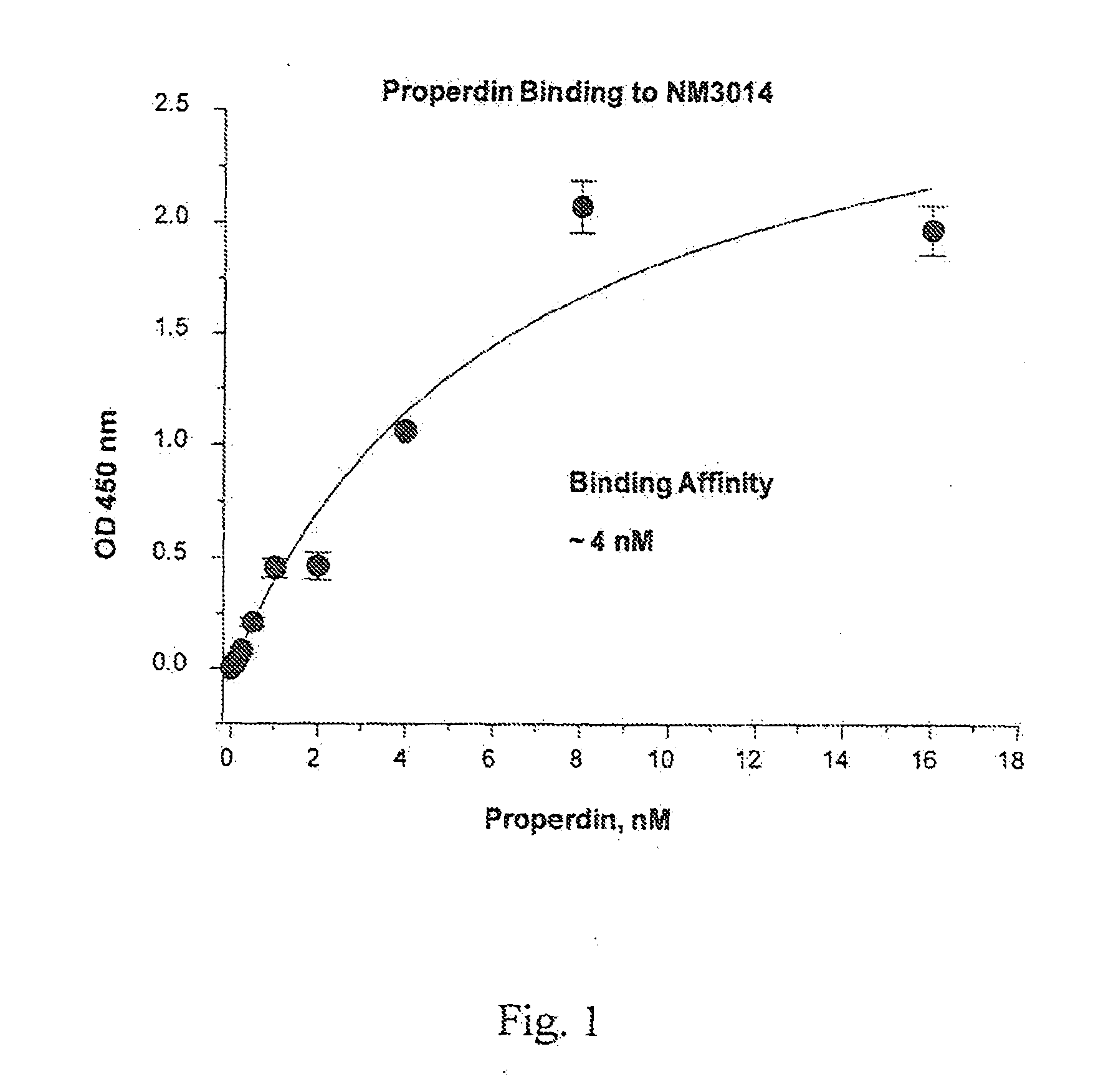
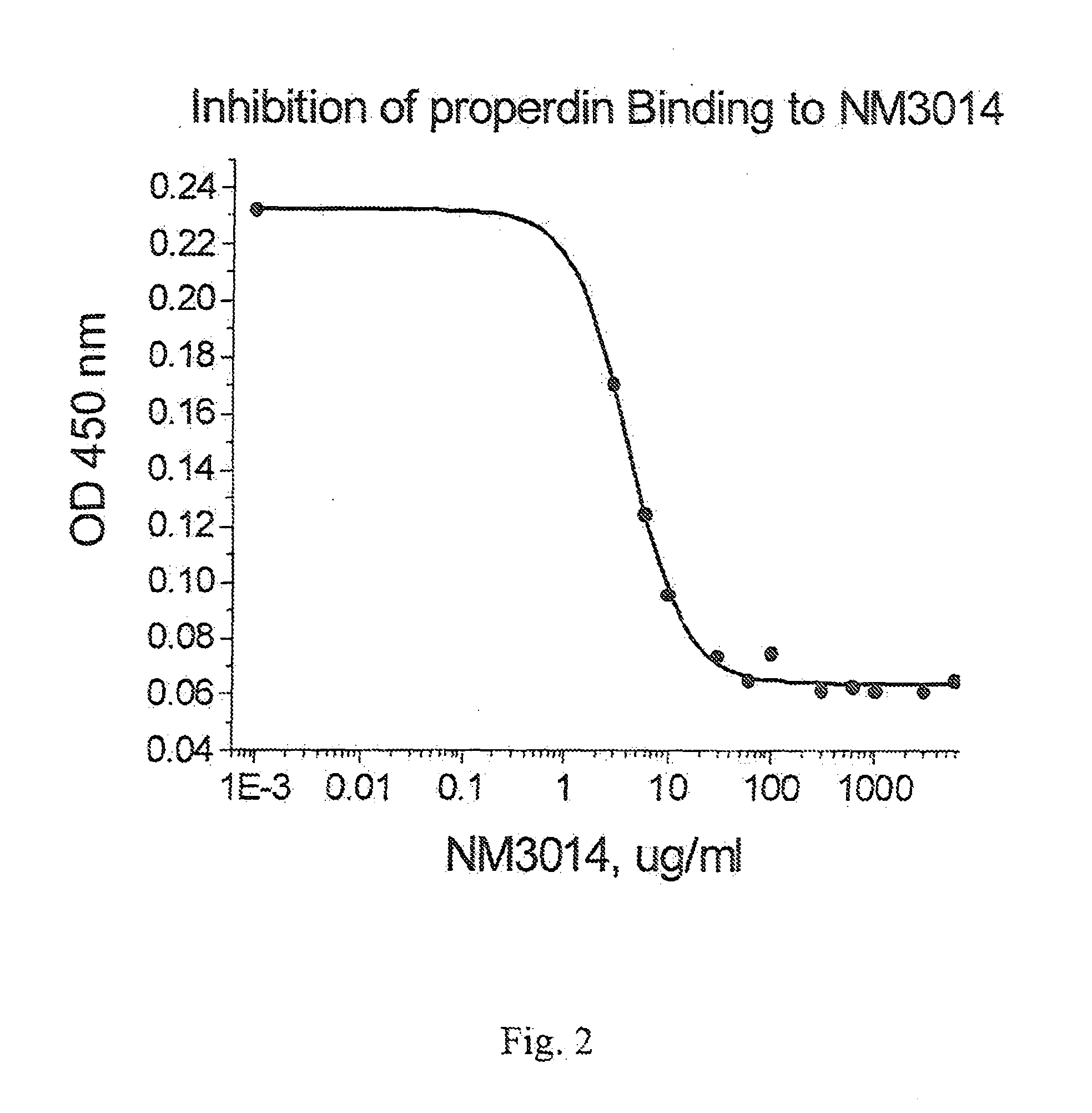
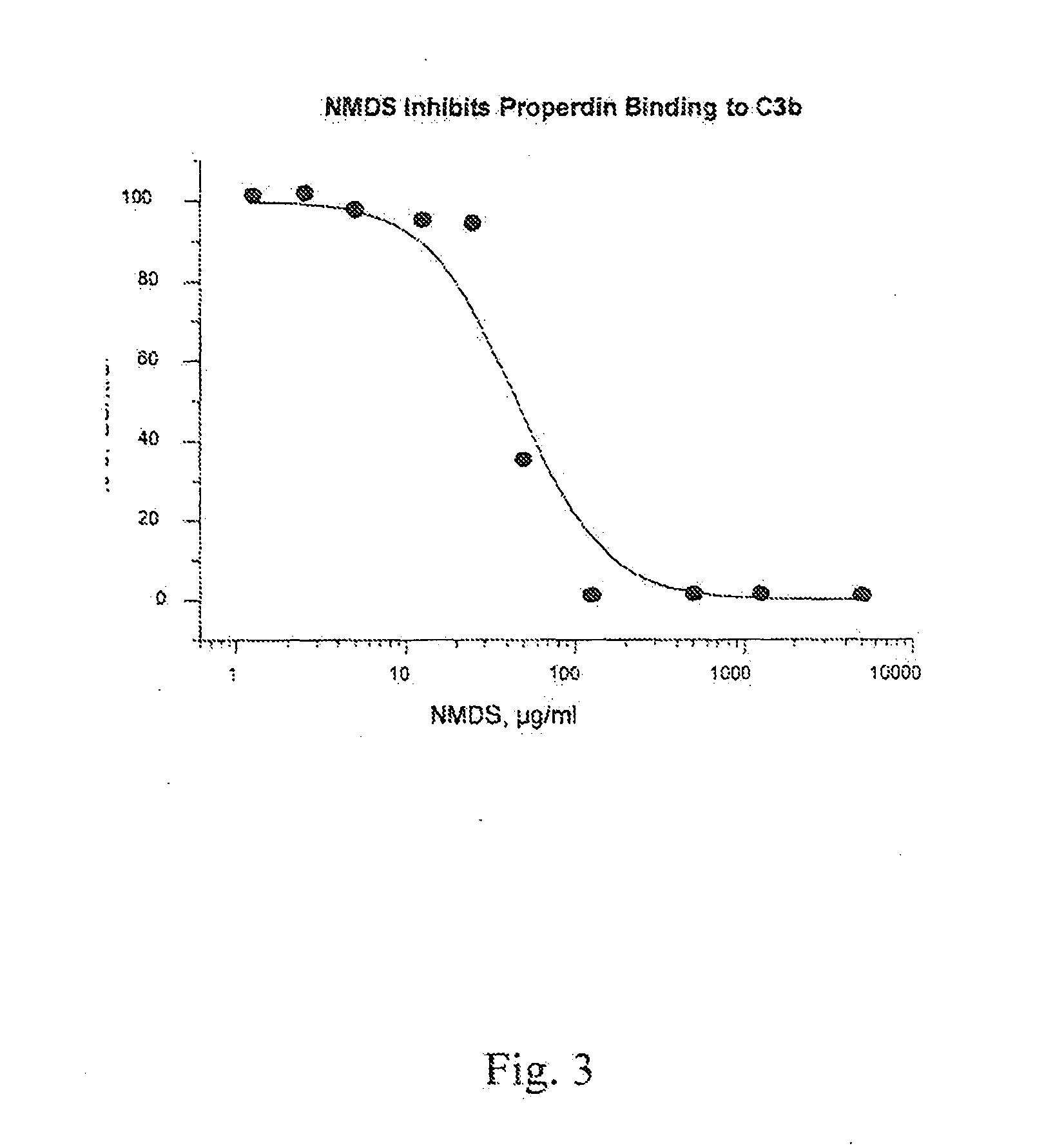
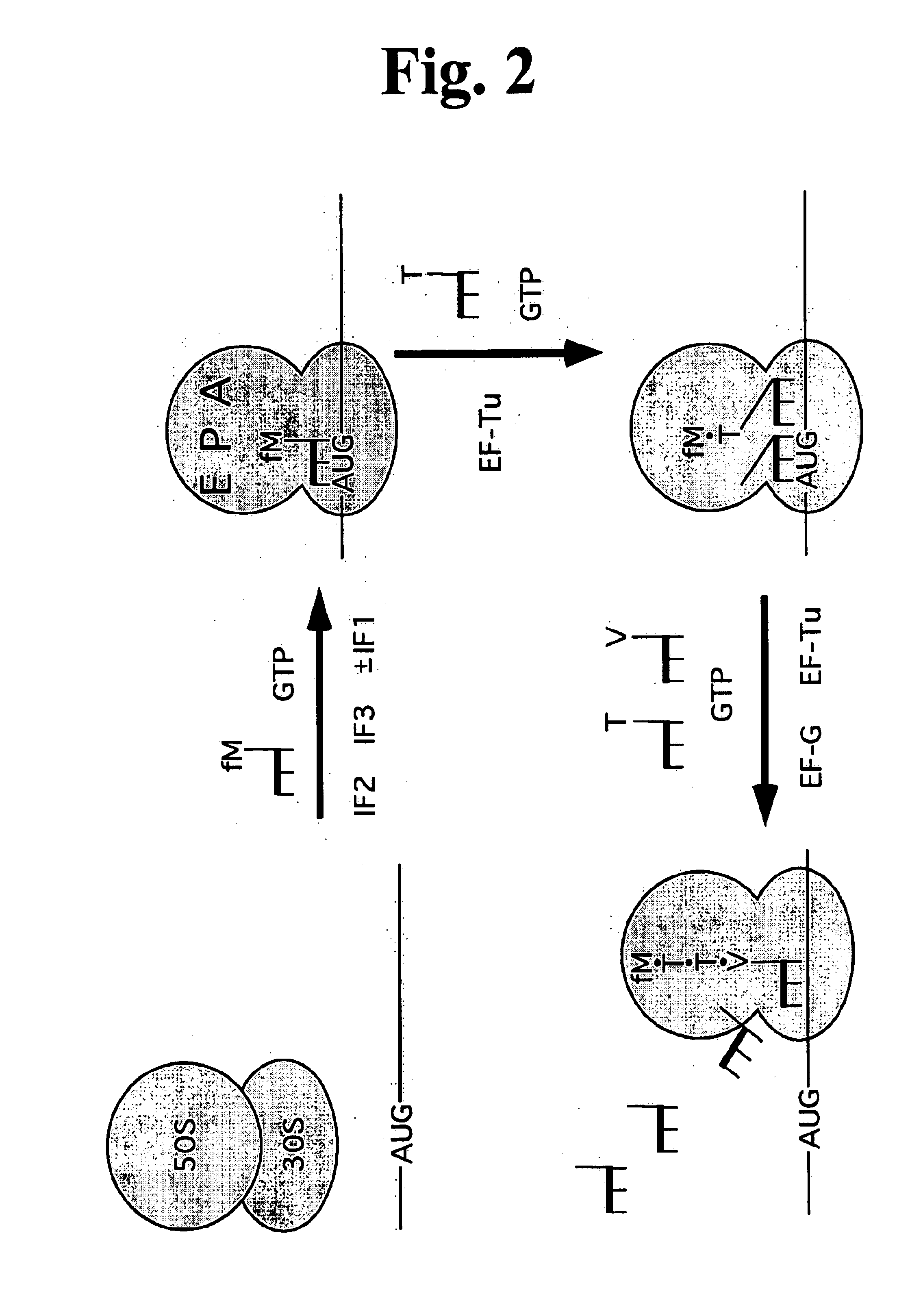
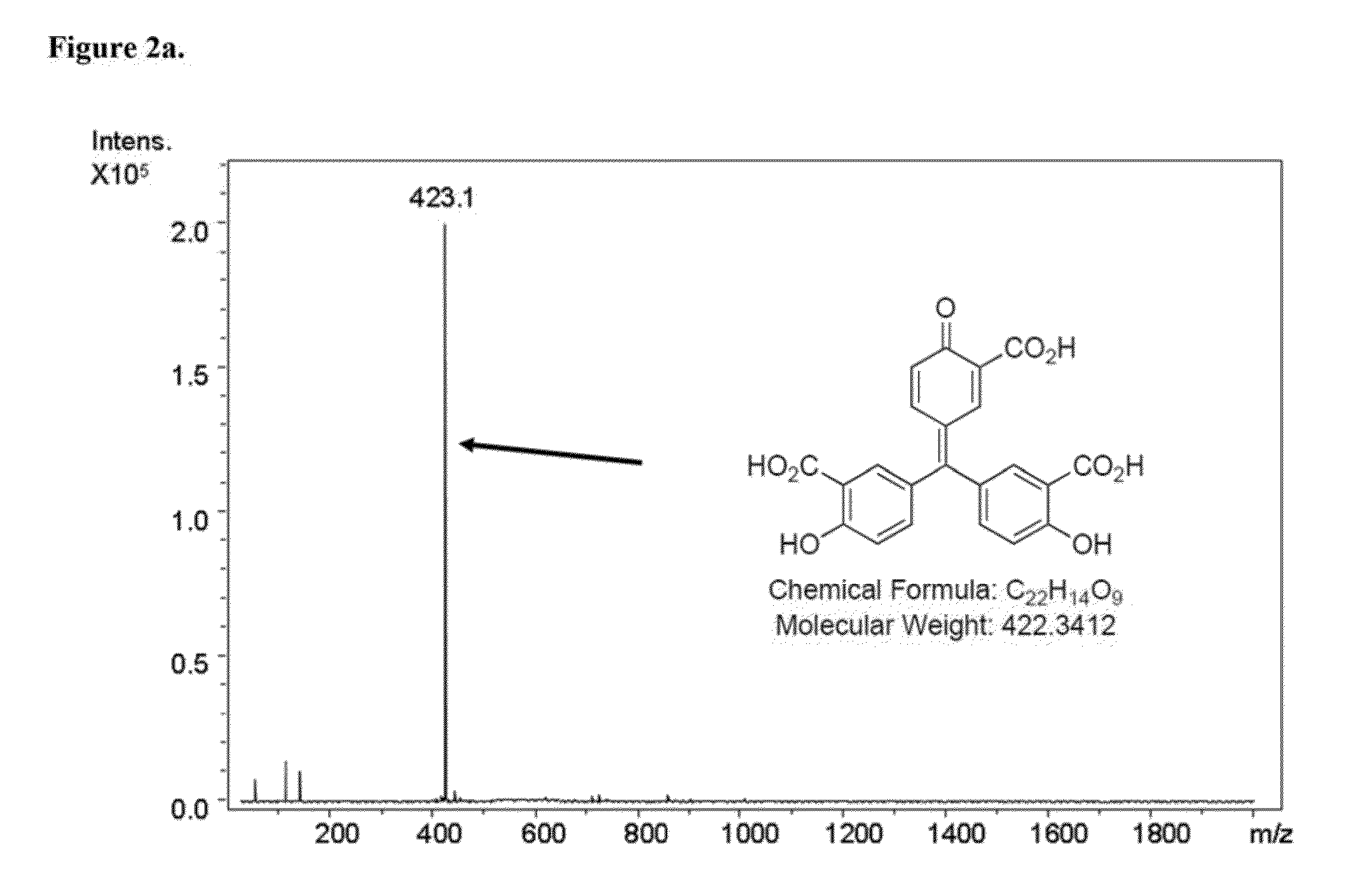
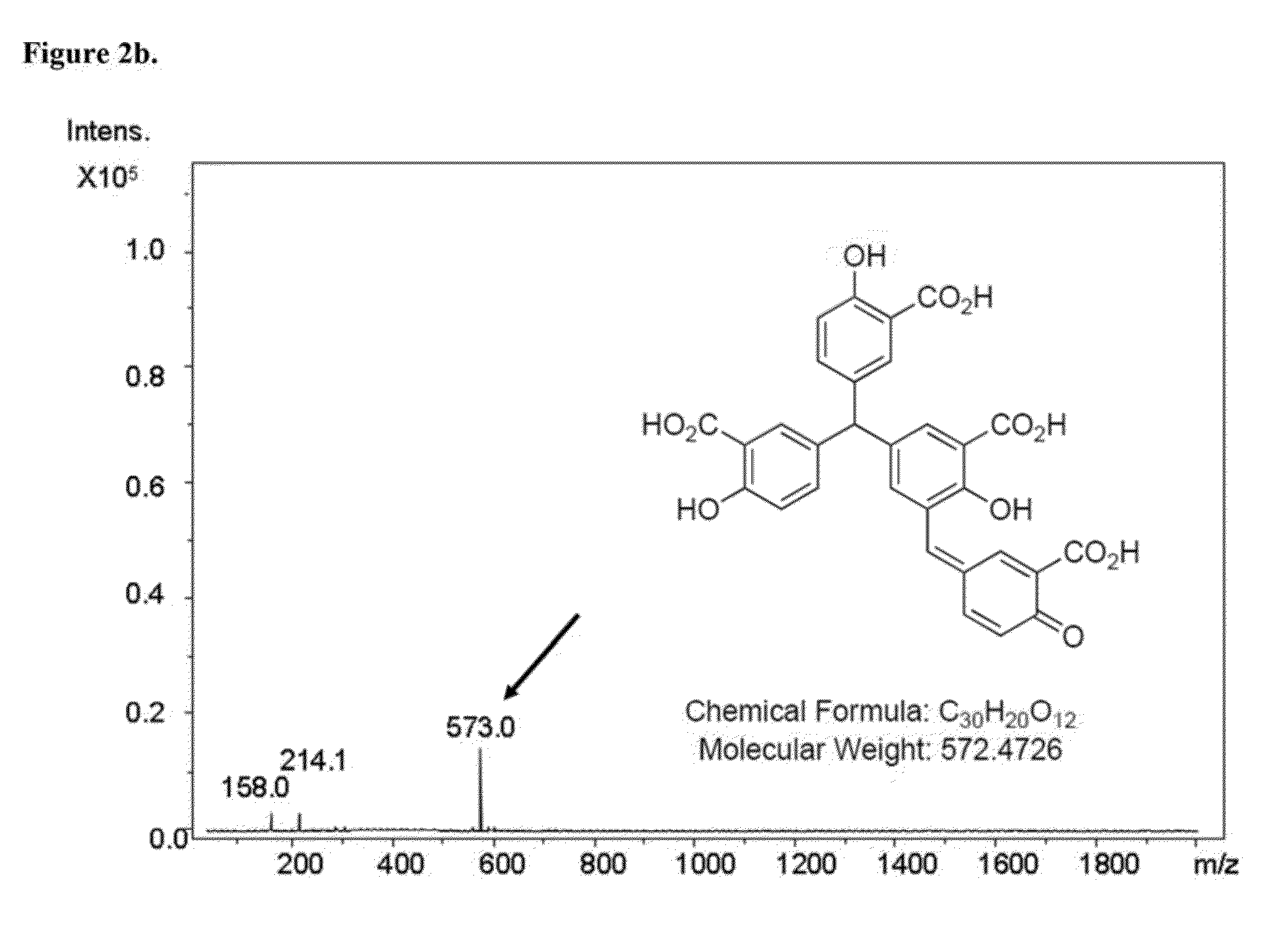
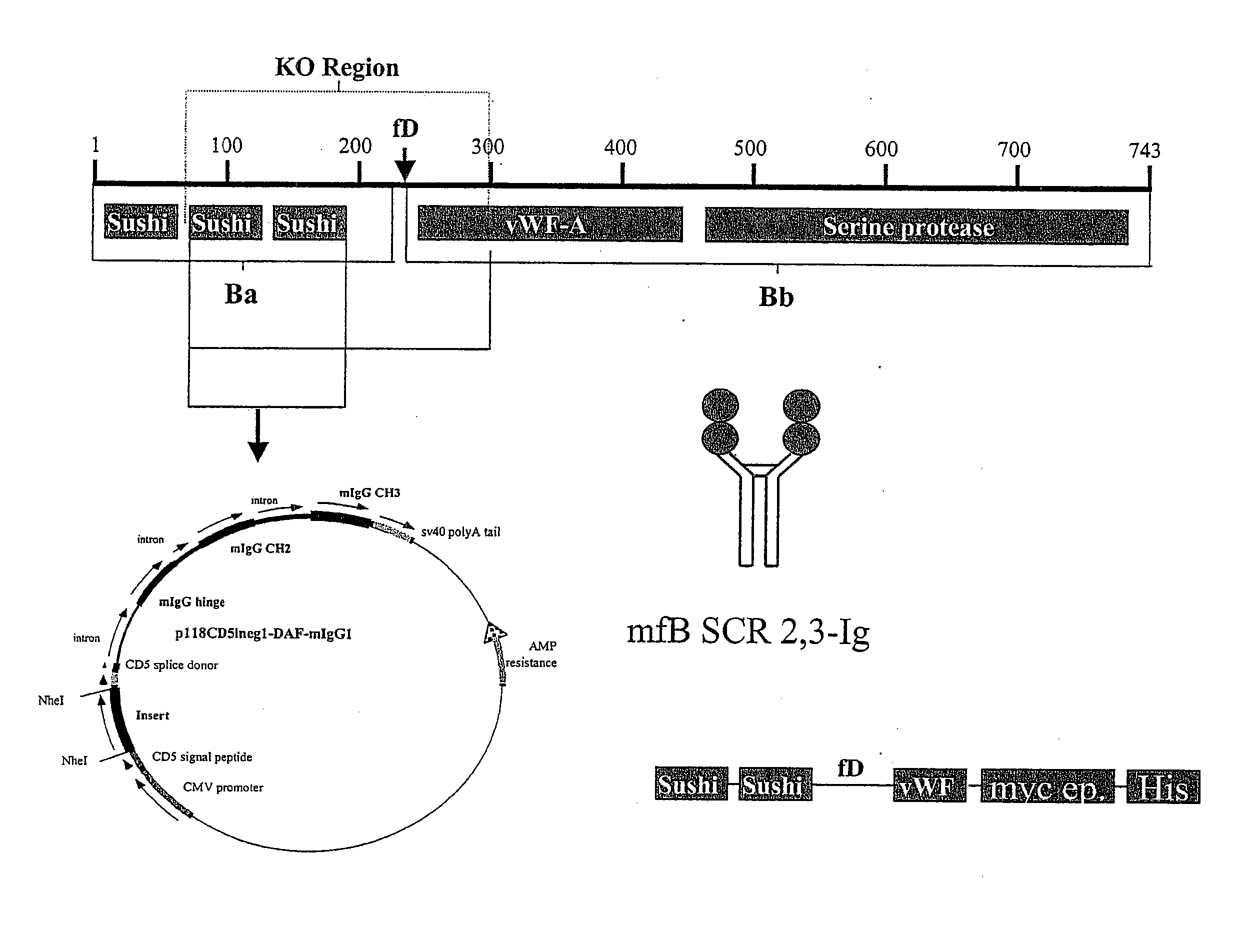
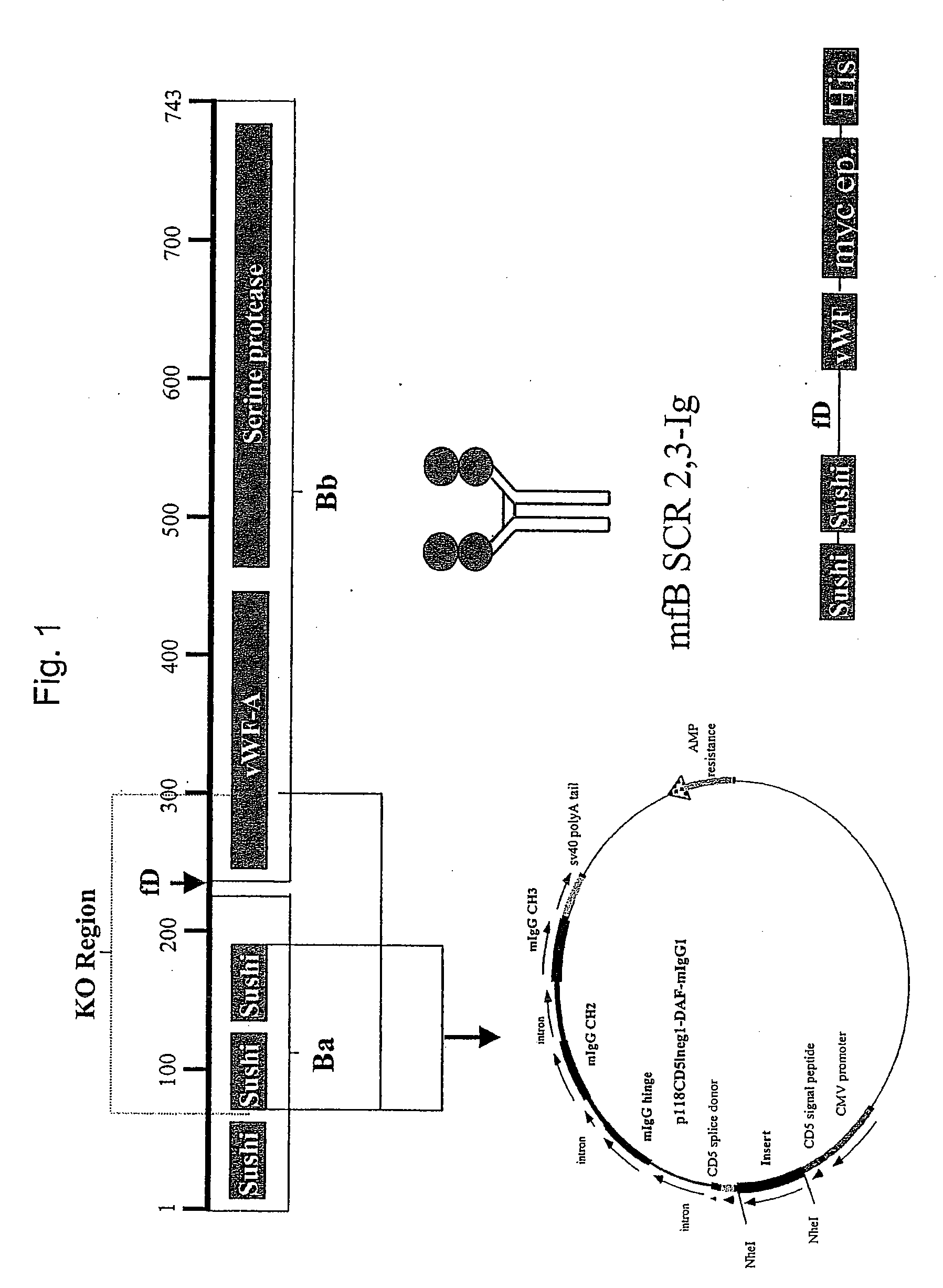
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77 results about "Alternate pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
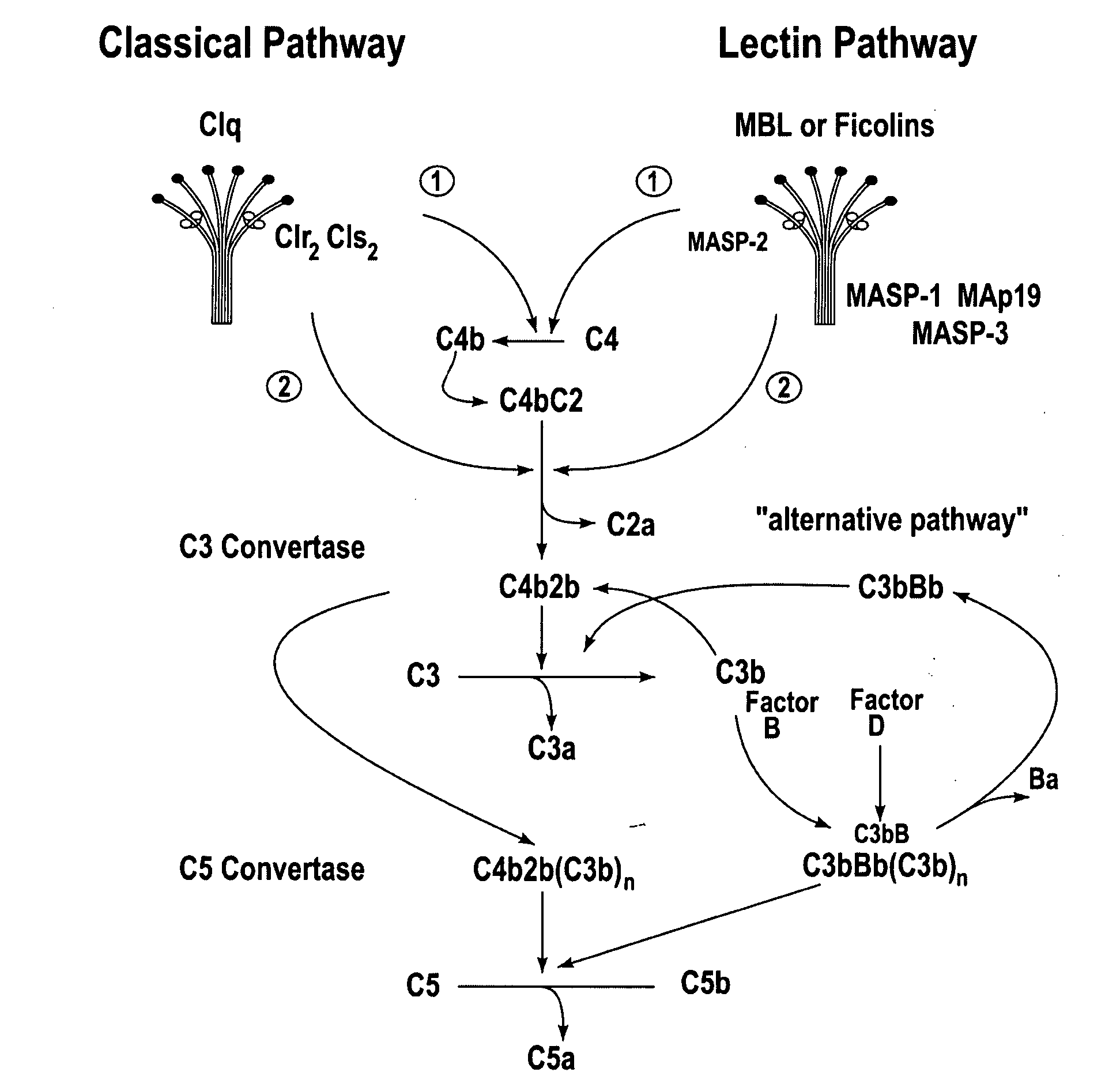
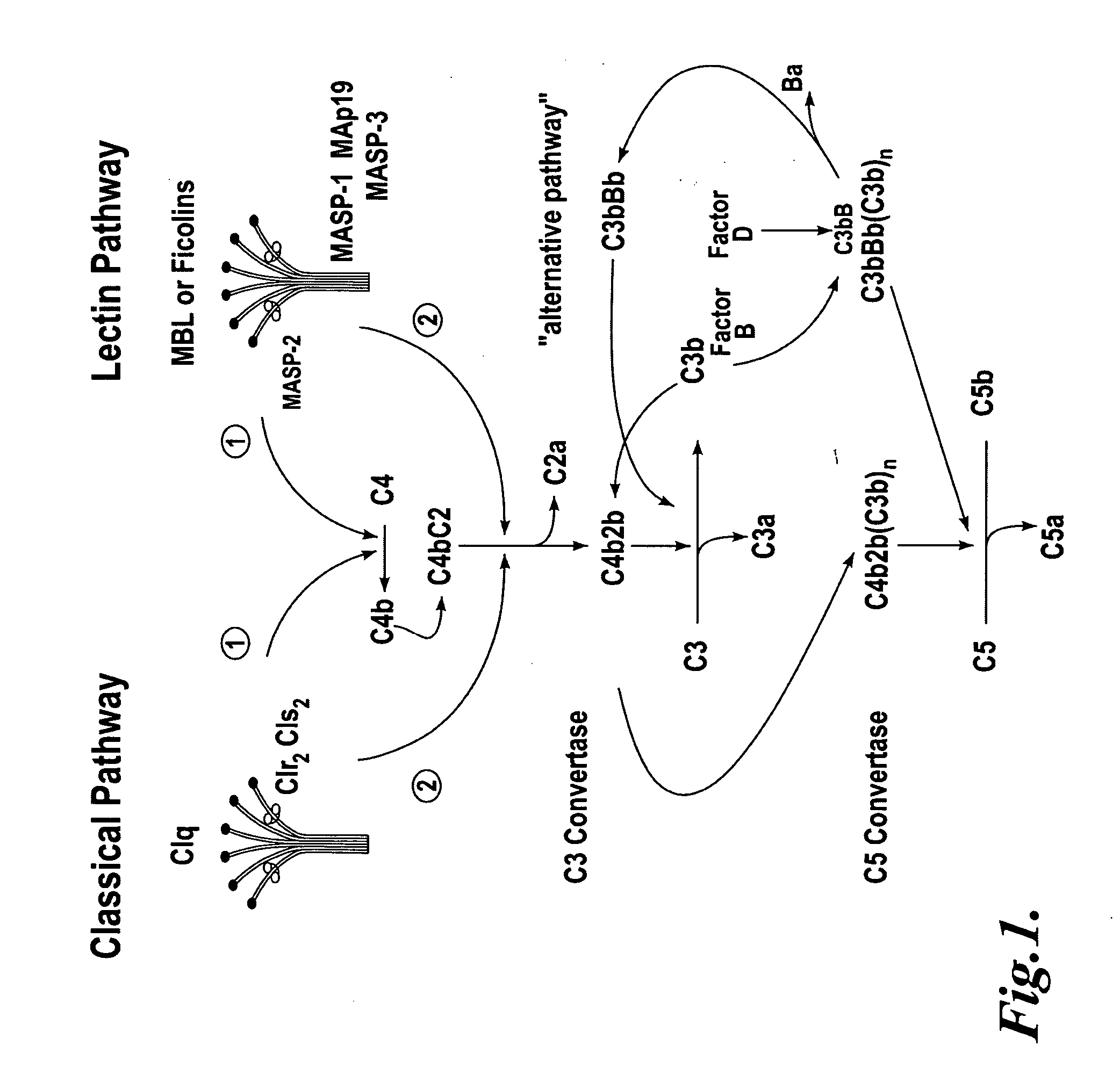
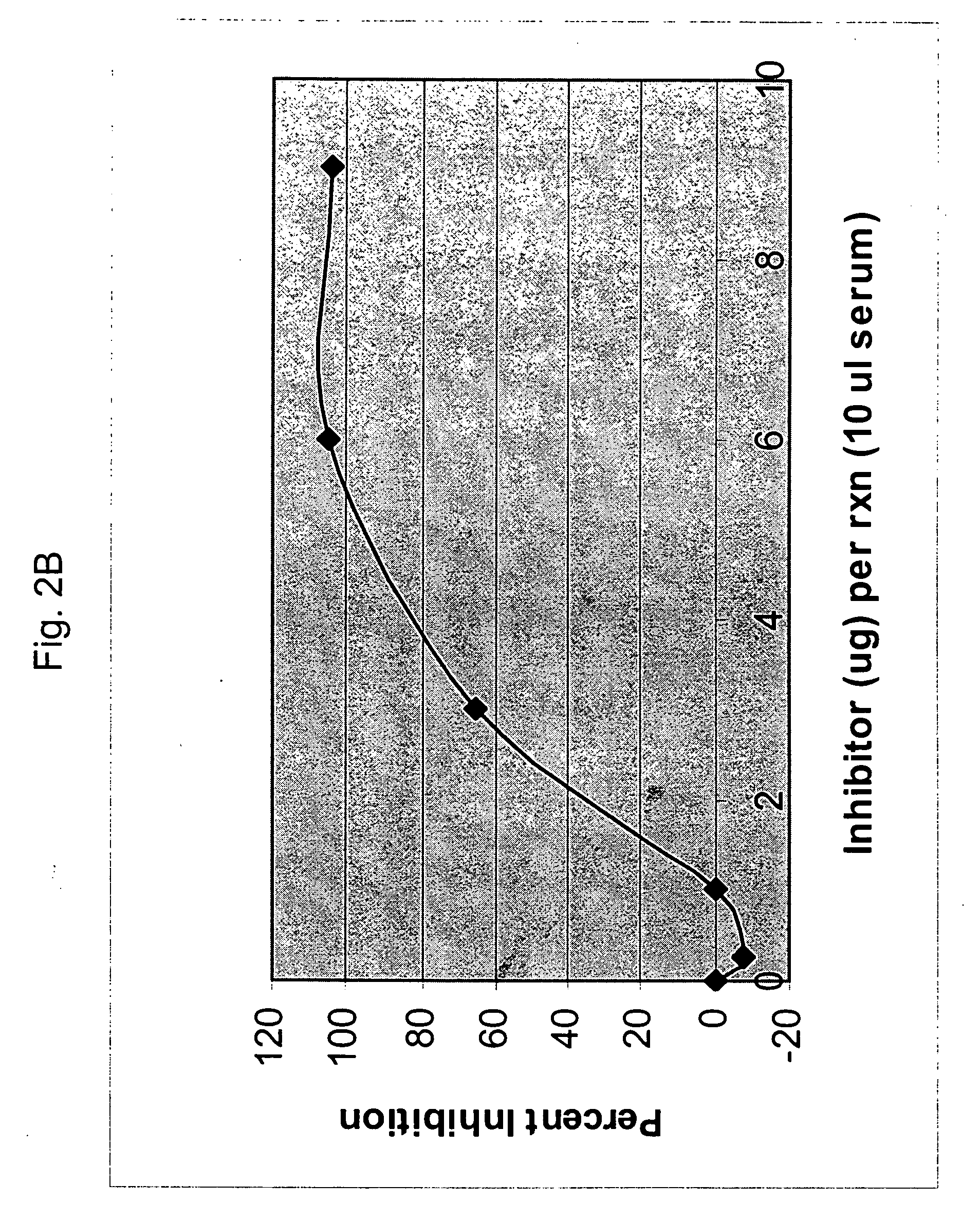
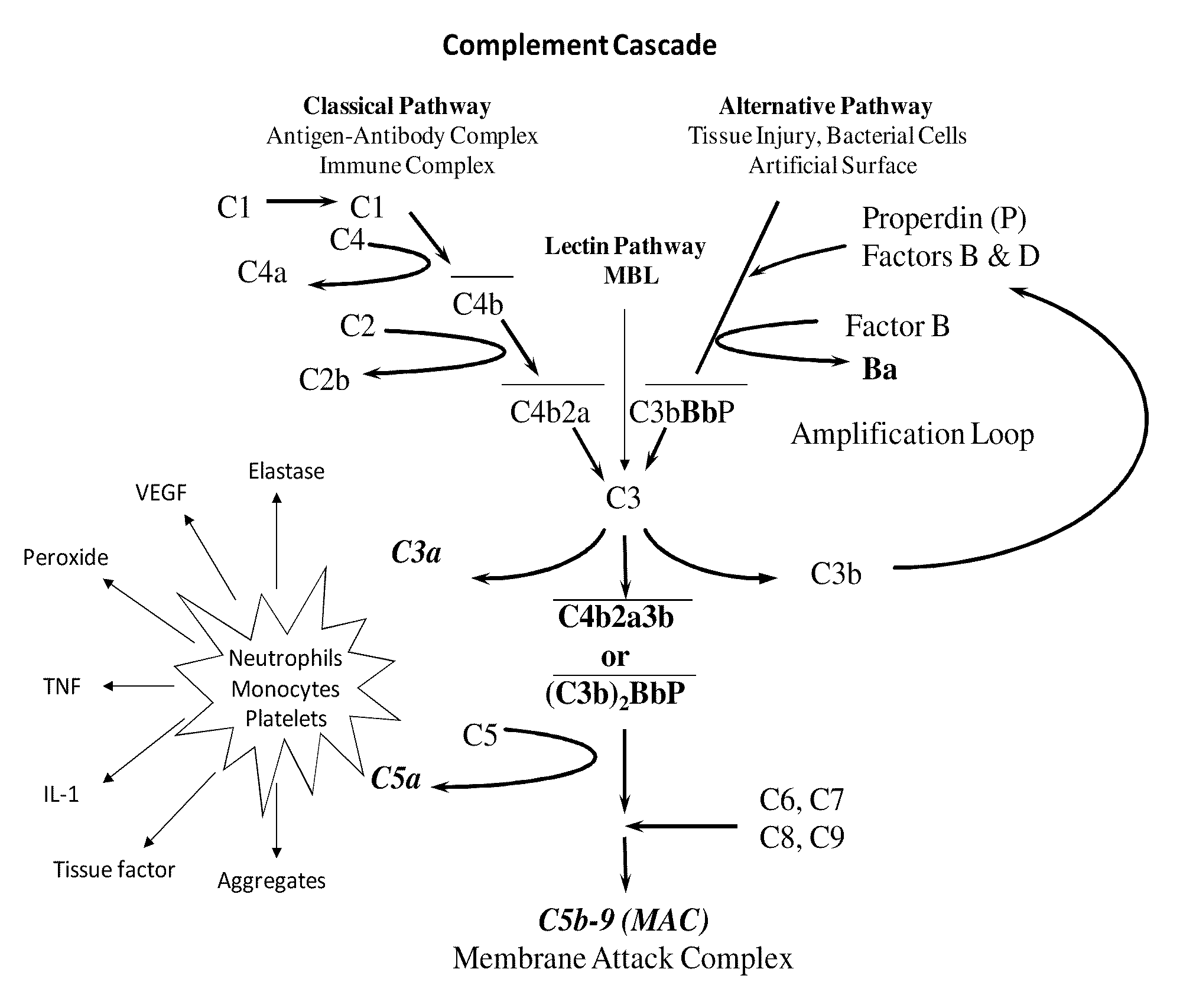
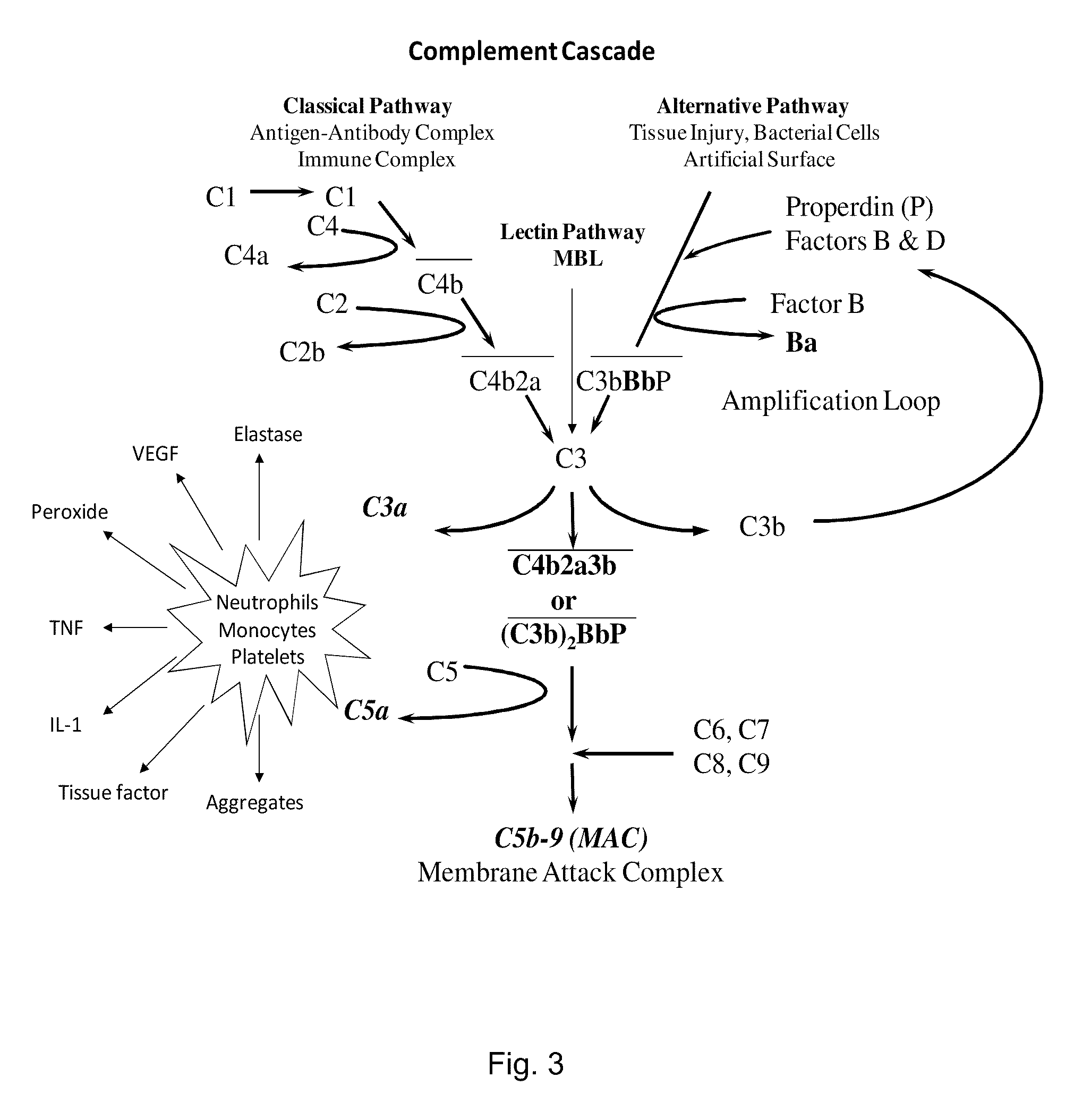
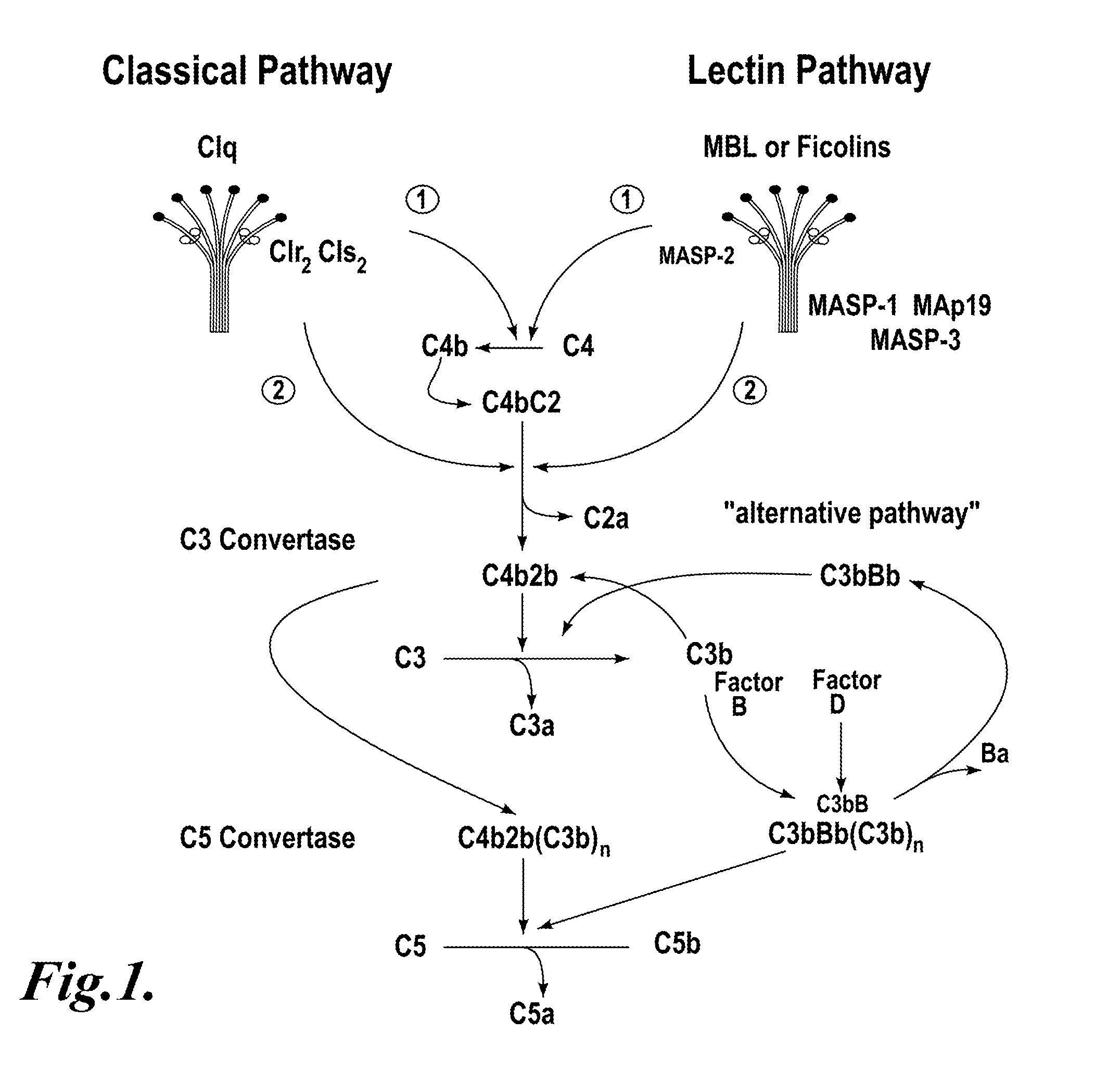
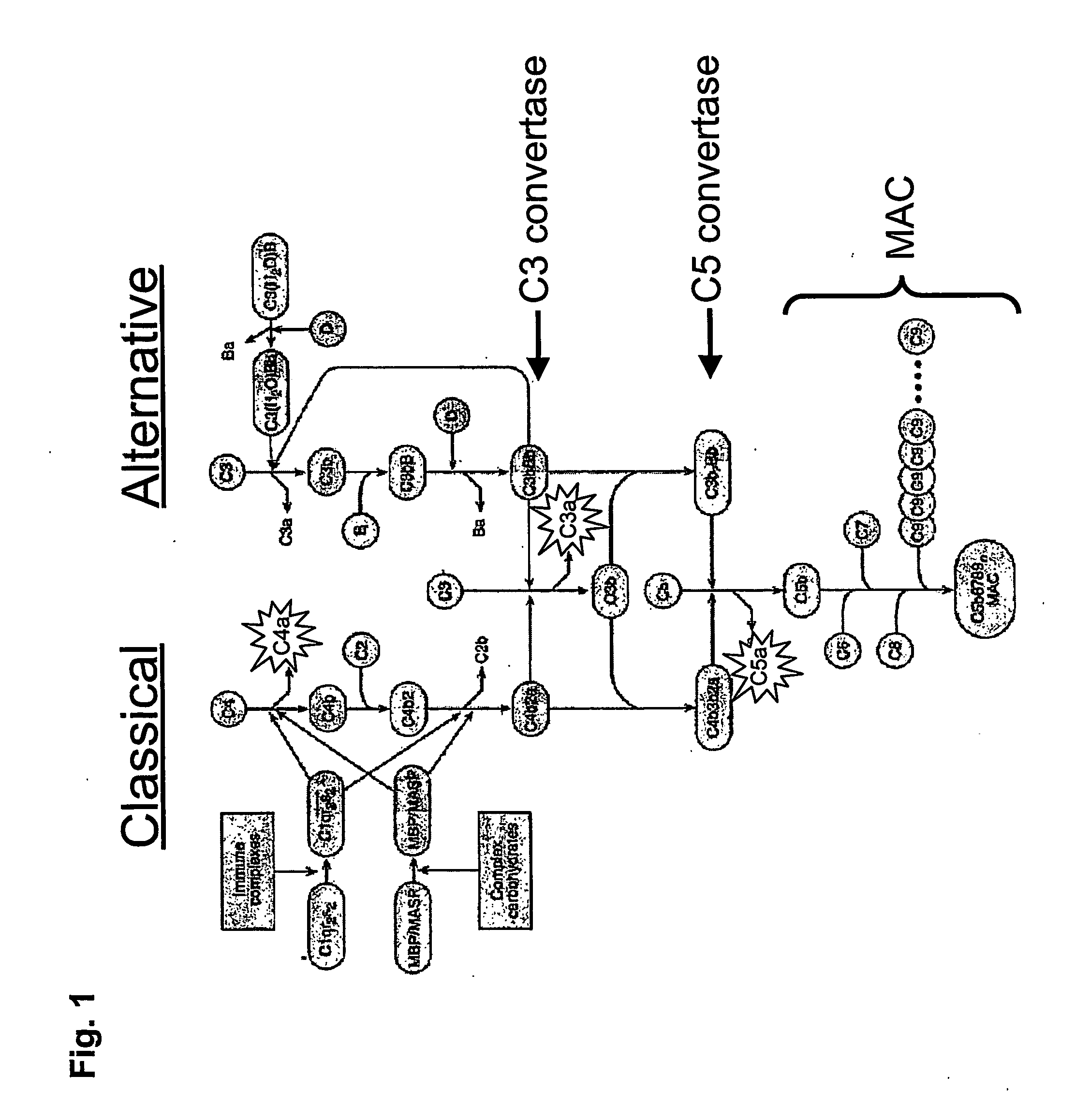
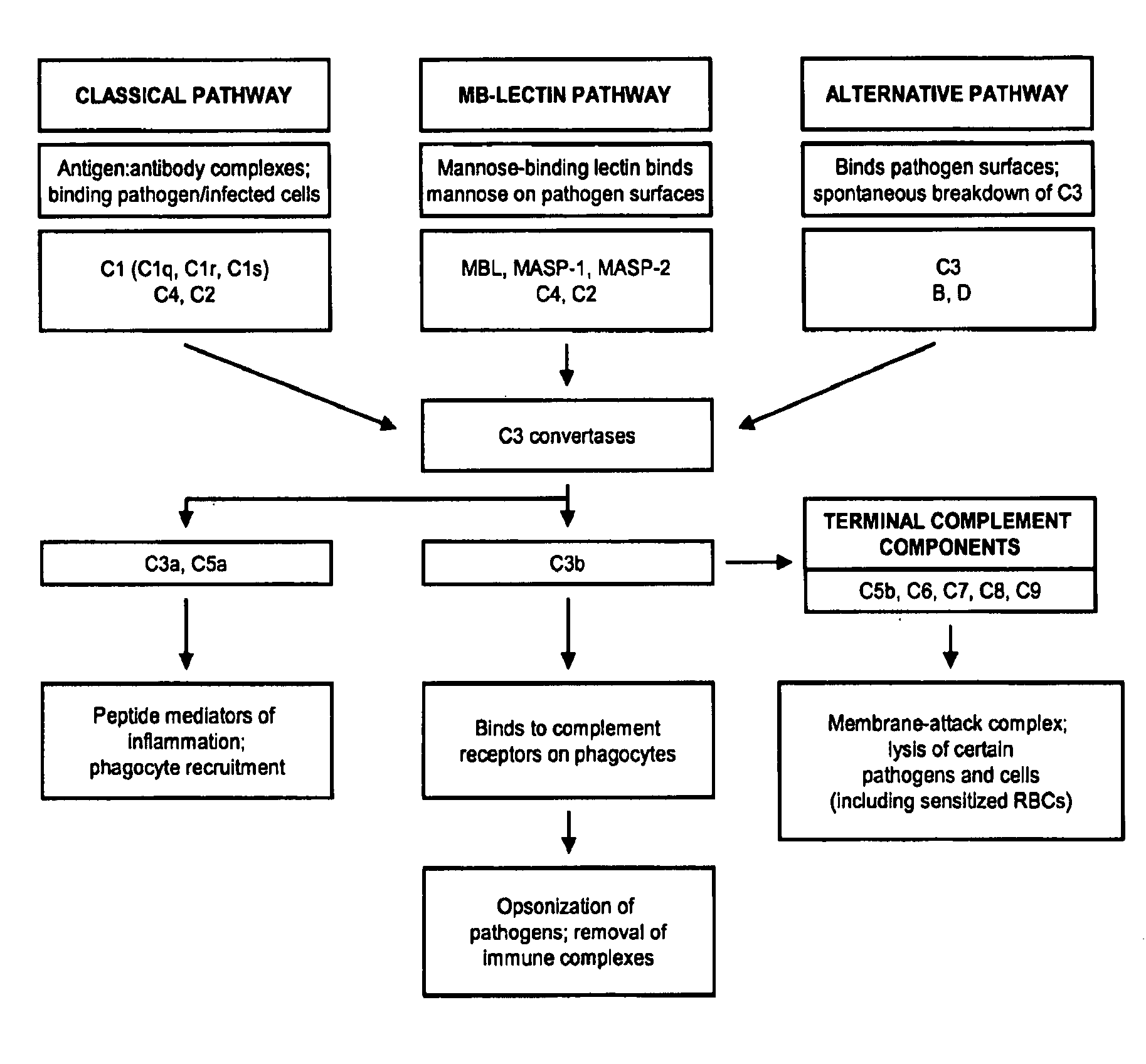
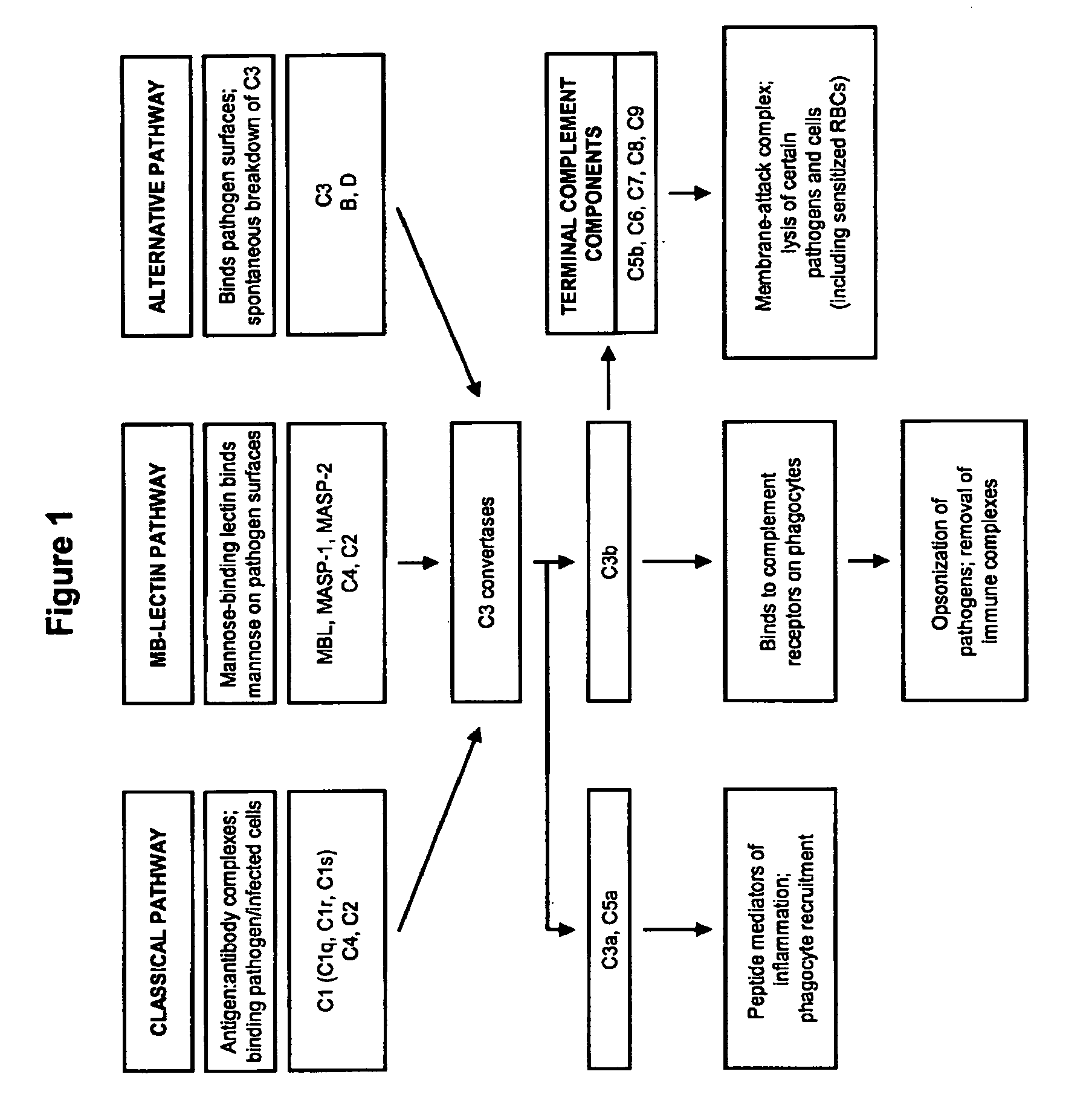
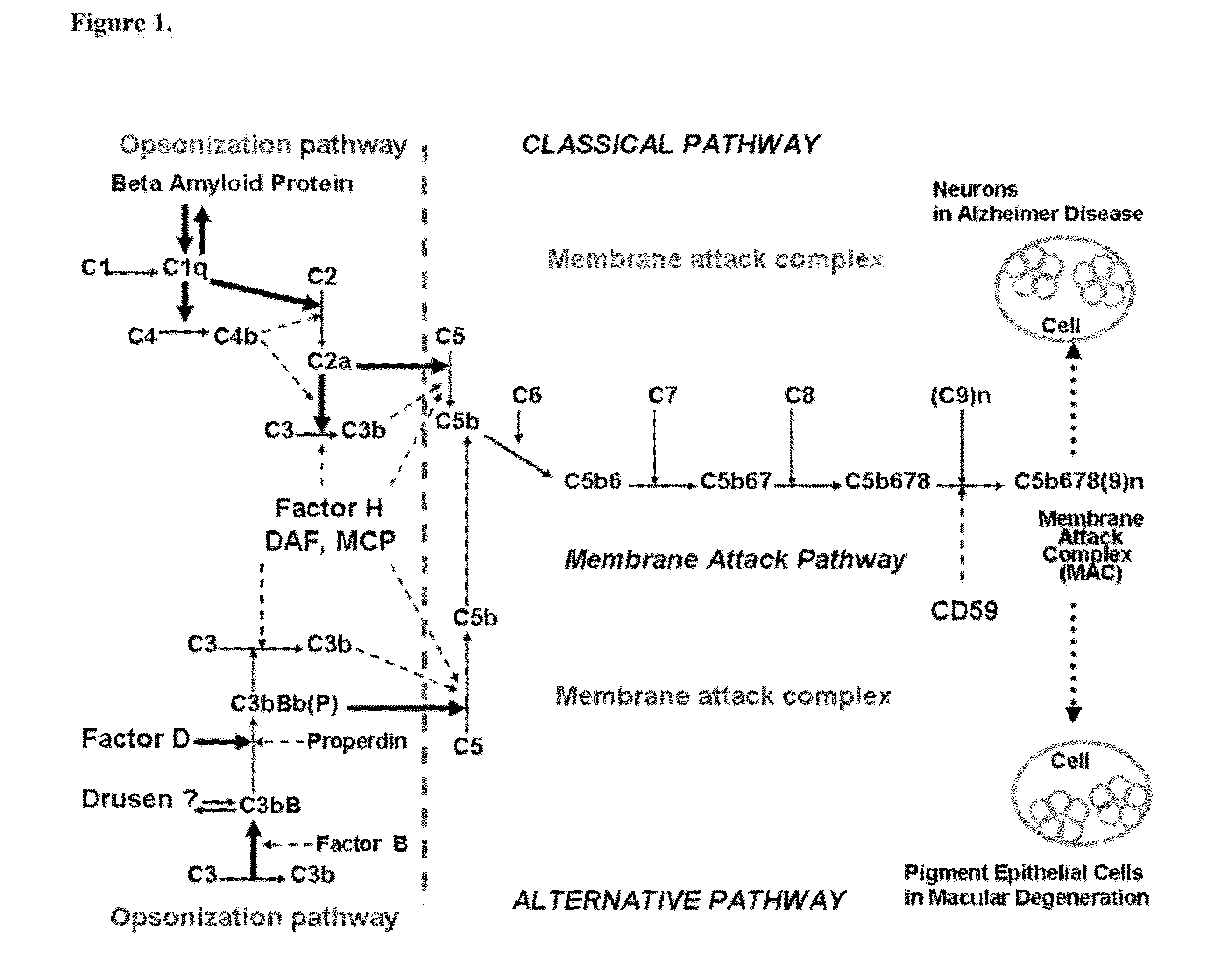
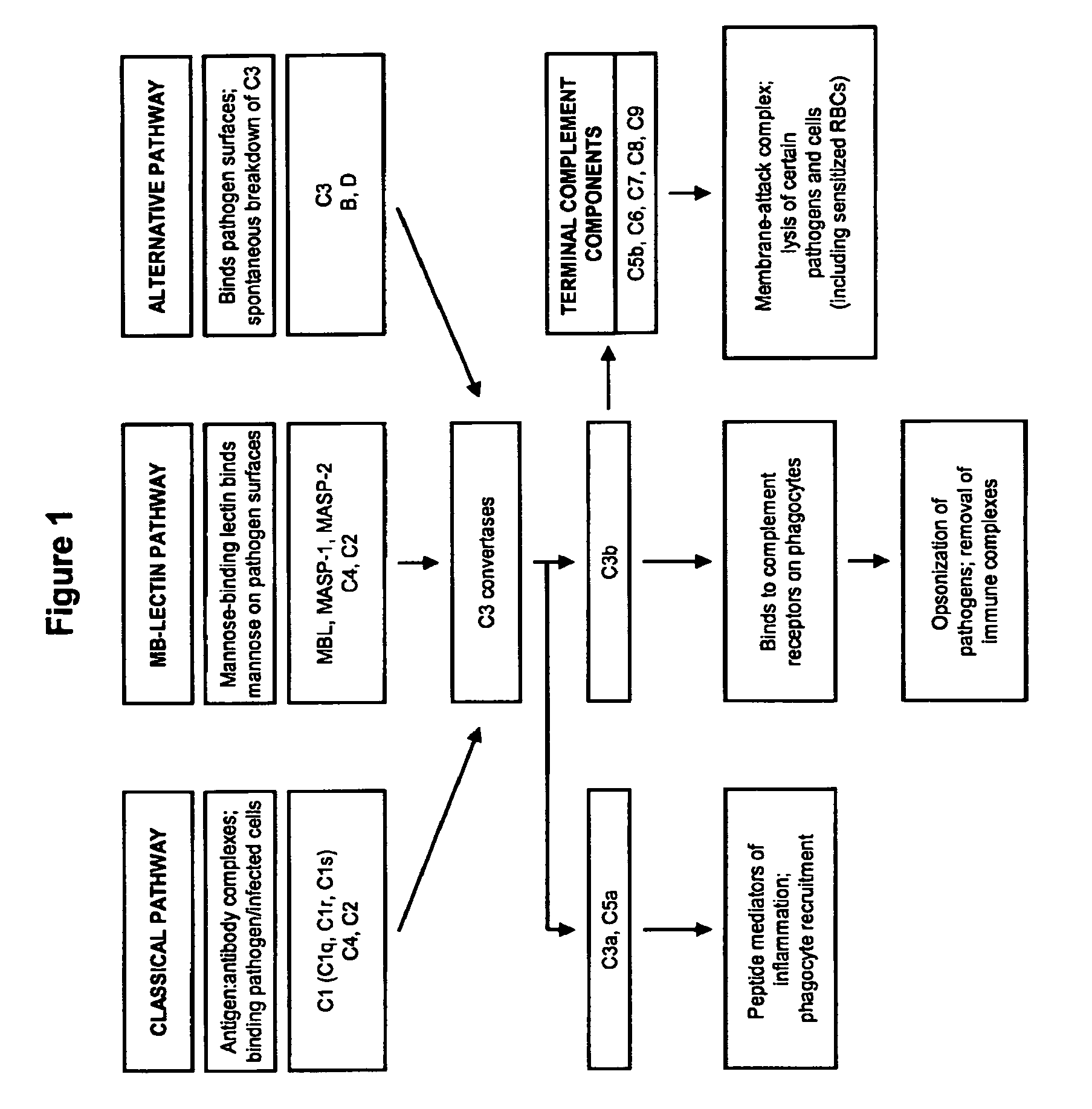
The alternative pathway of the complement system is an innate component of the immune system's natural defense against infections. The alternative pathway is one of three complement pathways that opsonize and kill pathogens. The pathway is triggered when the C3b protein directly binds a microbe.
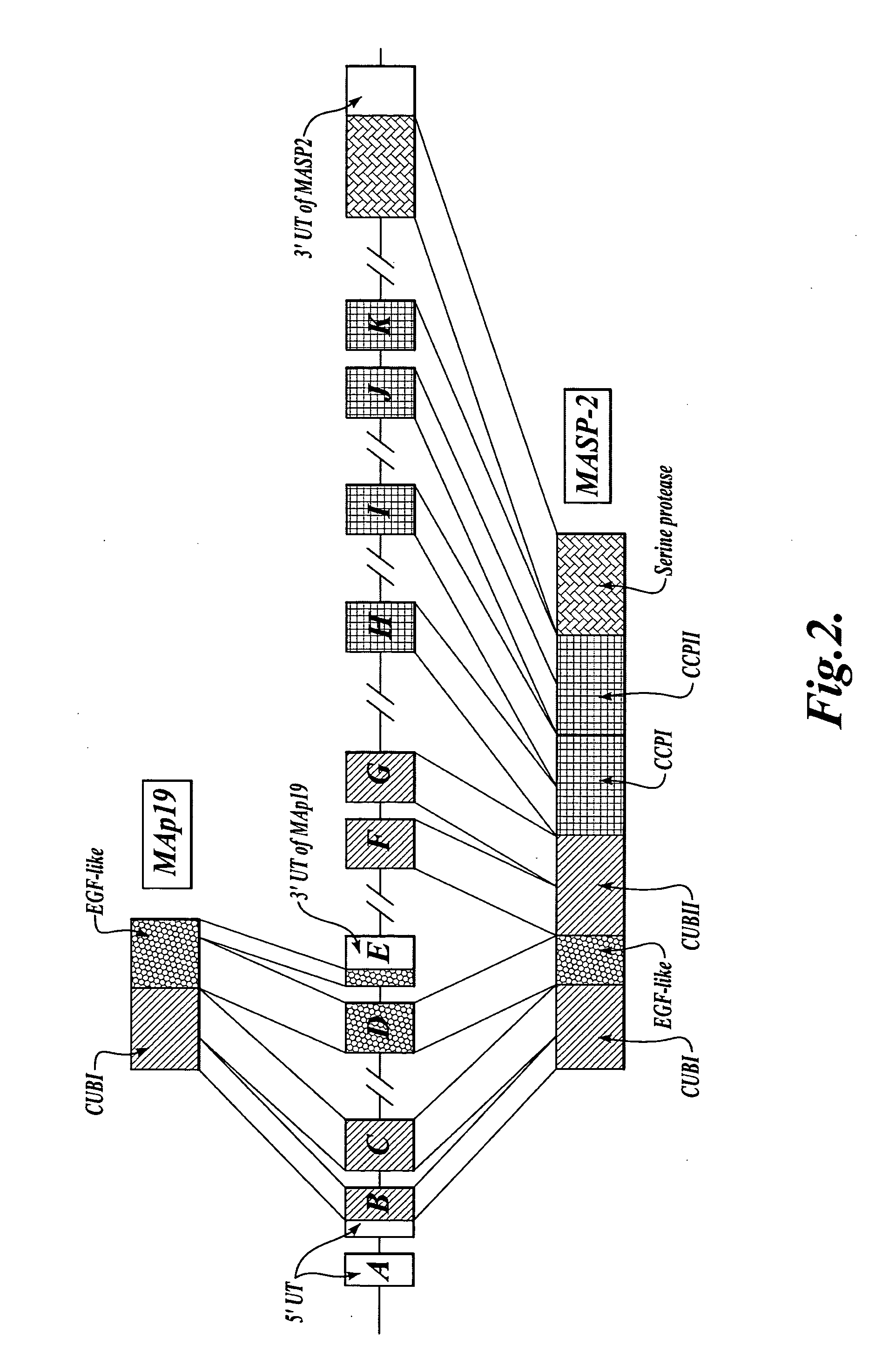
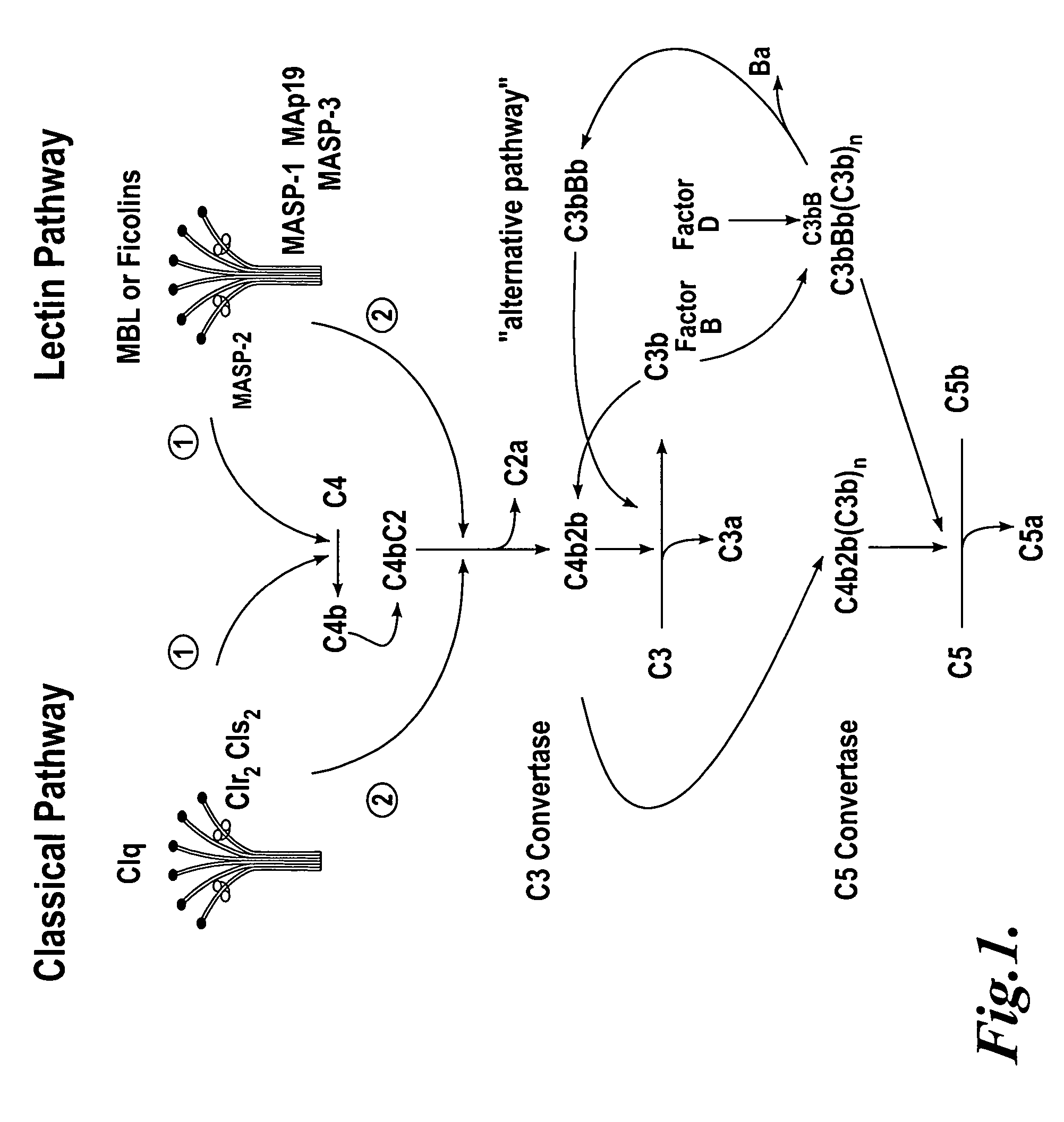
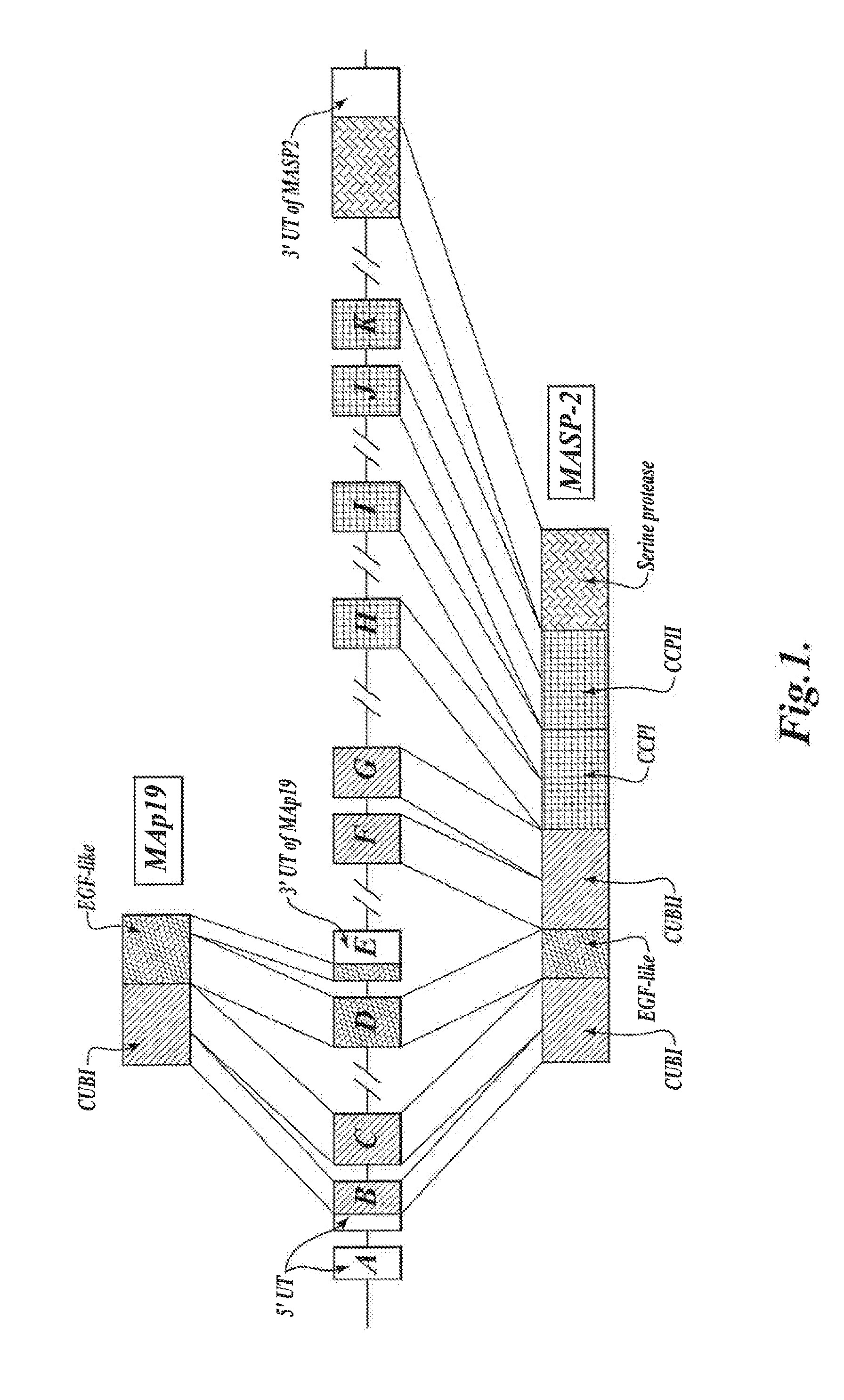
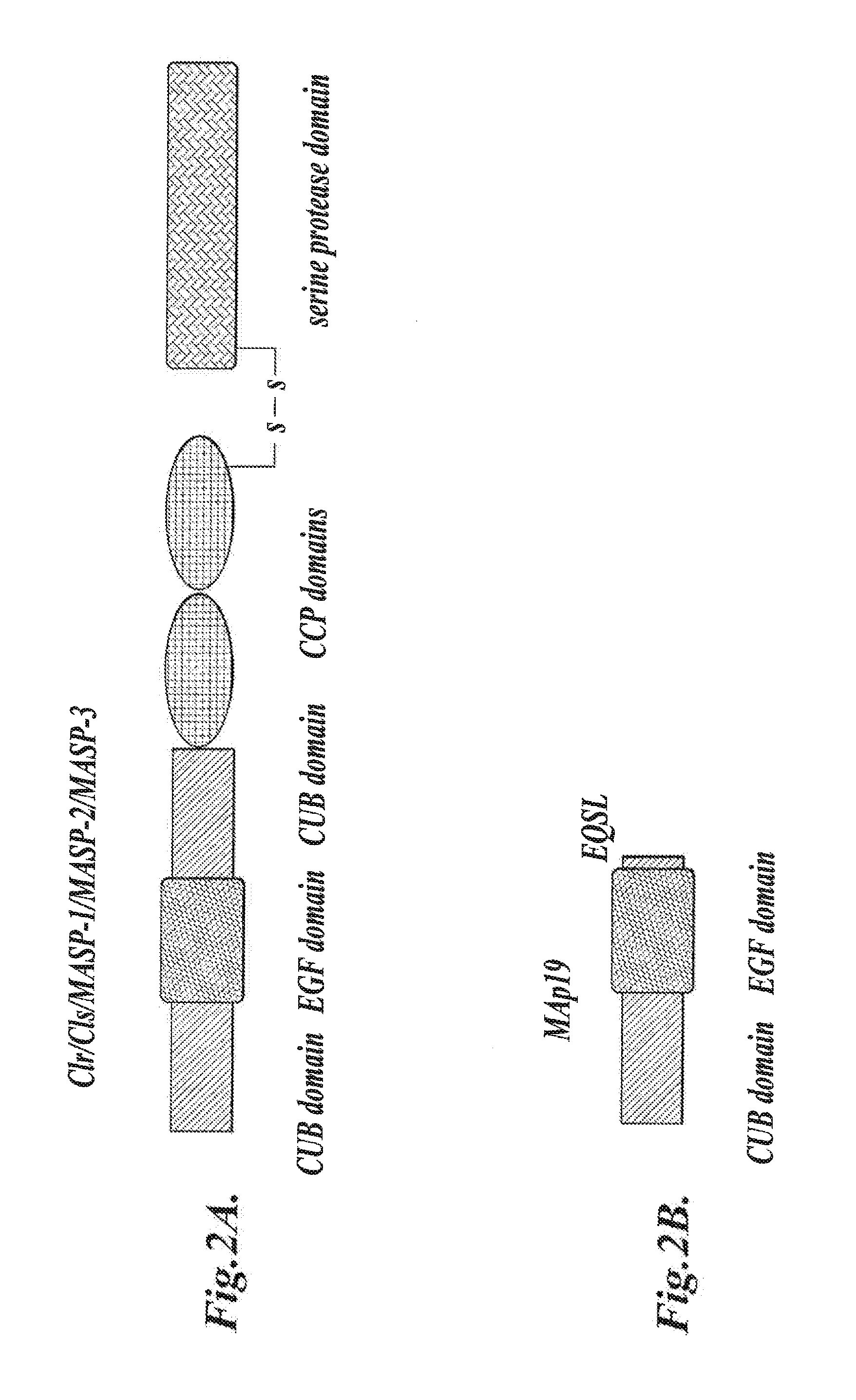
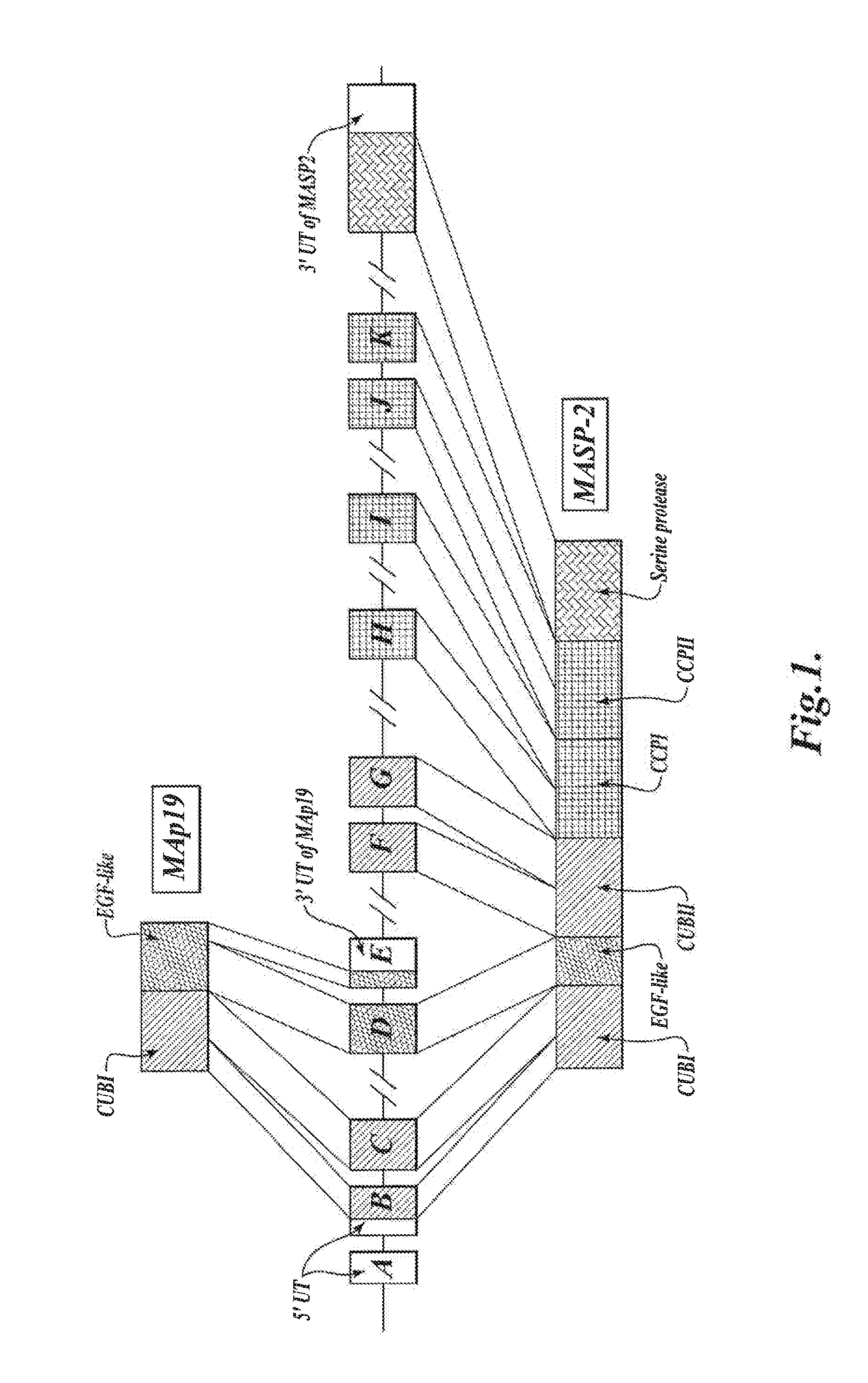
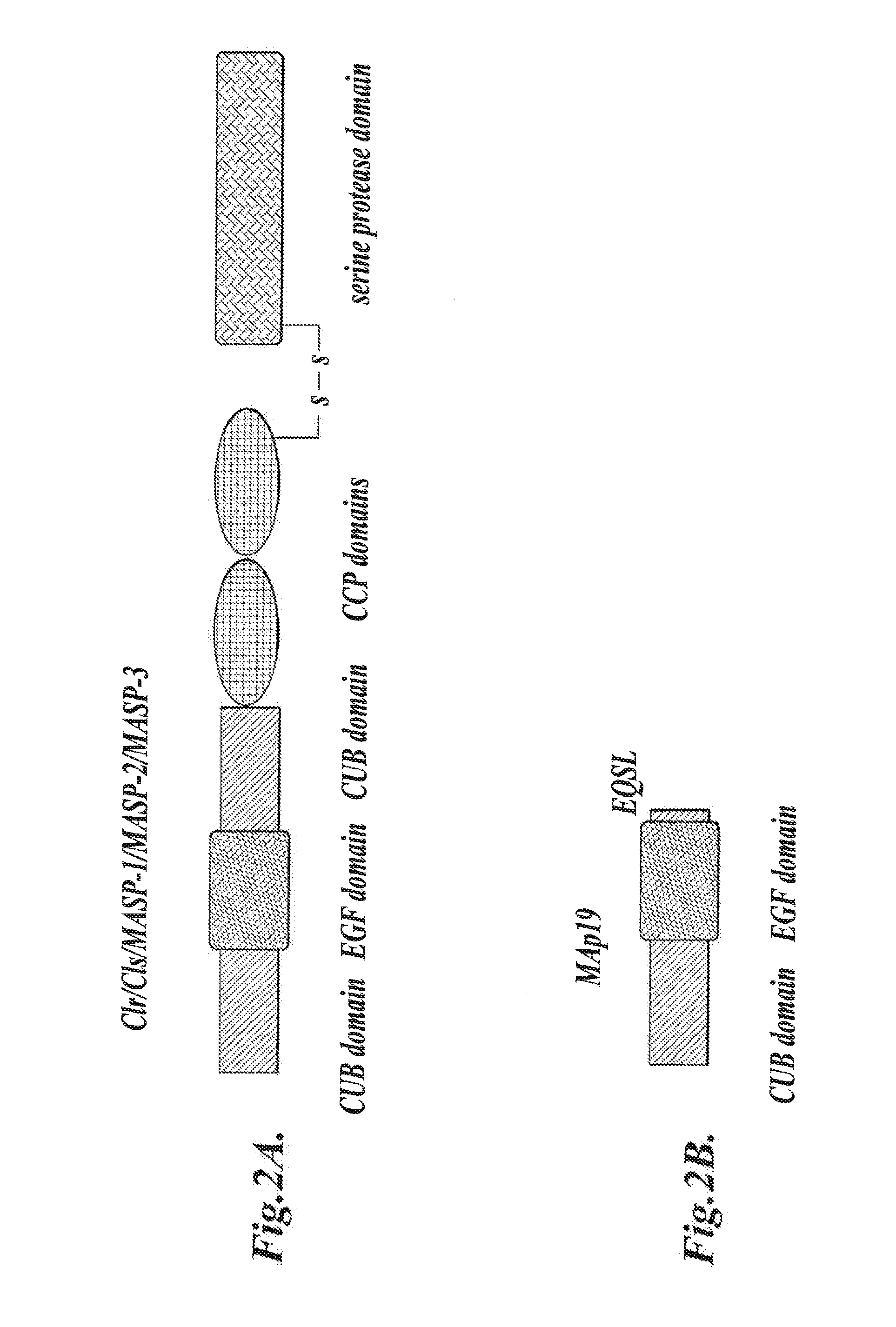
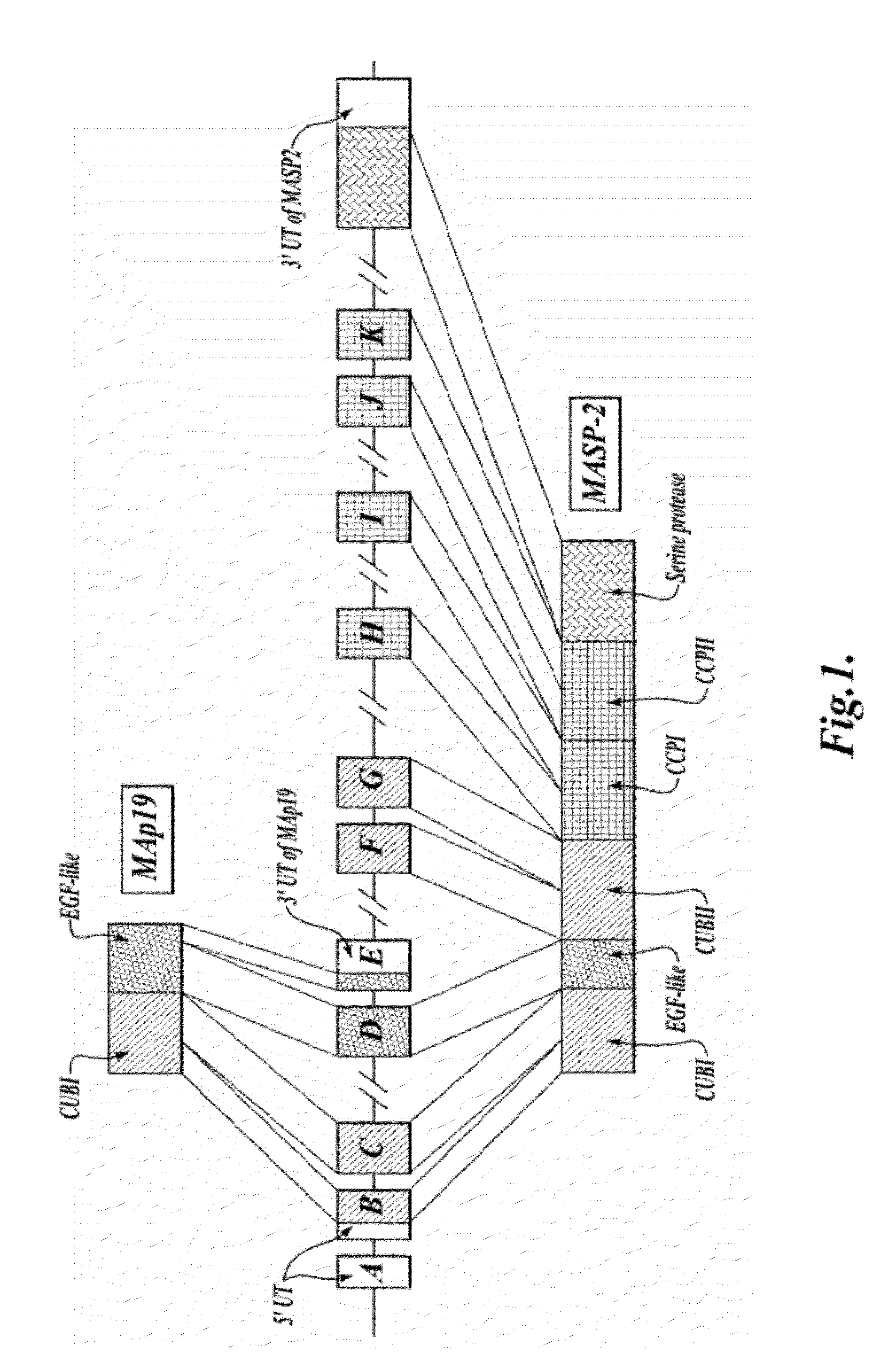
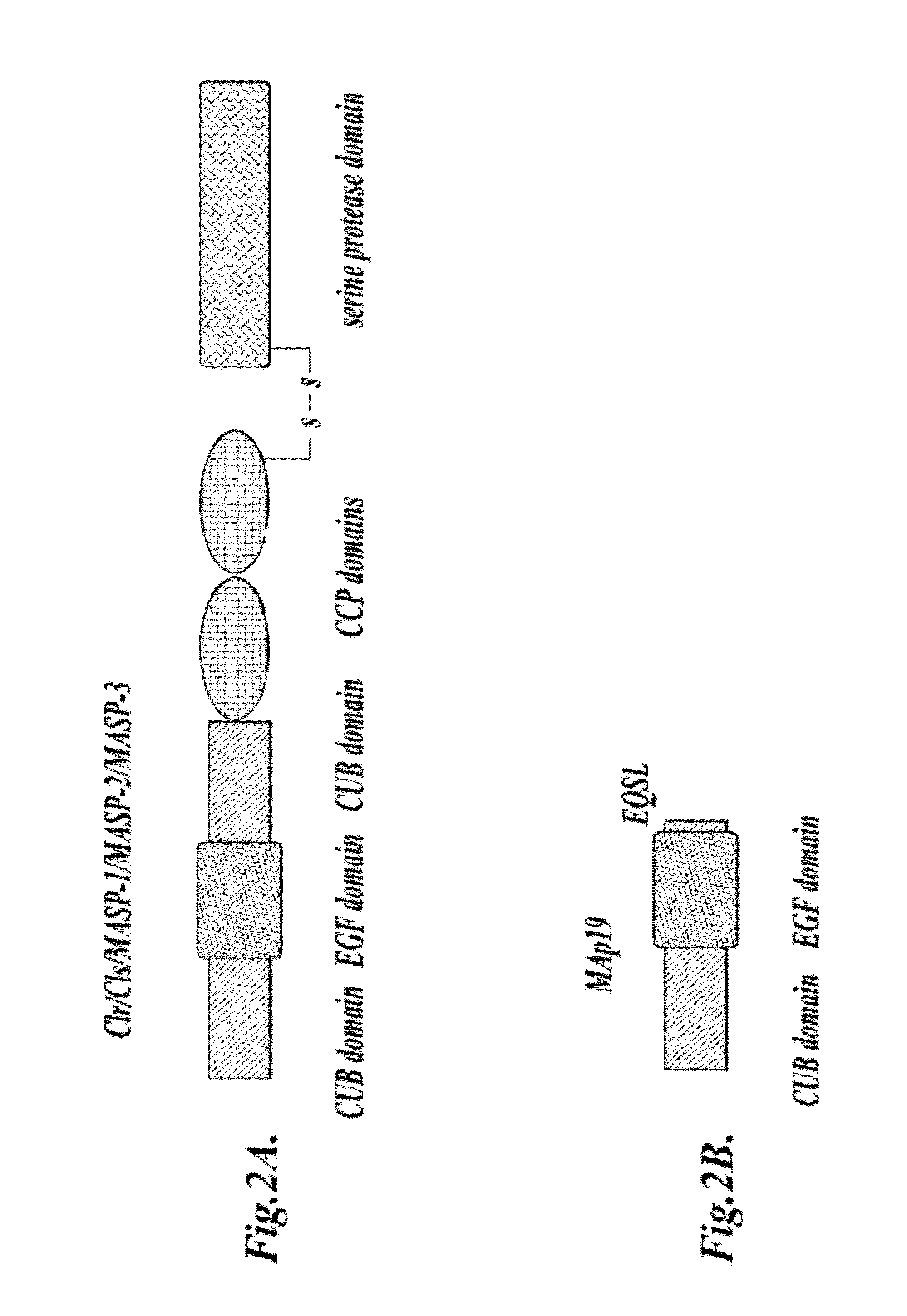
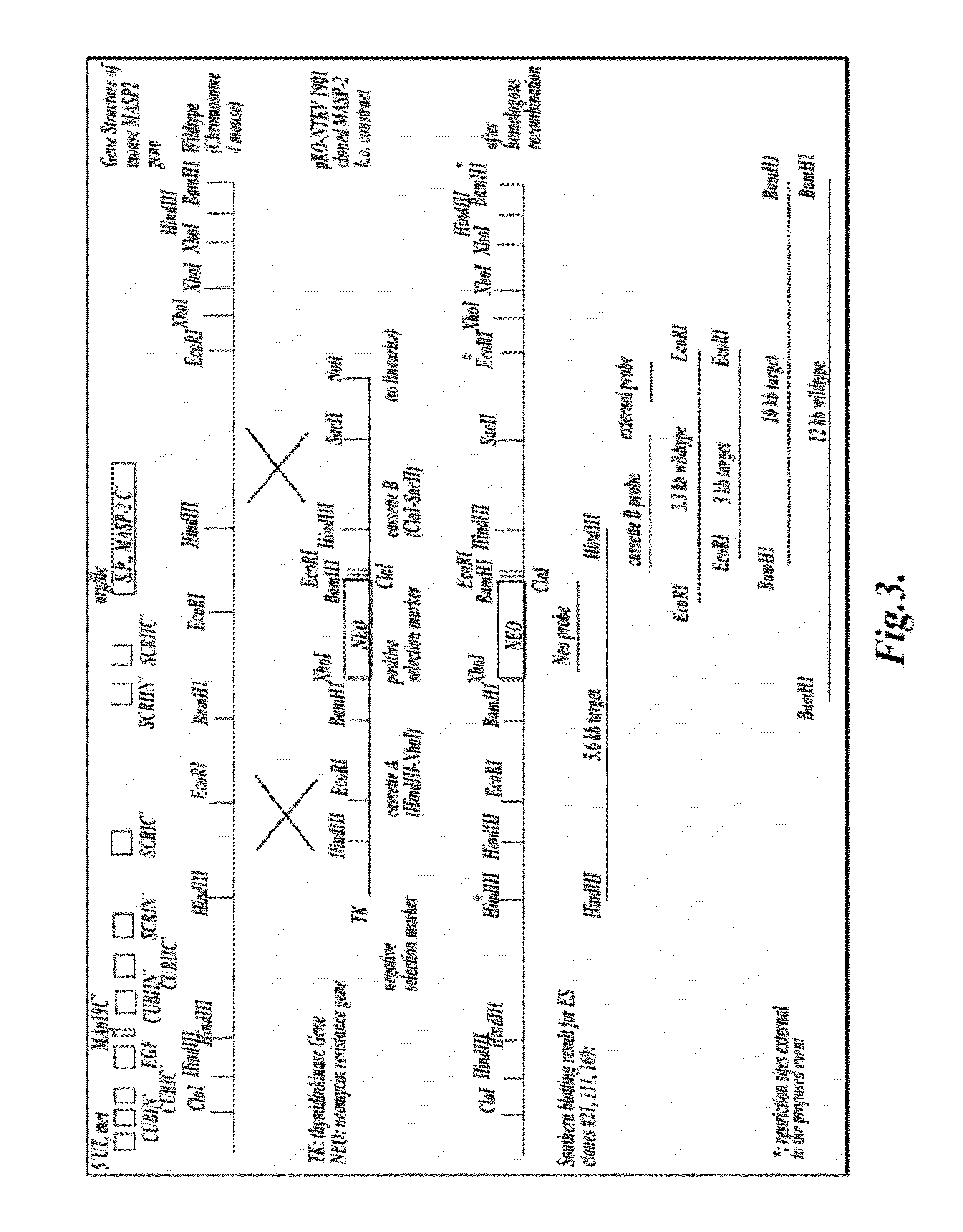
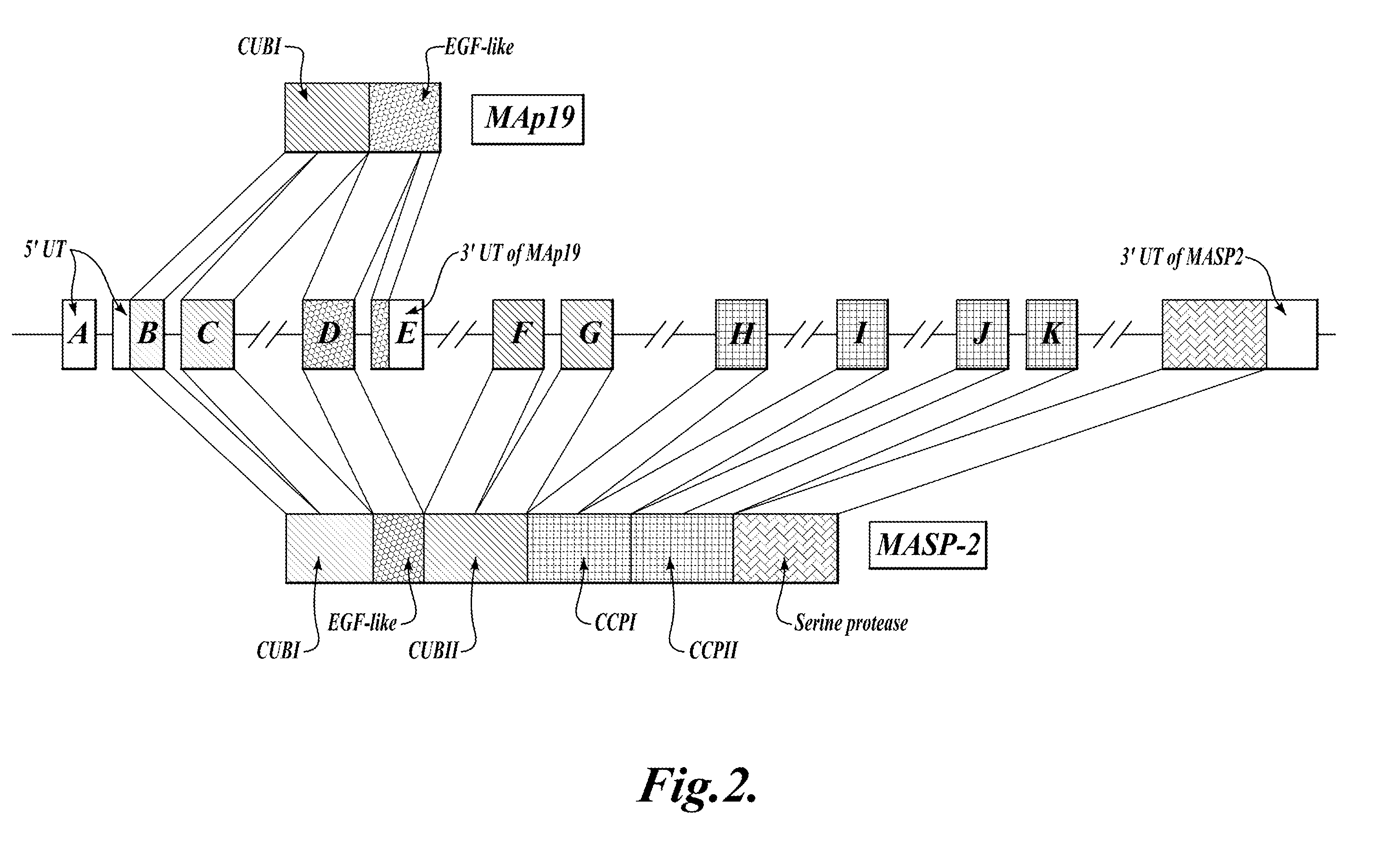
Methods for treating conditions associated with MASP-2 dependent complement activation
ActiveUS20070172483A1Eliminate side effectsInhibiting complement activationCompounds screening/testingAntibody ingredientsBiological activationAlternative complement pathway
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:OMEROS CORP +1
Compounds useful in the complement, coagulat and kallikrein pathways and method for their preparation
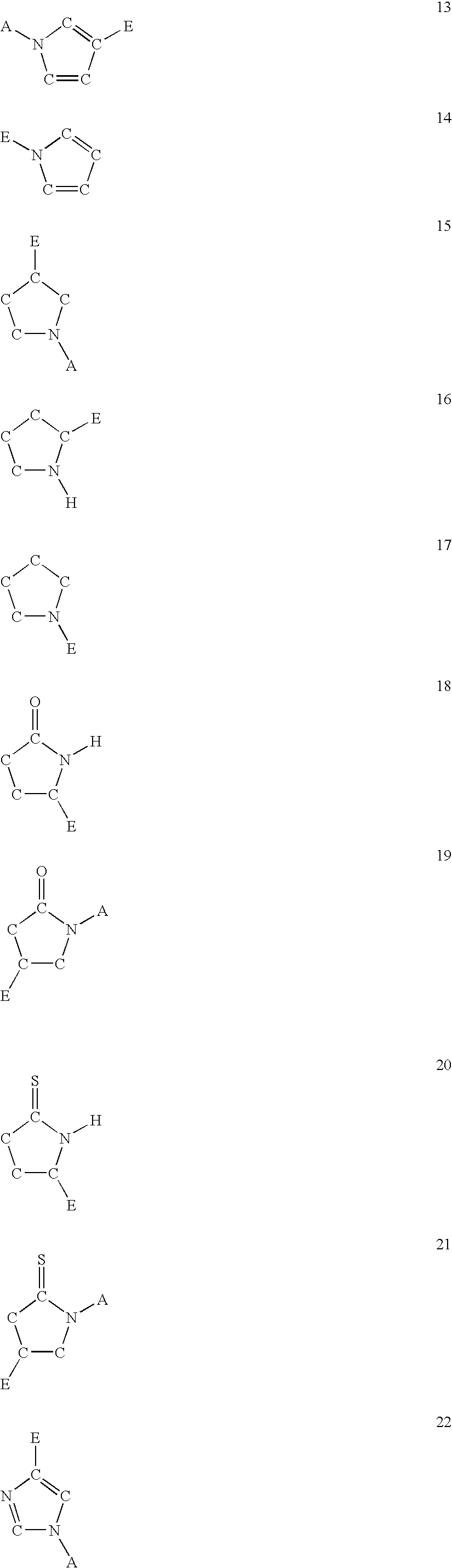
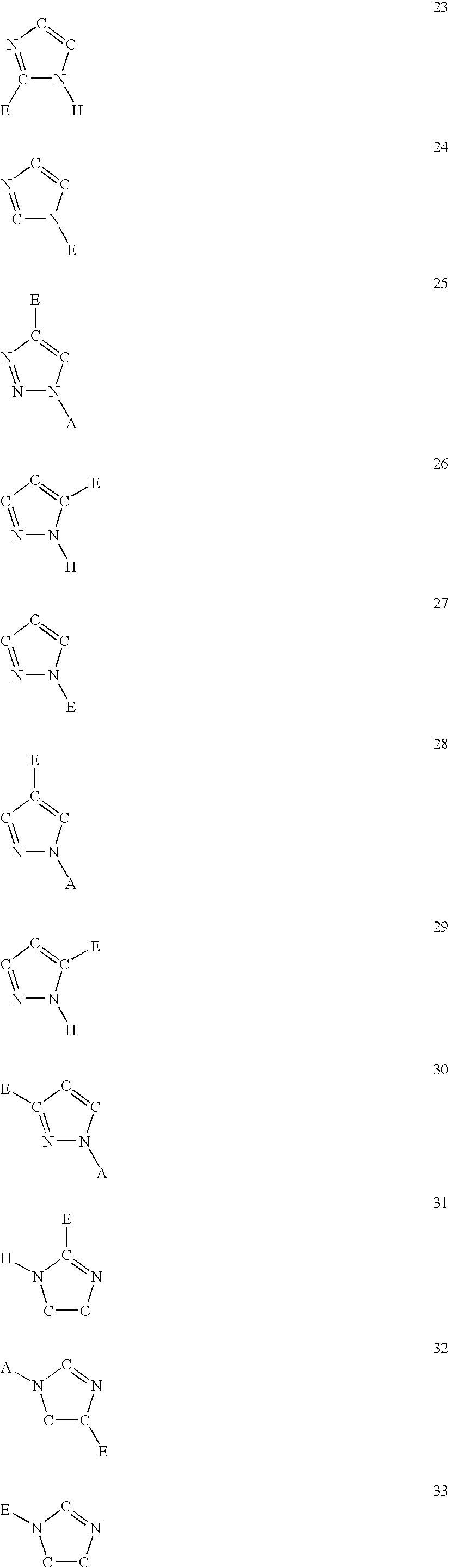
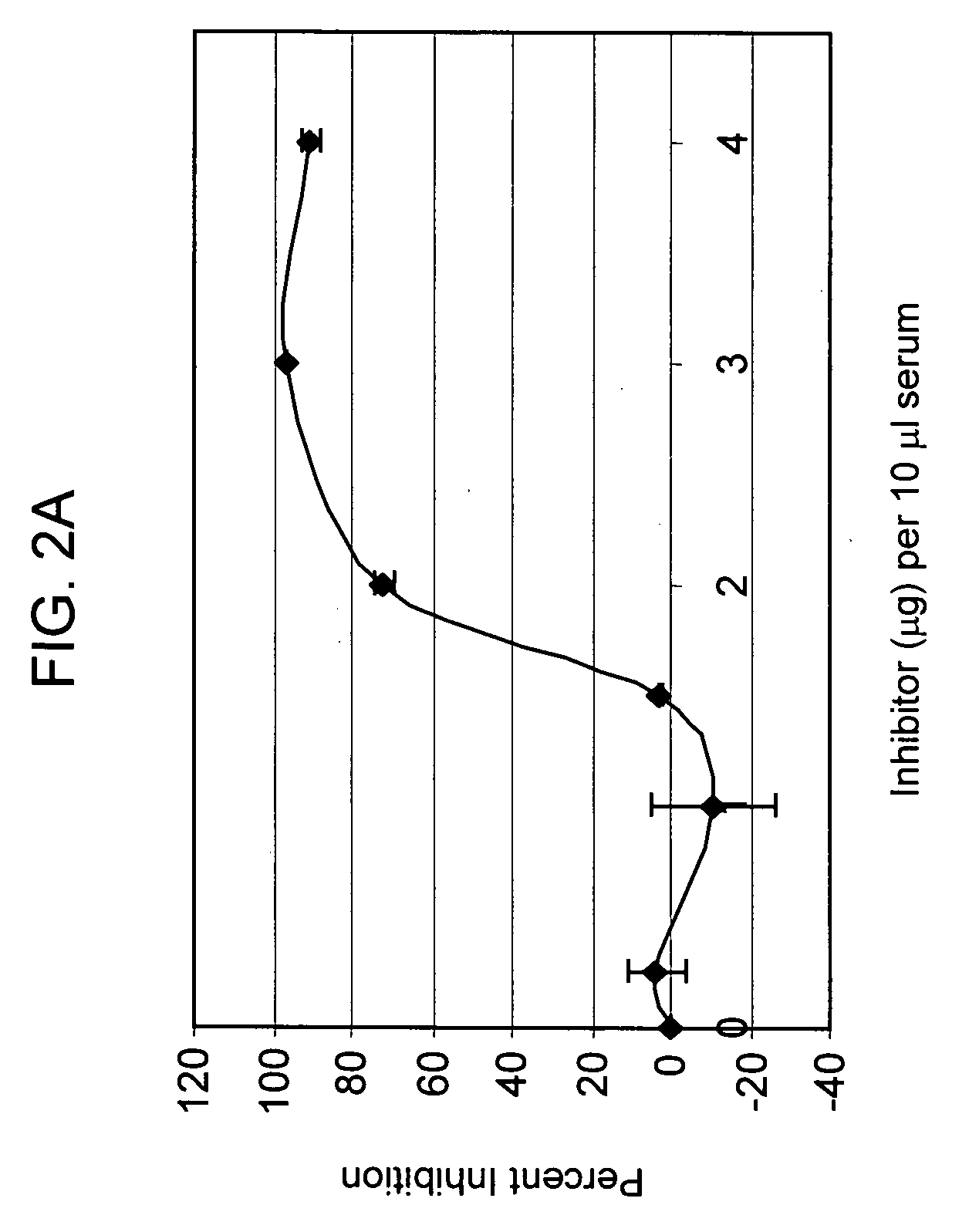
The present invention is concerned with new compounds, and particularly those having a fused bicyclic ring substituted with an amidine moiety. These compounds are each potent inhibitors of Factor D of the alternate pathway of complement, C1s of the classical pathway of complement, Factors Xa, XIIa, VIIa and thrombin of the coagulation pathway, plasmin in the fibrinolytic pathway, and kallikrein and high molecular weight kininogen in the inflammatory pathways. These proteases, which have serine in their active site, are called serine proteases and they are pivotal to most of the processes of inflammation and coagulation. In fact, these various systems are interactive with one another and it is difficult to activate one pathway without it influencing the others.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Inhibition of factor B, the alternative complement pathway and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20050260198A1Reduce or prevent airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) or airway inflammationSenses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReperfusion injuryMedicine
Disclosed are novel inhibitors of the alternative complement pathway and particularly, novel anti-factor B antibodies. Also disclosed is the use of such inhibitors to reduce or prevent airway hyperresponsiveness and / or airway inflammation by selectively inhibiting the alternative complement pathway, thereby treating diseases in which such conditions play a role. Also disclosed is the use of such inhibitors to reduce or prevent other diseases and conditions, including ischemia-reperfusion injury, by inhibition of the alternative complement pathway.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +2
Methods for treating conditions associated with MASP-2 dependent complement activation
InactiveUS20060002937A1Eliminate side effectsInhibiting complement activationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationAlternative complement pathway
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASp-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:OMEROS CORP +1
Inhibition of factor B, the alternative complement pathway and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20080075720A1Reduce or prevent airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) or airway inflammationSenses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReperfusion injuryMedicine
Disclosed are novel inhibitors of the alternative complement pathway and particularly, novel anti-factor B antibodies. Also disclosed is the use of such inhibitors to reduce or prevent airway hyperresponsiveness and / or airway inflammation by selectively inhibiting the alternative complement pathway, thereby treating diseases in which such conditions play a role. Also disclosed is the use of such inhibitors to reduce or prevent other diseases and conditions, including ischemia-reperfusion injury, by inhibition of the alternative complement pathway.
Owner:NAT JEWISH HEALTH +2
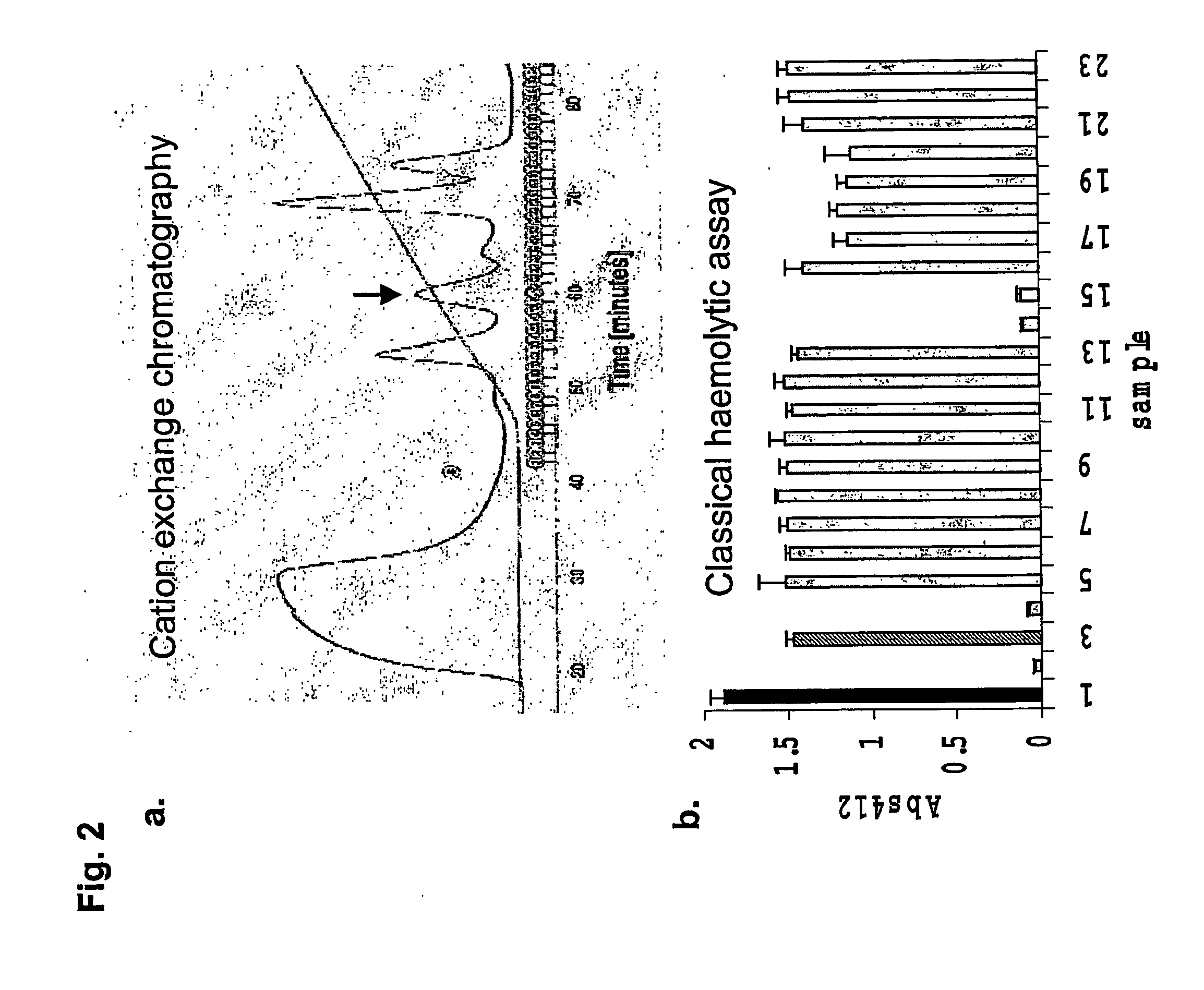
METHOD OF INHIBITING COMPLEMENT ACTIVATION WITH FACTOR Ba SPECIFIC ANTIBODIES AND USE THEREOF
InactiveUS20100015139A1Inhibiting complement activationEliminate side effectsAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulins against enzymesFactor iiNeutrophil granulocyte
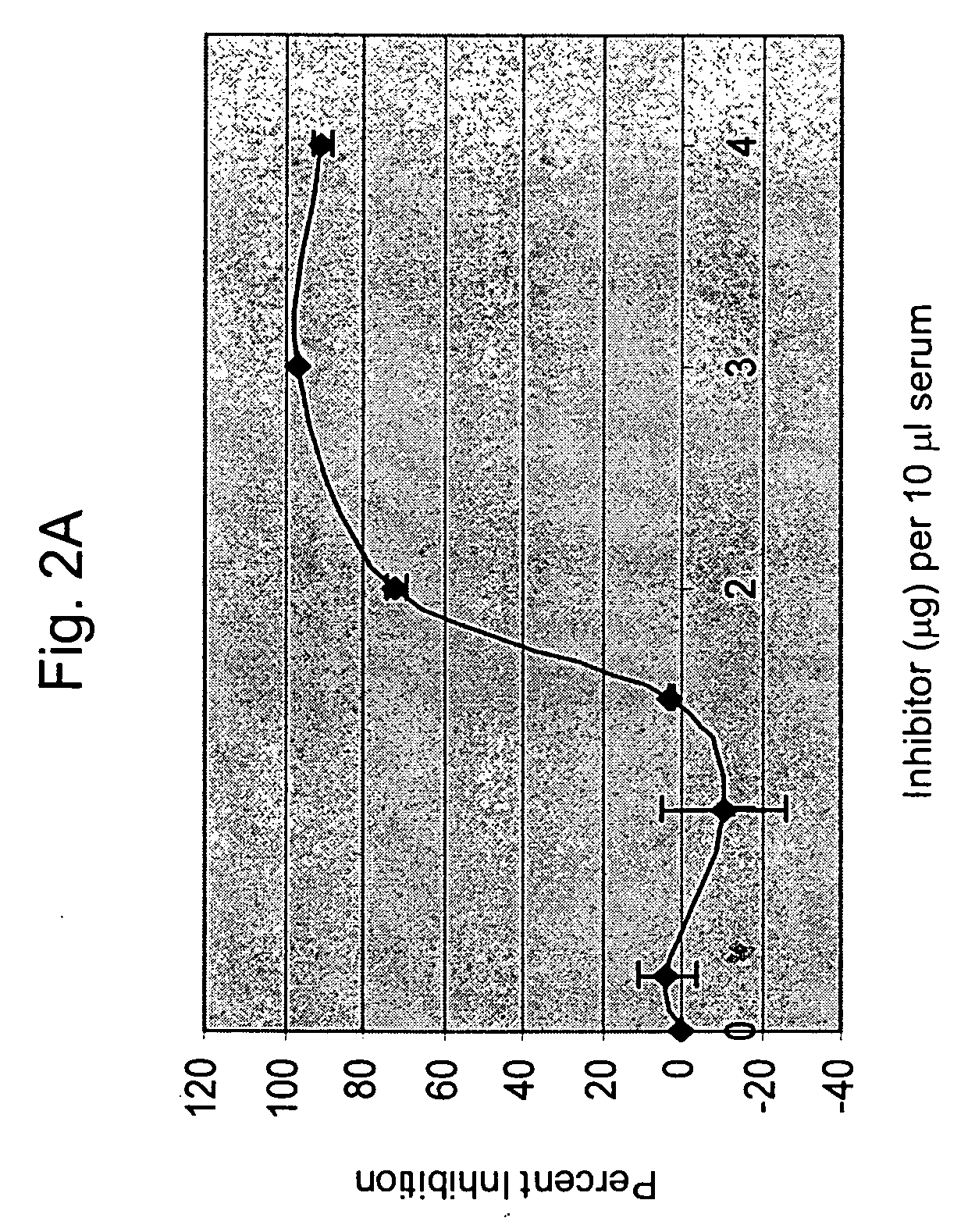
A method of inhibiting the adverse effects of alternative complement pathway activation products in a subject comprising administering to the subject an amount of anti-factor Ba antibody effective to selectively inhibit formation of an alternative complement pathway activation products C3a, C5a, and C5b-9, and activation of neutrophils, monocytes, and platelets.
Owner:NOVELMED THERAPEUTICS
Inhibition of the alternative complement pathway for treatment of traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury and related conditions
InactiveUS8911733B2Reduce or prevent at least one symptom of physiological damagePromote recoveryAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderTraumatic brain injuryBrain traumas
Disclosed is the use of agents and compositions that selectively inhibit the alternative complement pathway for the inhibiting or treating physiological damage resulting from traumatic brain injury (TBI), spinal cord injury (SCI), or related conditions. Preferred reagents for use in inhibition of damage resulting from TBI or SCI include those that inhibit factor B, with anti-factor B antibodies representing a particularly preferred agent.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
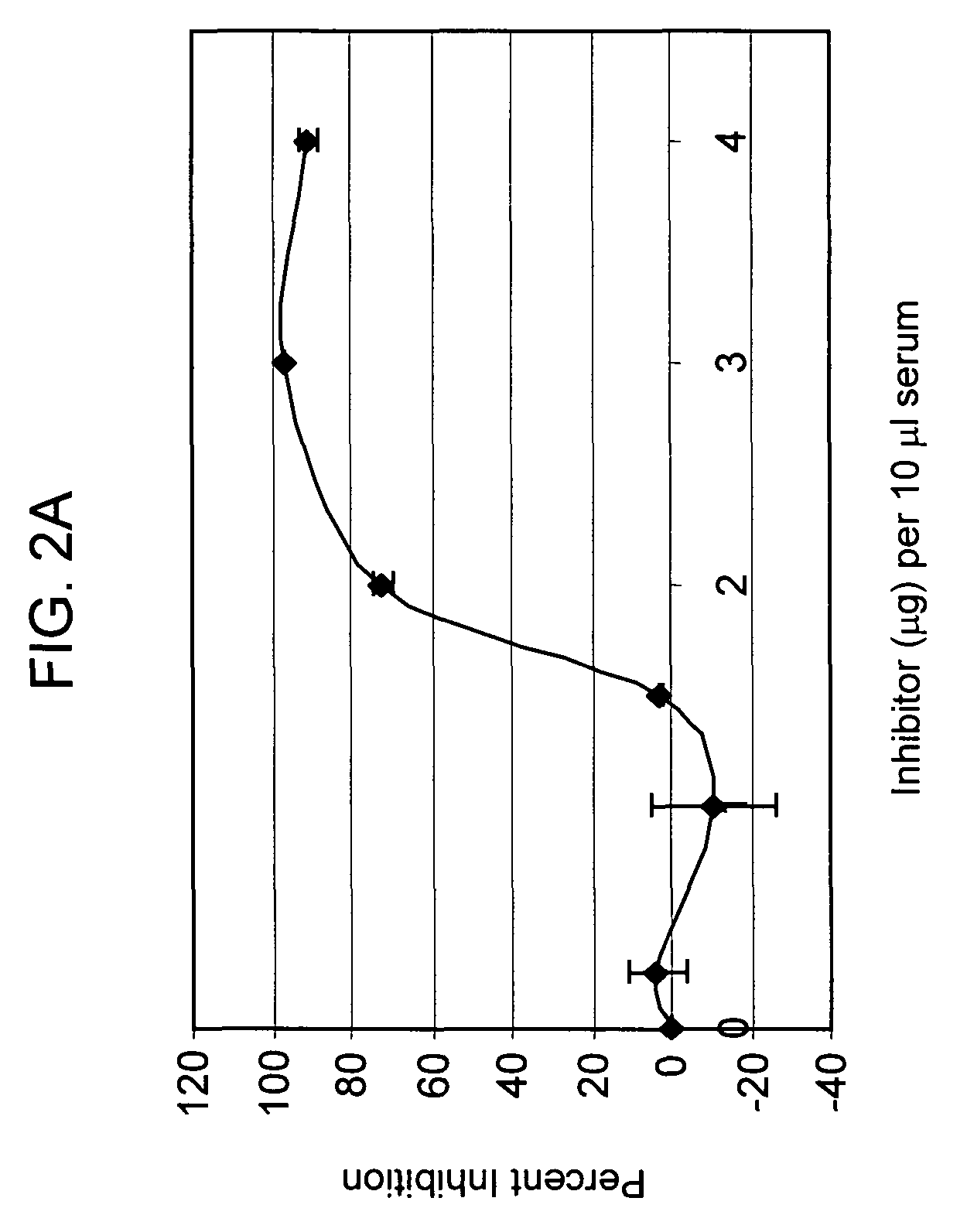
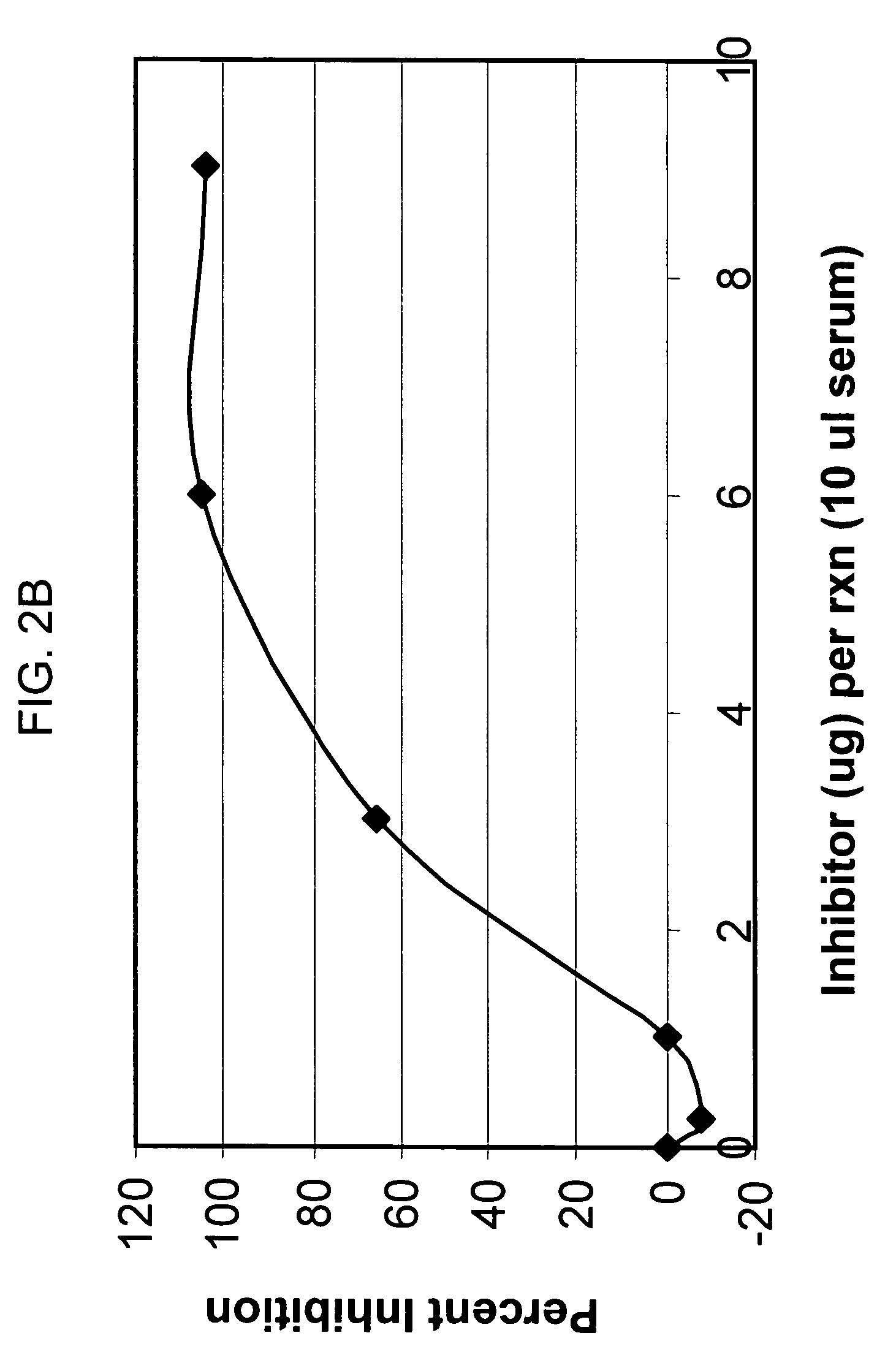
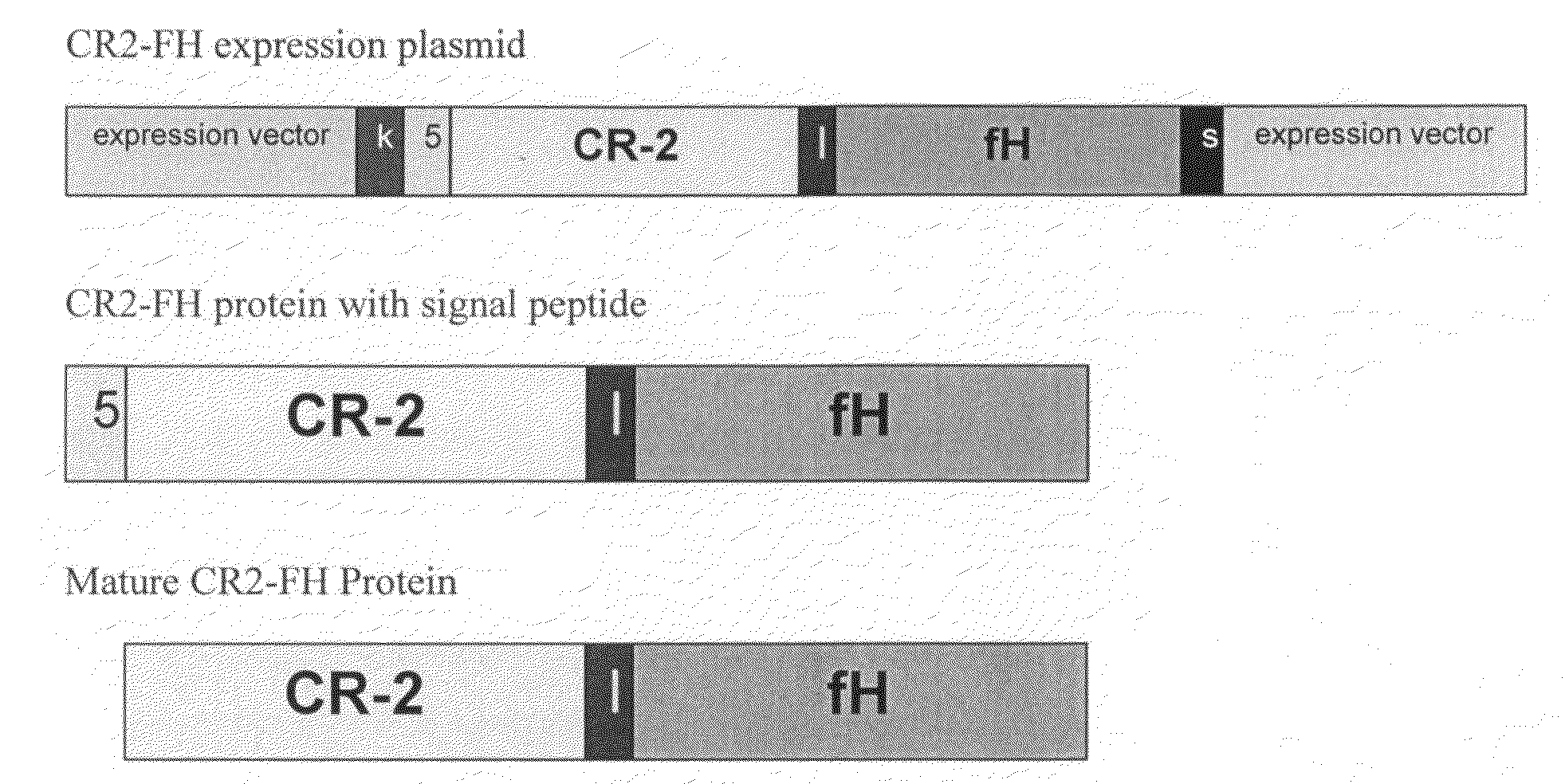
Targeting complement factor H for treatment of diseases
ActiveUS20080221011A1Improve survivalSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor iiComplement factor I
The invention provides a CR2-FH molecule comprising a CR2 portion comprising CR2 protein or a fragment thereof and a FH portion comprising a factor H protein or a fragment thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a CR2-FH molecule. Also provided are methods of using the compositions for treatment diseases in which the alternative complement pathway is implicated, such as age-related macular degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, and ischemia reperfusion.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
ActiveUS20130266560A1Improve survivalReduced survival rateAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulins against enzymesDiseasePharmaceutical medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER +1
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
InactiveUS20150166675A1Inhibiting complement activationReduce the possibilityAntibody ingredientsDermatological disorderCvd riskBiological activation
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject suffering from, or at risk for developing a thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
ActiveUS20120258095A1Improve survivalReduced survival rateAntibacterial agentsAntibody ingredientsPharmaceutical medicinePharmacology
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
Inhibition of factor B and the alternative complement pathway for treatment of traumatic brain injury and related conditions
InactiveUS20060292141A1Promote recoveryReduce or prevent at least one symptom of physiological damageAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderTraumatic brain injuryBrain traumas
Disclosed is the use of agents and compositions that selectively inhibit the alternative complement pathway for the inhibiting or treating physiological damage resulting from traumatic brain injury (TBI), spinal cord injury (SCI), or related conditions. Preferred reagents for use in inhibition of damage resulting from TBI or SCI include those that inhibit factor B, with anti-factor B antibodies representing a particularly preferred agent.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Humaneered Anti-factor b antibody
ActiveUS20080299114A1Inhibition formationInhibition of activationAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticShort Consensus RepeatDisease
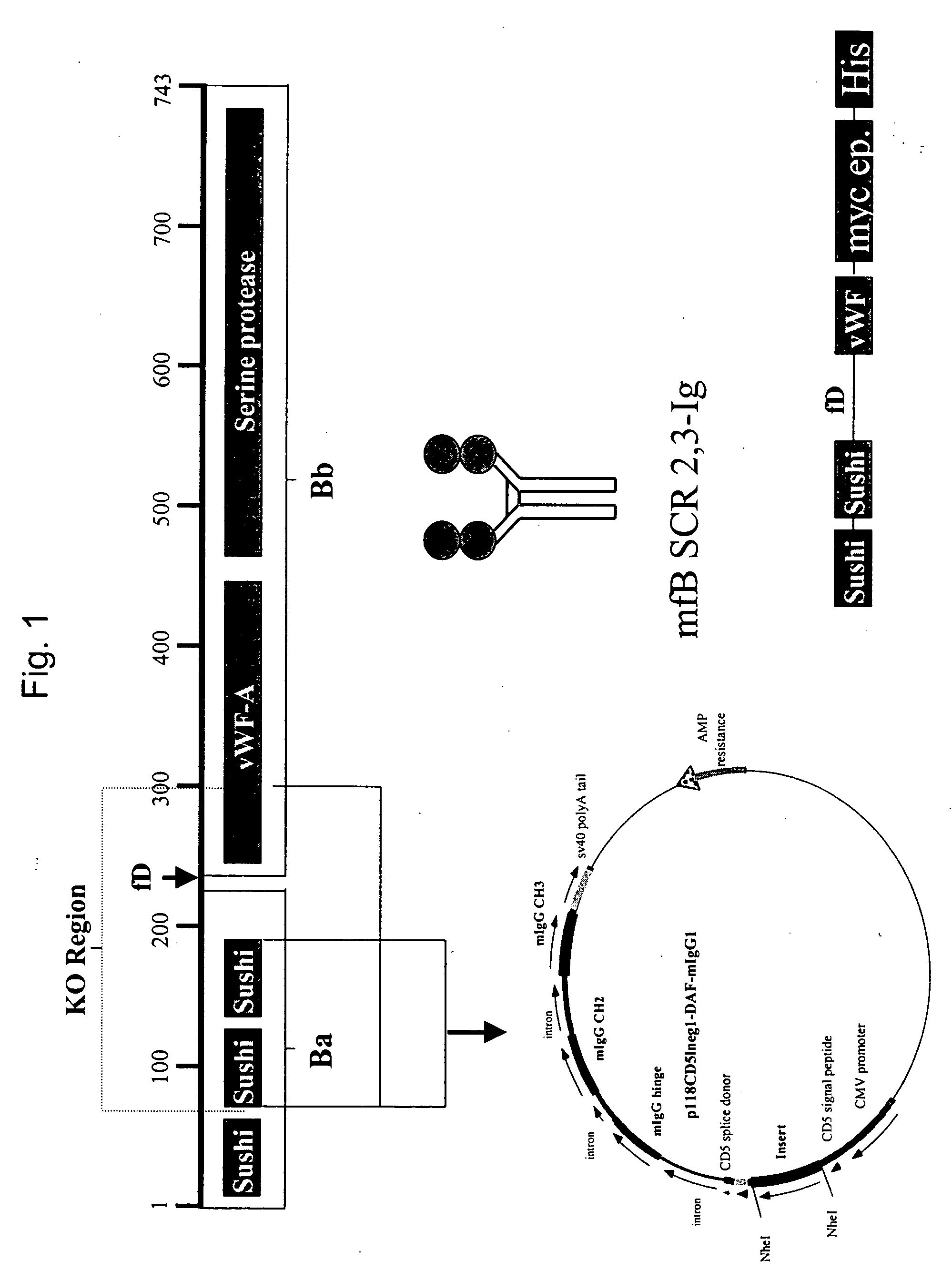
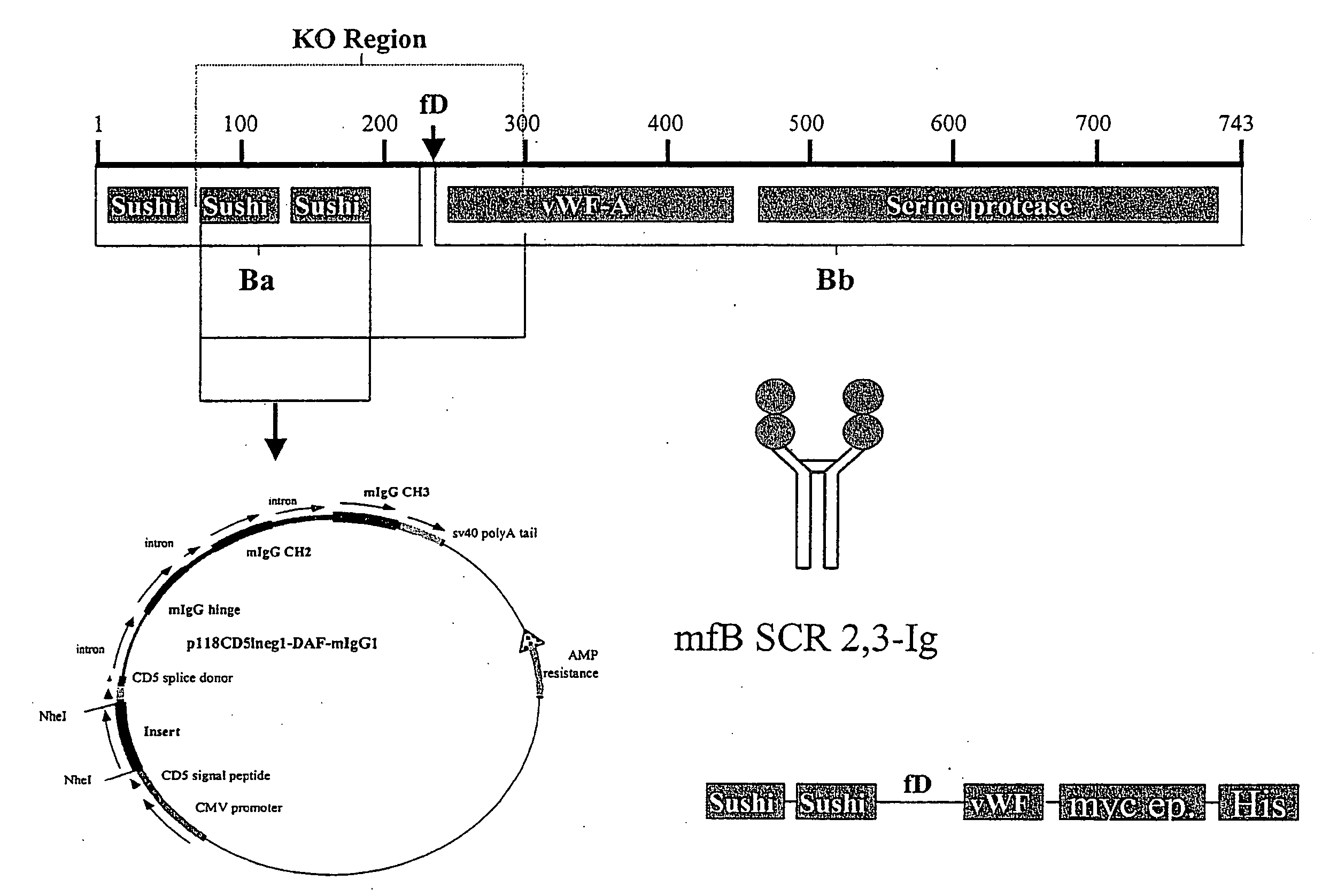
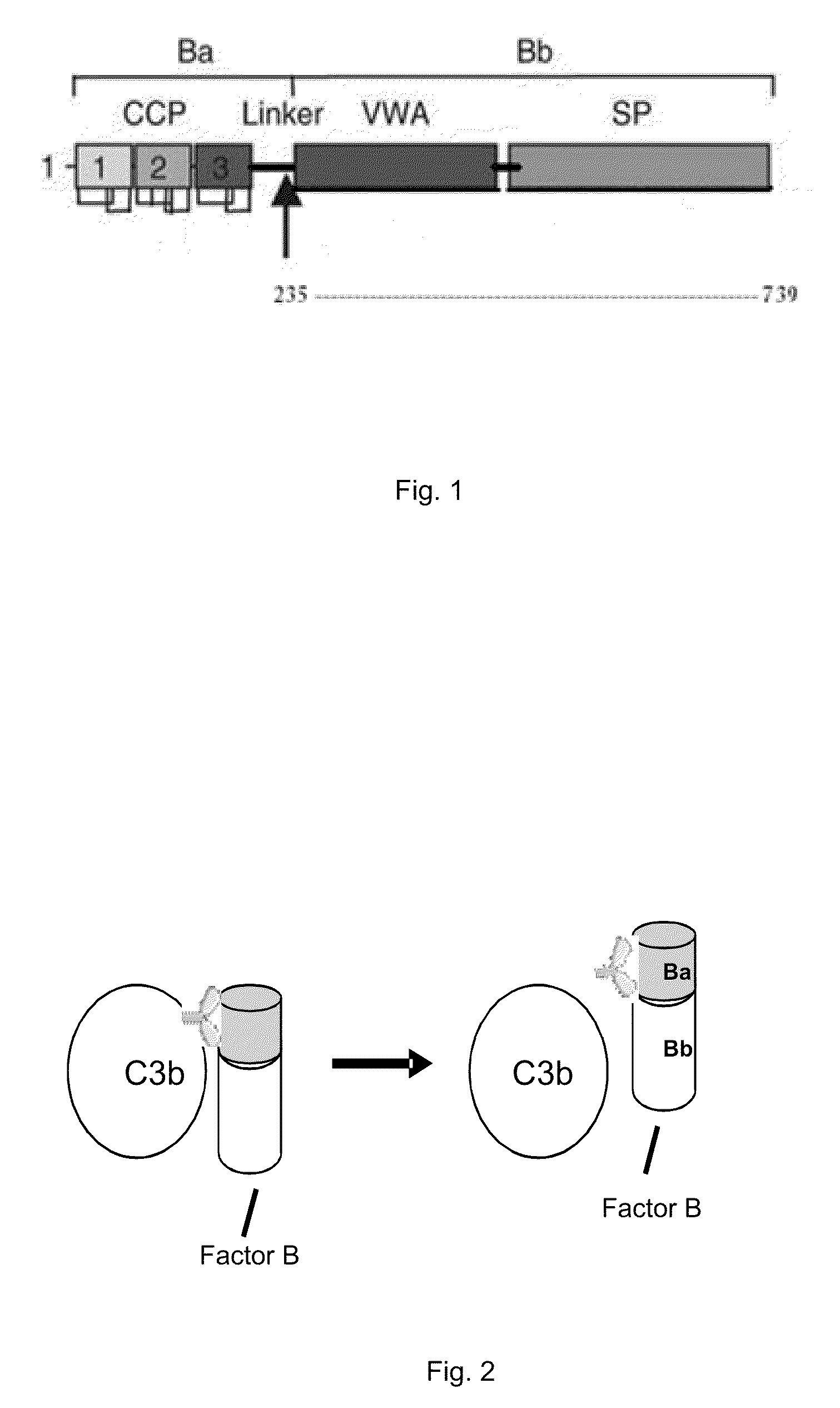
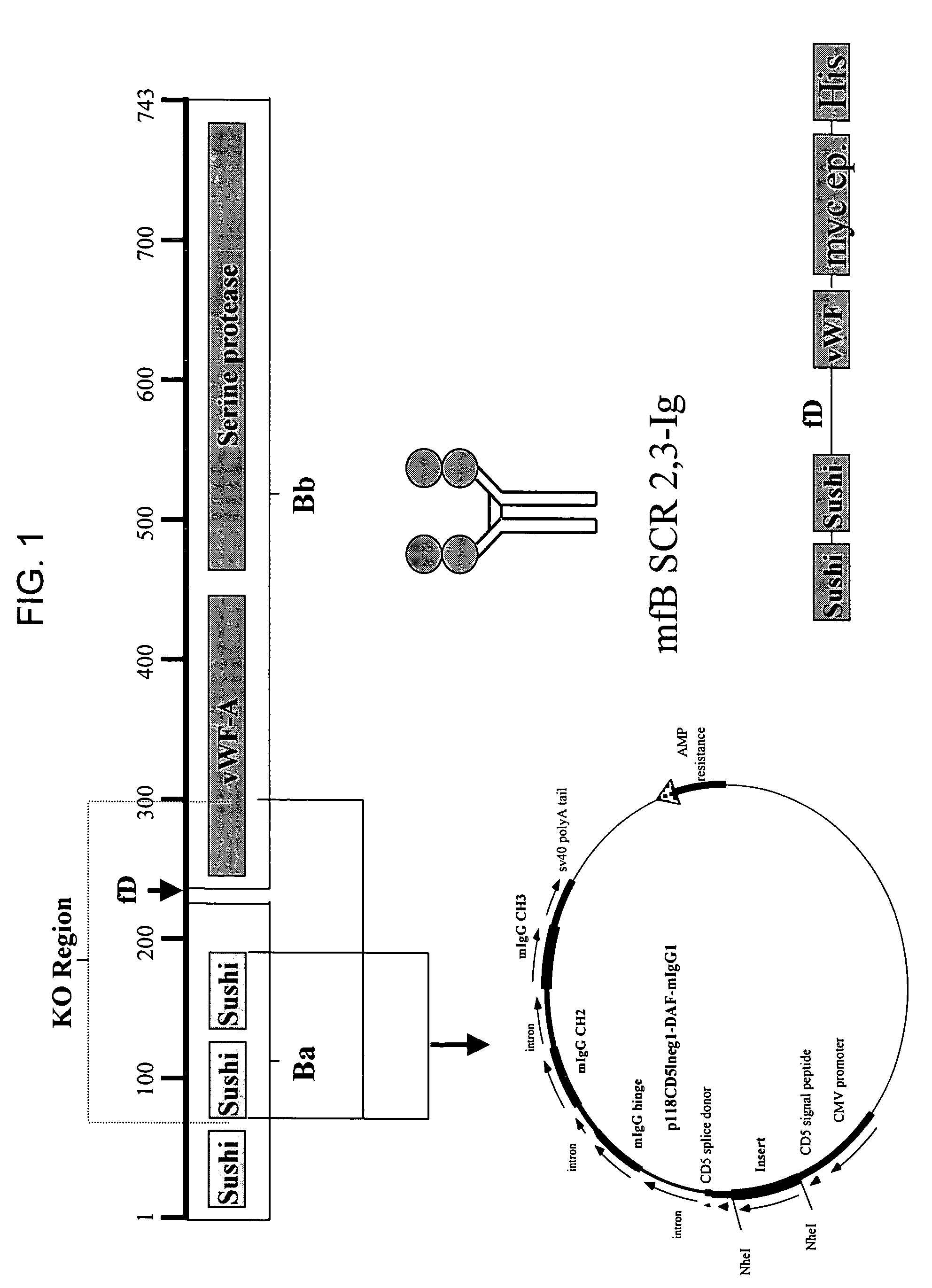
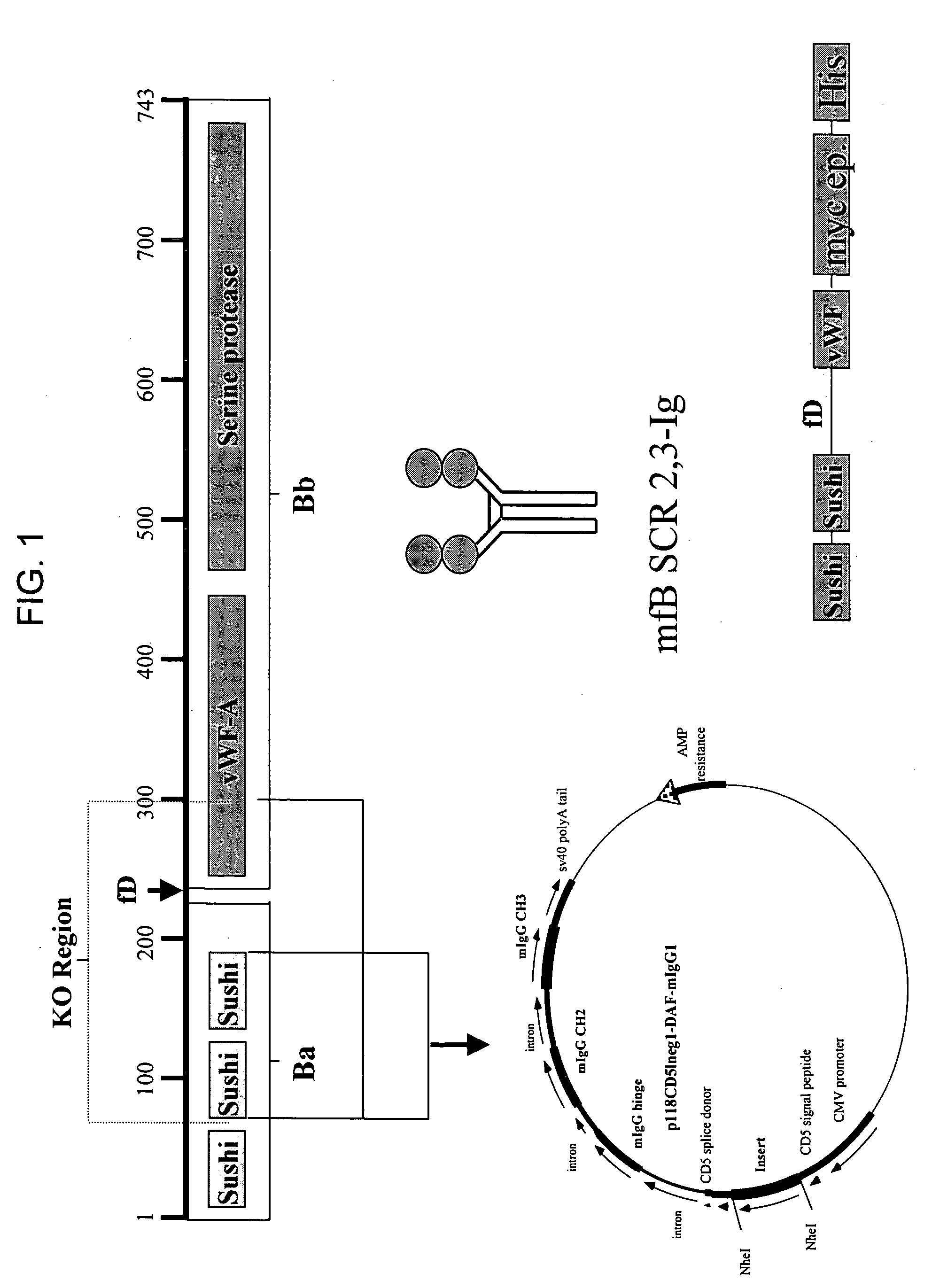
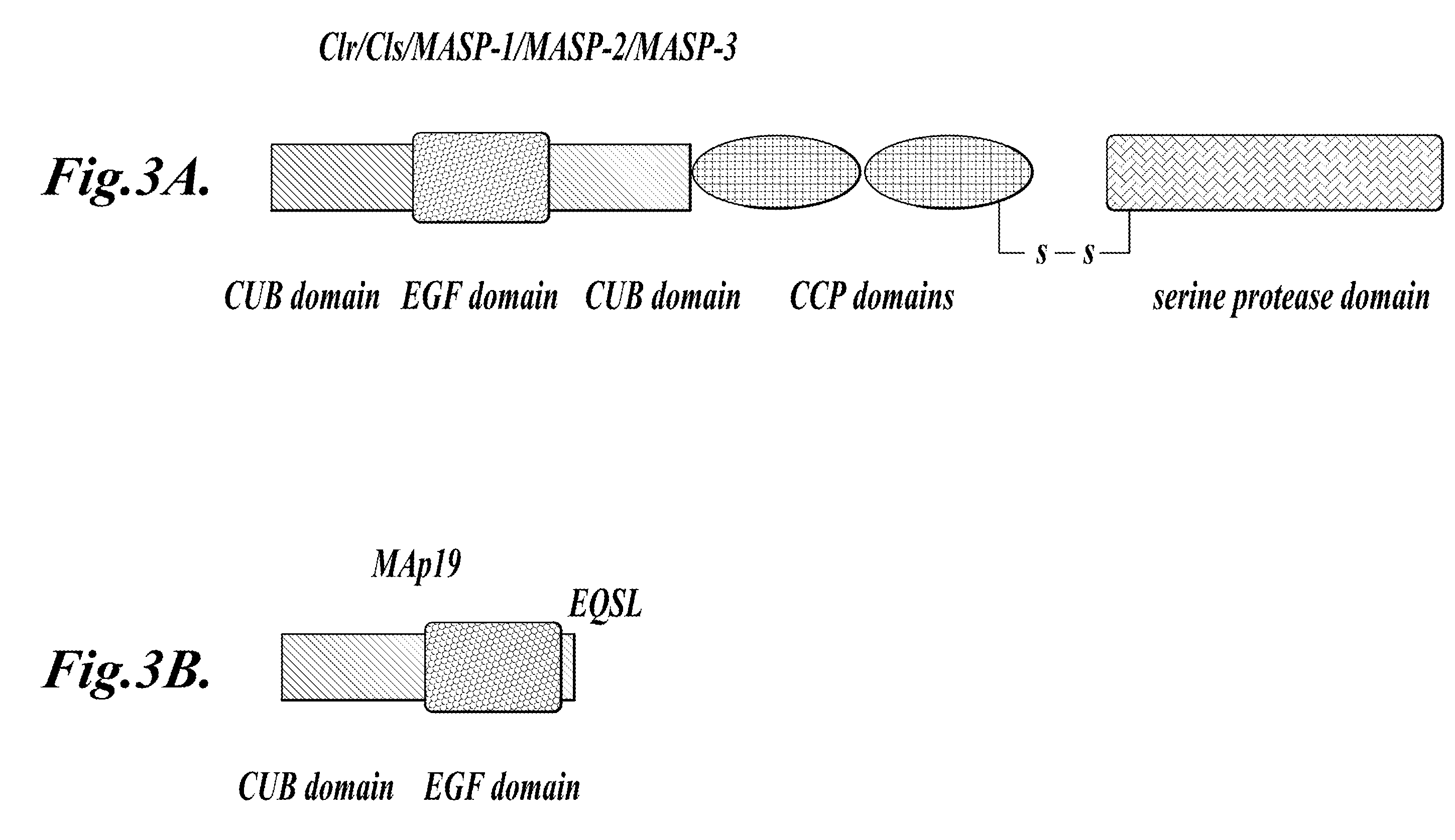
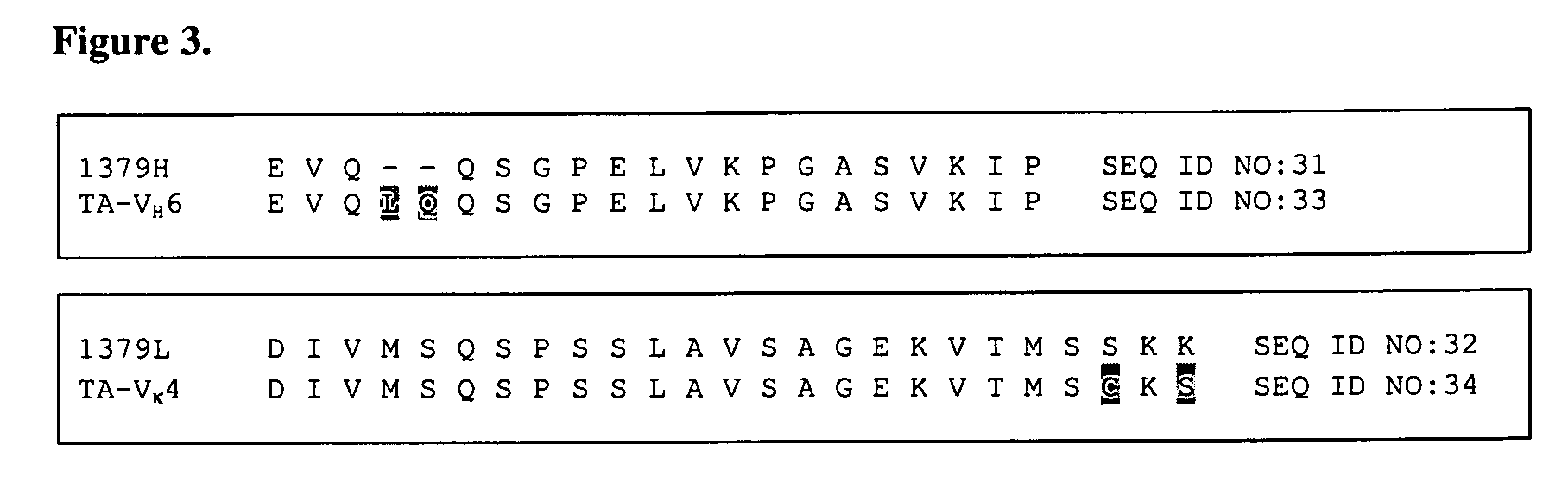
This invention relates to humaneered anti-factor B antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof with reduced immunogenicity. The humaneered anti-factor B antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof are derived from murine monoclonal antibody 1379, which binds factor B in the third short consensus repeat (“SCR”) domain and selectively inhibits activation of the alternative complement pathway by preventing formation of the C3bBb complex. The invention also relates to methods of treating diseases or disorders in which activation of the alternative complement pathway plays a role, and methods of selectively inhibiting activation of the alternative complement pathway in an individual in need thereof.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Methods for treating disseminated intravascular coagulation by inhibiting MASP-2 dependent complement activation
ActiveUS20110091450A1Reduce adverse effectsInhibiting complement activationAntibacterial agentsBiocideDisseminated coagulopathyCoagulation Disorder
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. In one embodiment, the invention provides methods of treating a subject suffering from a complement mediated coagulation disorder, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:OMEROS CORP +1
Targeting complement factor H for treatment of diseases
ActiveUS7759304B2Improve survivalSenses disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsComplement factor IDisease cause
The invention provides a CR2-FH molecule comprising a CR2 portion comprising CR2 protein or a fragment thereof and a FH portion comprising a factor H protein or a fragment thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a CR2-FH molecule. Also provided are methods of using the compositions for treatment diseases in which the alternative complement pathway is implicated, such as age-related macular degeneration, rheumatoid arthritis, and ischemia reperfusion.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +1
Humaneered anti-factor B antibody
ActiveUS7964705B2Inhibition formationAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticShort Consensus RepeatAntigen Binding Fragment
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
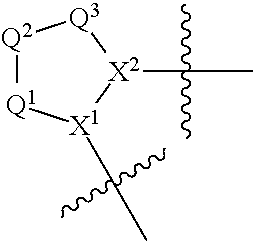
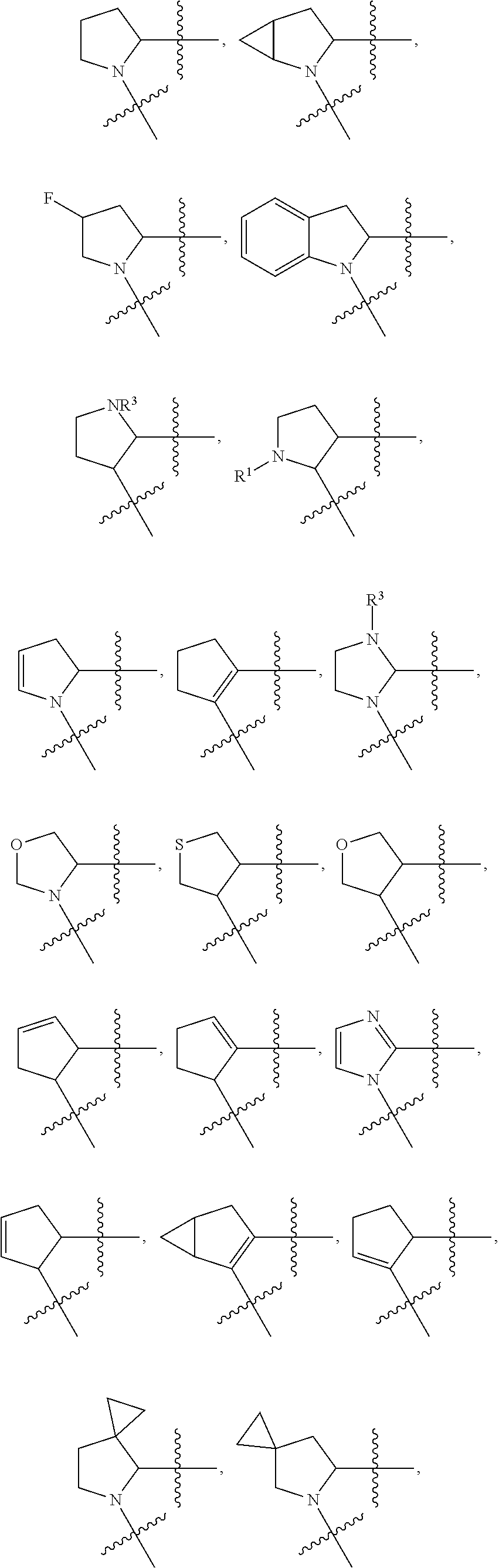
Compounds for Treatment of Complement Mediated Disorders
ActiveUS20180022767A1Dampen and inhibit detrimental complement activitySenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseReperfusion injury
Compounds, methods of use, and processes for making inhibitors of complement factor D comprising Formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or composition thereof are provided. The inhibitors described herein target factor D and inhibit or regulate the complement cascade at an early and essential point in the alternative complement pathway, and reduce factor D's ability to modulate the classical and lectin complement pathways. The inhibitors of factor D described herein are capable of reducing the excessive activation of complement, which has been linked to certain autoimmune, inflammatory, and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as ischemia-reperfusion injury and cancer.
Owner:ACHILLION PHARMA INC
Methods for treating conditions associated with MASP-2 dependent complement activation
ActiveUS8951522B2Reduce adverse effectsInhibition of activationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderBiological activationLectin
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
Complement inhibitors
ActiveUS20070141573A1Increase deposition rateConvenient treatmentAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention relates to complement inhibitors that inhibit both the classical and alternative complement pathways. In particular, the invention relates to complement inhibitors derived from the salivary glands of haematophagous arthropods that inhibit both the classical and alternative complement pathways. The invention also relates to the use of such complement inhibitors in the treatment and prevention of diseases.
Owner:VOLUTION IMMUNO PHARMA
Amide compounds for treatment of complement mediated disorders
ActiveUS20160362398A1Dampen and inhibit detrimental complement activitySenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseFactor D
Compounds, methods of use, and processes for making inhibitors of complement factor D comprising Formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or composition thereof, wherein R12 or R13 on the A group is an amide substituent (R32) are provided. The inhibitors described herein target factor D and inhibit or regulate the complement cascade in the alternative complement pathway. The inhibitors of factor D described herein reduce the excessive activation of complement.
Owner:ACHILLION PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions of inhibiting complement and cellular activation with dextran sulfate
InactiveUS20100087393A1Minimized and reduced hemorrhagic propertyHigh selectivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBiological activationCell biology
A method of inhibiting the adverse effects of complement pathway, activation products in a subject comprising administering to the subject an amount of Dextran Sulfate effective to inhibit formation of alternative complement pathway activation product.
Owner:NOVELMED THERAPEUTICS
Process and compositions for peptide, protein and peptidomimetic synthesis
InactiveUS6977150B2Overcome limitationsAvoid problemsHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsTranslation systemTranslation factor
The present invention is a simplified, highly-purified, processive translation system that does not require the addition of translation factors EF-P, W, W2 or rescue. A new translation process offers new, potentially improved, routes to all peptides, proteins and peptidomimetics currently synthesized by alternative routes.
Owner:ANTHONY C FORSTER DR
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
InactiveUS20150166676A1Reduce adverse effectsAvoid injuryMammal material medical ingredientsAntibody ingredientsBiological activationAlternative complement pathway
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER +1
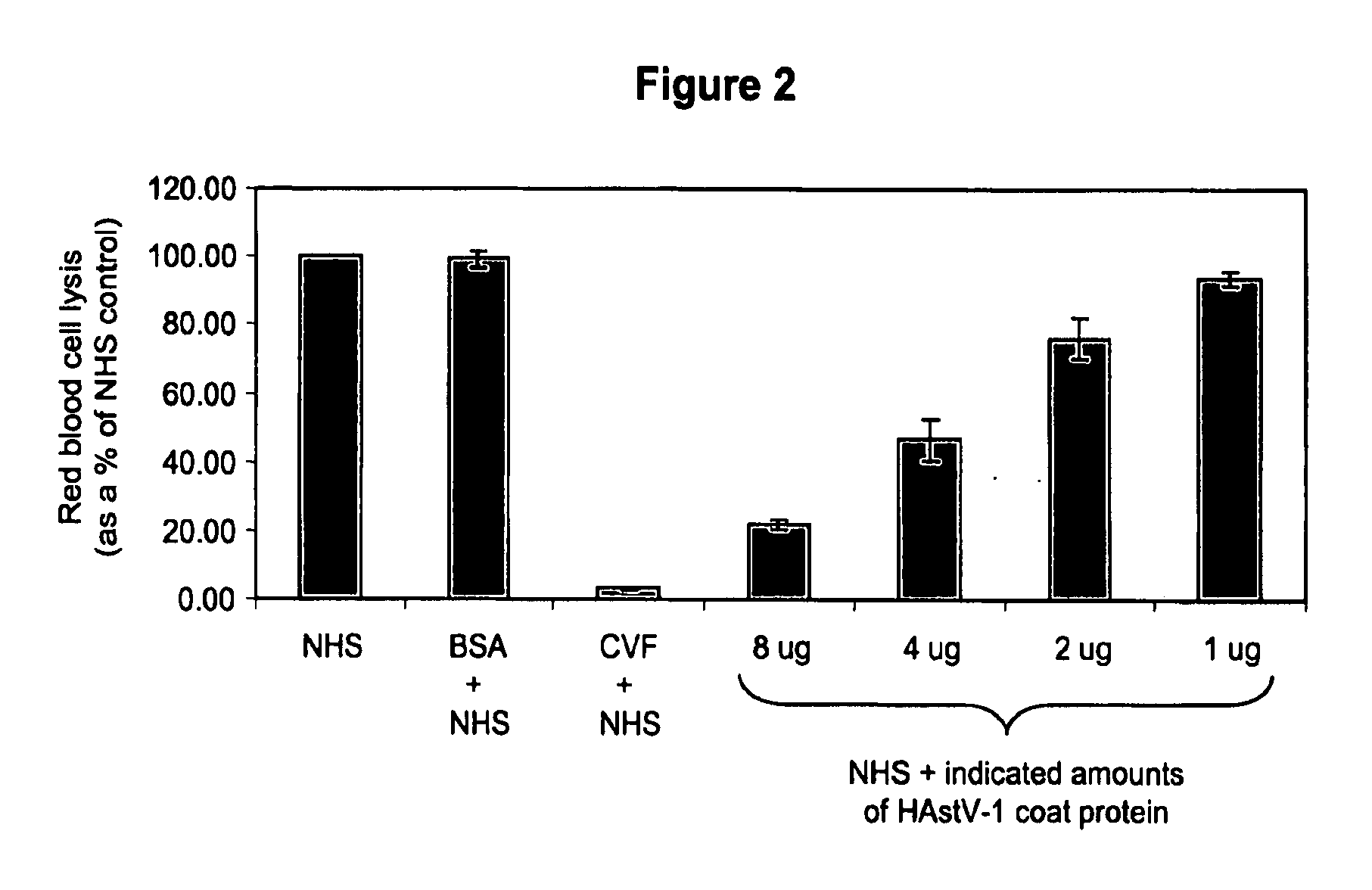
Methods for regulating complement cascade proteins using astrovirus coat protein and derivatives thereof
ActiveUS20100055106A1Decrease complement-related tissue damageReduce tissue damageNervous disorderSsRNA viruses positive-senseDiseaseFunctional activity
The present invention provides a method for modulating the complement cascade by depleting the plasma of the functional activity of complement proteins and thereby reducing or eliminating complement-mediated cell lysis. The invention provides a method for the therapeutic use of coat proteins and derivatives thereof from the Astroviradae family of viruses in the treatment of complement-mediated cell lysis and peptide mediators of inflammation. The invention provides a method for the therapeutic use of coat proteins and derivatives thereof from the Astroviradae family of viruses in the treatment of complement-mediated diseases. Methods are described herein where complement cascade, triggered by either the classical or alternative complement pathways, is prevented from effecting cell lysis and inflammation due to inhibition or depletion of one or more complement components in the serum following administration of astrovirus coat proteins or derivatives.
Owner:CHILDRENS RES HLDG LLC +1
Device and method for inhibiting complement activation
InactiveUS20110160636A1Inhibition of activationLower Level RequirementsHaemofiltrationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological activationAntibody
An extracorporeal device for inhibiting alternative complement pathway activation includes a support structure an anti-complement antibody disposed on or within the support structure and a first conduit for conducting blood of the subject to the anti-complement antibody. The anti-complement antibody can bind to the complement protein and remove the complement protein from the blood.
Owner:NOVELMED THERAPEUTICS
Selective inhibition of the membrane attack complex of complement and C3 convertase by low molecular weight components of the aurin tricarboxylic acid synthetic complex
InactiveUS20130035392A1Inhibit heinolysisInhibit MAC formationBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseC5-convertase
It pertains to selective inhibition of C3 convertase of the alternative pathway of complement as well as the previously claimed assembly of the membrane attack complex of complement by use of less than 1 kDa molecular weight forms of the aurin tricarboxylic acid synthetic complex (ATAC), and their derivatives. It further pertains to the use of these materials to treat human conditions where there is evidence of self destruction of host tissue by C3 convertase activation of the alternative complement pathway, or the membrane attack complex, or both pathways. These diseases include, but are not limited to, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinemia, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, malaria infection, Alzheimer disease, age related macular degeneration, and atherosclerosis.
Owner:AURIN BIOTECH
Inhibition of factor b, the alternative complement pathway and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20080102040A1Reduce or prevent airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) or airway inflammationPowder deliverySenses disorderReperfusion injuryMedicine
Disclosed are novel inhibitors of the alternative complement pathway and particularly, novel anti-factor B antibodies. Also disclosed is the use of such inhibitors to reduce or prevent airway hyperresponsiveness and / or airway inflammation by selectively inhibiting the alternative complement pathway, thereby treating diseases in which such conditions play a role. Also disclosed is the use of such inhibitors to reduce or prevent other diseases and conditions, including ischemia-reperfusion injury, by inhibition of the alternative complement pathway.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +2
Modulating the Alternative Complement Pathway
ActiveUS20110229497A1Modulate activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAlternative complement pathwayProtein C
Provided herein are compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions, and methods for modulating, i.e., stimulating or inhibiting, activity of the alternative complement pathway, and methods of identifying factor H-binding proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods for treating conditions associated with MASP-2 dependent complement activation
InactiveUS20100074899A1Eliminate side effectsCompounds screening/testingAntibacterial agentsBiological activationAlternative complement pathway
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:OMEROS CORP +1
Methods for regulating complement cascade proteins using astrovirus coat protein and derivatives thereof
ActiveUS8241843B2Reduce tissue damageSsRNA viruses positive-senseNervous disorderDiseaseFunctional activity
The present invention provides a method for modulating the complement cascade by depleting the plasma of the functional activity of complement proteins and thereby reducing or eliminating complement-mediated cell lysis. The invention provides a method for the therapeutic use of coat proteins and derivatives thereof from the Astroviradae family of viruses in the treatment of complement-mediated cell lysis and peptide mediators of inflammation. The invention provides a method for the therapeutic use of coat proteins and derivatives thereof from the Astroviradae family of viruses in the treatment of complement-mediated diseases. Methods are described herein where complement cascade, triggered by either the classical or alternative complement pathways, is prevented from effecting cell lysis and inflammation due to inhibition or depletion of one or more complement components in the serum following administration of astrovirus coat proteins or derivatives.
Owner:CHILDRENS RES HLDG LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com