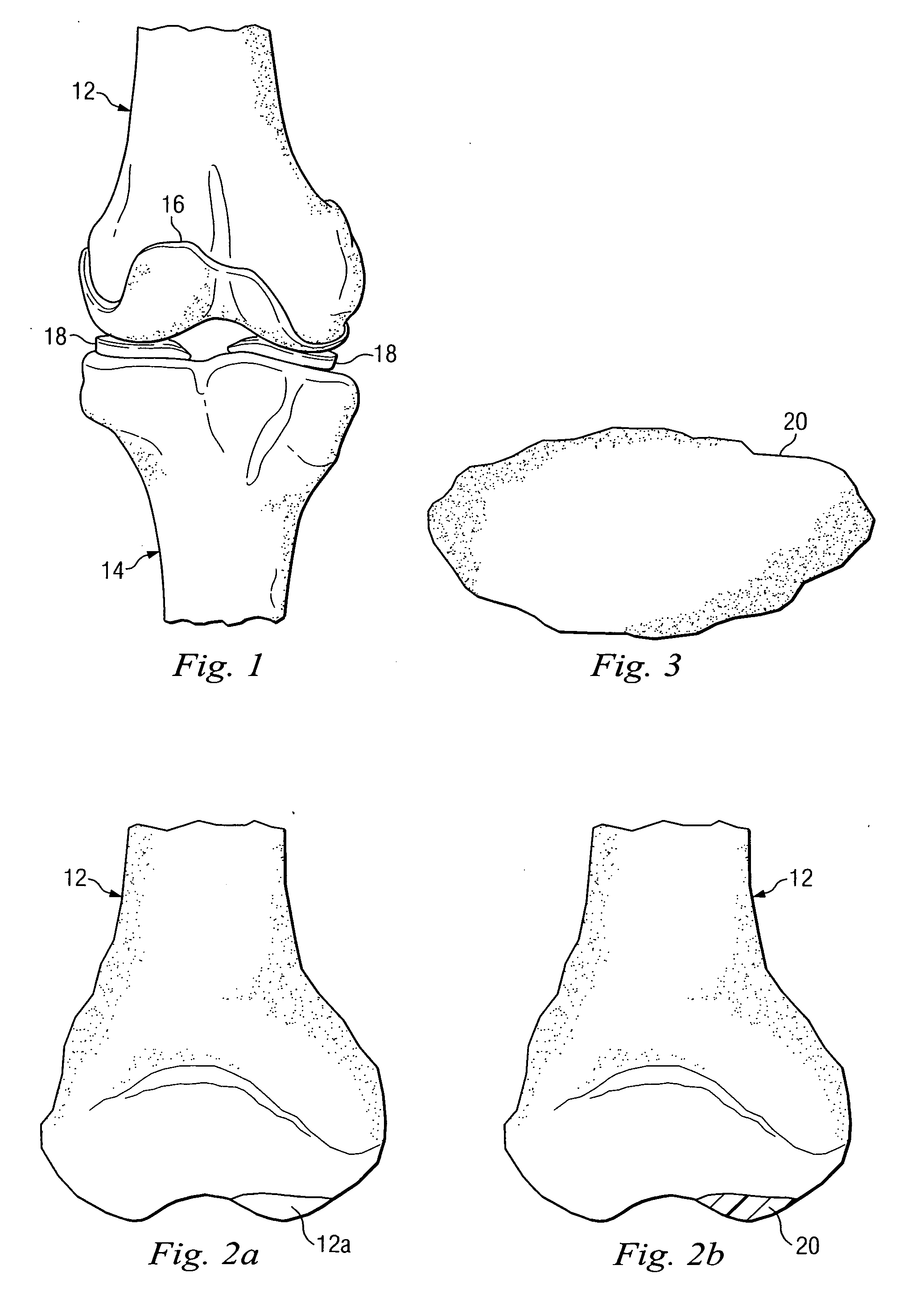
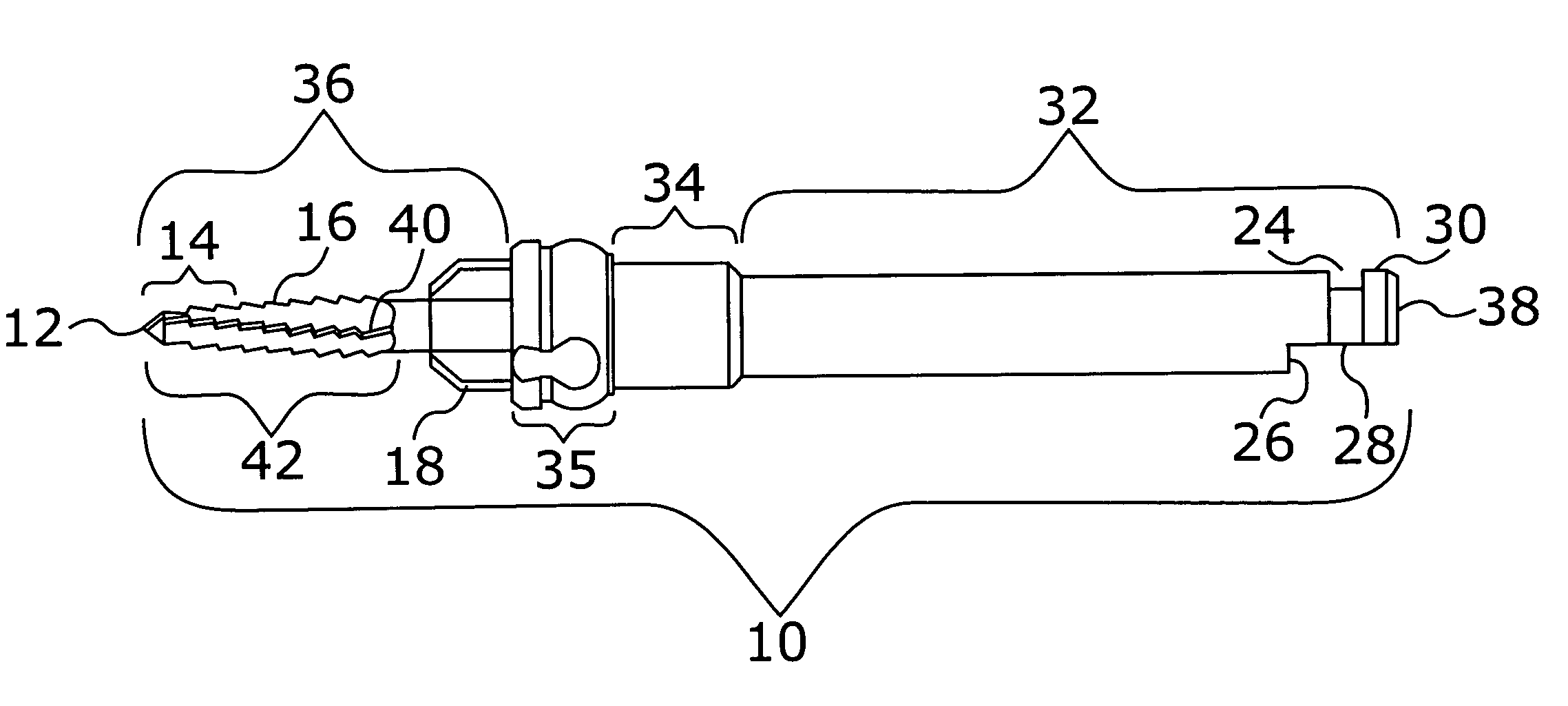
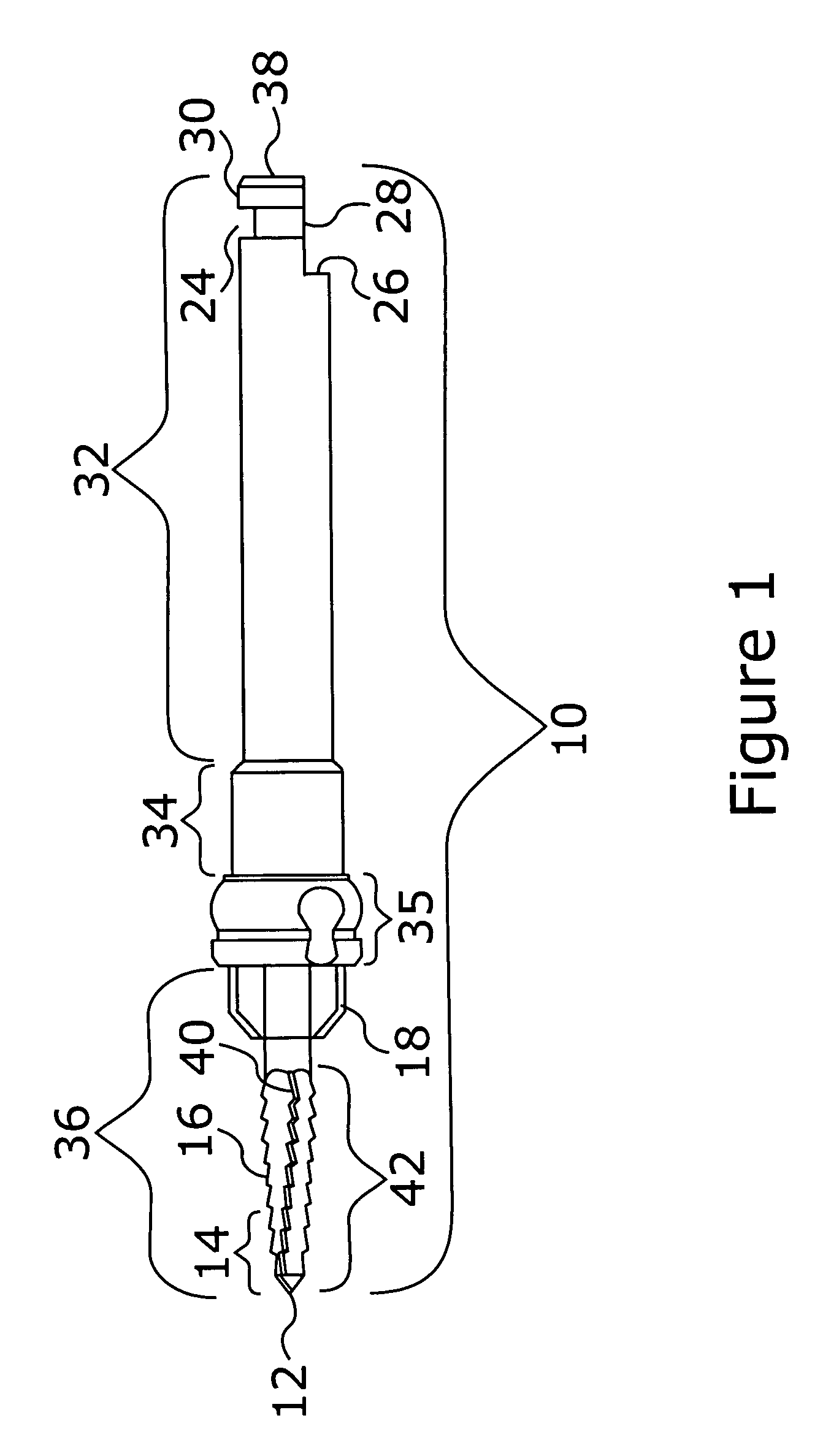
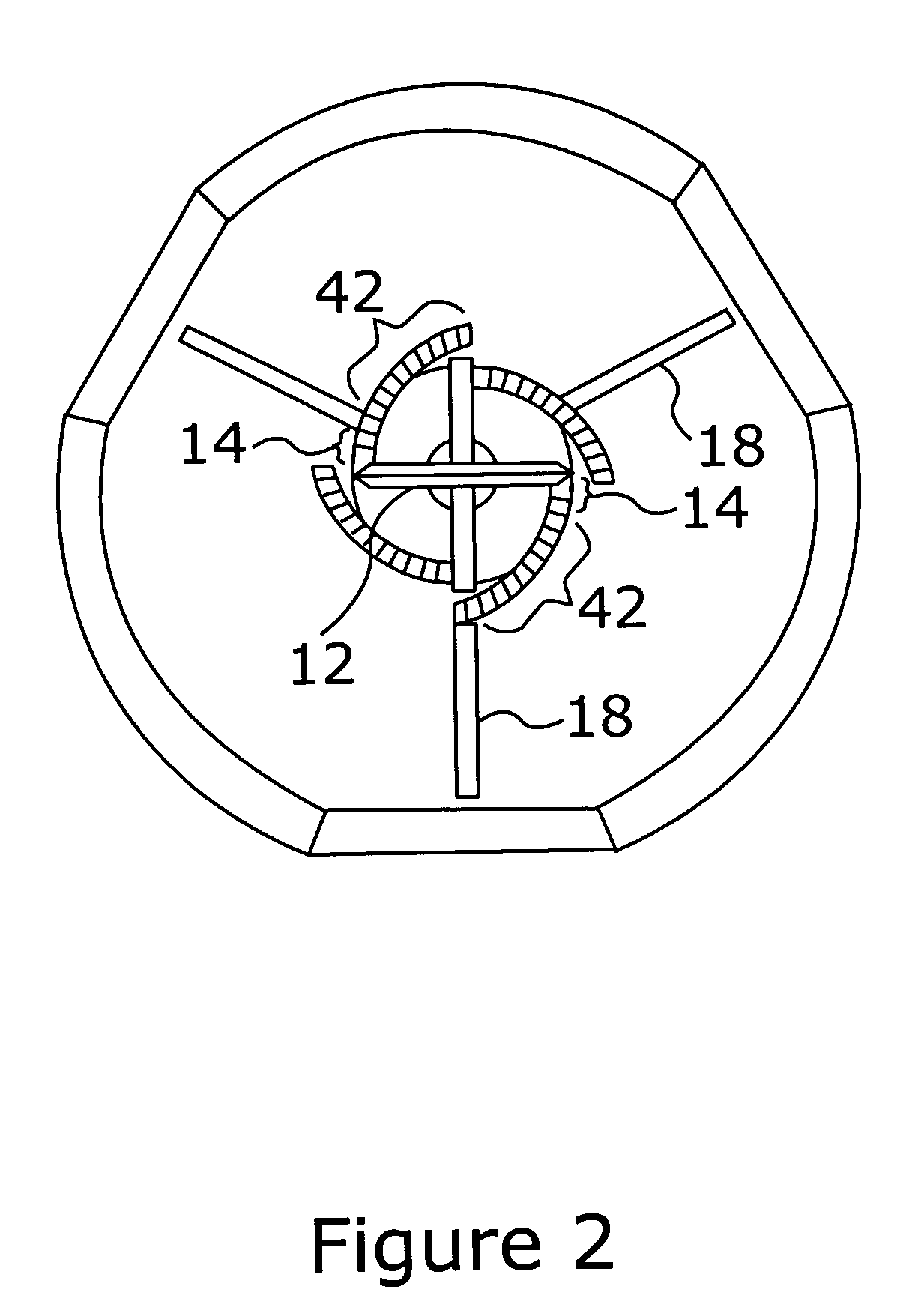
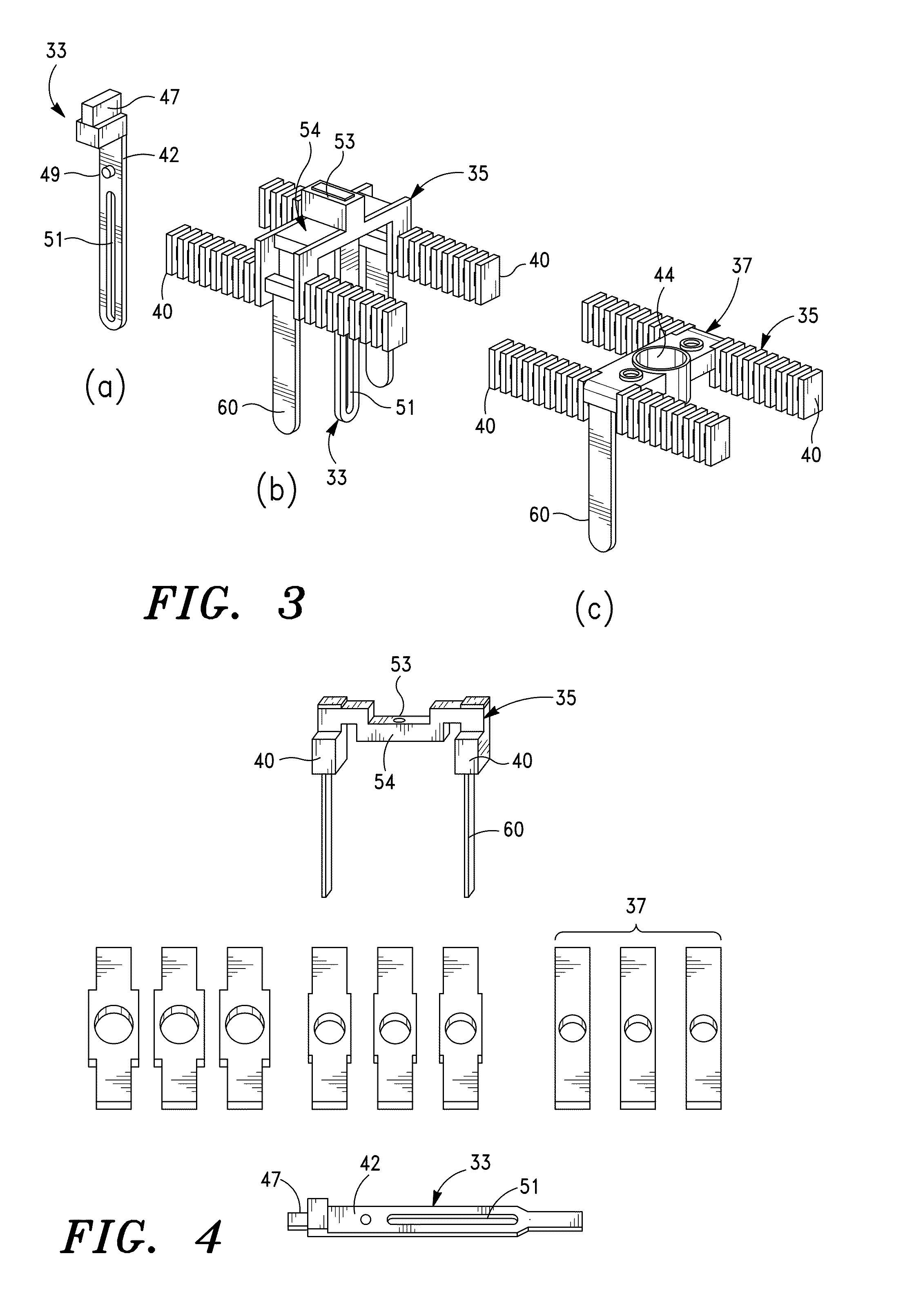
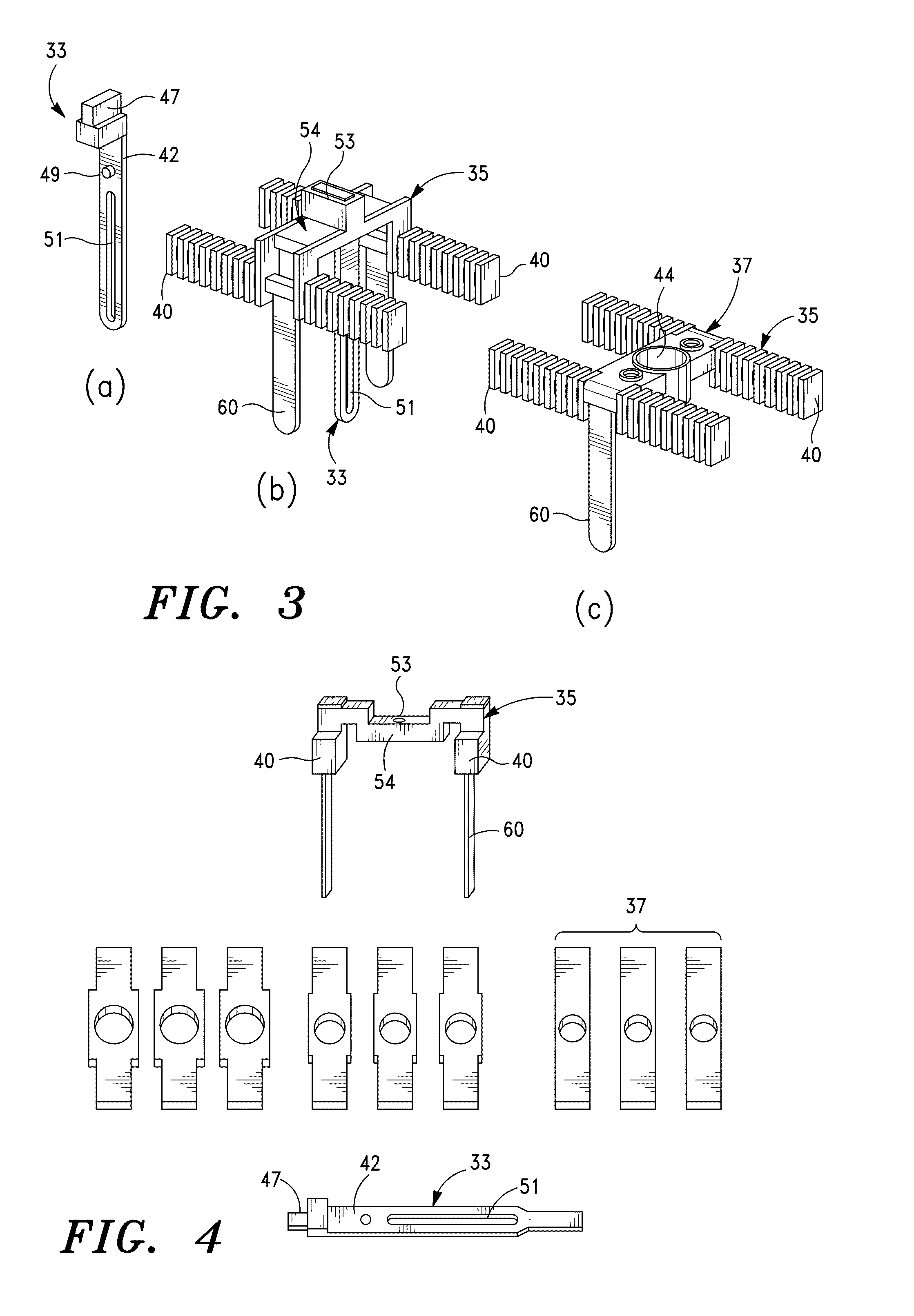
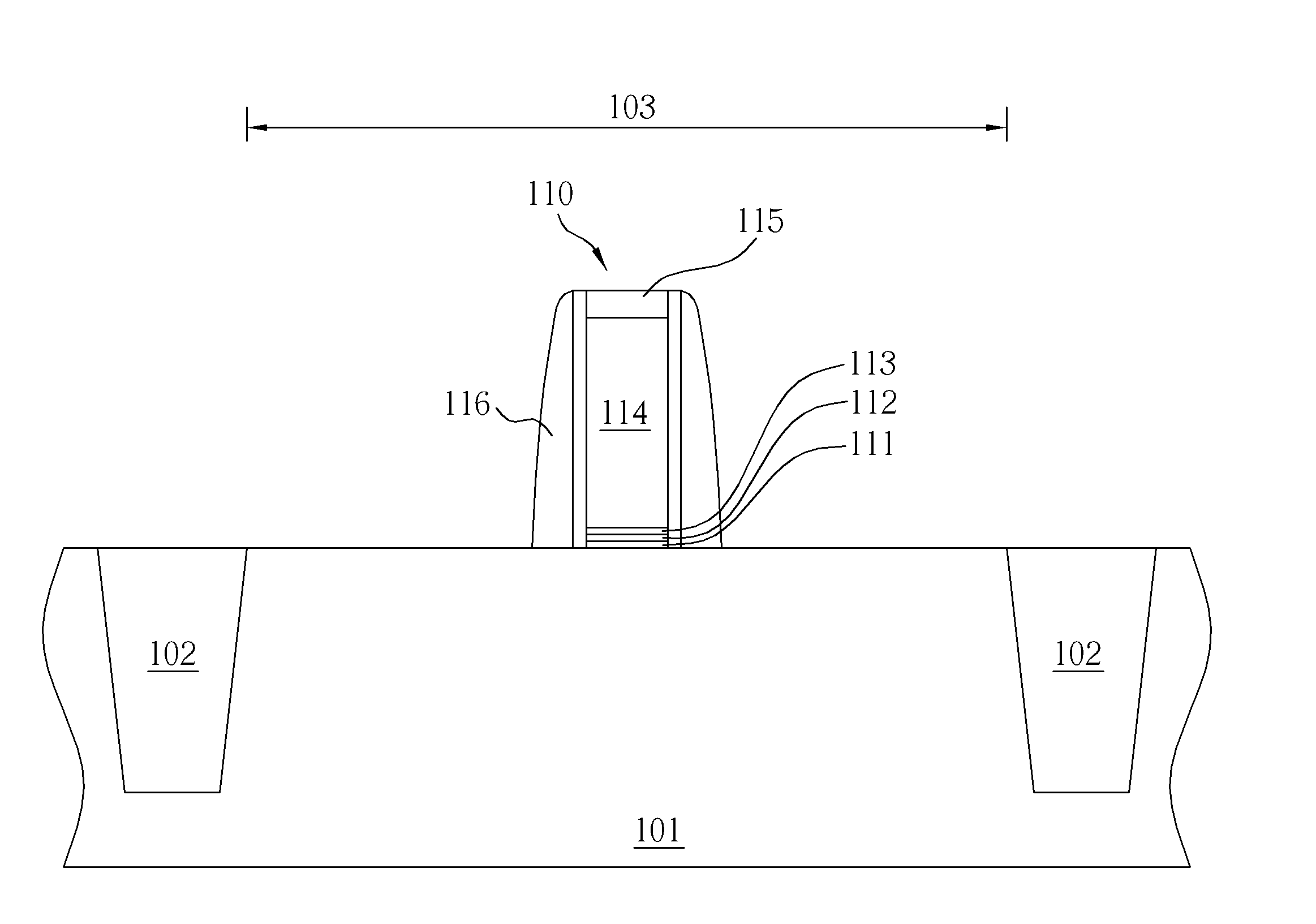
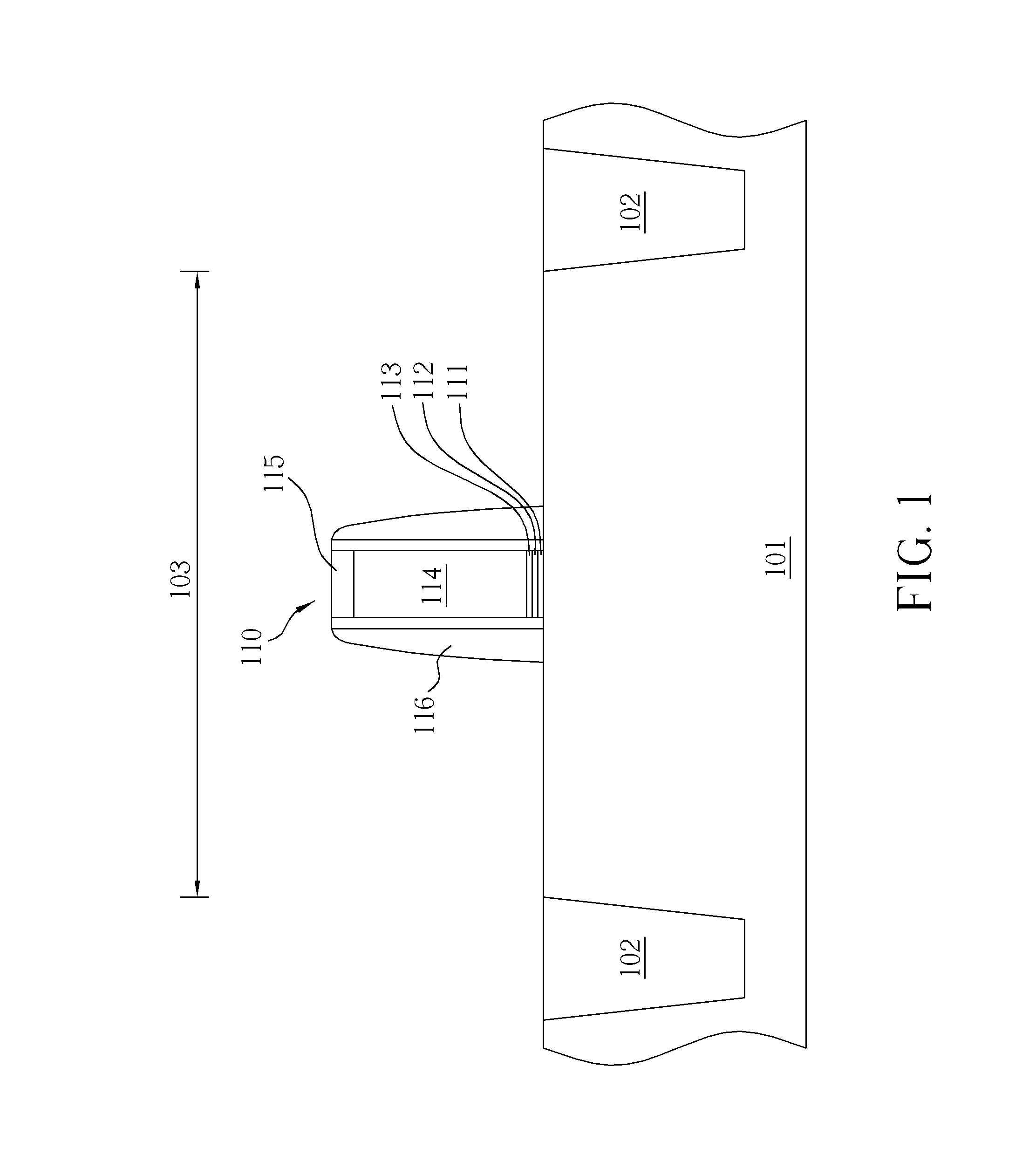
Deployable medical lead fixation system and method
InactiveUS7107105B2Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesReticular formationLead extraction
An improved medical lead assembly and method of use is provided. The lead assembly includes a lead body, and a spring member positioned adjacent to the lead body. The spring member may be deployed a selectable amount to maintain the lead body in a fixed location within a patient's body. The spring member may be an expandable coil, a mesh structure that is similar to a stent, or any other similar device that may be positioned in a low-profile state during a lead implant procedure. After the lead is positioned at a target destination, the spring member may be deployed an amount that is selected based on the characteristics of the surrounding tissue, including vessel size. According to one aspect of the invention, the lead assembly may provide means for facilitating chronic lead extraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
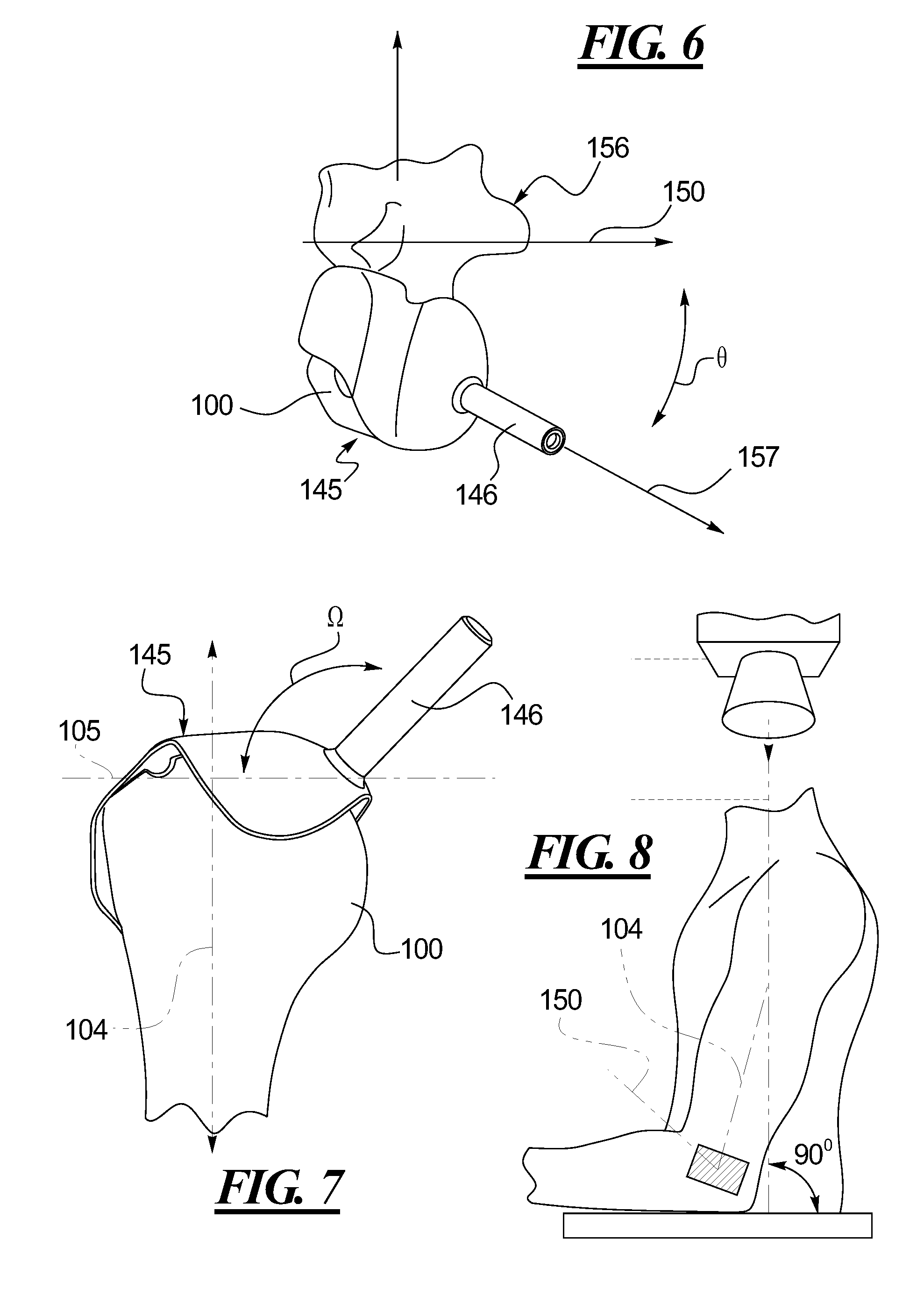
Methods and devices for installing standard and reverse shoulder implants
Surgical procedures, tools and implants are disclosed for both conventional and reverse shoulder implant surgeries. The improved procedures, tools and implants relate to humeral head resurfacing, humeral head resection for standard implants, humeral head resection for reverse shoulder implants, glenoid resurfacing for standard shoulder implants and glenoid resurfacing for reverse shoulder implants. 3D scans and x-rays are used to develop virtual models of the patient anatomy, identify patient specific landmarks for anchoring guide wire installation blocks, templates and drill guides. 3D scans are also used to design patient specific tools and implants for the shoulder implant procedures and to pre-operatively determine the appropriate inclination and retroversion angles.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
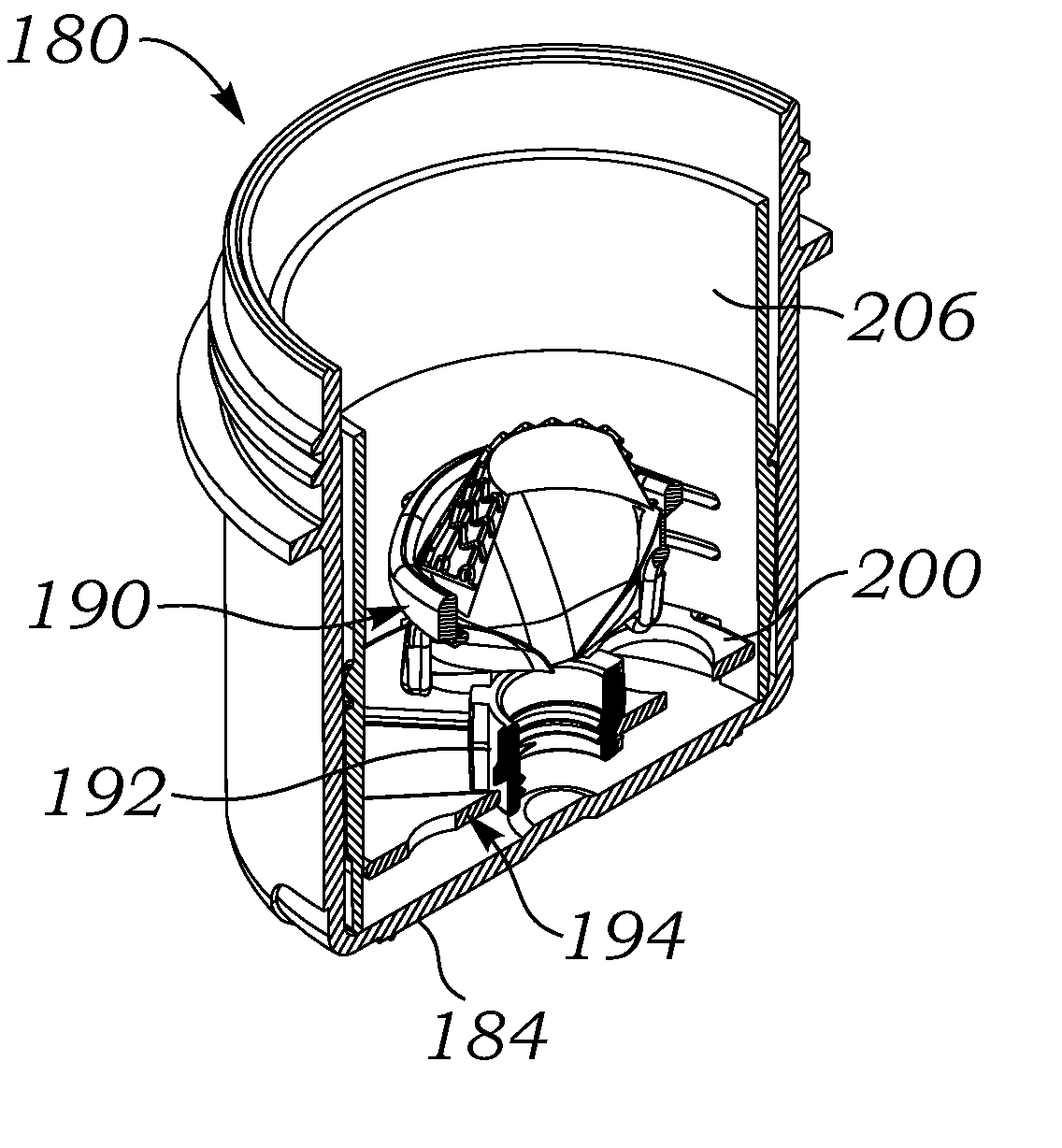
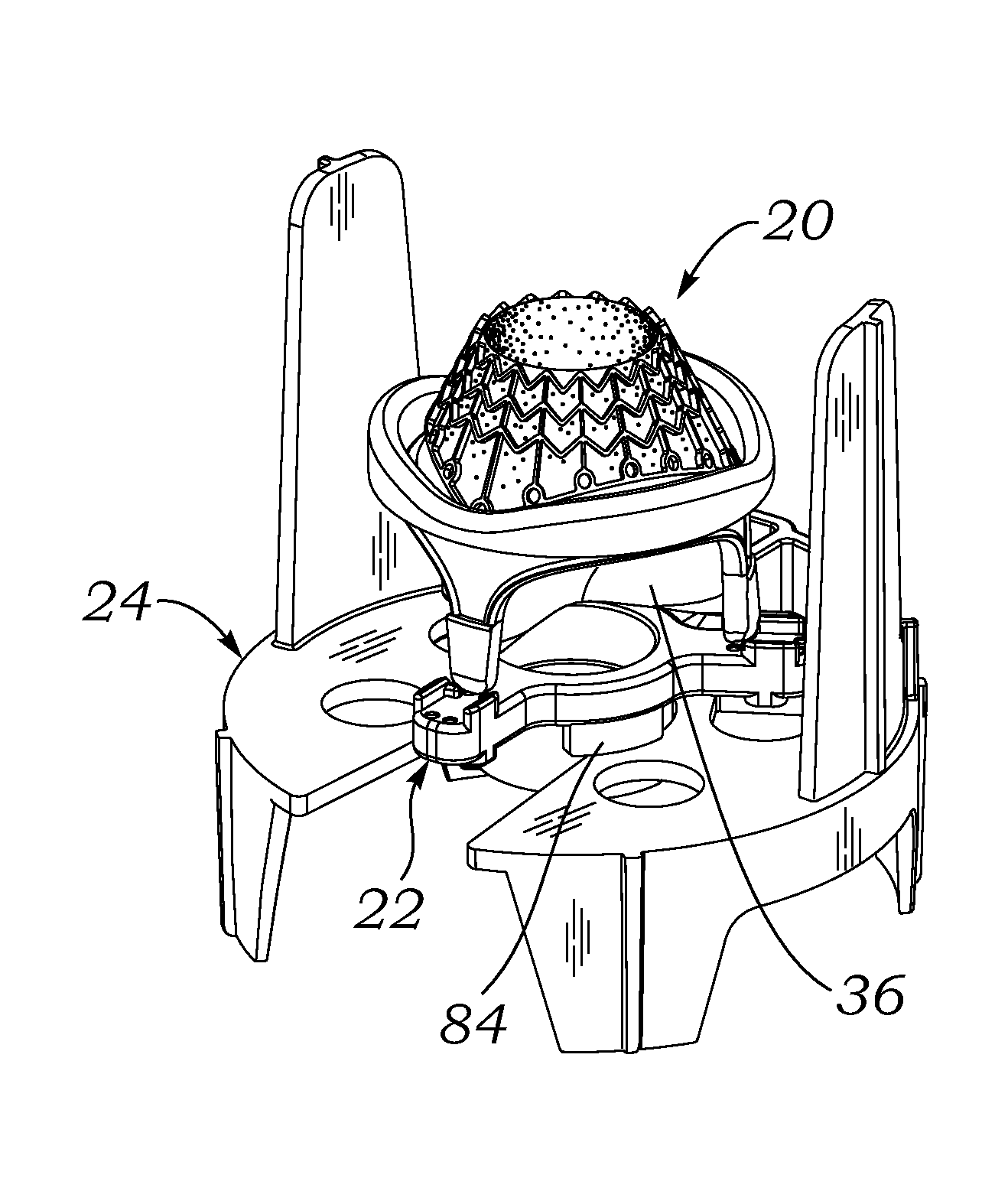
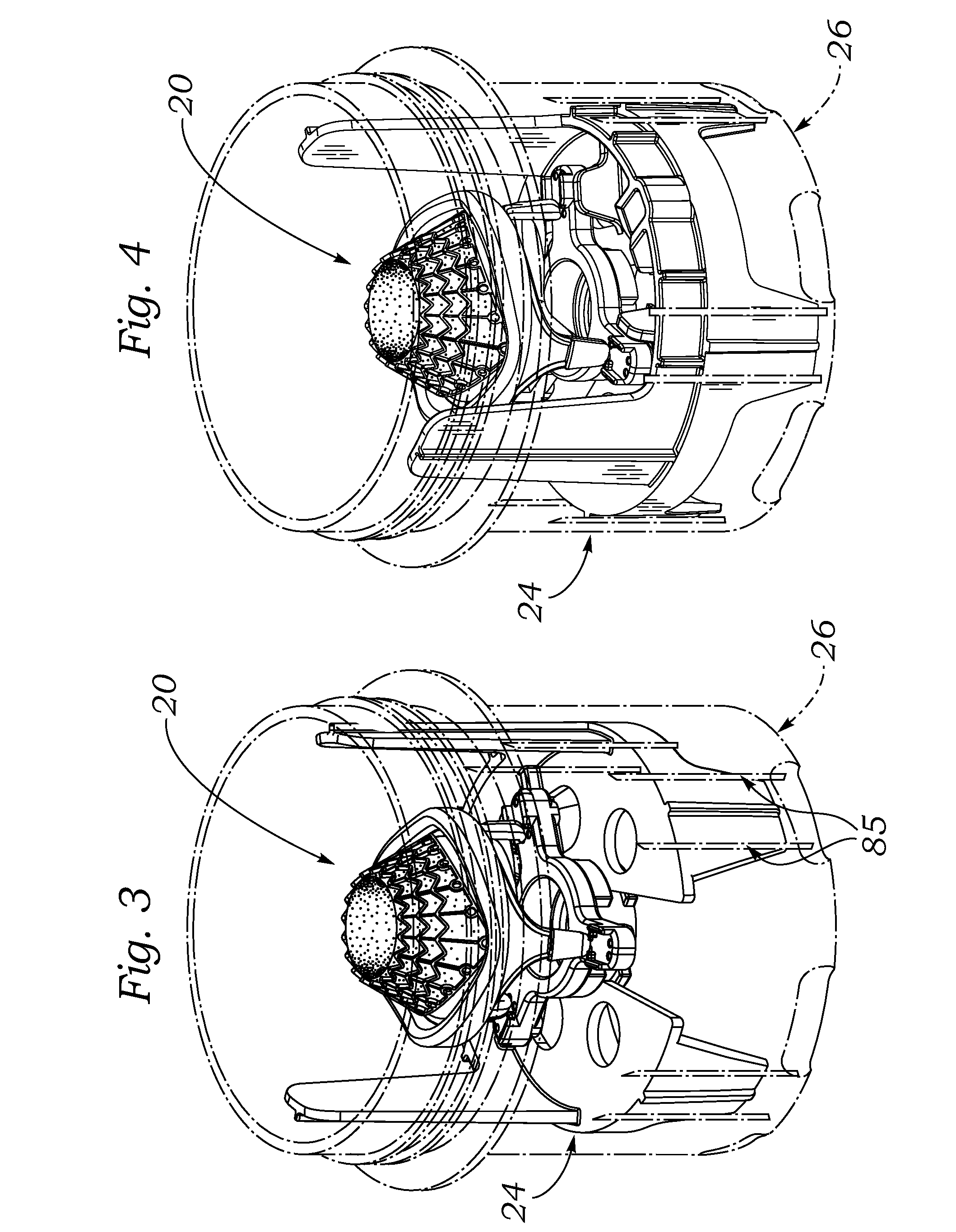
Prosthetic heart valve packaging and deployment system
ActiveUS20110147251A1Easy retrievalGood adhesionHeart valvesDiagnosticsInsertion stentProsthetic heart
Packaging for prosthetic heart valves including an assembly for securely retaining a heart valve within a jar and facilitating retrieval therefrom. The assembly includes a packaging sleeve that fits closely within the jar and has a clip structure for securing a valve holder. Contrary to previous designs, in one embodiment the valve holder is directed downward into the jar, and the valve is retained with an inflow end upward. The valve may have flexible leaflets, and a leaflet parting member on the end of the shaft extends through the leaflets and couples with the valve holder. The assembly of the packaging sleeve, valve, and holder can then be removed from the jar and a valve delivery tube connected with the holder, or to the leaflet parting member. The packaging sleeve may be bifurcated into two halves connected at a living hinge to facilitate removal from around the valve / holder subassembly. The packaging system facilitates attachment of the valve delivery tube for use in a quick-connect valve implant procedure.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device for regeneration of articular cartilage and other tissue
InactiveUS20050074481A1Good adhesionMinimizes procedural discomfortBone implantMammal material medical ingredientsSubchondral boneOsteoblast
An implantable device for facilitating the healing of voids in bone, cartilage and soft tissue is disclosed. A preferred embodiment includes a cartilage region comprising a polyelectrolytic complex joined with a subchondral bone region. The cartilage region, of this embodiment, enhances the environment for chondrocytes to grow articular cartilage; while the subchondral bone region enhances the environment for cells which migrate into that region's macrostructure and which differentiate into osteoblasts. A hydrophobic barrier exists between the regions, of this embodiment. In one embodiment, the polyelectrolytic complex transforms to hydrogel, following the implant procedure.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Transmyocardial implant procedure and tools
A blood flow path is formed from a heart chamber to a coronary vessel on an exterior surface of a heart wall. A hollow conduit has a vessel portion and a myocardial portion. The vessel portion has an open leading end sized to be inserted into the coronary vessel. The myocardial portion has an open leading end and the myocardium portion is sized to extend through a thickness of the heart wall. The myocardial portion is placed in the heart wall with the open leading end of the myocardial portion protruding into the heart chamber. Blood flow through the conduit from the heart chamber is at least partially blocked. The leading end of the vessel portion is placed in the coronary vessel. Blood flow through the conduit from the heart chamber and into the vessel is then opened.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
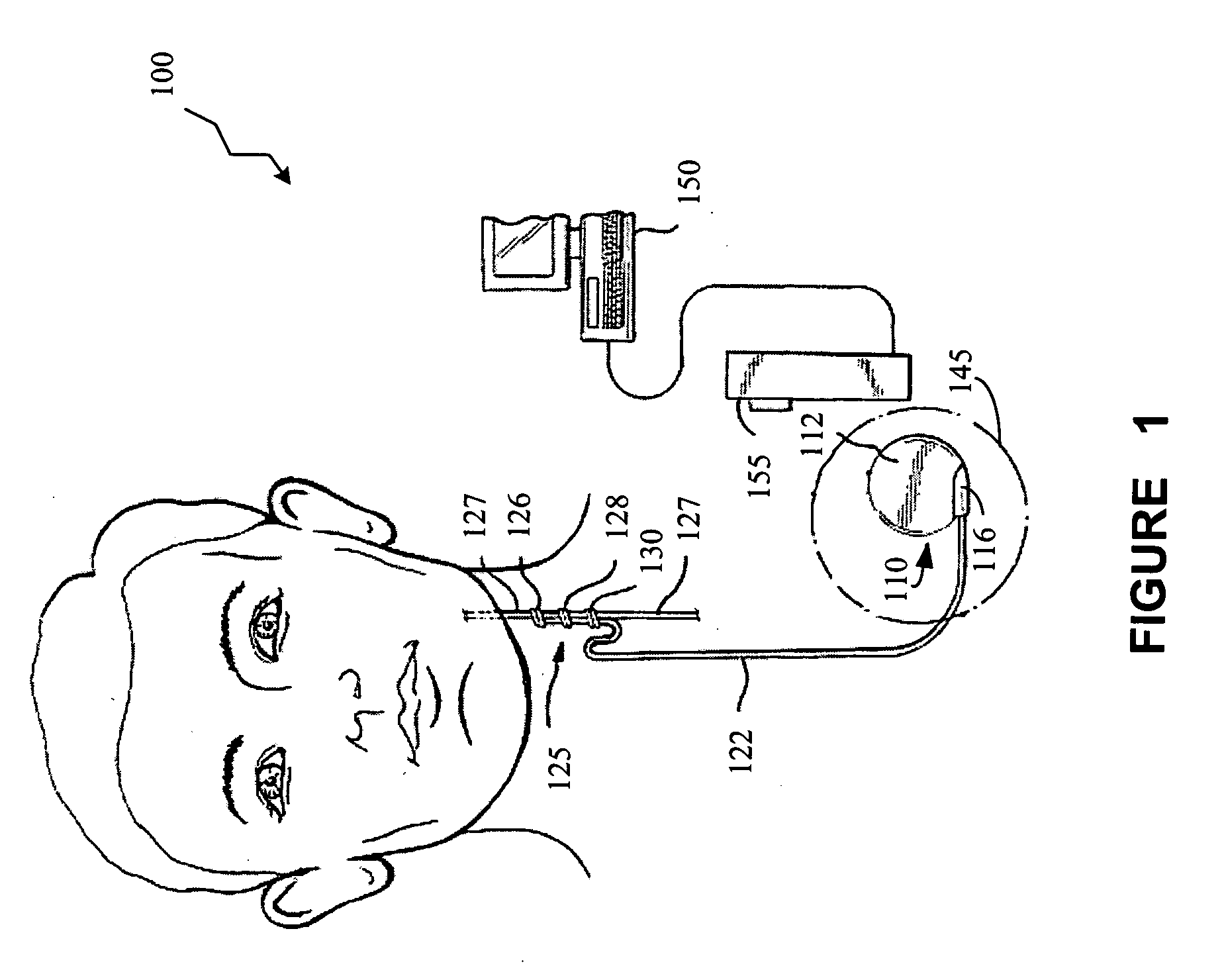
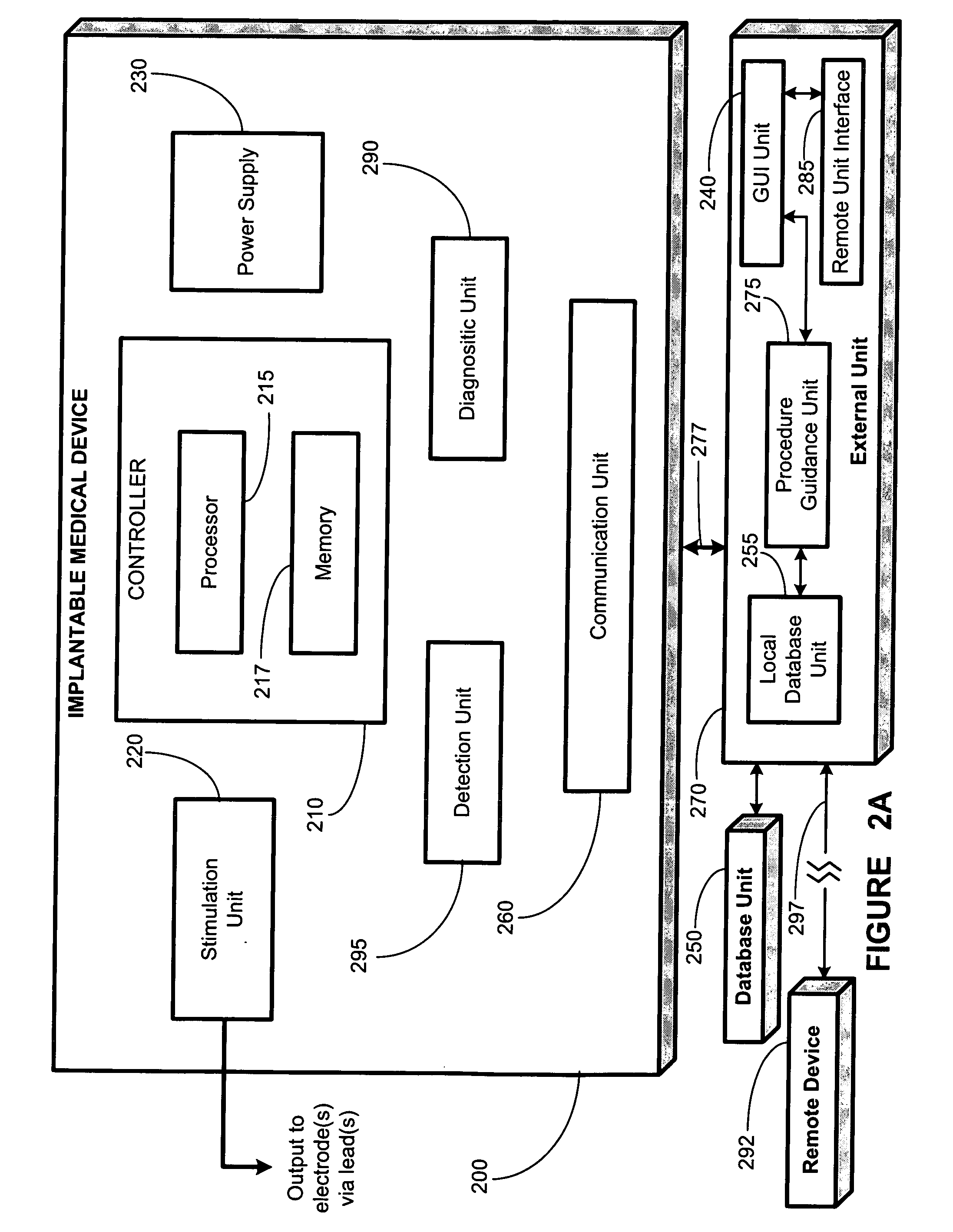
Method, apparatus and system for guiding a procedure relating to an implantable medical device
A method, apparatus, and system, are provided for guiding a medical procedure relating to an implantable medical device operatively coupled to a cranial nerve. Communications between the implantable medical device and an external device are established. An implant procedure is performed for implanting the implantable medical device. A first diagnostic process of the implantable medical device is performed. Using the external device a first signal is received from the implantable medical device based on the first diagnostic process. A first instruction is displayed using the external device based upon the first signal received by the external device. The first instruction includes information relating to guiding the implant procedure.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
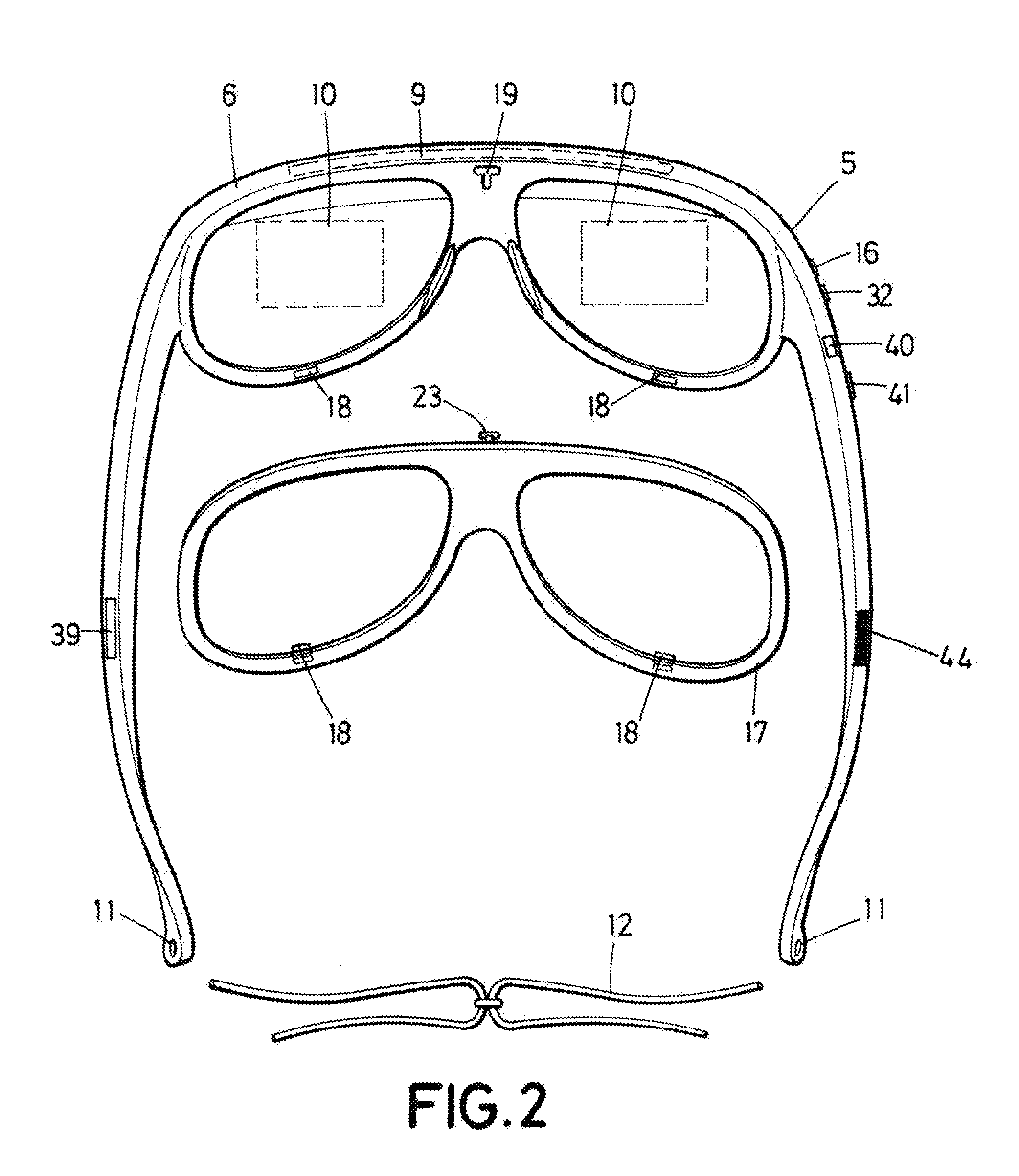
Enhanced-reality electronic device for low-vision pathologies, and implant procedure
InactiveUS20170038607A1Increase autonomyOptimise the residual sightSpectales/gogglesTelevision system detailsThe InternetPatient data
An electronic enhanced-reality device for low-vision pathologies and an implant procedure to optimise the residual vision of persons with low-vision pathologies, to enhance or recover certain functionalities and autonomy for daily activities, Internet-assisted in cloud mode and which, using patient data along with other data and ophthalmological metadata (big data), plus the adjustment and adaptation of the image captured by a video camera, allows the residual visual of persons affected by low-vision pathologies to be optimised, and operating in such a way that with the optimal parametrisations selected and loaded on to the device, the cameras switch on automatically and their images replace the previous image pre-loaded in the projection area (10).These images are processed by the signal processor (9) and projected by the image projector (31) on to the projection areas (10).These images are the ones which the patient will perceive.Ophthalmologist-patient interaction will enable the ophthalmologist to place the images in the right place for the patient in the projection area (10), suitably adapting the images from the camera in each eye independently or simultaneously in both, to optimise their residual vision.
Owner:CAMARA RAFAEL
Transmyocardial implant procedure
A blood flow path is formed from a heart chamber to a coronary vessel on an exterior surface of a heart wall. A hollow conduit has a vessel portion and a myocardial portion. The vessel portion has an open leading end sized to be inserted into the coronary vessel. The myocardial portion has an open leading end and the myocardium portion is sized to extend through a thickness of the heart wall. The myocardial portion is placed in the heart wall with the open leading end of the myocardial portion protruding into the heart chamber. Blood flow through the conduit from the heart chamber is at least partially blocked. The leading end of the vessel portion is placed in the coronary vessel. Blood flow through the conduit from the heart chamber and into the vessel is then opened.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Multilayer composite vascular access graft
ActiveUS7297158B2Improve performanceDesirable characteristicStentsMedical devicesMedicineBlood vessel
A multilayer composite vascular access graft and a method of constructing such a graft are disclosed. The mcVAG has improved performance characteristics, which include desirable handling characteristics such as ease of suturing, kink resistance and the ability to serve as a cannulation route soon after the implant procedure.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Methods and devices for installing standard and reverse shoulder implants
Surgical procedures, tools and implants are disclosed for both conventional and reverse shoulder implant surgeries. The improved procedures, tools and implants relate to humeral head resurfacing, humeral head resection for standard implants, humeral head resection for reverse shoulder implants, glenoid resurfacing for standard shoulder implants and glenoid resurfacing for reverse shoulder implants. 3D scans and x-rays are used to develop virtual models of the patient anatomy, identify patient specific landmarks for anchoring guide wire installation blocks, templates and drill guides. 3D scans are also used to design patient specific tools and implants for the shoulder implant procedures and to pre-operatively determine the appropriate inclination and retroversion angles.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Dental implantation system and method using magnetic sensors
Provided herein, inter alia, is a system for indicating the location of a dental drill includes a dental handpiece, which further includes the dental drill. A plurality of sensors detect a magnetic field and produce a set of outputs, which are usable at least in part to indicate the location of the dental drill. The sensor outputs may be processed to produce an indication of the spatial relationship of the drill to a patient's dentition. The indication is preferably graphical, and may be presented to a dental professional using the system during an implant procedure to provide visual feedback about the procedure. The indication may be repeatedly updated, substantially in real time.
Owner:PRECISION THROUGH IMAGING
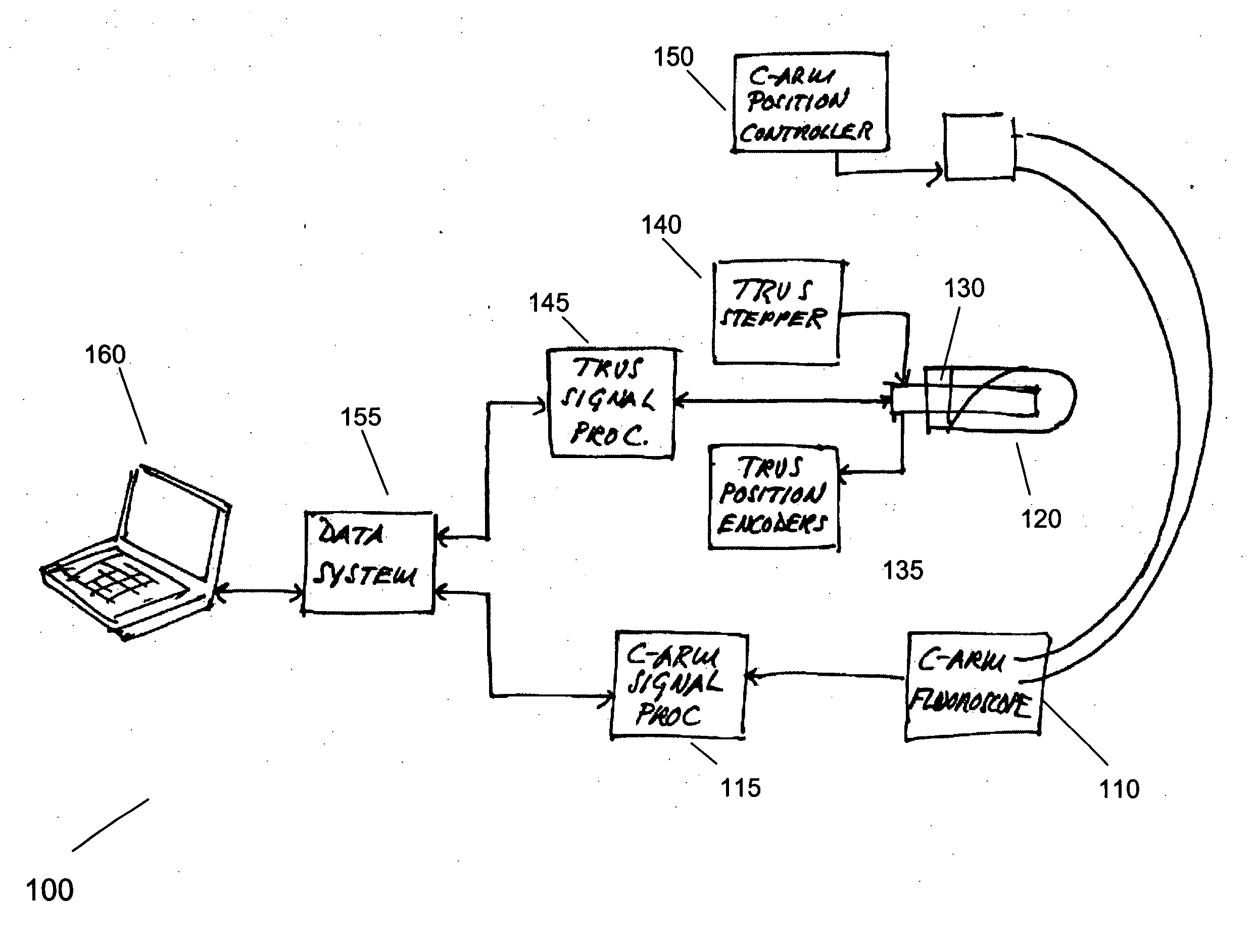
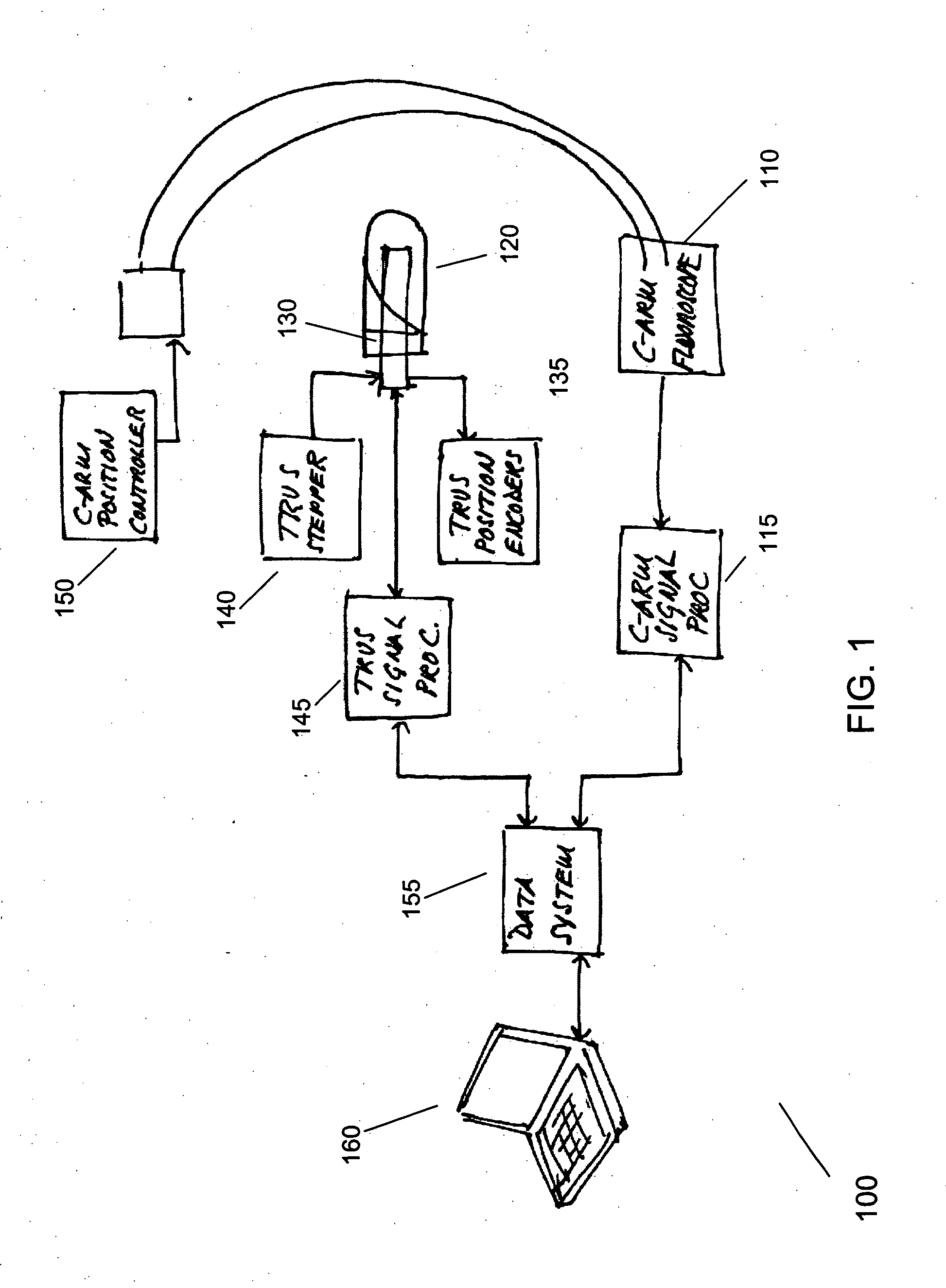
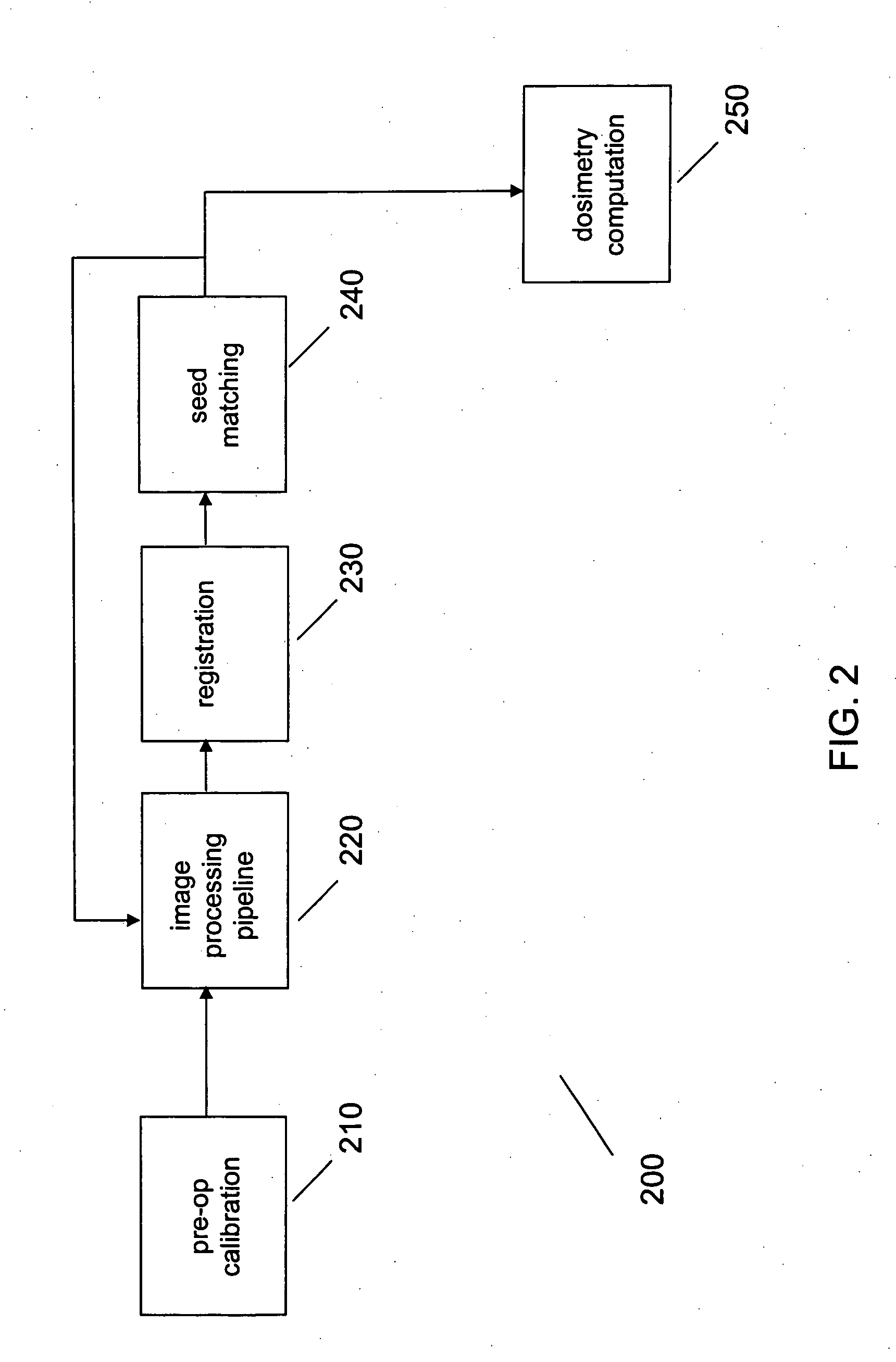
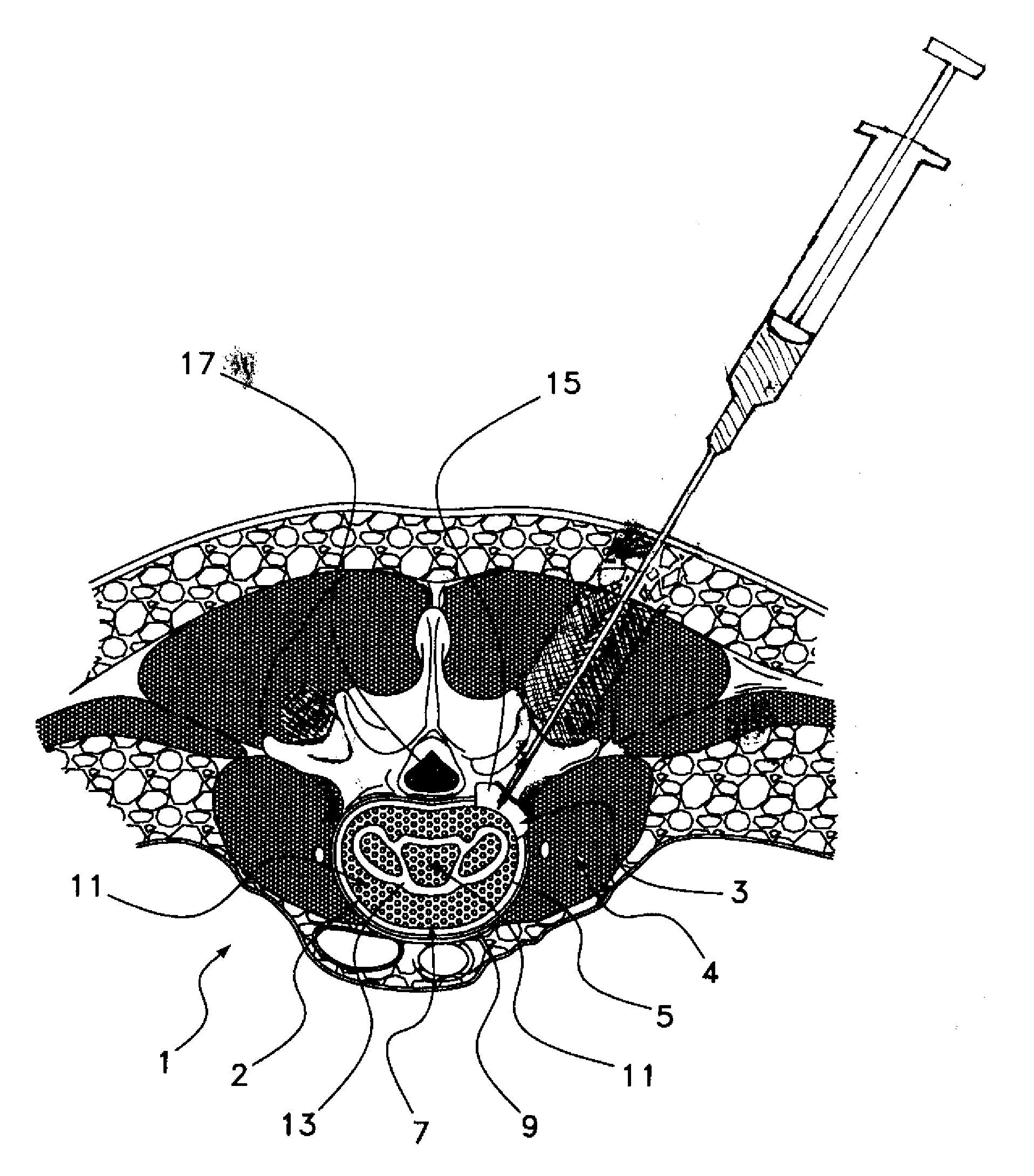
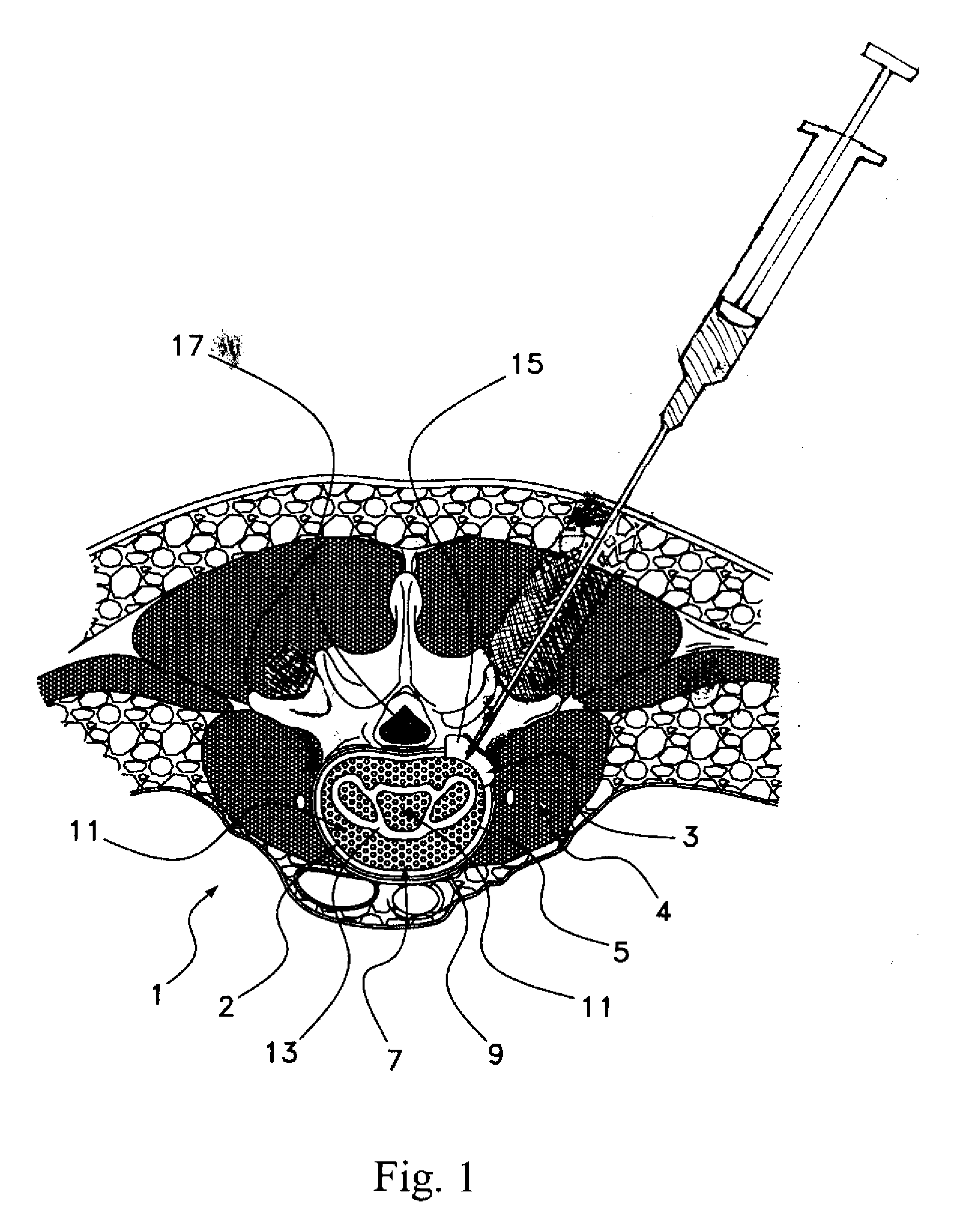
Registration of ultrasound to fluoroscopy for real time optimization of radiation implant procedures
InactiveUS20050171428A1Easy to controlImprove visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonificationFluorescence
Transrectal ultrasound guided transperineal low dose-rate brachytherapy has been emerged as one of the definitive treatments of low-risk prostate cancer. Ultrasound has been an excellent tool in guiding the implant needles with respect to prostate anatomy, yet it cannot show reliably the location of radioactive seeds after they are released in the prostate. Intraoperative C-arm fluoroscopy can show the implanted seeds, but it cannot detect prostate anatomy. Intra-operative fusion of these two complementary modalities offers significant clinical benefit by allowing for real-time optimization of the brachytherapy implant as the procedure progresses in the operating room. Disclosed is a system and method for mitigating this problem and providing registration of seeds seen by fluoroscopy with live prostate anatomy visualized by transrectal ultrasound.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
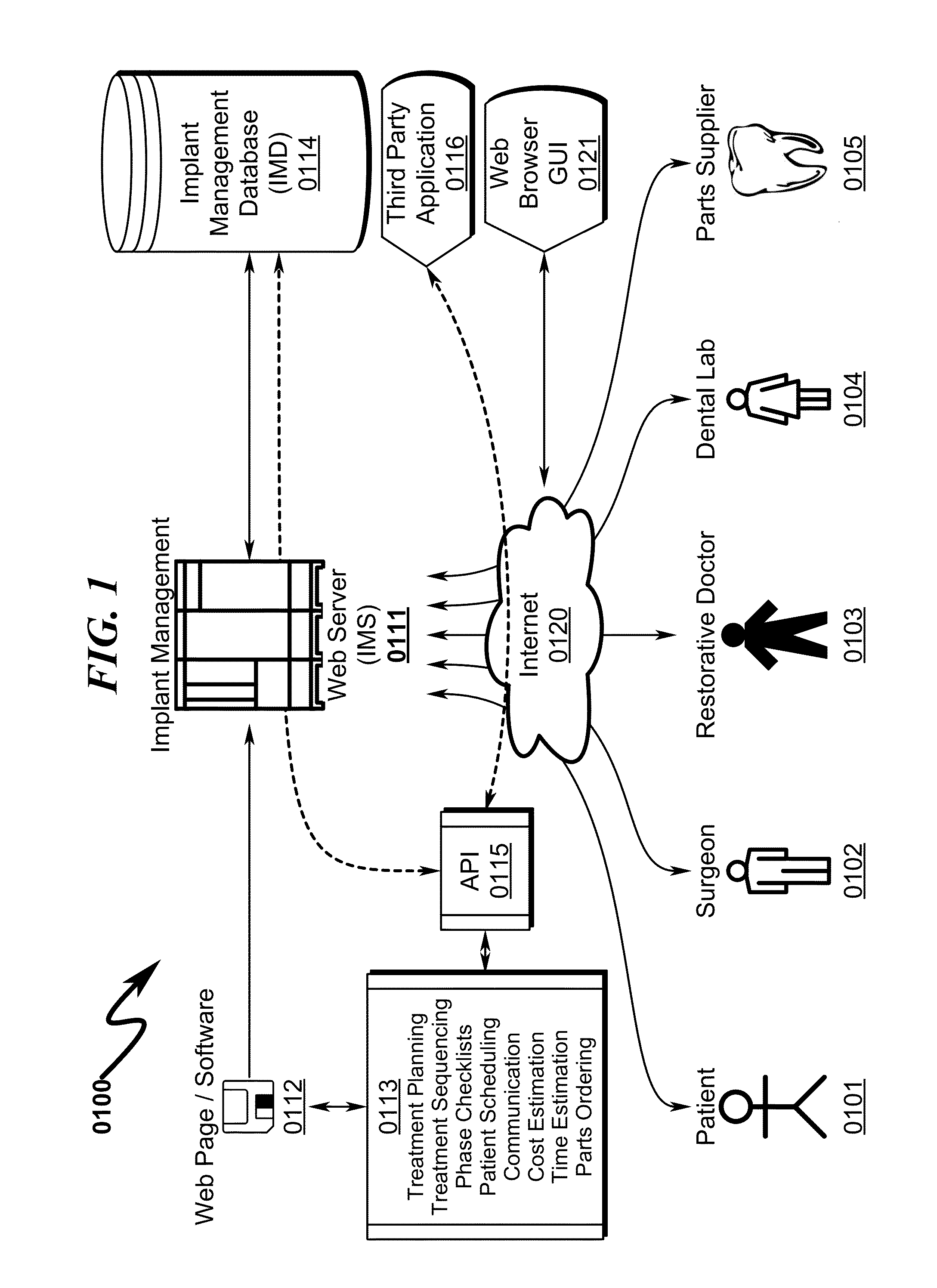
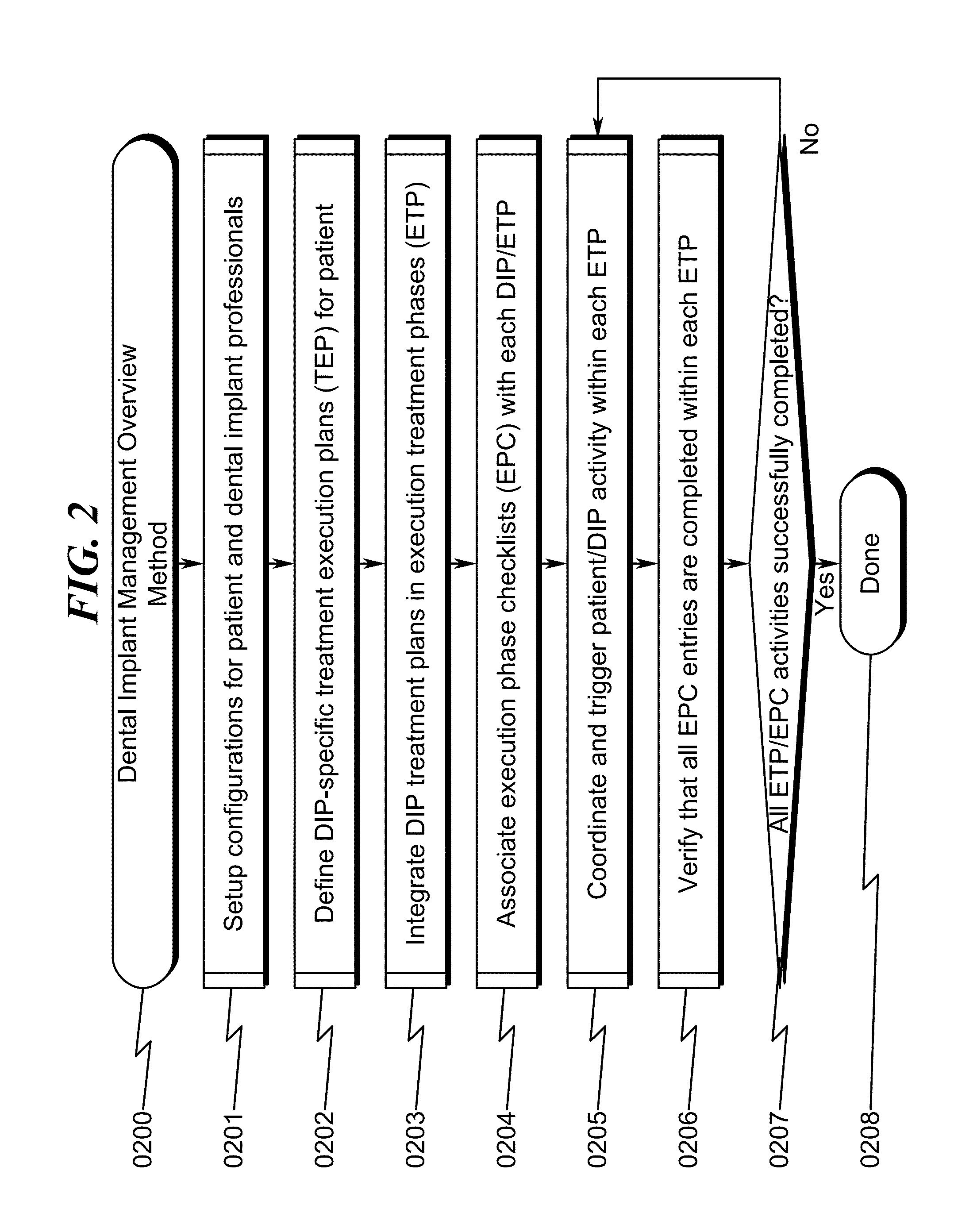
Dental implant management system and method
InactiveUS20150019252A1Good for dental healthFacilitate communicationDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesExecution planDental laboratory
A dental implant management system / method that improves communication and coordination between parties associated with dental implant procedures is disclosed. The system / method operates to permit each dental implant professional (DIP) (typically a surgeon, restorative doctor, and dental laboratory) to iteratively generate a patient treatment execution plan (TEP) for the dental implant procedure that is generally structured within execution treatment phases (ETP) and automatically coordinated among each DIP. The ETP typically defines FOUNDATION, IMPLANT PLACEMENT, RESTORATIVE, and MAINTENANCE phases that may each incorporate custom execution phase checklists (EPC) that permit each DIP to ensure that critical elements of their TEP are properly executed. Coordination of the various DIP-generated TEPs is integrated with treatment planning / sequencing, patient scheduling, DIP fee estimation, and dental parts procurement to ensure maximum revenue to each DIP while simultaneously improving the probability of a successful dental implant procedure for the patient.
Owner:CENTGISTIX
Osteochondral implant procedure
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method of using an Anti-growth matrix as a barrier for cell attachment and osteo-inductive factors
The present invention generally relates to a method of using a matrix as a barrier for unwanted cell attachment and bone formation in unwanted areas of the human body during implant procedures. More specifically, a growth-inhibiting matrix may be used to prevent migration of osteo-inductive agents or bone tissue from an intervertebral disc space through the outer bands of annulus fibrosis that abuts the spinal tissue, canal, and other surrounding areas.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
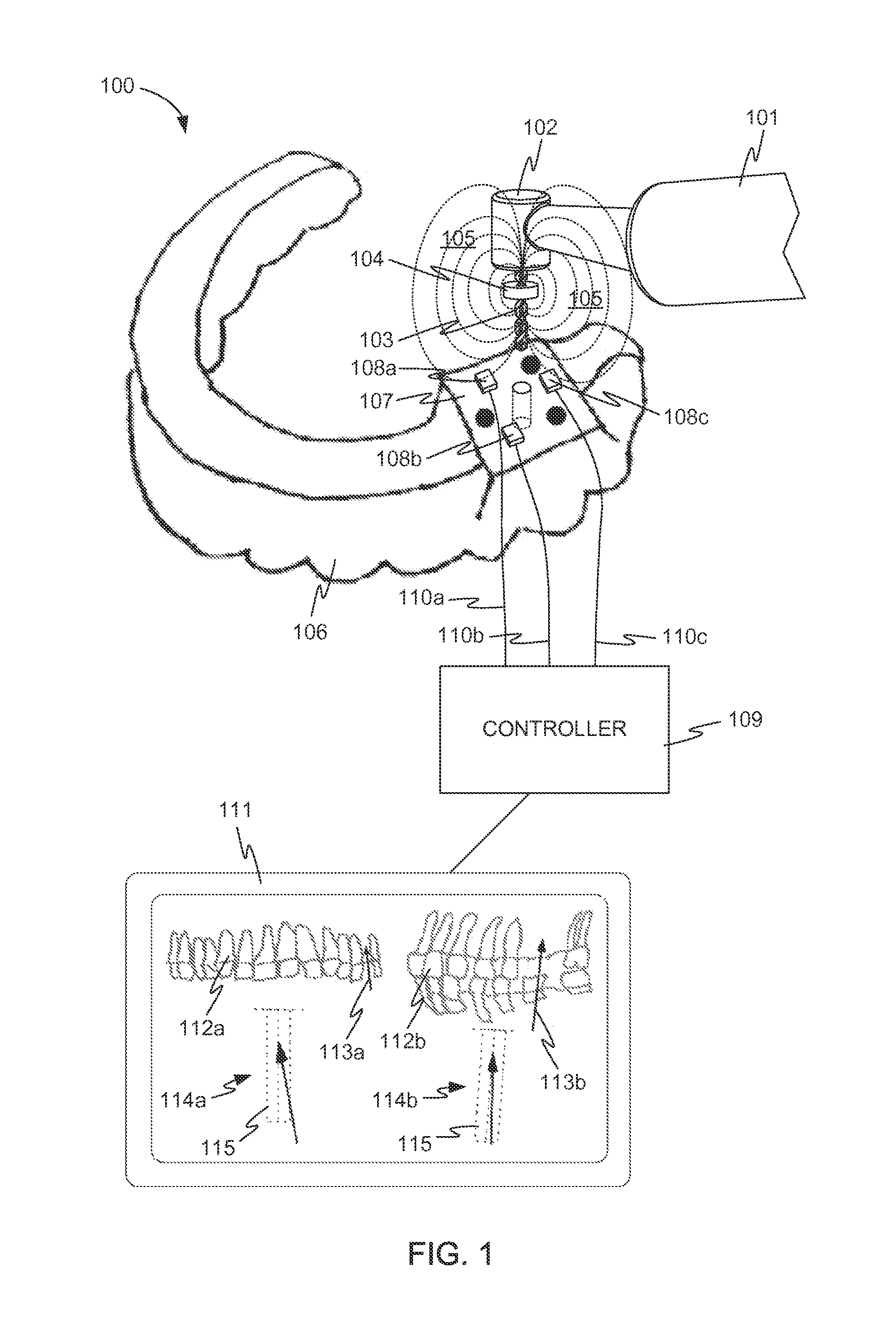
Method for optimizing location of implanted electrode array during implant surgery
InactiveUS20050203588A1Simple processShorten the timeElectrotherapySurgeryElectricityImplant electrode
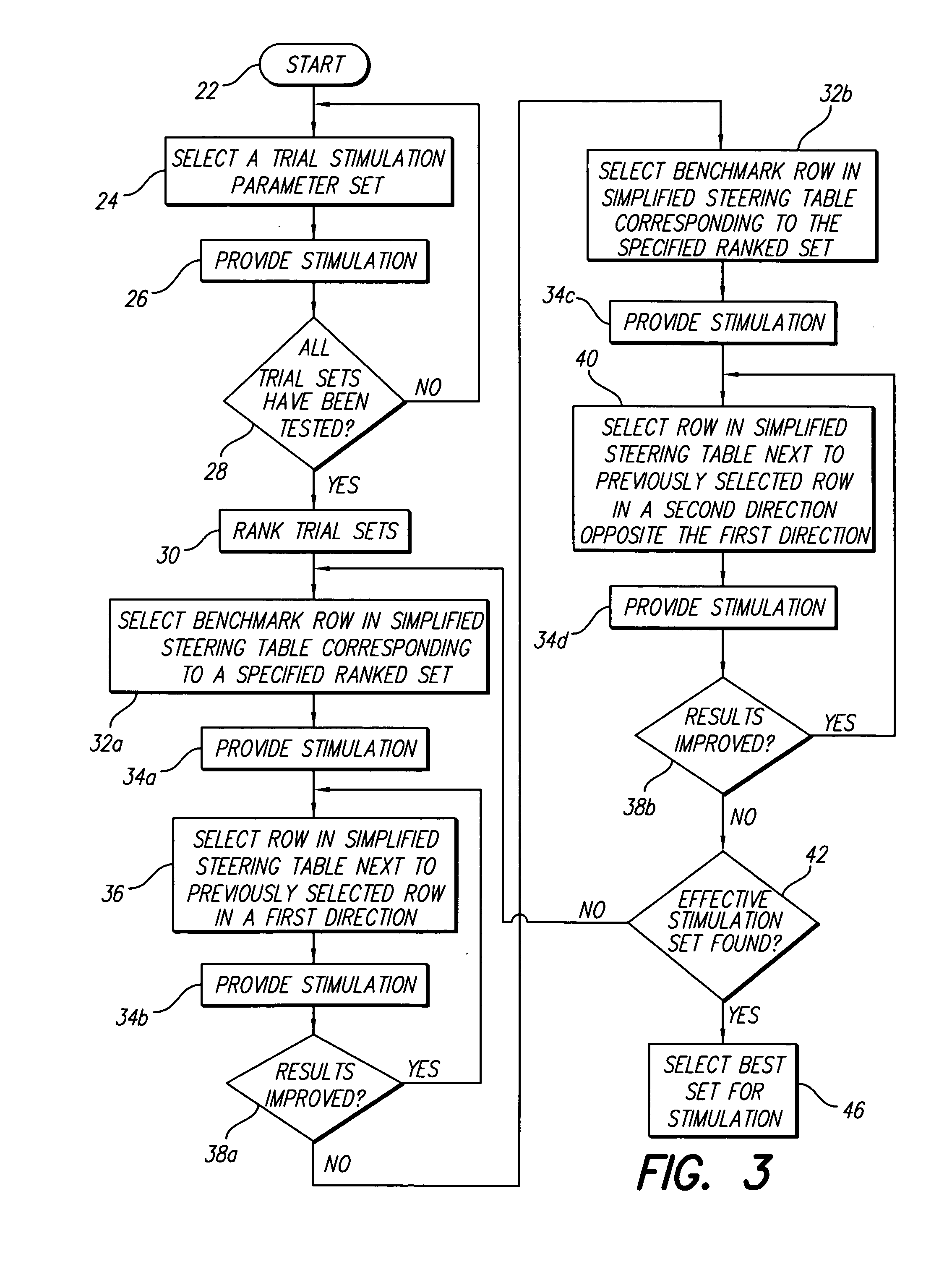
A method for determining an effectual placement of an electrode array during a surgical procedure to implant the lead is provided. This method involves placing a lead having electrodes in a first location in a patient then (1) activating electrical stimulation to produce paresthesia, (2) “electronically trolling” the length of the electrode array and (3) determining whether the paresthesia is in an effective location. If the paresthesia is not in an effective location to match the location of the pain, the lead is moved to a different location steps (1) through (3) are repeated. The process of electronically trolling involves moving the electrical stimulation along the electrode array so that all regions of the electrode array provide stimulation. This method reduces or eliminates the need to move the lead during the implant procedure and thus simplifies the implant procedure compared to the currently used physical trolling method, reducing the risks to the patient. Additionally, this method saves time and improves outcomes by allowing multiple electrode combinations to be tested in a relatively short amount of time.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Universal, multifunctional, single unit, rotary osteotome
InactiveUS7547210B1Precise positioningReduce crestal bone heightDental implantsTeeth fillingSurgical dentistrySurgical department
A multifunctional surgical rotary instrument with a corrosion resistant wear reducing hard coating, to be used in a surgical dental motor driven handpiece for preparing an osteotomy for implant insertion, combining the functions of six surgical instruments is described. The multifunctional surgical rotary instrument has structural features that provide the functions of a crestal bone height reducer, an osteotomy locator, an osteotomy lateral redirector, osteotomy drill, tapered countersink, and an osteocompressor. These structural features include a dual-lobed single plane tip that remains where the drilling is initiated without wandering, and facilitates the precise location of the osseous implant site. Advantageously, the instrument can save time and cost in the implant procedure.
Owner:IMPLADENT
Surgical guide and method
A method for preparing a surgical guide for positioning of a dental implementation. The method includes positioning a positioning device relative to a model jawbone, translating the positioning device in a BL direction, adjusting a BL angle of the positioning device about a BL pivot axis corresponding to a desired position of a top of the dental implementation, and fixing the BL position, BL angle, and z-height of the positioning device. A mounting assembly mounts to the positioning device and includes a removable rotation block with a guide hole. The mounting assembly is movable in the MD direction while the BL position is fixed. A template fixes the mounting assembly for transferring the positioning information to a patient's mouth. Various aspects of the design process can be performed on a computer. The guide and a method of using the guide to perform an implant procedure are also disclosed.
Owner:STUMPEL LAMBERT J
Device for regeneration of articular cartilage and other tissue
InactiveUS7776100B2Minimize or prevent foreign body giant cell responsesGood adhesionBone implantMammal material medical ingredientsSubchondral boneOsteoblast
An implantable device for facilitating the healing of voids in bone, cartilage and soft tissue is disclosed. A preferred embodiment includes a cartilage region comprising a polyelectrolytic complex joined with a subchondral bone region. The cartilage region, of this embodiment, enhances the environment for chondrocytes to grow articular cartilage; while the subchondral bone region enhances the environment for cells which migrate into that region's macrostructure and which differentiate into osteoblasts. A hydrophobic barrier exists between the regions, of this embodiment. In one embodiment, the polyelectrolytic complex transforms to hydrogel, following the implant procedure.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Multilayer composite vascular access graft
ActiveUS20050278018A1Improve performanceDesirable characteristicStentsPharmaceutical containersMedicineBlood vessel
A multilayer composite vascular access graft and a method of constructing such a graft are disclosed. The mcVAG has improved performance characteristics, which include desirable handling characteristics such as ease of suturing, kink resistance and the ability to serve as a cannulation route soon after the implant procedure.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Surgical guide and method
A method for preparing a surgical guide for positioning of a dental implementation. The method includes positioning a positioning device relative to a model jawbone, translating the positioning device in a BL direction, adjusting a BL angle of the positioning device about a BL pivot axis corresponding to a desired position of a top of the dental implementation, and fixing the BL position, BL angle, and z-height of the positioning device. A mounting assembly mounts to the positioning device and includes a removable rotation block with a guide hole. The mounting assembly is movable in the MD direction while the BL position is fixed. A template fixes the mounting assembly for transferring the positioning information to a patient's mouth. Various aspects of the design process can be performed on a computer. The guide and a method of using the guide to perform an implant procedure are also disclosed.
Owner:STUMPEL LAMBERT J
Method of deployable medical lead fixation
InactiveUS20060292912A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesCoupling contact membersLead extractionFixed position
An improved medical lead assembly and method of use is provided. The lead assembly includes a lead body, and a spring member positioned adjacent to the lead body. The spring member may be deployed a selectable amount to maintain the lead body in a fixed location within a patient's body. The spring member may be an expandable coil, a mesh structure that is similar to a stent, or any other similar device that may be positioned in a low-profile state during a lead implant procedure. After the lead is positioned at a target destination, the spring member may be deployed an amount that is selected based on the characteristics of the surrounding tissue, including vessel size. According to one aspect of the invention, the lead assembly may provide means for facilitating chronic lead extraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prosthetic heart valve packaging and deployment system
ActiveUS8869982B2Easy retrievalGood adhesionDispensing apparatusHeart valvesProsthetic heartBiomedical engineering
Packaging for prosthetic heart valves including an assembly for securely retaining a heart valve within a jar and facilitating retrieval therefrom. The assembly includes a packaging sleeve that fits closely within the jar and has a clip structure for securing a valve holder. Contrary to previous designs, in one embodiment the valve holder is directed downward into the jar, and the valve is retained with an inflow end upward. The valve may have flexible leaflets, and a leaflet parting member on the end of the shaft extends through the leaflets and couples with the valve holder. The assembly of the packaging sleeve, valve, and holder can then be removed from the jar and a valve delivery tube connected with the holder, or to the leaflet parting member. The packaging sleeve may be bifurcated into two halves connected at a living hinge to facilitate removal from around the valve / holder subassembly. The packaging system facilitates attachment of the valve delivery tube for use in a quick-connect valve implant procedure.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Semiconductor process
ActiveUS20130137243A1Improve device speedImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor packageEmbedded system
First, a substrate with a recess is provided in a semiconductor process. Second, an embedded SiGe layer is formed in the substrate. The embedded SiGe layer includes an epitaxial SiGe material which fills up the recess. Then, a pre-amorphization implant (PAI) procedure is carried out on the embedded SiGe layer to form an amorphous region. Next, a source / drain implanting procedure is carried out on the embedded SiGe layer to form a source doping region and a drain doping region. Later, a source / drain annealing procedure is carried out to form a source and a drain in the substrate. At least one of the pre-amorphization implant procedure and the source / drain implanting procedure is carried out in a cryogenic procedure below −30° C.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
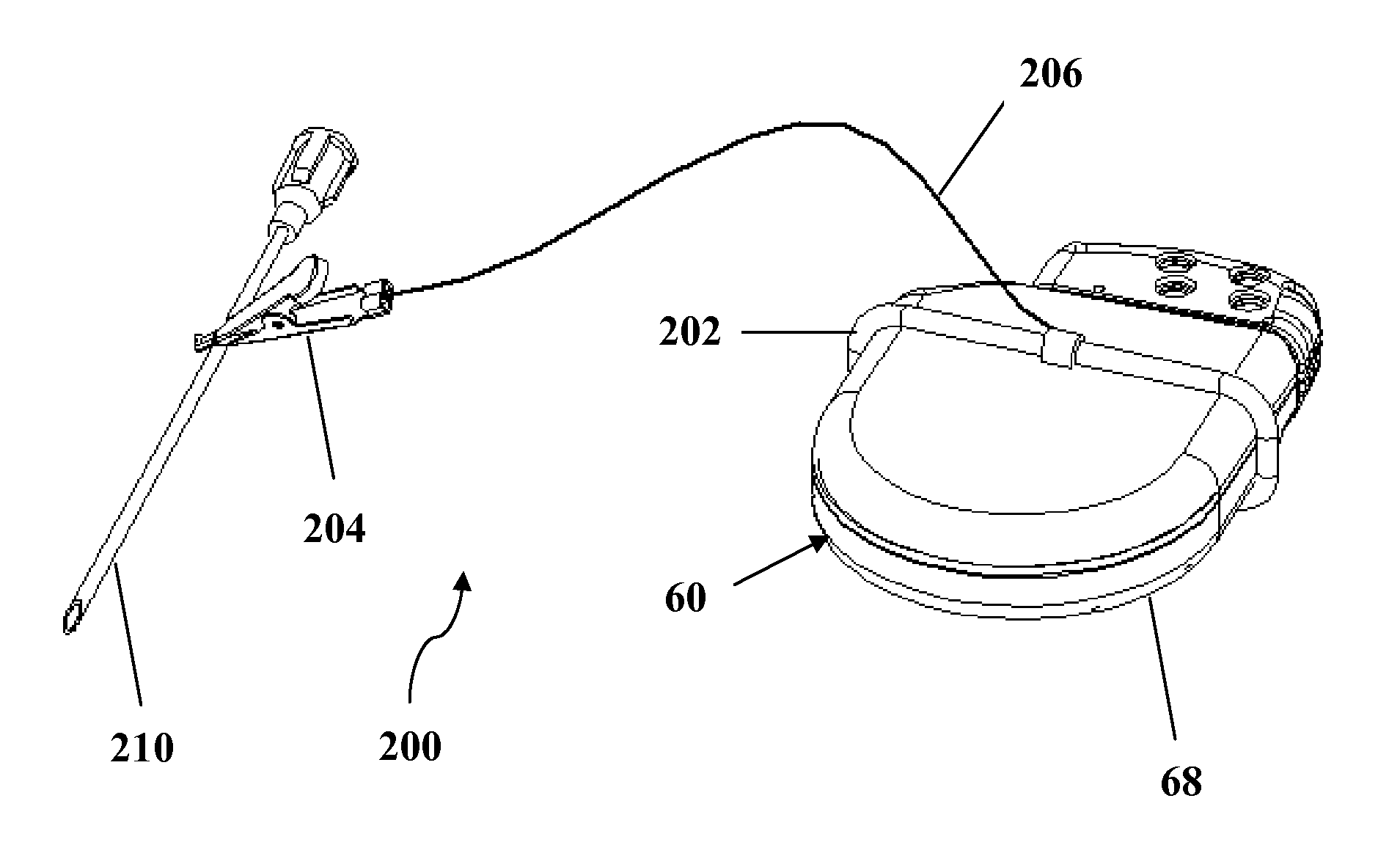
Adapter for connection to pulse generator
Embodiments of the present invention generally pertain to devices and methods for use in conjunction with implanting a baroreflex therapy system which includes an implantable pulse generator and associated circuitry contained within a hermetically sealed housing, an elongate flexible electrical lead connectable to the housing, and a monopolar electrode structure coupled with the electrical lead. More specifically, the devices and methods of the present invention allow for a mapping procedure to be conducted as part of the implant procedure prior to fully implanting the baroreflex therapy system.
Owner:CVRX
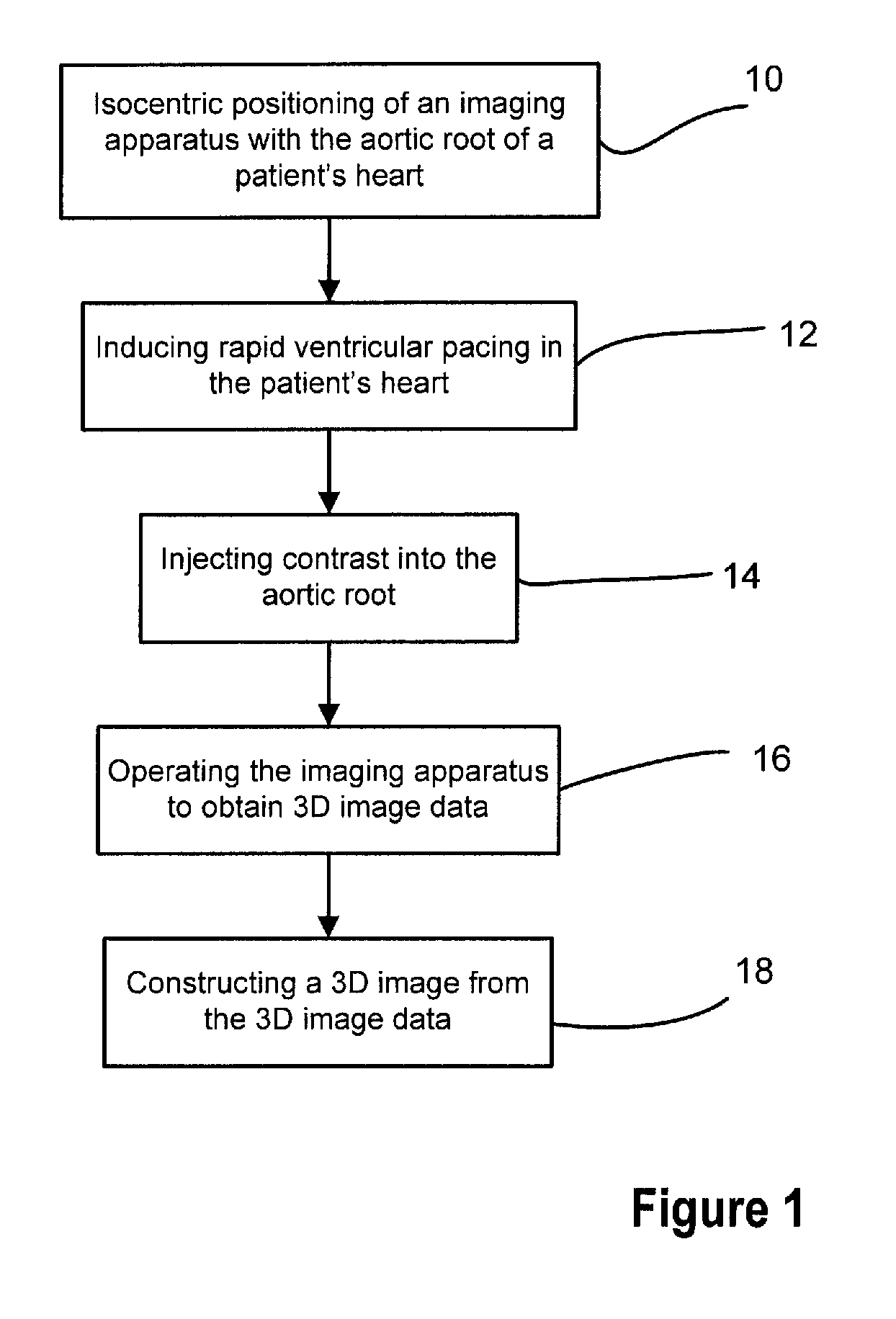
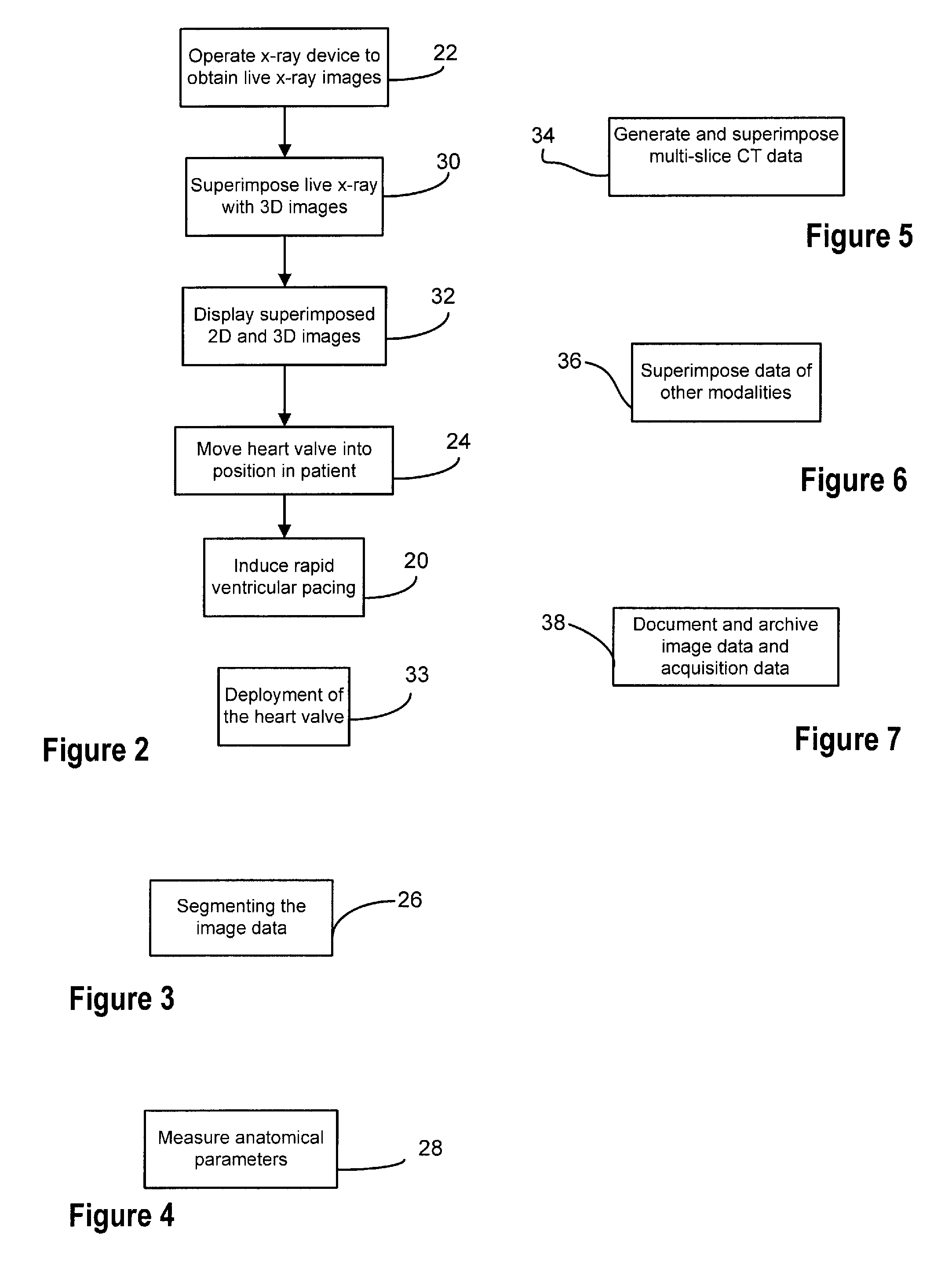
Method of imaging for heart valve implant procedure
InactiveUS20110046725A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesJoint imagingMethod of images
A method as a workflow for imaging for a heart valve implant procedure includes positioning the patient and an articulated imaging apparatus relative to one another, inducing rapid ventricular pacing in the patient, and imaging a region of the patient's heart to obtain image date for a three-dimensional image. The three-dimensional data is used to construct a three-dimensional image of the region of the patient's heart an the three-dimensional image is displayed for use in the implanting of the replacement heart valve. Optional steps may include obtaining a real time two-dimensional image of the patient's heart and superimposing the real time two-dimensional image with the constructed three dimensional image. The replacement valve is moved into position in the patient's heart during rapid ventricular pacing and breath hold using the superimposed two-dimensional and three-dimensional image information.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Catheter feed through guide
InactiveUS20060116608A1Easy to eatAvoid damageGuide wiresSurgical needlesCatheter deviceImplant procedures
A catheter feed through guide apparatus and method which facilitates the feeding of a catheter through a tunneler during implant procedures and avoids damage to the catheter and catheter tip during the catheter feed through procedure. The apparatus comprises a guide element configured to fit through a tunneler and to releasibly engage a catheter or catheter end.
Owner:DURECT CORP
Bone Implant Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20150202045A1Bone implantSpecial data processing applicationsFixation pointImplanted device
A bone implant apparatus and method includes a programmable device for creating a bone implant. A computer program is connected with the programmable device and the computer program includes a repository of implant programs for standard bones and spacers of preselected dimensions and forms and where the repository of implant programs are customizable and where the bone implant includes a fixation point.
Owner:BESPA
Surgical implant instrument and method
InactiveUS7211100B2Easy to installBone implantJoint implantsSurgical instrumentationSurgical implant
A surgical instrument suitable for use in an implant procedure is disclosed. A surgical instrument of the invention can be particularly advantageous for use in grasping, holding and placement of implants in an intervertebral disc space. In a typical embodiment, the surgical instrument has a grasping region to hold the implant, and an impact head for receiving a force in order to insert the implant.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
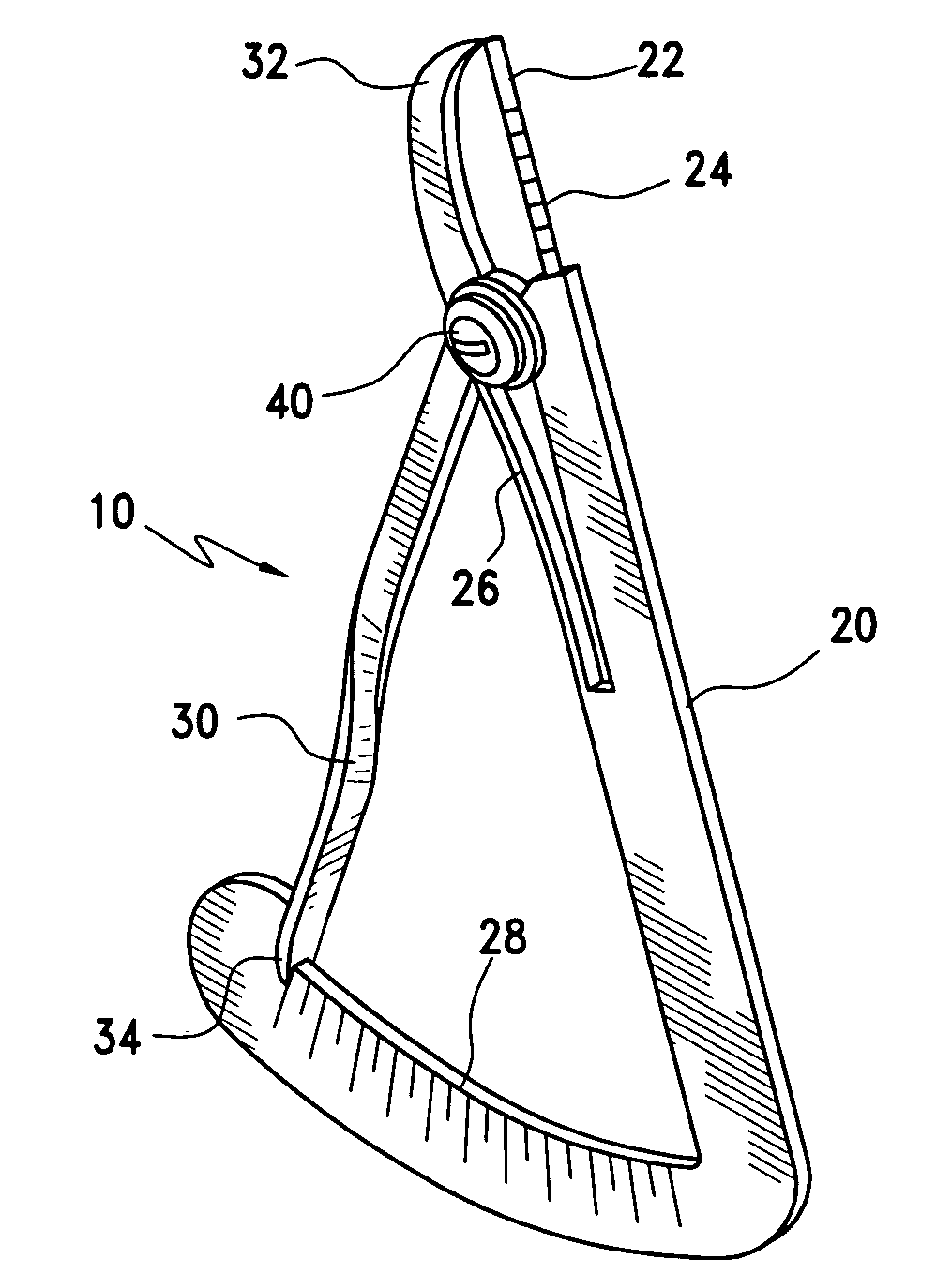
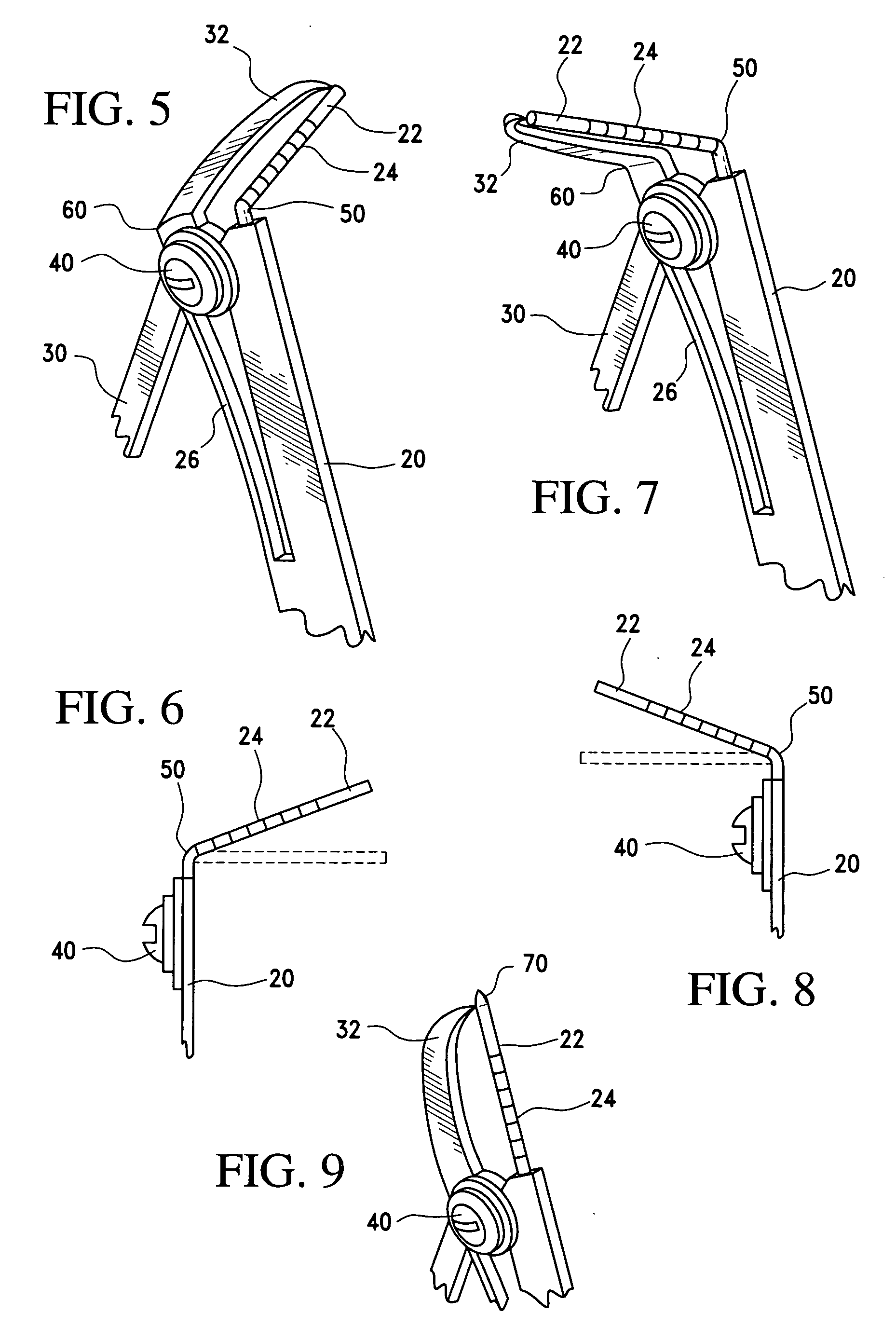
Bone measurement device for use during oral implant surgery
InactiveUS20070209221A1Improve efficiencyImprove placement accuracyDental implantsMeasurement devicesBone MeasurementsDentistry
The present invention is a tool to measure depth and width of bone cavities prior to and during oral implant placement. The tool includes a passive-depth gauge arm and an active spring caliper arm. The tool can be used to define the extraction socket for oral implant placement and allows measurement verifications after each step of the bone bed preparation prior to or during the actual implant placement in the extraction socket. There are multiple modifications of the primary design into separate embodiments to accommodate usage in different parts of the jaw and different points during the implant procedure.
Owner:ZIPPLIES ROBERT ERNST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com